.gif)
Battle of Lepanto (1571)
Encyclopedia
The Battle of Lepanto took place on 7 October 1571 when a fleet of the Holy League, a coalition of Catholic
maritime states
, decisively defeated the main fleet of the Ottoman Empire
in five hours of fighting on the northern edge of the Gulf of Patras
, off western Greece
. The Ottoman forces sailing westwards from their naval station in Lepanto
met the Holy League forces, which had come from Messina
.
The Victory of the Holy League prevented the Mediterranean Sea
from becoming an uncontested highway for Muslim forces, protected Italy from a major Ottoman invasion, and prevented the Ottomans from advancing further into the southern flank of Europe. Lepanto was the last major naval battle
in the Mediterranean fought entirely between galleys, and has been assigned great symbolic importance.
The members of the Holy League were Spain
(including its territories of Naples
, Sicily
and Sardinia
), the Republic of Venice
, the Papacy
, the Republic of Genoa
, the Duchy of Savoy
, the Knights Hospitaller
and others. Its fleet consisted of 206 galleys and 6 galleass
es (large new galleys, invented by the Venetians, which carried substantial artillery
) and was commanded by John of Austria, the illegitimate son of Emperor Charles V
and half brother of King Philip II of Spain
.
Vessels had been contributed by the various Christian states: 109 galleys and 6 galleasses from the Republic of Venice
, 80 galleys from Spain
, 12 Tuscan
galleys of the Order of Saint Stephen
, 3 galleys each from the Republic of Genoa
, the Knights of Malta
, and the Duchy of Savoy
, and some privately owned galleys. All members of the alliance viewed the Ottoman navy
as a significant threat, both to the security of maritime trade in the Mediterranean Sea
and to the security of continental Europe itself. Notwithstanding, Spain preferred to preserve its galleys for its own wars against the nearby sultanates of the Barbary Coast
rather than expend its naval strength for Venetian benefit, although it contributed the bulk of the Christian infantry. The various Christian contingents met the main force, that of Venice (under Venier
), in July and August 1571 at Messina, Sicily
. John of Austria arrived on 23 August.
This fleet of the Christian alliance was manned by 40,000 sailors and oarsmen. In addition, it carried almost 28,000 fighting troops: 10,000 Spanish
regular infantry of excellent quality, 7,000 Germans
and Croatians in Spanish pay, 5,000 Italian mercenaries
and 5,000 Venetian
soldiers, including Greeks
from Crete
and the Ionian Islands
. Also, Venetian oarsmen were mainly free citizens and were able to bear arms adding to the fighting power of their ship, whereas convicts were used to row many of the galleys in other Holy League squadrons.
Many of the galleys in the Ottoman fleet were also rowed by slaves, often Christians who had been captured in previous conquests and engagements. Free oarsmen were generally acknowledged to be superior by all combatants, but were gradually replaced in all galley fleets (including those of Venice from 1549) during the 16th century by cheaper slaves, convicts and prisoners-of-war owing to rapidly rising costs.
The Ottoman galleys were manned by 13,000 experienced sailors - generally drawn from the maritime nations of the Ottoman Empire, namely Berbers
, Greeks
, Syria
ns, and Egyptians
—and 34,000 soldiers. Ali Pasha, the Ottoman admiral (Kapudan-i Derya ), supported by the corsairs Chulouk Bey
of Alexandria
and Uluç Ali, commanded an Ottoman force of 222 war galleys, 56 galliots
, and some smaller vessels. The Turks had skilled and experienced crews of sailors but were significantly deficient in their elite corps of Janissaries
. The number of oarsmen was about 37,000, virtually all of them slaves.
An advantage for the Christians was their numerical superiority in guns and cannon aboard their ships, and probably the better fighting quality of the Spanish infantry. It is estimated the Christians had 1,815 guns, while the Turks had only 750 with insufficient ammunition. The Christians embarked with their much improved arquebusier and musketeer
forces, while the Ottomans trusted in their greatly feared composite bow
men.
colony of Famagusta
, on the island of Cyprus
, which was being besieged by the Turks in early 1571 subsequent to the fall of Nicosia
and other Venetian possessions in Cyprus in the course of 1570.
The banner for the fleet, blessed by the pope, reached the Kingdom of Naples
(then ruled by the King of Spain
) on August 14, 1571. There in the Basilica of Santa Chiara it was solemnly consigned to John of Austria, who had been named leader of the coalition after long discussions between the allies. The fleet moved to Sicily
, leaving Messina and reaching the port of Viscando, where news arrived of the fall of Famagusta and of the torture inflicted by the Turks on the Venetian commander of the fortress, Marco Antonio Bragadin
.
On August 1 the Venetians had surrendered after being reassured that they could leave Cyprus freely. However, the Ottoman commander, Lala Kara Mustafa Pasha
, who had lost some 52,000 men in the siege (including his son), broke his word, imprisoning the Venetians. On 17 August Bragadin was flayed alive
and his corpse hung on Mustafa's galley together with the heads of the Venetian commanders, Astorre Baglioni
, Alvise Martinengo and Gianantonio Querini.
Despite bad weather, the Christian ships sailed to Kefalonia
, where they remained for a while. On 6 October they reached the Gulf of Patras
. On 7 October they encountered the Ottoman fleet. While neither fleet had immediate strategic resources or objectives in the gulf, both chose to engage. The Ottoman fleet had an express order from the Sultan
to fight, and John of Austria found it necessary to attack in order to maintain the integrity of the expedition in the face of personal and political disagreements within the Holy League.
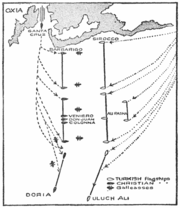 The Christian fleet formed up in four divisions in a North-South line. At the northern end, closest to the coast, was the Left Division of 53 galleys, mainly Venetian, led by Agostino Barbarigo
The Christian fleet formed up in four divisions in a North-South line. At the northern end, closest to the coast, was the Left Division of 53 galleys, mainly Venetian, led by Agostino Barbarigo
, with Marco Querini and Antonio da Canale in support. The Centre Division consisted of 62 galleys under John of Austria himself in his Real
, along with Sebastiano Venier
, later Doge of Venice
, Mathurin Romegas and Marcantonio Colonna
.
The Right Division to the south consisted of another 53 galleys under the Genoese Giovanni Andrea Doria
, great-nephew of admiral Andrea Doria
. Two galleasses, which had side-mounted cannon, were positioned in front of each main division, for the purpose, according to Miguel de Cervantes
(who served on the galley Marquesa during the battle), of preventing the Turks from sneaking in small boats and sapping, sabotaging or boarding the Christian vessels. A Reserve Division was stationed behind (that is, to the west of) the main fleet, to lend support wherever it might be needed.
This reserve division consisted of 38 galleys - 30 behind the Centre Division commanded by Álvaro de Bazán
, and four behind each wing. A scouting group was formed, from two Right Wing and six Reserve Division galleys. As the Christian fleet was slowly turning around Point Scropha, Doria's Right Division, at the off-shore side, was delayed at the start of the battle and the Right's galleasses did not get into position.
The Ottoman fleet consisted of 57 galleys and 2 galliots on its Right under Chulouk Bey, 61 galleys and 32 galliots in the Centre under Ali Pasha in the Sultana, and about 63 galleys and 30 galliots in the South off-shore under Uluç Ali. A small reserve existed of 8 galleys, 22 galliots and 64 fusta
s, behind the Centre body. Ali Pasha is supposed to have told his Christian galley-slaves: "If I win the battle, I promise you your liberty. If the day is yours, then God has given it to you." John of Austria, more laconically, warned his crew: "There is no paradise for cowards."
 The left and centre galleass
The left and centre galleass
es had been towed half a mile ahead of the Christian line. When the battle started, the Turks mistook the galleasses to be merchant supply vessels and set out to attack them. This proved to be disastrous, the galleasses, with their many guns, alone were said to have sunk up to 70 Ottoman galleys, before the Ottoman fleet left them behind. Their attacks also disrupted the Ottoman formations.
As the battle started, Doria found that Uluç Ali's galleys extended further to the south than his own, and so headed south to avoid being out-flanked, instead of holding the Christian line. After the battle Doria was accused of having maneuvered his fleet away from the bulk of the battle to avoid taking damage and casualties. Regardless, he ended up being out maneuvered by Uluç Ali, who turned back and attacked the southern end of the Centre Division, taking advantage of the big gap that Doria had left.
In the north, Chulouk Bey had managed to get between the shore and the Christian North Division, with six galleys in an outflanking move, and initially the Christian fleet suffered. Commander Barbarigo was killed by an arrow, but the Venetians, turning to face the threat, held their line. The return of a galleass saved the Christian North Division. The Christian Centre also held the line with the help of the Reserve, after taking a great deal of damage, and caused great damage to the Muslim Centre. In the south, off-shore side, Doria was engaged in a melee with Uluç Ali's ships, taking the worse part. Meanwhile Uluç Ali himself commanded 16 galleys in a fast attack on the Christian Centre, taking six galleys - amongst them the Maltese Capitana, killing all but three men on board. Its commander, Pietro Giustiniani, Prior to the Order of St. John
, was severely wounded by five arrows, but was found alive in his cabin. The intervention of the Spaniards Álvaro de Bazán and Juan de Cardona with the reserve turned the battle, both in the Centre and in Doria's South Wing.
Uluç Ali was forced to flee with 16 galleys and 24 galliots, abandoning all but one of his captures. During the course of the battle, the Ottoman Commander's ship was boarded
and the Spanish tercio
s from 3 galleys and the Ottoman Janissaries
from seven galleys fought on the deck of the Sultana. Twice the Spanish were repelled with heavy casualties, but at the third attempt, with reinforcements from Álvaro de Bazán's galley, they took the ship. Müezzinzade Ali Pasha was killed and beheaded, against the wishes of Don Juan. However, when his severed head was displayed on a pike from the Spanish flagship, it contributed greatly to the destruction of Turkish morale. Even after the battle had clearly turned against the Turks, groups of Janissaries still kept fighting with all they had. It is said that at some point the Janissaries ran out of weapons and started throwing oranges and lemons at their Christian adversaries, leading to awkward scenes of laughter among the general misery of battle.
The battle concluded around 4 pm. The Ottoman fleet suffered the loss of about 210 ships—of which 117 galleys, 10 galliots and three fustas were captured and in good enough condition for the Christians to keep. On the Christian side 20 galleys were destroyed and 30 were damaged so seriously that they had to be scuttled. One Venetian galley was the only prize kept by the Turks; all others were abandoned by them and recaptured.
Uluç Ali, who had captured the flagship of the Maltese Knights, succeeded in extricating most of his ships from the battle when defeat was certain. Although he had cut the tow on the Maltese flagship in order to get away, he sailed to Constantinople
, gathering up other Ottoman ships along the way and finally arriving there with 87 vessels. He presented the huge Maltese flag to Sultan
Selim II
who thereupon bestowed upon him the honorary title of "kιlιç" (Sword); Uluç thus became known as Kılıç Ali Pasha.
The Holy League had suffered around 7,500 soldiers, sailors and rowers dead, but freed about as many Christian prisoners. Ottoman casualties were around 15,000, and at least 3,500 were captured.
 The engagement was a significant defeat for the Ottomans, who had not lost a major naval battle since the fifteenth century. The defeat was mourned by them as an act of Divine Will, contemporary chronicles recording that "the Imperial fleet encountered the fleet of the wretched infidels and the will of God turned another way." To half of Christendom, this event encouraged hope for the downfall of "the Turk", the Satan-like personification of the Ottoman Empire,http://www.columbia.edu/cu/history/resource-library/ugrad_szabla_thesis.pdf who was regarded as the "Sempiternal Enemy of the Christian". Indeed, the Empire lost all but 30 of its ships and as many as 30,000 men, and some Western historians have held it to be the most decisive naval battle anywhere on the globe since the Battle of Actium
The engagement was a significant defeat for the Ottomans, who had not lost a major naval battle since the fifteenth century. The defeat was mourned by them as an act of Divine Will, contemporary chronicles recording that "the Imperial fleet encountered the fleet of the wretched infidels and the will of God turned another way." To half of Christendom, this event encouraged hope for the downfall of "the Turk", the Satan-like personification of the Ottoman Empire,http://www.columbia.edu/cu/history/resource-library/ugrad_szabla_thesis.pdf who was regarded as the "Sempiternal Enemy of the Christian". Indeed, the Empire lost all but 30 of its ships and as many as 30,000 men, and some Western historians have held it to be the most decisive naval battle anywhere on the globe since the Battle of Actium
of 31 BC.
Despite the decisive defeat, the Ottoman Empire rebuilt its navy with a massive effort, by largely imitating the successful Venetian galeasses, in a very short time. By 1572, about six months after the defeat, more than 150 galleys and 8 galleasses, in total 250 ships had been built, including eight of the largest capital ships ever seen in the Mediterranean. With this new fleet the Ottoman Empire was able to reassert its supremacy in the Eastern Mediterranean On 7 March 1573 the Venetians thus recognized by treaty the Ottoman possession of Cyprus
, whose last Venetian possession, Famagosta, had fallen to the Turks under Piyale Pasha
on 3 August 1571, just two months before Lepanto, and remained Turkish for the next three centuries, and that summer the Ottoman navy attacked the geographically vulnerable coasts of Sicily and southern Italy. Sultan Selim II's Chief Minister, the Grand Vizier Mehmed Sokullu, argued to the Venetian emissary Marcantonio Barbaro
that the Christian triumph at Lepanto made no lasting harm to the Ottoman Empire, while the capture of Cyprus by the Ottomans in the same year was a significant blow, saying that:
Numerous historians pointed out the historical importance of the battle and how it served as a turning point in history. For instance, it is argued that while the ships were relatively easily replaced, it proved much harder to man them, since so many experienced sailors, oarsmen and soldiers had been lost. The loss of so many of its experienced sailors at Lepanto sapped the fighting effectiveness of the Ottoman navy, a fact emphasized by their avoidance of major confrontations with Christian navies in the years following the battle. After 1580, the discouraged Ottomans left the fleet to rot in the waters of the Horn. Especially critical was the loss of most of the caliphate's composite bow
men, which, far beyond ship rams and early firearms, were the Ottoman's main embarked weapon. British historian John Keegan
noted that the losses in this highly specialised class of warrior were irreplaceable in a generation, and in fact represented "the death of a living tradition" for the Ottomans. Historian Paul K. Davis has argued that:
In 1574, the Ottomans retook the strategic city of Tunis
from the Spanish supported Hafsid dynasty, that had been re-installed when Don Juan's forces reconquered the city from the Ottomans the year before. With the long-standing Franco-Ottoman alliance
coming into play they were able to resume naval activity in the western Mediterranean. In 1579 the capture of Fez
completed Ottoman conquests in Morocco
that had begun under Süleyman the Magnificent
. The establishment of Ottoman suzerainty
over the area placed the entire coast of the Mediterranean from the Straits of Gibraltar
to Greece
(with the exceptions of the Spanish controlled trading city of Oran
and strategic settlements such as Melilla
and Ceuta
) – under Ottoman authority.
Thus, this victory for the Holy League was historically important not only because the Turks lost 80 ships sunk and 130 captured by the Allies, and 30,000 men killed (not including 12,000 Christian galley slaves who were freed) while allied losses were 7,500 men and 17 galleys - but because the victory heralded the end of Turkish supremacy in the Mediterranean. It has been said that "after Lepanto the pendulum swung back the other way and the wealth began to flow from East to West", as well as "a crucial turning point in the ongoing conflict between the Middle East and Europe, which has not yet completely been resolved."
with God they had implored for victory through the use of the Rosary
. Andrea Doria had kept a copy of the miraculous image of Our Lady of Guadalupe given to him by King Philip II of Spain
in his ship's state room.
Pope Pius V
instituted a new Catholic feast day of Our Lady of Victory to commemorate the battle, which is now celebrated by the Catholic Church as the feast of Our Lady of the Rosary
.
The only known commemorative music composed after the victory is the motet Canticum Moysis (Song of Moses Exodus 15
) Pro victoria navali contra Turcas by the Spanish composer based in Rome Fernando de las Infantas
There are many pictorial representations of the battle, including one in the Doge's Palace in Venice, by Andrea Vicentino
on the walls of the Sala dello Scrutinio, which replaced Tintoretto
's Victory of Lepanto, destroyed by fire in 1577. A painting by Paolo Veronese
is in the collection of the Gallerie dell'Accademia in Venice and Titian
's Allegory of the Battle of Lepanto, using the battle as a background, hangs in the Prado
in Madrid
. A painting by Filipino painter Juan Luna
depicting the Battle of Lepanto is also displayed at the Spanish Senate in Madrid.
The battle has also appeared in literature and poetry. Spanish poet Fernando de Herrera
wrote the poem "Canción en alabanza de la divina majestad por la victoria del Señor Don Juan" in 1572. The English author G. K. Chesterton
wrote a poem Lepanto, first published in 1911 and republished many times since. It provides a series of poetic visions of the major characters in the battle, particularly the leader of the Christian forces, Don Juan of Austria (John of Austria). It closes with verses linking Miguel de Cervantes
, who fought in the battle, with the "lean and foolish knight" he would later immortalize in Don Quixote. Miguel de Cervantes lost the use of an arm in this battle and therefore he is known as el manco de Lepanto in the Hispanic world.
The battle also features prominently in "Scenes from an Execution" by British playwright Howard Barker
, in which a fictional artist is commissioned to create a painting of the battle.
Roman Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the world's largest Christian church, with over a billion members. Led by the Pope, it defines its mission as spreading the gospel of Jesus Christ, administering the sacraments and exercising charity...
maritime states
Maritime nation
A maritime nation is any nation which borders the sea and uses it for any of the following: commerce and transport, war, to define a territorial boundary, or for any maritime activity ....
, decisively defeated the main fleet of the Ottoman Empire
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman EmpireIt was usually referred to as the "Ottoman Empire", the "Turkish Empire", the "Ottoman Caliphate" or more commonly "Turkey" by its contemporaries...
in five hours of fighting on the northern edge of the Gulf of Patras
Gulf of Patras
The Gulf of Patras is a branch of the Ionian Sea. On the east, it is closed by the Strait of Rion between capes Rio, Greece and Antirrio, near the Rio-Antirio bridge. On the west, it is bounded by a line from Oxeia island to Cape Araxos...
, off western Greece
Greece
Greece , officially the Hellenic Republic , and historically Hellas or the Republic of Greece in English, is a country in southeastern Europe....
. The Ottoman forces sailing westwards from their naval station in Lepanto
Naupactus
Naupactus or Nafpaktos , is a town and a former municipality in Aetolia-Acarnania, West Greece, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Nafpaktia, of which it is the seat and a municipal unit...
met the Holy League forces, which had come from Messina
Messina, Italy
Messina is the third largest city on the island of Sicily, Italy and the capital of the province of Messina. It has a population of about 250,000 inhabitants in the city proper and about 650,000 in the province...
.
The Victory of the Holy League prevented the Mediterranean Sea
Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean surrounded by the Mediterranean region and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Anatolia and Europe, on the south by North Africa, and on the east by the Levant...
from becoming an uncontested highway for Muslim forces, protected Italy from a major Ottoman invasion, and prevented the Ottomans from advancing further into the southern flank of Europe. Lepanto was the last major naval battle
Naval battle
A naval battle is a battle fought using boats, ships or other waterborne vessels. Most naval battles have occurred at sea, but a few have taken place on lakes or rivers. The earliest recorded naval battle took place in 1210 BC near Cyprus...
in the Mediterranean fought entirely between galleys, and has been assigned great symbolic importance.
Forces
- See Battle of Lepanto order of battleBattle of Lepanto order of battleThis is the order of battle during the Battle of Lepanto on 7 October 1571 in which the Holy League deployed 6 galleasses and 206 galleys, while the Ottoman forces numbered 216 galleys and 56 galliots.-The Fleet of the Holy League¹:...
for a detailed list of ships and commanders involved in the battle.
The members of the Holy League were Spain
Spain
Spain , officially the Kingdom of Spain languages]] under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, Spain's official name is as follows:;;;;;;), is a country and member state of the European Union located in southwestern Europe on the Iberian Peninsula...
(including its territories of Naples
Naples
Naples is a city in Southern Italy, situated on the country's west coast by the Gulf of Naples. Lying between two notable volcanic regions, Mount Vesuvius and the Phlegraean Fields, it is the capital of the region of Campania and of the province of Naples...
, Sicily
Sicily
Sicily is a region of Italy, and is the largest island in the Mediterranean Sea. Along with the surrounding minor islands, it constitutes an autonomous region of Italy, the Regione Autonoma Siciliana Sicily has a rich and unique culture, especially with regard to the arts, music, literature,...
and Sardinia
Sardinia
Sardinia is the second-largest island in the Mediterranean Sea . It is an autonomous region of Italy, and the nearest land masses are the French island of Corsica, the Italian Peninsula, Sicily, Tunisia and the Spanish Balearic Islands.The name Sardinia is from the pre-Roman noun *sard[],...
), the Republic of Venice
Republic of Venice
The Republic of Venice or Venetian Republic was a state originating from the city of Venice in Northeastern Italy. It existed for over a millennium, from the late 7th century until 1797. It was formally known as the Most Serene Republic of Venice and is often referred to as La Serenissima, in...
, the Papacy
Papal States
The Papal State, State of the Church, or Pontifical States were among the major historical states of Italy from roughly the 6th century until the Italian peninsula was unified in 1861 by the Kingdom of Piedmont-Sardinia .The Papal States comprised territories under...
, the Republic of Genoa
Republic of Genoa
The Most Serene Republic of Genoa |Ligurian]]: Repúbrica de Zêna) was an independent state from 1005 to 1797 in Liguria on the northwestern Italian coast, as well as Corsica from 1347 to 1768, and numerous other territories throughout the Mediterranean....
, the Duchy of Savoy
Duchy of Savoy
From 1416 to 1847, the House of Savoy ruled the eponymous Duchy of Savoy . The Duchy was a state in the northern part of the Italian Peninsula, with some territories that are now in France. It was a continuation of the County of Savoy...
, the Knights Hospitaller
Knights Hospitaller
The Sovereign Military Hospitaller Order of Saint John of Jerusalem of Rhodes and of Malta , also known as the Sovereign Military Order of Malta , Order of Malta or Knights of Malta, is a Roman Catholic lay religious order, traditionally of military, chivalrous, noble nature. It is the world's...
and others. Its fleet consisted of 206 galleys and 6 galleass
Galleass
The galleass developed from large merchant galleys.Converted for military use they were higher and larger than regular galleys. They had up to 32 oars, each worked by up to 5 men. They usually had three masts and a forecastle and aftcastle. Much effort was made in Venice to make these galleasses...
es (large new galleys, invented by the Venetians, which carried substantial artillery
Naval artillery
Naval artillery, or naval riflery, is artillery mounted on a warship for use in naval warfare. Naval artillery has historically been used to engage either other ships, or targets on land; in the latter role it is currently termed naval gunfire fire support...
) and was commanded by John of Austria, the illegitimate son of Emperor Charles V
Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor
Charles V was ruler of the Holy Roman Empire from 1519 and, as Charles I, of the Spanish Empire from 1516 until his voluntary retirement and abdication in favor of his younger brother Ferdinand I and his son Philip II in 1556.As...
and half brother of King Philip II of Spain
Philip II of Spain
Philip II was King of Spain, Portugal, Naples, Sicily, and, while married to Mary I, King of England and Ireland. He was lord of the Seventeen Provinces from 1556 until 1581, holding various titles for the individual territories such as duke or count....
.
Vessels had been contributed by the various Christian states: 109 galleys and 6 galleasses from the Republic of Venice
Republic of Venice
The Republic of Venice or Venetian Republic was a state originating from the city of Venice in Northeastern Italy. It existed for over a millennium, from the late 7th century until 1797. It was formally known as the Most Serene Republic of Venice and is often referred to as La Serenissima, in...
, 80 galleys from Spain
Spanish Empire
The Spanish Empire comprised territories and colonies administered directly by Spain in Europe, in America, Africa, Asia and Oceania. It originated during the Age of Exploration and was therefore one of the first global empires. At the time of Habsburgs, Spain reached the peak of its world power....
, 12 Tuscan
Grand Duchy of Tuscany
The Grand Duchy of Tuscany was a central Italian monarchy that existed, with interruptions, from 1569 to 1859, replacing the Duchy of Florence. The grand duchy's capital was Florence...
galleys of the Order of Saint Stephen
Order of Saint Stephen
The Order of Saint Stephen is a Tuscan dynastic-military order founded in 1561. The order was created by Cosimo I de' Medici, first Grand Duke of Tuscany. The last member of the Medici dynasty to be a leader of the order was Gian Gastone de Medici in 1737...
, 3 galleys each from the Republic of Genoa
Republic of Genoa
The Most Serene Republic of Genoa |Ligurian]]: Repúbrica de Zêna) was an independent state from 1005 to 1797 in Liguria on the northwestern Italian coast, as well as Corsica from 1347 to 1768, and numerous other territories throughout the Mediterranean....
, the Knights of Malta
Knights Hospitaller
The Sovereign Military Hospitaller Order of Saint John of Jerusalem of Rhodes and of Malta , also known as the Sovereign Military Order of Malta , Order of Malta or Knights of Malta, is a Roman Catholic lay religious order, traditionally of military, chivalrous, noble nature. It is the world's...
, and the Duchy of Savoy
Duchy of Savoy
From 1416 to 1847, the House of Savoy ruled the eponymous Duchy of Savoy . The Duchy was a state in the northern part of the Italian Peninsula, with some territories that are now in France. It was a continuation of the County of Savoy...
, and some privately owned galleys. All members of the alliance viewed the Ottoman navy
Ottoman Navy
The Ottoman Navy was established in the early 14th century. During its long existence it was involved in many conflicts; refer to list of Ottoman sieges and landings and list of Admirals in the Ottoman Empire for a brief chronology.- Pre-Ottoman:...
as a significant threat, both to the security of maritime trade in the Mediterranean Sea
Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean surrounded by the Mediterranean region and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Anatolia and Europe, on the south by North Africa, and on the east by the Levant...
and to the security of continental Europe itself. Notwithstanding, Spain preferred to preserve its galleys for its own wars against the nearby sultanates of the Barbary Coast
Barbary Coast
The Barbary Coast, or Barbary, was the term used by Europeans from the 16th until the 19th century to refer to much of the collective land of the Berber people. Today, the terms Maghreb and "Tamazgha" correspond roughly to "Barbary"...
rather than expend its naval strength for Venetian benefit, although it contributed the bulk of the Christian infantry. The various Christian contingents met the main force, that of Venice (under Venier
Sebastiano Venier
Sebastiano Venier was Doge of Venice from June 11, 1577 to March 3, 1578.-Biography:Venier was born in Venice around 1496. He was a son of Moisè Venier and Elena Donà, and a nephew of Zuan Francesco Venier, Co-Lord of Cerigo. He was a paternal grandson of Moisé Venier...
), in July and August 1571 at Messina, Sicily
Sicily
Sicily is a region of Italy, and is the largest island in the Mediterranean Sea. Along with the surrounding minor islands, it constitutes an autonomous region of Italy, the Regione Autonoma Siciliana Sicily has a rich and unique culture, especially with regard to the arts, music, literature,...
. John of Austria arrived on 23 August.
This fleet of the Christian alliance was manned by 40,000 sailors and oarsmen. In addition, it carried almost 28,000 fighting troops: 10,000 Spanish
Spain
Spain , officially the Kingdom of Spain languages]] under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, Spain's official name is as follows:;;;;;;), is a country and member state of the European Union located in southwestern Europe on the Iberian Peninsula...
regular infantry of excellent quality, 7,000 Germans
Germans
The Germans are a Germanic ethnic group native to Central Europe. The English term Germans has referred to the German-speaking population of the Holy Roman Empire since the Late Middle Ages....
and Croatians in Spanish pay, 5,000 Italian mercenaries
Italian people
The Italian people are an ethnic group that share a common Italian culture, ancestry and speak the Italian language as a mother tongue. Within Italy, Italians are defined by citizenship, regardless of ancestry or country of residence , and are distinguished from people...
and 5,000 Venetian
Republic of Venice
The Republic of Venice or Venetian Republic was a state originating from the city of Venice in Northeastern Italy. It existed for over a millennium, from the late 7th century until 1797. It was formally known as the Most Serene Republic of Venice and is often referred to as La Serenissima, in...
soldiers, including Greeks
Greeks
The Greeks, also known as the Hellenes , are a nation and ethnic group native to Greece, Cyprus and neighboring regions. They also form a significant diaspora, with Greek communities established around the world....
from Crete
Crete
Crete is the largest and most populous of the Greek islands, the fifth largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, and one of the thirteen administrative regions of Greece. It forms a significant part of the economy and cultural heritage of Greece while retaining its own local cultural traits...
and the Ionian Islands
Ionian Islands
The Ionian Islands are a group of islands in Greece. They are traditionally called the Heptanese, i.e...
. Also, Venetian oarsmen were mainly free citizens and were able to bear arms adding to the fighting power of their ship, whereas convicts were used to row many of the galleys in other Holy League squadrons.
Many of the galleys in the Ottoman fleet were also rowed by slaves, often Christians who had been captured in previous conquests and engagements. Free oarsmen were generally acknowledged to be superior by all combatants, but were gradually replaced in all galley fleets (including those of Venice from 1549) during the 16th century by cheaper slaves, convicts and prisoners-of-war owing to rapidly rising costs.
The Ottoman galleys were manned by 13,000 experienced sailors - generally drawn from the maritime nations of the Ottoman Empire, namely Berbers
Berber people
Berbers are the indigenous peoples of North Africa west of the Nile Valley. They are continuously distributed from the Atlantic to the Siwa oasis, in Egypt, and from the Mediterranean to the Niger River. Historically they spoke the Berber language or varieties of it, which together form a branch...
, Greeks
Greeks
The Greeks, also known as the Hellenes , are a nation and ethnic group native to Greece, Cyprus and neighboring regions. They also form a significant diaspora, with Greek communities established around the world....
, Syria
Syria
Syria , officially the Syrian Arab Republic , is a country in Western Asia, bordering Lebanon and the Mediterranean Sea to the West, Turkey to the north, Iraq to the east, Jordan to the south, and Israel to the southwest....
ns, and Egyptians
Egyptians
Egyptians are nation an ethnic group made up of Mediterranean North Africans, the indigenous people of Egypt.Egyptian identity is closely tied to geography. The population of Egypt is concentrated in the lower Nile Valley, the small strip of cultivable land stretching from the First Cataract to...
—and 34,000 soldiers. Ali Pasha, the Ottoman admiral (Kapudan-i Derya ), supported by the corsairs Chulouk Bey
Suluc Mehmed Pasha
Suluc Mehmed Pasha, better known in Europe as Mohammed Sirocco or Mehmed Siroco, was the Ottoman viceroy of Egypt and Governor of Alexandria, in the mid 16th century....
of Alexandria
Alexandria
Alexandria is the second-largest city of Egypt, with a population of 4.1 million, extending about along the coast of the Mediterranean Sea in the north central part of the country; it is also the largest city lying directly on the Mediterranean coast. It is Egypt's largest seaport, serving...
and Uluç Ali, commanded an Ottoman force of 222 war galleys, 56 galliots
Galiot
Galiots were types of ships from the Age of Sail.In the Mediterranean, galiots were a type of small galley, with one or two masts and about twenty oars, using both sails and oars for propulsion...
, and some smaller vessels. The Turks had skilled and experienced crews of sailors but were significantly deficient in their elite corps of Janissaries
Janissary
The Janissaries were infantry units that formed the Ottoman sultan's household troops and bodyguards...
. The number of oarsmen was about 37,000, virtually all of them slaves.
An advantage for the Christians was their numerical superiority in guns and cannon aboard their ships, and probably the better fighting quality of the Spanish infantry. It is estimated the Christians had 1,815 guns, while the Turks had only 750 with insufficient ammunition. The Christians embarked with their much improved arquebusier and musketeer
Musketeer
A musketeer was an early modern type of infantry soldier equipped with a musket. Musketeers were an important part of early modern armies, particularly in Europe. They sometimes could fight on horseback, like a dragoon or a cavalryman...
forces, while the Ottomans trusted in their greatly feared composite bow
Composite bow
A composite bow is a bow made from horn, wood, and sinew laminated together. The horn is on the belly, facing the archer, and sinew on the back of a wooden core. Sinew and horn will store more energy than wood for the same length of bow...
men.
Background
The Christian coalition had been promoted by Pope Pius V to rescue the VenetianRepublic of Venice
The Republic of Venice or Venetian Republic was a state originating from the city of Venice in Northeastern Italy. It existed for over a millennium, from the late 7th century until 1797. It was formally known as the Most Serene Republic of Venice and is often referred to as La Serenissima, in...
colony of Famagusta
Famagusta
Famagusta is a city on the east coast of Cyprus and is capital of the Famagusta District. It is located east of Nicosia, and possesses the deepest harbour of the island.-Name:...
, on the island of Cyprus
Cyprus
Cyprus , officially the Republic of Cyprus , is a Eurasian island country, member of the European Union, in the Eastern Mediterranean, east of Greece, south of Turkey, west of Syria and north of Egypt. It is the third largest island in the Mediterranean Sea.The earliest known human activity on the...
, which was being besieged by the Turks in early 1571 subsequent to the fall of Nicosia
Nicosia
Nicosia from , known locally as Lefkosia , is the capital and largest city in Cyprus, as well as its main business center. Nicosia is the only divided capital in the world, with the southern and the northern portions divided by a Green Line...
and other Venetian possessions in Cyprus in the course of 1570.
The banner for the fleet, blessed by the pope, reached the Kingdom of Naples
Kingdom of Naples
The Kingdom of Naples, comprising the southern part of the Italian peninsula, was the remainder of the old Kingdom of Sicily after secession of the island of Sicily as a result of the Sicilian Vespers rebellion of 1282. Known to contemporaries as the Kingdom of Sicily, it is dubbed Kingdom of...
(then ruled by the King of Spain
Spanish Empire
The Spanish Empire comprised territories and colonies administered directly by Spain in Europe, in America, Africa, Asia and Oceania. It originated during the Age of Exploration and was therefore one of the first global empires. At the time of Habsburgs, Spain reached the peak of its world power....
) on August 14, 1571. There in the Basilica of Santa Chiara it was solemnly consigned to John of Austria, who had been named leader of the coalition after long discussions between the allies. The fleet moved to Sicily
Sicily
Sicily is a region of Italy, and is the largest island in the Mediterranean Sea. Along with the surrounding minor islands, it constitutes an autonomous region of Italy, the Regione Autonoma Siciliana Sicily has a rich and unique culture, especially with regard to the arts, music, literature,...
, leaving Messina and reaching the port of Viscando, where news arrived of the fall of Famagusta and of the torture inflicted by the Turks on the Venetian commander of the fortress, Marco Antonio Bragadin
Marco Antonio Bragadin
Marco Antonio Bragadin, also Marcantonio Bragadin was an Italian lawyer and military officer of the Republic of Venice....
.
On August 1 the Venetians had surrendered after being reassured that they could leave Cyprus freely. However, the Ottoman commander, Lala Kara Mustafa Pasha
Lala Kara Mustafa Pasha
Lala Kara Mustafa Pasha was an Ottoman general and Grand Vizier of the Ottoman Empire.He had risen to the position of Beylerbey of Damascus and then to that of Fifth Vizier...
, who had lost some 52,000 men in the siege (including his son), broke his word, imprisoning the Venetians. On 17 August Bragadin was flayed alive
Flaying
Flaying is the removal of skin from the body. Generally, an attempt is made to keep the removed portion of skin intact.-Scope:An animal may be flayed in preparation for human consumption, or for its hide or fur; this is more commonly called skinning....
and his corpse hung on Mustafa's galley together with the heads of the Venetian commanders, Astorre Baglioni
Astorre Baglioni
Astorre Baglioni was an Italian condottiero and military commander.-Biography:He was born in Perugia, the son of Gentile Baglioni, a member of a condottieri family of central Italy...
, Alvise Martinengo and Gianantonio Querini.
Despite bad weather, the Christian ships sailed to Kefalonia
Kefalonia
The island of Cephalonia, also known as Kefalonia, Cephallenia, Cephallonia, Kefallinia, or Kefallonia , is the largest of the Ionian Islands in western Greece, with an area of . It is also a separate regional unit of the Ionian Islands region, and the only municipality of the regional unit...
, where they remained for a while. On 6 October they reached the Gulf of Patras
Gulf of Patras
The Gulf of Patras is a branch of the Ionian Sea. On the east, it is closed by the Strait of Rion between capes Rio, Greece and Antirrio, near the Rio-Antirio bridge. On the west, it is bounded by a line from Oxeia island to Cape Araxos...
. On 7 October they encountered the Ottoman fleet. While neither fleet had immediate strategic resources or objectives in the gulf, both chose to engage. The Ottoman fleet had an express order from the Sultan
Selim II
Selim II Sarkhosh Hashoink , also known as "Selim the Sot " or "Selim the Drunkard"; and as "Sarı Selim" or "Selim the Blond", was the Sultan of the Ottoman Empire from 1566 until his death in 1574.-Early years:He was born in Constantinople a son of Suleiman the...
to fight, and John of Austria found it necessary to attack in order to maintain the integrity of the expedition in the face of personal and political disagreements within the Holy League.
Deployment

Agostino Barbarigo
Agostino Barbarigo was Doge of Venice from 1486 until his death in 1501.While he was Doge, the imposing Clock Tower in the Piazza San Marco with its archway through which the street known as the Merceria leads to the Rialto, was designed and completed...
, with Marco Querini and Antonio da Canale in support. The Centre Division consisted of 62 galleys under John of Austria himself in his Real
Real (galley)
The Real, built in Barcelona, was the largest galley of its time and the flagship of Don Juan de Austria in the Battle of Lepanto in 1571, the largest battle between galleys in history, in which a fleet of the Holy League, an alliance of Christian powers of the Mediterranean, decisively defeated an...
, along with Sebastiano Venier
Sebastiano Venier
Sebastiano Venier was Doge of Venice from June 11, 1577 to March 3, 1578.-Biography:Venier was born in Venice around 1496. He was a son of Moisè Venier and Elena Donà, and a nephew of Zuan Francesco Venier, Co-Lord of Cerigo. He was a paternal grandson of Moisé Venier...
, later Doge of Venice
Doge of Venice
The Doge of Venice , often mistranslated Duke was the chief magistrate and leader of the Most Serene Republic of Venice for over a thousand years. Doges of Venice were elected for life by the city-state's aristocracy. Commonly the person selected as Doge was the shrewdest elder in the city...
, Mathurin Romegas and Marcantonio Colonna
Marcantonio Colonna
Marcantonio II Colonna , Duke and Prince of Paliano, was an Italian general and admiral.-Biography:...
.
The Right Division to the south consisted of another 53 galleys under the Genoese Giovanni Andrea Doria
Giovanni Andrea Doria
Giovanni Andrea Doria, also Giannandrea Doria , was an Italian admiral from Genoa. He was the son of Giannettino Doria and the great-nephew of the famed Genoese admiral Andrea Doria, by whom he was later adopted...
, great-nephew of admiral Andrea Doria
Andrea Doria
Andrea Doria was an Italian condottiere and admiral from Genoa.-Early life:Doria was born at Oneglia from the ancient Genoese family, the Doria di Oneglia branch of the old Doria, de Oria or de Auria family. His parents were related: Ceva Doria, co-lord of Oneglia, and Caracosa Doria, of the...
. Two galleasses, which had side-mounted cannon, were positioned in front of each main division, for the purpose, according to Miguel de Cervantes
Miguel de Cervantes
Miguel de Cervantes Saavedra was a Spanish novelist, poet, and playwright. His magnum opus, Don Quixote, considered the first modern novel, is a classic of Western literature, and is regarded amongst the best works of fiction ever written...
(who served on the galley Marquesa during the battle), of preventing the Turks from sneaking in small boats and sapping, sabotaging or boarding the Christian vessels. A Reserve Division was stationed behind (that is, to the west of) the main fleet, to lend support wherever it might be needed.
This reserve division consisted of 38 galleys - 30 behind the Centre Division commanded by Álvaro de Bazán
Álvaro de Bazán, 1st Marquis of Santa Cruz
Álvaro de Bazán, 1st Marquis of Santa Cruz de Mudela , was a Spanish admiral.-Biography:Álvaro de Bazán was born in Granada....
, and four behind each wing. A scouting group was formed, from two Right Wing and six Reserve Division galleys. As the Christian fleet was slowly turning around Point Scropha, Doria's Right Division, at the off-shore side, was delayed at the start of the battle and the Right's galleasses did not get into position.
The Ottoman fleet consisted of 57 galleys and 2 galliots on its Right under Chulouk Bey, 61 galleys and 32 galliots in the Centre under Ali Pasha in the Sultana, and about 63 galleys and 30 galliots in the South off-shore under Uluç Ali. A small reserve existed of 8 galleys, 22 galliots and 64 fusta
Fusta
The fusta or fuste was a narrow, light and fast ship with shallow draft, powered by both oars and sail -– in essence a small galley. It typically had 12 to 18 two-man rowing benches on each side, a single mast with a lateen sail, and usually carried two or three guns...
s, behind the Centre body. Ali Pasha is supposed to have told his Christian galley-slaves: "If I win the battle, I promise you your liberty. If the day is yours, then God has given it to you." John of Austria, more laconically, warned his crew: "There is no paradise for cowards."
The battle

Galleass
The galleass developed from large merchant galleys.Converted for military use they were higher and larger than regular galleys. They had up to 32 oars, each worked by up to 5 men. They usually had three masts and a forecastle and aftcastle. Much effort was made in Venice to make these galleasses...
es had been towed half a mile ahead of the Christian line. When the battle started, the Turks mistook the galleasses to be merchant supply vessels and set out to attack them. This proved to be disastrous, the galleasses, with their many guns, alone were said to have sunk up to 70 Ottoman galleys, before the Ottoman fleet left them behind. Their attacks also disrupted the Ottoman formations.
As the battle started, Doria found that Uluç Ali's galleys extended further to the south than his own, and so headed south to avoid being out-flanked, instead of holding the Christian line. After the battle Doria was accused of having maneuvered his fleet away from the bulk of the battle to avoid taking damage and casualties. Regardless, he ended up being out maneuvered by Uluç Ali, who turned back and attacked the southern end of the Centre Division, taking advantage of the big gap that Doria had left.
In the north, Chulouk Bey had managed to get between the shore and the Christian North Division, with six galleys in an outflanking move, and initially the Christian fleet suffered. Commander Barbarigo was killed by an arrow, but the Venetians, turning to face the threat, held their line. The return of a galleass saved the Christian North Division. The Christian Centre also held the line with the help of the Reserve, after taking a great deal of damage, and caused great damage to the Muslim Centre. In the south, off-shore side, Doria was engaged in a melee with Uluç Ali's ships, taking the worse part. Meanwhile Uluç Ali himself commanded 16 galleys in a fast attack on the Christian Centre, taking six galleys - amongst them the Maltese Capitana, killing all but three men on board. Its commander, Pietro Giustiniani, Prior to the Order of St. John
Knights Hospitaller
The Sovereign Military Hospitaller Order of Saint John of Jerusalem of Rhodes and of Malta , also known as the Sovereign Military Order of Malta , Order of Malta or Knights of Malta, is a Roman Catholic lay religious order, traditionally of military, chivalrous, noble nature. It is the world's...
, was severely wounded by five arrows, but was found alive in his cabin. The intervention of the Spaniards Álvaro de Bazán and Juan de Cardona with the reserve turned the battle, both in the Centre and in Doria's South Wing.
Uluç Ali was forced to flee with 16 galleys and 24 galliots, abandoning all but one of his captures. During the course of the battle, the Ottoman Commander's ship was boarded
Boarding (attack)
Boarding, in its simplest sense, refers to the insertion on to a ship's deck of individuals. However, when it is classified as an attack, in most contexts, it refers to the forcible insertion of personnel that are not members of the crew by another party without the consent of the captain or crew...
and the Spanish tercio
Tercio
The tercio was a Renaissance era military formation made up of a mixed infantry formation of about 3,000 pikemen, swordsmen and arquebusiers or musketeers in a mutually supportive formation. It was also sometimes referred to as the Spanish Square...
s from 3 galleys and the Ottoman Janissaries
Janissary
The Janissaries were infantry units that formed the Ottoman sultan's household troops and bodyguards...
from seven galleys fought on the deck of the Sultana. Twice the Spanish were repelled with heavy casualties, but at the third attempt, with reinforcements from Álvaro de Bazán's galley, they took the ship. Müezzinzade Ali Pasha was killed and beheaded, against the wishes of Don Juan. However, when his severed head was displayed on a pike from the Spanish flagship, it contributed greatly to the destruction of Turkish morale. Even after the battle had clearly turned against the Turks, groups of Janissaries still kept fighting with all they had. It is said that at some point the Janissaries ran out of weapons and started throwing oranges and lemons at their Christian adversaries, leading to awkward scenes of laughter among the general misery of battle.
The battle concluded around 4 pm. The Ottoman fleet suffered the loss of about 210 ships—of which 117 galleys, 10 galliots and three fustas were captured and in good enough condition for the Christians to keep. On the Christian side 20 galleys were destroyed and 30 were damaged so seriously that they had to be scuttled. One Venetian galley was the only prize kept by the Turks; all others were abandoned by them and recaptured.
Uluç Ali, who had captured the flagship of the Maltese Knights, succeeded in extricating most of his ships from the battle when defeat was certain. Although he had cut the tow on the Maltese flagship in order to get away, he sailed to Constantinople
Constantinople
Constantinople was the capital of the Roman, Eastern Roman, Byzantine, Latin, and Ottoman Empires. Throughout most of the Middle Ages, Constantinople was Europe's largest and wealthiest city.-Names:...
, gathering up other Ottoman ships along the way and finally arriving there with 87 vessels. He presented the huge Maltese flag to Sultan
Sultan
Sultan is a title with several historical meanings. Originally, it was an Arabic language abstract noun meaning "strength", "authority", "rulership", and "dictatorship", derived from the masdar سلطة , meaning "authority" or "power". Later, it came to be used as the title of certain rulers who...
Selim II
Selim II
Selim II Sarkhosh Hashoink , also known as "Selim the Sot " or "Selim the Drunkard"; and as "Sarı Selim" or "Selim the Blond", was the Sultan of the Ottoman Empire from 1566 until his death in 1574.-Early years:He was born in Constantinople a son of Suleiman the...
who thereupon bestowed upon him the honorary title of "kιlιç" (Sword); Uluç thus became known as Kılıç Ali Pasha.
The Holy League had suffered around 7,500 soldiers, sailors and rowers dead, but freed about as many Christian prisoners. Ottoman casualties were around 15,000, and at least 3,500 were captured.
Aftermath

Battle of Actium
The Battle of Actium was the decisive confrontation of the Final War of the Roman Republic. It was fought between the forces of Octavian and the combined forces of Mark Antony and Cleopatra VII. The battle took place on 2 September 31 BC, on the Ionian Sea near the city of Actium, at the Roman...
of 31 BC.
Despite the decisive defeat, the Ottoman Empire rebuilt its navy with a massive effort, by largely imitating the successful Venetian galeasses, in a very short time. By 1572, about six months after the defeat, more than 150 galleys and 8 galleasses, in total 250 ships had been built, including eight of the largest capital ships ever seen in the Mediterranean. With this new fleet the Ottoman Empire was able to reassert its supremacy in the Eastern Mediterranean On 7 March 1573 the Venetians thus recognized by treaty the Ottoman possession of Cyprus
Cyprus
Cyprus , officially the Republic of Cyprus , is a Eurasian island country, member of the European Union, in the Eastern Mediterranean, east of Greece, south of Turkey, west of Syria and north of Egypt. It is the third largest island in the Mediterranean Sea.The earliest known human activity on the...
, whose last Venetian possession, Famagosta, had fallen to the Turks under Piyale Pasha
Piyale Pasha
Piyale Pasha , born in Viganj on the Pelješac peninsula, was a Croatian Ottoman admiral between 1553 and 1567 and an Ottoman Vizier after 1568. He was also known as Piale Pasha in the West or Pialí Bajá in Spain; )....
on 3 August 1571, just two months before Lepanto, and remained Turkish for the next three centuries, and that summer the Ottoman navy attacked the geographically vulnerable coasts of Sicily and southern Italy. Sultan Selim II's Chief Minister, the Grand Vizier Mehmed Sokullu, argued to the Venetian emissary Marcantonio Barbaro
Marcantonio Barbaro
Marcantonio Barbaro was an Italian diplomat of the Republic of Venice.-Family:He was born in Venice into the aristocratic Barbaro family...
that the Christian triumph at Lepanto made no lasting harm to the Ottoman Empire, while the capture of Cyprus by the Ottomans in the same year was a significant blow, saying that:
Numerous historians pointed out the historical importance of the battle and how it served as a turning point in history. For instance, it is argued that while the ships were relatively easily replaced, it proved much harder to man them, since so many experienced sailors, oarsmen and soldiers had been lost. The loss of so many of its experienced sailors at Lepanto sapped the fighting effectiveness of the Ottoman navy, a fact emphasized by their avoidance of major confrontations with Christian navies in the years following the battle. After 1580, the discouraged Ottomans left the fleet to rot in the waters of the Horn. Especially critical was the loss of most of the caliphate's composite bow
Composite bow
A composite bow is a bow made from horn, wood, and sinew laminated together. The horn is on the belly, facing the archer, and sinew on the back of a wooden core. Sinew and horn will store more energy than wood for the same length of bow...
men, which, far beyond ship rams and early firearms, were the Ottoman's main embarked weapon. British historian John Keegan
John Keegan
Sir John Keegan OBE FRSL is a British military historian, lecturer, writer and journalist. He has published many works on the nature of combat between the 14th and 21st centuries concerning land, air, maritime, and intelligence warfare, as well as the psychology of battle.-Life and career:John...
noted that the losses in this highly specialised class of warrior were irreplaceable in a generation, and in fact represented "the death of a living tradition" for the Ottomans. Historian Paul K. Davis has argued that:
In 1574, the Ottomans retook the strategic city of Tunis
Capture of Tunis
The Conquest of Tunis in 1574 marked the final conquest of Tunis by the Ottoman Empire over the Spanish Empire. This was an event of great significance as it decided that North Africa would be under Muslim rather than Christian rule, ended the Spanish Conquista of Northern Africa started under...
from the Spanish supported Hafsid dynasty, that had been re-installed when Don Juan's forces reconquered the city from the Ottomans the year before. With the long-standing Franco-Ottoman alliance
Franco-Ottoman alliance
The Franco-Ottoman alliance, also Franco-Turkish alliance, was an alliance established in 1536 between the king of France Francis I and the Turkish ruler of the Ottoman Empire Suleiman the Magnificent. The alliance has been called "the first non-ideological diplomatic alliance of its kind between a...
coming into play they were able to resume naval activity in the western Mediterranean. In 1579 the capture of Fez
Fes, Morocco
Fes or Fez is the second largest city of Morocco, after Casablanca, with a population of approximately 1 million . It is the capital of the Fès-Boulemane region....
completed Ottoman conquests in Morocco
Morocco
Morocco , officially the Kingdom of Morocco , is a country located in North Africa. It has a population of more than 32 million and an area of 710,850 km², and also primarily administers the disputed region of the Western Sahara...
that had begun under Süleyman the Magnificent
Suleiman the Magnificent
Suleiman I was the tenth and longest-reigning Sultan of the Ottoman Empire, from 1520 to his death in 1566. He is known in the West as Suleiman the Magnificent and in the East, as "The Lawgiver" , for his complete reconstruction of the Ottoman legal system...
. The establishment of Ottoman suzerainty
Suzerainty
Suzerainty occurs where a region or people is a tributary to a more powerful entity which controls its foreign affairs while allowing the tributary vassal state some limited domestic autonomy. The dominant entity in the suzerainty relationship, or the more powerful entity itself, is called a...
over the area placed the entire coast of the Mediterranean from the Straits of Gibraltar
Gibraltar
Gibraltar is a British overseas territory located on the southern end of the Iberian Peninsula at the entrance of the Mediterranean. A peninsula with an area of , it has a northern border with Andalusia, Spain. The Rock of Gibraltar is the major landmark of the region...
to Greece
Greece
Greece , officially the Hellenic Republic , and historically Hellas or the Republic of Greece in English, is a country in southeastern Europe....
(with the exceptions of the Spanish controlled trading city of Oran
Oran
Oran is a major city on the northwestern Mediterranean coast of Algeria, and the second largest city of the country.It is the capital of the Oran Province . The city has a population of 759,645 , while the metropolitan area has a population of approximately 1,500,000, making it the second largest...
and strategic settlements such as Melilla
Melilla
Melilla is a autonomous city of Spain and an exclave on the north coast of Morocco. Melilla, along with the Spanish exclave Ceuta, is one of the two Spanish territories located in mainland Africa...
and Ceuta
Ceuta
Ceuta is an autonomous city of Spain and an exclave located on the north coast of North Africa surrounded by Morocco. Separated from the Iberian peninsula by the Strait of Gibraltar, Ceuta lies on the border of the Mediterranean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean. Ceuta along with the other Spanish...
) – under Ottoman authority.
Thus, this victory for the Holy League was historically important not only because the Turks lost 80 ships sunk and 130 captured by the Allies, and 30,000 men killed (not including 12,000 Christian galley slaves who were freed) while allied losses were 7,500 men and 17 galleys - but because the victory heralded the end of Turkish supremacy in the Mediterranean. It has been said that "after Lepanto the pendulum swung back the other way and the wealth began to flow from East to West", as well as "a crucial turning point in the ongoing conflict between the Middle East and Europe, which has not yet completely been resolved."
Religious significance
The Holy League credited the victory to the Virgin Mary, whose intercessionIntercession
Intercession is the act of interceding between two parties. In both Christian and Islamic religious usage, it is a prayer to God on behalf of others....
with God they had implored for victory through the use of the Rosary
Rosary
The rosary or "garland of roses" is a traditional Catholic devotion. The term denotes the prayer beads used to count the series of prayers that make up the rosary...
. Andrea Doria had kept a copy of the miraculous image of Our Lady of Guadalupe given to him by King Philip II of Spain
Philip II of Spain
Philip II was King of Spain, Portugal, Naples, Sicily, and, while married to Mary I, King of England and Ireland. He was lord of the Seventeen Provinces from 1556 until 1581, holding various titles for the individual territories such as duke or count....
in his ship's state room.
Pope Pius V
Pope Pius V
Pope Saint Pius V , born Antonio Ghislieri , was Pope from 1566 to 1572 and is a saint of the Catholic Church. He is chiefly notable for his role in the Council of Trent, the Counter-Reformation, and the standardization of the Roman liturgy within the Latin Church...
instituted a new Catholic feast day of Our Lady of Victory to commemorate the battle, which is now celebrated by the Catholic Church as the feast of Our Lady of the Rosary
Our Lady of the Rosary
Our Lady of the Rosary is a title of the Blessed Virgin Mary in relation to the rosary....
.
Depictions in art and culture
The significance of Lepanto has inspired artists in various fields.The only known commemorative music composed after the victory is the motet Canticum Moysis (Song of Moses Exodus 15
Song of the sea
The Song of the Sea is a poem that appears in the Book of Exodus of the Hebrew Bible, at . It is followed in verses 20 and 21 by a much shorter song sung by Miriam and the other women...
) Pro victoria navali contra Turcas by the Spanish composer based in Rome Fernando de las Infantas
Fernando de las Infantas
- Life :Infantas was born in Córdoba in 1534, a descendant of Juan Fernández de Córdoba who had conveyed the two daughters, infantas , of Pedro I of Castile to safety after the Battle of Montiel in 1369...
There are many pictorial representations of the battle, including one in the Doge's Palace in Venice, by Andrea Vicentino
Andrea Vicentino
Andrea Vicentino was an Italian painter of the late-Renaissance or Mannerist period. He was a pupil of the painter Giovanni Battista Maganza. Born in Vicenza, he was also known as Andrea Michieli or Michelli. He moved to Venice in the mid-1570s and registered in the “Fraglia” or guild of Venetian...
on the walls of the Sala dello Scrutinio, which replaced Tintoretto
Tintoretto
Tintoretto , real name Jacopo Comin, was a Venetian painter and a notable exponent of the Renaissance school. For his phenomenal energy in painting he was termed Il Furioso...
's Victory of Lepanto, destroyed by fire in 1577. A painting by Paolo Veronese
Paolo Veronese
Paolo Veronese was an Italian painter of the Renaissance in Venice, famous for paintings such as The Wedding at Cana and The Feast in the House of Levi...
is in the collection of the Gallerie dell'Accademia in Venice and Titian
Titian
Tiziano Vecelli or Tiziano Vecellio Tiziano Vecelli or Tiziano Vecellio Tiziano Vecelli or Tiziano Vecellio (c. 1488/1490 – 27 August 1576 better known as Titian was an Italian painter, the most important member of the 16th-century Venetian school. He was born in Pieve di Cadore, near...
's Allegory of the Battle of Lepanto, using the battle as a background, hangs in the Prado
Museo del Prado
The Museo del Prado is the main Spanish national art museum, located in central Madrid. It features one of the world's finest collections of European art, from the 12th century to the early 19th century, based on the former Spanish Royal Collection, and unquestionably the best single collection of...
in Madrid
Madrid
Madrid is the capital and largest city of Spain. The population of the city is roughly 3.3 million and the entire population of the Madrid metropolitan area is calculated to be 6.271 million. It is the third largest city in the European Union, after London and Berlin, and its metropolitan...
. A painting by Filipino painter Juan Luna
Juan Luna
Juan Luna y Novicio was an Ilocano Filipino painter, sculptor and a political activist of the Philippine Revolution during the late 19th century...
depicting the Battle of Lepanto is also displayed at the Spanish Senate in Madrid.
The battle has also appeared in literature and poetry. Spanish poet Fernando de Herrera
Fernando de Herrera
Fernando de Herrera , called "El Divino", was a 16th-century Spanish poet and man of letters. He was born in Seville. Much of what is known about him comes from Libro de descripción de verdaderos retratos de illustres y memorables varones by Francisco Pacheco.-Biography:Although...
wrote the poem "Canción en alabanza de la divina majestad por la victoria del Señor Don Juan" in 1572. The English author G. K. Chesterton
G. K. Chesterton
Gilbert Keith Chesterton, KC*SG was an English writer. His prolific and diverse output included philosophy, ontology, poetry, plays, journalism, public lectures and debates, literary and art criticism, biography, Christian apologetics, and fiction, including fantasy and detective fiction....
wrote a poem Lepanto, first published in 1911 and republished many times since. It provides a series of poetic visions of the major characters in the battle, particularly the leader of the Christian forces, Don Juan of Austria (John of Austria). It closes with verses linking Miguel de Cervantes
Miguel de Cervantes
Miguel de Cervantes Saavedra was a Spanish novelist, poet, and playwright. His magnum opus, Don Quixote, considered the first modern novel, is a classic of Western literature, and is regarded amongst the best works of fiction ever written...
, who fought in the battle, with the "lean and foolish knight" he would later immortalize in Don Quixote. Miguel de Cervantes lost the use of an arm in this battle and therefore he is known as el manco de Lepanto in the Hispanic world.
The battle also features prominently in "Scenes from an Execution" by British playwright Howard Barker
Howard Barker
Howard E. Barker is a British playwright.-The Theatre of Catastrophe :Barker has coined the term "Theatre of Catastrophe" to describe his work...
, in which a fictional artist is commissioned to create a painting of the battle.
See also
- Battle of Preveza (1538)
- Battle of Djerba (1560)Battle of DjerbaThe naval Battle of Djerba took place in May 1560 near the island of Djerba, Tunisia in which the Ottomans under Piyale Pasha's command overwhelmed a large joint European fleet, chiefly Spanish forces, sinking half its ships.-Background:...
- Siege of Malta (1565)Siege of Malta (1565)The Siege of Malta took place in 1565 when the Ottoman Empire invaded the island, then held by the Knights Hospitaller .The Knights, together with between 4-5,000 Maltese men,...
- Ottoman-Habsburg warsOttoman-Habsburg warsThe Ottoman–Habsburg wars refers to the military conflicts between the Ottoman Empire and the Habsburg dynasties of the Austrian Empire, Habsburg Spain and in certain times, the Holy Roman Empire and the Kingdom of Hungary. The war would be dominated by land campaigns in Hungary and present day...
- Our Lady of the RosaryOur Lady of the RosaryOur Lady of the Rosary is a title of the Blessed Virgin Mary in relation to the rosary....
External links
- Battle of Lepanto animated battle map by Jonathan Webb
- Chronicle of the battle of Lepanto by Luis Coloma, SJ
- "Lepanto cultural center"
- The Battle that Saved the Christian West by Christopher Check
- Overview of the battle
- Lepanto: The Battle that Saved Christendom?
- "The Tactics of the Battle of Lepanto Clarified: The Impact of Social, Economic, and Political Factors on Sixteenth Century Galley Warfare"

