History of geography
Encyclopedia
The history of geography includes various histories
of geography
which have differed over time and between different cultural and political groups. In more recent developments, geography has become a distinct academic discipline. 'Geography' derives from the from Greek
- geographia,, a literal translation of which would be "to describe or write about the Earth". The first person to use the word "geography" was Eratosthenes
(276-194 BC). However there is evidence for recognizable practices of geography, such as cartography
(or map-making) prior to the use of the term geography.
from the 9th century BC. The best known Babylonia
n world map, however, is the Imago Mundi of 600 BC. The map as reconstructed by Eckhard Unger
shows Babylon
on the Euphrates
, surrounded by a circular landmass showing Assyria
, Urartu
and several cities, in turn surrounded by a "bitter river" (Oceanus
), with seven islands arranged around it so as to form a seven-pointed star. The accompanying text mentions seven outer regions beyond the encircling ocean. The descriptions of five of them have survived.
In contrast to the Imago Mundi, an earlier Babylonian world map
dating back to the 9th century BC depicted Babylon as being further north from the center of the world, though it is not certain what that center was supposed to represent.
saw the poet Homer
as the founder of geography. His works the Iliad
and the Odyssey
are works of literature, but both contain a great deal of geographical information. Homer describes a circular world ringed by a single massive ocean. The works show that the Greeks
by the 8th century BC had considerable knowledge of the geography of the eastern Mediterranean. The poems contain a large number of place names and descriptions, but for many of these it is uncertain what real location, if any, is actually being referred to.
Thales
of Miletus is one of the first known philosophers known to have wondered about the shape of the world. He proposed that the world was based on water, and that all things grew out of it. He also laid down many of the astronomical and mathematical rules that would allow geography to be studied scientifically. His successor Anaximander
is the first person known to have attempted to create a scale map of the known world and to have introduced the gnomon
to Ancient Greece.
Hecataeus of Miletus initiated a different form of geography, avoiding the mathematical calculations of Thales and Anaximander he learnt about the world by gathering previous works and speaking to the sailors who came through the busy port of Miletus. From these accounts he wrote a detailed prose account of what was known of the world. A similar work, and one that mostly survives today, is Herodotus
' Histories
. While primarily a work of history, the book contains a wealth of geographic descriptions covering much of the known world. Egypt, Scythia, Persia, and Asia Minor are all described in great detail. Little is known about areas further a field, and descriptions of areas such as India
are almost wholly fanciful. Herodotus also made important observations about geography. He is the first to have noted the process by which large rivers, such as the Nile, build up deltas
, and is also the first recorded as observing that winds tend to blow from colder regions to warmer ones.
Pythagoras
was perhaps the first to propose a spherical world, arguing that the sphere was the most perfect form. This idea was embraced by Plato
and Aristotle
presented empirical evidence to verify this. He noted that the Earth's shadow during an eclipse is curved, and also that stars increase in height as one moves north. Eudoxus of Cnidus
used the idea of a sphere to explain how the sun created differing climatic zones based on latitude. This led the Greeks to believe in a division of the world into five regions. At each of the poles was an uncharitably cold region. While extrapolating from the heat of the Sahara it was deduced that the area around the equator was unbearably hot. Between these extreme regions both the northern and southern hemispheres had a temperate belt suitable for human habitation.
had traveled as far south as Sierra Leone
, and it is possible other Phoenicians had circumnavigated Africa. In the 4th century BC the Greek explorer Pytheas
traveled through northwest Europe, and circled the British Isles. He found that the region was considerably more habitable than theory expected, but his discoveries were largely dismissed as fanciful by his contemporaries because of this. Conquerors also carried out exploration, for example, Caesar's invasions of Britain
and Germany
, expeditions/invasions sent by Augustus
to Arabia Felix and Ethiopia
(Res Gestae
26), and perhaps the greatest Ancient Greek explorer of all, Alexander the Great, who deliberately set out to learn more about the east through his military expeditions and so took a large number of geographers and writers with his army who recorded their observations as they moved east.
The ancient Greeks divided the world into three continents, Europe, Asia, and Libya
(Africa). The Hellespont formed the border between Europe and Asia. The border between Asia and Libya was generally considered to be the Nile river, but some geographers, such as Herodotus objected to this. Herodotus argued that there was no difference between the people on the east and west sides of the Nile, and that the Red Sea
was a better border. The relatively narrow habitable band was considered to run from the Atlantic Ocean in the west to an unknown sea somewhere east of India in the east. The southern portion of Africa was unknown, as was the northern portion of Europe and Asia, so it was believed that they were circled by a sea. These areas were generally considered uninhabitable.
The size of the Earth was an important question to the Ancient Greeks. Eratosthenes
attempted to calculate its circumference by measuring the angle of the sun at two different locations. While his numbers were problematic, most of the errors cancelled themselves out and he got quite an accurate figure. Since the distance from the Atlantic to India was roughly known, this raised the important question of what was in the vast region east of Asia and to the west of Europe. Crates of Mallus
proposed that there were in fact four inhabitable land masses, two in each hemisphere. In Rome a large globe was created depicting this world. That some of the figures Eratosthenes had used in his calculation were considerably in error became known, and Posidonius
set out to get a more accurate measurement. This number actually was considerably smaller than the real one, but it became accepted that the eastern part of Asia was not a huge distance from Europe.
 While the works of almost all earlier geographers have been lost, many of them are partially known through quotations found in Strabo
While the works of almost all earlier geographers have been lost, many of them are partially known through quotations found in Strabo
. Strabo's seventeen volume work of geography is almost completely extant, and is one of the most important sources of information on classical geography. Strabo accepted the narrow band of habitation theory, and rejected the accounts of Hanno and Pytheas as fables. None of Strabo's maps survive, but his detailed descriptions give a clear picture of the status of geographical knowledge of the time. A century after Strabo Ptolemy
launched a similar undertaking. By this time the Roman Empire had expanded through much of Europe, and previously unknown areas such as the British Isles had been explored. The Silk Road
was also in operation, and for the first time knowledge of the far east began to be known. Ptolemy's Geographia
opens with a theoretical discussion about the nature and techniques of geographical inquiry, and then moves to detailed descriptions of much the known world. Ptolemy lists a huge number of cities, tribes, and sites and places them in the world. It is uncertain what Ptolemy's names correspond to in the modern world, and a vast amount of scholarship has gone into trying to link Ptolemaic descriptions to know locations.
Pliny the Elder
's Natural History also has sections on geography. For the most part Ancient Greek geography was an academic field. There is little evidence that maps or charts were used for navigation. It does, however, seem that at least in Athens the people were acquainted with maps and that several were on public display. It was the Romans who made far more extensive practical use of geography and maps.

 In China
In China
, the earliest known geographical Chinese writing dates back to the 5th century BC, during the beginning of the Warring States (481 BC
-221 BC
). This was the 'Yu Gong' ('Tribute of Yu') chapter of the book Shu Jing (Classic of History
). The book describes the traditional nine provinces, their kinds of soil, their characteristic products and economic goods, their tributary goods, their trades and vocations, their state revenues and agricultural systems, and the various rivers and lakes listed and placed accordingly. The nine provinces in the time of this geographical work was very small in terrain size compared to what modern China occupies today. In fact, its description pertained to areas of the Yellow River
, the lower valleys of the Yangtze, with the plain between them and the Shandong peninsula, and to the west the most northern parts of the Wei River
and the Han River
were known (along with the southern parts of modern day Shanxi
province).
In this ancient geographical treatise (which would greatly influence later Chinese geographers and cartographers), the Chinese used the mythological figure of Yu the Great
to describe the known earth (of the Chinese). Apart from the appearance of Yu, however, the work was devoid of magic, fantasy, Chinese folklore, or legend. Although the Chinese geographical writing in the time of Herodotus
and Strabo
were of lesser quality and contained less systematic approach, this would change from the 3rd century onwards, as Chinese methods of documenting geography became more complex than found in Europe (until the 13th century).
The earliest extant maps found in archeological sites of China date to the 4th century BC and were made in the ancient State of Qin
. The earliest known reference to the application of a geometric grid and mathematically graduated scale to a map was contained in the writings of the cartographer Pei Xiu
(224–271). From the 1st century AD onwards, official Chinese historical texts contained a geographical section, which was often an enormous compilation of changes in place-names and local administrative divisions controlled by the ruling dynasty, descriptions of mountain ranges, river systems, taxable products, etc. The ancient Chinese historian Ban Gu
(32–92) most likely started the trend of the gazeteer in China, which became prominent in the Southern and Northern Dynasties
period and Sui Dynasty
. Local gazeteers would feature a wealth of geographic information, although its cartographic aspects were not as highly professional as the maps created by professional cartographers.
From the time of the 5th century BC Shu Jing forward, Chinese geographical writing provided more concrete information and less legendary element. This example can be seen in the 4th chapter of the Huainanzi
(Book of the Master of Huainan), compiled under the editorship of Prince Liu An
in 139 BC during the Han Dynasty
(202 BC
-202 AD). The chapter gave general descriptions of topography
in a systematic fashion, given visual aids by the use of maps (di tu) due to the efforts of Liu An and his associate Zuo Wu. In Chang Chu's Hua Yang Guo Chi (Historical Geography of Szechuan) of 347 AD, not only rivers, trade routes, and various tribes were described, but it also wrote of a 'Ba Jun Tu Jing' ('Map of Szechuan'), which had been made much earlier in 150 AD. The Shui Jing (Waterways Classic) was written anonymously in the 3rd century during the Three Kingdoms
era (attributed often to Guo Pu
), and gave a description of some 137 rivers found throughout China. In the 6th century AD, the book was expanded to forty times its original size by the geographers Li Daoyuan
, given the new title of Shui Jing Zhu
(The Waterways Classic Commented).
In later periods of the Song Dynasty
(960-1279 AD) and Ming Dynasty
(1368-1644 AD) there were much more systematic and professional approaches to geographic literature. The Song Dynasty poet, scholar, and government official Fan Chengda
(1126–1193) wrote the geographical treatise known as the Gui Hai Yu Heng Chi. It focused primarily on the topography
of the land, along with the agricultural, economic and commercial products of each region in China's southern provinces. The polymath
Chinese scientist Shen Kuo
(1031–1095) devoted a significant amount of his written work to geography, as well as a hypothesis of land formation (geomorphology
) due to the evidence of marine
fossil
s found far inland, along with bamboo
fossils found underground in a region far from where bamboo was suitable to grow. The 14th century Yuan Dynasty
(Mongol Empire
) geographer Na-xin wrote a treatise of archeological topography of all the regions north of the Yellow River, in his book He Shuo Fang Gu Ji. The Ming Dynasty geographer Xu Xiake
(1587–1641) traveled throughout the provinces of China (often on foot) to write his enormous geographical and topographical treatise, documenting various details of his travels, such as the locations of small gorges, or mineral
beds such as mica
schists. Xu's work was largely systematic, providing accurate details of measurement, and his work (translated later by Ding Wenjiang) read more like a 20th century field surveyor than an early 17th century scholar.
The Chinese were also concerned with documenting geographical information of foreign regions far outside of China. Although Chinese had been writing of civilizations of the Middle East, India, and Central Asia since the traveler Zhang Qian
(2nd century BC), later Chinese would provide more concrete and valid information on the topography and geographical aspects of foreign regions. The Tang Dynasty
(618
-907
AD) Chinese diplomat Wang Xuance
traveled to Magadha
(modern northeastern India
) during the 7th century AD. Afterwards he wrote the book Zhang Tian-zhu Guo Tu (Illustrated Accounts of Central India), which included a wealth of geographical information. Chinese geographers such as Jia Dan
(730–805) wrote accurate descriptions of places far abroad. In his work written between 785
and 805
AD, he described the sea route going into the mouth of the Persian Gulf
, and that the medieval Iranian
s (whom he called the people of the Luo-He-Yi country, i.e. Persia) had erected 'ornamental pillars' in the sea that acted as lighthouse
beacons for ships that might go astray. Confirming Jia's reports about lighthouses in the Persian Gulf, Arabic writers a century after Jia wrote of the same structures, writers such as al-Mas'udi and al-Muqaddasi
. The later Song Dynasty ambassador Xu Jing wrote his accounts of voyage and travel throughout Korea
in his work of 1124 AD, the Xuan-He Feng Shi Gao Li Tu Jing (Illustrated Record of an Embassy to Korea in the Xuan-He Reign Period). The geography of medieval Cambodia
(the Khmer Empire
) was documented in the book Zhen-La Feng Tu Ji of 1297 AD, written by Zhou Daguan
.
, al-Yaqubi, al-Masudi
, Ibn Khurdadhbih, Ibn al-Faqih
, al-Istakhri, Ibn Battuta
, Ibn Khaldun
, etc. maintained the Greek and Roman techniques and developed new ones. The Islamic empire
stretched from Spain
to India
, and Arab and Jewish traders (known as Radhanite
s) travelled throughout Eurasia
, Africa
and the Indian Ocean
. The Arabs added a great deal of knowledge to expand and correct the classical sources. There were some representatives of the West that produced geographical works of quality, such as the Syria
n bishop
Jacob of Edessa
(633
-708
), but this paled in comparison to the virtual mountain of work published by Islamic writers of the Middle Ages (who were largely responsible for the foundations of knowledge present in later Western geography).
During the Muslim conquests
of the seventh and early 8th centuries, Arab armies
established the Islam
ic Arab Empire
, reaching from Central Asia
to the Iberian Peninsula
. An early form of globalization
began emerging during the Islamic Golden Age, when the knowledge, trade and economies from many previously isolated regions and civilizations began integrating due to contacts with Muslim explorers, sailors, scholars, traders, and travelers. Subhi Y. Labib has called this period the Pax Islamica, and John M. Hobson has called it the Afro-Asiatic age of discovery
, in reference to the Muslim Southwest Asia
n and North Africa
n traders and explorers who travelled most of the Old World
, and established an early global economy across most of Asia
, Africa
, and Europe
, with their trade networks extending from the Atlantic Ocean
and Mediterranean Sea
in the west to the Indian Ocean
and China Seas in the east, and even as far as Japan
, Korea
and the Bering Strait
.
Arabic silver dirham
coins were also being circulated throughout the Afro-Eurasia
n landmass, as far as sub-Saharan Africa
in the south and northern Europe
in the north, often in exchange for goods and slaves. In England, for example, the Anglo-Saxon
king Offa of Mercia
(r. 757-796) had coins minted with the Shahadah in Arabic. These factors helped establish the Arab Empire (including the Rashidun
, Umayyad
, Abbasid
and Fatimid
caliphates) as the world's leading extensive economic power throughout the 7th–13th centuries.
In the 9th century, Alkindus
was the first to introduce experiment
ation into the Earth science
s. An early adherent of environmental determinism
was the medieval Afro-Arab
writer al-Jahiz
, who explained how the environment can determine the physical characteristics of the inhabitants of a certain community. He used his early theory of evolution
to explain the origins of different human skin color
s, particularly black skin
, which he believed to be the result of the environment. He cited a stony region of black basalt
in the northern Najd
as evidence for his theory. In the early 10th century, Abū Zayd al-Balkhī
, originally from Balkh
, founded the "Balkhī school" of terrestrial mapping in Baghdad
. The geographers of this school also wrote extensively of the peoples, products, and customs of areas in the Muslim world, with little interest in the non-Muslim realms. Suhrāb, a late 10th century Muslim geographer, accompanied a book of geographical coordinates with instructions for making a rectangular world map, with equirectangular projection
or cylindrical cylindrical equidistant projection. In the early 11th century, Avicenna
hypothesized on the geological
causes of mountain
s in The Book of Healing
(1027).
In mathematical geography, Abū Rayhān al-Bīrūnī, around 1025, was the first to describe a polar equi-azimuthal equidistant projection
of the celestial sphere
. He was also regarded as the most skilled when it came to mapping cities
and measuring the distances between them, which he did for many cities in the Middle East
and western Indian subcontinent
. He often combined astronomical readings and mathematical equations, in order to develop methods of pin-pointing locations by recording degrees of latitude
and longitude
. He also developed similar techniques when it came to measuring the heights of mountain
s, depths of valley
s, and expanse of the horizon
, in The Chronology of the Ancient Nations. He also discussed human geography
and the planetary habitability
of the Earth
. He hypothesized that roughly a quarter of the Earth's surface is habitable by human
s, and also argued that the shores of Asia
and Europe
were "separated by a vast sea, too dark and dense to navigate and too risky to try" in reference to the Atlantic Ocean
and Pacific Ocean
.
At the age of 17, al-Biruni calculated the latitude
of Kath, Khwarazm, using the maximum altitude of the Sun. Al-Biruni also solved a complex geodesic
equation in order to accurately compute the Earth
's circumference
, which were close to modern values of the Earth's circumference. His estimate of 6,339.9 km for the Earth radius
was only 16.8 km less than the modern value of 6,356.7 km. In contrast to his predecessors who measured the Earth's circumference by sighting the Sun simultaneously from two different locations, al-Biruni developed a new method of using trigonometric calculations based on the angle between a plain
and mountain
top which yielded more accurate measurements of the Earth's circumference and made it possible for it to be measured by a single person from a single location. By the age of 22, al-Biruni had written several short works, including a study of map projection
s, Cartography
, which included a method for projecting a hemisphere
on a plane
.
John J. O'Connor and Edmund F. Robertson write in the MacTutor History of Mathematics archive
:
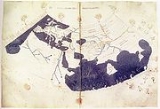
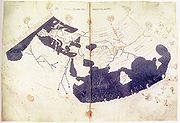
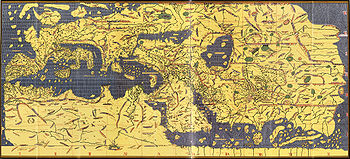 The Arab
The Arab
geographer Al-Idrisi's Mappa Mundi incorporated the knowledge of Africa
, the Indian Ocean
and the Far East
gathered by Arab merchants and explorers with the information inherited from the classical geographers to create one of the most accurate maps of the world to date. The Tabula Rogeriana
was drawn by Al-Idrisi in 1154 for the Norman
King Roger II of Sicily
, after a stay of eighteen years at his court, where he worked on the commentaries and illustrations of the map. The map, written in Arabic, shows the Eurasian continent in its entirety, but only shows the northern part of the African continent.
In the 14th century, Ibn Baṭṭūṭah
, a Moroccan
, began his travels. He started as a pilgrim to Mecca, but continued his journeys for the next 30 years, covering some 73,000 miles (117,000 km). Before returning home, he had visited most of the Muslim world and beyond, from Europe and southern Africa in the west to eastern Asia in the east. The universal use of Arabic in the Muslim world and his status as judge trained in law gave him access to royal courts at most locations he visited.
Ibn Battuta
(1304–1368) was a traveler and explorer, whose account documents his travels and excursions over a period of almost thirty years, covering some 73,000 miles (117,000 km). These journeys covered most of the known Old World
, extending from North Africa
, West Africa
, Southern Europe
and Eastern Europe
in the west, to the Middle East
, Indian subcontinent
, Central Asia
, Southeast Asia
and China
(then the Mongol Yuan Empire) in the east, a distance readily surpassing that of his predecessors and his near-contemporary Marco Polo
.
, geographical knowledge in Europe regressed (though it is a popular misconception that they thought the world was flat), and the simple T and O map
became the standard depiction of the world.
The trips of Venetian
explorer Marco Polo
in the 13th century, the Christian Crusades of the 12th and 13th centuries, and the Portuguese and Spanish voyages of exploration during the 15th and 16th centuries opened up new horizons and stimulated geographic writings.
During the 15th century, Henry the Navigator of Portugal supported explorations of the African coast and became a leader in the promotion of geographic studies. Among the most notable accounts of voyages and discoveries published during the 16th century were those by Giambattista Ramusio in Venice, by Richard Hakluyt
in England, and by Theodore de Bry in what is now Belgium.
 Following the journeys of Marco Polo
Following the journeys of Marco Polo
, interest in geography spread throughout Europe. From around circa 1400, the writings of Ptolemy
and his Islamic successors
provided a systematic framework to tie together and portray geographical information. The great voyages of exploration in 16th and 17th centuries revived a desire for both accurate geographic detail, and more solid theoretical foundations. The Geographia Generalis by Bernhardus Varenius
and Gerardus Mercator
's world map are prime examples of the new breed of scientific geography.
 The Mongols
The Mongols
also had wide ranging knowledge of the geography of Europe and Asia, based in their governance and ruling of much of this area and used this information for the undertaking of large military expeditions. The evidence for this is found in historical resources such as The Secret History of Mongols and other Persian chronicles written in 13th and 14th centuries. For example, during the rule of the Great Yuan Dynasty a world map was created and is currently kept in South Korea. See also: Maps of the Yuan Dynasty
The Muslim Ottoman
cartographer Piri Reis
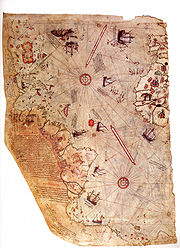
drawn navigational maps in his Kitab-ı Bahriye. The work includes an atlas of charts for small segments of the Mediterranean, accompanied by sailing instructions covering the sea. In the second version of the work, he included a map of the Americas. The Piri Reis map
drawn by the Ottoman cartographer Piri Reis
in 1513 is an early surviving map to show the Americas.
curriculum in Europe (especially Paris
and Berlin
), although not in the United Kingdom
where geography was generally taught as a sub-discipline of other subjects.
One of the great works of this time was Kosmos: a sketch of a physical description of the Universe, by Alexander von Humboldt
, the first volume of which was published in German in 1845. Such was the power of this work that Dr Mary Somerville, of Cambridge University
intended to scrap publication of her own Physical Geography on reading Kosmos. Von Humboldt himself persuaded her to publish (after the publisher sent him a copy).
In 1877, Thomas Henry Huxley published his Physiography with the philosophy of universality
presented as an integrated approach in the study of the natural environment. The philosophy of universality in geography was not a new one but can be seen as evolving from the works of Alexander von Humboldt
and Immanuel Kant
. The publication of Huxley physiography presented a new form of geography that analysed and classified cause and effect
at the micro-level and then applied these to the macro-scale (due to the view that the micro was part of the macro and thus an understanding of all the micro-scales was need to understand the macro level). This approach emphasized the empirical collection of data over the theoretical. The same approach was also used by Halford John Mackinder
in 1887. However, the integration of the Geosphere
, Atmosphere
and Biosphere
under physiography was soon over taken by Davisian geomorphology.
Over the past two centuries the quantity of knowledge and the number of tools has exploded. There are strong links between geography and the sciences of geology
and botany
, as well as economics
, sociology
and demographics
.
The Royal Geographical Society
was founded in England
in 1830, although the United Kingdom did not get its first full Chair of geography until 1917. The first real geographical intellect to emerge in United Kingdom
geography was Halford John Mackinder
, appointed reader at Oxford University
in 1887.
The National Geographic Society
was founded in the USA in 1888 and began publication of the National Geographic magazine which became and continues to be a great popularizer of geographic information. The society has long supported geographic research and education.
included Carl Ritter
, Ellen Churchill Semple
, and Ellsworth Huntington
. Popular hypotheses included "heat makes inhabitants of the tropics lazy" and "frequent changes in barometric pressure make inhabitants of temperate latitudes more intellectually agile." Environmental determinist geographers attempted to make the study of such influences scientific. Around the 1930s, this school of thought was widely repudiated as lacking any basis and being prone to (often bigoted) generalizations. Environmental determinism remains an embarrassment to many contemporary geographers, and leads to skepticism among many of them of claims of environmental influence on culture (such as the theories of Jared Diamond
).
in Germany and Paul Vidal de la Blache
in France. The philosophical basis of this field in United States was laid out by Richard Hartshorne
, who defined geography as a study of areal differentiation, which later led to criticism of this approach as overly descriptive and unscientific.
s. Well-known geographers from this period are Fred K. Schaefer
, Waldo Tobler, William Garrison
, Peter Haggett
, Richard J. Chorley
, William Bunge
, and Torsten Hägerstrand
.
and phenomenology, humanistic geographers (such as Yi-Fu Tuan
) focused on people's sense of, and relationship with, places. More influential was Marxist geography
, which applied the social theories of Karl Marx
and his followers to geographic phenomena. David Harvey
and Richard Peet are well-known Marxist geographers. Feminist geography
is, as the name suggests, the use of ideas from feminism
in geographic contexts. The most recent strain of critical geography is postmodernist geography, which employs the ideas of postmodernist
and poststructuralist theorists to explore the social construction of spatial relations.
History
History is the discovery, collection, organization, and presentation of information about past events. History can also mean the period of time after writing was invented. Scholars who write about history are called historians...
of geography
Geography
Geography is the science that studies the lands, features, inhabitants, and phenomena of Earth. A literal translation would be "to describe or write about the Earth". The first person to use the word "geography" was Eratosthenes...
which have differed over time and between different cultural and political groups. In more recent developments, geography has become a distinct academic discipline. 'Geography' derives from the from Greek
Greek language
Greek is an independent branch of the Indo-European family of languages. Native to the southern Balkans, it has the longest documented history of any Indo-European language, spanning 34 centuries of written records. Its writing system has been the Greek alphabet for the majority of its history;...
- geographia,, a literal translation of which would be "to describe or write about the Earth". The first person to use the word "geography" was Eratosthenes
Eratosthenes
Eratosthenes of Cyrene was a Greek mathematician, poet, athlete, geographer, astronomer, and music theorist.He was the first person to use the word "geography" and invented the discipline of geography as we understand it...
(276-194 BC). However there is evidence for recognizable practices of geography, such as cartography
Cartography
Cartography is the study and practice of making maps. Combining science, aesthetics, and technique, cartography builds on the premise that reality can be modeled in ways that communicate spatial information effectively.The fundamental problems of traditional cartography are to:*Set the map's...
(or map-making) prior to the use of the term geography.
Babylon
The oldest known world maps date back to ancient BabylonBabylon
Babylon was an Akkadian city-state of ancient Mesopotamia, the remains of which are found in present-day Al Hillah, Babil Province, Iraq, about 85 kilometers south of Baghdad...
from the 9th century BC. The best known Babylonia
Babylonia
Babylonia was an ancient cultural region in central-southern Mesopotamia , with Babylon as its capital. Babylonia emerged as a major power when Hammurabi Babylonia was an ancient cultural region in central-southern Mesopotamia (present-day Iraq), with Babylon as its capital. Babylonia emerged as...
n world map, however, is the Imago Mundi of 600 BC. The map as reconstructed by Eckhard Unger
Eckhard Unger
Eckhard Unger was a German assyriologist.In 1916, as curator of the Archeological Museum of Istanbul, he identified and described a copper-alloy object in the museum collection as an ell or measuring rod from Nippur...
shows Babylon
Babylon
Babylon was an Akkadian city-state of ancient Mesopotamia, the remains of which are found in present-day Al Hillah, Babil Province, Iraq, about 85 kilometers south of Baghdad...
on the Euphrates
Euphrates
The Euphrates is the longest and one of the most historically important rivers of Western Asia. Together with the Tigris, it is one of the two defining rivers of Mesopotamia...
, surrounded by a circular landmass showing Assyria
Assyria
Assyria was a Semitic Akkadian kingdom, extant as a nation state from the mid–23rd century BC to 608 BC centred on the Upper Tigris river, in northern Mesopotamia , that came to rule regional empires a number of times through history. It was named for its original capital, the ancient city of Assur...
, Urartu
Urartu
Urartu , corresponding to Ararat or Kingdom of Van was an Iron Age kingdom centered around Lake Van in the Armenian Highland....
and several cities, in turn surrounded by a "bitter river" (Oceanus
Oceanus
Oceanus ; , Ōkeanós) was a pseudo-geographical feature in classical antiquity, believed by the ancient Greeks and Romans to be the world-ocean, an enormous river encircling the world....
), with seven islands arranged around it so as to form a seven-pointed star. The accompanying text mentions seven outer regions beyond the encircling ocean. The descriptions of five of them have survived.
In contrast to the Imago Mundi, an earlier Babylonian world map
World map
A world map is a map of the surface of the Earth, which may be made using any of a number of different map projections. A map projection is any method of representing the surface of a sphere or other three-dimensional body on a plane....
dating back to the 9th century BC depicted Babylon as being further north from the center of the world, though it is not certain what that center was supposed to represent.
Greco-Roman world
The ancient GreeksAncient Greece
Ancient Greece is a civilization belonging to a period of Greek history that lasted from the Archaic period of the 8th to 6th centuries BC to the end of antiquity. Immediately following this period was the beginning of the Early Middle Ages and the Byzantine era. Included in Ancient Greece is the...
saw the poet Homer
Homer
In the Western classical tradition Homer , is the author of the Iliad and the Odyssey, and is revered as the greatest ancient Greek epic poet. These epics lie at the beginning of the Western canon of literature, and have had an enormous influence on the history of literature.When he lived is...
as the founder of geography. His works the Iliad
Iliad
The Iliad is an epic poem in dactylic hexameters, traditionally attributed to Homer. Set during the Trojan War, the ten-year siege of the city of Troy by a coalition of Greek states, it tells of the battles and events during the weeks of a quarrel between King Agamemnon and the warrior Achilles...
and the Odyssey
Odyssey
The Odyssey is one of two major ancient Greek epic poems attributed to Homer. It is, in part, a sequel to the Iliad, the other work ascribed to Homer. The poem is fundamental to the modern Western canon, and is the second—the Iliad being the first—extant work of Western literature...
are works of literature, but both contain a great deal of geographical information. Homer describes a circular world ringed by a single massive ocean. The works show that the Greeks
Greeks
The Greeks, also known as the Hellenes , are a nation and ethnic group native to Greece, Cyprus and neighboring regions. They also form a significant diaspora, with Greek communities established around the world....
by the 8th century BC had considerable knowledge of the geography of the eastern Mediterranean. The poems contain a large number of place names and descriptions, but for many of these it is uncertain what real location, if any, is actually being referred to.
Thales
Thales
Thales of Miletus was a pre-Socratic Greek philosopher from Miletus in Asia Minor, and one of the Seven Sages of Greece. Many, most notably Aristotle, regard him as the first philosopher in the Greek tradition...
of Miletus is one of the first known philosophers known to have wondered about the shape of the world. He proposed that the world was based on water, and that all things grew out of it. He also laid down many of the astronomical and mathematical rules that would allow geography to be studied scientifically. His successor Anaximander
Anaximander
Anaximander was a pre-Socratic Greek philosopher who lived in Miletus, a city of Ionia; Milet in modern Turkey. He belonged to the Milesian school and learned the teachings of his master Thales...
is the first person known to have attempted to create a scale map of the known world and to have introduced the gnomon
Gnomon
The gnomon is the part of a sundial that casts the shadow. Gnomon is an ancient Greek word meaning "indicator", "one who discerns," or "that which reveals."It has come to be used for a variety of purposes in mathematics and other fields....
to Ancient Greece.
Hecataeus of Miletus initiated a different form of geography, avoiding the mathematical calculations of Thales and Anaximander he learnt about the world by gathering previous works and speaking to the sailors who came through the busy port of Miletus. From these accounts he wrote a detailed prose account of what was known of the world. A similar work, and one that mostly survives today, is Herodotus
Herodotus
Herodotus was an ancient Greek historian who was born in Halicarnassus, Caria and lived in the 5th century BC . He has been called the "Father of History", and was the first historian known to collect his materials systematically, test their accuracy to a certain extent and arrange them in a...
' Histories
Histories (Herodotus)
The Histories of Herodotus is considered one of the seminal works of history in Western literature. Written from the 450s to the 420s BC in the Ionic dialect of classical Greek, The Histories serves as a record of the ancient traditions, politics, geography, and clashes of various cultures that...
. While primarily a work of history, the book contains a wealth of geographic descriptions covering much of the known world. Egypt, Scythia, Persia, and Asia Minor are all described in great detail. Little is known about areas further a field, and descriptions of areas such as India
India
India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
are almost wholly fanciful. Herodotus also made important observations about geography. He is the first to have noted the process by which large rivers, such as the Nile, build up deltas
River delta
A delta is a landform that is formed at the mouth of a river where that river flows into an ocean, sea, estuary, lake, reservoir, flat arid area, or another river. Deltas are formed from the deposition of the sediment carried by the river as the flow leaves the mouth of the river...
, and is also the first recorded as observing that winds tend to blow from colder regions to warmer ones.
Pythagoras
Pythagoras
Pythagoras of Samos was an Ionian Greek philosopher, mathematician, and founder of the religious movement called Pythagoreanism. Most of the information about Pythagoras was written down centuries after he lived, so very little reliable information is known about him...
was perhaps the first to propose a spherical world, arguing that the sphere was the most perfect form. This idea was embraced by Plato
Plato
Plato , was a Classical Greek philosopher, mathematician, student of Socrates, writer of philosophical dialogues, and founder of the Academy in Athens, the first institution of higher learning in the Western world. Along with his mentor, Socrates, and his student, Aristotle, Plato helped to lay the...
and Aristotle
Aristotle
Aristotle was a Greek philosopher and polymath, a student of Plato and teacher of Alexander the Great. His writings cover many subjects, including physics, metaphysics, poetry, theater, music, logic, rhetoric, linguistics, politics, government, ethics, biology, and zoology...
presented empirical evidence to verify this. He noted that the Earth's shadow during an eclipse is curved, and also that stars increase in height as one moves north. Eudoxus of Cnidus
Eudoxus of Cnidus
Eudoxus of Cnidus was a Greek astronomer, mathematician, scholar and student of Plato. Since all his own works are lost, our knowledge of him is obtained from secondary sources, such as Aratus's poem on astronomy...
used the idea of a sphere to explain how the sun created differing climatic zones based on latitude. This led the Greeks to believe in a division of the world into five regions. At each of the poles was an uncharitably cold region. While extrapolating from the heat of the Sahara it was deduced that the area around the equator was unbearably hot. Between these extreme regions both the northern and southern hemispheres had a temperate belt suitable for human habitation.
Hellenistic period
These theories clashed with the evidence of explorers, however. Hanno the NavigatorHanno the Navigator
Hanno the Navigator was a Carthaginian explorer c. 500 BC, best known for his naval exploration of the African coast...
had traveled as far south as Sierra Leone
Sierra Leone
Sierra Leone , officially the Republic of Sierra Leone, is a country in West Africa. It is bordered by Guinea to the north and east, Liberia to the southeast, and the Atlantic Ocean to the west and southwest. Sierra Leone covers a total area of and has an estimated population between 5.4 and 6.4...
, and it is possible other Phoenicians had circumnavigated Africa. In the 4th century BC the Greek explorer Pytheas
Pytheas
Pytheas of Massalia or Massilia , was a Greek geographer and explorer from the Greek colony, Massalia . He made a voyage of exploration to northwestern Europe at about 325 BC. He travelled around and visited a considerable part of Great Britain...
traveled through northwest Europe, and circled the British Isles. He found that the region was considerably more habitable than theory expected, but his discoveries were largely dismissed as fanciful by his contemporaries because of this. Conquerors also carried out exploration, for example, Caesar's invasions of Britain
Caesar's invasions of Britain
In his Gallic Wars, Julius Caesar invaded Britain twice, in 55 and 54 BC. The first invasion, made late in summer, was either intended as a full invasion or a reconnaissance-in-force expedition...
and Germany
Gallic Wars
The Gallic Wars were a series of military campaigns waged by the Roman proconsul Julius Caesar against several Gallic tribes. They lasted from 58 BC to 51 BC. The Gallic Wars culminated in the decisive Battle of Alesia in 52 BC, in which a complete Roman victory resulted in the expansion of the...
, expeditions/invasions sent by Augustus
Augustus
Augustus ;23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14) is considered the first emperor of the Roman Empire, which he ruled alone from 27 BC until his death in 14 AD.The dates of his rule are contemporary dates; Augustus lived under two calendars, the Roman Republican until 45 BC, and the Julian...
to Arabia Felix and Ethiopia
Axum
Axum or Aksum is a city in northern Ethiopia which was the original capital of the eponymous kingdom of Axum. Population 56,500 . Axum was a naval and trading power that ruled the region from ca. 400 BC into the 10th century...
(Res Gestae
Res gestae
Res gestae is a term found in substantive and procedural American jurisprudence and English law. In American substantive law, it refers to the start-to-end period of a felony. In American procedural law, it refers to an exception to the hearsay rule for statements made spontaneously or as part of...
26), and perhaps the greatest Ancient Greek explorer of all, Alexander the Great, who deliberately set out to learn more about the east through his military expeditions and so took a large number of geographers and writers with his army who recorded their observations as they moved east.
The ancient Greeks divided the world into three continents, Europe, Asia, and Libya
Libya
Libya is an African country in the Maghreb region of North Africa bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the north, Egypt to the east, Sudan to the southeast, Chad and Niger to the south, and Algeria and Tunisia to the west....
(Africa). The Hellespont formed the border between Europe and Asia. The border between Asia and Libya was generally considered to be the Nile river, but some geographers, such as Herodotus objected to this. Herodotus argued that there was no difference between the people on the east and west sides of the Nile, and that the Red Sea
Red Sea
The Red Sea is a seawater inlet of the Indian Ocean, lying between Africa and Asia. The connection to the ocean is in the south through the Bab el Mandeb strait and the Gulf of Aden. In the north, there is the Sinai Peninsula, the Gulf of Aqaba, and the Gulf of Suez...
was a better border. The relatively narrow habitable band was considered to run from the Atlantic Ocean in the west to an unknown sea somewhere east of India in the east. The southern portion of Africa was unknown, as was the northern portion of Europe and Asia, so it was believed that they were circled by a sea. These areas were generally considered uninhabitable.
The size of the Earth was an important question to the Ancient Greeks. Eratosthenes
Eratosthenes
Eratosthenes of Cyrene was a Greek mathematician, poet, athlete, geographer, astronomer, and music theorist.He was the first person to use the word "geography" and invented the discipline of geography as we understand it...
attempted to calculate its circumference by measuring the angle of the sun at two different locations. While his numbers were problematic, most of the errors cancelled themselves out and he got quite an accurate figure. Since the distance from the Atlantic to India was roughly known, this raised the important question of what was in the vast region east of Asia and to the west of Europe. Crates of Mallus
Crates of Mallus
Crates, of Mallus in Cilicia , was a Greek language grammarian and Stoic philosopher of the 2nd century BC, leader of the literary school and head of the library of Pergamum. His chief work was a critical and exegetical commentary on Homer...
proposed that there were in fact four inhabitable land masses, two in each hemisphere. In Rome a large globe was created depicting this world. That some of the figures Eratosthenes had used in his calculation were considerably in error became known, and Posidonius
Posidonius
Posidonius "of Apameia" or "of Rhodes" , was a Greek Stoic philosopher, politician, astronomer, geographer, historian and teacher native to Apamea, Syria. He was acclaimed as the greatest polymath of his age...
set out to get a more accurate measurement. This number actually was considerably smaller than the real one, but it became accepted that the eastern part of Asia was not a huge distance from Europe.
Roman period

Strabo
Strabo, also written Strabon was a Greek historian, geographer and philosopher.-Life:Strabo was born to an affluent family from Amaseia in Pontus , a city which he said was situated the approximate equivalent of 75 km from the Black Sea...
. Strabo's seventeen volume work of geography is almost completely extant, and is one of the most important sources of information on classical geography. Strabo accepted the narrow band of habitation theory, and rejected the accounts of Hanno and Pytheas as fables. None of Strabo's maps survive, but his detailed descriptions give a clear picture of the status of geographical knowledge of the time. A century after Strabo Ptolemy
Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy , was a Roman citizen of Egypt who wrote in Greek. He was a mathematician, astronomer, geographer, astrologer, and poet of a single epigram in the Greek Anthology. He lived in Egypt under Roman rule, and is believed to have been born in the town of Ptolemais Hermiou in the...
launched a similar undertaking. By this time the Roman Empire had expanded through much of Europe, and previously unknown areas such as the British Isles had been explored. The Silk Road
Silk Road
The Silk Road or Silk Route refers to a historical network of interlinking trade routes across the Afro-Eurasian landmass that connected East, South, and Western Asia with the Mediterranean and European world, as well as parts of North and East Africa...
was also in operation, and for the first time knowledge of the far east began to be known. Ptolemy's Geographia
Geographia (Ptolemy)
The Geography is Ptolemy's main work besides the Almagest...
opens with a theoretical discussion about the nature and techniques of geographical inquiry, and then moves to detailed descriptions of much the known world. Ptolemy lists a huge number of cities, tribes, and sites and places them in the world. It is uncertain what Ptolemy's names correspond to in the modern world, and a vast amount of scholarship has gone into trying to link Ptolemaic descriptions to know locations.
Pliny the Elder
Pliny the Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus , better known as Pliny the Elder, was a Roman author, naturalist, and natural philosopher, as well as naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and personal friend of the emperor Vespasian...
's Natural History also has sections on geography. For the most part Ancient Greek geography was an academic field. There is little evidence that maps or charts were used for navigation. It does, however, seem that at least in Athens the people were acquainted with maps and that several were on public display. It was the Romans who made far more extensive practical use of geography and maps.
China


China
Chinese civilization may refer to:* China for more general discussion of the country.* Chinese culture* Greater China, the transnational community of ethnic Chinese.* History of China* Sinosphere, the area historically affected by Chinese culture...
, the earliest known geographical Chinese writing dates back to the 5th century BC, during the beginning of the Warring States (481 BC
481 BC
Year 481 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Vibulanus and Fusus...
-221 BC
221 BC
Year 221 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Asina and Rufus/Lepidus...
). This was the 'Yu Gong' ('Tribute of Yu') chapter of the book Shu Jing (Classic of History
Classic of History
The Classic of History is a compilation of documentary records related to events in ancient history of China. It is also commonly known as the Shàngshū , or simply Shū...
). The book describes the traditional nine provinces, their kinds of soil, their characteristic products and economic goods, their tributary goods, their trades and vocations, their state revenues and agricultural systems, and the various rivers and lakes listed and placed accordingly. The nine provinces in the time of this geographical work was very small in terrain size compared to what modern China occupies today. In fact, its description pertained to areas of the Yellow River
Yellow River
The Yellow River or Huang He, formerly known as the Hwang Ho, is the second-longest river in China and the sixth-longest in the world at the estimated length of . Originating in the Bayan Har Mountains in Qinghai Province in western China, it flows through nine provinces of China and empties into...
, the lower valleys of the Yangtze, with the plain between them and the Shandong peninsula, and to the west the most northern parts of the Wei River
Wei River
The Wei River is a major river in west-central China's Gansu and Shaanxi provinces. It is the largest tributary of the Yellow River and very important in the early development of Chinese civilization....
and the Han River
Han River (Hanshui)
The Han River is a left tributary of the Yangtze River with a length of 1532 km. Historically it was referred to as Hànshuǐ and the name is still occasionally used today....
were known (along with the southern parts of modern day Shanxi
Shanxi
' is a province in Northern China. Its one-character abbreviation is "晋" , after the state of Jin that existed here during the Spring and Autumn Period....
province).
In this ancient geographical treatise (which would greatly influence later Chinese geographers and cartographers), the Chinese used the mythological figure of Yu the Great
Yu the Great
Yu the Great , was a legendary ruler of Ancient China famed for his introduction of flood control, inaugurating dynastic rule in China by founding the Xia Dynasty, and for his upright moral character....
to describe the known earth (of the Chinese). Apart from the appearance of Yu, however, the work was devoid of magic, fantasy, Chinese folklore, or legend. Although the Chinese geographical writing in the time of Herodotus
Herodotus
Herodotus was an ancient Greek historian who was born in Halicarnassus, Caria and lived in the 5th century BC . He has been called the "Father of History", and was the first historian known to collect his materials systematically, test their accuracy to a certain extent and arrange them in a...
and Strabo
Strabo
Strabo, also written Strabon was a Greek historian, geographer and philosopher.-Life:Strabo was born to an affluent family from Amaseia in Pontus , a city which he said was situated the approximate equivalent of 75 km from the Black Sea...
were of lesser quality and contained less systematic approach, this would change from the 3rd century onwards, as Chinese methods of documenting geography became more complex than found in Europe (until the 13th century).
The earliest extant maps found in archeological sites of China date to the 4th century BC and were made in the ancient State of Qin
Qin (state)
The State of Qin was a Chinese feudal state that existed during the Spring and Autumn and Warring States Periods of Chinese history...
. The earliest known reference to the application of a geometric grid and mathematically graduated scale to a map was contained in the writings of the cartographer Pei Xiu
Pei Xiu
Pei Xiu , style name Jiyan , was a minister, geographer, and cartographer of the state of Cao Wei during the Three Kingdoms period of Chinese history, as well as the subsequent Jin Dynasty. Pei Xiu was very much trusted by Sima Zhao, and participated in the suppression of Zhuge Dan's coup...
(224–271). From the 1st century AD onwards, official Chinese historical texts contained a geographical section, which was often an enormous compilation of changes in place-names and local administrative divisions controlled by the ruling dynasty, descriptions of mountain ranges, river systems, taxable products, etc. The ancient Chinese historian Ban Gu
Ban Gu
Ban Gu , courtesy name Mengjian , was a 1st century Chinese historian and poet best known for his part in compiling the Book of Han. He also wrote in the main poetic genre of the Han era, a kind of poetry interspersed with prose called fu. Some are anthologized by Xiao Tong in his Selections of...
(32–92) most likely started the trend of the gazeteer in China, which became prominent in the Southern and Northern Dynasties
Southern and Northern Dynasties
The Southern and Northern Dynasties was a period in the history of China that lasted from 420 to 589 AD. Though an age of civil war and political chaos, it was also a time of flourishing arts and culture, advancement in technology, and the spreading of Mahayana Buddhism and Daoism...
period and Sui Dynasty
Sui Dynasty
The Sui Dynasty was a powerful, but short-lived Imperial Chinese dynasty. Preceded by the Southern and Northern Dynasties, it ended nearly four centuries of division between rival regimes. It was followed by the Tang Dynasty....
. Local gazeteers would feature a wealth of geographic information, although its cartographic aspects were not as highly professional as the maps created by professional cartographers.
From the time of the 5th century BC Shu Jing forward, Chinese geographical writing provided more concrete information and less legendary element. This example can be seen in the 4th chapter of the Huainanzi
Huainanzi
The Huáinánzǐ is a 2nd century BCE Chinese philosophical classic from the Han dynasty that blends Daoist, Confucianist, and Legalist concepts, including theories such as Yin-Yang and the Five Phases. It was written under the patronage of Liu An, Prince of Huainan, a legendarily prodigious author...
(Book of the Master of Huainan), compiled under the editorship of Prince Liu An
Liu An
Líu Ān was a Chinese prince and advisor to his nephew, Emperor Wu of Han of the Han Dynasty in China and the legendary inventor of t'ai chi...
in 139 BC during the Han Dynasty
Han Dynasty
The Han Dynasty was the second imperial dynasty of China, preceded by the Qin Dynasty and succeeded by the Three Kingdoms . It was founded by the rebel leader Liu Bang, known posthumously as Emperor Gaozu of Han. It was briefly interrupted by the Xin Dynasty of the former regent Wang Mang...
(202 BC
202 BC
Year 202 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Geminus and Nero...
-202 AD). The chapter gave general descriptions of topography
Topography
Topography is the study of Earth's surface shape and features or those ofplanets, moons, and asteroids...
in a systematic fashion, given visual aids by the use of maps (di tu) due to the efforts of Liu An and his associate Zuo Wu. In Chang Chu's Hua Yang Guo Chi (Historical Geography of Szechuan) of 347 AD, not only rivers, trade routes, and various tribes were described, but it also wrote of a 'Ba Jun Tu Jing' ('Map of Szechuan'), which had been made much earlier in 150 AD. The Shui Jing (Waterways Classic) was written anonymously in the 3rd century during the Three Kingdoms
Three Kingdoms
The Three Kingdoms period was a period in Chinese history, part of an era of disunity called the "Six Dynasties" following immediately the loss of de facto power of the Han Dynasty rulers. In a strict academic sense it refers to the period between the foundation of the state of Wei in 220 and the...
era (attributed often to Guo Pu
Guo Pu
Guo Pu , courtesy name Jingchun , born in Yuncheng, Shanxi, was a Chinese writer.-Biography:Guo Pu was a Taoist mystic, geomancer, collector of strange tales, editor of old texts, and erudite commentator...
), and gave a description of some 137 rivers found throughout China. In the 6th century AD, the book was expanded to forty times its original size by the geographers Li Daoyuan
Li Daoyuan
Li Daoyuan was a Chinese geographer during thetimes of the Northern Wei Dynasty. He is known as the author ofthe Commentary to the River Classic ....
, given the new title of Shui Jing Zhu
Shui Jing Zhu
Shui Jing Zhu is a work on the ancient geography of China. It is an annotated and much expanded version of an older text, the Shui Jing , which has been lost.The annotated version was compiled by Li Daoyuan Shui Jing Zhu is a work on the ancient geography of China. It is an annotated and much...
(The Waterways Classic Commented).
In later periods of the Song Dynasty
Song Dynasty
The Song Dynasty was a ruling dynasty in China between 960 and 1279; it succeeded the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms Period, and was followed by the Yuan Dynasty. It was the first government in world history to issue banknotes or paper money, and the first Chinese government to establish a...
(960-1279 AD) and Ming Dynasty
Ming Dynasty
The Ming Dynasty, also Empire of the Great Ming, was the ruling dynasty of China from 1368 to 1644, following the collapse of the Mongol-led Yuan Dynasty. The Ming, "one of the greatest eras of orderly government and social stability in human history", was the last dynasty in China ruled by ethnic...
(1368-1644 AD) there were much more systematic and professional approaches to geographic literature. The Song Dynasty poet, scholar, and government official Fan Chengda
Fan Chengda
Fan Chengda , courtesy name Zhineng , was one of the best-known Chinese poets of the Song Dynasty , a government official, and an academic authority in geography , especially the southern provinces of China...
(1126–1193) wrote the geographical treatise known as the Gui Hai Yu Heng Chi. It focused primarily on the topography
Topography
Topography is the study of Earth's surface shape and features or those ofplanets, moons, and asteroids...
of the land, along with the agricultural, economic and commercial products of each region in China's southern provinces. The polymath
Polymath
A polymath is a person whose expertise spans a significant number of different subject areas. In less formal terms, a polymath may simply be someone who is very knowledgeable...
Chinese scientist Shen Kuo
Shen Kuo
Shen Kuo or Shen Gua , style name Cunzhong and pseudonym Mengqi Weng , was a polymathic Chinese scientist and statesman of the Song Dynasty...
(1031–1095) devoted a significant amount of his written work to geography, as well as a hypothesis of land formation (geomorphology
Geomorphology
Geomorphology is the scientific study of landforms and the processes that shape them...
) due to the evidence of marine
Marine (ocean)
Marine is an umbrella term. As an adjective it is usually applicable to things relating to the sea or ocean, such as marine biology, marine ecology and marine geology...
fossil
Fossil
Fossils are the preserved remains or traces of animals , plants, and other organisms from the remote past...
s found far inland, along with bamboo
Bamboo
Bamboo is a group of perennial evergreens in the true grass family Poaceae, subfamily Bambusoideae, tribe Bambuseae. Giant bamboos are the largest members of the grass family....
fossils found underground in a region far from where bamboo was suitable to grow. The 14th century Yuan Dynasty
Yuan Dynasty
The Yuan Dynasty , or Great Yuan Empire was a ruling dynasty founded by the Mongol leader Kublai Khan, who ruled most of present-day China, all of modern Mongolia and its surrounding areas, lasting officially from 1271 to 1368. It is considered both as a division of the Mongol Empire and as an...
(Mongol Empire
Mongol Empire
The Mongol Empire , initially named as Greater Mongol State was a great empire during the 13th and 14th centuries...
) geographer Na-xin wrote a treatise of archeological topography of all the regions north of the Yellow River, in his book He Shuo Fang Gu Ji. The Ming Dynasty geographer Xu Xiake
Xu Xiake
Xu Xiake , born Xu Hongzu , courtesy name Zhenzhi , was a Chinese travel writer and geographer of the Ming Dynasty known best for his famous geographical treatise, and noted for his bravery and humility. He traveled throughout China for more than 30 years, documenting his travels extensively...
(1587–1641) traveled throughout the provinces of China (often on foot) to write his enormous geographical and topographical treatise, documenting various details of his travels, such as the locations of small gorges, or mineral
Mineral
A mineral is a naturally occurring solid chemical substance formed through biogeochemical processes, having characteristic chemical composition, highly ordered atomic structure, and specific physical properties. By comparison, a rock is an aggregate of minerals and/or mineraloids and does not...
beds such as mica
Mica
The mica group of sheet silicate minerals includes several closely related materials having highly perfect basal cleavage. All are monoclinic, with a tendency towards pseudohexagonal crystals, and are similar in chemical composition...
schists. Xu's work was largely systematic, providing accurate details of measurement, and his work (translated later by Ding Wenjiang) read more like a 20th century field surveyor than an early 17th century scholar.
The Chinese were also concerned with documenting geographical information of foreign regions far outside of China. Although Chinese had been writing of civilizations of the Middle East, India, and Central Asia since the traveler Zhang Qian
Zhang Qian
Zhang Qian was an imperial envoy to the world outside of China in the 2nd century BCE, during the time of the Han Dynasty...
(2nd century BC), later Chinese would provide more concrete and valid information on the topography and geographical aspects of foreign regions. The Tang Dynasty
Tang Dynasty
The Tang Dynasty was an imperial dynasty of China preceded by the Sui Dynasty and followed by the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms Period. It was founded by the Li family, who seized power during the decline and collapse of the Sui Empire...
(618
618
Year 618 was a common year starting on Sunday of the Julian calendar. The denomination 618 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.- Asia :* The Sui Dynasty ends and the Tang Dynasty...
-907
907
Year 907 was a common year starting on Thursday of the Julian calendar.- Asia :* Oleg leads the Kievan Rus' in a campaign against Constantinople ....
AD) Chinese diplomat Wang Xuance
Wang Xuance
Wang Xuance , fl. 7th century) was a Tang Dynasty guard officer and diplomat. In 648, Tang Taizong sent him to India in response to Harshavardhana sending an ambassador to China. However once in India he discovered Harshavardhana had died and the new king attacked Wang and his 30 mounted subordinates...
traveled to Magadha
Magadha
Magadha formed one of the sixteen Mahājanapadas or kingdoms in ancient India. The core of the kingdom was the area of Bihar south of the Ganga; its first capital was Rajagriha then Pataliputra...
(modern northeastern India
India
India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
) during the 7th century AD. Afterwards he wrote the book Zhang Tian-zhu Guo Tu (Illustrated Accounts of Central India), which included a wealth of geographical information. Chinese geographers such as Jia Dan
Jia Dan
Jia Dan , courtesy name Dunshi , formally Duke Yuanjing of Wei , was a Chinese scholar-official, general, geographer, and cartographer from Cangzhou, Hebei during the Tang Dynasty of China.- Background :...
(730–805) wrote accurate descriptions of places far abroad. In his work written between 785
785
Year 785 was a common year starting on Saturday of the Julian calendar. The article denomination 785 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years...
and 805
805
Year 805 was a common year starting on Wednesday of the Julian calendar.- Byzantine Empire :* Emperor Nicephorus I of Byzantium suffers a major defeat against the Saracens at Crasus.- Asia :...
AD, he described the sea route going into the mouth of the Persian Gulf
Persian Gulf
The Persian Gulf, in Southwest Asia, is an extension of the Indian Ocean located between Iran and the Arabian Peninsula.The Persian Gulf was the focus of the 1980–1988 Iran-Iraq War, in which each side attacked the other's oil tankers...
, and that the medieval Iranian
Iranian peoples
The Iranian peoples are an Indo-European ethnic-linguistic group, consisting of the speakers of Iranian languages, a major branch of the Indo-European language family, as such forming a branch of Indo-European-speaking peoples...
s (whom he called the people of the Luo-He-Yi country, i.e. Persia) had erected 'ornamental pillars' in the sea that acted as lighthouse
Lighthouse
A lighthouse is a tower, building, or other type of structure designed to emit light from a system of lamps and lenses or, in older times, from a fire, and used as an aid to navigation for maritime pilots at sea or on inland waterways....
beacons for ships that might go astray. Confirming Jia's reports about lighthouses in the Persian Gulf, Arabic writers a century after Jia wrote of the same structures, writers such as al-Mas'udi and al-Muqaddasi
Al-Muqaddasi
Muhammad ibn Ahmad Shams al-Din Al-Muqaddasi , also transliterated as Al-Maqdisi and el-Mukaddasi, was a medieval Arab geographer, author of Ahsan at-Taqasim fi Ma`rifat il-Aqalim .-Biography:Al-Muqaddasi, "the Hierosolomite" was born in Jerusalem in 946 AD...
. The later Song Dynasty ambassador Xu Jing wrote his accounts of voyage and travel throughout Korea
Korea
Korea ) is an East Asian geographic region that is currently divided into two separate sovereign states — North Korea and South Korea. Located on the Korean Peninsula, Korea is bordered by the People's Republic of China to the northwest, Russia to the northeast, and is separated from Japan to the...
in his work of 1124 AD, the Xuan-He Feng Shi Gao Li Tu Jing (Illustrated Record of an Embassy to Korea in the Xuan-He Reign Period). The geography of medieval Cambodia
Cambodia
Cambodia , officially known as the Kingdom of Cambodia, is a country located in the southern portion of the Indochina Peninsula in Southeast Asia...
(the Khmer Empire
Khmer Empire
The Khmer Empire was one of the most powerful empires in Southeast Asia. The empire, which grew out of the former kingdom of Chenla, at times ruled over and/or vassalized parts of modern-day Laos, Thailand, Vietnam, Burma, and Malaysia. Its greatest legacy is Angkor, the site of the capital city...
) was documented in the book Zhen-La Feng Tu Ji of 1297 AD, written by Zhou Daguan
Zhou Daguan
Zhou Daguan was a Chinese diplomat under the Temür Khan, Emperor Chengzong of Yuan. He is most well known for his accounts of the customs of Cambodia and the Angkor temple complexes during his visit there. He arrived at Angkor in August 1296, and remained at the court of King Indravarman III...
.
Medieval Islamic world
In the Middle East, Muslim geographers such as al-IdrisiMuhammad al-Idrisi
Abu Abd Allah Muhammad al-Idrisi al-Qurtubi al-Hasani al-Sabti or simply Al Idrisi was a Moroccan Muslim geographer, cartographer, Egyptologist and traveller who lived in Sicily, at the court of King Roger II. Muhammed al-Idrisi was born in Ceuta then belonging to the Almoravid Empire and died in...
, al-Yaqubi, al-Masudi
Al-Masudi
Abu al-Hasan Ali ibn al-Husayn ibn Ali al-Mas'udi , was an Arab historian and geographer, known as the "Herodotus of the Arabs." Al-Masudi was one of the first to combine history and scientific geography in a large-scale work, Muruj adh-dhahab...
, Ibn Khurdadhbih, Ibn al-Faqih
Ibn al-Faqih
Ibn al-Faqih al-Hamadani was a 10th century Persian historian and geographer, famous for his Mukhtasar Kitab al-Buldan .-References:...
, al-Istakhri, Ibn Battuta
Ibn Battuta
Abu Abdullah Muhammad Ibn Battuta , or simply Ibn Battuta, also known as Shams ad–Din , was a Muslim Moroccan Berber explorer, known for his extensive travels published in the Rihla...
, Ibn Khaldun
Ibn Khaldun
Ibn Khaldūn or Ibn Khaldoun was an Arab Tunisian historiographer and historian who is often viewed as one of the forerunners of modern historiography, sociology and economics...
, etc. maintained the Greek and Roman techniques and developed new ones. The Islamic empire
Caliphate
The term caliphate, "dominion of a caliph " , refers to the first system of government established in Islam and represented the political unity of the Muslim Ummah...
stretched from Spain
Spain
Spain , officially the Kingdom of Spain languages]] under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, Spain's official name is as follows:;;;;;;), is a country and member state of the European Union located in southwestern Europe on the Iberian Peninsula...
to India
India
India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
, and Arab and Jewish traders (known as Radhanite
Radhanite
The Radhanites were medieval Jewish merchants. Whether the term, which is used by only a limited number of primary sources, refers to a specific guild, or a clan, or is a generic term for Jewish merchants in the trans-Eurasian trade network is unclear...
s) travelled throughout Eurasia
Eurasia
Eurasia is a continent or supercontinent comprising the traditional continents of Europe and Asia ; covering about 52,990,000 km2 or about 10.6% of the Earth's surface located primarily in the eastern and northern hemispheres...
, Africa
Africa
Africa is the world's second largest and second most populous continent, after Asia. At about 30.2 million km² including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of the Earth's total surface area and 20.4% of the total land area...
and the Indian Ocean
Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third largest of the world's oceanic divisions, covering approximately 20% of the water on the Earth's surface. It is bounded on the north by the Indian Subcontinent and Arabian Peninsula ; on the west by eastern Africa; on the east by Indochina, the Sunda Islands, and...
. The Arabs added a great deal of knowledge to expand and correct the classical sources. There were some representatives of the West that produced geographical works of quality, such as the Syria
Syria
Syria , officially the Syrian Arab Republic , is a country in Western Asia, bordering Lebanon and the Mediterranean Sea to the West, Turkey to the north, Iraq to the east, Jordan to the south, and Israel to the southwest....
n bishop
Bishop
A bishop is an ordained or consecrated member of the Christian clergy who is generally entrusted with a position of authority and oversight. Within the Catholic Church, Eastern Orthodox, Oriental Orthodox Churches, in the Assyrian Church of the East, in the Independent Catholic Churches, and in the...
Jacob of Edessa
Jacob of Edessa
Jacob of Edessa was one of the most distinguished of Syriac writers.-Life:Jacob of Edessa was born in Aindaba near Aleppo, around 640...
(633
633
Year 633 was a common year starting on Friday of the Julian calendar. The denomination 633 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.- Europe :* Oswald of Bernicia becomes Bretwalda.* Osric...
-708
708
Year 708 was a leap year starting on Sunday of the Julian calendar. The denomination 708 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.- Asia :* Byzantine Empire: March – The Umayyads...
), but this paled in comparison to the virtual mountain of work published by Islamic writers of the Middle Ages (who were largely responsible for the foundations of knowledge present in later Western geography).
During the Muslim conquests
Muslim conquests
Muslim conquests also referred to as the Islamic conquests or Arab conquests, began with the Islamic prophet Muhammad. He established a new unified polity in the Arabian Peninsula which under the subsequent Rashidun and Umayyad Caliphates saw a century of rapid expansion of Muslim power.They...
of the seventh and early 8th centuries, Arab armies
Rashidun army
The Rashidun Caliphate Army or Rashidun army was the primary military body of the Rashidun Caliphate's armed forces during the Muslim conquests of the 7th century, serving alongside the Rashidun Navy...
established the Islam
Islam
Islam . The most common are and . : Arabic pronunciation varies regionally. The first vowel ranges from ~~. The second vowel ranges from ~~~...
ic Arab Empire
Caliphate
The term caliphate, "dominion of a caliph " , refers to the first system of government established in Islam and represented the political unity of the Muslim Ummah...
, reaching from Central Asia
Central Asia
Central Asia is a core region of the Asian continent from the Caspian Sea in the west, China in the east, Afghanistan in the south, and Russia in the north...
to the Iberian Peninsula
Iberian Peninsula
The Iberian Peninsula , sometimes called Iberia, is located in the extreme southwest of Europe and includes the modern-day sovereign states of Spain, Portugal and Andorra, as well as the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar...
. An early form of globalization
Globalization
Globalization refers to the increasingly global relationships of culture, people and economic activity. Most often, it refers to economics: the global distribution of the production of goods and services, through reduction of barriers to international trade such as tariffs, export fees, and import...
began emerging during the Islamic Golden Age, when the knowledge, trade and economies from many previously isolated regions and civilizations began integrating due to contacts with Muslim explorers, sailors, scholars, traders, and travelers. Subhi Y. Labib has called this period the Pax Islamica, and John M. Hobson has called it the Afro-Asiatic age of discovery
Age of Discovery
The Age of Discovery, also known as the Age of Exploration and the Great Navigations , was a period in history starting in the early 15th century and continuing into the early 17th century during which Europeans engaged in intensive exploration of the world, establishing direct contacts with...
, in reference to the Muslim Southwest Asia
Southwest Asia
Western Asia, West Asia, Southwest Asia or Southwestern Asia are terms that describe the westernmost portion of Asia. The terms are partly coterminous with the Middle East, which describes a geographical position in relation to Western Europe rather than its location within Asia...
n and North Africa
North Africa
North Africa or Northern Africa is the northernmost region of the African continent, linked by the Sahara to Sub-Saharan Africa. Geopolitically, the United Nations definition of Northern Africa includes eight countries or territories; Algeria, Egypt, Libya, Morocco, South Sudan, Sudan, Tunisia, and...
n traders and explorers who travelled most of the Old World
Old World
The Old World consists of those parts of the world known to classical antiquity and the European Middle Ages. It is used in the context of, and contrast with, the "New World" ....
, and established an early global economy across most of Asia
Asia
Asia is the world's largest and most populous continent, located primarily in the eastern and northern hemispheres. It covers 8.7% of the Earth's total surface area and with approximately 3.879 billion people, it hosts 60% of the world's current human population...
, Africa
Africa
Africa is the world's second largest and second most populous continent, after Asia. At about 30.2 million km² including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of the Earth's total surface area and 20.4% of the total land area...
, and Europe
Europe
Europe is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting...
, with their trade networks extending from the Atlantic Ocean
Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's oceanic divisions. With a total area of about , it covers approximately 20% of the Earth's surface and about 26% of its water surface area...
and Mediterranean Sea
Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean surrounded by the Mediterranean region and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Anatolia and Europe, on the south by North Africa, and on the east by the Levant...
in the west to the Indian Ocean
Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third largest of the world's oceanic divisions, covering approximately 20% of the water on the Earth's surface. It is bounded on the north by the Indian Subcontinent and Arabian Peninsula ; on the west by eastern Africa; on the east by Indochina, the Sunda Islands, and...
and China Seas in the east, and even as far as Japan
Japan
Japan is an island nation in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean, it lies to the east of the Sea of Japan, China, North Korea, South Korea and Russia, stretching from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea and Taiwan in the south...
, Korea
Korea
Korea ) is an East Asian geographic region that is currently divided into two separate sovereign states — North Korea and South Korea. Located on the Korean Peninsula, Korea is bordered by the People's Republic of China to the northwest, Russia to the northeast, and is separated from Japan to the...
and the Bering Strait
Bering Strait
The Bering Strait , known to natives as Imakpik, is a sea strait between Cape Dezhnev, Chukotka Autonomous Okrug, Russia, the easternmost point of the Asian continent and Cape Prince of Wales, Alaska, USA, the westernmost point of the North American continent, with latitude of about 65°40'N,...
.
Arabic silver dirham
Dirham
Dirham or dirhem is a unit of currency in several Arab or Berber nations, and formerly the related unit of mass in the Ottoman Empire and Persian states...
coins were also being circulated throughout the Afro-Eurasia
Afro-Eurasia
Afro-Eurasia or less commonly Afrasia or Eurafrasia is the term used to describe the largest landmass on earth. It may be defined as a supercontinent, consisting of Africa and Eurasia...
n landmass, as far as sub-Saharan Africa
Sub-Saharan Africa
Sub-Saharan Africa as a geographical term refers to the area of the African continent which lies south of the Sahara. A political definition of Sub-Saharan Africa, instead, covers all African countries which are fully or partially located south of the Sahara...
in the south and northern Europe
Northern Europe
Northern Europe is the northern part or region of Europe. Northern Europe typically refers to the seven countries in the northern part of the European subcontinent which includes Denmark, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Norway, Finland and Sweden...
in the north, often in exchange for goods and slaves. In England, for example, the Anglo-Saxon
Anglo-Saxons
Anglo-Saxon is a term used by historians to designate the Germanic tribes who invaded and settled the south and east of Great Britain beginning in the early 5th century AD, and the period from their creation of the English nation to the Norman conquest. The Anglo-Saxon Era denotes the period of...
king Offa of Mercia
Offa of Mercia
Offa was the King of Mercia from 757 until his death in July 796. The son of Thingfrith and a descendant of Eowa, Offa came to the throne after a period of civil war following the assassination of Æthelbald after defeating the other claimant Beornred. In the early years of Offa's reign it is likely...
(r. 757-796) had coins minted with the Shahadah in Arabic. These factors helped establish the Arab Empire (including the Rashidun
Rashidun Empire
The Rashidun Caliphate , comprising the first four caliphs in Islam's history, was founded after Muhammad's death in 632, Year 10 A.H.. At its height, the Caliphate extended from the Arabian Peninsula, to the Levant, Caucasus and North Africa in the west, to the Iranian highlands and Central Asia...
, Umayyad
Umayyad
The Umayyad Caliphate was the second of the four major Arab caliphates established after the death of Muhammad. It was ruled by the Umayyad dynasty, whose name derives from Umayya ibn Abd Shams, the great-grandfather of the first Umayyad caliph. Although the Umayyad family originally came from the...
, Abbasid
Abbasid
The Abbasid Caliphate or, more simply, the Abbasids , was the third of the Islamic caliphates. It was ruled by the Abbasid dynasty of caliphs, who built their capital in Baghdad after overthrowing the Umayyad caliphate from all but the al-Andalus region....
and Fatimid
Fatimid
The Fatimid Islamic Caliphate or al-Fāṭimiyyūn was a Berber Shia Muslim caliphate first centered in Tunisia and later in Egypt that ruled over varying areas of the Maghreb, Sudan, Sicily, the Levant, and Hijaz from 5 January 909 to 1171.The caliphate was ruled by the Fatimids, who established the...
caliphates) as the world's leading extensive economic power throughout the 7th–13th centuries.
In the 9th century, Alkindus
Al-Kindi
' , known as "the Philosopher of the Arabs", was a Muslim Arab philosopher, mathematician, physician, and musician. Al-Kindi was the first of the Muslim peripatetic philosophers, and is unanimously hailed as the "father of Islamic or Arabic philosophy" for his synthesis, adaptation and promotion...
was the first to introduce experiment
Experiment
An experiment is a methodical procedure carried out with the goal of verifying, falsifying, or establishing the validity of a hypothesis. Experiments vary greatly in their goal and scale, but always rely on repeatable procedure and logical analysis of the results...
ation into the Earth science
Earth science
Earth science is an all-embracing term for the sciences related to the planet Earth. It is arguably a special case in planetary science, the Earth being the only known life-bearing planet. There are both reductionist and holistic approaches to Earth sciences...
s. An early adherent of environmental determinism
Environmental determinism
Environmental determinism, also known as climatic determinism or geographical determinism, is the view that the physical environment, rather than social conditions, determines culture...
was the medieval Afro-Arab
Afro-Arab
Afro-Arab refers to people of mixed Black African and genealogical Arab ancestral heritage and/or linguistically and culturally Arabized Black Africans...
writer al-Jahiz
Al-Jahiz
Al-Jāḥiẓ was an Arabic prose writer and author of works of literature, Mu'tazili theology, and politico-religious polemics.In biology, Al-Jahiz introduced the concept of food chains and also proposed a scheme of animal evolution that entailed...
, who explained how the environment can determine the physical characteristics of the inhabitants of a certain community. He used his early theory of evolution
Evolution
Evolution is any change across successive generations in the heritable characteristics of biological populations. Evolutionary processes give rise to diversity at every level of biological organisation, including species, individual organisms and molecules such as DNA and proteins.Life on Earth...
to explain the origins of different human skin color
Human skin color
Human skin color is primarily due to the presence of melanin in the skin. Skin color ranges from almost black to white with a pinkish tinge due to blood vessels underneath. Variation in natural skin color is mainly due to genetics, although the evolutionary causes are not completely certain...
s, particularly black skin
Black people
The term black people is used in systems of racial classification for humans of a dark skinned phenotype, relative to other racial groups.Different societies apply different criteria regarding who is classified as "black", and often social variables such as class, socio-economic status also plays a...
, which he believed to be the result of the environment. He cited a stony region of black basalt
Basalt
Basalt is a common extrusive volcanic rock. It is usually grey to black and fine-grained due to rapid cooling of lava at the surface of a planet. It may be porphyritic containing larger crystals in a fine matrix, or vesicular, or frothy scoria. Unweathered basalt is black or grey...
in the northern Najd
Najd
Najd or Nejd , literally Highland, is the central region of the Arabian Peninsula.-Boundaries :The Arabic word nejd literally means "upland" and was once applied to a variety of regions within the Arabian Peninsula...
as evidence for his theory. In the early 10th century, Abū Zayd al-Balkhī
Ahmed ibn Sahl al-Balkhi
Abu Zayd Ahmed ibn Sahl Balkhi was a Persian Muslim polymath: a geographer, mathematician, physician, psychologist and scientist. Born in 850 CE in Shamistiyan, in the Persian province of Balkh, Khorasan , he was a disciple of al-Kindi...
, originally from Balkh
Balkh
Balkh , was an ancient city and centre of Zoroastrianism in what is now northern Afghanistan. Today it is a small town in the province of Balkh, about 20 kilometers northwest of the provincial capital, Mazar-e Sharif, and some south of the Amu Darya. It was one of the major cities of Khorasan...
, founded the "Balkhī school" of terrestrial mapping in Baghdad
Baghdad
Baghdad is the capital of Iraq, as well as the coterminous Baghdad Governorate. The population of Baghdad in 2011 is approximately 7,216,040...
. The geographers of this school also wrote extensively of the peoples, products, and customs of areas in the Muslim world, with little interest in the non-Muslim realms. Suhrāb, a late 10th century Muslim geographer, accompanied a book of geographical coordinates with instructions for making a rectangular world map, with equirectangular projection
Equirectangular projection
The equirectangular projection is a very simple map projection attributed to Marinus of Tyre, who Ptolemy claims invented the projection about AD 100...
or cylindrical cylindrical equidistant projection. In the early 11th century, Avicenna
Avicenna
Abū ʿAlī al-Ḥusayn ibn ʿAbd Allāh ibn Sīnā , commonly known as Ibn Sīnā or by his Latinized name Avicenna, was a Persian polymath, who wrote almost 450 treatises on a wide range of subjects, of which around 240 have survived...
hypothesized on the geological
Geology
Geology is the science comprising the study of solid Earth, the rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which it evolves. Geology gives insight into the history of the Earth, as it provides the primary evidence for plate tectonics, the evolutionary history of life, and past climates...
causes of mountain
Mountain
Image:Himalaya_annotated.jpg|thumb|right|The Himalayan mountain range with Mount Everestrect 58 14 160 49 Chomo Lonzorect 200 28 335 52 Makalurect 378 24 566 45 Mount Everestrect 188 581 920 656 Tibetan Plateaurect 250 406 340 427 Rong River...
s in The Book of Healing
The Book of Healing
The Book of Healing is a scientific and philosophical encyclopedia written by Abū Alī ibn Sīnā from Asfahana, near Bukhara in Greater Persia. Despite its English title, it is not in fact concerned with medicine...
(1027).
In mathematical geography, Abū Rayhān al-Bīrūnī, around 1025, was the first to describe a polar equi-azimuthal equidistant projection
Azimuthal equidistant projection
The azimuthal equidistant projection is a type of map projection.A useful application for this type of projection is a polar projection in which all distances measured from the center of the map along any longitudinal line are accurate; an example of a polar azimuthal equidistant projection can be...
of the celestial sphere
Celestial sphere
In astronomy and navigation, the celestial sphere is an imaginary sphere of arbitrarily large radius, concentric with the Earth and rotating upon the same axis. All objects in the sky can be thought of as projected upon the celestial sphere. Projected upward from Earth's equator and poles are the...
. He was also regarded as the most skilled when it came to mapping cities
City
A city is a relatively large and permanent settlement. Although there is no agreement on how a city is distinguished from a town within general English language meanings, many cities have a particular administrative, legal, or historical status based on local law.For example, in the U.S...
and measuring the distances between them, which he did for many cities in the Middle East
Middle East
The Middle East is a region that encompasses Western Asia and Northern Africa. It is often used as a synonym for Near East, in opposition to Far East...
and western Indian subcontinent
Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent, also Indian Subcontinent, Indo-Pak Subcontinent or South Asian Subcontinent is a region of the Asian continent on the Indian tectonic plate from the Hindu Kush or Hindu Koh, Himalayas and including the Kuen Lun and Karakoram ranges, forming a land mass which extends...
. He often combined astronomical readings and mathematical equations, in order to develop methods of pin-pointing locations by recording degrees of latitude
Latitude
In geography, the latitude of a location on the Earth is the angular distance of that location south or north of the Equator. The latitude is an angle, and is usually measured in degrees . The equator has a latitude of 0°, the North pole has a latitude of 90° north , and the South pole has a...
and longitude
Longitude
Longitude is a geographic coordinate that specifies the east-west position of a point on the Earth's surface. It is an angular measurement, usually expressed in degrees, minutes and seconds, and denoted by the Greek letter lambda ....
. He also developed similar techniques when it came to measuring the heights of mountain
Mountain
Image:Himalaya_annotated.jpg|thumb|right|The Himalayan mountain range with Mount Everestrect 58 14 160 49 Chomo Lonzorect 200 28 335 52 Makalurect 378 24 566 45 Mount Everestrect 188 581 920 656 Tibetan Plateaurect 250 406 340 427 Rong River...
s, depths of valley
Valley
In geology, a valley or dale is a depression with predominant extent in one direction. A very deep river valley may be called a canyon or gorge.The terms U-shaped and V-shaped are descriptive terms of geography to characterize the form of valleys...
s, and expanse of the horizon
Horizon
The horizon is the apparent line that separates earth from sky, the line that divides all visible directions into two categories: those that intersect the Earth's surface, and those that do not. At many locations, the true horizon is obscured by trees, buildings, mountains, etc., and the resulting...
, in The Chronology of the Ancient Nations. He also discussed human geography
Human geography
Human geography is one of the two major sub-fields of the discipline of geography. Human geography is the study of the world, its people, communities, and cultures. Human geography differs from physical geography mainly in that it has a greater focus on studying human activities and is more...
and the planetary habitability
Planetary habitability
Planetary habitability is the measure of a planet's or a natural satellite's potential to sustain life. Life may develop directly on a planet or satellite or be transferred to it from another body, a theoretical process known as panspermia...
of the Earth
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun, and the densest and fifth-largest of the eight planets in the Solar System. It is also the largest of the Solar System's four terrestrial planets...
. He hypothesized that roughly a quarter of the Earth's surface is habitable by human
Human
Humans are the only living species in the Homo genus...
s, and also argued that the shores of Asia
Asia
Asia is the world's largest and most populous continent, located primarily in the eastern and northern hemispheres. It covers 8.7% of the Earth's total surface area and with approximately 3.879 billion people, it hosts 60% of the world's current human population...
and Europe
Europe
Europe is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting...
were "separated by a vast sea, too dark and dense to navigate and too risky to try" in reference to the Atlantic Ocean
Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's oceanic divisions. With a total area of about , it covers approximately 20% of the Earth's surface and about 26% of its water surface area...
and Pacific Ocean
Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest of the Earth's oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic in the north to the Southern Ocean in the south, bounded by Asia and Australia in the west, and the Americas in the east.At 165.2 million square kilometres in area, this largest division of the World...
.
At the age of 17, al-Biruni calculated the latitude
Latitude
In geography, the latitude of a location on the Earth is the angular distance of that location south or north of the Equator. The latitude is an angle, and is usually measured in degrees . The equator has a latitude of 0°, the North pole has a latitude of 90° north , and the South pole has a...
of Kath, Khwarazm, using the maximum altitude of the Sun. Al-Biruni also solved a complex geodesic
Geodesy
Geodesy , also named geodetics, a branch of earth sciences, is the scientific discipline that deals with the measurement and representation of the Earth, including its gravitational field, in a three-dimensional time-varying space. Geodesists also study geodynamical phenomena such as crustal...
equation in order to accurately compute the Earth
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun, and the densest and fifth-largest of the eight planets in the Solar System. It is also the largest of the Solar System's four terrestrial planets...
's circumference
Circumference
The circumference is the distance around a closed curve. Circumference is a special perimeter.-Circumference of a circle:The circumference of a circle is the length around it....
, which were close to modern values of the Earth's circumference. His estimate of 6,339.9 km for the Earth radius
Earth radius
Because the Earth is not perfectly spherical, no single value serves as its natural radius. Distances from points on the surface to the center range from 6,353 km to 6,384 km...
was only 16.8 km less than the modern value of 6,356.7 km. In contrast to his predecessors who measured the Earth's circumference by sighting the Sun simultaneously from two different locations, al-Biruni developed a new method of using trigonometric calculations based on the angle between a plain
Plain
In geography, a plain is land with relatively low relief, that is flat or gently rolling. Prairies and steppes are types of plains, and the archetype for a plain is often thought of as a grassland, but plains in their natural state may also be covered in shrublands, woodland and forest, or...
and mountain
Mountain
Image:Himalaya_annotated.jpg|thumb|right|The Himalayan mountain range with Mount Everestrect 58 14 160 49 Chomo Lonzorect 200 28 335 52 Makalurect 378 24 566 45 Mount Everestrect 188 581 920 656 Tibetan Plateaurect 250 406 340 427 Rong River...
top which yielded more accurate measurements of the Earth's circumference and made it possible for it to be measured by a single person from a single location. By the age of 22, al-Biruni had written several short works, including a study of map projection
Map projection
A map projection is any method of representing the surface of a sphere or other three-dimensional body on a plane. Map projections are necessary for creating maps. All map projections distort the surface in some fashion...
s, Cartography
Cartography
Cartography is the study and practice of making maps. Combining science, aesthetics, and technique, cartography builds on the premise that reality can be modeled in ways that communicate spatial information effectively.The fundamental problems of traditional cartography are to:*Set the map's...
, which included a method for projecting a hemisphere
Sphere
A sphere is a perfectly round geometrical object in three-dimensional space, such as the shape of a round ball. Like a circle in two dimensions, a perfect sphere is completely symmetrical around its center, with all points on the surface lying the same distance r from the center point...
on a plane
Plane (mathematics)
In mathematics, a plane is a flat, two-dimensional surface. A plane is the two dimensional analogue of a point , a line and a space...
.
John J. O'Connor and Edmund F. Robertson write in the MacTutor History of Mathematics archive
MacTutor History of Mathematics archive
The MacTutor History of Mathematics archive is a website maintained by John J. O'Connor and Edmund F. Robertson and hosted by the University of St Andrews in Scotland...
:

Arab
Arab people, also known as Arabs , are a panethnicity primarily living in the Arab world, which is located in Western Asia and North Africa. They are identified as such on one or more of genealogical, linguistic, or cultural grounds, with tribal affiliations, and intra-tribal relationships playing...
geographer Al-Idrisi's Mappa Mundi incorporated the knowledge of Africa
Africa
Africa is the world's second largest and second most populous continent, after Asia. At about 30.2 million km² including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of the Earth's total surface area and 20.4% of the total land area...
, the Indian Ocean
Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third largest of the world's oceanic divisions, covering approximately 20% of the water on the Earth's surface. It is bounded on the north by the Indian Subcontinent and Arabian Peninsula ; on the west by eastern Africa; on the east by Indochina, the Sunda Islands, and...
and the Far East
Far East
The Far East is an English term mostly describing East Asia and Southeast Asia, with South Asia sometimes also included for economic and cultural reasons.The term came into use in European geopolitical discourse in the 19th century,...
gathered by Arab merchants and explorers with the information inherited from the classical geographers to create one of the most accurate maps of the world to date. The Tabula Rogeriana
Tabula Rogeriana
The Nuzhat al-mushtaq fi'khtiraq al-afaq lit. "the book of pleasant journeys into faraway lands", most often known as the Tabula Rogeriana , is a description of the world and world map created by the Arab geographer, Muhammad al-Idrisi, in 1154...
was drawn by Al-Idrisi in 1154 for the Norman
Normans
The Normans were the people who gave their name to Normandy, a region in northern France. They were descended from Norse Viking conquerors of the territory and the native population of Frankish and Gallo-Roman stock...
King Roger II of Sicily
Roger II of Sicily
Roger II was King of Sicily, son of Roger I of Sicily and successor to his brother Simon. He began his rule as Count of Sicily in 1105, later became Duke of Apulia and Calabria , then King of Sicily...
, after a stay of eighteen years at his court, where he worked on the commentaries and illustrations of the map. The map, written in Arabic, shows the Eurasian continent in its entirety, but only shows the northern part of the African continent.
In the 14th century, Ibn Baṭṭūṭah
Ibn Battuta
Abu Abdullah Muhammad Ibn Battuta , or simply Ibn Battuta, also known as Shams ad–Din , was a Muslim Moroccan Berber explorer, known for his extensive travels published in the Rihla...
, a Moroccan
Morocco
Morocco , officially the Kingdom of Morocco , is a country located in North Africa. It has a population of more than 32 million and an area of 710,850 km², and also primarily administers the disputed region of the Western Sahara...
, began his travels. He started as a pilgrim to Mecca, but continued his journeys for the next 30 years, covering some 73,000 miles (117,000 km). Before returning home, he had visited most of the Muslim world and beyond, from Europe and southern Africa in the west to eastern Asia in the east. The universal use of Arabic in the Muslim world and his status as judge trained in law gave him access to royal courts at most locations he visited.
Ibn Battuta
Ibn Battuta
Abu Abdullah Muhammad Ibn Battuta , or simply Ibn Battuta, also known as Shams ad–Din , was a Muslim Moroccan Berber explorer, known for his extensive travels published in the Rihla...
(1304–1368) was a traveler and explorer, whose account documents his travels and excursions over a period of almost thirty years, covering some 73,000 miles (117,000 km). These journeys covered most of the known Old World
Old World
The Old World consists of those parts of the world known to classical antiquity and the European Middle Ages. It is used in the context of, and contrast with, the "New World" ....
, extending from North Africa
North Africa
North Africa or Northern Africa is the northernmost region of the African continent, linked by the Sahara to Sub-Saharan Africa. Geopolitically, the United Nations definition of Northern Africa includes eight countries or territories; Algeria, Egypt, Libya, Morocco, South Sudan, Sudan, Tunisia, and...
, West Africa
West Africa
West Africa or Western Africa is the westernmost region of the African continent. Geopolitically, the UN definition of Western Africa includes the following 16 countries and an area of approximately 5 million square km:-Flags of West Africa:...
, Southern Europe
Southern Europe
The term Southern Europe, at its most general definition, is used to mean "all countries in the south of Europe". However, the concept, at different times, has had different meanings, providing additional political, linguistic and cultural context to the definition in addition to the typical...
and Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is the eastern part of Europe. The term has widely disparate geopolitical, geographical, cultural and socioeconomic readings, which makes it highly context-dependent and even volatile, and there are "almost as many definitions of Eastern Europe as there are scholars of the region"...
in the west, to the Middle East
Middle East
The Middle East is a region that encompasses Western Asia and Northern Africa. It is often used as a synonym for Near East, in opposition to Far East...
, Indian subcontinent
Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent, also Indian Subcontinent, Indo-Pak Subcontinent or South Asian Subcontinent is a region of the Asian continent on the Indian tectonic plate from the Hindu Kush or Hindu Koh, Himalayas and including the Kuen Lun and Karakoram ranges, forming a land mass which extends...
, Central Asia
Central Asia
Central Asia is a core region of the Asian continent from the Caspian Sea in the west, China in the east, Afghanistan in the south, and Russia in the north...
, Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia, South-East Asia, South East Asia or Southeastern Asia is a subregion of Asia, consisting of the countries that are geographically south of China, east of India, west of New Guinea and north of Australia. The region lies on the intersection of geological plates, with heavy seismic...
and China
China
Chinese civilization may refer to:* China for more general discussion of the country.* Chinese culture* Greater China, the transnational community of ethnic Chinese.* History of China* Sinosphere, the area historically affected by Chinese culture...
(then the Mongol Yuan Empire) in the east, a distance readily surpassing that of his predecessors and his near-contemporary Marco Polo
Marco Polo
Marco Polo was a Venetian merchant traveler from the Venetian Republic whose travels are recorded in Il Milione, a book which did much to introduce Europeans to Central Asia and China. He learned about trading whilst his father and uncle, Niccolò and Maffeo, travelled through Asia and apparently...
.
Medieval Europe
During the Early Middle AgesEarly Middle Ages
The Early Middle Ages was the period of European history lasting from the 5th century to approximately 1000. The Early Middle Ages followed the decline of the Western Roman Empire and preceded the High Middle Ages...
, geographical knowledge in Europe regressed (though it is a popular misconception that they thought the world was flat), and the simple T and O map
T and O map
A T and O map or O-T or T-O map , is a type of medieval world map, sometimes also called a Beatine map or a Beatus map because one of the earliest known representations of this sort is attributed to Beatus of Liébana, an 8th-century Spanish monk...
became the standard depiction of the world.
The trips of Venetian
Republic of Venice
The Republic of Venice or Venetian Republic was a state originating from the city of Venice in Northeastern Italy. It existed for over a millennium, from the late 7th century until 1797. It was formally known as the Most Serene Republic of Venice and is often referred to as La Serenissima, in...
explorer Marco Polo
Marco Polo
Marco Polo was a Venetian merchant traveler from the Venetian Republic whose travels are recorded in Il Milione, a book which did much to introduce Europeans to Central Asia and China. He learned about trading whilst his father and uncle, Niccolò and Maffeo, travelled through Asia and apparently...
in the 13th century, the Christian Crusades of the 12th and 13th centuries, and the Portuguese and Spanish voyages of exploration during the 15th and 16th centuries opened up new horizons and stimulated geographic writings.
During the 15th century, Henry the Navigator of Portugal supported explorations of the African coast and became a leader in the promotion of geographic studies. Among the most notable accounts of voyages and discoveries published during the 16th century were those by Giambattista Ramusio in Venice, by Richard Hakluyt
Richard Hakluyt
Richard Hakluyt was an English writer. He is principally remembered for his efforts in promoting and supporting the settlement of North America by the English through his works, notably Divers Voyages Touching the Discoverie of America and The Principal Navigations, Voiages, Traffiques and...
in England, and by Theodore de Bry in what is now Belgium.
Early modern period

Marco Polo
Marco Polo was a Venetian merchant traveler from the Venetian Republic whose travels are recorded in Il Milione, a book which did much to introduce Europeans to Central Asia and China. He learned about trading whilst his father and uncle, Niccolò and Maffeo, travelled through Asia and apparently...
, interest in geography spread throughout Europe. From around circa 1400, the writings of Ptolemy
Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy , was a Roman citizen of Egypt who wrote in Greek. He was a mathematician, astronomer, geographer, astrologer, and poet of a single epigram in the Greek Anthology. He lived in Egypt under Roman rule, and is believed to have been born in the town of Ptolemais Hermiou in the...
and his Islamic successors
Islamic geography
Geography and cartography in medieval Islam refers to the advancement of geography, cartography and the earth sciences in the medieval Islamic civilization....
provided a systematic framework to tie together and portray geographical information. The great voyages of exploration in 16th and 17th centuries revived a desire for both accurate geographic detail, and more solid theoretical foundations. The Geographia Generalis by Bernhardus Varenius
Bernhardus Varenius
Bernhardus Varenius was a German geographer.-Life:His early years were spent at Uelzen, where his father was court preacher to the duke of Brunswick...
and Gerardus Mercator
Gerardus Mercator
thumb|right|200px|Gerardus MercatorGerardus Mercator was a cartographer, born in Rupelmonde in the Hapsburg County of Flanders, part of the Holy Roman Empire. He is remembered for the Mercator projection world map, which is named after him...
's world map are prime examples of the new breed of scientific geography.

Mongols
Mongols ) are a Central-East Asian ethnic group that lives mainly in the countries of Mongolia, China, and Russia. In China, ethnic Mongols can be found mainly in the central north region of China such as Inner Mongolia...
also had wide ranging knowledge of the geography of Europe and Asia, based in their governance and ruling of much of this area and used this information for the undertaking of large military expeditions. The evidence for this is found in historical resources such as The Secret History of Mongols and other Persian chronicles written in 13th and 14th centuries. For example, during the rule of the Great Yuan Dynasty a world map was created and is currently kept in South Korea. See also: Maps of the Yuan Dynasty
The Muslim Ottoman
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman EmpireIt was usually referred to as the "Ottoman Empire", the "Turkish Empire", the "Ottoman Caliphate" or more commonly "Turkey" by its contemporaries...
cartographer Piri Reis
Piri Reis
Piri Reis was an Turkish Ottoman admiral, geographer and cartographer born between 1465 and 1470 and died in 1554 or 1555....
drawn navigational maps in his Kitab-ı Bahriye. The work includes an atlas of charts for small segments of the Mediterranean, accompanied by sailing instructions covering the sea. In the second version of the work, he included a map of the Americas. The Piri Reis map
Piri Reis map
The Piri Reis map is a pre-modern world map compiled in 1513 from military intelligence by the Ottoman-Turkish admiral and cartographer Piri Reis. The half of the map that survives shows the western coasts of Europe and North Africa and the coast of Brazil with reasonable accuracy...
drawn by the Ottoman cartographer Piri Reis
Piri Reis
Piri Reis was an Turkish Ottoman admiral, geographer and cartographer born between 1465 and 1470 and died in 1554 or 1555....
in 1513 is an early surviving map to show the Americas.
19th century
By the 18th century, geography had become recognized as a discrete discipline and became part of a typical universityUniversity
A university is an institution of higher education and research, which grants academic degrees in a variety of subjects. A university is an organisation that provides both undergraduate education and postgraduate education...
curriculum in Europe (especially Paris
Paris
Paris is the capital and largest city in France, situated on the river Seine, in northern France, at the heart of the Île-de-France region...
and Berlin
Berlin
Berlin is the capital city of Germany and is one of the 16 states of Germany. With a population of 3.45 million people, Berlin is Germany's largest city. It is the second most populous city proper and the seventh most populous urban area in the European Union...
), although not in the United Kingdom
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
where geography was generally taught as a sub-discipline of other subjects.
One of the great works of this time was Kosmos: a sketch of a physical description of the Universe, by Alexander von Humboldt
Alexander von Humboldt
Friedrich Wilhelm Heinrich Alexander Freiherr von Humboldt was a German naturalist and explorer, and the younger brother of the Prussian minister, philosopher and linguist Wilhelm von Humboldt...
, the first volume of which was published in German in 1845. Such was the power of this work that Dr Mary Somerville, of Cambridge University
University of Cambridge
The University of Cambridge is a public research university located in Cambridge, United Kingdom. It is the second-oldest university in both the United Kingdom and the English-speaking world , and the seventh-oldest globally...
intended to scrap publication of her own Physical Geography on reading Kosmos. Von Humboldt himself persuaded her to publish (after the publisher sent him a copy).
In 1877, Thomas Henry Huxley published his Physiography with the philosophy of universality
Universality (philosophy)
In philosophy, universalism is a doctrine or school claiming universal facts can be discovered and is therefore understood as being in opposition to relativism. In certain religions, universality is the quality ascribed to an entity whose existence is consistent throughout the universe...
presented as an integrated approach in the study of the natural environment. The philosophy of universality in geography was not a new one but can be seen as evolving from the works of Alexander von Humboldt
Alexander von Humboldt
Friedrich Wilhelm Heinrich Alexander Freiherr von Humboldt was a German naturalist and explorer, and the younger brother of the Prussian minister, philosopher and linguist Wilhelm von Humboldt...
and Immanuel Kant
Immanuel Kant
Immanuel Kant was a German philosopher from Königsberg , researching, lecturing and writing on philosophy and anthropology at the end of the 18th Century Enlightenment....
. The publication of Huxley physiography presented a new form of geography that analysed and classified cause and effect
Causality
Causality is the relationship between an event and a second event , where the second event is understood as a consequence of the first....
at the micro-level and then applied these to the macro-scale (due to the view that the micro was part of the macro and thus an understanding of all the micro-scales was need to understand the macro level). This approach emphasized the empirical collection of data over the theoretical. The same approach was also used by Halford John Mackinder
Halford John Mackinder
Sir Halford John Mackinder PC was an English geographer and is considered one of the founding fathers of both geopolitics and geostrategy.-Early life and education:...
in 1887. However, the integration of the Geosphere
Geosphere
The term geosphere is often used to refer to the densest parts of Earth, which consist mostly of rock and regolith. The geosphere consists of the inside of the Earth or other planets or bodies....
, Atmosphere
Atmosphere
An atmosphere is a layer of gases that may surround a material body of sufficient mass, and that is held in place by the gravity of the body. An atmosphere may be retained for a longer duration, if the gravity is high and the atmosphere's temperature is low...
and Biosphere
Biosphere
The biosphere is the global sum of all ecosystems. It can also be called the zone of life on Earth, a closed and self-regulating system...
under physiography was soon over taken by Davisian geomorphology.
Over the past two centuries the quantity of knowledge and the number of tools has exploded. There are strong links between geography and the sciences of geology
Geology
Geology is the science comprising the study of solid Earth, the rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which it evolves. Geology gives insight into the history of the Earth, as it provides the primary evidence for plate tectonics, the evolutionary history of life, and past climates...
and botany
Botany
Botany, plant science, or plant biology is a branch of biology that involves the scientific study of plant life. Traditionally, botany also included the study of fungi, algae and viruses...
, as well as economics
Economics
Economics is the social science that analyzes the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services. The term economics comes from the Ancient Greek from + , hence "rules of the house"...
, sociology
Sociology
Sociology is the study of society. It is a social science—a term with which it is sometimes synonymous—which uses various methods of empirical investigation and critical analysis to develop a body of knowledge about human social activity...
and demographics
Demographics
Demographics are the most recent statistical characteristics of a population. These types of data are used widely in sociology , public policy, and marketing. Commonly examined demographics include gender, race, age, disabilities, mobility, home ownership, employment status, and even location...
.
The Royal Geographical Society
Royal Geographical Society
The Royal Geographical Society is a British learned society founded in 1830 for the advancement of geographical sciences...
was founded in England
England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Scotland to the north and Wales to the west; the Irish Sea is to the north west, the Celtic Sea to the south west, with the North Sea to the east and the English Channel to the south separating it from continental...
in 1830, although the United Kingdom did not get its first full Chair of geography until 1917. The first real geographical intellect to emerge in United Kingdom
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
geography was Halford John Mackinder
Halford John Mackinder
Sir Halford John Mackinder PC was an English geographer and is considered one of the founding fathers of both geopolitics and geostrategy.-Early life and education:...
, appointed reader at Oxford University
University of Oxford
The University of Oxford is a university located in Oxford, United Kingdom. It is the second-oldest surviving university in the world and the oldest in the English-speaking world. Although its exact date of foundation is unclear, there is evidence of teaching as far back as 1096...
in 1887.
The National Geographic Society
National Geographic Society
The National Geographic Society , headquartered in Washington, D.C. in the United States, is one of the largest non-profit scientific and educational institutions in the world. Its interests include geography, archaeology and natural science, the promotion of environmental and historical...
was founded in the USA in 1888 and began publication of the National Geographic magazine which became and continues to be a great popularizer of geographic information. The society has long supported geographic research and education.
20th century
In the West during the second half of the 19th and the 20th century, the discipline of geography went through four major phases: environmental determinism, regional geography, the quantitative revolution, and critical geography.Environmental determinism
Environmental determinism is the theory that a people's physical, mental and moral habits are directly due to the influence of their natural environment. Prominent environmental deterministsEnvironmental determinism
Environmental determinism, also known as climatic determinism or geographical determinism, is the view that the physical environment, rather than social conditions, determines culture...
included Carl Ritter
Carl Ritter
Carl Ritter was a German geographer. Along with Alexander von Humboldt, he is considered one of the founders of modern geography. From 1825 until his death, he occupied the first chair in geography at the University of Berlin.-Biography:Ritter was born in Quedlinburg, one of the six children of a...
, Ellen Churchill Semple
Ellen Churchill Semple
Ellen Churchill Semple was an American geographer. Ellen was born in Louisville, Kentucky, the youngest of five children by Alexander Bonner Semple and Emerine Price. She is most closely associated with work in anthropogeography and environmentalism...
, and Ellsworth Huntington
Ellsworth Huntington
Ellsworth Huntington was a professor of geography at Yale University during the early 20th century, known for his studies on climatic determinism, economic growth and economic geography...
. Popular hypotheses included "heat makes inhabitants of the tropics lazy" and "frequent changes in barometric pressure make inhabitants of temperate latitudes more intellectually agile." Environmental determinist geographers attempted to make the study of such influences scientific. Around the 1930s, this school of thought was widely repudiated as lacking any basis and being prone to (often bigoted) generalizations. Environmental determinism remains an embarrassment to many contemporary geographers, and leads to skepticism among many of them of claims of environmental influence on culture (such as the theories of Jared Diamond
Jared Diamond
Jared Mason Diamond is an American scientist and author whose work draws from a variety of fields. He is currently Professor of Geography and Physiology at UCLA...
).
Regional geography
Regional geography was coined by a group of geographers known as possibilists and represented a reaffirmation that the proper topic of geography was study of places (regions). Regional geographers focused on the collection of descriptive information about places, as well as the proper methods for dividing the earth up into regions. Well-known names from these period are Alfred HettnerAlfred Hettner
Alfred Hettner was a German geographer.He is known for his concept of chorology, the study of places and regions....
in Germany and Paul Vidal de la Blache
Paul Vidal de la Blache
Paul Vidal de la Blache was a French geographer. He is considered to be the founder of the modern French geography and also the founder of the French School of Geopolitics...
in France. The philosophical basis of this field in United States was laid out by Richard Hartshorne
Richard Hartshorne
Richard Hartshorne was a prominent American geographer. He completed his undergraduate studies at Princeton University and his doctorate at the University of Chicago , then taught at the University of Minnesota and the University of Wisconsin , with war-time interruption to...
, who defined geography as a study of areal differentiation, which later led to criticism of this approach as overly descriptive and unscientific.
The Quantitative revolution
The quantitative revolution in geography began in the 1950s. Geographers formulated geographical theories and subjected the theories to empirical tests, usually using statistical methods (especially hypothesis testing). This quantitative revolution laid the groundwork for the development of geographic information systemGeographic Information System
A geographic information system, geographical information science, or geospatial information studies is a system designed to capture, store, manipulate, analyze, manage, and present all types of geographically referenced data...
s. Well-known geographers from this period are Fred K. Schaefer
Fred K. Schaefer
Fred K. Schaefer was a geographer. He is considered as one of the pioneers of quantitative revolution.-Life:Fred K. Schaefer was born in Berlin, Germany in the family of metal worker. He was involved in politics as a member of Social Democratic party and after the rise of fascism he fled from Nazi...
, Waldo Tobler, William Garrison
William Garrison (geographer)
William Louis Garrison is an American geographer and transportation analyst, currently a professor emeritus at the University of California, Berkeley. While at the University of Washington in the 1950s, Garrison led the "quantitative revolution" in geography, which applied computers and statistics...
, Peter Haggett
Peter Haggett
Peter Haggett, CBE Sc.D. FBA is an eminent British geographer and academic, Professor Emeritus and Senior Research Fellow in Urban and Regional Geography at the School of Geographical Sciences, University of Bristol....
, Richard J. Chorley
Richard Chorley
Richard John Chorley was a leading figure in the late 20th century for his work in quantitative geography, and played an instrumental role in bringing in the use of systems theory to geography.-Early Education:...
, William Bunge
William Bunge
William Wheeler Bunge Jr. is an American geographer active mainly as a quantitative geographer and spatial theorist. He also became a radical geographer and anti-war activist in the USA and Canada.-Personal life:...
, and Torsten Hägerstrand
Torsten Hägerstrand
Torsten Hägerstrand , was a Swedish geographer. He is known for his work on migration, cultural diffusion and time geography....
.
Critical geography
Though positivist approaches remain important in geography, critical geography arose as a critique of positivism. The first strain of critical geography to emerge was humanistic geography. Drawing on the philosophies of existentialismExistentialism
Existentialism is a term applied to a school of 19th- and 20th-century philosophers who, despite profound doctrinal differences, shared the belief that philosophical thinking begins with the human subject—not merely the thinking subject, but the acting, feeling, living human individual...
and phenomenology, humanistic geographers (such as Yi-Fu Tuan
Yi-Fu Tuan
Yi-Fu Tuan is a Chinese-U.S. geographer.Tuan was born in 1930 in Tientsin, China. He was the son of a rich oligarch and was part of the top class in the Republic of China....
) focused on people's sense of, and relationship with, places. More influential was Marxist geography
Marxist geography
Marxist geography is a critical geography which utilises the theories and philosophy of Marxism to examine the spatial relations of human geography. In Marxist geography the relations that geography has traditionally analyzed - natural environment and spatial relations - are reviewed as outcomes of...
, which applied the social theories of Karl Marx
Karl Marx
Karl Heinrich Marx was a German philosopher, economist, sociologist, historian, journalist, and revolutionary socialist. His ideas played a significant role in the development of social science and the socialist political movement...
and his followers to geographic phenomena. David Harvey
David Harvey (geographer)
David Harvey is the Distinguished Professor of Anthropology at the Graduate Center of the City University of New York . A leading social theorist of international standing, he received his PhD in Geography from University of Cambridge in 1961. Widely influential, he is among the top 20 most cited...
and Richard Peet are well-known Marxist geographers. Feminist geography
Feminist geography
Feminist geography is an approach in human geography which applies the theories, methods and critiques of feminism to the study of the human environment, society and geographical space.-Areas of study:...
is, as the name suggests, the use of ideas from feminism
Feminism
Feminism is a collection of movements aimed at defining, establishing, and defending equal political, economic, and social rights and equal opportunities for women. Its concepts overlap with those of women's rights...
in geographic contexts. The most recent strain of critical geography is postmodernist geography, which employs the ideas of postmodernist
Postmodernism
Postmodernism is a philosophical movement evolved in reaction to modernism, the tendency in contemporary culture to accept only objective truth and to be inherently suspicious towards a global cultural narrative or meta-narrative. Postmodernist thought is an intentional departure from the...
and poststructuralist theorists to explore the social construction of spatial relations.
See also
- Human geographyHuman geographyHuman geography is one of the two major sub-fields of the discipline of geography. Human geography is the study of the world, its people, communities, and cultures. Human geography differs from physical geography mainly in that it has a greater focus on studying human activities and is more...
- Physical geographyPhysical geographyPhysical geography is one of the two major subfields of geography. Physical geography is that branch of natural science which deals with the study of processes and patterns in the natural environment like the atmosphere, biosphere and geosphere, as opposed to the cultural or built environment, the...
- CartographyCartographyCartography is the study and practice of making maps. Combining science, aesthetics, and technique, cartography builds on the premise that reality can be modeled in ways that communicate spatial information effectively.The fundamental problems of traditional cartography are to:*Set the map's...
- ChorographyChorographyChorography is a term deriving from the writings of the ancient geographer Ptolemy, meaning the geographical description of regions...
- Economic geographyEconomic geographyEconomic geography is the study of the location, distribution and spatial organization of economic activities across the world. The subject matter investigated is strongly influenced by the researcher's methodological approach. Neoclassical location theorists, following in the tradition of Alfred...
- Royal Scottish Geographical SocietyRoyal Scottish Geographical SocietyThe Royal Scottish Geographical Society is a learned society founded in 1884 and based in Perth. The Society has a membership of 2500 and aims to advance the science of geography worldwide by supporting education, research, expeditions, through its journal , its newsletter and other publications...
- Royal Geographical SocietyRoyal Geographical SocietyThe Royal Geographical Society is a British learned society founded in 1830 for the advancement of geographical sciences...
- List of maritime explorers
- List of explorers
External links
- The encyclopædia of geography: comprising a complete description of the earth, physical, statistical, civil, and political, 1852, Hugh Murray, 1779–1846, et al. (Philadelphia: Blanchard and Lea) at the University of Michigan Making of America site.
- The Story of Maps at Google Book Search, a history of cartographyCartographyCartography is the study and practice of making maps. Combining science, aesthetics, and technique, cartography builds on the premise that reality can be modeled in ways that communicate spatial information effectively.The fundamental problems of traditional cartography are to:*Set the map's...
; why North is at the "top" of a map, how they surveyed all of Europe and other interesting facts.

