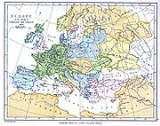
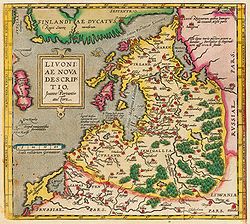
Livonia
Encyclopedia
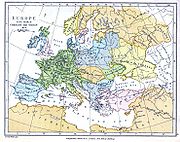
Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is a brackish mediterranean sea located in Northern Europe, from 53°N to 66°N latitude and from 20°E to 26°E longitude. It is bounded by the Scandinavian Peninsula, the mainland of Europe, and the Danish islands. It drains into the Kattegat by way of the Øresund, the Great Belt and...
. It was once the land of the Finnic
Finnic peoples
The Finnic or Fennic peoples were historic ethnic groups who spoke various languages traditionally classified as Finno-Permic...
Livonians inhabiting the principal ancient Livonian County Metsepole
Metsepole
Mõtsa Pūol, Metsepole , was an ancient Livonian county inhabited by a Finnic people Livonians, on the east coast of the Gulf of Riga, at the northwest of what is now the Vidzeme region of Latvia...
with its center at Turaida
Turaida Castle
Turaida Castle is a recently reconstructed medieval castle in Turaida, in the Vidzeme region of Latvia, on the opposite bank of the Gauja River from Sigulda....
. The most prominent ruler of ancient Livonia was Caupo of Turaida
Caupo of Turaida
Caupo of Turaida, or Kaupo was a leader of the Finnic-speaking Livonian people in the beginning of the 13th century, in what is now Latvia. He is sometimes called 'King of Livonia', Chronicle of Henry of Livonia calls him quasi rex, 'like a king'.He was the first prominent Livonian to be christened...
.
During the Livonian Crusade
Livonian Crusade
The Livonian Crusade refers to the German and Danish conquest and colonization of medieval Livonia, the territory constituting modern Latvia and Estonia, during the Northern Crusades...
, ancient Livonia was colonized by the Livonian Brothers of the Sword
Livonian Brothers of the Sword
The Livonian Brothers of the Sword were a military order founded by Bishop Albert of Riga in 1202. Pope Innocent III sanctioned the establishment in 1204. The membership of the order comprised German "warrior monks"...
, later called the Livonian Order
Livonian Order
The Livonian Order was an autonomous Livonian branch of the Teutonic Order and a member of the Livonian Confederation from 1435–1561. After being defeated by Samogitians in the 1236 Battle of Schaulen , the remnants of the Livonian Brothers of the Sword were incorporated into the Teutonic Knights...
, and the name Livonia came to designate a much broader territory: Terra Mariana on the eastern coasts of the Baltic Sea, in present-day Latvia
Latvia
Latvia , officially the Republic of Latvia , is a country in the Baltic region of Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by Estonia , to the south by Lithuania , to the east by the Russian Federation , to the southeast by Belarus and shares maritime borders to the west with Sweden...
and Estonia
Estonia
Estonia , officially the Republic of Estonia , is a state in the Baltic region of Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland, to the west by the Baltic Sea, to the south by Latvia , and to the east by Lake Peipsi and the Russian Federation . Across the Baltic Sea lies...
. Its frontiers were the Gulf of Riga
Gulf of Riga
The Gulf of Riga, or Bay of Riga, is a bay of the Baltic Sea between Latvia and Estonia. According to C.Michael Hogan, a saline stratification layer is found at a depth of approximately seventy metres....
and the Gulf of Finland
Gulf of Finland
The Gulf of Finland is the easternmost arm of the Baltic Sea. It extends between Finland and Estonia all the way to Saint Petersburg in Russia, where the river Neva drains into it. Other major cities around the gulf include Helsinki and Tallinn...
in the north-west, Lake Peipus
Lake Peipus
Lake Peipus, ) is the biggest transboundary lake in Europe on the border between Estonia and Russia.The lake is the fifth largest in Europe after Lake Ladoga and Lake Onega in Russia north of St...
and Russia
Russia
Russia or , officially known as both Russia and the Russian Federation , is a country in northern Eurasia. It is a federal semi-presidential republic, comprising 83 federal subjects...
to the east, and Lithuania
Lithuania
Lithuania , officially the Republic of Lithuania is a country in Northern Europe, the biggest of the three Baltic states. It is situated along the southeastern shore of the Baltic Sea, whereby to the west lie Sweden and Denmark...
to the south.
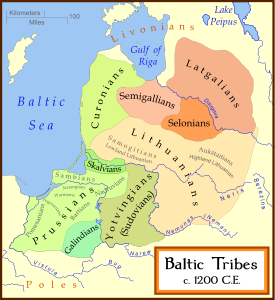
Livonia was inhabited by various Baltic
Balts
The Balts or Baltic peoples , defined as speakers of one of the Baltic languages, a branch of the Indo-European language family, are descended from a group of Indo-European tribes who settled the area between the Jutland peninsula in the west and Moscow, Oka and Volga rivers basins in the east...
and Finnic peoples
Finnic peoples
The Finnic or Fennic peoples were historic ethnic groups who spoke various languages traditionally classified as Finno-Permic...
, ruled by an upper class of Baltic Germans. Over the course of time, some nobles were polonized
Polonization
Polonization was the acquisition or imposition of elements of Polish culture, in particular, Polish language, as experienced in some historic periods by non-Polish populations of territories controlled or substantially influenced by Poland...
into the Polish–Lithuanian nobility (Szlachta
Szlachta
The szlachta was a legally privileged noble class with origins in the Kingdom of Poland. It gained considerable institutional privileges during the 1333-1370 reign of Casimir the Great. In 1413, following a series of tentative personal unions between the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and the Kingdom of...
) or russified
Russification
Russification is an adoption of the Russian language or some other Russian attributes by non-Russian communities...
into the Russian nobility (Dvoryanstvo).
History
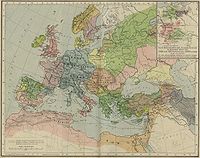
Germans
The Germans are a Germanic ethnic group native to Central Europe. The English term Germans has referred to the German-speaking population of the Holy Roman Empire since the Late Middle Ages....
, particularly by the Hanseatic League
Hanseatic League
The Hanseatic League was an economic alliance of trading cities and their merchant guilds that dominated trade along the coast of Northern Europe...
and the Cistercian Order.
Around 1160, Hanseatic traders from Lübeck
Lübeck
The Hanseatic City of Lübeck is the second-largest city in Schleswig-Holstein, in northern Germany, and one of the major ports of Germany. It was for several centuries the "capital" of the Hanseatic League and, because of its Brick Gothic architectural heritage, is listed by UNESCO as a World...
established a trading post on the site of the future city of Riga
Riga
Riga is the capital and largest city of Latvia. With 702,891 inhabitants Riga is the largest city of the Baltic states, one of the largest cities in Northern Europe and home to more than one third of Latvia's population. The city is an important seaport and a major industrial, commercial,...
, which Albrecht von Buxthoeven founded in 1201. He ordered the construction of a cathedral and became the first Prince-Bishop
Prince-Bishop
A Prince-Bishop is a bishop who is a territorial Prince of the Church on account of one or more secular principalities, usually pre-existent titles of nobility held concurrently with their inherent clerical office...
of Livonia.
Livonian Brothers of the Sword 1204–1237
Military order
A military order is a Christian society of knights that was founded for crusading, i.e. propagating or defending the faith , either in the Holy Land or against Islam or pagans in Europe...
of the Livonian Brothers of the Sword in 1202; Pope Innocent III
Pope Innocent III
Pope Innocent III was Pope from 8 January 1198 until his death. His birth name was Lotario dei Conti di Segni, sometimes anglicised to Lothar of Segni....
sanctioned the establishment in 1204. The membership of the order comprised German
Germans
The Germans are a Germanic ethnic group native to Central Europe. The English term Germans has referred to the German-speaking population of the Holy Roman Empire since the Late Middle Ages....
"warrior monk
Monk
A monk is a person who practices religious asceticism, living either alone or with any number of monks, while always maintaining some degree of physical separation from those not sharing the same purpose...
s". Alternative names of the order include the Christ Knights, Sword Brethren, and The Militia of Christ of Livonia. Following their defeat by Lithuania
History of Lithuania (1219–1295)
The history of Lithuania between 1219 and 1295 deals with the establishment and early history of the first Lithuanian state, the Grand Duchy of Lithuania. The beginning of the 13th century marks the end of the prehistory of Lithuania. From this point on the history of Lithuania is recorded in...
in the Battle of Saule in 1236, the surviving Brothers merged into the Teutonic Order as an autonomous branch and became known as the Livonian Order
Livonian Order
The Livonian Order was an autonomous Livonian branch of the Teutonic Order and a member of the Livonian Confederation from 1435–1561. After being defeated by Samogitians in the 1236 Battle of Schaulen , the remnants of the Livonian Brothers of the Sword were incorporated into the Teutonic Knights...
.

Riga
Riga is the capital and largest city of Latvia. With 702,891 inhabitants Riga is the largest city of the Baltic states, one of the largest cities in Northern Europe and home to more than one third of Latvia's population. The city is an important seaport and a major industrial, commercial,...
(or Prince-Bishop
Prince-Bishop
A Prince-Bishop is a bishop who is a territorial Prince of the Church on account of one or more secular principalities, usually pre-existent titles of nobility held concurrently with their inherent clerical office...
of Livonia), founded the Brotherhood to aid the Bishopric of Riga in the conversion of the pagan
Paganism
Paganism is a blanket term, typically used to refer to non-Abrahamic, indigenous polytheistic religious traditions....
Curonians
Curonians
The Curonians or Kurs were a Baltic tribe living on the shores of the Baltic sea in what are now the western parts of Latvia and Lithuania from the 5th to the 16th centuries, when they merged with other Baltic tribes. They gave their name to the region of Courland , and they spoke the Old...
, Livonians
Livonian people
The Livonians or Livs are the indigenous inhabitants of Livonia, a large part of what is today northwestern Latvia and southwestern Estonia. They spoke the Uralic Livonian language, a language which is closely related to Estonian and Finnish...
, Semigallians
Semigallians
Semigallians were the Baltic tribe that lived in the southcentral part of contemporary Latvia and northern Lithuania...
, and Latgalians
Latgalians
The term Latgalians The term Latgalians The term Latgalians (Latgalian: latgalīši, latgali, (also spelt Latgallians and sometimes known as Lettigalls, Latgolans, or Lettigallians) can refer to the inhabitants of the Latgale region in eastern Latvia in general, the ethnic Latvians of Latgale...
living on the shores of the Gulf of Riga
Gulf of Riga
The Gulf of Riga, or Bay of Riga, is a bay of the Baltic Sea between Latvia and Estonia. According to C.Michael Hogan, a saline stratification layer is found at a depth of approximately seventy metres....
. From its foundation, the undisciplined Order tended to ignore its supposed vassal
Vassal
A vassal or feudatory is a person who has entered into a mutual obligation to a lord or monarch in the context of the feudal system in medieval Europe. The obligations often included military support and mutual protection, in exchange for certain privileges, usually including the grant of land held...
age to the bishops. In 1218, Albert asked King Valdemar II
Valdemar II of Denmark
Valdemar II , called Valdemar the Victorious or Valdemar the Conqueror , was the King of Denmark from 1202 until his death in 1241. The nickname Sejr is a later invention and was not used during the King's own lifetime...
of Denmark
Denmark
Denmark is a Scandinavian country in Northern Europe. The countries of Denmark and Greenland, as well as the Faroe Islands, constitute the Kingdom of Denmark . It is the southernmost of the Nordic countries, southwest of Sweden and south of Norway, and bordered to the south by Germany. Denmark...
for assistance, but Valdemar instead arranged a deal with the Brotherhood and conquered the north of Estonia
Danish Estonia
Danish Estonia refers to the territories of present-day Estonia that were ruled by Denmark firstly during the 13th–14th centuries and again in the 16th–17th centuries....
for Denmark. The Brotherhood had its headquarters at Fellin (Viljandi)
Viljandi
Viljandi is a town and municipality in southern Estonia with a population of 19,150 . It is the capital of Viljandi County. The town was first mentioned in 1283, upon being granted its town charter by Wilhelm von Endorpe....
in present-day Estonia
Estonia
Estonia , officially the Republic of Estonia , is a state in the Baltic region of Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland, to the west by the Baltic Sea, to the south by Latvia , and to the east by Lake Peipsi and the Russian Federation . Across the Baltic Sea lies...
, where the walls of the Master's castle stand. Other strongholds included Wenden (Cēsis)
Cesis
Cēsis , is a town in Latvia located in the northern part of the Central Vidzeme Upland. Cēsis is on the Gauja River valley, and is built on a series of ridges above the river overlooking the woods below...
, Segewold (Sigulda)
Sigulda
Other twinnings: Keila, Estonia chiatura Georgia-References:* , , , , , and -External links:*...
and Ascheraden (Aizkraukle)
Aizkraukle
Aizkraukle is a town in Vidzeme region in Latvia, the administrative centre of Aizkraukle municipality on the right bank of the Daugava River.-History:Aizkraukle before the World War I was formerly known by its German name of Ascheraden...
. The commanders of Fellin, Goldingen (Kuldīga)
Kuldiga
Kuldīga is a town in western Latvia. It is the center of Kuldīga municipality with a population of approximately 13,500.Kuldīga was first mentioned in 1242. It joined the Hanseatic League in 1368...
, Marienburg (Alūksne)
Aluksne
Alūksne is a town on the shores of Lake Alūksne in northeastern Latvia near the borders with Estonia and Russia. It is the seat of Alūksne municipality.- History :...
, Reval (Tallinn)
Tallinn
Tallinn is the capital and largest city of Estonia. It occupies an area of with a population of 414,940. It is situated on the northern coast of the country, on the banks of the Gulf of Finland, south of Helsinki, east of Stockholm and west of Saint Petersburg. Tallinn's Old Town is in the list...
, and the bailiff
Bailiff
A bailiff is a governor or custodian ; a legal officer to whom some degree of authority, care or jurisdiction is committed...
of Weißenstein (Paide)
Paide
Paide is the capital of Järva County, Estonia.A castle built by the Livonian Brothers of the Sword is located here. The town was formally founded 30 September 1291 by Halt, master of the Livonian Order....
belonged to the five-member entourage of the Order's Master.

Pope Gregory IX
Pope Gregory IX, born Ugolino di Conti, was pope from March 19, 1227 to August 22, 1241.The successor of Pope Honorius III , he fully inherited the traditions of Pope Gregory VII and of his uncle Pope Innocent III , and zealously continued their policy of Papal supremacy.-Early life:Ugolino was...
asked the Brothers to defend Finland
Finland
Finland , officially the Republic of Finland, is a Nordic country situated in the Fennoscandian region of Northern Europe. It is bordered by Sweden in the west, Norway in the north and Russia in the east, while Estonia lies to its south across the Gulf of Finland.Around 5.4 million people reside...
from the Novgorodian attacks
Finnish-Novgorodian wars
The Finnish–Novgorodian wars were a series of conflicts that took place between Finnic tribes in eastern Fennoscandia called "Yem", and the Republic of Novgorod from the 11th or 12th century to early 13th century. The wars seem to have contributed to the eventual Swedish conquest of Finland in...
in his letter of November 24, 1232;
however, no known information regarding the knights' possible activities in Finland has survived. (Sweden
Swedish Empire
The Swedish Empire refers to the Kingdom of Sweden between 1561 and 1721 . During this time, Sweden was one of the great European powers. In Swedish, the period is called Stormaktstiden, literally meaning "the Great Power Era"...
eventually took over Finland after the Second Swedish Crusade
Second Swedish Crusade
The Second Swedish Crusade was a Swedish military expedition to areas in present-day Finland by Birger jarl in the 13th century. As a result of the crusade, Finland became permanently part of Sweden for the next 550 years.-Year of the crusade:...
in 1249.) In the Battle of Saule in 1236 the Lithuanians
Lithuanians
Lithuanians are the Baltic ethnic group native to Lithuania, where they number around 2,765,600 people. Another million or more make up the Lithuanian diaspora, largely found in countries such as the United States, Brazil, Canada, Colombia, Russia, United Kingdom and Ireland. Their native language...
and Semigallians
Semigallians
Semigallians were the Baltic tribe that lived in the southcentral part of contemporary Latvia and northern Lithuania...
decimated the Order. This disaster led the surviving Brothers to become incorporated into the Order of Teutonic Knights
Teutonic Knights
The Order of Brothers of the German House of Saint Mary in Jerusalem , commonly the Teutonic Order , is a German medieval military order, in modern times a purely religious Catholic order...
in the following year, and from that point on they became known as the Livonian Order
Livonian Order
The Livonian Order was an autonomous Livonian branch of the Teutonic Order and a member of the Livonian Confederation from 1435–1561. After being defeated by Samogitians in the 1236 Battle of Schaulen , the remnants of the Livonian Brothers of the Sword were incorporated into the Teutonic Knights...
. They continued, however, to function in all respects (rule, clothing and policy) as an autonomous branch of the Teutonic Order, headed by their own Master (himself de jure subject to the Teutonic Order's Grand Master
Hochmeister
The grand master is the holder of the supreme office of the Teutonic Order. It is equivalent to the grand master of other military orders and the superior general in non-military Roman Catholic religious orders...
).
Livonian Crusade 1206-1227
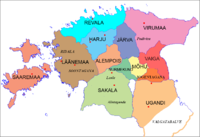
Chronicle of Henry of Livonia
The Livonian Chronicle of Henry is a document describing historic events in Livonia and surrounding areas from 1180 to 1227. Apart from the few references in the Primary Chronicle compiled in Kievan Rus' in the twelfth century, it is the oldest known written document about the history of these...
from the 1220s gives a firsthand account of the Christianization of Livonia, granted as a fief by the Hohenstaufen
Hohenstaufen
The House of Hohenstaufen was a dynasty of German kings in the High Middle Ages, lasting from 1138 to 1254. Three of these kings were also crowned Holy Roman Emperor. In 1194 the Hohenstaufens also became Kings of Sicily...
King of Germany, Philip of Swabia
Philip of Swabia
Philip of Swabia was king of Germany and duke of Swabia, the rival of the emperor Otto IV.-Biography:Philip was the fifth and youngest son of Emperor Frederick I and Beatrice I, Countess of Burgundy, daughter of Renaud III, count of Burgundy, and brother of the emperor Henry VI...
, to Bishop Albert of Buxthoeven, nephew of the Hartwig II
Hartwig of Uthlede
Hartwig of Uthlede was - as Hartwig II - Prince-Archbishop of Bremen and one of the originators of the Livonian Crusade. Coming from a family of the Bremian Ministerialis at Uthlede, he was a canon of Bremen Cathedral and a clerk of Duke Henry the Lion of Saxony, House of Guelph, before becoming...
, Archbishop of Bremen, who sailed with a convoy of ships filled with armed crusaders to carve out a Catholic territory in the east during the Livonian Crusade
Livonian Crusade
The Livonian Crusade refers to the German and Danish conquest and colonization of medieval Livonia, the territory constituting modern Latvia and Estonia, during the Northern Crusades...
.
Monastic state of the Teutonic Knights 1224-1237
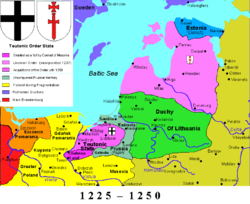
- a state ruled by the Livonian OrderLivonian Brothers of the SwordThe Livonian Brothers of the Sword were a military order founded by Bishop Albert of Riga in 1202. Pope Innocent III sanctioned the establishment in 1204. The membership of the order comprised German "warrior monks"...
founded by Albert in 1202, which was assimilated into the Teutonic KnightsTeutonic KnightsThe Order of Brothers of the German House of Saint Mary in Jerusalem , commonly the Teutonic Order , is a German medieval military order, in modern times a purely religious Catholic order...
in 1237; - the Bishopric of Riga (an archbishopric since 1255);
- the Bishoprics of CourlandBishopric of CourlandThe Bishopric of Courland was the second smallest ecclesiastical state in the Livonian Confederation founded in the aftermath of the Livonian Crusade...
, Ösel-WiekBishopric of Ösel-WiekThe Bishopric of Ösel–Wiek was a semi-independent Roman Catholic prince-bishopric in what is now Saare, Hiiu and Lääne counties of Estonia.The bishopric was created as a state of Holy Roman Empire on 1 October 1228, by Henry, King of the Romans...
, and DorpatBishopric of DorpatThe Bishopric of Dorpat was a medieval principality and a catholic diocese which existed from 1224 to 1558, generally encompassing what are now Tartu, Põlva, Võru and Jõgeva counties in Estonia. The Bishopric was part of Livonian Confederation...
, where Albert's brother Hermann established himself as the prince-bishop (Terra Mariana). The conquest of Livonia by the Germans is described in the Livonian Rhymed ChronicleLivonian Rhymed ChronicleThe Livonian Rhymed Chronicle was a chronicle written in Low German by an anonymous writer. It covers the period 1180 – 1290 and contains a wealth of detail about Livonia — modern Estonia and Latvia....
.
Livonian Order 1237-1561
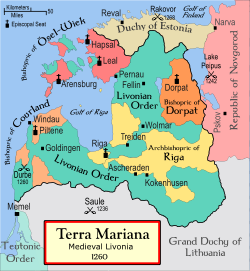
Teutonic Knights
The Order of Brothers of the German House of Saint Mary in Jerusalem , commonly the Teutonic Order , is a German medieval military order, in modern times a purely religious Catholic order...
(or Teutonic Order) and a member of the Livonian Confederation
Livonian Confederation
Terra Mariana was the official name for Medieval Livonia or Old Livonia which was formed in the aftermath of the Livonian Crusade in the territories comprising present day Estonia and Latvia...
from 1418–1561. After being defeated by Lithuania
History of Lithuania (1219–1295)
The history of Lithuania between 1219 and 1295 deals with the establishment and early history of the first Lithuanian state, the Grand Duchy of Lithuania. The beginning of the 13th century marks the end of the prehistory of Lithuania. From this point on the history of Lithuania is recorded in...
in the 1236 Battle of Saule, the remnants of the Livonian Brothers of the Sword
Livonian Brothers of the Sword
The Livonian Brothers of the Sword were a military order founded by Bishop Albert of Riga in 1202. Pope Innocent III sanctioned the establishment in 1204. The membership of the order comprised German "warrior monks"...
were incorporated into the Teutonic Knights as the Livonian Order in 1237. Between 1237 and 1290, the Livonian Order conquered all of Courland
Courland
Courland is one of the historical and cultural regions of Latvia. The regions of Semigallia and Selonia are sometimes considered as part of Courland.- Geography and climate :...
, Livonia, and Semigallia, but their attack on northern Russia was repelled in the Battle of Rakvere (1268). In 1346, after St. George's Night Uprising
St. George's Night Uprising
St. George’s Night Uprising in 1343–1346 was an unsuccessful attempt by the indigenous Estonian population in the Duchy of Estonia, the Bishopric of Ösel-Wiek, and the insular territories of the State of the Teutonic Order to annihilate the Danish and German rulers and landlords, who had conquered...
the Order bought the rest of Estonia
Estonia
Estonia , officially the Republic of Estonia , is a state in the Baltic region of Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland, to the west by the Baltic Sea, to the south by Latvia , and to the east by Lake Peipsi and the Russian Federation . Across the Baltic Sea lies...
from King Valdemar IV of Denmark
Valdemar IV of Denmark
Valdemar IV of Denmark or Waldemar ; , was King of Denmark from 1340 to 1375.-Ascension to the throne:...
. Life within the Order's territory is described in the Chronicle of Henry of Livonia
Chronicle of Henry of Livonia
The Livonian Chronicle of Henry is a document describing historic events in Livonia and surrounding areas from 1180 to 1227. Apart from the few references in the Primary Chronicle compiled in Kievan Rus' in the twelfth century, it is the oldest known written document about the history of these...
and the Livonian Rhymed Chronicle
Livonian Rhymed Chronicle
The Livonian Rhymed Chronicle was a chronicle written in Low German by an anonymous writer. It covers the period 1180 – 1290 and contains a wealth of detail about Livonia — modern Estonia and Latvia....
. The Teutonic Order fell into decline following its defeat in the Battle of Grunwald
Battle of Grunwald
The Battle of Grunwald or 1st Battle of Tannenberg was fought on 15 July 1410, during the Polish–Lithuanian–Teutonic War. The alliance of the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, led respectively by King Jogaila and Grand Duke Vytautas , decisively defeated the Teutonic Knights, led...
in 1410 and the secularization of its Prussian territories by Albert of Brandenburg in 1525, but the Livonian Order managed to maintain an independent existence. During many years of Livonian War
Livonian War
The Livonian War was fought for control of Old Livonia in the territory of present-day Estonia and Latvia when the Tsardom of Russia faced a varying coalition of Denmark–Norway, the Kingdom of Sweden, the Union of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and the Kingdom of Poland.During the period 1558–1578,...
(1558–1582), however, they suffered a decisive defeat by troops of Muscovite Russia in the Battle of Ergeme
Battle of Ergeme
The Battle of Ērģeme was fought on 2 August 1560 in present-day Latvia as part of the Livonian War between the forces of Ivan IV of Russia and the Livonian Confederation. It was the last battle fought by the German knights in Livonia and an important Russian victory...
in 1560 and continued living under great threat. Letters to the Emperor arrived from many European countries, warning, that Moscow has its eyes on much more than only a few harbors or the province of Liefland... the East Sea (Ostsee-Baltic Sea
Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is a brackish mediterranean sea located in Northern Europe, from 53°N to 66°N latitude and from 20°E to 26°E longitude. It is bounded by the Scandinavian Peninsula, the mainland of Europe, and the Danish islands. It drains into the Kattegat by way of the Øresund, the Great Belt and...
and the West Sea (Atlantic) are equally in danger. Duke Barnim the Elder, 50 years duke of Pomerania, warned, that never before did he experience the fear than now, where even in his land, where people send by Moscow are everywhere. At stake was the Narva
Narva
Narva is the third largest city in Estonia. It is located at the eastern extreme point of Estonia, by the Russian border, on the Narva River which drains Lake Peipus.-Early history:...
-Trade-Route and practically all trade in the North, and with that all of Europe. Due to religious upheavals of the Reformation
Protestant Reformation
The Protestant Reformation was a 16th-century split within Western Christianity initiated by Martin Luther, John Calvin and other early Protestants. The efforts of the self-described "reformers", who objected to the doctrines, rituals and ecclesiastical structure of the Roman Catholic Church, led...
the empire could not send troops, which it could not afford and which were too far away anyway. Prussia was not able to help for much of the same reason, and Duke Albrecht was under continuous ban by the emperor. The Hanseatic League was greatly weakened by this and the city state of Luebeck fought its last great war. The emperor Maximilian II
Maximilian II, Holy Roman Emperor
Maximilian II was king of Bohemia and king of the Romans from 1562, king of Hungary and Croatia from 1563, emperor of the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation from 1564 until his death...
diffused the greatest threat by remaining on friendly terms with the czar, but not sending him troops as requested, in his struggles with the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth.
Czar Ivan of Moscow installed Duke Magnus as King of Livonia. This was opposed by the other forces. The Livonian Order saw no other way than to seek protection from Sigismund II Augustus
Sigismund II Augustus
Sigismund II Augustus I was King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania, the only son of Sigismund I the Old, whom Sigismund II succeeded in 1548...
, the King of Poland
Kingdom of Poland (1385–1569)
The Kingdom of Poland of the Jagiellons was the Polish state created by the accession of Jogaila , Grand Duke of Lithuania, to the Polish throne in 1386. The Union of Krewo or Krėva Act, united Poland and Lithuania under the rule of a single monarch...
and the Grand Duke of Lithuania
Grand Duchy of Lithuania
The Grand Duchy of Lithuania was a European state from the 12th /13th century until 1569 and then as a constituent part of Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth until 1791 when Constitution of May 3, 1791 abolished it in favor of unitary state. It was founded by the Lithuanians, one of the polytheistic...
, who had intervened in a war between Bishop William
William of Brandenburg
Wilhelm von Brandenburg was the Archbishop of Riga from 1539 to 1561.A member of the House of Hohenzollern, Wilhelm was the son of Frederick I, Margrave of Brandenburg-Ansbach, the brother of Albert, Duke of Prussia, and the grandson of Albert III Achilles, Elector of Brandenburg and Casimir IV...
of Riga and the Brothers in 1557. After coming to an agreement with Sigismund II Augustus and his representatives (especially Mikołaj "the Black" Radziwiłł), the last Livonian Master, Gotthard Kettler
Gotthard Kettler
Gotthard von Kettler was the last Master of the Livonian Order and the first Duke of Courland and Semigallia....
, secularized the Order and converted to Lutheranism
Lutheranism
Lutheranism is a major branch of Western Christianity that identifies with the theology of Martin Luther, a German reformer. Luther's efforts to reform the theology and practice of the church launched the Protestant Reformation...
. In the southern part of the Brothers' lands he created the Duchy of Courland and Semigallia
Duchy of Courland and Semigallia
The Duchy of Courland and Semigallia is the name of a duchy in the Baltic region that existed from 1562 to 1569 as a vassal state of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and from 1569...
for his family. Most of the remaining lands were seized by the Grand Duchy of Lithuania. The north of Estonia was taken back by Denmark and Sweden
Swedish Empire
The Swedish Empire refers to the Kingdom of Sweden between 1561 and 1721 . During this time, Sweden was one of the great European powers. In Swedish, the period is called Stormaktstiden, literally meaning "the Great Power Era"...
.
From the 14th to the 16th centuries, Middle Low German
Middle Low German
Middle Low German is a language that is the descendant of Old Saxon and is the ancestor of modern Low German. It served as the international lingua franca of the Hanseatic League...
as spoken in the towns of the Hanseatic League
Hanseatic League
The Hanseatic League was an economic alliance of trading cities and their merchant guilds that dominated trade along the coast of Northern Europe...
was the established language, but was subsequently succeeded by High German as official language in the course of the 16th and 17th centuries.
Livonian Confederation 1418-1561
The 5 Ecclesiastical states of the Holy Roman Empire in Medieval Livonia were organized into the Livonian ConfederationLivonian Confederation
Terra Mariana was the official name for Medieval Livonia or Old Livonia which was formed in the aftermath of the Livonian Crusade in the territories comprising present day Estonia and Latvia...
in 1418 A diet or Landtag
Landtag
A Landtag is a representative assembly or parliament in German-speaking countries with some legislative authority.- Name :...
was formed in 1419. The city of Walk
Walk, Livonia
Walk was the historical German name for the town that is now divided into Valga in Estonia and Valka in Latvia. After 1419 it was the seat of the Landtag of the Livonian Confederation.-See also:*List of German exonyms for places in Estonia...
was chosen as the site of the diet.
Livonian War 1558–1583
Ferdinand I, Holy Roman Emperor
Ferdinand I was Holy Roman Emperor from 1558 and king of Bohemia and Hungary from 1526 until his death. Before his accession, he ruled the Austrian hereditary lands of the Habsburgs in the name of his elder brother, Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor.The key events during his reign were the contest...
once again asked for help of Gustav I of Sweden
Gustav I of Sweden
Gustav I of Sweden, born Gustav Eriksson of the Vasa noble family and later known simply as Gustav Vasa , was King of Sweden from 1523 until his death....
, and The Kingdom of Poland (1385–1569)
Kingdom of Poland (1385–1569)
The Kingdom of Poland of the Jagiellons was the Polish state created by the accession of Jogaila , Grand Duke of Lithuania, to the Polish throne in 1386. The Union of Krewo or Krėva Act, united Poland and Lithuania under the rule of a single monarch...
also began direct negotiation
Negotiation
Negotiation is a dialogue between two or more people or parties, intended to reach an understanding, resolve point of difference, or gain advantage in outcome of dialogue, to produce an agreement upon courses of action, to bargain for individual or collective advantage, to craft outcomes to satisfy...
s with Gustav, but nothing resulted because on September 29, 1560, Gustav I Vasa died. The chances for success of Magnus and his supporters looked particularly good in 1560 (and 1570). In the former case, he had been recognised as their sovereign
Sovereign
A sovereign is the supreme lawmaking authority within its jurisdiction.Sovereign may also refer to:*Monarch, the sovereign of a monarchy*Sovereign Bank, banking institution in the United States*Sovereign...
by The Bishopric of Ösel-Wiek
Bishopric of Ösel-Wiek
The Bishopric of Ösel–Wiek was a semi-independent Roman Catholic prince-bishopric in what is now Saare, Hiiu and Lääne counties of Estonia.The bishopric was created as a state of Holy Roman Empire on 1 October 1228, by Henry, King of the Romans...
and The Bishopric of Courland
Bishopric of Courland
The Bishopric of Courland was the second smallest ecclesiastical state in the Livonian Confederation founded in the aftermath of the Livonian Crusade...
, and as their prospective ruler by the authorities of The Bishopric of Dorpat
Bishopric of Dorpat
The Bishopric of Dorpat was a medieval principality and a catholic diocese which existed from 1224 to 1558, generally encompassing what are now Tartu, Põlva, Võru and Jõgeva counties in Estonia. The Bishopric was part of Livonian Confederation...
; The Bishopric of Reval
Bishopric of Reval
The Bishopric of Reval was created in Duchy of Estonia by Valdemar II of Denmark in 1240. Contradictory to canon law Valdemar II reserved the right to appoint the bishops of Reval to himself and his successor kings of Denmark. The decision to simply nominate the holy see of Reval was unique in the...
with the Harrien-Wierland gentry
Gentry
Gentry denotes "well-born and well-bred people" of high social class, especially in the past....
were on his side; Livonian Order
Livonian Order
The Livonian Order was an autonomous Livonian branch of the Teutonic Order and a member of the Livonian Confederation from 1435–1561. After being defeated by Samogitians in the 1236 Battle of Schaulen , the remnants of the Livonian Brothers of the Sword were incorporated into the Teutonic Knights...
conditionally recognised his right of ownership
Ownership
Ownership is the state or fact of exclusive rights and control over property, which may be an object, land/real estate or intellectual property. Ownership involves multiple rights, collectively referred to as title, which may be separated and held by different parties. The concept of ownership has...
of Estonia
Estonia
Estonia , officially the Republic of Estonia , is a state in the Baltic region of Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland, to the west by the Baltic Sea, to the south by Latvia , and to the east by Lake Peipsi and the Russian Federation . Across the Baltic Sea lies...
(Principality of Estonia). Then along with Archbishop
Archbishop
An archbishop is a bishop of higher rank, but not of higher sacramental order above that of the three orders of deacon, priest , and bishop...
Wilhelm von Brandenburg of The Archbishopric of Riga and his Coadjutor Christoph von Mecklenburg, Kettler gave to Magnus the portions of The Kingdom of Livonia
Kingdom of Livonia
The Kingdom of Livonia was a nominal state in what is now the territory of the present-day Estonia and Latvia, declared as such by Ivan IV during the Livonian War but never properly established. On June 10, 1570 the Danish Duke Magnus of Holstein arrived in Moscow where he was crowned King of Livonia...
, which he had taken possession of, but they refused to give him any more land. Once Eric XIV of Sweden
Eric XIV of Sweden
-Family and descendants:Eric XIV had several relationships before his marriage. With Agda Persdotter he had four daughters:#Margareta Eriksdotter , married 1592 to Olov Simonsson, vicar of Horn....
became king he took quick actions to get involved in the war. He negotiated a continued peace
Peace
Peace is a state of harmony characterized by the lack of violent conflict. Commonly understood as the absence of hostility, peace also suggests the existence of healthy or newly healed interpersonal or international relationships, prosperity in matters of social or economic welfare, the...
with Muscovy and spoke to the burghers of Reval city
City
A city is a relatively large and permanent settlement. Although there is no agreement on how a city is distinguished from a town within general English language meanings, many cities have a particular administrative, legal, or historical status based on local law.For example, in the U.S...
. He offered them goods to submit to him as well as threatening them. By June 6, 1561 they submitted to him contrary to the persuasion
Persuasion
Persuasion is a form of social influence. It is the process of guiding or bringing oneself or another toward the adoption of an idea, attitude, or action by rational and symbolic means.- Methods :...
s of Kettler to the burghers. The King's brother Johan married the Polish princess
Princess
Princess is the feminine form of prince . Most often, the term has been used for the consort of a prince, or his daughters....
Catherine Jagiellon
Catherine Jagiellon
Catherine the Jagiellonian of Poland was Duchess of Finland , Queen Consort of Sweden , Grand Princess of Finland and heir to her mother's claim to the title of King of Jerusalem....
. Wanting to obtain his own land in Livonia, he loaned Poland money and then claimed the castle
Castle
A castle is a type of fortified structure built in Europe and the Middle East during the Middle Ages by European nobility. Scholars debate the scope of the word castle, but usually consider it to be the private fortified residence of a lord or noble...
s they had pawned as his own instead of using them to pressure Poland. After Johan returned to Finland
Finland
Finland , officially the Republic of Finland, is a Nordic country situated in the Fennoscandian region of Northern Europe. It is bordered by Sweden in the west, Norway in the north and Russia in the east, while Estonia lies to its south across the Gulf of Finland.Around 5.4 million people reside...
, Erik XIV forbade him to deal with any foreign countries without his consent. Shortly after that Erik XIV started acting quickly lost any allies he was about to obtain, either from Magnus or the Archbishop of Riga
Riga
Riga is the capital and largest city of Latvia. With 702,891 inhabitants Riga is the largest city of the Baltic states, one of the largest cities in Northern Europe and home to more than one third of Latvia's population. The city is an important seaport and a major industrial, commercial,...
. Magnus was upset he had been tricked out of his inheritance
Inheritance
Inheritance is the practice of passing on property, titles, debts, rights and obligations upon the death of an individual. It has long played an important role in human societies...
of Holstein
Holstein
Holstein is the region between the rivers Elbe and Eider. It is part of Schleswig-Holstein, the northernmost state of Germany....
. After Sweden occupied
Military occupation
Military occupation occurs when the control and authority over a territory passes to a hostile army. The territory then becomes occupied territory.-Military occupation and the laws of war:...
Reval, Frederick II of Denmark
Frederick II of Denmark
Frederick II was King of Denmark and Norway and duke of Schleswig from 1559 until his death.-King of Denmark:Frederick II was the son of King Christian III of Denmark and Norway and Dorothea of Saxe-Lauenburg. Frederick II stands as the typical renaissance ruler of Denmark. Unlike his father, he...
made a treaty with Erik XIV of Sweden in August 1561. The brothers were in great disagreement and Frederick II negotiated a treaty with Ivan IV on August 7, 1562 in order to help his brother obtain more land and stall further Swedish advance. Erik XIV did not like this and The Northern Seven Years' War
Northern Seven Years' War
The Northern Seven Years' War was the war between Kingdom of Sweden and a coalition of Denmark–Norway, Lübeck and the Polish–Lithuanian union, fought between 1563 and 1570...
between The Free City of Lübeck, Denmark, Poland, and Sweden broke out. While only losing land and trade, Frederick II and Magnus were not faring well. But in 1568 Erik XIV became insane and his brother Johan III took his place. Johan III ascended to the throne
Throne
A throne is the official chair or seat upon which a monarch is seated on state or ceremonial occasions. "Throne" in an abstract sense can also refer to the monarchy or the Crown itself, an instance of metonymy, and is also used in many expressions such as "the power behind the...
of Sweden and due to his friendship with Poland he began a policy against Muscovy. He would try to obtain more land in Livonia and exercise strength over Denmark. After all parties had been financially drained, Frederick II let his ally, King Sigismund II Augustus
Sigismund II Augustus
Sigismund II Augustus I was King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania, the only son of Sigismund I the Old, whom Sigismund II succeeded in 1548...
of Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, know that he was ready for peace. On December 15, 1570, the Treaty of Stettin was concluded. It is, however, more difficult to estimate the scope and magnitude of the support Magnus received in Livonian cities. Compared to the Harrien-Wierland gentry, the Reval city council, and hence probably the majority of citizens, demonstrated a much more reserved attitude towards Denmark and King Magnus of Livonia. Nevertheless, there is no reason to speak about any strong pro-Swedish sentiments among the residents of Reval. The citizens who had fled to The Bishopric of Dorpat or had been deported to Muscovy hailed Magnus as their saviour until 1571. The analysis indicates that during the Livonian War
Livonian War
The Livonian War was fought for control of Old Livonia in the territory of present-day Estonia and Latvia when the Tsardom of Russia faced a varying coalition of Denmark–Norway, the Kingdom of Sweden, the Union of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and the Kingdom of Poland.During the period 1558–1578,...
a pro-independence
Independence
Independence is a condition of a nation, country, or state in which its residents and population, or some portion thereof, exercise self-government, and usually sovereignty, over its territory....
wing emerged among the Livonian gentry and townspeople, forming the so-called "Peace Party
Peace Party
The Peace Party is a small political party in the United Kingdom and represents some who totally oppose war. The party was founded in 1996 as the Pacifist Party by a group of activists in Guildford, Surrey....
". Dismissing hostilities, these forces perceived an agreement with Muscovy as a chance to escape the atrocities of war and avoid the division of Livonia. That is why Magnus, who represented Denmark and later struck a deal with Ivan the Terrible, proved a suitable figurehead for this faction.
The Peace Party, however, had its own armed forces – scattered bands of household troops (Hofleute) under diverse command, which only united in action in 1565 (Battle of Pärnu, 1565 and Siege of Reval, 1999), in 1570–1571 (Siege of Reval, 1570-1571; 30 weeks), and in 1574–1576 (first on Sweden’s side, then came the sale of Wiek
Wiek
Wiek may refer to:*the old German name for Lääne County, Estonia*Wiek, Rügen, a municipality on the island of Rügen, GermanySee also:*Wieck *Wyk *Wick...
to the Danish Crown
Danish Crown
Danish Crown may refer to several things.* Danish krone, currency used in Denmark* The monarchy of Denmark* Danish Crown Regalia, symbols of the Danish monarchy.* Danish Crown AmbA, a large meat processing company....
, and the loss of the territory to Muscovites). In 1575 after Muscovy attacked Danish claims in Livonia, Frederick II dropped out of the competition as well as the Holy Roman Emperor. After this Johan III held off on his pursuit for more land due to Muscovy obtaining lands that Sweden controlled. He used the next two years of truce to get in a better position. In 1578, he resumed the fight for not only Livonia, but also everywhere due to an understanding he made with Rzeczpospolita. In 1578 Magnus retired to Rzeczpospolita and his brother all but gave up the land in Livonia.
Duchy of Livonia 1561-1621
In 1561, during the Livonian WarLivonian War
The Livonian War was fought for control of Old Livonia in the territory of present-day Estonia and Latvia when the Tsardom of Russia faced a varying coalition of Denmark–Norway, the Kingdom of Sweden, the Union of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and the Kingdom of Poland.During the period 1558–1578,...
, Livonia fell to the Grand Duchy of Lithuania
Grand Duchy of Lithuania
The Grand Duchy of Lithuania was a European state from the 12th /13th century until 1569 and then as a constituent part of Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth until 1791 when Constitution of May 3, 1791 abolished it in favor of unitary state. It was founded by the Lithuanians, one of the polytheistic...
with vassal dependency from Lithuania. Eight years later, in 1569, when the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and Kingdom of Poland formed Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, Livonia became a joint domain administered directly by the king and grand duke.
Having rejected peace proposals from its enemies, Ivan the Terrible found himself in a difficult position by 1579, when Crimean Khanate
Crimean Khanate
Crimean Khanate, or Khanate of Crimea , was a state ruled by Crimean Tatars from 1441 to 1783. Its native name was . Its khans were the patrilineal descendants of Toqa Temür, the thirteenth son of Jochi and grandson of Genghis Khan...
devastated Muscovian territories and burnt down Moscow
Moscow
Moscow is the capital, the most populous city, and the most populous federal subject of Russia. The city is a major political, economic, cultural, scientific, religious, financial, educational, and transportation centre of Russia and the continent...
(see Russo-Crimean Wars
Russo-Crimean Wars
The Russo-Crimean Wars were fought between the forces of the Muscovy and the invading Tatars of the Crimean Khanate.-History:...
), the drought
Drought
A drought is an extended period of months or years when a region notes a deficiency in its water supply. Generally, this occurs when a region receives consistently below average precipitation. It can have a substantial impact on the ecosystem and agriculture of the affected region...
and epidemics have fatally affected the economy, Oprichnina
Oprichnina
The oprichnina is the period of Russian history between Tsar Ivan the Terrible's 1565 initiation and his 1572 disbanding of a domestic policy of secret police, mass repressions, public executions, and confiscation of land from Russian aristocrats...
had thoroughly disrupted the government, while The Grand Principality of Lithuania had united with
Union of Lublin
The Union of Lublin replaced the personal union of the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania with a real union and an elective monarchy, since Sigismund II Augustus, the last of the Jagiellons, remained childless after three marriages. In addition, the autonomy of Royal Prussia was...
The Kingdom of Poland (1385–1569)
Kingdom of Poland (1385–1569)
The Kingdom of Poland of the Jagiellons was the Polish state created by the accession of Jogaila , Grand Duke of Lithuania, to the Polish throne in 1386. The Union of Krewo or Krėva Act, united Poland and Lithuania under the rule of a single monarch...
and acquired an energetic leader, Stefan Batory
Stefan Batory
Stephen Báthory was a Hungarian noble Prince of Transylvania , then King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania . He was a member of the Somlyó branch of the noble Hungarian Báthory family...
, supported by Ottoman Empire
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman EmpireIt was usually referred to as the "Ottoman Empire", the "Turkish Empire", the "Ottoman Caliphate" or more commonly "Turkey" by its contemporaries...
(1576). Stefan Batory replied with a series of three offensives
Offensive (military)
An offensive is a military operation that seeks through aggressive projection of armed force to occupy territory, gain an objective or achieve some larger strategic, operational or tactical goal...
against Muscovy, trying to cut The Kingdom of Livonia
Kingdom of Livonia
The Kingdom of Livonia was a nominal state in what is now the territory of the present-day Estonia and Latvia, declared as such by Ivan IV during the Livonian War but never properly established. On June 10, 1570 the Danish Duke Magnus of Holstein arrived in Moscow where he was crowned King of Livonia...
from Muscovian territories. During his first offensive in 1579, with 22,000 men, he retook Polotsk
Polatsk
Polotsk , is a historical city in Belarus, situated on the Dvina river. It is the center of Polotsk district in Vitsebsk Voblast. Its population is more than 80,000 people...
; during the second, in 1580, with 29,000-strong army, he took Velikie Luki, and in 1581 with a 100,000-strong army he started the Siege of Pskov
Siege of Pskov
The Siege of Pskov, known as the Pskov Defense in Russia took place between August of 1581 and February of 1582, when the army of the Polish king and Grand Duke of Lithuania Stefan Batory laid an unsuccessful siege and successful blockade of the city of Pskov during the final stage of the Livonian...
. Frederick II of Denmark and Norway had trouble continuing the fight against Muscovy unlike Sweden
Swedish Empire
The Swedish Empire refers to the Kingdom of Sweden between 1561 and 1721 . During this time, Sweden was one of the great European powers. In Swedish, the period is called Stormaktstiden, literally meaning "the Great Power Era"...
and Poland. He came to an agreement with John III
John III of Sweden
-Family:John married his first wife, Catherine Jagellonica of Poland , house of Jagiello, in Vilnius on 4 October 1562. In Sweden, she is known as Katarina Jagellonica. She was the sister of king Sigismund II Augustus of Poland...
in 1580 giving him the titles in Livonia. That war would last from 1577 to 1582. Muscovy recognized Polish–Lithuanian control of Ducatus Ultradunensis only in 1582. After Magnus von Lyffland died in 1583, Poland invaded his territories in The Duchy of Courland and Frederick II decided to sell his rights of inheritance
Inheritance
Inheritance is the practice of passing on property, titles, debts, rights and obligations upon the death of an individual. It has long played an important role in human societies...
. Except for the island of Œsel, Denmark
Denmark
Denmark is a Scandinavian country in Northern Europe. The countries of Denmark and Greenland, as well as the Faroe Islands, constitute the Kingdom of Denmark . It is the southernmost of the Nordic countries, southwest of Sweden and south of Norway, and bordered to the south by Germany. Denmark...
was out of the Baltic
Baltic region
The terms Baltic region, Baltic Rim countries, and Baltic Rim refer to slightly different combinations of countries in the general area surrounding the Baltic Sea.- Etymology :...
by 1585. As of 1598 Inflanty Voivodeship was divided onto:
- Wenden VoivodeshipWenden VoivodeshipWenden Voivodeship was a unit of administrative division and local government in the Duchy of Livonia, part of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, since it was formed in 1598 till the Swedish conquest of Livonia in the 1620s...
(województwo wendeńskie, Kieś) - Dorpat VoivodeshipDorpat VoivodeshipThe Dorpat Voivodeship was a unit of administrative division and local government in the Duchy of Livonia, part of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, from 1598 till the Swedish conquest of Livonia in the 1620s.The seat of the voivode was Dorpat...
(województwo dorpackie, Dorpat) - Parnawa VoivodeshipParnawa VoivodeshipThe Parnawa Voivodeship was a unit of administrative division and local government in the Duchy of Livonia, part of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, since it was formed in 1598 till the Swedish conquest of Livonia in the 1620s....
(województwo parnawskie, Parnawa)
Based on a guarantee by Sigismund II Augustus from the 1560s, the German language retained its official status.
Kingdom of Livonia 1570-1578
The armies of Ivan the TerribleIvan IV of Russia
Ivan IV Vasilyevich , known in English as Ivan the Terrible , was Grand Prince of Moscow from 1533 until his death. His long reign saw the conquest of the Khanates of Kazan, Astrakhan, and Siberia, transforming Russia into a multiethnic and multiconfessional state spanning almost one billion acres,...
were initially successful, taking Polock (1563) and Parnawa (1575) and overrunning much of Grand Duchy of Lithuania up to Vilnius
Vilnius
Vilnius is the capital of Lithuania, and its largest city, with a population of 560,190 as of 2010. It is the seat of the Vilnius city municipality and of the Vilnius district municipality. It is also the capital of Vilnius County...
. Eventually, Grand Duchy of Lithuania and Kingdom of Poland formed Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth in 1569 under the Union of Lublin
Union of Lublin
The Union of Lublin replaced the personal union of the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania with a real union and an elective monarchy, since Sigismund II Augustus, the last of the Jagiellons, remained childless after three marriages. In addition, the autonomy of Royal Prussia was...
. Eric XIV of Sweden
Eric XIV of Sweden
-Family and descendants:Eric XIV had several relationships before his marriage. With Agda Persdotter he had four daughters:#Margareta Eriksdotter , married 1592 to Olov Simonsson, vicar of Horn....
did not like this and The Northern Seven Years' War
Northern Seven Years' War
The Northern Seven Years' War was the war between Kingdom of Sweden and a coalition of Denmark–Norway, Lübeck and the Polish–Lithuanian union, fought between 1563 and 1570...
between Free City of Lübeck, Denmark, Poland, and Sweden broke out. While only losing land and trade, Frederick II of Denmark
Frederick II of Denmark
Frederick II was King of Denmark and Norway and duke of Schleswig from 1559 until his death.-King of Denmark:Frederick II was the son of King Christian III of Denmark and Norway and Dorothea of Saxe-Lauenburg. Frederick II stands as the typical renaissance ruler of Denmark. Unlike his father, he...
and Magnus von Lyffland of Œsel-Wiek
Bishopric of Ösel-Wiek
The Bishopric of Ösel–Wiek was a semi-independent Roman Catholic prince-bishopric in what is now Saare, Hiiu and Lääne counties of Estonia.The bishopric was created as a state of Holy Roman Empire on 1 October 1228, by Henry, King of the Romans...
were not faring well. But in 1569, Erik XIV became insane and his brother John III of Sweden
John III of Sweden
-Family:John married his first wife, Catherine Jagellonica of Poland , house of Jagiello, in Vilnius on 4 October 1562. In Sweden, she is known as Katarina Jagellonica. She was the sister of king Sigismund II Augustus of Poland...
took his place. After all parties had been financially drained, Frederick II let his ally, King Zygmunt II August
Sigismund II Augustus
Sigismund II Augustus I was King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania, the only son of Sigismund I the Old, whom Sigismund II succeeded in 1548...
, know that he was ready for peace. On December 15, 1570, the Treaty of Stettin was concluded.
Gdansk
Gdańsk is a Polish city on the Baltic coast, at the centre of the country's fourth-largest metropolitan area.The city lies on the southern edge of Gdańsk Bay , in a conurbation with the city of Gdynia, spa town of Sopot, and suburban communities, which together form a metropolitan area called the...
in Polish historiography), and during the reign of Stefan Batory
Stefan Batory
Stephen Báthory was a Hungarian noble Prince of Transylvania , then King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania . He was a member of the Somlyó branch of the noble Hungarian Báthory family...
in Poland invaded Livonia, quickly taking almost the entire territory, with the exception of Riga
Riga
Riga is the capital and largest city of Latvia. With 702,891 inhabitants Riga is the largest city of the Baltic states, one of the largest cities in Northern Europe and home to more than one third of Latvia's population. The city is an important seaport and a major industrial, commercial,...
and Rewel. In 1578, Magnus of Livonia
Magnus of Livonia
Magnus of Holstein was a Prince of Denmark and a member of the House of Oldenburg. As a vassal of Ivan IV of Russia, he was the titular King of Livonia from 1570 to 1578.-Early life:...
recognized the sovereignty
Sovereignty
Sovereignty is the quality of having supreme, independent authority over a geographic area, such as a territory. It can be found in a power to rule and make law that rests on a political fact for which no purely legal explanation can be provided...
of Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth (not ratified
Ratification
Ratification is a principal's approval of an act of its agent where the agent lacked authority to legally bind the principal. The term applies to private contract law, international treaties, and constitutionals in federations such as the United States and Canada.- Private law :In contract law, the...
by the Sejm
Sejm
The Sejm is the lower house of the Polish parliament. The Sejm is made up of 460 deputies, or Poseł in Polish . It is elected by universal ballot and is presided over by a speaker called the Marshal of the Sejm ....
of Poland-Lithuania, or recognized by Denmark). The Kingdom of Livonia was beaten back by Muscovy on all fronts. In 1578, Magnus of Livonia retired to The Bishopric of Courland
Bishopric of Courland
The Bishopric of Courland was the second smallest ecclesiastical state in the Livonian Confederation founded in the aftermath of the Livonian Crusade...
and his brother all but gave up the land in Livonia.
Swedish Livonia 1629-1721
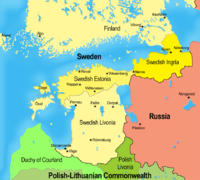
Swedish Empire
The Swedish Empire refers to the Kingdom of Sweden between 1561 and 1721 . During this time, Sweden was one of the great European powers. In Swedish, the period is called Stormaktstiden, literally meaning "the Great Power Era"...
was given roughly the same area as the former Duchy of Livonia after the 1626-1629 Polish–Swedish War
Polish–Swedish War (1626–1629)
The Polish–Swedish War of 1626–1629 was the fourth stage in a series of conflicts between Sweden and Poland fought in the 17th century...
. The area, usually known as Swedish Livonia
Swedish Livonia
- Swedish infantry and cavalry regiments:Infantry regiments:* Garnisonsregementet i Riga * Guvenörsregementet i Riga * Livländsk infanteribataljon I...
, became a very important Swedish dominion, with Riga being the second largest Swedish city and Livonia paying for one third of the Swedish war costs. Sweden lost Swedish Livonia, Swedish Estonia
Swedish Estonia
The Duchy of Estonia , also known as Swedish Estonia, was a dominion of the Swedish Empire from 1561 until 1721, when it was ceded to Russia in the Treaty of Nystad, following its capitulation in the Great Northern War. The dominion arose when the northern parts of present-day Estonia were united...
and Ingria
Ingria
Ingria is a historical region in the eastern Baltic, now part of Russia, comprising the southern bank of the river Neva, between the Gulf of Finland, the Narva River, Lake Peipus in the west, and Lake Ladoga and the western bank of the Volkhov river in the east...
to Russia
Russia
Russia or , officially known as both Russia and the Russian Federation , is a country in northern Eurasia. It is a federal semi-presidential republic, comprising 83 federal subjects...
almost 100 years later, by the Capitulation of Estonia and Livonia
Capitulation of Estonia and Livonia
With the Capitulation of Estonia and Livonia in 1710 the Swedish dominions Estonia and Livonia were integrated into the Russian Empire following their conquest during the Great Northern War...
in 1710 and the Treaty of Nystad
Treaty of Nystad
The Treaty of Nystad was the last peace treaty of the Great Northern War. It was concluded between the Tsardom of Russia and Swedish Empire on 30 August / 10 September 1721 in the then Swedish town of Nystad , after Sweden had settled with the other parties in Stockholm and Frederiksborg.During...
in 1721.
Livonian Voivodeship 1620s-1772
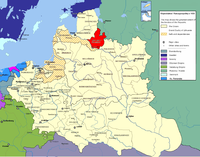
Inflanty
Inflanty is the Polish name for Livonia.Inflanty may also refer to*the Inflanty Voivodeship, also known as Polish Livonia.*the Principality of Inflanty, also known as the Duchy of Livonia....
, part of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, since it was formed in the 1620s out of the Wenden Voivodeship
Wenden Voivodeship
Wenden Voivodeship was a unit of administrative division and local government in the Duchy of Livonia, part of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, since it was formed in 1598 till the Swedish conquest of Livonia in the 1620s...
till the First Partition of Poland
Partitions of Poland
The Partitions of Poland or Partitions of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth took place in the second half of the 18th century and ended the existence of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, resulting in the elimination of sovereign Poland for 123 years...
in 1772.
Inflanty 1660-1772
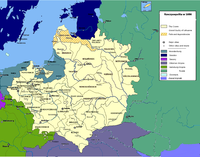
Treaty of Oliva
The Treaty or Peace of Oliva of 23 April /3 May 1660 was one of the peace treaties ending the Second Northern War...
in 1660 was known as Polish Livonia, or Inflanty Voivodeship. It consisted mainly of the southern Latvian region Latgale
Latgale
Latgale is one of the four historical and cultural regions of Latvia recognised in the Constitution of the Latvian Republic. It is the easternmost region north of the Daugava River...
within the Inflanty Voivodeship with the capital of Daugavpils
Daugavpils
Daugavpils is a city in southeastern Latvia, located on the banks of the Daugava River, from which the city gets its name. Daugavpils literally means "Daugava Castle". With a population of over 100,000, it is the second largest city in the country after the capital Riga, which is located some...
, or Dyneburg. This division of Livonia was codified in the Treaty of Oliva in 1660.
Riga Governorate 1721-1796
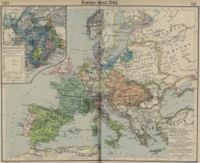
Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was a state that existed from 1721 until the Russian Revolution of 1917. It was the successor to the Tsardom of Russia and the predecessor of the Soviet Union...
conquered Swedish Livonia during the course of the Great Northern War
Great Northern War
The Great Northern War was a conflict in which a coalition led by the Tsardom of Russia successfully contested the supremacy of the Swedish Empire in northern Central Europe and Eastern Europe. The initial leaders of the anti-Swedish alliance were Peter I the Great of Russia, Frederick IV of...
and acquired the province in the Capitulation of Estonia and Livonia
Capitulation of Estonia and Livonia
With the Capitulation of Estonia and Livonia in 1710 the Swedish dominions Estonia and Livonia were integrated into the Russian Empire following their conquest during the Great Northern War...
in 1710, confirmed by the Treaty of Nystad
Treaty of Nystad
The Treaty of Nystad was the last peace treaty of the Great Northern War. It was concluded between the Tsardom of Russia and Swedish Empire on 30 August / 10 September 1721 in the then Swedish town of Nystad , after Sweden had settled with the other parties in Stockholm and Frederiksborg.During...
in 1721. Peter the Great confirmed German as the exclusive official language. Russia then added Polish Livonia in 1772 during the Partitions of Poland
Partitions of Poland
The Partitions of Poland or Partitions of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth took place in the second half of the 18th century and ended the existence of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, resulting in the elimination of sovereign Poland for 123 years...
.
Governorate of Livonia 1796-1918
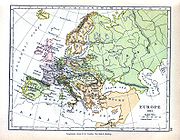
World War I
World War I , which was predominantly called the World War or the Great War from its occurrence until 1939, and the First World War or World War I thereafter, was a major war centred in Europe that began on 28 July 1914 and lasted until 11 November 1918...
, when it was split between the newly independent states of Latvia and Estonia. In 1918–1920, both Soviet troops and German Freikorps
Freikorps
Freikorps are German volunteer military or paramilitary units. The term was originally applied to voluntary armies formed in German lands from the middle of the 18th century onwards. Between World War I and World War II the term was also used for the paramilitary organizations that arose during...
fought against Latvian and Estonian troops for control over Livonia, but their attempts were defeated.
Governors-General of Estonia, Livonia, and Courland 1845-1876
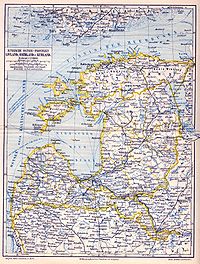
Governorate of Estonia
The Governorate of Estonia or Estland, also known as the Government of Estonia or Province of Estonia, was a governorate of the Russian Empire in what is now northern Estonia.-Historical overview:...
, Livonia, and Courland
Courland Governorate
Courland Governorate, also known as the Province of Courland, Governorate of Kurland , and Government of Courland , was one of the Baltic governorates of the Russian Empire, that is now part of the Republic of Latvia....
—an area roughly corresponding to the historical medieval Livonia —were administratively subordinated to a common Governor-General
Governor-General
A Governor-General, is a vice-regal person of a monarch in an independent realm or a major colonial circonscription. Depending on the political arrangement of the territory, a Governor General can be a governor of high rank, or a principal governor ranking above "ordinary" governors.- Current uses...
. Amongst the holders of this post were Count Alexander Arkadyevich Suvorov
Alexander Arkadyevich Suvorov
Alexander Arkadyevich Suvorov, Prince of Italy, Count Rymniksky was a Russian general, diplomat and politician.-Education:...
and Count Pyotr Andreyevich Shuvalov
Pyotr Andreyevich Shuvalov
Count Pyotr Andreyevich Shuvalov was an influential Russian statesman and a counselor to Tsar Alexander II...
.
Vidzeme in Independent Latvia 1918-1940

Latvia
Latvia , officially the Republic of Latvia , is a country in the Baltic region of Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by Estonia , to the south by Lithuania , to the east by the Russian Federation , to the southeast by Belarus and shares maritime borders to the west with Sweden...
between the World Wars, southern Livonia became an administrative region under the traditional Latvian name Vidzeme
Vidzeme
Vidzeme is one of the historical and cultural regions of Latvia. Literally meaning "the Middle Land" it is situated in north-central Latvia north of the Daugava River...
, encompassing the then much larger counties of Riga
Riga District
Riga District was an administrative division of Latvia, located in Semigallia and Vidzeme regions, in the centre of the country. The district had the two cities of Riga and Jūrmala with the Gulf of Riga to the north. Beginning from the west and counterclockwise to the east, Riga District had...
, Cēsis
Cesis District
Cēsis District was an administrative division of Latvia, located in the Vidzeme region, in the country's north-east. It bordered the former districts of Valmiera and Valka to the north, Limbaži and Riga to the west, Gulbene to the east, Ogre and Madona to the south. It was organized into two...
, Valmiera
Valmiera District
The Valmiera district was an administrative division of Latvia, located in the Vidzeme region, in the country's north-east. Its administrative center was Valmiera. It bordered Estonia to the north and the former districts of Limbaži to the west, Valka to the east and Cēsis to the south...
, and Valka
Valka District
Valka district was an administrative division of Latvia, located in Vidzeme region, in the country's north-east. The district's area was 2441 km2. The population was 31,314 inhabitants in 2008.The district contained 4 towns and 17 parishes...
.
Ostland 1941-1944
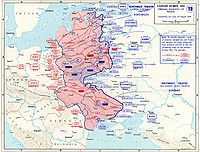
Reichsleiter
Reichsleiter , was the second highest political rank of the NSDAP next only to the office of Führer. Reichsleiter also served as a paramilitary rank, for the Nazi Party and was the highest position attainable in any Nazi-Organisation.The Reichsleiter reported directly to Adolf Hitler, in whose...
Alfred Rosenberg
Alfred Rosenberg
' was an early and intellectually influential member of the Nazi Party. Rosenberg was first introduced to Adolf Hitler by Dietrich Eckart; he later held several important posts in the Nazi government...
, Minister für die besetzten Ostgebiete (Reich Ministry for the Occupied Eastern Territories). The structure of the Reichskommissariats was defined by the same decree. Local administration in the Reichskommissariats was to be organized under a "National Director" (Reichskomissar) in Estonia, a "General Director" in Latvia and a "General Adviser" in Lithuania. The local administration of the Reichskommissariat Ostland was under Reichskomissar Hinrich Lohse
Hinrich Lohse
Hinrich Lohse was a Nazi German politician, best known for his World War II rule of the Baltic states.-Early life:...
. Below him there was an administrative hierarchy: a Generalkomissar led each Generalbezirke, Gebietskomissars and Hauptkommissars administered Kreigsbietes and Hauptgenbietes, respectively. Rosenberg's ministerial authority was, in practice, severely limited. The first reason was that many of the practicalities were commanded elsewhere: the Wehrmacht
Wehrmacht
The Wehrmacht – from , to defend and , the might/power) were the unified armed forces of Nazi Germany from 1935 to 1945. It consisted of the Heer , the Kriegsmarine and the Luftwaffe .-Origin and use of the term:...
and the SS
Schutzstaffel
The Schutzstaffel |Sig runes]]) was a major paramilitary organization under Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party. Built upon the Nazi ideology, the SS under Heinrich Himmler's command was responsible for many of the crimes against humanity during World War II...
managed the military and security aspects, Fritz Saukel (Reich Director of Labour) had control over manpower and working areas, Hermann Göring
Hermann Göring
Hermann Wilhelm Göring, was a German politician, military leader, and a leading member of the Nazi Party. He was a veteran of World War I as an ace fighter pilot, and a recipient of the coveted Pour le Mérite, also known as "The Blue Max"...
and Albert Speer
Albert Speer
Albert Speer, born Berthold Konrad Hermann Albert Speer, was a German architect who was, for a part of World War II, Minister of Armaments and War Production for the Third Reich. Speer was Adolf Hitler's chief architect before assuming ministerial office...
had total management of economic aspects in the territories and the Reich postal service administered the East territories' postal services. These German central government interventions in the affairs of Ostland, overriding the appropriate ministries was known as "Sonderverwaltungen" (special administration). Later, from September, the civil administration that had been decreed in the previous July was actually set up. Lohse and, for that matter, Koch would not bow to his authority seeking to administer their territories with the independence and authority of gauleiters. on 1 April 1942 an arbeitsbereich (lit. "working sphere", a name for the party cadre organisation outside the reich proper) was established in the civil administration part of the occupied Soviet territories, whereupon Koch and Lohse gradually ceased communication with him preferring to deal directly with Hitler through Martin Bormann
Martin Bormann
Martin Ludwig Bormann was a prominent Nazi official. He became head of the Party Chancellery and private secretary to Adolf Hitler...
and the party chancellery. In the process they also displaced all other actors including notably the SS, except in central Belarus where HSSPF 'Erich von dem Bach-Zelewsky had a special command encompassing both military and civil administration territories and engaged in "anti-partisan" atrocities.
Baltic countries since 1990
The historical land of Livonia has been split between LatviaLatvia
Latvia , officially the Republic of Latvia , is a country in the Baltic region of Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by Estonia , to the south by Lithuania , to the east by the Russian Federation , to the southeast by Belarus and shares maritime borders to the west with Sweden...
and Estonia
Estonia
Estonia , officially the Republic of Estonia , is a state in the Baltic region of Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland, to the west by the Baltic Sea, to the south by Latvia , and to the east by Lake Peipsi and the Russian Federation . Across the Baltic Sea lies...
ever since. The Livonian language
Livonian language
Livonian belongs to the Finnic branch of the Uralic languages. It is a nearly extinct language, with one of its last native speakers having died in February 2009. It is closely related to Estonian...
is spoken by fewer than 100 individuals as a second language, and is understood to be fast approaching extinction. The last native Livonian speaker died in February 2009.
The anthem (unofficial) of Livonians is Min izāmō, min sindimō sharing the melody of Finnish
Finland
Finland , officially the Republic of Finland, is a Nordic country situated in the Fennoscandian region of Northern Europe. It is bordered by Sweden in the west, Norway in the north and Russia in the east, while Estonia lies to its south across the Gulf of Finland.Around 5.4 million people reside...
and Estonia
Estonia
Estonia , officially the Republic of Estonia , is a state in the Baltic region of Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland, to the west by the Baltic Sea, to the south by Latvia , and to the east by Lake Peipsi and the Russian Federation . Across the Baltic Sea lies...
n anthems.
See also
|
History of Estonia Estonia was settled near the end of the last glacial era, beginning from around 8500 BC. Before the German invasions in the 13th century proto-Estonians of the Ancient Estonia worshipped the spirits of nature... History of Latvia The History of Latvia began when the area which is today Latvia was settled following the end of the last glacial period, around 9000 BC. Ancient Baltic peoples appeared during the second millennium BC and four distinct tribal realms in Latvia's territories were identifiable towards the end of the... History of Lithuania The history of Lithuania dates back to at least 1009, the first recorded written use of the term. Lithuanians, a branch of the Baltic peoples, later conquered neighboring lands, establishing the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and in the 13th century the short-lived Kingdom of Lithuania. The Grand Duchy... History of Poland The History of Poland is rooted in the arrival of the Slavs, who gave rise to permanent settlement and historic development on Polish lands. During the Piast dynasty Christianity was adopted in 966 and medieval monarchy established... |
External links
|
|

