
Estonian Constituent Assembly
Encyclopedia
The Estonian Constituent Assembly was elected on 5-7 April 1919, called by the Estonian Provisional Government
during the Estonian War of Independence. The Assembly was elected by proportional representation. Eligible voters included soldiers at the front. The elections were won by left-wing and centrist parties.
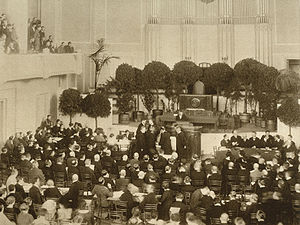 The 120 members of the Constituent Assembly met at the opening session on 23 April 1919, the birthday of the Estonian Parliament and elected the chairman, Social Democrat August Rei
The 120 members of the Constituent Assembly met at the opening session on 23 April 1919, the birthday of the Estonian Parliament and elected the chairman, Social Democrat August Rei
. On 7 May the Assembly passed the Public Elementary Schools Act: The principle of compulsory and free primary 6-year elementary school education was established. On 8 May 1919 the Estonian provisional government resigned, and the first fully democratically elected Government of Estonia headed by Prime Minister
Otto Strandman
(Estonian Labor Party) took office. On 15 May the assembly reaffirmed the Estonian Declaration of Independence
, aimed at the international community for recognizing Estonia as an independent state. On 4 June 1919 the Assembly adopted a temporary Constitution of Estonia. On 10 October 1919 The Land Reform
Act was passed which confiscated and redistributed the Baltic German
estates, ending the 700 years possession of the regions that the Germans had gained after the Livonian Crusade
. On 13 February the Peace Treaty of Tartu
was ratified, signed by Estonia and Russian SFSR on 2 February. The first Constitution of Estonia was adopted on 15 June 1920. After the constitution had entered into effect and the first parliamentary elections
were held, the Constituent Assembly disbanded itself on 20 December 1920.
Estonian Provisional Government
The Estonian Provisional Government was formed on February 24, 1918 by the Salvation Committee appointed by Maapäev the Estonian Province Assembly. The Provisional Government was led by Konstantin Päts...
during the Estonian War of Independence. The Assembly was elected by proportional representation. Eligible voters included soldiers at the front. The elections were won by left-wing and centrist parties.

August Rei
August Rei VR III/1 was an Estonian Social Democratic politician. He was born in Pilistvere, Kõo Parish, Viljandi County.- Education :...
. On 7 May the Assembly passed the Public Elementary Schools Act: The principle of compulsory and free primary 6-year elementary school education was established. On 8 May 1919 the Estonian provisional government resigned, and the first fully democratically elected Government of Estonia headed by Prime Minister
Prime minister
A prime minister is the most senior minister of cabinet in the executive branch of government in a parliamentary system. In many systems, the prime minister selects and may dismiss other members of the cabinet, and allocates posts to members within the government. In most systems, the prime...
Otto Strandman
Otto Strandman
Otto August Strandman VR III/1 was an Estonian politician, who served as Prime Minister and State Elder of Estonia . He was one of the leaders of the centre-left Estonian Labour Party, that saw its biggest support after the 1919 and 1920 elections...
(Estonian Labor Party) took office. On 15 May the assembly reaffirmed the Estonian Declaration of Independence
Estonian Declaration of Independence
The Estonian Declaration of Independence, also known as the Manifesto to the Peoples of Estonia , is the founding act of the Republic of Estonia from 1918. It is celebrated on 24 February, the National Day or Estonian Independence Day....
, aimed at the international community for recognizing Estonia as an independent state. On 4 June 1919 the Assembly adopted a temporary Constitution of Estonia. On 10 October 1919 The Land Reform
Land reform
[Image:Jakarta farmers protest23.jpg|300px|thumb|right|Farmers protesting for Land Reform in Indonesia]Land reform involves the changing of laws, regulations or customs regarding land ownership. Land reform may consist of a government-initiated or government-backed property redistribution,...
Act was passed which confiscated and redistributed the Baltic German
Baltic German
The Baltic Germans were mostly ethnically German inhabitants of the eastern shore of the Baltic Sea, which today form the countries of Estonia and Latvia. The Baltic German population never made up more than 10% of the total. They formed the social, commercial, political and cultural élite in...
estates, ending the 700 years possession of the regions that the Germans had gained after the Livonian Crusade
Livonian Crusade
The Livonian Crusade refers to the German and Danish conquest and colonization of medieval Livonia, the territory constituting modern Latvia and Estonia, during the Northern Crusades...
. On 13 February the Peace Treaty of Tartu
Treaty of Tartu (Russian–Estonian)
Tartu Peace Treaty or Treaty of Tartu was a peace treaty between Estonia and Russian SFSR signed on February 2, 1920 ending the Estonian War of Independence. The terms of the treaty stated that "Russia unreservedly recognises" the independence of Republic of Estonia de jure and renounced in...
was ratified, signed by Estonia and Russian SFSR on 2 February. The first Constitution of Estonia was adopted on 15 June 1920. After the constitution had entered into effect and the first parliamentary elections
Estonian parliamentary election, 1920
Estonian parliamentary elections, 1920 to form the I Riigikogu were held from 27 to 29 November 1920. Those were the first elections by the constitution of 1920. 100 deputies were elected into the new parliament by party lists in 10 regions, by which one party or electoral bloc could put up several...
were held, the Constituent Assembly disbanded itself on 20 December 1920.
Results
| Party Political party A political party is a political organization that typically seeks to influence government policy, usually by nominating their own candidates and trying to seat them in political office. Parties participate in electoral campaigns, educational outreach or protest actions... |
Ideology | Votes | % | MPs Member of Parliament A Member of Parliament is a representative of the voters to a :parliament. In many countries with bicameral parliaments, the term applies specifically to members of the lower house, as upper houses often have a different title, such as senate, and thus also have different titles for its members,... |
% of MPs | % of MPs swing Swing (politics) An electoral swing analysis shows the extent of change in voter support from one election to another. It is an indicator of voter support for individual candidates or political parties, or voter preference between two or more candidates or parties... |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Estonian Social Democratic Workers' Party (Eesti Sotsiaaldemokraatline Tööliste Partei) |
Social democracy Social democracy Social democracy is a political ideology of the center-left on the political spectrum. Social democracy is officially a form of evolutionary reformist socialism. It supports class collaboration as the course to achieve socialism... |
152,341 | 32.6% | 41 | 34.2% | 17.8% |
| Estonian Labour Party (Eesti Tööerakond) |
Centre-left Centre-left Centre-left is a political term that describes individuals, political parties or organisations such as think tanks whose ideology lies between the centre and the left on the left-right spectrum... |
114,879 | 24.6% | 30 | 25.0% | 17.7% |
| Estonian People's Party (Eesti Rahvaerakond) |
Centre-right Centre-right The centre-right or center-right is a political term commonly used to describe or denote individuals, political parties, or organizations whose views stretch from the centre to the right on the left-right spectrum, excluding far right stances. Centre-right can also describe a coalition of centrist... |
94,892 | 20.3% | 25 | 20.8% | 8.1% |
| Estonian Country People's Union (Eesti Maarahva Liit) |
Agrarianism Agrarianism Agrarianism has two common meanings. The first meaning refers to a social philosophy or political philosophy which values rural society as superior to urban society, the independent farmer as superior to the paid worker, and sees farming as a way of life that can shape the ideal social values... , conservative |
29,989 | 6.4% | 8 | 6.7% | 17.0% |
| Party of Estonian Socialists-Revolutionaries (Eesti Sotsialistide-Revolutsionääride Partei) |
Socialist revolutionary Socialist-Revolutionary Party thumb|right|200px|Socialist-Revolutionary election poster, 1917. The caption in red reads "партия соц-рев" , short for Party of the Socialist Revolutionaries... |
26,536 | 5.7% | 7 | 5.8% | 8.7% |
| Estonian Christian Peoples Party (Eesti Kristlik Rahvaerakond) |
Christian conservatism Christian conservative Christian conservative may refer to political position:*Christian right*Christian agrarian conservatism of Europe... |
20,157 | 4.3% | 5 | 4.2% | 4.2% |
| German Party in Estonia (Saksa erakond Eestis) |
Minority interests Political parties of minorities Ethnic parties aim to represent an ethnic group in a political system, be it a sovereign state or a subnational entity. An alternate designation is 'Political parties of minorities', but they should not be mistaken with regionalist or separatist parties, whose purpose is territorial autonomy.-... |
11,462 | 2.4% | 3 | 2.5% | 0.7% |
| Party of the Residents of Hiiumaa Hiiumaa Hiiumaa is the second largest island belonging to Estonia. It is located in the Baltic Sea, north of the island of Saaremaa, a part of the West Estonian archipelago. Its largest town is Kärdla.-Name:... island (Hiiu saare elanike partei) |
Regional interests Regionalism (politics) Regionalism is a term used in international relations. Regionalism also constitutes one of the three constituents of the international commercial system... |
11,090 | 2.4% | — | — | — |
| Russian Citizens' Assembly (Vene Kodanike Kogu) |
Minority interests Political parties of minorities Ethnic parties aim to represent an ethnic group in a political system, be it a sovereign state or a subnational entity. An alternate designation is 'Political parties of minorities', but they should not be mistaken with regionalist or separatist parties, whose purpose is territorial autonomy.-... |
5,765 | 1.2% | 1 | 0.8% | 0.2% |
| All-Estonian Sailors' Union (Üle-eestimaaline Meremeeste Liit) |
Interest group Advocacy group Advocacy groups use various forms of advocacy to influence public opinion and/or policy; they have played and continue to play an important part in the development of political and social systems... |
795 | 0.2% | — | — | — |
| Total valid votes | Turnout 80% | 467,906 | 100.00% | 120 | ||
|
||||||

