
History of Protestantism
Encyclopedia
The Protestant Reformation
of the early 16th century was an attempt to reform the Catholic Church.
German theologian Martin Luther
wrote his Ninety-Five Theses on the sale of indulgences in 1517. Parallel to events in Germany, a movement began in Switzerland under the leadership of Ulrich Zwingli. The political separation of the Church of England
from Rome under Henry VIII
, beginning in 1529 and completed in 1536, brought England alongside this broad Reformed movement.
The Scottish Reformation
of 1560 decisively shaped the Church of Scotland
and, through it, all other Presbyterian churches worldwide.
Following the excommunication
of Luther and condemnation of the Reformation by the Pope, the work and writings of John Calvin
were influential in establishing a loose consensus among various groups in Switzerland, Scotland
, Hungary, Germany and elsewhere.
In the course of this religious upheaval, the German Peasants' War
of 1524–1525 swept through the Bavaria
n, Thuringia
n and Swabia
n principalities. The confessional division of the states of the Holy Roman Empire eventually erupted in the Thirty Years' War
of 1618–1648. This left Germany weakened and fragmented
for more than two centuries, until the unification of Germany under the German Empire
of 1871.
The success of the Counter-Reformation
on the Continent and the growth of a Puritan
party dedicated to further Protestant reform polarized the Elizabethan Age, although it was not until the Civil War
of the 1640s that England underwent religious strife comparable to that which its neighbours had suffered some generations before.
The "Great Awakenings" were periods of rapid and dramatic religious revival
in Anglo-American religious history, generally recognized as beginning in the 1730s. They have also been described as periodic revolutions in colonial religious thought
.
In the 20th century, Protestantism, especially in the United States
, was characterized by accelerating fragmentation. The century saw the rise of both liberal and conservative splinter groups, as well as a general secularization of Western society.
Notable developments in the 20th century of US Protestantism was the rise of Pentecostalism
, Christian fundamentalism and Evangelicalism
.
While these movements have spilled over to Europe to a limited degree, the development of Protestantism in Europe was more dominated by secularization, leading to an increasingly "post-Christian Europe".
, so called because the movement received support from the magistrates (that is, the civil authorities) as opposed to the Radical Reformation
, which had no state sponsorship. Older Protestant churches, such as the Unitas Fratrum
(Unity of the Brethren
), Moravian Brethren or the Bohemian Brethren trace their origin to the time of Jan Hus
in the early 15th century. As the Hussite
movement was led by a majority of Bohemian nobles and recognized for a time by the Basel Compacts, this is considered by some to be the first Magisterial Reformation in Europe. In Germany, a hundred years later, protests against the Roman Catholic authorities erupted in many places at once, during a time of threatened Islamic Ottoman
invasion
¹ which distracted German princes in particular. To some degree, the protest can be explained by the events of the previous two centuries in Europe and particularly in Bohemia. Earlier in the south of France, where the old influence of the Cathars led to the growing protests against the pope and his authorities, Guillaume Farel (b. 1489) preached reformation as early as 1522 in Dauphiné
, where the French Wars of Religion
later originated in 1562, also known as Huguenot
wars. These also spread later to other parts of Europe.
and the Papal Schism
in the Roman Catholic Church (1378–1416) had excited wars between princes, uprisings among the peasants, and widespread concern over corruption in the Church. A new nationalism
also challenged the relatively internationalist medieval world. The first of a series of disruptive and new perspectives came from John Wycliffe
at Oxford University, then from Jan Hus
at the University of Prague
(Hus had been previously influenced by Wycliffe during a trip to England) . The Catholic Church officially concluded debate over Hus' teachings at the Council of Constance
(1414–1417). The conclave condemned Jan Hus, who was executed by burning in spite of a promise of safe-conduct. At the command of Pope Martin V
, Wycliffe was posthumously exhumed and burned as a heretic
twelve years after his burial.
The Council of Constance confirmed and strengthened the traditional medieval conception of Churches and Empires. It did not address the national tensions, or the theological tensions which had been stirred up during the previous century. The council could not prevents schism
and the Hussite Wars
in Bohemia
.
Historical upheaval usually yields much new thinking as to how society should be organized. This was the case leading up to the Protestant Reformation. Following the breakdown of monastic institutions and scholasticism
in late medieval Europe, which were accentuated by the "Babylonian Captivity" of the Papacy, the Papal Schism, and the failure of the Conciliar movement, the sixteenth century saw the fomenting of a great cultural debate about religious reforms and later fundamental religious values (See German mysticism
). Historians would generally assume that the failure to reform (too many vested interests, lack of coordination in the reforming coalition) would eventually lead to a greater upheaval or even revolution, since the system must eventually be adjusted or disintegrate, and the failure of the Conciliar movement helped lead to the Protestant Reformation in Europe. These frustrated reformist movements ranged from nominalism
, devotio moderna (modern devotion)
, to humanism
occurring in conjunction with economic, political and demographic forces that contributed to a growing disaffection with the wealth and power of the elite
clergy
, sensitizing the population to the financial and moral corruption of the secular Renaissance
church.
The outcome of the Black Death
encouraged a radical reorganization of the economy, and eventually of European society. In the emerging urban centers, however, the calamities of the fourteenth and early fifteenth century, and the resultant labor shortages, provided a strong impetus for economic diversification and technological innovations. Following the Black Death, the initial loss of life due to famine, plague, and pestilence contributed to an intensification of capital accumulation in the urban areas, and thus a stimulus to trade, industry, and burgeoning urban growth in fields as diverse as banking (the Fugger
banking family in Augsburg
and the Medici
family of Florence
being the most prominent); textiles, armaments
, especially stimulated by the Hundred Years' War
, and mining of iron ore due, in large part, to the booming armaments industry. Accumulation of surplus, competitive overproduction
, and heightened competition to maximize economic advantage, contributed to civil war, aggressive militarism
, and thus to centralization. As a direct result of the move toward centralization, leaders like Louis XI of France
(1461–1483), the "spider king", sought to remove all constitutional restrictions on the exercise of their authority. In England
, France
, and Spain
the move toward centralization begun in the thirteenth century was carried to a successful conclusion.
But as recovery and prosperity progressed, enabling the population to reach its former levels in the late 15th and 16th centuries, the combination of both a newly-abundant labor supply as well as improved productivity, were 'mixed blessings' for many segments of Western European society. Despite tradition, landlords started the move to exclude peasant
s from "common land
s". With trade stimulated, landowners increasingly moved away from the manorial
economy. Woollen manufacturing greatly expanded in France
, Germany
, and the Netherlands
and new textile industries began to develop.
The invention of movable type
would lead to the Protestant zeal for translating the Bible and getting it into the hands of the laity. This would advance the culture of Biblical literacy.
The "humanism" of the Renaissance
period stimulated unprecedented academic ferment, and a concern for academic freedom
. Ongoing, earnest theoretical debates occurred in the universities about the nature of the church, and the source and extent of the authority of the papacy, of councils, and of princes.
 The protests against Rome began in earnest when Martin Luther
The protests against Rome began in earnest when Martin Luther
, an Augustinian monk and professor at the university of Wittenberg
, called in 1517 for a reopening of the debate on the sale of indulgence
s. Luther's dissent marked a sudden outbreak of a new and irresistible force of discontent which had been pushed underground but not resolved. The quick spread of discontent occurred to a large degree because of the printing press
and the resulting swift movement of both ideas and documents, including the 95 Theses
. Information was also widely disseminated in manuscript form, as well as by cheap prints and woodcuts amongst the poorer sections of society.
Parallel to events in Germany, a movement began in Switzerland under the leadership of Ulrich Zwingli. These two movements quickly agreed on most issues, as the recently introduced printing press
spread ideas rapidly from place to place, but some unresolved differences kept them separate. Some followers of Zwingli believed that the Reformation was too conservative, and moved independently toward more radical positions, some of which survive among modern day Anabaptist
s. Other Protestant movements grew up along lines of mysticism or humanism (cf.
Erasmus), sometimes breaking from Rome or from the Protestants, or forming outside of the churches.
 After this first stage of the Reformation, following the excommunication
After this first stage of the Reformation, following the excommunication
of Luther and condemnation of the Reformation by the Pope, the work and writings of John Calvin
were influential in establishing a loose consensus among various groups in Switzerland, Scotland
, Hungary, Germany and elsewhere.
The Reformation foundations engaged with Augustinianism
. Both Luther and Calvin thought along lines linked with the theological teachings of Augustine of Hippo
. The Augustinianism of the Reformers struggled against Pelagianism
, a heresy that they perceived in the Catholic Church of their day. In the course of this religious upheaval, the German Peasants' War
of 1524–1525 swept through the Bavaria
n, Thuringia
n and Swabia
n principalities, leaving scores of Catholics slaughtered at the hands of Protestant bands, including the Black Company
of Florian Geier,a knight from Giebelstadt
who joined the peasants in the general outrage against the Catholic hierarchy.
Even though Luther and Calvin had very similar theological teachings, the relationship between their followers turned quickly to conflict. Frenchman Michel de Montaigne
told a story of a Lutheran pastor who once claimed that he would rather celebrate the mass of Rome than participate in a Calvinist service.
The political separation of the Church of England
from Rome under Henry VIII
, beginning in 1529 and completed in 1536, brought England alongside this broad Reformed movement. However, religious changes in the English national church proceeded more conservatively than elsewhere in Europe. Reformers in the Church of England alternated, for centuries, between sympathies for Catholic traditions and Protestantism, progressively forging a stable compromise between adherence to ancient tradition and Protestantism, which is now sometimes called the via media.
 Martin Luther, John Calvin, and Ulrich Zwingli are considered Magisterial Reformers because their reform movements were supported by ruling authorities or "magistrates". Frederick the Wise not only supported Luther, who was a professor at the university he founded, but also protected him by hiding Luther in Wartburg Castle in Eisenach. Zwingli and Calvin were supported by the city councils in Zurich
Martin Luther, John Calvin, and Ulrich Zwingli are considered Magisterial Reformers because their reform movements were supported by ruling authorities or "magistrates". Frederick the Wise not only supported Luther, who was a professor at the university he founded, but also protected him by hiding Luther in Wartburg Castle in Eisenach. Zwingli and Calvin were supported by the city councils in Zurich
and Geneva
. Since the term "magister" also means "teacher", the Magisterial Reformation is also characterized by an emphasis on the authority of a teacher. This is made evident in the prominence of Luther, Calvin, and Zwingli as leaders of the reform movements in their respective areas of ministry. Because of their authority, they were often criticized by Radical Reformers
as being too much like the Roman Popes. For example, Radical Reformer Andreas von Bodenstein Karlstadt referred to the Wittenberg theologians as the "new papists".
, contributed to a growing impatience among reformers. Erasmus and later figures like Martin Luther and Zwingli would emerge from this debate and eventually contribute to another major schism of Christendom. The crisis of theology beginning with William of Ockham
in the fourteenth century was occurring in conjunction with the new burgher
discontent. Since the breakdown of the philosophical
foundations of scholasticism
, the new nominalism
did not bode well for an institutional church legitimized as an intermediary between man and God. New thinking favored the notion that no religious doctrine
can be supported by philosophical arguments, eroding the old alliance between reason
and faith
of the medieval period laid out by Thomas Aquinas
.
 The major individualistic reform movements that revolted against medieval scholasticism and the institutions that underpinned it were humanism
The major individualistic reform movements that revolted against medieval scholasticism and the institutions that underpinned it were humanism
, devotionalism, (see for example, the Brothers of the Common Life and Jan Standonck
) and the observantine tradition. In Germany
, "the modern way" or devotionalism caught on in the universities, requiring a redefinition of God, who was no longer a rational governing principle but an arbitrary, unknowable will that cannot be limited. God was now a ruler, and religion would be more fervent and emotional. Thus, the ensuing revival of Augustinian theology, stating that man cannot be saved by his own efforts but only by the grace of God, would erode the legitimacy of the rigid institutions of the church meant to provide a channel for man to do good works and get into heaven
. Humanism, however, was more of an educational reform movement with origins in the Renaissance
's revival of classical learning
and thought. A revolt against Aristotelian
logic, it placed great emphasis on reforming individuals through eloquence as opposed to reason. The European Renaissance laid the foundation for the Northern humanists in its reinforcement of the traditional use of Latin
as the great unifying language of European culture.
The polarization of the scholarly community in Germany over the Reuchlin (1455–1522) affair, attacked by the elite clergy for his study of Hebrew
and Jewish texts, brought Luther fully in line with the humanist educational reforms who favored academic freedom
. At the same time, the impact of the Renaissance would soon backfire against traditional Catholicism, ushering in an age of reform and a repudiation of much of medieval Latin tradition. Led by Erasmus, the humanists condemned various forms of corruption within the Church, forms of corruption that might not have been any more prevalent than during the medieval zenith of the church. Erasmus held that true religion was a matter of inward devotion rather than outward symbols of ceremony and ritual. Going back to ancient texts, scriptures, from this viewpoint the greatest culmination of the ancient tradition, are the guides to life. Favoring moral
reforms and de-emphasizing didactic ritual, Erasmus laid the groundwork for Luther.
Humanism's intellectual anti-clericalism
would profoundly influence Luther. The increasingly well-educated middle
sectors of Northern Germany, namely the educated community and city dwellers would turn to Luther's rethinking of religion to conceptualize their discontent according to the cultural medium of the era. The great rise of the burghers, the desire to run their new businesses free of institutional barriers or outmoded cultural practices, contributed to the appeal of humanist individualism
. To many, papal
institutions were rigid, especially regarding their views on just price and usury
. In the North, burghers and monarchs were united in their frustration for not paying any tax
es to the nation, but collecting taxes from subjects
and sending the revenues disproportionately to the Pope in Italy
.
These trends heightened demands for significant reform and revitalization along with anticlericalism. New thinkers began noticing the divide between the priests and the flock. The clergy, for instance, were not always well-educated. Parish priests often did not know Latin
and rural parishes often did not have great opportunities for theological education for many at the time. Due to its large landholdings and institutional rigidity, a rigidity to which the excessively large ranks of the clergy contributed, many bishop
s studied law
, not theology, being relegated to the role of property managers trained in administration. While priests emphasized works of religiosity, the respectability of the church began diminishing, especially among well educated urbanites, and especially considering the recent strings of political humiliation, such as the apprehension of Pope Boniface VIII
by Philip IV of France
, the "Babylonian Captivity", the Great Schism, and the failure of Conciliar reformism. In a sense, the campaign by Pope Leo X
to raise funds to rebuild St. Peter's Basilica was too much of an excess by the secular Renaissance
church, prompting high-pressure indulgences that rendered the clergy establishments even more disliked in the cities.
Luther borrowed from the humanists the sense of individualism, that each man can be his own priest (an attitude likely to find popular support considering the rapid rise of an educated urban middle class in the North), and that the only true authority is the Bible
, echoing the reformist zeal of the Conciliar movement and opening up the debate once again on limiting the authority of the Pope. While his ideas called for the sharp redefinition of the dividing lines between the laity
and the clergy, his ideas were still, by this point, reformist in nature. Luther's contention that the human will was incapable of following good, however, resulted in his rift with Erasmus finally distinguishing Lutheran reformism from humanism
.
called Real Presence
, a doctrine of the presence of Christ in the Eucharist which affirms the real presence yet upholding that the bread and wine are not "changed" into the body and blood; rather the divine elements adhere "in, with, and under" the earthly elements. He took this understanding of Christ's presence in the Eucharist to be more harmonious with the Church's teaching on the Incarnation. Just as Christ is the union of the fully human and the fully divine (cf. Council of Chalcedon) so to the Eucharist is a union of Bread and Body, Wine and Blood. According to the doctrine of real presence, the substances of the body and the blood of Christ and of the bread and the wine were held to coexist together in the consecrated Host during the communion service. While Luther seemed to maintain the perpetual consecration of the elements, other Lutherans argued that any consecrated bread or wine left over would revert to its former state the moment the service ended. Most Lutherans accept the latter.
 A Lutheran understanding of the Eucharist is distinct from the Reformed doctrine of the Eucharist in that Lutherans affirm a real, physical presence of Christ in the Eucharist (as opposed to either a "spiritual presence" or a "memorial") and Lutherans affirm that the presence of Christ does not depend on the faith of the recipient; the repentant receive Christ in the Eucharist worthily, the unrepentant who receive the Eucharist risk the wrath of Christ.
A Lutheran understanding of the Eucharist is distinct from the Reformed doctrine of the Eucharist in that Lutherans affirm a real, physical presence of Christ in the Eucharist (as opposed to either a "spiritual presence" or a "memorial") and Lutherans affirm that the presence of Christ does not depend on the faith of the recipient; the repentant receive Christ in the Eucharist worthily, the unrepentant who receive the Eucharist risk the wrath of Christ.
Luther, along with his colleague Philipp Melanchthon
, emphasized this point in his plea for the Reformation at the Reichstag
in 1529 amid charges of heresy
. But the changes he proposed were of such a fundamental nature that by their own logic they would automatically overthrow the old order; neither the Emperor nor the Church could possibly accept them, as Luther well knew. As was only to be expected, the edict by the Diet of Worms
(1521) prohibited all innovations. Meanwhile, in these efforts to retain the guise of a Catholic reformer as opposed to a heretical revolutionary, and to appeal to German princes with his religious condemnation of the peasant revolts backed up by the Doctrine of the Two Kingdoms
, Luther's growing conservatism would provoke more radical reformers.
At a religious conference with the Zwinglians in 1529, Melanchthon joined with Luther in opposing a union with Zwingli. There would finally be a schism in the reform movement due to Luther's belief in real presence
—the real (as opposed to symbolic) presence of Christ at the Eucharist. His original intention was not schism, but with the Reichstag of Augsburg (1530) and its rejection of the Lutheran "Augsburg Confession", a separate Lutheran church finally emerged. In a sense, Luther would take theology further in its deviation from established Catholic dogma, forcing a rift between the humanist Erasmus and Luther. Similarly, Zwingli would further repudiate ritualism, and break with the increasingly conservative Luther.
 Aside from the enclosing of the lower classes, the middle sectors of northern Germany, namely the educated community and city dwellers, would turn to religion to conceptualize their discontent according to the cultural medium of the era. The great rise of the burghers, the desire to run their new businesses free of institutional barriers or outmoded cultural practices contributed to the appeal of individualism. To many, papal institutions were rigid, especially regarding their views on just price and usury
Aside from the enclosing of the lower classes, the middle sectors of northern Germany, namely the educated community and city dwellers, would turn to religion to conceptualize their discontent according to the cultural medium of the era. The great rise of the burghers, the desire to run their new businesses free of institutional barriers or outmoded cultural practices contributed to the appeal of individualism. To many, papal institutions were rigid, especially regarding their views on just price and usury
. In the North, burghers and monarchs were united in their frustration for not paying any taxes to the nation, but collecting taxes from subjects and sending the revenues disproportionately to Italy. In northern Europe, Luther appealed to the growing national consciousness of the German states because he denounced the Pope for involvement in politics as well as religion. Moreover, he backed the nobility, which was now justified to crush the Great Peasant Revolt of 1525 and to confiscate church property by Luther's Doctrine of the Two Kingdoms
. This explains the attraction of some territorial princes to Lutheranism, especially its Doctrine of the Two Kingdoms. However, the Elector of Brandenburg, Joachim I, blamed Lutheranism for the revolt and so did others. In Brandenburg, it was only under his successor Joachim II that Lutheranism was established, and the old religion was not formally extinct in Brandenburg until the death of the last Catholic bishop there, Georg von Blumenthal, who was Bishop of Lebus and sovereign Prince-Bishop of Ratzeburg.
With the church subordinate to and the agent of civil authority and peasant rebellions condemned on strict religious terms, Lutheranism and German nationalist sentiment were ideally suited to coincide.
Though Charles V
fought the Reformation, it is no coincidence either that the reign of his nationalistic predecessor Maximilian I
saw the beginning of the movement. While the centralized states of western Europe had reached accords with the Vatican permitting them to draw on the rich property of the church for government expenditures, enabling them to form state churches that were greatly autonomous of Rome, similar moves on behalf of the Reich were unsuccessful so long as princes and prince bishops fought reforms to drop the pretension of the secular universal empire.
to the traditional teaching on the church's doctrinal authority and to many of its practices as well. The seeming inability of Pope Leo X
(1513–1521) and those popes who succeeded him to comprehend the significance of the threat that Luther posed - or, indeed, the alienation of many Christians by the corruption that had spread throughout the church - was a major factor in the rapid growth of the Protestant Reformation. By the time the need for a vigorous, reforming papal leadership was recognized, much of northern Europe had already converted to Protestantism.
 Martin Luther (10 November 148318 February 1546) was a German
Martin Luther (10 November 148318 February 1546) was a German
monk
, theologian
, university professor, priest, father of Protestantism
, and church reformer
whose ideas started the Protestant Reformation
.
Luther taught that salvation is a free gift of God and received only through true faith
in Jesus
as redeemer from sin. His theology
challenged the authority
of the papacy
by adducing the Bible
as the only infallible source of Christian
doctrine
and countering "sacerdotalism
" in the doctrine that all baptized
Christians are a universal priesthood
.
Luther's refusal to retract his writings in confrontation with the Holy Roman Emperor Charles V
at the Diet of Worms
in 1521 resulted in his excommunication
by Pope Leo X
and declaration as an outlaw
. His translation of the Bible
into the language of the people made the Scriptures more accessible, causing a tremendous impact on the church and on German culture. It fostered the development of a standard version of the German language
, added several principles to the art of translation, and influenced the translation of the King James Bible. His hymn
s inspired the development of congregational singing within Christianity. His marriage to Katharina von Bora
set a model for the practice of clerical marriage
within Protestantism.

 In 1516-17, Johann Tetzel
In 1516-17, Johann Tetzel
, a Dominican friar and papal commissioner for indulgences, was sent to Germany by the Roman Catholic Church to sell indulgences to raise money to rebuild St Peter's Basilica in Rome. Roman Catholic theology stated that faith alone, whether fiduciary or dogmatic, cannot justify man; and that only such faith as is active in charity and good works (fides caritate formata) can justify man. These good works could be obtained by donating money to the church.
On 31 October 1517, Luther wrote to Albrecht, Archbishop of Mainz and Magdeburg, protesting the sale of indulgences. He enclosed in his letter a copy of his "Disputation of Martin Luther on the Power and Efficacy of Indulgences," which came to be known as The 95 Theses.
Luther objected to a saying attributed to Johann Tetzel that "As soon as the coin in the coffer rings, the soul from purgatory springs," insisting that, since forgiveness was God's alone to grant, those who claimed that indulgences absolved buyers from all punishments and granted them salvation were in error. Christians, he said, must not slacken in following Christ on account of such false assurances.
 According to Walter Krämer, Götz Trenkler, Gerhard Ritter and Gerhard Prause, the story of the posting on the door has settled as one of the pillars of history, but its foundations in truth are minimal. In the preface of the second pressing of Luther’s compiled work, released after his death, humanist and reformist Philipp Melanchthon
According to Walter Krämer, Götz Trenkler, Gerhard Ritter and Gerhard Prause, the story of the posting on the door has settled as one of the pillars of history, but its foundations in truth are minimal. In the preface of the second pressing of Luther’s compiled work, released after his death, humanist and reformist Philipp Melanchthon
writes ‘reportedly, Luther, burning with passion and just devoutness, posted the Ninety-Five Theses at the Castle Church in Wittenberg
, Germany at All Saints Eve, October 31 (Old calendar)”. At the time of the writing of the preface Melanchton lived in Tübingen
, far from Wittenberg. In the preface, Melanchton presents more facts that are not true: He writes that indulgence sales man Johann Tetzel
publicly burned Luther’s Ninety-Five Theses, that Luther held colleges on nature and physics, and that Luther had visited Rome in 1511.For a professor of the Wittenberg University to post thesis on doors is unparalleled in history. Even further, Luther is known as strongly law abiding, and to publish his thoughts and direction in such a way would be strongly against his character. Luther has never mentioned anything in this direction in his writings, and the only contemporary account of the publishing of the thesis is the account of Luther’s servant Agricola
, written in Latin. In this account, Agricola states that Luther presents ‘certain thesis in the year of 1517 according to the customs of University of Wittenberg as part of a scientific discussion. The presentation of the thesis was done in a modest and respectful way, preventing to mock or insult anybody”. There is no mention of nailing the thesis to a door, nor does any other source report this. In reality, Luther presented a hand-written copy, accompanied with honourable comments to the archbishop Albrecht of Mainz
and Magdenburg, responsible for the practice of the indulgence sales, and to the bishop of Brandenburg
, the superior of Luther.
It wasn’t until January 1518 that friends of Luther translated the 95 Theses from Latin into German, printed, and widely copied, making the controversy one of the first in history to be aided by the printing press
. Within two weeks, copies of the theses had spread throughout Germany; within two months throughout Europe. In contrast to the speed with which the theses were distributed, the response of the papacy was painstakingly slow. After three years of debate and negotiations involving Luther, government, and church officials, on 15 June 1520, the Pope warned Luther with the papal bull
(edict) Exsurge Domine
that he risked excommunication
unless he recanted 41 sentences drawn from his writings, including the 95 Theses
, within 60 days.
That autumn, Johann Eck
proclaimed the bull in Meissen and other towns. Karl von Miltitz
, a papal nuncio
, attempted to broker a solution, but Luther, who had sent the Pope a copy of his concilatory On the Freedom of a Christian (which the Pope refused to read) in October, publicly set fire to the bull and decretal
s at Wittenberg on 10 December 1520, an act he defended in Why the Pope and his Recent Book are Burned and Assertions Concerning All Articles.
As a consequence, Luther was excommunicated by Leo X
on 3 January 1521, in the bull Decet Romanum Pontificem
.
(died 1531). These two movements quickly agreed on most issues, as the recently introduced printing press
spread ideas rapidly from place to place, but some unresolved differences kept them separate. Some followers of Zwingli believed that the Reformation was too conservative, and moved independently toward more radical positions, some of which survive among modern day Anabaptist
s. Other Protestant movements grew up along lines of mysticism or humanism (cf.
Erasmus), sometimes breaking from Rome or from the Protestants, or forming outside of the churches.

 Following the excommunication
Following the excommunication
of Luther and condemnation of the Reformation by the Pope, the work and writings of John Calvin
were influential in establishing a loose consensus among various groups in Switzerland, Scotland
, Hungary, Germany and elsewhere.
Geneva became the unofficial capital of the Protestant movement, led by the Frenchman, Jean Calvin, until his death in 1564 (when Calvin's ally, William Farel
, assumed the spiritual leadership of the group).
The Reformation foundations engaged with Augustinianism. Both Luther and Calvin thought along lines linked with the theological teachings of Augustine of Hippo. The Augustinianism of the Reformers struggled against Pelagianism
, a heresy that they perceived in the Catholic Church of their day. Ironically, even though both Luther and Calvin both had very similar theological teachings, the relationship between Lutherans and Calvinists evolved into one of conflict.
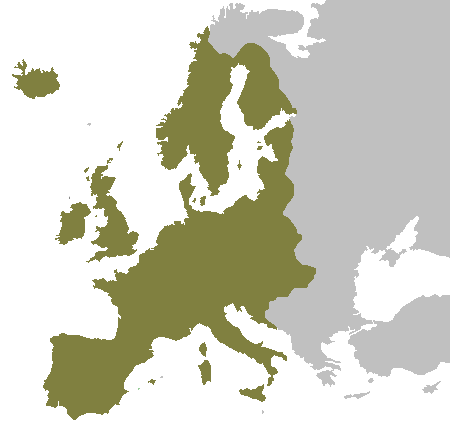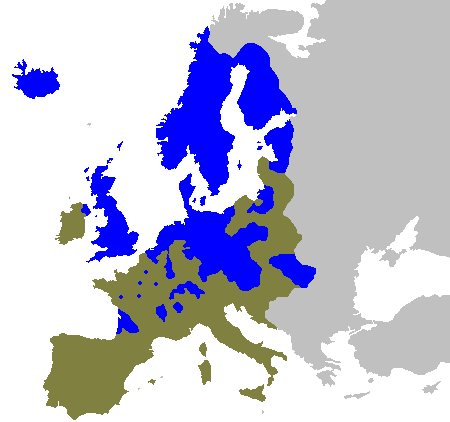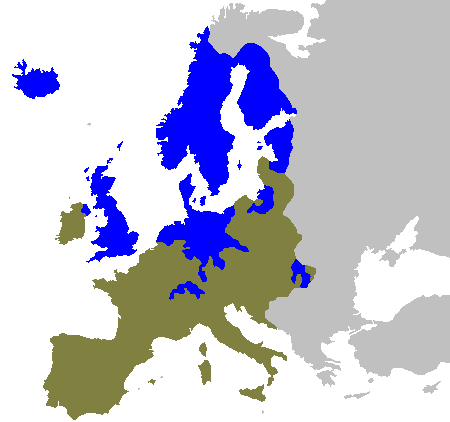
ultimately adopted Lutheranism over the course of the sixteenth century, as the monarchs of Denmark
(who also ruled Norway
and Iceland
) and Sweden
(who also ruled Finland
) converted to that faith.
In Sweden the Reformation was spearheaded by Gustav Vasa, elected king in 1523. Friction with the pope over the latter's interference in Swedish ecclesiastical affairs led to the discontinuance of any official connection between Sweden and the papacy from 1523. Four years later, at the Diet of Västerås, the king succeeded in forcing the diet to accept his dominion over the national church. The king was given possession of all church property, church appointments required royal approval, the clergy were subject to the civil law, and the "pure Word of God" was to be preached in the churches and taught in the schools—effectively granting official sanction to Lutheran ideas.
Under the reign of Frederick I
(1523–33), Denmark remained officially Catholic. But though Frederick initially pledged to persecute Lutherans, he soon adopted a policy of protecting Lutheran preachers and reformers, of whom the most famous was Hans Tausen
. During his reign, Lutheranism made significant inroads among the Danish population. Frederick's son, Christian, was openly Lutheran, which prevented his election to the throne upon his father's death. However, following his victory in the civil war that followed, in 1537 he became Christian III
and began a reformation of the official state church.

or Anglican Church from Rome under Henry VIII
, beginning in 1529 and completed in 1536, brought England alongside this broad Reformed movement. However, religious changes in the English national church proceeded more conservatively than elsewhere in Europe. Reformers in the Church of England alternated, for centuries, between sympathies for Catholic traditions and Protestantism, progressively forging a stable compromise between adherence to ancient tradition and Protestantism, which is now sometimes called the via media (middle way).
In England, the Reformation followed a different course than elsewhere in Europe. There had long been a strong strain of anti-clericalism, and England had already given rise to the Lollard movement of John Wycliffe
, which played an important part in inspiring the Hussite
s in Bohemia
. Lollardy was suppressed and became an underground movement so the extent of its influence in the 1520s is difficult to assess. The different character of the English Reformation came rather from the fact that it was driven initially by the political necessities of Henry VIII
. Henry had once been a sincere Catholic and had even authored a book strongly criticizing Luther, but he later found it expedient and profitable to break with the Papacy. His wife, Catherine of Aragon
, bore him only a single child, Mary
. As England had recently gone through a lengthy dynastic conflict (see Wars of the Roses
), Henry feared that his lack of a male heir might jeopardize his descendants' claim to the throne. However, Pope Clement VII, concentrating more on Charles V's "sack of Rome", denied his request for an annulment. Had Clement granted the annulment and therefore admitted that his predecessor, Julius II, had erred, Clement would have given support to the Lutheran assertion that Popes replaced their own judgement for the will of God. King Henry decided to remove the Church of England
from the authority of Rome. In 1534, the Act of Supremacy made Henry the Supreme Head
of the Church of England. Between 1535 and 1540, under Thomas Cromwell
, the policy known as the Dissolution of the Monasteries
was put into effect. The veneration of some saint
s, certain pilgrimages and some pilgrim shrines were also attacked. Huge amounts of church land and property passed into the hands of the crown and ultimately into those of the nobility and gentry. The vested interest thus created made for a powerful force in support of the dissolutions.
There were some notable opponents to the Henrician Reformation, such as Thomas More
and Bishop John Fisher
, who were executed for their opposition. There was also a growing party of reformers who were imbued with the Zwinglian and Calvinistic doctrines now current on the Continent. When Henry died he was succeeded by his Protestant son Edward VI, who, through his empowered councillors (with the King being only nine years old at his succession and not yet sixteen at his death) the Duke of Somerset and the Duke of Northumberland, ordered the destruction of images in churches, and the closing of the chantries
. Under Edward VI the reform of the Church of England
was established unequivocally in doctrinal terms. Yet, at a popular level, religion in England was still in a state of flux. Following a brief Roman Catholic restoration during the reign of Mary
1553–1558, a loose consensus developed during the reign of Elizabeth I
, though this point is one of considerable debate among historians. Yet it is the so-called "Elizabethan Religious Settlement
" to which the origins of Anglicanism
are traditionally ascribed. The compromise was uneasy and was capable of veering between extreme Calvinism
on the one hand and Catholicism on the other, but compared to the bloody and chaotic state of affairs in contemporary France, it was relatively successful until the Puritan Revolution or English Civil War
in the seventeenth century.
on the Continent and the growth of a Puritan
party dedicated to further Protestant reform polarized the Elizabethan Age, although it was not until the 1640s that England underwent religious strife comparable to that which its neighbours had suffered some generations before.
The early Puritan movement (late 16th century-17th century) was Reformed or Calvinist
and was a movement for reform in the Church of England
. Its origins lay in the discontent with the Elizabethan Religious Settlement
. The desire was for the Church of England to resemble more closely the Protestant churches of Europe, especially Geneva
. The Puritans objected to ornaments and ritual in the churches as idolatrous
(vestments, surplices, organs, genuflection), which they castigated as "popish pomp and rags". (See Vestments controversy
.) They also objected to ecclesiastical courts. They refused to endorse completely all of the ritual directions and formulas of the Book of Common Prayer
; the imposition of its liturgical order by legal force and inspection sharpened Puritanism into a definite opposition movement.
The later Puritan movement were often referred to as Dissenters and Nonconformists and eventually led to the formation of various Reformed denominations
.
The most famous and well-known emigration to America
was the migration of the Puritan separatists from the Anglican Church of England, who fled first to Holland, and then later to America, to establish the English colonies of New England
, which later became the United States
.
These Puritan separatists were also known as "the pilgrims". After establishing a colony at Plymouth (in what would become later Massachusetts) in 1620, the Puritan pilgrims received a charter from the King of England which legitimized their colony, allowing them to do trade and commerce with merchants in England, in accordance with the principles of mercantilism
. This successful, though initially quite difficult, colony marked the beginning of the Protestant presence in America (the earlier French, Spanish and Portuguese settlements had been Catholic), and became a kind of oasis of spiritual and economic freedom
, to which persecuted Protestants and other minorities from the British Isles and Europe (and later, from all over the world) fled to for peace, freedom and opportunity.
The original intent of the colonists was to establish spiritual Puritanism, which had been denied to them in England and the rest of Europe to engage in peaceful commerce with England and the native American Indians and to Christianize the peoples of the Americas.
influence over that of France
. John Knox
is regarded as the leader of the Scottish Reformation
The Reformation Parliament
of 1560, which repudiated the pope's authority, forbade the celebration of the mass
and approved a Protestant Confession of Faith
, was made possible by a revolution against French
hegemony under the regime of the regent
Mary of Guise
, who had governed Scotland in the name of her absent daughter Mary, Queen of Scots, (then also Queen
of France).
The Scottish Reformation decisively shaped the Church of Scotland
and, through it, all other Presbyterian churches worldwide.
A spiritual revival also broke out among Catholics soon after Martin Luther's actions, and led to the Scottish Covenanters' movement
, the precursor to Scottish
Presbyterianism
. This movement spread, and greatly influenced the formation of Puritan
ism among the Anglican Church in England
. The Scottish Covenanters were persecuted by the Roman Catholic Church. This persecution by the Catholics drove some of the Protestant Covenanter leadership out of Scotland, and into France
and later, Switzerland
.
d "Huguenots", and this touched off decades of warfare in France, after initial support by Henry of Navarre was lost due to the "Night of the Placards
" affair. Many French Huguenots however, still contributed to the Protestant movement, including many who emigrated to the English colonies.
 Though he was not personally interested in religious reform, Francis I
Though he was not personally interested in religious reform, Francis I
(1515–47) initially maintained an attitude of tolerance, arising from his interest in the humanist
movement. This changed in 1534 with the Affair of the Placards
. In this act, Protestants denounced the mass in placards that appeared across France, even reaching the royal apartments. The issue of religious faith having been thrown into the arena of politics, Francis was prompted to view the movement as a threat to the kingdom's stability. This led to the first major phase of anti-Protestant persecution in France, in which the Chambre Ardente
("Burning Chamber") was established within the Parlement of Paris to handle with the rise in prosecutions for heresy. Several thousand French Protestants fled the country during this time, most notably John Calvin
, who settled in Geneva
.
Calvin continued to take an interest in the religious affairs of his native land and, from his base in Geneva, beyond the reach of the French king, regularly trained pastors to lead congregations in France. Despite heavy persecution by Henry II
, the Reformed Church of France
, largely Calvinist in direction, made steady progress across large sections of the nation, in the urban bourgeoisie
and parts of the aristocracy
, appealing to people alienated by the obduracy and the complacency of the Catholic establishment.
French Protestantism, though its appeal increased under persecution, came to acquire a distinctly political character, made all the more obvious by the noble conversions of the 1550s. This had the effect of creating the preconditions for a series of destructive and intermittent conflicts, known as the Wars of Religion
. The civil wars were helped along by the sudden death of Henry II
in 1559, which saw the beginning of a prolonged period of weakness for the French crown. Atrocity and outrage became the defining characteristic of the time, illustrated at its most intense in the St. Bartholomew's Day massacre
of August 1572, when the Catholic Church annihilated between 30,000 and 100,000 Huguenots across France. The wars only concluded when Henry IV
, himself a former Huguenot, issued the Edict of Nantes
, promising official toleration of the Protestant minority, but under highly restricted conditions. Catholicism remained the official state religion, and the fortunes of French Protestants gradually declined over the next century, culminating in Louis XIV's Edict of Fontainebleau
—which revoked the Edict of Nantes and made Catholicism the sole legal religion of France. In response to the Edict of Fontainebleau, Frederick William
of Brandenburg
declared the Edict of Potsdam
, giving free passage to French Huguenot refugees, and tax-free status to them for 10 years.
 The Reformation in the Netherlands, unlike in many other countries, was not initiated by the rulers of the Seventeen Provinces
The Reformation in the Netherlands, unlike in many other countries, was not initiated by the rulers of the Seventeen Provinces
, but instead by multiple popular movements, which in turn were bolstered by the arrival of Protestant refugees from other parts of the continent. While the Anabaptist
movement enjoyed popularity in the region in the early decades of the Reformation, Calvinism, in the form of the Dutch Reformed Church
, became the dominant Protestant faith in the country from the 1560s onward.
Harsh persecution of Protestants by the Spanish government of Philip II
contributed to a desire for independence in the provinces, which led to the Eighty Years' War and eventually, the separation of the largely Protestant Dutch Republic
from the Catholic-dominated Southern Netherlands
, the present-day Belgium
.
adopted Protestantism during the sixteenth century. After the 1526 Battle of Mohács
the Hungarian people were disillusioned by the ability of the government to protect them and turned to the faith which would infuse them with the strength necessary to resist the Turkish invaders. They found this in the teaching of the Protestant Reformers such as Martin Luther
. The spread of Protestantism in the country was aided by its large ethnic German minority, which could understand and translate the writings of Martin Luther
. While Lutheranism gained a foothold among the German-speaking population, Calvinism
became widely accepted among ethnic Hungarians.
In the more independent northwest the rulers and priests, protected now by the Habsburg Monarchy
which had taken the field to fight the Turks, defended the old Catholic faith. They dragged the Protestants to prison and the stake wherever they could. Such strong measures only fanned the flames of protest, however. Leaders of the Protestants included Matthias Biro Devai, Michael Sztarai, and Stephen Kis Szegedi.
Protestants likely formed a majority of Hungary's population at the close of the sixteenth century, but Counter-Reformation
efforts in the seventeenth century reconverted a majority of the kingdom to Catholicism. A significant Protestant minority remained, most of it adhering to the Calvinist faith.
In 1558 the Transylvania
n Diet
of Turda
declared free practice of both the Catholic
and Lutheran
religions, but prohibited Calvinism
. Ten years later, in 1568, the Diet extended this freedom, declaring that "It is not allowed to anybody to intimidate anybody with captivity or expelling for his religion". Four religions were declared as accepted (recepta) religions, while Orthodox Christianity
was "tolerated" (though the building of stone Orthodox churches was forbidden).
Hungary entered the Thirty Years' War
, Royal (Habsburg) Hungary joined the catholic side, until Transylvania joined the Protestant side.
There were a series of other successful and unsuccessful anti-Habsburg /i.e. anti-Austrian/ (requiring equal rights and freedom for all Christian religions) uprisings between 1604 and 1711, the uprisings were usually organized from Transylvania. The constrained Habsburg Counter-Reformation efforts in the seventeenth century reconverted the majority of the kingdom to Catholicism.
in Anglo-American religious history, generally recognized as beginning in the 1730s. They have also been described as periodic revolutions in colonial religious thought
.
in Germany
, the Evangelical Revival
, and Methodism
in England
. It had a major impact in reshaping the Congregational
, Presbyterian
, Dutch Reformed
, and German Reformed denominations, and strengthened the small Baptist
and Methodist
denominations. It brought Christianity to the slaves and was an apocalyptic event in New England
that challenged established authority. It incited rancor and division between the old traditionalists who insisted on ritual and doctrine and the new revivalists. It had little impact on Anglicans
and Quakers
.
Unlike the Second Great Awakening
that began about 1800 and which reached out to the unchurched, the First Great Awakening focused on people who were already church members. It changed their rituals, their piety, and their self awareness. The new style of sermons and the way people practiced their faith breathed new life into religion in America
. People became passionately and emotionally involved in their religion, rather than passively listening to intellectual discourse in a detached manner. Ministers who used this new style of preaching were generally called "new lights", while the preachers of old were called "old lights". People began to study the Bible at home, which effectively decentralized the means of informing the public on religious manners and was akin to the individualistic trends present in Europe during the Protestant Reformation
.
history and, unlike the First Great Awakening
of the 18th century
, focused on the unchurched and sought to instil in them a deep sense of personal salvation as experienced in revival meeting
s. It also sparked the beginnings of groups such as the Mormons
and the Holiness movement
. Leaders included Charles Grandison Finney
, Lyman Beecher
, Barton W. Stone
, Peter Cartwright
and James Finley
.
In New England
, the renewed interest in religion inspired a wave of social activism. In western New York
, the spirit of revival encouraged the emergence of the Restoration Movement
, the Latter Day Saint movement
, Adventism and the Holiness movement
. In the west especially—at Cane Ridge, Kentucky
and in Tennessee
—the revival strengthened the Methodists
and the Baptists and introduced into America a new form of religious expression—the Scottish camp meeting
.
The Second Great Awakening made its way across the frontier territories, fed by intense longing for a prominent place for God in the life of the new nation, a new liberal attitude toward fresh interpretations of the Bible, and a contagious experience of zeal for authentic spirituality. As these revivals spread, they gathered converts to Protestant sects of the time. However, the revivals eventually moved freely across denominational lines, with practically identical results, and went farther than ever toward breaking down the allegiances which kept adherents to these denominations loyal to their own. Consequently, the revivals were accompanied by a growing dissatisfaction with Evangelical churches and especially with the doctrine of Calvinism
, which was nominally accepted or at least tolerated in most Evangelical churches at the time. Various unaffiliated movements arose that were often restorationist in outlook, considering contemporary Christianity of the time to be a deviation from the true, original Christianity. These groups attempted to transcend Protestant denominationalism and orthodox Christian
creeds to restore Christianity to its original form.
of Christ would come after mankind had reformed the entire earth. The Social Gospel
Movement gained its force from the Awakening, as did the worldwide missionary movement. New groupings emerged, such as the Holiness movement
and Nazarene
movements, and Christian Science
. Significant names include Dwight L. Moody
, Ira D. Sankey
, William Booth
and Catherine Booth (founders of the Salvation Army
), Charles Spurgeon
and James Caughey. Hudson Taylor
began the China Inland Mission
and Thomas John Barnardo
founded his famous orphanages. The Keswick Convention
movement began out of the British Holiness movement
, encouraging a lifestyle of holiness
, unity and prayer.
Mary Baker Eddy
introduced Christian Science
, which gained a national following. In 1880, the Salvation Army
denomination arrived in America. Although its theology was based on ideals expressed during the Second Great Awakening
, its focus on poverty was of the Third. The Society for Ethical Culture was established in New York
in 1876 by Felix Adler attracted a Reform Jewish clientele. Charles Taze Russell
Founded a Bible Student Institute now known as The Jehovah's Witnesses
With Jane Addams
's Hull House
in Chicago as its center, the settlement house movement and the vocation of social work were deeply influenced by the Tolstoy
an reworking of Christian idealism. The final group to emerge from this awakening in North America was Pentecostalism
, which had its roots in the Methodist, Wesleyan, and Holiness movement
s, and began in 1906 on Azusa Street
, in Los Angeles
. Pentecostalism would later lead to the Charismatic movement
.
and the Mexican Revolution
there was a distinct anti-clerical
tone in those countries that exists to this day. In some cases, opposition to the clergy turned into opposition to religion itself; thus, for example, Karl Marx
condemned religion as the "opium of the people
" http://www.baylor.edu/~Scott_Moore/texts/Marx_Opium.html as he considered it a false sense of hope in an afterlife withholding the people from facing their worldly situation. Based on a similar quote ("opium for the people"), Lenin believed religion was being used by ruling classes as tool of suppression of the people. The Marxist-Leninist
governments of the twentieth century were generally atheistic. All of them restricted the exercise of religion to a greater or lesser degree, but only Albania
actually banned religion and officially declared itself to be an atheistic state.
, establishing further followings in China
, Taiwan
, and Japan
. At the same time, state-promoted atheism in Communist Eastern Europe and the Soviet Union brought many Eastern Orthodox Christians to Western Europe and the United States, leading to greatly increased contact between Western and Eastern Christianity. Nevertheless, church attendance declined more in Western Europe than it did in the East. Christian ecumenism grew in importance, beginning at the Edinburgh Missionary Conference
in 1910, and accelerated after the Second Vatican Council
(1962–1965) of the Catholic Church, The Liturgical Movement
became significant in both Catholic and Protestant Christianity, especially in Anglicanism
.
Another movement which has grown up over the 20th century has been Christian anarchism
which rejects the church, state or any power other than God. They usually also believe in absolute nonviolence
. Leo Tolstoy
's book The Kingdom of God is Within You
published in 1894, is believed to be the catalyst for this movement. Because of its extremist political views, however, its appeal has been largely limited to the highly educated, especially those with erstwhile humanist
sentiments; the thoroughgoing aversion to institutionalism on Christian anarchists' part has also hindered acceptance of this philosophy on a large scale.
The 1950s saw a boom in the Evangelical church in America. The post–World War II prosperity experienced in the U.S. also had its effects on the church. Although simplistically referred to as "morphological fundamentalism", the phrase nonetheless does accurately describe the physical developments experienced. Church buildings were erected in large numbers, and the Evangelical church's activities grew along with this expansive physical growth.
within already established denominations, continues to be an important force in western Christianity.
began to be felt in the Protestant churches, especially in the 19th century, Liberal Christianity
, exemplified especially by numerous theologians in Germany
in the 19th century, sought to bring the churches alongside of the broad revolution that Modernism represented. In doing so, new critical approaches to the Bible were developed, new attitudes became evident about the role of religion in society, and a new openness to questioning the nearly universally accepted definitions of Christian orthodoxy began to become obvious.
In reaction to these developments, Christian fundamentalism was a movement to reject the radical influences of philosophical humanism, as this was affecting the Christian religion. Especially targeting critical approaches to the interpretation of the Bible, and trying to blockade the inroads made into their churches by atheistic scientific assumptions, the fundamentalists began to appear in various denominations as numerous independent movements of resistance to the drift away from historic Christianity. Over time, the Fundamentalist Evangelical movement has divided into two main wings, with the label Fundamentalist following one branch, while Evangelical has become the preferred banner of the more moderate movement. Although both movements primarily originated in the English speaking world, the majority of Evangelicals now live elsewhere in the world.
A third, but less popular, option than either liberalism or fundamentalism was the neo-orthodox movement, which generally affirmed a higher view of Scripture than liberalism but did not tie the main doctrines of the Christian faith to precise theories of Biblical inspiration. If anything, thinkers in this camp denounced such quibbling between liberals and conservatives as a dangerous distraction from the duties of Christian discipleship. This branch of thought arose in the early 20th century in the context of the rise of the Third Reich in Germany and the accompanying political and ecclesiastical destabilization of Europe in the years before and during World War II
. Neo-orthodoxy's highly contextual, dialectical modes of argument and reasoning often rendered its main premises incomprehensible to American thinkers and clergy, and it was frequently either dismissed out of hand as unrealistic or cast into the reigning left- or right-wing molds of theologizing. Karl Barth
, a Swiss
Reformed pastor and professor, brought this movement into being by drawing upon earlier criticisms of established (largely modernist) Protestant thought made by the likes of Søren Kierkegaard
and Franz Overbeck
; Dietrich Bonhoeffer
, murdered by the Nazis for allegedly taking part in an attempt to overthrow the Hitler
regime, adhered to this school of thought; his classic The Cost of Discipleship
is likely the best-known and accessible statement of the neo-orthodox position.
wing of Protestant denominations, especially those that are more exclusively evangelical, and a corresponding decline in the mainstream liberal churches. In the post–World War I era, Liberalism
was the faster growing sector of the American church. Liberal wings of denominations were on the rise, and a considerable number of seminaries held and taught from a liberal perspective as well. In the post–World war II era, the trend began to swing back towards the conservative camp in America's seminaries and church structures. Those entering seminaries and other postgraduate theologically related programs have shown more conservative leanings than their average predecessors.
The neo-Evangelical push of the 1940s and 1950s produced a movement that continues to have wide influence. In the southern U.S., the more moderate neo-Evangelicals, represented by leaders such as Billy Graham
, have experienced a notable surge displacing the caricature of the pulpit pounding country preachers of fundamentalism. The stereotypes have gradually shifted. Some, such as Jerry Falwell
, have managed to maintain credibility in the eyes of many fundamentalists, as well as to gain stature as a more moderate Evangelical.
Evangelicalism is not a single, monolithic entity. The Evangelical churches and their adherents cannot be easily stereotyped. Most are not fundamentalist, in the narrow sense that this term has come to represent; though many still refer to themselves as such. There have always been diverse views on issues, such as openness to cooperation with non-Evangelicals, the applicability of the Bible to political choices and social or scientific issues, and even the limited inerrancy of the Bible.
However, the movement has managed in an informal way, to reserve the name Evangelical for those who adhere to an historic Christian faith, a paleo-orthodoxy, as some have put it. Those who call themselves "moderate evangelicals"(although considered conservative in relation to society as a whole) still hold fast to the fundamentals of the historic Christian faith. Even "Liberal" Evangelicals label themselves as such not so much in terms of their theology, but rather to advertise that they are progressive in their civic, social, or scientific perspective.
There is some debate as to whether Pentecostals are considered to be Evangelical. Their roots in Pietism
and the Holiness movement
are undisputedly Evangelical, but their doctrinal distinctives differ from the more traditional Evangelicals, who are less likely to have an expectation of private revelations from God, and differ from the Pentecostal perspective on miracle
s, angels, and demons. Typically, those who include the Pentecostals in the Evangelical camp are labeled neo-evangelical by those who do not. The National Association of Evangelicals
and the Evangelical Alliance
have numerous Trinitarian Pentecostal denominations among their membership. Another relatively late entrant to wide acceptance within the Evangelical fold is the Seventh-day Adventist Church
.
Evangelicals are as diverse as the names that appear—Billy Graham, Chuck Colson, J. Vernon McGee, Benny Hinn
, J.I. Packer, John R.W. Stott
, Pat Robertson
, Jimmy Carter
, etc.—or even Evangelical institutions such as Dallas Theological Seminary (dispensationalist), Gordon-Conwell Theological Seminary (Boston), Trinity Evangelical Divinity School
(Chicago), Wheaton College (Illinois), the Christian Coalition, The Christian Embassy (Jerusalem), etc. Although there exists a diversity in the Evangelical community worldwide, the ties that bind all Evangelicals are still apparent. These include but are not limited to a high view of Scripture, belief in the Deity of Christ, the Trinity, salvation by grace alone through faith alone, and the bodily resurrection of Christ.
and 40 degrees North
of the equator and stretching from North Africa across to China. This area is mostly dominated by Muslim nations, many who do not allow missionaries of other religions to enter their countries.
In Europe
there has been a general move away from religious observance and belief in Christian teachings and a move towards secularism
. The "secularization of society", attributed to the time of the Enlightenment
and its following years, is largely responsible for the spread of secularism. For example the Gallup International Millennium Survey http://www.gallup-international.com/survey15.htm showed that only about one sixth of Europeans attend regular religious services, less than half gave God "high importance", and only about 40% believe in a "personal God". Nevertheless the large majority considered that they "belong" to a religious denomination
.
The Americas and Australia
In North America
, South America
and Australia
, the other three continents where Christianity is the dominant professed religion, religious observance is much higher than in Europe. At the same time, these regions are often seen by other nations as being uptight and "Victorian", in their social mores. In general, the United States leans toward the conservative in comparison to other western nations in its general culture, in part due to the Christian element found primarily in its Midwestern and southern states.
South America, historically Catholic, has experienced a large Evangelical and Pentecostal infusion in the 20th century due to the influx of Christian missionaries from abroad. For example: Brazil
, South America's largest country, is the largest Catholic country in the world, and at the same time is the largest Evangelical country in the world (based on population). Some of the largest Christian congregations in the world are found in Brazil.
The following link provides quantitative data related to Christianity and other major religions, including rates of adherence at different points in time:
Protestant Reformation
The Protestant Reformation was a 16th-century split within Western Christianity initiated by Martin Luther, John Calvin and other early Protestants. The efforts of the self-described "reformers", who objected to the doctrines, rituals and ecclesiastical structure of the Roman Catholic Church, led...
of the early 16th century was an attempt to reform the Catholic Church.
German theologian Martin Luther
Martin Luther
Martin Luther was a German priest, professor of theology and iconic figure of the Protestant Reformation. He strongly disputed the claim that freedom from God's punishment for sin could be purchased with money. He confronted indulgence salesman Johann Tetzel with his Ninety-Five Theses in 1517...
wrote his Ninety-Five Theses on the sale of indulgences in 1517. Parallel to events in Germany, a movement began in Switzerland under the leadership of Ulrich Zwingli. The political separation of the Church of England
Church of England
The Church of England is the officially established Christian church in England and the Mother Church of the worldwide Anglican Communion. The church considers itself within the tradition of Western Christianity and dates its formal establishment principally to the mission to England by St...
from Rome under Henry VIII
Henry VIII of England
Henry VIII was King of England from 21 April 1509 until his death. He was Lord, and later King, of Ireland, as well as continuing the nominal claim by the English monarchs to the Kingdom of France...
, beginning in 1529 and completed in 1536, brought England alongside this broad Reformed movement.
The Scottish Reformation
Scottish Reformation
The Scottish Reformation was Scotland's formal break with the Papacy in 1560, and the events surrounding this. It was part of the wider European Protestant Reformation; and in Scotland's case culminated ecclesiastically in the re-establishment of the church along Reformed lines, and politically in...
of 1560 decisively shaped the Church of Scotland
Church of Scotland
The Church of Scotland, known informally by its Scots language name, the Kirk, is a Presbyterian church, decisively shaped by the Scottish Reformation....
and, through it, all other Presbyterian churches worldwide.
Following the excommunication
Excommunication
Excommunication is a religious censure used to deprive, suspend or limit membership in a religious community. The word means putting [someone] out of communion. In some religions, excommunication includes spiritual condemnation of the member or group...
of Luther and condemnation of the Reformation by the Pope, the work and writings of John Calvin
John Calvin
John Calvin was an influential French theologian and pastor during the Protestant Reformation. He was a principal figure in the development of the system of Christian theology later called Calvinism. Originally trained as a humanist lawyer, he broke from the Roman Catholic Church around 1530...
were influential in establishing a loose consensus among various groups in Switzerland, Scotland
Scotland
Scotland is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Occupying the northern third of the island of Great Britain, it shares a border with England to the south and is bounded by the North Sea to the east, the Atlantic Ocean to the north and west, and the North Channel and Irish Sea to the...
, Hungary, Germany and elsewhere.
In the course of this religious upheaval, the German Peasants' War
German Peasants' War
The German Peasants' War or Great Peasants' Revolt was a widespread popular revolt in the German-speaking areas of Central Europe, 1524–1526. At its height in the spring and summer of 1525, the conflict involved an estimated 300,000 peasants: contemporary estimates put the dead at 100,000...
of 1524–1525 swept through the Bavaria
Bavaria
Bavaria, formally the Free State of Bavaria is a state of Germany, located in the southeast of Germany. With an area of , it is the largest state by area, forming almost 20% of the total land area of Germany...
n, Thuringia
Thuringia
The Free State of Thuringia is a state of Germany, located in the central part of the country.It has an area of and 2.29 million inhabitants, making it the sixth smallest by area and the fifth smallest by population of Germany's sixteen states....
n and Swabia
Swabia
Swabia is a cultural, historic and linguistic region in southwestern Germany.-Geography:Like many cultural regions of Europe, Swabia's borders are not clearly defined...
n principalities. The confessional division of the states of the Holy Roman Empire eventually erupted in the Thirty Years' War
Thirty Years' War
The Thirty Years' War was fought primarily in what is now Germany, and at various points involved most countries in Europe. It was one of the most destructive conflicts in European history....
of 1618–1648. This left Germany weakened and fragmented
Kleinstaaterei
is a German word, mainly used for the political situation in Germany and neighbouring regions during the Holy Roman Empire and during the German Confederation...
for more than two centuries, until the unification of Germany under the German Empire
German Empire
The German Empire refers to Germany during the "Second Reich" period from the unification of Germany and proclamation of Wilhelm I as German Emperor on 18 January 1871, to 1918, when it became a federal republic after defeat in World War I and the abdication of the Emperor, Wilhelm II.The German...
of 1871.
The success of the Counter-Reformation
Counter-Reformation
The Counter-Reformation was the period of Catholic revival beginning with the Council of Trent and ending at the close of the Thirty Years' War, 1648 as a response to the Protestant Reformation.The Counter-Reformation was a comprehensive effort, composed of four major elements:#Ecclesiastical or...
on the Continent and the growth of a Puritan
Puritan
The Puritans were a significant grouping of English Protestants in the 16th and 17th centuries. Puritanism in this sense was founded by some Marian exiles from the clergy shortly after the accession of Elizabeth I of England in 1558, as an activist movement within the Church of England...
party dedicated to further Protestant reform polarized the Elizabethan Age, although it was not until the Civil War
English Civil War
The English Civil War was a series of armed conflicts and political machinations between Parliamentarians and Royalists...
of the 1640s that England underwent religious strife comparable to that which its neighbours had suffered some generations before.
The "Great Awakenings" were periods of rapid and dramatic religious revival
Religious revival
Religious revival may refer to:* Christian Revivalism* Revival meeting* Islamic revival...
in Anglo-American religious history, generally recognized as beginning in the 1730s. They have also been described as periodic revolutions in colonial religious thought
Christianity in the United States
Christianity is the largest and most popular religion in the United States, with around 77% of those polled identifying themselves as Christian, as of 2009. This is down from 86% in 1990, and slightly lower than 78.6% in 2001. About 62% of those polled claim to be members of a church congregation...
.
In the 20th century, Protestantism, especially in the United States
Protestantism in the United States
-Mainline vs. Evangelical:In typical usage, the term mainline is contrasted with evangelical. Theologically conservative critics accuse the mainline churches of "the substitution of leftist social action for Christian evangelizing, and the disappearance of biblical theology," and maintain that "All...
, was characterized by accelerating fragmentation. The century saw the rise of both liberal and conservative splinter groups, as well as a general secularization of Western society.
Notable developments in the 20th century of US Protestantism was the rise of Pentecostalism
Pentecostalism
Pentecostalism is a diverse and complex movement within Christianity that places special emphasis on a direct personal experience of God through the baptism in the Holy Spirit, has an eschatological focus, and is an experiential religion. The term Pentecostal is derived from Pentecost, the Greek...
, Christian fundamentalism and Evangelicalism
Evangelicalism
Evangelicalism is a Protestant Christian movement which began in Great Britain in the 1730s and gained popularity in the United States during the series of Great Awakenings of the 18th and 19th century.Its key commitments are:...
.
While these movements have spilled over to Europe to a limited degree, the development of Protestantism in Europe was more dominated by secularization, leading to an increasingly "post-Christian Europe".
History and origins
Protestants generally trace to the 16th century their separation from the Catholic Church. Mainstream Protestantism began with the Magisterial ReformationMagisterial Reformation
The Magisterial Reformation is a phrase that "draws attention to the manner in which the Lutheran and Calvinist reformers related to secular authorities, such as princes, magistrates, or city councils", i.e. "the magistracy"...
, so called because the movement received support from the magistrates (that is, the civil authorities) as opposed to the Radical Reformation
Radical Reformation
The Radical Reformation was a 16th century response to what was believed to be both the corruption in the Roman Catholic Church and the expanding Magisterial Protestant movement led by Martin Luther and many others. Beginning in Germany and Switzerland, the Radical Reformation birthed many radical...
, which had no state sponsorship. Older Protestant churches, such as the Unitas Fratrum
Unitas Fratrum
This article is about the coordinating body of the Moravian Church worldwide. For the Christian denomination based in Texas see Unity of the Brethren....
(Unity of the Brethren
Unity of the Brethren
The Unity of the Brethren is a Christian denomination whose roots are in the pre-reformation work of priest and philosopher Jan Hus, who was martyred in 1415.-History in Bohemia:...
), Moravian Brethren or the Bohemian Brethren trace their origin to the time of Jan Hus
Jan Hus
Jan Hus , often referred to in English as John Hus or John Huss, was a Czech priest, philosopher, reformer, and master at Charles University in Prague...
in the early 15th century. As the Hussite
Hussite
The Hussites were a Christian movement following the teachings of Czech reformer Jan Hus , who became one of the forerunners of the Protestant Reformation...
movement was led by a majority of Bohemian nobles and recognized for a time by the Basel Compacts, this is considered by some to be the first Magisterial Reformation in Europe. In Germany, a hundred years later, protests against the Roman Catholic authorities erupted in many places at once, during a time of threatened Islamic Ottoman
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman EmpireIt was usually referred to as the "Ottoman Empire", the "Turkish Empire", the "Ottoman Caliphate" or more commonly "Turkey" by its contemporaries...
invasion
Ottoman wars in Europe
The wars of the Ottoman Empire in Europe are also sometimes referred to as the Ottoman Wars or as Turkish Wars, particularly in older, European texts.- Rise :...
¹ which distracted German princes in particular. To some degree, the protest can be explained by the events of the previous two centuries in Europe and particularly in Bohemia. Earlier in the south of France, where the old influence of the Cathars led to the growing protests against the pope and his authorities, Guillaume Farel (b. 1489) preached reformation as early as 1522 in Dauphiné
Dauphiné
The Dauphiné or Dauphiné Viennois is a former province in southeastern France, whose area roughly corresponded to that of the present departments of :Isère, :Drôme, and :Hautes-Alpes....
, where the French Wars of Religion
French Wars of Religion
The French Wars of Religion is the name given to a period of civil infighting and military operations, primarily fought between French Catholics and Protestants . The conflict involved the factional disputes between the aristocratic houses of France, such as the House of Bourbon and House of Guise...
later originated in 1562, also known as Huguenot
Huguenot
The Huguenots were members of the Protestant Reformed Church of France during the 16th and 17th centuries. Since the 17th century, people who formerly would have been called Huguenots have instead simply been called French Protestants, a title suggested by their German co-religionists, the...
wars. These also spread later to other parts of Europe.
Roots and precursors: 14th century and 15th century
Unrest due to the Avignon PapacyAvignon Papacy
The Avignon Papacy was the period from 1309 to 1376 during which seven Popes resided in Avignon, in modern-day France. This arose from the conflict between the Papacy and the French crown....
and the Papal Schism
Western Schism
The Western Schism or Papal Schism was a split within the Catholic Church from 1378 to 1417. Two men simultaneously claimed to be the true pope. Driven by politics rather than any theological disagreement, the schism was ended by the Council of Constance . The simultaneous claims to the papal chair...
in the Roman Catholic Church (1378–1416) had excited wars between princes, uprisings among the peasants, and widespread concern over corruption in the Church. A new nationalism
Nationalism
Nationalism is a political ideology that involves a strong identification of a group of individuals with a political entity defined in national terms, i.e. a nation. In the 'modernist' image of the nation, it is nationalism that creates national identity. There are various definitions for what...
also challenged the relatively internationalist medieval world. The first of a series of disruptive and new perspectives came from John Wycliffe
John Wycliffe
John Wycliffe was an English Scholastic philosopher, theologian, lay preacher, translator, reformer and university teacher who was known as an early dissident in the Roman Catholic Church during the 14th century. His followers were known as Lollards, a somewhat rebellious movement, which preached...
at Oxford University, then from Jan Hus
Jan Hus
Jan Hus , often referred to in English as John Hus or John Huss, was a Czech priest, philosopher, reformer, and master at Charles University in Prague...
at the University of Prague
Charles University in Prague
Charles University in Prague is the oldest and largest university in the Czech Republic. Founded in 1348, it was the first university in Central Europe and is also considered the earliest German university...
(Hus had been previously influenced by Wycliffe during a trip to England) . The Catholic Church officially concluded debate over Hus' teachings at the Council of Constance
Council of Constance
The Council of Constance is the 15th ecumenical council recognized by the Roman Catholic Church, held from 1414 to 1418. The council ended the Three-Popes Controversy, by deposing or accepting the resignation of the remaining Papal claimants and electing Pope Martin V.The Council also condemned and...
(1414–1417). The conclave condemned Jan Hus, who was executed by burning in spite of a promise of safe-conduct. At the command of Pope Martin V
Pope Martin V
Pope Martin V , born Odo Colonna, was Pope from 1417 to 1431. His election effectively ended the Western Schism .-Biography:...
, Wycliffe was posthumously exhumed and burned as a heretic
Heresy
Heresy is a controversial or novel change to a system of beliefs, especially a religion, that conflicts with established dogma. It is distinct from apostasy, which is the formal denunciation of one's religion, principles or cause, and blasphemy, which is irreverence toward religion...
twelve years after his burial.
The Council of Constance confirmed and strengthened the traditional medieval conception of Churches and Empires. It did not address the national tensions, or the theological tensions which had been stirred up during the previous century. The council could not prevents schism
Schism (religion)
A schism , from Greek σχίσμα, skhísma , is a division between people, usually belonging to an organization or movement religious denomination. The word is most frequently applied to a break of communion between two sections of Christianity that were previously a single body, or to a division within...
and the Hussite Wars
Hussite Wars
The Hussite Wars, also called the Bohemian Wars involved the military actions against and amongst the followers of Jan Hus in Bohemia in the period 1419 to circa 1434. The Hussite Wars were notable for the extensive use of early hand-held gunpowder weapons such as hand cannons...
in Bohemia
Bohemia
Bohemia is a historical region in central Europe, occupying the western two-thirds of the traditional Czech Lands. It is located in the contemporary Czech Republic with its capital in Prague...
.
Historical upheaval usually yields much new thinking as to how society should be organized. This was the case leading up to the Protestant Reformation. Following the breakdown of monastic institutions and scholasticism
Scholasticism
Scholasticism is a method of critical thought which dominated teaching by the academics of medieval universities in Europe from about 1100–1500, and a program of employing that method in articulating and defending orthodoxy in an increasingly pluralistic context...
in late medieval Europe, which were accentuated by the "Babylonian Captivity" of the Papacy, the Papal Schism, and the failure of the Conciliar movement, the sixteenth century saw the fomenting of a great cultural debate about religious reforms and later fundamental religious values (See German mysticism
German mysticism
German mysticism, sometimes called Dominican mysticism or Rhineland mysticism, was a late medieval Christian mystical movement, that was especially prominent within the Dominican order and in Germany. Although its origins can be traced back to Hildegard of Bingen, it is mostly represented by...
). Historians would generally assume that the failure to reform (too many vested interests, lack of coordination in the reforming coalition) would eventually lead to a greater upheaval or even revolution, since the system must eventually be adjusted or disintegrate, and the failure of the Conciliar movement helped lead to the Protestant Reformation in Europe. These frustrated reformist movements ranged from nominalism
Nominalism
Nominalism is a metaphysical view in philosophy according to which general or abstract terms and predicates exist, while universals or abstract objects, which are sometimes thought to correspond to these terms, do not exist. Thus, there are at least two main versions of nominalism...
, devotio moderna (modern devotion)
Devotio Moderna
Devotio Moderna, or Modern Devotion, was a 14th century new religious movement, with Gerard Groote as a key founder. Other well known members included Thomas à Kempis who was the likely author of the book The Imitation of Christ which proved to be highly influential for centuries.Groote's initial...
, to humanism
Humanism
Humanism is an approach in study, philosophy, world view or practice that focuses on human values and concerns. In philosophy and social science, humanism is a perspective which affirms some notion of human nature, and is contrasted with anti-humanism....
occurring in conjunction with economic, political and demographic forces that contributed to a growing disaffection with the wealth and power of the elite
Elite
Elite refers to an exceptional or privileged group that wields considerable power within its sphere of influence...
clergy
Clergy
Clergy is the generic term used to describe the formal religious leadership within a given religion. A clergyman, churchman or cleric is a member of the clergy, especially one who is a priest, preacher, pastor, or other religious professional....
, sensitizing the population to the financial and moral corruption of the secular Renaissance
Renaissance
The Renaissance was a cultural movement that spanned roughly the 14th to the 17th century, beginning in Italy in the Late Middle Ages and later spreading to the rest of Europe. The term is also used more loosely to refer to the historical era, but since the changes of the Renaissance were not...
church.
The outcome of the Black Death
Black Death
The Black Death was one of the most devastating pandemics in human history, peaking in Europe between 1348 and 1350. Of several competing theories, the dominant explanation for the Black Death is the plague theory, which attributes the outbreak to the bacterium Yersinia pestis. Thought to have...
encouraged a radical reorganization of the economy, and eventually of European society. In the emerging urban centers, however, the calamities of the fourteenth and early fifteenth century, and the resultant labor shortages, provided a strong impetus for economic diversification and technological innovations. Following the Black Death, the initial loss of life due to famine, plague, and pestilence contributed to an intensification of capital accumulation in the urban areas, and thus a stimulus to trade, industry, and burgeoning urban growth in fields as diverse as banking (the Fugger
Fugger
The Fugger family was a historically prominent group of European bankers, members of the fifteenth and sixteenth-century mercantile patriciate of Augsburg, international mercantile bankers, and venture capitalists like the Welser and the Höchstetter families. This banking family replaced the de'...
banking family in Augsburg
Augsburg
Augsburg is a city in the south-west of Bavaria, Germany. It is a university town and home of the Regierungsbezirk Schwaben and the Bezirk Schwaben. Augsburg is an urban district and home to the institutions of the Landkreis Augsburg. It is, as of 2008, the third-largest city in Bavaria with a...
and the Medici
Medici
The House of Medici or Famiglia de' Medici was a political dynasty, banking family and later royal house that first began to gather prominence under Cosimo de' Medici in the Republic of Florence during the late 14th century. The family originated in the Mugello region of the Tuscan countryside,...
family of Florence
Florence
Florence is the capital city of the Italian region of Tuscany and of the province of Florence. It is the most populous city in Tuscany, with approximately 370,000 inhabitants, expanding to over 1.5 million in the metropolitan area....
being the most prominent); textiles, armaments
Weapon
A weapon, arm, or armament is a tool or instrument used with the aim of causing damage or harm to living beings or artificial structures or systems...
, especially stimulated by the Hundred Years' War
Hundred Years' War
The Hundred Years' War was a series of separate wars waged from 1337 to 1453 by the House of Valois and the House of Plantagenet, also known as the House of Anjou, for the French throne, which had become vacant upon the extinction of the senior Capetian line of French kings...
, and mining of iron ore due, in large part, to the booming armaments industry. Accumulation of surplus, competitive overproduction
Overproduction
In economics, overproduction, oversupply or excess of supply refers to excess of supply over demand of products being offered to the market...
, and heightened competition to maximize economic advantage, contributed to civil war, aggressive militarism
Militarism
Militarism is defined as: the belief or desire of a government or people that a country should maintain a strong military capability and be prepared to use it aggressively to defend or promote national interests....
, and thus to centralization. As a direct result of the move toward centralization, leaders like Louis XI of France
Louis XI of France
Louis XI , called the Prudent , was the King of France from 1461 to 1483. He was the son of Charles VII of France and Mary of Anjou, a member of the House of Valois....
(1461–1483), the "spider king", sought to remove all constitutional restrictions on the exercise of their authority. In England
England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Scotland to the north and Wales to the west; the Irish Sea is to the north west, the Celtic Sea to the south west, with the North Sea to the east and the English Channel to the south separating it from continental...
, France
France
The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
, and Spain
Spain
Spain , officially the Kingdom of Spain languages]] under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, Spain's official name is as follows:;;;;;;), is a country and member state of the European Union located in southwestern Europe on the Iberian Peninsula...
the move toward centralization begun in the thirteenth century was carried to a successful conclusion.
But as recovery and prosperity progressed, enabling the population to reach its former levels in the late 15th and 16th centuries, the combination of both a newly-abundant labor supply as well as improved productivity, were 'mixed blessings' for many segments of Western European society. Despite tradition, landlords started the move to exclude peasant
Peasant
A peasant is an agricultural worker who generally tend to be poor and homeless-Etymology:The word is derived from 15th century French païsant meaning one from the pays, or countryside, ultimately from the Latin pagus, or outlying administrative district.- Position in society :Peasants typically...
s from "common land
Common land
Common land is land owned collectively or by one person, but over which other people have certain traditional rights, such as to allow their livestock to graze upon it, to collect firewood, or to cut turf for fuel...
s". With trade stimulated, landowners increasingly moved away from the manorial
Manorialism
Manorialism, an essential element of feudal society, was the organizing principle of rural economy that originated in the villa system of the Late Roman Empire, was widely practiced in medieval western and parts of central Europe, and was slowly replaced by the advent of a money-based market...
economy. Woollen manufacturing greatly expanded in France
France
The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
, Germany
Germany
Germany , officially the Federal Republic of Germany , is a federal parliamentary republic in Europe. The country consists of 16 states while the capital and largest city is Berlin. Germany covers an area of 357,021 km2 and has a largely temperate seasonal climate...
, and the Netherlands
Netherlands
The Netherlands is a constituent country of the Kingdom of the Netherlands, located mainly in North-West Europe and with several islands in the Caribbean. Mainland Netherlands borders the North Sea to the north and west, Belgium to the south, and Germany to the east, and shares maritime borders...
and new textile industries began to develop.
The invention of movable type
Movable type
Movable type is the system of printing and typography that uses movable components to reproduce the elements of a document ....
would lead to the Protestant zeal for translating the Bible and getting it into the hands of the laity. This would advance the culture of Biblical literacy.
The "humanism" of the Renaissance
Renaissance
The Renaissance was a cultural movement that spanned roughly the 14th to the 17th century, beginning in Italy in the Late Middle Ages and later spreading to the rest of Europe. The term is also used more loosely to refer to the historical era, but since the changes of the Renaissance were not...
period stimulated unprecedented academic ferment, and a concern for academic freedom
Academic freedom
Academic freedom is the belief that the freedom of inquiry by students and faculty members is essential to the mission of the academy, and that scholars should have freedom to teach or communicate ideas or facts without being targeted for repression, job loss, or imprisonment.Academic freedom is a...
. Ongoing, earnest theoretical debates occurred in the universities about the nature of the church, and the source and extent of the authority of the papacy, of councils, and of princes.
16th century

Martin Luther
Martin Luther was a German priest, professor of theology and iconic figure of the Protestant Reformation. He strongly disputed the claim that freedom from God's punishment for sin could be purchased with money. He confronted indulgence salesman Johann Tetzel with his Ninety-Five Theses in 1517...
, an Augustinian monk and professor at the university of Wittenberg
Wittenberg
Wittenberg, officially Lutherstadt Wittenberg, is a city in Germany in the Bundesland Saxony-Anhalt, on the river Elbe. It has a population of about 50,000....
, called in 1517 for a reopening of the debate on the sale of indulgence
Indulgence
In Catholic theology, an indulgence is the full or partial remission of temporal punishment due for sins which have already been forgiven. The indulgence is granted by the Catholic Church after the sinner has confessed and received absolution...
s. Luther's dissent marked a sudden outbreak of a new and irresistible force of discontent which had been pushed underground but not resolved. The quick spread of discontent occurred to a large degree because of the printing press
Printing press
A printing press is a device for applying pressure to an inked surface resting upon a print medium , thereby transferring the ink...
and the resulting swift movement of both ideas and documents, including the 95 Theses
95 Theses
The Ninety-Five Theses on the Power and Efficacy of Indulgences , commonly known as , was written by Martin Luther, 1517 and is widely regarded as the primary catalyst for the Protestant Reformation...
. Information was also widely disseminated in manuscript form, as well as by cheap prints and woodcuts amongst the poorer sections of society.
Parallel to events in Germany, a movement began in Switzerland under the leadership of Ulrich Zwingli. These two movements quickly agreed on most issues, as the recently introduced printing press
Printing press
A printing press is a device for applying pressure to an inked surface resting upon a print medium , thereby transferring the ink...
spread ideas rapidly from place to place, but some unresolved differences kept them separate. Some followers of Zwingli believed that the Reformation was too conservative, and moved independently toward more radical positions, some of which survive among modern day Anabaptist
Anabaptist
Anabaptists are Protestant Christians of the Radical Reformation of 16th-century Europe, and their direct descendants, particularly the Amish, Brethren, Hutterites, and Mennonites....
s. Other Protestant movements grew up along lines of mysticism or humanism (cf.
Cf.
cf., an abbreviation for the Latin word confer , literally meaning "bring together", is used to refer to other material or ideas which may provide similar or different information or arguments. It is mainly used in scholarly contexts, such as in academic or legal texts...
Erasmus), sometimes breaking from Rome or from the Protestants, or forming outside of the churches.

Excommunication
Excommunication is a religious censure used to deprive, suspend or limit membership in a religious community. The word means putting [someone] out of communion. In some religions, excommunication includes spiritual condemnation of the member or group...
of Luther and condemnation of the Reformation by the Pope, the work and writings of John Calvin
John Calvin
John Calvin was an influential French theologian and pastor during the Protestant Reformation. He was a principal figure in the development of the system of Christian theology later called Calvinism. Originally trained as a humanist lawyer, he broke from the Roman Catholic Church around 1530...
were influential in establishing a loose consensus among various groups in Switzerland, Scotland
Scotland
Scotland is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Occupying the northern third of the island of Great Britain, it shares a border with England to the south and is bounded by the North Sea to the east, the Atlantic Ocean to the north and west, and the North Channel and Irish Sea to the...
, Hungary, Germany and elsewhere.
The Reformation foundations engaged with Augustinianism
Augustinians
The term Augustinians, named after Saint Augustine of Hippo , applies to two separate and unrelated types of Catholic religious orders:...
. Both Luther and Calvin thought along lines linked with the theological teachings of Augustine of Hippo
Augustine of Hippo
Augustine of Hippo , also known as Augustine, St. Augustine, St. Austin, St. Augoustinos, Blessed Augustine, or St. Augustine the Blessed, was Bishop of Hippo Regius . He was a Latin-speaking philosopher and theologian who lived in the Roman Africa Province...
. The Augustinianism of the Reformers struggled against Pelagianism
Pelagianism
Pelagianism is a theological theory named after Pelagius , although he denied, at least at some point in his life, many of the doctrines associated with his name. It is the belief that original sin did not taint human nature and that mortal will is still capable of choosing good or evil without...
, a heresy that they perceived in the Catholic Church of their day. In the course of this religious upheaval, the German Peasants' War
German Peasants' War
The German Peasants' War or Great Peasants' Revolt was a widespread popular revolt in the German-speaking areas of Central Europe, 1524–1526. At its height in the spring and summer of 1525, the conflict involved an estimated 300,000 peasants: contemporary estimates put the dead at 100,000...
of 1524–1525 swept through the Bavaria
Bavaria
Bavaria, formally the Free State of Bavaria is a state of Germany, located in the southeast of Germany. With an area of , it is the largest state by area, forming almost 20% of the total land area of Germany...
n, Thuringia
Thuringia
The Free State of Thuringia is a state of Germany, located in the central part of the country.It has an area of and 2.29 million inhabitants, making it the sixth smallest by area and the fifth smallest by population of Germany's sixteen states....
n and Swabia
Swabia
Swabia is a cultural, historic and linguistic region in southwestern Germany.-Geography:Like many cultural regions of Europe, Swabia's borders are not clearly defined...
n principalities, leaving scores of Catholics slaughtered at the hands of Protestant bands, including the Black Company
Black Company
The Black Company or the Black Troops was a unit of Franconian mercenaries during the Peasant's Revolt in the 1520s during the Protestant Reformation in Germany.The original German name of the Black Company was "Schwarzer Haufen"...
of Florian Geier,a knight from Giebelstadt
Giebelstadt
Giebelstadt is a municipality in the district of Würzburg in Bavaria in Germany.History of GiebelstadtThe town is the birthplace of Florian Geyer , also known as "Florian Geier from Giebelstadt", a Franconian nobleman who led the Black Company during the Peasants War resulting from the Protestant...
who joined the peasants in the general outrage against the Catholic hierarchy.
Even though Luther and Calvin had very similar theological teachings, the relationship between their followers turned quickly to conflict. Frenchman Michel de Montaigne
Michel de Montaigne
Lord Michel Eyquem de Montaigne , February 28, 1533 – September 13, 1592, was one of the most influential writers of the French Renaissance, known for popularising the essay as a literary genre and is popularly thought of as the father of Modern Skepticism...
told a story of a Lutheran pastor who once claimed that he would rather celebrate the mass of Rome than participate in a Calvinist service.
The political separation of the Church of England
Church of England
The Church of England is the officially established Christian church in England and the Mother Church of the worldwide Anglican Communion. The church considers itself within the tradition of Western Christianity and dates its formal establishment principally to the mission to England by St...
from Rome under Henry VIII
Henry VIII of England
Henry VIII was King of England from 21 April 1509 until his death. He was Lord, and later King, of Ireland, as well as continuing the nominal claim by the English monarchs to the Kingdom of France...
, beginning in 1529 and completed in 1536, brought England alongside this broad Reformed movement. However, religious changes in the English national church proceeded more conservatively than elsewhere in Europe. Reformers in the Church of England alternated, for centuries, between sympathies for Catholic traditions and Protestantism, progressively forging a stable compromise between adherence to ancient tradition and Protestantism, which is now sometimes called the via media.

Zürich
Zurich is the largest city in Switzerland and the capital of the canton of Zurich. It is located in central Switzerland at the northwestern tip of Lake Zurich...
and Geneva
Geneva
Geneva In the national languages of Switzerland the city is known as Genf , Ginevra and Genevra is the second-most-populous city in Switzerland and is the most populous city of Romandie, the French-speaking part of Switzerland...
. Since the term "magister" also means "teacher", the Magisterial Reformation is also characterized by an emphasis on the authority of a teacher. This is made evident in the prominence of Luther, Calvin, and Zwingli as leaders of the reform movements in their respective areas of ministry. Because of their authority, they were often criticized by Radical Reformers
Radical Reformation
The Radical Reformation was a 16th century response to what was believed to be both the corruption in the Roman Catholic Church and the expanding Magisterial Protestant movement led by Martin Luther and many others. Beginning in Germany and Switzerland, the Radical Reformation birthed many radical...
as being too much like the Roman Popes. For example, Radical Reformer Andreas von Bodenstein Karlstadt referred to the Wittenberg theologians as the "new papists".
Humanism to Protestantism
The frustrated reformism of the humanists, ushered in by the RenaissanceRenaissance
The Renaissance was a cultural movement that spanned roughly the 14th to the 17th century, beginning in Italy in the Late Middle Ages and later spreading to the rest of Europe. The term is also used more loosely to refer to the historical era, but since the changes of the Renaissance were not...
, contributed to a growing impatience among reformers. Erasmus and later figures like Martin Luther and Zwingli would emerge from this debate and eventually contribute to another major schism of Christendom. The crisis of theology beginning with William of Ockham
William of Ockham
William of Ockham was an English Franciscan friar and scholastic philosopher, who is believed to have been born in Ockham, a small village in Surrey. He is considered to be one of the major figures of medieval thought and was at the centre of the major intellectual and political controversies of...
in the fourteenth century was occurring in conjunction with the new burgher
Bourgeoisie
In sociology and political science, bourgeoisie describes a range of groups across history. In the Western world, between the late 18th century and the present day, the bourgeoisie is a social class "characterized by their ownership of capital and their related culture." A member of the...
discontent. Since the breakdown of the philosophical
Philosophy
Philosophy is the study of general and fundamental problems, such as those connected with existence, knowledge, values, reason, mind, and language. Philosophy is distinguished from other ways of addressing such problems by its critical, generally systematic approach and its reliance on rational...
foundations of scholasticism
Scholasticism
Scholasticism is a method of critical thought which dominated teaching by the academics of medieval universities in Europe from about 1100–1500, and a program of employing that method in articulating and defending orthodoxy in an increasingly pluralistic context...
, the new nominalism
Nominalism
Nominalism is a metaphysical view in philosophy according to which general or abstract terms and predicates exist, while universals or abstract objects, which are sometimes thought to correspond to these terms, do not exist. Thus, there are at least two main versions of nominalism...
did not bode well for an institutional church legitimized as an intermediary between man and God. New thinking favored the notion that no religious doctrine
Doctrine
Doctrine is a codification of beliefs or a body of teachings or instructions, taught principles or positions, as the body of teachings in a branch of knowledge or belief system...
can be supported by philosophical arguments, eroding the old alliance between reason
Reason
Reason is a term that refers to the capacity human beings have to make sense of things, to establish and verify facts, and to change or justify practices, institutions, and beliefs. It is closely associated with such characteristically human activities as philosophy, science, language, ...
and faith
Faith
Faith is confidence or trust in a person or thing, or a belief that is not based on proof. In religion, faith is a belief in a transcendent reality, a religious teacher, a set of teachings or a Supreme Being. Generally speaking, it is offered as a means by which the truth of the proposition,...
of the medieval period laid out by Thomas Aquinas
Thomas Aquinas
Thomas Aquinas, O.P. , also Thomas of Aquin or Aquino, was an Italian Dominican priest of the Catholic Church, and an immensely influential philosopher and theologian in the tradition of scholasticism, known as Doctor Angelicus, Doctor Communis, or Doctor Universalis...
.

Humanism
Humanism is an approach in study, philosophy, world view or practice that focuses on human values and concerns. In philosophy and social science, humanism is a perspective which affirms some notion of human nature, and is contrasted with anti-humanism....
, devotionalism, (see for example, the Brothers of the Common Life and Jan Standonck
Jan Standonck
Jan Standonck was a Dutch priest, Scholastic, and reformer.He was part of the great movement for reform in the 15th century French church. His approach was to reform the recruitment and education of the clergy, along very ascetic lines, heavily influenced by the hermit saint Francis of Paola...
) and the observantine tradition. In Germany
Germany
Germany , officially the Federal Republic of Germany , is a federal parliamentary republic in Europe. The country consists of 16 states while the capital and largest city is Berlin. Germany covers an area of 357,021 km2 and has a largely temperate seasonal climate...
, "the modern way" or devotionalism caught on in the universities, requiring a redefinition of God, who was no longer a rational governing principle but an arbitrary, unknowable will that cannot be limited. God was now a ruler, and religion would be more fervent and emotional. Thus, the ensuing revival of Augustinian theology, stating that man cannot be saved by his own efforts but only by the grace of God, would erode the legitimacy of the rigid institutions of the church meant to provide a channel for man to do good works and get into heaven
Heaven
Heaven, the Heavens or Seven Heavens, is a common religious cosmological or metaphysical term for the physical or transcendent place from which heavenly beings originate, are enthroned or inhabit...
. Humanism, however, was more of an educational reform movement with origins in the Renaissance
Renaissance
The Renaissance was a cultural movement that spanned roughly the 14th to the 17th century, beginning in Italy in the Late Middle Ages and later spreading to the rest of Europe. The term is also used more loosely to refer to the historical era, but since the changes of the Renaissance were not...
's revival of classical learning
Classical education movement
The Classical education movement advocates a form of education based in the traditions of Western culture, with a particular focus on education as understood and taught in the Middle Ages. The curricula and pedagogy of classical education was first developed during the Middle Ages by Martianus...
and thought. A revolt against Aristotelian
Aristotle
Aristotle was a Greek philosopher and polymath, a student of Plato and teacher of Alexander the Great. His writings cover many subjects, including physics, metaphysics, poetry, theater, music, logic, rhetoric, linguistics, politics, government, ethics, biology, and zoology...
logic, it placed great emphasis on reforming individuals through eloquence as opposed to reason. The European Renaissance laid the foundation for the Northern humanists in its reinforcement of the traditional use of Latin
Latin
Latin is an Italic language originally spoken in Latium and Ancient Rome. It, along with most European languages, is a descendant of the ancient Proto-Indo-European language. Although it is considered a dead language, a number of scholars and members of the Christian clergy speak it fluently, and...
as the great unifying language of European culture.
The polarization of the scholarly community in Germany over the Reuchlin (1455–1522) affair, attacked by the elite clergy for his study of Hebrew
Biblical Hebrew language
Biblical Hebrew , also called Classical Hebrew , is the archaic form of the Hebrew language, a Canaanite Semitic language spoken in the area known as Canaan between the Jordan River and the Mediterranean Sea. Biblical Hebrew is attested from about the 10th century BCE, and persisted through...
and Jewish texts, brought Luther fully in line with the humanist educational reforms who favored academic freedom
Academic freedom
Academic freedom is the belief that the freedom of inquiry by students and faculty members is essential to the mission of the academy, and that scholars should have freedom to teach or communicate ideas or facts without being targeted for repression, job loss, or imprisonment.Academic freedom is a...
. At the same time, the impact of the Renaissance would soon backfire against traditional Catholicism, ushering in an age of reform and a repudiation of much of medieval Latin tradition. Led by Erasmus, the humanists condemned various forms of corruption within the Church, forms of corruption that might not have been any more prevalent than during the medieval zenith of the church. Erasmus held that true religion was a matter of inward devotion rather than outward symbols of ceremony and ritual. Going back to ancient texts, scriptures, from this viewpoint the greatest culmination of the ancient tradition, are the guides to life. Favoring moral
Morality
Morality is the differentiation among intentions, decisions, and actions between those that are good and bad . A moral code is a system of morality and a moral is any one practice or teaching within a moral code...
reforms and de-emphasizing didactic ritual, Erasmus laid the groundwork for Luther.
Humanism's intellectual anti-clericalism
Anti-clericalism
Anti-clericalism is a historical movement that opposes religious institutional power and influence, real or alleged, in all aspects of public and political life, and the involvement of religion in the everyday life of the citizen...
would profoundly influence Luther. The increasingly well-educated middle
Middle class
The middle class is any class of people in the middle of a societal hierarchy. In Weberian socio-economic terms, the middle class is the broad group of people in contemporary society who fall socio-economically between the working class and upper class....
sectors of Northern Germany, namely the educated community and city dwellers would turn to Luther's rethinking of religion to conceptualize their discontent according to the cultural medium of the era. The great rise of the burghers, the desire to run their new businesses free of institutional barriers or outmoded cultural practices, contributed to the appeal of humanist individualism
Individualism
Individualism is the moral stance, political philosophy, ideology, or social outlook that stresses "the moral worth of the individual". Individualists promote the exercise of one's goals and desires and so value independence and self-reliance while opposing most external interference upon one's own...
. To many, papal
Pope
The Pope is the Bishop of Rome, a position that makes him the leader of the worldwide Catholic Church . In the Catholic Church, the Pope is regarded as the successor of Saint Peter, the Apostle...
institutions were rigid, especially regarding their views on just price and usury
Usury
Usury Originally, when the charging of interest was still banned by Christian churches, usury simply meant the charging of interest at any rate . In countries where the charging of interest became acceptable, the term came to be used for interest above the rate allowed by law...
. In the North, burghers and monarchs were united in their frustration for not paying any tax
Tax
To tax is to impose a financial charge or other levy upon a taxpayer by a state or the functional equivalent of a state such that failure to pay is punishable by law. Taxes are also imposed by many subnational entities...
es to the nation, but collecting taxes from subjects
Citizenship
Citizenship is the state of being a citizen of a particular social, political, national, or human resource community. Citizenship status, under social contract theory, carries with it both rights and responsibilities...
and sending the revenues disproportionately to the Pope in Italy
Italy
Italy , officially the Italian Republic languages]] under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, Italy's official name is as follows:;;;;;;;;), is a unitary parliamentary republic in South-Central Europe. To the north it borders France, Switzerland, Austria and...
.
These trends heightened demands for significant reform and revitalization along with anticlericalism. New thinkers began noticing the divide between the priests and the flock. The clergy, for instance, were not always well-educated. Parish priests often did not know Latin
Latin
Latin is an Italic language originally spoken in Latium and Ancient Rome. It, along with most European languages, is a descendant of the ancient Proto-Indo-European language. Although it is considered a dead language, a number of scholars and members of the Christian clergy speak it fluently, and...
and rural parishes often did not have great opportunities for theological education for many at the time. Due to its large landholdings and institutional rigidity, a rigidity to which the excessively large ranks of the clergy contributed, many bishop
Bishop
A bishop is an ordained or consecrated member of the Christian clergy who is generally entrusted with a position of authority and oversight. Within the Catholic Church, Eastern Orthodox, Oriental Orthodox Churches, in the Assyrian Church of the East, in the Independent Catholic Churches, and in the...
s studied law
Law
Law is a system of rules and guidelines which are enforced through social institutions to govern behavior, wherever possible. It shapes politics, economics and society in numerous ways and serves as a social mediator of relations between people. Contract law regulates everything from buying a bus...
, not theology, being relegated to the role of property managers trained in administration. While priests emphasized works of religiosity, the respectability of the church began diminishing, especially among well educated urbanites, and especially considering the recent strings of political humiliation, such as the apprehension of Pope Boniface VIII
Pope Boniface VIII
Pope Boniface VIII , born Benedetto Gaetani, was Pope of the Catholic Church from 1294 to 1303. Today, Boniface VIII is probably best remembered for his feuds with Dante, who placed him in the Eighth circle of Hell in his Divina Commedia, among the Simonists.- Biography :Gaetani was born in 1235 in...
by Philip IV of France
Philip IV of France
Philip the Fair was, as Philip IV, King of France from 1285 until his death. He was the husband of Joan I of Navarre, by virtue of which he was, as Philip I, King of Navarre and Count of Champagne from 1284 to 1305.-Youth:A member of the House of Capet, Philip was born at the Palace of...
, the "Babylonian Captivity", the Great Schism, and the failure of Conciliar reformism. In a sense, the campaign by Pope Leo X
Pope Leo X
Pope Leo X , born Giovanni di Lorenzo de' Medici, was the Pope from 1513 to his death in 1521. He was the last non-priest to be elected Pope. He is known for granting indulgences for those who donated to reconstruct St. Peter's Basilica and his challenging of Martin Luther's 95 Theses...
to raise funds to rebuild St. Peter's Basilica was too much of an excess by the secular Renaissance
Renaissance
The Renaissance was a cultural movement that spanned roughly the 14th to the 17th century, beginning in Italy in the Late Middle Ages and later spreading to the rest of Europe. The term is also used more loosely to refer to the historical era, but since the changes of the Renaissance were not...
church, prompting high-pressure indulgences that rendered the clergy establishments even more disliked in the cities.
Luther borrowed from the humanists the sense of individualism, that each man can be his own priest (an attitude likely to find popular support considering the rapid rise of an educated urban middle class in the North), and that the only true authority is the Bible
Bible
The Bible refers to any one of the collections of the primary religious texts of Judaism and Christianity. There is no common version of the Bible, as the individual books , their contents and their order vary among denominations...
, echoing the reformist zeal of the Conciliar movement and opening up the debate once again on limiting the authority of the Pope. While his ideas called for the sharp redefinition of the dividing lines between the laity
Laity
In religious organizations, the laity comprises all people who are not in the clergy. A person who is a member of a religious order who is not ordained legitimate clergy is considered as a member of the laity, even though they are members of a religious order .In the past in Christian cultures, the...
and the clergy, his ideas were still, by this point, reformist in nature. Luther's contention that the human will was incapable of following good, however, resulted in his rift with Erasmus finally distinguishing Lutheran reformism from humanism
Humanism
Humanism is an approach in study, philosophy, world view or practice that focuses on human values and concerns. In philosophy and social science, humanism is a perspective which affirms some notion of human nature, and is contrasted with anti-humanism....
.
Lutheranism adopted by the German princes
Luther affirmed a theology of the EucharistEucharist
The Eucharist , also called Holy Communion, the Sacrament of the Altar, the Blessed Sacrament, the Lord's Supper, and other names, is a Christian sacrament or ordinance...
called Real Presence
Real Presence
Real Presence is a term used in various Christian traditions to express belief that in the Eucharist, Jesus Christ is really present in what was previously just bread and wine, and not merely present in symbol, a figure of speech , or by his power .Not all Christian traditions accept this dogma...
, a doctrine of the presence of Christ in the Eucharist which affirms the real presence yet upholding that the bread and wine are not "changed" into the body and blood; rather the divine elements adhere "in, with, and under" the earthly elements. He took this understanding of Christ's presence in the Eucharist to be more harmonious with the Church's teaching on the Incarnation. Just as Christ is the union of the fully human and the fully divine (cf. Council of Chalcedon) so to the Eucharist is a union of Bread and Body, Wine and Blood. According to the doctrine of real presence, the substances of the body and the blood of Christ and of the bread and the wine were held to coexist together in the consecrated Host during the communion service. While Luther seemed to maintain the perpetual consecration of the elements, other Lutherans argued that any consecrated bread or wine left over would revert to its former state the moment the service ended. Most Lutherans accept the latter.

Luther, along with his colleague Philipp Melanchthon
Philipp Melanchthon
Philipp Melanchthon , born Philipp Schwartzerdt, was a German reformer, collaborator with Martin Luther, the first systematic theologian of the Protestant Reformation, intellectual leader of the Lutheran Reformation, and an influential designer of educational systems...
, emphasized this point in his plea for the Reformation at the Reichstag
Reichstag (Holy Roman Empire)
The Imperial Diet was the Diet, or general assembly, of the Imperial Estates of the Holy Roman Empire.During the period of the Empire, which lasted formally until 1806, the Diet was not a parliament in today's sense; instead, it was an assembly of the various estates of the realm...
in 1529 amid charges of heresy
Heresy
Heresy is a controversial or novel change to a system of beliefs, especially a religion, that conflicts with established dogma. It is distinct from apostasy, which is the formal denunciation of one's religion, principles or cause, and blasphemy, which is irreverence toward religion...
. But the changes he proposed were of such a fundamental nature that by their own logic they would automatically overthrow the old order; neither the Emperor nor the Church could possibly accept them, as Luther well knew. As was only to be expected, the edict by the Diet of Worms
Diet of Worms
The Diet of Worms 1521 was a diet that took place in Worms, Germany, and is most memorable for the Edict of Worms , which addressed Martin Luther and the effects of the Protestant Reformation.It was conducted from 28 January to 25 May 1521, with Emperor Charles V presiding.Other Imperial diets at...
(1521) prohibited all innovations. Meanwhile, in these efforts to retain the guise of a Catholic reformer as opposed to a heretical revolutionary, and to appeal to German princes with his religious condemnation of the peasant revolts backed up by the Doctrine of the Two Kingdoms
Doctrine of the two kingdoms
Martin Luther's doctrine of the two kingdoms of God teaches that God is the ruler of the whole world and that he rules in two ways....
, Luther's growing conservatism would provoke more radical reformers.
At a religious conference with the Zwinglians in 1529, Melanchthon joined with Luther in opposing a union with Zwingli. There would finally be a schism in the reform movement due to Luther's belief in real presence
Real Presence
Real Presence is a term used in various Christian traditions to express belief that in the Eucharist, Jesus Christ is really present in what was previously just bread and wine, and not merely present in symbol, a figure of speech , or by his power .Not all Christian traditions accept this dogma...
—the real (as opposed to symbolic) presence of Christ at the Eucharist. His original intention was not schism, but with the Reichstag of Augsburg (1530) and its rejection of the Lutheran "Augsburg Confession", a separate Lutheran church finally emerged. In a sense, Luther would take theology further in its deviation from established Catholic dogma, forcing a rift between the humanist Erasmus and Luther. Similarly, Zwingli would further repudiate ritualism, and break with the increasingly conservative Luther.

Usury
Usury Originally, when the charging of interest was still banned by Christian churches, usury simply meant the charging of interest at any rate . In countries where the charging of interest became acceptable, the term came to be used for interest above the rate allowed by law...
. In the North, burghers and monarchs were united in their frustration for not paying any taxes to the nation, but collecting taxes from subjects and sending the revenues disproportionately to Italy. In northern Europe, Luther appealed to the growing national consciousness of the German states because he denounced the Pope for involvement in politics as well as religion. Moreover, he backed the nobility, which was now justified to crush the Great Peasant Revolt of 1525 and to confiscate church property by Luther's Doctrine of the Two Kingdoms
Doctrine of the two kingdoms
Martin Luther's doctrine of the two kingdoms of God teaches that God is the ruler of the whole world and that he rules in two ways....
. This explains the attraction of some territorial princes to Lutheranism, especially its Doctrine of the Two Kingdoms. However, the Elector of Brandenburg, Joachim I, blamed Lutheranism for the revolt and so did others. In Brandenburg, it was only under his successor Joachim II that Lutheranism was established, and the old religion was not formally extinct in Brandenburg until the death of the last Catholic bishop there, Georg von Blumenthal, who was Bishop of Lebus and sovereign Prince-Bishop of Ratzeburg.
With the church subordinate to and the agent of civil authority and peasant rebellions condemned on strict religious terms, Lutheranism and German nationalist sentiment were ideally suited to coincide.
Though Charles V
Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor
Charles V was ruler of the Holy Roman Empire from 1519 and, as Charles I, of the Spanish Empire from 1516 until his voluntary retirement and abdication in favor of his younger brother Ferdinand I and his son Philip II in 1556.As...
fought the Reformation, it is no coincidence either that the reign of his nationalistic predecessor Maximilian I
Maximilian I, Holy Roman Emperor
Maximilian I , the son of Frederick III, Holy Roman Emperor and Eleanor of Portugal, was King of the Romans from 1486 and Holy Roman Emperor from 1493 until his death, though he was never in fact crowned by the Pope, the journey to Rome always being too risky...
saw the beginning of the movement. While the centralized states of western Europe had reached accords with the Vatican permitting them to draw on the rich property of the church for government expenditures, enabling them to form state churches that were greatly autonomous of Rome, similar moves on behalf of the Reich were unsuccessful so long as princes and prince bishops fought reforms to drop the pretension of the secular universal empire.
Protestant Reformation (1517 – 1579)
In the early 16th century, the church was confronted with the challenge posed by Martin LutherMartin Luther
Martin Luther was a German priest, professor of theology and iconic figure of the Protestant Reformation. He strongly disputed the claim that freedom from God's punishment for sin could be purchased with money. He confronted indulgence salesman Johann Tetzel with his Ninety-Five Theses in 1517...
to the traditional teaching on the church's doctrinal authority and to many of its practices as well. The seeming inability of Pope Leo X
Pope Leo X
Pope Leo X , born Giovanni di Lorenzo de' Medici, was the Pope from 1513 to his death in 1521. He was the last non-priest to be elected Pope. He is known for granting indulgences for those who donated to reconstruct St. Peter's Basilica and his challenging of Martin Luther's 95 Theses...
(1513–1521) and those popes who succeeded him to comprehend the significance of the threat that Luther posed - or, indeed, the alienation of many Christians by the corruption that had spread throughout the church - was a major factor in the rapid growth of the Protestant Reformation. By the time the need for a vigorous, reforming papal leadership was recognized, much of northern Europe had already converted to Protestantism.
Germany

Germans
The Germans are a Germanic ethnic group native to Central Europe. The English term Germans has referred to the German-speaking population of the Holy Roman Empire since the Late Middle Ages....
monk
Monk
A monk is a person who practices religious asceticism, living either alone or with any number of monks, while always maintaining some degree of physical separation from those not sharing the same purpose...
, theologian
Theology
Theology is the systematic and rational study of religion and its influences and of the nature of religious truths, or the learned profession acquired by completing specialized training in religious studies, usually at a university or school of divinity or seminary.-Definition:Augustine of Hippo...
, university professor, priest, father of Protestantism
Protestantism
Protestantism is one of the three major groupings within Christianity. It is a movement that began in Germany in the early 16th century as a reaction against medieval Roman Catholic doctrines and practices, especially in regards to salvation, justification, and ecclesiology.The doctrines of the...
, and church reformer
Protestant Reformers
Protestant Reformers were those theologians, churchmen, and statesmen whose careers, works, and actions brought about the Protestant Reformation of the sixteenth century...
whose ideas started the Protestant Reformation
Protestant Reformation
The Protestant Reformation was a 16th-century split within Western Christianity initiated by Martin Luther, John Calvin and other early Protestants. The efforts of the self-described "reformers", who objected to the doctrines, rituals and ecclesiastical structure of the Roman Catholic Church, led...
.
Luther taught that salvation is a free gift of God and received only through true faith
Faith
Faith is confidence or trust in a person or thing, or a belief that is not based on proof. In religion, faith is a belief in a transcendent reality, a religious teacher, a set of teachings or a Supreme Being. Generally speaking, it is offered as a means by which the truth of the proposition,...
in Jesus
Jesus
Jesus of Nazareth , commonly referred to as Jesus Christ or simply as Jesus or Christ, is the central figure of Christianity...
as redeemer from sin. His theology
Theology of Martin Luther
The theology of Martin Luther was instrumental in influencing the Protestant Reformation, specifically topics dealing with Justification by Faith, the relationship between the Law and the Gospel , and various other theological ideas. Although Luther never wrote a "systematic theology" or a...
challenged the authority
Authority
The word Authority is derived mainly from the Latin word auctoritas, meaning invention, advice, opinion, influence, or command. In English, the word 'authority' can be used to mean power given by the state or by academic knowledge of an area .-Authority in Philosophy:In...
of the papacy
Pope
The Pope is the Bishop of Rome, a position that makes him the leader of the worldwide Catholic Church . In the Catholic Church, the Pope is regarded as the successor of Saint Peter, the Apostle...
by adducing the Bible
Bible
The Bible refers to any one of the collections of the primary religious texts of Judaism and Christianity. There is no common version of the Bible, as the individual books , their contents and their order vary among denominations...
as the only infallible source of Christian
Christianity
Christianity is a monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus as presented in canonical gospels and other New Testament writings...
doctrine
Doctrine
Doctrine is a codification of beliefs or a body of teachings or instructions, taught principles or positions, as the body of teachings in a branch of knowledge or belief system...
and countering "sacerdotalism
Sacerdotalism
Sacerdotalism is the idea that a propitiatory sacrifice for sin must be offered by the intervention of an order of men separated to the priesthood...
" in the doctrine that all baptized
Baptism
In Christianity, baptism is for the majority the rite of admission , almost invariably with the use of water, into the Christian Church generally and also membership of a particular church tradition...
Christians are a universal priesthood
Priesthood of all believers
The universal priesthood or the priesthood of all believers, as it would come to be known in the present day, is a Christian doctrine believed to be derived from several passages of the New Testament...
.
Luther's refusal to retract his writings in confrontation with the Holy Roman Emperor Charles V
Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor
Charles V was ruler of the Holy Roman Empire from 1519 and, as Charles I, of the Spanish Empire from 1516 until his voluntary retirement and abdication in favor of his younger brother Ferdinand I and his son Philip II in 1556.As...
at the Diet of Worms
Diet of Worms
The Diet of Worms 1521 was a diet that took place in Worms, Germany, and is most memorable for the Edict of Worms , which addressed Martin Luther and the effects of the Protestant Reformation.It was conducted from 28 January to 25 May 1521, with Emperor Charles V presiding.Other Imperial diets at...
in 1521 resulted in his excommunication
Excommunication
Excommunication is a religious censure used to deprive, suspend or limit membership in a religious community. The word means putting [someone] out of communion. In some religions, excommunication includes spiritual condemnation of the member or group...
by Pope Leo X
Pope Leo X
Pope Leo X , born Giovanni di Lorenzo de' Medici, was the Pope from 1513 to his death in 1521. He was the last non-priest to be elected Pope. He is known for granting indulgences for those who donated to reconstruct St. Peter's Basilica and his challenging of Martin Luther's 95 Theses...
and declaration as an outlaw
Outlaw
In historical legal systems, an outlaw is declared as outside the protection of the law. In pre-modern societies, this takes the burden of active prosecution of a criminal from the authorities. Instead, the criminal is withdrawn all legal protection, so that anyone is legally empowered to persecute...
. His translation of the Bible
Luther Bible
The Luther Bible is a German Bible translation by Martin Luther, first printed with both testaments in 1534. This translation became a force in shaping the Modern High German language. The project absorbed Luther's later years. The new translation was very widely disseminated thanks to the printing...
into the language of the people made the Scriptures more accessible, causing a tremendous impact on the church and on German culture. It fostered the development of a standard version of the German language
German language
German is a West Germanic language, related to and classified alongside English and Dutch. With an estimated 90 – 98 million native speakers, German is one of the world's major languages and is the most widely-spoken first language in the European Union....
, added several principles to the art of translation, and influenced the translation of the King James Bible. His hymn
Hymn
A hymn is a type of song, usually religious, specifically written for the purpose of praise, adoration or prayer, and typically addressed to a deity or deities, or to a prominent figure or personification...
s inspired the development of congregational singing within Christianity. His marriage to Katharina von Bora
Katharina von Bora
Katharina von Bora, referred to as "die Lutherin", was the wife of Martin Luther, Germanleader of the Protestant Reformation. Beyond what is found in the writings of Luther and some of his contemporaries, little is known about her...
set a model for the practice of clerical marriage
Clerical marriage
Clerical marriage is the practice of allowing clergy to marry. Churches such as the Eastern Orthodox and the Oriental Orthodox exclude this practice for their priests, while accepting already married men for ordination to priesthood...
within Protestantism.


Johann Tetzel
Johann Tetzel was a German Dominican preacher known for selling indulgences.-Life:Tetzel was born in Pirna, Saxony, and studied theology and philosophy at the university of his native city...
, a Dominican friar and papal commissioner for indulgences, was sent to Germany by the Roman Catholic Church to sell indulgences to raise money to rebuild St Peter's Basilica in Rome. Roman Catholic theology stated that faith alone, whether fiduciary or dogmatic, cannot justify man; and that only such faith as is active in charity and good works (fides caritate formata) can justify man. These good works could be obtained by donating money to the church.
On 31 October 1517, Luther wrote to Albrecht, Archbishop of Mainz and Magdeburg, protesting the sale of indulgences. He enclosed in his letter a copy of his "Disputation of Martin Luther on the Power and Efficacy of Indulgences," which came to be known as The 95 Theses.
Luther objected to a saying attributed to Johann Tetzel that "As soon as the coin in the coffer rings, the soul from purgatory springs," insisting that, since forgiveness was God's alone to grant, those who claimed that indulgences absolved buyers from all punishments and granted them salvation were in error. Christians, he said, must not slacken in following Christ on account of such false assurances.

Philipp Melanchthon
Philipp Melanchthon , born Philipp Schwartzerdt, was a German reformer, collaborator with Martin Luther, the first systematic theologian of the Protestant Reformation, intellectual leader of the Lutheran Reformation, and an influential designer of educational systems...
writes ‘reportedly, Luther, burning with passion and just devoutness, posted the Ninety-Five Theses at the Castle Church in Wittenberg
Wittenberg
Wittenberg, officially Lutherstadt Wittenberg, is a city in Germany in the Bundesland Saxony-Anhalt, on the river Elbe. It has a population of about 50,000....
, Germany at All Saints Eve, October 31 (Old calendar)”. At the time of the writing of the preface Melanchton lived in Tübingen
Tübingen
Tübingen is a traditional university town in central Baden-Württemberg, Germany. It is situated south of the state capital, Stuttgart, on a ridge between the Neckar and Ammer rivers.-Geography:...
, far from Wittenberg. In the preface, Melanchton presents more facts that are not true: He writes that indulgence sales man Johann Tetzel
Johann Tetzel
Johann Tetzel was a German Dominican preacher known for selling indulgences.-Life:Tetzel was born in Pirna, Saxony, and studied theology and philosophy at the university of his native city...
publicly burned Luther’s Ninety-Five Theses, that Luther held colleges on nature and physics, and that Luther had visited Rome in 1511.For a professor of the Wittenberg University to post thesis on doors is unparalleled in history. Even further, Luther is known as strongly law abiding, and to publish his thoughts and direction in such a way would be strongly against his character. Luther has never mentioned anything in this direction in his writings, and the only contemporary account of the publishing of the thesis is the account of Luther’s servant Agricola
Johannes Agricola
Johannes Agricola was a German Protestant reformer and humanist. He was a follower and friend of Martin Luther, who became his antagonist in the matter of the binding obligation of the law on Christians.-Early life:Agricola was born at Eisleben, whence he is sometimes called Magister Islebius...
, written in Latin. In this account, Agricola states that Luther presents ‘certain thesis in the year of 1517 according to the customs of University of Wittenberg as part of a scientific discussion. The presentation of the thesis was done in a modest and respectful way, preventing to mock or insult anybody”. There is no mention of nailing the thesis to a door, nor does any other source report this. In reality, Luther presented a hand-written copy, accompanied with honourable comments to the archbishop Albrecht of Mainz
Mainz
Mainz under the Holy Roman Empire, and previously was a Roman fort city which commanded the west bank of the Rhine and formed part of the northernmost frontier of the Roman Empire...
and Magdenburg, responsible for the practice of the indulgence sales, and to the bishop of Brandenburg
Brandenburg
Brandenburg is one of the sixteen federal-states of Germany. It lies in the east of the country and is one of the new federal states that were re-created in 1990 upon the reunification of the former West Germany and East Germany. The capital is Potsdam...
, the superior of Luther.
It wasn’t until January 1518 that friends of Luther translated the 95 Theses from Latin into German, printed, and widely copied, making the controversy one of the first in history to be aided by the printing press
Printing press
A printing press is a device for applying pressure to an inked surface resting upon a print medium , thereby transferring the ink...
. Within two weeks, copies of the theses had spread throughout Germany; within two months throughout Europe. In contrast to the speed with which the theses were distributed, the response of the papacy was painstakingly slow. After three years of debate and negotiations involving Luther, government, and church officials, on 15 June 1520, the Pope warned Luther with the papal bull
Papal bull
A Papal bull is a particular type of letters patent or charter issued by a Pope of the Catholic Church. It is named after the bulla that was appended to the end in order to authenticate it....
(edict) Exsurge Domine
Exsurge Domine
220px|thumb|Title page of first printed edition of Exsurge DomineExsurge Domine is a papal bull issued on 15 June 1520 by Pope Leo X in response to the teachings of Martin Luther in his 95 theses and subsequent writings which opposed the views of the papacy...
that he risked excommunication
Excommunication
Excommunication is a religious censure used to deprive, suspend or limit membership in a religious community. The word means putting [someone] out of communion. In some religions, excommunication includes spiritual condemnation of the member or group...
unless he recanted 41 sentences drawn from his writings, including the 95 Theses
95 Theses
The Ninety-Five Theses on the Power and Efficacy of Indulgences , commonly known as , was written by Martin Luther, 1517 and is widely regarded as the primary catalyst for the Protestant Reformation...
, within 60 days.
That autumn, Johann Eck
Johann Eck
Dr. Johann Maier von Eck was a German Scholastic theologian and defender of Catholicism during the Protestant Reformation. It was Eck who argued that the beliefs of Martin Luther and Jan Hus were similar.-Life:...
proclaimed the bull in Meissen and other towns. Karl von Miltitz
Karl von Miltitz
Karl von Miltitz was a papal nuncio and a Mainz Cathedral canon.-Biography:He was born in Rabenau near Meißen and Dresden, his family stemming from the lesser Saxon nobility. He studied at Mainz, Trier, Cologne , and Bologna , but his deficient Latin reveals that he was not especially learned...
, a papal nuncio
Nuncio
Nuncio is an ecclesiastical diplomatic title, derived from the ancient Latin word, Nuntius, meaning "envoy." This article addresses this title as well as derived similar titles, all within the structure of the Roman Catholic Church...
, attempted to broker a solution, but Luther, who had sent the Pope a copy of his concilatory On the Freedom of a Christian (which the Pope refused to read) in October, publicly set fire to the bull and decretal
Decretal
Decretals is the name that is given in Canon law to those letters of the pope which formulate decisions in ecclesiastical law.They are generally given in answer to consultations, but are sometimes due to the initiative of the popes...
s at Wittenberg on 10 December 1520, an act he defended in Why the Pope and his Recent Book are Burned and Assertions Concerning All Articles.
As a consequence, Luther was excommunicated by Leo X
Pope Leo X
Pope Leo X , born Giovanni di Lorenzo de' Medici, was the Pope from 1513 to his death in 1521. He was the last non-priest to be elected Pope. He is known for granting indulgences for those who donated to reconstruct St. Peter's Basilica and his challenging of Martin Luther's 95 Theses...
on 3 January 1521, in the bull Decet Romanum Pontificem
Decet Romanum Pontificem
Decet Romanum Pontificem is the papal bull excommunicating Martin Luther, bearing the title of the first three Latin words of the text. It was issued on January 3, 1521, by Pope Leo X to effect the excommunication threatened in his earlier papal bull Exsurge Domine since Luther failed to recant...
.
Zwingli
Parallel to events in Germany, a movement began in Switzerland under the leadership of Huldrych ZwingliHuldrych Zwingli
Ulrich Zwingli was a leader of the Reformation in Switzerland. Born during a time of emerging Swiss patriotism and increasing criticism of the Swiss mercenary system, he attended the University of Vienna and the University of Basel, a scholarly centre of humanism...
(died 1531). These two movements quickly agreed on most issues, as the recently introduced printing press
Printing press
A printing press is a device for applying pressure to an inked surface resting upon a print medium , thereby transferring the ink...
spread ideas rapidly from place to place, but some unresolved differences kept them separate. Some followers of Zwingli believed that the Reformation was too conservative, and moved independently toward more radical positions, some of which survive among modern day Anabaptist
Anabaptist
Anabaptists are Protestant Christians of the Radical Reformation of 16th-century Europe, and their direct descendants, particularly the Amish, Brethren, Hutterites, and Mennonites....
s. Other Protestant movements grew up along lines of mysticism or humanism (cf.
Cf.
cf., an abbreviation for the Latin word confer , literally meaning "bring together", is used to refer to other material or ideas which may provide similar or different information or arguments. It is mainly used in scholarly contexts, such as in academic or legal texts...
Erasmus), sometimes breaking from Rome or from the Protestants, or forming outside of the churches.

John Calvin

Excommunication
Excommunication is a religious censure used to deprive, suspend or limit membership in a religious community. The word means putting [someone] out of communion. In some religions, excommunication includes spiritual condemnation of the member or group...
of Luther and condemnation of the Reformation by the Pope, the work and writings of John Calvin
John Calvin
John Calvin was an influential French theologian and pastor during the Protestant Reformation. He was a principal figure in the development of the system of Christian theology later called Calvinism. Originally trained as a humanist lawyer, he broke from the Roman Catholic Church around 1530...
were influential in establishing a loose consensus among various groups in Switzerland, Scotland
Scotland
Scotland is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Occupying the northern third of the island of Great Britain, it shares a border with England to the south and is bounded by the North Sea to the east, the Atlantic Ocean to the north and west, and the North Channel and Irish Sea to the...
, Hungary, Germany and elsewhere.
Geneva became the unofficial capital of the Protestant movement, led by the Frenchman, Jean Calvin, until his death in 1564 (when Calvin's ally, William Farel
William Farel
William Farel , né Guilhem Farel, 1489 in Gap, Dauphiné, in south-eastern France, was a French evangelist, and a founder of the Reformed Church in the cantons of Neuchâtel, Berne, Geneva, and Vaud in Switzerland...
, assumed the spiritual leadership of the group).
The Reformation foundations engaged with Augustinianism. Both Luther and Calvin thought along lines linked with the theological teachings of Augustine of Hippo. The Augustinianism of the Reformers struggled against Pelagianism
Pelagianism
Pelagianism is a theological theory named after Pelagius , although he denied, at least at some point in his life, many of the doctrines associated with his name. It is the belief that original sin did not taint human nature and that mortal will is still capable of choosing good or evil without...
, a heresy that they perceived in the Catholic Church of their day. Ironically, even though both Luther and Calvin both had very similar theological teachings, the relationship between Lutherans and Calvinists evolved into one of conflict.
Scandinavia
All of ScandinaviaScandinavia
Scandinavia is a cultural, historical and ethno-linguistic region in northern Europe that includes the three kingdoms of Denmark, Norway and Sweden, characterized by their common ethno-cultural heritage and language. Modern Norway and Sweden proper are situated on the Scandinavian Peninsula,...
ultimately adopted Lutheranism over the course of the sixteenth century, as the monarchs of Denmark
Denmark
Denmark is a Scandinavian country in Northern Europe. The countries of Denmark and Greenland, as well as the Faroe Islands, constitute the Kingdom of Denmark . It is the southernmost of the Nordic countries, southwest of Sweden and south of Norway, and bordered to the south by Germany. Denmark...
(who also ruled Norway
Norway
Norway , officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic unitary constitutional monarchy whose territory comprises the western portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula, Jan Mayen, and the Arctic archipelago of Svalbard and Bouvet Island. Norway has a total area of and a population of about 4.9 million...
and Iceland
Iceland
Iceland , described as the Republic of Iceland, is a Nordic and European island country in the North Atlantic Ocean, on the Mid-Atlantic Ridge. Iceland also refers to the main island of the country, which contains almost all the population and almost all the land area. The country has a population...
) and Sweden
Sweden
Sweden , officially the Kingdom of Sweden , is a Nordic country on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. Sweden borders with Norway and Finland and is connected to Denmark by a bridge-tunnel across the Öresund....
(who also ruled Finland
Finland
Finland , officially the Republic of Finland, is a Nordic country situated in the Fennoscandian region of Northern Europe. It is bordered by Sweden in the west, Norway in the north and Russia in the east, while Estonia lies to its south across the Gulf of Finland.Around 5.4 million people reside...
) converted to that faith.
In Sweden the Reformation was spearheaded by Gustav Vasa, elected king in 1523. Friction with the pope over the latter's interference in Swedish ecclesiastical affairs led to the discontinuance of any official connection between Sweden and the papacy from 1523. Four years later, at the Diet of Västerås, the king succeeded in forcing the diet to accept his dominion over the national church. The king was given possession of all church property, church appointments required royal approval, the clergy were subject to the civil law, and the "pure Word of God" was to be preached in the churches and taught in the schools—effectively granting official sanction to Lutheran ideas.
Under the reign of Frederick I
Frederick I of Denmark
Frederick I of Denmark and Norway was the King of Denmark and Norway. The name is also spelled Friedrich in German, Frederik in Danish, and Fredrik in Swedish and Norwegian...
(1523–33), Denmark remained officially Catholic. But though Frederick initially pledged to persecute Lutherans, he soon adopted a policy of protecting Lutheran preachers and reformers, of whom the most famous was Hans Tausen
Hans Tausen
Hans Tausen , the protagonist of the Danish Reformation, was born at Birkende on Funen in 1494 and died in Ribe in 1561.- Life :...
. During his reign, Lutheranism made significant inroads among the Danish population. Frederick's son, Christian, was openly Lutheran, which prevented his election to the throne upon his father's death. However, following his victory in the civil war that followed, in 1537 he became Christian III
Christian III of Denmark
Christian III reigned as king of Denmark and Norway. He was the eldest son of King Frederick I and Anna of Brandenburg.-Childhood:...
and began a reformation of the official state church.
England

Church of England
The separation of the Church of EnglandChurch of England
The Church of England is the officially established Christian church in England and the Mother Church of the worldwide Anglican Communion. The church considers itself within the tradition of Western Christianity and dates its formal establishment principally to the mission to England by St...
or Anglican Church from Rome under Henry VIII
Henry VIII of England
Henry VIII was King of England from 21 April 1509 until his death. He was Lord, and later King, of Ireland, as well as continuing the nominal claim by the English monarchs to the Kingdom of France...
, beginning in 1529 and completed in 1536, brought England alongside this broad Reformed movement. However, religious changes in the English national church proceeded more conservatively than elsewhere in Europe. Reformers in the Church of England alternated, for centuries, between sympathies for Catholic traditions and Protestantism, progressively forging a stable compromise between adherence to ancient tradition and Protestantism, which is now sometimes called the via media (middle way).
In England, the Reformation followed a different course than elsewhere in Europe. There had long been a strong strain of anti-clericalism, and England had already given rise to the Lollard movement of John Wycliffe
John Wycliffe
John Wycliffe was an English Scholastic philosopher, theologian, lay preacher, translator, reformer and university teacher who was known as an early dissident in the Roman Catholic Church during the 14th century. His followers were known as Lollards, a somewhat rebellious movement, which preached...
, which played an important part in inspiring the Hussite
Hussite
The Hussites were a Christian movement following the teachings of Czech reformer Jan Hus , who became one of the forerunners of the Protestant Reformation...
s in Bohemia
Bohemia
Bohemia is a historical region in central Europe, occupying the western two-thirds of the traditional Czech Lands. It is located in the contemporary Czech Republic with its capital in Prague...
. Lollardy was suppressed and became an underground movement so the extent of its influence in the 1520s is difficult to assess. The different character of the English Reformation came rather from the fact that it was driven initially by the political necessities of Henry VIII
Henry VIII of England
Henry VIII was King of England from 21 April 1509 until his death. He was Lord, and later King, of Ireland, as well as continuing the nominal claim by the English monarchs to the Kingdom of France...
. Henry had once been a sincere Catholic and had even authored a book strongly criticizing Luther, but he later found it expedient and profitable to break with the Papacy. His wife, Catherine of Aragon
Catherine of Aragon
Catherine of Aragon , also known as Katherine or Katharine, was Queen consort of England as the first wife of King Henry VIII of England and Princess of Wales as the wife to Arthur, Prince of Wales...
, bore him only a single child, Mary
Mary I of England
Mary I was queen regnant of England and Ireland from July 1553 until her death.She was the only surviving child born of the ill-fated marriage of Henry VIII and his first wife Catherine of Aragon. Her younger half-brother, Edward VI, succeeded Henry in 1547...
. As England had recently gone through a lengthy dynastic conflict (see Wars of the Roses
Wars of the Roses
The Wars of the Roses were a series of dynastic civil wars for the throne of England fought between supporters of two rival branches of the royal House of Plantagenet: the houses of Lancaster and York...
), Henry feared that his lack of a male heir might jeopardize his descendants' claim to the throne. However, Pope Clement VII, concentrating more on Charles V's "sack of Rome", denied his request for an annulment. Had Clement granted the annulment and therefore admitted that his predecessor, Julius II, had erred, Clement would have given support to the Lutheran assertion that Popes replaced their own judgement for the will of God. King Henry decided to remove the Church of England
Church of England
The Church of England is the officially established Christian church in England and the Mother Church of the worldwide Anglican Communion. The church considers itself within the tradition of Western Christianity and dates its formal establishment principally to the mission to England by St...
from the authority of Rome. In 1534, the Act of Supremacy made Henry the Supreme Head
Supreme Head
Supreme Head of the Church of England was a title held by King Henry VIII of England signifying his leadership of the Church of England.-History:...
of the Church of England. Between 1535 and 1540, under Thomas Cromwell
Thomas Cromwell, 1st Earl of Essex
Thomas Cromwell, 1st Earl of Essex, , was an English statesman who served as chief minister of King Henry VIII of England from 1532 to 1540....
, the policy known as the Dissolution of the Monasteries
Dissolution of the Monasteries
The Dissolution of the Monasteries, sometimes referred to as the Suppression of the Monasteries, was the set of administrative and legal processes between 1536 and 1541 by which Henry VIII disbanded monasteries, priories, convents and friaries in England, Wales and Ireland; appropriated their...
was put into effect. The veneration of some saint
Saint
A saint is a holy person. In various religions, saints are people who are believed to have exceptional holiness.In Christian usage, "saint" refers to any believer who is "in Christ", and in whom Christ dwells, whether in heaven or in earth...
s, certain pilgrimages and some pilgrim shrines were also attacked. Huge amounts of church land and property passed into the hands of the crown and ultimately into those of the nobility and gentry. The vested interest thus created made for a powerful force in support of the dissolutions.
There were some notable opponents to the Henrician Reformation, such as Thomas More
Thomas More
Sir Thomas More , also known by Catholics as Saint Thomas More, was an English lawyer, social philosopher, author, statesman and noted Renaissance humanist. He was an important councillor to Henry VIII of England and, for three years toward the end of his life, Lord Chancellor...
and Bishop John Fisher
John Fisher
Saint John Fisher was an English Roman Catholic scholastic, bishop, cardinal and martyr. He shares his feast day with Saint Thomas More on 22 June in the Roman Catholic calendar of saints and 6 July on the Church of England calendar of saints...
, who were executed for their opposition. There was also a growing party of reformers who were imbued with the Zwinglian and Calvinistic doctrines now current on the Continent. When Henry died he was succeeded by his Protestant son Edward VI, who, through his empowered councillors (with the King being only nine years old at his succession and not yet sixteen at his death) the Duke of Somerset and the Duke of Northumberland, ordered the destruction of images in churches, and the closing of the chantries
Chantry
Chantry is the English term for a fund established to pay for a priest to celebrate sung Masses for a specified purpose, generally for the soul of the deceased donor. Chantries were endowed with lands given by donors, the income from which maintained the chantry priest...
. Under Edward VI the reform of the Church of England
Church of England
The Church of England is the officially established Christian church in England and the Mother Church of the worldwide Anglican Communion. The church considers itself within the tradition of Western Christianity and dates its formal establishment principally to the mission to England by St...
was established unequivocally in doctrinal terms. Yet, at a popular level, religion in England was still in a state of flux. Following a brief Roman Catholic restoration during the reign of Mary
Mary I of England
Mary I was queen regnant of England and Ireland from July 1553 until her death.She was the only surviving child born of the ill-fated marriage of Henry VIII and his first wife Catherine of Aragon. Her younger half-brother, Edward VI, succeeded Henry in 1547...
1553–1558, a loose consensus developed during the reign of Elizabeth I
Elizabeth I of England
Elizabeth I was queen regnant of England and Ireland from 17 November 1558 until her death. Sometimes called The Virgin Queen, Gloriana, or Good Queen Bess, Elizabeth was the fifth and last monarch of the Tudor dynasty...
, though this point is one of considerable debate among historians. Yet it is the so-called "Elizabethan Religious Settlement
Elizabethan Religious Settlement
The Elizabethan Religious Settlement was Elizabeth I’s response to the religious divisions created over the reigns of Henry VIII, Edward VI and Mary I. This response, described as "The Revolution of 1559", was set out in two Acts of the Parliament of England...
" to which the origins of Anglicanism
Anglicanism
Anglicanism is a tradition within Christianity comprising churches with historical connections to the Church of England or similar beliefs, worship and church structures. The word Anglican originates in ecclesia anglicana, a medieval Latin phrase dating to at least 1246 that means the English...
are traditionally ascribed. The compromise was uneasy and was capable of veering between extreme Calvinism
Calvinism
Calvinism is a Protestant theological system and an approach to the Christian life...
on the one hand and Catholicism on the other, but compared to the bloody and chaotic state of affairs in contemporary France, it was relatively successful until the Puritan Revolution or English Civil War
English Civil War
The English Civil War was a series of armed conflicts and political machinations between Parliamentarians and Royalists...
in the seventeenth century.
Puritan movement
The success of the Counter-ReformationCounter-Reformation
The Counter-Reformation was the period of Catholic revival beginning with the Council of Trent and ending at the close of the Thirty Years' War, 1648 as a response to the Protestant Reformation.The Counter-Reformation was a comprehensive effort, composed of four major elements:#Ecclesiastical or...
on the Continent and the growth of a Puritan
Puritan
The Puritans were a significant grouping of English Protestants in the 16th and 17th centuries. Puritanism in this sense was founded by some Marian exiles from the clergy shortly after the accession of Elizabeth I of England in 1558, as an activist movement within the Church of England...
party dedicated to further Protestant reform polarized the Elizabethan Age, although it was not until the 1640s that England underwent religious strife comparable to that which its neighbours had suffered some generations before.
The early Puritan movement (late 16th century-17th century) was Reformed or Calvinist
Calvinism
Calvinism is a Protestant theological system and an approach to the Christian life...
and was a movement for reform in the Church of England
Church of England
The Church of England is the officially established Christian church in England and the Mother Church of the worldwide Anglican Communion. The church considers itself within the tradition of Western Christianity and dates its formal establishment principally to the mission to England by St...
. Its origins lay in the discontent with the Elizabethan Religious Settlement
Elizabethan Religious Settlement
The Elizabethan Religious Settlement was Elizabeth I’s response to the religious divisions created over the reigns of Henry VIII, Edward VI and Mary I. This response, described as "The Revolution of 1559", was set out in two Acts of the Parliament of England...
. The desire was for the Church of England to resemble more closely the Protestant churches of Europe, especially Geneva
Geneva
Geneva In the national languages of Switzerland the city is known as Genf , Ginevra and Genevra is the second-most-populous city in Switzerland and is the most populous city of Romandie, the French-speaking part of Switzerland...
. The Puritans objected to ornaments and ritual in the churches as idolatrous
Idolatry
Idolatry is a pejorative term for the worship of an idol, a physical object such as a cult image, as a god, or practices believed to verge on worship, such as giving undue honour and regard to created forms other than God. In all the Abrahamic religions idolatry is strongly forbidden, although...
(vestments, surplices, organs, genuflection), which they castigated as "popish pomp and rags". (See Vestments controversy
Vestments controversy
The vestments controversy arose in the English Reformation, ostensibly concerning vestments, but more fundamentally concerned with English Protestant identity, doctrine, and various church practices...
.) They also objected to ecclesiastical courts. They refused to endorse completely all of the ritual directions and formulas of the Book of Common Prayer
Book of Common Prayer
The Book of Common Prayer is the short title of a number of related prayer books used in the Anglican Communion, as well as by the Continuing Anglican, "Anglican realignment" and other Anglican churches. The original book, published in 1549 , in the reign of Edward VI, was a product of the English...
; the imposition of its liturgical order by legal force and inspection sharpened Puritanism into a definite opposition movement.
The later Puritan movement were often referred to as Dissenters and Nonconformists and eventually led to the formation of various Reformed denominations
Christian denomination
A Christian denomination is an identifiable religious body under a common name, structure, and doctrine within Christianity. In the Orthodox tradition, Churches are divided often along ethnic and linguistic lines, into separate churches and traditions. Technically, divisions between one group and...
.
The most famous and well-known emigration to America
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
was the migration of the Puritan separatists from the Anglican Church of England, who fled first to Holland, and then later to America, to establish the English colonies of New England
New England
New England is a region in the northeastern corner of the United States consisting of the six states of Maine, New Hampshire, Vermont, Massachusetts, Rhode Island, and Connecticut...
, which later became the United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
.
These Puritan separatists were also known as "the pilgrims". After establishing a colony at Plymouth (in what would become later Massachusetts) in 1620, the Puritan pilgrims received a charter from the King of England which legitimized their colony, allowing them to do trade and commerce with merchants in England, in accordance with the principles of mercantilism
Mercantilism
Mercantilism is the economic doctrine in which government control of foreign trade is of paramount importance for ensuring the prosperity and security of the state. In particular, it demands a positive balance of trade. Mercantilism dominated Western European economic policy and discourse from...
. This successful, though initially quite difficult, colony marked the beginning of the Protestant presence in America (the earlier French, Spanish and Portuguese settlements had been Catholic), and became a kind of oasis of spiritual and economic freedom
Economic freedom
Economic freedom is a term used in economic and policy debates. As with freedom generally, there are various definitions, but no universally accepted concept of economic freedom...
, to which persecuted Protestants and other minorities from the British Isles and Europe (and later, from all over the world) fled to for peace, freedom and opportunity.
The original intent of the colonists was to establish spiritual Puritanism, which had been denied to them in England and the rest of Europe to engage in peaceful commerce with England and the native American Indians and to Christianize the peoples of the Americas.
Scotland
The Reformation in Scotland's case culminated ecclesiastically in the re-establishment of the church along Reformed lines, and politically in the triumph of EnglishEngland
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Scotland to the north and Wales to the west; the Irish Sea is to the north west, the Celtic Sea to the south west, with the North Sea to the east and the English Channel to the south separating it from continental...
influence over that of France
France
The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
. John Knox
John Knox
John Knox was a Scottish clergyman and a leader of the Protestant Reformation who brought reformation to the church in Scotland. He was educated at the University of St Andrews or possibly the University of Glasgow and was ordained to the Catholic priesthood in 1536...
is regarded as the leader of the Scottish Reformation
The Reformation Parliament
Scottish Reformation Parliament
The Scottish Reformation Parliament is the name given to the Scottish Parliament commencing in 1560 that passed the major pieces of legislation leading to the Scottish Reformation, most importantly Confession of Faith Ratification Act 1560; and Papal Jurisdiction Act 1560 .right|thumb|[[John...
of 1560, which repudiated the pope's authority, forbade the celebration of the mass
Mass (liturgy)
"Mass" is one of the names by which the sacrament of the Eucharist is called in the Roman Catholic Church: others are "Eucharist", the "Lord's Supper", the "Breaking of Bread", the "Eucharistic assembly ", the "memorial of the Lord's Passion and Resurrection", the "Holy Sacrifice", the "Holy and...
and approved a Protestant Confession of Faith
Confession of Faith
A Confession of Faith is a statement of doctrine very similar to a creed, but usually longer and polemical, as well as didactic.Confessions of Faith are in the main, though not exclusively, associated with Protestantism...
, was made possible by a revolution against French
France
The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
hegemony under the regime of the regent
Regent
A regent, from the Latin regens "one who reigns", is a person selected to act as head of state because the ruler is a minor, not present, or debilitated. Currently there are only two ruling Regencies in the world, sovereign Liechtenstein and the Malaysian constitutive state of Terengganu...
Mary of Guise
Mary of Guise
Mary of Guise was a queen consort of Scotland as the second spouse of King James V. She was the mother of Mary, Queen of Scots, and served as regent of Scotland in her daughter's name from 1554 to 1560...
, who had governed Scotland in the name of her absent daughter Mary, Queen of Scots, (then also Queen
Queen consort
A queen consort is the wife of a reigning king. A queen consort usually shares her husband's rank and holds the feminine equivalent of the king's monarchical titles. Historically, queens consort do not share the king regnant's political and military powers. Most queens in history were queens consort...
of France).
The Scottish Reformation decisively shaped the Church of Scotland
Church of Scotland
The Church of Scotland, known informally by its Scots language name, the Kirk, is a Presbyterian church, decisively shaped by the Scottish Reformation....
and, through it, all other Presbyterian churches worldwide.
A spiritual revival also broke out among Catholics soon after Martin Luther's actions, and led to the Scottish Covenanters' movement
Covenanter
The Covenanters were a Scottish Presbyterian movement that played an important part in the history of Scotland, and to a lesser extent in that of England and Ireland, during the 17th century...
, the precursor to Scottish
Scotland
Scotland is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Occupying the northern third of the island of Great Britain, it shares a border with England to the south and is bounded by the North Sea to the east, the Atlantic Ocean to the north and west, and the North Channel and Irish Sea to the...
Presbyterianism
Presbyterianism
Presbyterianism refers to a number of Christian churches adhering to the Calvinist theological tradition within Protestantism, which are organized according to a characteristic Presbyterian polity. Presbyterian theology typically emphasizes the sovereignty of God, the authority of the Scriptures,...
. This movement spread, and greatly influenced the formation of Puritan
Puritan
The Puritans were a significant grouping of English Protestants in the 16th and 17th centuries. Puritanism in this sense was founded by some Marian exiles from the clergy shortly after the accession of Elizabeth I of England in 1558, as an activist movement within the Church of England...
ism among the Anglican Church in England
England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Scotland to the north and Wales to the west; the Irish Sea is to the north west, the Celtic Sea to the south west, with the North Sea to the east and the English Channel to the south separating it from continental...
. The Scottish Covenanters were persecuted by the Roman Catholic Church. This persecution by the Catholics drove some of the Protestant Covenanter leadership out of Scotland, and into France
France
The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
and later, Switzerland
Switzerland
Switzerland name of one of the Swiss cantons. ; ; ; or ), in its full name the Swiss Confederation , is a federal republic consisting of 26 cantons, with Bern as the seat of the federal authorities. The country is situated in Western Europe,Or Central Europe depending on the definition....
.
France
Protestantism also spread into France, where the Protestants were nicknameNickname
A nickname is "a usually familiar or humorous but sometimes pointed or cruel name given to a person or place, as a supposedly appropriate replacement for or addition to the proper name.", or a name similar in origin and pronunciation from the original name....
d "Huguenots", and this touched off decades of warfare in France, after initial support by Henry of Navarre was lost due to the "Night of the Placards
Affair of the placards
The Affair of the Placards was an incident in which anti-Catholic posters appeared in public places in Paris and in four major provincial cities: Blois, Rouen, Tours and Orléans, overnight during 17 October 1534. One was actually posted on the bedchamber door of King Francis I at Amboise, an...
" affair. Many French Huguenots however, still contributed to the Protestant movement, including many who emigrated to the English colonies.

Francis I of France
Francis I was King of France from 1515 until his death. During his reign, huge cultural changes took place in France and he has been called France's original Renaissance monarch...
(1515–47) initially maintained an attitude of tolerance, arising from his interest in the humanist
Renaissance humanism
Renaissance humanism was an activity of cultural and educational reform engaged by scholars, writers, and civic leaders who are today known as Renaissance humanists. It developed during the fourteenth and the beginning of the fifteenth centuries, and was a response to the challenge of Mediæval...
movement. This changed in 1534 with the Affair of the Placards
Affair of the placards
The Affair of the Placards was an incident in which anti-Catholic posters appeared in public places in Paris and in four major provincial cities: Blois, Rouen, Tours and Orléans, overnight during 17 October 1534. One was actually posted on the bedchamber door of King Francis I at Amboise, an...
. In this act, Protestants denounced the mass in placards that appeared across France, even reaching the royal apartments. The issue of religious faith having been thrown into the arena of politics, Francis was prompted to view the movement as a threat to the kingdom's stability. This led to the first major phase of anti-Protestant persecution in France, in which the Chambre Ardente
Chambre Ardente
A Chambre ardente was an extraordinary court of justice in Ancien Régime France, mainly held for the trials of heretics.The name is perhaps an allusion to the fact that the proceedings took place in a room from which all daylight was excluded, the only illumination being from torches, or there may...
("Burning Chamber") was established within the Parlement of Paris to handle with the rise in prosecutions for heresy. Several thousand French Protestants fled the country during this time, most notably John Calvin
John Calvin
John Calvin was an influential French theologian and pastor during the Protestant Reformation. He was a principal figure in the development of the system of Christian theology later called Calvinism. Originally trained as a humanist lawyer, he broke from the Roman Catholic Church around 1530...
, who settled in Geneva
Geneva
Geneva In the national languages of Switzerland the city is known as Genf , Ginevra and Genevra is the second-most-populous city in Switzerland and is the most populous city of Romandie, the French-speaking part of Switzerland...
.
Calvin continued to take an interest in the religious affairs of his native land and, from his base in Geneva, beyond the reach of the French king, regularly trained pastors to lead congregations in France. Despite heavy persecution by Henry II
Henry II of France
Henry II was King of France from 31 March 1547 until his death in 1559.-Early years:Henry was born in the royal Château de Saint-Germain-en-Laye, near Paris, the son of Francis I and Claude, Duchess of Brittany .His father was captured at the Battle of Pavia in 1525 by his sworn enemy,...
, the Reformed Church of France
Reformed Church of France
The Reformed Church of France is a denomination in France with Calvinist origins. It is the original and largest Protestant denomination in France....
, largely Calvinist in direction, made steady progress across large sections of the nation, in the urban bourgeoisie
Bourgeoisie
In sociology and political science, bourgeoisie describes a range of groups across history. In the Western world, between the late 18th century and the present day, the bourgeoisie is a social class "characterized by their ownership of capital and their related culture." A member of the...
and parts of the aristocracy
Aristocracy
Aristocracy , is a form of government in which a few elite citizens rule. The term derives from the Greek aristokratia, meaning "rule of the best". In origin in Ancient Greece, it was conceived of as rule by the best qualified citizens, and contrasted with monarchy...
, appealing to people alienated by the obduracy and the complacency of the Catholic establishment.
French Protestantism, though its appeal increased under persecution, came to acquire a distinctly political character, made all the more obvious by the noble conversions of the 1550s. This had the effect of creating the preconditions for a series of destructive and intermittent conflicts, known as the Wars of Religion
French Wars of Religion
The French Wars of Religion is the name given to a period of civil infighting and military operations, primarily fought between French Catholics and Protestants . The conflict involved the factional disputes between the aristocratic houses of France, such as the House of Bourbon and House of Guise...
. The civil wars were helped along by the sudden death of Henry II
Henry II of France
Henry II was King of France from 31 March 1547 until his death in 1559.-Early years:Henry was born in the royal Château de Saint-Germain-en-Laye, near Paris, the son of Francis I and Claude, Duchess of Brittany .His father was captured at the Battle of Pavia in 1525 by his sworn enemy,...
in 1559, which saw the beginning of a prolonged period of weakness for the French crown. Atrocity and outrage became the defining characteristic of the time, illustrated at its most intense in the St. Bartholomew's Day massacre
St. Bartholomew's Day massacre
The St. Bartholomew's Day massacre in 1572 was a targeted group of assassinations, followed by a wave of Roman Catholic mob violence, both directed against the Huguenots , during the French Wars of Religion...
of August 1572, when the Catholic Church annihilated between 30,000 and 100,000 Huguenots across France. The wars only concluded when Henry IV
Henry IV of France
Henry IV , Henri-Quatre, was King of France from 1589 to 1610 and King of Navarre from 1572 to 1610. He was the first monarch of the Bourbon branch of the Capetian dynasty in France....
, himself a former Huguenot, issued the Edict of Nantes
Edict of Nantes
The Edict of Nantes, issued on 13 April 1598, by Henry IV of France, granted the Calvinist Protestants of France substantial rights in a nation still considered essentially Catholic. In the Edict, Henry aimed primarily to promote civil unity...
, promising official toleration of the Protestant minority, but under highly restricted conditions. Catholicism remained the official state religion, and the fortunes of French Protestants gradually declined over the next century, culminating in Louis XIV's Edict of Fontainebleau
Edict of Fontainebleau
The Edict of Fontainebleau was an edict issued by Louis XIV of France, also known as the Revocation of the Edict of Nantes. The Edict of Nantes of 1598, had granted the Huguenots the right to practice their religion without persecution from the state...
—which revoked the Edict of Nantes and made Catholicism the sole legal religion of France. In response to the Edict of Fontainebleau, Frederick William
Frederick William
The name Frederick William usually refers to several monarchs and princes of the Hohenzollern dynasty:*Frederick William, Elector of Brandenburg *Frederick William I , King of Prussia*Frederick William II , King of Prussia...
of Brandenburg
Brandenburg
Brandenburg is one of the sixteen federal-states of Germany. It lies in the east of the country and is one of the new federal states that were re-created in 1990 upon the reunification of the former West Germany and East Germany. The capital is Potsdam...
declared the Edict of Potsdam
Edict of Potsdam
The Edict of Potsdam was a proclamation issued by Frederick William, Elector of Brandenburg and Duke of Prussia, in Potsdam on October 29, 1685, as a response to the revocation of the Edict of Nantes by the Edict of Fontainebleau.- Background :...
, giving free passage to French Huguenot refugees, and tax-free status to them for 10 years.
Netherlands

Seventeen Provinces
The Seventeen Provinces were a personal union of states in the Low Countries in the 15th century and 16th century, roughly covering the current Netherlands, Belgium, Luxembourg, a good part of the North of France , and a small part of Western Germany.The Seventeen Provinces were originally held by...
, but instead by multiple popular movements, which in turn were bolstered by the arrival of Protestant refugees from other parts of the continent. While the Anabaptist
Anabaptist
Anabaptists are Protestant Christians of the Radical Reformation of 16th-century Europe, and their direct descendants, particularly the Amish, Brethren, Hutterites, and Mennonites....
movement enjoyed popularity in the region in the early decades of the Reformation, Calvinism, in the form of the Dutch Reformed Church
Dutch Reformed Church
The Dutch Reformed Church was a Reformed Christian denomination in the Netherlands. It existed from the 1570s to 2004, the year it merged with the Reformed Churches in the Netherlands and the Evangelical Lutheran Church in the Kingdom of the Netherlands to form the Protestant Church in the...
, became the dominant Protestant faith in the country from the 1560s onward.
Harsh persecution of Protestants by the Spanish government of Philip II
Philip II of Spain
Philip II was King of Spain, Portugal, Naples, Sicily, and, while married to Mary I, King of England and Ireland. He was lord of the Seventeen Provinces from 1556 until 1581, holding various titles for the individual territories such as duke or count....
contributed to a desire for independence in the provinces, which led to the Eighty Years' War and eventually, the separation of the largely Protestant Dutch Republic
Dutch Republic
The Dutch Republic — officially known as the Republic of the Seven United Netherlands , the Republic of the United Netherlands, or the Republic of the Seven United Provinces — was a republic in Europe existing from 1581 to 1795, preceding the Batavian Republic and ultimately...
from the Catholic-dominated Southern Netherlands
Southern Netherlands
Southern Netherlands were a part of the Low Countries controlled by Spain , Austria and annexed by France...
, the present-day Belgium
Belgium
Belgium , officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a federal state in Western Europe. It is a founding member of the European Union and hosts the EU's headquarters, and those of several other major international organisations such as NATO.Belgium is also a member of, or affiliated to, many...
.
Hungary
Much of the population of Kingdom of HungaryKingdom of Hungary
The Kingdom of Hungary comprised present-day Hungary, Slovakia and Croatia , Transylvania , Carpatho Ruthenia , Vojvodina , Burgenland , and other smaller territories surrounding present-day Hungary's borders...
adopted Protestantism during the sixteenth century. After the 1526 Battle of Mohács
Battle of Mohács
The Battle of Mohács was fought on August 29, 1526 near Mohács, Hungary. In the battle, forces of the Kingdom of Hungary led by King Louis II of Hungary and Bohemia were defeated by forces of the Ottoman Empire led by Sultan Suleiman the Magnificent....
the Hungarian people were disillusioned by the ability of the government to protect them and turned to the faith which would infuse them with the strength necessary to resist the Turkish invaders. They found this in the teaching of the Protestant Reformers such as Martin Luther
Martin Luther
Martin Luther was a German priest, professor of theology and iconic figure of the Protestant Reformation. He strongly disputed the claim that freedom from God's punishment for sin could be purchased with money. He confronted indulgence salesman Johann Tetzel with his Ninety-Five Theses in 1517...
. The spread of Protestantism in the country was aided by its large ethnic German minority, which could understand and translate the writings of Martin Luther
Martin Luther (resources)
-Wittenberg edition:Nineteen volumes published between 1539-1558. Twelve volumes of German and seven volumes of Latin works.*, 1558, Wittenberg, Thomam Klug-Jena edition:...
. While Lutheranism gained a foothold among the German-speaking population, Calvinism
Calvinism
Calvinism is a Protestant theological system and an approach to the Christian life...
became widely accepted among ethnic Hungarians.
In the more independent northwest the rulers and priests, protected now by the Habsburg Monarchy
Habsburg Monarchy
The Habsburg Monarchy covered the territories ruled by the junior Austrian branch of the House of Habsburg , and then by the successor House of Habsburg-Lorraine , between 1526 and 1867/1918. The Imperial capital was Vienna, except from 1583 to 1611, when it was moved to Prague...
which had taken the field to fight the Turks, defended the old Catholic faith. They dragged the Protestants to prison and the stake wherever they could. Such strong measures only fanned the flames of protest, however. Leaders of the Protestants included Matthias Biro Devai, Michael Sztarai, and Stephen Kis Szegedi.
Protestants likely formed a majority of Hungary's population at the close of the sixteenth century, but Counter-Reformation
Counter-Reformation
The Counter-Reformation was the period of Catholic revival beginning with the Council of Trent and ending at the close of the Thirty Years' War, 1648 as a response to the Protestant Reformation.The Counter-Reformation was a comprehensive effort, composed of four major elements:#Ecclesiastical or...
efforts in the seventeenth century reconverted a majority of the kingdom to Catholicism. A significant Protestant minority remained, most of it adhering to the Calvinist faith.
In 1558 the Transylvania
Transylvania
Transylvania is a historical region in the central part of Romania. Bounded on the east and south by the Carpathian mountain range, historical Transylvania extended in the west to the Apuseni Mountains; however, the term sometimes encompasses not only Transylvania proper, but also the historical...
n Diet
Diet (assembly)
In politics, a diet is a formal deliberative assembly. The term is mainly used historically for the Imperial Diet, the general assembly of the Imperial Estates of the Holy Roman Empire, and for the legislative bodies of certain countries.-Etymology:...
of Turda
Turda
Turda is a city and Municipality in Cluj County, Romania, situated on the Arieş River.- Ancient times :The city was founded by Dacians under the name Patavissa or Potaissa...
declared free practice of both the Catholic
Roman Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the world's largest Christian church, with over a billion members. Led by the Pope, it defines its mission as spreading the gospel of Jesus Christ, administering the sacraments and exercising charity...
and Lutheran
Lutheranism
Lutheranism is a major branch of Western Christianity that identifies with the theology of Martin Luther, a German reformer. Luther's efforts to reform the theology and practice of the church launched the Protestant Reformation...
religions, but prohibited Calvinism
Calvinism
Calvinism is a Protestant theological system and an approach to the Christian life...
. Ten years later, in 1568, the Diet extended this freedom, declaring that "It is not allowed to anybody to intimidate anybody with captivity or expelling for his religion". Four religions were declared as accepted (recepta) religions, while Orthodox Christianity
Orthodox Christianity
The term Orthodox Christianity may refer to:* the Eastern Orthodox Church and its various geographical subdivisions...
was "tolerated" (though the building of stone Orthodox churches was forbidden).
Hungary entered the Thirty Years' War
Thirty Years' War
The Thirty Years' War was fought primarily in what is now Germany, and at various points involved most countries in Europe. It was one of the most destructive conflicts in European history....
, Royal (Habsburg) Hungary joined the catholic side, until Transylvania joined the Protestant side.
There were a series of other successful and unsuccessful anti-Habsburg /i.e. anti-Austrian/ (requiring equal rights and freedom for all Christian religions) uprisings between 1604 and 1711, the uprisings were usually organized from Transylvania. The constrained Habsburg Counter-Reformation efforts in the seventeenth century reconverted the majority of the kingdom to Catholicism.
The Great Awakenings
The "Great Awakenings" were periods of rapid and dramatic religious revivalReligious revival
Religious revival may refer to:* Christian Revivalism* Revival meeting* Islamic revival...
in Anglo-American religious history, generally recognized as beginning in the 1730s. They have also been described as periodic revolutions in colonial religious thought
Christianity in the United States
Christianity is the largest and most popular religion in the United States, with around 77% of those polled identifying themselves as Christian, as of 2009. This is down from 86% in 1990, and slightly lower than 78.6% in 2001. About 62% of those polled claim to be members of a church congregation...
.
First Great Awakening
The "First Great Awakening" (or sometimes "The Great Awakening") was a wave of religious enthusiasm among Protestants that swept the American colonies in the 1730s and 1740s, leaving a permanent impact on American religion. It emphasising the traditional Reformed virtues of Godly preaching, rudimentary liturgy, and a deep sense of personal guilt and redemption by Christ Jesus. It resulted from powerful preaching that deeply affected listeners (already church members) with a deep sense of personal guilt and salvation by Christ. Pulling away from ritual and ceremony, the Great Awakening made religion intensely personal to the average person by creating a deep sense of spiritual guilt and redemption. Historian Sydney E. Ahlstrom saw it as part of a "great international Protestant upheaval" that also created PietismPietism
Pietism was a movement within Lutheranism, lasting from the late 17th century to the mid-18th century and later. It proved to be very influential throughout Protestantism and Anabaptism, inspiring not only Anglican priest John Wesley to begin the Methodist movement, but also Alexander Mack to...
in Germany
Germany
Germany , officially the Federal Republic of Germany , is a federal parliamentary republic in Europe. The country consists of 16 states while the capital and largest city is Berlin. Germany covers an area of 357,021 km2 and has a largely temperate seasonal climate...
, the Evangelical Revival
Evangelicalism
Evangelicalism is a Protestant Christian movement which began in Great Britain in the 1730s and gained popularity in the United States during the series of Great Awakenings of the 18th and 19th century.Its key commitments are:...
, and Methodism
Methodism
Methodism is a movement of Protestant Christianity represented by a number of denominations and organizations, claiming a total of approximately seventy million adherents worldwide. The movement traces its roots to John Wesley's evangelistic revival movement within Anglicanism. His younger brother...
in England
England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Scotland to the north and Wales to the west; the Irish Sea is to the north west, the Celtic Sea to the south west, with the North Sea to the east and the English Channel to the south separating it from continental...
. It had a major impact in reshaping the Congregational
Congregational church
Congregational churches are Protestant Christian churches practicing Congregationalist church governance, in which each congregation independently and autonomously runs its own affairs....
, Presbyterian
Presbyterianism
Presbyterianism refers to a number of Christian churches adhering to the Calvinist theological tradition within Protestantism, which are organized according to a characteristic Presbyterian polity. Presbyterian theology typically emphasizes the sovereignty of God, the authority of the Scriptures,...
, Dutch Reformed
Dutch Reformed Church
The Dutch Reformed Church was a Reformed Christian denomination in the Netherlands. It existed from the 1570s to 2004, the year it merged with the Reformed Churches in the Netherlands and the Evangelical Lutheran Church in the Kingdom of the Netherlands to form the Protestant Church in the...
, and German Reformed denominations, and strengthened the small Baptist
Baptist
Baptists comprise a group of Christian denominations and churches that subscribe to a doctrine that baptism should be performed only for professing believers , and that it must be done by immersion...
and Methodist
Methodism
Methodism is a movement of Protestant Christianity represented by a number of denominations and organizations, claiming a total of approximately seventy million adherents worldwide. The movement traces its roots to John Wesley's evangelistic revival movement within Anglicanism. His younger brother...
denominations. It brought Christianity to the slaves and was an apocalyptic event in New England
New England
New England is a region in the northeastern corner of the United States consisting of the six states of Maine, New Hampshire, Vermont, Massachusetts, Rhode Island, and Connecticut...
that challenged established authority. It incited rancor and division between the old traditionalists who insisted on ritual and doctrine and the new revivalists. It had little impact on Anglicans
Anglicanism
Anglicanism is a tradition within Christianity comprising churches with historical connections to the Church of England or similar beliefs, worship and church structures. The word Anglican originates in ecclesia anglicana, a medieval Latin phrase dating to at least 1246 that means the English...
and Quakers
Religious Society of Friends
The Religious Society of Friends, or Friends Church, is a Christian movement which stresses the doctrine of the priesthood of all believers. Members are known as Friends, or popularly as Quakers. It is made of independent organisations, which have split from one another due to doctrinal differences...
.
Unlike the Second Great Awakening
Second Great Awakening
The Second Great Awakening was a Christian revival movement during the early 19th century in the United States. The movement began around 1800, had begun to gain momentum by 1820, and was in decline by 1870. The Second Great Awakening expressed Arminian theology, by which every person could be...
that began about 1800 and which reached out to the unchurched, the First Great Awakening focused on people who were already church members. It changed their rituals, their piety, and their self awareness. The new style of sermons and the way people practiced their faith breathed new life into religion in America
Religion in the United States
Religion in the United States is characterized by both a wide diversity in religious beliefs and practices, and by a high adherence level. According to recent surveys, 83 percent of Americans claim to belong to a religious denomination, 40 percent claim to attend services nearly every week or...
. People became passionately and emotionally involved in their religion, rather than passively listening to intellectual discourse in a detached manner. Ministers who used this new style of preaching were generally called "new lights", while the preachers of old were called "old lights". People began to study the Bible at home, which effectively decentralized the means of informing the public on religious manners and was akin to the individualistic trends present in Europe during the Protestant Reformation
Protestant Reformation
The Protestant Reformation was a 16th-century split within Western Christianity initiated by Martin Luther, John Calvin and other early Protestants. The efforts of the self-described "reformers", who objected to the doctrines, rituals and ecclesiastical structure of the Roman Catholic Church, led...
.
Second Great Awakening
The "Second Great Awakening" (1790-1840s) was the second great religious revival in United StatesUnited States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
history and, unlike the First Great Awakening
First Great Awakening
The First Awakening was a Christian revitalization movement that swept Protestant Europe and British America, and especially the American colonies in the 1730s and 1740s, leaving a permanent impact on American religion. It resulted from powerful preaching that gave listeners a sense of personal...
of the 18th century
Christianity in the 18th century
-Revivalism:Revivalism refers to the Calvinist and Wesleyan revival, called the Great Awakening, in North America which saw the development of evangelical Congregationalist, Presbyterian, Baptist, and new Methodist churches....
, focused on the unchurched and sought to instil in them a deep sense of personal salvation as experienced in revival meeting
Revival meeting
A revival meeting is a series of Christian religious services held in order to inspire active members of a church body, to raise funds and to gain new converts...
s. It also sparked the beginnings of groups such as the Mormons
Mormons
The Mormons are a religious and cultural group related to Mormonism, a religion started by Joseph Smith during the American Second Great Awakening. A vast majority of Mormons are members of The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints while a minority are members of other independent churches....
and the Holiness movement
Holiness movement
The holiness movement refers to a set of beliefs and practices emerging from the Methodist Christian church in the mid 19th century. The movement is distinguished by its emphasis on John Wesley's doctrine of "Christian perfection" - the belief that it is possible to live free of voluntary sin - and...
. Leaders included Charles Grandison Finney
Charles Grandison Finney
Charles Grandison Finney was a leader in the Second Great Awakening. He has been called The Father of Modern Revivalism. Finney was best known as an innovative revivalist, an opponent of Old School Presbyterian theology, an advocate of Christian perfectionism, a pioneer in social reforms in favor...
, Lyman Beecher
Lyman Beecher
Lyman Beecher was a Presbyterian minister, American Temperance Society co-founder and leader, and the father of 13 children, many of whom were noted leaders, including Harriet Beecher Stowe, Henry Ward Beecher, Charles Beecher, Edward Beecher, Isabella Beecher Hooker, Catharine Beecher, and Thomas...
, Barton W. Stone
Barton W. Stone
Barton Warren Stone was an important preacher during the Second Great Awakening of the early 19th century. He was first ordained a Presbyterian minister, then was expelled from the church after the Cane Ridge, Kentucky revival for his stated beliefs in faith as the sole prerequisite for salvation...
, Peter Cartwright
Peter Cartwright (exhorter)
Peter Cartwright was an American Methodist revivalist and politician in Illinois. Born in Amherst County, Virginia, Cartwright was a missionary who helped start the Second Great Awakening and personally baptized twelve thousand converts. He settled in Illinois. He lost against Abraham Lincoln...
and James Finley
James Finley (minister)
James Finley was an American Presbyterian minister and politician who was a pioneer resident of western Pennsylvania...
.
In New England
New England
New England is a region in the northeastern corner of the United States consisting of the six states of Maine, New Hampshire, Vermont, Massachusetts, Rhode Island, and Connecticut...
, the renewed interest in religion inspired a wave of social activism. In western New York
New York
New York is a state in the Northeastern region of the United States. It is the nation's third most populous state. New York is bordered by New Jersey and Pennsylvania to the south, and by Connecticut, Massachusetts and Vermont to the east...
, the spirit of revival encouraged the emergence of the Restoration Movement
Restoration Movement
The Restoration Movement is a Christian movement that began on the American frontier during the Second Great Awakening of the early 19th century...
, the Latter Day Saint movement
Latter Day Saint movement
The Latter Day Saint movement is a group of independent churches tracing their origin to a Christian primitivist movement founded by Joseph Smith, Jr. in the late 1820s. Collectively, these churches have over 14 million members...
, Adventism and the Holiness movement
Holiness movement
The holiness movement refers to a set of beliefs and practices emerging from the Methodist Christian church in the mid 19th century. The movement is distinguished by its emphasis on John Wesley's doctrine of "Christian perfection" - the belief that it is possible to live free of voluntary sin - and...
. In the west especially—at Cane Ridge, Kentucky
Cane Ridge, Kentucky
Cane Ridge, Kentucky, USA was the site, in 1801, of a large camp meeting that drew thousands of people and had a lasting influence as one of the landmark events of the Second Great Awakening. Methodists, Baptists and Presbyterians all participated, and many of the "spiritual exercises", such as...
and in Tennessee
Tennessee
Tennessee is a U.S. state located in the Southeastern United States. It has a population of 6,346,105, making it the nation's 17th-largest state by population, and covers , making it the 36th-largest by total land area...
—the revival strengthened the Methodists
Methodism
Methodism is a movement of Protestant Christianity represented by a number of denominations and organizations, claiming a total of approximately seventy million adherents worldwide. The movement traces its roots to John Wesley's evangelistic revival movement within Anglicanism. His younger brother...
and the Baptists and introduced into America a new form of religious expression—the Scottish camp meeting
Camp meeting
The camp meeting is a form of Protestant Christian religious service originating in Britain and once common in some parts of the United States, wherein people would travel from a large area to a particular site to camp out, listen to itinerant preachers, and pray...
.
The Second Great Awakening made its way across the frontier territories, fed by intense longing for a prominent place for God in the life of the new nation, a new liberal attitude toward fresh interpretations of the Bible, and a contagious experience of zeal for authentic spirituality. As these revivals spread, they gathered converts to Protestant sects of the time. However, the revivals eventually moved freely across denominational lines, with practically identical results, and went farther than ever toward breaking down the allegiances which kept adherents to these denominations loyal to their own. Consequently, the revivals were accompanied by a growing dissatisfaction with Evangelical churches and especially with the doctrine of Calvinism
Calvinism
Calvinism is a Protestant theological system and an approach to the Christian life...
, which was nominally accepted or at least tolerated in most Evangelical churches at the time. Various unaffiliated movements arose that were often restorationist in outlook, considering contemporary Christianity of the time to be a deviation from the true, original Christianity. These groups attempted to transcend Protestant denominationalism and orthodox Christian
Christianity
Christianity is a monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus as presented in canonical gospels and other New Testament writings...
creeds to restore Christianity to its original form.
Third Great Awakening
The "Third Great Awakening" was a period of religious activism in American history from the late 1850s to the 1900s. It affected pietistic Protestant denominations and had a strong sense of social activism. It gathered strength from the postmillennial theology that the Second ComingSecond Coming
In Christian doctrine, the Second Coming of Christ, the Second Advent, or the Parousia, is the anticipated return of Jesus Christ from Heaven, where he sits at the Right Hand of God, to Earth. This prophecy is found in the canonical gospels and in most Christian and Islamic eschatologies...
of Christ would come after mankind had reformed the entire earth. The Social Gospel
Social Gospel
The Social Gospel movement is a Protestant Christian intellectual movement that was most prominent in the early 20th century United States and Canada...
Movement gained its force from the Awakening, as did the worldwide missionary movement. New groupings emerged, such as the Holiness movement
Holiness movement
The holiness movement refers to a set of beliefs and practices emerging from the Methodist Christian church in the mid 19th century. The movement is distinguished by its emphasis on John Wesley's doctrine of "Christian perfection" - the belief that it is possible to live free of voluntary sin - and...
and Nazarene
Church of the Nazarene
The Church of the Nazarene is an evangelical Christian denomination that emerged from the 19th century Holiness movement in North America with its members colloquially referred to as Nazarenes. It is the largest Wesleyan-holiness denomination in the world. At the end of 2010, the Church of the...
movements, and Christian Science
Christian Science
Christian Science is a system of thought and practice derived from the writings of Mary Baker Eddy and the Bible. It is practiced by members of The First Church of Christ, Scientist as well as some others who are nonmembers. Its central texts are the Bible and the Christian Science textbook,...
. Significant names include Dwight L. Moody
Dwight L. Moody
Dwight Lyman Moody , also known as D.L. Moody, was an American evangelist and publisher who founded the Moody Church, Northfield School and Mount Hermon School in Massachusetts , the Moody Bible Institute and Moody Publishers.-Early life:Dwight Moody was born in Northfield, Massachusetts to a large...
, Ira D. Sankey
Ira D. Sankey
Ira D. Sankey , known as The Sweet Singer of Methodism, was an American gospel singer and composer, associated with evangelist Dwight L...
, William Booth
William Booth
William Booth was a British Methodist preacher who founded The Salvation Army and became its first General...
and Catherine Booth (founders of the Salvation Army
Salvation Army
The Salvation Army is a Protestant Christian church known for its thrift stores and charity work. It is an international movement that currently works in over a hundred countries....
), Charles Spurgeon
Charles Spurgeon
Charles Haddon Spurgeon was a large British Particular Baptist preacher who remains highly influential among Christians of different denominations, among whom he is still known as the "Prince of Preachers"...
and James Caughey. Hudson Taylor
Hudson Taylor
James Hudson Taylor , was a British Protestant Christian missionary to China, and founder of the China Inland Mission . Taylor spent 51 years in China...
began the China Inland Mission
China Inland Mission
OMF International is an interdenominational Protestant Christian missionary society, founded in Britain by Hudson Taylor on 25 June 1865.-Overview:...
and Thomas John Barnardo
Thomas John Barnardo
Thomas John Barnardo was a philanthropist and founder and director of homes for poor children, born in Dublin. From the foundation of the first Barnardo's home in 1870 to the date of Barnardo’s death, nearly 100,000 children had been rescued, trained and given a better life.- Early life :Barnardo...
founded his famous orphanages. The Keswick Convention
Keswick Convention
The Keswick Convention is an annual gathering of evangelical Christians in Keswick, in the English county of Cumbria.- History :The Keswick Convention began in 1875 as a catalyst and focal point for the emerging Higher Life movement in the United Kingdom. It was founded by an Anglican, Canon T. D....
movement began out of the British Holiness movement
Higher Life movement
The Higher Life movement was a movement devoted to Christian holiness in England. Its name comes from a book by William Boardman, entitled The Higher Christian Life, which was published in 1858...
, encouraging a lifestyle of holiness
Sacred
Holiness, or sanctity, is in general the state of being holy or sacred...
, unity and prayer.
Mary Baker Eddy
Mary Baker Eddy
Mary Baker Eddy was the founder of Christian Science , a Protestant American system of religious thought and practice religion adopted by the Church of Christ, Scientist, and others...
introduced Christian Science
Christian Science
Christian Science is a system of thought and practice derived from the writings of Mary Baker Eddy and the Bible. It is practiced by members of The First Church of Christ, Scientist as well as some others who are nonmembers. Its central texts are the Bible and the Christian Science textbook,...
, which gained a national following. In 1880, the Salvation Army
Salvation Army
The Salvation Army is a Protestant Christian church known for its thrift stores and charity work. It is an international movement that currently works in over a hundred countries....
denomination arrived in America. Although its theology was based on ideals expressed during the Second Great Awakening
Second Great Awakening
The Second Great Awakening was a Christian revival movement during the early 19th century in the United States. The movement began around 1800, had begun to gain momentum by 1820, and was in decline by 1870. The Second Great Awakening expressed Arminian theology, by which every person could be...
, its focus on poverty was of the Third. The Society for Ethical Culture was established in New York
New York
New York is a state in the Northeastern region of the United States. It is the nation's third most populous state. New York is bordered by New Jersey and Pennsylvania to the south, and by Connecticut, Massachusetts and Vermont to the east...
in 1876 by Felix Adler attracted a Reform Jewish clientele. Charles Taze Russell
Charles Taze Russell
Charles Taze Russell , or Pastor Russell, was a prominent early 20th century Christian restorationist minister from Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, USA, and founder of what is now known as the Bible Student movement, from which Jehovah's Witnesses and numerous independent Bible Student groups emerged...
Founded a Bible Student Institute now known as The Jehovah's Witnesses
Jehovah's Witnesses
Jehovah's Witnesses is a millenarian restorationist Christian denomination with nontrinitarian beliefs distinct from mainstream Christianity. The religion reports worldwide membership of over 7 million adherents involved in evangelism, convention attendance of over 12 million, and annual...
With Jane Addams
Jane Addams
Jane Addams was a pioneer settlement worker, founder of Hull House in Chicago, public philosopher, sociologist, author, and leader in woman suffrage and world peace...
's Hull House
Hull House
Hull House is a settlement house in the United States that was co-founded in 1889 by Jane Addams and Ellen Gates Starr. Located in the Near West Side of , Hull House opened its doors to the recently arrived European immigrants. By 1911, Hull House had grown to 13 buildings. In 1912 the Hull...
in Chicago as its center, the settlement house movement and the vocation of social work were deeply influenced by the Tolstoy
Tolstoy
Tolstoy, or Tolstoi is a prominent family of Russian nobility, descending from Andrey Kharitonovich Tolstoy who served under Vasily II of Moscow...
an reworking of Christian idealism. The final group to emerge from this awakening in North America was Pentecostalism
Pentecostalism
Pentecostalism is a diverse and complex movement within Christianity that places special emphasis on a direct personal experience of God through the baptism in the Holy Spirit, has an eschatological focus, and is an experiential religion. The term Pentecostal is derived from Pentecost, the Greek...
, which had its roots in the Methodist, Wesleyan, and Holiness movement
Holiness movement
The holiness movement refers to a set of beliefs and practices emerging from the Methodist Christian church in the mid 19th century. The movement is distinguished by its emphasis on John Wesley's doctrine of "Christian perfection" - the belief that it is possible to live free of voluntary sin - and...
s, and began in 1906 on Azusa Street
Azusa Street Revival
The Azusa Street Revival was a historic Pentecostal revival meeting that took place in Los Angeles, California and is the origin of the Pentecostal movement. It was led by William J. Seymour, an African American preacher. It began with a meeting on April 14, 1906, and continued until roughly 1915...
, in Los Angeles
Los Ángeles
Los Ángeles is the capital of the province of Biobío, in the commune of the same name, in Region VIII , in the center-south of Chile. It is located between the Laja and Biobío rivers. The population is 123,445 inhabitants...
. Pentecostalism would later lead to the Charismatic movement
Charismatic movement
The term charismatic movement is used in varying senses to describe 20th century developments in various Christian denominations. It describes an ongoing international, cross-denominational/non-denominational Christian movement in which individual, historically mainstream congregations adopt...
.
Anti-clericalism and atheistic communism
In many revolutionary movements the church was associated with the established repressive regimes. Thus, for example, after the French RevolutionFrench Revolution
The French Revolution , sometimes distinguished as the 'Great French Revolution' , was a period of radical social and political upheaval in France and Europe. The absolute monarchy that had ruled France for centuries collapsed in three years...
and the Mexican Revolution
Mexican Revolution
The Mexican Revolution was a major armed struggle that started in 1910, with an uprising led by Francisco I. Madero against longtime autocrat Porfirio Díaz. The Revolution was characterized by several socialist, liberal, anarchist, populist, and agrarianist movements. Over time the Revolution...
there was a distinct anti-clerical
Anti-clericalism
Anti-clericalism is a historical movement that opposes religious institutional power and influence, real or alleged, in all aspects of public and political life, and the involvement of religion in the everyday life of the citizen...
tone in those countries that exists to this day. In some cases, opposition to the clergy turned into opposition to religion itself; thus, for example, Karl Marx
Karl Marx
Karl Heinrich Marx was a German philosopher, economist, sociologist, historian, journalist, and revolutionary socialist. His ideas played a significant role in the development of social science and the socialist political movement...
condemned religion as the "opium of the people
Opium of the People
"Religion is the opium of the people" is one of the most frequently paraphrased statements of Karl Marx. It was translated from the German original, "Die Religion .....
" http://www.baylor.edu/~Scott_Moore/texts/Marx_Opium.html as he considered it a false sense of hope in an afterlife withholding the people from facing their worldly situation. Based on a similar quote ("opium for the people"), Lenin believed religion was being used by ruling classes as tool of suppression of the people. The Marxist-Leninist
Marxism-Leninism
Marxism–Leninism is a communist ideology, officially based upon the theories of Marxism and Vladimir Lenin, that promotes the development and creation of a international communist society through the leadership of a vanguard party over a revolutionary socialist state that represents a dictatorship...
governments of the twentieth century were generally atheistic. All of them restricted the exercise of religion to a greater or lesser degree, but only Albania
Albania
Albania , officially known as the Republic of Albania , is a country in Southeastern Europe, in the Balkans region. It is bordered by Montenegro to the northwest, Kosovo to the northeast, the Republic of Macedonia to the east and Greece to the south and southeast. It has a coast on the Adriatic Sea...
actually banned religion and officially declared itself to be an atheistic state.
20th century
Protestant Christianity in the 20th century was characterized by accelerating fragmentation. The century saw the rise of both liberal and conservative splinter groups, as well as a general secularization of Western society. The Roman Catholic Church instituted many reforms in order to modernize. Missionaries also made inroads in the Far EastFar East
The Far East is an English term mostly describing East Asia and Southeast Asia, with South Asia sometimes also included for economic and cultural reasons.The term came into use in European geopolitical discourse in the 19th century,...
, establishing further followings in China
China
Chinese civilization may refer to:* China for more general discussion of the country.* Chinese culture* Greater China, the transnational community of ethnic Chinese.* History of China* Sinosphere, the area historically affected by Chinese culture...
, Taiwan
Taiwan
Taiwan , also known, especially in the past, as Formosa , is the largest island of the same-named island group of East Asia in the western Pacific Ocean and located off the southeastern coast of mainland China. The island forms over 99% of the current territory of the Republic of China following...
, and Japan
Japan
Japan is an island nation in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean, it lies to the east of the Sea of Japan, China, North Korea, South Korea and Russia, stretching from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea and Taiwan in the south...
. At the same time, state-promoted atheism in Communist Eastern Europe and the Soviet Union brought many Eastern Orthodox Christians to Western Europe and the United States, leading to greatly increased contact between Western and Eastern Christianity. Nevertheless, church attendance declined more in Western Europe than it did in the East. Christian ecumenism grew in importance, beginning at the Edinburgh Missionary Conference
Edinburgh Missionary Conference
The 1910 World Missionary Conference, or the Edinburgh Missionary Conference, was held June 14 to 23, 1910. Some have seen it as both the culmination of nineteenth-century Protestant Christian missions and the formal beginning of the modern Protestant Christian ecumenical movement.- Edinburgh 1910...
in 1910, and accelerated after the Second Vatican Council
Second Vatican Council
The Second Vatican Council addressed relations between the Roman Catholic Church and the modern world. It was the twenty-first Ecumenical Council of the Catholic Church and the second to be held at St. Peter's Basilica in the Vatican. It opened under Pope John XXIII on 11 October 1962 and closed...
(1962–1965) of the Catholic Church, The Liturgical Movement
Liturgical Movement
The Liturgical Movement began as a movement of scholarship for the reform of worship within the Roman Catholic Church. It has grown over the last century and a half and has affected many other Christian Churches, including the Church of England and other Churches of the Anglican Communion, and some...
became significant in both Catholic and Protestant Christianity, especially in Anglicanism
Anglicanism
Anglicanism is a tradition within Christianity comprising churches with historical connections to the Church of England or similar beliefs, worship and church structures. The word Anglican originates in ecclesia anglicana, a medieval Latin phrase dating to at least 1246 that means the English...
.
Another movement which has grown up over the 20th century has been Christian anarchism
Christian anarchism
Christian anarchism is a movement in political theology that combines anarchism and Christianity. It is the belief that there is only one source of authority to which Christians are ultimately answerable, the authority of God as embodied in the teachings of Jesus...
which rejects the church, state or any power other than God. They usually also believe in absolute nonviolence
Nonviolence
Nonviolence has two meanings. It can refer, first, to a general philosophy of abstention from violence because of moral or religious principle It can refer to the behaviour of people using nonviolent action Nonviolence has two (closely related) meanings. (1) It can refer, first, to a general...
. Leo Tolstoy
Leo Tolstoy
Lev Nikolayevich Tolstoy was a Russian writer who primarily wrote novels and short stories. Later in life, he also wrote plays and essays. His two most famous works, the novels War and Peace and Anna Karenina, are acknowledged as two of the greatest novels of all time and a pinnacle of realist...
's book The Kingdom of God is Within You
The Kingdom of God Is Within You
The Kingdom of God Is Within You is the non-fiction magnum opus of Leo Tolstoy and was first published in Germany in 1894, after being banned in his home country of Russia...
published in 1894, is believed to be the catalyst for this movement. Because of its extremist political views, however, its appeal has been largely limited to the highly educated, especially those with erstwhile humanist
Humanism
Humanism is an approach in study, philosophy, world view or practice that focuses on human values and concerns. In philosophy and social science, humanism is a perspective which affirms some notion of human nature, and is contrasted with anti-humanism....
sentiments; the thoroughgoing aversion to institutionalism on Christian anarchists' part has also hindered acceptance of this philosophy on a large scale.
The 1950s saw a boom in the Evangelical church in America. The post–World War II prosperity experienced in the U.S. also had its effects on the church. Although simplistically referred to as "morphological fundamentalism", the phrase nonetheless does accurately describe the physical developments experienced. Church buildings were erected in large numbers, and the Evangelical church's activities grew along with this expansive physical growth.
Pentecostal movement
Another noteworthy development in 20th-century Christianity was the rise of the modern Pentecostal movement. Although its roots predate the year 1900, its actual birth is commonly attributed to the 20th century. Sprung from Methodist and Wesleyan roots, it arose out of the meetings at an urban mission on Azusa Street in Los Angeles. From there it spread around the world, carried by those who experienced what they believed to be miraculous moves of God there. These Pentecost-like manifestations have steadily been in evidence throughout the history of Christianity—such as seen in the two Great Awakenings that started in the United States. However, Azusa Street is widely accepted as the fount of the modern Pentecostal movement. Pentecostalism, which in turn birthed the Charismatic movementCharismatic movement
The term charismatic movement is used in varying senses to describe 20th century developments in various Christian denominations. It describes an ongoing international, cross-denominational/non-denominational Christian movement in which individual, historically mainstream congregations adopt...
within already established denominations, continues to be an important force in western Christianity.
Modernism, fundamentalism, and neo-orthodoxy
As the more radical implications of the scientific and cultural influences of the EnlightenmentAge of Enlightenment
The Age of Enlightenment was an elite cultural movement of intellectuals in 18th century Europe that sought to mobilize the power of reason in order to reform society and advance knowledge. It promoted intellectual interchange and opposed intolerance and abuses in church and state...
began to be felt in the Protestant churches, especially in the 19th century, Liberal Christianity
Liberal Christianity
Liberal Christianity, sometimes called liberal theology, is an umbrella term covering diverse, philosophically and biblically informed religious movements and ideas within Christianity from the late 18th century and onward...
, exemplified especially by numerous theologians in Germany
Germany
Germany , officially the Federal Republic of Germany , is a federal parliamentary republic in Europe. The country consists of 16 states while the capital and largest city is Berlin. Germany covers an area of 357,021 km2 and has a largely temperate seasonal climate...
in the 19th century, sought to bring the churches alongside of the broad revolution that Modernism represented. In doing so, new critical approaches to the Bible were developed, new attitudes became evident about the role of religion in society, and a new openness to questioning the nearly universally accepted definitions of Christian orthodoxy began to become obvious.
In reaction to these developments, Christian fundamentalism was a movement to reject the radical influences of philosophical humanism, as this was affecting the Christian religion. Especially targeting critical approaches to the interpretation of the Bible, and trying to blockade the inroads made into their churches by atheistic scientific assumptions, the fundamentalists began to appear in various denominations as numerous independent movements of resistance to the drift away from historic Christianity. Over time, the Fundamentalist Evangelical movement has divided into two main wings, with the label Fundamentalist following one branch, while Evangelical has become the preferred banner of the more moderate movement. Although both movements primarily originated in the English speaking world, the majority of Evangelicals now live elsewhere in the world.
A third, but less popular, option than either liberalism or fundamentalism was the neo-orthodox movement, which generally affirmed a higher view of Scripture than liberalism but did not tie the main doctrines of the Christian faith to precise theories of Biblical inspiration. If anything, thinkers in this camp denounced such quibbling between liberals and conservatives as a dangerous distraction from the duties of Christian discipleship. This branch of thought arose in the early 20th century in the context of the rise of the Third Reich in Germany and the accompanying political and ecclesiastical destabilization of Europe in the years before and during World War II
World War II
World War II, or the Second World War , was a global conflict lasting from 1939 to 1945, involving most of the world's nations—including all of the great powers—eventually forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis...
. Neo-orthodoxy's highly contextual, dialectical modes of argument and reasoning often rendered its main premises incomprehensible to American thinkers and clergy, and it was frequently either dismissed out of hand as unrealistic or cast into the reigning left- or right-wing molds of theologizing. Karl Barth
Karl Barth
Karl Barth was a Swiss Reformed theologian whom critics hold to be among the most important Christian thinkers of the 20th century; Pope Pius XII described him as the most important theologian since Thomas Aquinas...
, a Swiss
Switzerland
Switzerland name of one of the Swiss cantons. ; ; ; or ), in its full name the Swiss Confederation , is a federal republic consisting of 26 cantons, with Bern as the seat of the federal authorities. The country is situated in Western Europe,Or Central Europe depending on the definition....
Reformed pastor and professor, brought this movement into being by drawing upon earlier criticisms of established (largely modernist) Protestant thought made by the likes of Søren Kierkegaard
Søren Kierkegaard
Søren Aabye Kierkegaard was a Danish Christian philosopher, theologian and religious author. He was a critic of idealist intellectuals and philosophers of his time, such as Georg Wilhelm Friedrich Hegel, Friedrich Wilhelm Joseph Schelling and Karl Wilhelm Friedrich Schlegel...
and Franz Overbeck
Franz Overbeck
Franz Camille Overbeck was a German Protestant theologian. In Anglo-American discourse, he is perhaps best known in regard to his friendship with Friedrich Nietzsche; while in German theological circles, Overbeck remains discussed for his own contributions.- Youth :Franz Overbeck was born in Saint...
; Dietrich Bonhoeffer
Dietrich Bonhoeffer
Dietrich Bonhoeffer was a German Lutheran pastor, theologian and martyr. He was a participant in the German resistance movement against Nazism and a founding member of the Confessing Church. He was involved in plans by members of the Abwehr to assassinate Adolf Hitler...
, murdered by the Nazis for allegedly taking part in an attempt to overthrow the Hitler
Adolf Hitler
Adolf Hitler was an Austrian-born German politician and the leader of the National Socialist German Workers Party , commonly referred to as the Nazi Party). He was Chancellor of Germany from 1933 to 1945, and head of state from 1934 to 1945...
regime, adhered to this school of thought; his classic The Cost of Discipleship
The Cost of Discipleship
The Cost of Discipleship is a book by the German Theologian Dietrich Bonhoeffer, considered a classic of Christian thought. The original German title is simply . It is centred around an exposition of the Sermon on the Mount, in which Bonhoeffer spells out what he believes it means to follow Christ...
is likely the best-known and accessible statement of the neo-orthodox position.
Evangelicalism
In the U.S. and elsewhere in the world, there has been a marked rise in the evangelicalEvangelicalism
Evangelicalism is a Protestant Christian movement which began in Great Britain in the 1730s and gained popularity in the United States during the series of Great Awakenings of the 18th and 19th century.Its key commitments are:...
wing of Protestant denominations, especially those that are more exclusively evangelical, and a corresponding decline in the mainstream liberal churches. In the post–World War I era, Liberalism
Liberal Christianity
Liberal Christianity, sometimes called liberal theology, is an umbrella term covering diverse, philosophically and biblically informed religious movements and ideas within Christianity from the late 18th century and onward...
was the faster growing sector of the American church. Liberal wings of denominations were on the rise, and a considerable number of seminaries held and taught from a liberal perspective as well. In the post–World war II era, the trend began to swing back towards the conservative camp in America's seminaries and church structures. Those entering seminaries and other postgraduate theologically related programs have shown more conservative leanings than their average predecessors.
The neo-Evangelical push of the 1940s and 1950s produced a movement that continues to have wide influence. In the southern U.S., the more moderate neo-Evangelicals, represented by leaders such as Billy Graham
Billy Graham
William Franklin "Billy" Graham, Jr. is an American evangelical Christian evangelist. As of April 25, 2010, when he met with Barack Obama, Graham has spent personal time with twelve United States Presidents dating back to Harry S. Truman, and is number seven on Gallup's list of admired people for...
, have experienced a notable surge displacing the caricature of the pulpit pounding country preachers of fundamentalism. The stereotypes have gradually shifted. Some, such as Jerry Falwell
Jerry Falwell
Jerry Lamon Falwell, Sr. was an evangelical fundamentalist Southern Baptist pastor, televangelist, and a conservative commentator from the United States. He was the founding pastor of the Thomas Road Baptist Church, a megachurch in Lynchburg, Virginia...
, have managed to maintain credibility in the eyes of many fundamentalists, as well as to gain stature as a more moderate Evangelical.
Evangelicalism is not a single, monolithic entity. The Evangelical churches and their adherents cannot be easily stereotyped. Most are not fundamentalist, in the narrow sense that this term has come to represent; though many still refer to themselves as such. There have always been diverse views on issues, such as openness to cooperation with non-Evangelicals, the applicability of the Bible to political choices and social or scientific issues, and even the limited inerrancy of the Bible.
However, the movement has managed in an informal way, to reserve the name Evangelical for those who adhere to an historic Christian faith, a paleo-orthodoxy, as some have put it. Those who call themselves "moderate evangelicals"(although considered conservative in relation to society as a whole) still hold fast to the fundamentals of the historic Christian faith. Even "Liberal" Evangelicals label themselves as such not so much in terms of their theology, but rather to advertise that they are progressive in their civic, social, or scientific perspective.
There is some debate as to whether Pentecostals are considered to be Evangelical. Their roots in Pietism
Pietism
Pietism was a movement within Lutheranism, lasting from the late 17th century to the mid-18th century and later. It proved to be very influential throughout Protestantism and Anabaptism, inspiring not only Anglican priest John Wesley to begin the Methodist movement, but also Alexander Mack to...
and the Holiness movement
Holiness movement
The holiness movement refers to a set of beliefs and practices emerging from the Methodist Christian church in the mid 19th century. The movement is distinguished by its emphasis on John Wesley's doctrine of "Christian perfection" - the belief that it is possible to live free of voluntary sin - and...
are undisputedly Evangelical, but their doctrinal distinctives differ from the more traditional Evangelicals, who are less likely to have an expectation of private revelations from God, and differ from the Pentecostal perspective on miracle
Miracle
A miracle often denotes an event attributed to divine intervention. Alternatively, it may be an event attributed to a miracle worker, saint, or religious leader. A miracle is sometimes thought of as a perceptible interruption of the laws of nature. Others suggest that a god may work with the laws...
s, angels, and demons. Typically, those who include the Pentecostals in the Evangelical camp are labeled neo-evangelical by those who do not. The National Association of Evangelicals
National Association of Evangelicals
The National Association of Evangelicals is a fellowship of member denominations, churches, organizations, and individuals. Its goal is to honor God by connecting and representing evangelicals in the United States. Today it works in four main areas: Church & Faith Partners, Government Relations,...
and the Evangelical Alliance
Evangelical Alliance
The Evangelical Alliance is a London-based charitable organization founded in 1846. It has a claimed representation of over 1,000,000 evangelical Christians in the United Kingdom and is the oldest alliance of evangelical Christians in the world....
have numerous Trinitarian Pentecostal denominations among their membership. Another relatively late entrant to wide acceptance within the Evangelical fold is the Seventh-day Adventist Church
Seventh-day Adventist Church
The Seventh-day Adventist Church is a Protestant Christian denomination distinguished by its observance of Saturday, the original seventh day of the Judeo-Christian week, as the Sabbath, and by its emphasis on the imminent second coming of Jesus Christ...
.
Evangelicals are as diverse as the names that appear—Billy Graham, Chuck Colson, J. Vernon McGee, Benny Hinn
Benny Hinn
Toufik Benedictus "Benny" Hinn הין; born December 3, 1952) is a televangelist, best known for his regular "Miracle Crusades" – revival meeting/faith healing summits that are usually held in large stadiums in major cities, which are later broadcast worldwide on his television program, This Is Your...
, J.I. Packer, John R.W. Stott
John Stott
John Robert Walmsley Stott CBE was an English Christian leader and Anglican cleric who was noted as a leader of the worldwide Evangelical movement. He was one of the principal authors of the Lausanne Covenant in 1974...
, Pat Robertson
Pat Robertson
Marion Gordon "Pat" Robertson is a media mogul, television evangelist, ex-Baptist minister and businessman who is politically aligned with the Christian Right in the United States....
, Jimmy Carter
Jimmy Carter
James Earl "Jimmy" Carter, Jr. is an American politician who served as the 39th President of the United States and was the recipient of the 2002 Nobel Peace Prize, the only U.S. President to have received the Prize after leaving office...
, etc.—or even Evangelical institutions such as Dallas Theological Seminary (dispensationalist), Gordon-Conwell Theological Seminary (Boston), Trinity Evangelical Divinity School
Trinity Evangelical Divinity School
Trinity Evangelical Divinity School is an evangelical Christian seminary located in Deerfield, Illinois. TEDS is one of the largest seminaries in the world, enrolling more than 1,200 graduate students in professional and academic programs, including more than 150 in its PhD programs...
(Chicago), Wheaton College (Illinois), the Christian Coalition, The Christian Embassy (Jerusalem), etc. Although there exists a diversity in the Evangelical community worldwide, the ties that bind all Evangelicals are still apparent. These include but are not limited to a high view of Scripture, belief in the Deity of Christ, the Trinity, salvation by grace alone through faith alone, and the bodily resurrection of Christ.
10/40 Window
Evangelicals defined and prioritized efforts to reach the "unreached" in the late 20th and early 21st centuries by focusing on countries located between 10 degrees10th parallel north
The 10th parallel north is a circle of latitude that is 10 degrees north of the Earth's equatorial plane. It crosses Africa, the Indian Ocean, South Asia, Southeast Asia, the Pacific Ocean, Central America, South America and the Atlantic Ocean....
and 40 degrees North
40th parallel north
The 40th parallel north is a circle of latitude that is 40 degrees north of the Earth's equatorial plane. It crosses Europe, the Mediterranean Sea, Asia, the Pacific Ocean, North America, and the Atlantic Ocean....
of the equator and stretching from North Africa across to China. This area is mostly dominated by Muslim nations, many who do not allow missionaries of other religions to enter their countries.
Spread of secularism
EuropeIn Europe
Europe
Europe is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting...
there has been a general move away from religious observance and belief in Christian teachings and a move towards secularism
Secularism
Secularism is the principle of separation between government institutions and the persons mandated to represent the State from religious institutions and religious dignitaries...
. The "secularization of society", attributed to the time of the Enlightenment
Age of Enlightenment
The Age of Enlightenment was an elite cultural movement of intellectuals in 18th century Europe that sought to mobilize the power of reason in order to reform society and advance knowledge. It promoted intellectual interchange and opposed intolerance and abuses in church and state...
and its following years, is largely responsible for the spread of secularism. For example the Gallup International Millennium Survey http://www.gallup-international.com/survey15.htm showed that only about one sixth of Europeans attend regular religious services, less than half gave God "high importance", and only about 40% believe in a "personal God". Nevertheless the large majority considered that they "belong" to a religious denomination
Religious denomination
A religious denomination is a subgroup within a religion that operates under a common name, tradition, and identity.The term describes various Christian denominations...
.
The Americas and Australia
In North America
North America
North America is a continent wholly within the Northern Hemisphere and almost wholly within the Western Hemisphere. It is also considered a northern subcontinent of the Americas...
, South America
South America
South America is a continent situated in the Western Hemisphere, mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere. The continent is also considered a subcontinent of the Americas. It is bordered on the west by the Pacific Ocean and on the north and east...
and Australia
Australia
Australia , officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country in the Southern Hemisphere comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands in the Indian and Pacific Oceans. It is the world's sixth-largest country by total area...
, the other three continents where Christianity is the dominant professed religion, religious observance is much higher than in Europe. At the same time, these regions are often seen by other nations as being uptight and "Victorian", in their social mores. In general, the United States leans toward the conservative in comparison to other western nations in its general culture, in part due to the Christian element found primarily in its Midwestern and southern states.
South America, historically Catholic, has experienced a large Evangelical and Pentecostal infusion in the 20th century due to the influx of Christian missionaries from abroad. For example: Brazil
Brazil
Brazil , officially the Federative Republic of Brazil , is the largest country in South America. It is the world's fifth largest country, both by geographical area and by population with over 192 million people...
, South America's largest country, is the largest Catholic country in the world, and at the same time is the largest Evangelical country in the world (based on population). Some of the largest Christian congregations in the world are found in Brazil.
Key dates
- 1516: Sir Thomas More publishes "UtopiaUtopiaUtopia is an ideal community or society possessing a perfect socio-politico-legal system. The word was imported from Greek by Sir Thomas More for his 1516 book Utopia, describing a fictional island in the Atlantic Ocean. The term has been used to describe both intentional communities that attempt...
" in Latin - October 31, 1517: Martin LutherMartin LutherMartin Luther was a German priest, professor of theology and iconic figure of the Protestant Reformation. He strongly disputed the claim that freedom from God's punishment for sin could be purchased with money. He confronted indulgence salesman Johann Tetzel with his Ninety-Five Theses in 1517...
posts his 95 Theses95 ThesesThe Ninety-Five Theses on the Power and Efficacy of Indulgences , commonly known as , was written by Martin Luther, 1517 and is widely regarded as the primary catalyst for the Protestant Reformation...
, protesting the sale of indulgences. - August 15, 1534: Saint Ignatius of Loyola and six others, including Francis XavierFrancis XavierFrancis Xavier, born Francisco de Jasso y Azpilicueta was a pioneering Roman Catholic missionary born in the Kingdom of Navarre and co-founder of the Society of Jesus. He was a student of Saint Ignatius of Loyola and one of the first seven Jesuits, dedicated at Montmartre in 1534...
met in Montmartre outside Paris to found the missionary Jesuit OrderSociety of JesusThe Society of Jesus is a Catholic male religious order that follows the teachings of the Catholic Church. The members are called Jesuits, and are also known colloquially as "God's Army" and as "The Company," these being references to founder Ignatius of Loyola's military background and a...
. - October 30, 1534: English Parliament passes Act of Supremacy making the King of England Supreme Head of the Church of England. Anglican schism with Rome.
- 1536 To 1540: Dissolution of the MonasteriesDissolution of the MonasteriesThe Dissolution of the Monasteries, sometimes referred to as the Suppression of the Monasteries, was the set of administrative and legal processes between 1536 and 1541 by which Henry VIII disbanded monasteries, priories, convents and friaries in England, Wales and Ireland; appropriated their...
in England, Wales and Ireland. - December 17, 1538: Pope Paul III excommunicates King Henry VIII of England.
- 1543: A full account of the heliocentric Copernican theory titled, On the Revolutions of the Heavenly Spheres (De Revolutionibus Orbium Coelestium) is published. Considered as the start of the Scientific RevolutionScientific revolutionThe Scientific Revolution is an era associated primarily with the 16th and 17th centuries during which new ideas and knowledge in physics, astronomy, biology, medicine and chemistry transformed medieval and ancient views of nature and laid the foundations for modern science...
. - December 13, 1545: Ecumenical Council of TrentCouncil of TrentThe Council of Trent was the 16th-century Ecumenical Council of the Roman Catholic Church. It is considered to be one of the Church's most important councils. It convened in Trent between December 13, 1545, and December 4, 1563 in twenty-five sessions for three periods...
convened during the pontificate of Paul III, to prepare the Catholic response to the Protestant ReformationProtestant ReformationThe Protestant Reformation was a 16th-century split within Western Christianity initiated by Martin Luther, John Calvin and other early Protestants. The efforts of the self-described "reformers", who objected to the doctrines, rituals and ecclesiastical structure of the Roman Catholic Church, led...
. Its rulings set the tone of Catholic society for at least three centuries. - 1568: St. John Chrysostom, St. Basil, St. Gregory of NazianzusGregory of NazianzusGregory of Nazianzus was a 4th-century Archbishop of Constantinople. He is widely considered the most accomplished rhetorical stylist of the patristic age...
, St. Athanasius and St. Thomas Aquinas are made Doctors of the ChurchDoctor of the ChurchDoctor of the Church is a title given by a variety of Christian churches to individuals whom they recognize as having been of particular importance, particularly regarding their contribution to theology or doctrine.-Catholic Church:In the Catholic Church, this name is given to a saint from whose...
. - July 14, 1570: Pope St. Pius V issues the Apostolic Constitution on the Tridentine MassTridentine MassThe Tridentine Mass is the form of the Roman Rite Mass contained in the typical editions of the Roman Missal that were published from 1570 to 1962. It was the most widely celebrated Mass liturgy in the world until the introduction of the Mass of Paul VI in December 1969...
, Quo Primum. - October 7, 1571: Christian fleet of the Holy League defeats the Ottoman Turks in the Battle of LepantoBattle of Lepanto (1571)The Battle of Lepanto took place on 7 October 1571 when a fleet of the Holy League, a coalition of Catholic maritime states, decisively defeated the main fleet of the Ottoman Empire in five hours of fighting on the northern edge of the Gulf of Patras, off western Greece...
. - Histoire des Protestants du Dauphiné 1522-1598; E. Arnaud
See also
- History of the Roman Catholic ChurchHistory of the Roman Catholic ChurchAs the oldest branch of Christianity, along with Eastern Orthodoxy, the history of the Catholic Church plays an integral part of the History of Christianity as a whole. This article covers a period of just under 2,000 years....
- Revival (religious)
- Timeline of ChristianityTimeline of ChristianityThe purpose of this timeline is to give a detailed account of Christianity from the beginning of the current era to the present. Question marks on dates indicate approximate dates....
- Bible beltBible BeltBible Belt is an informal term for a region in the southeastern and south-central United States in which socially conservative evangelical Protestantism is a significant part of the culture and Christian church attendance across the denominations is generally higher than the nation's average.The...
- Cathars
- Esoteric ChristianityEsoteric ChristianityEsoteric Christianity is a term which refers to an ensemble of spiritual currents which regard Christianity as a mystery religion, and profess the existence and possession of certain esoteric doctrines or practices, hidden from the public but accessible only to a narrow circle of "enlightened",...
Christian religion as a Mystery religion - Jesus in the Christian Bible
- Cultural and historical background of JesusCultural and historical background of JesusMost scholars who study the Historical Jesus and Early Christianity believe that the Canonical Gospels and life of Jesus must be viewed as firmly placed within his historical and cultural context, rather than purely in terms of Christian orthodoxy...
- WaldensiansWaldensiansWaldensians, Waldenses or Vaudois are names for a Christian movement of the later Middle Ages, descendants of which still exist in various regions, primarily in North-Western Italy. There is considerable uncertainty about the earlier history of the Waldenses because of a lack of extant source...
External links
The following links give an overview of the history of Christianity:- Dictionary of the History of Ideas: Christianity in History
- Dictionary of the History of Ideas: Church as an Institution
- Church History in the 1911 Encyclopædia BritannicaEncyclopædia BritannicaThe Encyclopædia Britannica , published by Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc., is a general knowledge English-language encyclopaedia that is available in print, as a DVD, and on the Internet. It is written and continuously updated by about 100 full-time editors and more than 4,000 expert...
The following link provides quantitative data related to Christianity and other major religions, including rates of adherence at different points in time:
- American Religion Data Archive
- Historical Christianity, A time line with references to the descendants of the early church.

