
Anglo-French relations
Encyclopedia
United Kingdom – French relations are the relations between the governments of France
and the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland
(UK). In recent years the two countries have experienced a very close relationship.
The designation "Anglo-" specifically refers to England, not the UK. However, modern intergovernmental relations between these two nations are habitually called Anglo-French relations, and understood to refer to the UK and not only England. The term Franco-British relations is also used.
Early Franco-British interactions occurred before Caesar's invasion of Gaul, when the two regions were inhabited by loosely trading Celts fighting the Romans as a common enemy. They continued under the Roman Empire
as both modern day states were ruled from Rome. Both were provinces in the larger Roman Empire.
Recently relations have been cordial and cooperative, with an edge of wariness on both sides due to historical differences and more recent disagreements between two of the leaders of the two countries: former French President, Jacques Chirac
, and former British Prime Minister, Tony Blair
. French author Jose-Alain Fralon characterised the relationship between the countries by describing the British as "our most dear enemies". Tony Blair is regarded as being a francophile
by the French media and the current French President Nicolas Sarkozy
is known for his will to transform the "Entente Cordiale" into an "Entente amicale" (that is, a friendlier and closer relation).
Much of the two countries' histories has been defined by the relationship between the two countries. Today, both France and the United Kingdom are member states of the European Union
(EU), and it is estimated that about 400,000 French people live in the UK, and vice versa.
invaded Gaul
, he encountered allies of the Gauls and Belgae
from southeastern Britain offering assistance, some of whom even acknowledged the king of the Belgae as their sovereign.
Although all peoples concerned were Celts (and the Germanic
Angles and Franks had not yet invaded either country that would later bear their names), this could arguably be seen as the first major example of Anglo-French cooperation in recorded history. As a consequence, Caesar felt compelled to invade in an attempt to subdue Britain.
For the next five hundred years, there was much interaction between the two regions, as both Britain and France were under Roman rule. This was followed by another five hundred years with very little interaction between the two, as both were invaded by different Germanic
tribes. At the turn of the second millennium, the British Isles
were primarily involved with the Scandinavia
n world, while France's main foreign relationship was with the Holy Roman Empire
.
, who were of Viking stock, invaded England under their duke William the Conqueror and took over following the Battle of Hastings
in 1066, and crowned themselves Kings of England.
The Norman feudal culture took root in England, and for the next 150 years England was generally considered of secondary importance to the dynasty's Continental territories. The language of the aristocracy
was French. To this day the coat of arms
of the United Kingdom reads 'Dieu et mon Droit' ('God and my right'). Scotland
, Wales and Ireland gradually also were summed into this new influence.
The first Norman kings were also the Dukes of Normandy
, so relations were somewhat complicated between the countries. Though they were dukes ostensibly under the king of France, their higher level of organisation in Normandy gave them more de facto power. In addition, they were kings of England in their own right; England was not officially a province of France, nor even, officially at least, a province of Normandy.
, half of France was under Angevin control as well as all of England. However, almost all of the Angevin empire was lost to Philip II of France
under Richard the Lionheart, John and Henry III of England. This finally gave the English a separate identity as an Anglo-Saxon people under a Francophone, but not French, crown.
While the English and French had been frequently acrimonious, they had always had a common culture and little fundamental difference in identity. Nationalism had been minimal in days when most wars took place between rival feudal lords on a sub-national scale. The last attempt to unite the two cultures under such lines was probably a failed French-supported rebellion to depose Edward II. It was also during the Middle Ages that a Franco-Scottish alliance, known as the Auld Alliance
was signed by King John of Scotland
and Philip IV of France
.
 The English monarchy increasingly integrated with its subjects and turned to the English language wholeheartedly during the Hundred Years' War
The English monarchy increasingly integrated with its subjects and turned to the English language wholeheartedly during the Hundred Years' War
between 1337 and 1453. Though the war was in principle a mere dispute over territory, it drastically changed societies on both sides of the Channel. The English, although already politically united, for the first time found pride in their language and identity, while the French united politically.
Several of the most famous Anglo-French battles took place during the Hundred Years' War: Crécy
, Poitiers
, Agincourt
, Orléans
, and Paris. Major sources of French pride stemmed from their leadership during the war. Bertrand du Guesclin
was a brilliant tactician who forced the English out of the lands they had procured at the Treaty of Brétigny
, a compromising treaty that most Frenchmen saw as a humiliation. Joan of Arc
was another unifying figure who to this day represents a combination of religious fervour and French patriotism to all France. After her inspirational victory at Orléans and what many saw as Joan's martyrdom at the hands of Burgundians and Englishmen, Jean de Dunois
eventually forced the English out of all of France except Calais
, which was only lost in 1558. Apart from setting national identities, the Hundred Years' War is often cited as the root of the traditional rivalry and at times hatred between the two countries.
During this era, the English lost their last territories in France, except Calais, though the English monarchs continued to style themselves as Kings of France until 1800.
agreed to defend each other in the event of an attack on either from England in several treaties
, the most notable of which were in 1327 and 1490. There had always been intermarriage between the Scottish and French royal households, but this solidified the bond between the royals even further.
 The English and French were engaged in numerous wars in the following centuries. They took opposite sides in all of the Italian Wars
The English and French were engaged in numerous wars in the following centuries. They took opposite sides in all of the Italian Wars
between 1494 and 1559.
An even deeper division set in during the English Reformation
, when most of England converted to Protestantism and France remained Roman Catholic. This enabled each side to see the other as not only a foreign evil but also a heretical one. In both countries there was intense civil religious conflict. Because of the oppression by Roman Catholic King Louis XIII of France
, many Protestant Huguenots fled to England. Similarly, many Catholics fled from England to France.
Henry VIII of England
had initially sought an alliance with France, and the Field of the Cloth of Gold
saw a face to face meeting between him and King Francis I of France
.
in the sixteenth and early seventeenth centuries, the English had often sided with France as a counterweight against them. This design was intended to keep a European balance of power
, and prevent one country gaining overwhelming supremacy. Key to English strategy, was the fear that a universal monarchy
of Europe would be able to overwhelm the British Isles
.
Following the Treaty of Westphalia in 1648, as Spain's power weakened, France began to take on a more assertive role under King Louis XIV of France
with an expansionist policy both in Europe and across the globe. English foreign policy was now directed towards preventing France gaining supremacy on the continent and creating a universal monarchy. To the French, England was an isolated and piratical nation heavily reliant on naval power, and particularly privateers, which they referred to as Perfidious Albion
.
There was a sharp diversion in political philosophies in the two states. In England King Charles I
had been executed during the English Civil War
for exceeding his powers, and later King James II
had been overthrown in the Glorious Revolution
. In France the power of the monarchs and their advisors went largely unchecked.
England
and France
fought each other in the War of the League of Augsburg from 1688 to 1697 which set the pattern for relations between France and Great Britain during the eighteenth century. Wars were fought intermittently, with each nation part of a constantly shifting pattern of alliances known as the stately quadrille
.
.svg.png) Partly out of fear of a continental intervention an Act of Union was passed in 1707 creating the Kingdom of Great Britain
Partly out of fear of a continental intervention an Act of Union was passed in 1707 creating the Kingdom of Great Britain
, formally merging the kingdoms of Scotland
and England
(of which Wales
was a part). While the new Britain grew increasingly parliamentarian
, France continued its system of absolute monarchy
.
The newly united Britain fought France in the War of the Spanish Succession
from 1702 to 1713, and the War of the Austrian Succession
from 1740 to 1748, attempting to maintain the balance of power in Europe. The British had a massive navy but maintained a small land army, so Britain always acted on the continent in alliance with other states such as Prussia
and Austria
as they were unable to fight France alone. Equally France, lacking a superior navy, was unable to ever launch a successful invasion of Britain.
France lent support to the Jacobite
pretenders who claimed the British throne, hoping that a restored Jacobite monarchy would be inclined to be more pro-French. Despite this support the Jacobites failed to overthrow the Hanoverian
monarchs.
As the century wore on, there was a distinct passage of power to Britain and France, at the expense of traditional major powers such as Portugal
, Spain and the Dutch Republic
. Some observers saw the frequent conflicts between the two states during the eighteenth century as a battle for control of Europe, though most of these wars ended without a conclusive victory for either side. France largely had greater influence on the continent while Britain posed dominant at sea and trade threatening French colonies abroad.
increasingly became a battleground between the two powers. The Western Design of Oliver Cromwell
intended to build up an increasing British presence in North America, beginning with the acquisition of Jamaica
from the Spanish Empire
in 1652. The first British settlement on continental North America was founded in 1603, by the 1760s these had grown into thirteen separate colonies
.
The French had settled the province of Canada to the North, and controlled Saint-Domingue
in the Caribbean, the wealthiest colony in the world. Both countries, recognising the potential of India, established trading post
s there. Wars between the two states increasingly took place in these other continents, as well as Europe.
 The French and British fought each other and made treaties with Native American
The French and British fought each other and made treaties with Native American
tribes to gain control of North America. Both nations coveted the Ohio Territory and in 1753 a British expedition there led by George Washington
clashed with a French force. Shortly afterwards the French and Indian War
broke out, initially taking place only in North America but in 1756 becoming part of the wider Seven Years' War
in which Britain and France were part of opposing coalitions.
The war was described by Winston Churchill
as the first "world war
", because fighting took place on several different continents. In 1759 the British enjoyed victories over the French in Europe, Canada and India, severely weakening the French position around the world. In 1762 the British captured the cities of Manila
and Havana
from Spain, France's strongest ally, which led ultimately to a peace settlement
the following year that saw a large number of territories come under British control.
The Seven Years' War is regarded as a critical moment in the history of Anglo-French relations, which laid the foundations for the dominance of the Anglosphere
during the next two and a half centuries, and arguably the spread of democracy and English common law
.
 In 1778 France, hoping to capitalise on the British defeat at Saratoga and fearing a rapprochement between the British and the Americans, entered the war and in 1779 persuaded their Spanish allies to do likewise. France despatched troops to fight alongside the American rebels, and besieged Gibraltar
In 1778 France, hoping to capitalise on the British defeat at Saratoga and fearing a rapprochement between the British and the Americans, entered the war and in 1779 persuaded their Spanish allies to do likewise. France despatched troops to fight alongside the American rebels, and besieged Gibraltar
with Spain. Plans were drawn up, but never put into action, to launch an invasion of England.
The British were forced to withdraw forces from the American mainland to protect their more valuable possessions in the West Indies. While the French were initially unable to break the string of British victories, the combined actions of a French fleet and army, forced the British into a decisive surrender at Yorktown
in 1781.
In 1783 the French-led alliance managed to gain a number of concessions out of the British at the Treaty of Paris
most notably the recognition of American independence. For a brief period after the war, Britain's naval power was subdued by an alliance between France and Spain.
The crippling debts incurred by France during the war, and the cost of rebuilding the French navy during the 1780s caused a financial crisis, leading directly to the French Revolution
of 1789. The loss of the colonies was taken by some, such as the Emperor Joseph II
of Austria, to mark the end of Britain as a major power.

During the French Revolution
, the anti-monarchical ideals of France were regarded with alarm throughout Europe. While France was plunged into chaos, Britain took advantage of its temporary weakness to stir up the civil war occurring in France
and build up its naval forces. The Revolution was initially popular with many Britons, both because it appeared to weaken France and was perceived to be based on British liberal ideals. This began to change as the Jacobin
faction took over, and began the Reign of Terror
.
The French were intent on spreading their revolutionary republicanism to other European states, including Britain. The British initially stayed out of the alliances of European states which unsuccessfully attacked France trying to restore the monarchy. In France a new, strong nationalism took hold enabling them to mobilise large and motivated forces.
Following the execution of King Louis XVI of France
in 1793, Britain declared war on France. Except for a brief pause in the fighting from 1802–03
, the war lasted continuously for twenty one years. During this time Britain raised several coalitions against the French, continually subsidising other European states with the Golden Cavalry of St George
, enabling them to put large armies in the field. In spite of this, the French armies were very successful on land, creating several client states such as the Batavian Republic
, and the British devoted much of their own forces to campaigns against the French in the Caribbean, with mixed results.
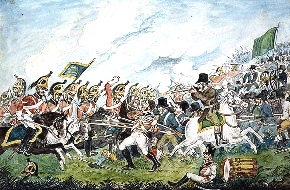
, where they were joined by thousands of rebels but defeated by British and Irish loyalist
forces. The fear of further attempts to create a French satellite in Ireland, led to the Act of Union merging of the crowns of Great Britain and Ireland to create the United Kingdom in 1801.

came to power in France, ending the revolutionary era and creating a dictatorship (crowning himself Emperor
in 1804). After he had triumphed on the European continent against the other major European powers, Napoleon contemplated an invasion of the British mainland, but was dissuaded by an Austrian
attack over its Bavaria
n allies.
In response Napoleon established a continental system
by which no nation was permitted to trade with the British. Napoleon hoped the embargo would isolate the British Isles
severely weakening them, but a number of countries continued to trade with them in defiance of the policy. In spite of this, the Napoleonic influence stretched across much of Europe.
In 1808 French forces invaded Portugal trying to attempt to halt trade with the United Kingdom, turning Spain into a satellite state
in the process. The British responded by dispatching a force under Sir Arthur Wellesley
which captured Lisbon. Napoleon dispatched increasing forces into the Iberian Peninsula
, which became the key battleground between the two nations. Allied with Spanish and Portuguese forces, the British inflicted a number of defeats on the French, confronted with a new kind of warfare called "guerrilla" which led Napoleon to brand it the "Spanish Ulcer". Allied to an increasingly resurgent European coalition, the British invaded southern France forcing Napoleon to abdicate and go into exile on Elba
in 1814.
 After escaping and briefly threatening to restore the French Empire, Napoleon was defeated by combined British, German and Dutch forces at Battle of Waterloo
After escaping and briefly threatening to restore the French Empire, Napoleon was defeated by combined British, German and Dutch forces at Battle of Waterloo
. With strong British support, the Bourbon
monarchy was restored and Louis XVIII was crowned King of France. The Napoleonic era
was the last occasion on which Britain and France went to war with each other, but by no means marked the end of the rivalry between the two nations. Despite his final defeat, Napoleon continues to be regarded as a national hero figure in France for his numerous victories over coalised monarchies.
 Despite having entered the Napoleonic era
Despite having entered the Napoleonic era
regarded by many as a spent force, the UK had emerged from the 1815 Congress of Vienna
as one of the leading financial, military and cultural powers of the world. France also recovered from the defeat at Waterloo
to quickly retake its position on the world stage.
Despite their historic enmity, the British and French eventually became strained political allies, as both began to turn their attentions to acquiring new territories beyond Europe. The British developed India and Canada and settled Australia, spreading their powers to several different continents as the Second British Empire.
They frequently made stereotypical jokes about each other, and even side by side in war were critical of each other's tactics.
As a Royal Navy
officer said to the French corsair
Robert Surcouf
"You French fight for money, while we British fight for honour.", Surcouf
replied "Sir, a man fights for what he lacks the most." According to one story, a French diplomat once said to Lord Palmerston "If I were not a Frenchman, I should wish to be an Englishman"; to which Palmerston replied: "If I were not an Englishman, I should wish to be an Englishman." According to another, upon seeing the disastrous British Charge of the Light Brigade
in the Crimean War
against Russia, French marshal Pierre Bosquet
said 'C'est magnifique, mais ce n'est pas la guerre.' ('It's magnificent, but it's not war.') Eventually, relations settled down as the two empires tried to consolidate themselves rather than extend themselves.
, and the Orléanist
Louis-Phillipe
subsequently ascended to the throne; by contrast, the reign of Queen Victoria
began in 1837 in a much more peaceful fashion. The major European powers—Russia
, Austria
, the UK, and to some extent Prussia
—were determined to keep France in check, and so France generally pursued a cautious foreign policy. Louis-Phillipe allied with Britain, the country with which France shared the most similar form of government, and its combative Foreign Secretary Lord Palmerston. In Louis-Philippe's first year in power, he refused to annex Belgium during its revolution
, instead following the British line of supporting independence. Despite posturings from leading French minister Adolphe Thiers
in 1839–1840 that France would protect the increasingly powerful Muhammad Ali of Egypt
(a viceroy of the Ottoman Empire
), any reinforcements were not forthcoming, and in 1840, much to France's embarrassment, Ali was forced to sign the Convention of London
by the powers. Relations cooled again under the governments of François Guizot
and Robert Peel
. They soured once more in 1844 though when, with Palmerston back as Foreign Secretary, the French government hastily agreed to have Isabella II of Spain
and her sister marry members of the Bourbon
and Orléanist dynasties, respectively. Palmerston had hoped to arrange a marriage, and "The Affair of the Spanish Marriages" has generally been viewed unfavourably by British historians ("By the dispassionate judgment of history it has been universally condemned"), although a more sympathetic view has been taken in recent years.
 Louis-Napoléon Bonaparte came to power in France in 1848 (elected by universal male suffrage in a presidential election
Louis-Napoléon Bonaparte came to power in France in 1848 (elected by universal male suffrage in a presidential election
), soon restoring the position of Emperor, as Napoleon III, which had been vacant since his uncle Napoleon I
. The new Emperor had an expansionist foreign policy, which saw the French deepen the colonisation of Africa
and establish new colonies, in particular Indochina
. The British were initially alarmed, and commissioned a series of forts in southern England designed to resist a French invasion.
Despite this Napoleon had a very pro-British foreign policy, and was eager not to displease the British government whose friendship he saw as important to France.
The expanding Russia and the prospect of a United Germany became greater concerns to the British, and the two nations worked together during the Crimean War
which aimed to curb Russia's expansion westwards. The two nations also co-operated during the Second Opium War
, dispatching a joint force to the Chinese capital Peking to agree a treaty with the Chinese Qing Dynasty
. In 1859 Napoleon, bypassing the Corps législatif
which he feared would not approve of free trade, met with influential reformer Richard Cobden
, and in 1860 the Cobden-Chevalier Treaty
was signed between the two countries, reducing tariffs on goods sold between the UK and France.
During the American Civil War
both nations remained neutral. France came close to entering on the side of the Confederate States of America
, but did not want to become involved without the support of the British, which was not forthcoming due to concerns over slavery
. France also attempted to gain British support for a scheme to put an Austrian Prince, Maximilian I
, on the throne of Mexico, but the British were not willing to support any action other than the collection of debts owed by the Mexicans. This forced to French to act alone in the French Intervention in Mexico
, which ultimately proved disastrous.
When Napoleon was overthrown in 1870, he fled to take refuge in England where he and his family lived in exile. The republic
which replaced his rule continued the warm relations with the UK, especially following the creation of the German Empire
, which they perceived as a serious threat.
when French troops tried to claim an area in the Southern Sudan, and a British force purporting to be acting in the interests of the Khedive of Egypt arrived. Under heavy pressure the French withdrew securing Anglo-Egyptian control over the area. The status quo
was recognised by an agreement between the two states acknowledging British control over Egypt, while France became the dominant power in Morocco
.
During the Scramble for Africa
the British and French generally recognised each other's spheres of influence. The Suez Canal
, initially built by the French, became a joint British-French project in 1875, as both saw it as vital to maintaining their influence and empires in Asia. In 1882, ongoing civil disturbances in Egypt (see Urabi Revolt
) prompted Britain to intervene, extending a hand to France. France's expansionist Prime Minister Jules Ferry
was out of office, and the Chamber of Deputies
was unwilling to send more than an intimidatory fleet to the region. The UK established a protectorate, as France had a year earlier in Tunisia
, and popular opinion in France later put this action down to duplicity. It was about this time that the two nations established co-ownership of Vanuatu
. The Anglo-French Convention of 1882
was also signed to resolve territory disagreements in western Africa.
 From about 1900, Francophiles in Britain and Anglophiles in France began to spread a study and mutual respect and love of the culture of the country on the other side of the English Channel
From about 1900, Francophiles in Britain and Anglophiles in France began to spread a study and mutual respect and love of the culture of the country on the other side of the English Channel
. Francophile and Anglophile societies developed, further introducing Britain to French food and wine, and France to English sports like rugby
. French and English were already the second languages of choice in Britain and France respectively. Eventually this developed into a political policy as the new united Germany was seen as a potential threat. Louis Blériot
, for example, crossed the Channel in an aeroplane in 1909. Many saw this as symbolic of the connection between the two countries. This period in the first decade of the 20th century became known as the Entente cordiale, and continued in spirit until the 1940s. Up to the 1920s, relations between the UK and France were arguably closer than those between the UK and the US.
after Belgium and a small part of northern France had been invaded by the German army
.
There was strong co-operation between the British and French forces. The battles took place on several different fronts, but most particularly to Anglo-French relations in the trenches in France and Belgium against the Germans. Unable to advance against the combined primary alliance powers of the British, French, and later American forces as well as the embargo of German controlled North Sea seaports, the Germans eventually surrendered after four years of heavy fighting.
 Following the war, at the Treaty of Versailles the British and French worked closely together, as their interests were largely similar. Both countries were interested in creating a weakened Germany, as opposed to a more moderate American position. Both were also keen to protect and expand their empires, in the face of calls for self-determination. On a visit to London, French leader Georges Clemenceau
Following the war, at the Treaty of Versailles the British and French worked closely together, as their interests were largely similar. Both countries were interested in creating a weakened Germany, as opposed to a more moderate American position. Both were also keen to protect and expand their empires, in the face of calls for self-determination. On a visit to London, French leader Georges Clemenceau
was hailed by the British crowds. Lloyd George
was given a similar reception in Paris.
Both states joined the League of Nations
, and both signed agreements of defence of several countries, most significantly Poland
. The Treaty of Sèvres
split the Middle East between the two states, in the form of mandates
. However the outlook of the nations were different during the inter-war years; while France saw itself inherently as a European power, the UK enjoyed close relationships with Australia, Canada and New Zealand and at one time flirted with the idea of Empire Free Trade, a form of protectionism
that would have seen large tariffs placed on goods from France.
 In contradiction to the German disarmament provisions of the Treaty of Versailles
In contradiction to the German disarmament provisions of the Treaty of Versailles
(1919), the Anglo-German Naval Agreement
was signed between the United Kingdom and the German Reich in 1935. This bilateral agreement, which allowed Hitler to reinforce his Kriegsmarine
, was regarded by the French as the ruining of the anti-Hitlerian Stresa front
.
In the years leading up to World War II, both countries followed a similar diplomatic path of appeasement
of Germany in Czechoslovakia
, despite a French military excursion there. As Nazi intentions became clear, France pushed for a harder line but the British demurred, believing diplomacy could solve the disputes.
After guaranteeing the independence of Poland, both declared war on Germany on the same day, the 3rd of September 1939, after the Germans ignored an ultimatum to withdraw from the country. When Germany began its attack on France in 1940, British troops and French troops again fought side by side. Eventually, after the Germans came through the Ardennes
, it became clear that France would not be able to fend off the German attack, and Winston Churchill
pledged that the United Kingdom would continue to fight for France's freedom, even if it must do so alone. The final bond between the two nations was so strong that members of the British cabinet had proposed a temporary union of the two countries for the sake of morale: the plan was drawn up by Jean Monnet
, who later created the Common Market
. The idea was not popular with a majority on either side, and the French government felt that, in the circumstances, the plan for union would reduce France to the level of a British Dominion. The proposal was turned down, shortly before France fell to the Germans. The Free French resistance, led by Charles de Gaulle
, were formed in London, after de Gaulle gave his famous 'Appeal of the 18th of June', widely broadcast by the BBC
.
 In southern France a collaborative government known as Vichy France
In southern France a collaborative government known as Vichy France
was set up, allied to Germany. The British were soon at war with the Vichy state, destroying much of its navy and moving into many of its colonies, such as Senegal
, on behalf of the Free French government.
Following D-Day
, relations between the two peoples were at a high, as the British were greeted as liberators. Following the surrender of Germany in 1945, the UK and France became close as both feared the Americans would withdraw from Europe leaving them vulnerable to the Soviet Union
's expanding communist bloc. The UK strongly advocated that France be given a zone of occupied Germany. Both states were amongst the five Permanent Members of the new UN Security Council, where they commonly collaborated.
, previously owned by an Anglo-French company, was nationalised by the Egyptian government. The British and the French were both strongly committed to taking the canal back by force. Both the British and French governments saw the actions of the Egypt president Gamal Abdel Nasser
as potentially dangerous to their interests in trade, and within the framework of the Cold War and the tensions of the newly independent. During the initial stages of the crisis, French Prime Minister Guy Mollet
proposed a union between Britain and France, but the British were less enthusiastic. British Prime Minister Anthony Eden
called it a "good idea in substance" but thought it "a bit premature".
The Americans, while opposed to Nasser, refused to become involved with what many regarded as European colonialism, putting severe strain on the Anglo-American special relationship
. The relations between Britain and France were not entirely harmonious, as the French kept the British in the dark about the involvement of Israel
until very close to the commencement of military operations.
was probably the last time that Anglo-French relations have been more comfortable than Anglo-American relations.
Immediately after the crisis Anglo-French relations started to sour again, only since the last few years of the 20th century have they begun to improve and climb towards the peak they did in the years between 1900 and 1940.
Shortly after this, France, West Germany
, Italy, Belgium
, the Netherlands
and Luxembourg
formed what would become the European Economic Community
and later the European Union
, and did not at first allow the UK to join. President Charles de Gaulle
's attempts to exclude the British from European affairs during the beginning of France's Fifth Republic are now seen by many in Britain to be a betrayal of the bond between the countries, and Anthony Eden
's exclusion of France from the commonwealth is seen in a similar light in France. The French partly feared that were the British to join the EEC they would attempt to dominate it.
Over the years, the UK and France have often taken diverging courses within the European Community. British policy has favoured an expansion of the Community and free trade
while France has advocated protectionism
and restricting membership of the Community to a core of Western European states.
, Charles de Gaulle
, the wartime leader of the Free French, returned to power in France. He created the Fifth French Republic, ending the post-war parliamentary system and replacing it with a strong Presidency, which became dominated by his followers—the Gaullists.
De Gaulle made ambitious changes to French foreign policy—first ending the war in Algeria, and then withdrawing France from the NATO command structure. De Gaulle declared a new policy of "in every direction", meaning that French military forces were prepared to fight a war against the UK and the United States as much as they were against the Soviet Union
.
In 1967 de Gaulle visited Quebec
, a French-speaking province of Canada and spoke out in favour
of its independence. This was received as a snub to the English-speaking world
, and the British in particular because of the close relationship between Britain and Canada. It was poorly received in Britain and was criticized even in the French press, and it was opposed by many French and French-Canadians including the future Canadian Prime Minister, Pierre Trudeau
, a French-Canadian from Montreal. He also vetoed the UK's first attempt to enter the European Communities.
were prepared to open a more friendly dialogue with Britain and, although they did not reverse much of De Gaulle's foreign policy , they removed their objections to British membership of the EEC
opening the way for the United Kingdom to join the Common Market in 1973.
These differing points of view came to a head in the lead-up to the 2003 War in Iraq. The UK, and their American allies, strongly advocated the use of force to remove Saddam Hussein
while France (with China, Russia, and other nations) strongly opposed such action, with French President Jacques Chirac
threatening to veto
any resolution proposed to the UN Security Council. However, despite such differences Chirac and then British Prime Minister Tony Blair
maintained a fairly close relationship during their years in office even after the Iraq War started.
Both states asserted the importance of the Entente cordiale
alliance, and the role it had played during the twentieth century.
 Following his election in 2007, President Nicolas Sarkozy
Following his election in 2007, President Nicolas Sarkozy
has attempted to forge closer relations between France and the United Kingdom: in March 2008, Prime Minister Gordon Brown
said that "there has never been greater cooperation between France and Britain as there is now". Sarkozy also urged both countries to "overcome our long-standing rivalries and build together a future that will be stronger because we will be together". He also said "If we want to change Europe my dear British friends—and we Frenchmen do wish to change Europe—we need you inside Europe to help us do so, not standing on the outside." On 26 March 2008, Sarkozy had the privilege of giving a speech to both British Houses of Parliament, where he called for a "brotherhood" between the two countries and stated that "France will never forget Britain's war sacrifice" during World War II.
In March 2008, Sarkozy made a state visit
to Britain. He attended a state dinner
with Elizabeth II and addressed a joint session
of the British parliament where he promised closer cooperation between the two countries' governments in the future.
Relations took a slight turn for the worse when Nicolas Sarkozy said that the D-Day Landing Memorials in 2009 were a French and American affair and therefore did not invite Queen Elizabeth II, and did not consider Britain's involvement in the D-Day landings; the matter was quickly resolved with Charles, Prince of Wales
and Gordon Brown attending the event as the British representatives.
On 18 June 2010, Nicolas Sarkozy went to London to commemorate the 70th anniversary of the Appeal of 18 June, with notably David Cameron
and the Prince of Wales, in a way that was considered to be a strong affirmation of the French-British friendship. He is the first French president to go to London to commemorate this event. Sarkozy notably declared that he and the French delegation "come as friends, and friends who remember the past and what France owes you"
On 2 November 2010, France and the UK signed two defence co-operation treaties. They provide for the sharing of aircraft carriers, a 1000-strong joint reaction force, a common nuclear simulation centre in France, a common nuclear research centre in the UK, sharing air-refuelling tankers and joint training.
French classical music has always been popular in Britain. British popular music
is in turn popular in France. English literature
, in particular the works of William Shakespeare
, have been immensely popular in France. French artist Eugène Delacroix
based many of his paintings on scenes from his plays. In turn, French writers such as Molière
and Voltaire
have been translated
numerous times into English. In general, most of the more popular books in either language are translated into the other.
there is a rivalry between England and France
. Both countries compete in the Six Nations Championship
and the Rugby World Cup
. England have the edge in both tournaments having the most outright wins in the Six Nations (and its previous version the Five Nations), and most recently knocking the French sides out of the 2003
and 2007
World Cups at the semifinal stage and France knocked England out of the rugby World Cup 2011 with a convincing score in their quarter final match. Though rugby is originally a British sport, French rugby
has developed to such an extent that the English and French teams are now stiff competitors, with neither side greatly superior to the other.
The influence of French players and coaches on British football has been increasing in recent years and is often cited as an example of Anglo-French cooperation. In particular the Premier League club Arsenal
has become known for its Anglo-French connection due to a heavy influx of French players since the advent of French manager Arsène Wenger
in 1996. In March 2008 their Emirates stadium
was chosen as the venue for a meeting during a state visit
by the French President precisely for this reason. Despite rivalry in rugby, there is no significant rivalry between the international football teams.
Many people blamed the then French President Jacques Chirac for contributing to Paris' loss to London in its bid for the 2012 Summer Olympics
after he made rude remarks about British cuisine
and saying that "only Finnish food is worse". The IOC committee which would ultimately decide to give the games to London had two members from Finland.
There are lists of twinnings
(including those to towns in other countries) at List of twin towns and sister cities in France and at List of twin towns and sister cities in the United Kingdom.
France
The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
and the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
(UK). In recent years the two countries have experienced a very close relationship.
The designation "Anglo-" specifically refers to England, not the UK. However, modern intergovernmental relations between these two nations are habitually called Anglo-French relations, and understood to refer to the UK and not only England. The term Franco-British relations is also used.
Early Franco-British interactions occurred before Caesar's invasion of Gaul, when the two regions were inhabited by loosely trading Celts fighting the Romans as a common enemy. They continued under the Roman Empire
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire was the post-Republican period of the ancient Roman civilization, characterised by an autocratic form of government and large territorial holdings in Europe and around the Mediterranean....
as both modern day states were ruled from Rome. Both were provinces in the larger Roman Empire.
Recently relations have been cordial and cooperative, with an edge of wariness on both sides due to historical differences and more recent disagreements between two of the leaders of the two countries: former French President, Jacques Chirac
Jacques Chirac
Jacques René Chirac is a French politician who served as President of France from 1995 to 2007. He previously served as Prime Minister of France from 1974 to 1976 and from 1986 to 1988 , and as Mayor of Paris from 1977 to 1995.After completing his studies of the DEA's degree at the...
, and former British Prime Minister, Tony Blair
Tony Blair
Anthony Charles Lynton Blair is a former British Labour Party politician who served as the Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 2 May 1997 to 27 June 2007. He was the Member of Parliament for Sedgefield from 1983 to 2007 and Leader of the Labour Party from 1994 to 2007...
. French author Jose-Alain Fralon characterised the relationship between the countries by describing the British as "our most dear enemies". Tony Blair is regarded as being a francophile
Francophile
Is a person with a positive predisposition or interest toward the government, culture, history, or people of France. This could include France itself and its history, the French language, French cuisine, literature, etc...
by the French media and the current French President Nicolas Sarkozy
Nicolas Sarkozy
Nicolas Sarkozy is the 23rd and current President of the French Republic and ex officio Co-Prince of Andorra. He assumed the office on 16 May 2007 after defeating the Socialist Party candidate Ségolène Royal 10 days earlier....
is known for his will to transform the "Entente Cordiale" into an "Entente amicale" (that is, a friendlier and closer relation).
Much of the two countries' histories has been defined by the relationship between the two countries. Today, both France and the United Kingdom are member states of the European Union
Member State of the European Union
A member state of the European Union is a state that is party to treaties of the European Union and has thereby undertaken the privileges and obligations that EU membership entails. Unlike membership of an international organisation, being an EU member state places a country under binding laws in...
(EU), and it is estimated that about 400,000 French people live in the UK, and vice versa.
Roman era
When Julius CaesarJulius Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar was a Roman general and statesman and a distinguished writer of Latin prose. He played a critical role in the gradual transformation of the Roman Republic into the Roman Empire....
invaded Gaul
Gaul
Gaul was a region of Western Europe during the Iron Age and Roman era, encompassing present day France, Luxembourg and Belgium, most of Switzerland, the western part of Northern Italy, as well as the parts of the Netherlands and Germany on the left bank of the Rhine. The Gauls were the speakers of...
, he encountered allies of the Gauls and Belgae
Belgae
The Belgae were a group of tribes living in northern Gaul, on the west bank of the Rhine, in the 3rd century BC, and later also in Britain, and possibly even Ireland...
from southeastern Britain offering assistance, some of whom even acknowledged the king of the Belgae as their sovereign.
Although all peoples concerned were Celts (and the Germanic
Germanic peoples
The Germanic peoples are an Indo-European ethno-linguistic group of Northern European origin, identified by their use of the Indo-European Germanic languages which diversified out of Proto-Germanic during the Pre-Roman Iron Age.Originating about 1800 BCE from the Corded Ware Culture on the North...
Angles and Franks had not yet invaded either country that would later bear their names), this could arguably be seen as the first major example of Anglo-French cooperation in recorded history. As a consequence, Caesar felt compelled to invade in an attempt to subdue Britain.
For the next five hundred years, there was much interaction between the two regions, as both Britain and France were under Roman rule. This was followed by another five hundred years with very little interaction between the two, as both were invaded by different Germanic
Germanic peoples
The Germanic peoples are an Indo-European ethno-linguistic group of Northern European origin, identified by their use of the Indo-European Germanic languages which diversified out of Proto-Germanic during the Pre-Roman Iron Age.Originating about 1800 BCE from the Corded Ware Culture on the North...
tribes. At the turn of the second millennium, the British Isles
British Isles
The British Isles are a group of islands off the northwest coast of continental Europe that include the islands of Great Britain and Ireland and over six thousand smaller isles. There are two sovereign states located on the islands: the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland and...
were primarily involved with the Scandinavia
Scandinavia
Scandinavia is a cultural, historical and ethno-linguistic region in northern Europe that includes the three kingdoms of Denmark, Norway and Sweden, characterized by their common ethno-cultural heritage and language. Modern Norway and Sweden proper are situated on the Scandinavian Peninsula,...
n world, while France's main foreign relationship was with the Holy Roman Empire
Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a realm that existed from 962 to 1806 in Central Europe.It was ruled by the Holy Roman Emperor. Its character changed during the Middle Ages and the Early Modern period, when the power of the emperor gradually weakened in favour of the princes...
.
Norman conquest
However, in the mid-eleventh century there was a dispute over the English throne, and the French-speaking NormansNormans
The Normans were the people who gave their name to Normandy, a region in northern France. They were descended from Norse Viking conquerors of the territory and the native population of Frankish and Gallo-Roman stock...
, who were of Viking stock, invaded England under their duke William the Conqueror and took over following the Battle of Hastings
Battle of Hastings
The Battle of Hastings occurred on 14 October 1066 during the Norman conquest of England, between the Norman-French army of Duke William II of Normandy and the English army under King Harold II...
in 1066, and crowned themselves Kings of England.
The Norman feudal culture took root in England, and for the next 150 years England was generally considered of secondary importance to the dynasty's Continental territories. The language of the aristocracy
Aristocracy
Aristocracy , is a form of government in which a few elite citizens rule. The term derives from the Greek aristokratia, meaning "rule of the best". In origin in Ancient Greece, it was conceived of as rule by the best qualified citizens, and contrasted with monarchy...
was French. To this day the coat of arms
Coat of arms
A coat of arms is a unique heraldic design on a shield or escutcheon or on a surcoat or tabard used to cover and protect armour and to identify the wearer. Thus the term is often stated as "coat-armour", because it was anciently displayed on the front of a coat of cloth...
of the United Kingdom reads 'Dieu et mon Droit' ('God and my right'). Scotland
Scotland
Scotland is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Occupying the northern third of the island of Great Britain, it shares a border with England to the south and is bounded by the North Sea to the east, the Atlantic Ocean to the north and west, and the North Channel and Irish Sea to the...
, Wales and Ireland gradually also were summed into this new influence.
The first Norman kings were also the Dukes of Normandy
Duke of Normandy
The Duke of Normandy is the title of the reigning monarch of the British Crown Dependancies of the Bailiwick of Guernsey and the Bailiwick of Jersey. The title traces its roots to the Duchy of Normandy . Whether the reigning sovereign is a male or female, they are always titled as the "Duke of...
, so relations were somewhat complicated between the countries. Though they were dukes ostensibly under the king of France, their higher level of organisation in Normandy gave them more de facto power. In addition, they were kings of England in their own right; England was not officially a province of France, nor even, officially at least, a province of Normandy.
High Medieval era
During the reign of the closely related Plantagenet dynasty, which was based in its Angevin EmpireAngevin Empire
The term Angevin Empire is a modern term describing the collection of states once ruled by the Angevin Plantagenet dynasty.The Plantagenets ruled over an area stretching from the Pyrenees to Ireland during the 12th and early 13th centuries, located north of Moorish Iberia. This "empire" extended...
, half of France was under Angevin control as well as all of England. However, almost all of the Angevin empire was lost to Philip II of France
Philip II of France
Philip II Augustus was the King of France from 1180 until his death. A member of the House of Capet, Philip Augustus was born at Gonesse in the Val-d'Oise, the son of Louis VII and his third wife, Adela of Champagne...
under Richard the Lionheart, John and Henry III of England. This finally gave the English a separate identity as an Anglo-Saxon people under a Francophone, but not French, crown.
While the English and French had been frequently acrimonious, they had always had a common culture and little fundamental difference in identity. Nationalism had been minimal in days when most wars took place between rival feudal lords on a sub-national scale. The last attempt to unite the two cultures under such lines was probably a failed French-supported rebellion to depose Edward II. It was also during the Middle Ages that a Franco-Scottish alliance, known as the Auld Alliance
Auld Alliance
The Auld Alliance was an alliance between the kingdoms of Scotland and France. It played a significant role in the relations between Scotland, France and England from its beginning in 1295 until the 1560 Treaty of Edinburgh. The alliance was renewed by all the French and Scottish monarchs of that...
was signed by King John of Scotland
John of Scotland
John Balliol , known to the Scots as Toom Tabard , was King of Scots from 1292 to 1296.-Early life:Little of John's early life is known. He was born between 1248 and 1250 at an unknown location, possibilities include Galloway, Picardy and Barnard Castle, County Durham...
and Philip IV of France
Philip IV of France
Philip the Fair was, as Philip IV, King of France from 1285 until his death. He was the husband of Joan I of Navarre, by virtue of which he was, as Philip I, King of Navarre and Count of Champagne from 1284 to 1305.-Youth:A member of the House of Capet, Philip was born at the Palace of...
.
The Hundred Years' War

Hundred Years' War
The Hundred Years' War was a series of separate wars waged from 1337 to 1453 by the House of Valois and the House of Plantagenet, also known as the House of Anjou, for the French throne, which had become vacant upon the extinction of the senior Capetian line of French kings...
between 1337 and 1453. Though the war was in principle a mere dispute over territory, it drastically changed societies on both sides of the Channel. The English, although already politically united, for the first time found pride in their language and identity, while the French united politically.
Several of the most famous Anglo-French battles took place during the Hundred Years' War: Crécy
Battle of Crécy
The Battle of Crécy took place on 26 August 1346 near Crécy in northern France, and was one of the most important battles of the Hundred Years' War...
, Poitiers
Battle of Poitiers (1356)
The Battle of Poitiers was fought between the Kingdoms of England and France on 19 September 1356 near Poitiers, resulting in the second of the three great English victories of the Hundred Years' War: Crécy, Poitiers, and Agincourt....
, Agincourt
Battle of Agincourt
The Battle of Agincourt was a major English victory against a numerically superior French army in the Hundred Years' War. The battle occurred on Friday, 25 October 1415 , near modern-day Azincourt, in northern France...
, Orléans
Siege of Orléans
The Siege of Orléans marked a turning point in the Hundred Years' War between France and England. This was Joan of Arc's first major military victory and the first major French success to follow the crushing defeat at Agincourt in 1415. The outset of this siege marked the pinnacle of English power...
, and Paris. Major sources of French pride stemmed from their leadership during the war. Bertrand du Guesclin
Bertrand du Guesclin
Bertrand du Guesclin , known as the Eagle of Brittany or the Black Dog of Brocéliande, was a Breton knight and French military commander during the Hundred Years' War. He was Constable of France from 1370 to his death...
was a brilliant tactician who forced the English out of the lands they had procured at the Treaty of Brétigny
Treaty of Brétigny
The Treaty of Brétigny was a treaty signed on May 9, 1360, between King Edward III of England and King John II of France. In retrospect it is seen as having marked the end of the first phase of the Hundred Years' War —as well as the height of English hegemony on the Continent.It was signed...
, a compromising treaty that most Frenchmen saw as a humiliation. Joan of Arc
Joan of Arc
Saint Joan of Arc, nicknamed "The Maid of Orléans" , is a national heroine of France and a Roman Catholic saint. A peasant girl born in eastern France who claimed divine guidance, she led the French army to several important victories during the Hundred Years' War, which paved the way for the...
was another unifying figure who to this day represents a combination of religious fervour and French patriotism to all France. After her inspirational victory at Orléans and what many saw as Joan's martyrdom at the hands of Burgundians and Englishmen, Jean de Dunois
Jean de Dunois
John of Orléans, Count of Dunois was the illegitimate son of Louis d'Orléans by Mariette d'Enghien.The term "Bastard of Orléans" John of Orléans, Count of Dunois (French born "Jean Levieux Valois des Orléans" better known as Jean d'Orléans, comte de Dunois, also known as John of Orléans and...
eventually forced the English out of all of France except Calais
Calais
Calais is a town in Northern France in the department of Pas-de-Calais, of which it is a sub-prefecture. Although Calais is by far the largest city in Pas-de-Calais, the department's capital is its third-largest city of Arras....
, which was only lost in 1558. Apart from setting national identities, the Hundred Years' War is often cited as the root of the traditional rivalry and at times hatred between the two countries.
During this era, the English lost their last territories in France, except Calais, though the English monarchs continued to style themselves as Kings of France until 1800.
The Franco-Scots Alliance
France and ScotlandScotland
Scotland is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Occupying the northern third of the island of Great Britain, it shares a border with England to the south and is bounded by the North Sea to the east, the Atlantic Ocean to the north and west, and the North Channel and Irish Sea to the...
agreed to defend each other in the event of an attack on either from England in several treaties
Treaty
A treaty is an express agreement under international law entered into by actors in international law, namely sovereign states and international organizations. A treaty may also be known as an agreement, protocol, covenant, convention or exchange of letters, among other terms...
, the most notable of which were in 1327 and 1490. There had always been intermarriage between the Scottish and French royal households, but this solidified the bond between the royals even further.
The early modern period

Italian Wars
The Italian Wars, often referred to as the Great Italian Wars or the Great Wars of Italy and sometimes as the Habsburg–Valois Wars, were a series of conflicts from 1494 to 1559 that involved, at various times, most of the city-states of Italy, the Papal States, most of the major states of Western...
between 1494 and 1559.
An even deeper division set in during the English Reformation
English Reformation
The English Reformation was the series of events in 16th-century England by which the Church of England broke away from the authority of the Pope and the Roman Catholic Church....
, when most of England converted to Protestantism and France remained Roman Catholic. This enabled each side to see the other as not only a foreign evil but also a heretical one. In both countries there was intense civil religious conflict. Because of the oppression by Roman Catholic King Louis XIII of France
Louis XIII of France
Louis XIII was a Bourbon monarch who ruled as King of France and of Navarre from 1610 to 1643.Louis was only eight years old when he succeeded his father. His mother, Marie de Medici, acted as regent during Louis' minority...
, many Protestant Huguenots fled to England. Similarly, many Catholics fled from England to France.
Henry VIII of England
Henry VIII of England
Henry VIII was King of England from 21 April 1509 until his death. He was Lord, and later King, of Ireland, as well as continuing the nominal claim by the English monarchs to the Kingdom of France...
had initially sought an alliance with France, and the Field of the Cloth of Gold
Field of the Cloth of Gold
The Field of Cloth of Gold is the name given to a place in Balinghem, between Guînes and Ardres, in France, near Calais. It was the site of a meeting that took place from 7 June to 24 June 1520, between King Henry VIII of England and King Francis I of France. The meeting was arranged to increase...
saw a face to face meeting between him and King Francis I of France
Francis I of France
Francis I was King of France from 1515 until his death. During his reign, huge cultural changes took place in France and he has been called France's original Renaissance monarch...
.
Universal Monarchy
While Spain had been the dominant world powerWorld Power
World Power is the debut album of German Eurodance project Snap!, released in 1990 on Bookmark/Ariola Records. The album received generally positive reviews from music critics, as the project's musical style and its vocalists, Turbo B and Penny "Tiny" Ford, were well-received...
in the sixteenth and early seventeenth centuries, the English had often sided with France as a counterweight against them. This design was intended to keep a European balance of power
Balance of power in international relations
In international relations, a balance of power exists when there is parity or stability between competing forces. The concept describes a state of affairs in the international system and explains the behavior of states in that system...
, and prevent one country gaining overwhelming supremacy. Key to English strategy, was the fear that a universal monarchy
Universal Monarchy
A Universal Monarchy is a concept and a political situation where one monarchy is deemed to have either sole rule over everywhere or to have a special supremacy over all other states .-Concept:Universal Monarchy is differentiated from ordinary monarchy in...
of Europe would be able to overwhelm the British Isles
British Isles
The British Isles are a group of islands off the northwest coast of continental Europe that include the islands of Great Britain and Ireland and over six thousand smaller isles. There are two sovereign states located on the islands: the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland and...
.
Following the Treaty of Westphalia in 1648, as Spain's power weakened, France began to take on a more assertive role under King Louis XIV of France
Louis XIV of France
Louis XIV , known as Louis the Great or the Sun King , was a Bourbon monarch who ruled as King of France and Navarre. His reign, from 1643 to his death in 1715, began at the age of four and lasted seventy-two years, three months, and eighteen days...
with an expansionist policy both in Europe and across the globe. English foreign policy was now directed towards preventing France gaining supremacy on the continent and creating a universal monarchy. To the French, England was an isolated and piratical nation heavily reliant on naval power, and particularly privateers, which they referred to as Perfidious Albion
Perfidious Albion
'Perfidious Albion' is a pejorative phrase used within the context of international relations and diplomacy to refer to acts of duplicity, treachery and hence infidelity by monarchs or governments of Britain in their pursuit of self-interest and the requirements of...
.
There was a sharp diversion in political philosophies in the two states. In England King Charles I
Charles I of England
Charles I was King of England, King of Scotland, and King of Ireland from 27 March 1625 until his execution in 1649. Charles engaged in a struggle for power with the Parliament of England, attempting to obtain royal revenue whilst Parliament sought to curb his Royal prerogative which Charles...
had been executed during the English Civil War
English Civil War
The English Civil War was a series of armed conflicts and political machinations between Parliamentarians and Royalists...
for exceeding his powers, and later King James II
James II of England
James II & VII was King of England and King of Ireland as James II and King of Scotland as James VII, from 6 February 1685. He was the last Catholic monarch to reign over the Kingdoms of England, Scotland, and Ireland...
had been overthrown in the Glorious Revolution
Glorious Revolution
The Glorious Revolution, also called the Revolution of 1688, is the overthrow of King James II of England by a union of English Parliamentarians with the Dutch stadtholder William III of Orange-Nassau...
. In France the power of the monarchs and their advisors went largely unchecked.
England
Kingdom of England
The Kingdom of England was, from 927 to 1707, a sovereign state to the northwest of continental Europe. At its height, the Kingdom of England spanned the southern two-thirds of the island of Great Britain and several smaller outlying islands; what today comprises the legal jurisdiction of England...
and France
Kingdom of France
The Kingdom of France was one of the most powerful states to exist in Europe during the second millennium.It originated from the Western portion of the Frankish empire, and consolidated significant power and influence over the next thousand years. Louis XIV, also known as the Sun King, developed a...
fought each other in the War of the League of Augsburg from 1688 to 1697 which set the pattern for relations between France and Great Britain during the eighteenth century. Wars were fought intermittently, with each nation part of a constantly shifting pattern of alliances known as the stately quadrille
Stately quadrille
The stately quadrille is a term popularly used to describe the constantly shifting alliances between the Great Powers of Europe during the 18th century. The ultimate objective was to maintain the balance of power in Europe, and to stop any one alliance or country becoming too strong...
.
Union of England and Scotland
.svg.png)
Kingdom of Great Britain
The former Kingdom of Great Britain, sometimes described as the 'United Kingdom of Great Britain', That the Two Kingdoms of Scotland and England, shall upon the 1st May next ensuing the date hereof, and forever after, be United into One Kingdom by the Name of GREAT BRITAIN. was a sovereign...
, formally merging the kingdoms of Scotland
Kingdom of Scotland
The Kingdom of Scotland was a Sovereign state in North-West Europe that existed from 843 until 1707. It occupied the northern third of the island of Great Britain and shared a land border to the south with the Kingdom of England...
and England
Kingdom of England
The Kingdom of England was, from 927 to 1707, a sovereign state to the northwest of continental Europe. At its height, the Kingdom of England spanned the southern two-thirds of the island of Great Britain and several smaller outlying islands; what today comprises the legal jurisdiction of England...
(of which Wales
Wales
Wales is a country that is part of the United Kingdom and the island of Great Britain, bordered by England to its east and the Atlantic Ocean and Irish Sea to its west. It has a population of three million, and a total area of 20,779 km²...
was a part). While the new Britain grew increasingly parliamentarian
Parliament of Great Britain
The Parliament of Great Britain was formed in 1707 following the ratification of the Acts of Union by both the Parliament of England and Parliament of Scotland...
, France continued its system of absolute monarchy
Absolute monarchy
Absolute monarchy is a monarchical form of government in which the monarch exercises ultimate governing authority as head of state and head of government, his or her power not being limited by a constitution or by the law. An absolute monarch thus wields unrestricted political power over the...
.
The newly united Britain fought France in the War of the Spanish Succession
War of the Spanish Succession
The War of the Spanish Succession was fought among several European powers, including a divided Spain, over the possible unification of the Kingdoms of Spain and France under one Bourbon monarch. As France and Spain were among the most powerful states of Europe, such a unification would have...
from 1702 to 1713, and the War of the Austrian Succession
War of the Austrian Succession
The War of the Austrian Succession – including King George's War in North America, the Anglo-Spanish War of Jenkins' Ear, and two of the three Silesian wars – involved most of the powers of Europe over the question of Maria Theresa's succession to the realms of the House of Habsburg.The...
from 1740 to 1748, attempting to maintain the balance of power in Europe. The British had a massive navy but maintained a small land army, so Britain always acted on the continent in alliance with other states such as Prussia
Prussia
Prussia was a German kingdom and historic state originating out of the Duchy of Prussia and the Margraviate of Brandenburg. For centuries, the House of Hohenzollern ruled Prussia, successfully expanding its size by way of an unusually well-organized and effective army. Prussia shaped the history...
and Austria
Austria
Austria , officially the Republic of Austria , is a landlocked country of roughly 8.4 million people in Central Europe. It is bordered by the Czech Republic and Germany to the north, Slovakia and Hungary to the east, Slovenia and Italy to the south, and Switzerland and Liechtenstein to the...
as they were unable to fight France alone. Equally France, lacking a superior navy, was unable to ever launch a successful invasion of Britain.
France lent support to the Jacobite
Jacobitism
Jacobitism was the political movement in Britain dedicated to the restoration of the Stuart kings to the thrones of England, Scotland, later the Kingdom of Great Britain, and the Kingdom of Ireland...
pretenders who claimed the British throne, hoping that a restored Jacobite monarchy would be inclined to be more pro-French. Despite this support the Jacobites failed to overthrow the Hanoverian
House of Hanover
The House of Hanover is a deposed German royal dynasty which has ruled the Duchy of Brunswick-Lüneburg , the Kingdom of Hanover, the Kingdom of Great Britain, the Kingdom of Ireland and the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland...
monarchs.
As the century wore on, there was a distinct passage of power to Britain and France, at the expense of traditional major powers such as Portugal
Portugal
Portugal , officially the Portuguese Republic is a country situated in southwestern Europe on the Iberian Peninsula. Portugal is the westernmost country of Europe, and is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the West and South and by Spain to the North and East. The Atlantic archipelagos of the...
, Spain and the Dutch Republic
Dutch Republic
The Dutch Republic — officially known as the Republic of the Seven United Netherlands , the Republic of the United Netherlands, or the Republic of the Seven United Provinces — was a republic in Europe existing from 1581 to 1795, preceding the Batavian Republic and ultimately...
. Some observers saw the frequent conflicts between the two states during the eighteenth century as a battle for control of Europe, though most of these wars ended without a conclusive victory for either side. France largely had greater influence on the continent while Britain posed dominant at sea and trade threatening French colonies abroad.
Overseas expansion
From the 1650s, the New WorldNew World
The New World is one of the names used for the Western Hemisphere, specifically America and sometimes Oceania . The term originated in the late 15th century, when America had been recently discovered by European explorers, expanding the geographical horizon of the people of the European middle...
increasingly became a battleground between the two powers. The Western Design of Oliver Cromwell
Oliver Cromwell
Oliver Cromwell was an English military and political leader who overthrew the English monarchy and temporarily turned England into a republican Commonwealth, and served as Lord Protector of England, Scotland, and Ireland....
intended to build up an increasing British presence in North America, beginning with the acquisition of Jamaica
Jamaica
Jamaica is an island nation of the Greater Antilles, in length, up to in width and 10,990 square kilometres in area. It is situated in the Caribbean Sea, about south of Cuba, and west of Hispaniola, the island harbouring the nation-states Haiti and the Dominican Republic...
from the Spanish Empire
Spanish Empire
The Spanish Empire comprised territories and colonies administered directly by Spain in Europe, in America, Africa, Asia and Oceania. It originated during the Age of Exploration and was therefore one of the first global empires. At the time of Habsburgs, Spain reached the peak of its world power....
in 1652. The first British settlement on continental North America was founded in 1603, by the 1760s these had grown into thirteen separate colonies
Thirteen Colonies
The Thirteen Colonies were English and later British colonies established on the Atlantic coast of North America between 1607 and 1733. They declared their independence in the American Revolution and formed the United States of America...
.
The French had settled the province of Canada to the North, and controlled Saint-Domingue
Saint-Domingue
The labour for these plantations was provided by an estimated 790,000 African slaves . Between 1764 and 1771, the average annual importation of slaves varied between 10,000-15,000; by 1786 it was about 28,000, and from 1787 onward, the colony received more than 40,000 slaves a year...
in the Caribbean, the wealthiest colony in the world. Both countries, recognising the potential of India, established trading post
Trading post
A trading post was a place or establishment in historic Northern America where the trading of goods took place. The preferred travel route to a trading post or between trading posts, was known as a trade route....
s there. Wars between the two states increasingly took place in these other continents, as well as Europe.
Seven Years' War

Indigenous peoples of the Americas
The indigenous peoples of the Americas are the pre-Columbian inhabitants of North and South America, their descendants and other ethnic groups who are identified with those peoples. Indigenous peoples are known in Canada as Aboriginal peoples, and in the United States as Native Americans...
tribes to gain control of North America. Both nations coveted the Ohio Territory and in 1753 a British expedition there led by George Washington
George Washington
George Washington was the dominant military and political leader of the new United States of America from 1775 to 1799. He led the American victory over Great Britain in the American Revolutionary War as commander-in-chief of the Continental Army from 1775 to 1783, and presided over the writing of...
clashed with a French force. Shortly afterwards the French and Indian War
French and Indian War
The French and Indian War is the common American name for the war between Great Britain and France in North America from 1754 to 1763. In 1756, the war erupted into the world-wide conflict known as the Seven Years' War and thus came to be regarded as the North American theater of that war...
broke out, initially taking place only in North America but in 1756 becoming part of the wider Seven Years' War
Seven Years' War
The Seven Years' War was a global military war between 1756 and 1763, involving most of the great powers of the time and affecting Europe, North America, Central America, the West African coast, India, and the Philippines...
in which Britain and France were part of opposing coalitions.
The war was described by Winston Churchill
Winston Churchill
Sir Winston Leonard Spencer-Churchill, was a predominantly Conservative British politician and statesman known for his leadership of the United Kingdom during the Second World War. He is widely regarded as one of the greatest wartime leaders of the century and served as Prime Minister twice...
as the first "world war
World war
A world war is a war affecting the majority of the world's most powerful and populous nations. World wars span multiple countries on multiple continents, with battles fought in multiple theaters....
", because fighting took place on several different continents. In 1759 the British enjoyed victories over the French in Europe, Canada and India, severely weakening the French position around the world. In 1762 the British captured the cities of Manila
Manila
Manila is the capital of the Philippines. It is one of the sixteen cities forming Metro Manila.Manila is located on the eastern shores of Manila Bay and is bordered by Navotas and Caloocan to the north, Quezon City to the northeast, San Juan and Mandaluyong to the east, Makati on the southeast,...
and Havana
Havana
Havana is the capital city, province, major port, and leading commercial centre of Cuba. The city proper has a population of 2.1 million inhabitants, and it spans a total of — making it the largest city in the Caribbean region, and the most populous...
from Spain, France's strongest ally, which led ultimately to a peace settlement
Treaty of Paris (1763)
The Treaty of Paris, often called the Peace of Paris, or the Treaty of 1763, was signed on 10 February 1763, by the kingdoms of Great Britain, France and Spain, with Portugal in agreement. It ended the French and Indian War/Seven Years' War...
the following year that saw a large number of territories come under British control.
The Seven Years' War is regarded as a critical moment in the history of Anglo-French relations, which laid the foundations for the dominance of the Anglosphere
Anglosphere
Anglosphere is a neologism which refers to those nations with English as the most common language. The term can be used more specifically to refer to those nations which share certain characteristics within their cultures based on a linguistic heritage, through being former British colonies...
during the next two and a half centuries, and arguably the spread of democracy and English common law
Common law
Common law is law developed by judges through decisions of courts and similar tribunals rather than through legislative statutes or executive branch action...
.
American War of Independence
The Anglo-American settlers had originally fought on the side of the British, but as some Americans grew dissatisfied with British policies the French saw an opportunity to undermine British overseas power. When the American War of Independence broke out in 1775, the French began sending covert supplies and intelligence to the American rebels.
Gibraltar
Gibraltar is a British overseas territory located on the southern end of the Iberian Peninsula at the entrance of the Mediterranean. A peninsula with an area of , it has a northern border with Andalusia, Spain. The Rock of Gibraltar is the major landmark of the region...
with Spain. Plans were drawn up, but never put into action, to launch an invasion of England.
The British were forced to withdraw forces from the American mainland to protect their more valuable possessions in the West Indies. While the French were initially unable to break the string of British victories, the combined actions of a French fleet and army, forced the British into a decisive surrender at Yorktown
Siege of Yorktown
The Siege of Yorktown, Battle of Yorktown, or Surrender of Yorktown in 1781 was a decisive victory by a combined assault of American forces led by General George Washington and French forces led by the Comte de Rochambeau over a British Army commanded by Lieutenant General Lord Cornwallis...
in 1781.
In 1783 the French-led alliance managed to gain a number of concessions out of the British at the Treaty of Paris
Treaty of Paris (1783)
The Treaty of Paris, signed on September 3, 1783, ended the American Revolutionary War between Great Britain on the one hand and the United States of America and its allies on the other. The other combatant nations, France, Spain and the Dutch Republic had separate agreements; for details of...
most notably the recognition of American independence. For a brief period after the war, Britain's naval power was subdued by an alliance between France and Spain.
The crippling debts incurred by France during the war, and the cost of rebuilding the French navy during the 1780s caused a financial crisis, leading directly to the French Revolution
French Revolution
The French Revolution , sometimes distinguished as the 'Great French Revolution' , was a period of radical social and political upheaval in France and Europe. The absolute monarchy that had ruled France for centuries collapsed in three years...
of 1789. The loss of the colonies was taken by some, such as the Emperor Joseph II
Joseph II, Holy Roman Emperor
Joseph II was Holy Roman Emperor from 1765 to 1790 and ruler of the Habsburg lands from 1780 to 1790. He was the eldest son of Empress Maria Theresa and her husband, Francis I...
of Austria, to mark the end of Britain as a major power.
The French Revolution

During the French Revolution
French Revolution
The French Revolution , sometimes distinguished as the 'Great French Revolution' , was a period of radical social and political upheaval in France and Europe. The absolute monarchy that had ruled France for centuries collapsed in three years...
, the anti-monarchical ideals of France were regarded with alarm throughout Europe. While France was plunged into chaos, Britain took advantage of its temporary weakness to stir up the civil war occurring in France
French Counter-Revolution
The French Counter-Revolution was a period in the history of France where certain individuals, groups and nations openly opposed the French Revolution.- Causes :During the early stages of the French Revolution many were not content with the status of France...
and build up its naval forces. The Revolution was initially popular with many Britons, both because it appeared to weaken France and was perceived to be based on British liberal ideals. This began to change as the Jacobin
Jacobin (politics)
A Jacobin , in the context of the French Revolution, was a member of the Jacobin Club, a revolutionary far-left political movement. The Jacobin Club was the most famous political club of the French Revolution. So called from the Dominican convent where they originally met, in the Rue St. Jacques ,...
faction took over, and began the Reign of Terror
Reign of Terror
The Reign of Terror , also known simply as The Terror , was a period of violence that occurred after the onset of the French Revolution, incited by conflict between rival political factions, the Girondins and the Jacobins, and marked by mass executions of "enemies of...
.
The French were intent on spreading their revolutionary republicanism to other European states, including Britain. The British initially stayed out of the alliances of European states which unsuccessfully attacked France trying to restore the monarchy. In France a new, strong nationalism took hold enabling them to mobilise large and motivated forces.
Following the execution of King Louis XVI of France
Louis XVI of France
Louis XVI was a Bourbon monarch who ruled as King of France and Navarre until 1791, and then as King of the French from 1791 to 1792, before being executed in 1793....
in 1793, Britain declared war on France. Except for a brief pause in the fighting from 1802–03
Treaty of Amiens
The Treaty of Amiens temporarily ended hostilities between the French Republic and the United Kingdom during the French Revolutionary Wars. It was signed in the city of Amiens on 25 March 1802 , by Joseph Bonaparte and the Marquess Cornwallis as a "Definitive Treaty of Peace"...
, the war lasted continuously for twenty one years. During this time Britain raised several coalitions against the French, continually subsidising other European states with the Golden Cavalry of St George
Golden Cavalry of St George
The Golden Cavalry of St George was the colloquial name of subsidies paid out by the British government to other European states in the eighteenth and nineteenth centuries, through particularly during the Napoleonic Wars...
, enabling them to put large armies in the field. In spite of this, the French armies were very successful on land, creating several client states such as the Batavian Republic
Batavian Republic
The Batavian Republic was the successor of the Republic of the United Netherlands. It was proclaimed on January 19, 1795, and ended on June 5, 1806, with the accession of Louis Bonaparte to the throne of the Kingdom of Holland....
, and the British devoted much of their own forces to campaigns against the French in the Caribbean, with mixed results.
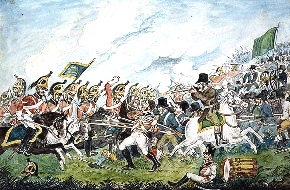
Union of Great Britain and Ireland
In 1798 French forces invaded Ireland to assist the United Irishmen who had launched a rebellionIrish Rebellion of 1798
The Irish Rebellion of 1798 , also known as the United Irishmen Rebellion , was an uprising in 1798, lasting several months, against British rule in Ireland...
, where they were joined by thousands of rebels but defeated by British and Irish loyalist
Loyalist
In general, a loyalist is someone who maintains loyalty to an established government, political party, or sovereign, especially during war or revolutionary change. In modern English usage, the most common application is to loyalty to the British Crown....
forces. The fear of further attempts to create a French satellite in Ireland, led to the Act of Union merging of the crowns of Great Britain and Ireland to create the United Kingdom in 1801.

The Napoleonic Wars
In 1799, NapoleonNapoleon I
Napoleon Bonaparte was a French military and political leader during the latter stages of the French Revolution.As Napoleon I, he was Emperor of the French from 1804 to 1815...
came to power in France, ending the revolutionary era and creating a dictatorship (crowning himself Emperor
Emperor of the French
The Emperor of the French was the title used by the Bonaparte Dynasty starting when Napoleon Bonaparte was given the title Emperor on 18 May 1804 by the French Senate and was crowned emperor of the French on 02 December 1804 at the cathedral of Notre Dame de Paris, in Paris with the Crown of...
in 1804). After he had triumphed on the European continent against the other major European powers, Napoleon contemplated an invasion of the British mainland, but was dissuaded by an Austrian
Austrian Empire
The Austrian Empire was a modern era successor empire, which was centered on what is today's Austria and which officially lasted from 1804 to 1867. It was followed by the Empire of Austria-Hungary, whose proclamation was a diplomatic move that elevated Hungary's status within the Austrian Empire...
attack over its Bavaria
Bavaria
Bavaria, formally the Free State of Bavaria is a state of Germany, located in the southeast of Germany. With an area of , it is the largest state by area, forming almost 20% of the total land area of Germany...
n allies.
In response Napoleon established a continental system
Continental System
The Continental System or Continental Blockade was the foreign policy of Napoleon I of France in his struggle against the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland during the Napoleonic Wars. It was a large-scale embargo against British trade, which began on November 21, 1806...
by which no nation was permitted to trade with the British. Napoleon hoped the embargo would isolate the British Isles
British Isles
The British Isles are a group of islands off the northwest coast of continental Europe that include the islands of Great Britain and Ireland and over six thousand smaller isles. There are two sovereign states located on the islands: the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland and...
severely weakening them, but a number of countries continued to trade with them in defiance of the policy. In spite of this, the Napoleonic influence stretched across much of Europe.
In 1808 French forces invaded Portugal trying to attempt to halt trade with the United Kingdom, turning Spain into a satellite state
Satellite state
A satellite state is a political term that refers to a country that is formally independent, but under heavy political and economic influence or control by another country...
in the process. The British responded by dispatching a force under Sir Arthur Wellesley
Arthur Wellesley, 1st Duke of Wellington
Field Marshal Arthur Wellesley, 1st Duke of Wellington, KG, GCB, GCH, PC, FRS , was an Irish-born British soldier and statesman, and one of the leading military and political figures of the 19th century...
which captured Lisbon. Napoleon dispatched increasing forces into the Iberian Peninsula
Iberian Peninsula
The Iberian Peninsula , sometimes called Iberia, is located in the extreme southwest of Europe and includes the modern-day sovereign states of Spain, Portugal and Andorra, as well as the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar...
, which became the key battleground between the two nations. Allied with Spanish and Portuguese forces, the British inflicted a number of defeats on the French, confronted with a new kind of warfare called "guerrilla" which led Napoleon to brand it the "Spanish Ulcer". Allied to an increasingly resurgent European coalition, the British invaded southern France forcing Napoleon to abdicate and go into exile on Elba
Elba
Elba is a Mediterranean island in Tuscany, Italy, from the coastal town of Piombino. The largest island of the Tuscan Archipelago, Elba is also part of the National Park of the Tuscan Archipelago and the third largest island in Italy after Sicily and Sardinia...
in 1814.

Battle of Waterloo
The Battle of Waterloo was fought on Sunday 18 June 1815 near Waterloo in present-day Belgium, then part of the United Kingdom of the Netherlands...
. With strong British support, the Bourbon
House of Bourbon
The House of Bourbon is a European royal house, a branch of the Capetian dynasty . Bourbon kings first ruled Navarre and France in the 16th century. By the 18th century, members of the Bourbon dynasty also held thrones in Spain, Naples, Sicily, and Parma...
monarchy was restored and Louis XVIII was crowned King of France. The Napoleonic era
Napoleonic Era
The Napoleonic Era is a period in the history of France and Europe. It is generally classified as including the fourth and final stage of the French Revolution, the first being the National Assembly, the second being the Legislative Assembly, and the third being the Directory...
was the last occasion on which Britain and France went to war with each other, but by no means marked the end of the rivalry between the two nations. Despite his final defeat, Napoleon continues to be regarded as a national hero figure in France for his numerous victories over coalised monarchies.
Early 19th century

Napoleonic Era
The Napoleonic Era is a period in the history of France and Europe. It is generally classified as including the fourth and final stage of the French Revolution, the first being the National Assembly, the second being the Legislative Assembly, and the third being the Directory...
regarded by many as a spent force, the UK had emerged from the 1815 Congress of Vienna
Congress of Vienna
The Congress of Vienna was a conference of ambassadors of European states chaired by Klemens Wenzel von Metternich, and held in Vienna from September, 1814 to June, 1815. The objective of the Congress was to settle the many issues arising from the French Revolutionary Wars, the Napoleonic Wars,...
as one of the leading financial, military and cultural powers of the world. France also recovered from the defeat at Waterloo
Battle of Waterloo
The Battle of Waterloo was fought on Sunday 18 June 1815 near Waterloo in present-day Belgium, then part of the United Kingdom of the Netherlands...
to quickly retake its position on the world stage.
Despite their historic enmity, the British and French eventually became strained political allies, as both began to turn their attentions to acquiring new territories beyond Europe. The British developed India and Canada and settled Australia, spreading their powers to several different continents as the Second British Empire.
They frequently made stereotypical jokes about each other, and even side by side in war were critical of each other's tactics.
As a Royal Navy
Royal Navy
The Royal Navy is the naval warfare service branch of the British Armed Forces. Founded in the 16th century, it is the oldest service branch and is known as the Senior Service...
officer said to the French corsair
Corsair
Corsairs were privateers, authorized to conduct raids on shipping of a nation at war with France, on behalf of the French Crown. Seized vessels and cargo were sold at auction, with the corsair captain entitled to a portion of the proceeds...
Robert Surcouf
Robert Surcouf
Robert Surcouf was a famous French corsair. During his legendary career, he captured 47 ships and was renowned for his gallantry and chivalry, earning the nickname of Roi des Corsaires .- Youth :...
"You French fight for money, while we British fight for honour.", Surcouf
Surcouf
Surcouf is a French surname. It may refer to:* Robert Surcouf , a French corsair** For boats and ships named after him, see French ship Surcouf.* Jaques Surcouf , a French entomologist...
replied "Sir, a man fights for what he lacks the most." According to one story, a French diplomat once said to Lord Palmerston "If I were not a Frenchman, I should wish to be an Englishman"; to which Palmerston replied: "If I were not an Englishman, I should wish to be an Englishman." According to another, upon seeing the disastrous British Charge of the Light Brigade
Charge of the Light Brigade
The Charge of the Light Brigade was a charge of British cavalry led by Lord Cardigan against Russian forces during the Battle of Balaclava on 25 October 1854 in the Crimean War. The charge was the result of a miscommunication in such a way that the brigade attempted a much more difficult objective...
in the Crimean War
Crimean War
The Crimean War was a conflict fought between the Russian Empire and an alliance of the French Empire, the British Empire, the Ottoman Empire, and the Kingdom of Sardinia. The war was part of a long-running contest between the major European powers for influence over territories of the declining...
against Russia, French marshal Pierre Bosquet
Pierre Bosquet
Pierre François Joseph Bosquet was a French Army general. He served during the conquest of Algeria and the Crimean War; returning from Crimea he was made Marshal of France and senator.-Biography:...
said 'C'est magnifique, mais ce n'est pas la guerre.' ('It's magnificent, but it's not war.') Eventually, relations settled down as the two empires tried to consolidate themselves rather than extend themselves.
The July Monarchy and the beginning of the Victorian age
In 1830, France underwent the July RevolutionJuly Revolution
The French Revolution of 1830, also known as the July Revolution or in French, saw the overthrow of King Charles X of France, the French Bourbon monarch, and the ascent of his cousin Louis-Philippe, Duke of Orléans, who himself, after 18 precarious years on the throne, would in turn be overthrown...
, and the Orléanist
House of Orleans
Orléans is the name used by several branches of the Royal House of France, all descended in the legitimate male line from the dynasty's founder, Hugh Capet. It became a tradition during France's ancien régime for the duchy of Orléans to be granted as an appanage to a younger son of the king...
Louis-Phillipe
Louis-Philippe of France
Louis Philippe I was King of the French from 1830 to 1848 in what was known as the July Monarchy. His father was a duke who supported the French Revolution but was nevertheless guillotined. Louis Philippe fled France as a young man and spent 21 years in exile, including considerable time in the...
subsequently ascended to the throne; by contrast, the reign of Queen Victoria
Victoria of the United Kingdom
Victoria was the monarch of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland from 20 June 1837 until her death. From 1 May 1876, she used the additional title of Empress of India....
began in 1837 in a much more peaceful fashion. The major European powers—Russia
Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was a state that existed from 1721 until the Russian Revolution of 1917. It was the successor to the Tsardom of Russia and the predecessor of the Soviet Union...
, Austria
Austrian Empire
The Austrian Empire was a modern era successor empire, which was centered on what is today's Austria and which officially lasted from 1804 to 1867. It was followed by the Empire of Austria-Hungary, whose proclamation was a diplomatic move that elevated Hungary's status within the Austrian Empire...
, the UK, and to some extent Prussia
Prussia
Prussia was a German kingdom and historic state originating out of the Duchy of Prussia and the Margraviate of Brandenburg. For centuries, the House of Hohenzollern ruled Prussia, successfully expanding its size by way of an unusually well-organized and effective army. Prussia shaped the history...
—were determined to keep France in check, and so France generally pursued a cautious foreign policy. Louis-Phillipe allied with Britain, the country with which France shared the most similar form of government, and its combative Foreign Secretary Lord Palmerston. In Louis-Philippe's first year in power, he refused to annex Belgium during its revolution
Belgian Revolution
The Belgian Revolution was the conflict which led to the secession of the Southern provinces from the United Kingdom of the Netherlands and established an independent Kingdom of Belgium....
, instead following the British line of supporting independence. Despite posturings from leading French minister Adolphe Thiers
Adolphe Thiers
Marie Joseph Louis Adolphe Thiers was a French politician and historian. was a prime minister under King Louis-Philippe of France. Following the overthrow of the Second Empire he again came to prominence as the French leader who suppressed the revolutionary Paris Commune of 1871...
in 1839–1840 that France would protect the increasingly powerful Muhammad Ali of Egypt
Muhammad Ali of Egypt
Muhammad Ali Pasha al-Mas'ud ibn Agha was a commander in the Ottoman army, who became Wāli, and self-declared Khedive of Egypt and Sudan...
(a viceroy of the Ottoman Empire
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman EmpireIt was usually referred to as the "Ottoman Empire", the "Turkish Empire", the "Ottoman Caliphate" or more commonly "Turkey" by its contemporaries...
), any reinforcements were not forthcoming, and in 1840, much to France's embarrassment, Ali was forced to sign the Convention of London
Convention of London (1840)
The Convention of London of 1840 was a treaty with the formal title of Convention for the Pacification of the Levant, signed on 15 July 1840 between the European Great Powers of United Kingdom, Austria, Prussia, Russia on the one hand, and the Ottoman Empire on the other.The treaty summarized...
by the powers. Relations cooled again under the governments of François Guizot
François Guizot
François Pierre Guillaume Guizot was a French historian, orator, and statesman. Guizot was a dominant figure in French politics prior to the Revolution of 1848, a conservative liberal who opposed the attempt by King Charles X to usurp legislative power, and worked to sustain a constitutional...
and Robert Peel
Robert Peel
Sir Robert Peel, 2nd Baronet was a British Conservative statesman who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 10 December 1834 to 8 April 1835, and again from 30 August 1841 to 29 June 1846...
. They soured once more in 1844 though when, with Palmerston back as Foreign Secretary, the French government hastily agreed to have Isabella II of Spain
Isabella II of Spain
Isabella II was the only female monarch of Spain in modern times. She came to the throne as an infant, but her succession was disputed by the Carlists, who refused to recognise a female sovereign, leading to the Carlist Wars. After a troubled reign, she was deposed in the Glorious Revolution of...
and her sister marry members of the Bourbon
House of Bourbon
The House of Bourbon is a European royal house, a branch of the Capetian dynasty . Bourbon kings first ruled Navarre and France in the 16th century. By the 18th century, members of the Bourbon dynasty also held thrones in Spain, Naples, Sicily, and Parma...
and Orléanist dynasties, respectively. Palmerston had hoped to arrange a marriage, and "The Affair of the Spanish Marriages" has generally been viewed unfavourably by British historians ("By the dispassionate judgment of history it has been universally condemned"), although a more sympathetic view has been taken in recent years.
Second French Empire

French presidential election, 1848
The first-ever French presidential election of 1848 elected the first—and only—President of the Second Republic. The election was held on 10 December 1848 and led to the surprise victory of Louis-Napoléon Bonaparte with 74% of the vote.-Election:...
), soon restoring the position of Emperor, as Napoleon III, which had been vacant since his uncle Napoleon I
Napoleon I
Napoleon Bonaparte was a French military and political leader during the latter stages of the French Revolution.As Napoleon I, he was Emperor of the French from 1804 to 1815...
. The new Emperor had an expansionist foreign policy, which saw the French deepen the colonisation of Africa
Colonisation of Africa
The colonisation of Africa has a long history, the most famous phase being the European Scramble for Africa during the late 19th and early 20th century.- Ancient colonialism :...
and establish new colonies, in particular Indochina
Indochina
The Indochinese peninsula, is a region in Southeast Asia. It lies roughly southwest of China, and east of India. The name has its origins in the French, Indochine, as a combination of the names of "China" and "India", and was adopted when French colonizers in Vietnam began expanding their territory...
. The British were initially alarmed, and commissioned a series of forts in southern England designed to resist a French invasion.
Despite this Napoleon had a very pro-British foreign policy, and was eager not to displease the British government whose friendship he saw as important to France.
The expanding Russia and the prospect of a United Germany became greater concerns to the British, and the two nations worked together during the Crimean War
Crimean War
The Crimean War was a conflict fought between the Russian Empire and an alliance of the French Empire, the British Empire, the Ottoman Empire, and the Kingdom of Sardinia. The war was part of a long-running contest between the major European powers for influence over territories of the declining...
which aimed to curb Russia's expansion westwards. The two nations also co-operated during the Second Opium War
Second Opium War
The Second Opium War, the Second Anglo-Chinese War, the Second China War, the Arrow War, or the Anglo-French expedition to China, was a war pitting the British Empire and the Second French Empire against the Qing Dynasty of China, lasting from 1856 to 1860...
, dispatching a joint force to the Chinese capital Peking to agree a treaty with the Chinese Qing Dynasty
Qing Dynasty
The Qing Dynasty was the last dynasty of China, ruling from 1644 to 1912 with a brief, abortive restoration in 1917. It was preceded by the Ming Dynasty and followed by the Republic of China....
. In 1859 Napoleon, bypassing the Corps législatif
Corps législatif
The Corps législatif was a part of the French legislature during the French Revolution and beyond. It is also the generic French term used to refer to any legislative body.-History:The Constitution of the Year I foresaw the need for a corps législatif...
which he feared would not approve of free trade, met with influential reformer Richard Cobden
Richard Cobden
Richard Cobden was a British manufacturer and Radical and Liberal statesman, associated with John Bright in the formation of the Anti-Corn Law League as well as with the Cobden-Chevalier Treaty...
, and in 1860 the Cobden-Chevalier Treaty
Cobden-Chevalier Treaty
The Cobden–Chevalier Treaty was a Free Trade treaty signed between the United Kingdom and France on 23 January, 1860. It is named after the main British and French originators of the treaty, Richard Cobden MP and Michel Chevalier.-Origins and negotiations:...
was signed between the two countries, reducing tariffs on goods sold between the UK and France.
During the American Civil War
American Civil War
The American Civil War was a civil war fought in the United States of America. In response to the election of Abraham Lincoln as President of the United States, 11 southern slave states declared their secession from the United States and formed the Confederate States of America ; the other 25...
both nations remained neutral. France came close to entering on the side of the Confederate States of America
Confederate States of America
The Confederate States of America was a government set up from 1861 to 1865 by 11 Southern slave states of the United States of America that had declared their secession from the U.S...
, but did not want to become involved without the support of the British, which was not forthcoming due to concerns over slavery
Slavery
Slavery is a system under which people are treated as property to be bought and sold, and are forced to work. Slaves can be held against their will from the time of their capture, purchase or birth, and deprived of the right to leave, to refuse to work, or to demand compensation...
. France also attempted to gain British support for a scheme to put an Austrian Prince, Maximilian I
Maximilian I of Mexico
Maximilian I was the only monarch of the Second Mexican Empire.After a distinguished career in the Austrian Navy, he was proclaimed Emperor of Mexico on April 10, 1864, with the backing of Napoleon III of France and a group of Mexican monarchists who sought to revive the Mexican monarchy...
, on the throne of Mexico, but the British were not willing to support any action other than the collection of debts owed by the Mexicans. This forced to French to act alone in the French Intervention in Mexico
French intervention in Mexico
The French intervention in Mexico , also known as The Maximilian Affair, War of the French Intervention, and The Franco-Mexican War, was an invasion of Mexico by an expeditionary force sent by the Second French Empire, supported in the beginning by the United Kingdom and the Kingdom of Spain...
, which ultimately proved disastrous.
When Napoleon was overthrown in 1870, he fled to take refuge in England where he and his family lived in exile. The republic
French Third Republic
The French Third Republic was the republican government of France from 1870, when the Second French Empire collapsed due to the French defeat in the Franco-Prussian War, to 1940, when France was overrun by Nazi Germany during World War II, resulting in the German and Italian occupations of France...
which replaced his rule continued the warm relations with the UK, especially following the creation of the German Empire
German Empire
The German Empire refers to Germany during the "Second Reich" period from the unification of Germany and proclamation of Wilhelm I as German Emperor on 18 January 1871, to 1918, when it became a federal republic after defeat in World War I and the abdication of the Emperor, Wilhelm II.The German...
, which they perceived as a serious threat.
Later Victorian Era
One brief dispute occurred during the Fashoda IncidentFashoda Incident
The Fashoda Incident was the climax of imperial territorial disputes between Britain and France in Eastern Africa. A French expedition to Fashoda on the White Nile sought to gain control of the Nile River and thereby force Britain out of Egypt. The British held firm as Britain and France were on...
when French troops tried to claim an area in the Southern Sudan, and a British force purporting to be acting in the interests of the Khedive of Egypt arrived. Under heavy pressure the French withdrew securing Anglo-Egyptian control over the area. The status quo
Status quo
Statu quo, a commonly used form of the original Latin "statu quo" – literally "the state in which" – is a Latin term meaning the current or existing state of affairs. To maintain the status quo is to keep the things the way they presently are...
was recognised by an agreement between the two states acknowledging British control over Egypt, while France became the dominant power in Morocco
Morocco
Morocco , officially the Kingdom of Morocco , is a country located in North Africa. It has a population of more than 32 million and an area of 710,850 km², and also primarily administers the disputed region of the Western Sahara...
.
During the Scramble for Africa
Scramble for Africa
The Scramble for Africa, also known as the Race for Africa or Partition of Africa was a process of invasion, occupation, colonization and annexation of African territory by European powers during the New Imperialism period, between 1881 and World War I in 1914...
the British and French generally recognised each other's spheres of influence. The Suez Canal
Suez Canal
The Suez Canal , also known by the nickname "The Highway to India", is an artificial sea-level waterway in Egypt, connecting the Mediterranean Sea and the Red Sea. Opened in November 1869 after 10 years of construction work, it allows water transportation between Europe and Asia without navigation...
, initially built by the French, became a joint British-French project in 1875, as both saw it as vital to maintaining their influence and empires in Asia. In 1882, ongoing civil disturbances in Egypt (see Urabi Revolt
Urabi Revolt
The Urabi Revolt or Orabi Revolt , also known as the Orabi Revolution, was an uprising in Egypt in 1879-82 against the Khedive and European influence in the country...
) prompted Britain to intervene, extending a hand to France. France's expansionist Prime Minister Jules Ferry
Jules Ferry
Jules François Camille Ferry was a French statesman and republican. He was a promoter of laicism and colonial expansion.- Early life :Born in Saint-Dié, in the Vosges département, France, he studied law, and was called to the bar at Paris in 1854, but soon went into politics, contributing to...
was out of office, and the Chamber of Deputies
Chamber of Deputies of France
Chamber of Deputies was the name given to several parliamentary bodies in France in the nineteenth and twentieth centuries:* 1814–1848 during the Bourbon Restoration and the July Monarchy, the Chamber of Deputies was the Lower chamber of the French Parliament, elected by census suffrage.*...
was unwilling to send more than an intimidatory fleet to the region. The UK established a protectorate, as France had a year earlier in Tunisia
Tunisia
Tunisia , officially the Tunisian RepublicThe long name of Tunisia in other languages used in the country is: , is the northernmost country in Africa. It is a Maghreb country and is bordered by Algeria to the west, Libya to the southeast, and the Mediterranean Sea to the north and east. Its area...
, and popular opinion in France later put this action down to duplicity. It was about this time that the two nations established co-ownership of Vanuatu
Vanuatu
Vanuatu , officially the Republic of Vanuatu , is an island nation located in the South Pacific Ocean. The archipelago, which is of volcanic origin, is some east of northern Australia, northeast of New Caledonia, west of Fiji, and southeast of the Solomon Islands, near New Guinea.Vanuatu was...
. The Anglo-French Convention of 1882
Anglo-French Convention of 1882
The Anglo-French Convention of 1882 was signed on June 28, 1882 between the United Kingdom and France. It confirmed the territorial boundaries between Guinea and Sierra Leone around Conakry and Freetown. However, it was never fully ratified by the French Chamber of Deputies although was officially...
was also signed to resolve territory disagreements in western Africa.
The Entente cordiale

English Channel
The English Channel , often referred to simply as the Channel, is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that separates southern England from northern France, and joins the North Sea to the Atlantic. It is about long and varies in width from at its widest to in the Strait of Dover...
. Francophile and Anglophile societies developed, further introducing Britain to French food and wine, and France to English sports like rugby
Rugby union
Rugby union, often simply referred to as rugby, is a full contact team sport which originated in England in the early 19th century. One of the two codes of rugby football, it is based on running with the ball in hand...
. French and English were already the second languages of choice in Britain and France respectively. Eventually this developed into a political policy as the new united Germany was seen as a potential threat. Louis Blériot
Louis Blériot
Louis Charles Joseph Blériot was a French aviator, inventor and engineer. In 1909 he completed the first flight across a large body of water in a heavier-than-air craft, when he crossed the English Channel. For this achievement, he received a prize of £1,000...
, for example, crossed the Channel in an aeroplane in 1909. Many saw this as symbolic of the connection between the two countries. This period in the first decade of the 20th century became known as the Entente cordiale, and continued in spirit until the 1940s. Up to the 1920s, relations between the UK and France were arguably closer than those between the UK and the US.
First World War
Between 1914 and 1918 the British and French were allies against the Central PowersCentral Powers
The Central Powers were one of the two warring factions in World War I , composed of the German Empire, the Austro-Hungarian Empire, the Ottoman Empire, and the Kingdom of Bulgaria...
after Belgium and a small part of northern France had been invaded by the German army
German Army
The German Army is the land component of the armed forces of the Federal Republic of Germany. Following the disbanding of the Wehrmacht after World War II, it was re-established in 1955 as the Bundesheer, part of the newly formed West German Bundeswehr along with the Navy and the Air Force...
.
There was strong co-operation between the British and French forces. The battles took place on several different fronts, but most particularly to Anglo-French relations in the trenches in France and Belgium against the Germans. Unable to advance against the combined primary alliance powers of the British, French, and later American forces as well as the embargo of German controlled North Sea seaports, the Germans eventually surrendered after four years of heavy fighting.
Treaty of Versailles

Georges Clemenceau
Georges Benjamin Clemenceau was a French statesman, physician and journalist. He served as the Prime Minister of France from 1906 to 1909, and again from 1917 to 1920. For nearly the final year of World War I he led France, and was one of the major voices behind the Treaty of Versailles at the...
was hailed by the British crowds. Lloyd George
David Lloyd George
David Lloyd George, 1st Earl Lloyd-George of Dwyfor OM, PC was a British Liberal politician and statesman...
was given a similar reception in Paris.
Both states joined the League of Nations
League of Nations
The League of Nations was an intergovernmental organization founded as a result of the Paris Peace Conference that ended the First World War. It was the first permanent international organization whose principal mission was to maintain world peace...
, and both signed agreements of defence of several countries, most significantly Poland
Poland
Poland , officially the Republic of Poland , is a country in Central Europe bordered by Germany to the west; the Czech Republic and Slovakia to the south; Ukraine, Belarus and Lithuania to the east; and the Baltic Sea and Kaliningrad Oblast, a Russian exclave, to the north...
. The Treaty of Sèvres
Treaty of Sèvres
The Treaty of Sèvres was the peace treaty between the Ottoman Empire and Allies at the end of World War I. The Treaty of Versailles was signed with Germany before this treaty to annul the German concessions including the economic rights and enterprises. Also, France, Great Britain and Italy...
split the Middle East between the two states, in the form of mandates
League of Nations mandate
A League of Nations mandate was a legal status for certain territories transferred from the control of one country to another following World War I, or the legal instruments that contained the internationally agreed-upon terms for administering the territory on behalf of the League...
. However the outlook of the nations were different during the inter-war years; while France saw itself inherently as a European power, the UK enjoyed close relationships with Australia, Canada and New Zealand and at one time flirted with the idea of Empire Free Trade, a form of protectionism
Protectionism
Protectionism is the economic policy of restraining trade between states through methods such as tariffs on imported goods, restrictive quotas, and a variety of other government regulations designed to allow "fair competition" between imports and goods and services produced domestically.This...
that would have seen large tariffs placed on goods from France.
Second World War

Treaty of Versailles
The Treaty of Versailles was one of the peace treaties at the end of World War I. It ended the state of war between Germany and the Allied Powers. It was signed on 28 June 1919, exactly five years after the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand. The other Central Powers on the German side of...
(1919), the Anglo-German Naval Agreement
Anglo-German Naval Agreement
The Anglo-German Naval Agreement of June 18, 1935 was a bilateral agreement between the United Kingdom and German Reich regulating the size of the Kriegsmarine in relation to the Royal Navy. The A.G.N.A fixed a ratio whereby the total tonnage of the Kriegsmarine was to be 35% of the total tonnage...
was signed between the United Kingdom and the German Reich in 1935. This bilateral agreement, which allowed Hitler to reinforce his Kriegsmarine
Kriegsmarine
The Kriegsmarine was the name of the German Navy during the Nazi regime . It superseded the Kaiserliche Marine of World War I and the post-war Reichsmarine. The Kriegsmarine was one of three official branches of the Wehrmacht, the unified armed forces of Nazi Germany.The Kriegsmarine grew rapidly...
, was regarded by the French as the ruining of the anti-Hitlerian Stresa front
Stresa Front
The Stresa Front was an agreement made in Stresa, a town on the banks of Lake Maggiore in Italy, between French foreign minister Pierre Laval, British prime minister Ramsay MacDonald, and Italian prime minister Benito Mussolini on April 14, 1935...
.
In the years leading up to World War II, both countries followed a similar diplomatic path of appeasement
Appeasement
The term appeasement is commonly understood to refer to a diplomatic policy aimed at avoiding war by making concessions to another power. Historian Paul Kennedy defines it as "the policy of settling international quarrels by admitting and satisfying grievances through rational negotiation and...
of Germany in Czechoslovakia
Czechoslovakia
Czechoslovakia or Czecho-Slovakia was a sovereign state in Central Europe which existed from October 1918, when it declared its independence from the Austro-Hungarian Empire, until 1992...
, despite a French military excursion there. As Nazi intentions became clear, France pushed for a harder line but the British demurred, believing diplomacy could solve the disputes.
After guaranteeing the independence of Poland, both declared war on Germany on the same day, the 3rd of September 1939, after the Germans ignored an ultimatum to withdraw from the country. When Germany began its attack on France in 1940, British troops and French troops again fought side by side. Eventually, after the Germans came through the Ardennes
Ardennes
The Ardennes is a region of extensive forests, rolling hills and ridges formed within the Givetian Ardennes mountain range, primarily in Belgium and Luxembourg, but stretching into France , and geologically into the Eifel...
, it became clear that France would not be able to fend off the German attack, and Winston Churchill
Winston Churchill
Sir Winston Leonard Spencer-Churchill, was a predominantly Conservative British politician and statesman known for his leadership of the United Kingdom during the Second World War. He is widely regarded as one of the greatest wartime leaders of the century and served as Prime Minister twice...
pledged that the United Kingdom would continue to fight for France's freedom, even if it must do so alone. The final bond between the two nations was so strong that members of the British cabinet had proposed a temporary union of the two countries for the sake of morale: the plan was drawn up by Jean Monnet
Jean Monnet
Jean Omer Marie Gabriel Monnet was a French political economist and diplomat. He is regarded by many as a chief architect of European Unity and is regarded as one of its founding fathers...
, who later created the Common Market
European Economic Community
The European Economic Community The European Economic Community (EEC) The European Economic Community (EEC) (also known as the Common Market in the English-speaking world, renamed the European Community (EC) in 1993The information in this article primarily covers the EEC's time as an independent...
. The idea was not popular with a majority on either side, and the French government felt that, in the circumstances, the plan for union would reduce France to the level of a British Dominion. The proposal was turned down, shortly before France fell to the Germans. The Free French resistance, led by Charles de Gaulle
Charles de Gaulle
Charles André Joseph Marie de Gaulle was a French general and statesman who led the Free French Forces during World War II. He later founded the French Fifth Republic in 1958 and served as its first President from 1959 to 1969....
, were formed in London, after de Gaulle gave his famous 'Appeal of the 18th of June', widely broadcast by the BBC
BBC
The British Broadcasting Corporation is a British public service broadcaster. Its headquarters is at Broadcasting House in the City of Westminster, London. It is the largest broadcaster in the world, with about 23,000 staff...
.

Vichy France
Vichy France, Vichy Regime, or Vichy Government, are common terms used to describe the government of France that collaborated with the Axis powers from July 1940 to August 1944. This government succeeded the Third Republic and preceded the Provisional Government of the French Republic...
was set up, allied to Germany. The British were soon at war with the Vichy state, destroying much of its navy and moving into many of its colonies, such as Senegal
Senegal
Senegal , officially the Republic of Senegal , is a country in western Africa. It owes its name to the Sénégal River that borders it to the east and north...
, on behalf of the Free French government.
Following D-Day
D-Day
D-Day is a term often used in military parlance to denote the day on which a combat attack or operation is to be initiated. "D-Day" often represents a variable, designating the day upon which some significant event will occur or has occurred; see Military designation of days and hours for similar...
, relations between the two peoples were at a high, as the British were greeted as liberators. Following the surrender of Germany in 1945, the UK and France became close as both feared the Americans would withdraw from Europe leaving them vulnerable to the Soviet Union
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union , officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics , was a constitutionally socialist state that existed in Eurasia between 1922 and 1991....
's expanding communist bloc. The UK strongly advocated that France be given a zone of occupied Germany. Both states were amongst the five Permanent Members of the new UN Security Council, where they commonly collaborated.
Suez Crisis
In 1956 the Suez CanalSuez Canal
The Suez Canal , also known by the nickname "The Highway to India", is an artificial sea-level waterway in Egypt, connecting the Mediterranean Sea and the Red Sea. Opened in November 1869 after 10 years of construction work, it allows water transportation between Europe and Asia without navigation...
, previously owned by an Anglo-French company, was nationalised by the Egyptian government. The British and the French were both strongly committed to taking the canal back by force. Both the British and French governments saw the actions of the Egypt president Gamal Abdel Nasser
Gamal Abdel Nasser
Gamal Abdel Nasser Hussein was the second President of Egypt from 1956 until his death. A colonel in the Egyptian army, Nasser led the Egyptian Revolution of 1952 along with Muhammad Naguib, the first president, which overthrew the monarchy of Egypt and Sudan, and heralded a new period of...
as potentially dangerous to their interests in trade, and within the framework of the Cold War and the tensions of the newly independent. During the initial stages of the crisis, French Prime Minister Guy Mollet
Guy Mollet
Guy Mollet was a French Socialist politician. He led the French Section of the Workers' International party from 1946 to 1969 and was Prime Minister in 1956–1957.-Early life and World War II:...
proposed a union between Britain and France, but the British were less enthusiastic. British Prime Minister Anthony Eden
Anthony Eden
Robert Anthony Eden, 1st Earl of Avon, KG, MC, PC was a British Conservative politician, who was Prime Minister from 1955 to 1957...
called it a "good idea in substance" but thought it "a bit premature".
The Americans, while opposed to Nasser, refused to become involved with what many regarded as European colonialism, putting severe strain on the Anglo-American special relationship
Special relationship
The Special Relationship is a phrase used to describe the exceptionally close political, diplomatic, cultural, economic, military and historical relations between the United Kingdom and the United States, following its use in a 1946 speech by British statesman Winston Churchill...
. The relations between Britain and France were not entirely harmonious, as the French kept the British in the dark about the involvement of Israel
Israel
The State of Israel is a parliamentary republic located in the Middle East, along the eastern shore of the Mediterranean Sea...
until very close to the commencement of military operations.
Common market
The Suez CrisisSuez Crisis
The Suez Crisis, also referred to as the Tripartite Aggression, Suez War was an offensive war fought by France, the United Kingdom, and Israel against Egypt beginning on 29 October 1956. Less than a day after Israel invaded Egypt, Britain and France issued a joint ultimatum to Egypt and Israel,...
was probably the last time that Anglo-French relations have been more comfortable than Anglo-American relations.
Immediately after the crisis Anglo-French relations started to sour again, only since the last few years of the 20th century have they begun to improve and climb towards the peak they did in the years between 1900 and 1940.
Shortly after this, France, West Germany
West Germany
West Germany is the common English, but not official, name for the Federal Republic of Germany or FRG in the period between its creation in May 1949 to German reunification on 3 October 1990....
, Italy, Belgium
Belgium
Belgium , officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a federal state in Western Europe. It is a founding member of the European Union and hosts the EU's headquarters, and those of several other major international organisations such as NATO.Belgium is also a member of, or affiliated to, many...
, the Netherlands
Netherlands
The Netherlands is a constituent country of the Kingdom of the Netherlands, located mainly in North-West Europe and with several islands in the Caribbean. Mainland Netherlands borders the North Sea to the north and west, Belgium to the south, and Germany to the east, and shares maritime borders...
and Luxembourg
Luxembourg
Luxembourg , officially the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg , is a landlocked country in western Europe, bordered by Belgium, France, and Germany. It has two principal regions: the Oesling in the North as part of the Ardennes massif, and the Gutland in the south...
formed what would become the European Economic Community
European Economic Community
The European Economic Community The European Economic Community (EEC) The European Economic Community (EEC) (also known as the Common Market in the English-speaking world, renamed the European Community (EC) in 1993The information in this article primarily covers the EEC's time as an independent...
and later the European Union
European Union
The European Union is an economic and political union of 27 independent member states which are located primarily in Europe. The EU traces its origins from the European Coal and Steel Community and the European Economic Community , formed by six countries in 1958...
, and did not at first allow the UK to join. President Charles de Gaulle
Charles de Gaulle
Charles André Joseph Marie de Gaulle was a French general and statesman who led the Free French Forces during World War II. He later founded the French Fifth Republic in 1958 and served as its first President from 1959 to 1969....
's attempts to exclude the British from European affairs during the beginning of France's Fifth Republic are now seen by many in Britain to be a betrayal of the bond between the countries, and Anthony Eden
Anthony Eden
Robert Anthony Eden, 1st Earl of Avon, KG, MC, PC was a British Conservative politician, who was Prime Minister from 1955 to 1957...
's exclusion of France from the commonwealth is seen in a similar light in France. The French partly feared that were the British to join the EEC they would attempt to dominate it.
Over the years, the UK and France have often taken diverging courses within the European Community. British policy has favoured an expansion of the Community and free trade
Free trade
Under a free trade policy, prices emerge from supply and demand, and are the sole determinant of resource allocation. 'Free' trade differs from other forms of trade policy where the allocation of goods and services among trading countries are determined by price strategies that may differ from...
while France has advocated protectionism
Protectionism
Protectionism is the economic policy of restraining trade between states through methods such as tariffs on imported goods, restrictive quotas, and a variety of other government regulations designed to allow "fair competition" between imports and goods and services produced domestically.This...
and restricting membership of the Community to a core of Western European states.
De Gaulle
In 1958 with France mired in a seemingly unwinnable war in AlgeriaAlgeria
Algeria , officially the People's Democratic Republic of Algeria , also formally referred to as the Democratic and Popular Republic of Algeria, is a country in the Maghreb region of Northwest Africa with Algiers as its capital.In terms of land area, it is the largest country in Africa and the Arab...
, Charles de Gaulle
Charles de Gaulle
Charles André Joseph Marie de Gaulle was a French general and statesman who led the Free French Forces during World War II. He later founded the French Fifth Republic in 1958 and served as its first President from 1959 to 1969....
, the wartime leader of the Free French, returned to power in France. He created the Fifth French Republic, ending the post-war parliamentary system and replacing it with a strong Presidency, which became dominated by his followers—the Gaullists.
De Gaulle made ambitious changes to French foreign policy—first ending the war in Algeria, and then withdrawing France from the NATO command structure. De Gaulle declared a new policy of "in every direction", meaning that French military forces were prepared to fight a war against the UK and the United States as much as they were against the Soviet Union
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union , officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics , was a constitutionally socialist state that existed in Eurasia between 1922 and 1991....
.
In 1967 de Gaulle visited Quebec
Quebec
Quebec or is a province in east-central Canada. It is the only Canadian province with a predominantly French-speaking population and the only one whose sole official language is French at the provincial level....
, a French-speaking province of Canada and spoke out in favour
Vive le Québec libre speech
"Vive le Québec libre !" was a controversial phrase in a speech delivered by French president Charles de Gaulle in Montreal on July 24, 1967.De Gaulle was in Canada on an official visit under the pretext of attending Expo 67...
of its independence. This was received as a snub to the English-speaking world
Anglosphere
Anglosphere is a neologism which refers to those nations with English as the most common language. The term can be used more specifically to refer to those nations which share certain characteristics within their cultures based on a linguistic heritage, through being former British colonies...
, and the British in particular because of the close relationship between Britain and Canada. It was poorly received in Britain and was criticized even in the French press, and it was opposed by many French and French-Canadians including the future Canadian Prime Minister, Pierre Trudeau
Pierre Trudeau
Joseph Philippe Pierre Yves Elliott Trudeau, , usually known as Pierre Trudeau or Pierre Elliott Trudeau, was the 15th Prime Minister of Canada from April 20, 1968 to June 4, 1979, and again from March 3, 1980 to June 30, 1984.Trudeau began his political career campaigning for socialist ideals,...
, a French-Canadian from Montreal. He also vetoed the UK's first attempt to enter the European Communities.
Recent relations
When de Gaulle resigned in 1969, a new French government under Georges PompidouGeorges Pompidou
Georges Jean Raymond Pompidou was a French politician. He was Prime Minister of France from 1962 to 1968, holding the longest tenure in this position, and later President of the French Republic from 1969 until his death in 1974.-Biography:...
were prepared to open a more friendly dialogue with Britain and, although they did not reverse much of De Gaulle's foreign policy , they removed their objections to British membership of the EEC
European Economic Community
The European Economic Community The European Economic Community (EEC) The European Economic Community (EEC) (also known as the Common Market in the English-speaking world, renamed the European Community (EC) in 1993The information in this article primarily covers the EEC's time as an independent...
opening the way for the United Kingdom to join the Common Market in 1973.
These differing points of view came to a head in the lead-up to the 2003 War in Iraq. The UK, and their American allies, strongly advocated the use of force to remove Saddam Hussein
Saddam Hussein
Saddam Hussein Abd al-Majid al-Tikriti was the fifth President of Iraq, serving in this capacity from 16 July 1979 until 9 April 2003...
while France (with China, Russia, and other nations) strongly opposed such action, with French President Jacques Chirac
Jacques Chirac
Jacques René Chirac is a French politician who served as President of France from 1995 to 2007. He previously served as Prime Minister of France from 1974 to 1976 and from 1986 to 1988 , and as Mayor of Paris from 1977 to 1995.After completing his studies of the DEA's degree at the...
threatening to veto
Veto
A veto, Latin for "I forbid", is the power of an officer of the state to unilaterally stop an official action, especially enactment of a piece of legislation...
any resolution proposed to the UN Security Council. However, despite such differences Chirac and then British Prime Minister Tony Blair
Tony Blair
Anthony Charles Lynton Blair is a former British Labour Party politician who served as the Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 2 May 1997 to 27 June 2007. He was the Member of Parliament for Sedgefield from 1983 to 2007 and Leader of the Labour Party from 1994 to 2007...
maintained a fairly close relationship during their years in office even after the Iraq War started.
Both states asserted the importance of the Entente cordiale
Entente Cordiale
The Entente Cordiale was a series of agreements signed on 8 April 1904 between the United Kingdom and the French Republic. Beyond the immediate concerns of colonial expansion addressed by the agreement, the signing of the Entente Cordiale marked the end of almost a millennium of intermittent...
alliance, and the role it had played during the twentieth century.
Sarkozy era

Nicolas Sarkozy
Nicolas Sarkozy is the 23rd and current President of the French Republic and ex officio Co-Prince of Andorra. He assumed the office on 16 May 2007 after defeating the Socialist Party candidate Ségolène Royal 10 days earlier....
has attempted to forge closer relations between France and the United Kingdom: in March 2008, Prime Minister Gordon Brown
Gordon Brown
James Gordon Brown is a British Labour Party politician who was the Prime Minister of the United Kingdom and Leader of the Labour Party from 2007 until 2010. He previously served as Chancellor of the Exchequer in the Labour Government from 1997 to 2007...
said that "there has never been greater cooperation between France and Britain as there is now". Sarkozy also urged both countries to "overcome our long-standing rivalries and build together a future that will be stronger because we will be together". He also said "If we want to change Europe my dear British friends—and we Frenchmen do wish to change Europe—we need you inside Europe to help us do so, not standing on the outside." On 26 March 2008, Sarkozy had the privilege of giving a speech to both British Houses of Parliament, where he called for a "brotherhood" between the two countries and stated that "France will never forget Britain's war sacrifice" during World War II.
In March 2008, Sarkozy made a state visit
State visit
A state visit is a formal visit by a foreign head of state to another nation, at the invitation of that nation's head of state. State visits are the highest form of diplomatic contact between two nations, and are marked by ceremonial pomp and diplomatic protocol. In parliamentary democracies, heads...
to Britain. He attended a state dinner
State dinner
A state dinner is a dinner or banquet paid by a government and hosted by a head of state in his or her official residence in order to renew and celebrate diplomatic ties between the host country and the country of a foreign head of state or head of government who was issued an invitation. In many...
with Elizabeth II and addressed a joint session
Joint session
A joint session or joint convention is, most broadly, when two normally-separate decision-making groups meet together, often in a special session or other extraordinary meeting, for a specific purpose....
of the British parliament where he promised closer cooperation between the two countries' governments in the future.
Relations took a slight turn for the worse when Nicolas Sarkozy said that the D-Day Landing Memorials in 2009 were a French and American affair and therefore did not invite Queen Elizabeth II, and did not consider Britain's involvement in the D-Day landings; the matter was quickly resolved with Charles, Prince of Wales
Charles, Prince of Wales
Prince Charles, Prince of Wales is the heir apparent and eldest son of Queen Elizabeth II and Prince Philip, Duke of Edinburgh. Since 1958 his major title has been His Royal Highness The Prince of Wales. In Scotland he is additionally known as The Duke of Rothesay...
and Gordon Brown attending the event as the British representatives.
On 18 June 2010, Nicolas Sarkozy went to London to commemorate the 70th anniversary of the Appeal of 18 June, with notably David Cameron
David Cameron
David William Donald Cameron is the current Prime Minister of the United Kingdom, First Lord of the Treasury, Minister for the Civil Service and Leader of the Conservative Party. Cameron represents Witney as its Member of Parliament ....
and the Prince of Wales, in a way that was considered to be a strong affirmation of the French-British friendship. He is the first French president to go to London to commemorate this event. Sarkozy notably declared that he and the French delegation "come as friends, and friends who remember the past and what France owes you"
On 2 November 2010, France and the UK signed two defence co-operation treaties. They provide for the sharing of aircraft carriers, a 1000-strong joint reaction force, a common nuclear simulation centre in France, a common nuclear research centre in the UK, sharing air-refuelling tankers and joint training.
The sciences
There have been some major patriotic issues between the French and British scientific communities, despite overall cooperation. As a first example, Newtonian mechanics was not generally accepted in France for about half a century because of what was seen as a competing formulation by Descartes. As a second example of stiff competition, the scandal about which of the two countries deserves credit for the discovery of the planet Neptune has still not died down, though the consensus weighs in France's favour.Arts and culture
In general, France is regarded with favour by Britain in regard to its high culture and is seen as an ideal holiday destination, whilst France sees Britain as a major trading partner. Both countries are contemptuous of each other's cooking, the French claiming all British food is bland and boring whilst the British claim French food is inedible. Much of the apparent disdain for French food and culture in Britain takes the form of self-effacing humour, and British comedy often uses French culture as a butt of jokes. Whether this is representative of true opinion is open to debate.French classical music has always been popular in Britain. British popular music
British popular music
British popular music and popular music in general, can be defined in a number of ways, but is used here to describe music which is not part of the art/classical music or Church music traditions, including folk music, jazz, pop and rock music...
is in turn popular in France. English literature
English literature
English literature is the literature written in the English language, including literature composed in English by writers not necessarily from England; for example, Robert Burns was Scottish, James Joyce was Irish, Joseph Conrad was Polish, Dylan Thomas was Welsh, Edgar Allan Poe was American, J....
, in particular the works of William Shakespeare
William Shakespeare
William Shakespeare was an English poet and playwright, widely regarded as the greatest writer in the English language and the world's pre-eminent dramatist. He is often called England's national poet and the "Bard of Avon"...
, have been immensely popular in France. French artist Eugène Delacroix
Eugène Delacroix
Ferdinand Victor Eugène Delacroix was a French Romantic artist regarded from the outset of his career as the leader of the French Romantic school...
based many of his paintings on scenes from his plays. In turn, French writers such as Molière
Molière
Jean-Baptiste Poquelin, known by his stage name Molière, was a French playwright and actor who is considered to be one of the greatest masters of comedy in Western literature...
and Voltaire
Voltaire
François-Marie Arouet , better known by the pen name Voltaire , was a French Enlightenment writer, historian and philosopher famous for his wit and for his advocacy of civil liberties, including freedom of religion, free trade and separation of church and state...
have been translated
Translation
Translation is the communication of the meaning of a source-language text by means of an equivalent target-language text. Whereas interpreting undoubtedly antedates writing, translation began only after the appearance of written literature; there exist partial translations of the Sumerian Epic of...
numerous times into English. In general, most of the more popular books in either language are translated into the other.
Language
The most common second language taught in schools in Britain is French, and the most commonly taught second language in France is English. A higher proportion of the French population is proficient in English than vice versa.Sports
In the sport of rugby unionRugby union
Rugby union, often simply referred to as rugby, is a full contact team sport which originated in England in the early 19th century. One of the two codes of rugby football, it is based on running with the ball in hand...
there is a rivalry between England and France
Le Crunch
The first Anglo-French rugby union match was held on March 22, 1906 at Parc des Princes in Paris.The traditional name for the annual England versus France rugby union match in the Six Nations Championship as used on both sides of the English Channel is Le Crunch. Games have also been played as...
. Both countries compete in the Six Nations Championship
Six Nations Championship
The Six Nations Championship is an annual international rugby union competition involving six European sides: England, France, Ireland, Italy, Scotland and Wales....
and the Rugby World Cup
Rugby World Cup
The Rugby World Cup is an international rugby union competition organised by the International Rugby Board and held every four years since 1987....
. England have the edge in both tournaments having the most outright wins in the Six Nations (and its previous version the Five Nations), and most recently knocking the French sides out of the 2003
2003 Rugby World Cup
The 2003 Rugby World Cup was the fifth Rugby World Cup and was won by England. Originally planned to be co-hosted by Australia and New Zealand, all games were shifted to Australia following a contractual dispute over ground signage rights between the New Zealand Rugby Football Union and Rugby World...
and 2007
2007 Rugby World Cup
The 2007 Rugby World Cup was the sixth Rugby World Cup, a quadrennial international rugby union competition inaugurated in 1987. Twenty nations competed for the Webb Ellis Cup in the tournament, which was hosted by France from 7 September to 20 October. France won the hosting rights in 2003,...
World Cups at the semifinal stage and France knocked England out of the rugby World Cup 2011 with a convincing score in their quarter final match. Though rugby is originally a British sport, French rugby
Rugby union in France
Rugby union is the second most popular team sport in France, after association football, and is the dominant sport in most of the southern half of the country. It was first introduced in the early 1870s by British residents. Elite French clubs participate in the professional domestic club league,...
has developed to such an extent that the English and French teams are now stiff competitors, with neither side greatly superior to the other.
The influence of French players and coaches on British football has been increasing in recent years and is often cited as an example of Anglo-French cooperation. In particular the Premier League club Arsenal
Arsenal F.C.
Arsenal Football Club is a professional English Premier League football club based in North London. One of the most successful clubs in English football, it has won 13 First Division and Premier League titles and 10 FA Cups...
has become known for its Anglo-French connection due to a heavy influx of French players since the advent of French manager Arsène Wenger
Arsène Wenger
Arsène Wenger, OBE is a French association football manager and former player, who has managed English Premier League side Arsenal since 1996...
in 1996. In March 2008 their Emirates stadium
Emirates Stadium
Ashburton Grove, currently known as the Emirates Stadium, is a UEFA elite football stadium which is home to Arsenal FC, where they moved from Highbury in 2006. It has an current capacity of 60,361, and there have been rumours of an expansion...
was chosen as the venue for a meeting during a state visit
State visit
A state visit is a formal visit by a foreign head of state to another nation, at the invitation of that nation's head of state. State visits are the highest form of diplomatic contact between two nations, and are marked by ceremonial pomp and diplomatic protocol. In parliamentary democracies, heads...
by the French President precisely for this reason. Despite rivalry in rugby, there is no significant rivalry between the international football teams.
Many people blamed the then French President Jacques Chirac for contributing to Paris' loss to London in its bid for the 2012 Summer Olympics
2012 Summer Olympics
The 2012 Summer Olympic Games, officially known as the "London 2012 Olympic Games", are scheduled to take place in London, England, United Kingdom from 27 July to 12 August 2012...
after he made rude remarks about British cuisine
British cuisine
English cuisine encompasses the cooking styles, traditions and recipes associated with England. It has distinctive attributes of its own, but also shares much with wider British cuisine, largely due to the importation of ingredients and ideas from places such as North America, China, and India...
and saying that "only Finnish food is worse". The IOC committee which would ultimately decide to give the games to London had two members from Finland.
Twinnings
- BasingstokeBasingstokeBasingstoke is a town in northeast Hampshire, in south central England. It lies across a valley at the source of the River Loddon. It is southwest of London, northeast of Southampton, southwest of Reading and northeast of the county town, Winchester. In 2008 it had an estimated population of...
, HampshireHampshireHampshire is a county on the southern coast of England in the United Kingdom. The county town of Hampshire is Winchester, a historic cathedral city that was once the capital of England. Hampshire is notable for housing the original birthplaces of the Royal Navy, British Army, and Royal Air Force...
and AlençonAlençonAlençon is a commune in Normandy, France, capital of the Orne department. It is situated west of Paris. Alençon belongs to the intercommunality of Alençon .-History:...
, Basse-NormandieBasse-NormandieLower Normandy is an administrative region of France. It was created in 1956, when the Normandy region was divided into Lower Normandy and Upper Normandy... - BuryBuryBury is a town in Greater Manchester, England. It lies on the River Irwell, east of Bolton, west-southwest of Rochdale, and north-northwest of the city of Manchester...
, Greater ManchesterGreater ManchesterGreater Manchester is a metropolitan county in North West England, with a population of 2.6 million. It encompasses one of the largest metropolitan areas in the United Kingdom and comprises ten metropolitan boroughs: Bolton, Bury, Oldham, Rochdale, Stockport, Tameside, Trafford, Wigan, and the...
and AngoulêmeAngoulême-Main sights:In place of its ancient fortifications, Angoulême is encircled by boulevards above the old city walls, known as the Remparts, from which fine views may be obtained in all directions. Within the town the streets are often narrow. Apart from the cathedral and the hôtel de ville, the...
, CharenteCharenteCharente is a department in southwestern France, in the Poitou-Charentes region, named after the Charente River, the most important river in the department, and also the river beside which the department's two largest towns, Angoulême and Cognac, are sited.-History:Charente is one of the original... - FarnboroughFarnborough, Hampshire-History:Name changes: Ferneberga ; Farnburghe, Farenberg ; Farnborowe, Fremborough, Fameborough .Tower Hill, Cove: There is substantial evidence...
, HampshireHampshireHampshire is a county on the southern coast of England in the United Kingdom. The county town of Hampshire is Winchester, a historic cathedral city that was once the capital of England. Hampshire is notable for housing the original birthplaces of the Royal Navy, British Army, and Royal Air Force...
and MeudonMeudonMeudon is a municipality in the southwestern suburbs of Paris, France. It is in the département of Hauts-de-Seine. It is located from the center of Paris.-Geography:...
, Ile-de-FranceÎle-de-France (région)Île-de-France is the wealthiest and most populated of the twenty-two administrative regions of France, composed mostly of the Paris metropolitan area.... - ChelmsfordChelmsfordChelmsford is the county town of Essex, England and the principal settlement of the borough of Chelmsford. It is located in the London commuter belt, approximately northeast of Charing Cross, London, and approximately the same distance from the once provincial Roman capital at Colchester...
, EssexEssexEssex is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in the East region of England, and one of the home counties. It is located to the northeast of Greater London. It borders with Cambridgeshire and Suffolk to the north, Hertfordshire to the west, Kent to the South and London to the south west...
and AnnonayAnnonayAnnonay is a commune in the north of the Ardèche department in the Rhône-Alpes region in southern France. It is the most populous commune in the Ardèche department, although it is not the capital, which resides in the smaller town of Privas.-Geography:...
, Rhône-AlpesRhône-AlpesRhône-Alpes is one of the 27 regions of France, located on the eastern border of the country, towards the south. The region was named after the Rhône River and the Alps mountain range. Its capital, Lyon, is the second-largest metropolitan area in France after Paris... - CockermouthCockermouth-History:The Romans created a fort at Derventio, now the adjoining village of Papcastle, to protect the river crossing, which had become located on a major route for troops heading towards Hadrian's Wall....
, CumbriaCumbriaCumbria , is a non-metropolitan county in North West England. The county and Cumbria County Council, its local authority, came into existence in 1974 after the passage of the Local Government Act 1972. Cumbria's largest settlement and county town is Carlisle. It consists of six districts, and in...
and MarvejolsMarvejolsMarvejols , is a commune in the Lozère department in southern France.Its inhabitants are known as Marvejolais.-Geography:The commune is located in the Massif central...
, LozèreLozèreLozère , is a department in southeast France near the Massif Central, named after Mont Lozère.- History :Lozère is one of the original 83 departments created during the French Revolution on March 4, 1790... - DundeeDundeeDundee is the fourth-largest city in Scotland and the 39th most populous settlement in the United Kingdom. It lies within the eastern central Lowlands on the north bank of the Firth of Tay, which feeds into the North Sea...
, Scotland and OrléansOrléans-Prehistory and Roman:Cenabum was a Gallic stronghold, one of the principal towns of the Carnutes tribe where the Druids held their annual assembly. It was conquered and destroyed by Julius Caesar in 52 BC, then rebuilt under the Roman Empire...
, LoiretLoiretLoiret is a department in north-central FranceThe department is named after the river Loiret, a tributary of the Loire. The Loiret is located wholly within the department.- History :... - EalingEalingEaling is a suburban area of west London, England and the administrative centre of the London Borough of Ealing. It is located west of Charing Cross and around from the City of London. It is one of the major metropolitan centres identified in the London Plan. It was historically a rural village...
, London and Marcq-en-BarœulMarcq-en-BarœulMarcq-en-Barœul is a commune in the Nord department in the Nord-Pas-de-Calais region in northern France.It is a suburb of the city of Lille, and is adjacent to it on the northeast...
, Nord-Pas-de-Calais - EdinburghEdinburghEdinburgh is the capital city of Scotland, the second largest city in Scotland, and the eighth most populous in the United Kingdom. The City of Edinburgh Council governs one of Scotland's 32 local government council areas. The council area includes urban Edinburgh and a rural area...
, Scotland and NiceNiceNice is the fifth most populous city in France, after Paris, Marseille, Lyon and Toulouse, with a population of 348,721 within its administrative limits on a land area of . The urban area of Nice extends beyond the administrative city limits with a population of more than 955,000 on an area of...
, Provence-Alpes-Côte d'AzurProvence-Alpes-Côte d'AzurProvence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur or PACA is one of the 27 regions of France.It is made up of:* the former French province of Provence* the former papal territory of Avignon, known as Comtat Venaissin... - GlasgowGlasgowGlasgow is the largest city in Scotland and third most populous in the United Kingdom. The city is situated on the River Clyde in the country's west central lowlands...
, Scotland and MarseilleMarseilleMarseille , known in antiquity as Massalia , is the second largest city in France, after Paris, with a population of 852,395 within its administrative limits on a land area of . The urban area of Marseille extends beyond the city limits with a population of over 1,420,000 on an area of...
, Provence-Alpes-Côte d'AzurProvence-Alpes-Côte d'AzurProvence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur or PACA is one of the 27 regions of France.It is made up of:* the former French province of Provence* the former papal territory of Avignon, known as Comtat Venaissin... - CardiffCardiffCardiff is the capital, largest city and most populous county of Wales and the 10th largest city in the United Kingdom. The city is Wales' chief commercial centre, the base for most national cultural and sporting institutions, the Welsh national media, and the seat of the National Assembly for...
, Wales and NantesNantesNantes is a city in western France, located on the Loire River, from the Atlantic coast. The city is the 6th largest in France, while its metropolitan area ranks 8th with over 800,000 inhabitants....
, BrittanyBrittanyBrittany is a cultural and administrative region in the north-west of France. Previously a kingdom and then a duchy, Brittany was united to the Kingdom of France in 1532 as a province. Brittany has also been referred to as Less, Lesser or Little Britain... - PlymouthPlymouthPlymouth is a city and unitary authority area on the coast of Devon, England, about south-west of London. It is built between the mouths of the rivers Plym to the east and Tamar to the west, where they join Plymouth Sound...
, England and BrestBrest, FranceBrest is a city in the Finistère department in Brittany in northwestern France. Located in a sheltered position not far from the western tip of the Breton peninsula, and the western extremity of metropolitan France, Brest is an important harbour and the second French military port after Toulon...
, BrittanyBrittanyBrittany is a cultural and administrative region in the north-west of France. Previously a kingdom and then a duchy, Brittany was united to the Kingdom of France in 1532 as a province. Brittany has also been referred to as Less, Lesser or Little Britain... - NorwichNorwichNorwich is a city in England. It is the regional administrative centre and county town of Norfolk. During the 11th century, Norwich was the largest city in England after London, and one of the most important places in the kingdom...
, East AngliaEast AngliaEast Anglia is a traditional name for a region of eastern England, named after an ancient Anglo-Saxon kingdom, the Kingdom of the East Angles. The Angles took their name from their homeland Angeln, in northern Germany. East Anglia initially consisted of Norfolk and Suffolk, but upon the marriage of...
and RouenRouenRouen , in northern France on the River Seine, is the capital of the Haute-Normandie region and the historic capital city of Normandy. Once one of the largest and most prosperous cities of medieval Europe , it was the seat of the Exchequer of Normandy in the Middle Ages...
, Haute-NormandieHaute-NormandieUpper Normandy is one of the 27 regions of France. It was created in 1984 from two départements: Seine-Maritime and Eure, when Normandy was divided into Lower Normandy and Upper Normandy. This division continues to provoke controversy, and some continue to call for reuniting the two regions... - OxfordOxfordThe city of Oxford is the county town of Oxfordshire, England. The city, made prominent by its medieval university, has a population of just under 165,000, with 153,900 living within the district boundary. It lies about 50 miles north-west of London. The rivers Cherwell and Thames run through...
, OxfordshireOxfordshireOxfordshire is a county in the South East region of England, bordering on Warwickshire and Northamptonshire , Buckinghamshire , Berkshire , Wiltshire and Gloucestershire ....
and GrenobleGrenobleGrenoble is a city in southeastern France, at the foot of the French Alps where the river Drac joins the Isère. Located in the Rhône-Alpes region, Grenoble is the capital of the department of Isère...
, Rhône-AlpesRhône-AlpesRhône-Alpes is one of the 27 regions of France, located on the eastern border of the country, towards the south. The region was named after the Rhône River and the Alps mountain range. Its capital, Lyon, is the second-largest metropolitan area in France after Paris... - DroylsdenDroylsdenDroylsden is a town within the Metropolitan Borough of Tameside, in Greater Manchester, England. It is to the east of Manchester city centre, and west-southwest of Ashton-under-Lyne, it has a population of 23,172....
, TamesideTamesideThe Metropolitan Borough of Tameside is a metropolitan borough of Greater Manchester in North West England. It is named after the River Tame which flows through the borough and spans the towns of Ashton-under-Lyne, Audenshaw, Denton, Droylsden, Dukinfield, Hyde, Mossley and Stalybridge. Its western...
and VillemombleVillemombleVillemomble is a commune in the eastern suburbs of Paris, France. It is located from the center of Paris.-Heraldry:-Transport:Villemomble is served by Le Raincy – Villemomble – Montfermeil station on Paris RER line E.-Demography:...
, Ile-de-FranceÎle-de-France (région)Île-de-France is the wealthiest and most populated of the twenty-two administrative regions of France, composed mostly of the Paris metropolitan area.... - BirminghamBirminghamBirmingham is a city and metropolitan borough in the West Midlands of England. It is the most populous British city outside the capital London, with a population of 1,036,900 , and lies at the heart of the West Midlands conurbation, the second most populous urban area in the United Kingdom with a...
, West MidlandsWest Midlands (county)The West Midlands is a metropolitan county in western central England with a 2009 estimated population of 2,638,700. It came into existence as a metropolitan county in 1974 after the passage of the Local Government Act 1972, formed from parts of Staffordshire, Worcestershire and Warwickshire. The...
and LyonLyonLyon , is a city in east-central France in the Rhône-Alpes region, situated between Paris and Marseille. Lyon is located at from Paris, from Marseille, from Geneva, from Turin, and from Barcelona. The residents of the city are called Lyonnais....
, Rhône-AlpesRhône-AlpesRhône-Alpes is one of the 27 regions of France, located on the eastern border of the country, towards the south. The region was named after the Rhône River and the Alps mountain range. Its capital, Lyon, is the second-largest metropolitan area in France after Paris... - SunderlandCity of SunderlandThe City of Sunderland is a local government district of Tyne and Wear, in North East England, with the status of a city and metropolitan borough...
, Tyne & Wear and Saint Nazaire, BrittanyBrittanyBrittany is a cultural and administrative region in the north-west of France. Previously a kingdom and then a duchy, Brittany was united to the Kingdom of France in 1532 as a province. Brittany has also been referred to as Less, Lesser or Little Britain... - ExeterExeterExeter is a historic city in Devon, England. It lies within the ceremonial county of Devon, of which it is the county town as well as the home of Devon County Council. Currently the administrative area has the status of a non-metropolitan district, and is therefore under the administration of the...
, DevonDevonDevon is a large county in southwestern England. The county is sometimes referred to as Devonshire, although the term is rarely used inside the county itself as the county has never been officially "shired", it often indicates a traditional or historical context.The county shares borders with...
and RennesRennesRennes is a city in the east of Brittany in northwestern France. Rennes is the capital of the region of Brittany, as well as the Ille-et-Vilaine department.-History:...
, BrittanyBrittanyBrittany is a cultural and administrative region in the north-west of France. Previously a kingdom and then a duchy, Brittany was united to the Kingdom of France in 1532 as a province. Brittany has also been referred to as Less, Lesser or Little Britain... - StockportStockportStockport is a town in Greater Manchester, England. It lies on elevated ground southeast of Manchester city centre, at the point where the rivers Goyt and Tame join and create the River Mersey. Stockport is the largest settlement in the metropolitan borough of the same name...
, Greater ManchesterGreater ManchesterGreater Manchester is a metropolitan county in North West England, with a population of 2.6 million. It encompasses one of the largest metropolitan areas in the United Kingdom and comprises ten metropolitan boroughs: Bolton, Bury, Oldham, Rochdale, Stockport, Tameside, Trafford, Wigan, and the...
and BéziersBéziersBéziers is a town in Languedoc in southern France. It is a sub-prefecture of the Hérault department. Béziers hosts the famous Feria de Béziers, centred around bullfighting, every August. A million visitors are attracted to the five-day event...
, Languedoc-RoussillonLanguedoc-RoussillonLanguedoc-Roussillon is one of the 27 regions of France. It comprises five departments, and borders the other French regions of Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur, Rhône-Alpes, Auvergne, Midi-Pyrénées on the one side, and Spain, Andorra and the Mediterranean sea on the other side.-Geography:The region is... - Bath, Bath and North East SomersetBath and North East SomersetBath and North East Somerset is a unitary authority that was created on 1 April 1996 following the abolition of the County of Avon. It is part of the Ceremonial county of Somerset...
and Aix-en-ProvenceAix-en-ProvenceAix , or Aix-en-Provence to distinguish it from other cities built over hot springs, is a city-commune in southern France, some north of Marseille. It is in the region of Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur, in the département of Bouches-du-Rhône, of which it is a subprefecture. The population of Aix is... - Metropolitan Borough of WirralMetropolitan Borough of WirralThe Metropolitan Borough of Wirral is a metropolitan borough of Merseyside, in North West England. It has a population of 311,200, and encompasses of the northern part of the Wirral Peninsula. Major settlements include Birkenhead, Wallasey, Bebington, Heswall, Hoylake and West Kirby. The city of...
, MerseysideMerseysideMerseyside is a metropolitan county in North West England, with a population of 1,365,900. It encompasses the metropolitan area centred on both banks of the lower reaches of the Mersey Estuary, and comprises five metropolitan boroughs: Knowsley, St Helens, Sefton, Wirral, and the city of Liverpool...
and LorientLorientLorient, or L'Orient, is a commune and a seaport in the Morbihan department in Brittany in north-western France.-History:At the beginning of the 17th century, merchants who were trading with India had established warehouses in Port-Louis... - BoltonBoltonBolton is a town in Greater Manchester, in the North West of England. Close to the West Pennine Moors, it is north west of the city of Manchester. Bolton is surrounded by several smaller towns and villages which together form the Metropolitan Borough of Bolton, of which Bolton is the...
, Greater ManchesterGreater ManchesterGreater Manchester is a metropolitan county in North West England, with a population of 2.6 million. It encompasses one of the largest metropolitan areas in the United Kingdom and comprises ten metropolitan boroughs: Bolton, Bury, Oldham, Rochdale, Stockport, Tameside, Trafford, Wigan, and the...
and Le MansLe MansLe Mans is a city in France, located on the Sarthe River. Traditionally the capital of the province of Maine, it is now the capital of the Sarthe department and the seat of the Roman Catholic diocese of Le Mans. Le Mans is a part of the Pays de la Loire region.Its inhabitants are called Manceaux...
, SartheSartheSarthe is a French department, named after the Sarthe River.- History :The department was created during the French Revolution on March 4, 1790, pursuant to the law of December 22, 1789, starting from a part of the province of Maine which was divided into two departments, Sarthe to the east and... - BuryBuryBury is a town in Greater Manchester, England. It lies on the River Irwell, east of Bolton, west-southwest of Rochdale, and north-northwest of the city of Manchester...
, Greater ManchesterGreater ManchesterGreater Manchester is a metropolitan county in North West England, with a population of 2.6 million. It encompasses one of the largest metropolitan areas in the United Kingdom and comprises ten metropolitan boroughs: Bolton, Bury, Oldham, Rochdale, Stockport, Tameside, Trafford, Wigan, and the...
and AngoulêmeAngoulême-Main sights:In place of its ancient fortifications, Angoulême is encircled by boulevards above the old city walls, known as the Remparts, from which fine views may be obtained in all directions. Within the town the streets are often narrow. Apart from the cathedral and the hôtel de ville, the...
, Poitou-CharentesPoitou-CharentesPoitou-Charentes is an administrative region in central western France comprising four departments: Charente, Charente-Maritime, Deux-Sèvres and Vienne. The regional capital is Poitiers.-Politics:The regional council is composed of 56 members... - WiganWiganWigan is a town in Greater Manchester, England. It stands on the River Douglas, south-west of Bolton, north of Warrington and west-northwest of Manchester. Wigan is the largest settlement in the Metropolitan Borough of Wigan and is its administrative centre. The town of Wigan had a total...
, Greater ManchesterGreater ManchesterGreater Manchester is a metropolitan county in North West England, with a population of 2.6 million. It encompasses one of the largest metropolitan areas in the United Kingdom and comprises ten metropolitan boroughs: Bolton, Bury, Oldham, Rochdale, Stockport, Tameside, Trafford, Wigan, and the...
and AngersAngersAngers is the main city in the Maine-et-Loire department in western France about south-west of Paris. Angers is located in the French region known by its pre-revolutionary, provincial name, Anjou, and its inhabitants are called Angevins....
, Maine et Loire - London and Paris, Île-de-FranceÎle-de-France (région)Île-de-France is the wealthiest and most populated of the twenty-two administrative regions of France, composed mostly of the Paris metropolitan area....
- Preston, LancashireLancashireLancashire is a non-metropolitan county of historic origin in the North West of England. It takes its name from the city of Lancaster, and is sometimes known as the County of Lancaster. Although Lancaster is still considered to be the county town, Lancashire County Council is based in Preston...
and NîmesNîmesNîmes is the capital of the Gard department in the Languedoc-Roussillon region in southern France. Nîmes has a rich history, dating back to the Roman Empire, and is a popular tourist destination.-History:...
, Languedoc-RoussillonLanguedoc-RoussillonLanguedoc-Roussillon is one of the 27 regions of France. It comprises five departments, and borders the other French regions of Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur, Rhône-Alpes, Auvergne, Midi-Pyrénées on the one side, and Spain, Andorra and the Mediterranean sea on the other side.-Geography:The region is... - LichfieldLichfieldLichfield is a cathedral city, civil parish and district in Staffordshire, England. One of eight civil parishes with city status in England, Lichfield is situated roughly north of Birmingham...
, StaffordshireStaffordshireStaffordshire is a landlocked county in the West Midlands region of England. For Eurostat purposes, the county is a NUTS 3 region and is one of four counties or unitary districts that comprise the "Shropshire and Staffordshire" NUTS 2 region. Part of the National Forest lies within its borders...
and Sainte-Foy-lès-LyonSainte-Foy-lès-LyonSainte-Foy-lès-Lyon is a commune in the Rhône department in eastern France.It is a suburb of the city of Lyon, being located to the west of the city. It is thus a component of the metropolitan Urban Community of Lyon.... - SpelthorneSpelthorneSpelthorne is a local government district and borough in Surrey, England. It includes the towns of Ashford, Laleham, Shepperton, Staines, Stanwell and Sunbury...
, SurreySurreySurrey is a county in the South East of England and is one of the Home Counties. The county borders Greater London, Kent, East Sussex, West Sussex, Hampshire and Berkshire. The historic county town is Guildford. Surrey County Council sits at Kingston upon Thames, although this has been part of...
and MelunMelunMelun is a commune in the Seine-et-Marne department in the Île-de-France region in north-central France. Located in the south-eastern suburbs of Paris, Melun is the capital of the department, as the seat of an arrondissement... - StalybridgeStalybridgeStalybridge is a town in the Metropolitan Borough of Tameside in Greater Manchester, England, with a population of 22,568. Historically a part of Cheshire, it is east of Manchester city centre and northwest of Glossop. With the construction of a cotton mill in 1776, Stalybridge became one of...
, TamesideTamesideThe Metropolitan Borough of Tameside is a metropolitan borough of Greater Manchester in North West England. It is named after the River Tame which flows through the borough and spans the towns of Ashton-under-Lyne, Audenshaw, Denton, Droylsden, Dukinfield, Hyde, Mossley and Stalybridge. Its western...
and ArmentièresArmentièresArmentières is a commune in the Nord department in the Nord-Pas-de-Calais region in northern France. It is part of the Urban Community of Lille Métropole, and lies on the Belgian border, northwest of the city of Lille, on the right bank of the river Lys....
, Nord-Pas-de-Calais
There are lists of twinnings
Town twinning
Twin towns and sister cities are two of many terms used to describe the cooperative agreements between towns, cities, and even counties in geographically and politically distinct areas to promote cultural and commercial ties.- Terminology :...
(including those to towns in other countries) at List of twin towns and sister cities in France and at List of twin towns and sister cities in the United Kingdom.
See also
- Angevin EmpireAngevin EmpireThe term Angevin Empire is a modern term describing the collection of states once ruled by the Angevin Plantagenet dynasty.The Plantagenets ruled over an area stretching from the Pyrenees to Ireland during the 12th and early 13th centuries, located north of Moorish Iberia. This "empire" extended...
- Attack on Mers-el-Kébir
- Auld AllianceAuld AllianceThe Auld Alliance was an alliance between the kingdoms of Scotland and France. It played a significant role in the relations between Scotland, France and England from its beginning in 1295 until the 1560 Treaty of Edinburgh. The alliance was renewed by all the French and Scottish monarchs of that...
- Channel TunnelChannel TunnelThe Channel Tunnel is a undersea rail tunnel linking Folkestone, Kent in the United Kingdom with Coquelles, Pas-de-Calais near Calais in northern France beneath the English Channel at the Strait of Dover. At its lowest point, it is deep...
- ConcordeConcordeAérospatiale-BAC Concorde was a turbojet-powered supersonic passenger airliner, a supersonic transport . It was a product of an Anglo-French government treaty, combining the manufacturing efforts of Aérospatiale and the British Aircraft Corporation...
- English claims to the French throneEnglish claims to the French throneThe English claims to the French throne have a long and complex history between the 1340s and the 19th century.From 1340 to 1801, with only brief intervals in 1360-1369 and 1420–1422, the kings and queens of England, and after the Acts of Union in 1707 the kings and queens of Great Britain, also...
- Entente cordialeEntente CordialeThe Entente Cordiale was a series of agreements signed on 8 April 1904 between the United Kingdom and the French Republic. Beyond the immediate concerns of colonial expansion addressed by the agreement, the signing of the Entente Cordiale marked the end of almost a millennium of intermittent...
- Common Security and Defence Policy
- Franco-British UnionFranco-British UnionA Franco-British Union is a concept for a union between the two independent sovereign states of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and France, known as the French Republic...
- Franco-British Council
- French migration to the United KingdomFrench migration to the United KingdomFrench migration to the United Kingdom is a phenomenon that has occurred at various points in history. Today, many British people have French ancestry...
- HuguenotHuguenotThe Huguenots were members of the Protestant Reformed Church of France during the 16th and 17th centuries. Since the 17th century, people who formerly would have been called Huguenots have instead simply been called French Protestants, a title suggested by their German co-religionists, the...
- Hundred Years' WarHundred Years' WarThe Hundred Years' War was a series of separate wars waged from 1337 to 1453 by the House of Valois and the House of Plantagenet, also known as the House of Anjou, for the French throne, which had become vacant upon the extinction of the senior Capetian line of French kings...
- List of British French
- List of wars involving England and France
- Norman conquest of EnglandNorman conquest of EnglandThe Norman conquest of England began on 28 September 1066 with the invasion of England by William, Duke of Normandy. William became known as William the Conqueror after his victory at the Battle of Hastings on 14 October 1066, defeating King Harold II of England...
- Pax BritannicaPax BritannicaPax Britannica was the period of relative peace in Europe when the British Empire controlled most of the key maritime trade routes and enjoyed unchallenged sea power...
- Perfidious AlbionPerfidious Albion'Perfidious Albion' is a pejorative phrase used within the context of international relations and diplomacy to refer to acts of duplicity, treachery and hence infidelity by monarchs or governments of Britain in their pursuit of self-interest and the requirements of...
- Second Hundred Years' WarSecond Hundred Years' WarThe Second Hundred Years' War is a periodization used by some historians to describe the series of military conflicts between the Kingdom of England and France that occurred from about 1689 to 1815. The term appears to have been coined by J. R...
- SEPECAT JaguarSEPECAT JaguarThe SEPECAT Jaguar is an Anglo-French jet ground attack aircraft, originally used by the British Royal Air Force and the French Armée de l'Air in the close air support and nuclear strike role, and still in service with several export customers, notably the Indian Air Force and the Royal Air Force...
- Siege of YorktownSiege of YorktownThe Siege of Yorktown, Battle of Yorktown, or Surrender of Yorktown in 1781 was a decisive victory by a combined assault of American forces led by General George Washington and French forces led by the Comte de Rochambeau over a British Army commanded by Lieutenant General Lord Cornwallis...
- Triple EntenteTriple EntenteThe Triple Entente was the name given to the alliance among Britain, France and Russia after the signing of the Anglo-Russian Entente in 1907....
- University of London Institute in ParisUniversity of London Institute in ParisThe University of London Institute in Paris is a college of the University of London located in Paris. It is currently the only UK University Institute in Continental Europe.-History:...
- 1983 France – United Kingdom Maritime Boundary Convention1983 France – United Kingdom Maritime Boundary ConventionThe 1983 France – United Kingdom Maritime Boundary Convention is a 1983 treaty between France and the United Kingdom which establishes the maritime boundary between French Polynesia and the British territory of the Pitcairn Islands....
External links
- Reassessing what we collect website – French London History of French London with objects and images
- Franco-British Council Links
- University of London in Paris (ULIP)

