
History of Estonia
Encyclopedia
Estonia
was settled near the end of the last glacial era
, beginning from around 8500 BC. Before the German invasions in the 13th century proto-Estonians of the Ancient Estonia
worshipped the spirits of nature. Since the Northern Crusades
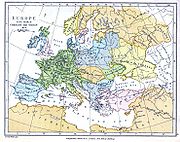
Estonia became a battleground for centuries where Denmark, Germany, Russia, Sweden and Poland fought their many wars over controlling the important geographical position of the country as a gateway between East and West.
Being conquered by Danes and Germans in 1227, Estonia was ruled initially by Denmark
in the north, by the Livonian Order
, an autonomous part of the Monastic state of the Teutonic Knights
and Baltic German
ecclesiastical states of the Holy Roman Empire. From 1418–1562 the whole of Estonia was part of the Livonian Confederation
. After the Livonian War
, Estonia became part of the Swedish Empire
from the 16th century to 1710/1721, when it was ceded
to the Russian Empire
as the result of the Great Northern War
. Throughout this period the Baltic German
nobility enjoyed autonomy, where the language of administration and education was German.
The Estophile Enlightenment Period 1750–1840 led to the Estonian national awakening
in the middle of the 19th century. In 1918 the Estonian Declaration of Independence
was issued. The Estonian War of Independence ensued on two fronts between the newly proclaimed state and Bolshevist Russia
to the east and the forces of the United Baltic Duchy
(the Baltische Landeswehr
) to the south, resulting in the Tartu Peace Treaty
recognising Estonian independence in perpetuity. Prior to the Second World War, Estonia was occupied and according to the USA, the EU, and the European Court of Human Rights
illegally annexed by the Soviet Union as a result of the Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact. During the war Estonia was occupied by Nazi Germany
in 1941, then reoccupied by the Soviet Union in 1944. Estonia regained independence in 1991 after the collapse of the USSR and joined the European Union
in 2004.
 The region has been populated since the end of the Late Pleistocene
The region has been populated since the end of the Late Pleistocene
Ice Age
, about 10,000 BC. The earliest traces of human settlement in Estonia are connected with the Kunda culture
. The early Mesolithic
Pulli settlement
is located by the Pärnu
River. It has been dated to the beginning of the 9th millennium BC. The Kunda Culture received its name from the Lammasmäe settlement site in northern Estonia, which dates from earlier than 8500 BC. Bone and stone artifacts similar to those found at Kunda have been discovered elsewhere in Estonia, as well as in Latvia
, northern Lithuania
and southern Finland
. Among minerals, flint
and quartz
were used the most for making cutting tools.
 Around the beginning of 4th millennium Comb Ceramic culture arrived in Estonia. Until the early 1980s the arrival of Finnic peoples
Around the beginning of 4th millennium Comb Ceramic culture arrived in Estonia. Until the early 1980s the arrival of Finnic peoples
, the ancestors of the Estonians, Finns, and Livonians, on the shores of the Baltic sea was associated with the Comb Ceramic Culture. However , such a linking of archaeologically defined cultural entities with linguistic ones cannot be proven and it has been suggested that the increase of settlement finds in the period is more likely to have been associated with an economic boom related to the warming of climate. Some researchers have even argued that a Uralic form of language may have been spoken in Estonia and Finland since the end of the last glaciation.
 The burial customs of the comb pottery people included additions of figures of animals, birds, snakes and men carved from bone and amber
The burial customs of the comb pottery people included additions of figures of animals, birds, snakes and men carved from bone and amber
. Antiquities from comb pottery culture are found from Northern Finland to Eastern Prussia.
The beginning of the Late Neolithic Period about 2200 BC is characterized by the appearance of the Corded Ware culture
, pottery with corded decoration and well-polished stone axes (s.c. boat-shape axes). Evidence of agriculture is provided by charred grains of wheat on the wall of a corded-ware vessel found in Iru settlement. Osteological analysis show an attempt was made to domesticate the wild boar.
Specific burial customs were characterized by the dead being laid on their sides with their knees pressed against their breast, one hand under the head. Objects placed into the graves were made of the bones of domesticated animals.
 The beginning of the Bronze Age
The beginning of the Bronze Age
in Estonia is dated to approximately 1800 BC. The development of the borders between the Finnic peoples
and the Balts
was under way. The first fortified settlements, Asva and Ridala on the island of Saaremaa
and Iru in the Northern Estonia began to be built. The development of shipbuilding facilitated the spread of bronze. Changes took place in burial customs, a new type of burial ground spread from Germanic to Estonian areas, stone cist graves and cremation burials became increasingly common aside a small number of boat-shaped stone graves.
About 7th century BC, a big meteorite hit Saaremaa
island and created the Kaali crater
s.
c. 325 BC, a Greek explorer Pytheas
probably visited Estonia. Thule
island he described has been frequently identified as Saaremaa
.
began in Estonia about 500 BC and lasted until the middle of the 1st century AD. The oldest iron items were imported, although since the 1st century iron was smelted from local marsh and lake ore. Settlement sites were located mostly in places that offered natural protection. Fortresses were built, although used temporarily. The appearance of square Celtic fields surrounded by enclosures in Estonia date from the Pre-Roman Iron Age. The majority of stones with man-made indents, which presumably were connected with magic designed to increase crop fertility, date from this period. A new type of grave, quadrangular burial mounds began to develop. Burial traditions show the clear beginning of social stratification.
The Roman Iron Age
in Estonia is roughly dated to between 50 and 450 AD, the era that was affected by the influence of the Roman Empire
. In material culture this is reflected by a few Roman coins, some jewellery
and artefacts. The abundance of iron artefacts in Southern Estonia speaks of closer mainland ties with southern areas while the islands of western and northern Estonia communicated with their neighbors mainly by sea. By the end of the period three clearly defined tribal dialectical areas: Northern Estonia, Southern Estonia, and Western Estonia including the islands had emerged, the population of each having formed its own understanding of identity.
 The name of Estonia occurs first in a form of Aestii in the 1st century AD by Tacitus
The name of Estonia occurs first in a form of Aestii in the 1st century AD by Tacitus
; however, it might have indicated Baltic tribes living in the area. In the Northern Sagas (9th century) the term started to be used to indicate the Estonians.
Ptolemy
in his Geography III in the middle of the 2nd century CE mentions the Osilians among other dwellers on the Baltic shore.
According to the 5th-century Roman historian Cassiodorus
the people known to Tacitius as the Aestii were the Estonians. The extent of their territory in early medieval times is disputed but the nature of their religion is not. They were known to the Scandinavians as experts in wind-magic, as were the Lapps (known at the time as Finns) in the North. Cassiodorus mentions Estonia in his book V. Letters 1–2 dating from the 6th century.
The Chudes, as mentioned by a monk Nestor in the earliest Russian chronicles, were the Ests or Esthonians.
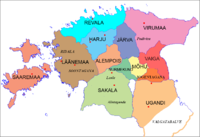
 In the 1st centuries AD political and administrative subdivisions began to emerge in Estonia. Two larger subdivisions appeared: the parish (kihelkond) and the county (maakond). The parish consisted of several villages. Nearly all parishes had at least one fortress. The defense of the local area was directed by the highest official, the parish elder. The county was composed of several parishes, also headed by an elder. By the 13th century the following major counties had developed in Estonia: Saaremaa
In the 1st centuries AD political and administrative subdivisions began to emerge in Estonia. Two larger subdivisions appeared: the parish (kihelkond) and the county (maakond). The parish consisted of several villages. Nearly all parishes had at least one fortress. The defense of the local area was directed by the highest official, the parish elder. The county was composed of several parishes, also headed by an elder. By the 13th century the following major counties had developed in Estonia: Saaremaa
(Osilia), Läänemaa (Rotalia or Maritima), Harjumaa (Harria), Rävala (Revalia), Virumaa
(Vironia), Järvamaa (Jervia), Sakala (Saccala), and Ugandi (Ugaunia).
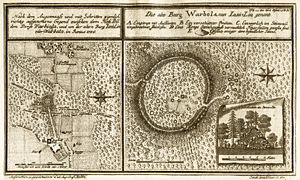
Varbola Stronghold
was one of the largest circular rampart fortresses and trading centers built in Estonia
, Harju County
at the time.
In the 11th century the Scandinavians are frequently chronicled as combating the Vikings from the eastern shores of the Baltic Sea.
With the rise of Christianity
, centralized authority in Scandinavia and Germany eventually led to the Baltic crusades.
The east Baltic world was transformed by military conquest: first the Livs, and Estonians
, then the Prussians and the Finns underwent defeat, baptism
, military occupation
and sometimes extermination by groups of Germans, Danes and Swedes.

Estonia remained one of the last corners of medieval Europe to be Christianized
. In 1193 Pope Celestine III
called for a crusade against pagan
s in Northern Europe
. The Northern Crusades
from Northern Germany
established the stronghold of Riga
(in modern Latvia). With the help of the newly converted local tribes of Livs
and Letts
, the crusaders initiated raids into part of what is present-day Estonia in 1208. Estonian tribes fiercely resisted the attacks from Riga and occasionally themselves sacked territories controlled by the crusaders. In 1217 the German crusading order the Sword Brethren
and their recently converted allies won a major battle in which the Estonian commander Lembitu was killed. The period of the several Northern Crusade battles in Estonia between 1208 and 1227 is also known as the period of the ancient Estonian fight for independence.
 Northern Estonia was conquered by Danish
Northern Estonia was conquered by Danish
crusaders led by king Waldemar II
, who arrived in 1219 on the site of the Estonian town of Lindanisse (now Tallinn
) at (Latin) Revelia (Estonian) Revala or Rävala, the adjacent ancient Estonian county. The Danish Army defeated the Estonians at Battle of Lyndanisse
.
The Estonians of Harria started a rebellion in 1343 (St.George's Night Uprising). The province was occupied by the Livonian Order
as a result. In 1346, the Danish dominions in Estonia (Harria and Vironia) were sold for 10 000 marks to the Livonian Order
.
comes from 1294, in the laws of the town of Haapsalu
. Estonian Swedes are one of the earliest known minorities in Estonia. They have also been called Coastal Swedes ("Rannarootslased" in Estonian
), or according to their settlement area Ruhnu
Swedes, Hiiu Swedes etc. They themselves used the expression aibofolke – Island People.
The ancient areas of Swedish settlement in Estonia were Ruhnu Island, Hiiumaa
Island, the west coast and smaller islands (Vormsi
, Noarootsi, Sutlepa, Riguldi, Osmussaar
), the north-west coast of the Harju District (Nõva, Vihterpalu, Kurkse, the Pakri Peninsula and the Pakri Islands) and Naissaar
Island near Tallinn. The towns with a significant percentage of Swedish population have been Haapsalu
and Tallinn.
In earlier times Swedes also lived on the coasts of Saaremaa, the southern part of Läänemaa, the eastern part of Harjumaa
and the western part of Virumaa
.
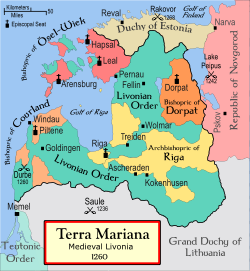
In 1227 the Sword Brethren conquered the last indigenous stronghold on the Estonian island of Saaremaa
. After the conquest, all the remaining local pagans of Estonia were ostensibly Christianized
. An ecclesiastical state Terra Mariana was established .
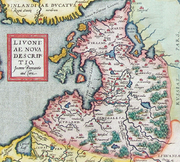 The territory was then divided between the Livonian branch
The territory was then divided between the Livonian branch
of the Teutonic Order, the Bishopric of Dorpat
(in Estonian: Tartu piiskopkond) and the Bishopric of Ösel-Wiek
(in Estonian: Saare-Lääne piiskopkond). The Northern part of Estonia – more exactly Harjumaa and Virumaa districts (in German: Harrien und Wierland) – was a nominal possession of Denmark
until 1346. Tallinn
(Reval) was given the Lübeck Rights
in 1248 and joined the Hanseatic League
at the end of the 13th century. In 1343 the people of northern Estonia and Saaremaa (Oesel) Island started a rebellion (St. George's Night Uprising
) against the rule of their German-speaking landlords. The uprising was put down, and four elected Estonian "kings" were killed in Paide
during peace negotiations in 1343 and Vesse, the rebel King of Saaremaa, was hanged in 1344.
Despite local rebellions and Muscovian invasions in 1481 and 1558, the local Low German
-speaking upper class continued to rule Estonia and from 1524 preserved Estonian commitment to the Protestant Reformation
.
(1483–1546) and his 95 Theses.
The Reformation resulted in great change in the Baltic. Ideas entered the Livonian Confederation very quickly and by the 1520s they were well known. Language, education, religion and politics were greatly transformed. Church services were now given in the local vernacular, instead of Latin, as was previously used.
once again asked for help of Gustav I of Sweden
, and The Kingdom of Poland (1385–1569)
also began direct negotiations with Gustavus, but nothing resulted because on September 29, 1560, Gustavus I Vasa died. The chances for success of Magnus von Lyffland and his supporters looked particularly good in 1560 (and 1570). In the former case he had been recognised as their sovereign
by The Bishopric of Ösel-Wiek
and The Bishopric of Courland
, and as their prospective ruler by the authorities of The Bishopric of Dorpat
; The Bishopric of Reval
with the Harrien-Wierland gentry
were on his side; Livonian Order
conditionally recognised his right of ownership of Estonia (Principality of Estonia). Then along with Archbishop
Wilhelm von Brandenburg of The Archbishopric of Riga and his coadjutor Christoph von Mecklenburg, Kettler gave to Magnus the portions of The Kingdom of Livonia
, which he had taken possession of, but they refused to give him any more land. Once Eric XIV of Sweden
became king he took quick actions to get involved in the war. He negotiated a continued peace with Muscovy and spoke to the burgher
s of Reval city. He offered them goods to submit to him as well as threatening them. By June 6, 1561 they submitted to him contrary to the persuasions of Kettler to the burghers. The King's brother Johan married the Polish princess Catherine Jagiellon
. Wanting to obtain his own land in Livonia, he loaned Poland money and then claimed the castle
s they had pawned as his own instead of using them to pressure Poland. After Johan returned to Finland
, Erik XIV forbade him to deal with any foreign countries without his consent. Shortly after that Erik XIV started acting quickly lost any allies he was about to obtain, either from Magnus or the Archbishop of Riga
. Magnus was upset he had been tricked out of his inheritance
of Holstein
. After Sweden occupied
Reval, Frederick II of Denmark
made a treaty with Erik XIV of Sweden in August 1561. The brothers were in great disagreement and Frederick II negotiated a treaty with Ivan IV on August 7, 1562 in order to help his brother obtain more land and stall further Swedish advance. Erik XIV did not like this and The Northern Seven Years' War
between The Free City of Lübeck, Denmark, Poland, and Sweden broke out. While only losing land and trade, Frederick II and Magnus were not faring well. But in 1568 Erik XIV became insane and his brother Johan III took his place. Johan III ascended to the throne
of Sweden and due to his friendship with Poland he began a policy against Muscovy. He would try to obtain more land in Livonia and exercise strength over Denmark. After all parties had been financially drained, Frederick II let his ally, King Sigismund II Augustus
of Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, know that he was ready for peace. On December 15, 1570, the Treaty of Stettin was concluded. It is, however, more difficult to estimate the scope and magnitude of the support Magnus received in Livonian cities. Compared to the Harrien-Wierland gentry, the Reval city council, and hence probably the majority of citizens, demonstrated a much more reserved attitude towards Denmark and King Magnus of Livonia. Nevertheless, there is no reason to speak about any strong pro-Swedish sentiments among the residents of Reval. The citizens who had fled to The Bishopric of Dorpat or had been deported to Muscovy hailed Magnus as their saviour until 1571. The analysis indicates that during the Livonian War
a pro-independence
wing emerged among the Livonian gentry and townspeople, forming the so-called "". Dismissing hostilities, these forces perceived an agreement with Muscovy as a chance to escape the atrocities of war and avoid the division of Livonia. That is why Magnus, who represented Denmark and later struck a deal with Ivan the Terrible, proved a suitable figurehead for this faction.
 The Peace Party, however, had its own armed forces – scattered bands of household troops (Hofleute) under diverse command, which only united in action in 1565 (Battle of Pärnu, 1565 and Siege of Reval, 1565), in 1570–1571 (Siege of Reval, 1570–1571; 30 weeks), and in 1574–1576 (first on Sweden’s side, then came the sale of to the Danish Crown, and the loss of the territory to ). In 1575 after Muscovy attacked Danish claims in Livonia, Frederick II dropped out of the competition as well as the Holy Roman Emperor. After this Johan III held off on his pursuit for more land due to Muscovy obtaining lands that Sweden controlled. He used the next two years of truce to get in a better position. In 1578, he resumed the fight for not only Livonia, but also everywhere due to an understanding he made with Rzeczpospolita. In 1578 Magnus retired to Rzeczpospolita and his brother all but gave up the land in Livonia.
The Peace Party, however, had its own armed forces – scattered bands of household troops (Hofleute) under diverse command, which only united in action in 1565 (Battle of Pärnu, 1565 and Siege of Reval, 1565), in 1570–1571 (Siege of Reval, 1570–1571; 30 weeks), and in 1574–1576 (first on Sweden’s side, then came the sale of to the Danish Crown, and the loss of the territory to ). In 1575 after Muscovy attacked Danish claims in Livonia, Frederick II dropped out of the competition as well as the Holy Roman Emperor. After this Johan III held off on his pursuit for more land due to Muscovy obtaining lands that Sweden controlled. He used the next two years of truce to get in a better position. In 1578, he resumed the fight for not only Livonia, but also everywhere due to an understanding he made with Rzeczpospolita. In 1578 Magnus retired to Rzeczpospolita and his brother all but gave up the land in Livonia.
Having rejected peace proposals from its enemies, Ivan the Terrible found himself in a difficult position by 1579, when Crimean Khanate
devastated Muscovian territories and burnt down Moscow
(see Russo-Crimean Wars
), the drought
and epidemic
s have fatally affected the economy, Oprichnina
had thoroughly disrupted the government, while The Grand Principality of Lithuania had united with
The Kingdom of Poland (1385–1569)
and acquired an energetic leader, Stefan Batory
, supported by Ottoman Empire
(1576). Stefan Batory replied with a series of three offensive
s against Muscovy, trying to cut The Kingdom of Livonia
from Muscovian territories. During his first offensive in 1579 with 22,000 men he retook Polotsk
, during the second, in 1580, with 29,000-strong army he took Velikie Luki, and in 1581 with a 100,000-strong army he started the Siege of Pskov
. Frederick II had trouble continuing the fight against Muscovy unlike Sweden
and Poland. He came to an agreement with John III
in 1580 giving him the titles in Livonia. That war would last from 1577 to 1582. Muscovy recognized Polish–Lithuanian control of Ducatus Ultradunensis only in 1582. After Magnus von Lyffland died in 1583, Poland invaded his territories in The Duchy of Courland and Frederick II decided to sell his rights of inheritance
. Except for the island of Œsel, Denmark
was out of the Baltic
by 1585. As of 1598 Polish Livonia was divided onto:
During the Livonian War
in 1561, northern Estonia submitted to Swedish control, while southern Estonia briefly came under the control of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth in the 1580s. In 1625, mainland Estonia came entirely under Swedish rule. Estonia was administratively divided between the provinces of Estonia in the north and Livonia
in southern Estonia and northern Latvia, a division which persisted until the early 20th century.
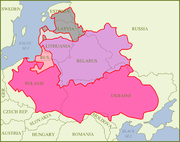
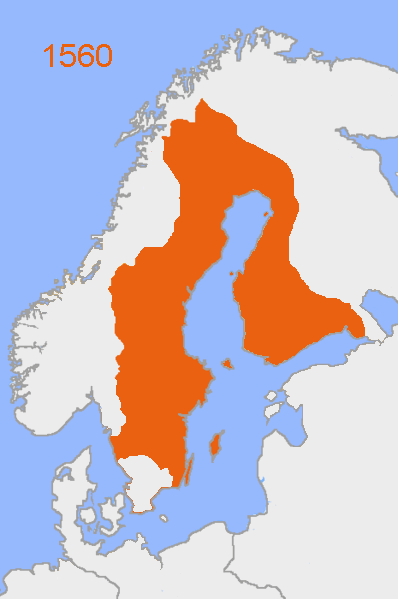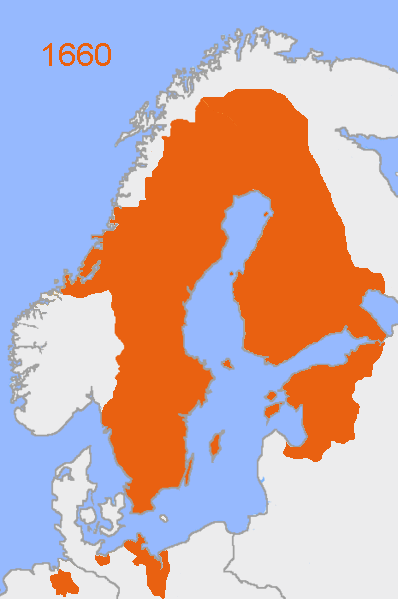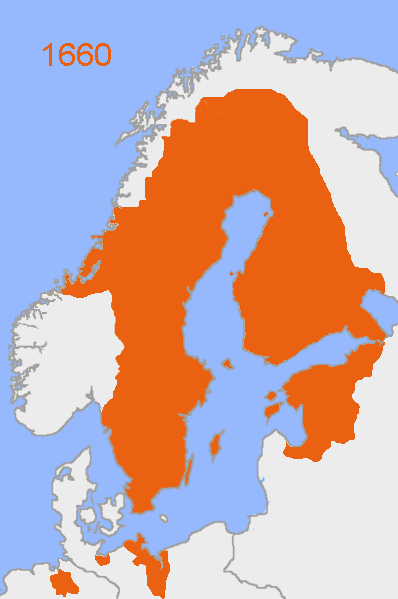 During 1582–83 southern Estonia (Livonia
During 1582–83 southern Estonia (Livonia
) became part of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth.
as the Livonian Order
lost their foothold in the Baltic provinces. Territorially it represented the northern part of present-day Estonia.
Livonia was conquered from the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth by 1629 in the Polish–Swedish War
. By the Treaty of Oliva
between the Commonwealth and Sweden in 1660 following the Northern Wars
the Polish–Lithuanian king
renounced all claims to the Swedish throne and Livonia was formally ceded to Sweden. Swedish Livonia represents the southern part of present-day Estonia and the northern part of present-day Latvia
(Vidzeme
region)
In 1631, Gustavus II Adolphus of Sweden forced the nobility
to grant the peasantry greater autonomy, and in 1632 established a printing press
and University
in the city of Tartu
.
 Sweden's defeat by Russia in the Great Northern War
Sweden's defeat by Russia in the Great Northern War
resulted in the Capitulation of Estonia and Livonia
in 1710, confirmed by the Treaty of Nystad
in 1721, and Russian rule was then imposed on what later became modern Estonia. Nonetheless, the legal system, Lutheran church, local and town governments, and education remained mostly German until the late 19th century and partially until 1918.
By 1819, the Baltic provinces
were the first in the Russian empire in which serfdom was abolished, the largely autonomous nobility allowing the peasants to own their own land or move to the cities. These moves created the economic foundation for the coming to life of the local national identity and culture as Estonia was caught in a current of national awakening that began sweeping through Europe in the mid-19th century.
of rational thinking, ideas that propagated freedom of thinking and brotherhood and equality. The French Revolution
provided a powerful motive for the enlightened local upper class to create literature for the peasantry. The freeing of the peasantry from serfdom on the nobles' estates in 1816 in Southern Estonia: Governorate of Livonia (Russian: Лифляндская губерния) and 1819 in Northern Estonia: Governorate of Estonia
(Russian: Эстляндская губерния) by Alexander I of Russia
gave rise to a debate as to the future fate of the former enslaved peoples. Although Baltic Germans by and large regarded the future of the Estonians as being a fusion with the Baltic Germans, the Estophile educated class admired the ancient culture of the Estonians and their era of freedom before the conquests by Danes and Germans in the 13th century. The Estophile Enlightenment Period formed the transition from religious Estonian literature to newspapers written in Estonian for the mass public.
as the language of instruction in schools, all-Estonian song festivals were held regularly after 1869, and a national literature in Estonian developed. "Kalevipoeg
", Estonia's national epic, was published in 1861 in both Estonian and German.
1889 marked the beginning of the central government-sponsored policy of Russification
. The impact of this was that many of the Baltic German
legal institutions were either abolished or had to do their work in Russian – a good example of this is the University of Tartu
.
As the Russian Revolution of 1905
swept through Estonia, the Estonians called for freedom of the press
and assembly
, for universal franchise
, and for national autonomy. Estonian gains were minimal, but the tense stability that prevailed between 1905 and 1917 allowed Estonians to advance the aspiration of national statehood.
 Estonia as a unified political entity first emerged after the Russian February Revolution
Estonia as a unified political entity first emerged after the Russian February Revolution
of 1917. With the collapse of the Russian Empire
in World War I
, Russia's Provisional Government granted national autonomy to an unified Estonia
in April. The Governorate of Estonia
in the north (corresponding to the historic Danish Estonia
) was united with the northern part of the Governorate of Livonia. Elections for a provisional parliament, Maapäev
was organized, with the Menshevik
and Bolshevik
factions of the Russian Social Democratic Labour Party
obtaining a part of the vote. On November 5, 1917, two days before the October Revolution
in Saint Petersburg
, Estonian Bolshevik
leader Jaan Anvelt
violently usurped power from the legally constituted Maapäev in a coup d'état, forcing the Maapäev underground.
In February, after the collapse of the peace talks between Soviet Russia and the German Empire
, mainland Estonia was occupied by the Germans. Bolshevik forces retreated to Russia. Between the Russian Red Army's retreat and the arrival of advancing German troops, the Salvation Committee
of the Estonian National Council Maapäev issued the Estonian Declaration of Independence
in Pärnu
on February 23, 1918.
 After the collapse of the short-lived puppet government of the United Baltic Duchy
After the collapse of the short-lived puppet government of the United Baltic Duchy
and the withdrawal of German troops in November 1918, an Estonian provisional Government retook office. A military invasion by the Red Army
followed a few days later, however, marking the beginning of the Estonian War of Independence (1918–1920). The Estonian army cleared the entire territory of Estonia of the Red Army by February 1919.
was elected. On February 2, 1920, the Treaty of Tartu
was signed by the Republic of Estonia and the Russian SFSR. The terms of the treaty stated that Russia renounced in perpetuity all rights to the territory of Estonia. The first Constitution of Estonia
was adopted on June 15, 1920. The Republic of Estonia obtained international recognition and became a member of the League of Nations
in 1921.
In nearby Finland
similar circumstances resulted in a bloody civil war. Despite repeated threats from fascist movements, Finland became and remained a free democracy under the rule of law. By contrast Estonia, without a civil war, started as a democracy and was turned into a dictatorship in 1934.
 The first period of independence lasted 22 years, beginning in 1918. Estonia underwent a number of economic, social, and political reforms necessary to come to terms with its new status as a sovereign state
The first period of independence lasted 22 years, beginning in 1918. Estonia underwent a number of economic, social, and political reforms necessary to come to terms with its new status as a sovereign state
. Economically and socially, land reform in 1919 was the most important step. Large estate holdings belonging to the Baltic nobility
were redistributed among the peasants and especially among volunteers in the Estonian War of Independence. Estonia's principal markets became Scandinavia
, the United Kingdom
, and western Europe, with some exports to the United States
and to the Soviet Union
.
The first constitution of the Republic of Estonia, adopted in 1920, established a parliamentary form of government. The parliament (Riigikogu
) consisted of 100 members elected for 3-year terms. Between 1920 and 1934, Estonia had 21 governments.
A mass anticommunist and antiparliamentary Vaps Movement emerged in the 1930s.
In October 1933 a referendum
on constitutional reform initiated by the Vaps Movement was approved by 72.7 percent. The league spearheaded replacement of the parliamentary system
with a presidential form of government
and laid the groundwork for an April 1934 presidential election, which it expected to win. However, the Vaps Movement was thwarted by a pre-emptive coup d'état
on March 12, 1934, by Head of State Konstantin Päts
, who then established his own authoritarian rule until a new constitution came to force. During the Era of Silence
, political parties were banned and the parliament was not in session between 1934 and 1938 as the country was ruled by decree
by Konstantin Päts
. The Vaps Movement was officially banned and finally disbanded in December 1935. On May 6, 1936, 150 members of the league went on trial and 143 of them were convicted to long-term prison sentences. They were granted an amnesty and freed in 1938, by which time the league had lost most of its popular support.
The independence period was one of great cultural advancement. Estonian language schools were established, and artistic life of all kinds flourished. One of the more notable cultural acts of the independence period, unique in western Europe at the time of its passage in 1925, was a guarantee of cultural autonomy to minority group
s comprising at least 3,000 persons, including Jews (see history of the Jews in Estonia
). Historians see the lack of any bloodshed after a nearly "700-year German rule" as indication that it must have been mild by comparison.
Estonia had pursued a policy of neutrality, but it was of no consequence after the Soviet Union
and Nazi Germany
signed the Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact on August 23, 1939. In the agreement, the two great powers agreed to divide up the countries situated between them (Poland
, Lithuania
, Latvia
, Estonia, and Finland
) with Estonia falling in the Soviet "sphere of influence
". After the invasion of Poland, the Orzeł incident took place when Polish submarine ORP Orzeł
looked for shelter in Tallinn
but escaped after the Soviet Union
attacked Poland on September 17. Estonian's lack of will and/or inability to disarm and intern the crew caused the Soviet Union to accuse Estonia of "helping them escape" and claim that Estonia was not neutral. On September 24, 1939, the Soviet Union threatened Estonia with war unless provided with military bases in the country –- an ultimatum with which the Estonian government complied.

On September 24, 1939, warships of the Red Navy appeared off Estonian ports and Soviet bombers began a threatening patrol over Tallinn
and the nearby countryside. Moscow demanded Estonia assent to an agreement which allowed the USSR to establish military bases and station 25,000 troops on Estonian soil for the duration of the European war. The government of Estonia accepted the ultimatum, signing the corresponding agreement on September 28, 1939.
On June 12, 1940, the order for a total military blockade of Estonia by the Soviet Baltic Fleet
was given.
On June 14, 1940, while the world's attention was focused on the fall of Paris
to Nazi Germany
a day earlier, the Soviet military blockade of Estonia went into effect, and two Soviet bombers downed Finnish passenger airplane "Kaleva
" flying from Tallinn to Helsinki carrying three diplomatic pouches from the U.S. legations in Tallinn
, Riga
and Helsinki
. US Foreign Service employee Henry W. Antheil, Jr.
was killed in the crash.
On June 16, 1940, the Soviet Union invaded Estonia. Molotov
accused the Baltic states of conspiracy against the Soviet Union and delivered an ultimatum to Estonia for the establishment of a government approved of by the Soviets.
The Estonian government decided, given the overwhelming Soviet force both on the borders and inside the country, not to resist, to avoid bloodshed and open war. Estonia accepted the ultimatum and the statehood of Estonia de facto
ceased to exist as the Red Army exited from their military bases in Estonia on June 17. The following day, some 90,000 additional troops entered the country. The military occupation
of the Republic of Estonia was rendered "official" by a communist coup d'état
supported by the Soviet troops, followed by "parliamentary elections" where all but pro-Communist candidates were outlawed. The "parliament" so elected proclaimed Estonia a Socialist Republic on July 21, 1940 and unanimously requested Estonia to be "accepted" into the Soviet Union
. Those who had fallen short of the "political duty" of voting Estonia into the USSR, who had failed to have their passports stamped for so voting, were allowed to be shot in the back of the head by Soviet tribunals. Estonia was formally annexed into the Soviet Union on August 6 and renamed the Estonian Soviet Socialist Republic
. See, for instance, position expressed by European Parliament, which condemned "the fact that the occupation of these formerly independent and neutral States by the Soviet Union occurred in 1940 following the Molotov/Ribbentrop pact, and continues."
The Soviet authorities, having gained control over Estonia, immediately imposed a regime of terror. During the first year of Soviet occupation (1940–1941) over 8,000 people, including most of the country's leading politicians and military officers, were arrested. About 2,200 of the arrested were executed in Estonia, while most others were moved to prison camps in Russia, from where very few were later able to return alive. On June 14, 1941, when mass deportation
s took place simultaneously in all three Baltic countries, about 10,000 Estonian civilians were deported to Siberia
and other remote areas of the Soviet Union, where nearly half of them later perished. Of the 32,100 Estonian men who were forcibly relocated to Russia under the pretext of mobilisation into the Soviet army after the German invasion of the Soviet Union in 1941, nearly 40 percent died within the next year in the so-called "labour battalion
s" of hunger, cold and overworking. During the first Soviet occupation of 1940–41 about 500 Jews were deported to Siberia
.
Estonian graveyards and monuments were destroyed. Among others, the Tallinn Military Cemetery had the majority of gravestones from 1918–1944 destroyed by the Soviet authorities, and this graveyard became reused by the Red Army
.
Other cemeteries destroyed by the authorities during the Soviet era in Estonia include Baltic German
cemeteries established in 1774 (Kopli cemetery
, Mõigu cemetery
) and the oldest cemetery in Tallinn, from the 16th century, Kalamaja cemetery
.
Many countries including the United States did not recognize the seizure of Estonia by the USSR. Such countries recognized Estonian diplomats and consuls who still functioned in many countries in the name of their former governments. These aging diplomats persisted in this anomalous situation until the ultimate restoration of Baltic independence.
Ernst Jaakson
, the longest-serving foreign diplomatic representative to the United States, served as vice-consul from 1934, and as consul general in charge of the Estonian legation in the United States from 1965 until reestablishment of Estonia's independence. On November 25, 1991 he presented credentials as Estonian ambassador to the United States.

After Nazi Germany
invaded the Soviet Union
on June 22, 1941, and the Wehrmacht reached Estonia in July 1941, most Estonians greeted the Germans with relatively open arms and hoped to restore independence. But it soon became clear that sovereignty was out of the question. Estonia became a part of the German-occupied "Ostland
". A Sicherheitspolizei
was established for internal security under the leadership of Ain-Ervin Mere
. The initial enthusiasm that accompanied the liberation from Soviet occupation quickly waned as a result and the Germans had limited success in recruiting volunteers. The draft was introduced in 1942, resulting in some 3,400 men fleeing to Finland to fight in the Finnish Army rather than join the Germans. Finnish Infantry Regiment 200
AKA (Estonian: soomepoisid) was formed out of Estonian volunteers in Finland. With the Allied victory over Germany becoming certain in 1944, the only option to save Estonia's independence was to stave off a new Soviet invasion of Estonia until Germany's capitulation.
By January 1944, the front was pushed back by the Soviet Army almost all the way to the former Estonian border. Narva
was evacuated. Jüri Uluots
, the last legitimate prime minister of the Republic of Estonia (according to the Constitution of the Republic of Estonia) prior to its fall to the Soviet Union in 1940, delivered a radio address that implored all able-bodied men born from 1904 through 1923 to report for military service (before this, Uluots had opposed Estonian mobilization.) The call drew support from all across the country: 38,000 volunteers jammed registration centers. Several thousand Estonians who had joined the Finnish army came back across the Gulf of Finland
to join the newly formed Territorial Defense Force, assigned to defend Estonia against the Soviet advance. It was hoped that by engaging in such a war Estonia would be able to attract Western support for the cause of Estonia's independence from the USSR and thus ultimately succeed in achieving independence.
The initial formation of the volunteer SS Estonian legion created in 1942 was eventually expanded to become a full-sized conscript division of the Waffen-SS
in 1944, the 20th Waffen Grenadier Division of the SS (1st Estonian). The Estonian units saw action defending the Narva line
throughout 1944.
As the Germans started to retreat on 18 September 1944, Jüri Uluots
, the last Prime Minister of the Estonian Republic prior to Soviet occupation, assumed the responsibilities of president (as dictated in the Constitution) and appointed a new government while seeking recognition from the Allies
. On 22 September 1944, as the last German units pulled out of Tallinn, the city was re-occupied by the Soviet Red Army. The new Estonian government fled to Stockholm
, Sweden
and operated in exile until 1992, when Heinrich Mark
, the prime minister of the Estonian government in exile acting as president, presented his credentials to incoming president Lennart Meri
.
granted them the right to enter the region. The creation of the Republic of Estonia in 1918 marked the beginning of a new era for the Jews. Approximately 200 Jews fought in combat for the creation of the Republic of Estonia and 70 of these men were volunteers. From the very first days of her existence as a state, Estonia showed her tolerance towards all the peoples inhabiting her territories. On 12 February 1925 The Estonian government passed a law pertaining to the cultural autonomy of minority peoples. The Jewish community quickly prepared its application for cultural autonomy. Statistics on Jewish citizens were compiled. They totaled 3,045, fulfilling the minimum requirement of 3000. In June 1926 the Jewish Cultural Council was elected and Jewish cultural autonomy was declared. Jewish cultural autonomy was of great interest to the global Jewish community. The Jewish National Endowment presented the Government of the Republic of Estonia
with a certificate of gratitude for this achievement.
There were, at the time of Soviet occupation in 1940, approximately 2000 Estonian Jews. Many Jewish people were deported to Siberia along with other Estonians by the Soviets. It is estimated that 500 Jews suffered this fate. With the invasion of the Baltics, it was the intention of the Nazi government to use the Baltic countries as their main area of mass genocide. Consequently, Jews from countries outside the Baltics were shipped there to be exterminated. Out of the approximately 4,300 Jews in Estonia prior to the war, between 1,500 and 2,000 were entrapped by the Nazis,
and an estimated 10,000 Jews were killed in Estonia after having been deported to camps there from elsewhere in Eastern Europe.
There are known to have been 7 ethnic Estonians
– Ralf Gerrets, Ain-Ervin Mere
, Jaan Viik, Juhan Jüriste, Karl Linnas
, Aleksander Laak and Ervin Viks – that have faced trials for crimes against humanity.
Since the reestablishment of Estonian independence the Estonian International Commission for Investigation of Crimes Against Humanity
has been established. Markers were put in place for the 60th anniversary of the mass executions that were carried out at the Lagedi, Vaivara and Klooga (Kalevi-Liiva) camps in September 1944.
Almost all the remaining Estonian Swedes
fled in August 1944, often in their small boats to the Swedish island of Gotland
.
The Russian minority grew significantly in numbers during the postwar era.
Estonia had suffered huge losses. Ports had been destroyed, and 45% of industry and 40% of the railways had become damaged. Estonia's population had decreased by one-fifth, about 200,000 people. Some 10% of the population (over 80,000 people) had fled to the West between 1940 and 1944. More than 30,000 soldiers had been killed in action. In 1944 Russian air raids
had destroyed Narva
and one-third of the residential area in Tallinn
. By the late autumn of 1944, Soviet forces had ushered in a second phase of Soviet rule on the heels of the German troops withdrawing from Estonia, and followed it up by a new wave of arrests and executions of people considered disloyal to the Soviets.
 An anti-Soviet guerrilla
An anti-Soviet guerrilla
movement known as the "Metsavennad" ("Forest Brothers")
developed in the countryside, reaching its zenith in 1946–48. It is hard to tell how many people were in the ranks of the Metsavennad; however, it is estimated that at different times there could have been about 30,000–35,000 people. Probably the last Forest Brother was caught in September 1978, and killed himself during his apprehension.
In March 1949, 20,722 people (2.5% of the population) were deported to Siberia. By the beginning of the 1950s, the occupying regime had suppressed the resistance movement.
After the war the Communist Party of the Estonian Soviet Socialist Republic (ECP) became the pre-eminent organization in the republic. The ethnic Estonian share in the total ECP membership decreased from 90% in 1941 to 48% in 1952.

's death, Party membership vastly expanded its social base to include more ethnic Estonians. By the mid-1960s, the percentage of ethnic Estonian membership stabilized near 50%. On the eve of perestroika
the ECP claimed about 100,000 members; less than half were ethnic Estonians and they totalled less than 7% of the country's population.
One positive aspect of the post-Stalin era in Estonia was the regranting of permission in the late 1950s for citizens to make contact with foreign countries. Ties were reactivated with Finland
, and in the 1960s, a ferry connection was opened from Tallinn to Helsinki
and Estonians began watching Finnish television. This electronic "window on the West" afforded Estonians more information on current affairs and more access to Western culture and thought than any other group in the Soviet Union. This heightened media environment was important in preparing Estonians for their vanguard role in extending perestroika during the Gorbachev
era.
, the venue for the song festivals, were built in 1960
period of 1956 did healthcare networks start to stabilise. Due to natural development, science and technology advanced and popular welfare increased. All demographic indicators improved; birth rate increased, mortality decreased. Healthcare became freely available to everybody during the Soviet era.

which led to controversy since many governments had not de jure recognized ESSR as part of the USSR. During the preparations to the Olympics
, sports buildings were built in Tallinn, along with other general infrastructure and broadcasting facilities. This wave of investment included Tallinn Airport, Hotell Olumpia, Tallinn TV Tower
, Pirita Yachting Centre
and Linnahall
.
died and was succeeded by Yuri Andropov
, the former head of the KGB
. Andropov introduced limited economic reforms and established an anti-corruption program. On February 9, 1984 Andropov died and was succeeded by Konstantin Chernenko
who in turn died on March 10, 1985.
became a growing health issue. Up until 1985 and the beginning of glasnost
, it was illegal to publish statistical data on alcohol sales. It is estimated that alcoholism peaked in 1982–1984, when consumption reached 11.2 litres of absolute alcohol per person per annum. (In comparison, in Finland during the same period consumption only 6–7 litres per person per annum).
and the dissident-led Estonian National Independence Party soon followed.
was issued on November 16, 1988. By 1989 the political spectrum had widened, and new parties were formed and re-formed almost daily. The republic's Supreme Soviet
transformed into an authentic regional lawmaking body. This relatively conservative legislature passed an early declaration of sovereignty (November 16, 1988); a law on economic independence (May 1989) confirmed by the Supreme Soviet of the Soviet Union that November; a language law making Estonian the official language
(January 1989); and local and republic election laws stipulating residency requirements for voting and candidacy (August, November 1989).
Despite the emergence of the Popular Front and the Supreme Soviet as a new lawmaking body, since 1989 the different segments of the indigenous Estonian population had been politically mobilized by different and competing actors. The Popular Front's proposal, to declare the independence of Estonia as a new, so-called "third republic" whose citizens would be all those living there at the moment found less and less support over time.
A grassroots Estonian Citizens' Committees Movement launched in 1989 with the objective of registering all pre-war citizens of the Republic of Estonia and their descendants in order to convene a Congress of Estonia
. Their emphasis was on the illegal nature of the Soviet system and that hundreds of thousands of inhabitants of Estonia had not ceased to be citizens of the Estonian Republic which still existed de jure, recognized by the majority of Western nations. Despite the hostility of the mainstream official press and intimidation by Soviet Estonian authorities, dozens of local citizens' committees were elected by popular initiative all over the country. These quickly organized into a nation-wide structure and by the beginning of 1990, over 900,000 people had registered themselves as citizens of the Republic of Estonia.
The spring of 1990 saw two free elections and two alternative legislatures developed in Estonia. On 24 February 1990, the 464-member Congress of Estonia (including 35 delegates of refugee communities abroad) was elected by the registered citizens of the republic. The Congress of Estonia convened for the first time in Tallinn March 11–12, 1990, passing 14 declarations and resolutions. A 70-member standing committee (Eesti Komitee) was elected with Tunne Kelam
as its chairman.
In March 1991 a referendum was held on the issue of independence. This was somewhat controversial, as holding a referendum could be taken as signalling that Estonian independence would be established rather than "re"-established. There was some discussion about whether it was appropriate to allow the Russian immigrant minority to vote, or if this decision should be reserved exclusively for citizens of Estonia. In the end all major political parties backed the referendum, considering it most important to send a strong signal to the world. To further legitimise the vote, all residents of Estonia were allowed to participate. The result vindicated these decisions, as the referendum produced a strong endorsement for independence. Turnout was 82%, and 64% of all possible voters in the country backed independence, with only 17% against.
Although the majority of Estonia's large Russian-speaking diaspora of Soviet-era immigrants did not support full independence, they were divided in their goals for the republic. In March 1990 some 18% of Russian
speakers supported the idea of a fully independent Estonia, up from 7% the previous autumn, and by early 1990 only a small minority of ethnic Estonians were opposed to full independence.
In the March 18, 1990 elections for the 105-member Supreme Soviet all residents of Estonia were eligible to participate, including all Soviet-era immigrants from the U.S.S.R. and approximately 50,000 Soviet troops stationed there. The Popular Front coalition, composed of left
and centrist parties
and led by former Central Planning Committee official Edgar Savisaar
, gained a parliamentary majority.
 On May 8, 1990, the Supreme Council of the Republic of Estonia (created the previous day) restored the Republic of Estonia
On May 8, 1990, the Supreme Council of the Republic of Estonia (created the previous day) restored the Republic of Estonia
. Through a strict, non-confrontational policy in pursuing independence, Estonia managed to avoid the violence which Latvia
and Lithuania
incurred in the bloody January 1991 crackdowns and in the border customs-post guard murders that summer. During the August coup in the U.S.S.R., Estonia was able to maintain constant operation and control of its telecommunication
s facilities, thereby offering the West
a clear view into the latest coup developments and serving as a conduit for swift Western support and recognition of Estonia's "confirmation" of independence on August 20, 1991. August 20 remains a national holiday in Estonia because of this. Following Europe's lead, the United States formally reestablished diplomatic relations with Estonia on September 2, and the U.S.S.R. Supreme Soviet offered recognition on September 6.
Since the debates about whether the future independent Estonia would be established as a new republic or a continuation of the first republic were not yet complete by the time of the August coup, while the members of the Supreme Soviet generally agreed that independence should be declared rapidly, a compromise was hatched between the two main sides: instead of "declaring" independence, which would imply a new start, or explicitly asserting continuity, the declaration would "confirm" Estonia as a state independent of the Soviet Union, and willing to reestablish diplomatic relations of its own accord. The full text of the statement is available at.
After more than 3 years of negotiations, on August 31, 1994, the armed forces of Russia
withdrew from Estonia. Since fully regaining independence Estonia has had 12 governments with 8 prime ministers: Mart Laar
, Andres Tarand
, Tiit Vähi
, Mart Siimann
, Siim Kallas
, Juhan Parts
, and Andrus Ansip
. The PMs of the interim government (1990–1992) were Edgar Savisaar
and Tiit Vähi
.
Since the last Russian troops left in 1994, Estonia has been free to promote economic and political ties with Western Europe. Estonia opened accession negotiations with the European Union
in 1998 and joined in 2004, shortly after becoming a member of NATO.
n voters approved the constitutional assembly's draft constitution and implementation act, which established a parliamentary government with a president as chief of state and with a government headed by a prime minister.
The Riigikogu
, a unicameral legislative body, is the highest organ of state authority. It initiates and approves legislation sponsored by the prime minister. The prime minister has full responsibility and control over his cabinet.
, an outstanding writer and former Minister of Foreign Affairs
, won this election and became president
. He chose 32-year-old historian and Christian Democratic Party founder Mart Laar
as prime minister.
In February 1992, and with amendments in January 1995, the Riigikogu
renewed Estonia's 1938 citizenship law, which also provides equal civil protection to resident aliens.
In 1996, Estonia ratified a border agreement with Latvia
and completed work with Russia
on a technical border agreement. President Meri
was re-elected in free and fair indirect elections in August and September in 1996. During parliamentary elections in 1999, the seats in Riigikogu
were divided as follows: the Centre Party
received 28, the Pro Patria Union 18, the Reform Party
18, the People's Party Moderates (election cartel between Moderates and People's Party) 17, Coalition Party 7, Country People's Party (now People's Union
) 7, United People's Party's electoral cartel 6 seats. Pro Patria Union, the Reform Party, and the Moderates formed a government with Mart Laar
as prime minister whereas the Centre Party with the Coalition Party, People's Union, United People's Party, and Members of Parliament who were not members of factions formed the opposition in the Riigikogu
.
The 1999 Parliamentary election
, with a 5% threshold and no electoral cartel allowed, resulted in a disaster for the Coalition Party, which achieved only seven seats together with two of its smaller allies. Estonian Ruralfolk Party, which participated the election on its own list, obtained seven seats as well.
The programme of Mart Laar
's government was signed by Pro Patria Union, Reform Party
, Moderates
and People’s Party. The latter two merged soon after, so Mart Laar’s second government is widely known as Kolmikliit, or Tripartite coalition. Notwithstanding the different political orientation of the ruling parties, the coalition stayed united until Mart Laar resigned in December 2001, after Reform Party had broken up the same coalition in Tallinn
municipality, making opposition leader Edgar Savisaar
new Mayor of Tallinn. After resignation of Laar, Reform Party and Estonian Centre Party
formed a coalition that lasted until next parliamentary election, 2003.
The Moderates joined with the People's Party on 27 November 1999, forming the People's Party Moderates.
became the President of the Republic of Estonia, and in January 2002 Prime Minister Laar
stepped down. On January 28, 2002 the new government was formed from a coalition of the centre-right
Estonian Reform Party
and the more left wing Centre Party
, with Siim Kallas
from the Reform Party of Estonia as Prime Minister
.
In 2003, Estonia joined the NATO defense alliance.
in 2003, the seats were allocated as follows (the United People's Party failed to meet the 5% threshold):
Voter turnout
was higher than expected at 58%.
The results saw the Centre Party win the most votes but they were only 0.8% ahead of the new Res Publica party. As a result both parties won 28 seats, which was a disappointment for the Centre Party who had expected to win the most seats. Altogether the right of centre parties won 60 seats, compared to only 41 for the left wing, and so were expected to form the next government.
Both the Centre and Res Publica parties said that they should get the chance to try and form the next government, while ruling out any deal between themselves. President Rüütel had to decide who he should nominate as Prime Minister and therefore be given the first chance at forming a government. On the 2 April he invited the leader of the Res Publica party, Juhan Parts
to form a government and after negotiations a coalition government composed of Res Publica, the Reform Party and the People's Union of Estonia
was formed on the 10 April.
On 14 September 2003, following negotiations that began in 1998, the citizens of Estonia were asked in a referendum whether or not they wished to join the European Union
. With 64% of the electorate turning out the referendum passed with a 66.83% margin in favor, 33.17% against. Accession to the EU took place on 1 May of the following year.
In February 2004 the People's Party Moderates renamed themselves as Social Democratic Party of Estonia.
On the 8 May 2004, a defection of several Centre Party members to form a new party, the Social Liberal Party, over a row concerning the Centrists' "no" stance to joining the European Union changed the allocation of the seats in Riigikogu. Social-liberals had 8 seats, but a hope to form a new party disappeared by the 10 May 2005, because most members in the social-liberal group joined other parties.
announced his resignation following a vote of no confidence in the Riigikogu against Minister of Justice
Ken-Marti Vaher
, which was held on the 21 March. Result: 54 pro (Social Democrats, Social Liberals, People's Union, Pro Patria Union and Reform Party) without no against or neutral MPs. 32 MPs (Res Publica and Centre Party) did not take part.
On 4 April 2005, President Rüütel nominated Reform party leader Andrus Ansip
as Prime Minister designate by and asked him to form a new government, the 8th in 12 years. Ansip formed a government out of a coalition of his Reform Party with the People’s Union and the Centre Party. Approval by the Riigikogu, which by law must decide within 14 days of his nomination, came on 12 April 2005. Ansip was backed by 53 out of 101 members of the Estonian parliament. Forty deputies voted against his candidature.
The general consensus in the Estonian media seems to be that the new Andrus Ansip's cabinet
, on the level of competence, is not necessarily an improvement over the old one.
On 18 May 2005, Estonia signed a border treaty with the Russian Federation in Moscow. The treaty was ratified by the Riigikogu
on 20 June 2005. However, in the end of June the Russian Ministry of Foreign Affairs informed that it did not intend to become a party to the border treaty and did not consider itself bound by the circumstances concerning the object and the purposes of the treaty because Riigikogu had attached a preambula to the ratification act that referenced earlier documents that mentioned the Soviet occupation and the uninterrupted legal continuity of the Republic of Estonia during the Soviet period. The issue remains unsolved and is in focus of European level discussions.
On 4 April 2006, Fatherland Union and Res Publica decided to form a united right-conservative party. The two parties joining was approved on 4 June by both parties in Pärnu. The joined party name is Isamaa ja Res Publica Liit (Union of Pro Patria and Res Publica
).
have shown an improvement in the scores of the Reform Party, gaining 12 seats and reaching 31 MPs; the Centre Party held, while the unified right-conservative Union of Pro Patria and Res Publica
lost 16. Socialdemocrats gained 4 seats, while the Greens entered the Parliaments with 7 seats, at the expenses of the agrarian People's Union
which lost 6. The new configuration of the Estonian Parliament shows a prevalence of the centre-left parties. The Centre Party, led by the mayor of Tallinn Edgar Savisaar
, has been increasingly excluded from collaboration, since his open collaboration with Putin
's United Russia
party, real estate scandals in Tallinn, and the Bronze Soldier controversy, considered as a deliberate attempt of splitting the Estonian society by provoking the Russian minority. The lack of a concrete possibility for government alternance in Estonia has been quoted as a concern.
. With 64% of the electorate turning out the referendum passed with a 66.83% margin in favor, 33.17% against. Accession to the EU took place on 1 May of the following year.
In its first European Parliament elections in 2004
, Estonia
elected 3 MEPs for the Social Democratic Party (PES), while the governing Res Publica Party
and People's Union
polled poorly, not being able to gain any of the other 3 MEPs posts.
The voter turnout
in Estonia was one of the lowest of all member countries at only 26.8%. A similar trend was visible in most of the new member states that joined the EU in 2004.
The European Parliament election of 2009 in Estonia
scored a 43.9% turnout – about 17.1% higher than during the previous election
, and slightly above the European average of 42.94%.
Six seats were up for taking in this election: two of them were won by the Estonian Centre Party
. Estonian Reform Party
, Union of Pro Patria and Res Publica
, Social Democratic Party
and an independent candidate Indrek Tarand
(who gathered the support of 102,460 voters, only 1,046 votes less than the winner of the election) all won one seat each. The success of independent candidates has been attributed both to general disillusionment with major parties and use of closed lists which rendered voters incapable to cast a vote for specific candidates in party lists.
On 1 January 2011 Estonia
adopted the Euro
. The enlargement of the eurozone
, although limited, was hailed as a good sign in a period of global financial crisis and instability of the euro
. To cope with crisis and financial targets, the government cut down public service salaries; the only opposition, in the absence of organised unions, came from Estonian teachers, whose salary cuts were therefore limited.
Estonian euro coins
entered circulation on 1 January 2011. Estonia is the fifth of ten states that joined the EU in 2004, and the first ex-Soviet republic, to join the eurozone
. Of the ten new member states, Estonia was the first to unveil its design. It originally planned to adopt the euro on 1 January 2007; however, it did not formally apply when Slovenia
did, and officially changed its target date to 1 January 2008, and later, to 1 January 2011. On 12 May 2010 the European Commission
announced that Estonia had met all criteria to join the eurozone. On 8 June 2010, the EU finance ministers agreed that Estonia would be able to join the euro on 1 January 2011. On 13 July 2010, Estonia received the final approval from the ECOFIN to adopt the euro as from 1 January 2011. On the same date the exchange rate at which the kroon
would be exchanged for the euro (€1 = 15.6466 krooni) was also announced. On 20 July 2010, mass production of Estonian euro coins began in the mint of Finland.
Being a member of the eurozone
, NATO and the EU
, Estonia is the most integrated in Western European organizations of all Nordic states
remain tense. According to the Estonian Security Police, Russian influence operations in Estonia form a complex system of financial, political, economic and espionage activities in Republic of Estonia for the purposes of influencing Estonia's political and economic decisions in ways considered favourable to Russian Federation and conducted under the doctrine of near abroad
. According to the Centre for Geopolitical Studies, the Russian information campaign which the centre characterises as a "real mud throwing" exercise, has provoked a split in Estonian society amongst Russian speakers, inciting some to riot over the relocation of the Bronze Soldier. The 2007 cyberattacks on Estonia
is considered to be an information operation against Estonia, with the intent to influence the decisions and actions of the Estonian government; while Russia denies any direct involvement in the attacks, hostile rhetoric from the political elite via the media influenced people to attack. Following the 2007 cyber-attacks
, the NATO Cooperative Cyber Defence Centre of Excellence (CCDCOE
) was established in Tallinn
.
Estonia
Estonia , officially the Republic of Estonia , is a state in the Baltic region of Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland, to the west by the Baltic Sea, to the south by Latvia , and to the east by Lake Peipsi and the Russian Federation . Across the Baltic Sea lies...
was settled near the end of the last glacial era
Ice age
An ice age or, more precisely, glacial age, is a generic geological period of long-term reduction in the temperature of the Earth's surface and atmosphere, resulting in the presence or expansion of continental ice sheets, polar ice sheets and alpine glaciers...
, beginning from around 8500 BC. Before the German invasions in the 13th century proto-Estonians of the Ancient Estonia
Ancient Estonia
Ancient Estonia refers to a period covering History of Estonia from the middle of the 8th millennium BC until the conquest and subjugation of the Estonian people in the first quarter of the 13th century during the Northern Crusades.-The Mesolithic Period:...
worshipped the spirits of nature. Since the Northern Crusades
Northern Crusades
The Northern Crusades or Baltic Crusades were crusades undertaken by the Christian kings of Denmark and Sweden, the German Livonian and Teutonic military orders, and their allies against the pagan peoples of Northern Europe around the southern and eastern shores of the Baltic Sea...
Estonia became a battleground for centuries where Denmark, Germany, Russia, Sweden and Poland fought their many wars over controlling the important geographical position of the country as a gateway between East and West.
Being conquered by Danes and Germans in 1227, Estonia was ruled initially by Denmark
Denmark
Denmark is a Scandinavian country in Northern Europe. The countries of Denmark and Greenland, as well as the Faroe Islands, constitute the Kingdom of Denmark . It is the southernmost of the Nordic countries, southwest of Sweden and south of Norway, and bordered to the south by Germany. Denmark...
in the north, by the Livonian Order
Livonian Order
The Livonian Order was an autonomous Livonian branch of the Teutonic Order and a member of the Livonian Confederation from 1435–1561. After being defeated by Samogitians in the 1236 Battle of Schaulen , the remnants of the Livonian Brothers of the Sword were incorporated into the Teutonic Knights...
, an autonomous part of the Monastic state of the Teutonic Knights
Monastic State of the Teutonic Knights
The State of the Teutonic Order, , also Monastic State of the Teutonic Knights or Ordensstaat , was formed in 1224 during the Northern Crusades, the Teutonic Knights' conquest of the pagan West-Baltic Old Prussians in the 13th century....
and Baltic German
Baltic German
The Baltic Germans were mostly ethnically German inhabitants of the eastern shore of the Baltic Sea, which today form the countries of Estonia and Latvia. The Baltic German population never made up more than 10% of the total. They formed the social, commercial, political and cultural élite in...
ecclesiastical states of the Holy Roman Empire. From 1418–1562 the whole of Estonia was part of the Livonian Confederation
Livonian Confederation
Terra Mariana was the official name for Medieval Livonia or Old Livonia which was formed in the aftermath of the Livonian Crusade in the territories comprising present day Estonia and Latvia...
. After the Livonian War
Livonian War
The Livonian War was fought for control of Old Livonia in the territory of present-day Estonia and Latvia when the Tsardom of Russia faced a varying coalition of Denmark–Norway, the Kingdom of Sweden, the Union of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and the Kingdom of Poland.During the period 1558–1578,...
, Estonia became part of the Swedish Empire
Swedish Empire
The Swedish Empire refers to the Kingdom of Sweden between 1561 and 1721 . During this time, Sweden was one of the great European powers. In Swedish, the period is called Stormaktstiden, literally meaning "the Great Power Era"...
from the 16th century to 1710/1721, when it was ceded
Capitulation of Estonia and Livonia
With the Capitulation of Estonia and Livonia in 1710 the Swedish dominions Estonia and Livonia were integrated into the Russian Empire following their conquest during the Great Northern War...
to the Russian Empire
Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was a state that existed from 1721 until the Russian Revolution of 1917. It was the successor to the Tsardom of Russia and the predecessor of the Soviet Union...
as the result of the Great Northern War
Great Northern War
The Great Northern War was a conflict in which a coalition led by the Tsardom of Russia successfully contested the supremacy of the Swedish Empire in northern Central Europe and Eastern Europe. The initial leaders of the anti-Swedish alliance were Peter I the Great of Russia, Frederick IV of...
. Throughout this period the Baltic German
Baltic German
The Baltic Germans were mostly ethnically German inhabitants of the eastern shore of the Baltic Sea, which today form the countries of Estonia and Latvia. The Baltic German population never made up more than 10% of the total. They formed the social, commercial, political and cultural élite in...
nobility enjoyed autonomy, where the language of administration and education was German.
The Estophile Enlightenment Period 1750–1840 led to the Estonian national awakening
Estonian national awakening
The Estonian Age of Awakening is a period in history where Estonians came to acknowledge themselves as a nation deserving the right to govern themselves. This period is considered to begin in 1850s with greater rights being granted to commoners and to end with the declaration of the Republic of...
in the middle of the 19th century. In 1918 the Estonian Declaration of Independence
Estonian Declaration of Independence
The Estonian Declaration of Independence, also known as the Manifesto to the Peoples of Estonia , is the founding act of the Republic of Estonia from 1918. It is celebrated on 24 February, the National Day or Estonian Independence Day....
was issued. The Estonian War of Independence ensued on two fronts between the newly proclaimed state and Bolshevist Russia
Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic
The Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic , commonly referred to as Soviet Russia, Bolshevik Russia, or simply Russia, was the largest, most populous and economically developed republic in the former Soviet Union....
to the east and the forces of the United Baltic Duchy
United Baltic Duchy
The proposed United Baltic Duchy also known as the Grand Duchy of Livonia was a state proposed by the Baltic German nobility and exiled Russian nobility after the Russian revolution and German occupation of the Courland, Livonian and Estonian governorates of the Russian Empire.The idea comprised...
(the Baltische Landeswehr
Baltische Landeswehr
Baltische Landeswehr was the name of the unified armed forces of the Couronian and Livonian nobility from 7 December 1918 to 3 July 1919.- Command structure :...
) to the south, resulting in the Tartu Peace Treaty
Treaty of Tartu (Russian–Estonian)
Tartu Peace Treaty or Treaty of Tartu was a peace treaty between Estonia and Russian SFSR signed on February 2, 1920 ending the Estonian War of Independence. The terms of the treaty stated that "Russia unreservedly recognises" the independence of Republic of Estonia de jure and renounced in...
recognising Estonian independence in perpetuity. Prior to the Second World War, Estonia was occupied and according to the USA, the EU, and the European Court of Human Rights
European Court of Human Rights
The European Court of Human Rights in Strasbourg is a supra-national court established by the European Convention on Human Rights and hears complaints that a contracting state has violated the human rights enshrined in the Convention and its protocols. Complaints can be brought by individuals or...
illegally annexed by the Soviet Union as a result of the Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact. During the war Estonia was occupied by Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany , also known as the Third Reich , but officially called German Reich from 1933 to 1943 and Greater German Reich from 26 June 1943 onward, is the name commonly used to refer to the state of Germany from 1933 to 1945, when it was a totalitarian dictatorship ruled by...
in 1941, then reoccupied by the Soviet Union in 1944. Estonia regained independence in 1991 after the collapse of the USSR and joined the European Union
European Union
The European Union is an economic and political union of 27 independent member states which are located primarily in Europe. The EU traces its origins from the European Coal and Steel Community and the European Economic Community , formed by six countries in 1958...
in 2004.
The Mesolithic Period

Late Pleistocene
The Late Pleistocene is a stage of the Pleistocene Epoch. The beginning of the stage is defined by the base of the Eemian interglacial phase before the final glacial episode of the Pleistocene 126,000 ± 5,000 years ago. The end of the stage is defined exactly at 10,000 Carbon-14 years BP...
Ice Age
Ice age
An ice age or, more precisely, glacial age, is a generic geological period of long-term reduction in the temperature of the Earth's surface and atmosphere, resulting in the presence or expansion of continental ice sheets, polar ice sheets and alpine glaciers...
, about 10,000 BC. The earliest traces of human settlement in Estonia are connected with the Kunda culture
Kunda culture
Kunda Culture, with its roots in Swiderian culture is a mesolithic hunter-gatherer communities of the Baltic forest zone extending eastwards through Latvia into northern Russia dating to the period 8000–5000 BC by calibrated radiocarbon dating...
. The early Mesolithic
Mesolithic
The Mesolithic is an archaeological concept used to refer to certain groups of archaeological cultures defined as falling between the Paleolithic and the Neolithic....
Pulli settlement
Pulli settlement
Pulli settlement, located on the right bank of the Pärnu River, is the oldest known human settlement in Estonia. It is located two kilometers from the town of Sindi, which is 14 kilometers from Pärnu...
is located by the Pärnu
Pärnu
Pärnu is a city in southwestern Estonia on the coast of Pärnu Bay, an inlet of the Gulf of Riga in the Baltic Sea. It is a popular summer vacation resort with many hotels, restaurants, and large beaches. The Pärnu River flows through the city and drains into the Gulf of Riga...
River. It has been dated to the beginning of the 9th millennium BC. The Kunda Culture received its name from the Lammasmäe settlement site in northern Estonia, which dates from earlier than 8500 BC. Bone and stone artifacts similar to those found at Kunda have been discovered elsewhere in Estonia, as well as in Latvia
Latvia
Latvia , officially the Republic of Latvia , is a country in the Baltic region of Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by Estonia , to the south by Lithuania , to the east by the Russian Federation , to the southeast by Belarus and shares maritime borders to the west with Sweden...
, northern Lithuania
Lithuania
Lithuania , officially the Republic of Lithuania is a country in Northern Europe, the biggest of the three Baltic states. It is situated along the southeastern shore of the Baltic Sea, whereby to the west lie Sweden and Denmark...
and southern Finland
Finland
Finland , officially the Republic of Finland, is a Nordic country situated in the Fennoscandian region of Northern Europe. It is bordered by Sweden in the west, Norway in the north and Russia in the east, while Estonia lies to its south across the Gulf of Finland.Around 5.4 million people reside...
. Among minerals, flint
Flint
Flint is a hard, sedimentary cryptocrystalline form of the mineral quartz, categorized as a variety of chert. It occurs chiefly as nodules and masses in sedimentary rocks, such as chalks and limestones. Inside the nodule, flint is usually dark grey, black, green, white, or brown in colour, and...
and quartz
Quartz
Quartz is the second-most-abundant mineral in the Earth's continental crust, after feldspar. It is made up of a continuous framework of SiO4 silicon–oxygen tetrahedra, with each oxygen being shared between two tetrahedra, giving an overall formula SiO2. There are many different varieties of quartz,...
were used the most for making cutting tools.
The Neolithic Period
The beginning of the Neolithic Period is marked by the ceramics of the Narva culture, and appear in Estonia at the beginning of the 5th millennium. The oldest finds date from around 4900 BC. The first pottery was made of thick clay mixed with pebbles, shells or plants. The Narva-type ceramics are found throughout almost the entire Estonian coastal region and on the islands. The stone and bone tools of the era have a notable similarity with the artifacts of the Kunda culture.
Finnic peoples
The Finnic or Fennic peoples were historic ethnic groups who spoke various languages traditionally classified as Finno-Permic...
, the ancestors of the Estonians, Finns, and Livonians, on the shores of the Baltic sea was associated with the Comb Ceramic Culture. However , such a linking of archaeologically defined cultural entities with linguistic ones cannot be proven and it has been suggested that the increase of settlement finds in the period is more likely to have been associated with an economic boom related to the warming of climate. Some researchers have even argued that a Uralic form of language may have been spoken in Estonia and Finland since the end of the last glaciation.

Amber
Amber is fossilized tree resin , which has been appreciated for its color and natural beauty since Neolithic times. Amber is used as an ingredient in perfumes, as a healing agent in folk medicine, and as jewelry. There are five classes of amber, defined on the basis of their chemical constituents...
. Antiquities from comb pottery culture are found from Northern Finland to Eastern Prussia.
The beginning of the Late Neolithic Period about 2200 BC is characterized by the appearance of the Corded Ware culture
Corded Ware culture
The Corded Ware culture , alternatively characterized as the Battle Axe culture or Single Grave culture, is an enormous European archaeological horizon that begins in the late Neolithic , flourishes through the Copper Age and culminates in the early Bronze Age.Corded Ware culture is associated with...
, pottery with corded decoration and well-polished stone axes (s.c. boat-shape axes). Evidence of agriculture is provided by charred grains of wheat on the wall of a corded-ware vessel found in Iru settlement. Osteological analysis show an attempt was made to domesticate the wild boar.
Specific burial customs were characterized by the dead being laid on their sides with their knees pressed against their breast, one hand under the head. Objects placed into the graves were made of the bones of domesticated animals.
The Bronze Age

Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a period characterized by the use of copper and its alloy bronze as the chief hard materials in the manufacture of some implements and weapons. Chronologically, it stands between the Stone Age and Iron Age...
in Estonia is dated to approximately 1800 BC. The development of the borders between the Finnic peoples
Finnic peoples
The Finnic or Fennic peoples were historic ethnic groups who spoke various languages traditionally classified as Finno-Permic...
and the Balts
Balts
The Balts or Baltic peoples , defined as speakers of one of the Baltic languages, a branch of the Indo-European language family, are descended from a group of Indo-European tribes who settled the area between the Jutland peninsula in the west and Moscow, Oka and Volga rivers basins in the east...
was under way. The first fortified settlements, Asva and Ridala on the island of Saaremaa
Saaremaa
Saaremaa is the largest island in Estonia, measuring 2,673 km². The main island of Saare County, it is located in the Baltic Sea, south of Hiiumaa island, and belongs to the West Estonian Archipelago...
and Iru in the Northern Estonia began to be built. The development of shipbuilding facilitated the spread of bronze. Changes took place in burial customs, a new type of burial ground spread from Germanic to Estonian areas, stone cist graves and cremation burials became increasingly common aside a small number of boat-shaped stone graves.
About 7th century BC, a big meteorite hit Saaremaa
Saaremaa
Saaremaa is the largest island in Estonia, measuring 2,673 km². The main island of Saare County, it is located in the Baltic Sea, south of Hiiumaa island, and belongs to the West Estonian Archipelago...
island and created the Kaali crater
Kaali crater
Kaali is a group of 9 meteorite craters located on the Estonian island of Saaremaa. Formed in the 7th century BC or about 4000 years ago , it is one of the most recent craters created by an impact event and the only known major impact event that has occurred in a populated area.Prior to the 1930s,...
s.
c. 325 BC, a Greek explorer Pytheas
Pytheas
Pytheas of Massalia or Massilia , was a Greek geographer and explorer from the Greek colony, Massalia . He made a voyage of exploration to northwestern Europe at about 325 BC. He travelled around and visited a considerable part of Great Britain...
probably visited Estonia. Thule
Thule
Thule Greek: Θούλη, Thoulē), also spelled Thula, Thila, or Thyïlea, is, in classical European literature and maps, a region in the far north. Though often considered to be an island in antiquity, modern interpretations of what was meant by Thule often identify it as Norway. Other interpretations...
island he described has been frequently identified as Saaremaa
Saaremaa
Saaremaa is the largest island in Estonia, measuring 2,673 km². The main island of Saare County, it is located in the Baltic Sea, south of Hiiumaa island, and belongs to the West Estonian Archipelago...
.
The Iron Age
The Pre-Roman Iron AgePre-Roman Iron Age
The Pre-Roman Iron Age of Northern Europe designates the earliest part of the Iron Age in Scandinavia, northern Germany, and the Netherlands north of the Rhine River. These regions feature many extensive archaeological excavation sites, which have yielded a wealth of artifacts...
began in Estonia about 500 BC and lasted until the middle of the 1st century AD. The oldest iron items were imported, although since the 1st century iron was smelted from local marsh and lake ore. Settlement sites were located mostly in places that offered natural protection. Fortresses were built, although used temporarily. The appearance of square Celtic fields surrounded by enclosures in Estonia date from the Pre-Roman Iron Age. The majority of stones with man-made indents, which presumably were connected with magic designed to increase crop fertility, date from this period. A new type of grave, quadrangular burial mounds began to develop. Burial traditions show the clear beginning of social stratification.
The Roman Iron Age
Roman Iron Age
The Roman Iron Age is the name that Swedish archaeologist Oscar Montelius gave to a part of the Iron Age in Scandinavia, Northern Germany and the Netherlands....
in Estonia is roughly dated to between 50 and 450 AD, the era that was affected by the influence of the Roman Empire
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire was the post-Republican period of the ancient Roman civilization, characterised by an autocratic form of government and large territorial holdings in Europe and around the Mediterranean....
. In material culture this is reflected by a few Roman coins, some jewellery
Jewellery
Jewellery or jewelry is a form of personal adornment, such as brooches, rings, necklaces, earrings, and bracelets.With some exceptions, such as medical alert bracelets or military dog tags, jewellery normally differs from other items of personal adornment in that it has no other purpose than to...
and artefacts. The abundance of iron artefacts in Southern Estonia speaks of closer mainland ties with southern areas while the islands of western and northern Estonia communicated with their neighbors mainly by sea. By the end of the period three clearly defined tribal dialectical areas: Northern Estonia, Southern Estonia, and Western Estonia including the islands had emerged, the population of each having formed its own understanding of identity.
Early Middle Ages

Tacitus
Publius Cornelius Tacitus was a senator and a historian of the Roman Empire. The surviving portions of his two major works—the Annals and the Histories—examine the reigns of the Roman Emperors Tiberius, Claudius, Nero and those who reigned in the Year of the Four Emperors...
; however, it might have indicated Baltic tribes living in the area. In the Northern Sagas (9th century) the term started to be used to indicate the Estonians.
Ptolemy
Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy , was a Roman citizen of Egypt who wrote in Greek. He was a mathematician, astronomer, geographer, astrologer, and poet of a single epigram in the Greek Anthology. He lived in Egypt under Roman rule, and is believed to have been born in the town of Ptolemais Hermiou in the...
in his Geography III in the middle of the 2nd century CE mentions the Osilians among other dwellers on the Baltic shore.
According to the 5th-century Roman historian Cassiodorus
Cassiodorus
Flavius Magnus Aurelius Cassiodorus Senator , commonly known as Cassiodorus, was a Roman statesman and writer, serving in the administration of Theodoric the Great, king of the Ostrogoths. Senator was part of his surname, not his rank.- Life :Cassiodorus was born at Scylletium, near Catanzaro in...
the people known to Tacitius as the Aestii were the Estonians. The extent of their territory in early medieval times is disputed but the nature of their religion is not. They were known to the Scandinavians as experts in wind-magic, as were the Lapps (known at the time as Finns) in the North. Cassiodorus mentions Estonia in his book V. Letters 1–2 dating from the 6th century.
The Chudes, as mentioned by a monk Nestor in the earliest Russian chronicles, were the Ests or Esthonians.

Saare County
Saare County , or Saaremaa, is one of 15 counties of Estonia. It consists of Saaremaa , the largest island of Estonia, and several smaller islands near it. The county borders Lääne County to the east and Hiiu County to the north...
(Osilia), Läänemaa (Rotalia or Maritima), Harjumaa (Harria), Rävala (Revalia), Virumaa
Virumaa
Virumaa is a former independent county in Ancient Estonia. Now it is divided into Ida-Viru County or Eastern Vironia and Lääne-Viru County or Western Vironia...
(Vironia), Järvamaa (Jervia), Sakala (Saccala), and Ugandi (Ugaunia).
Varbola Stronghold
Varbola Stronghold
The Varbola Stronghold was the largest circular rampart fortress and trading centre built in Estonia, in Harju County in the 10th – 12th centuries. Parts of the ruins of the 580 metre long and 8-10 metre high limestone wall of the fortress stand til this day. The long gateways with...
was one of the largest circular rampart fortresses and trading centers built in Estonia
Estonia
Estonia , officially the Republic of Estonia , is a state in the Baltic region of Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland, to the west by the Baltic Sea, to the south by Latvia , and to the east by Lake Peipsi and the Russian Federation . Across the Baltic Sea lies...
, Harju County
Harju County
Harju County , or Harjumaa , nowadays one of 15 counties of Estonia. It is situated in northern Estonia, on the south coast of the Gulf of Finland, and borders Lääne-Viru County to the east, Järva County to the south-east, Rapla County to the south, and Lääne County to the south-west.528,468 people...
at the time.
In the 11th century the Scandinavians are frequently chronicled as combating the Vikings from the eastern shores of the Baltic Sea.
With the rise of Christianity
Christianity
Christianity is a monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus as presented in canonical gospels and other New Testament writings...
, centralized authority in Scandinavia and Germany eventually led to the Baltic crusades.
The east Baltic world was transformed by military conquest: first the Livs, and Estonians
Estonians
Estonians are a Finnic people closely related to the Finns and inhabiting, primarily, the country of Estonia. They speak a Finnic language known as Estonian...
, then the Prussians and the Finns underwent defeat, baptism
Baptism
In Christianity, baptism is for the majority the rite of admission , almost invariably with the use of water, into the Christian Church generally and also membership of a particular church tradition...
, military occupation
Military occupation
Military occupation occurs when the control and authority over a territory passes to a hostile army. The territory then becomes occupied territory.-Military occupation and the laws of war:...
and sometimes extermination by groups of Germans, Danes and Swedes.
Estonian Crusade: The Middle Ages


Estonia remained one of the last corners of medieval Europe to be Christianized
Christianity
Christianity is a monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus as presented in canonical gospels and other New Testament writings...
. In 1193 Pope Celestine III
Pope Celestine III
Pope Celestine III , born Giacinto Bobone, was elected Pope on March 21, 1191, and reigned until his death. He was born into the noble Orsini family in Rome, though he was only a cardinal deacon before becoming Pope...
called for a crusade against pagan
Paganism
Paganism is a blanket term, typically used to refer to non-Abrahamic, indigenous polytheistic religious traditions....
s in Northern Europe
Northern Europe
Northern Europe is the northern part or region of Europe. Northern Europe typically refers to the seven countries in the northern part of the European subcontinent which includes Denmark, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Norway, Finland and Sweden...
. The Northern Crusades
Northern Crusades
The Northern Crusades or Baltic Crusades were crusades undertaken by the Christian kings of Denmark and Sweden, the German Livonian and Teutonic military orders, and their allies against the pagan peoples of Northern Europe around the southern and eastern shores of the Baltic Sea...
from Northern Germany
Germany
Germany , officially the Federal Republic of Germany , is a federal parliamentary republic in Europe. The country consists of 16 states while the capital and largest city is Berlin. Germany covers an area of 357,021 km2 and has a largely temperate seasonal climate...
established the stronghold of Riga
Riga
Riga is the capital and largest city of Latvia. With 702,891 inhabitants Riga is the largest city of the Baltic states, one of the largest cities in Northern Europe and home to more than one third of Latvia's population. The city is an important seaport and a major industrial, commercial,...
(in modern Latvia). With the help of the newly converted local tribes of Livs
Livonian people
The Livonians or Livs are the indigenous inhabitants of Livonia, a large part of what is today northwestern Latvia and southwestern Estonia. They spoke the Uralic Livonian language, a language which is closely related to Estonian and Finnish...
and Letts
Latvians
Latvians or Letts are the indigenous Baltic people of Latvia.-History:Latvians occasionally refer to themselves by the ancient name of Latvji, which may have originated from the word Latve which is a name of the river that presumably flowed through what is now eastern Latvia...
, the crusaders initiated raids into part of what is present-day Estonia in 1208. Estonian tribes fiercely resisted the attacks from Riga and occasionally themselves sacked territories controlled by the crusaders. In 1217 the German crusading order the Sword Brethren
Livonian Brothers of the Sword
The Livonian Brothers of the Sword were a military order founded by Bishop Albert of Riga in 1202. Pope Innocent III sanctioned the establishment in 1204. The membership of the order comprised German "warrior monks"...
and their recently converted allies won a major battle in which the Estonian commander Lembitu was killed. The period of the several Northern Crusade battles in Estonia between 1208 and 1227 is also known as the period of the ancient Estonian fight for independence.
Danish Estonia

Denmark
Denmark is a Scandinavian country in Northern Europe. The countries of Denmark and Greenland, as well as the Faroe Islands, constitute the Kingdom of Denmark . It is the southernmost of the Nordic countries, southwest of Sweden and south of Norway, and bordered to the south by Germany. Denmark...
crusaders led by king Waldemar II
Valdemar II of Denmark
Valdemar II , called Valdemar the Victorious or Valdemar the Conqueror , was the King of Denmark from 1202 until his death in 1241. The nickname Sejr is a later invention and was not used during the King's own lifetime...
, who arrived in 1219 on the site of the Estonian town of Lindanisse (now Tallinn
Tallinn
Tallinn is the capital and largest city of Estonia. It occupies an area of with a population of 414,940. It is situated on the northern coast of the country, on the banks of the Gulf of Finland, south of Helsinki, east of Stockholm and west of Saint Petersburg. Tallinn's Old Town is in the list...
) at (Latin) Revelia (Estonian) Revala or Rävala, the adjacent ancient Estonian county. The Danish Army defeated the Estonians at Battle of Lyndanisse
Battle of Lyndanisse
The Battle of Lyndanisse was a battle which helped King Valdemar II of Denmark establish the territory of Danish Estonia during the Northern Crusades. Valdemar II defeated the Estonians at Lyndanisse , during the Northern Crusades, by orders from the Pope...
.
The Estonians of Harria started a rebellion in 1343 (St.George's Night Uprising). The province was occupied by the Livonian Order
Livonian Order
The Livonian Order was an autonomous Livonian branch of the Teutonic Order and a member of the Livonian Confederation from 1435–1561. After being defeated by Samogitians in the 1236 Battle of Schaulen , the remnants of the Livonian Brothers of the Sword were incorporated into the Teutonic Knights...
as a result. In 1346, the Danish dominions in Estonia (Harria and Vironia) were sold for 10 000 marks to the Livonian Order
Livonian Order
The Livonian Order was an autonomous Livonian branch of the Teutonic Order and a member of the Livonian Confederation from 1435–1561. After being defeated by Samogitians in the 1236 Battle of Schaulen , the remnants of the Livonian Brothers of the Sword were incorporated into the Teutonic Knights...
.
Swedish coastal settlements
The first written mention of the Estonian SwedesEstonian Swedes
The Estonian Swedes, Estonia-Swedes, or Coastal Swedes are a Swedish-speaking linguistic minority traditionally residing in the coastal areas and islands of what is now western and northern Estonia...
comes from 1294, in the laws of the town of Haapsalu
Haapsalu
Haapsalu is a seaside resort town located on the west coast of Estonia. It's the administrative centre of Lääne County and has a population of 11,618 ....
. Estonian Swedes are one of the earliest known minorities in Estonia. They have also been called Coastal Swedes ("Rannarootslased" in Estonian
Estonian language
Estonian is the official language of Estonia, spoken by about 1.1 million people in Estonia and tens of thousands in various émigré communities...
), or according to their settlement area Ruhnu
Ruhnu
Ruhnu is an island situated in the Gulf of Riga in the Baltic Sea. It belongs to Estonia and is an administrative part of Saare County. At 11.9 km2 it has currently less than 100, mostly ethnic Estonian permanent inhabitants...
Swedes, Hiiu Swedes etc. They themselves used the expression aibofolke – Island People.
The ancient areas of Swedish settlement in Estonia were Ruhnu Island, Hiiumaa
Hiiumaa
Hiiumaa is the second largest island belonging to Estonia. It is located in the Baltic Sea, north of the island of Saaremaa, a part of the West Estonian archipelago. Its largest town is Kärdla.-Name:...
Island, the west coast and smaller islands (Vormsi
Vormsi
Estonia's fourth largest island, Vormsi , is located between Hiiumaa and the mainland with a total area of 93 square kilometers. It is part of a rural municipality Vormsi Parish. From mainland, Vormsi is separated by a narrow strait – Voosi Kurk, and from Hiiumaa by a bit wider Hari...
, Noarootsi, Sutlepa, Riguldi, Osmussaar
Osmussaar
Osmussaar is an Estonian island situated in the mouth of the Gulf of Finland in the Baltic Sea, 7.5 km off the Estonian mainland. Administratively the island is part of Noarootsi Parish in Lääne County. Its area is ....
), the north-west coast of the Harju District (Nõva, Vihterpalu, Kurkse, the Pakri Peninsula and the Pakri Islands) and Naissaar
Naissaar
Naissaar is an island northwest of Tallinn in Estonia. The island covers an area of 18.6 km². It is 13-14 km long and 6 km wide, and lies about 8.5 km from the mainland. The highest point on the island is Kunilamägi, which is 27 meters above sea-level. The island consists predominantly of...
Island near Tallinn. The towns with a significant percentage of Swedish population have been Haapsalu
Haapsalu
Haapsalu is a seaside resort town located on the west coast of Estonia. It's the administrative centre of Lääne County and has a population of 11,618 ....
and Tallinn.
In earlier times Swedes also lived on the coasts of Saaremaa, the southern part of Läänemaa, the eastern part of Harjumaa
Harjumaa
Harjumaa, , was an ancient Estonian county. It corresponded roughly to the present territory of Rapla County.- See also :*Danish Estonia*Harju County*Rapla County*History of Estonia*Livonian Crusade*Rulers of Estonia...
and the western part of Virumaa
Virumaa
Virumaa is a former independent county in Ancient Estonia. Now it is divided into Ida-Viru County or Eastern Vironia and Lääne-Viru County or Western Vironia...
.
Terra Mariana
Estonia in Terra Mariana from 1228 to the 1560s.In 1227 the Sword Brethren conquered the last indigenous stronghold on the Estonian island of Saaremaa
Saaremaa
Saaremaa is the largest island in Estonia, measuring 2,673 km². The main island of Saare County, it is located in the Baltic Sea, south of Hiiumaa island, and belongs to the West Estonian Archipelago...
. After the conquest, all the remaining local pagans of Estonia were ostensibly Christianized
Christianity
Christianity is a monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus as presented in canonical gospels and other New Testament writings...
. An ecclesiastical state Terra Mariana was established .

Livonian Order
The Livonian Order was an autonomous Livonian branch of the Teutonic Order and a member of the Livonian Confederation from 1435–1561. After being defeated by Samogitians in the 1236 Battle of Schaulen , the remnants of the Livonian Brothers of the Sword were incorporated into the Teutonic Knights...
of the Teutonic Order, the Bishopric of Dorpat
Bishopric of Dorpat
The Bishopric of Dorpat was a medieval principality and a catholic diocese which existed from 1224 to 1558, generally encompassing what are now Tartu, Põlva, Võru and Jõgeva counties in Estonia. The Bishopric was part of Livonian Confederation...
(in Estonian: Tartu piiskopkond) and the Bishopric of Ösel-Wiek
Bishopric of Ösel-Wiek
The Bishopric of Ösel–Wiek was a semi-independent Roman Catholic prince-bishopric in what is now Saare, Hiiu and Lääne counties of Estonia.The bishopric was created as a state of Holy Roman Empire on 1 October 1228, by Henry, King of the Romans...
(in Estonian: Saare-Lääne piiskopkond). The Northern part of Estonia – more exactly Harjumaa and Virumaa districts (in German: Harrien und Wierland) – was a nominal possession of Denmark
Denmark
Denmark is a Scandinavian country in Northern Europe. The countries of Denmark and Greenland, as well as the Faroe Islands, constitute the Kingdom of Denmark . It is the southernmost of the Nordic countries, southwest of Sweden and south of Norway, and bordered to the south by Germany. Denmark...
until 1346. Tallinn
Tallinn
Tallinn is the capital and largest city of Estonia. It occupies an area of with a population of 414,940. It is situated on the northern coast of the country, on the banks of the Gulf of Finland, south of Helsinki, east of Stockholm and west of Saint Petersburg. Tallinn's Old Town is in the list...
(Reval) was given the Lübeck Rights
Lübeck law
The Lübeck law was the constitution of a municipal form of government developed at Lübeck in Schleswig-Holstein after it was made a free city in 1226. The law provides for self-government. It replaced the personal rule of tribal monarchs descending from ancient times or the rule of the regional...
in 1248 and joined the Hanseatic League
Hanseatic League
The Hanseatic League was an economic alliance of trading cities and their merchant guilds that dominated trade along the coast of Northern Europe...
at the end of the 13th century. In 1343 the people of northern Estonia and Saaremaa (Oesel) Island started a rebellion (St. George's Night Uprising
St. George's Night Uprising
St. George’s Night Uprising in 1343–1346 was an unsuccessful attempt by the indigenous Estonian population in the Duchy of Estonia, the Bishopric of Ösel-Wiek, and the insular territories of the State of the Teutonic Order to annihilate the Danish and German rulers and landlords, who had conquered...
) against the rule of their German-speaking landlords. The uprising was put down, and four elected Estonian "kings" were killed in Paide
Paide
Paide is the capital of Järva County, Estonia.A castle built by the Livonian Brothers of the Sword is located here. The town was formally founded 30 September 1291 by Halt, master of the Livonian Order....
during peace negotiations in 1343 and Vesse, the rebel King of Saaremaa, was hanged in 1344.
Despite local rebellions and Muscovian invasions in 1481 and 1558, the local Low German
Low German
Low German or Low Saxon is an Ingvaeonic West Germanic language spoken mainly in northern Germany and the eastern part of the Netherlands...
-speaking upper class continued to rule Estonia and from 1524 preserved Estonian commitment to the Protestant Reformation
Protestant Reformation
The Protestant Reformation was a 16th-century split within Western Christianity initiated by Martin Luther, John Calvin and other early Protestants. The efforts of the self-described "reformers", who objected to the doctrines, rituals and ecclesiastical structure of the Roman Catholic Church, led...
.
The Reformation Period
The Reformation in Europe began in 1517 with Martin LutherMartin Luther
Martin Luther was a German priest, professor of theology and iconic figure of the Protestant Reformation. He strongly disputed the claim that freedom from God's punishment for sin could be purchased with money. He confronted indulgence salesman Johann Tetzel with his Ninety-Five Theses in 1517...
(1483–1546) and his 95 Theses.
The Reformation resulted in great change in the Baltic. Ideas entered the Livonian Confederation very quickly and by the 1520s they were well known. Language, education, religion and politics were greatly transformed. Church services were now given in the local vernacular, instead of Latin, as was previously used.
Division of Estonia in the Livonian War
Ferdinand I, Holy Roman EmperorFerdinand I, Holy Roman Emperor
Ferdinand I was Holy Roman Emperor from 1558 and king of Bohemia and Hungary from 1526 until his death. Before his accession, he ruled the Austrian hereditary lands of the Habsburgs in the name of his elder brother, Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor.The key events during his reign were the contest...
once again asked for help of Gustav I of Sweden
Gustav I of Sweden
Gustav I of Sweden, born Gustav Eriksson of the Vasa noble family and later known simply as Gustav Vasa , was King of Sweden from 1523 until his death....
, and The Kingdom of Poland (1385–1569)
Kingdom of Poland (1385–1569)
The Kingdom of Poland of the Jagiellons was the Polish state created by the accession of Jogaila , Grand Duke of Lithuania, to the Polish throne in 1386. The Union of Krewo or Krėva Act, united Poland and Lithuania under the rule of a single monarch...
also began direct negotiations with Gustavus, but nothing resulted because on September 29, 1560, Gustavus I Vasa died. The chances for success of Magnus von Lyffland and his supporters looked particularly good in 1560 (and 1570). In the former case he had been recognised as their sovereign
Sovereign
A sovereign is the supreme lawmaking authority within its jurisdiction.Sovereign may also refer to:*Monarch, the sovereign of a monarchy*Sovereign Bank, banking institution in the United States*Sovereign...
by The Bishopric of Ösel-Wiek
Bishopric of Ösel-Wiek
The Bishopric of Ösel–Wiek was a semi-independent Roman Catholic prince-bishopric in what is now Saare, Hiiu and Lääne counties of Estonia.The bishopric was created as a state of Holy Roman Empire on 1 October 1228, by Henry, King of the Romans...
and The Bishopric of Courland
Bishopric of Courland
The Bishopric of Courland was the second smallest ecclesiastical state in the Livonian Confederation founded in the aftermath of the Livonian Crusade...
, and as their prospective ruler by the authorities of The Bishopric of Dorpat
Bishopric of Dorpat
The Bishopric of Dorpat was a medieval principality and a catholic diocese which existed from 1224 to 1558, generally encompassing what are now Tartu, Põlva, Võru and Jõgeva counties in Estonia. The Bishopric was part of Livonian Confederation...
; The Bishopric of Reval
Bishopric of Reval
The Bishopric of Reval was created in Duchy of Estonia by Valdemar II of Denmark in 1240. Contradictory to canon law Valdemar II reserved the right to appoint the bishops of Reval to himself and his successor kings of Denmark. The decision to simply nominate the holy see of Reval was unique in the...
with the Harrien-Wierland gentry
Gentry
Gentry denotes "well-born and well-bred people" of high social class, especially in the past....
were on his side; Livonian Order
Livonian Order
The Livonian Order was an autonomous Livonian branch of the Teutonic Order and a member of the Livonian Confederation from 1435–1561. After being defeated by Samogitians in the 1236 Battle of Schaulen , the remnants of the Livonian Brothers of the Sword were incorporated into the Teutonic Knights...
conditionally recognised his right of ownership of Estonia (Principality of Estonia). Then along with Archbishop
Archbishop
An archbishop is a bishop of higher rank, but not of higher sacramental order above that of the three orders of deacon, priest , and bishop...
Wilhelm von Brandenburg of The Archbishopric of Riga and his coadjutor Christoph von Mecklenburg, Kettler gave to Magnus the portions of The Kingdom of Livonia
Kingdom of Livonia
The Kingdom of Livonia was a nominal state in what is now the territory of the present-day Estonia and Latvia, declared as such by Ivan IV during the Livonian War but never properly established. On June 10, 1570 the Danish Duke Magnus of Holstein arrived in Moscow where he was crowned King of Livonia...
, which he had taken possession of, but they refused to give him any more land. Once Eric XIV of Sweden
Eric XIV of Sweden
-Family and descendants:Eric XIV had several relationships before his marriage. With Agda Persdotter he had four daughters:#Margareta Eriksdotter , married 1592 to Olov Simonsson, vicar of Horn....
became king he took quick actions to get involved in the war. He negotiated a continued peace with Muscovy and spoke to the burgher
Bourgeoisie
In sociology and political science, bourgeoisie describes a range of groups across history. In the Western world, between the late 18th century and the present day, the bourgeoisie is a social class "characterized by their ownership of capital and their related culture." A member of the...
s of Reval city. He offered them goods to submit to him as well as threatening them. By June 6, 1561 they submitted to him contrary to the persuasions of Kettler to the burghers. The King's brother Johan married the Polish princess Catherine Jagiellon
Catherine Jagiellon
Catherine the Jagiellonian of Poland was Duchess of Finland , Queen Consort of Sweden , Grand Princess of Finland and heir to her mother's claim to the title of King of Jerusalem....
. Wanting to obtain his own land in Livonia, he loaned Poland money and then claimed the castle
Castle
A castle is a type of fortified structure built in Europe and the Middle East during the Middle Ages by European nobility. Scholars debate the scope of the word castle, but usually consider it to be the private fortified residence of a lord or noble...
s they had pawned as his own instead of using them to pressure Poland. After Johan returned to Finland
Finland
Finland , officially the Republic of Finland, is a Nordic country situated in the Fennoscandian region of Northern Europe. It is bordered by Sweden in the west, Norway in the north and Russia in the east, while Estonia lies to its south across the Gulf of Finland.Around 5.4 million people reside...
, Erik XIV forbade him to deal with any foreign countries without his consent. Shortly after that Erik XIV started acting quickly lost any allies he was about to obtain, either from Magnus or the Archbishop of Riga
Riga
Riga is the capital and largest city of Latvia. With 702,891 inhabitants Riga is the largest city of the Baltic states, one of the largest cities in Northern Europe and home to more than one third of Latvia's population. The city is an important seaport and a major industrial, commercial,...
. Magnus was upset he had been tricked out of his inheritance
Inheritance
Inheritance is the practice of passing on property, titles, debts, rights and obligations upon the death of an individual. It has long played an important role in human societies...
of Holstein
Holstein
Holstein is the region between the rivers Elbe and Eider. It is part of Schleswig-Holstein, the northernmost state of Germany....
. After Sweden occupied
Military occupation
Military occupation occurs when the control and authority over a territory passes to a hostile army. The territory then becomes occupied territory.-Military occupation and the laws of war:...
Reval, Frederick II of Denmark
Frederick II of Denmark
Frederick II was King of Denmark and Norway and duke of Schleswig from 1559 until his death.-King of Denmark:Frederick II was the son of King Christian III of Denmark and Norway and Dorothea of Saxe-Lauenburg. Frederick II stands as the typical renaissance ruler of Denmark. Unlike his father, he...
made a treaty with Erik XIV of Sweden in August 1561. The brothers were in great disagreement and Frederick II negotiated a treaty with Ivan IV on August 7, 1562 in order to help his brother obtain more land and stall further Swedish advance. Erik XIV did not like this and The Northern Seven Years' War
Northern Seven Years' War
The Northern Seven Years' War was the war between Kingdom of Sweden and a coalition of Denmark–Norway, Lübeck and the Polish–Lithuanian union, fought between 1563 and 1570...
between The Free City of Lübeck, Denmark, Poland, and Sweden broke out. While only losing land and trade, Frederick II and Magnus were not faring well. But in 1568 Erik XIV became insane and his brother Johan III took his place. Johan III ascended to the throne
Throne
A throne is the official chair or seat upon which a monarch is seated on state or ceremonial occasions. "Throne" in an abstract sense can also refer to the monarchy or the Crown itself, an instance of metonymy, and is also used in many expressions such as "the power behind the...
of Sweden and due to his friendship with Poland he began a policy against Muscovy. He would try to obtain more land in Livonia and exercise strength over Denmark. After all parties had been financially drained, Frederick II let his ally, King Sigismund II Augustus
Sigismund II Augustus
Sigismund II Augustus I was King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania, the only son of Sigismund I the Old, whom Sigismund II succeeded in 1548...
of Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, know that he was ready for peace. On December 15, 1570, the Treaty of Stettin was concluded. It is, however, more difficult to estimate the scope and magnitude of the support Magnus received in Livonian cities. Compared to the Harrien-Wierland gentry, the Reval city council, and hence probably the majority of citizens, demonstrated a much more reserved attitude towards Denmark and King Magnus of Livonia. Nevertheless, there is no reason to speak about any strong pro-Swedish sentiments among the residents of Reval. The citizens who had fled to The Bishopric of Dorpat or had been deported to Muscovy hailed Magnus as their saviour until 1571. The analysis indicates that during the Livonian War
Livonian War
The Livonian War was fought for control of Old Livonia in the territory of present-day Estonia and Latvia when the Tsardom of Russia faced a varying coalition of Denmark–Norway, the Kingdom of Sweden, the Union of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and the Kingdom of Poland.During the period 1558–1578,...
a pro-independence
Independence
Independence is a condition of a nation, country, or state in which its residents and population, or some portion thereof, exercise self-government, and usually sovereignty, over its territory....
wing emerged among the Livonian gentry and townspeople, forming the so-called "". Dismissing hostilities, these forces perceived an agreement with Muscovy as a chance to escape the atrocities of war and avoid the division of Livonia. That is why Magnus, who represented Denmark and later struck a deal with Ivan the Terrible, proved a suitable figurehead for this faction.

Having rejected peace proposals from its enemies, Ivan the Terrible found himself in a difficult position by 1579, when Crimean Khanate
Crimean Khanate
Crimean Khanate, or Khanate of Crimea , was a state ruled by Crimean Tatars from 1441 to 1783. Its native name was . Its khans were the patrilineal descendants of Toqa Temür, the thirteenth son of Jochi and grandson of Genghis Khan...
devastated Muscovian territories and burnt down Moscow
Moscow
Moscow is the capital, the most populous city, and the most populous federal subject of Russia. The city is a major political, economic, cultural, scientific, religious, financial, educational, and transportation centre of Russia and the continent...
(see Russo-Crimean Wars
Russo-Crimean Wars
The Russo-Crimean Wars were fought between the forces of the Muscovy and the invading Tatars of the Crimean Khanate.-History:...
), the drought
Drought
A drought is an extended period of months or years when a region notes a deficiency in its water supply. Generally, this occurs when a region receives consistently below average precipitation. It can have a substantial impact on the ecosystem and agriculture of the affected region...
and epidemic
Epidemic
In epidemiology, an epidemic , occurs when new cases of a certain disease, in a given human population, and during a given period, substantially exceed what is expected based on recent experience...
s have fatally affected the economy, Oprichnina
Oprichnina
The oprichnina is the period of Russian history between Tsar Ivan the Terrible's 1565 initiation and his 1572 disbanding of a domestic policy of secret police, mass repressions, public executions, and confiscation of land from Russian aristocrats...
had thoroughly disrupted the government, while The Grand Principality of Lithuania had united with
Union of Lublin
The Union of Lublin replaced the personal union of the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania with a real union and an elective monarchy, since Sigismund II Augustus, the last of the Jagiellons, remained childless after three marriages. In addition, the autonomy of Royal Prussia was...
The Kingdom of Poland (1385–1569)
Kingdom of Poland (1385–1569)
The Kingdom of Poland of the Jagiellons was the Polish state created by the accession of Jogaila , Grand Duke of Lithuania, to the Polish throne in 1386. The Union of Krewo or Krėva Act, united Poland and Lithuania under the rule of a single monarch...
and acquired an energetic leader, Stefan Batory
Stefan Batory
Stephen Báthory was a Hungarian noble Prince of Transylvania , then King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania . He was a member of the Somlyó branch of the noble Hungarian Báthory family...
, supported by Ottoman Empire
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman EmpireIt was usually referred to as the "Ottoman Empire", the "Turkish Empire", the "Ottoman Caliphate" or more commonly "Turkey" by its contemporaries...
(1576). Stefan Batory replied with a series of three offensive
Offensive (military)
An offensive is a military operation that seeks through aggressive projection of armed force to occupy territory, gain an objective or achieve some larger strategic, operational or tactical goal...
s against Muscovy, trying to cut The Kingdom of Livonia
Kingdom of Livonia
The Kingdom of Livonia was a nominal state in what is now the territory of the present-day Estonia and Latvia, declared as such by Ivan IV during the Livonian War but never properly established. On June 10, 1570 the Danish Duke Magnus of Holstein arrived in Moscow where he was crowned King of Livonia...
from Muscovian territories. During his first offensive in 1579 with 22,000 men he retook Polotsk
Polatsk
Polotsk , is a historical city in Belarus, situated on the Dvina river. It is the center of Polotsk district in Vitsebsk Voblast. Its population is more than 80,000 people...
, during the second, in 1580, with 29,000-strong army he took Velikie Luki, and in 1581 with a 100,000-strong army he started the Siege of Pskov
Siege of Pskov
The Siege of Pskov, known as the Pskov Defense in Russia took place between August of 1581 and February of 1582, when the army of the Polish king and Grand Duke of Lithuania Stefan Batory laid an unsuccessful siege and successful blockade of the city of Pskov during the final stage of the Livonian...
. Frederick II had trouble continuing the fight against Muscovy unlike Sweden
Sweden
Sweden , officially the Kingdom of Sweden , is a Nordic country on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. Sweden borders with Norway and Finland and is connected to Denmark by a bridge-tunnel across the Öresund....
and Poland. He came to an agreement with John III
John III of Sweden
-Family:John married his first wife, Catherine Jagellonica of Poland , house of Jagiello, in Vilnius on 4 October 1562. In Sweden, she is known as Katarina Jagellonica. She was the sister of king Sigismund II Augustus of Poland...
in 1580 giving him the titles in Livonia. That war would last from 1577 to 1582. Muscovy recognized Polish–Lithuanian control of Ducatus Ultradunensis only in 1582. After Magnus von Lyffland died in 1583, Poland invaded his territories in The Duchy of Courland and Frederick II decided to sell his rights of inheritance
Inheritance
Inheritance is the practice of passing on property, titles, debts, rights and obligations upon the death of an individual. It has long played an important role in human societies...
. Except for the island of Œsel, Denmark
Denmark
Denmark is a Scandinavian country in Northern Europe. The countries of Denmark and Greenland, as well as the Faroe Islands, constitute the Kingdom of Denmark . It is the southernmost of the Nordic countries, southwest of Sweden and south of Norway, and bordered to the south by Germany. Denmark...
was out of the Baltic
Baltic region
The terms Baltic region, Baltic Rim countries, and Baltic Rim refer to slightly different combinations of countries in the general area surrounding the Baltic Sea.- Etymology :...
by 1585. As of 1598 Polish Livonia was divided onto:
- Wenden VoivodeshipWenden VoivodeshipWenden Voivodeship was a unit of administrative division and local government in the Duchy of Livonia, part of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, since it was formed in 1598 till the Swedish conquest of Livonia in the 1620s...
(województwo wendeńskie, Kieś) - Dorpat VoivodeshipDorpat VoivodeshipThe Dorpat Voivodeship was a unit of administrative division and local government in the Duchy of Livonia, part of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, from 1598 till the Swedish conquest of Livonia in the 1620s.The seat of the voivode was Dorpat...
(województwo dorpackie, Dorpat) - Parnawa VoivodeshipParnawa VoivodeshipThe Parnawa Voivodeship was a unit of administrative division and local government in the Duchy of Livonia, part of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, since it was formed in 1598 till the Swedish conquest of Livonia in the 1620s....
(województwo parnawskie, Parnawa)
During the Livonian War
Livonian War
The Livonian War was fought for control of Old Livonia in the territory of present-day Estonia and Latvia when the Tsardom of Russia faced a varying coalition of Denmark–Norway, the Kingdom of Sweden, the Union of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and the Kingdom of Poland.During the period 1558–1578,...
in 1561, northern Estonia submitted to Swedish control, while southern Estonia briefly came under the control of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth in the 1580s. In 1625, mainland Estonia came entirely under Swedish rule. Estonia was administratively divided between the provinces of Estonia in the north and Livonia
Livonia
Livonia is a historic region along the eastern shores of the Baltic Sea. It was once the land of the Finnic Livonians inhabiting the principal ancient Livonian County Metsepole with its center at Turaida...
in southern Estonia and northern Latvia, a division which persisted until the early 20th century.
Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth


Livonia
Livonia is a historic region along the eastern shores of the Baltic Sea. It was once the land of the Finnic Livonians inhabiting the principal ancient Livonian County Metsepole with its center at Turaida...
) became part of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth.
Estonia in the Swedish Empire
Estonia placed itself under Swedish rule in 1561 to receive protection against Russia and PolandPoland
Poland , officially the Republic of Poland , is a country in Central Europe bordered by Germany to the west; the Czech Republic and Slovakia to the south; Ukraine, Belarus and Lithuania to the east; and the Baltic Sea and Kaliningrad Oblast, a Russian exclave, to the north...
as the Livonian Order
Livonian Brothers of the Sword
The Livonian Brothers of the Sword were a military order founded by Bishop Albert of Riga in 1202. Pope Innocent III sanctioned the establishment in 1204. The membership of the order comprised German "warrior monks"...
lost their foothold in the Baltic provinces. Territorially it represented the northern part of present-day Estonia.
Livonia was conquered from the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth by 1629 in the Polish–Swedish War
Polish–Swedish War (1626–1629)
The Polish–Swedish War of 1626–1629 was the fourth stage in a series of conflicts between Sweden and Poland fought in the 17th century...
. By the Treaty of Oliva
Treaty of Oliva
The Treaty or Peace of Oliva of 23 April /3 May 1660 was one of the peace treaties ending the Second Northern War...
between the Commonwealth and Sweden in 1660 following the Northern Wars
Northern Wars
Northern Wars is a term used for a series of wars fought in northern and northeastern Europe in the 16th and 17th century. An internationally agreed nomenclature for these wars has not yet been devised...
the Polish–Lithuanian king
House of Vasa
The House of Vasa was the Royal House of Sweden 1523-1654 and of Poland 1587-1668. It originated from a noble family in Uppland of which several members had high offices during the 15th century....
renounced all claims to the Swedish throne and Livonia was formally ceded to Sweden. Swedish Livonia represents the southern part of present-day Estonia and the northern part of present-day Latvia
Latvia
Latvia , officially the Republic of Latvia , is a country in the Baltic region of Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by Estonia , to the south by Lithuania , to the east by the Russian Federation , to the southeast by Belarus and shares maritime borders to the west with Sweden...
(Vidzeme
Vidzeme
Vidzeme is one of the historical and cultural regions of Latvia. Literally meaning "the Middle Land" it is situated in north-central Latvia north of the Daugava River...
region)
In 1631, Gustavus II Adolphus of Sweden forced the nobility
Nobility
Nobility is a social class which possesses more acknowledged privileges or eminence than members of most other classes in a society, membership therein typically being hereditary. The privileges associated with nobility may constitute substantial advantages over or relative to non-nobles, or may be...
to grant the peasantry greater autonomy, and in 1632 established a printing press
Printing press
A printing press is a device for applying pressure to an inked surface resting upon a print medium , thereby transferring the ink...
and University
University of Tartu
The University of Tartu is a classical university in the city of Tartu, Estonia. University of Tartu is the national university of Estonia; it is the biggest and highest-ranked university in Estonia...
in the city of Tartu
Tartu
Tartu is the second largest city of Estonia. In contrast to Estonia's political and financial capital Tallinn, Tartu is often considered the intellectual and cultural hub, especially since it is home to Estonia's oldest and most renowned university. Situated 186 km southeast of Tallinn, the...
.
Estonia in the Russian Empire

Great Northern War
The Great Northern War was a conflict in which a coalition led by the Tsardom of Russia successfully contested the supremacy of the Swedish Empire in northern Central Europe and Eastern Europe. The initial leaders of the anti-Swedish alliance were Peter I the Great of Russia, Frederick IV of...
resulted in the Capitulation of Estonia and Livonia
Capitulation of Estonia and Livonia
With the Capitulation of Estonia and Livonia in 1710 the Swedish dominions Estonia and Livonia were integrated into the Russian Empire following their conquest during the Great Northern War...
in 1710, confirmed by the Treaty of Nystad
Treaty of Nystad
The Treaty of Nystad was the last peace treaty of the Great Northern War. It was concluded between the Tsardom of Russia and Swedish Empire on 30 August / 10 September 1721 in the then Swedish town of Nystad , after Sweden had settled with the other parties in Stockholm and Frederiksborg.During...
in 1721, and Russian rule was then imposed on what later became modern Estonia. Nonetheless, the legal system, Lutheran church, local and town governments, and education remained mostly German until the late 19th century and partially until 1918.
By 1819, the Baltic provinces
Baltic provinces
The Baltic governorates , originally the Ostsee governorates is a collective name for the administrative units of the Russian Empire set up at the territories of Swedish Estonia, Swedish Livonia and, afterwards, of Duchy of Courland and Semigallia .-History:The Treaty of Vilnius of 1561 included...
were the first in the Russian empire in which serfdom was abolished, the largely autonomous nobility allowing the peasants to own their own land or move to the cities. These moves created the economic foundation for the coming to life of the local national identity and culture as Estonia was caught in a current of national awakening that began sweeping through Europe in the mid-19th century.
Estophile Enlightenment Period (1750–1840)
Educated German immigrants and local Baltic Germans in Estonia, educated at German universities, introduced Enlightenment ideasAge of Enlightenment
The Age of Enlightenment was an elite cultural movement of intellectuals in 18th century Europe that sought to mobilize the power of reason in order to reform society and advance knowledge. It promoted intellectual interchange and opposed intolerance and abuses in church and state...
of rational thinking, ideas that propagated freedom of thinking and brotherhood and equality. The French Revolution
French Revolution
The French Revolution , sometimes distinguished as the 'Great French Revolution' , was a period of radical social and political upheaval in France and Europe. The absolute monarchy that had ruled France for centuries collapsed in three years...
provided a powerful motive for the enlightened local upper class to create literature for the peasantry. The freeing of the peasantry from serfdom on the nobles' estates in 1816 in Southern Estonia: Governorate of Livonia (Russian: Лифляндская губерния) and 1819 in Northern Estonia: Governorate of Estonia
Governorate of Estonia
The Governorate of Estonia or Estland, also known as the Government of Estonia or Province of Estonia, was a governorate of the Russian Empire in what is now northern Estonia.-Historical overview:...
(Russian: Эстляндская губерния) by Alexander I of Russia
Alexander I of Russia
Alexander I of Russia , served as Emperor of Russia from 23 March 1801 to 1 December 1825 and the first Russian King of Poland from 1815 to 1825. He was also the first Russian Grand Duke of Finland and Lithuania....
gave rise to a debate as to the future fate of the former enslaved peoples. Although Baltic Germans by and large regarded the future of the Estonians as being a fusion with the Baltic Germans, the Estophile educated class admired the ancient culture of the Estonians and their era of freedom before the conquests by Danes and Germans in the 13th century. The Estophile Enlightenment Period formed the transition from religious Estonian literature to newspapers written in Estonian for the mass public.
National awakening
A cultural movement sprang forth to adopt the use of EstonianEstonian language
Estonian is the official language of Estonia, spoken by about 1.1 million people in Estonia and tens of thousands in various émigré communities...
as the language of instruction in schools, all-Estonian song festivals were held regularly after 1869, and a national literature in Estonian developed. "Kalevipoeg
Kalevipoeg
Kalevipoeg is an epic poem by Friedrich Reinhold Kreutzwald held to be the Estonian national epic.- Origins : There existed an oral tradition within Ancient Estonia of legends explaining the origin of the world...
", Estonia's national epic, was published in 1861 in both Estonian and German.
1889 marked the beginning of the central government-sponsored policy of Russification
Russification
Russification is an adoption of the Russian language or some other Russian attributes by non-Russian communities...
. The impact of this was that many of the Baltic German
Baltic German
The Baltic Germans were mostly ethnically German inhabitants of the eastern shore of the Baltic Sea, which today form the countries of Estonia and Latvia. The Baltic German population never made up more than 10% of the total. They formed the social, commercial, political and cultural élite in...
legal institutions were either abolished or had to do their work in Russian – a good example of this is the University of Tartu
University of Tartu
The University of Tartu is a classical university in the city of Tartu, Estonia. University of Tartu is the national university of Estonia; it is the biggest and highest-ranked university in Estonia...
.
As the Russian Revolution of 1905
Russian Revolution of 1905
The 1905 Russian Revolution was a wave of mass political and social unrest that spread through vast areas of the Russian Empire. Some of it was directed against the government, while some was undirected. It included worker strikes, peasant unrest, and military mutinies...
swept through Estonia, the Estonians called for freedom of the press
Freedom of the press
Freedom of the press or freedom of the media is the freedom of communication and expression through vehicles including various electronic media and published materials...
and assembly
Freedom of assembly
Freedom of assembly, sometimes used interchangeably with the freedom of association, is the individual right to come together and collectively express, promote, pursue and defend common interests...
, for universal franchise
Suffrage
Suffrage, political franchise, or simply the franchise, distinct from mere voting rights, is the civil right to vote gained through the democratic process...
, and for national autonomy. Estonian gains were minimal, but the tense stability that prevailed between 1905 and 1917 allowed Estonians to advance the aspiration of national statehood.
Road to Republic

February Revolution
The February Revolution of 1917 was the first of two revolutions in Russia in 1917. Centered around the then capital Petrograd in March . Its immediate result was the abdication of Tsar Nicholas II, the end of the Romanov dynasty, and the end of the Russian Empire...
of 1917. With the collapse of the Russian Empire
Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was a state that existed from 1721 until the Russian Revolution of 1917. It was the successor to the Tsardom of Russia and the predecessor of the Soviet Union...
in World War I
World War I
World War I , which was predominantly called the World War or the Great War from its occurrence until 1939, and the First World War or World War I thereafter, was a major war centred in Europe that began on 28 July 1914 and lasted until 11 November 1918...
, Russia's Provisional Government granted national autonomy to an unified Estonia
Autonomous Governorate of Estonia
The local autonomy in Estonia was established as a result of the Russian Revolution of 1917. For the duration of control by Imperial Russia, Estonia was divided between two governorates . The Governorate of Estonia in the north corresponded roughly to the area of Danish Estonia and the northern...
in April. The Governorate of Estonia
Governorate of Estonia
The Governorate of Estonia or Estland, also known as the Government of Estonia or Province of Estonia, was a governorate of the Russian Empire in what is now northern Estonia.-Historical overview:...
in the north (corresponding to the historic Danish Estonia
Danish Estonia
Danish Estonia refers to the territories of present-day Estonia that were ruled by Denmark firstly during the 13th–14th centuries and again in the 16th–17th centuries....
) was united with the northern part of the Governorate of Livonia. Elections for a provisional parliament, Maapäev
Maapäev
The Estonian Provincial Assembly was elected after the February Revolution in 1917 as the national diet of the Autonomous Governorate of Estonia in Russian Empire....
was organized, with the Menshevik
Menshevik
The Mensheviks were a faction of the Russian revolutionary movement that emerged in 1904 after a dispute between Vladimir Lenin and Julius Martov, both members of the Russian Social-Democratic Labour Party. The dispute originated at the Second Congress of that party, ostensibly over minor issues...
and Bolshevik
Bolshevik
The Bolsheviks, originally also Bolshevists , derived from bol'shinstvo, "majority") were a faction of the Marxist Russian Social Democratic Labour Party which split apart from the Menshevik faction at the Second Party Congress in 1903....
factions of the Russian Social Democratic Labour Party
Russian Social Democratic Labour Party
The Russian Social Democratic Labour Party , also known as Russian Social Democratic Workers' Party or Russian Social Democratic Party, was a revolutionary socialist Russian political party formed in 1898 in Minsk to unite the various revolutionary organizations into one party...
obtaining a part of the vote. On November 5, 1917, two days before the October Revolution
October Revolution
The October Revolution , also known as the Great October Socialist Revolution , Red October, the October Uprising or the Bolshevik Revolution, was a political revolution and a part of the Russian Revolution of 1917...
in Saint Petersburg
Saint Petersburg
Saint Petersburg is a city and a federal subject of Russia located on the Neva River at the head of the Gulf of Finland on the Baltic Sea...
, Estonian Bolshevik
Bolshevik
The Bolsheviks, originally also Bolshevists , derived from bol'shinstvo, "majority") were a faction of the Marxist Russian Social Democratic Labour Party which split apart from the Menshevik faction at the Second Party Congress in 1903....
leader Jaan Anvelt
Jaan Anvelt
Jaan Anvelt Jaan Anvelt Jaan Anvelt (in Russian Ян Анвельт, also known by the pseudonyms Eessaare Aadu, Jaan Holm, Jaan Hulmu, Kaarel Maatamees, Onkel Kaak or Н...
violently usurped power from the legally constituted Maapäev in a coup d'état, forcing the Maapäev underground.
In February, after the collapse of the peace talks between Soviet Russia and the German Empire
German Empire
The German Empire refers to Germany during the "Second Reich" period from the unification of Germany and proclamation of Wilhelm I as German Emperor on 18 January 1871, to 1918, when it became a federal republic after defeat in World War I and the abdication of the Emperor, Wilhelm II.The German...
, mainland Estonia was occupied by the Germans. Bolshevik forces retreated to Russia. Between the Russian Red Army's retreat and the arrival of advancing German troops, the Salvation Committee
Salvation Committee
The Estonian Salvation Committee was the executive body of the Estonian Provincial Assembly that issued the Estonian Declaration of Independence....
of the Estonian National Council Maapäev issued the Estonian Declaration of Independence
Estonian Declaration of Independence
The Estonian Declaration of Independence, also known as the Manifesto to the Peoples of Estonia , is the founding act of the Republic of Estonia from 1918. It is celebrated on 24 February, the National Day or Estonian Independence Day....
in Pärnu
Pärnu
Pärnu is a city in southwestern Estonia on the coast of Pärnu Bay, an inlet of the Gulf of Riga in the Baltic Sea. It is a popular summer vacation resort with many hotels, restaurants, and large beaches. The Pärnu River flows through the city and drains into the Gulf of Riga...
on February 23, 1918.
German occupation

United Baltic Duchy
The proposed United Baltic Duchy also known as the Grand Duchy of Livonia was a state proposed by the Baltic German nobility and exiled Russian nobility after the Russian revolution and German occupation of the Courland, Livonian and Estonian governorates of the Russian Empire.The idea comprised...
and the withdrawal of German troops in November 1918, an Estonian provisional Government retook office. A military invasion by the Red Army
Red Army
The Workers' and Peasants' Red Army started out as the Soviet Union's revolutionary communist combat groups during the Russian Civil War of 1918-1922. It grew into the national army of the Soviet Union. By the 1930s the Red Army was among the largest armies in history.The "Red Army" name refers to...
followed a few days later, however, marking the beginning of the Estonian War of Independence (1918–1920). The Estonian army cleared the entire territory of Estonia of the Red Army by February 1919.
Independence
On 5–7 April 1919 The Estonian Constituent AssemblyEstonian Constituent Assembly
The Estonian Constituent Assembly was elected on 5-7 April 1919, called by the Estonian Provisional Government during the Estonian War of Independence. The Assembly was elected by proportional representation. Eligible voters included soldiers at the front...
was elected. On February 2, 1920, the Treaty of Tartu
Treaty of Tartu (Russian–Estonian)
Tartu Peace Treaty or Treaty of Tartu was a peace treaty between Estonia and Russian SFSR signed on February 2, 1920 ending the Estonian War of Independence. The terms of the treaty stated that "Russia unreservedly recognises" the independence of Republic of Estonia de jure and renounced in...
was signed by the Republic of Estonia and the Russian SFSR. The terms of the treaty stated that Russia renounced in perpetuity all rights to the territory of Estonia. The first Constitution of Estonia
Constitution of Estonia
The Constitution of Estonia is the fundamental law of the Republic of Estonia and establishes the state order as that of a democratic republic where the supreme power is vested in its citizens. It was adopted in a freely elected Estonian Constituent Assembly on 15 June 1920 and came into force on...
was adopted on June 15, 1920. The Republic of Estonia obtained international recognition and became a member of the League of Nations
League of Nations
The League of Nations was an intergovernmental organization founded as a result of the Paris Peace Conference that ended the First World War. It was the first permanent international organization whose principal mission was to maintain world peace...
in 1921.
In nearby Finland
History of Finland
The land area that now makes up Finland was settled immediately after the Ice Age, beginning from around 8500 BCE. Most of the region was part of the Kingdom of Sweden from the 13th century to 1809, when it was ceded to the Russian Empire, becoming the autonomous Grand Duchy of Finland. The...
similar circumstances resulted in a bloody civil war. Despite repeated threats from fascist movements, Finland became and remained a free democracy under the rule of law. By contrast Estonia, without a civil war, started as a democracy and was turned into a dictatorship in 1934.
Republic of Estonia

Sovereign state
A sovereign state, or simply, state, is a state with a defined territory on which it exercises internal and external sovereignty, a permanent population, a government, and the capacity to enter into relations with other sovereign states. It is also normally understood to be a state which is neither...
. Economically and socially, land reform in 1919 was the most important step. Large estate holdings belonging to the Baltic nobility
Baltic nobility
The Baltic nobility was the privileged social class in the territories of today's Estonia and Latvia. It existed continuously since the medieval foundation of Terra Mariana...
were redistributed among the peasants and especially among volunteers in the Estonian War of Independence. Estonia's principal markets became Scandinavia
Scandinavia
Scandinavia is a cultural, historical and ethno-linguistic region in northern Europe that includes the three kingdoms of Denmark, Norway and Sweden, characterized by their common ethno-cultural heritage and language. Modern Norway and Sweden proper are situated on the Scandinavian Peninsula,...
, the United Kingdom
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
, and western Europe, with some exports to the United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
and to the Soviet Union
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union , officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics , was a constitutionally socialist state that existed in Eurasia between 1922 and 1991....
.
The first constitution of the Republic of Estonia, adopted in 1920, established a parliamentary form of government. The parliament (Riigikogu
Riigikogu
The Riigikogu is the unicameral parliament of Estonia. All important state-related questions pass through the Riigikogu...
) consisted of 100 members elected for 3-year terms. Between 1920 and 1934, Estonia had 21 governments.
A mass anticommunist and antiparliamentary Vaps Movement emerged in the 1930s.
In October 1933 a referendum
Referendum
A referendum is a direct vote in which an entire electorate is asked to either accept or reject a particular proposal. This may result in the adoption of a new constitution, a constitutional amendment, a law, the recall of an elected official or simply a specific government policy. It is a form of...
on constitutional reform initiated by the Vaps Movement was approved by 72.7 percent. The league spearheaded replacement of the parliamentary system
Parliamentary system
A parliamentary system is a system of government in which the ministers of the executive branch get their democratic legitimacy from the legislature and are accountable to that body, such that the executive and legislative branches are intertwined....
with a presidential form of government
Presidential system
A presidential system is a system of government where an executive branch exists and presides separately from the legislature, to which it is not responsible and which cannot, in normal circumstances, dismiss it....
and laid the groundwork for an April 1934 presidential election, which it expected to win. However, the Vaps Movement was thwarted by a pre-emptive coup d'état
Coup d'état
A coup d'état state, literally: strike/blow of state)—also known as a coup, putsch, and overthrow—is the sudden, extrajudicial deposition of a government, usually by a small group of the existing state establishment—typically the military—to replace the deposed government with another body; either...
on March 12, 1934, by Head of State Konstantin Päts
Konstantin Päts
Konstantin Päts VR I/1 and III/1 was the most influential politician of interwar Estonia. He was one of the first Estonians to become active in politics and started an almost 40-year political rivalry with Jaan Tõnisson, first through journalism with his newspaper Teataja, later through politics...
, who then established his own authoritarian rule until a new constitution came to force. During the Era of Silence
Era of Silence
"Era of Silence" is a term used to describe the years 1934-1938 or 1940. in Estonian history. It was introduced by Kaarel Eenpalu, Prime Minister of Estonia in 1938-39 and a strong supporter of Konstantin Päts, Estonia's dictator during that period...
, political parties were banned and the parliament was not in session between 1934 and 1938 as the country was ruled by decree
Rule by decree
Rule by decree is a style of governance allowing quick, unchallenged creation of law by a single person or group, and is used primarily by dictators and absolute monarchs, although philosophers such as Giorgio Agamben have argued that it has been generalized since World War I in all modern states,...
by Konstantin Päts
Konstantin Päts
Konstantin Päts VR I/1 and III/1 was the most influential politician of interwar Estonia. He was one of the first Estonians to become active in politics and started an almost 40-year political rivalry with Jaan Tõnisson, first through journalism with his newspaper Teataja, later through politics...
. The Vaps Movement was officially banned and finally disbanded in December 1935. On May 6, 1936, 150 members of the league went on trial and 143 of them were convicted to long-term prison sentences. They were granted an amnesty and freed in 1938, by which time the league had lost most of its popular support.
The independence period was one of great cultural advancement. Estonian language schools were established, and artistic life of all kinds flourished. One of the more notable cultural acts of the independence period, unique in western Europe at the time of its passage in 1925, was a guarantee of cultural autonomy to minority group
Minority group
A minority is a sociological group within a demographic. The demographic could be based on many factors from ethnicity, gender, wealth, power, etc. The term extends to numerous situations, and civilizations within history, despite the misnomer of minorities associated with a numerical statistic...
s comprising at least 3,000 persons, including Jews (see history of the Jews in Estonia
History of the Jews in Estonia
The history of the Jews in Estonia starts with individual reports of Jews in what is now Estonia from as early as the 14th century. However, the process of permanent Jewish settlement in Estonia began in the 19th century, especially after they were granted the official right to enter the region by...
). Historians see the lack of any bloodshed after a nearly "700-year German rule" as indication that it must have been mild by comparison.
Estonia had pursued a policy of neutrality, but it was of no consequence after the Soviet Union
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union , officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics , was a constitutionally socialist state that existed in Eurasia between 1922 and 1991....
and Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany , also known as the Third Reich , but officially called German Reich from 1933 to 1943 and Greater German Reich from 26 June 1943 onward, is the name commonly used to refer to the state of Germany from 1933 to 1945, when it was a totalitarian dictatorship ruled by...
signed the Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact on August 23, 1939. In the agreement, the two great powers agreed to divide up the countries situated between them (Poland
Poland
Poland , officially the Republic of Poland , is a country in Central Europe bordered by Germany to the west; the Czech Republic and Slovakia to the south; Ukraine, Belarus and Lithuania to the east; and the Baltic Sea and Kaliningrad Oblast, a Russian exclave, to the north...
, Lithuania
Lithuania
Lithuania , officially the Republic of Lithuania is a country in Northern Europe, the biggest of the three Baltic states. It is situated along the southeastern shore of the Baltic Sea, whereby to the west lie Sweden and Denmark...
, Latvia
Latvia
Latvia , officially the Republic of Latvia , is a country in the Baltic region of Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by Estonia , to the south by Lithuania , to the east by the Russian Federation , to the southeast by Belarus and shares maritime borders to the west with Sweden...
, Estonia, and Finland
Finland
Finland , officially the Republic of Finland, is a Nordic country situated in the Fennoscandian region of Northern Europe. It is bordered by Sweden in the west, Norway in the north and Russia in the east, while Estonia lies to its south across the Gulf of Finland.Around 5.4 million people reside...
) with Estonia falling in the Soviet "sphere of influence
Sphere of influence
In the field of international relations, a sphere of influence is a spatial region or conceptual division over which a state or organization has significant cultural, economic, military or political influence....
". After the invasion of Poland, the Orzeł incident took place when Polish submarine ORP Orzeł
ORP Orzeł
Three boats of the Polish Navy have been named ORP Orzeł :* ORP Orzeł was an commissioned in 1939 and lost in 1940.* ORP Orzeł was a commissioned in 1962 and decommissioned in 1983....
looked for shelter in Tallinn
Tallinn
Tallinn is the capital and largest city of Estonia. It occupies an area of with a population of 414,940. It is situated on the northern coast of the country, on the banks of the Gulf of Finland, south of Helsinki, east of Stockholm and west of Saint Petersburg. Tallinn's Old Town is in the list...
but escaped after the Soviet Union
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union , officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics , was a constitutionally socialist state that existed in Eurasia between 1922 and 1991....
attacked Poland on September 17. Estonian's lack of will and/or inability to disarm and intern the crew caused the Soviet Union to accuse Estonia of "helping them escape" and claim that Estonia was not neutral. On September 24, 1939, the Soviet Union threatened Estonia with war unless provided with military bases in the country –- an ultimatum with which the Estonian government complied.

Soviet occupation (1940)
The Republic of Estonia was occupied by the Soviet Union in June 1940.On September 24, 1939, warships of the Red Navy appeared off Estonian ports and Soviet bombers began a threatening patrol over Tallinn
Tallinn
Tallinn is the capital and largest city of Estonia. It occupies an area of with a population of 414,940. It is situated on the northern coast of the country, on the banks of the Gulf of Finland, south of Helsinki, east of Stockholm and west of Saint Petersburg. Tallinn's Old Town is in the list...
and the nearby countryside. Moscow demanded Estonia assent to an agreement which allowed the USSR to establish military bases and station 25,000 troops on Estonian soil for the duration of the European war. The government of Estonia accepted the ultimatum, signing the corresponding agreement on September 28, 1939.
On June 12, 1940, the order for a total military blockade of Estonia by the Soviet Baltic Fleet
Baltic Fleet
The Twice Red Banner Baltic Fleet - is the Russian Navy's presence in the Baltic Sea. In previous historical periods, it has been part of the navy of Imperial Russia and later the Soviet Union. The Fleet gained the 'Twice Red Banner' appellation during the Soviet period, indicating two awards of...
was given.
On June 14, 1940, while the world's attention was focused on the fall of Paris
Paris
Paris is the capital and largest city in France, situated on the river Seine, in northern France, at the heart of the Île-de-France region...
to Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany , also known as the Third Reich , but officially called German Reich from 1933 to 1943 and Greater German Reich from 26 June 1943 onward, is the name commonly used to refer to the state of Germany from 1933 to 1945, when it was a totalitarian dictatorship ruled by...
a day earlier, the Soviet military blockade of Estonia went into effect, and two Soviet bombers downed Finnish passenger airplane "Kaleva
Kaleva (airplane)
Kaleva, registered OH-ALL, was a civilian Junkers Ju 52 passenger and transport plane, belonging to the Finnish carrier Aero O/Y. The aircraft was shot down by two Soviet Ilyushin DB-3 bombers during peacetime between the Soviet Union and Finland on June 14, 1940, while en route from Tallinn to...
" flying from Tallinn to Helsinki carrying three diplomatic pouches from the U.S. legations in Tallinn
Tallinn
Tallinn is the capital and largest city of Estonia. It occupies an area of with a population of 414,940. It is situated on the northern coast of the country, on the banks of the Gulf of Finland, south of Helsinki, east of Stockholm and west of Saint Petersburg. Tallinn's Old Town is in the list...
, Riga
Riga
Riga is the capital and largest city of Latvia. With 702,891 inhabitants Riga is the largest city of the Baltic states, one of the largest cities in Northern Europe and home to more than one third of Latvia's population. The city is an important seaport and a major industrial, commercial,...
and Helsinki
Helsinki
Helsinki is the capital and largest city in Finland. It is in the region of Uusimaa, located in southern Finland, on the shore of the Gulf of Finland, an arm of the Baltic Sea. The population of the city of Helsinki is , making it by far the most populous municipality in Finland. Helsinki is...
. US Foreign Service employee Henry W. Antheil, Jr.
Henry W. Antheil, Jr.
Henry William Antheil, Jr. was born in Trenton, New Jersey, USA.Henry W. Antheil, Jr., younger brother of noted composer George Antheil, was a clerk at the U.S. legation in Helsinki...
was killed in the crash.
On June 16, 1940, the Soviet Union invaded Estonia. Molotov
Vyacheslav Molotov
Vyacheslav Mikhailovich Molotov was a Soviet politician and diplomat, an Old Bolshevik and a leading figure in the Soviet government from the 1920s, when he rose to power as a protégé of Joseph Stalin, to 1957, when he was dismissed from the Presidium of the Central Committee by Nikita Khrushchev...
accused the Baltic states of conspiracy against the Soviet Union and delivered an ultimatum to Estonia for the establishment of a government approved of by the Soviets.
The Estonian government decided, given the overwhelming Soviet force both on the borders and inside the country, not to resist, to avoid bloodshed and open war. Estonia accepted the ultimatum and the statehood of Estonia de facto
De facto
De facto is a Latin expression that means "concerning fact." In law, it often means "in practice but not necessarily ordained by law" or "in practice or actuality, but not officially established." It is commonly used in contrast to de jure when referring to matters of law, governance, or...
ceased to exist as the Red Army exited from their military bases in Estonia on June 17. The following day, some 90,000 additional troops entered the country. The military occupation
Military occupation
Military occupation occurs when the control and authority over a territory passes to a hostile army. The territory then becomes occupied territory.-Military occupation and the laws of war:...
of the Republic of Estonia was rendered "official" by a communist coup d'état
Coup d'état
A coup d'état state, literally: strike/blow of state)—also known as a coup, putsch, and overthrow—is the sudden, extrajudicial deposition of a government, usually by a small group of the existing state establishment—typically the military—to replace the deposed government with another body; either...
supported by the Soviet troops, followed by "parliamentary elections" where all but pro-Communist candidates were outlawed. The "parliament" so elected proclaimed Estonia a Socialist Republic on July 21, 1940 and unanimously requested Estonia to be "accepted" into the Soviet Union
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union , officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics , was a constitutionally socialist state that existed in Eurasia between 1922 and 1991....
. Those who had fallen short of the "political duty" of voting Estonia into the USSR, who had failed to have their passports stamped for so voting, were allowed to be shot in the back of the head by Soviet tribunals. Estonia was formally annexed into the Soviet Union on August 6 and renamed the Estonian Soviet Socialist Republic
Estonian Soviet Socialist Republic
The Estonian Soviet Socialist Republic , often abbreviated as Estonian SSR or ESSR, was a republic of the Soviet Union, administered by and subordinated to the Government of the Soviet Union...
. See, for instance, position expressed by European Parliament, which condemned "the fact that the occupation of these formerly independent and neutral States by the Soviet Union occurred in 1940 following the Molotov/Ribbentrop pact, and continues."
The Soviet authorities, having gained control over Estonia, immediately imposed a regime of terror. During the first year of Soviet occupation (1940–1941) over 8,000 people, including most of the country's leading politicians and military officers, were arrested. About 2,200 of the arrested were executed in Estonia, while most others were moved to prison camps in Russia, from where very few were later able to return alive. On June 14, 1941, when mass deportation
Deportation
Deportation means the expulsion of a person or group of people from a place or country. Today it often refers to the expulsion of foreign nationals whereas the expulsion of nationals is called banishment, exile, or penal transportation...
s took place simultaneously in all three Baltic countries, about 10,000 Estonian civilians were deported to Siberia
Siberia
Siberia is an extensive region constituting almost all of Northern Asia. Comprising the central and eastern portion of the Russian Federation, it was part of the Soviet Union from its beginning, as its predecessor states, the Tsardom of Russia and the Russian Empire, conquered it during the 16th...
and other remote areas of the Soviet Union, where nearly half of them later perished. Of the 32,100 Estonian men who were forcibly relocated to Russia under the pretext of mobilisation into the Soviet army after the German invasion of the Soviet Union in 1941, nearly 40 percent died within the next year in the so-called "labour battalion
Labour battalion
Labour battalions have been a form of alternative service or unfree labour in various countries in lieu of or resembling regular military service...
s" of hunger, cold and overworking. During the first Soviet occupation of 1940–41 about 500 Jews were deported to Siberia
Siberia
Siberia is an extensive region constituting almost all of Northern Asia. Comprising the central and eastern portion of the Russian Federation, it was part of the Soviet Union from its beginning, as its predecessor states, the Tsardom of Russia and the Russian Empire, conquered it during the 16th...
.
Estonian graveyards and monuments were destroyed. Among others, the Tallinn Military Cemetery had the majority of gravestones from 1918–1944 destroyed by the Soviet authorities, and this graveyard became reused by the Red Army
Red Army
The Workers' and Peasants' Red Army started out as the Soviet Union's revolutionary communist combat groups during the Russian Civil War of 1918-1922. It grew into the national army of the Soviet Union. By the 1930s the Red Army was among the largest armies in history.The "Red Army" name refers to...
.
Other cemeteries destroyed by the authorities during the Soviet era in Estonia include Baltic German
Baltic German
The Baltic Germans were mostly ethnically German inhabitants of the eastern shore of the Baltic Sea, which today form the countries of Estonia and Latvia. The Baltic German population never made up more than 10% of the total. They formed the social, commercial, political and cultural élite in...
cemeteries established in 1774 (Kopli cemetery
Kopli cemetery
Kopli cemetery was Estonia's largest Lutheran Baltic German cemetery, located in the suburb of Kopli in Tallinn. It contained thousands of graves of prominent citizens of Tallinn and stood for over 170 years from 1774 to shortly after World War II when it was completely flattened and destroyed by...
, Mõigu cemetery
Mõigu cemetery
The Mõigu cemetery ) was a large Baltic German cemetery, located in the Tallinn suburb of Mõigu in Estonia. It served as the primary burial ground for the usually wealthy and noble citizens of the Toompea parish of Tallinn...
) and the oldest cemetery in Tallinn, from the 16th century, Kalamaja cemetery
Kalamaja cemetery
The Kalamaja cemetery in Tallinn in Estonia was once the city's oldest existing cemetery, located in the suburb of Kalamaja in the north of the city...
.
- See also Soviet deportations from EstoniaSoviet deportations from EstoniaAs the Soviet Union had occupied Estonia in 1940 and retaken it from Nazi Germany again in 1944, tens of thousands of Estonia's citizens underwent deportation in the 1940s...
Many countries including the United States did not recognize the seizure of Estonia by the USSR. Such countries recognized Estonian diplomats and consuls who still functioned in many countries in the name of their former governments. These aging diplomats persisted in this anomalous situation until the ultimate restoration of Baltic independence.
Ernst Jaakson
Ernst Jaakson
Ernst Jaakson was an Estonian diplomat whose unique contribution was to keep Estonia's legal continuity with his uninterrupted diplomatic service for 69 years.-Education:...
, the longest-serving foreign diplomatic representative to the United States, served as vice-consul from 1934, and as consul general in charge of the Estonian legation in the United States from 1965 until reestablishment of Estonia's independence. On November 25, 1991 he presented credentials as Estonian ambassador to the United States.
German occupation (1941–1944)

After Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany , also known as the Third Reich , but officially called German Reich from 1933 to 1943 and Greater German Reich from 26 June 1943 onward, is the name commonly used to refer to the state of Germany from 1933 to 1945, when it was a totalitarian dictatorship ruled by...
invaded the Soviet Union
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union , officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics , was a constitutionally socialist state that existed in Eurasia between 1922 and 1991....
on June 22, 1941, and the Wehrmacht reached Estonia in July 1941, most Estonians greeted the Germans with relatively open arms and hoped to restore independence. But it soon became clear that sovereignty was out of the question. Estonia became a part of the German-occupied "Ostland
Reichskommissariat Ostland
Reichskommissariat Ostland, literally "Reich Commissariat Eastland", was the civilian occupation regime established by Nazi Germany in the Baltic states and much of Belarus during World War II. It was also known as Reichskommissariat Baltenland initially...
". A Sicherheitspolizei
Sicherheitspolizei
The Sicherheitspolizei , often abbreviated as SiPo, was a term used in Nazi Germany to describe the state political and criminal investigation security agencies. It was made up by the combined forces of the Gestapo and the Kripo between 1936 and 1939...
was established for internal security under the leadership of Ain-Ervin Mere
Ain-Ervin Mere
Ain Mere was an Estonian military officer. During the World War II, he was an Obersturmbannführer in the Waffen SS and also the head of the Sicherheitspolizei in Estonia following its creation in 1942.He was born in Vändra and fought voluntarily in the Estonian War...
. The initial enthusiasm that accompanied the liberation from Soviet occupation quickly waned as a result and the Germans had limited success in recruiting volunteers. The draft was introduced in 1942, resulting in some 3,400 men fleeing to Finland to fight in the Finnish Army rather than join the Germans. Finnish Infantry Regiment 200
Finnish Infantry Regiment 200
Infantry Regiment 200 or Soomepoisid was a unit in the Finnish army during World War II made up mostly of Estonian volunteers, who preferred to fight against the Soviet Union in the ranks of the Finnish army instead of the armed forces of Germany....
AKA (Estonian: soomepoisid) was formed out of Estonian volunteers in Finland. With the Allied victory over Germany becoming certain in 1944, the only option to save Estonia's independence was to stave off a new Soviet invasion of Estonia until Germany's capitulation.
By January 1944, the front was pushed back by the Soviet Army almost all the way to the former Estonian border. Narva
Narva
Narva is the third largest city in Estonia. It is located at the eastern extreme point of Estonia, by the Russian border, on the Narva River which drains Lake Peipus.-Early history:...
was evacuated. Jüri Uluots
Jüri Uluots
Jüri Uluots was an Estonian prime minister, journalist, prominent attorney and distinguished Professor and Dean of the Faculty of Law at the University of Tartu....
, the last legitimate prime minister of the Republic of Estonia (according to the Constitution of the Republic of Estonia) prior to its fall to the Soviet Union in 1940, delivered a radio address that implored all able-bodied men born from 1904 through 1923 to report for military service (before this, Uluots had opposed Estonian mobilization.) The call drew support from all across the country: 38,000 volunteers jammed registration centers. Several thousand Estonians who had joined the Finnish army came back across the Gulf of Finland
Gulf of Finland
The Gulf of Finland is the easternmost arm of the Baltic Sea. It extends between Finland and Estonia all the way to Saint Petersburg in Russia, where the river Neva drains into it. Other major cities around the gulf include Helsinki and Tallinn...
to join the newly formed Territorial Defense Force, assigned to defend Estonia against the Soviet advance. It was hoped that by engaging in such a war Estonia would be able to attract Western support for the cause of Estonia's independence from the USSR and thus ultimately succeed in achieving independence.
The initial formation of the volunteer SS Estonian legion created in 1942 was eventually expanded to become a full-sized conscript division of the Waffen-SS
Waffen-SS
The Waffen-SS was a multi-ethnic and multi-national military force of the Third Reich. It constituted the armed wing of the Schutzstaffel or SS, an organ of the Nazi Party. The Waffen-SS saw action throughout World War II and grew from three regiments to over 38 divisions, and served alongside...
in 1944, the 20th Waffen Grenadier Division of the SS (1st Estonian). The Estonian units saw action defending the Narva line
Battle of Narva (1944)
The Battle of Narva was a military campaign between the German Army Detachment "Narwa" and the Soviet Leningrad Front fought for possession of the strategically important Narva Isthmus on 2 February – 10 August 1944 during World War II....
throughout 1944.
As the Germans started to retreat on 18 September 1944, Jüri Uluots
Jüri Uluots
Jüri Uluots was an Estonian prime minister, journalist, prominent attorney and distinguished Professor and Dean of the Faculty of Law at the University of Tartu....
, the last Prime Minister of the Estonian Republic prior to Soviet occupation, assumed the responsibilities of president (as dictated in the Constitution) and appointed a new government while seeking recognition from the Allies
Allies of World War II
The Allies of World War II were the countries that opposed the Axis powers during the Second World War . Former Axis states contributing to the Allied victory are not considered Allied states...
. On 22 September 1944, as the last German units pulled out of Tallinn, the city was re-occupied by the Soviet Red Army. The new Estonian government fled to Stockholm
Stockholm
Stockholm is the capital and the largest city of Sweden and constitutes the most populated urban area in Scandinavia. Stockholm is the most populous city in Sweden, with a population of 851,155 in the municipality , 1.37 million in the urban area , and around 2.1 million in the metropolitan area...
, Sweden
Sweden
Sweden , officially the Kingdom of Sweden , is a Nordic country on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. Sweden borders with Norway and Finland and is connected to Denmark by a bridge-tunnel across the Öresund....
and operated in exile until 1992, when Heinrich Mark
Heinrich Mark
Heinrich Mark was born on October 1, 1911, in Krootuse, Kõlleste Parish, now in Põlva County, Estonia. He died on August 2, 2004, in Stockholm, Sweden....
, the prime minister of the Estonian government in exile acting as president, presented his credentials to incoming president Lennart Meri
Lennart Meri
Lennart Georg Meri was a writer, film director and statesman who served as the second President of Estonia from 1992 to 2001. Meri was a leader of the Estonian independence movement.-Early life:...
.
The Holocaust in Estonia
The process of Jewish settlement in Estonia began in the 19th century, when in 1865 Russian Tsar Alexander IIAlexander II of Russia
Alexander II , also known as Alexander the Liberator was the Emperor of the Russian Empire from 3 March 1855 until his assassination in 1881...
granted them the right to enter the region. The creation of the Republic of Estonia in 1918 marked the beginning of a new era for the Jews. Approximately 200 Jews fought in combat for the creation of the Republic of Estonia and 70 of these men were volunteers. From the very first days of her existence as a state, Estonia showed her tolerance towards all the peoples inhabiting her territories. On 12 February 1925 The Estonian government passed a law pertaining to the cultural autonomy of minority peoples. The Jewish community quickly prepared its application for cultural autonomy. Statistics on Jewish citizens were compiled. They totaled 3,045, fulfilling the minimum requirement of 3000. In June 1926 the Jewish Cultural Council was elected and Jewish cultural autonomy was declared. Jewish cultural autonomy was of great interest to the global Jewish community. The Jewish National Endowment presented the Government of the Republic of Estonia
Government of the Republic of Estonia
The Government of the Republic of Estonia exercises executive power pursuant to the Constitution and the laws of the Republic of Estonia...
with a certificate of gratitude for this achievement.
There were, at the time of Soviet occupation in 1940, approximately 2000 Estonian Jews. Many Jewish people were deported to Siberia along with other Estonians by the Soviets. It is estimated that 500 Jews suffered this fate. With the invasion of the Baltics, it was the intention of the Nazi government to use the Baltic countries as their main area of mass genocide. Consequently, Jews from countries outside the Baltics were shipped there to be exterminated. Out of the approximately 4,300 Jews in Estonia prior to the war, between 1,500 and 2,000 were entrapped by the Nazis,
and an estimated 10,000 Jews were killed in Estonia after having been deported to camps there from elsewhere in Eastern Europe.
There are known to have been 7 ethnic Estonians
Holocaust trials in Soviet Estonia
A number of Holocaust trials in Soviet Estonia were held in the 1960s.The best-known trial was brought in 1961, by the local Soviet authorities against Estonian collaborators who had participated in the execution of the Holocaust during the Nazi German occupation...
– Ralf Gerrets, Ain-Ervin Mere
Ain-Ervin Mere
Ain Mere was an Estonian military officer. During the World War II, he was an Obersturmbannführer in the Waffen SS and also the head of the Sicherheitspolizei in Estonia following its creation in 1942.He was born in Vändra and fought voluntarily in the Estonian War...
, Jaan Viik, Juhan Jüriste, Karl Linnas
Karl Linnas
Karl Linnas was an Estonian who was sentenced to capital punishment during the Holocaust trials in Soviet Estonia in 1961. He was later deported from the United States to the Soviet Union...
, Aleksander Laak and Ervin Viks – that have faced trials for crimes against humanity.
Since the reestablishment of Estonian independence the Estonian International Commission for Investigation of Crimes Against Humanity
Estonian International Commission for Investigation of Crimes Against Humanity
The Estonian International Commission for Investigation of Crimes Against Humanity is the commission established by President of Estonia Lennart Meri in October 1998 to investigate crimes against humanity committed in Estonia or against its citizens during the Soviet and German occupation, such as...
has been established. Markers were put in place for the 60th anniversary of the mass executions that were carried out at the Lagedi, Vaivara and Klooga (Kalevi-Liiva) camps in September 1944.
Fate of other minorities in and after World War II
The Baltic Germans had mainly been evacuated to Germany following the Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact.Almost all the remaining Estonian Swedes
Estonian Swedes
The Estonian Swedes, Estonia-Swedes, or Coastal Swedes are a Swedish-speaking linguistic minority traditionally residing in the coastal areas and islands of what is now western and northern Estonia...
fled in August 1944, often in their small boats to the Swedish island of Gotland
Gotland
Gotland is a county, province, municipality and diocese of Sweden; it is Sweden's largest island and the largest island in the Baltic Sea. At 3,140 square kilometers in area, the region makes up less than one percent of Sweden's total land area...
.
The Russian minority grew significantly in numbers during the postwar era.

Stalinism
In World War IIWorld War II
World War II, or the Second World War , was a global conflict lasting from 1939 to 1945, involving most of the world's nations—including all of the great powers—eventually forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis...
Estonia had suffered huge losses. Ports had been destroyed, and 45% of industry and 40% of the railways had become damaged. Estonia's population had decreased by one-fifth, about 200,000 people. Some 10% of the population (over 80,000 people) had fled to the West between 1940 and 1944. More than 30,000 soldiers had been killed in action. In 1944 Russian air raids
Airstrike
An air strike is an attack on a specific objective by military aircraft during an offensive mission. Air strikes are commonly delivered from aircraft such as fighters, bombers, ground attack aircraft, attack helicopters, and others...
had destroyed Narva
Narva
Narva is the third largest city in Estonia. It is located at the eastern extreme point of Estonia, by the Russian border, on the Narva River which drains Lake Peipus.-Early history:...
and one-third of the residential area in Tallinn
Tallinn
Tallinn is the capital and largest city of Estonia. It occupies an area of with a population of 414,940. It is situated on the northern coast of the country, on the banks of the Gulf of Finland, south of Helsinki, east of Stockholm and west of Saint Petersburg. Tallinn's Old Town is in the list...
. By the late autumn of 1944, Soviet forces had ushered in a second phase of Soviet rule on the heels of the German troops withdrawing from Estonia, and followed it up by a new wave of arrests and executions of people considered disloyal to the Soviets.

Guerrilla warfare
Guerrilla warfare is a form of irregular warfare and refers to conflicts in which a small group of combatants including, but not limited to, armed civilians use military tactics, such as ambushes, sabotage, raids, the element of surprise, and extraordinary mobility to harass a larger and...
movement known as the "Metsavennad" ("Forest Brothers")
Forest Brothers
The Forest Brothers were Estonian, Latvian, and Lithuanian partisans who waged a guerrilla war against Soviet rule during the Soviet invasion and occupation of the three Baltic states during, and after, World War II...
developed in the countryside, reaching its zenith in 1946–48. It is hard to tell how many people were in the ranks of the Metsavennad; however, it is estimated that at different times there could have been about 30,000–35,000 people. Probably the last Forest Brother was caught in September 1978, and killed himself during his apprehension.
In March 1949, 20,722 people (2.5% of the population) were deported to Siberia. By the beginning of the 1950s, the occupying regime had suppressed the resistance movement.
After the war the Communist Party of the Estonian Soviet Socialist Republic (ECP) became the pre-eminent organization in the republic. The ethnic Estonian share in the total ECP membership decreased from 90% in 1941 to 48% in 1952.

Khrushchev era
After StalinJoseph Stalin
Joseph Vissarionovich Stalin was the Premier of the Soviet Union from 6 May 1941 to 5 March 1953. He was among the Bolshevik revolutionaries who brought about the October Revolution and had held the position of first General Secretary of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union's Central Committee...
's death, Party membership vastly expanded its social base to include more ethnic Estonians. By the mid-1960s, the percentage of ethnic Estonian membership stabilized near 50%. On the eve of perestroika
Perestroika
Perestroika was a political movement within the Communist Party of the Soviet Union during 1980s, widely associated with the Soviet leader Mikhail Gorbachev...
the ECP claimed about 100,000 members; less than half were ethnic Estonians and they totalled less than 7% of the country's population.
One positive aspect of the post-Stalin era in Estonia was the regranting of permission in the late 1950s for citizens to make contact with foreign countries. Ties were reactivated with Finland
Finland
Finland , officially the Republic of Finland, is a Nordic country situated in the Fennoscandian region of Northern Europe. It is bordered by Sweden in the west, Norway in the north and Russia in the east, while Estonia lies to its south across the Gulf of Finland.Around 5.4 million people reside...
, and in the 1960s, a ferry connection was opened from Tallinn to Helsinki
Helsinki
Helsinki is the capital and largest city in Finland. It is in the region of Uusimaa, located in southern Finland, on the shore of the Gulf of Finland, an arm of the Baltic Sea. The population of the city of Helsinki is , making it by far the most populous municipality in Finland. Helsinki is...
and Estonians began watching Finnish television. This electronic "window on the West" afforded Estonians more information on current affairs and more access to Western culture and thought than any other group in the Soviet Union. This heightened media environment was important in preparing Estonians for their vanguard role in extending perestroika during the Gorbachev
Mikhail Gorbachev
Mikhail Sergeyevich Gorbachev is a former Soviet statesman, having served as General Secretary of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union from 1985 until 1991, and as the last head of state of the USSR, having served from 1988 until its dissolution in 1991...
era.
Capital investments
In 1955 the TV Centre was built in Tallinn, that began TV broadcasts on June 29 of that year. The Tallinn Song Festival GroundsTallinn Song Festival Grounds
-History of Song Festivals:In 1869 Johann Voldemar Jannsen established the Estonian Song Festival while the nation was still a province of the Russian Empire. This festival was considered responsible for fostering an Estonian national awakening...
, the venue for the song festivals, were built in 1960
Health care
Only after the Khrushchev ThawKhrushchev Thaw
The Khrushchev Thaw refers to the period from the mid 1950s to the early 1960s, when repression and censorship in the Soviet Union were partially reversed and millions of Soviet political prisoners were released from Gulag labor camps, due to Nikita Khrushchev's policies of de-Stalinization and...
period of 1956 did healthcare networks start to stabilise. Due to natural development, science and technology advanced and popular welfare increased. All demographic indicators improved; birth rate increased, mortality decreased. Healthcare became freely available to everybody during the Soviet era.
Brezhnev era
In the late 1970s, Estonian society grew increasingly concerned about the threat of cultural Russification to the Estonian language and national identity. By 1981, Russian was taught in the first grade of Estonian-language schools and was also introduced into Estonian pre-school teaching.
Moscow Olympic Games of 1980
Tallinn was selected as the host of the sailing eventsSailing at the 1980 Summer Olympics
Sailing/Yachting is a Olympic sport starting from the Games of the 1st Olympiad . With the exception of 1904 and possible 1916 sailing was always a part of the Olympic program....
which led to controversy since many governments had not de jure recognized ESSR as part of the USSR. During the preparations to the Olympics
1980 Summer Olympics
The 1980 Summer Olympics, officially known as the Games of the XXII Olympiad, was an international multi-sport event celebrated in Moscow in the Soviet Union. In addition, the yachting events were held in Tallinn, and some of the preliminary matches and the quarter-finals of the football tournament...
, sports buildings were built in Tallinn, along with other general infrastructure and broadcasting facilities. This wave of investment included Tallinn Airport, Hotell Olumpia, Tallinn TV Tower
Tallinn TV Tower
The Tallinn TV Tower is a free-standing structure with an observation deck, built to provide better telecommunication services for the 1980 Moscow Summer Olympics regatta event . It is located near Pirita, six km north-east of the Tallinn city center...
, Pirita Yachting Centre
Sailing at the 1980 Summer Olympics
Sailing/Yachting is a Olympic sport starting from the Games of the 1st Olympiad . With the exception of 1904 and possible 1916 sailing was always a part of the Olympic program....
and Linnahall
Linnahall
Linnahall is a concert/sports venue in Tallinn, Estonia. It is situated on the harbour, just beyond the walls of the Old Town and was completed in 1980....
.
Andropov and Chernenko era
On November 10, 1982 Leonid BrezhnevLeonid Brezhnev
Leonid Ilyich Brezhnev – 10 November 1982) was the General Secretary of the Central Committee of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union , presiding over the country from 1964 until his death in 1982. His eighteen-year term as General Secretary was second only to that of Joseph Stalin in...
died and was succeeded by Yuri Andropov
Yuri Andropov
Yuri Vladimirovich Andropov was a Soviet politician and the General Secretary of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union from 12 November 1982 until his death fifteen months later.-Early life:...
, the former head of the KGB
KGB
The KGB was the commonly used acronym for the . It was the national security agency of the Soviet Union from 1954 until 1991, and was the premier internal security, intelligence, and secret police organization during that time.The State Security Agency of the Republic of Belarus currently uses the...
. Andropov introduced limited economic reforms and established an anti-corruption program. On February 9, 1984 Andropov died and was succeeded by Konstantin Chernenko
Konstantin Chernenko
Konstantin Ustinovich Chernenko was a Soviet politician and the fifth General Secretary of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union. He led the Soviet Union from 13 February 1984 until his death thirteen months later, on 10 March 1985...
who in turn died on March 10, 1985.
Alcoholism
AlcoholismAlcoholism
Alcoholism is a broad term for problems with alcohol, and is generally used to mean compulsive and uncontrolled consumption of alcoholic beverages, usually to the detriment of the drinker's health, personal relationships, and social standing...
became a growing health issue. Up until 1985 and the beginning of glasnost
Glasnost
Glasnost was the policy of maximal publicity, openness, and transparency in the activities of all government institutions in the Soviet Union, together with freedom of information, introduced by Mikhail Gorbachev in the second half of the 1980s...
, it was illegal to publish statistical data on alcohol sales. It is estimated that alcoholism peaked in 1982–1984, when consumption reached 11.2 litres of absolute alcohol per person per annum. (In comparison, in Finland during the same period consumption only 6–7 litres per person per annum).
Gorbachev era
By the beginning of the Gorbachev era, concern over the cultural survival of the Estonian people had reached a critical point. The ECP remained stable in the early perestroika years but waned in the late 1980s. Other political movements, groupings and parties moved to fill the power vacuum. The first and most important was the Estonian Popular Front, established in April 1988 with its own platform, leadership and broad constituency. The GreensEstonian Greens
Estonian Greens is an Estonian green political party. Valdur Lahtvee, an organizer, reported that on 2006-11-01, more than 1000 members had been recruited for the Green Party Initiative Group to register as a political party under Estonian law, opening doors for running at the coming parliament...
and the dissident-led Estonian National Independence Party soon followed.
Regaining independence
The Estonian Sovereignty DeclarationEstonian Sovereignty Declaration
The Estonian Sovereignty Declaration , fully: Declaration on the Sovereignty of the Estonian SSR was issued on November 16, 1988 during the Singing Revolution in Estonia. The declaration asserted Estonia's sovereignty and the supremacy of the Estonian laws over the laws of the Soviet Union...
was issued on November 16, 1988. By 1989 the political spectrum had widened, and new parties were formed and re-formed almost daily. The republic's Supreme Soviet
Supreme Soviet
The Supreme Soviet of the Soviet Union was the Supreme Soviet in the Soviet Union and the only one with the power to pass constitutional amendments...
transformed into an authentic regional lawmaking body. This relatively conservative legislature passed an early declaration of sovereignty (November 16, 1988); a law on economic independence (May 1989) confirmed by the Supreme Soviet of the Soviet Union that November; a language law making Estonian the official language
Official language
An official language is a language that is given a special legal status in a particular country, state, or other jurisdiction. Typically a nation's official language will be the one used in that nation's courts, parliament and administration. However, official status can also be used to give a...
(January 1989); and local and republic election laws stipulating residency requirements for voting and candidacy (August, November 1989).
Despite the emergence of the Popular Front and the Supreme Soviet as a new lawmaking body, since 1989 the different segments of the indigenous Estonian population had been politically mobilized by different and competing actors. The Popular Front's proposal, to declare the independence of Estonia as a new, so-called "third republic" whose citizens would be all those living there at the moment found less and less support over time.
A grassroots Estonian Citizens' Committees Movement launched in 1989 with the objective of registering all pre-war citizens of the Republic of Estonia and their descendants in order to convene a Congress of Estonia
Congress of Estonia
The Congress of Estonia was an innovative grassroots parliament established in Estonia as a part of the process of regaining of independence from the Soviet Union. It also challenged the power and authority of the pre-existing quasi-parliament in the country, called the Supreme Soviet of the...
. Their emphasis was on the illegal nature of the Soviet system and that hundreds of thousands of inhabitants of Estonia had not ceased to be citizens of the Estonian Republic which still existed de jure, recognized by the majority of Western nations. Despite the hostility of the mainstream official press and intimidation by Soviet Estonian authorities, dozens of local citizens' committees were elected by popular initiative all over the country. These quickly organized into a nation-wide structure and by the beginning of 1990, over 900,000 people had registered themselves as citizens of the Republic of Estonia.
The spring of 1990 saw two free elections and two alternative legislatures developed in Estonia. On 24 February 1990, the 464-member Congress of Estonia (including 35 delegates of refugee communities abroad) was elected by the registered citizens of the republic. The Congress of Estonia convened for the first time in Tallinn March 11–12, 1990, passing 14 declarations and resolutions. A 70-member standing committee (Eesti Komitee) was elected with Tunne Kelam
Tunne Kelam
Tunne-Väldo Kelam MEP is an Estonian politician and Member of the European Parliament for the Pro Patria Union , part of the European People's Party....
as its chairman.
In March 1991 a referendum was held on the issue of independence. This was somewhat controversial, as holding a referendum could be taken as signalling that Estonian independence would be established rather than "re"-established. There was some discussion about whether it was appropriate to allow the Russian immigrant minority to vote, or if this decision should be reserved exclusively for citizens of Estonia. In the end all major political parties backed the referendum, considering it most important to send a strong signal to the world. To further legitimise the vote, all residents of Estonia were allowed to participate. The result vindicated these decisions, as the referendum produced a strong endorsement for independence. Turnout was 82%, and 64% of all possible voters in the country backed independence, with only 17% against.
Although the majority of Estonia's large Russian-speaking diaspora of Soviet-era immigrants did not support full independence, they were divided in their goals for the republic. In March 1990 some 18% of Russian
Russian language
Russian is a Slavic language used primarily in Russia, Belarus, Uzbekistan, Kazakhstan, Tajikistan and Kyrgyzstan. It is an unofficial but widely spoken language in Ukraine, Moldova, Latvia, Turkmenistan and Estonia and, to a lesser extent, the other countries that were once constituent republics...
speakers supported the idea of a fully independent Estonia, up from 7% the previous autumn, and by early 1990 only a small minority of ethnic Estonians were opposed to full independence.
In the March 18, 1990 elections for the 105-member Supreme Soviet all residents of Estonia were eligible to participate, including all Soviet-era immigrants from the U.S.S.R. and approximately 50,000 Soviet troops stationed there. The Popular Front coalition, composed of left
Left-wing politics
In politics, Left, left-wing and leftist generally refer to support for social change to create a more egalitarian society...
and centrist parties
Centrism
In politics, centrism is the ideal or the practice of promoting policies that lie different from the standard political left and political right. Most commonly, this is visualized as part of the one-dimensional political spectrum of left-right politics, with centrism landing in the middle between...
and led by former Central Planning Committee official Edgar Savisaar
Edgar Savisaar
Edgar Savisaar , is an Estonian politician, one of the founding members of Popular Front of Estonia and the leader of the Centre Party. He has served as the acting Prime Minister of Estonia, Minister of Internal affairs and Minister of Economic Affairs and Communications...
, gained a parliamentary majority.

Estonia
Estonia , officially the Republic of Estonia , is a state in the Baltic region of Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland, to the west by the Baltic Sea, to the south by Latvia , and to the east by Lake Peipsi and the Russian Federation . Across the Baltic Sea lies...
. Through a strict, non-confrontational policy in pursuing independence, Estonia managed to avoid the violence which Latvia
Latvia
Latvia , officially the Republic of Latvia , is a country in the Baltic region of Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by Estonia , to the south by Lithuania , to the east by the Russian Federation , to the southeast by Belarus and shares maritime borders to the west with Sweden...
and Lithuania
Lithuania
Lithuania , officially the Republic of Lithuania is a country in Northern Europe, the biggest of the three Baltic states. It is situated along the southeastern shore of the Baltic Sea, whereby to the west lie Sweden and Denmark...
incurred in the bloody January 1991 crackdowns and in the border customs-post guard murders that summer. During the August coup in the U.S.S.R., Estonia was able to maintain constant operation and control of its telecommunication
Telecommunication
Telecommunication is the transmission of information over significant distances to communicate. In earlier times, telecommunications involved the use of visual signals, such as beacons, smoke signals, semaphore telegraphs, signal flags, and optical heliographs, or audio messages via coded...
s facilities, thereby offering the West
Western world
The Western world, also known as the West and the Occident , is a term referring to the countries of Western Europe , the countries of the Americas, as well all countries of Northern and Central Europe, Australia and New Zealand...
a clear view into the latest coup developments and serving as a conduit for swift Western support and recognition of Estonia's "confirmation" of independence on August 20, 1991. August 20 remains a national holiday in Estonia because of this. Following Europe's lead, the United States formally reestablished diplomatic relations with Estonia on September 2, and the U.S.S.R. Supreme Soviet offered recognition on September 6.
Since the debates about whether the future independent Estonia would be established as a new republic or a continuation of the first republic were not yet complete by the time of the August coup, while the members of the Supreme Soviet generally agreed that independence should be declared rapidly, a compromise was hatched between the two main sides: instead of "declaring" independence, which would imply a new start, or explicitly asserting continuity, the declaration would "confirm" Estonia as a state independent of the Soviet Union, and willing to reestablish diplomatic relations of its own accord. The full text of the statement is available at.
After more than 3 years of negotiations, on August 31, 1994, the armed forces of Russia
Russia
Russia or , officially known as both Russia and the Russian Federation , is a country in northern Eurasia. It is a federal semi-presidential republic, comprising 83 federal subjects...
withdrew from Estonia. Since fully regaining independence Estonia has had 12 governments with 8 prime ministers: Mart Laar
Mart Laar
Mart Laar is an Estonian statesman, historian and a founding member of the Foundation for the Investigation of Communist Crimes. He was the Prime Minister of Estonia from 1992 to 1994 and from 1999 to 2002, and is the leader of the conservative party Union of Pro Patria and Res Publica...
, Andres Tarand
Andres Tarand
Andres Tarand , is an Estonian politician and former Member of the European Parliament for the Social Democratic Party, part of the Party of European Socialists between 2004 and 2009. Tarand also served as the Prime Minister of Estonia from 1994 to 1995.Born in Tallinn, Tarand graduated from the...
, Tiit Vähi
Tiit Vähi
Tiit Vähi is an Estonian politician, Prime Minister of Estonia from 1995 to 1997, and acting Prime Minister for several months during 1992 under the transitional government....
, Mart Siimann
Mart Siimann
Mart Siimann was the Prime Minister of Estonia from 1997 to 1999. Since 2001, he has been the president of the Estonian Olympic Committee....
, Siim Kallas
Siim Kallas
Siim Kallas is an Estonian politician, currently serving as European Commissioner for Transport. He is also one of five vice-presidents of the 27-member Barroso Commission...
, Juhan Parts
Juhan Parts
Juhan Parts is an Estonian politician who was Prime Minister of Estonia from 2003 to 2005. He was chairman of the Res Publica Party for a time. Since 5 April 2007 he is the Minister of Economy and Communication in Andrus Ansip's second government...
, and Andrus Ansip
Andrus Ansip
Andrus Ansip is the current Prime Minister of Estonia, and chairman of the market liberal Estonian Reform Party .-Early life and career:...
. The PMs of the interim government (1990–1992) were Edgar Savisaar
Edgar Savisaar
Edgar Savisaar , is an Estonian politician, one of the founding members of Popular Front of Estonia and the leader of the Centre Party. He has served as the acting Prime Minister of Estonia, Minister of Internal affairs and Minister of Economic Affairs and Communications...
and Tiit Vähi
Tiit Vähi
Tiit Vähi is an Estonian politician, Prime Minister of Estonia from 1995 to 1997, and acting Prime Minister for several months during 1992 under the transitional government....
.
Since the last Russian troops left in 1994, Estonia has been free to promote economic and political ties with Western Europe. Estonia opened accession negotiations with the European Union
European Union
The European Union is an economic and political union of 27 independent member states which are located primarily in Europe. The EU traces its origins from the European Coal and Steel Community and the European Economic Community , formed by six countries in 1958...
in 1998 and joined in 2004, shortly after becoming a member of NATO.
Independent Estonia
On June 28, 1992, EstoniaEstonia
Estonia , officially the Republic of Estonia , is a state in the Baltic region of Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland, to the west by the Baltic Sea, to the south by Latvia , and to the east by Lake Peipsi and the Russian Federation . Across the Baltic Sea lies...
n voters approved the constitutional assembly's draft constitution and implementation act, which established a parliamentary government with a president as chief of state and with a government headed by a prime minister.
The Riigikogu
Riigikogu
The Riigikogu is the unicameral parliament of Estonia. All important state-related questions pass through the Riigikogu...
, a unicameral legislative body, is the highest organ of state authority. It initiates and approves legislation sponsored by the prime minister. The prime minister has full responsibility and control over his cabinet.
Meri presidency and Laar premiership (1992–2001)
Parliamentary and presidential elections were held on September 20, 1992. Approximately 68% of the country's 637,000 registered voters cast ballots. Lennart MeriLennart Meri
Lennart Georg Meri was a writer, film director and statesman who served as the second President of Estonia from 1992 to 2001. Meri was a leader of the Estonian independence movement.-Early life:...
, an outstanding writer and former Minister of Foreign Affairs
Estonian Minister of Foreign Affairs
The Minister of Foreign Affairs is the senior minister at the Ministry of Foreign Affairs in the Estonian Government. The Minister is one of the most important members of the Estonian government, with responsibility for the relations between Estonia and foreign states.The Foreign Minister is...
, won this election and became president
President of Estonia
The President of the Republic is the head of state of the Republic of Estonia.Estonia is a parliamentary republic, therefore President is mainly a symbolic figure and holds no executive power. The President has to suspend his membership in any political party for his term in office...
. He chose 32-year-old historian and Christian Democratic Party founder Mart Laar
Mart Laar
Mart Laar is an Estonian statesman, historian and a founding member of the Foundation for the Investigation of Communist Crimes. He was the Prime Minister of Estonia from 1992 to 1994 and from 1999 to 2002, and is the leader of the conservative party Union of Pro Patria and Res Publica...
as prime minister.
In February 1992, and with amendments in January 1995, the Riigikogu
Riigikogu
The Riigikogu is the unicameral parliament of Estonia. All important state-related questions pass through the Riigikogu...
renewed Estonia's 1938 citizenship law, which also provides equal civil protection to resident aliens.
In 1996, Estonia ratified a border agreement with Latvia
Latvia
Latvia , officially the Republic of Latvia , is a country in the Baltic region of Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by Estonia , to the south by Lithuania , to the east by the Russian Federation , to the southeast by Belarus and shares maritime borders to the west with Sweden...
and completed work with Russia
Russia
Russia or , officially known as both Russia and the Russian Federation , is a country in northern Eurasia. It is a federal semi-presidential republic, comprising 83 federal subjects...
on a technical border agreement. President Meri
Lennart Meri
Lennart Georg Meri was a writer, film director and statesman who served as the second President of Estonia from 1992 to 2001. Meri was a leader of the Estonian independence movement.-Early life:...
was re-elected in free and fair indirect elections in August and September in 1996. During parliamentary elections in 1999, the seats in Riigikogu
Riigikogu
The Riigikogu is the unicameral parliament of Estonia. All important state-related questions pass through the Riigikogu...
were divided as follows: the Centre Party
Estonian Centre Party
The Estonian Centre Party is a centrist, social liberal party in Estonia. Keskerakond is a member of the European Liberal Democrat and Reform Party. It has the largest membership of an Estonian party, with over 12 000 members....
received 28, the Pro Patria Union 18, the Reform Party
Estonian Reform Party
The Estonian Reform Party is a centre-right, free market liberal party in Estonia. It is led by Estonian Prime Minister Andrus Ansip, and has 33 members in the 101-member Riigikogu, making it the largest party in the legislature...
18, the People's Party Moderates (election cartel between Moderates and People's Party) 17, Coalition Party 7, Country People's Party (now People's Union
People's Union of Estonia
The People's Union of Estonia is a political party in Estonia, currently led by Margo Miljand.In the 2003 parliamentary election, the party collected 64,463 votes, which made 13.0% share of all votes and 13 mandates out of 101. In 2007's election, this dropped to 39,211 votes , and six seats in...
) 7, United People's Party's electoral cartel 6 seats. Pro Patria Union, the Reform Party, and the Moderates formed a government with Mart Laar
Mart Laar
Mart Laar is an Estonian statesman, historian and a founding member of the Foundation for the Investigation of Communist Crimes. He was the Prime Minister of Estonia from 1992 to 1994 and from 1999 to 2002, and is the leader of the conservative party Union of Pro Patria and Res Publica...
as prime minister whereas the Centre Party with the Coalition Party, People's Union, United People's Party, and Members of Parliament who were not members of factions formed the opposition in the Riigikogu
Riigikogu
The Riigikogu is the unicameral parliament of Estonia. All important state-related questions pass through the Riigikogu...
.
The 1999 Parliamentary election
Estonian parliamentary election, 1999
Estonian parliamentary election of 1999 was held on 7 March 1999. The threshold was 5% of the national vote, and seven lists passed the threshold...
, with a 5% threshold and no electoral cartel allowed, resulted in a disaster for the Coalition Party, which achieved only seven seats together with two of its smaller allies. Estonian Ruralfolk Party, which participated the election on its own list, obtained seven seats as well.
The programme of Mart Laar
Mart Laar
Mart Laar is an Estonian statesman, historian and a founding member of the Foundation for the Investigation of Communist Crimes. He was the Prime Minister of Estonia from 1992 to 1994 and from 1999 to 2002, and is the leader of the conservative party Union of Pro Patria and Res Publica...
's government was signed by Pro Patria Union, Reform Party
Estonian Reform Party
The Estonian Reform Party is a centre-right, free market liberal party in Estonia. It is led by Estonian Prime Minister Andrus Ansip, and has 33 members in the 101-member Riigikogu, making it the largest party in the legislature...
, Moderates
Social Democratic Party (Estonia)
The Social Democratic Party is a social-democratic party in Estonia, led by Sven Mikser. It has been a member of the Party of European Socialists since 16 May 2003 and a member of the Socialist International since November 1990....
and People’s Party. The latter two merged soon after, so Mart Laar’s second government is widely known as Kolmikliit, or Tripartite coalition. Notwithstanding the different political orientation of the ruling parties, the coalition stayed united until Mart Laar resigned in December 2001, after Reform Party had broken up the same coalition in Tallinn
Tallinn
Tallinn is the capital and largest city of Estonia. It occupies an area of with a population of 414,940. It is situated on the northern coast of the country, on the banks of the Gulf of Finland, south of Helsinki, east of Stockholm and west of Saint Petersburg. Tallinn's Old Town is in the list...
municipality, making opposition leader Edgar Savisaar
Edgar Savisaar
Edgar Savisaar , is an Estonian politician, one of the founding members of Popular Front of Estonia and the leader of the Centre Party. He has served as the acting Prime Minister of Estonia, Minister of Internal affairs and Minister of Economic Affairs and Communications...
new Mayor of Tallinn. After resignation of Laar, Reform Party and Estonian Centre Party
Estonian Centre Party
The Estonian Centre Party is a centrist, social liberal party in Estonia. Keskerakond is a member of the European Liberal Democrat and Reform Party. It has the largest membership of an Estonian party, with over 12 000 members....
formed a coalition that lasted until next parliamentary election, 2003.
The Moderates joined with the People's Party on 27 November 1999, forming the People's Party Moderates.
Rüütel presidency and Siim Kallas government (2001–2002)
In fall 2001 Arnold RüütelArnold Rüütel
Arnold Rüütel OIH was the third President of the Republic of Estonia from October 8, 2001 to October 9, 2006. He was the second President since Estonia regained its independence in 1991....
became the President of the Republic of Estonia, and in January 2002 Prime Minister Laar
Mart Laar
Mart Laar is an Estonian statesman, historian and a founding member of the Foundation for the Investigation of Communist Crimes. He was the Prime Minister of Estonia from 1992 to 1994 and from 1999 to 2002, and is the leader of the conservative party Union of Pro Patria and Res Publica...
stepped down. On January 28, 2002 the new government was formed from a coalition of the centre-right
Centre-right
The centre-right or center-right is a political term commonly used to describe or denote individuals, political parties, or organizations whose views stretch from the centre to the right on the left-right spectrum, excluding far right stances. Centre-right can also describe a coalition of centrist...
Estonian Reform Party
Estonian Reform Party
The Estonian Reform Party is a centre-right, free market liberal party in Estonia. It is led by Estonian Prime Minister Andrus Ansip, and has 33 members in the 101-member Riigikogu, making it the largest party in the legislature...
and the more left wing Centre Party
Estonian Centre Party
The Estonian Centre Party is a centrist, social liberal party in Estonia. Keskerakond is a member of the European Liberal Democrat and Reform Party. It has the largest membership of an Estonian party, with over 12 000 members....
, with Siim Kallas
Siim Kallas
Siim Kallas is an Estonian politician, currently serving as European Commissioner for Transport. He is also one of five vice-presidents of the 27-member Barroso Commission...
from the Reform Party of Estonia as Prime Minister
Prime Minister of Estonia
The Prime Minister of Estonia is the head of government of the Republic of Estonia. The prime minister is nominated by the President after appropriate consultations with the parliamentary factions and confirmed by the Parliament. In case of disagreement, the Parliament can reject the President's...
.
In 2003, Estonia joined the NATO defense alliance.
Juhan Parts government (2003)
Following parliamentary electionsEstonian parliamentary election, 2003
The 2003 Estonian parliamentary election was held in Estonia on 2 March 2003 to elect the members of the Riigikogu . Two opposing parties won the most seats, with both the Centre Party and Res Publica Party winning 28 seats...
in 2003, the seats were allocated as follows (the United People's Party failed to meet the 5% threshold):
- Centre PartyEstonian Centre PartyThe Estonian Centre Party is a centrist, social liberal party in Estonia. Keskerakond is a member of the European Liberal Democrat and Reform Party. It has the largest membership of an Estonian party, with over 12 000 members....
28, - Res Publica 28,
- Reform PartyEstonian Reform PartyThe Estonian Reform Party is a centre-right, free market liberal party in Estonia. It is led by Estonian Prime Minister Andrus Ansip, and has 33 members in the 101-member Riigikogu, making it the largest party in the legislature...
19, - People's UnionPeople's Union of EstoniaThe People's Union of Estonia is a political party in Estonia, currently led by Margo Miljand.In the 2003 parliamentary election, the party collected 64,463 votes, which made 13.0% share of all votes and 13 mandates out of 101. In 2007's election, this dropped to 39,211 votes , and six seats in...
13, - Pro Patria UnionPro Patria UnionThe Pro Patria Union was a conservative political party in Estonia. The party was founded on 2 December 1995 by merging the Estonian National Independence Party and the National Coalition Party Pro Patria .On April 4, 2006, representatives of the Pro Patria Union and the representatives of Res...
7, - People's Party Moderates 6
Voter turnout
Voter turnout
Voter turnout is the percentage of eligible voters who cast a ballot in an election . After increasing for many decades, there has been a trend of decreasing voter turnout in most established democracies since the 1960s...
was higher than expected at 58%.
The results saw the Centre Party win the most votes but they were only 0.8% ahead of the new Res Publica party. As a result both parties won 28 seats, which was a disappointment for the Centre Party who had expected to win the most seats. Altogether the right of centre parties won 60 seats, compared to only 41 for the left wing, and so were expected to form the next government.
Both the Centre and Res Publica parties said that they should get the chance to try and form the next government, while ruling out any deal between themselves. President Rüütel had to decide who he should nominate as Prime Minister and therefore be given the first chance at forming a government. On the 2 April he invited the leader of the Res Publica party, Juhan Parts
Juhan Parts
Juhan Parts is an Estonian politician who was Prime Minister of Estonia from 2003 to 2005. He was chairman of the Res Publica Party for a time. Since 5 April 2007 he is the Minister of Economy and Communication in Andrus Ansip's second government...
to form a government and after negotiations a coalition government composed of Res Publica, the Reform Party and the People's Union of Estonia
People's Union of Estonia
The People's Union of Estonia is a political party in Estonia, currently led by Margo Miljand.In the 2003 parliamentary election, the party collected 64,463 votes, which made 13.0% share of all votes and 13 mandates out of 101. In 2007's election, this dropped to 39,211 votes , and six seats in...
was formed on the 10 April.
On 14 September 2003, following negotiations that began in 1998, the citizens of Estonia were asked in a referendum whether or not they wished to join the European Union
European Union
The European Union is an economic and political union of 27 independent member states which are located primarily in Europe. The EU traces its origins from the European Coal and Steel Community and the European Economic Community , formed by six countries in 1958...
. With 64% of the electorate turning out the referendum passed with a 66.83% margin in favor, 33.17% against. Accession to the EU took place on 1 May of the following year.
In February 2004 the People's Party Moderates renamed themselves as Social Democratic Party of Estonia.
On the 8 May 2004, a defection of several Centre Party members to form a new party, the Social Liberal Party, over a row concerning the Centrists' "no" stance to joining the European Union changed the allocation of the seats in Riigikogu. Social-liberals had 8 seats, but a hope to form a new party disappeared by the 10 May 2005, because most members in the social-liberal group joined other parties.
Andrus Ansip government (2004)
On 24 March Prime Minister Juhan PartsJuhan Parts
Juhan Parts is an Estonian politician who was Prime Minister of Estonia from 2003 to 2005. He was chairman of the Res Publica Party for a time. Since 5 April 2007 he is the Minister of Economy and Communication in Andrus Ansip's second government...
announced his resignation following a vote of no confidence in the Riigikogu against Minister of Justice
Estonian Minister of Justice
The Estonian Ministry of Justice is Ministry of Justice in Estonia., the current Minister of Justice is Kristen Michal.- Estonian Ministers of Justice :...
Ken-Marti Vaher
Ken-Marti Vaher
Ken-Marti Vaher is a leading member of the Estonian Pro Patria and Res Publica Union party, and the current Estonian Minister of Internal Affairs.-Career:...
, which was held on the 21 March. Result: 54 pro (Social Democrats, Social Liberals, People's Union, Pro Patria Union and Reform Party) without no against or neutral MPs. 32 MPs (Res Publica and Centre Party) did not take part.
On 4 April 2005, President Rüütel nominated Reform party leader Andrus Ansip
Andrus Ansip
Andrus Ansip is the current Prime Minister of Estonia, and chairman of the market liberal Estonian Reform Party .-Early life and career:...
as Prime Minister designate by and asked him to form a new government, the 8th in 12 years. Ansip formed a government out of a coalition of his Reform Party with the People’s Union and the Centre Party. Approval by the Riigikogu, which by law must decide within 14 days of his nomination, came on 12 April 2005. Ansip was backed by 53 out of 101 members of the Estonian parliament. Forty deputies voted against his candidature.
The general consensus in the Estonian media seems to be that the new Andrus Ansip's cabinet
Andrus Ansip's cabinet
Andrus Ansip is the current Prime Minister of Estonia; his first cabinet took office on 12 April 2005 after being approved by Riigikogu by 53 members out of 101. His cabinet was formed with pragmatic calculations, as it consisted of ministers from free market liberal Reform Party of Estonia,...
, on the level of competence, is not necessarily an improvement over the old one.
On 18 May 2005, Estonia signed a border treaty with the Russian Federation in Moscow. The treaty was ratified by the Riigikogu
Riigikogu
The Riigikogu is the unicameral parliament of Estonia. All important state-related questions pass through the Riigikogu...
on 20 June 2005. However, in the end of June the Russian Ministry of Foreign Affairs informed that it did not intend to become a party to the border treaty and did not consider itself bound by the circumstances concerning the object and the purposes of the treaty because Riigikogu had attached a preambula to the ratification act that referenced earlier documents that mentioned the Soviet occupation and the uninterrupted legal continuity of the Republic of Estonia during the Soviet period. The issue remains unsolved and is in focus of European level discussions.
On 4 April 2006, Fatherland Union and Res Publica decided to form a united right-conservative party. The two parties joining was approved on 4 June by both parties in Pärnu. The joined party name is Isamaa ja Res Publica Liit (Union of Pro Patria and Res Publica
Union of Pro Patria and Res Publica
Union of Pro Patria and Res Publica is an Estonian Liberal Conservative political party. It was founded on 4 June 2006 when two conservative parties, Pro Patria Union and Res Publica merged. Up to the 2007 parliamentary elections, the party held 32 seats out of 101 in the Riigikogu and one of...
).
2007 elections
The 2007 Parliamentary ElectionsEstonian parliamentary election, 2007
Parliamentary elections took place in Estonia on Sunday, March 4, 2007 to elect members of the Riigikogu. The electoral system was a two-tier semi-open list proportional representation system with a 5% election threshold...
have shown an improvement in the scores of the Reform Party, gaining 12 seats and reaching 31 MPs; the Centre Party held, while the unified right-conservative Union of Pro Patria and Res Publica
Union of Pro Patria and Res Publica
Union of Pro Patria and Res Publica is an Estonian Liberal Conservative political party. It was founded on 4 June 2006 when two conservative parties, Pro Patria Union and Res Publica merged. Up to the 2007 parliamentary elections, the party held 32 seats out of 101 in the Riigikogu and one of...
lost 16. Socialdemocrats gained 4 seats, while the Greens entered the Parliaments with 7 seats, at the expenses of the agrarian People's Union
People's Union
People's Union may refer to one of the following political parties:*People's Union *People's Union of Estonia*People's Union *People's Union *People's Union *People's Union "Our Ukraine"...
which lost 6. The new configuration of the Estonian Parliament shows a prevalence of the centre-left parties. The Centre Party, led by the mayor of Tallinn Edgar Savisaar
Edgar Savisaar
Edgar Savisaar , is an Estonian politician, one of the founding members of Popular Front of Estonia and the leader of the Centre Party. He has served as the acting Prime Minister of Estonia, Minister of Internal affairs and Minister of Economic Affairs and Communications...
, has been increasingly excluded from collaboration, since his open collaboration with Putin
Vladimir Putin
Vladimir Vladimirovich Putin served as the second President of the Russian Federation and is the current Prime Minister of Russia, as well as chairman of United Russia and Chairman of the Council of Ministers of the Union of Russia and Belarus. He became acting President on 31 December 1999, when...
's United Russia
United Russia
United Russia is a centrist political party in Russia and the largest party in the country, currently holding 315 of the 450 seats in the State Duma. The party was founded in December 2001, through a merger of the Unity and Fatherland-All Russia parties...
party, real estate scandals in Tallinn, and the Bronze Soldier controversy, considered as a deliberate attempt of splitting the Estonian society by provoking the Russian minority. The lack of a concrete possibility for government alternance in Estonia has been quoted as a concern.
Estonia and the European Union
On 14 September 2003, following negotiations that began in 1998, the citizens of Estonia were asked in a referendum whether or not they wished to join the European UnionEuropean Union
The European Union is an economic and political union of 27 independent member states which are located primarily in Europe. The EU traces its origins from the European Coal and Steel Community and the European Economic Community , formed by six countries in 1958...
. With 64% of the electorate turning out the referendum passed with a 66.83% margin in favor, 33.17% against. Accession to the EU took place on 1 May of the following year.
In its first European Parliament elections in 2004
European Parliament election, 2004 (Estonia)
The European Parliament election of 2004 in Estonia was the election of MEP representing Estonia constituency for the 2004-2009 term of the European Parliament. It was part of the wider 2004 European election. The vote took place on June 13....
, Estonia
Estonia (European Parliament constituency)
In European elections, Estonia is a constituency of the European Parliament, currently represented by six MEPs. It covers the member state of Estonia. The elections uses the D'Hondt method with an open list.-Current MEPs:As of October 2007-2004:...
elected 3 MEPs for the Social Democratic Party (PES), while the governing Res Publica Party
Res Publica Party
Res Publica Party was a political party in Estonia that self-identified as conservative and therefore member of IDU, but considering its vague platform for 2003 election, the genuineness of this ideology is disputed...
and People's Union
People's Union of Estonia
The People's Union of Estonia is a political party in Estonia, currently led by Margo Miljand.In the 2003 parliamentary election, the party collected 64,463 votes, which made 13.0% share of all votes and 13 mandates out of 101. In 2007's election, this dropped to 39,211 votes , and six seats in...
polled poorly, not being able to gain any of the other 3 MEPs posts.
The voter turnout
Voter turnout
Voter turnout is the percentage of eligible voters who cast a ballot in an election . After increasing for many decades, there has been a trend of decreasing voter turnout in most established democracies since the 1960s...
in Estonia was one of the lowest of all member countries at only 26.8%. A similar trend was visible in most of the new member states that joined the EU in 2004.
The European Parliament election of 2009 in Estonia
European Parliament election, 2009
Elections to the European Parliament were held in the 27 member states of the European Union between 4 and 7 June 2009. A total of 736 Members of the European Parliament were elected to represent some 500 million Europeans, making these the biggest trans-national elections in history...
scored a 43.9% turnout – about 17.1% higher than during the previous election
European Parliament election, 2004 (Estonia)
The European Parliament election of 2004 in Estonia was the election of MEP representing Estonia constituency for the 2004-2009 term of the European Parliament. It was part of the wider 2004 European election. The vote took place on June 13....
, and slightly above the European average of 42.94%.
Six seats were up for taking in this election: two of them were won by the Estonian Centre Party
Estonian Centre Party
The Estonian Centre Party is a centrist, social liberal party in Estonia. Keskerakond is a member of the European Liberal Democrat and Reform Party. It has the largest membership of an Estonian party, with over 12 000 members....
. Estonian Reform Party
Estonian Reform Party
The Estonian Reform Party is a centre-right, free market liberal party in Estonia. It is led by Estonian Prime Minister Andrus Ansip, and has 33 members in the 101-member Riigikogu, making it the largest party in the legislature...
, Union of Pro Patria and Res Publica
Union of Pro Patria and Res Publica
Union of Pro Patria and Res Publica is an Estonian Liberal Conservative political party. It was founded on 4 June 2006 when two conservative parties, Pro Patria Union and Res Publica merged. Up to the 2007 parliamentary elections, the party held 32 seats out of 101 in the Riigikogu and one of...
, Social Democratic Party
Social Democratic Party (Estonia)
The Social Democratic Party is a social-democratic party in Estonia, led by Sven Mikser. It has been a member of the Party of European Socialists since 16 May 2003 and a member of the Socialist International since November 1990....
and an independent candidate Indrek Tarand
Indrek Tarand
Indrek Tarand MEP is an Estonian politician, reserve officer, civil servant, journalist and historian.Tarand has served as an advisor to the Prime Minister of Estonia and as the Secretary General of the Estonian Ministry of Foreign Affairs.-Biography:Tarand is the eldest son of Andres Tarand...
(who gathered the support of 102,460 voters, only 1,046 votes less than the winner of the election) all won one seat each. The success of independent candidates has been attributed both to general disillusionment with major parties and use of closed lists which rendered voters incapable to cast a vote for specific candidates in party lists.
On 1 January 2011 Estonia
Estonia
Estonia , officially the Republic of Estonia , is a state in the Baltic region of Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland, to the west by the Baltic Sea, to the south by Latvia , and to the east by Lake Peipsi and the Russian Federation . Across the Baltic Sea lies...
adopted the Euro
Euro
The euro is the official currency of the eurozone: 17 of the 27 member states of the European Union. It is also the currency used by the Institutions of the European Union. The eurozone consists of Austria, Belgium, Cyprus, Estonia, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Ireland, Italy, Luxembourg,...
. The enlargement of the eurozone
Eurozone
The eurozone , officially called the euro area, is an economic and monetary union of seventeen European Union member states that have adopted the euro as their common currency and sole legal tender...
, although limited, was hailed as a good sign in a period of global financial crisis and instability of the euro
Euro
The euro is the official currency of the eurozone: 17 of the 27 member states of the European Union. It is also the currency used by the Institutions of the European Union. The eurozone consists of Austria, Belgium, Cyprus, Estonia, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Ireland, Italy, Luxembourg,...
. To cope with crisis and financial targets, the government cut down public service salaries; the only opposition, in the absence of organised unions, came from Estonian teachers, whose salary cuts were therefore limited.
Estonian euro coins
Estonian euro coins
Estonian euro coins feature a single design for all eight coins. This is a design by Lembit Lõhmus and features a silhouette map of Estonia together with the word Eesti and twelve stars, symbolic of the European Union, surrounding the map...
entered circulation on 1 January 2011. Estonia is the fifth of ten states that joined the EU in 2004, and the first ex-Soviet republic, to join the eurozone
Eurozone
The eurozone , officially called the euro area, is an economic and monetary union of seventeen European Union member states that have adopted the euro as their common currency and sole legal tender...
. Of the ten new member states, Estonia was the first to unveil its design. It originally planned to adopt the euro on 1 January 2007; however, it did not formally apply when Slovenia
Slovenia
Slovenia , officially the Republic of Slovenia , is a country in Central and Southeastern Europe touching the Alps and bordering the Mediterranean. Slovenia borders Italy to the west, Croatia to the south and east, Hungary to the northeast, and Austria to the north, and also has a small portion of...
did, and officially changed its target date to 1 January 2008, and later, to 1 January 2011. On 12 May 2010 the European Commission
European Commission
The European Commission is the executive body of the European Union. The body is responsible for proposing legislation, implementing decisions, upholding the Union's treaties and the general day-to-day running of the Union....
announced that Estonia had met all criteria to join the eurozone. On 8 June 2010, the EU finance ministers agreed that Estonia would be able to join the euro on 1 January 2011. On 13 July 2010, Estonia received the final approval from the ECOFIN to adopt the euro as from 1 January 2011. On the same date the exchange rate at which the kroon
Estonian kroon
In 1992, coins were introduced in denominations of 5, 10, 20 & 50 senti, as well as 1 kroon. The 1 kroon was struck in cupronickel, the others in aluminum-bronze. However, in 1997, nickel-plated steel 20 senti were introduced, followed by aluminum-bronze 1 kroon in 1998. 5 senti coins were not...
would be exchanged for the euro (€1 = 15.6466 krooni) was also announced. On 20 July 2010, mass production of Estonian euro coins began in the mint of Finland.
Being a member of the eurozone
Eurozone
The eurozone , officially called the euro area, is an economic and monetary union of seventeen European Union member states that have adopted the euro as their common currency and sole legal tender...
, NATO and the EU
European Union
The European Union is an economic and political union of 27 independent member states which are located primarily in Europe. The EU traces its origins from the European Coal and Steel Community and the European Economic Community , formed by six countries in 1958...
, Estonia is the most integrated in Western European organizations of all Nordic states
Estonia–Russia relations in the late 2000s
Estonia–Russia relationsEstonia–Russia relations
Estonia–Russia relations refers to bilateral foreign relations between Estonia and Russia. Diplomatic relations between the Republic of Estonia and the Russian SFSR were established on 2 February 1920, when Bolshevist Russia recognized de jure the independence of the Republic of Estonia, and...
remain tense. According to the Estonian Security Police, Russian influence operations in Estonia form a complex system of financial, political, economic and espionage activities in Republic of Estonia for the purposes of influencing Estonia's political and economic decisions in ways considered favourable to Russian Federation and conducted under the doctrine of near abroad
Near abroad
In political language of Russia and some other post-Soviet states, the near abroad refers to the newly independent republics which emerged after the dissolution of the Soviet Union, and sometimes other nearby countries such as Finland and Mongolia....
. According to the Centre for Geopolitical Studies, the Russian information campaign which the centre characterises as a "real mud throwing" exercise, has provoked a split in Estonian society amongst Russian speakers, inciting some to riot over the relocation of the Bronze Soldier. The 2007 cyberattacks on Estonia
2007 cyberattacks on Estonia
Cyberattacks on Estonia refers to a series of cyber attacks that began April 27, 2007 and swamped websites of Estonian organizations, including Estonian parliament, banks, ministries, newspapers and broadcasters, amid the country's row with Russia about the relocation of the Bronze Soldier of...
is considered to be an information operation against Estonia, with the intent to influence the decisions and actions of the Estonian government; while Russia denies any direct involvement in the attacks, hostile rhetoric from the political elite via the media influenced people to attack. Following the 2007 cyber-attacks
2007 cyberattacks on Estonia
Cyberattacks on Estonia refers to a series of cyber attacks that began April 27, 2007 and swamped websites of Estonian organizations, including Estonian parliament, banks, ministries, newspapers and broadcasters, amid the country's row with Russia about the relocation of the Bronze Soldier of...
, the NATO Cooperative Cyber Defence Centre of Excellence (CCDCOE
CCDCOE
CCDCOE, officially the Cooperative Cyber Defence Centre of Excellence is one of NATO Centres of Excellence, located in Tallinn, Estonia.The CCDCOE was established in the wake of the 2007 cyberattacks on Estonia and the Bronze Night events.-History:...
) was established in Tallinn
Tallinn
Tallinn is the capital and largest city of Estonia. It occupies an area of with a population of 414,940. It is situated on the northern coast of the country, on the banks of the Gulf of Finland, south of Helsinki, east of Stockholm and west of Saint Petersburg. Tallinn's Old Town is in the list...
.
See also
- List of rulers of Estonia
- President of EstoniaPresident of EstoniaThe President of the Republic is the head of state of the Republic of Estonia.Estonia is a parliamentary republic, therefore President is mainly a symbolic figure and holds no executive power. The President has to suspend his membership in any political party for his term in office...
- Prime Minister of EstoniaPrime Minister of EstoniaThe Prime Minister of Estonia is the head of government of the Republic of Estonia. The prime minister is nominated by the President after appropriate consultations with the parliamentary factions and confirmed by the Parliament. In case of disagreement, the Parliament can reject the President's...
- RiigihoidjaRiigihoidjaRiigihoidja was the name of the office of the head of state and head of government of Estonia from 3 September 1937 to 24 April 1938. The only person to hold this position was Konstantin Päts, five time former State Elder...
- Northern CrusadesNorthern CrusadesThe Northern Crusades or Baltic Crusades were crusades undertaken by the Christian kings of Denmark and Sweden, the German Livonian and Teutonic military orders, and their allies against the pagan peoples of Northern Europe around the southern and eastern shores of the Baltic Sea...
- Conquest of Estonia
- UgauniansUgauniansUngannians or Ugandians , referred to as Chudes by the earliest Russian chronicles were historical Finnic people inhabiting the ancient southern Estonian Ugandi County :Ungannia) that is now Tartu, Põlva, Võru and Valga counties of Estonia.-The name and the territory:In modern Estonian...
- VironiansVironiansThe Vironians were one of the Finnic tribes that later formed the Estonian nation.-History:They lived in Vironia...
- Livonian OrderLivonian OrderThe Livonian Order was an autonomous Livonian branch of the Teutonic Order and a member of the Livonian Confederation from 1435–1561. After being defeated by Samogitians in the 1236 Battle of Schaulen , the remnants of the Livonian Brothers of the Sword were incorporated into the Teutonic Knights...
- Bishopric of DorpatBishopric of DorpatThe Bishopric of Dorpat was a medieval principality and a catholic diocese which existed from 1224 to 1558, generally encompassing what are now Tartu, Põlva, Võru and Jõgeva counties in Estonia. The Bishopric was part of Livonian Confederation...
- Hanseatic LeagueHanseatic LeagueThe Hanseatic League was an economic alliance of trading cities and their merchant guilds that dominated trade along the coast of Northern Europe...
- Soviet UnionSoviet UnionThe Soviet Union , officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics , was a constitutionally socialist state that existed in Eurasia between 1922 and 1991....
- Estonian SSR
- Dissolution of the Soviet UnionDissolution of the Soviet UnionThe dissolution of the Soviet Union was the disintegration of the federal political structures and central government of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics , resulting in the independence of all fifteen republics of the Soviet Union between March 11, 1990 and December 25, 1991...
- History of EuropeHistory of EuropeHistory of Europe describes the history of humans inhabiting the European continent since it was first populated in prehistoric times to present, with the first human settlement between 45,000 and 25,000 BC.-Overview:...
- History of the European UnionHistory of the European UnionThe European Union is a geo-political entity covering a large portion of the European continent. It is founded upon numerous treaties and has undergone expansions that have taken it from 7 member states to 27, a majority of states in Europe....
- History of DenmarkHistory of DenmarkThe history of Denmark dates back about 12,000 years, to the end of the last ice age, with the earliest evidence of human inhabitation. The Danes were first documented in written sources around 500 AD, including in the writings of Jordanes and Procopius. With the Christianization of the Danes c...
- History of FinlandHistory of FinlandThe land area that now makes up Finland was settled immediately after the Ice Age, beginning from around 8500 BCE. Most of the region was part of the Kingdom of Sweden from the 13th century to 1809, when it was ceded to the Russian Empire, becoming the autonomous Grand Duchy of Finland. The...
- History of GermanyHistory of GermanyThe concept of Germany as a distinct region in central Europe can be traced to Roman commander Julius Caesar, who referred to the unconquered area east of the Rhine as Germania, thus distinguishing it from Gaul , which he had conquered. The victory of the Germanic tribes in the Battle of the...
- History of LatviaHistory of LatviaThe History of Latvia began when the area which is today Latvia was settled following the end of the last glacial period, around 9000 BC. Ancient Baltic peoples appeared during the second millennium BC and four distinct tribal realms in Latvia's territories were identifiable towards the end of the...
- History of LithuaniaHistory of LithuaniaThe history of Lithuania dates back to at least 1009, the first recorded written use of the term. Lithuanians, a branch of the Baltic peoples, later conquered neighboring lands, establishing the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and in the 13th century the short-lived Kingdom of Lithuania. The Grand Duchy...
- History of RussiaHistory of RussiaThe history of Russia begins with that of the Eastern Slavs and the Finno-Ugric peoples. The state of Garðaríki , which was centered in Novgorod and included the entire areas inhabited by Ilmen Slavs, Veps and Votes, was established by the Varangian chieftain Rurik in 862...
- History of SwedenHistory of SwedenModern Sweden started out of the Kalmar Union formed in 1397 and by the unification of the country by King Gustav Vasa in the 16th century. In the 17th century Sweden expanded its territories to form the Swedish empire. Most of these conquered territories had to be given up during the 18th century...
- Occupation of Estonia by Nazi GermanyOccupation of Estonia by Nazi GermanyAfter Nazi Germany invaded the Soviet Union on June 22, 1941, Army Group North reached Estonia in July.Initially the Germans were perceived by most Estonians as liberators from the USSR and its repressions, having arrived only a week after the first mass deportations from the Baltics...
- Politics of EstoniaPolitics of EstoniaPolitics in Estonia takes place in a framework of a parliamentary representative democratic republic, whereby the Prime Minister of Estonia is the head of government, and of a multi-party system. Legislative power is vested in the Estonian parliament. Executive power is exercised by the Government...
External links
- Estonian History in Pictures an Estonian Institute publication
- Association Of Baltic German Knighthoods
- Crimes against humanity during Soviet and German occupation of Estonia
- Historical maps of Estonia in the 16th, 17th and 18th century
- History of Estonian Manors, part of English version of the Estonian Manors Portal
- Cultural treasures National Library Estonia
- A Brief History of Estonia by Mel Huang

