
History of the United States
Encyclopedia
The history of the United States traditionally starts with the Declaration of Independence
in the year 1776, although its territory was inhabited by Native Americans
since prehistoric times and then by European colonists
who followed the voyages of Christopher Columbus
starting in 1492. The largest settlements were by the English on the East Coast, starting in 1607. By the 1770s the Thirteen Colonies
contained two and half million people, were prosperous, and had developed their own political and legal systems. The British government's threat to American self-government led to war in 1775 and the Declaration of Independence in 1776. With major military and financial support from France, the patriots won the American Revolution
. In 1789 the Constitution
became the basis for the United States federal government, with war hero George Washington
as the first president. The young nation continued to struggle with the scope of central government and with European influence, creating the first political parties in the 1790s
, and fighting a second war for independence in 1812
.
U.S. territory expanded westward across the continent, brushing aside Native Americans and Mexico, and overcoming modernizers who wanted to deepen the economy rather than expand the geography. Slavery of Africans was abolished in the North, but heavy world demand for cotton let it flourish in the Southern states
. The 1860 election of Abraham Lincoln
calling for no more expansion of slavery triggered a crisis as eleven slave states seceded to found the Confederate States of America
in 1861. The bloody American Civil War
(1861–65) redefined the nation and remains the central iconic event. The South was defeated and, in the Reconstruction era, the U.S. ended slavery, extended rights to African American
s, and readmitted secessionist states with loyal governments. The national government was much stronger, and it now had the explicit duty to protect individuals. Reconstruction was never completed by the US government and left the blacks in a world of Jim Crow political, social and economic inferiority. The entire South remained poor while the North and West grew rapidly.
Thanks to an outburst of entrepreneurship in the North and the arrival of millions of immigrant workers from Europe, the U.S. became the leading industrialized power by 1900. Disgust with corruption, waste, and traditional politics stimulated the Progressive movement
, 1890s-1920s, which pushed for reform in industry and politics and put into the Constitution women's suffrage and Prohibition
of alcohol (the latter repealed in 1933). Initially neutral in World War I
, the U.S. declared war on Germany in 1917, and funded the Allied victory. The nation refused to follow President Woodrow Wilson
's leadership and never joined the League of Nations
. After a prosperous decade in the 1920s the Wall Street Crash of 1929
marked the onset of the decade-long world-wide Great Depression
. A political realignment expelled the Republicans from power and installed Democrat Franklin D. Roosevelt
and his elaborate and expensive New Deal
programs for relief, recovery, and reform. Roosevelt's Democratic coalition
, comprising ethnics in the north, labor unions, big-city machines, intellectuals, and the white South, dominated national politics into the 1960s. After the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor
in December 1941, the U.S. entered World War II
alongside the Allies
and helped defeat Nazi Germany
in Europe and, with the detonation of newly-invented atomic bombs, Japan
in Asia and the Pacific.
The Soviet Union
and the U.S. emerged as opposing superpower
s after the war and began the Cold War
confronting indirectly in an arms race
, the Space Race
, and intervention in Europe and eastern Asia. Liberalism
reflected in the civil rights movement
and opposition to war in Vietnam peaked in the 1960s–70s before giving way to conservatism in the early 1980s. The Cold War ended when the Soviet Union dissolved
in 1991, leaving the U.S. to prosper in the booming Information Age
economy that was boosted, at least in part, by information technology
. International conflict and economic uncertainty heightened by 2001 with the September 11 attacks and subsequent War on Terror
and the late-2000s recession.
first settled the Americas and the present-day United States. The prevailing theory proposes that people migrated from Eurasia
across Beringia, a land bridge
that connected Siberia
to present-day Alaska
, and then spread southward throughout the Americas. This migration might have begun as early as 30,000 years ago and continued through to about 10,000 years ago, when the land bridge became submerged by the rising sea level caused by the ending of the last glacial period. These early inhabitants, called Paleoamericans, soon diversified into many hundreds of culturally distinct nations and tribes.
The pre-Columbian era
incorporates all period subdivisions
in the history and prehistory of the Americas
before the appearance of significant Europe
an influences on the American
continents, spanning the time of the original settlement in the Upper Paleolithic
period to European colonization
during the Early Modern period
. While technically referring to the era before Christopher Columbus
' voyages of 1492 to 1504, in practice the term usually includes the history of American indigenous cultures
until they were conquered or significantly influenced by Europeans, even if this happened decades or even centuries after Columbus' initial landing.
 After a period of exploration by people from various European countries, Spanish
After a period of exploration by people from various European countries, Spanish
, Dutch
, English
, French
, Swedish
, and Portuguese
settlements were established. In the 16th century, Europeans brought horses, cattle, and hogs to the Americas and, in turn, took back to Europe maize, potato
es, tobacco
, beans, and squash. The disease environment was very unhealthy for explorers and early settlers. The Native Americans became exposed to new diseases such as smallpox and measles and died in very large numbers
, usually before large-scale European settlement began.
' second expedition
, which reached Puerto Rico on November 19, 1493; others reached Florida in 1513. Quickly Spanish expeditions reached the Appalachian Mountains
, the Mississippi River
, the Grand Canyon
and the Great Plains
. In 1540, Hernando de Soto undertook an extensive exploration of Southeast. Also in 1540 Francisco Vázquez de Coronado explored from Arizona to central Kansas. The Spanish sent some settlers, creating the first permanent European settlement in the continental United States at St. Augustine, Florida
in 1565, but it attracted few permanent settlers. Much larger and more important Spanish settlements included Santa Fe
, Albuquerque
, San Antonio, Tucson, San Diego, Los Angeles
and San Francisco.
New Netherland
was the 17th century Dutch colony centered on New York City and the Hudson River Valley, where they traded furs with the Native Americans to the north and were a barrier to Yankee
expansion from New England
. The Dutch were Calvinists who built the Reformed Church in America
, but they were tolerant of other religions and cultures. The colony was taken over by Britain in 1664. It left an enduring legacy on American cultural and political life, including a secular broadmindedness and mercantile pragmatism in the city, a rural traditionalism in the countryside typified by the story of Rip Van Winkle
, and politicians such as Martin Van Buren
, Theodore Roosevelt
, Franklin D. Roosevelt
and Eleanor Roosevelt
.
New France
was the area colonized by France
from 1534 to 1763. There were few permanent settlers outside Quebec
, but Indian tribes often became military allies in France's wars with Britain. After 1750 the Acadians—French settlers who had been expelled by the British from Acadia (Nova Scotia
)—resettled in Louisiana, where they developed a distinctive rural Cajun
culture that still exists. They became American citizens in 1803 with the Louisiana Purchase
. Other French villages along the Mississippi
and Illinois rivers
were absorbed when the Americans started arriving after 1770.
 The strip of land along the eastern seacoast was settled primarily by English colonists in the 17th century, along with much smaller numbers of Dutch
The strip of land along the eastern seacoast was settled primarily by English colonists in the 17th century, along with much smaller numbers of Dutch
and Swedes. Colonial America was defined by a severe labor shortage that employed forms of unfree labor such as slavery and indentured servitude, and by a British policy of benign neglect (salutary neglect
) that permitted the development of an American spirit distinct from that of its European founders. Over half of all European immigrants to Colonial America arrived as indentured servants.
The first successful English colony was established in 1607, on the James River
at Jamestown
. It languished for decades until a new wave of settlers arrived in the late 17th century and established commercial agriculture based on tobacco. Between the late 1610s and the Revolution, the British shipped an estimated 50,000 convicts to their American colonies. One example of conflict between Native Americans and English settlers was the 1622 Powhatan
uprising in Virginia, in which Native Americans had killed hundreds of English settlers. The largest conflict between Native Americans and English settlers in the 17th century was King Philip's War
in New England
, although the Yamasee War
may have been bloodier.
New England
was initially settled primarily by Puritans who established the Massachusetts Bay Colony
in 1630, although there was a small earlier settlement in 1620 by a similar group, the Pilgrims, at Plymouth Colony
. The Middle Colonies, consisting of the present-day states of New York
, New Jersey
, Pennsylvania
, and Delaware
, were characterized by a large degree of diversity. The first attempted English settlement south of Virginia was the Province of Carolina
, with Georgia Colony the last of the Thirteen Colonies
established in 1733. The colonies were characterized by religious diversity, with many Congregationalists in New England, German and Dutch Reformed in the Middle Colonies, Catholics in Maryland, and Scotch Irish Presbyterians on the frontier The First Great Awakening
. Many royal officials and merchants were Anglicans. Religion expanded greatly after the First Great Awakening
, a religious revival in the 1740s led by preachers such as Jonathan Edwards. American Evangelicals affected by the Awakening added a new emphasis on divine outpourings of the Holy Spirit and conversions that implanted within new believers an intense love for God. Revivals encapsulated those hallmarks and forwarded the newly created evangelicalism into the early republic, setting the stage for the Second Great Awakening
beginning in the late 1790s.
(1754–1763) was a watershed event in the political development of the colonies. The influence of the main rivals of the British Crown in the colonies and Canada, the French and North American Indians, was significantly reduced. Moreover, the war effort resulted in greater political integration of the colonies, as symbolized by Benjamin Franklin's call for the colonies to "Join or Die".
Following Britain's acquisition of French territory in North America, King George III issued the Royal Proclamation of 1763
with the goal of organizing the new North American empire and stabilizing relations with the native Indians. In ensuing years, strains developed in the relations between the colonists and the Crown. The British Parliament passed the Stamp Act of 1765, imposing a tax on the colonies to help pay for troops stationed in North America following the British victory in the Seven Years' War
.
The British government felt that the colonies were the primary beneficiaries of this military presence, and should pay at least a portion of the expense. The colonists did not share this view. Rather, with the French and Indian threat diminished, the primary outside influence remained that of Britain. A conflict of economic interests increased with the right of the British Parliament to govern the colonies without representation being called into question.
 The Boston Tea Party
The Boston Tea Party
in 1773 was a direct action by colonists in the town of Boston
to protest against the taxes levied by the British government. Parliament responded the next year with the Coercive Acts, which sparked outrage and resistance in the Thirteen Colonies
. Colonists convened the First Continental Congress
to coordinate their resistance to the Coercive Acts. The Congress called for a boycott of British trade, published a list of rights and grievances, and petitioned the king
for redress of those grievances.
The Congress also called for another meeting if their petition did not halt enforcement of the Coercive Acts. Their appeal to the Crown had no effect, and so the Second Continental Congress
was convened in 1775 to organize the defense of the colonies at the onset of the American Revolutionary War
.
began a rebellion against British rule in 1775 and proclaimed their independence in 1776 as the United States of America. In the American Revolutionary War
(1775–1783) the American capture of the British invasion army at Saratoga in 1777 secured the Northeast and encouraged the French to make a military alliance with the United States. France brought in Spain and the Netherlands, thus balancing the military and naval forces on each side as Britain had no allies. General George Washington
(1732–1799) proved an excellent organizer and administrator, who worked successfully with Congress and the state governors, selecting and mentoring his senior officers, supporting and training his troops, and maintaining an idealistic Republican Army. His biggest challenge was logistics, since neither Congress nor the states had the funding to provide adequately for the equipment, munitions, clothing, paychecks, or even the food supply of the soldiers. As a battlefield tactician Washington was often outmaneuvered by his British counterparts. As a strategist, however, he had a better idea of how to win the war than they did. The British sent four invasion armies. Washington's strategy forced the first army out of Boston in 1776, and was responsible for the surrender of the second and third armies at Saratoga (1777) and Yorktown (1781). He limited the British control to New York and a few places while keeping Patriot control of the great majority of the population. The Loyalists, whom the British counted upon too heavily, comprised about 20% of the population but never were well organized. As the war ended, Washington watched proudly as the final British army quietly sailed out of New York City in November 1783, taking the Loyalist leadership with them. Washington astonished the world when, instead of seizing power for himself, he retired quietly to his farm in Virginia. Political scientist Seymour Martin Lipset
observes, "The United States was the first major colony successfully to revolt against colonial rule. In this sense, it was the first 'new nation'."
 On July 4, 1776, the Second Continental Congress
On July 4, 1776, the Second Continental Congress
, meeting in Philadelphia, declared the independence of "the United States of America" in the Declaration of Independence
. July 4 is celebrated as the nation's birthday. The new nation was founded on Enlightenment
ideals of liberalism
in what Thomas Jefferson
called the unalienable rights to "life, liberty and the pursuit of happiness," and dedicated strongly to republican
principles. Republicanism emphasized the people are sovereign (not hereditary kings), demanded civic duty, feared corruption, and rejected any aristocracy.
In the 1780s the national government was able to settle the issue of the western territories, which were ceded by the states to Congress and became territories; soon they became states. Nationalists worried that the new nation was too fragile to withstand an international war, or even internal revolts such as the Shays' Rebellion
of 1786 in Massachusetts. Nationalists—most of them war veterans—organized in every state and convinced Congress to call the Philadelphia Convention
in 1787. The delegates from every state wrote a new Constitution
that created a much more powerful and efficient central government, one with a strong president, and powers of taxation. The new government reflected the prevailing republican ideals of guarantees of individual liberty
and upon constraining the power of government through a system of separation of powers
.
To assuage the Anti-Federalists who feared a too-powerful national government, the nation adopted the United States Bill of Rights
in 1791. Comprising the first ten amendments of the Constitution, it guaranteed individual liberties such as freedom of speech and religious practice, jury trials, and stated that citizens and states had reserved rights (which were not specified).
 George Washington
George Washington
—a renowned hero of the American Revolutionary War
, commander-in-chief of the Continental Army
, and president of the Constitutional Convention
—became the first President of the United States
under the new Constitution
in 1789.
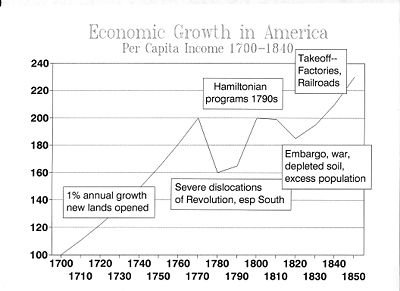
The major accomplishments of the Washington Administration
were creating a strong national government that was recognized without question by all Americans, and, following the plans of Treasury Secretary Alexander Hamilton
, assuming the debts of the states (the debt holders received federal bonds), creating the Bank of the United States
to stabilize the financial system, setting up a uniform system of tariffs (taxes on imports) and other taxes to pay off the debt and provide a financial infrastructure. To support his programs Hamilton created a new political party—the first in the world based on voters—the Federalist Party
. Thomas Jefferson
and James Madison
led the opposition, forming an opposition Republican Party (usually called the Democratic-Republican Party by historians). Hamilton and Washington presented the country in 1794 with the Jay Treaty
that reestablished good relations with Britain. The Jeffersonians vehemently protested, and the voters aligned behind one party or the other, thus setting up the First Party System
. The treaty passed, but politics became very heated.
The Whiskey Rebellion
in 1794, when western settlers protested against a federal tax on liquor, was the first serious test of the federal government. Washington called out the state militia and personally led an army, as the insurgents melted away and the power of the national government was firmly established.
Washington refused to serve more than two terms—setting a precedent—and in famous his farewell address
, he extolled the benefits of federal government and importance of ethics and morality while warning against foreign alliances and formation of political parties.
John Adams
, a Federalist, defeated Jefferson in the 1796 election. War loomed with France and the Federalists used the opportunity to try to silence the Republicans with the Alien and Sedition Acts
, build up a large army with Hamilton at the head, and prepare for a French invasion. However, the Federalists became divided after Adams sent a successful peace mission to France that ended the Quasi-War
of 1798. Jefferson defeated Adams for the presidency in the 1800 election
.
 Although the Constitution included a Supreme Court
Although the Constitution included a Supreme Court
, its functions were vague until John Marshall
, the Chief Justice (1801–35), defined them, especially the power to overturn acts of Congress that violated the Constitution, first enunciated in 1803 in Marbury v. Madison
. The Louisiana Purchase
, in 1803, removed the French presence from the western border of the United States and provided U.S. settlers with vast potential for expansion west of the Mississippi River
.
In response to multiple grievances, the Congress
declared war on Britain
in 1812. The grievances included humiliating the Americans in the Chesapeake incident of 1807
, continued British impressment
of American sailors into the Royal Navy
, restrictions on trade with France, and arming hostile Indians in Ohio and the western territories. The War of 1812
ended in a draw after bitter fighting that lasted until January 8, 1815, during the Battle of New Orleans
. The Americans gained no territory but were cheered by a sense of victory in what they called a "second war of independence". The war was a major loss for Native American
tribes in the Northwest and Southeast who had allied themselves with Britain and were defeated on the battlefield.
As strong opponents of the war, the Federalists held the Hartford Convention
in 1814 that hinted at disunion. National euphoria after the victory at New Orleans ruined the prestige of the Federalists and they no longer played a significant role. President Madison and most Republicans realized it had been a mistake to let the Bank of the United States close down, for its absence greatly hindered the financing of the war. So they chartered the Second Bank of the United States
in 1816. The Republicans also imposed tariffs designed to protect the infant industries that had been created when Britain was blockading the U.S. With the collapse of the Federalists as a party, the adoption of many Federalist principles by the Republicans, and the systematic policy of President James Monroe
in his two terms (1817–25) to downplay partisanship, the nation entered an Era of Good Feelings
, with far less partisanship than before (or after), and closed out the First Party System
.
The Monroe Doctrine
, expressed in 1823, proclaimed the United States' opinion that European powers should no longer colonize or interfere in the Americas
. This was a defining moment in the foreign policy
of the United States. The Monroe Doctrine was adopted in response to American and British fears over Russian and French expansion into the Western Hemisphere
.
 In 1830, Congress passed the Indian Removal Act
In 1830, Congress passed the Indian Removal Act
, which authorized the president to negotiate treaties that exchanged Native American tribal lands in the eastern states for lands west of the Mississippi River. This established Andrew Jackson
, a military hero and President, as a proponent of the forcible removal of native populations to the West. The act resulted most notably in the Trail of Tears
, a forced migration of several native tribes to the West, with several thousand people dying en route. Many of the Seminole Indians in Florida refused to move west; they fought the Army for years in the Seminole Wars
.
After 1840 the abolitionist movement redefined itself as a crusade against the sin of slave ownership. It mobilized support (especially among religious women in the Northeast affected by the Second Great Awakening
). William Lloyd Garrison
published the most influential of the many anti-slavery newspapers, The Liberator, while Frederick Douglass
, an ex-slave, began writing for that newspaper around 1840 and started his own abolitionist newspaper North Star
in 1847. The great majority of anti-slavery elements rejected its moralism and held that slavery was an unfortunate social evil, not a sin.
The Republic of Texas was annexed
in 1845, which Mexico had warned meant war. The U.S. army, using regulars and large numbers of volunteers, easily won the Mexican-American War, 1846-48. Public sentiment in the U.S. was divided as Whigs and anti-slavery elements opposed the war. The 1848 Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo
ceded California, New Mexico, and adjacent areas to the United States, with the residents given full citizenship. Simultaneously gold was discovered, pulling over 100,000 men to northern California in a matter of months in the California Gold Rush
.
.png) The churches split on slavery, with the Methodists and Baptists dividing into northern and southern denominations. In the North, the Methodists, Congregationalists and Quakers included many abolitionists, especially among women activists. The Catholic, Episcopal and Lutheran denominations ignored the slavery issue.
The churches split on slavery, with the Methodists and Baptists dividing into northern and southern denominations. In the North, the Methodists, Congregationalists and Quakers included many abolitionists, especially among women activists. The Catholic, Episcopal and Lutheran denominations ignored the slavery issue.
The issue of slavery in the new territories was seemingly settled by the Compromise of 1850
brokered by Whig Henry Clay
and Democrat Stephen Douglas; the Compromise included admission of California
as a free state. The sore point was the Fugitive Slave Act to make it easier for masters to reclaim runaway slaves; with abolitionists used it to attack slavery, as in Uncle Tom's Cabin by Harriet Beecher Stowe
. The Compromise of 1820 was repealed in 1854 with the Kansas-Nebraska Act
, promoted by Senator Douglas in the name of "opular sovereignty" and democracy. It permitted settlers to decide on slavery in each territory, and allowed Douglas to say he was neutral on the slavery issue. Antislavery forces rose in anger and alarm, forming the new Republican Party. Pro and anti-forces rushed to Kansas to vote slavery up or down, resulting in a mini civil war called Bleeding Kansas
. By the late 1850s the young Republican Party dominated nearly all northern states and thus the electoral college, and insisted that slavery would never be allowed to expand (and thus would slowly die out).
By 1860, there were nearly four million slaves residing in the United States, nearly eight times as many from 1790; within the same time period, cotton
production in the U.S. boomed from less than a thousand tons to nearly one million tons per year. There were some slave rebellions—including by Gabriel Prosser
(1800), Denmark Vesey
(1822), and Nat Turner
(1831)—but they all failed and led to tighter slave oversight in the south and distrust of Yankees as abolitionists. The Supreme Court's 1857 decision in the Dred Scott Case took the Southern position of making slavery legal everywhere, which outraged northerners.
 After Abraham Lincoln
After Abraham Lincoln
won the 1860 election, eleven Southern states seceded from the union between late 1860 and 1861, establishing a new government, the Confederate States of America
, on February 8, 1861. Along with the northwestern portion of Virginia, which became West Virginia
, four of the five northernmost "slave states" did not secede and became known as the Border States.
began on April 12, 1861, when Confederate forces attacked a U.S. military installation
at Fort Sumter
in South Carolina
. In response to the attack, on April 15, Lincoln called on the states to send detachments totaling 75,000 troops to recapture forts, protect the capital, and "preserve the Union", which in his view still existed intact despite the actions of the seceding states. The two armies had their first major clash at the First Battle of Bull Run
, which ended in a surprising Union defeat, but, more importantly, proved to both the Union and Confederacy that the war was going to be much longer and bloodier than they had originally anticipated.
The war soon divided into two theaters: Eastern
and Western
. In the western theater, the Union was quite successful, with major battles, such as Perryville
, producing strategic Union victories and destroying major confederate operations.
 In the Eastern theater, things did not start well for the Union as the Confederates won at Manassas Junction (Bull Run), just outside Washington. Major General George B. McClellan
In the Eastern theater, things did not start well for the Union as the Confederates won at Manassas Junction (Bull Run), just outside Washington. Major General George B. McClellan
was put in charge of the Union armies. After reorganizing the new Army of the Potomac
, McClellan failed to capture the Confederate capital of Richmond, Virginia
in his Peninsula Campaign
and retreated after attacks from newly appointed Confederate General Robert E. Lee
.
Feeling confident in his army after defeating the Union at Second Bull Run, Lee embarked on an invasion of the north
that was stopped by McClellan at the bloody Battle of Antietam
. Despite this, McClellan was relieved from command for refusing to pursue Lee's crippled army. The next commander, General Ambrose Burnside
, suffered a humiliating defeat by Lee's smaller army at the Battle of Fredericksburg
late in 1862, causing yet another change in commanders. Lee won again at the Battle of Chancellorsville
in May 1863, while losing his top aide, Stonewall Jackson
. But Lee pushed too hard and ignored the Union threat in the west. Lee invaded Pennsylvania in search of supplies and to cause war weariness in the North. In perhaps the turning point of the war
, Lee's army was badly beaten at the Battle of Gettysburg
, July 1–3, 1863, and barely made it back to Virginia.
Simultaneously on July 4, 1863, Union forces under the command of General Ulysses S. Grant
gained control of the Mississippi River at the Battle of Vicksburg
, thereby splitting the Confederacy. Lincoln made General Grant commander of all Union armies.
The last two years of the war was bloody for both sides, with Grant launching a war of attrition
against General Lee's Army of Northern Virginia
. This war of attrition was divided into three main campaigns. The first of these, the Overland Campaign
forced Lee to retreat into the city of Petersburg where Grant launched his second major offensive, the Richmond-Petersburg Campaign in which he sieged Petersburg
. After a near ten-month siege, Petersburg surrendered. However, the defense of Fort Gregg allowed Lee to move his army out of Petersburg. Grant pursued and launched the final, Appomattox Campaign
which resulted in Lee surrendering his Army of Northern Virginia on April 9, 1865, at Appomattox Court House
. Other Confederate armies followed suit and the war ended.
Based on 1860 census
figures, about 8% of all white males aged 13 to 43 died in the war, including about 6% in the North and approximately 18% in the South, establishing the American Civil War as the deadliest war in American history. Its legacy includes ending slavery in the United States, restoring the Union, and strengthening the role of the federal government. The social, political, economic and racial issues of the war decisively shaped the Reconstruction era, which lasted through 1877, and brought about changes that would eventually help make the country a united superpower.
 Reconstruction took place for most of the decade following the Civil War. During this era, the "Reconstruction Amendments
Reconstruction took place for most of the decade following the Civil War. During this era, the "Reconstruction Amendments
" were passed to expand civil rights for black Americans. Those amendments included the Thirteenth Amendment
, which outlawed slavery, the Fourteenth Amendment
that guaranteed citizenship for all people born or naturalized within U.S. territory, and the Fifteenth Amendment
that granted the vote for all men regardless of race. While the Civil Rights Act of 1875
forbade discrimination in the service of public facilities, the Black Codes denied blacks privileges readily available to whites.
In response to Reconstruction, the Ku Klux Klan
(KKK) emerged around the late 1860s as a white-supremacist organization opposed to black civil rights. Congress passed the Ku Klux Klan Act of 1870 and vigorous enforcement closed down the Klan and classified the KKK as a terrorist group. However, an 1883 Supreme Court decision nullified the Civil Rights Act of 1875 and ended federal efforts to stop private acts of violence designed to suppress legal rights.
During the era, many regions of the southern U.S. were military-governed
and often corrupt; Reconstruction ended after the disputed 1876 election
between Republican candidate Rutherford B. Hayes
and Democratic candidate Samuel J. Tilden
. Hayes won the election, and the South soon re-entered the national political scene.
" was a term that Mark Twain
used to describe the period of the late 19th century when there had been a dramatic expansion of American wealth and prosperity. Reform of the Age included the Civil Service Act
, which mandated a competitive examination for applicants for government jobs. Other important legislation included the Interstate Commerce Act, which ended railroads' discrimination against small shippers, and the Sherman Antitrust Act
, which outlawed monopolies in business. Twain believed that this age was corrupted by such elements as land speculators, scandalous politics, and unethical business practices.
By 1890 American industrial production and per capita income
exceeded those of all other world nations. In response to heavy debts and decreasing farm prices, wheat and cotton farmers joined the Populist Party. An unprecedented wave of immigration
from Europe served to both provide the labor for American industry and create diverse communities in previously undeveloped areas. From 1880 to 1914, peak years of immigration, more than 22 million people migrated to the United States. The workers' demand for control of their workplace led to the often-violent rise of the labor movement in the cities and mining camps. Industrial leaders included John D. Rockefeller
in oil and Andrew Carnegie
in steel; both became leaders of philanthropy, giving away their fortunes to create the modern system of hospitals, universities, libraries and foundations.
 Dissatisfaction on the part of the growing middle class with the corruption and inefficiency of politics as usual, and the failure to deal with increasingly important urban and industrial problems, led to the dynamic Progressive Movement starting in the 1890s. In every major city and state, and at the national level as well, and in education, medicine, and industry, the progressives called for the modernization and reform of decrepit institutions, the elimination of corruption in politics, and the introduction of efficiency as a criterion for change. Leading politicians from both parties, most notably Theodore Roosevelt
Dissatisfaction on the part of the growing middle class with the corruption and inefficiency of politics as usual, and the failure to deal with increasingly important urban and industrial problems, led to the dynamic Progressive Movement starting in the 1890s. In every major city and state, and at the national level as well, and in education, medicine, and industry, the progressives called for the modernization and reform of decrepit institutions, the elimination of corruption in politics, and the introduction of efficiency as a criterion for change. Leading politicians from both parties, most notably Theodore Roosevelt
, Charles Evans Hughes
, and Robert LaFollette
on the Republican side, and William Jennings Bryan
on the Democratic side, took up the cause of progressive reform. Women became especially involved in demands for woman suffrage, prohibition, and better schools; their most prominent leader was Jane Addams
of Chicago. Progressives implemented anti-trust laws and regulated such industries of meat-packing, drugs, and railroads. Four new constitutional amendments—the Sixteenth
through Nineteenth
—resulted from progressive activism, bringing the federal income tax, direct election of Senators, prohibition, and woman suffrage. The Progressive Movement lasted through the 1920s; the most active period was 1900–1918.
. The "splendid little war", as one official called it, involved a series of quick American victories on land and at sea. At the Treaty of Paris
peace conference the United States acquired the Philippines
, Puerto Rico
, and Guam
. Cuba became an independent country, under close American tutelage. Although the war itself was widely popular, the peace terms proved controversial. William Jennings Bryan led his Democratic Party in opposition to control of the Philippines, which he denounced as imperialism unbecoming to American democracy. President William McKinley
defended the acquisition, and was riding high as the nation had returned to prosperity and felt triumphant in the war. McKinley easily defeated Bryan in a rematch in the 1900 presidential election
. After defeating an insurrection by Filipino nationalists, the United States engaged in a large-scale program to modernize the economy of the Philippines, and dramatically upgrade the public health facilities. By 1908, however, Americans lost interest in an empire, and turned their international attention to the Caribbean, and especially the building of the Panama Canal
. The canal opened in 1914, and increased trade with Japan and the rest of the Far East. A key innovation was the Open Door Policy
, whereby the imperial powers were given equal access to Chinese business, with no one of them allowed to take control of China.
raged in Europe from 1914, President Woodrow Wilson took full control of foreign policy, declaring neutrality but warning Germany that resumption unrestricted submarine warfare
against American ships would mean war. Germany decided to take the risk and try to win by cutting off Britain; the U.S. declared of war in April 1917. American money, food and munitions arrived quickly, but troops had to be drafted, trained; by summer 1918 American soldiers under General John J. Pershing
arrived at the rate of 10,000 a day, while Germany was unable to replace its losses. The result was Allied
victory in November 1918. President Woodrow Wilson
demanded Germany depose the Kaiser and accept his terms, the Fourteen Points
. Wilson dominated the 1919 Paris Peace Conference
but Germany was treated harshly by the Allies in the Treaty of Versailles
(1919) as Wilson put all his hopes in the new League of Nations
. Wilson refused to compromise with Senate Republicans over the issue of Congressional power to declare war, and the Senate rejected the Treaty and the League.
 The women's suffrage movement began with the 1848 Seneca Falls Convention
The women's suffrage movement began with the 1848 Seneca Falls Convention
, organized by Elizabeth Cady Stanton
and Lucretia Mott
, and the Declaration of Sentiments
demanding equal rights for women. Many of the activists became politically aware during the abolitionist movement. The women's rights campaign during "first-wave feminism
" was led by Mott, Stanton, Susan B. Anthony
, among many others. The movement reorganized after the Civil War, gaining experienced campaigners, many of whom had worked for prohibition in the Women's Christian Temperance Union. By the end of the 19th century a few western states had granted women full voting rights, though women had made significant legal victories, gaining rights in areas such as property and child custody.
Around 1912 the feminist movement
, which had grown sluggish, began to reawaken, putting an emphasis on its demands for equality and arguing that the corruption of American politics demanded purification by women, because men could not do that job. Protests became increasingly common as suffragette
Alice Paul
led parades through the capital and major cities. Paul split from the large National American Woman Suffrage Association
(NAWSA), which favored a more moderate approach and supported the Democratic Party and Woodrow Wilson, led by Carrie Chapman Catt
, and formed the more militant National Woman's Party
. Suffragists were arrested during their "Silent Sentinels
" pickets at the White House, the first time such a tactic was used, and were taken as political prisoner
s.
Finally, the suffragettes were ordered released from prison, and Wilson urged Congress to pass a Constitutional amendment enfranchising women. The old anti-suffragist argument that only men could fight a war, and therefore only men deserve the right to vote, was refuted by the enthusiastic participation of tens of thousands of American women on the home front in World War I. Across the world, grateful nations gave women the right to vote. Furthermore, most of the Western states had already given the women the right to vote in state and national elections, and the representatives from those states, including the first woman Jeannette Rankin
of Montana, demonstrated that woman suffrage was a success. The main resistance came from the south, where white leaders were worried about the threat of black women voting. Nevertheless Congress passed the Nineteenth Amendment
in 1919. It became constitutional law on August 26, 1920, after ratification by the 36th required state.
NAWSA became the League of Women Voters
and the National Woman's Party began lobbying for full equality and the Equal Rights Amendment
which would pass Congress during the second wave of the women's movement in 1972. Politicians responded to the new electorate by emphasizing issues of special interest to women, especially prohibition, child health, and world peace. The main surge of women voting came in 1928, when the big-city machines realized they needed the support of women to elect Al Smith
, while rural organizations mobilized women to support Prohibition and vote for Republican Herbert Hoover
.
 Following World War I, the U.S. grew steadily in stature as an economic and military world power. The United States Senate did not ratify the Treaty of Versailles
Following World War I, the U.S. grew steadily in stature as an economic and military world power. The United States Senate did not ratify the Treaty of Versailles
imposed by its Allies
on the defeated Central Powers
; instead, the United States chose to pursue unilateralism
, if not isolationism
. The aftershock of Russia's October Revolution
resulted in real fears of communism
in the United States, leading to a three-year Red Scare
. In 1918 the U.S. lost 675,000 people to the Spanish flu
pandemic
.
In 1920, the manufacture, sale, import and export of alcohol were prohibited by the Eighteenth Amendment
. Prohibition
encouraged illegal breweries and dealers to make substantial amounts of money selling alcohol illegally. The Prohibition ended in 1933, a failure. Additionally, the KKK re-formed during that decade and gathered nearly 4.5 million members by 1924, and the U.S. government passed the Immigration Act of 1924
restricting foreign immigration. The 1920s were also known as the Roaring Twenties
, due to the great economic prosperity during this period. Jazz
became popular among the younger generation, and thus was also called the Jazz Age
.
 During most of the 1920s, the United States enjoyed a period of unbalanced prosperity: farm prices and wages fell, while new industries and industrial profits grew. The boom was fueled by an inflated stock market
During most of the 1920s, the United States enjoyed a period of unbalanced prosperity: farm prices and wages fell, while new industries and industrial profits grew. The boom was fueled by an inflated stock market
, which later led to the Stock Market Crash
on October 29, 1929. This, along with many other economic factors
, triggered a worldwide depression known as the Great Depression
. During this time, the United States experienced deflation
, unemployment soared from 3% in 1929 to 25% in 1933, and manufacturing output collapsed by one-third.
In 1932, Democratic
presidential nominee Franklin D. Roosevelt
promised "a new deal
for the American people", a phrase that has endured as a label for his administration and its many domestic achievements. The desperate economic situation, along with the substantial Democratic victories in the 1932 elections, gave Roosevelt unusual influence over Congress in the "First Hundred Days" of his administration. He used his leverage to win rapid passage of a series of measures to create welfare programs and regulate the banking system, stock market, industry and agriculture, along with many other government efforts to end the Great Depression and reform the American economy. Some programs that were a part of Roosevelt's New Deal
include the Works Progress Administration
(WPA) relief program, the Social Security Act
, the Emergency Banking Act
, and the Economy Act
.
 In the Depression years the United States remained focused on domestic concerns while democracy declined across the world and many countries fell under the control of dictators. Imperial Japan
In the Depression years the United States remained focused on domestic concerns while democracy declined across the world and many countries fell under the control of dictators. Imperial Japan
asserted dominance in East Asia and in the Pacific. Nazi Germany
and Fascist Italy
militarized to and threatened conquests, while Britain and France attempted appeasement
to avert another war in Europe. U.S. legislation in the Neutrality Acts sought to avoid foreign conflicts; however policy clashed with increasing anti-Nazi feelings following the German invasion of Poland in September 1939 that started World War II
. Roosevelt positioned the U.S. as the "Arsenal of Democracy
" pledging full-scale financial and munitions support for the Allies—but no soldiers. Japan tried to neutralize America's power in the Pacific by attacking Pearl Harbor
on December 7, 1941, which catalyzed American support to enter the war and seek revenge.
The main contributions of the U.S. to the Allied war effort comprised money, industrial output, food, petroleum, technological innovation, and (especially 1944-45), soldiers. Much of the focus in Washington was maximizing the economic output of the nation. The overall result was a dramatic increase in GDP, the export of vast quantities of supplies to the Allies and to American forces overseas, the end of unemployment, and a rise in civilian consumption even as 40% of the GDP went to the war effort. This was achieved by tens of millions of workers moving from low-productivity occupations to high efficiency jobs, improvements in productivity through better technology and management, and the move into the active labor force of students, retired people, housewives, and the unemployed, and an increase in hours worked. It was exhausting; leisure activities declined sharply. People tolerated the extra work because of patriotism, the pay, and the confidence it was only "for the duration" and life would return to normal as soon as the war was won. Most durable goods became unavailable, and meat, clothing, and gasoline were tightly rationed. In industrial areas housing was in short supply as people doubled up and lived in cramped quarters. Prices and wages were controlled, and Americans saved a high portion of their incomes, which led to renewed growth after the war instead of a return to depression.
The Allies
--the U.S., Britain and the Soviet Union, as well as China, Canada and other countries—fought the Axis powers
of Germany, Italy, and Japan. The Allies saw Germany as the main threat, and gave highest priority to Europe. The U.S. dominated the war against Japan, and stopped Japanese expansion in the Pacific in 1942. After losing to the Japanese Pearl Harbor and in the Philippines, and drawing the Battle of the Coral Sea
(May 1942), the American Navy inflicted a decisive blow at Midway
(June 1942). American ground forces assisted in the North African Campaign
that eventually concluded with the collapse of Mussolini's fascist government in 1943, as Italy switched to the Allied side. A more significant European front was opened on D-Day
, June 6, 1944, in which American and Allied forces invaded Nazi-occupied France from Britain.
 On the home front
On the home front
, mobilization of the U.S. economy was managed by Roosevelt's War Production Board
. The wartime production boom led to full employment, wiping out this vestige of the Great Depression. Indeed, labor shortage
s encouraged industry to look for new sources of workers, finding new roles for women and blacks.
However the fervor also inspired anti-Japanese sentiment
, which responded by removing everyone of Japanese descent from the West Coast war zone
. Research and development
took flight as well, best seen in the Manhattan Project
, a secret effort to harness nuclear fission
to produce highly destructive atomic bombs.
The Allied pushed the Germans out of France, but faced an unexpected counterattack at the Battle of the Bulge
in December. The final German effort failed, and as 1945 opened Allied armies in East and West were converging on Berlin, as the Nazis hurriedly tried to kill the last remaining Jews. The western front stopped short, leaving Berlin
to the Soviets as the Nazi regime formally capitulated in May 1945, ending the war in Europe. Over in the Pacific, the U.S. implemented an island hopping strategy toward Tokyo
, establishing airfields for bombing runs against mainland Japan from the Mariana Islands
and achieving hard-fought victories at Iwo Jima
and Okinawa
in 1945. Bloodied at Okinawa, the U.S. prepared to invade Japan's home islands when B-29's dropped two atomic bombs on Japanese cities
, forcing the empire's surrender in a matter of days and thus ending World War II. The U.S. occupied Japan (and part of Germany), sending Douglas MacArthur
to restructure the Japanese economy and political system along American lines.
Though the nation lost more than 400,000 soldiers, the mainland prospered untouched by the devastation of war that inflicted a heavy toll on Europe and Asia.
Participation in postwar foreign affairs marked the end of predominant American isolationism. The awesome threat of nuclear weapons inspired both optimism
and fear
. Nuclear weapons were never used after 1945, as both sides drew back from the brink and a "long peace" characterized the Cold War
years, 1947–1991. There were, however, regional wars in Korea and Vietnam.
 Following World War II, the United States emerged as one of the two dominant superpower
Following World War II, the United States emerged as one of the two dominant superpower
s. The U.S. Senate on a bipartisan vote approved U.S. participation in the United Nations
(UN), which marked a turn away from the traditional isolationism
of the U.S. and toward increased international involvement.
The primary American goal of 1945–48 was to rescue Europe from the devastation of World War II and to contain the expansion of Communism
, represented by the Soviet Union
. The Truman Doctrine
of 1947 provided military and economic aid to Greece and Turkey to counteract the threat of Communist expansion in the Balkans. In 1948, the United States replaced piecemeal financial aid programs with a comprehensive Marshall Plan
, which pumped money into the economy of Western Europe, and removed trade barriers, while modernizing the managerial practices of businesses and governments. The Plan's $13 billion budget was in the context of a U.S. GDP of $258 billion in 1948, and was on top of $12 billion in American aid to Europe between the end of the war and the start of the Marshall Plan. Soviet head of state Joseph Stalin
prevented his satellites from participating, and from that point on Eastern Europe, with inefficient centralized economies, fell further and further behind Western Europe in terms of economic development and prosperity. In 1949, the United States, rejecting the long-standing policy of no military alliances in peacetime, formed the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) alliance, which continues into the 21st century. In response the Soviets formed the Warsaw Pact
of communist states.
In August 1949 the Soviets tested their first nuclear weapon, thereby escalating the risk of warfare. Indeed, the threat of mutually assured destruction prevented both powers from going too far, and resulted in proxy wars, especially in Korea
and Vietnam
, in which the two sides did not directly confront each other. Within the United States, the Cold War prompted concerns about Communist influence. The unexpected leapfrogging of American technology by the Soviets in 1957 with Sputnik, the first Earth satellite, began the Space Race
, won by the Americans as Apollo 11
landed astronauts on the moon in 1969. The angst about the weaknesses of American education led to large-scale federal support for science education and research.
In the decades after World War II, the United States became a global influence in economic, political, military, cultural, and technological affairs. Beginning in the 1950s, middle-class culture became obsessed with consumer goods. White Americans made up nearly 90% of the population in 1950.
In 1960
, the charismatic politician John F. Kennedy
was elected as the first and—thus far—only Roman Catholic President of the United States. The Kennedy family brought a new life and vigor to the atmosphere of the White House
. His time in office was marked by such notable events as the acceleration of the United States' role in the Space Race
; escalation of the American role in the Vietnam War
; the Cuban missile crisis
; the Bay of Pigs Invasion
; the jailing of Martin Luther King, Jr.
during the Birmingham campaign
; and the appointment of his brother Robert F. Kennedy
to his Cabinet as Attorney General
. Kennedy was assassinated
in Dallas, Texas
, on November 22, 1963, leaving the nation in profound shock.
(1963–69) in securing congressional passage of his Great Society
programs, including civil rights, the end of segregation
, Medicare
, extension of welfare
, federal aid to education at all levels, subsidies for the arts and humanities, environmental activism, and a series of programs designed to wipe out poverty. As recent historians have explained:
Johnson was rewarded with an electoral landslide in 1964
against conservative Barry Goldwater
, which broke the decades-long control of Congress by the Conservative coalition
. But the Republicans bounced back in 1966 and elected Richard Nixon
in 1968. Nixon largely continued the New Deal and Great Society programs he inherited; conservative reaction would come with the election of Ronald Reagan
in 1980.
Meanwhile, the American people completed a great migration from farms into the cities and experienced a period of sustained economic expansion. At the same time, institutionalized racism across the United States
, but especially in the South
, was increasingly challenged by the growing Civil Rights movement. The activism of African American
leaders Rosa Parks
and Martin Luther King, Jr.
led to the Montgomery Bus Boycott
, which launched the movement. For years African Americans would struggle with violence against them, but would achieve great steps towards equality with Supreme Court decisions, including Brown v. Board of Education
and Loving v. Virginia
, the Civil Rights Act of 1964
, the Voting Rights Act of 1965, and the Fair Housing Act of 1968, which ended the Jim Crow laws
that legalized racial segregation
between Whites and Blacks.
Martin Luther King, Jr., who had won the Nobel Peace Prize
for his efforts to achieve equality of the races, was assassinated in 1968. Following his death others led the movement, most notably King's widow, Coretta Scott King
, who was also active, like her husband, in the Opposition to the Vietnam War
, and in the Women's Liberation Movement. Over the first nine months of 1967, 128 American cities suffered 164 riot
s. The late 1960s and early 1970s saw the strengthening of Black Power
, however the decade would ultimately bring about positive strides toward integration.
 A new consciousness of the inequality of American women began sweeping the nation, starting with the 1963 publication of Betty Friedan
A new consciousness of the inequality of American women began sweeping the nation, starting with the 1963 publication of Betty Friedan
's best-seller, The Feminine Mystique
, which explained how many housewives felt trapped and unfulfilled, assaulted American culture for its creation of the notion that women could only find fulfillment through their roles as wives, mothers, and keepers of the home, and argued that women were just as able as men to do every type of job. In 1966 Friedan and others established the National Organization for Women
, or NOW, to act for women as the NAACP did for African Americans.
Protests began, and the new Women's Liberation Movement grew in size and power, gained much media attention, and, by 1968, had replaced the Civil Rights Movement as the U.S.'s main social revolution. Marches, parades, rallies, boycotts, and pickets brought out thousands, sometimes millions; Friedan's Women's Strike for Equality
(1970) was a nation-wide success. The Movement was split into factions by political ideology early on, however (with NOW on the left, the Women's Equity Action League
(WEAL) on the right, the National Women's Political Caucus
(NWPC) in the center, and more radical groups formed by younger women on the far left).
Along with Friedan, Gloria Steinem
was an important feminist leader, co-founding the NWPC, the Women's Action Alliance
, and editing the Movement's magazine, Ms. The proposed Equal Rights Amendment
to the Constitution, passed by Congress in 1972 and favored by about seventy percent of the American public, failed to be ratified in 1982, with only three more states needed to make it law. The nation's conservative women, led by activist Phyllis Schlafly
, defeated the ERA by arguing that it degraded the position of the housewife, and made young women susceptible to the military draft
.
However, many federal laws (i.e. those equalizing pay, employment, education
, employment opportunities, credit
, ending pregnancy discrimination, and requiring NASA
, the Military Academies, and other organizations to admit women), state laws (i.e. those ending spousal abuse and marital rape
), Supreme Court rulings (i.e. ruling the equal protection clause of the Fourteenth Amendment applied to women), and state ERAs established women's equal status under the law, and social custom and consciousness began to change, accepting women's equality. The controversial issue of abortion
, deemed by the Supreme Court as a fundamental right in Roe v. Wade
(1973), is still a point of debate
today.
Amid the Cold War, the United States entered the Vietnam War
, whose growing unpopularity fed already existing social movements, including those among women, minorities and young people. President Lyndon B. Johnson
's Great Society
social programs and numerous rulings by the Warren Court
added to the wide range of social reform during the 1960s and 1970s. Feminism
and the environmental movement became political forces, and progress continued toward civil rights
for all Americans. The Counterculture Revolution
swept through the nation and much of the western world in the late sixties and early seventies, dividing the already hostile environment but also bringing forth more liberated social views.
Johnson was succeeded in 1969 by Republican Richard Nixon
, who turned the war over to the South Vietnamese forces and ended American combat roles; he negotiated a peace treaty in 1973
, secured the release of POWs and ended the draft. The war had cost the lives of 58,000 American troops. Nixon manipulated the fierce distrust between the Soviet Union and China to the advantage of the United States, achieving détente
(cooperation) with both parties. The Watergate scandal
, involving Nixon's cover-up of his operatives break-in into the Democratic National Committee
headquarters at the Watergate office complex
destroyed his political base, sent many aides to prison, and forced Nixon's resignation on August 9, 1974. He was succeeded by Vice President Gerald Ford
, who was subsequently helpless to prevent the conquest of South Vietnam when North Vietnam invaded in 1975.
The OPEC oil embargo
marked a long-term economic transition, as for the first time energy prices skyrocketed and American factories faced serious competition from foreign automobiles, clothing, electronics and consumer goods. By the late 1970s the economy suffered an energy crisis
, slow economic growth, high unemployment, and very high inflation coupled with high interest rates (the term stagflation
was coined). While economists agreed on the wisdom of deregulation
, many of the New Deal era regulations were ended, as in transportation, banking and telecommunications.
Jimmy Carter
, running as someone who was not a part of the Washington political establishment, was elected president in 1976. On the world stage, Carter brokered the Camp David Accords
between Israel and Egypt. In 1979, Iranian students stormed the U.S. embassy in Tehran
and took 66 Americans hostage, resulting in the Iran hostage crisis
. With the hostage crisis and continuing stagflation, Carter lost the 1980 election
to the Republican Ronald Reagan
. On January 20, 1981, minutes after Carter's term in office ended, the remaining U.S. captives held at the U.S. embassy in Iran were released, ending the 444-day hostage crisis.
 Ronald Reagan
Ronald Reagan
produced a major realignment
with his 1980 and 1984 landslide elections. Reagan's economic policies (dubbed "Reaganomics
") and the implementation of the Economic Recovery Tax Act of 1981 lowered income taxes from 70% to 28% over the course of seven years. Reagan continued to downsize government taxation and regulation. The U.S. experienced a recession in 1982 but the negative indicators reversed, as the inflation rate decreased from 11% to 2%, the unemployment rate decreased from 10.8% in December 1982 to 7.5% in November 1984, and the economic growth rate increased from 4.5% to 7.2%.
Reagan ordered a massive buildup of the U.S. military, incurring a costly budget deficit. Reagan introduced a complicated missile defense system known as the Strategic Defense Initiative
(dubbed "Star Wars" by opponents) in which, theoretically, the U.S. could shoot down missiles with laser systems in space. Though it was never fully developed or deployed, the Soviets were genuinely concerned about the possible effects of the program and the research and technologies of SDI paved the way for the anti-ballistic missile systems of today.
The Reagan administration also provided covert funding and assistance to anti-Communist resistance movements worldwide. Reagan's interventions against Grenada and Libya were popular in the U.S., though his backing of the Contra rebels was mired in controversy. The arms-for-hostages scandal led to the convictions of such figures as Oliver North
and John Poindexter
.
Reagan met four times with Soviet leader Mikhail Gorbachev
, who ascended to power in 1985, and their summit conferences led to the signing of the Intermediate-Range Nuclear Forces Treaty
. Gorbachev tried to save Communism in the Soviet Union first by ending the expensive arms race with America, then by shedding the East European empire in 1989. The Soviet Union collapsed
in 1991, ending the U.S.–Soviet Cold War
.
 The United States emerged as the world's sole remaining superpower
The United States emerged as the world's sole remaining superpower
and continued to intervene in international affairs during the 1990s, including the 1991 Gulf War
against Iraq
. Following his election in 1992
, President Bill Clinton
oversaw one of the longest periods of economic expansion and unprecedented gains in securities values, a side effect of the digital revolution
and new business opportunities created by the Internet
. He also worked with the Republican Congress to pass the first balanced federal budget in 30 years. In 1998, Clinton was impeached
by the House of Representatives on charges of "high crimes and misdemeanors" for lying about a sexual relationship with White House intern Monica Lewinsky
, but was later acquitted by the Senate. The failure of impeachment and the Democratic gains in the 1998 election forced House Speaker Newt Gingrich
, a Republican, to resign from Congress.
The presidential election in 2000
between George W. Bush
and Al Gore
was one of the closest in U.S. history, and helped lay the seeds for political polarization to come. The vote in the decisive state of Florida was extremely close and produced a dramatic dispute over the counting of votes
. The U.S. Supreme Court in Bush v. Gore
ended the recount with a 5–4 vote. That meant Bush, then in the lead, carried Florida and the election.
 Once again the United States was attacked by terrorism
Once again the United States was attacked by terrorism
with the September 11, 2001 attacks
(9/11) in which al-Qaeda
terrorists hijacked four transcontinental airliners and intentionally crashed two of them into the twin towers of the World Trade Center
and one into the Pentagon
killing 3,000 people. President George W. Bush
announced a "War on Terror
" in response. The United States and NATO launched an invasion of Afghanistan
to overthrow the Taliban regime that had harbored al-Qaeda and its leader Osama bin Laden
. The federal government established new domestic efforts to prevent future attacks. The controversial USA PATRIOT Act
increased government's power to monitor communications and removed legal restrictions on information sharing between federal law enforcement and intelligence services. A cabinet-level agency called the Department of Homeland Security
was created to lead and coordinate federal counter-terrorism
activities. Some of these anti-terrorism efforts, particularly the U.S. government's handling of detainees at the prison at Guantanamo Bay, led to allegations toward the U.S. government of human rights violations.
In 2003, the United States launched an invasion of Iraq
, which led to the collapse of the Iraqi government and the eventual capture of Iraqi dictator Saddam Hussein
, with whom the U.S. had long-standing tense relations. The reasons for the invasion cited by the Bush administration included the spreading of democracy, the elimination of weapons of mass destruction
(a key demand of the UN as well, though later investigations found parts of the intelligence reports to be inaccurate) and the liberation of the Iraqi people. The invasion and continued Iraq War fueled international protests
and gradually saw domestic support waver, despite initial successes early in the invasion. In 2007, after years of violence by the Iraqi insurgency
, President Bush deployed more troops in a strategy dubbed "the surge
". While the death toll decreased, the political stability of Iraq remained in doubt.
In 2008, the unpopularity of President Bush and the Iraq war, along with the 2008 financial crisis, led to the election of Barack Obama
, the first African American
President of the United States. After he took office, Obama began to decrease troop levels in Iraq, and officially ended combat operations in the country on August 31, 2010. At the same time, he kept 50,000 in Iraq to assist Iraqi forces, help protect withdrawing forces, and work on counter-terrorism until December 31, 2011, the date Bush scheduled for the full withdrawal. Obama increased American involvement in Afghanistan, starting a surge strategy using an additional 30,000 troops, while proposing to begin withdrawing troops in July 2011. In May 2011, after nearly a decade in hiding, Osama bin Laden
was killed by U.S. armed forces acting under President Obama's direct orders.
 In December 2007, the United States, and most of Europe, entered the longest post–World War II recession, which included a housing market crisis
In December 2007, the United States, and most of Europe, entered the longest post–World War II recession, which included a housing market crisis
, a subprime mortgage crisis
, soaring oil prices, an automotive industry crisis, rising unemployment, and the worst financial crisis since the Great Depression
. The financial crisis hit a critical point in September 2008 when Lehman Brothers
and other important financial institutions failed. Starting the following month the federal government lent $245 billion to financial institutions through the Troubled Asset Relief Program which was signed into law under the Bush administration. Shortly after taking office, Obama signed into law a $787 billion economic stimulus package
aimed at helping the economy recover from the deepening recession. In addition to the economic stimulus, the government took steps to rescue the auto industry and prevent future economic meltdowns. These included a bailout of General Motors
and Chrysler
, putting ownership temporarily in the hands of the government, and the "cash for clunkers" program which temporarily boosted new car sales. Congress enacted the Dodd–Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act, a bill that makes sweeping changes to the financial regulatory system. The recession officially ended in June 2009 as the U.S. economy began to expand once again; however the unemployment rate has continued to linger near 9% and above into 2011.
In the 111th Congress
Democratic legislative initiatives ran into strong Republican opposition. National debates emerged over numerous issues such as health care reform
, which was rekindled by the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act
. In the 2010 midterm elections
, the Republicans regained control of the House and installed John Boehner
as Speaker. They also made some gains in the Senate. A factor in these results was the conservative Tea Party movement
that has promoted political candidates and protests, and has called for significant reductions in taxes and spending. On August 2, 2011, after a lengthy congressional debate over whether to raise the nation's debt limit, Congress passed the bipartisan Budget Control Act of 2011
. The legislation enforces limits on discretionary spending until 2021, establishes a procedure to increase the debt limit, creates a two-party Congressional Joint Select Committee on Deficit Reduction to propose further deficit reduction with a stated goal of achieving at least $1.5 trillion in budgetary savings over 10 years, and establishes automatic procedures for reducing spending by as much as $1.2 trillion if legislation originating with the new joint select committee does not achieve such savings. By passing the legislation, Congress was able to prevent an unprecedented U.S. government default on its obligations, though credit ratings agency Standard & Poor's still lowered the ratings on America's long term debt to AA+, reasoning that the political blockage endangered future debt payments and that the legislation fell short of what would be necessary to stabilize the country's growing national debt.
As of November 2011, debates continue over the economy, the 9% unemployment rate, deficit spending, health care reform
, the financial crisis in state government, the role of corporate spending in election campaigns, and U.S. involvement in Afghanistan
.
Lists:
Timelines:
United States Declaration of Independence
The Declaration of Independence was a statement adopted by the Continental Congress on July 4, 1776, which announced that the thirteen American colonies then at war with Great Britain regarded themselves as independent states, and no longer a part of the British Empire. John Adams put forth a...
in the year 1776, although its territory was inhabited by Native Americans
Native Americans in the United States
Native Americans in the United States are the indigenous peoples in North America within the boundaries of the present-day continental United States, parts of Alaska, and the island state of Hawaii. They are composed of numerous, distinct tribes, states, and ethnic groups, many of which survive as...
since prehistoric times and then by European colonists
European colonization of the Americas
The start of the European colonization of the Americas is typically dated to 1492. The first Europeans to reach the Americas were the Vikings during the 11th century, who established several colonies in Greenland and one short-lived settlement in present day Newfoundland...
who followed the voyages of Christopher Columbus
Voyages of Christopher Columbus
In the early modern period, the voyages of Columbus initiated European exploration and colonization of the American continents, and are thus of great significance in world history. Christopher Columbus was a navigator and an admiral for Castile, a country that later founded modern Spain...
starting in 1492. The largest settlements were by the English on the East Coast, starting in 1607. By the 1770s the Thirteen Colonies
Thirteen Colonies
The Thirteen Colonies were English and later British colonies established on the Atlantic coast of North America between 1607 and 1733. They declared their independence in the American Revolution and formed the United States of America...
contained two and half million people, were prosperous, and had developed their own political and legal systems. The British government's threat to American self-government led to war in 1775 and the Declaration of Independence in 1776. With major military and financial support from France, the patriots won the American Revolution
American Revolution
The American Revolution was the political upheaval during the last half of the 18th century in which thirteen colonies in North America joined together to break free from the British Empire, combining to become the United States of America...
. In 1789 the Constitution
United States Constitution
The Constitution of the United States is the supreme law of the United States of America. It is the framework for the organization of the United States government and for the relationship of the federal government with the states, citizens, and all people within the United States.The first three...
became the basis for the United States federal government, with war hero George Washington
George Washington
George Washington was the dominant military and political leader of the new United States of America from 1775 to 1799. He led the American victory over Great Britain in the American Revolutionary War as commander-in-chief of the Continental Army from 1775 to 1783, and presided over the writing of...
as the first president. The young nation continued to struggle with the scope of central government and with European influence, creating the first political parties in the 1790s
First Party System
The First Party System is a model of American politics used by political scientists and historians to periodize the political party system existing in the United States between roughly 1792 and 1824. It featured two national parties competing for control of the presidency, Congress, and the states:...
, and fighting a second war for independence in 1812
War of 1812
The War of 1812 was a military conflict fought between the forces of the United States of America and those of the British Empire. The Americans declared war in 1812 for several reasons, including trade restrictions because of Britain's ongoing war with France, impressment of American merchant...
.
U.S. territory expanded westward across the continent, brushing aside Native Americans and Mexico, and overcoming modernizers who wanted to deepen the economy rather than expand the geography. Slavery of Africans was abolished in the North, but heavy world demand for cotton let it flourish in the Southern states
Southern United States
The Southern United States—commonly referred to as the American South, Dixie, or simply the South—constitutes a large distinctive area in the southeastern and south-central United States...
. The 1860 election of Abraham Lincoln
Abraham Lincoln
Abraham Lincoln was the 16th President of the United States, serving from March 1861 until his assassination in April 1865. He successfully led his country through a great constitutional, military and moral crisis – the American Civil War – preserving the Union, while ending slavery, and...
calling for no more expansion of slavery triggered a crisis as eleven slave states seceded to found the Confederate States of America
Confederate States of America
The Confederate States of America was a government set up from 1861 to 1865 by 11 Southern slave states of the United States of America that had declared their secession from the U.S...
in 1861. The bloody American Civil War
American Civil War
The American Civil War was a civil war fought in the United States of America. In response to the election of Abraham Lincoln as President of the United States, 11 southern slave states declared their secession from the United States and formed the Confederate States of America ; the other 25...
(1861–65) redefined the nation and remains the central iconic event. The South was defeated and, in the Reconstruction era, the U.S. ended slavery, extended rights to African American
African American
African Americans are citizens or residents of the United States who have at least partial ancestry from any of the native populations of Sub-Saharan Africa and are the direct descendants of enslaved Africans within the boundaries of the present United States...
s, and readmitted secessionist states with loyal governments. The national government was much stronger, and it now had the explicit duty to protect individuals. Reconstruction was never completed by the US government and left the blacks in a world of Jim Crow political, social and economic inferiority. The entire South remained poor while the North and West grew rapidly.
Thanks to an outburst of entrepreneurship in the North and the arrival of millions of immigrant workers from Europe, the U.S. became the leading industrialized power by 1900. Disgust with corruption, waste, and traditional politics stimulated the Progressive movement
Progressive Era
The Progressive Era in the United States was a period of social activism and political reform that flourished from the 1890s to the 1920s. One main goal of the Progressive movement was purification of government, as Progressives tried to eliminate corruption by exposing and undercutting political...
, 1890s-1920s, which pushed for reform in industry and politics and put into the Constitution women's suffrage and Prohibition
Prohibition in the United States
Prohibition in the United States was a national ban on the sale, manufacture, and transportation of alcohol, in place from 1920 to 1933. The ban was mandated by the Eighteenth Amendment to the Constitution, and the Volstead Act set down the rules for enforcing the ban, as well as defining which...
of alcohol (the latter repealed in 1933). Initially neutral in World War I
American entry into World War I
American entry into World War I came in April 1917, after 2½ years of efforts by President Woodrow Wilson to keep the United States neutral. Americans had no idea that a war was approaching in 1914...
, the U.S. declared war on Germany in 1917, and funded the Allied victory. The nation refused to follow President Woodrow Wilson
Woodrow Wilson
Thomas Woodrow Wilson was the 28th President of the United States, from 1913 to 1921. A leader of the Progressive Movement, he served as President of Princeton University from 1902 to 1910, and then as the Governor of New Jersey from 1911 to 1913...
's leadership and never joined the League of Nations
League of Nations
The League of Nations was an intergovernmental organization founded as a result of the Paris Peace Conference that ended the First World War. It was the first permanent international organization whose principal mission was to maintain world peace...
. After a prosperous decade in the 1920s the Wall Street Crash of 1929
Wall Street Crash of 1929
The Wall Street Crash of 1929 , also known as the Great Crash, and the Stock Market Crash of 1929, was the most devastating stock market crash in the history of the United States, taking into consideration the full extent and duration of its fallout...
marked the onset of the decade-long world-wide Great Depression
Great Depression in the United States
The Great Depression began with the Wall Street Crash of October, 1929 and rapidly spread worldwide. The market crash marked the beginning of a decade of high unemployment, poverty, low profits, deflation, plunging farm incomes, and lost opportunities for economic growth and personal advancement...
. A political realignment expelled the Republicans from power and installed Democrat Franklin D. Roosevelt
Franklin D. Roosevelt
Franklin Delano Roosevelt , also known by his initials, FDR, was the 32nd President of the United States and a central figure in world events during the mid-20th century, leading the United States during a time of worldwide economic crisis and world war...
and his elaborate and expensive New Deal
New Deal
The New Deal was a series of economic programs implemented in the United States between 1933 and 1936. They were passed by the U.S. Congress during the first term of President Franklin D. Roosevelt. The programs were Roosevelt's responses to the Great Depression, and focused on what historians call...
programs for relief, recovery, and reform. Roosevelt's Democratic coalition
New Deal coalition
The New Deal Coalition was the alignment of interest groups and voting blocs that supported the New Deal and voted for Democratic presidential candidates from 1932 until the late 1960s. It made the Democratic Party the majority party during that period, losing only to Dwight D. Eisenhower in 1952...
, comprising ethnics in the north, labor unions, big-city machines, intellectuals, and the white South, dominated national politics into the 1960s. After the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor
Attack on Pearl Harbor
The attack on Pearl Harbor was a surprise military strike conducted by the Imperial Japanese Navy against the United States naval base at Pearl Harbor, Hawaii, on the morning of December 7, 1941...
in December 1941, the U.S. entered World War II
World War II
World War II, or the Second World War , was a global conflict lasting from 1939 to 1945, involving most of the world's nations—including all of the great powers—eventually forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis...
alongside the Allies
Allies of World War II
The Allies of World War II were the countries that opposed the Axis powers during the Second World War . Former Axis states contributing to the Allied victory are not considered Allied states...
and helped defeat Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany , also known as the Third Reich , but officially called German Reich from 1933 to 1943 and Greater German Reich from 26 June 1943 onward, is the name commonly used to refer to the state of Germany from 1933 to 1945, when it was a totalitarian dictatorship ruled by...
in Europe and, with the detonation of newly-invented atomic bombs, Japan
Empire of Japan
The Empire of Japan is the name of the state of Japan that existed from the Meiji Restoration on 3 January 1868 to the enactment of the post-World War II Constitution of...
in Asia and the Pacific.
The Soviet Union
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union , officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics , was a constitutionally socialist state that existed in Eurasia between 1922 and 1991....
and the U.S. emerged as opposing superpower
Superpower
A superpower is a state with a dominant position in the international system which has the ability to influence events and its own interests and project power on a worldwide scale to protect those interests...
s after the war and began the Cold War
Cold War
The Cold War was the continuing state from roughly 1946 to 1991 of political conflict, military tension, proxy wars, and economic competition between the Communist World—primarily the Soviet Union and its satellite states and allies—and the powers of the Western world, primarily the United States...
confronting indirectly in an arms race
Arms race
The term arms race, in its original usage, describes a competition between two or more parties for the best armed forces. Each party competes to produce larger numbers of weapons, greater armies, or superior military technology in a technological escalation...
, the Space Race
Space Race
The Space Race was a mid-to-late 20th century competition between the Soviet Union and the United States for supremacy in space exploration. Between 1957 and 1975, Cold War rivalry between the two nations focused on attaining firsts in space exploration, which were seen as necessary for national...
, and intervention in Europe and eastern Asia. Liberalism
Liberalism in the United States
Liberalism in the United States is a broad political philosophy centered on the unalienable rights of the individual. The fundamental liberal ideals of freedom of speech, freedom of the press, freedom of religion for all belief systems, and the separation of church and state, right to due process...
reflected in the civil rights movement
Civil rights movement
The civil rights movement was a worldwide political movement for equality before the law occurring between approximately 1950 and 1980. In many situations it took the form of campaigns of civil resistance aimed at achieving change by nonviolent forms of resistance. In some situations it was...
and opposition to war in Vietnam peaked in the 1960s–70s before giving way to conservatism in the early 1980s. The Cold War ended when the Soviet Union dissolved
Dissolution of the Soviet Union
The dissolution of the Soviet Union was the disintegration of the federal political structures and central government of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics , resulting in the independence of all fifteen republics of the Soviet Union between March 11, 1990 and December 25, 1991...
in 1991, leaving the U.S. to prosper in the booming Information Age
Information Age
The Information Age, also commonly known as the Computer Age or Digital Age, is an idea that the current age will be characterized by the ability of individuals to transfer information freely, and to have instant access to knowledge that would have been difficult or impossible to find previously...
economy that was boosted, at least in part, by information technology
Information technology
Information technology is the acquisition, processing, storage and dissemination of vocal, pictorial, textual and numerical information by a microelectronics-based combination of computing and telecommunications...
. International conflict and economic uncertainty heightened by 2001 with the September 11 attacks and subsequent War on Terror
War on Terror
The War on Terror is a term commonly applied to an international military campaign led by the United States and the United Kingdom with the support of other North Atlantic Treaty Organisation as well as non-NATO countries...
and the late-2000s recession.
Pre-Columbian era
It is not definitively known how or when the Native AmericansNative Americans in the United States
Native Americans in the United States are the indigenous peoples in North America within the boundaries of the present-day continental United States, parts of Alaska, and the island state of Hawaii. They are composed of numerous, distinct tribes, states, and ethnic groups, many of which survive as...
first settled the Americas and the present-day United States. The prevailing theory proposes that people migrated from Eurasia
Eurasia
Eurasia is a continent or supercontinent comprising the traditional continents of Europe and Asia ; covering about 52,990,000 km2 or about 10.6% of the Earth's surface located primarily in the eastern and northern hemispheres...
across Beringia, a land bridge
Land bridge
A land bridge, in biogeography, is an isthmus or wider land connection between otherwise separate areas, over which animals and plants are able to cross and colonise new lands...
that connected Siberia
Siberia
Siberia is an extensive region constituting almost all of Northern Asia. Comprising the central and eastern portion of the Russian Federation, it was part of the Soviet Union from its beginning, as its predecessor states, the Tsardom of Russia and the Russian Empire, conquered it during the 16th...
to present-day Alaska
Alaska
Alaska is the largest state in the United States by area. It is situated in the northwest extremity of the North American continent, with Canada to the east, the Arctic Ocean to the north, and the Pacific Ocean to the west and south, with Russia further west across the Bering Strait...
, and then spread southward throughout the Americas. This migration might have begun as early as 30,000 years ago and continued through to about 10,000 years ago, when the land bridge became submerged by the rising sea level caused by the ending of the last glacial period. These early inhabitants, called Paleoamericans, soon diversified into many hundreds of culturally distinct nations and tribes.
The pre-Columbian era
Pre-Columbian era
The pre-Columbian era incorporates all period subdivisions in the history and prehistory of the Americas before the appearance of significant European influences on the American continents, spanning the time of the original settlement in the Upper Paleolithic period to European colonization during...
incorporates all period subdivisions
Archaeology of the Americas
The archaeology of the Americas is the study of the archaeology of North America , Central America, South America and the Caribbean...
in the history and prehistory of the Americas
History of the Americas
The history of the Americas is the collective history of the American landmass, which includes North and South America, as well as Central America and the Caribbean. It begins with people migrating to these areas from Asia during the height of an Ice Age...
before the appearance of significant Europe
Europe
Europe is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting...
an influences on the American
Americas
The Americas, or America , are lands in the Western hemisphere, also known as the New World. In English, the plural form the Americas is often used to refer to the landmasses of North America and South America with their associated islands and regions, while the singular form America is primarily...
continents, spanning the time of the original settlement in the Upper Paleolithic
Upper Paleolithic
The Upper Paleolithic is the third and last subdivision of the Paleolithic or Old Stone Age as it is understood in Europe, Africa and Asia. Very broadly it dates to between 40,000 and 10,000 years ago, roughly coinciding with the appearance of behavioral modernity and before the advent of...
period to European colonization
European colonization of the Americas
The start of the European colonization of the Americas is typically dated to 1492. The first Europeans to reach the Americas were the Vikings during the 11th century, who established several colonies in Greenland and one short-lived settlement in present day Newfoundland...
during the Early Modern period
Early modern period
In history, the early modern period of modern history follows the late Middle Ages. Although the chronological limits of the period are open to debate, the timeframe spans the period after the late portion of the Middle Ages through the beginning of the Age of Revolutions...
. While technically referring to the era before Christopher Columbus
Christopher Columbus
Christopher Columbus was an explorer, colonizer, and navigator, born in the Republic of Genoa, in northwestern Italy. Under the auspices of the Catholic Monarchs of Spain, he completed four voyages across the Atlantic Ocean that led to general European awareness of the American continents in the...
' voyages of 1492 to 1504, in practice the term usually includes the history of American indigenous cultures
Indigenous peoples of the Americas
The indigenous peoples of the Americas are the pre-Columbian inhabitants of North and South America, their descendants and other ethnic groups who are identified with those peoples. Indigenous peoples are known in Canada as Aboriginal peoples, and in the United States as Native Americans...
until they were conquered or significantly influenced by Europeans, even if this happened decades or even centuries after Columbus' initial landing.
Colonial period

Spain
Spain , officially the Kingdom of Spain languages]] under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, Spain's official name is as follows:;;;;;;), is a country and member state of the European Union located in southwestern Europe on the Iberian Peninsula...
, Dutch
Netherlands
The Netherlands is a constituent country of the Kingdom of the Netherlands, located mainly in North-West Europe and with several islands in the Caribbean. Mainland Netherlands borders the North Sea to the north and west, Belgium to the south, and Germany to the east, and shares maritime borders...
, English
Kingdom of England
The Kingdom of England was, from 927 to 1707, a sovereign state to the northwest of continental Europe. At its height, the Kingdom of England spanned the southern two-thirds of the island of Great Britain and several smaller outlying islands; what today comprises the legal jurisdiction of England...
, French
France
The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
, Swedish
Sweden
Sweden , officially the Kingdom of Sweden , is a Nordic country on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. Sweden borders with Norway and Finland and is connected to Denmark by a bridge-tunnel across the Öresund....
, and Portuguese
Portugal
Portugal , officially the Portuguese Republic is a country situated in southwestern Europe on the Iberian Peninsula. Portugal is the westernmost country of Europe, and is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the West and South and by Spain to the North and East. The Atlantic archipelagos of the...
settlements were established. In the 16th century, Europeans brought horses, cattle, and hogs to the Americas and, in turn, took back to Europe maize, potato
Potato
The potato is a starchy, tuberous crop from the perennial Solanum tuberosum of the Solanaceae family . The word potato may refer to the plant itself as well as the edible tuber. In the region of the Andes, there are some other closely related cultivated potato species...
es, tobacco
Tobacco
Tobacco is an agricultural product processed from the leaves of plants in the genus Nicotiana. It can be consumed, used as a pesticide and, in the form of nicotine tartrate, used in some medicines...
, beans, and squash. The disease environment was very unhealthy for explorers and early settlers. The Native Americans became exposed to new diseases such as smallpox and measles and died in very large numbers
Native American disease and epidemics
Native American disease and epidemics pervade many aspects of Native American life, both throughout history and in the modern day. Diseases and epidemics can be chronicled from centuries ago when European settlers brought diseases that devastated entire tribes to the modern day when Native...
, usually before large-scale European settlement began.
Spanish, Dutch, and French colonization
Spanish explorers were the first Europeans to arrive in what is now the United States with Christopher ColumbusChristopher Columbus
Christopher Columbus was an explorer, colonizer, and navigator, born in the Republic of Genoa, in northwestern Italy. Under the auspices of the Catholic Monarchs of Spain, he completed four voyages across the Atlantic Ocean that led to general European awareness of the American continents in the...
' second expedition
Voyages of Christopher Columbus
In the early modern period, the voyages of Columbus initiated European exploration and colonization of the American continents, and are thus of great significance in world history. Christopher Columbus was a navigator and an admiral for Castile, a country that later founded modern Spain...
, which reached Puerto Rico on November 19, 1493; others reached Florida in 1513. Quickly Spanish expeditions reached the Appalachian Mountains
Appalachian Mountains
The Appalachian Mountains #Whether the stressed vowel is or ,#Whether the "ch" is pronounced as a fricative or an affricate , and#Whether the final vowel is the monophthong or the diphthong .), often called the Appalachians, are a system of mountains in eastern North America. The Appalachians...
, the Mississippi River
Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the largest river system in North America. Flowing entirely in the United States, this river rises in western Minnesota and meanders slowly southwards for to the Mississippi River Delta at the Gulf of Mexico. With its many tributaries, the Mississippi's watershed drains...
, the Grand Canyon
Grand Canyon
The Grand Canyon is a steep-sided canyon carved by the Colorado River in the United States in the state of Arizona. It is largely contained within the Grand Canyon National Park, the 15th national park in the United States...
and the Great Plains
Great Plains
The Great Plains are a broad expanse of flat land, much of it covered in prairie, steppe and grassland, which lies west of the Mississippi River and east of the Rocky Mountains in the United States and Canada. This area covers parts of the U.S...
. In 1540, Hernando de Soto undertook an extensive exploration of Southeast. Also in 1540 Francisco Vázquez de Coronado explored from Arizona to central Kansas. The Spanish sent some settlers, creating the first permanent European settlement in the continental United States at St. Augustine, Florida
St. Augustine, Florida
St. Augustine is a city in the northeast section of Florida and the county seat of St. Johns County, Florida, United States. Founded in 1565 by Spanish explorer and admiral Pedro Menéndez de Avilés, it is the oldest continuously occupied European-established city and port in the continental United...
in 1565, but it attracted few permanent settlers. Much larger and more important Spanish settlements included Santa Fe
Santa Fe, New Mexico
Santa Fe is the capital of the U.S. state of New Mexico. It is the fourth-largest city in the state and is the seat of . Santa Fe had a population of 67,947 in the 2010 census...
, Albuquerque
Albuquerque, New Mexico
Albuquerque is the largest city in the state of New Mexico, United States. It is the county seat of Bernalillo County and is situated in the central part of the state, straddling the Rio Grande. The city population was 545,852 as of the 2010 Census and ranks as the 32nd-largest city in the U.S. As...
, San Antonio, Tucson, San Diego, Los Angeles
Los Ángeles
Los Ángeles is the capital of the province of Biobío, in the commune of the same name, in Region VIII , in the center-south of Chile. It is located between the Laja and Biobío rivers. The population is 123,445 inhabitants...
and San Francisco.
New Netherland
New Netherland
New Netherland, or Nieuw-Nederland in Dutch, was the 17th-century colonial province of the Republic of the Seven United Netherlands on the East Coast of North America. The claimed territories were the lands from the Delmarva Peninsula to extreme southwestern Cape Cod...
was the 17th century Dutch colony centered on New York City and the Hudson River Valley, where they traded furs with the Native Americans to the north and were a barrier to Yankee
Yankee
The term Yankee has several interrelated and often pejorative meanings, usually referring to people originating in the northeastern United States, or still more narrowly New England, where application of the term is largely restricted to descendants of the English settlers of the region.The...
expansion from New England
New England
New England is a region in the northeastern corner of the United States consisting of the six states of Maine, New Hampshire, Vermont, Massachusetts, Rhode Island, and Connecticut...
. The Dutch were Calvinists who built the Reformed Church in America
Reformed Church in America
The Reformed Church in America is a mainline Reformed Protestant denomination in Canada and the United States. It has about 170,000 members, with the total declining in recent decades. From its beginning in 1628 until 1819, it was the North American branch of the Dutch Reformed Church. In 1819, it...
, but they were tolerant of other religions and cultures. The colony was taken over by Britain in 1664. It left an enduring legacy on American cultural and political life, including a secular broadmindedness and mercantile pragmatism in the city, a rural traditionalism in the countryside typified by the story of Rip Van Winkle
Rip Van Winkle
"Rip Van Winkle" is a short story by the American author Washington Irving published in 1819, as well as the name of the story's fictional protagonist. Written while Irving was living in Birmingham, England, it was part of a collection entitled The Sketch Book of Geoffrey Crayon...
, and politicians such as Martin Van Buren
Martin Van Buren
Martin Van Buren was the eighth President of the United States . Before his presidency, he was the eighth Vice President and the tenth Secretary of State, under Andrew Jackson ....
, Theodore Roosevelt
Theodore Roosevelt
Theodore "Teddy" Roosevelt was the 26th President of the United States . He is noted for his exuberant personality, range of interests and achievements, and his leadership of the Progressive Movement, as well as his "cowboy" persona and robust masculinity...
, Franklin D. Roosevelt
Franklin D. Roosevelt
Franklin Delano Roosevelt , also known by his initials, FDR, was the 32nd President of the United States and a central figure in world events during the mid-20th century, leading the United States during a time of worldwide economic crisis and world war...
and Eleanor Roosevelt
Eleanor Roosevelt
Anna Eleanor Roosevelt was the First Lady of the United States from 1933 to 1945. She supported the New Deal policies of her husband, distant cousin Franklin Delano Roosevelt, and became an advocate for civil rights. After her husband's death in 1945, Roosevelt continued to be an international...
.
New France
New France
New France was the area colonized by France in North America during a period beginning with the exploration of the Saint Lawrence River by Jacques Cartier in 1534 and ending with the cession of New France to Spain and Great Britain in 1763...
was the area colonized by France
French colonization of the Americas
The French colonization of the Americas began in the 16th century, and continued in the following centuries as France established a colonial empire in the Western Hemisphere. France founded colonies in much of eastern North America, on a number of Caribbean islands, and in South America...
from 1534 to 1763. There were few permanent settlers outside Quebec
Quebec
Quebec or is a province in east-central Canada. It is the only Canadian province with a predominantly French-speaking population and the only one whose sole official language is French at the provincial level....
, but Indian tribes often became military allies in France's wars with Britain. After 1750 the Acadians—French settlers who had been expelled by the British from Acadia (Nova Scotia
Nova Scotia
Nova Scotia is one of Canada's three Maritime provinces and is the most populous province in Atlantic Canada. The name of the province is Latin for "New Scotland," but "Nova Scotia" is the recognized, English-language name of the province. The provincial capital is Halifax. Nova Scotia is the...
)—resettled in Louisiana, where they developed a distinctive rural Cajun
Cajun
Cajuns are an ethnic group mainly living in the U.S. state of Louisiana, consisting of the descendants of Acadian exiles...
culture that still exists. They became American citizens in 1803 with the Louisiana Purchase
Louisiana Purchase
The Louisiana Purchase was the acquisition by the United States of America of of France's claim to the territory of Louisiana in 1803. The U.S...
. Other French villages along the Mississippi
Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the largest river system in North America. Flowing entirely in the United States, this river rises in western Minnesota and meanders slowly southwards for to the Mississippi River Delta at the Gulf of Mexico. With its many tributaries, the Mississippi's watershed drains...
and Illinois rivers
Illinois River
The Illinois River is a principal tributary of the Mississippi River, approximately long, in the State of Illinois. The river drains a large section of central Illinois, with a drainage basin of . This river was important among Native Americans and early French traders as the principal water route...
were absorbed when the Americans started arriving after 1770.
British colonization

Dutch people
The Dutch people are an ethnic group native to the Netherlands. They share a common culture and speak the Dutch language. Dutch people and their descendants are found in migrant communities worldwide, notably in Suriname, Chile, Brazil, Canada, Australia, South Africa, New Zealand, and the United...
and Swedes. Colonial America was defined by a severe labor shortage that employed forms of unfree labor such as slavery and indentured servitude, and by a British policy of benign neglect (salutary neglect
Salutary neglect
Salutary neglect was an undocumented, though long-lasting, British policy of avoiding strict enforcement of parliamentary laws, meant to keep the American colonies obedient to Great Britain. Prime Minister Robert Walpole stated that "If no restrictions were placed on the colonies, they would...
) that permitted the development of an American spirit distinct from that of its European founders. Over half of all European immigrants to Colonial America arrived as indentured servants.
The first successful English colony was established in 1607, on the James River
James River (Virginia)
The James River is a river in the U.S. state of Virginia. It is long, extending to if one includes the Jackson River, the longer of its two source tributaries. The James River drains a catchment comprising . The watershed includes about 4% open water and an area with a population of 2.5 million...
at Jamestown
Jamestown, Virginia
Jamestown was a settlement in the Colony of Virginia. Established by the Virginia Company of London as "James Fort" on May 14, 1607 , it was the first permanent English settlement in what is now the United States, following several earlier failed attempts, including the Lost Colony of Roanoke...
. It languished for decades until a new wave of settlers arrived in the late 17th century and established commercial agriculture based on tobacco. Between the late 1610s and the Revolution, the British shipped an estimated 50,000 convicts to their American colonies. One example of conflict between Native Americans and English settlers was the 1622 Powhatan
Powhatan
The Powhatan is the name of a Virginia Indian confederation of tribes. It is estimated that there were about 14,000–21,000 of these native Powhatan people in eastern Virginia when the English settled Jamestown in 1607...
uprising in Virginia, in which Native Americans had killed hundreds of English settlers. The largest conflict between Native Americans and English settlers in the 17th century was King Philip's War
King Philip's War
King Philip's War, sometimes called Metacom's War, Metacomet's War, or Metacom's Rebellion, was an armed conflict between Native American inhabitants of present-day southern New England and English colonists and their Native American allies in 1675–76. The war is named after the main leader of the...
in New England
New England
New England is a region in the northeastern corner of the United States consisting of the six states of Maine, New Hampshire, Vermont, Massachusetts, Rhode Island, and Connecticut...
, although the Yamasee War
Yamasee War
The Yamasee War was a conflict between British settlers of colonial South Carolina and various Native American Indian tribes, including the Yamasee, Muscogee, Cherokee, Chickasaw, Catawba, Apalachee, Apalachicola, Yuchi, Savannah River Shawnee, Congaree, Waxhaw, Pee Dee, Cape Fear, Cheraw, and...
may have been bloodier.
New England
New England
New England is a region in the northeastern corner of the United States consisting of the six states of Maine, New Hampshire, Vermont, Massachusetts, Rhode Island, and Connecticut...
was initially settled primarily by Puritans who established the Massachusetts Bay Colony
Massachusetts Bay Colony
The Massachusetts Bay Colony was an English settlement on the east coast of North America in the 17th century, in New England, situated around the present-day cities of Salem and Boston. The territory administered by the colony included much of present-day central New England, including portions...
in 1630, although there was a small earlier settlement in 1620 by a similar group, the Pilgrims, at Plymouth Colony
Plymouth Colony
Plymouth Colony was an English colonial venture in North America from 1620 to 1691. The first settlement of the Plymouth Colony was at New Plymouth, a location previously surveyed and named by Captain John Smith. The settlement, which served as the capital of the colony, is today the modern town...
. The Middle Colonies, consisting of the present-day states of New York
History of New York
The history of New York begins around 10,000 BCE, when the first Native Americans arrived. By 1100 CE, New York's main tribes, the Iroquoian and Algonquian cultures, had developed. New York was discovered by the French in 1524 and first claimed in 1609 by the Dutch...
, New Jersey
History of New Jersey
The history of New Jersey began at the end of the Younger Dryas climate, about 10 millennia ago. Native Americans moved into New Jersey soon after the reversal of the Younger Dryas, which had made the area uninhabitable and, during the preceding ice age, unreachable.European contact began with the...
, Pennsylvania
History of Pennsylvania
The history of Pennsylvania is as varied as any in the American experience and reflects the salad bowl vision of the United States. Before Pennsylvania was settled by Europeans, the area was home to the Delaware , Susquehannock, Iroquois, Eries, Shawnee and other Native American tribes...
, and Delaware
History of Delaware
The history of Delaware is the story of a small American state, in the middle of the original colonies, and yet until recently often overlooked by outsiders...
, were characterized by a large degree of diversity. The first attempted English settlement south of Virginia was the Province of Carolina
Province of Carolina
The Province of Carolina, originally chartered in 1629, was an English and later British colony of North America. Because the original Heath charter was unrealized and was ruled invalid, a new charter was issued to a group of eight English noblemen, the Lords Proprietors, in 1663...
, with Georgia Colony the last of the Thirteen Colonies
Thirteen Colonies
The Thirteen Colonies were English and later British colonies established on the Atlantic coast of North America between 1607 and 1733. They declared their independence in the American Revolution and formed the United States of America...
established in 1733. The colonies were characterized by religious diversity, with many Congregationalists in New England, German and Dutch Reformed in the Middle Colonies, Catholics in Maryland, and Scotch Irish Presbyterians on the frontier The First Great Awakening
First Great Awakening
The First Awakening was a Christian revitalization movement that swept Protestant Europe and British America, and especially the American colonies in the 1730s and 1740s, leaving a permanent impact on American religion. It resulted from powerful preaching that gave listeners a sense of personal...
. Many royal officials and merchants were Anglicans. Religion expanded greatly after the First Great Awakening
First Great Awakening
The First Awakening was a Christian revitalization movement that swept Protestant Europe and British America, and especially the American colonies in the 1730s and 1740s, leaving a permanent impact on American religion. It resulted from powerful preaching that gave listeners a sense of personal...
, a religious revival in the 1740s led by preachers such as Jonathan Edwards. American Evangelicals affected by the Awakening added a new emphasis on divine outpourings of the Holy Spirit and conversions that implanted within new believers an intense love for God. Revivals encapsulated those hallmarks and forwarded the newly created evangelicalism into the early republic, setting the stage for the Second Great Awakening
Second Great Awakening
The Second Great Awakening was a Christian revival movement during the early 19th century in the United States. The movement began around 1800, had begun to gain momentum by 1820, and was in decline by 1870. The Second Great Awakening expressed Arminian theology, by which every person could be...
beginning in the late 1790s.
Political integration and autonomy
The French and Indian WarFrench and Indian War
The French and Indian War is the common American name for the war between Great Britain and France in North America from 1754 to 1763. In 1756, the war erupted into the world-wide conflict known as the Seven Years' War and thus came to be regarded as the North American theater of that war...
(1754–1763) was a watershed event in the political development of the colonies. The influence of the main rivals of the British Crown in the colonies and Canada, the French and North American Indians, was significantly reduced. Moreover, the war effort resulted in greater political integration of the colonies, as symbolized by Benjamin Franklin's call for the colonies to "Join or Die".
Following Britain's acquisition of French territory in North America, King George III issued the Royal Proclamation of 1763
Royal Proclamation of 1763
The Royal Proclamation of 1763 was issued October 7, 1763, by King George III following Great Britain's acquisition of French territory in North America after the end of the French and Indian War/Seven Years' War...
with the goal of organizing the new North American empire and stabilizing relations with the native Indians. In ensuing years, strains developed in the relations between the colonists and the Crown. The British Parliament passed the Stamp Act of 1765, imposing a tax on the colonies to help pay for troops stationed in North America following the British victory in the Seven Years' War
Great Britain in the Seven Years War
The Kingdom of Great Britain was one of the major participants in the Seven Years' War which lasted between 1756 and 1763. Britain emerged from the war as the world's leading colonial power having gained a number of new territories at the Treaty of Paris in 1763 and established itself as the...
.
The British government felt that the colonies were the primary beneficiaries of this military presence, and should pay at least a portion of the expense. The colonists did not share this view. Rather, with the French and Indian threat diminished, the primary outside influence remained that of Britain. A conflict of economic interests increased with the right of the British Parliament to govern the colonies without representation being called into question.

Boston Tea Party
The Boston Tea Party was a direct action by colonists in Boston, a town in the British colony of Massachusetts, against the British government and the monopolistic East India Company that controlled all the tea imported into the colonies...
in 1773 was a direct action by colonists in the town of Boston
Boston
Boston is the capital of and largest city in Massachusetts, and is one of the oldest cities in the United States. The largest city in New England, Boston is regarded as the unofficial "Capital of New England" for its economic and cultural impact on the entire New England region. The city proper had...
to protest against the taxes levied by the British government. Parliament responded the next year with the Coercive Acts, which sparked outrage and resistance in the Thirteen Colonies
Thirteen Colonies
The Thirteen Colonies were English and later British colonies established on the Atlantic coast of North America between 1607 and 1733. They declared their independence in the American Revolution and formed the United States of America...
. Colonists convened the First Continental Congress
First Continental Congress
The First Continental Congress was a convention of delegates from twelve of the thirteen North American colonies that met on September 5, 1774, at Carpenters' Hall in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, early in the American Revolution. It was called in response to the passage of the Coercive Acts by the...
to coordinate their resistance to the Coercive Acts. The Congress called for a boycott of British trade, published a list of rights and grievances, and petitioned the king
Petition to the King (1774)
The Petition to the King was a petition sent to George III of Great Britain by the First Continental Congress. The petition expressed loyalty to the king and hoped for redress of grievances relating to the Intolerable Acts and other issues that helped foment the American Revolution.-Further...
for redress of those grievances.
The Congress also called for another meeting if their petition did not halt enforcement of the Coercive Acts. Their appeal to the Crown had no effect, and so the Second Continental Congress
Second Continental Congress
The Second Continental Congress was a convention of delegates from the Thirteen Colonies that started meeting on May 10, 1775, in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, soon after warfare in the American Revolutionary War had begun. It succeeded the First Continental Congress, which met briefly during 1774,...
was convened in 1775 to organize the defense of the colonies at the onset of the American Revolutionary War
American Revolutionary War
The American Revolutionary War , the American War of Independence, or simply the Revolutionary War, began as a war between the Kingdom of Great Britain and thirteen British colonies in North America, and ended in a global war between several European great powers.The war was the result of the...
.
Formation of the United States of America (1776–1789)
The Thirteen ColoniesThirteen Colonies
The Thirteen Colonies were English and later British colonies established on the Atlantic coast of North America between 1607 and 1733. They declared their independence in the American Revolution and formed the United States of America...
began a rebellion against British rule in 1775 and proclaimed their independence in 1776 as the United States of America. In the American Revolutionary War
American Revolutionary War
The American Revolutionary War , the American War of Independence, or simply the Revolutionary War, began as a war between the Kingdom of Great Britain and thirteen British colonies in North America, and ended in a global war between several European great powers.The war was the result of the...
(1775–1783) the American capture of the British invasion army at Saratoga in 1777 secured the Northeast and encouraged the French to make a military alliance with the United States. France brought in Spain and the Netherlands, thus balancing the military and naval forces on each side as Britain had no allies. General George Washington
George Washington
George Washington was the dominant military and political leader of the new United States of America from 1775 to 1799. He led the American victory over Great Britain in the American Revolutionary War as commander-in-chief of the Continental Army from 1775 to 1783, and presided over the writing of...
(1732–1799) proved an excellent organizer and administrator, who worked successfully with Congress and the state governors, selecting and mentoring his senior officers, supporting and training his troops, and maintaining an idealistic Republican Army. His biggest challenge was logistics, since neither Congress nor the states had the funding to provide adequately for the equipment, munitions, clothing, paychecks, or even the food supply of the soldiers. As a battlefield tactician Washington was often outmaneuvered by his British counterparts. As a strategist, however, he had a better idea of how to win the war than they did. The British sent four invasion armies. Washington's strategy forced the first army out of Boston in 1776, and was responsible for the surrender of the second and third armies at Saratoga (1777) and Yorktown (1781). He limited the British control to New York and a few places while keeping Patriot control of the great majority of the population. The Loyalists, whom the British counted upon too heavily, comprised about 20% of the population but never were well organized. As the war ended, Washington watched proudly as the final British army quietly sailed out of New York City in November 1783, taking the Loyalist leadership with them. Washington astonished the world when, instead of seizing power for himself, he retired quietly to his farm in Virginia. Political scientist Seymour Martin Lipset
Seymour Martin Lipset
Seymour Martin Lipset was an American political sociologist, senior fellow at the Hoover Institution, and the Hazel Professor of Public Policy at George Mason University. His major work was in the fields of political sociology, trade union organization, social stratification, public opinion, and...
observes, "The United States was the first major colony successfully to revolt against colonial rule. In this sense, it was the first 'new nation'."

Second Continental Congress
The Second Continental Congress was a convention of delegates from the Thirteen Colonies that started meeting on May 10, 1775, in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, soon after warfare in the American Revolutionary War had begun. It succeeded the First Continental Congress, which met briefly during 1774,...
, meeting in Philadelphia, declared the independence of "the United States of America" in the Declaration of Independence
United States Declaration of Independence
The Declaration of Independence was a statement adopted by the Continental Congress on July 4, 1776, which announced that the thirteen American colonies then at war with Great Britain regarded themselves as independent states, and no longer a part of the British Empire. John Adams put forth a...
. July 4 is celebrated as the nation's birthday. The new nation was founded on Enlightenment
Age of Enlightenment
The Age of Enlightenment was an elite cultural movement of intellectuals in 18th century Europe that sought to mobilize the power of reason in order to reform society and advance knowledge. It promoted intellectual interchange and opposed intolerance and abuses in church and state...
ideals of liberalism
Liberalism
Liberalism is the belief in the importance of liberty and equal rights. Liberals espouse a wide array of views depending on their understanding of these principles, but generally, liberals support ideas such as constitutionalism, liberal democracy, free and fair elections, human rights,...
in what Thomas Jefferson
Thomas Jefferson
Thomas Jefferson was the principal author of the United States Declaration of Independence and the Statute of Virginia for Religious Freedom , the third President of the United States and founder of the University of Virginia...
called the unalienable rights to "life, liberty and the pursuit of happiness," and dedicated strongly to republican
Republicanism in the United States
Republicanism is the political value system that has been a major part of American civic thought since the American Revolution. It stresses liberty and inalienable rights as central values, makes the people as a whole sovereign, supports activist government to promote the common good, rejects...
principles. Republicanism emphasized the people are sovereign (not hereditary kings), demanded civic duty, feared corruption, and rejected any aristocracy.
In the 1780s the national government was able to settle the issue of the western territories, which were ceded by the states to Congress and became territories; soon they became states. Nationalists worried that the new nation was too fragile to withstand an international war, or even internal revolts such as the Shays' Rebellion
Shays' Rebellion
Shays' Rebellion was an armed uprising in central and western Massachusetts from 1786 to 1787. The rebellion is named after Daniel Shays, a veteran of the American Revolutionary War....
of 1786 in Massachusetts. Nationalists—most of them war veterans—organized in every state and convinced Congress to call the Philadelphia Convention
Philadelphia Convention
The Constitutional Convention took place from May 14 to September 17, 1787, in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, to address problems in governing the United States of America, which had been operating under the Articles of Confederation following independence from...
in 1787. The delegates from every state wrote a new Constitution
United States Constitution
The Constitution of the United States is the supreme law of the United States of America. It is the framework for the organization of the United States government and for the relationship of the federal government with the states, citizens, and all people within the United States.The first three...
that created a much more powerful and efficient central government, one with a strong president, and powers of taxation. The new government reflected the prevailing republican ideals of guarantees of individual liberty
Natural rights
Natural and legal rights are two types of rights theoretically distinct according to philosophers and political scientists. Natural rights are rights not contingent upon the laws, customs, or beliefs of any particular culture or government, and therefore universal and inalienable...
and upon constraining the power of government through a system of separation of powers
Separation of powers
The separation of powers, often imprecisely used interchangeably with the trias politica principle, is a model for the governance of a state. The model was first developed in ancient Greece and came into widespread use by the Roman Republic as part of the unmodified Constitution of the Roman Republic...
.
To assuage the Anti-Federalists who feared a too-powerful national government, the nation adopted the United States Bill of Rights
United States Bill of Rights
The Bill of Rights is the collective name for the first ten amendments to the United States Constitution. These limitations serve to protect the natural rights of liberty and property. They guarantee a number of personal freedoms, limit the government's power in judicial and other proceedings, and...
in 1791. Comprising the first ten amendments of the Constitution, it guaranteed individual liberties such as freedom of speech and religious practice, jury trials, and stated that citizens and states had reserved rights (which were not specified).
Early national era (1789–1849)

George Washington
George Washington was the dominant military and political leader of the new United States of America from 1775 to 1799. He led the American victory over Great Britain in the American Revolutionary War as commander-in-chief of the Continental Army from 1775 to 1783, and presided over the writing of...
—a renowned hero of the American Revolutionary War
American Revolutionary War
The American Revolutionary War , the American War of Independence, or simply the Revolutionary War, began as a war between the Kingdom of Great Britain and thirteen British colonies in North America, and ended in a global war between several European great powers.The war was the result of the...
, commander-in-chief of the Continental Army
Continental Army
The Continental Army was formed after the outbreak of the American Revolutionary War by the colonies that became the United States of America. Established by a resolution of the Continental Congress on June 14, 1775, it was created to coordinate the military efforts of the Thirteen Colonies in...
, and president of the Constitutional Convention
Philadelphia Convention
The Constitutional Convention took place from May 14 to September 17, 1787, in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, to address problems in governing the United States of America, which had been operating under the Articles of Confederation following independence from...
—became the first President of the United States
President of the United States
The President of the United States of America is the head of state and head of government of the United States. The president leads the executive branch of the federal government and is the commander-in-chief of the United States Armed Forces....
under the new Constitution
United States Constitution
The Constitution of the United States is the supreme law of the United States of America. It is the framework for the organization of the United States government and for the relationship of the federal government with the states, citizens, and all people within the United States.The first three...
in 1789.
The major accomplishments of the Washington Administration
Presidency of George Washington
With inauguration on April 30, 1789, the presidency of George Washington initiated a significant leadership role over the United States. President Washington entered office with the full support of the national and state leadership, and established the executive and judicial branches of the federal...
were creating a strong national government that was recognized without question by all Americans, and, following the plans of Treasury Secretary Alexander Hamilton
Alexander Hamilton
Alexander Hamilton was a Founding Father, soldier, economist, political philosopher, one of America's first constitutional lawyers and the first United States Secretary of the Treasury...
, assuming the debts of the states (the debt holders received federal bonds), creating the Bank of the United States
First Bank of the United States
The First Bank of the United States is a National Historic Landmark located in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania within Independence National Historical Park.-Banking History:...
to stabilize the financial system, setting up a uniform system of tariffs (taxes on imports) and other taxes to pay off the debt and provide a financial infrastructure. To support his programs Hamilton created a new political party—the first in the world based on voters—the Federalist Party
Federalist Party (United States)
The Federalist Party was the first American political party, from the early 1790s to 1816, the era of the First Party System, with remnants lasting into the 1820s. The Federalists controlled the federal government until 1801...
. Thomas Jefferson
Thomas Jefferson
Thomas Jefferson was the principal author of the United States Declaration of Independence and the Statute of Virginia for Religious Freedom , the third President of the United States and founder of the University of Virginia...
and James Madison
James Madison
James Madison, Jr. was an American statesman and political theorist. He was the fourth President of the United States and is hailed as the “Father of the Constitution” for being the primary author of the United States Constitution and at first an opponent of, and then a key author of the United...
led the opposition, forming an opposition Republican Party (usually called the Democratic-Republican Party by historians). Hamilton and Washington presented the country in 1794 with the Jay Treaty
Jay Treaty
Jay's Treaty, , also known as Jay's Treaty, The British Treaty, and the Treaty of London of 1794, was a treaty between the United States and Great Britain that is credited with averting war,, resolving issues remaining since the Treaty of Paris of 1783, which ended the American Revolution,, and...
that reestablished good relations with Britain. The Jeffersonians vehemently protested, and the voters aligned behind one party or the other, thus setting up the First Party System
First Party System
The First Party System is a model of American politics used by political scientists and historians to periodize the political party system existing in the United States between roughly 1792 and 1824. It featured two national parties competing for control of the presidency, Congress, and the states:...
. The treaty passed, but politics became very heated.
The Whiskey Rebellion
Whiskey Rebellion
The Whiskey Rebellion, or Whiskey Insurrection, was a tax protest in the United States in the 1790s, during the presidency of George Washington. Farmers who sold their corn in the form of whiskey had to pay a new tax which they strongly resented...
in 1794, when western settlers protested against a federal tax on liquor, was the first serious test of the federal government. Washington called out the state militia and personally led an army, as the insurgents melted away and the power of the national government was firmly established.
Washington refused to serve more than two terms—setting a precedent—and in famous his farewell address
George Washington's Farewell Address
George Washington's Farewell Address was written to "The People of the United States" near the end of his second term as President of the United States and before his retirement to his home at Mount Vernon....
, he extolled the benefits of federal government and importance of ethics and morality while warning against foreign alliances and formation of political parties.
John Adams
John Adams
John Adams was an American lawyer, statesman, diplomat and political theorist. A leading champion of independence in 1776, he was the second President of the United States...
, a Federalist, defeated Jefferson in the 1796 election. War loomed with France and the Federalists used the opportunity to try to silence the Republicans with the Alien and Sedition Acts
Alien and Sedition Acts
The Alien and Sedition Acts were four bills passed in 1798 by the Federalists in the 5th United States Congress in the aftermath of the French Revolution's reign of terror and during an undeclared naval war with France, later known as the Quasi-War. They were signed into law by President John Adams...
, build up a large army with Hamilton at the head, and prepare for a French invasion. However, the Federalists became divided after Adams sent a successful peace mission to France that ended the Quasi-War
Quasi-War
The Quasi-War was an undeclared war fought mostly at sea between the United States and French Republic from 1798 to 1800. In the United States, the conflict was sometimes also referred to as the Franco-American War, the Pirate Wars, or the Half-War.-Background:The Kingdom of France had been a...
of 1798. Jefferson defeated Adams for the presidency in the 1800 election
United States presidential election, 1800
In the United States Presidential election of 1800, sometimes referred to as the "Revolution of 1800," Vice-President Thomas Jefferson defeated President John Adams. The election was a realigning election that ushered in a generation of Democratic-Republican Party rule and the eventual demise of...
.

Supreme Court of the United States
The Supreme Court of the United States is the highest court in the United States. It has ultimate appellate jurisdiction over all state and federal courts, and original jurisdiction over a small range of cases...
, its functions were vague until John Marshall
John Marshall
John Marshall was the Chief Justice of the United States whose court opinions helped lay the basis for American constitutional law and made the Supreme Court of the United States a coequal branch of government along with the legislative and executive branches...
, the Chief Justice (1801–35), defined them, especially the power to overturn acts of Congress that violated the Constitution, first enunciated in 1803 in Marbury v. Madison
Marbury v. Madison
Marbury v. Madison, is a landmark case in United States law and in the history of law worldwide. It formed the basis for the exercise of judicial review in the United States under Article III of the Constitution. It was also the first time in Western history a court invalidated a law by declaring...
. The Louisiana Purchase
Louisiana Purchase
The Louisiana Purchase was the acquisition by the United States of America of of France's claim to the territory of Louisiana in 1803. The U.S...
, in 1803, removed the French presence from the western border of the United States and provided U.S. settlers with vast potential for expansion west of the Mississippi River
Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the largest river system in North America. Flowing entirely in the United States, this river rises in western Minnesota and meanders slowly southwards for to the Mississippi River Delta at the Gulf of Mexico. With its many tributaries, the Mississippi's watershed drains...
.
In response to multiple grievances, the Congress
United States Congress
The United States Congress is the bicameral legislature of the federal government of the United States, consisting of the Senate and the House of Representatives. The Congress meets in the United States Capitol in Washington, D.C....
declared war on Britain
United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland was the formal name of the United Kingdom during the period when what is now the Republic of Ireland formed a part of it....
in 1812. The grievances included humiliating the Americans in the Chesapeake incident of 1807
Chesapeake–Leopard Affair
The Chesapeake-Leopard Affair was a naval engagement which occurred off the coast of Norfolk, Virginia on June 22, 1807, between the British warship HMS Leopard and the American frigate, the USS Chesapeake, when the crew of the Leopard pursued, attacked and boarded the American frigate looking for...
, continued British impressment
Impressment
Impressment, colloquially, "the Press", was the act of taking men into a navy by force and without notice. It was used by the Royal Navy, beginning in 1664 and during the 18th and early 19th centuries, in wartime, as a means of crewing warships, although legal sanction for the practice goes back to...
of American sailors into the Royal Navy
Royal Navy
The Royal Navy is the naval warfare service branch of the British Armed Forces. Founded in the 16th century, it is the oldest service branch and is known as the Senior Service...
, restrictions on trade with France, and arming hostile Indians in Ohio and the western territories. The War of 1812
War of 1812
The War of 1812 was a military conflict fought between the forces of the United States of America and those of the British Empire. The Americans declared war in 1812 for several reasons, including trade restrictions because of Britain's ongoing war with France, impressment of American merchant...
ended in a draw after bitter fighting that lasted until January 8, 1815, during the Battle of New Orleans
Battle of New Orleans
The Battle of New Orleans took place on January 8, 1815 and was the final major battle of the War of 1812. American forces, commanded by Major General Andrew Jackson, defeated an invading British Army intent on seizing New Orleans and the vast territory the United States had acquired with the...
. The Americans gained no territory but were cheered by a sense of victory in what they called a "second war of independence". The war was a major loss for Native American
Indigenous peoples of the Americas
The indigenous peoples of the Americas are the pre-Columbian inhabitants of North and South America, their descendants and other ethnic groups who are identified with those peoples. Indigenous peoples are known in Canada as Aboriginal peoples, and in the United States as Native Americans...
tribes in the Northwest and Southeast who had allied themselves with Britain and were defeated on the battlefield.
As strong opponents of the war, the Federalists held the Hartford Convention
Hartford Convention
The Hartford Convention was an event spanning from December 15, 1814–January 4, 1815 in the United States during the War of 1812 in which New England's opposition to the war reached the point where secession from the United States was discussed...
in 1814 that hinted at disunion. National euphoria after the victory at New Orleans ruined the prestige of the Federalists and they no longer played a significant role. President Madison and most Republicans realized it had been a mistake to let the Bank of the United States close down, for its absence greatly hindered the financing of the war. So they chartered the Second Bank of the United States
Second Bank of the United States
The Second Bank of the United States was chartered in 1816, five years after the First Bank of the United States lost its own charter. The Second Bank of the United States was initially headquartered in Carpenters' Hall, Philadelphia, the same as the First Bank, and had branches throughout the...
in 1816. The Republicans also imposed tariffs designed to protect the infant industries that had been created when Britain was blockading the U.S. With the collapse of the Federalists as a party, the adoption of many Federalist principles by the Republicans, and the systematic policy of President James Monroe
James Monroe
James Monroe was the fifth President of the United States . Monroe was the last president who was a Founding Father of the United States, and the last president from the Virginia dynasty and the Republican Generation...
in his two terms (1817–25) to downplay partisanship, the nation entered an Era of Good Feelings
Era of Good Feelings
The Era of Good Feelings was a period in United States political history in which partisan bitterness abated. It lasted approximately from 1815 to 1825, during the administration of U.S...
, with far less partisanship than before (or after), and closed out the First Party System
First Party System
The First Party System is a model of American politics used by political scientists and historians to periodize the political party system existing in the United States between roughly 1792 and 1824. It featured two national parties competing for control of the presidency, Congress, and the states:...
.
The Monroe Doctrine
Monroe Doctrine
The Monroe Doctrine is a policy of the United States introduced on December 2, 1823. It stated that further efforts by European nations to colonize land or interfere with states in North or South America would be viewed as acts of aggression requiring U.S. intervention...
, expressed in 1823, proclaimed the United States' opinion that European powers should no longer colonize or interfere in the Americas
Americas
The Americas, or America , are lands in the Western hemisphere, also known as the New World. In English, the plural form the Americas is often used to refer to the landmasses of North America and South America with their associated islands and regions, while the singular form America is primarily...
. This was a defining moment in the foreign policy
Foreign relations of the United States
The United States has formal diplomatic relations with most nations. The United States federal statutes relating to foreign relations can be found in Title 22 of the United States Code.-Pacific:-Americas:-Caribbean:...
of the United States. The Monroe Doctrine was adopted in response to American and British fears over Russian and French expansion into the Western Hemisphere
Western Hemisphere
The Western Hemisphere or western hemisphere is mainly used as a geographical term for the half of the Earth that lies west of the Prime Meridian and east of the Antimeridian , the other half being called the Eastern Hemisphere.In this sense, the western hemisphere consists of the western portions...
.

Indian Removal Act
The Indian Removal Act was signed into law by President Andrew Jackson on May 28, 1830.The Removal Act was strongly supported in the South, where states were eager to gain access to lands inhabited by the Five Civilized Tribes. In particular, Georgia, the largest state at that time, was involved in...
, which authorized the president to negotiate treaties that exchanged Native American tribal lands in the eastern states for lands west of the Mississippi River. This established Andrew Jackson
Andrew Jackson
Andrew Jackson was the seventh President of the United States . Based in frontier Tennessee, Jackson was a politician and army general who defeated the Creek Indians at the Battle of Horseshoe Bend , and the British at the Battle of New Orleans...
, a military hero and President, as a proponent of the forcible removal of native populations to the West. The act resulted most notably in the Trail of Tears
Trail of Tears
The Trail of Tears is a name given to the forced relocation and movement of Native American nations from southeastern parts of the United States following the Indian Removal Act of 1830...
, a forced migration of several native tribes to the West, with several thousand people dying en route. Many of the Seminole Indians in Florida refused to move west; they fought the Army for years in the Seminole Wars
Seminole Wars
The Seminole Wars, also known as the Florida Wars, were three conflicts in Florida between the Seminole — the collective name given to the amalgamation of various groups of native Americans and Black people who settled in Florida in the early 18th century — and the United States Army...
.
After 1840 the abolitionist movement redefined itself as a crusade against the sin of slave ownership. It mobilized support (especially among religious women in the Northeast affected by the Second Great Awakening
Second Great Awakening
The Second Great Awakening was a Christian revival movement during the early 19th century in the United States. The movement began around 1800, had begun to gain momentum by 1820, and was in decline by 1870. The Second Great Awakening expressed Arminian theology, by which every person could be...
). William Lloyd Garrison
William Lloyd Garrison
William Lloyd Garrison was a prominent American abolitionist, journalist, and social reformer. He is best known as the editor of the abolitionist newspaper The Liberator, and as one of the founders of the American Anti-Slavery Society, he promoted "immediate emancipation" of slaves in the United...
published the most influential of the many anti-slavery newspapers, The Liberator, while Frederick Douglass
Frederick Douglass
Frederick Douglass was an American social reformer, orator, writer and statesman. After escaping from slavery, he became a leader of the abolitionist movement, gaining note for his dazzling oratory and incisive antislavery writing...
, an ex-slave, began writing for that newspaper around 1840 and started his own abolitionist newspaper North Star
North Star (newspaper)
The North Star was an anti-slavery newspaper. Abolitionist Frederick Douglass published the North Star until June 1851, when Douglass and Gerrit Smith agreed to merge the North Star with the Liberty Party Paper to form Frederick Douglass's Paper...
in 1847. The great majority of anti-slavery elements rejected its moralism and held that slavery was an unfortunate social evil, not a sin.
The Republic of Texas was annexed
Texas Annexation
In 1845, United States of America annexed the Republic of Texas and admitted it to the Union as the 28th state. The U.S. thus inherited Texas's border dispute with Mexico; this quickly led to the Mexican-American War, during which the U.S. captured additional territory , extending the nation's...
in 1845, which Mexico had warned meant war. The U.S. army, using regulars and large numbers of volunteers, easily won the Mexican-American War, 1846-48. Public sentiment in the U.S. was divided as Whigs and anti-slavery elements opposed the war. The 1848 Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo
Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo
The Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo is the peace treaty, largely dictated by the United States to the interim government of a militarily occupied Mexico City, that ended the Mexican-American War on February 2, 1848...
ceded California, New Mexico, and adjacent areas to the United States, with the residents given full citizenship. Simultaneously gold was discovered, pulling over 100,000 men to northern California in a matter of months in the California Gold Rush
California Gold Rush
The California Gold Rush began on January 24, 1848, when gold was found by James W. Marshall at Sutter's Mill in Coloma, California. The first to hear confirmed information of the gold rush were the people in Oregon, the Sandwich Islands , and Latin America, who were the first to start flocking to...
.
Civil War era (1849–1865)
.png)
The issue of slavery in the new territories was seemingly settled by the Compromise of 1850
Compromise of 1850
The Compromise of 1850 was a package of five bills, passed in September 1850, which defused a four-year confrontation between the slave states of the South and the free states of the North regarding the status of territories acquired during the Mexican-American War...
brokered by Whig Henry Clay
Henry Clay
Henry Clay, Sr. , was a lawyer, politician and skilled orator who represented Kentucky separately in both the Senate and in the House of Representatives...
and Democrat Stephen Douglas; the Compromise included admission of California
California
California is a state located on the West Coast of the United States. It is by far the most populous U.S. state, and the third-largest by land area...
as a free state. The sore point was the Fugitive Slave Act to make it easier for masters to reclaim runaway slaves; with abolitionists used it to attack slavery, as in Uncle Tom's Cabin by Harriet Beecher Stowe
Harriet Beecher Stowe
Harriet Beecher Stowe was an American abolitionist and author. Her novel Uncle Tom's Cabin was a depiction of life for African-Americans under slavery; it reached millions as a novel and play, and became influential in the United States and United Kingdom...
. The Compromise of 1820 was repealed in 1854 with the Kansas-Nebraska Act
Kansas-Nebraska Act
The Kansas–Nebraska Act of 1854 created the territories of Kansas and Nebraska, opening new lands for settlement, and had the effect of repealing the Missouri Compromise of 1820 by allowing settlers in those territories to determine through Popular Sovereignty if they would allow slavery within...
, promoted by Senator Douglas in the name of "opular sovereignty" and democracy. It permitted settlers to decide on slavery in each territory, and allowed Douglas to say he was neutral on the slavery issue. Antislavery forces rose in anger and alarm, forming the new Republican Party. Pro and anti-forces rushed to Kansas to vote slavery up or down, resulting in a mini civil war called Bleeding Kansas
Bleeding Kansas
Bleeding Kansas, Bloody Kansas or the Border War, was a series of violent events, involving anti-slavery Free-Staters and pro-slavery "Border Ruffian" elements, that took place in the Kansas Territory and the western frontier towns of the U.S. state of Missouri roughly between 1854 and 1858...
. By the late 1850s the young Republican Party dominated nearly all northern states and thus the electoral college, and insisted that slavery would never be allowed to expand (and thus would slowly die out).
By 1860, there were nearly four million slaves residing in the United States, nearly eight times as many from 1790; within the same time period, cotton
Cotton
Cotton is a soft, fluffy staple fiber that grows in a boll, or protective capsule, around the seeds of cotton plants of the genus Gossypium. The fiber is almost pure cellulose. The botanical purpose of cotton fiber is to aid in seed dispersal....
production in the U.S. boomed from less than a thousand tons to nearly one million tons per year. There were some slave rebellions—including by Gabriel Prosser
Gabriel Prosser
Gabriel , today commonly – if incorrectly – known as Gabriel Prosser, was a literate enslaved blacksmith who planned to lead a large slave rebellion in the Richmond area in the summer of 1800. However, information regarding the revolt was leaked prior to its execution, thus Gabriel's plans were...
(1800), Denmark Vesey
Denmark Vesey
Denmark Vesey originally Telemaque, was an African American slave brought to the United States from the Caribbean of Coromantee background. After purchasing his freedom, he planned what would have been one of the largest slave rebellions in the United States...
(1822), and Nat Turner
Nat Turner
Nathaniel "Nat" Turner was an American slave who led a slave rebellion in Virginia on August 21, 1831 that resulted in 60 white deaths and at least 100 black deaths, the largest number of fatalities to occur in one uprising prior to the American Civil War in the southern United States. He gathered...
(1831)—but they all failed and led to tighter slave oversight in the south and distrust of Yankees as abolitionists. The Supreme Court's 1857 decision in the Dred Scott Case took the Southern position of making slavery legal everywhere, which outraged northerners.

Abraham Lincoln
Abraham Lincoln was the 16th President of the United States, serving from March 1861 until his assassination in April 1865. He successfully led his country through a great constitutional, military and moral crisis – the American Civil War – preserving the Union, while ending slavery, and...
won the 1860 election, eleven Southern states seceded from the union between late 1860 and 1861, establishing a new government, the Confederate States of America
Confederate States of America
The Confederate States of America was a government set up from 1861 to 1865 by 11 Southern slave states of the United States of America that had declared their secession from the U.S...
, on February 8, 1861. Along with the northwestern portion of Virginia, which became West Virginia
West Virginia
West Virginia is a state in the Appalachian and Southeastern regions of the United States, bordered by Virginia to the southeast, Kentucky to the southwest, Ohio to the northwest, Pennsylvania to the northeast and Maryland to the east...
, four of the five northernmost "slave states" did not secede and became known as the Border States.
Civil War
The Civil WarAmerican Civil War
The American Civil War was a civil war fought in the United States of America. In response to the election of Abraham Lincoln as President of the United States, 11 southern slave states declared their secession from the United States and formed the Confederate States of America ; the other 25...
began on April 12, 1861, when Confederate forces attacked a U.S. military installation
Battle of Fort Sumter
The Battle of Fort Sumter was the bombardment and surrender of Fort Sumter, near Charleston, South Carolina, that started the American Civil War. Following declarations of secession by seven Southern states, South Carolina demanded that the U.S. Army abandon its facilities in Charleston Harbor. On...
at Fort Sumter
Fort Sumter
Fort Sumter is a Third System masonry coastal fortification located in Charleston Harbor, South Carolina. The fort is best known as the site upon which the shots initiating the American Civil War were fired, at the Battle of Fort Sumter.- Construction :...
in South Carolina
South Carolina
South Carolina is a state in the Deep South of the United States that borders Georgia to the south, North Carolina to the north, and the Atlantic Ocean to the east. Originally part of the Province of Carolina, the Province of South Carolina was one of the 13 colonies that declared independence...
. In response to the attack, on April 15, Lincoln called on the states to send detachments totaling 75,000 troops to recapture forts, protect the capital, and "preserve the Union", which in his view still existed intact despite the actions of the seceding states. The two armies had their first major clash at the First Battle of Bull Run
First Battle of Bull Run
First Battle of Bull Run, also known as First Manassas , was fought on July 21, 1861, in Prince William County, Virginia, near the City of Manassas...
, which ended in a surprising Union defeat, but, more importantly, proved to both the Union and Confederacy that the war was going to be much longer and bloodier than they had originally anticipated.
The war soon divided into two theaters: Eastern
Eastern Theater of the American Civil War
The Eastern Theater of the American Civil War included the states of Virginia, West Virginia, Maryland, and Pennsylvania, the District of Columbia, and the coastal fortifications and seaports of North Carolina...
and Western
Western Theater of the American Civil War
This article presents an overview of major military and naval operations in the Western Theater of the American Civil War.-Theater of operations:...
. In the western theater, the Union was quite successful, with major battles, such as Perryville
Battle of Perryville
The Battle of Perryville, also known as the Battle of Chaplin Hills, was fought on October 8, 1862, in the Chaplin Hills west of Perryville, Kentucky, as the culmination of the Confederate Heartland Offensive during the American Civil War. Confederate Gen. Braxton Bragg's Army of Mississippi won a...
, producing strategic Union victories and destroying major confederate operations.

George B. McClellan
George Brinton McClellan was a major general during the American Civil War. He organized the famous Army of the Potomac and served briefly as the general-in-chief of the Union Army. Early in the war, McClellan played an important role in raising a well-trained and organized army for the Union...
was put in charge of the Union armies. After reorganizing the new Army of the Potomac
Army of the Potomac
The Army of the Potomac was the major Union Army in the Eastern Theater of the American Civil War.-History:The Army of the Potomac was created in 1861, but was then only the size of a corps . Its nucleus was called the Army of Northeastern Virginia, under Brig. Gen...
, McClellan failed to capture the Confederate capital of Richmond, Virginia
Richmond, Virginia
Richmond is the capital of the Commonwealth of Virginia, in the United States. It is an independent city and not part of any county. Richmond is the center of the Richmond Metropolitan Statistical Area and the Greater Richmond area...
in his Peninsula Campaign
Peninsula Campaign
The Peninsula Campaign of the American Civil War was a major Union operation launched in southeastern Virginia from March through July 1862, the first large-scale offensive in the Eastern Theater. The operation, commanded by Maj. Gen. George B...
and retreated after attacks from newly appointed Confederate General Robert E. Lee
Robert E. Lee
Robert Edward Lee was a career military officer who is best known for having commanded the Confederate Army of Northern Virginia in the American Civil War....
.
Feeling confident in his army after defeating the Union at Second Bull Run, Lee embarked on an invasion of the north
Maryland Campaign
The Maryland Campaign, or the Antietam Campaign is widely considered one of the major turning points of the American Civil War. Confederate Gen. Robert E. Lee's first invasion of the North was repulsed by Maj. Gen. George B...
that was stopped by McClellan at the bloody Battle of Antietam
Battle of Antietam
The Battle of Antietam , fought on September 17, 1862, near Sharpsburg, Maryland, and Antietam Creek, as part of the Maryland Campaign, was the first major battle in the American Civil War to take place on Northern soil. It was the bloodiest single-day battle in American history, with about 23,000...
. Despite this, McClellan was relieved from command for refusing to pursue Lee's crippled army. The next commander, General Ambrose Burnside
Ambrose Burnside
Ambrose Everett Burnside was an American soldier, railroad executive, inventor, industrialist, and politician from Rhode Island, serving as governor and a U.S. Senator...
, suffered a humiliating defeat by Lee's smaller army at the Battle of Fredericksburg
Battle of Fredericksburg
The Battle of Fredericksburg was fought December 11–15, 1862, in and around Fredericksburg, Virginia, between General Robert E. Lee's Confederate Army of Northern Virginia and the Union Army of the Potomac, commanded by Maj. Gen. Ambrose E. Burnside...
late in 1862, causing yet another change in commanders. Lee won again at the Battle of Chancellorsville
Battle of Chancellorsville
The Battle of Chancellorsville was a major battle of the American Civil War, and the principal engagement of the Chancellorsville Campaign. It was fought from April 30 to May 6, 1863, in Spotsylvania County, Virginia, near the village of Chancellorsville. Two related battles were fought nearby on...
in May 1863, while losing his top aide, Stonewall Jackson
Stonewall Jackson
ຄຽשת״ׇׂׂׂׂ֣|birth_place= Clarksburg, Virginia |death_place=Guinea Station, Virginia|placeofburial=Stonewall Jackson Memorial CemeteryLexington, Virginia|placeofburial_label= Place of burial|image=...
. But Lee pushed too hard and ignored the Union threat in the west. Lee invaded Pennsylvania in search of supplies and to cause war weariness in the North. In perhaps the turning point of the war
Turning point of the American Civil War
There is widespread disagreement over the turning point of the American Civil War. The idea of a turning point is an event after which most observers would agree that the eventual outcome was inevitable. While the Battle of Gettysburg is the most widely cited , there are several other arguable...
, Lee's army was badly beaten at the Battle of Gettysburg
Battle of Gettysburg
The Battle of Gettysburg , was fought July 1–3, 1863, in and around the town of Gettysburg, Pennsylvania. The battle with the largest number of casualties in the American Civil War, it is often described as the war's turning point. Union Maj. Gen. George Gordon Meade's Army of the Potomac...
, July 1–3, 1863, and barely made it back to Virginia.
Simultaneously on July 4, 1863, Union forces under the command of General Ulysses S. Grant
Ulysses S. Grant
Ulysses S. Grant was the 18th President of the United States as well as military commander during the Civil War and post-war Reconstruction periods. Under Grant's command, the Union Army defeated the Confederate military and ended the Confederate States of America...
gained control of the Mississippi River at the Battle of Vicksburg
Battle of Vicksburg
The Siege of Vicksburg was the final major military action in the Vicksburg Campaign of the American Civil War. In a series of maneuvers, Union Maj. Gen. Ulysses S. Grant and his Army of the Tennessee crossed the Mississippi River and drove the Confederate army of Lt. Gen. John C...
, thereby splitting the Confederacy. Lincoln made General Grant commander of all Union armies.
The last two years of the war was bloody for both sides, with Grant launching a war of attrition
Attrition warfare
Attrition warfare is a military strategy in which a belligerent side attempts to win a war by wearing down its enemy to the point of collapse through continuous losses in personnel and matériel....
against General Lee's Army of Northern Virginia
Army of Northern Virginia
The Army of Northern Virginia was the primary military force of the Confederate States of America in the Eastern Theater of the American Civil War, as well as the primary command structure of the Department of Northern Virginia. It was most often arrayed against the Union Army of the Potomac...
. This war of attrition was divided into three main campaigns. The first of these, the Overland Campaign
Overland Campaign
The Overland Campaign, also known as Grant's Overland Campaign and the Wilderness Campaign, was a series of battles fought in Virginia during May and June 1864, in the American Civil War. Lt. Gen. Ulysses S. Grant, general-in-chief of all Union armies, directed the actions of the Army of the...
forced Lee to retreat into the city of Petersburg where Grant launched his second major offensive, the Richmond-Petersburg Campaign in which he sieged Petersburg
Siege of Petersburg
The Richmond–Petersburg Campaign was a series of battles around Petersburg, Virginia, fought from June 9, 1864, to March 25, 1865, during the American Civil War...
. After a near ten-month siege, Petersburg surrendered. However, the defense of Fort Gregg allowed Lee to move his army out of Petersburg. Grant pursued and launched the final, Appomattox Campaign
Appomattox Campaign
The Appomattox Campaign was a series of battles fought March 29 – April 9, 1865, in Virginia that culminated in the surrender of Confederate General Robert E...
which resulted in Lee surrendering his Army of Northern Virginia on April 9, 1865, at Appomattox Court House
Appomattox Court House
The Appomattox Courthouse is the current courthouse in Appomattox, Virginia built in 1892. It is located in the middle of the state about three miles northwest of the Appomattox Court House National Historical Park, once known as Clover Hill - home of the original Old Appomattox Court House...
. Other Confederate armies followed suit and the war ended.
Based on 1860 census
United States Census, 1860
The United States Census of 1860 was the eighth Census conducted in the United States. It determined the population of the United States to be 31,443,321 — an increase of 35.4 percent over the 23,191,875 persons enumerated during the 1850 Census...
figures, about 8% of all white males aged 13 to 43 died in the war, including about 6% in the North and approximately 18% in the South, establishing the American Civil War as the deadliest war in American history. Its legacy includes ending slavery in the United States, restoring the Union, and strengthening the role of the federal government. The social, political, economic and racial issues of the war decisively shaped the Reconstruction era, which lasted through 1877, and brought about changes that would eventually help make the country a united superpower.
Reconstruction

Reconstruction Amendments
The Reconstruction Amendments are the Thirteenth, Fourteenth, and Fifteenth amendments to the United States Constitution, adopted between 1865 and 1870, the five years immediately following the Civil War...
" were passed to expand civil rights for black Americans. Those amendments included the Thirteenth Amendment
Thirteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution
The Thirteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution officially abolished and continues to prohibit slavery and involuntary servitude, except as punishment for a crime. It was passed by the Senate on April 8, 1864, passed by the House on January 31, 1865, and adopted on December 6, 1865. On...
, which outlawed slavery, the Fourteenth Amendment
Fourteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution
The Fourteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution was adopted on July 9, 1868, as one of the Reconstruction Amendments.Its Citizenship Clause provides a broad definition of citizenship that overruled the Dred Scott v...
that guaranteed citizenship for all people born or naturalized within U.S. territory, and the Fifteenth Amendment
Fifteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution
The Fifteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution prohibits each government in the United States from denying a citizen the right to vote based on that citizen's "race, color, or previous condition of servitude"...
that granted the vote for all men regardless of race. While the Civil Rights Act of 1875
Civil Rights Act of 1875
The Civil Rights Act of 1875 was a United States federal law proposed by Senator Charles Sumner and Representative Benjamin F. Butler in 1870...
forbade discrimination in the service of public facilities, the Black Codes denied blacks privileges readily available to whites.
In response to Reconstruction, the Ku Klux Klan
Ku Klux Klan
Ku Klux Klan, often abbreviated KKK and informally known as the Klan, is the name of three distinct past and present far-right organizations in the United States, which have advocated extremist reactionary currents such as white supremacy, white nationalism, and anti-immigration, historically...
(KKK) emerged around the late 1860s as a white-supremacist organization opposed to black civil rights. Congress passed the Ku Klux Klan Act of 1870 and vigorous enforcement closed down the Klan and classified the KKK as a terrorist group. However, an 1883 Supreme Court decision nullified the Civil Rights Act of 1875 and ended federal efforts to stop private acts of violence designed to suppress legal rights.
During the era, many regions of the southern U.S. were military-governed
Militarism
Militarism is defined as: the belief or desire of a government or people that a country should maintain a strong military capability and be prepared to use it aggressively to defend or promote national interests....
and often corrupt; Reconstruction ended after the disputed 1876 election
United States presidential election, 1876
The United States presidential election of 1876 was one of the most disputed and controversial presidential elections in American history. Samuel J. Tilden of New York outpolled Ohio's Rutherford B. Hayes in the popular vote, and had 184 electoral votes to Hayes's 165, with 20 votes uncounted...
between Republican candidate Rutherford B. Hayes
Rutherford B. Hayes
Rutherford Birchard Hayes was the 19th President of the United States . As president, he oversaw the end of Reconstruction and the United States' entry into the Second Industrial Revolution...
and Democratic candidate Samuel J. Tilden
Samuel J. Tilden
Samuel Jones Tilden was the Democratic candidate for the U.S. presidency in the disputed election of 1876, one of the most controversial American elections of the 19th century. He was the 25th Governor of New York...
. Hayes won the election, and the South soon re-entered the national political scene.
Gilded Age and Progressivism
The "Gilded AgeGilded Age
In United States history, the Gilded Age refers to the era of rapid economic and population growth in the United States during the post–Civil War and post-Reconstruction eras of the late 19th century. The term "Gilded Age" was coined by Mark Twain and Charles Dudley Warner in their book The Gilded...
" was a term that Mark Twain
Mark Twain
Samuel Langhorne Clemens , better known by his pen name Mark Twain, was an American author and humorist...
used to describe the period of the late 19th century when there had been a dramatic expansion of American wealth and prosperity. Reform of the Age included the Civil Service Act
Pendleton Civil Service Reform Act
The Pendleton Civil Service Reform Act of United States is a federal law established in 1883 that stipulated that government jobs should be awarded on the basis of merit. The act provided selection of government employees competitive exams, rather than ties to politicians or political affiliation...
, which mandated a competitive examination for applicants for government jobs. Other important legislation included the Interstate Commerce Act, which ended railroads' discrimination against small shippers, and the Sherman Antitrust Act
Sherman Antitrust Act
The Sherman Antitrust Act requires the United States federal government to investigate and pursue trusts, companies, and organizations suspected of violating the Act. It was the first Federal statute to limit cartels and monopolies, and today still forms the basis for most antitrust litigation by...
, which outlawed monopolies in business. Twain believed that this age was corrupted by such elements as land speculators, scandalous politics, and unethical business practices.
By 1890 American industrial production and per capita income
Per capita income
Per capita income or income per person is a measure of mean income within an economic aggregate, such as a country or city. It is calculated by taking a measure of all sources of income in the aggregate and dividing it by the total population...
exceeded those of all other world nations. In response to heavy debts and decreasing farm prices, wheat and cotton farmers joined the Populist Party. An unprecedented wave of immigration
Immigration to the United States
Immigration to the United States has been a major source of population growth and cultural change throughout much of the history of the United States. The economic, social, and political aspects of immigration have caused controversy regarding ethnicity, economic benefits, jobs for non-immigrants,...
from Europe served to both provide the labor for American industry and create diverse communities in previously undeveloped areas. From 1880 to 1914, peak years of immigration, more than 22 million people migrated to the United States. The workers' demand for control of their workplace led to the often-violent rise of the labor movement in the cities and mining camps. Industrial leaders included John D. Rockefeller
John D. Rockefeller
John Davison Rockefeller was an American oil industrialist, investor, and philanthropist. He was the founder of the Standard Oil Company, which dominated the oil industry and was the first great U.S. business trust. Rockefeller revolutionized the petroleum industry and defined the structure of...
in oil and Andrew Carnegie
Andrew Carnegie
Andrew Carnegie was a Scottish-American industrialist, businessman, and entrepreneur who led the enormous expansion of the American steel industry in the late 19th century...
in steel; both became leaders of philanthropy, giving away their fortunes to create the modern system of hospitals, universities, libraries and foundations.

Theodore Roosevelt
Theodore "Teddy" Roosevelt was the 26th President of the United States . He is noted for his exuberant personality, range of interests and achievements, and his leadership of the Progressive Movement, as well as his "cowboy" persona and robust masculinity...
, Charles Evans Hughes
Charles Evans Hughes
Charles Evans Hughes, Sr. was an American statesman, lawyer and Republican politician from New York. He served as the 36th Governor of New York , Associate Justice of the Supreme Court of the United States , United States Secretary of State , a judge on the Court of International Justice , and...
, and Robert LaFollette
Robert M. La Follette, Sr.
Robert Marion "Fighting Bob" La Follette, Sr. , was an American Republican politician. He served as a member of the U.S. House of Representatives, was the Governor of Wisconsin, and was also a U.S. Senator from Wisconsin...
on the Republican side, and William Jennings Bryan
William Jennings Bryan
William Jennings Bryan was an American politician in the late-19th and early-20th centuries. He was a dominant force in the liberal wing of the Democratic Party, standing three times as its candidate for President of the United States...
on the Democratic side, took up the cause of progressive reform. Women became especially involved in demands for woman suffrage, prohibition, and better schools; their most prominent leader was Jane Addams
Jane Addams
Jane Addams was a pioneer settlement worker, founder of Hull House in Chicago, public philosopher, sociologist, author, and leader in woman suffrage and world peace...
of Chicago. Progressives implemented anti-trust laws and regulated such industries of meat-packing, drugs, and railroads. Four new constitutional amendments—the Sixteenth
Sixteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution
The Sixteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution allows the Congress to levy an income tax without apportioning it among the states or basing it on Census results...
through Nineteenth
Nineteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution
The Nineteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution prohibits any United States citizen to be denied the right to vote based on sex. It was ratified on August 18, 1920....
—resulted from progressive activism, bringing the federal income tax, direct election of Senators, prohibition, and woman suffrage. The Progressive Movement lasted through the 1920s; the most active period was 1900–1918.
Imperialism
The United States emerged as a world economic and military power after 1890. The main episode was the Spanish–American War, which began when Spain refused American demands to reform its oppressive policies in CubaCuba
The Republic of Cuba is an island nation in the Caribbean. The nation of Cuba consists of the main island of Cuba, the Isla de la Juventud, and several archipelagos. Havana is the largest city in Cuba and the country's capital. Santiago de Cuba is the second largest city...
. The "splendid little war", as one official called it, involved a series of quick American victories on land and at sea. At the Treaty of Paris
Treaty of Paris (1898)
The Treaty of Paris of 1898 was signed on December 10, 1898, at the end of the Spanish-American War, and came into effect on April 11, 1899, when the ratifications were exchanged....
peace conference the United States acquired the Philippines
Philippines
The Philippines , officially known as the Republic of the Philippines , is a country in Southeast Asia in the western Pacific Ocean. To its north across the Luzon Strait lies Taiwan. West across the South China Sea sits Vietnam...
, Puerto Rico
Puerto Rico
Puerto Rico , officially the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico , is an unincorporated territory of the United States, located in the northeastern Caribbean, east of the Dominican Republic and west of both the United States Virgin Islands and the British Virgin Islands.Puerto Rico comprises an...
, and Guam
Guam
Guam is an organized, unincorporated territory of the United States located in the western Pacific Ocean. It is one of five U.S. territories with an established civilian government. Guam is listed as one of 16 Non-Self-Governing Territories by the Special Committee on Decolonization of the United...
. Cuba became an independent country, under close American tutelage. Although the war itself was widely popular, the peace terms proved controversial. William Jennings Bryan led his Democratic Party in opposition to control of the Philippines, which he denounced as imperialism unbecoming to American democracy. President William McKinley
William McKinley
William McKinley, Jr. was the 25th President of the United States . He is best known for winning fiercely fought elections, while supporting the gold standard and high tariffs; he succeeded in forging a Republican coalition that for the most part dominated national politics until the 1930s...
defended the acquisition, and was riding high as the nation had returned to prosperity and felt triumphant in the war. McKinley easily defeated Bryan in a rematch in the 1900 presidential election
United States presidential election, 1900
The United States presidential election of 1900 was a re-match of the 1896 race between Republican President William McKinley and his Democratic challenger, William Jennings Bryan. The return of economic prosperity and recent victory in the Spanish–American War helped McKinley to score a decisive...
. After defeating an insurrection by Filipino nationalists, the United States engaged in a large-scale program to modernize the economy of the Philippines, and dramatically upgrade the public health facilities. By 1908, however, Americans lost interest in an empire, and turned their international attention to the Caribbean, and especially the building of the Panama Canal
Panama Canal
The Panama Canal is a ship canal in Panama that joins the Atlantic Ocean and the Pacific Ocean and is a key conduit for international maritime trade. Built from 1904 to 1914, the canal has seen annual traffic rise from about 1,000 ships early on to 14,702 vessels measuring a total of 309.6...
. The canal opened in 1914, and increased trade with Japan and the rest of the Far East. A key innovation was the Open Door Policy
Open Door Policy
The Open Door Policy is a concept in foreign affairs, which usually refers to the policy in 1899 allowing multiple Imperial powers access to China, with none of them in control of that country. As a theory, the Open Door Policy originates with British commercial practice, as was reflected in...
, whereby the imperial powers were given equal access to Chinese business, with no one of them allowed to take control of China.
World War I
As World War IWorld War I
World War I , which was predominantly called the World War or the Great War from its occurrence until 1939, and the First World War or World War I thereafter, was a major war centred in Europe that began on 28 July 1914 and lasted until 11 November 1918...
raged in Europe from 1914, President Woodrow Wilson took full control of foreign policy, declaring neutrality but warning Germany that resumption unrestricted submarine warfare
Unrestricted submarine warfare
Unrestricted submarine warfare is a type of naval warfare in which submarines sink merchantmen without warning, as opposed to attacks per prize rules...
against American ships would mean war. Germany decided to take the risk and try to win by cutting off Britain; the U.S. declared of war in April 1917. American money, food and munitions arrived quickly, but troops had to be drafted, trained; by summer 1918 American soldiers under General John J. Pershing
John J. Pershing
John Joseph "Black Jack" Pershing, GCB , was a general officer in the United States Army who led the American Expeditionary Forces in World War I...
arrived at the rate of 10,000 a day, while Germany was unable to replace its losses. The result was Allied
Allies of World War I
The Entente Powers were the countries at war with the Central Powers during World War I. The members of the Triple Entente were the United Kingdom, France, and the Russian Empire; Italy entered the war on their side in 1915...
victory in November 1918. President Woodrow Wilson
Woodrow Wilson
Thomas Woodrow Wilson was the 28th President of the United States, from 1913 to 1921. A leader of the Progressive Movement, he served as President of Princeton University from 1902 to 1910, and then as the Governor of New Jersey from 1911 to 1913...
demanded Germany depose the Kaiser and accept his terms, the Fourteen Points
Fourteen Points
The Fourteen Points was a speech given by United States President Woodrow Wilson to a joint session of Congress on January 8, 1918. The address was intended to assure the country that the Great War was being fought for a moral cause and for postwar peace in Europe...
. Wilson dominated the 1919 Paris Peace Conference
Paris Peace Conference, 1919
The Paris Peace Conference was the meeting of the Allied victors following the end of World War I to set the peace terms for the defeated Central Powers following the armistices of 1918. It took place in Paris in 1919 and involved diplomats from more than 32 countries and nationalities...
but Germany was treated harshly by the Allies in the Treaty of Versailles
Treaty of Versailles
The Treaty of Versailles was one of the peace treaties at the end of World War I. It ended the state of war between Germany and the Allied Powers. It was signed on 28 June 1919, exactly five years after the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand. The other Central Powers on the German side of...
(1919) as Wilson put all his hopes in the new League of Nations
League of Nations
The League of Nations was an intergovernmental organization founded as a result of the Paris Peace Conference that ended the First World War. It was the first permanent international organization whose principal mission was to maintain world peace...
. Wilson refused to compromise with Senate Republicans over the issue of Congressional power to declare war, and the Senate rejected the Treaty and the League.
Woman suffrage

Seneca Falls Convention
The Seneca Falls Convention was an early and influential women's rights convention held in Seneca Falls, New York, July 19–20, 1848. It was organized by local New York women upon the occasion of a visit by Boston-based Lucretia Mott, a Quaker famous for her speaking ability, a skill rarely...
, organized by Elizabeth Cady Stanton
Elizabeth Cady Stanton
Elizabeth Cady Stanton was an American social activist, abolitionist, and leading figure of the early woman's movement...
and Lucretia Mott
Lucretia Mott
Lucretia Coffin Mott was an American Quaker, abolitionist, social reformer, and proponent of women's rights.- Early life and education:...
, and the Declaration of Sentiments
Declaration of Sentiments
The Declaration of Sentiments, also known as the Declaration of Rights and Sentiments, is a document signed in 1848 by 68 women and 32 men, 100 out of some 300 attendees at the first women's rights convention, in Seneca Falls, New York, now known as the Seneca Falls Convention...
demanding equal rights for women. Many of the activists became politically aware during the abolitionist movement. The women's rights campaign during "first-wave feminism
First-wave feminism
First-wave feminism refers to a period of feminist activity during the 19th and early twentieth century in the United Kingdom, Canada, and the United States. It focused on de jure inequalities, primarily on gaining women's suffrage .The term first-wave was coined retroactively in the 1970s...
" was led by Mott, Stanton, Susan B. Anthony
Susan B. Anthony
Susan Brownell Anthony was a prominent American civil rights leader who played a pivotal role in the 19th century women's rights movement to introduce women's suffrage into the United States. She was co-founder of the first Women's Temperance Movement with Elizabeth Cady Stanton as President...
, among many others. The movement reorganized after the Civil War, gaining experienced campaigners, many of whom had worked for prohibition in the Women's Christian Temperance Union. By the end of the 19th century a few western states had granted women full voting rights, though women had made significant legal victories, gaining rights in areas such as property and child custody.
Around 1912 the feminist movement
Feminist movement
The feminist movement refers to a series of campaigns for reforms on issues such as reproductive rights, domestic violence, maternity leave, equal pay, women's suffrage, sexual harassment and sexual violence...
, which had grown sluggish, began to reawaken, putting an emphasis on its demands for equality and arguing that the corruption of American politics demanded purification by women, because men could not do that job. Protests became increasingly common as suffragette
Suffragette
"Suffragette" is a term coined by the Daily Mail newspaper as a derogatory label for members of the late 19th and early 20th century movement for women's suffrage in the United Kingdom, in particular members of the Women's Social and Political Union...
Alice Paul
Alice Paul
Alice Stokes Paul was an American suffragist and activist. Along with Lucy Burns and others, she led a successful campaign for women's suffrage that resulted in the passage of the Nineteenth Amendment to the U.S. Constitution in 1920.-Activism: Alice Paul received her undergraduate education from...
led parades through the capital and major cities. Paul split from the large National American Woman Suffrage Association
National American Woman Suffrage Association
The National American Woman Suffrage Association was an American women's rights organization formed in May 1890 as a unification of the National Woman Suffrage Association and the American Woman Suffrage Association...
(NAWSA), which favored a more moderate approach and supported the Democratic Party and Woodrow Wilson, led by Carrie Chapman Catt
Carrie Chapman Catt
Carrie Chapman Catt was a women's suffrage leader who campaigned for the Nineteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution which gave U.S. women the right to vote in 1920...
, and formed the more militant National Woman's Party
National Woman's Party
The National Woman's Party , was a women's organization founded by Alice Paul in 1915 that fought for women's rights during the early 20th century in the United States, particularly for the right to vote on the same terms as men...
. Suffragists were arrested during their "Silent Sentinels
Silent Sentinels
The Silent Sentinels were a group of women in favor of women's suffrage organized by Alice Paul to protest in front of the White House during Woodrow Wilson's presidency. The protests started January 10, 1917 and lasted until June 1919 when the Nineteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution...
" pickets at the White House, the first time such a tactic was used, and were taken as political prisoner
Political prisoner
According to the Longman Dictionary of Contemporary English, a political prisoner is ‘someone who is in prison because they have opposed or criticized the government of their own country’....
s.
Finally, the suffragettes were ordered released from prison, and Wilson urged Congress to pass a Constitutional amendment enfranchising women. The old anti-suffragist argument that only men could fight a war, and therefore only men deserve the right to vote, was refuted by the enthusiastic participation of tens of thousands of American women on the home front in World War I. Across the world, grateful nations gave women the right to vote. Furthermore, most of the Western states had already given the women the right to vote in state and national elections, and the representatives from those states, including the first woman Jeannette Rankin
Jeannette Rankin
Jeannette Pickering Rankin was the first woman in the US Congress. A Republican, she was elected statewide in Montana in 1916 and again in 1940. A lifelong pacifist, she voted against the entry of the United States into both World War I in 1917 and World War II in 1941, the only member of Congress...
of Montana, demonstrated that woman suffrage was a success. The main resistance came from the south, where white leaders were worried about the threat of black women voting. Nevertheless Congress passed the Nineteenth Amendment
Nineteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution
The Nineteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution prohibits any United States citizen to be denied the right to vote based on sex. It was ratified on August 18, 1920....
in 1919. It became constitutional law on August 26, 1920, after ratification by the 36th required state.
NAWSA became the League of Women Voters
League of Women Voters
The League of Women Voters is an American political organization founded in 1920 by Carrie Chapman Catt during the last meeting of the National American Woman Suffrage Association approximately six months before the Nineteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution gave women the right to vote...
and the National Woman's Party began lobbying for full equality and the Equal Rights Amendment
Equal Rights Amendment
The Equal Rights Amendment was a proposed amendment to the United States Constitution. The ERA was originally written by Alice Paul and, in 1923, it was introduced in the Congress for the first time...
which would pass Congress during the second wave of the women's movement in 1972. Politicians responded to the new electorate by emphasizing issues of special interest to women, especially prohibition, child health, and world peace. The main surge of women voting came in 1928, when the big-city machines realized they needed the support of women to elect Al Smith
Al Smith
Alfred Emanuel Smith. , known in private and public life as Al Smith, was an American statesman who was elected the 42nd Governor of New York three times, and was the Democratic U.S. presidential candidate in 1928...
, while rural organizations mobilized women to support Prohibition and vote for Republican Herbert Hoover
Herbert Hoover
Herbert Clark Hoover was the 31st President of the United States . Hoover was originally a professional mining engineer and author. As the United States Secretary of Commerce in the 1920s under Presidents Warren Harding and Calvin Coolidge, he promoted partnerships between government and business...
.
Roaring Twenties, the Great Depression, and World War II (1918–1945)

Treaty of Versailles
The Treaty of Versailles was one of the peace treaties at the end of World War I. It ended the state of war between Germany and the Allied Powers. It was signed on 28 June 1919, exactly five years after the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand. The other Central Powers on the German side of...
imposed by its Allies
Allies of World War I
The Entente Powers were the countries at war with the Central Powers during World War I. The members of the Triple Entente were the United Kingdom, France, and the Russian Empire; Italy entered the war on their side in 1915...
on the defeated Central Powers
Central Powers
The Central Powers were one of the two warring factions in World War I , composed of the German Empire, the Austro-Hungarian Empire, the Ottoman Empire, and the Kingdom of Bulgaria...
; instead, the United States chose to pursue unilateralism
Unilateralism
Unilateralism is any doctrine or agenda that supports one-sided action. Such action may be in disregard for other parties, or as an expression of a commitment toward a direction which other parties may find agreeable...
, if not isolationism
Isolationism
Isolationism is the policy or doctrine of isolating one's country from the affairs of other nations by declining to enter into alliances, foreign economic commitments, international agreements, etc., seeking to devote the entire efforts of one's country to its own advancement and remain at peace by...
. The aftershock of Russia's October Revolution
October Revolution
The October Revolution , also known as the Great October Socialist Revolution , Red October, the October Uprising or the Bolshevik Revolution, was a political revolution and a part of the Russian Revolution of 1917...
resulted in real fears of communism
Communism
Communism is a social, political and economic ideology that aims at the establishment of a classless, moneyless, revolutionary and stateless socialist society structured upon common ownership of the means of production...
in the United States, leading to a three-year Red Scare
First Red Scare
In American history, the First Red Scare of 1919–1920 was marked by a widespread fear of Bolshevism and anarchism. Concerns over the effects of radical political agitation in American society and alleged spread in the American labor movement fueled the paranoia that defined the period.The First Red...
. In 1918 the U.S. lost 675,000 people to the Spanish flu
Spanish flu
The 1918 flu pandemic was an influenza pandemic, and the first of the two pandemics involving H1N1 influenza virus . It was an unusually severe and deadly pandemic that spread across the world. Historical and epidemiological data are inadequate to identify the geographic origin...
pandemic
Pandemic
A pandemic is an epidemic of infectious disease that is spreading through human populations across a large region; for instance multiple continents, or even worldwide. A widespread endemic disease that is stable in terms of how many people are getting sick from it is not a pandemic...
.
In 1920, the manufacture, sale, import and export of alcohol were prohibited by the Eighteenth Amendment
Eighteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution
The Eighteenth Amendment of the United States Constitution established Prohibition in the United States. The separate Volstead Act set down methods of enforcing the Eighteenth Amendment, and defined which "intoxicating liquors" were prohibited, and which were excluded from prohibition...
. Prohibition
Prohibition in the United States
Prohibition in the United States was a national ban on the sale, manufacture, and transportation of alcohol, in place from 1920 to 1933. The ban was mandated by the Eighteenth Amendment to the Constitution, and the Volstead Act set down the rules for enforcing the ban, as well as defining which...
encouraged illegal breweries and dealers to make substantial amounts of money selling alcohol illegally. The Prohibition ended in 1933, a failure. Additionally, the KKK re-formed during that decade and gathered nearly 4.5 million members by 1924, and the U.S. government passed the Immigration Act of 1924
Immigration Act of 1924
The Immigration Act of 1924, or Johnson–Reed Act, including the National Origins Act, and Asian Exclusion Act , was a United States federal law that limited the annual number of immigrants who could be admitted from any country to 2% of the number of people from that country who were already...
restricting foreign immigration. The 1920s were also known as the Roaring Twenties
Roaring Twenties
The Roaring Twenties is a phrase used to describe the 1920s, principally in North America, but also in London, Berlin and Paris for a period of sustained economic prosperity. The phrase was meant to emphasize the period's social, artistic, and cultural dynamism...
, due to the great economic prosperity during this period. Jazz
Jazz
Jazz is a musical style that originated at the beginning of the 20th century in African American communities in the Southern United States. It was born out of a mix of African and European music traditions. From its early development until the present, jazz has incorporated music from 19th and 20th...
became popular among the younger generation, and thus was also called the Jazz Age
Jazz Age
The Jazz Age was a movement that took place during the 1920s or the Roaring Twenties from which jazz music and dance emerged. The movement came about with the introduction of mainstream radio and the end of the war. This era ended in the 1930s with the beginning of The Great Depression but has...
.
Great Depression

Stock market
A stock market or equity market is a public entity for the trading of company stock and derivatives at an agreed price; these are securities listed on a stock exchange as well as those only traded privately.The size of the world stock market was estimated at about $36.6 trillion...
, which later led to the Stock Market Crash
Wall Street Crash of 1929
The Wall Street Crash of 1929 , also known as the Great Crash, and the Stock Market Crash of 1929, was the most devastating stock market crash in the history of the United States, taking into consideration the full extent and duration of its fallout...
on October 29, 1929. This, along with many other economic factors
Causes of the Great Depression
The causes of the Great Depression are still a matter of active debate among economists, and is part of the larger debate about economic crises, although the popular belief is that the Great Depression was caused by the crash of the stock market...
, triggered a worldwide depression known as the Great Depression
Great Depression
The Great Depression was a severe worldwide economic depression in the decade preceding World War II. The timing of the Great Depression varied across nations, but in most countries it started in about 1929 and lasted until the late 1930s or early 1940s...
. During this time, the United States experienced deflation
Deflation (economics)
In economics, deflation is a decrease in the general price level of goods and services. Deflation occurs when the inflation rate falls below 0% . This should not be confused with disinflation, a slow-down in the inflation rate...
, unemployment soared from 3% in 1929 to 25% in 1933, and manufacturing output collapsed by one-third.
In 1932, Democratic
Democratic Party (United States)
The Democratic Party is one of two major contemporary political parties in the United States, along with the Republican Party. The party's socially liberal and progressive platform is largely considered center-left in the U.S. political spectrum. The party has the lengthiest record of continuous...
presidential nominee Franklin D. Roosevelt
Franklin D. Roosevelt
Franklin Delano Roosevelt , also known by his initials, FDR, was the 32nd President of the United States and a central figure in world events during the mid-20th century, leading the United States during a time of worldwide economic crisis and world war...
promised "a new deal
New Deal
The New Deal was a series of economic programs implemented in the United States between 1933 and 1936. They were passed by the U.S. Congress during the first term of President Franklin D. Roosevelt. The programs were Roosevelt's responses to the Great Depression, and focused on what historians call...
for the American people", a phrase that has endured as a label for his administration and its many domestic achievements. The desperate economic situation, along with the substantial Democratic victories in the 1932 elections, gave Roosevelt unusual influence over Congress in the "First Hundred Days" of his administration. He used his leverage to win rapid passage of a series of measures to create welfare programs and regulate the banking system, stock market, industry and agriculture, along with many other government efforts to end the Great Depression and reform the American economy. Some programs that were a part of Roosevelt's New Deal
New Deal
The New Deal was a series of economic programs implemented in the United States between 1933 and 1936. They were passed by the U.S. Congress during the first term of President Franklin D. Roosevelt. The programs were Roosevelt's responses to the Great Depression, and focused on what historians call...
include the Works Progress Administration
Works Progress Administration
The Works Progress Administration was the largest and most ambitious New Deal agency, employing millions of unskilled workers to carry out public works projects, including the construction of public buildings and roads, and operated large arts, drama, media, and literacy projects...
(WPA) relief program, the Social Security Act
Social Security (United States)
In the United States, Social Security refers to the federal Old-Age, Survivors, and Disability Insurance program.The original Social Security Act and the current version of the Act, as amended encompass several social welfare and social insurance programs...
, the Emergency Banking Act
Emergency Banking Act
The Emergency Banking Act was an act of the United States Congress spearheaded by President Franklin D. Roosevelt during the Great Depression. It was passed on March 9, 1933...
, and the Economy Act
Economy Act
The Economy Act of 1933, officially titled the Act of March 20, 1933 , is an Act of Congress that cut the salaries of federal workers and reduced benefit payments to veterans, moves intended to reduce the federal deficit in the United States....
.
World War II

Empire of Japan
The Empire of Japan is the name of the state of Japan that existed from the Meiji Restoration on 3 January 1868 to the enactment of the post-World War II Constitution of...
asserted dominance in East Asia and in the Pacific. Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany , also known as the Third Reich , but officially called German Reich from 1933 to 1943 and Greater German Reich from 26 June 1943 onward, is the name commonly used to refer to the state of Germany from 1933 to 1945, when it was a totalitarian dictatorship ruled by...
and Fascist Italy
Kingdom of Italy (1861–1946)
The Kingdom of Italy was a state forged in 1861 by the unification of Italy under the influence of the Kingdom of Sardinia, which was its legal predecessor state...
militarized to and threatened conquests, while Britain and France attempted appeasement
Appeasement
The term appeasement is commonly understood to refer to a diplomatic policy aimed at avoiding war by making concessions to another power. Historian Paul Kennedy defines it as "the policy of settling international quarrels by admitting and satisfying grievances through rational negotiation and...
to avert another war in Europe. U.S. legislation in the Neutrality Acts sought to avoid foreign conflicts; however policy clashed with increasing anti-Nazi feelings following the German invasion of Poland in September 1939 that started World War II
World War II
World War II, or the Second World War , was a global conflict lasting from 1939 to 1945, involving most of the world's nations—including all of the great powers—eventually forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis...
. Roosevelt positioned the U.S. as the "Arsenal of Democracy
Arsenal of Democracy
"The Arsenal of Democracy" was a propaganda slogan coined by U.S. President Franklin D. Roosevelt, in a radio broadcast delivered on December 29, 1940. Roosevelt promised to help the United Kingdom fight Nazi Germany by giving them military supplies while the United States stayed out of the actual...
" pledging full-scale financial and munitions support for the Allies—but no soldiers. Japan tried to neutralize America's power in the Pacific by attacking Pearl Harbor
Attack on Pearl Harbor
The attack on Pearl Harbor was a surprise military strike conducted by the Imperial Japanese Navy against the United States naval base at Pearl Harbor, Hawaii, on the morning of December 7, 1941...
on December 7, 1941, which catalyzed American support to enter the war and seek revenge.
The main contributions of the U.S. to the Allied war effort comprised money, industrial output, food, petroleum, technological innovation, and (especially 1944-45), soldiers. Much of the focus in Washington was maximizing the economic output of the nation. The overall result was a dramatic increase in GDP, the export of vast quantities of supplies to the Allies and to American forces overseas, the end of unemployment, and a rise in civilian consumption even as 40% of the GDP went to the war effort. This was achieved by tens of millions of workers moving from low-productivity occupations to high efficiency jobs, improvements in productivity through better technology and management, and the move into the active labor force of students, retired people, housewives, and the unemployed, and an increase in hours worked. It was exhausting; leisure activities declined sharply. People tolerated the extra work because of patriotism, the pay, and the confidence it was only "for the duration" and life would return to normal as soon as the war was won. Most durable goods became unavailable, and meat, clothing, and gasoline were tightly rationed. In industrial areas housing was in short supply as people doubled up and lived in cramped quarters. Prices and wages were controlled, and Americans saved a high portion of their incomes, which led to renewed growth after the war instead of a return to depression.
The Allies
Allies of World War II
The Allies of World War II were the countries that opposed the Axis powers during the Second World War . Former Axis states contributing to the Allied victory are not considered Allied states...
--the U.S., Britain and the Soviet Union, as well as China, Canada and other countries—fought the Axis powers
Axis Powers
The Axis powers , also known as the Axis alliance, Axis nations, Axis countries, or just the Axis, was an alignment of great powers during the mid-20th century that fought World War II against the Allies. It began in 1936 with treaties of friendship between Germany and Italy and between Germany and...
of Germany, Italy, and Japan. The Allies saw Germany as the main threat, and gave highest priority to Europe. The U.S. dominated the war against Japan, and stopped Japanese expansion in the Pacific in 1942. After losing to the Japanese Pearl Harbor and in the Philippines, and drawing the Battle of the Coral Sea
Battle of the Coral Sea
The Battle of the Coral Sea, fought from 4–8 May 1942, was a major naval battle in the Pacific Theater of World War II between the Imperial Japanese Navy and Allied naval and air forces from the United States and Australia. The battle was the first fleet action in which aircraft carriers engaged...
(May 1942), the American Navy inflicted a decisive blow at Midway
Battle of Midway
The Battle of Midway is widely regarded as the most important naval battle of the Pacific Campaign of World War II. Between 4 and 7 June 1942, approximately one month after the Battle of the Coral Sea and six months after Japan's attack on Pearl Harbor, the United States Navy decisively defeated...
(June 1942). American ground forces assisted in the North African Campaign
North African campaign
During the Second World War, the North African Campaign took place in North Africa from 10 June 1940 to 13 May 1943. It included campaigns fought in the Libyan and Egyptian deserts and in Morocco and Algeria and Tunisia .The campaign was fought between the Allies and Axis powers, many of whom had...
that eventually concluded with the collapse of Mussolini's fascist government in 1943, as Italy switched to the Allied side. A more significant European front was opened on D-Day
D-Day
D-Day is a term often used in military parlance to denote the day on which a combat attack or operation is to be initiated. "D-Day" often represents a variable, designating the day upon which some significant event will occur or has occurred; see Military designation of days and hours for similar...
, June 6, 1944, in which American and Allied forces invaded Nazi-occupied France from Britain.

United States home front during World War II
This page, United States home front during World War II, covers the developments within the United States, 1940–1945, to support its efforts during World War II.-Economics:...
, mobilization of the U.S. economy was managed by Roosevelt's War Production Board
War Production Board
The War Production Board was established as a government agency on January 16, 1942 by executive order of Franklin D. Roosevelt.The purpose of the board was to regulate the production and allocation of materials and fuel during World War II in the United States...
. The wartime production boom led to full employment, wiping out this vestige of the Great Depression. Indeed, labor shortage
Labor shortage
In its narrowest definition, a labor shortage is an economic condition in which there are insufficient qualified candidates to fill the market-place demands for employment at any price...
s encouraged industry to look for new sources of workers, finding new roles for women and blacks.
However the fervor also inspired anti-Japanese sentiment
Anti-Japanese sentiment
Anti-Japanese sentiment involves hatred, grievance, distrust, dehumanization, intimidation, fear, hostility, and/or general dislike of the Japanese people and Japanese diaspora as ethnic or national group, Japan, Japanese culture, and/or anything Japanese. Sometimes the terms Japanophobia and...
, which responded by removing everyone of Japanese descent from the West Coast war zone
Japanese American internment
Japanese-American internment was the relocation and internment by the United States government in 1942 of approximately 110,000 Japanese Americans and Japanese who lived along the Pacific coast of the United States to camps called "War Relocation Camps," in the wake of Imperial Japan's attack on...
. Research and development
Research and development
The phrase research and development , according to the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development, refers to "creative work undertaken on a systematic basis in order to increase the stock of knowledge, including knowledge of man, culture and society, and the use of this stock of...
took flight as well, best seen in the Manhattan Project
Manhattan Project
The Manhattan Project was a research and development program, led by the United States with participation from the United Kingdom and Canada, that produced the first atomic bomb during World War II. From 1942 to 1946, the project was under the direction of Major General Leslie Groves of the US Army...
, a secret effort to harness nuclear fission
Nuclear fission
In nuclear physics and nuclear chemistry, nuclear fission is a nuclear reaction in which the nucleus of an atom splits into smaller parts , often producing free neutrons and photons , and releasing a tremendous amount of energy...
to produce highly destructive atomic bombs.
The Allied pushed the Germans out of France, but faced an unexpected counterattack at the Battle of the Bulge
Battle of the Bulge
The Battle of the Bulge was a major German offensive , launched toward the end of World War II through the densely forested Ardennes mountain region of Wallonia in Belgium, hence its French name , and France and...
in December. The final German effort failed, and as 1945 opened Allied armies in East and West were converging on Berlin, as the Nazis hurriedly tried to kill the last remaining Jews. The western front stopped short, leaving Berlin
Berlin
Berlin is the capital city of Germany and is one of the 16 states of Germany. With a population of 3.45 million people, Berlin is Germany's largest city. It is the second most populous city proper and the seventh most populous urban area in the European Union...
to the Soviets as the Nazi regime formally capitulated in May 1945, ending the war in Europe. Over in the Pacific, the U.S. implemented an island hopping strategy toward Tokyo
Tokyo
, ; officially , is one of the 47 prefectures of Japan. Tokyo is the capital of Japan, the center of the Greater Tokyo Area, and the largest metropolitan area of Japan. It is the seat of the Japanese government and the Imperial Palace, and the home of the Japanese Imperial Family...
, establishing airfields for bombing runs against mainland Japan from the Mariana Islands
Mariana Islands
The Mariana Islands are an arc-shaped archipelago made up by the summits of 15 volcanic mountains in the north-western Pacific Ocean between the 12th and 21st parallels north and along the 145th meridian east...
and achieving hard-fought victories at Iwo Jima
Battle of Iwo Jima
The Battle of Iwo Jima , or Operation Detachment, was a major battle in which the United States fought for and captured the island of Iwo Jima from the Empire of Japan. The U.S...
and Okinawa
Battle of Okinawa
The Battle of Okinawa, codenamed Operation Iceberg, was fought on the Ryukyu Islands of Okinawa and was the largest amphibious assault in the Pacific War of World War II. The 82-day-long battle lasted from early April until mid-June 1945...
in 1945. Bloodied at Okinawa, the U.S. prepared to invade Japan's home islands when B-29's dropped two atomic bombs on Japanese cities
Atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki
During the final stages of World War II in 1945, the United States conducted two atomic bombings against the cities of Hiroshima and Nagasaki in Japan, the first on August 6, 1945, and the second on August 9, 1945. These two events are the only use of nuclear weapons in war to date.For six months...
, forcing the empire's surrender in a matter of days and thus ending World War II. The U.S. occupied Japan (and part of Germany), sending Douglas MacArthur
Douglas MacArthur
General of the Army Douglas MacArthur was an American general and field marshal of the Philippine Army. He was a Chief of Staff of the United States Army during the 1930s and played a prominent role in the Pacific theater during World War II. He received the Medal of Honor for his service in the...
to restructure the Japanese economy and political system along American lines.
Though the nation lost more than 400,000 soldiers, the mainland prospered untouched by the devastation of war that inflicted a heavy toll on Europe and Asia.
Participation in postwar foreign affairs marked the end of predominant American isolationism. The awesome threat of nuclear weapons inspired both optimism
Nuclear power debate
The nuclear power debate is about the controversy which has surrounded the deployment and use of nuclear fission reactors to generate electricity from nuclear fuel for civilian purposes...
and fear
Mutual assured destruction
Mutual Assured Destruction, or mutually assured destruction , is a doctrine of military strategy and national security policy in which a full-scale use of high-yield weapons of mass destruction by two opposing sides would effectively result in the complete, utter and irrevocable annihilation of...
. Nuclear weapons were never used after 1945, as both sides drew back from the brink and a "long peace" characterized the Cold War
Cold War
The Cold War was the continuing state from roughly 1946 to 1991 of political conflict, military tension, proxy wars, and economic competition between the Communist World—primarily the Soviet Union and its satellite states and allies—and the powers of the Western world, primarily the United States...
years, 1947–1991. There were, however, regional wars in Korea and Vietnam.
The Cold War begins (1945–1964)

Superpower
A superpower is a state with a dominant position in the international system which has the ability to influence events and its own interests and project power on a worldwide scale to protect those interests...
s. The U.S. Senate on a bipartisan vote approved U.S. participation in the United Nations
United Nations
The United Nations is an international organization whose stated aims are facilitating cooperation in international law, international security, economic development, social progress, human rights, and achievement of world peace...
(UN), which marked a turn away from the traditional isolationism
Isolationism
Isolationism is the policy or doctrine of isolating one's country from the affairs of other nations by declining to enter into alliances, foreign economic commitments, international agreements, etc., seeking to devote the entire efforts of one's country to its own advancement and remain at peace by...
of the U.S. and toward increased international involvement.
The primary American goal of 1945–48 was to rescue Europe from the devastation of World War II and to contain the expansion of Communism
Communism
Communism is a social, political and economic ideology that aims at the establishment of a classless, moneyless, revolutionary and stateless socialist society structured upon common ownership of the means of production...
, represented by the Soviet Union
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union , officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics , was a constitutionally socialist state that existed in Eurasia between 1922 and 1991....
. The Truman Doctrine
Truman Doctrine
The Truman Doctrine was a policy set forth by U.S. President Harry S Truman in a speech on March 12, 1947 stating that the U.S. would support Greece and Turkey with economic and military aid to prevent their falling into the Soviet sphere...
of 1947 provided military and economic aid to Greece and Turkey to counteract the threat of Communist expansion in the Balkans. In 1948, the United States replaced piecemeal financial aid programs with a comprehensive Marshall Plan
Marshall Plan
The Marshall Plan was the large-scale American program to aid Europe where the United States gave monetary support to help rebuild European economies after the end of World War II in order to combat the spread of Soviet communism. The plan was in operation for four years beginning in April 1948...
, which pumped money into the economy of Western Europe, and removed trade barriers, while modernizing the managerial practices of businesses and governments. The Plan's $13 billion budget was in the context of a U.S. GDP of $258 billion in 1948, and was on top of $12 billion in American aid to Europe between the end of the war and the start of the Marshall Plan. Soviet head of state Joseph Stalin
Joseph Stalin
Joseph Vissarionovich Stalin was the Premier of the Soviet Union from 6 May 1941 to 5 March 1953. He was among the Bolshevik revolutionaries who brought about the October Revolution and had held the position of first General Secretary of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union's Central Committee...
prevented his satellites from participating, and from that point on Eastern Europe, with inefficient centralized economies, fell further and further behind Western Europe in terms of economic development and prosperity. In 1949, the United States, rejecting the long-standing policy of no military alliances in peacetime, formed the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) alliance, which continues into the 21st century. In response the Soviets formed the Warsaw Pact
Warsaw Pact
The Warsaw Treaty Organization of Friendship, Cooperation, and Mutual Assistance , or more commonly referred to as the Warsaw Pact, was a mutual defense treaty subscribed to by eight communist states in Eastern Europe...
of communist states.
In August 1949 the Soviets tested their first nuclear weapon, thereby escalating the risk of warfare. Indeed, the threat of mutually assured destruction prevented both powers from going too far, and resulted in proxy wars, especially in Korea
Korean War
The Korean War was a conventional war between South Korea, supported by the United Nations, and North Korea, supported by the People's Republic of China , with military material aid from the Soviet Union...
and Vietnam
Vietnam War
The Vietnam War was a Cold War-era military conflict that occurred in Vietnam, Laos, and Cambodia from 1 November 1955 to the fall of Saigon on 30 April 1975. This war followed the First Indochina War and was fought between North Vietnam, supported by its communist allies, and the government of...
, in which the two sides did not directly confront each other. Within the United States, the Cold War prompted concerns about Communist influence. The unexpected leapfrogging of American technology by the Soviets in 1957 with Sputnik, the first Earth satellite, began the Space Race
Space Race
The Space Race was a mid-to-late 20th century competition between the Soviet Union and the United States for supremacy in space exploration. Between 1957 and 1975, Cold War rivalry between the two nations focused on attaining firsts in space exploration, which were seen as necessary for national...
, won by the Americans as Apollo 11
Apollo 11
In early 1969, Bill Anders accepted a job with the National Space Council effective in August 1969 and announced his retirement as an astronaut. At that point Ken Mattingly was moved from the support crew into parallel training with Anders as backup Command Module Pilot in case Apollo 11 was...
landed astronauts on the moon in 1969. The angst about the weaknesses of American education led to large-scale federal support for science education and research.
In the decades after World War II, the United States became a global influence in economic, political, military, cultural, and technological affairs. Beginning in the 1950s, middle-class culture became obsessed with consumer goods. White Americans made up nearly 90% of the population in 1950.
In 1960
United States presidential election, 1960
The United States presidential election of 1960 was the 44th American presidential election, held on November 8, 1960, for the term beginning January 20, 1961, and ending January 20, 1965. The incumbent president, Republican Dwight D. Eisenhower, was not eligible to run again. The Republican Party...
, the charismatic politician John F. Kennedy
John F. Kennedy
John Fitzgerald "Jack" Kennedy , often referred to by his initials JFK, was the 35th President of the United States, serving from 1961 until his assassination in 1963....
was elected as the first and—thus far—only Roman Catholic President of the United States. The Kennedy family brought a new life and vigor to the atmosphere of the White House
White House
The White House is the official residence and principal workplace of the president of the United States. Located at 1600 Pennsylvania Avenue NW in Washington, D.C., the house was designed by Irish-born James Hoban, and built between 1792 and 1800 of white-painted Aquia sandstone in the Neoclassical...
. His time in office was marked by such notable events as the acceleration of the United States' role in the Space Race
Space Race
The Space Race was a mid-to-late 20th century competition between the Soviet Union and the United States for supremacy in space exploration. Between 1957 and 1975, Cold War rivalry between the two nations focused on attaining firsts in space exploration, which were seen as necessary for national...
; escalation of the American role in the Vietnam War
Vietnam War
The Vietnam War was a Cold War-era military conflict that occurred in Vietnam, Laos, and Cambodia from 1 November 1955 to the fall of Saigon on 30 April 1975. This war followed the First Indochina War and was fought between North Vietnam, supported by its communist allies, and the government of...
; the Cuban missile crisis
Cuban Missile Crisis
The Cuban Missile Crisis was a confrontation among the Soviet Union, Cuba and the United States in October 1962, during the Cold War...
; the Bay of Pigs Invasion
Bay of Pigs Invasion
The Bay of Pigs Invasion was an unsuccessful action by a CIA-trained force of Cuban exiles to invade southern Cuba, with support and encouragement from the US government, in an attempt to overthrow the Cuban government of Fidel Castro. The invasion was launched in April 1961, less than three months...
; the jailing of Martin Luther King, Jr.
Martin Luther King, Jr.
Martin Luther King, Jr. was an American clergyman, activist, and prominent leader in the African-American Civil Rights Movement. He is best known for being an iconic figure in the advancement of civil rights in the United States and around the world, using nonviolent methods following the...
during the Birmingham campaign
Birmingham campaign
The Birmingham campaign was a strategic movement organized by the Southern Christian Leadership Conference to bring attention to the unequal treatment that black Americans endured in Birmingham, Alabama...
; and the appointment of his brother Robert F. Kennedy
Robert F. Kennedy
Robert Francis "Bobby" Kennedy , also referred to by his initials RFK, was an American politician, a Democratic senator from New York, and a noted civil rights activist. An icon of modern American liberalism and member of the Kennedy family, he was a younger brother of President John F...
to his Cabinet as Attorney General
United States Attorney General
The United States Attorney General is the head of the United States Department of Justice concerned with legal affairs and is the chief law enforcement officer of the United States government. The attorney general is considered to be the chief lawyer of the U.S. government...
. Kennedy was assassinated
John F. Kennedy assassination
John Fitzgerald Kennedy, the thirty-fifth President of the United States, was assassinated at 12:30 p.m. Central Standard Time on Friday, November 22, 1963, in Dealey Plaza, Dallas, Texas...
in Dallas, Texas
Dallas, Texas
Dallas is the third-largest city in Texas and the ninth-largest in the United States. The Dallas-Fort Worth Metroplex is the largest metropolitan area in the South and fourth-largest metropolitan area in the United States...
, on November 22, 1963, leaving the nation in profound shock.
Climax of liberalism
The climax of liberalism came in the mid-1960s with the success of President Lyndon B. JohnsonLyndon B. Johnson
Lyndon Baines Johnson , often referred to as LBJ, was the 36th President of the United States after his service as the 37th Vice President of the United States...
(1963–69) in securing congressional passage of his Great Society
Great Society
The Great Society was a set of domestic programs in the United States promoted by President Lyndon B. Johnson and fellow Democrats in Congress in the 1960s. Two main goals of the Great Society social reforms were the elimination of poverty and racial injustice...
programs, including civil rights, the end of segregation
Racial segregation in the United States
Racial segregation in the United States, as a general term, included the racial segregation or hypersegregation of facilities, services, and opportunities such as housing, medical care, education, employment, and transportation along racial lines...
, Medicare
Medicare (United States)
Medicare is a social insurance program administered by the United States government, providing health insurance coverage to people who are aged 65 and over; to those who are under 65 and are permanently physically disabled or who have a congenital physical disability; or to those who meet other...
, extension of welfare
Welfare
Welfare refers to a broad discourse which may hold certain implications regarding the provision of a minimal level of wellbeing and social support for all citizens without the stigma of charity. This is termed "social solidarity"...
, federal aid to education at all levels, subsidies for the arts and humanities, environmental activism, and a series of programs designed to wipe out poverty. As recent historians have explained:
- "Gradually, liberal intellectuals crafted a new vision for achieving economic and social justice. The liberalism of the early 1960s contained no hint of radicalism, little disposition to revive new deal era crusades against concentrated economic power, and no intention to fast and class passions or redistribute wealth or restructure existing institutions. Internationally it was strongly anti-Communist. It aimed to defend the free world, to encourage economic growth at home, and to ensure that the resulting plenty was fairly distributed. Their agenda-much influenced by Keynesian economic theory-envisioned massive public expenditure that would speed economic growth, thus providing the public resources to fund larger welfare, housing, health, and educational programs."
Johnson was rewarded with an electoral landslide in 1964
United States presidential election, 1964
The United States presidential election of 1964 was held on November 3, 1964. Incumbent President Lyndon B. Johnson had come to office less than a year earlier following the assassination of his predecessor, John F. Kennedy. Johnson, who had successfully associated himself with Kennedy's...
against conservative Barry Goldwater
Barry Goldwater
Barry Morris Goldwater was a five-term United States Senator from Arizona and the Republican Party's nominee for President in the 1964 election. An articulate and charismatic figure during the first half of the 1960s, he was known as "Mr...
, which broke the decades-long control of Congress by the Conservative coalition
Conservative coalition
In the United States, the conservative coalition was an unofficial Congressional coalition bringing together the conservative majority of the Republican Party and the conservative, mostly Southern, wing of the Democratic Party...
. But the Republicans bounced back in 1966 and elected Richard Nixon
Richard Nixon
Richard Milhous Nixon was the 37th President of the United States, serving from 1969 to 1974. The only president to resign the office, Nixon had previously served as a US representative and senator from California and as the 36th Vice President of the United States from 1953 to 1961 under...
in 1968. Nixon largely continued the New Deal and Great Society programs he inherited; conservative reaction would come with the election of Ronald Reagan
Ronald Reagan
Ronald Wilson Reagan was the 40th President of the United States , the 33rd Governor of California and, prior to that, a radio, film and television actor....
in 1980.
Meanwhile, the American people completed a great migration from farms into the cities and experienced a period of sustained economic expansion. At the same time, institutionalized racism across the United States
Racism in the United States
Racism in the United States has been a major issue since the colonial era and the slave era. Legally sanctioned racism imposed a heavy burden on Native Americans, African Americans, Asian Americans, and Latin Americans...
, but especially in the South
Southern United States
The Southern United States—commonly referred to as the American South, Dixie, or simply the South—constitutes a large distinctive area in the southeastern and south-central United States...
, was increasingly challenged by the growing Civil Rights movement. The activism of African American
African American
African Americans are citizens or residents of the United States who have at least partial ancestry from any of the native populations of Sub-Saharan Africa and are the direct descendants of enslaved Africans within the boundaries of the present United States...
leaders Rosa Parks
Rosa Parks
Rosa Louise McCauley Parks was an African-American civil rights activist, whom the U.S. Congress called "the first lady of civil rights", and "the mother of the freedom movement"....
and Martin Luther King, Jr.
Martin Luther King, Jr.
Martin Luther King, Jr. was an American clergyman, activist, and prominent leader in the African-American Civil Rights Movement. He is best known for being an iconic figure in the advancement of civil rights in the United States and around the world, using nonviolent methods following the...
led to the Montgomery Bus Boycott
Montgomery Bus Boycott
The Montgomery Bus Boycott was a political and social protest campaign that started in 1955 in Montgomery, Alabama, USA, intended to oppose the city's policy of racial segregation on its public transit system. Many important figures in the civil rights movement were involved in the boycott,...
, which launched the movement. For years African Americans would struggle with violence against them, but would achieve great steps towards equality with Supreme Court decisions, including Brown v. Board of Education
Brown v. Board of Education
Brown v. Board of Education of Topeka, 347 U.S. 483 , was a landmark decision of the United States Supreme Court that declared state laws establishing separate public schools for black and white students unconstitutional. The decision overturned the Plessy v. Ferguson decision of 1896 which...
and Loving v. Virginia
Loving v. Virginia
Loving v. Virginia, , was a landmark civil rights case in which the United States Supreme Court, in a unanimous decision, declared Virginia's anti-miscegenation statute, the "Racial Integrity Act of 1924", unconstitutional, thereby overturning Pace v...
, the Civil Rights Act of 1964
Civil Rights Act of 1964
The Civil Rights Act of 1964 was a landmark piece of legislation in the United States that outlawed major forms of discrimination against African Americans and women, including racial segregation...
, the Voting Rights Act of 1965, and the Fair Housing Act of 1968, which ended the Jim Crow laws
Jim Crow laws
The Jim Crow laws were state and local laws in the United States enacted between 1876 and 1965. They mandated de jure racial segregation in all public facilities, with a supposedly "separate but equal" status for black Americans...
that legalized racial segregation
Racial segregation
Racial segregation is the separation of humans into racial groups in daily life. It may apply to activities such as eating in a restaurant, drinking from a water fountain, using a public toilet, attending school, going to the movies, or in the rental or purchase of a home...
between Whites and Blacks.
Martin Luther King, Jr., who had won the Nobel Peace Prize
Nobel Peace Prize
The Nobel Peace Prize is one of the five Nobel Prizes bequeathed by the Swedish industrialist and inventor Alfred Nobel.-Background:According to Nobel's will, the Peace Prize shall be awarded to the person who...
for his efforts to achieve equality of the races, was assassinated in 1968. Following his death others led the movement, most notably King's widow, Coretta Scott King
Coretta Scott King
Coretta Scott King was an American author, activist, and civil rights leader. The widow of Martin Luther King, Jr., Coretta Scott King helped lead the African-American Civil Rights Movement in the 1960s.Mrs...
, who was also active, like her husband, in the Opposition to the Vietnam War
Opposition to the Vietnam War
The movement against US involvment in the in Vietnam War began in the United States with demonstrations in 1964 and grew in strength in later years. The US became polarized between those who advocated continued involvement in Vietnam, and those who wanted peace. Peace movements consisted largely of...
, and in the Women's Liberation Movement. Over the first nine months of 1967, 128 American cities suffered 164 riot
Riot
A riot is a form of civil disorder characterized often by what is thought of as disorganized groups lashing out in a sudden and intense rash of violence against authority, property or people. While individuals may attempt to lead or control a riot, riots are thought to be typically chaotic and...
s. The late 1960s and early 1970s saw the strengthening of Black Power
Black Power
Black Power is a political slogan and a name for various associated ideologies. It is used in the movement among people of Black African descent throughout the world, though primarily by African Americans in the United States...
, however the decade would ultimately bring about positive strides toward integration.
The Women's Movement

Betty Friedan
Betty Friedan was an American writer, activist, and feminist.A leading figure in the Women's Movement in the United States, her 1963 book The Feminine Mystique is often credited with sparking the "second wave" of American feminism in the twentieth century...
's best-seller, The Feminine Mystique
The Feminine Mystique
The Feminine Mystique, published February 19, 1963, by W.W. Norton and Co., is a nonfiction book written by Betty Friedan. It is widely credited with sparking the beginning of second-wave feminism in the United States....
, which explained how many housewives felt trapped and unfulfilled, assaulted American culture for its creation of the notion that women could only find fulfillment through their roles as wives, mothers, and keepers of the home, and argued that women were just as able as men to do every type of job. In 1966 Friedan and others established the National Organization for Women
National Organization for Women
The National Organization for Women is the largest feminist organization in the United States. It was founded in 1966 and has a membership of 500,000 contributing members. The organization consists of 550 chapters in all 50 U.S...
, or NOW, to act for women as the NAACP did for African Americans.
Protests began, and the new Women's Liberation Movement grew in size and power, gained much media attention, and, by 1968, had replaced the Civil Rights Movement as the U.S.'s main social revolution. Marches, parades, rallies, boycotts, and pickets brought out thousands, sometimes millions; Friedan's Women's Strike for Equality
Women's Strike for Equality
The Women’s Strike for Equality was a strike which took place in the United States on August 26, 1970. It celebrated the 50th anniversary of the passing of the Nineteenth Amendment, which effectively gave American women the right to vote. The rally was sponsored by the National Organization for...
(1970) was a nation-wide success. The Movement was split into factions by political ideology early on, however (with NOW on the left, the Women's Equity Action League
Women's Equity Action League
The Women's Equity Action League, or WEAL, was a United States women's rights organization founded in 1968, during the feminist movement. The Women's Equity Action League was founded in Ohio and headquartered in Washington, D.C., as a "spin-off" of the National Organization for Women by more...
(WEAL) on the right, the National Women's Political Caucus
National Women's Political Caucus
The National Women's Political Caucus is a national bipartisan grassroots organization in the United States dedicated to recruiting, training, and supporting women who seek elected and appointed offices....
(NWPC) in the center, and more radical groups formed by younger women on the far left).
Along with Friedan, Gloria Steinem
Gloria Steinem
Gloria Marie Steinem is an American feminist, journalist, and social and political activist who became nationally recognized as a leader of, and media spokeswoman for, the women's liberation movement in the late 1960s and 1970s...
was an important feminist leader, co-founding the NWPC, the Women's Action Alliance
Women's Action Alliance
The Women's Action Alliance was a feminist organization in the United States, founded during the Women's Movmement of the 1960s and 1970s. It was founded by Gloria Steinem, the noted journalist, activist, and feminist leader...
, and editing the Movement's magazine, Ms. The proposed Equal Rights Amendment
Equal Rights Amendment
The Equal Rights Amendment was a proposed amendment to the United States Constitution. The ERA was originally written by Alice Paul and, in 1923, it was introduced in the Congress for the first time...
to the Constitution, passed by Congress in 1972 and favored by about seventy percent of the American public, failed to be ratified in 1982, with only three more states needed to make it law. The nation's conservative women, led by activist Phyllis Schlafly
Phyllis Schlafly
Phyllis McAlpin Stewart Schlafly is a Constitutional lawyer and an American politically conservative activist and author who founded the Eagle Forum. She is known for her opposition to modern feminism ideas and for her campaign against the proposed Equal Rights Amendment...
, defeated the ERA by arguing that it degraded the position of the housewife, and made young women susceptible to the military draft
Conscription in the United States
Conscription in the United States has been employed several times, usually during war but also during the nominal peace of the Cold War...
.
However, many federal laws (i.e. those equalizing pay, employment, education
Title IX
Title IX of the Education Amendments of 1972 is a United States law, enacted on June 23, 1972, that amended Title IX of the Civil Rights Act of 1964. In 2002 it was renamed the Patsy T. Mink Equal Opportunity in Education Act, in honor of its principal author Congresswoman Mink, but is most...
, employment opportunities, credit
Equal Credit Opportunity Act
The Equal Credit Opportunity Act is a United States law , enacted in 1974, that makes it unlawful for any creditor to discriminate against any applicant, with respect to any aspect of a credit transaction, on the basis of race, color, religion, national origin, sex, marital status, or age ; to the...
, ending pregnancy discrimination, and requiring NASA
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research...
, the Military Academies, and other organizations to admit women), state laws (i.e. those ending spousal abuse and marital rape
Spousal rape
Marital rape, also known as spousal rape, is non-consensual sex in which the perpetrator is the victim's spouse. As such, it as a form of partner rape, of domestic violence, and of sexual abuse. Once widely condoned or ignored by law, spousal rape is now repudiated by international conventions and...
), Supreme Court rulings (i.e. ruling the equal protection clause of the Fourteenth Amendment applied to women), and state ERAs established women's equal status under the law, and social custom and consciousness began to change, accepting women's equality. The controversial issue of abortion
Abortion
Abortion is defined as the termination of pregnancy by the removal or expulsion from the uterus of a fetus or embryo prior to viability. An abortion can occur spontaneously, in which case it is usually called a miscarriage, or it can be purposely induced...
, deemed by the Supreme Court as a fundamental right in Roe v. Wade
Roe v. Wade
Roe v. Wade, , was a controversial landmark decision by the United States Supreme Court on the issue of abortion. The Court decided that a right to privacy under the due process clause in the Fourteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution extends to a woman's decision to have an abortion,...
(1973), is still a point of debate
Abortion debate
The abortion debate refers to discussion and controversy surrounding the moral and legal status of abortion. The two main groups involved in the abortion debate are the self-described "pro-choice" movement and the "pro-life" movement...
today.
The Counterculture Revolution and Cold War Détente (1964–1980)
Amid the Cold War, the United States entered the Vietnam War
Vietnam War
The Vietnam War was a Cold War-era military conflict that occurred in Vietnam, Laos, and Cambodia from 1 November 1955 to the fall of Saigon on 30 April 1975. This war followed the First Indochina War and was fought between North Vietnam, supported by its communist allies, and the government of...
, whose growing unpopularity fed already existing social movements, including those among women, minorities and young people. President Lyndon B. Johnson
Lyndon B. Johnson
Lyndon Baines Johnson , often referred to as LBJ, was the 36th President of the United States after his service as the 37th Vice President of the United States...
's Great Society
Great Society
The Great Society was a set of domestic programs in the United States promoted by President Lyndon B. Johnson and fellow Democrats in Congress in the 1960s. Two main goals of the Great Society social reforms were the elimination of poverty and racial injustice...
social programs and numerous rulings by the Warren Court
Warren Court
The Warren Court refers to the Supreme Court of the United States between 1953 and 1969, when Earl Warren served as Chief Justice. Warren led a liberal majority that used judicial power in dramatic fashion, to the consternation of conservative opponents...
added to the wide range of social reform during the 1960s and 1970s. Feminism
Feminism
Feminism is a collection of movements aimed at defining, establishing, and defending equal political, economic, and social rights and equal opportunities for women. Its concepts overlap with those of women's rights...
and the environmental movement became political forces, and progress continued toward civil rights
Civil rights
Civil and political rights are a class of rights that protect individuals' freedom from unwarranted infringement by governments and private organizations, and ensure one's ability to participate in the civil and political life of the state without discrimination or repression.Civil rights include...
for all Americans. The Counterculture Revolution
Counterculture of the 1960s
The counterculture of the 1960s refers to a cultural movement that mainly developed in the United States and spread throughout much of the western world between 1960 and 1973. The movement gained momentum during the U.S. government's extensive military intervention in Vietnam...
swept through the nation and much of the western world in the late sixties and early seventies, dividing the already hostile environment but also bringing forth more liberated social views.
Johnson was succeeded in 1969 by Republican Richard Nixon
Richard Nixon
Richard Milhous Nixon was the 37th President of the United States, serving from 1969 to 1974. The only president to resign the office, Nixon had previously served as a US representative and senator from California and as the 36th Vice President of the United States from 1953 to 1961 under...
, who turned the war over to the South Vietnamese forces and ended American combat roles; he negotiated a peace treaty in 1973
Paris Peace Accords
The Paris Peace Accords of 1973 intended to establish peace in Vietnam and an end to the Vietnam War, ended direct U.S. military involvement, and temporarily stopped the fighting between North and South Vietnam...
, secured the release of POWs and ended the draft. The war had cost the lives of 58,000 American troops. Nixon manipulated the fierce distrust between the Soviet Union and China to the advantage of the United States, achieving détente
Détente
Détente is the easing of strained relations, especially in a political situation. The term is often used in reference to the general easing of relations between the Soviet Union and the United States in the 1970s, a thawing at a period roughly in the middle of the Cold War...
(cooperation) with both parties. The Watergate scandal
Watergate scandal
The Watergate scandal was a political scandal during the 1970s in the United States resulting from the break-in of the Democratic National Committee headquarters at the Watergate office complex in Washington, D.C., and the Nixon administration's attempted cover-up of its involvement...
, involving Nixon's cover-up of his operatives break-in into the Democratic National Committee
Democratic National Committee
The Democratic National Committee is the principal organization governing the United States Democratic Party on a day to day basis. While it is responsible for overseeing the process of writing a platform every four years, the DNC's central focus is on campaign and political activity in support...
headquarters at the Watergate office complex
Watergate complex
The Watergate complex is a group of five buildings next to the John F. Kennedy Center for the Performing Arts in the Foggy Bottom neighborhood of Washington, D.C. in the United States. The site contains an office building, three apartment buildings, and a hotel-office building...
destroyed his political base, sent many aides to prison, and forced Nixon's resignation on August 9, 1974. He was succeeded by Vice President Gerald Ford
Gerald Ford
Gerald Rudolph "Jerry" Ford, Jr. was the 38th President of the United States, serving from 1974 to 1977, and the 40th Vice President of the United States serving from 1973 to 1974...
, who was subsequently helpless to prevent the conquest of South Vietnam when North Vietnam invaded in 1975.
The OPEC oil embargo
1973 oil crisis
The 1973 oil crisis started in October 1973, when the members of Organization of Arab Petroleum Exporting Countries or the OAPEC proclaimed an oil embargo. This was "in response to the U.S. decision to re-supply the Israeli military" during the Yom Kippur war. It lasted until March 1974. With the...
marked a long-term economic transition, as for the first time energy prices skyrocketed and American factories faced serious competition from foreign automobiles, clothing, electronics and consumer goods. By the late 1970s the economy suffered an energy crisis
1970s energy crisis
The 1970s energy crisis was a period in which the major industrial countries of the world, particularly the United States, faced substantial shortages, both perceived and real, of petroleum...
, slow economic growth, high unemployment, and very high inflation coupled with high interest rates (the term stagflation
Stagflation
In economics, stagflation is a situation in which the inflation rate is high and the economic growth rate slows down and unemployment remains steadily high...
was coined). While economists agreed on the wisdom of deregulation
Deregulation
Deregulation is the removal or simplification of government rules and regulations that constrain the operation of market forces.Deregulation is the removal or simplification of government rules and regulations that constrain the operation of market forces.Deregulation is the removal or...
, many of the New Deal era regulations were ended, as in transportation, banking and telecommunications.
Jimmy Carter
Jimmy Carter
James Earl "Jimmy" Carter, Jr. is an American politician who served as the 39th President of the United States and was the recipient of the 2002 Nobel Peace Prize, the only U.S. President to have received the Prize after leaving office...
, running as someone who was not a part of the Washington political establishment, was elected president in 1976. On the world stage, Carter brokered the Camp David Accords
Camp David Accords
The Camp David Accords were signed by Egyptian President Anwar El Sadat and Israeli Prime Minister Menachem Begin on September 17, 1978, following thirteen days of secret negotiations at Camp David. The two framework agreements were signed at the White House, and were witnessed by United States...
between Israel and Egypt. In 1979, Iranian students stormed the U.S. embassy in Tehran
Tehran
Tehran , sometimes spelled Teheran, is the capital of Iran and Tehran Province. With an estimated population of 8,429,807; it is also Iran's largest urban area and city, one of the largest cities in Western Asia, and is the world's 19th largest city.In the 20th century, Tehran was subject to...
and took 66 Americans hostage, resulting in the Iran hostage crisis
Iran hostage crisis
The Iran hostage crisis was a diplomatic crisis between Iran and the United States where 52 Americans were held hostage for 444 days from November 4, 1979 to January 20, 1981, after a group of Islamist students and militants took over the American Embassy in Tehran in support of the Iranian...
. With the hostage crisis and continuing stagflation, Carter lost the 1980 election
United States presidential election, 1980
The United States presidential election of 1980 featured a contest between incumbent Democrat Jimmy Carter and his Republican opponent, Ronald Reagan, as well as Republican Congressman John B. Anderson, who ran as an independent...
to the Republican Ronald Reagan
Ronald Reagan
Ronald Wilson Reagan was the 40th President of the United States , the 33rd Governor of California and, prior to that, a radio, film and television actor....
. On January 20, 1981, minutes after Carter's term in office ended, the remaining U.S. captives held at the U.S. embassy in Iran were released, ending the 444-day hostage crisis.
The end of the Cold War (1980–1991)

Ronald Reagan
Ronald Wilson Reagan was the 40th President of the United States , the 33rd Governor of California and, prior to that, a radio, film and television actor....
produced a major realignment
Realigning election
Realigning election are terms from political science and political history describing a dramatic change in the political system. Scholars frequently apply the term to American elections and occasionally to other countries...
with his 1980 and 1984 landslide elections. Reagan's economic policies (dubbed "Reaganomics
Reaganomics
Reaganomics refers to the economic policies promoted by the U.S. President Ronald Reagan during the 1980s, also known as supply-side economics and called trickle-down economics, particularly by critics...
") and the implementation of the Economic Recovery Tax Act of 1981 lowered income taxes from 70% to 28% over the course of seven years. Reagan continued to downsize government taxation and regulation. The U.S. experienced a recession in 1982 but the negative indicators reversed, as the inflation rate decreased from 11% to 2%, the unemployment rate decreased from 10.8% in December 1982 to 7.5% in November 1984, and the economic growth rate increased from 4.5% to 7.2%.
Reagan ordered a massive buildup of the U.S. military, incurring a costly budget deficit. Reagan introduced a complicated missile defense system known as the Strategic Defense Initiative
Strategic Defense Initiative
The Strategic Defense Initiative was proposed by U.S. President Ronald Reagan on March 23, 1983 to use ground and space-based systems to protect the United States from attack by strategic nuclear ballistic missiles. The initiative focused on strategic defense rather than the prior strategic...
(dubbed "Star Wars" by opponents) in which, theoretically, the U.S. could shoot down missiles with laser systems in space. Though it was never fully developed or deployed, the Soviets were genuinely concerned about the possible effects of the program and the research and technologies of SDI paved the way for the anti-ballistic missile systems of today.
The Reagan administration also provided covert funding and assistance to anti-Communist resistance movements worldwide. Reagan's interventions against Grenada and Libya were popular in the U.S., though his backing of the Contra rebels was mired in controversy. The arms-for-hostages scandal led to the convictions of such figures as Oliver North
Oliver North
Oliver Laurence North is a retired U.S. Marine Corps officer, political commentator, host of War Stories with Oliver North on Fox News Channel, a military historian, and a New York Times best-selling author....
and John Poindexter
John Poindexter
John Marlan Poindexter is a retired United States naval officer and Department of Defense official. He was Deputy National Security Advisor and National Security Advisor for the Reagan administration. He was convicted in April 1990 of multiple felonies as a result of his actions in the Iran-Contra...
.
Reagan met four times with Soviet leader Mikhail Gorbachev
Mikhail Gorbachev
Mikhail Sergeyevich Gorbachev is a former Soviet statesman, having served as General Secretary of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union from 1985 until 1991, and as the last head of state of the USSR, having served from 1988 until its dissolution in 1991...
, who ascended to power in 1985, and their summit conferences led to the signing of the Intermediate-Range Nuclear Forces Treaty
Intermediate-Range Nuclear Forces Treaty
The Intermediate-Range Nuclear Forces Treaty is a 1987 agreement between the United States and the Soviet Union. Signed in Washington, D.C. by U.S. President Ronald Reagan and General Secretary Mikhail Gorbachev on December 8, 1987, it was ratified by the United States Senate on May 27, 1988 and...
. Gorbachev tried to save Communism in the Soviet Union first by ending the expensive arms race with America, then by shedding the East European empire in 1989. The Soviet Union collapsed
Dissolution of the Soviet Union
The dissolution of the Soviet Union was the disintegration of the federal political structures and central government of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics , resulting in the independence of all fifteen republics of the Soviet Union between March 11, 1990 and December 25, 1991...
in 1991, ending the U.S.–Soviet Cold War
Cold War
The Cold War was the continuing state from roughly 1946 to 1991 of political conflict, military tension, proxy wars, and economic competition between the Communist World—primarily the Soviet Union and its satellite states and allies—and the powers of the Western world, primarily the United States...
.
World superpower (1991–present)

Superpower
A superpower is a state with a dominant position in the international system which has the ability to influence events and its own interests and project power on a worldwide scale to protect those interests...
and continued to intervene in international affairs during the 1990s, including the 1991 Gulf War
Gulf War
The Persian Gulf War , commonly referred to as simply the Gulf War, was a war waged by a U.N.-authorized coalition force from 34 nations led by the United States, against Iraq in response to Iraq's invasion and annexation of Kuwait.The war is also known under other names, such as the First Gulf...
against Iraq
Iraq
Iraq ; officially the Republic of Iraq is a country in Western Asia spanning most of the northwestern end of the Zagros mountain range, the eastern part of the Syrian Desert and the northern part of the Arabian Desert....
. Following his election in 1992
United States presidential election, 1992
The United States presidential election of 1992 had three major candidates: Incumbent Republican President George Bush; Democratic Arkansas Governor Bill Clinton, and independent Texas businessman Ross Perot....
, President Bill Clinton
Bill Clinton
William Jefferson "Bill" Clinton is an American politician who served as the 42nd President of the United States from 1993 to 2001. Inaugurated at age 46, he was the third-youngest president. He took office at the end of the Cold War, and was the first president of the baby boomer generation...
oversaw one of the longest periods of economic expansion and unprecedented gains in securities values, a side effect of the digital revolution
Digital Revolution
The Digital Revolution is the change from analog mechanical and electronic technology to digital technology that has taken place since c. 1980 and continues to the present day. Implicitly, the term also refers to the sweeping changes brought about by digital computing and communication technology...
and new business opportunities created by the Internet
Internet
The Internet is a global system of interconnected computer networks that use the standard Internet protocol suite to serve billions of users worldwide...
. He also worked with the Republican Congress to pass the first balanced federal budget in 30 years. In 1998, Clinton was impeached
Impeachment of Bill Clinton
Bill Clinton, President of the United States, was impeached by the House of Representatives on charges of perjury and obstruction of justice on December 19, 1998, but acquitted by the Senate on February 12, 1999. Two other impeachment articles, a second perjury charge and a charge of abuse of...
by the House of Representatives on charges of "high crimes and misdemeanors" for lying about a sexual relationship with White House intern Monica Lewinsky
Monica Lewinsky
Monica Samille Lewinsky is an American woman with whom United States President Bill Clinton admitted to having had an "improper relationship" while she worked at the White House in 1995 and 1996...
, but was later acquitted by the Senate. The failure of impeachment and the Democratic gains in the 1998 election forced House Speaker Newt Gingrich
Newt Gingrich
Newton Leroy "Newt" Gingrich is a U.S. Republican Party politician who served as the House Minority Whip from 1989 to 1995 and as the 58th Speaker of the U.S. House of Representatives from 1995 to 1999....
, a Republican, to resign from Congress.
The presidential election in 2000
United States presidential election, 2000
The United States presidential election of 2000 was a contest between Republican candidate George W. Bush, then-governor of Texas and son of former president George H. W. Bush , and Democratic candidate Al Gore, then-Vice President....
between George W. Bush
George W. Bush
George Walker Bush is an American politician who served as the 43rd President of the United States, from 2001 to 2009. Before that, he was the 46th Governor of Texas, having served from 1995 to 2000....
and Al Gore
Al Gore
Albert Arnold "Al" Gore, Jr. served as the 45th Vice President of the United States , under President Bill Clinton. He was the Democratic Party's nominee for President in the 2000 U.S. presidential election....
was one of the closest in U.S. history, and helped lay the seeds for political polarization to come. The vote in the decisive state of Florida was extremely close and produced a dramatic dispute over the counting of votes
Florida election recount
The Florida election recount of 2000 was a period of vote re-counting that occurred following the unclear results of the 2000 United States presidential election between George W. Bush and Al Gore, specifically the Florida results. The election was ultimately settled in favor of George W. Bush when...
. The U.S. Supreme Court in Bush v. Gore
Bush v. Gore
Bush v. Gore, , is the landmark United States Supreme Court decision on December 12, 2000, that effectively resolved the 2000 presidential election in favor of George W. Bush. Only eight days earlier, the United States Supreme Court had unanimously decided the closely related case of Bush v...
ended the recount with a 5–4 vote. That meant Bush, then in the lead, carried Florida and the election.
9/11 and the War on Terror

Terrorism
Terrorism is the systematic use of terror, especially as a means of coercion. In the international community, however, terrorism has no universally agreed, legally binding, criminal law definition...
with the September 11, 2001 attacks
September 11, 2001 attacks
The September 11 attacks The September 11 attacks The September 11 attacks (also referred to as September 11, September 11th or 9/119/11 is pronounced "nine eleven". The slash is not part of the pronunciation...
(9/11) in which al-Qaeda
Al-Qaeda
Al-Qaeda is a global broad-based militant Islamist terrorist organization founded by Osama bin Laden sometime between August 1988 and late 1989. It operates as a network comprising both a multinational, stateless army and a radical Sunni Muslim movement calling for global Jihad...
terrorists hijacked four transcontinental airliners and intentionally crashed two of them into the twin towers of the World Trade Center
World Trade Center
The original World Trade Center was a complex with seven buildings featuring landmark twin towers in Lower Manhattan, New York City, United States. The complex opened on April 4, 1973, and was destroyed in 2001 during the September 11 attacks. The site is currently being rebuilt with five new...
and one into the Pentagon
The Pentagon
The Pentagon is the headquarters of the United States Department of Defense, located in Arlington County, Virginia. As a symbol of the U.S. military, "the Pentagon" is often used metonymically to refer to the Department of Defense rather than the building itself.Designed by the American architect...
killing 3,000 people. President George W. Bush
George W. Bush
George Walker Bush is an American politician who served as the 43rd President of the United States, from 2001 to 2009. Before that, he was the 46th Governor of Texas, having served from 1995 to 2000....
announced a "War on Terror
War on Terror
The War on Terror is a term commonly applied to an international military campaign led by the United States and the United Kingdom with the support of other North Atlantic Treaty Organisation as well as non-NATO countries...
" in response. The United States and NATO launched an invasion of Afghanistan
War in Afghanistan (2001–present)
The War in Afghanistan began on October 7, 2001, as the armed forces of the United States of America, the United Kingdom, Australia, and the Afghan United Front launched Operation Enduring Freedom...
to overthrow the Taliban regime that had harbored al-Qaeda and its leader Osama bin Laden
Osama bin Laden
Osama bin Mohammed bin Awad bin Laden was the founder of the militant Islamist organization Al-Qaeda, the jihadist organization responsible for the September 11 attacks on the United States and numerous other mass-casualty attacks against civilian and military targets...
. The federal government established new domestic efforts to prevent future attacks. The controversial USA PATRIOT Act
USA PATRIOT Act
The USA PATRIOT Act is an Act of the U.S. Congress that was signed into law by President George W. Bush on October 26, 2001...
increased government's power to monitor communications and removed legal restrictions on information sharing between federal law enforcement and intelligence services. A cabinet-level agency called the Department of Homeland Security
United States Department of Homeland Security
The United States Department of Homeland Security is a cabinet department of the United States federal government, created in response to the September 11 attacks, and with the primary responsibilities of protecting the territory of the United States and protectorates from and responding to...
was created to lead and coordinate federal counter-terrorism
Counter-terrorism
Counter-terrorism is the practices, tactics, techniques, and strategies that governments, militaries, police departments and corporations adopt to prevent or in response to terrorist threats and/or acts, both real and imputed.The tactic of terrorism is available to insurgents and governments...
activities. Some of these anti-terrorism efforts, particularly the U.S. government's handling of detainees at the prison at Guantanamo Bay, led to allegations toward the U.S. government of human rights violations.
In 2003, the United States launched an invasion of Iraq
2003 invasion of Iraq
The 2003 invasion of Iraq , was the start of the conflict known as the Iraq War, or Operation Iraqi Freedom, in which a combined force of troops from the United States, the United Kingdom, Australia and Poland invaded Iraq and toppled the regime of Saddam Hussein in 21 days of major combat operations...
, which led to the collapse of the Iraqi government and the eventual capture of Iraqi dictator Saddam Hussein
Saddam Hussein
Saddam Hussein Abd al-Majid al-Tikriti was the fifth President of Iraq, serving in this capacity from 16 July 1979 until 9 April 2003...
, with whom the U.S. had long-standing tense relations. The reasons for the invasion cited by the Bush administration included the spreading of democracy, the elimination of weapons of mass destruction
Weapons of mass destruction
A weapon of mass destruction is a weapon that can kill and bring significant harm to a large number of humans and/or cause great damage to man-made structures , natural structures , or the biosphere in general...
(a key demand of the UN as well, though later investigations found parts of the intelligence reports to be inaccurate) and the liberation of the Iraqi people. The invasion and continued Iraq War fueled international protests
Protests against the Iraq War
Beginning in 2002, and continuing after the 2003 invasion of Iraq, protests against the Iraq War were held in many cities worldwide, often coordinated to occur simultaneously around the world...
and gradually saw domestic support waver, despite initial successes early in the invasion. In 2007, after years of violence by the Iraqi insurgency
Iraqi insurgency
The Iraqi Resistance is composed of a diverse mix of militias, foreign fighters, all-Iraqi units or mixtures opposing the United States-led multinational force in Iraq and the post-2003 Iraqi government...
, President Bush deployed more troops in a strategy dubbed "the surge
Iraq War troop surge of 2007
In the context of the Iraq War, the surge refers to United States President George W. Bush's 2007 increase in the number of American troops in order to provide security to Baghdad and Al Anbar Province....
". While the death toll decreased, the political stability of Iraq remained in doubt.
In 2008, the unpopularity of President Bush and the Iraq war, along with the 2008 financial crisis, led to the election of Barack Obama
Barack Obama
Barack Hussein Obama II is the 44th and current President of the United States. He is the first African American to hold the office. Obama previously served as a United States Senator from Illinois, from January 2005 until he resigned following his victory in the 2008 presidential election.Born in...
, the first African American
African American
African Americans are citizens or residents of the United States who have at least partial ancestry from any of the native populations of Sub-Saharan Africa and are the direct descendants of enslaved Africans within the boundaries of the present United States...
President of the United States. After he took office, Obama began to decrease troop levels in Iraq, and officially ended combat operations in the country on August 31, 2010. At the same time, he kept 50,000 in Iraq to assist Iraqi forces, help protect withdrawing forces, and work on counter-terrorism until December 31, 2011, the date Bush scheduled for the full withdrawal. Obama increased American involvement in Afghanistan, starting a surge strategy using an additional 30,000 troops, while proposing to begin withdrawing troops in July 2011. In May 2011, after nearly a decade in hiding, Osama bin Laden
Osama bin Laden
Osama bin Mohammed bin Awad bin Laden was the founder of the militant Islamist organization Al-Qaeda, the jihadist organization responsible for the September 11 attacks on the United States and numerous other mass-casualty attacks against civilian and military targets...
was killed by U.S. armed forces acting under President Obama's direct orders.
Recent events

United States housing market correction
A United States housing market correction is a market correction or "bubble bursting" of a United States housing bubble; the most recent began following a national home price peak first identified in July 2006. Because realty trades in illiquid markets relative to financial assets such as common...
, a subprime mortgage crisis
Subprime mortgage crisis
The U.S. subprime mortgage crisis was one of the first indicators of the late-2000s financial crisis, characterized by a rise in subprime mortgage delinquencies and foreclosures, and the resulting decline of securities backed by said mortgages....
, soaring oil prices, an automotive industry crisis, rising unemployment, and the worst financial crisis since the Great Depression
Great Depression
The Great Depression was a severe worldwide economic depression in the decade preceding World War II. The timing of the Great Depression varied across nations, but in most countries it started in about 1929 and lasted until the late 1930s or early 1940s...
. The financial crisis hit a critical point in September 2008 when Lehman Brothers
Lehman Brothers
Lehman Brothers Holdings Inc. was a global financial services firm. Before declaring bankruptcy in 2008, Lehman was the fourth largest investment bank in the USA , doing business in investment banking, equity and fixed-income sales and trading Lehman Brothers Holdings Inc. (former NYSE ticker...
and other important financial institutions failed. Starting the following month the federal government lent $245 billion to financial institutions through the Troubled Asset Relief Program which was signed into law under the Bush administration. Shortly after taking office, Obama signed into law a $787 billion economic stimulus package
American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009
The American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009, abbreviated ARRA and commonly referred to as the Stimulus or The Recovery Act, is an economic stimulus package enacted by the 111th United States Congress in February 2009 and signed into law on February 17, 2009, by President Barack Obama.To...
aimed at helping the economy recover from the deepening recession. In addition to the economic stimulus, the government took steps to rescue the auto industry and prevent future economic meltdowns. These included a bailout of General Motors
General Motors
General Motors Company , commonly known as GM, formerly incorporated as General Motors Corporation, is an American multinational automotive corporation headquartered in Detroit, Michigan and the world's second-largest automaker in 2010...
and Chrysler
Chrysler
Chrysler Group LLC is a multinational automaker headquartered in Auburn Hills, Michigan, USA. Chrysler was first organized as the Chrysler Corporation in 1925....
, putting ownership temporarily in the hands of the government, and the "cash for clunkers" program which temporarily boosted new car sales. Congress enacted the Dodd–Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act, a bill that makes sweeping changes to the financial regulatory system. The recession officially ended in June 2009 as the U.S. economy began to expand once again; however the unemployment rate has continued to linger near 9% and above into 2011.
In the 111th Congress
111th United States Congress
The One Hundred Eleventh United States Congress was the meeting of the legislative branch of the United States federal government from January 3, 2009 until January 3, 2011. It began during the last two weeks of the George W. Bush administration, with the remainder spanning the first two years of...
Democratic legislative initiatives ran into strong Republican opposition. National debates emerged over numerous issues such as health care reform
Health care reform in the United States
Health care reform in the United States has a long history, of which the most recent results were two federal statutes enacted in 2010: the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act , signed March 23, 2010, and the Health Care and Education Reconciliation Act of 2010 , which amended the PPACA and...
, which was rekindled by the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act
Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act
The Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act is a United States federal statute signed into law by President Barack Obama on March 23, 2010. The law is the principal health care reform legislation of the 111th United States Congress...
. In the 2010 midterm elections
United States elections, 2010
The 2010 United States elections were held on Tuesday, November 2, 2010. During this midterm election year, all 435 seats in the United States House of Representatives and 37 of the 100 seats in the United States Senate were contested in this election along with 38 state and territorial...
, the Republicans regained control of the House and installed John Boehner
John Boehner
John Andrew Boehner is the 61st and current Speaker of the United States House of Representatives. A member of the Republican Party, he is the U.S. Representative from , serving since 1991...
as Speaker. They also made some gains in the Senate. A factor in these results was the conservative Tea Party movement
Tea Party movement
The Tea Party movement is an American populist political movement that is generally recognized as conservative and libertarian, and has sponsored protests and supported political candidates since 2009...
that has promoted political candidates and protests, and has called for significant reductions in taxes and spending. On August 2, 2011, after a lengthy congressional debate over whether to raise the nation's debt limit, Congress passed the bipartisan Budget Control Act of 2011
Budget Control Act of 2011
The Budget Control Act of 2011 was passed by the 112th United States Congress signed into law by President Barack Obama. It brought conclusion to the 2011 United States debt ceiling crisis, which had threatened to lead the United States into sovereign default on or about August 3, 2011.The law...
. The legislation enforces limits on discretionary spending until 2021, establishes a procedure to increase the debt limit, creates a two-party Congressional Joint Select Committee on Deficit Reduction to propose further deficit reduction with a stated goal of achieving at least $1.5 trillion in budgetary savings over 10 years, and establishes automatic procedures for reducing spending by as much as $1.2 trillion if legislation originating with the new joint select committee does not achieve such savings. By passing the legislation, Congress was able to prevent an unprecedented U.S. government default on its obligations, though credit ratings agency Standard & Poor's still lowered the ratings on America's long term debt to AA+, reasoning that the political blockage endangered future debt payments and that the legislation fell short of what would be necessary to stabilize the country's growing national debt.
As of November 2011, debates continue over the economy, the 9% unemployment rate, deficit spending, health care reform
Health care reform in the United States
Health care reform in the United States has a long history, of which the most recent results were two federal statutes enacted in 2010: the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act , signed March 23, 2010, and the Health Care and Education Reconciliation Act of 2010 , which amended the PPACA and...
, the financial crisis in state government, the role of corporate spending in election campaigns, and U.S. involvement in Afghanistan
War in Afghanistan (2001–present)
The War in Afghanistan began on October 7, 2001, as the armed forces of the United States of America, the United Kingdom, Australia, and the Afghan United Front launched Operation Enduring Freedom...
.
See also
- Cultural history of the United StatesCultural history of the United StatesThe cultural history of the United States is a broad topic, covering or having influence in many of the world's cultural aspects. Since the founding of the United States, in the 18th century various immigrant groups have been at play in the formation of the nation's culture...
- Economic history of the United StatesEconomic history of the United StatesThe economic history of the United States has its roots in European colonization in the 16th, 17th, and 18th centuries. Marginal colonial economies grew into 13 small, independent farming economies, which joined together in 1776 to form the United States of America...
- History of agriculture in the United StatesHistory of agriculture in the United StatesThe history of agriculture in the United States covers the period from the first settlers to the present day. In Colonial America agriculture fund a livelihood for 90 percent of the population; most towns were shipping points for the export of agricultural products. Most farms were geared toward...
- History of the AmericasHistory of the AmericasThe history of the Americas is the collective history of the American landmass, which includes North and South America, as well as Central America and the Caribbean. It begins with people migrating to these areas from Asia during the height of an Ice Age...
- History of education in the United StatesHistory of education in the United StatesThe history of education in the United States, or foundations of education, covers the trends in educational philosophy, policy, institutions, as well as formal and informal learning in America from the 17th century to today.-New England:...
- History of North AmericaHistory of North AmericaThe history of North America is the study of the past, particularly the written record, oral histories, and traditions, passed down from generation to generation on the continent in the Earth's northern hemisphere and western hemisphere....
- History of religion in the United States
- Military history of the United StatesMilitary history of the United StatesThe military history of the United States spans a period of over two centuries. During the course of those years, the United States evolved from a new nation fighting the British Empire for independence without a professional military , through a monumental American Civil War to the world's sole...
- Outline of United States history
- Politics of the United StatesPolitics of the United StatesThe United States is a federal constitutional republic, in which the President of the United States , Congress, and judiciary share powers reserved to the national government, and the federal government shares sovereignty with the state governments.The executive branch is headed by the President...
- Technological and industrial history of the United States
- Territorial evolution of the United StatesTerritorial evolution of the United StatesThis is a list of the evolution of the borders of the United States. This lists each change to the internal and external borders of the country, as well as status and name changes. It also shows the surrounding areas that eventually became part of the United States...
Lists:
- List of conflicts in the United States
- List of Presidents of the United States
- List of United States treaties
- List of wars involving the United States
Timelines:
- Timeline of United States historyTimeline of United States historyThis is a timeline of United States history.The United States Constitution was completed on September 17, 1787 and the history of the United States is divided below into pre- and post-constitution.-Pre-Constitution:*Pre–United States...
- Timeline of United States military operations
Further reading
- Agnew, Jean-Christophe, and Roy Rosenzweig, eds. A Companion to Post-1945 America (2006)
- Anderson, Fred, ed. The Oxford Companion to American Military History (2000)
- Carnes, Mark C., and John A. Garraty, The American Nation: A History of the United States (14th ed. 2011); university and AP textbook
- Diner, Hasia, ed. Encyclopedia of American Women's History (2010)
- Foner, Eric. Give Me Liberty! An American History (3rd ed. 2011), university textbook
- Gilbert, Martin. The Routledge Atlas of American History (2010)
- Howe, Daniel Walker. What Hath God Wrought: The Transformation of America, 1815-1848;; (Oxford History of the United States) (2009); Pulitzer Prize excerpt and text search
- Hornsby Jr., Alton. A Companion to African American History (2008) excerpt and text search
- Kazin, Michael, et al. eds. The Concise Princeton Encyclopedia of American Political History (2011) excerpt and text search
- Kennedy, David M. Freedom from Fear: The American People in Depression and War, 1929-1945 (Oxford History of the United States) (2001), Pulitzer Prize
- Lancaster, Bruce, Bruce Catton, and Thomas Fleming. The American Heritage History of the American Revolution (2004)
- McPherson, James M. Battle Cry of Freedom: The Civil War Era (Oxford History of the United States) (2003), Pulitzer Prize excerpt and text search
- Middleton, Richard, and Anne Lombard. Colonial America: A History to 1763 (4th ed. 2011)
- Milner, Clyde A., Carol A. O'Connor, and Martha A. Sandweiss, eds. The Oxford History of the American West (1996) excerpt and text search
- Patterson, James T. Grand Expectations: The United States, 1945-1974 (Oxford History of the United States) (1997) excerpt and text search
- Patterson, James T. Restless Giant: The United States from Watergate to Bush v. Gore (Oxford History of the United States) (2007) excerpt and text search
- Perry, Elisabeth Israels, and Karen Manners Smith, eds. The Gilded Age & Progressive Era: A Student Companion (2006)
- Pole, Jack P. and J.R. Pole. A Companion to the American Revolution (2003) excerpt and text search
- Resch, John, ed. Americans at War: Society, Culture, and the Homefront (4 vol 2004)
- Schweikart, Larry, and Michael Allen. A Patriot's History of the United States: From Columbus's Great Discovery to the War on Terror (2007), view from the right excerpt and text search
- Tindall, George Brown, and David E. Shi. America: A Narrative History (8th ed. 2009), university textbook
- Troy, Gil, et al. eds. History of American Presidential Elections, 1789-2008 (2011) 3 vol; detailed analysis of each election, with primary documents
- Vickers, Daniel, ed. A Companion to Colonial America (2006)
- Wood, Gordon S. Empire of Liberty: A History of the Early Republic, 1789-1815 (Oxford History of the United States) (2009) excerpt and text search
- Zophy, Angela Howard, ed. Handbook of American Women's History. (2nd ed. 2000). 763 pp. articles by experts
External links
- Outline of U.S. History, an American history e-book from the U.S. Department of State
- US History map animation Animated map of the US, showing territorial expansion and statehood by year (Quick Maps, Theodora.com).
- US History map animation Animated map of the US, showing territorial expansion and statehood by year (Houston Institute for Culture).
- Edsitement, History & Social Studies, lesson plans from the National Endowment for the Humanities
- The Gilder Lehrman Institute of American History, includes curriculum modules covering the Revolution to the present
- BackStory, American history public radio show hosted by Ed AyersEdward L. AyersEdward Lynn Ayers is an American historian. He is the current president of the University of Richmond, having served in this capacity since July 1, 2007. Prior to his appointment, he had been on the faculty of the University of Virginia since 1980, most recently as the Buckner W. Clay Dean of the...
, Brian Balogh, and Peter Onuf - Early 20th century USA High Quality photographs

