
Fungus
Encyclopedia
A fungus is a member of a large group of eukaryotic
organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeast
s and mold
s (British English: moulds), as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom
, Fungi, which is separate from plant
s, animal
s, and bacteria
. One major difference is that fungal cells have cell wall
s that contain chitin
, unlike the cell walls of plants, which contain cellulose
. These and other differences show that the fungi form a single group of related organisms, named the Eumycota (true fungi or Eumycetes), that share a common ancestor (a monophyletic group). This fungal group is distinct from the structurally similar myxomycetes (slime molds) and oomycetes (water molds). The discipline of biology
devoted to the study of fungi is known as mycology
, which is often regarded as a branch of botany
, even though genetic studies have shown that fungi are more closely related to animals than to plants.
Abundant worldwide, most fungi are inconspicuous because of the small size of their structures, and their cryptic
lifestyles in soil, on dead matter, and as symbionts
of plants, animals, or other fungi. They may become noticeable when fruiting
, either as mushrooms or molds. Fungi perform an essential role in the decomposition of organic matter and have fundamental roles in nutrient cycling
and exchange. They have long been used as a direct source of food, such as mushrooms and truffles, as a leavening agent for bread, and in fermentation
of various food products, such as wine
, beer
, and soy sauce
. Since the 1940s, fungi have been used for the production of antibiotic
s, and, more recently, various enzyme
s produced by fungi are used industrially and in detergents. Fungi are also used as biological pesticides to control weeds, plant diseases and insect pests. Many species produce bioactive compounds called mycotoxin
s, such as alkaloid
s and polyketide
s, that are toxic to animals including humans. The fruiting structures of a few species contain psychotropic compounds and are consumed recreationally
or in traditional spiritual ceremonies. Fungi can break down manufactured materials and buildings, and become significant pathogen
s of humans and other animals. Losses of crops due to fungal diseases (e.g. rice blast disease) or food spoilage can have a large impact on human food supplies
and local economies.
The fungus kingdom encompasses an enormous diversity of taxa
with varied ecologies, life cycle
strategies, and morphologies
ranging from single-celled aquatic chytrids to large mushrooms. However, little is known of the true biodiversity
of Kingdom Fungi, which has been estimated at around 1.5 million species, with about 5% of these having been formally classified. Ever since the pioneering 18th and 19th century taxonomical
works of Carl Linnaeus, Christian Hendrik Persoon
, and Elias Magnus Fries
, fungi have been classified
according to their morphology (e.g., characteristics such as spore color or microscopic features) or physiology
. Advances in molecular genetics
have opened the way for DNA analysis
to be incorporated into taxonomy, which has sometimes challenged the historical groupings based on morphology and other traits. Phylogenetic studies published in the last decade have helped reshape the classification of Kingdom Fungi, which is divided into one subkingdom
, seven phyla
, and ten subphyla.
fungus (mushroom), used in the writings of Horace
and Pliny
. This in turn is derived from the Greek
word sphongos/σφογγος ("sponge"), which refers to the macroscopic
structures and morphology of mushrooms and molds; the root is also used in other languages, such as the German Schwamm ("sponge") and Schimmel ("mold"). The use of the word mycology, which is derived from the Greek mykes/μύκης (mushroom) and logos/λόγος (discourse), to denote the scientific study of fungi is thought to have originated in 1836 with English naturalist Miles Joseph Berkeley
's publication The English Flora of Sir James Edward Smith, Vol. 5.
considered fungi to be members of the Plant Kingdom
because of similarities in lifestyle: both fungi and plants are mainly immobile
, and have similarities in general morphology and growth habitat. Like plants, fungi often grow in soil, and in the case of mushroom
s form conspicuous fruiting bodies, which sometimes bear resemblance to plants such as mosses. The fungi are now considered a separate kingdom, distinct from both plants and animals, from which they appear to have diverged around one billion years ago. Some morphological, biochemical, and genetic features are shared with other organisms, while others are unique to the fungi, clearly separating them from the other kingdoms:
Shared features:
Unique features:
 Most fungi lack an efficient system for long-distance transport of water and nutrients, such as the xylem
Most fungi lack an efficient system for long-distance transport of water and nutrients, such as the xylem
and phloem
in many plants. To overcome these limitations, some fungi, such as Armillaria, form rhizomorphs
, that resemble and perform functions similar to the root
s of plants. Another characteristic shared with plants includes a biosynthetic pathway for producing terpene
s that uses mevalonic acid
and pyrophosphate
as chemical building blocks
. However, plants have an additional terpene pathway in their chloroplasts, a structure fungi do not possess. Fungi produce several secondary metabolite
s that are similar or identical in structure to those made by plants. Many of the plant and fungal enzymes that make these compounds differ from each other in sequence
and other characteristics, which indicates separate origins and evolution of these enzymes in the fungi and plants.
or areas with high salt concentrations or ionizing radiation
, as well as in deep sea
sediments. Some can survive the intense UV and cosmic radiation encountered during space travel. Most grow in terrestrial environments, though several species live partly or solely in aquatic habitats, such as the chytrid fungus Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis
, a parasite that has been responsible for a worldwide decline in amphibian
populations. This organism spends part of its life cycle as a motile zoospore
, enabling it to propel itself through water and enter its amphibian host. Other examples of aquatic fungi include those living in hydrothermal areas of the ocean.
Around 100,000 species of fungi have been formally described by taxonomists
, but the global biodiversity of the fungus kingdom is not fully understood. On the basis of observations of the ratio of the number of fungal species to the number of plant species in selected environments, the fungal kingdom has been estimated to contain about 1.5 million species; a recent (2011) estimate suggests there may be over 5 million species. In mycology, species
have historically been distinguished by a variety of methods and concepts. Classification based on morphological
characteristics, such as the size and shape of spores or fruiting structures, has traditionally dominated fungal taxonomy. Species may also be distinguished by their biochemical
and physiological
characteristics, such as their ability to metabolize certain biochemicals, or their reaction to chemical tests
. The biological species concept discriminates species based on their ability to mate
. The application of molecular
tools, such as DNA sequencing
and phylogenetic analysis, to study diversity has greatly enhanced the resolution and added robustness to estimates of genetic diversity
within various taxonomic groups.
e, which are cylindrical, thread-like structures 2–10 µm in diameter and up to several centimeters in length. Hyphae grow at their tips (apices); new hyphae are typically formed by emergence of new tips along existing hyphae by a process called branching, or occasionally growing hyphal tips bifurcate (fork) giving rise to two parallel-growing hyphae. The combination of apical growth and branching/forking leads to the development of a mycelium
, an interconnected network of hyphae. Hyphae can be either septate or coenocytic: septate hyphae are divided into compartments separated by cross walls (internal cell walls, called septa, that are formed at right angle
s to the cell wall giving the hypha its shape), with each compartment containing one or more nuclei; coenocytic hyphae are not compartmentalized. Septa have pores that allow cytoplasm
, organelle
s, and sometimes nuclei to pass through; an example is the dolipore septum in the fungi of the phylum Basidiomycota. Coenocytic hyphae are essentially multinucleate
supercells.
Many species have developed specialized hyphal structures for nutrient uptake from living hosts; examples include haustoria in plant-parasitic species of most fungal phyla, and arbuscules
of several mycorrhiza
l fungi, which penetrate into the host cells to consume nutrients.
Although fungi are opisthokont
s—a grouping of evolutionarily related organisms broadly characterized by a single posterior flagellum
—all phyla except for the chytrids have lost their posterior flagella. Fungi are unusual among the eukaryotes in having a cell wall that, in addition to glucan
s (e.g., β-1,3-glucan) and other typical components, also contains the biopolymer
chitin.
s. Mycelia grown on solid agar
media in laboratory petri dish
es are usually referred to as colonies
. These colonies can exhibit growth shapes and colors (due to spores or pigment
ation) that can be used as diagnostic features in the identification of species or groups. Some individual fungal colonies can reach extraordinary dimensions and ages as in the case of a clonal
colony of Armillaria solidipes, which extends over an area of more than 900 ha
(3.5 square miles), with an estimated age of nearly 9,000 years.
The apothecium—a specialized structure important in sexual reproduction
in the ascomycetes—is a cup-shaped fruiting body that holds the hymenium
, a layer of tissue containing the spore-bearing cells. The fruiting bodies of the basidiomycetes (basidiocarp
s) and some ascomycetes can sometimes grow very large, and many are well-known as mushroom
s.
 The growth of fungi as hyphae on or in solid substrates or as single cells in aquatic environments is adapted for the efficient extraction of nutrients, because these growth forms have high surface area to volume ratio
The growth of fungi as hyphae on or in solid substrates or as single cells in aquatic environments is adapted for the efficient extraction of nutrients, because these growth forms have high surface area to volume ratio
s. Hyphae are specifically adapted for growth on solid surfaces, and to invade substrates
and tissues. They can exert large penetrative mechanical forces; for example, the plant pathogen Magnaporthe grisea
forms a structure called an appressorium
that evolved to puncture plant tissues. The pressure generated by the appressorium, directed against the plant epidermis
, can exceed 8 megapascals (1,160.3 psi). The filamentous fungus Paecilomyces lilacinus uses a similar structure to penetrate the eggs of nematode
s.
The mechanical pressure exerted by the appressorium is generated from physiological processes that increase intracellular turgor by producing osmolyte
s such as glycerol
. Morphological adaptations such as these are complemented by hydrolytic enzymes
secreted into the environment to digest large organic molecules—such as polysaccharide
s, protein
s, lipid
s, and other organic substrates—into smaller molecules that may then be absorbed as nutrients. The vast majority of filamentous fungi grow in a polar fashion—i.e., by extension into one direction—by elongation at the tip (apex) of the hypha. Alternative forms of fungal growth include intercalary extension (i.e., by longitudinal expansion of hyphal compartments that are below the apex) as in the case of some endophytic
fungi, or growth by volume expansion during the development of mushroom stipes and other large organs. Growth of fungi as multicellular structures consisting of somatic
and reproductive cells—a feature independently evolved in animals and plants—has several functions, including the development of fruiting bodies for dissemination of sexual spores (see above) and biofilm
s for substrate colonization and intercellular communication.
Traditionally, the fungi are considered heterotroph
s, organisms that rely solely on carbon fixed
by other organisms for metabolism
. Fungi have evolved
a high degree of metabolic versatility that allows them to use a diverse range of organic substrates for growth, including simple compounds such as nitrate
, ammonia
, acetate
, or ethanol
. For some species it has been shown that the pigment melanin
may play a role in extracting energy from ionizing radiation
, such as gamma radiation; however, this form of "radiotrophic"
growth has only been described for a few species, the effects on growth rates are small, and the underlying biophysical
and biochemical processes are not known. The authors speculate that this process might bear similarity to CO2 fixation
via visible light
, but instead utilizing ionizing radiation as a source of energy.
 Fungal reproduction is complex, reflecting the differences in lifestyles and genetic makeup within this kingdom of organisms. It is estimated that a third of all fungi reproduce by different modes of propagation; for example, reproduction may occur in two well-differentiated stages within the life cycle
Fungal reproduction is complex, reflecting the differences in lifestyles and genetic makeup within this kingdom of organisms. It is estimated that a third of all fungi reproduce by different modes of propagation; for example, reproduction may occur in two well-differentiated stages within the life cycle
of a species, the teleomorph and the anamorph. Environmental conditions trigger genetically determined developmental states that lead to the creation of specialized structures for sexual or asexual reproduction. These structures aid reproduction by efficiently dispersing spores or spore-containing propagule
s.
via vegetative spores (conidia
) or through mycelial fragmentation is common; it maintains clonal populations adapted to a specific niche
, and allows more rapid dispersal than sexual reproduction. The "Fungi imperfecti" (fungi lacking the perfect or sexual stage) or Deuteromycota comprise all the species which lack an observable sexual cycle.
exists in all fungal phyla (with the exception of the Glomeromycota
).
A fungus is a member of a large group of eukaryotic
organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeast
s and mold
s (British English: moulds), as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom
, Fungi, which is separate from plant
s, animal
s, and bacteria
. One major difference is that fungal cells have cell wall
s that contain chitin
, unlike the cell walls of plants, which contain cellulose
. These and other differences show that the fungi form a single group of related organisms, named the Eumycota (true fungi or Eumycetes), that share a common ancestor (a monophyletic group). This fungal group is distinct from the structurally similar myxomycetes (slime molds) and oomycetes (water molds). The discipline of biology
devoted to the study of fungi is known as mycology
, which is often regarded as a branch of botany
, even though genetic studies have shown that fungi are more closely related to animals than to plants.
Abundant worldwide, most fungi are inconspicuous because of the small size of their structures, and their cryptic
lifestyles in soil, on dead matter, and as symbionts
of plants, animals, or other fungi. They may become noticeable when fruiting
, either as mushrooms or molds. Fungi perform an essential role in the decomposition of organic matter and have fundamental roles in nutrient cycling
and exchange. They have long been used as a direct source of food, such as mushrooms and truffles, as a leavening agent for bread, and in fermentation
of various food products, such as wine
, beer
, and soy sauce
. Since the 1940s, fungi have been used for the production of antibiotic
s, and, more recently, various enzyme
s produced by fungi are used industrially and in detergents. Fungi are also used as biological pesticides to control weeds, plant diseases and insect pests. Many species produce bioactive compounds called mycotoxin
s, such as alkaloid
s and polyketide
s, that are toxic to animals including humans. The fruiting structures of a few species contain psychotropic compounds and are consumed recreationally
or in traditional spiritual ceremonies. Fungi can break down manufactured materials and buildings, and become significant pathogen
s of humans and other animals. Losses of crops due to fungal diseases (e.g. rice blast disease) or food spoilage can have a large impact on human food supplies
and local economies.
The fungus kingdom encompasses an enormous diversity of taxa
with varied ecologies, life cycle
strategies, and morphologies
ranging from single-celled aquatic chytrids to large mushrooms. However, little is known of the true biodiversity
of Kingdom Fungi, which has been estimated at around 1.5 million species, with about 5% of these having been formally classified. Ever since the pioneering 18th and 19th century taxonomical
works of Carl Linnaeus, Christian Hendrik Persoon
, and Elias Magnus Fries
, fungi have been classified
according to their morphology (e.g., characteristics such as spore color or microscopic features) or physiology
. Advances in molecular genetics
have opened the way for DNA analysis
to be incorporated into taxonomy, which has sometimes challenged the historical groupings based on morphology and other traits. Phylogenetic studies published in the last decade have helped reshape the classification of Kingdom Fungi, which is divided into one subkingdom
, seven phyla
, and ten subphyla.
fungus (mushroom), used in the writings of Horace
and Pliny
. This in turn is derived from the Greek
word sphongos/σφογγος ("sponge"), which refers to the macroscopic
structures and morphology of mushrooms and molds; the root is also used in other languages, such as the German Schwamm ("sponge") and Schimmel ("mold"). The use of the word mycology, which is derived from the Greek mykes/μύκης (mushroom) and logos/λόγος (discourse), to denote the scientific study of fungi is thought to have originated in 1836 with English naturalist Miles Joseph Berkeley
's publication The English Flora of Sir James Edward Smith, Vol. 5.Ainsworth, p. 2.
considered fungi to be members of the Plant Kingdom
because of similarities in lifestyle: both fungi and plants are mainly immobile
, and have similarities in general morphology and growth habitat. Like plants, fungi often grow in soil, and in the case of mushroom
s form conspicuous fruiting bodies, which sometimes bear resemblance to plants such as mosses. The fungi are now considered a separate kingdom, distinct from both plants and animals, from which they appear to have diverged around one billion years ago. Some morphological, biochemical, and genetic features are shared with other organisms, while others are unique to the fungi, clearly separating them from the other kingdoms:
Shared features:
Unique features:
 Most fungi lack an efficient system for long-distance transport of water and nutrients, such as the xylem
Most fungi lack an efficient system for long-distance transport of water and nutrients, such as the xylem
and phloem
in many plants. To overcome these limitations, some fungi, such as Armillaria, form rhizomorphs
, that resemble and perform functions similar to the root
s of plants. Another characteristic shared with plants includes a biosynthetic pathway for producing terpene
s that uses mevalonic acid
and pyrophosphate
as chemical building blocks
. However, plants have an additional terpene pathway in their chloroplasts, a structure fungi do not possess. Fungi produce several secondary metabolite
s that are similar or identical in structure to those made by plants. Many of the plant and fungal enzymes that make these compounds differ from each other in sequence
and other characteristics, which indicates separate origins and evolution of these enzymes in the fungi and plants.
or areas with high salt concentrations or ionizing radiation
, as well as in deep sea
sediments. Some can survive the intense UV and cosmic radiation encountered during space travel. Most grow in terrestrial environments, though several species live partly or solely in aquatic habitats, such as the chytrid fungus Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis
, a parasite that has been responsible for a worldwide decline in amphibian
populations. This organism spends part of its life cycle as a motile zoospore
, enabling it to propel itself through water and enter its amphibian host. Other examples of aquatic fungi include those living in hydrothermal areas of the ocean.
Around 100,000 species of fungi have been formally described by taxonomists
, but the global biodiversity of the fungus kingdom is not fully understood. On the basis of observations of the ratio of the number of fungal species to the number of plant species in selected environments, the fungal kingdom has been estimated to contain about 1.5 million species; a recent (2011) estimate suggests there may be over 5 million species. In mycology, species
have historically been distinguished by a variety of methods and concepts. Classification based on morphological
characteristics, such as the size and shape of spores or fruiting structures, has traditionally dominated fungal taxonomy.Kirk et al., p. 489. Species may also be distinguished by their biochemical
and physiological
characteristics, such as their ability to metabolize certain biochemicals, or their reaction to chemical tests
. The biological species concept discriminates species based on their ability to mate
. The application of molecular
tools, such as DNA sequencing
and phylogenetic analysis, to study diversity has greatly enhanced the resolution and added robustness to estimates of genetic diversity
within various taxonomic groups.
e, which are cylindrical, thread-like structures 2–10 µm in diameter and up to several centimeters in length. Hyphae grow at their tips (apices); new hyphae are typically formed by emergence of new tips along existing hyphae by a process called branching, or occasionally growing hyphal tips bifurcate (fork) giving rise to two parallel-growing hyphae. The combination of apical growth and branching/forking leads to the development of a mycelium
, an interconnected network of hyphae. Hyphae can be either septate or coenocytic: septate hyphae are divided into compartments separated by cross walls (internal cell walls, called septa, that are formed at right angle
s to the cell wall giving the hypha its shape), with each compartment containing one or more nuclei; coenocytic hyphae are not compartmentalized. Septa have pores that allow cytoplasm
, organelle
s, and sometimes nuclei to pass through; an example is the dolipore septum in the fungi of the phylum Basidiomycota. Coenocytic hyphae are essentially multinucleate
supercells.
Many species have developed specialized hyphal structures for nutrient uptake from living hosts; examples include haustoria in plant-parasitic species of most fungal phyla, and arbuscules
of several mycorrhiza
l fungi, which penetrate into the host cells to consume nutrients.
Although fungi are opisthokont
s—a grouping of evolutionarily related organisms broadly characterized by a single posterior flagellum
—all phyla except for the chytrids have lost their posterior flagella. Fungi are unusual among the eukaryotes in having a cell wall that, in addition to glucan
s (e.g., β-1,3-glucan) and other typical components, also contains the biopolymer
chitin.
s. Mycelia grown on solid agar
media in laboratory petri dish
es are usually referred to as colonies
. These colonies can exhibit growth shapes and colors (due to spores or pigment
ation) that can be used as diagnostic features in the identification of species or groups. Some individual fungal colonies can reach extraordinary dimensions and ages as in the case of a clonal
colony of Armillaria solidipes, which extends over an area of more than 900 ha
(3.5 square miles), with an estimated age of nearly 9,000 years.
The apothecium—a specialized structure important in sexual reproduction
in the ascomycetes—is a cup-shaped fruiting body that holds the hymenium
, a layer of tissue containing the spore-bearing cells. The fruiting bodies of the basidiomycetes (basidiocarp
s) and some ascomycetes can sometimes grow very large, and many are well-known as mushroom
s.
 The growth of fungi as hyphae on or in solid substrates or as single cells in aquatic environments is adapted for the efficient extraction of nutrients, because these growth forms have high surface area to volume ratio
The growth of fungi as hyphae on or in solid substrates or as single cells in aquatic environments is adapted for the efficient extraction of nutrients, because these growth forms have high surface area to volume ratio
s. Hyphae are specifically adapted for growth on solid surfaces, and to invade substrates
and tissues. They can exert large penetrative mechanical forces; for example, the plant pathogen Magnaporthe grisea
forms a structure called an appressorium
that evolved to puncture plant tissues. The pressure generated by the appressorium, directed against the plant epidermis
, can exceed 8 megapascals (1,160.3 psi). The filamentous fungus Paecilomyces lilacinus uses a similar structure to penetrate the eggs of nematode
s.
The mechanical pressure exerted by the appressorium is generated from physiological processes that increase intracellular turgor by producing osmolyte
s such as glycerol
. Morphological adaptations such as these are complemented by hydrolytic enzymes
secreted into the environment to digest large organic molecules—such as polysaccharide
s, protein
s, lipid
s, and other organic substrates—into smaller molecules that may then be absorbed as nutrients. The vast majority of filamentous fungi grow in a polar fashion—i.e., by extension into one direction—by elongation at the tip (apex) of the hypha. Alternative forms of fungal growth include intercalary extension (i.e., by longitudinal expansion of hyphal compartments that are below the apex) as in the case of some endophytic
fungi, or growth by volume expansion during the development of mushroom stipes and other large organs. Growth of fungi as multicellular structures consisting of somatic
and reproductive cells—a feature independently evolved in animals and plants—has several functions, including the development of fruiting bodies for dissemination of sexual spores (see above) and biofilm
s for substrate colonization and intercellular communication.
Traditionally, the fungi are considered heterotroph
s, organisms that rely solely on carbon fixed
by other organisms for metabolism
. Fungi have evolved
a high degree of metabolic versatility that allows them to use a diverse range of organic substrates for growth, including simple compounds such as nitrate
, ammonia
, acetate
, or ethanol
. For some species it has been shown that the pigment melanin
may play a role in extracting energy from ionizing radiation
, such as gamma radiation; however, this form of "radiotrophic"
growth has only been described for a few species, the effects on growth rates are small, and the underlying biophysical
and biochemical processes are not known. The authors speculate that this process might bear similarity to CO2 fixation
via visible light
, but instead utilizing ionizing radiation as a source of energy.
 Fungal reproduction is complex, reflecting the differences in lifestyles and genetic makeup within this kingdom of organisms. It is estimated that a third of all fungi reproduce by different modes of propagation; for example, reproduction may occur in two well-differentiated stages within the life cycle
Fungal reproduction is complex, reflecting the differences in lifestyles and genetic makeup within this kingdom of organisms. It is estimated that a third of all fungi reproduce by different modes of propagation; for example, reproduction may occur in two well-differentiated stages within the life cycle
of a species, the teleomorph and the anamorph. Environmental conditions trigger genetically determined developmental states that lead to the creation of specialized structures for sexual or asexual reproduction. These structures aid reproduction by efficiently dispersing spores or spore-containing propagule
s.
via vegetative spores (conidia
) or through mycelial fragmentation is common; it maintains clonal populations adapted to a specific niche
, and allows more rapid dispersal than sexual reproduction. The "Fungi imperfecti" (fungi lacking the perfect or sexual stage) or Deuteromycota comprise all the species which lack an observable sexual cycle.
exists in all fungal phyla (with the exception of the Glomeromycota
).
A fungus is a member of a large group of eukaryotic
organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeast
s and mold
s (British English: moulds), as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom
, Fungi, which is separate from plant
s, animal
s, and bacteria
. One major difference is that fungal cells have cell wall
s that contain chitin
, unlike the cell walls of plants, which contain cellulose
. These and other differences show that the fungi form a single group of related organisms, named the Eumycota (true fungi or Eumycetes), that share a common ancestor (a monophyletic group). This fungal group is distinct from the structurally similar myxomycetes (slime molds) and oomycetes (water molds). The discipline of biology
devoted to the study of fungi is known as mycology
, which is often regarded as a branch of botany
, even though genetic studies have shown that fungi are more closely related to animals than to plants.
Abundant worldwide, most fungi are inconspicuous because of the small size of their structures, and their cryptic
lifestyles in soil, on dead matter, and as symbionts
of plants, animals, or other fungi. They may become noticeable when fruiting
, either as mushrooms or molds. Fungi perform an essential role in the decomposition of organic matter and have fundamental roles in nutrient cycling
and exchange. They have long been used as a direct source of food, such as mushrooms and truffles, as a leavening agent for bread, and in fermentation
of various food products, such as wine
, beer
, and soy sauce
. Since the 1940s, fungi have been used for the production of antibiotic
s, and, more recently, various enzyme
s produced by fungi are used industrially and in detergents. Fungi are also used as biological pesticides to control weeds, plant diseases and insect pests. Many species produce bioactive compounds called mycotoxin
s, such as alkaloid
s and polyketide
s, that are toxic to animals including humans. The fruiting structures of a few species contain psychotropic compounds and are consumed recreationally
or in traditional spiritual ceremonies. Fungi can break down manufactured materials and buildings, and become significant pathogen
s of humans and other animals. Losses of crops due to fungal diseases (e.g. rice blast disease) or food spoilage can have a large impact on human food supplies
and local economies.
The fungus kingdom encompasses an enormous diversity of taxa
with varied ecologies, life cycle
strategies, and morphologies
ranging from single-celled aquatic chytrids to large mushrooms. However, little is known of the true biodiversity
of Kingdom Fungi, which has been estimated at around 1.5 million species, with about 5% of these having been formally classified. Ever since the pioneering 18th and 19th century taxonomical
works of Carl Linnaeus, Christian Hendrik Persoon
, and Elias Magnus Fries
, fungi have been classified
according to their morphology (e.g., characteristics such as spore color or microscopic features) or physiology
. Advances in molecular genetics
have opened the way for DNA analysis
to be incorporated into taxonomy, which has sometimes challenged the historical groupings based on morphology and other traits. Phylogenetic studies published in the last decade have helped reshape the classification of Kingdom Fungi, which is divided into one subkingdom
, seven phyla
, and ten subphyla.
fungus (mushroom), used in the writings of Horace
and Pliny
. This in turn is derived from the Greek
word sphongos/σφογγος ("sponge"), which refers to the macroscopic
structures and morphology of mushrooms and molds; the root is also used in other languages, such as the German Schwamm ("sponge") and Schimmel ("mold"). The use of the word mycology, which is derived from the Greek mykes/μύκης (mushroom) and logos/λόγος (discourse), to denote the scientific study of fungi is thought to have originated in 1836 with English naturalist Miles Joseph Berkeley
's publication The English Flora of Sir James Edward Smith, Vol. 5.Ainsworth, p. 2.
considered fungi to be members of the Plant Kingdom
because of similarities in lifestyle: both fungi and plants are mainly immobile
, and have similarities in general morphology and growth habitat. Like plants, fungi often grow in soil, and in the case of mushroom
s form conspicuous fruiting bodies, which sometimes bear resemblance to plants such as mosses. The fungi are now considered a separate kingdom, distinct from both plants and animals, from which they appear to have diverged around one billion years ago. Some morphological, biochemical, and genetic features are shared with other organisms, while others are unique to the fungi, clearly separating them from the other kingdoms:
Shared features:
Unique features:
 Most fungi lack an efficient system for long-distance transport of water and nutrients, such as the xylem
Most fungi lack an efficient system for long-distance transport of water and nutrients, such as the xylem
and phloem
in many plants. To overcome these limitations, some fungi, such as Armillaria, form rhizomorphs
, that resemble and perform functions similar to the root
s of plants. Another characteristic shared with plants includes a biosynthetic pathway for producing terpene
s that uses mevalonic acid
and pyrophosphate
as chemical building blocks
. However, plants have an additional terpene pathway in their chloroplasts, a structure fungi do not possess. Fungi produce several secondary metabolite
s that are similar or identical in structure to those made by plants. Many of the plant and fungal enzymes that make these compounds differ from each other in sequence
and other characteristics, which indicates separate origins and evolution of these enzymes in the fungi and plants.
or areas with high salt concentrations or ionizing radiation
, as well as in deep sea
sediments. Some can survive the intense UV and cosmic radiation encountered during space travel. Most grow in terrestrial environments, though several species live partly or solely in aquatic habitats, such as the chytrid fungus Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis
, a parasite that has been responsible for a worldwide decline in amphibian
populations. This organism spends part of its life cycle as a motile zoospore
, enabling it to propel itself through water and enter its amphibian host. Other examples of aquatic fungi include those living in hydrothermal areas of the ocean.
Around 100,000 species of fungi have been formally described by taxonomists
, but the global biodiversity of the fungus kingdom is not fully understood. On the basis of observations of the ratio of the number of fungal species to the number of plant species in selected environments, the fungal kingdom has been estimated to contain about 1.5 million species; a recent (2011) estimate suggests there may be over 5 million species. In mycology, species
have historically been distinguished by a variety of methods and concepts. Classification based on morphological
characteristics, such as the size and shape of spores or fruiting structures, has traditionally dominated fungal taxonomy.Kirk et al., p. 489. Species may also be distinguished by their biochemical
and physiological
characteristics, such as their ability to metabolize certain biochemicals, or their reaction to chemical tests
. The biological species concept discriminates species based on their ability to mate
. The application of molecular
tools, such as DNA sequencing
and phylogenetic analysis, to study diversity has greatly enhanced the resolution and added robustness to estimates of genetic diversity
within various taxonomic groups.
e, which are cylindrical, thread-like structures 2–10 µm in diameter and up to several centimeters in length. Hyphae grow at their tips (apices); new hyphae are typically formed by emergence of new tips along existing hyphae by a process called branching, or occasionally growing hyphal tips bifurcate (fork) giving rise to two parallel-growing hyphae. The combination of apical growth and branching/forking leads to the development of a mycelium
, an interconnected network of hyphae. Hyphae can be either septate or coenocytic: septate hyphae are divided into compartments separated by cross walls (internal cell walls, called septa, that are formed at right angle
s to the cell wall giving the hypha its shape), with each compartment containing one or more nuclei; coenocytic hyphae are not compartmentalized. Septa have pores that allow cytoplasm
, organelle
s, and sometimes nuclei to pass through; an example is the dolipore septum in the fungi of the phylum Basidiomycota. Coenocytic hyphae are essentially multinucleate
supercells.
Many species have developed specialized hyphal structures for nutrient uptake from living hosts; examples include haustoria in plant-parasitic species of most fungal phyla, and arbuscules
of several mycorrhiza
l fungi, which penetrate into the host cells to consume nutrients.
Although fungi are opisthokont
s—a grouping of evolutionarily related organisms broadly characterized by a single posterior flagellum
—all phyla except for the chytrids have lost their posterior flagella. Fungi are unusual among the eukaryotes in having a cell wall that, in addition to glucan
s (e.g., β-1,3-glucan) and other typical components, also contains the biopolymer
chitin.
s. Mycelia grown on solid agar
media in laboratory petri dish
es are usually referred to as colonies
. These colonies can exhibit growth shapes and colors (due to spores or pigment
ation) that can be used as diagnostic features in the identification of species or groups. Some individual fungal colonies can reach extraordinary dimensions and ages as in the case of a clonal
colony of Armillaria solidipes, which extends over an area of more than 900 ha
(3.5 square miles), with an estimated age of nearly 9,000 years.
The apothecium—a specialized structure important in sexual reproduction
in the ascomycetes—is a cup-shaped fruiting body that holds the hymenium
, a layer of tissue containing the spore-bearing cells. The fruiting bodies of the basidiomycetes (basidiocarp
s) and some ascomycetes can sometimes grow very large, and many are well-known as mushroom
s.
 The growth of fungi as hyphae on or in solid substrates or as single cells in aquatic environments is adapted for the efficient extraction of nutrients, because these growth forms have high surface area to volume ratio
The growth of fungi as hyphae on or in solid substrates or as single cells in aquatic environments is adapted for the efficient extraction of nutrients, because these growth forms have high surface area to volume ratio
s. Hyphae are specifically adapted for growth on solid surfaces, and to invade substrates
and tissues. They can exert large penetrative mechanical forces; for example, the plant pathogen Magnaporthe grisea
forms a structure called an appressorium
that evolved to puncture plant tissues. The pressure generated by the appressorium, directed against the plant epidermis
, can exceed 8 megapascals (1,160.3 psi). The filamentous fungus Paecilomyces lilacinus uses a similar structure to penetrate the eggs of nematode
s.
The mechanical pressure exerted by the appressorium is generated from physiological processes that increase intracellular turgor by producing osmolyte
s such as glycerol
. Morphological adaptations such as these are complemented by hydrolytic enzymes
secreted into the environment to digest large organic molecules—such as polysaccharide
s, protein
s, lipid
s, and other organic substrates—into smaller molecules that may then be absorbed as nutrients. The vast majority of filamentous fungi grow in a polar fashion—i.e., by extension into one direction—by elongation at the tip (apex) of the hypha. Alternative forms of fungal growth include intercalary extension (i.e., by longitudinal expansion of hyphal compartments that are below the apex) as in the case of some endophytic
fungi, or growth by volume expansion during the development of mushroom stipes and other large organs. Growth of fungi as multicellular structures consisting of somatic
and reproductive cells—a feature independently evolved in animals and plants—has several functions, including the development of fruiting bodies for dissemination of sexual spores (see above) and biofilm
s for substrate colonization and intercellular communication.
Traditionally, the fungi are considered heterotroph
s, organisms that rely solely on carbon fixed
by other organisms for metabolism
. Fungi have evolved
a high degree of metabolic versatility that allows them to use a diverse range of organic substrates for growth, including simple compounds such as nitrate
, ammonia
, acetate
, or ethanol
. For some species it has been shown that the pigment melanin
may play a role in extracting energy from ionizing radiation
, such as gamma radiation; however, this form of "radiotrophic"
growth has only been described for a few species, the effects on growth rates are small, and the underlying biophysical
and biochemical processes are not known. The authors speculate that this process might bear similarity to CO2 fixation
via visible light
, but instead utilizing ionizing radiation as a source of energy.
 Fungal reproduction is complex, reflecting the differences in lifestyles and genetic makeup within this kingdom of organisms. It is estimated that a third of all fungi reproduce by different modes of propagation; for example, reproduction may occur in two well-differentiated stages within the life cycle
Fungal reproduction is complex, reflecting the differences in lifestyles and genetic makeup within this kingdom of organisms. It is estimated that a third of all fungi reproduce by different modes of propagation; for example, reproduction may occur in two well-differentiated stages within the life cycle
of a species, the teleomorph and the anamorph. Environmental conditions trigger genetically determined developmental states that lead to the creation of specialized structures for sexual or asexual reproduction. These structures aid reproduction by efficiently dispersing spores or spore-containing propagule
s.
via vegetative spores (conidia
) or through mycelial fragmentation is common; it maintains clonal populations adapted to a specific niche
, and allows more rapid dispersal than sexual reproduction. The "Fungi imperfecti" (fungi lacking the perfect or sexual stage) or Deuteromycota comprise all the species which lack an observable sexual cycle.
exists in all fungal phyla (with the exception of the Glomeromycota
). It differs in many aspects from sexual reproduction in animals or plants. Differences also exist between fungal groups and can be used to discriminate species by morphological differences in sexual structures and reproductive strategies. Mating
experiments between fungal isolates may identify species on the basis of biological species concepts. The major fungal groupings have initially been delineated based on the morphology of their sexual structures and spores; for example, the spore-containing structures, asci
and basidia
, can be used in the identification of ascomycetes and basidiomycetes, respectively. Some species may allow mating only between individuals of opposite mating type
, while others can mate and sexually reproduce with any other individual or itself. Species of the former mating system
are called heterothallic
, and of the latter homothallic
.
Most fungi have both an haploid and diploid stage in their life cycles. In sexually reproducing fungi, compatible individuals may combine by fusing their hyphae together into an interconnected network; this process, anastomosis
, is required for the initiation of the sexual cycle. Ascomycetes and basidiomycetes go through a dikaryotic stage, in which the nuclei inherited from the two parents do not combine immediately after cell fusion, but remain separate in the hyphal cells (see heterokaryosis
).
 In ascomycetes, dikaryotic hyphae of the hymenium
In ascomycetes, dikaryotic hyphae of the hymenium
(the spore-bearing tissue layer) form a characteristic hook at the hyphal septum. During cell division
, formation of the hook ensures proper distribution of the newly divided nuclei into the apical and basal hyphal compartments. An ascus (plural asci) is then formed, in which karyogamy
(nuclear fusion) occurs. Asci are embedded in an ascocarp
, or fruiting body. Karyogamy in the asci is followed immediately by meiosis and the production of ascospore
s. After dispersal, the ascospores may germinate and form a new haploid mycelium.
Sexual reproduction in basidiomycetes is similar to that of the ascomycetes. Compatible haploid hyphae fuse to produce a dikaryotic mycelium. However, the dikaryotic phase is more extensive in the basidiomycetes, often also present in the vegetatively growing mycelium. A specialized anatomical structure, called a clamp connection
, is formed at each hyphal septum. As with the structurally similar hook in the ascomycetes, the clamp connection in the basidiomycetes is required for controlled transfer of nuclei during cell division, to maintain the dikaryotic stage with two genetically different nuclei in each hyphal compartment. A basidiocarp
is formed in which club-like structures known as basidia generate haploid basidiospores after karyogamy and meiosis. The most commonly known basidiocarps are mushrooms, but they may also take other forms (see Morphology section).
In glomeromycetes (formerly zygomycetes), haploid hyphae of two individuals fuse, forming a gametangium, a specialized cell structure that becomes a fertile gamete
-producing cell. The gametangium develops into a zygospore
, a thick-walled spore formed by the union of gametes. When the zygospore germinates, it undergoes meiosis
, generating new haploid hyphae, which may then form asexual sporangiospores. These sporangiospores allow the fungus to rapidly disperse and germinate into new genetically identical haploid fungal mycelia.
 Specialized mechanical and physiological mechanisms, as well as spore surface structures (such as hydrophobin
Specialized mechanical and physiological mechanisms, as well as spore surface structures (such as hydrophobin
s), enable efficient spore ejection. For example, the structure of the spore-bearing cells
in some ascomycete species is such that the buildup of substances
affecting cell volume and fluid balance enables the explosive discharge of spores into the air. The forcible discharge of single spores termed ballistospores involves formation of a small drop of water (Buller's drop), which upon contact with the spore leads to its projectile release with an initial acceleration of more than 10,000 g
; the net result is that the spore is ejected 0.01–0.02 cm, sufficient distance for it to fall through the gills or pores into the air below. Other fungi, like the puffballs, rely on alternative mechanisms for spore release, such as external mechanical forces. The bird's nest fungi
use the force of falling water drops to liberate the spores from cup-shaped fruiting bodies. Another strategy is seen in the stinkhorns, a group of fungi with lively colors and putrid odor that attract insects to disperse their spores.
and Aspergillus
, may exchange genetic material via parasexual processes, initiated by anastomosis between hyphae and plasmogamy
of fungal cells. The frequency and relative importance of parasexual events is unclear and may be lower than other sexual processes. It is known to play a role in intraspecific hybridization and is likely required for hybridization between species, which has been associated with major events in fungal evolution.
and animals
, the early fossil record of the fungi is meager. Factors that likely contribute to the under-representation of fungal species among fossils include the nature of fungal fruiting bodies
, which are soft, fleshy, and easily degradable tissues and the microscopic dimensions of most fungal structures, which therefore are not readily evident. Fungal fossils are difficult to distinguish from those of other microbes, and are most easily identified when they resemble extant fungi. Often recovered from a permineralized
plant or animal host, these samples are typically studied by making thin-section preparations that can be examined with light microscopy
or transmission electron microscopy
. Compression fossil
s are studied by dissolving the surrounding matrix with acid and then using light or scanning electron microscopy to examine surface details.
The earliest fossils possessing features typical of fungi date to the Proterozoic
eon, some (Ma); these multicellular benthic organisms had filamentous structures with septa, and were capable of anastomosis. More recent studies (2009) estimate the arrival of fungal organisms at about 760–1060 Ma on the basis of comparisons of the rate of evolution in closely related groups. For much of the Paleozoic
Era (542–251 Ma), the fungi appear to have been aquatic and consisted of organisms similar to the extant chytrids in having flagellum-bearing spores. The evolutionary adaptation from an aquatic to a terrestrial lifestyle necessitated a diversification of ecological strategies for obtaining nutrients, including parasitism
, saprobism, and the development of mutualistic relationships such as mycorrhiza
and lichenization. Recent (2009) studies suggest that the ancestral ecological state of the Ascomycota
was saprobism, and that independent lichen
ization events have occurred multiple times.
The fungi probably colonized the land during the Cambrian
(542–488.3 Ma), long before land plants. Fossilized hyphae and spores recovered from the Ordovician
of Wisconsin (460 Ma) resemble modern-day Glomerales
, and existed at a time when the land flora likely consisted of only non-vascular bryophyte
-like plants. Prototaxites
, which was probably a fungus or lichen, would have been the tallest organism of the late Silurian
. Fungal fossils do not become common and uncontroversial until the early Devonian
(416–359.2 Ma), when they are abundant in the Rhynie chert
, mostly as Zygomycota
and Chytridiomycota
. At about this same time, approximately 400 Ma, the Ascomycota and Basidiomycota diverged, and all modern classes
of fungi were present by the Late Carboniferous
(Pennsylvanian
, 318.1–299 Ma).
Lichen
-like fossils have been found in the Doushantuo Formation
in southern China dating back to 635–551 Ma. Lichens were a component of the early terrestrial ecosystems, and the estimated age of the oldest terrestrial lichen fossil is 400 Ma; this date corresponds to the age of the oldest known sporocarp
fossil, a Paleopyrenomycites species found in the Rhynie Chert. The oldest fossil with microscopic features resembling modern-day basidiomycetes is Palaeoancistrus, found permineralized with a fern
from the Pennsylvanian. Rare in the fossil record are the Homobasidiomycetes (a taxon
roughly equivalent to the mushroom-producing species of the Agaricomycetes
). Two amber
-preserved specimens provide evidence that the earliest known mushroom-forming fungi (the extinct species Archaeomarasmius leggetti) appeared during the mid-Cretaceous
, 90 Ma.
Some time after the Permian–Triassic extinction event (251.4 Ma), a fungal spike (originally thought to be an extraordinary abundance of fungal spores in sediment
s) formed, suggesting that fungi were the dominant life form at this time, representing nearly 100% of the available fossil record for this period. However, the relative proportion of fungal spores relative to spores formed by algal
species is difficult to assess, the spike did not appear worldwide, and in many places it did not fall on the Permian–Triassic boundary.
s than to plants and are placed with the animals in the monophyletic group of opisthokont
s. Analyses using molecular phylogenetics support a monophyletic origin of the Fungi. The taxonomy
of the Fungi is in a state of constant flux, especially due to recent research based on DNA comparisons. These current phylogenetic analyses often overturn classifications based on older and sometimes less discriminative methods based on morphological features and biological species concepts obtained from experimental mating
s.
There is no unique generally accepted system at the higher taxonomic levels and there are frequent name changes at every level, from species upwards. Efforts among researchers are now underway to establish and encourage usage of a unified and more consistent nomenclature
. Fungal species can also have multiple scientific names depending on their life cycle and mode (sexual or asexual) of reproduction. Web sites such as Index Fungorum
and ITIS
list current names of fungal species (with cross-references to older synonyms).
The 2007 classification of Kingdom Fungi is the result of a large-scale collaborative research effort involving dozens of mycologists and other scientists working on fungal taxonomy. It recognizes seven phyla
, two of which—the Ascomycota and the Basidiomycota—are contained within a branch representing subkingdom Dikarya. The below cladogram
depicts the major fungal taxa
and their relationship to opisthokont and unikont organisms. The lengths of the branches in this tree are not proportional to evolutionary distances.
(sometimes called divisions) of fungi have been classified mainly on the basis of characteristics of their sexual reproductive structures. Currently, seven phyla are proposed: Microsporidia, Chytridiomycota, Blastocladiomycota, Neocallimastigomycota, Glomeromycota, Ascomycota, and Basidiomycota.
Phylogenetic analysis has demonstrated that the Microsporidia
, unicellular parasites of animals and protists, are fairly recent and highly derived endobiotic fungi (living within the tissue of another species). One 2006 study concludes that the Microsporidia are a sister group to the true fungi, that is, they are each other's closest evolutionary relative. Hibbett and colleagues suggest that this analysis does not clash with their classification of the Fungi, and although the Microsporidia are elevated to phylum status, it is acknowledged that further analysis is required to clarify evolutionary relationships within this group.
The Chytridiomycota
are commonly known as chytrids. These fungi are distributed worldwide. Chytrids produce zoospore
s that are capable of active movement through aqueous phases with a single flagellum
, leading early taxonomists to classify them as protist
s. Molecular phylogenies, inferred from rRNA sequences in ribosome
s, suggest that the Chytrids are a basal
group divergent from the other fungal phyla, consisting of four major clade
s with suggestive evidence for paraphyly
or possibly polyphyly
.
The Blastocladiomycota
were previously considered a taxonomic clade within the Chytridiomycota. Recent molecular data and ultrastructural
characteristics, however, place the Blastocladiomycota as a sister clade to the Zygomycota, Glomeromycota, and Dikarya (Ascomycota and Basidiomycota). The blastocladiomycetes are saprotrophs
, feeding on decomposing organic matter, and they are parasites of all eukaryotic groups. Unlike their close relatives, the chytrids, which mostly exhibit zygotic meiosis, the blastocladiomycetes undergo sporic meiosis.
The Neocallimastigomycota
were earlier placed in the phylum Chytridomycota. Members of this small phylum are anaerobic organism
s, living in the digestive system of larger herbivorous mammals and possibly in other terrestrial and aquatic environments. They lack mitochondria but contain hydrogenosome
s of mitochondrial origin. As the related chrytrids, neocallimastigomycetes form zoospores that are posteriorly uniflagellate or polyflagellate.
Members of the Glomeromycota
form arbuscular mycorrhizae, a form of symbiosis
where fungal hyphae invade plant root cells and both species benefit from the resulting increased supply of nutrients. All known Glomeromycota species reproduce asexually. The symbiotic association between the Glomeromycota and plants is ancient, with evidence dating to 400 million years ago. Formerly part of the Zygomycota
(commonly known as 'sugar' and 'pin' molds), the Glomeromycota were elevated to phylum status in 2001 and now replace the older phylum Zygomycota. Fungi that were placed in the Zygomycota are now being reassigned to the Glomeromycota, or the subphyla incertae sedis
Mucoromycotina
, Kickxellomycotina
, the Zoopagomycotina
and the Entomophthoromycotina
. Some well-known examples of fungi formerly in the Zygomycota include black bread mold (Rhizopus stolonifer), and Pilobolus
species, capable of ejecting spore
s several meters through the air. Medically relevant genera include Mucor
, Rhizomucor
, and Rhizopus
.
 The Ascomycota
The Ascomycota
, commonly known as sac fungi or ascomycetes, constitute the largest taxonomic group within the Eumycota. These fungi form meiotic spores called ascospore
s, which are enclosed in a special sac-like structure called an ascus
. This phylum includes morel
s, a few mushroom
s and truffles, single-celled yeast
s (e.g., of the genera Saccharomyces
, Kluyveromyces
, Pichia
, and Candida
), and many filamentous fungi living as saprotrophs, parasites, and mutualistic symbionts. Prominent and important genera of filamentous ascomycetes include Aspergillus
, Penicillium
, Fusarium
, and Claviceps. Many ascomycete species have only been observed undergoing asexual reproduction (called anamorphic species), but analysis of molecular data has often been able to identify their closest teleomorphs in the Ascomycota. Because the products of meiosis are retained within the sac-like ascus, ascomycetes have been used for elucidating principles of genetics and heredity (e.g. Neurospora crassa
).
Members of the Basidiomycota
, commonly known as the club fungi or basidiomycetes, produce meiospores called basidiospore
s on club-like stalks called basidia
. Most common mushrooms belong to this group, as well as rust
and smut fungi
, which are major pathogens of grains. Other important basidiomycetes include the maize
pathogen Ustilago maydis, human commensal
species of the genus Malassezia, and the opportunistic
human pathogen, Cryptococcus neoformans
.
s like fungi, but are grouped in the Amoebozoa
. Oomycetes are diploid bikont
s, grouped in the Chromalveolate
kingdom. Neither water molds nor slime molds are closely related to the true fungi, and, therefore, taxonomists no longer group them in the kingdom Fungi. Nonetheless, studies of the oomycetes and myxomycetes are still often included in mycology
textbooks and primary research literature.
The Rozellida
clade, including the "chytrid" Rozella
, is a genetically disparate group known mostly from environmental DNA sequences which is a sister group to fungi. Members of the group which have been isolated lack the chitinous cell wall which is characteristic of fungi.
The nucleariid
s, currently grouped in the Choanozoa
, may be the next sister group to the eumycete clade, and as such could be included in an expanded fungal kingdom.
and play very important roles in most ecosystems. Along with bacteria, fungi are the major decomposers in most terrestrial (and some aquatic) ecosystems, and therefore play a critical role in biogeochemical cycles and in many food webs. As decomposers, they play an essential role in nutrient cycling, especially as saprotrophs and symbionts, degrading organic matter
to inorganic molecules, which can then re-enter anabolic metabolic pathways in plants or other organisms.
s. These interactions can be mutualistic or antagonistic in nature, or in the case of commensal fungi are of no apparent benefit or detriment to the host.
l symbiosis between plants and fungi is one of the most well-known plant–fungus associations and is of significant importance for plant growth and persistence in many ecosystems; over 90% of all plant species engage in mycorrhizal relationships with fungi and are dependent upon this relationship for survival.
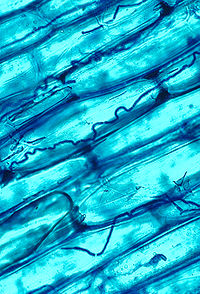 The mycorrhizal symbiosis is ancient, dating to at least 400 million years ago. It often increases the plant's uptake of inorganic compounds, such as nitrate
The mycorrhizal symbiosis is ancient, dating to at least 400 million years ago. It often increases the plant's uptake of inorganic compounds, such as nitrate
and phosphate
from soils having low concentrations of these key plant nutrients. The fungal partners may also mediate plant-to-plant transfer of carbohydrates and other nutrients. Such mycorrhizal communities are called "common mycorrhizal networks". A special case of mycorrhiza is myco-heterotrophy, whereby the plant parasitizes the fungus, obtaining all of its nutrients from its fungal symbiont. Some fungal species inhabit the tissues inside roots, stems, and leaves, in which case they are called endophytes. Similar to mycorrhiza, endophytic colonization by fungi may benefit both symbionts; for example, endophytes of grasses impart to their host increased resistance to herbivores and other environmental stresses and receive food and shelter from the plant in return.
 Lichens are formed by a symbiotic relationship between algae
Lichens are formed by a symbiotic relationship between algae
or cyanobacteria (referred to in lichen terminology as "photobionts") and fungi (mostly various species of ascomycetes and a few basidiomycetes), in which individual photobiont cells are embedded in a tissue formed by the fungus. Lichens occur in every ecosystem on all continents, play a key role in soil formation and the initiation of biological succession
, and are the dominating life forms in extreme environments, including polar
, alpine
, and semiarid desert regions. They are able to grow on inhospitable surfaces, including bare soil, rocks, tree bark
, wood, shells, barnacles and leaves. As in mycorrhiza
s, the photobiont provides sugars and other carbohydrates via photosynthesis
, while the fungus provides minerals and water. The functions of both symbiotic organisms are so closely intertwined that they function almost as a single organism; in most cases the resulting organism differs greatly from the individual components. Lichenization is a common mode of nutrition; around 20% of fungi—between 17,500 and 20,000 described species—are lichenized. Characteristics common to most lichens include obtaining organic carbon by photosynthesis, slow growth, small size, long life, long-lasting (seasonal) vegetative reproductive
structures, mineral nutrition obtained largely from airborne sources, and greater tolerance of desiccation
than most other photosynthetic organisms in the same habitat.
with fungi. Several groups of ants cultivate fungi in the order Agaricales
as their primary food source, while ambrosia beetles cultivate various species of fungi in the bark of trees that they infest. Similarly, females of several wood wasp
species (genus Sirex
) inject their eggs together with spores of the wood-rotting fungus Amylostereum areolatum into the sapwood of pine
trees; the growth of the fungus provides ideal nutritional conditions for the development of the wasp larvae. Termites on the African savannah
are also known to cultivate fungi, and yeasts of the genera Candida
and Lachancea inhabit the gut
of a wide range of insects, including neuroptera
ns, beetle
s, and cockroach
es; it is not known whether these fungi benefit their hosts.
 Many fungi are parasites on plants, animals (including humans), and other fungi. Serious pathogens of many cultivated plants causing extensive damage and losses to agriculture and forestry include the rice blast fungus Magnaporthe oryzae, tree pathogens such as Ophiostoma ulmi
Many fungi are parasites on plants, animals (including humans), and other fungi. Serious pathogens of many cultivated plants causing extensive damage and losses to agriculture and forestry include the rice blast fungus Magnaporthe oryzae, tree pathogens such as Ophiostoma ulmi
and Ophiostoma novo-ulmi causing Dutch elm disease
, and Cryphonectria parasitica responsible for chestnut blight
, and plant pathogens in the genera Fusarium
, Ustilago
, Alternaria
, and Cochliobolus
. Some carnivorous fungi, like Paecilomyces lilacinus, are predators
of nematodes, which they capture using an array of specialized structures such as constricting rings or adhesive nets.
Some fungi can cause serious diseases in humans, several of which may be fatal if untreated. These include aspergilloses
, candidoses, coccidioidomycosis
, cryptococcosis
, histoplasmosis
, mycetomas
, and paracoccidioidomycosis
. Furthermore, persons with immuno-deficiencies
are particularly susceptible to disease by genera such as Aspergillus
, Candida
, Cryptoccocus
, Histoplasma
, and Pneumocystis. Other fungi can attack eyes, nails, hair, and especially skin, the so-called dermatophytic
and keratinophilic fungi, and cause local infections such as ringworm and athlete’s foot. Fungal spores are also a cause of allergies, and fungi from different taxonomic groups can evoke allergic reactions.
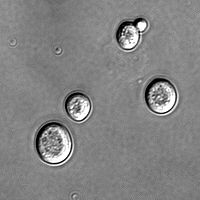 The human use of fungi for food preparation or preservation and other purposes is extensive and has a long history. Mushroom farming and mushroom gathering are large industries in many countries. The study of the historical uses and sociological impact of fungi is known as ethnomycology
The human use of fungi for food preparation or preservation and other purposes is extensive and has a long history. Mushroom farming and mushroom gathering are large industries in many countries. The study of the historical uses and sociological impact of fungi is known as ethnomycology
. Because of the capacity of this group to produce an enormous range of natural products with antimicrobial
or other biological activities, many species have long been used or are being developed for industrial production of antibiotics
, vitamins, and anti-cancer and cholesterol-lowering
drugs. More recently, methods have been developed for genetic engineering
of fungi, enabling metabolic engineering
of fungal species. For example, genetic modification of yeast species—which are easy to grow at fast rates in large fermentation vessels—has opened up ways of pharmaceutical production that are potentially more efficient than production by the original source organisms.
active drugs. Particularly important are the antibiotics, including the penicillin
s, a structurally related group of β-lactam antibiotics that are synthesized from small peptide
s. Although naturally occurring penicillins such as penicillin G (produced by Penicillium chrysogenum
) have a relatively narrow spectrum of biological activity, a wide range of other penicillins can be produced by chemical modification
of the natural penicillins. Modern penicillins are semisynthetic compounds, obtained initially from fermentation
cultures, but then structurally altered for specific desirable properties. Other antibiotics produced by fungi include: ciclosporin
, commonly used as an immunosuppressant
during transplant surgery
; and fusidic acid
, used to help control infection from methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus
bacteria. Widespread use of these antibiotics for the treatment of bacterial diseases, such as tuberculosis
, syphilis
, leprosy
, and many others began in the early 20th century and continues to play a major part in anti-bacterial
chemotherapy
. In nature, antibiotics of fungal or bacterial origin appear to play a dual role: at high concentrations they act as chemical defense against competition with other microorganisms in species-rich environments, such as the rhizosphere
, and at low concentrations as quorum-sensing
molecules for intra- or interspecies signaling.
Other drugs produced by fungi include griseofulvin
isolated from Penicillium griseofulvum, used to treat fungal infections, and statin
s (HMG-CoA reductase
inhibitors), used to inhibit cholesterol synthesis. Examples of statins found in fungi include mevastatin
from Penicillium citrinum and lovastatin
from Aspergillus terreus
and the oyster mushroom.
or Saccharomyces cerevisiae
, a single-celled fungus, is used to make bread
and other wheat-based products, such as pizza
dough and dumpling
s. Yeast species of the genus Saccharomyces
are also used to produce alcoholic beverage
s through fermentation. Shoyu koji mold (Aspergillus oryzae
) is an essential ingredient in brewing Shoyu (soy sauce
) and sake, and the preparation of miso
, while Rhizopus
species are used for making tempeh
. Several of these fungi are domesticated
species that were bred
or selected according to their capacity to ferment food without producing harmful mycotoxins (see below), which are produced by very closely related Aspergilli
. Quorn
, a meat substitute
, is made from Fusarium venenatum
.
s, such as Traditional Chinese medicine
. Notable medicinal mushrooms with a well-documented history of use include Agaricus subrufescens, Ganoderma lucidum, and Ophiocordyceps sinensis. Research has identified compounds produced by these and other fungi that have inhibitory biological effects against virus
es and cancer cells. Specific metabolites, such as polysaccharide-K
, ergotamine, and β-lactam antibiotics
, are routinely used in clinical medicine. The shiitake
mushroom is a source of lentinan
, a clinical drug approved for use in cancer treatments in several countries, including Japan
. In Europe
and Japan
, polysaccharide-K
(brand name Krestin), a chemical derived from Trametes versicolor
, is an approved adjuvant
for cancer therapy.
 Edible mushroom
Edible mushroom
s are well-known examples of fungi. Many are commercially raised, but others must be harvested from the wild. Agaricus bisporus, sold as button mushrooms when small or Portobello mushrooms when larger, is a commonly eaten species, used in salads, soups, and many other dishes. Many Asian fungi are commercially grown and have increased in popularity in the West. They are often available fresh in grocery store
s and markets, including straw mushrooms (Volvariella volvacea
), oyster mushrooms (Pleurotus ostreatus), shiitakes (Lentinula edodes), and enokitake
(Flammulina
spp.).
There are many more mushroom species that are harvested from the wild
for personal consumption or commercial sale. Milk mushrooms
, morel
s, chanterelle
s, truffles, black trumpets
, and porcini mushrooms (Boletus edulis
) (also known as king boletes) demand a high price on the market. They are often used in gourmet dishes.
Certain types of cheeses require inoculation of milk curds with fungal species that impart a unique flavor and texture to the cheese. Examples include the blue
color in cheeses such as Stilton or Roquefort, which are made by inoculation with Penicillium roqueforti
. Molds used in cheese production are non-toxic and are thus safe for human consumption; however, mycotoxins (e.g., aflatoxins, roquefortine C
, patulin, or others) may accumulate because of growth of other fungi during cheese ripening or storage.
 Many mushroom species are poisonous
Many mushroom species are poisonous
to humans, with toxicities ranging from slight digestive problems or allergic
reactions as well as hallucination
s to severe organ failures and death. Genera with mushrooms containing deadly toxins include Conocybe
, Galerina
, Lepiota
, and most infamously, Amanita
. The latter genus includes the destroying angel (A. virosa
) and the death cap (A. phalloides), the most common cause of deadly mushroom poisoning. The false morel (Gyromitra esculenta) is occasionally considered a delicacy when cooked, yet can be highly toxic when eaten raw. Tricholoma equestre
was considered edible until being implicated in serious poisonings causing rhabdomyolysis
. Fly agaric
mushrooms (Amanita muscaria) also cause occasional non-fatal poisonings, mostly as a result of ingestion for use as a recreational
drug for its hallucinogenic
properties. Historically, fly agaric was used by different peoples in Europe and Asia and its present usage for religious or shamanic
purposes is reported from some ethnic groups such as the Koryak people
of north-eastern Siberia
.
As it is difficult to accurately identify a safe mushroom without proper training and knowledge, it is often advised to assume that a wild mushroom is poisonous and not to consume it.
 In agriculture, fungi may be useful if they actively compete for nutrients and space with pathogen
In agriculture, fungi may be useful if they actively compete for nutrients and space with pathogen
ic microorganisms such as bacteria or other fungi via the competitive exclusion principle
, or if they are parasites
of these pathogens. For example, certain species may be used to eliminate or suppress the growth of harmful plant pathogens, such as insects, mites
, weed
s, nematodes and other fungi that cause diseases of important crop
plants. This has generated strong interest in practical applications that use these fungi in the biological control of these agricultural pests. Entomopathogenic fungi can be used as biopesticides, as they actively kill insects. Examples that have been used as biological insecticides are Beauveria bassiana
, Metarhizium
spp, Hirsutella
spp, Paecilomyces
(Isaria) spp, and Lecanicillium lecanii
. Endophytic fungi of grasses of the genus Neotyphodium
, such as N. coenophialum
, produce alkaloids that are toxic to a range of invertebrate and vertebrate herbivores. These alkaloids protect grass plants from herbivory, but several endophyte alkaloids can poison grazing animals, such as cattle and sheep. Infecting cultivars of pasture
or forage
grasses with Neotyphodium endophytes is one approach being used in grass breeding
programs; the fungal strains are selected for producing only alkaloids that increase resistance to herbivores such as insects, while being non-toxic to livestock.
s, herbicide
s, pentachlorophenol
, creosote
, coal tar
s, and heavy fuels and turn them into carbon dioxide
, water, and basic elements. Fungi have been shown to biomineralize uranium
oxide
s, suggesting they may have application in the bioremediation of radioactively polluted sites.
was formulated by scientists who used the bread mold Neurospora crassa
to test their biochemical theories. Other important model fungi are Aspergillus nidulans
and the yeasts, Saccaromyces cerevisiae and Schizosaccharomyces pombe
, each of which has a long history of use to investigate issues in eukaryotic cell biology
and genetics
, such as cell cycle
regulation, chromatin
structure, and gene regulation. Other fungal models have more recently emerged that each address specific biological questions relevant to medicine
, plant pathology, and industrial uses; examples include Candida albicans
, a dimorphic, opportunistic human pathogen, Magnaporthe grisea
, a plant pathogen, and Pichia pastoris
, a yeast widely used for eukaryotic protein expression
.
, gluconic
, lactic
, and malic
acids, and industrial enzymes, such as lipase
s used in biological detergent
s, cellulase
s used in making cellulosic ethanol
and stonewashed jeans, and amylase
s, invertase
s, protease
s and xylanase
s. Several species, most notably Psilocybin mushroom
s (colloquially known as magic mushrooms), are ingested for their psychedelic
properties, both recreationally and religiously.
 Many fungi produce biologically active
Many fungi produce biologically active
compounds, several of which are toxic
to animals or plants and are therefore called mycotoxins. Of particular relevance to humans are mycotoxins produced by molds causing food spoilage, and poisonous mushrooms (see above). Particularly infamous are the lethal amatoxin
s in some Amanita
mushrooms, and ergot alkaloids, which have a long history of causing serious epidemics of ergotism
(St Anthony's Fire) in people consuming rye
or related cereal
s contaminated with sclerotia of the ergot fungus, Claviceps purpurea
. Other notable mycotoxins include the aflatoxin
s, which are insidious liver toxins
and highly carcinogenic metabolites produced by certain Aspergillus
species often growing in or on grains and nuts consumed by humans, ochratoxin
s, patulin
, and trichothecene
s (e.g., T-2 mycotoxin
) and fumonisins, which have significant impact on human food supplies or animal livestock
.
Mycotoxins are secondary metabolites (or natural product
s), and research has established the existence of biochemical pathways solely for the purpose of producing mycotoxins and other natural products in fungi. Mycotoxins may provide fitness
benefits in terms of physiological adaptation, competition with other microbes and fungi, and protection from consumption (fungivory
).
is the branch of biology
concerned with the systematic study of fungi, including their genetic and biochemical properties, their taxonomy, and their use to humans as a source of medicine, food, and psychotropic substances
consumed for religious purposes, as well as their dangers, such as poisoning or infection. The field of phytopathology
, the study of plant diseases, is closely related because many plant pathogens are fungi.
Use of fungi by humans dates back to prehistory; Ötzi the Iceman
, a well-preserved mummy of a 5,300 year old Neolithic
man found frozen in the Austrian Alps, carried two species of polypore
mushrooms that may have been used as tinder
(Fomes fomentarius
), or for medicinal purposes (Piptoporus betulinus). Ancient peoples have used fungi as food sources–often unknowingly–for millennia, in the preparation of leavened bread and fermented juices. Some of the oldest written records contain references to the destruction of crops that were probably caused by pathogenic fungi.
in the 16th century. Although fungal spores were first observed by Giambattista della Porta
in 1588, the seminal work in the development of mycology is considered to be the publication of Pier Antonio Micheli
's 1729 work Nova plantarum genera. Micheli not only observed spores, but showed that under the proper conditions, they could be induced into growing into the same species of fungi from which they originated. Extending the use of the binomial system of nomenclature introduced by Carl Linnaeus in his Species plantarum
(1753), the Dutch Christian Hendrik Persoon
(1761–1836) established the first classification of mushrooms with such skill so as to be considered a founder of modern mycology. Later, Elias Magnus Fries
(1794–1878) further elaborated the classification
of fungi, using spore color and various microscopic characteristics, methods still used by taxonomists today. Other notable early contributors to mycology in the 17th–19th and early 20th centuries include Miles Joseph Berkeley
, August Carl Joseph Corda
, Anton de Bary
, the brothers Louis René
and Charles Tulasne
, Arthur H. R. Buller
, Curtis G. Lloyd
, and Pier Andrea Saccardo
. The 20th century has seen a modernization of mycology that has come from advances in biochemistry
, genetics
, molecular biology
, and biotechnology
. The use of DNA sequencing
technologies and phylogenetic analysis has provided new insights into fungal relationships and biodiversity
, and has challenged traditional morphology-based groupings in fungal taxonomy
.
Eukaryote
A eukaryote is an organism whose cells contain complex structures enclosed within membranes. Eukaryotes may more formally be referred to as the taxon Eukarya or Eukaryota. The defining membrane-bound structure that sets eukaryotic cells apart from prokaryotic cells is the nucleus, or nuclear...
organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeast
Yeast
Yeasts are eukaryotic micro-organisms classified in the kingdom Fungi, with 1,500 species currently described estimated to be only 1% of all fungal species. Most reproduce asexually by mitosis, and many do so by an asymmetric division process called budding...
s and mold
Mold
Molds are fungi that grow in the form of multicellular filaments called hyphae. Molds are not considered to be microbes but microscopic fungi that grow as single cells called yeasts...
s (British English: moulds), as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom
Kingdom (biology)
In biology, kingdom is a taxonomic rank, which is either the highest rank or in the more recent three-domain system, the rank below domain. Kingdoms are divided into smaller groups called phyla or divisions in botany...
, Fungi, which is separate from plant
Plant
Plants are living organisms belonging to the kingdom Plantae. Precise definitions of the kingdom vary, but as the term is used here, plants include familiar organisms such as trees, flowers, herbs, bushes, grasses, vines, ferns, mosses, and green algae. The group is also called green plants or...
s, animal
Animal
Animals are a major group of multicellular, eukaryotic organisms of the kingdom Animalia or Metazoa. Their body plan eventually becomes fixed as they develop, although some undergo a process of metamorphosis later on in their life. Most animals are motile, meaning they can move spontaneously and...
s, and bacteria
Bacteria
Bacteria are a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria have a wide range of shapes, ranging from spheres to rods and spirals...
. One major difference is that fungal cells have cell wall
Cell wall
The cell wall is the tough, usually flexible but sometimes fairly rigid layer that surrounds some types of cells. It is located outside the cell membrane and provides these cells with structural support and protection, and also acts as a filtering mechanism. A major function of the cell wall is to...
s that contain chitin
Chitin
Chitin n is a long-chain polymer of a N-acetylglucosamine, a derivative of glucose, and is found in many places throughout the natural world...
, unlike the cell walls of plants, which contain cellulose
Cellulose
Cellulose is an organic compound with the formula , a polysaccharide consisting of a linear chain of several hundred to over ten thousand β linked D-glucose units....
. These and other differences show that the fungi form a single group of related organisms, named the Eumycota (true fungi or Eumycetes), that share a common ancestor (a monophyletic group). This fungal group is distinct from the structurally similar myxomycetes (slime molds) and oomycetes (water molds). The discipline of biology
Biology
Biology is a natural science concerned with the study of life and living organisms, including their structure, function, growth, origin, evolution, distribution, and taxonomy. Biology is a vast subject containing many subdivisions, topics, and disciplines...
devoted to the study of fungi is known as mycology
Mycology
Mycology is the branch of biology concerned with the study of fungi, including their genetic and biochemical properties, their taxonomy and their use to humans as a source for tinder, medicinals , food and entheogens, as well as their dangers, such as poisoning or...
, which is often regarded as a branch of botany
Botany
Botany, plant science, or plant biology is a branch of biology that involves the scientific study of plant life. Traditionally, botany also included the study of fungi, algae and viruses...
, even though genetic studies have shown that fungi are more closely related to animals than to plants.
Abundant worldwide, most fungi are inconspicuous because of the small size of their structures, and their cryptic
Crypsis
In ecology, crypsis is the ability of an organism to avoid observation or detection by other organisms. It may be either a predation strategy or an antipredator adaptation, and methods include camouflage, nocturnality, subterranean lifestyle, transparency, and mimicry...
lifestyles in soil, on dead matter, and as symbionts
Symbiosis
Symbiosis is close and often long-term interaction between different biological species. In 1877 Bennett used the word symbiosis to describe the mutualistic relationship in lichens...
of plants, animals, or other fungi. They may become noticeable when fruiting
Sporocarp (fungi)
In fungi, the sporocarp is a multicellular structure on which spore-producing structures, such as basidia or asci, are borne...
, either as mushrooms or molds. Fungi perform an essential role in the decomposition of organic matter and have fundamental roles in nutrient cycling
Biogeochemical cycle
In ecology and Earth science, a biogeochemical cycle or substance turnover or cycling of substances is a pathway by which a chemical element or molecule moves through both biotic and abiotic compartments of Earth. A cycle is a series of change which comes back to the starting point and which can...
and exchange. They have long been used as a direct source of food, such as mushrooms and truffles, as a leavening agent for bread, and in fermentation
Fermentation (food)
Fermentation in food processing typically is the conversion of carbohydrates to alcohols and carbon dioxide or organic acids using yeasts, bacteria, or a combination thereof, under anaerobic conditions. Fermentation in simple terms is the chemical conversion of sugars into ethanol...
of various food products, such as wine
Wine
Wine is an alcoholic beverage, made of fermented fruit juice, usually from grapes. The natural chemical balance of grapes lets them ferment without the addition of sugars, acids, enzymes, or other nutrients. Grape wine is produced by fermenting crushed grapes using various types of yeast. Yeast...
, beer
Beer
Beer is the world's most widely consumed andprobably oldest alcoholic beverage; it is the third most popular drink overall, after water and tea. It is produced by the brewing and fermentation of sugars, mainly derived from malted cereal grains, most commonly malted barley and malted wheat...
, and soy sauce
Soy sauce
Soy sauce is a condiment produced by fermenting soybeans with Aspergillus oryzae or Aspergillus sojae molds, along with water and salt...
. Since the 1940s, fungi have been used for the production of antibiotic
Antibiotic
An antibacterial is a compound or substance that kills or slows down the growth of bacteria.The term is often used synonymously with the term antibiotic; today, however, with increased knowledge of the causative agents of various infectious diseases, antibiotic has come to denote a broader range of...
s, and, more recently, various enzyme
Enzyme
Enzymes are proteins that catalyze chemical reactions. In enzymatic reactions, the molecules at the beginning of the process, called substrates, are converted into different molecules, called products. Almost all chemical reactions in a biological cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates...
s produced by fungi are used industrially and in detergents. Fungi are also used as biological pesticides to control weeds, plant diseases and insect pests. Many species produce bioactive compounds called mycotoxin
Mycotoxin
A mycotoxin is a toxic secondary metabolite produced by organisms of the fungus kingdom, commonly known as molds. The term ‘mycotoxin’ is usually reserved for the toxic chemical products produced by fungi that readily colonize crops...
s, such as alkaloid
Alkaloid
Alkaloids are a group of naturally occurring chemical compounds that contain mostly basic nitrogen atoms. This group also includes some related compounds with neutral and even weakly acidic properties. Also some synthetic compounds of similar structure are attributed to alkaloids...
s and polyketide
Polyketide
Polyketides are secondary metabolites from bacteria, fungi, plants, and animals. Polyketides are usually biosynthesized through the decarboxylative condensation of malonyl-CoA derived extender units in a similar process to fatty acid synthesis...
s, that are toxic to animals including humans. The fruiting structures of a few species contain psychotropic compounds and are consumed recreationally
Recreational drug use
Recreational drug use is the use of a drug, usually psychoactive, with the intention of creating or enhancing recreational experience. Such use is controversial, however, often being considered to be also drug abuse, and it is often illegal...
or in traditional spiritual ceremonies. Fungi can break down manufactured materials and buildings, and become significant pathogen
Pathogenic fungi
Pathogenic fungi are fungi that cause disease in humans or other organisms. The study of pathogenic fungi is referred to as medical mycology. Although fungi are eukaryotic organisms many pathogenic fungi are also microorganisms.-Candida:...
s of humans and other animals. Losses of crops due to fungal diseases (e.g. rice blast disease) or food spoilage can have a large impact on human food supplies
Food security
Food security refers to the availability of food and one's access to it. A household is considered food-secure when its occupants do not live in hunger or fear of starvation. According to the World Resources Institute, global per capita food production has been increasing substantially for the past...
and local economies.
The fungus kingdom encompasses an enormous diversity of taxa
Taxon
|thumb|270px|[[African elephants]] form a widely-accepted taxon, the [[genus]] LoxodontaA taxon is a group of organisms, which a taxonomist adjudges to be a unit. Usually a taxon is given a name and a rank, although neither is a requirement...
with varied ecologies, life cycle
Biological life cycle
A life cycle is a period involving all different generations of a species succeeding each other through means of reproduction, whether through asexual reproduction or sexual reproduction...
strategies, and morphologies
Morphology (biology)
In biology, morphology is a branch of bioscience dealing with the study of the form and structure of organisms and their specific structural features....
ranging from single-celled aquatic chytrids to large mushrooms. However, little is known of the true biodiversity
Biodiversity
Biodiversity is the degree of variation of life forms within a given ecosystem, biome, or an entire planet. Biodiversity is a measure of the health of ecosystems. Biodiversity is in part a function of climate. In terrestrial habitats, tropical regions are typically rich whereas polar regions...
of Kingdom Fungi, which has been estimated at around 1.5 million species, with about 5% of these having been formally classified. Ever since the pioneering 18th and 19th century taxonomical
Taxonomy
Taxonomy is the science of identifying and naming species, and arranging them into a classification. The field of taxonomy, sometimes referred to as "biological taxonomy", revolves around the description and use of taxonomic units, known as taxa...
works of Carl Linnaeus, Christian Hendrik Persoon
Christian Hendrik Persoon
Christiaan Hendrik Persoon was a mycologist who made additions to Linnaeus' mushroom taxonomy.-Early life:...
, and Elias Magnus Fries
Elias Magnus Fries
-External links:*, Authors of fungal names, Mushroom, the Journal of Wild Mushrooming.*...
, fungi have been classified
Biological classification
Biological classification, or scientific classification in biology, is a method to group and categorize organisms by biological type, such as genus or species. Biological classification is part of scientific taxonomy....
according to their morphology (e.g., characteristics such as spore color or microscopic features) or physiology
Physiology
Physiology is the science of the function of living systems. This includes how organisms, organ systems, organs, cells, and bio-molecules carry out the chemical or physical functions that exist in a living system. The highest honor awarded in physiology is the Nobel Prize in Physiology or...
. Advances in molecular genetics
Molecular genetics
Molecular genetics is the field of biology and genetics that studies the structure and function of genes at a molecular level. The field studies how the genes are transferred from generation to generation. Molecular genetics employs the methods of genetics and molecular biology...
have opened the way for DNA analysis
DNA sequencing
DNA sequencing includes several methods and technologies that are used for determining the order of the nucleotide bases—adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine—in a molecule of DNA....
to be incorporated into taxonomy, which has sometimes challenged the historical groupings based on morphology and other traits. Phylogenetic studies published in the last decade have helped reshape the classification of Kingdom Fungi, which is divided into one subkingdom
Taxonomic rank
In biological classification, rank is the level in a taxonomic hierarchy. Examples of taxonomic ranks are species, genus, family, and class. Each rank subsumes under it a number of less general categories...
, seven phyla
Phylum
In biology, a phylum The term was coined by Georges Cuvier from Greek φῦλον phylon, "race, stock," related to φυλή phyle, "tribe, clan." is a taxonomic rank below kingdom and above class. "Phylum" is equivalent to the botanical term division....
, and ten subphyla.
Etymology
The English word fungus is directly adopted from the LatinLatin
Latin is an Italic language originally spoken in Latium and Ancient Rome. It, along with most European languages, is a descendant of the ancient Proto-Indo-European language. Although it is considered a dead language, a number of scholars and members of the Christian clergy speak it fluently, and...
fungus (mushroom), used in the writings of Horace
Horace
Quintus Horatius Flaccus , known in the English-speaking world as Horace, was the leading Roman lyric poet during the time of Augustus.-Life:...
and Pliny
Pliny the Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus , better known as Pliny the Elder, was a Roman author, naturalist, and natural philosopher, as well as naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and personal friend of the emperor Vespasian...
. This in turn is derived from the Greek
Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek is the stage of the Greek language in the periods spanning the times c. 9th–6th centuries BC, , c. 5th–4th centuries BC , and the c. 3rd century BC – 6th century AD of ancient Greece and the ancient world; being predated in the 2nd millennium BC by Mycenaean Greek...
word sphongos/σφογγος ("sponge"), which refers to the macroscopic
Macroscopic
The macroscopic scale is the length scale on which objects or processes are of a size which is measurable and observable by the naked eye.When applied to phenomena and abstract objects, the macroscopic scale describes existence in the world as we perceive it, often in contrast to experiences or...
structures and morphology of mushrooms and molds; the root is also used in other languages, such as the German Schwamm ("sponge") and Schimmel ("mold"). The use of the word mycology, which is derived from the Greek mykes/μύκης (mushroom) and logos/λόγος (discourse), to denote the scientific study of fungi is thought to have originated in 1836 with English naturalist Miles Joseph Berkeley
Miles Joseph Berkeley
Miles Joseph Berkeley was an English cryptogamist and clergyman, and one of the founders of the science of plant pathology....
's publication The English Flora of Sir James Edward Smith, Vol. 5.
Characteristics
Before the introduction of molecular methods for phylogenetic analysis, taxonomistsTaxonomy
Taxonomy is the science of identifying and naming species, and arranging them into a classification. The field of taxonomy, sometimes referred to as "biological taxonomy", revolves around the description and use of taxonomic units, known as taxa...
considered fungi to be members of the Plant Kingdom
Plant
Plants are living organisms belonging to the kingdom Plantae. Precise definitions of the kingdom vary, but as the term is used here, plants include familiar organisms such as trees, flowers, herbs, bushes, grasses, vines, ferns, mosses, and green algae. The group is also called green plants or...
because of similarities in lifestyle: both fungi and plants are mainly immobile
Sessility (zoology)
In zoology, sessility is a characteristic of animals which are not able to move about. They are usually permanently attached to a solid substrate of some kind, such as a part of a plant or dead tree trunk, a rock, or the hull of a ship in the case of barnacles. Corals lay down their own...
, and have similarities in general morphology and growth habitat. Like plants, fungi often grow in soil, and in the case of mushroom
Mushroom
A mushroom is the fleshy, spore-bearing fruiting body of a fungus, typically produced above ground on soil or on its food source. The standard for the name "mushroom" is the cultivated white button mushroom, Agaricus bisporus; hence the word "mushroom" is most often applied to those fungi that...
s form conspicuous fruiting bodies, which sometimes bear resemblance to plants such as mosses. The fungi are now considered a separate kingdom, distinct from both plants and animals, from which they appear to have diverged around one billion years ago. Some morphological, biochemical, and genetic features are shared with other organisms, while others are unique to the fungi, clearly separating them from the other kingdoms:
Shared features:
- With other eukaryoteEukaryoteA eukaryote is an organism whose cells contain complex structures enclosed within membranes. Eukaryotes may more formally be referred to as the taxon Eukarya or Eukaryota. The defining membrane-bound structure that sets eukaryotic cells apart from prokaryotic cells is the nucleus, or nuclear...
s: As other eukaryotes, fungal cells contain membrane-bound nucleiCell nucleusIn cell biology, the nucleus is a membrane-enclosed organelle found in eukaryotic cells. It contains most of the cell's genetic material, organized as multiple long linear DNA molecules in complex with a large variety of proteins, such as histones, to form chromosomes. The genes within these...
with chromosomes that contain DNA with noncoding regionsNoncoding DNAIn genetics, noncoding DNA describes components of an organism's DNA sequences that do not encode for protein sequences. In many eukaryotes, a large percentage of an organism's total genome size is noncoding DNA, although the amount of noncoding DNA, and the proportion of coding versus noncoding...
called intronIntronAn intron is any nucleotide sequence within a gene that is removed by RNA splicing to generate the final mature RNA product of a gene. The term intron refers to both the DNA sequence within a gene, and the corresponding sequence in RNA transcripts. Sequences that are joined together in the final...
s and coding regions called exons. In addition, fungi possess membrane-bound cytoplasmic organelles such as mitochondria, sterolSterolSterols, also known as steroid alcohols, are a subgroup of the steroids and an important class of organic molecules. They occur naturally in plants, animals, and fungi, with the most familiar type of animal sterol being cholesterol...
-containing membranes, and ribosomes of the 80S80S80S are ribosomes present in eukaryotes. Their small subunit is 40S and the large subunit is 60S. Ribosomes present in eukaryotes differ from those found in prokaryote in many ways: they are larger, contain larger proteins as well as a larger number of proteins, and have four molecules of RNA....
type. They have a characteristic range of soluble carbohydrates and storage compounds, including sugar alcoholSugar alcoholA sugar alcohol is a hydrogenated form of carbohydrate, whose carbonyl group has been reduced to a primary or secondary hydroxyl group . Sugar alcohols have the general formula Hn+1H, whereas sugars have HnHCO...
s (e.g., mannitolMannitolMannitol is a white, crystalline organic compound with the formula . This polyol is used as an osmotic diuretic agent and a weak renal vasodilator...
), disaccharideDisaccharideA disaccharide or biose is the carbohydrate formed when two monosaccharides undergo a condensation reaction which involves the elimination of a small molecule, such as water, from the functional groups only. Like monosaccharides, disaccharides form an aqueous solution when dissolved in water...
s, (e.g., trehaloseTrehaloseTrehalose, also known as mycose or tremalose, is a natural alpha-linked disaccharide formed by an α,α-1,1-glucoside bond between two α-glucose units. In 1832, H.A.L. Wiggers discovered trehalose in an ergot of rye, and in 1859 Marcellin Berthelot isolated it from trehala manna, a substance made...
), and polysaccharidePolysaccharidePolysaccharides are long carbohydrate molecules, of repeated monomer units joined together by glycosidic bonds. They range in structure from linear to highly branched. Polysaccharides are often quite heterogeneous, containing slight modifications of the repeating unit. Depending on the structure,...
s (e.g., glycogenGlycogenGlycogen is a molecule that serves as the secondary long-term energy storage in animal and fungal cells, with the primary energy stores being held in adipose tissue...
, which is also found in animals). - With animals: Fungi lack chloroplastChloroplastChloroplasts are organelles found in plant cells and other eukaryotic organisms that conduct photosynthesis. Chloroplasts capture light energy to conserve free energy in the form of ATP and reduce NADP to NADPH through a complex set of processes called photosynthesis.Chloroplasts are green...
s and are heterotrophHeterotrophA heterotroph is an organism that cannot fix carbon and uses organic carbon for growth. This contrasts with autotrophs, such as plants and algae, which can use energy from sunlight or inorganic compounds to produce organic compounds such as carbohydrates, fats, and proteins from inorganic carbon...
ic organisms, requiring preformed organic compoundOrganic compoundAn organic compound is any member of a large class of gaseous, liquid, or solid chemical compounds whose molecules contain carbon. For historical reasons discussed below, a few types of carbon-containing compounds such as carbides, carbonates, simple oxides of carbon, and cyanides, as well as the...
s as energy sources. - With plants: Fungi possess a cell wall and vacuoleVacuoleA vacuole is a membrane-bound organelle which is present in all plant and fungal cells and some protist, animal and bacterial cells. Vacuoles are essentially enclosed compartments which are filled with water containing inorganic and organic molecules including enzymes in solution, though in certain...
s. They reproduce by both sexual and asexual means, and like basal plant groups (such as fernFernA fern is any one of a group of about 12,000 species of plants belonging to the botanical group known as Pteridophyta. Unlike mosses, they have xylem and phloem . They have stems, leaves, and roots like other vascular plants...
s and mossMossMosses are small, soft plants that are typically 1–10 cm tall, though some species are much larger. They commonly grow close together in clumps or mats in damp or shady locations. They do not have flowers or seeds, and their simple leaves cover the thin wiry stems...
es) produce sporeSporeIn biology, a spore is a reproductive structure that is adapted for dispersal and surviving for extended periods of time in unfavorable conditions. Spores form part of the life cycles of many bacteria, plants, algae, fungi and some protozoa. According to scientist Dr...
s. Similar to mosses and algae, fungi typically have haploid nuclei. - With euglenoids and bacteria: Higher fungi, euglenoids, and some bacteria produce the amino acidAmino acidAmino acids are molecules containing an amine group, a carboxylic acid group and a side-chain that varies between different amino acids. The key elements of an amino acid are carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen...
L-lysine in specific biosynthesisBiosynthesisBiosynthesis is an enzyme-catalyzed process in cells of living organisms by which substrates are converted to more complex products. The biosynthesis process often consists of several enzymatic steps in which the product of one step is used as substrate in the following step...
steps, called the α-aminoadipate pathway. - The cells of most fungi grow as tubular, elongated, and thread-like (filamentous) structures and are called hyphae, which may contain multiple nuclei and extend at their tips. Each tip contains a set of aggregated vesiclesVesicle (biology)A vesicle is a bubble of liquid within another liquid, a supramolecular assembly made up of many different molecules. More technically, a vesicle is a small membrane-enclosed sack that can store or transport substances. Vesicles can form naturally because of the properties of lipid membranes , or...
—cellular structures consisting of proteinProteinProteins are biochemical compounds consisting of one or more polypeptides typically folded into a globular or fibrous form, facilitating a biological function. A polypeptide is a single linear polymer chain of amino acids bonded together by peptide bonds between the carboxyl and amino groups of...
s, lipidLipidLipids constitute a broad group of naturally occurring molecules that include fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins , monoglycerides, diglycerides, triglycerides, phospholipids, and others...
s, and other organic molecules—called SpitzenkörperSpitzenkörperThe Spitzenkörper is a structure found in fungal hyphae which is the organizing center for hyphal growth and morphogenesis. It consists of many small vesicles and is present in growing hyphal tips, during spore germination and where branch formation occurs. Its position in the hyphal tip correlates...
. Both fungi and oomycetes grow as filamentous hyphal cells. In contrast, similar-looking organisms, such as filamentous green algaeGreen algaeThe green algae are the large group of algae from which the embryophytes emerged. As such, they form a paraphyletic group, although the group including both green algae and embryophytes is monophyletic...
, grow by repeated cell division within a chain of cells. - In common with some plant and animal species, more than 60 fungal species display the phenomenon of bioluminescenceBioluminescenceBioluminescence is the production and emission of light by a living organism. Its name is a hybrid word, originating from the Greek bios for "living" and the Latin lumen "light". Bioluminescence is a naturally occurring form of chemiluminescence where energy is released by a chemical reaction in...
.
Unique features:
- Some species grow as single-celled yeasts that reproduce by buddingBuddingBudding is a form of asexual reproduction in which a new organism grows on another one. The new organism remains attached as it grows, separating from the parent organism only when it is mature. Since the reproduction is asexual, the newly created organism is a clone and is genetically identical...
or binary fission. Dimorphic fungiDimorphic fungiDimorphic fungi are fungi which can exist as mold/hyphal/filamentous form or as yeast. An example is Penicillium marneffei:* At room temperature, it grows as a mold.* At body temperature, it grows as a yeast....
can switch between a yeast phase and a hyphal phase in response to environmental conditions. - The fungal cell wall is composed of glucanGlucanA glucan molecule is a polysaccharide of D-glucose monomers linked by glycosidic bonds.Many beta-glucans are medically important.-Types:The following are glucans:-Alpha:...
s and chitinChitinChitin n is a long-chain polymer of a N-acetylglucosamine, a derivative of glucose, and is found in many places throughout the natural world...
; while the former compounds are also found in plants and the latter in the exoskeletonExoskeletonAn exoskeleton is the external skeleton that supports and protects an animal's body, in contrast to the internal skeleton of, for example, a human. In popular usage, some of the larger kinds of exoskeletons are known as "shells". Examples of exoskeleton animals include insects such as grasshoppers...
of arthropods, fungi are the only organisms that combine these two structural molecules in their cell wall. In contrast to plants and the oomycetes, fungal cell walls do not contain cellulose.

Xylem
Xylem is one of the two types of transport tissue in vascular plants. . The word xylem is derived from the Classical Greek word ξυλον , meaning "wood"; the best-known xylem tissue is wood, though it is found throughout the plant...
and phloem
Phloem
In vascular plants, phloem is the living tissue that carries organic nutrients , in particular, glucose, a sugar, to all parts of the plant where needed. In trees, the phloem is the innermost layer of the bark, hence the name, derived from the Greek word "bark"...
in many plants. To overcome these limitations, some fungi, such as Armillaria, form rhizomorphs
Mycelial cord
Mycelial cords are linear aggregations of parallel-oriented hyphae. The mature cords are composed of wide, empty vessel hyphae surrounded by narrower sheathing hyphae...
, that resemble and perform functions similar to the root
Root
In vascular plants, the root is the organ of a plant that typically lies below the surface of the soil. This is not always the case, however, since a root can also be aerial or aerating . Furthermore, a stem normally occurring below ground is not exceptional either...
s of plants. Another characteristic shared with plants includes a biosynthetic pathway for producing terpene
Terpene
Terpenes are a large and diverse class of organic compounds, produced by a variety of plants, particularly conifers, though also by some insects such as termites or swallowtail butterflies, which emit terpenes from their osmeterium. They are often strong smelling and thus may have had a protective...
s that uses mevalonic acid
Mevalonic acid
Mevalonic acid is a key organic compound in biochemistry. The anion of mevalonic acid, the predominant form in biological media, is known as mevalonate. This compound is of major pharmaceutical importance...
and pyrophosphate
Pyrophosphate
In chemistry, the anion, the salts, and the esters of pyrophosphoric acid are called pyrophosphates. Any salt or ester containing two phosphate groups is called a diphosphate. As a food additive, diphosphates are known as E450.- Chemistry :...
as chemical building blocks
Precursor (chemistry)
In chemistry, a precursor is a compound that participates in the chemical reaction that produces another compound. In biochemistry, the term "precursor" is used more specifically to refer to a chemical compound preceding another in a metabolic pathway....
. However, plants have an additional terpene pathway in their chloroplasts, a structure fungi do not possess. Fungi produce several secondary metabolite
Secondary metabolite
Secondary metabolites are organic compounds that are not directly involved in the normal growth, development, or reproduction of an organism. Unlike primary metabolites, absence of secondary metabolities does not result in immediate death, but rather in long-term impairment of the organism's...
s that are similar or identical in structure to those made by plants. Many of the plant and fungal enzymes that make these compounds differ from each other in sequence
Peptide sequence
Peptide sequence or amino acid sequence is the order in which amino acid residues, connected by peptide bonds, lie in the chain in peptides and proteins. The sequence is generally reported from the N-terminal end containing free amino group to the C-terminal end containing free carboxyl group...
and other characteristics, which indicates separate origins and evolution of these enzymes in the fungi and plants.
Diversity
Fungi have a worldwide distribution, and grow in a wide range of habitats, including extreme environments such as desertsDesert fungi
A variety of terricolous fungi inhabit the biological soil crust of arid regions. Those exposed to the sun typically contain melanin and are resistant to high temperatures, dryness and low nutrition. Species that are common elsewhere do not thrive in these conditions. Producing large dark...
or areas with high salt concentrations or ionizing radiation
Ionizing radiation
Ionizing radiation is radiation composed of particles that individually have sufficient energy to remove an electron from an atom or molecule. This ionization produces free radicals, which are atoms or molecules containing unpaired electrons...
, as well as in deep sea
Deep sea
The deep sea, or deep layer, is the lowest layer in the ocean, existing below the thermocline and above the seabed, at a depth of 1000 fathoms or more. Little or no light penetrates this part of the ocean and most of the organisms that live there rely for subsistence on falling organic matter...
sediments. Some can survive the intense UV and cosmic radiation encountered during space travel. Most grow in terrestrial environments, though several species live partly or solely in aquatic habitats, such as the chytrid fungus Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis
Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis
Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis is a chytrid fungus that causes the disease chytridiomycosis. In the decade after it was first discovered in amphibians in 1998, the disease devastated amphibian populations around the world, in a global decline towards multiple extinctions, part of the Holocene...
, a parasite that has been responsible for a worldwide decline in amphibian
Amphibian
Amphibians , are a class of vertebrate animals including animals such as toads, frogs, caecilians, and salamanders. They are characterized as non-amniote ectothermic tetrapods...
populations. This organism spends part of its life cycle as a motile zoospore
Zoospore
A zoospore is a motile asexual spore that uses a flagellum for locomotion. Also called a swarm spore, these spores are created by some algae, bacteria and fungi to propagate themselves.-Flagella:...
, enabling it to propel itself through water and enter its amphibian host. Other examples of aquatic fungi include those living in hydrothermal areas of the ocean.
Around 100,000 species of fungi have been formally described by taxonomists
Taxonomy
Taxonomy is the science of identifying and naming species, and arranging them into a classification. The field of taxonomy, sometimes referred to as "biological taxonomy", revolves around the description and use of taxonomic units, known as taxa...
, but the global biodiversity of the fungus kingdom is not fully understood. On the basis of observations of the ratio of the number of fungal species to the number of plant species in selected environments, the fungal kingdom has been estimated to contain about 1.5 million species; a recent (2011) estimate suggests there may be over 5 million species. In mycology, species
Species
In biology, a species is one of the basic units of biological classification and a taxonomic rank. A species is often defined as a group of organisms capable of interbreeding and producing fertile offspring. While in many cases this definition is adequate, more precise or differing measures are...
have historically been distinguished by a variety of methods and concepts. Classification based on morphological
Morphology (biology)
In biology, morphology is a branch of bioscience dealing with the study of the form and structure of organisms and their specific structural features....
characteristics, such as the size and shape of spores or fruiting structures, has traditionally dominated fungal taxonomy. Species may also be distinguished by their biochemical
Biochemistry
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes in living organisms, including, but not limited to, living matter. Biochemistry governs all living organisms and living processes...
and physiological
Physiology
Physiology is the science of the function of living systems. This includes how organisms, organ systems, organs, cells, and bio-molecules carry out the chemical or physical functions that exist in a living system. The highest honor awarded in physiology is the Nobel Prize in Physiology or...
characteristics, such as their ability to metabolize certain biochemicals, or their reaction to chemical tests
Chemical tests in mushroom identification
Chemical tests in mushroom identification are methods that aid in determining the variety of some fungi. The most useful tests are Melzer's reagent and potassium hydroxide.- Ammonia :Household ammonia can be used. A couple of drops are placed on the flesh...
. The biological species concept discriminates species based on their ability to mate
Mating in fungi
Mating in fungi is a complex process governed by mating types. Research on fungal mating has focused on only a few model species. Since not all of the fungi reproduce sexually and many that do are isogamous, the terms male and female do not apply to this kingdom...
. The application of molecular
Molecular biology
Molecular biology is the branch of biology that deals with the molecular basis of biological activity. This field overlaps with other areas of biology and chemistry, particularly genetics and biochemistry...
tools, such as DNA sequencing
DNA sequencing
DNA sequencing includes several methods and technologies that are used for determining the order of the nucleotide bases—adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine—in a molecule of DNA....
and phylogenetic analysis, to study diversity has greatly enhanced the resolution and added robustness to estimates of genetic diversity
Genetic diversity
Genetic diversity, the level of biodiversity, refers to the total number of genetic characteristics in the genetic makeup of a species. It is distinguished from genetic variability, which describes the tendency of genetic characteristics to vary....
within various taxonomic groups.
Microscopic structures
Most fungi grow as hyphaHypha
A hypha is a long, branching filamentous structure of a fungus, and also of unrelated Actinobacteria. In most fungi, hyphae are the main mode of vegetative growth, and are collectively called a mycelium; yeasts are unicellular fungi that do not grow as hyphae.-Structure:A hypha consists of one or...
e, which are cylindrical, thread-like structures 2–10 µm in diameter and up to several centimeters in length. Hyphae grow at their tips (apices); new hyphae are typically formed by emergence of new tips along existing hyphae by a process called branching, or occasionally growing hyphal tips bifurcate (fork) giving rise to two parallel-growing hyphae. The combination of apical growth and branching/forking leads to the development of a mycelium
Mycelium
thumb|right|Fungal myceliaMycelium is the vegetative part of a fungus, consisting of a mass of branching, thread-like hyphae. The mass of hyphae is sometimes called shiro, especially within the fairy ring fungi. Fungal colonies composed of mycelia are found in soil and on or within many other...
, an interconnected network of hyphae. Hyphae can be either septate or coenocytic: septate hyphae are divided into compartments separated by cross walls (internal cell walls, called septa, that are formed at right angle
Right angle
In geometry and trigonometry, a right angle is an angle that bisects the angle formed by two halves of a straight line. More precisely, if a ray is placed so that its endpoint is on a line and the adjacent angles are equal, then they are right angles...
s to the cell wall giving the hypha its shape), with each compartment containing one or more nuclei; coenocytic hyphae are not compartmentalized. Septa have pores that allow cytoplasm
Cytoplasm
The cytoplasm is a small gel-like substance residing between the cell membrane holding all the cell's internal sub-structures , except for the nucleus. All the contents of the cells of prokaryote organisms are contained within the cytoplasm...
, organelle
Organelle
In cell biology, an organelle is a specialized subunit within a cell that has a specific function, and is usually separately enclosed within its own lipid bilayer....
s, and sometimes nuclei to pass through; an example is the dolipore septum in the fungi of the phylum Basidiomycota. Coenocytic hyphae are essentially multinucleate
Multinucleate
Multinucleate cells have more than one nucleus per cell, which is the result of nuclear division not being followed by cytokinesis. As a consequence, multiple nuclei share one common cytoplasm. This can be the consequence of a disturbed cell cycle control Multinucleate (also multinucleated,...
supercells.
Many species have developed specialized hyphal structures for nutrient uptake from living hosts; examples include haustoria in plant-parasitic species of most fungal phyla, and arbuscules
Arbuscular mycorrhiza
An arbuscular mycorrhiza is a type of mycorrhiza in which the fungus penetrates the cortical cells of the roots of a vascular plant....
of several mycorrhiza
Mycorrhiza
A mycorrhiza is a symbiotic association between a fungus and the roots of a vascular plant....
l fungi, which penetrate into the host cells to consume nutrients.
Although fungi are opisthokont
Opisthokont
The opisthokonts or "Fungi/Metazoa group" are a broad group of eukaryotes, including both the animal and fungus kingdoms, together with the eukaryotic microorganisms that are sometimes grouped in the paraphyletic phylum Choanozoa...
s—a grouping of evolutionarily related organisms broadly characterized by a single posterior flagellum
Flagellum
A flagellum is a tail-like projection that protrudes from the cell body of certain prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, and plays the dual role of locomotion and sense organ, being sensitive to chemicals and temperatures outside the cell. There are some notable differences between prokaryotic and...
—all phyla except for the chytrids have lost their posterior flagella. Fungi are unusual among the eukaryotes in having a cell wall that, in addition to glucan
Glucan
A glucan molecule is a polysaccharide of D-glucose monomers linked by glycosidic bonds.Many beta-glucans are medically important.-Types:The following are glucans:-Alpha:...
s (e.g., β-1,3-glucan) and other typical components, also contains the biopolymer
Biopolymer
Biopolymers are polymers produced by living organisms. Since they are polymers, Biopolymers contain monomeric units that are covalently bonded to form larger structures. There are three main classes of biopolymers based on the differing monomeric units used and the structure of the biopolymer formed...
chitin.
Macroscopic structures
Fungal mycelia can become visible to the naked eye, for example, on various surfaces and substrates, such as damp walls and on spoiled food, where they are commonly called moldMold
Molds are fungi that grow in the form of multicellular filaments called hyphae. Molds are not considered to be microbes but microscopic fungi that grow as single cells called yeasts...
s. Mycelia grown on solid agar
Agar
Agar or agar-agar is a gelatinous substance derived from a polysaccharide that accumulates in the cell walls of agarophyte red algae. Throughout history into modern times, agar has been chiefly used as an ingredient in desserts throughout Asia and also as a solid substrate to contain culture medium...
media in laboratory petri dish
Petri dish
A Petri dish is a shallow glass or plastic cylindrical lidded dish that biologists use to culture cells or small moss plants. It was named after German bacteriologist Julius Richard Petri, who invented it when working as an assistant to Robert Koch...
es are usually referred to as colonies
Colony (biology)
In biology, a colony reference to several individual organisms of the same species living closely together, usually for mutual benefit, such as stronger defense or the ability to attack bigger prey. Some insects live only in colonies...
. These colonies can exhibit growth shapes and colors (due to spores or pigment
Pigment
A pigment is a material that changes the color of reflected or transmitted light as the result of wavelength-selective absorption. This physical process differs from fluorescence, phosphorescence, and other forms of luminescence, in which a material emits light.Many materials selectively absorb...
ation) that can be used as diagnostic features in the identification of species or groups. Some individual fungal colonies can reach extraordinary dimensions and ages as in the case of a clonal
Clone (cell biology)
A clone is a group of identical cells that share a common ancestry, meaning they are derived from the same mother cell.Clonality implies the state of a cell or a substance being derived from one source or the other...
colony of Armillaria solidipes, which extends over an area of more than 900 ha
Hectare
The hectare is a metric unit of area defined as 10,000 square metres , and primarily used in the measurement of land. In 1795, when the metric system was introduced, the are was defined as being 100 square metres and the hectare was thus 100 ares or 1/100 km2...
(3.5 square miles), with an estimated age of nearly 9,000 years.
The apothecium—a specialized structure important in sexual reproduction
Sexual reproduction
Sexual reproduction is the creation of a new organism by combining the genetic material of two organisms. There are two main processes during sexual reproduction; they are: meiosis, involving the halving of the number of chromosomes; and fertilization, involving the fusion of two gametes and the...
in the ascomycetes—is a cup-shaped fruiting body that holds the hymenium
Hymenium
The hymenium is the tissue layer on the hymenophore of a fungal fruiting body where the cells develop into basidia or asci, which produce spores. In some species all of the cells of the hymenium develop into basidia or asci, while in others some cells develop into sterile cells called cystidia or...
, a layer of tissue containing the spore-bearing cells. The fruiting bodies of the basidiomycetes (basidiocarp
Basidiocarp
In fungi, a basidiocarp, basidiome or basidioma , is the sporocarp of a basidiomycete, the multicellular structure on which the spore-producing hymenium is borne. Basidiocarps are characteristic of the hymenomycetes; rusts and smuts do not produce such structures...
s) and some ascomycetes can sometimes grow very large, and many are well-known as mushroom
Mushroom
A mushroom is the fleshy, spore-bearing fruiting body of a fungus, typically produced above ground on soil or on its food source. The standard for the name "mushroom" is the cultivated white button mushroom, Agaricus bisporus; hence the word "mushroom" is most often applied to those fungi that...
s.
Growth and physiology

Surface area to volume ratio
The surface-area-to-volume ratio also called the surface-to-volume ratio and variously denoted sa/vol or SA:V, is the amount of surface area per unit volume of an object or collection of objects. The surface-area-to-volume ratio is measured in units of inverse distance. A cube with sides of...
s. Hyphae are specifically adapted for growth on solid surfaces, and to invade substrates
Substrate (biology)
In biology a substrate is the surface a plant or animal lives upon and grows on. A substrate can include biotic or abiotic materials and animals. For example, encrusting algae that lives on a rock can be substrate for another animal that lives on top of the algae. See also substrate .-External...
and tissues. They can exert large penetrative mechanical forces; for example, the plant pathogen Magnaporthe grisea
Magnaporthe grisea
Magnaporthe grisea, also known as rice blast fungus, rice rotten neck, rice seedling blight, blast of rice, oval leaf spot of graminea, pitting disease, ryegrass blast, and Johnson spot, is a plant-pathogenic fungus that causes an important disease affecting rice. It is now known that M...
forms a structure called an appressorium
Appressorium
An appressorium is a flattened, hyphal "pressing" organ, from which a minute infection peg grows and enters the host, using turgor pressure capable of punching through even Mylar....
that evolved to puncture plant tissues. The pressure generated by the appressorium, directed against the plant epidermis
Epidermis (botany)
The epidermis is a single-layered group of cells that covers plants' leaves, flowers, roots and stems. It forms a boundary between the plant and the external environment. The epidermis serves several functions, it protects against water loss, regulates gas exchange, secretes metabolic compounds,...
, can exceed 8 megapascals (1,160.3 psi). The filamentous fungus Paecilomyces lilacinus uses a similar structure to penetrate the eggs of nematode
Nematode
The nematodes or roundworms are the most diverse phylum of pseudocoelomates, and one of the most diverse of all animals. Nematode species are very difficult to distinguish; over 28,000 have been described, of which over 16,000 are parasitic. It has been estimated that the total number of nematode...
s.
The mechanical pressure exerted by the appressorium is generated from physiological processes that increase intracellular turgor by producing osmolyte
Osmolyte
Osmolytes are compounds affecting osmosis. They are soluble in the solution within a cell, or in the surrounding fluid, e.g. as plasma osmolytes. They play a role in maintaining cell volume and fluid balance. For example, when a cell swells due to external osmotic pressure, membrane channels open...
s such as glycerol
Glycerol
Glycerol is a simple polyol compound. It is a colorless, odorless, viscous liquid that is widely used in pharmaceutical formulations. Glycerol has three hydroxyl groups that are responsible for its solubility in water and its hygroscopic nature. The glycerol backbone is central to all lipids...
. Morphological adaptations such as these are complemented by hydrolytic enzymes
Cellulase
400px|thumb|right|alt = Colored dice with checkered background|Ribbon representation of the Streptomyces lividans beta-1,4-endoglucanase catalytic domain - an example from the family 12 glycoside hydrolases...
secreted into the environment to digest large organic molecules—such as polysaccharide
Polysaccharide
Polysaccharides are long carbohydrate molecules, of repeated monomer units joined together by glycosidic bonds. They range in structure from linear to highly branched. Polysaccharides are often quite heterogeneous, containing slight modifications of the repeating unit. Depending on the structure,...
s, protein
Protein
Proteins are biochemical compounds consisting of one or more polypeptides typically folded into a globular or fibrous form, facilitating a biological function. A polypeptide is a single linear polymer chain of amino acids bonded together by peptide bonds between the carboxyl and amino groups of...
s, lipid
Lipid
Lipids constitute a broad group of naturally occurring molecules that include fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins , monoglycerides, diglycerides, triglycerides, phospholipids, and others...
s, and other organic substrates—into smaller molecules that may then be absorbed as nutrients. The vast majority of filamentous fungi grow in a polar fashion—i.e., by extension into one direction—by elongation at the tip (apex) of the hypha. Alternative forms of fungal growth include intercalary extension (i.e., by longitudinal expansion of hyphal compartments that are below the apex) as in the case of some endophytic
Endophyte
An endophyte is an endosymbiont, often a bacterium or fungus, that lives within a plant for at least part of its life without causing apparent disease. Endophytes are ubiquitous and have been found in all the species of plants studied to date; however, most of these endophyte/plant relationships...
fungi, or growth by volume expansion during the development of mushroom stipes and other large organs. Growth of fungi as multicellular structures consisting of somatic
Somatic
The term somatic means 'of the body',, relating to the body. In medicine, somatic illness is bodily, not mental, illness. The term is often used in biology to refer to the cells of the body in contrast to the germ line cells which usually give rise to the gametes...
and reproductive cells—a feature independently evolved in animals and plants—has several functions, including the development of fruiting bodies for dissemination of sexual spores (see above) and biofilm
Biofilm
A biofilm is an aggregate of microorganisms in which cells adhere to each other on a surface. These adherent cells are frequently embedded within a self-produced matrix of extracellular polymeric substance...
s for substrate colonization and intercellular communication.
Traditionally, the fungi are considered heterotroph
Heterotroph
A heterotroph is an organism that cannot fix carbon and uses organic carbon for growth. This contrasts with autotrophs, such as plants and algae, which can use energy from sunlight or inorganic compounds to produce organic compounds such as carbohydrates, fats, and proteins from inorganic carbon...
s, organisms that rely solely on carbon fixed
Carbon fixation
In biology, carbon fixation is the reduction of carbon dioxide to organic compounds by living organisms. The obvious example is photosynthesis. Carbon fixation requires both a source of energy such as sunlight, and an electron donor such as water. All life depends on fixed carbon. Organisms that...
by other organisms for metabolism
Metabolism
Metabolism is the set of chemical reactions that happen in the cells of living organisms to sustain life. These processes allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to their environments. Metabolism is usually divided into two categories...
. Fungi have evolved
Evolution
Evolution is any change across successive generations in the heritable characteristics of biological populations. Evolutionary processes give rise to diversity at every level of biological organisation, including species, individual organisms and molecules such as DNA and proteins.Life on Earth...
a high degree of metabolic versatility that allows them to use a diverse range of organic substrates for growth, including simple compounds such as nitrate
Nitrate
The nitrate ion is a polyatomic ion with the molecular formula NO and a molecular mass of 62.0049 g/mol. It is the conjugate base of nitric acid, consisting of one central nitrogen atom surrounded by three identically-bonded oxygen atoms in a trigonal planar arrangement. The nitrate ion carries a...
, ammonia
Ammonia
Ammonia is a compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the formula . It is a colourless gas with a characteristic pungent odour. Ammonia contributes significantly to the nutritional needs of terrestrial organisms by serving as a precursor to food and fertilizers. Ammonia, either directly or...
, acetate
Acetate
An acetate is a derivative of acetic acid. This term includes salts and esters, as well as the anion found in solution. Most of the approximately 5 billion kilograms of acetic acid produced annually in industry are used in the production of acetates, which usually take the form of polymers. In...
, or ethanol
Ethanol
Ethanol, also called ethyl alcohol, pure alcohol, grain alcohol, or drinking alcohol, is a volatile, flammable, colorless liquid. It is a psychoactive drug and one of the oldest recreational drugs. Best known as the type of alcohol found in alcoholic beverages, it is also used in thermometers, as a...
. For some species it has been shown that the pigment melanin
Melanin
Melanin is a pigment that is ubiquitous in nature, being found in most organisms . In animals melanin pigments are derivatives of the amino acid tyrosine. The most common form of biological melanin is eumelanin, a brown-black polymer of dihydroxyindole carboxylic acids, and their reduced forms...
may play a role in extracting energy from ionizing radiation
Ionizing radiation
Ionizing radiation is radiation composed of particles that individually have sufficient energy to remove an electron from an atom or molecule. This ionization produces free radicals, which are atoms or molecules containing unpaired electrons...
, such as gamma radiation; however, this form of "radiotrophic"
Radiotrophic fungus
Radiotrophic fungi are fungi which appear to use the pigment melanin to convert gamma radiation into chemical energy for growth. This proposed mechanism may be similar to anabolic pathways for the synthesis of reduced organic carbon in phototrophic organisms, which capture photons from visible...
growth has only been described for a few species, the effects on growth rates are small, and the underlying biophysical
Biophysics
Biophysics is an interdisciplinary science that uses the methods of physical science to study biological systems. Studies included under the branches of biophysics span all levels of biological organization, from the molecular scale to whole organisms and ecosystems...
and biochemical processes are not known. The authors speculate that this process might bear similarity to CO2 fixation
Carbon fixation
In biology, carbon fixation is the reduction of carbon dioxide to organic compounds by living organisms. The obvious example is photosynthesis. Carbon fixation requires both a source of energy such as sunlight, and an electron donor such as water. All life depends on fixed carbon. Organisms that...
via visible light
Visible spectrum
The visible spectrum is the portion of the electromagnetic spectrum that is visible to the human eye. Electromagnetic radiation in this range of wavelengths is called visible light or simply light. A typical human eye will respond to wavelengths from about 390 to 750 nm. In terms of...
, but instead utilizing ionizing radiation as a source of energy.
Reproduction

Biological life cycle
A life cycle is a period involving all different generations of a species succeeding each other through means of reproduction, whether through asexual reproduction or sexual reproduction...
of a species, the teleomorph and the anamorph. Environmental conditions trigger genetically determined developmental states that lead to the creation of specialized structures for sexual or asexual reproduction. These structures aid reproduction by efficiently dispersing spores or spore-containing propagule
Propagule
In horticulture, a propagule is any plant material used for the purpose of plant propagation. In asexual reproduction, a propagule may be a woody, semi-hardwood, or softwood cutting, leaf section, or any number of other plant parts. In sexual reproduction, a propagule is a seed or spore...
s.
Asexual reproduction
Asexual reproductionAsexual reproduction
Asexual reproduction is a mode of reproduction by which offspring arise from a single parent, and inherit the genes of that parent only, it is reproduction which does not involve meiosis, ploidy reduction, or fertilization. A more stringent definition is agamogenesis which is reproduction without...
via vegetative spores (conidia
Conidium
Conidia, sometimes termed conidiospores, are asexual, non-motile spores of a fungus and are named after the greek word for dust, konia. They are also called mitospores due to the way they are generated through the cellular process of mitosis...
) or through mycelial fragmentation is common; it maintains clonal populations adapted to a specific niche
Ecological niche
In ecology, a niche is a term describing the relational position of a species or population in its ecosystem to each other; e.g. a dolphin could potentially be in another ecological niche from one that travels in a different pod if the members of these pods utilize significantly different food...
, and allows more rapid dispersal than sexual reproduction. The "Fungi imperfecti" (fungi lacking the perfect or sexual stage) or Deuteromycota comprise all the species which lack an observable sexual cycle.
Sexual reproduction
Sexual reproduction with meiosisMeiosis
Meiosis is a special type of cell division necessary for sexual reproduction. The cells produced by meiosis are gametes or spores. The animals' gametes are called sperm and egg cells....
exists in all fungal phyla (with the exception of the Glomeromycota
Glomeromycota
Glomeromycota is one of seven currently recognized phyla within the kingdom Fungi, with approximately 230 described species. Members of the Glomeromycota form arbuscular mycorrhizas with the roots or thalli of land plants. Geosiphon pyriformis forms an endocytobiotic association with Nostoc...
).
A fungus is a member of a large group of eukaryotic
Eukaryote
A eukaryote is an organism whose cells contain complex structures enclosed within membranes. Eukaryotes may more formally be referred to as the taxon Eukarya or Eukaryota. The defining membrane-bound structure that sets eukaryotic cells apart from prokaryotic cells is the nucleus, or nuclear...
organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeast
Yeast
Yeasts are eukaryotic micro-organisms classified in the kingdom Fungi, with 1,500 species currently described estimated to be only 1% of all fungal species. Most reproduce asexually by mitosis, and many do so by an asymmetric division process called budding...
s and mold
Mold
Molds are fungi that grow in the form of multicellular filaments called hyphae. Molds are not considered to be microbes but microscopic fungi that grow as single cells called yeasts...
s (British English: moulds), as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom
Kingdom (biology)
In biology, kingdom is a taxonomic rank, which is either the highest rank or in the more recent three-domain system, the rank below domain. Kingdoms are divided into smaller groups called phyla or divisions in botany...
, Fungi, which is separate from plant
Plant
Plants are living organisms belonging to the kingdom Plantae. Precise definitions of the kingdom vary, but as the term is used here, plants include familiar organisms such as trees, flowers, herbs, bushes, grasses, vines, ferns, mosses, and green algae. The group is also called green plants or...
s, animal
Animal
Animals are a major group of multicellular, eukaryotic organisms of the kingdom Animalia or Metazoa. Their body plan eventually becomes fixed as they develop, although some undergo a process of metamorphosis later on in their life. Most animals are motile, meaning they can move spontaneously and...
s, and bacteria
Bacteria
Bacteria are a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria have a wide range of shapes, ranging from spheres to rods and spirals...
. One major difference is that fungal cells have cell wall
Cell wall
The cell wall is the tough, usually flexible but sometimes fairly rigid layer that surrounds some types of cells. It is located outside the cell membrane and provides these cells with structural support and protection, and also acts as a filtering mechanism. A major function of the cell wall is to...
s that contain chitin
Chitin
Chitin n is a long-chain polymer of a N-acetylglucosamine, a derivative of glucose, and is found in many places throughout the natural world...
, unlike the cell walls of plants, which contain cellulose
Cellulose
Cellulose is an organic compound with the formula , a polysaccharide consisting of a linear chain of several hundred to over ten thousand β linked D-glucose units....
. These and other differences show that the fungi form a single group of related organisms, named the Eumycota (true fungi or Eumycetes), that share a common ancestor (a monophyletic group). This fungal group is distinct from the structurally similar myxomycetes (slime molds) and oomycetes (water molds). The discipline of biology
Biology
Biology is a natural science concerned with the study of life and living organisms, including their structure, function, growth, origin, evolution, distribution, and taxonomy. Biology is a vast subject containing many subdivisions, topics, and disciplines...
devoted to the study of fungi is known as mycology
Mycology
Mycology is the branch of biology concerned with the study of fungi, including their genetic and biochemical properties, their taxonomy and their use to humans as a source for tinder, medicinals , food and entheogens, as well as their dangers, such as poisoning or...
, which is often regarded as a branch of botany
Botany
Botany, plant science, or plant biology is a branch of biology that involves the scientific study of plant life. Traditionally, botany also included the study of fungi, algae and viruses...
, even though genetic studies have shown that fungi are more closely related to animals than to plants.
Abundant worldwide, most fungi are inconspicuous because of the small size of their structures, and their cryptic
Crypsis
In ecology, crypsis is the ability of an organism to avoid observation or detection by other organisms. It may be either a predation strategy or an antipredator adaptation, and methods include camouflage, nocturnality, subterranean lifestyle, transparency, and mimicry...
lifestyles in soil, on dead matter, and as symbionts
Symbiosis
Symbiosis is close and often long-term interaction between different biological species. In 1877 Bennett used the word symbiosis to describe the mutualistic relationship in lichens...
of plants, animals, or other fungi. They may become noticeable when fruiting
Sporocarp (fungi)
In fungi, the sporocarp is a multicellular structure on which spore-producing structures, such as basidia or asci, are borne...
, either as mushrooms or molds. Fungi perform an essential role in the decomposition of organic matter and have fundamental roles in nutrient cycling
Biogeochemical cycle
In ecology and Earth science, a biogeochemical cycle or substance turnover or cycling of substances is a pathway by which a chemical element or molecule moves through both biotic and abiotic compartments of Earth. A cycle is a series of change which comes back to the starting point and which can...
and exchange. They have long been used as a direct source of food, such as mushrooms and truffles, as a leavening agent for bread, and in fermentation
Fermentation (food)
Fermentation in food processing typically is the conversion of carbohydrates to alcohols and carbon dioxide or organic acids using yeasts, bacteria, or a combination thereof, under anaerobic conditions. Fermentation in simple terms is the chemical conversion of sugars into ethanol...
of various food products, such as wine
Wine
Wine is an alcoholic beverage, made of fermented fruit juice, usually from grapes. The natural chemical balance of grapes lets them ferment without the addition of sugars, acids, enzymes, or other nutrients. Grape wine is produced by fermenting crushed grapes using various types of yeast. Yeast...
, beer
Beer
Beer is the world's most widely consumed andprobably oldest alcoholic beverage; it is the third most popular drink overall, after water and tea. It is produced by the brewing and fermentation of sugars, mainly derived from malted cereal grains, most commonly malted barley and malted wheat...
, and soy sauce
Soy sauce
Soy sauce is a condiment produced by fermenting soybeans with Aspergillus oryzae or Aspergillus sojae molds, along with water and salt...
. Since the 1940s, fungi have been used for the production of antibiotic
Antibiotic
An antibacterial is a compound or substance that kills or slows down the growth of bacteria.The term is often used synonymously with the term antibiotic; today, however, with increased knowledge of the causative agents of various infectious diseases, antibiotic has come to denote a broader range of...
s, and, more recently, various enzyme
Enzyme
Enzymes are proteins that catalyze chemical reactions. In enzymatic reactions, the molecules at the beginning of the process, called substrates, are converted into different molecules, called products. Almost all chemical reactions in a biological cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates...
s produced by fungi are used industrially and in detergents. Fungi are also used as biological pesticides to control weeds, plant diseases and insect pests. Many species produce bioactive compounds called mycotoxin
Mycotoxin
A mycotoxin is a toxic secondary metabolite produced by organisms of the fungus kingdom, commonly known as molds. The term ‘mycotoxin’ is usually reserved for the toxic chemical products produced by fungi that readily colonize crops...
s, such as alkaloid
Alkaloid
Alkaloids are a group of naturally occurring chemical compounds that contain mostly basic nitrogen atoms. This group also includes some related compounds with neutral and even weakly acidic properties. Also some synthetic compounds of similar structure are attributed to alkaloids...
s and polyketide
Polyketide
Polyketides are secondary metabolites from bacteria, fungi, plants, and animals. Polyketides are usually biosynthesized through the decarboxylative condensation of malonyl-CoA derived extender units in a similar process to fatty acid synthesis...
s, that are toxic to animals including humans. The fruiting structures of a few species contain psychotropic compounds and are consumed recreationally
Recreational drug use
Recreational drug use is the use of a drug, usually psychoactive, with the intention of creating or enhancing recreational experience. Such use is controversial, however, often being considered to be also drug abuse, and it is often illegal...
or in traditional spiritual ceremonies. Fungi can break down manufactured materials and buildings, and become significant pathogen
Pathogenic fungi
Pathogenic fungi are fungi that cause disease in humans or other organisms. The study of pathogenic fungi is referred to as medical mycology. Although fungi are eukaryotic organisms many pathogenic fungi are also microorganisms.-Candida:...
s of humans and other animals. Losses of crops due to fungal diseases (e.g. rice blast disease) or food spoilage can have a large impact on human food supplies
Food security
Food security refers to the availability of food and one's access to it. A household is considered food-secure when its occupants do not live in hunger or fear of starvation. According to the World Resources Institute, global per capita food production has been increasing substantially for the past...
and local economies.
The fungus kingdom encompasses an enormous diversity of taxa
Taxon
|thumb|270px|[[African elephants]] form a widely-accepted taxon, the [[genus]] LoxodontaA taxon is a group of organisms, which a taxonomist adjudges to be a unit. Usually a taxon is given a name and a rank, although neither is a requirement...
with varied ecologies, life cycle
Biological life cycle
A life cycle is a period involving all different generations of a species succeeding each other through means of reproduction, whether through asexual reproduction or sexual reproduction...
strategies, and morphologies
Morphology (biology)
In biology, morphology is a branch of bioscience dealing with the study of the form and structure of organisms and their specific structural features....
ranging from single-celled aquatic chytrids to large mushrooms. However, little is known of the true biodiversity
Biodiversity
Biodiversity is the degree of variation of life forms within a given ecosystem, biome, or an entire planet. Biodiversity is a measure of the health of ecosystems. Biodiversity is in part a function of climate. In terrestrial habitats, tropical regions are typically rich whereas polar regions...
of Kingdom Fungi, which has been estimated at around 1.5 million species, with about 5% of these having been formally classified. Ever since the pioneering 18th and 19th century taxonomical
Taxonomy
Taxonomy is the science of identifying and naming species, and arranging them into a classification. The field of taxonomy, sometimes referred to as "biological taxonomy", revolves around the description and use of taxonomic units, known as taxa...
works of Carl Linnaeus, Christian Hendrik Persoon
Christian Hendrik Persoon
Christiaan Hendrik Persoon was a mycologist who made additions to Linnaeus' mushroom taxonomy.-Early life:...
, and Elias Magnus Fries
Elias Magnus Fries
-External links:*, Authors of fungal names, Mushroom, the Journal of Wild Mushrooming.*...
, fungi have been classified
Biological classification
Biological classification, or scientific classification in biology, is a method to group and categorize organisms by biological type, such as genus or species. Biological classification is part of scientific taxonomy....
according to their morphology (e.g., characteristics such as spore color or microscopic features) or physiology
Physiology
Physiology is the science of the function of living systems. This includes how organisms, organ systems, organs, cells, and bio-molecules carry out the chemical or physical functions that exist in a living system. The highest honor awarded in physiology is the Nobel Prize in Physiology or...
. Advances in molecular genetics
Molecular genetics
Molecular genetics is the field of biology and genetics that studies the structure and function of genes at a molecular level. The field studies how the genes are transferred from generation to generation. Molecular genetics employs the methods of genetics and molecular biology...
have opened the way for DNA analysis
DNA sequencing
DNA sequencing includes several methods and technologies that are used for determining the order of the nucleotide bases—adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine—in a molecule of DNA....
to be incorporated into taxonomy, which has sometimes challenged the historical groupings based on morphology and other traits. Phylogenetic studies published in the last decade have helped reshape the classification of Kingdom Fungi, which is divided into one subkingdom
Taxonomic rank
In biological classification, rank is the level in a taxonomic hierarchy. Examples of taxonomic ranks are species, genus, family, and class. Each rank subsumes under it a number of less general categories...
, seven phyla
Phylum
In biology, a phylum The term was coined by Georges Cuvier from Greek φῦλον phylon, "race, stock," related to φυλή phyle, "tribe, clan." is a taxonomic rank below kingdom and above class. "Phylum" is equivalent to the botanical term division....
, and ten subphyla.
Etymology
The English word fungus is directly adopted from the LatinLatin
Latin is an Italic language originally spoken in Latium and Ancient Rome. It, along with most European languages, is a descendant of the ancient Proto-Indo-European language. Although it is considered a dead language, a number of scholars and members of the Christian clergy speak it fluently, and...
fungus (mushroom), used in the writings of Horace
Horace
Quintus Horatius Flaccus , known in the English-speaking world as Horace, was the leading Roman lyric poet during the time of Augustus.-Life:...
and Pliny
Pliny the Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus , better known as Pliny the Elder, was a Roman author, naturalist, and natural philosopher, as well as naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and personal friend of the emperor Vespasian...
. This in turn is derived from the Greek
Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek is the stage of the Greek language in the periods spanning the times c. 9th–6th centuries BC, , c. 5th–4th centuries BC , and the c. 3rd century BC – 6th century AD of ancient Greece and the ancient world; being predated in the 2nd millennium BC by Mycenaean Greek...
word sphongos/σφογγος ("sponge"), which refers to the macroscopic
Macroscopic
The macroscopic scale is the length scale on which objects or processes are of a size which is measurable and observable by the naked eye.When applied to phenomena and abstract objects, the macroscopic scale describes existence in the world as we perceive it, often in contrast to experiences or...
structures and morphology of mushrooms and molds; the root is also used in other languages, such as the German Schwamm ("sponge") and Schimmel ("mold"). The use of the word mycology, which is derived from the Greek mykes/μύκης (mushroom) and logos/λόγος (discourse), to denote the scientific study of fungi is thought to have originated in 1836 with English naturalist Miles Joseph Berkeley
Miles Joseph Berkeley
Miles Joseph Berkeley was an English cryptogamist and clergyman, and one of the founders of the science of plant pathology....
's publication The English Flora of Sir James Edward Smith, Vol. 5.Ainsworth, p. 2.
Characteristics
Before the introduction of molecular methods for phylogenetic analysis, taxonomistsTaxonomy
Taxonomy is the science of identifying and naming species, and arranging them into a classification. The field of taxonomy, sometimes referred to as "biological taxonomy", revolves around the description and use of taxonomic units, known as taxa...
considered fungi to be members of the Plant Kingdom
Plant
Plants are living organisms belonging to the kingdom Plantae. Precise definitions of the kingdom vary, but as the term is used here, plants include familiar organisms such as trees, flowers, herbs, bushes, grasses, vines, ferns, mosses, and green algae. The group is also called green plants or...
because of similarities in lifestyle: both fungi and plants are mainly immobile
Sessility (zoology)
In zoology, sessility is a characteristic of animals which are not able to move about. They are usually permanently attached to a solid substrate of some kind, such as a part of a plant or dead tree trunk, a rock, or the hull of a ship in the case of barnacles. Corals lay down their own...
, and have similarities in general morphology and growth habitat. Like plants, fungi often grow in soil, and in the case of mushroom
Mushroom
A mushroom is the fleshy, spore-bearing fruiting body of a fungus, typically produced above ground on soil or on its food source. The standard for the name "mushroom" is the cultivated white button mushroom, Agaricus bisporus; hence the word "mushroom" is most often applied to those fungi that...
s form conspicuous fruiting bodies, which sometimes bear resemblance to plants such as mosses. The fungi are now considered a separate kingdom, distinct from both plants and animals, from which they appear to have diverged around one billion years ago. Some morphological, biochemical, and genetic features are shared with other organisms, while others are unique to the fungi, clearly separating them from the other kingdoms:
Shared features:
- With other eukaryoteEukaryoteA eukaryote is an organism whose cells contain complex structures enclosed within membranes. Eukaryotes may more formally be referred to as the taxon Eukarya or Eukaryota. The defining membrane-bound structure that sets eukaryotic cells apart from prokaryotic cells is the nucleus, or nuclear...
s: As other eukaryotes, fungal cells contain membrane-bound nucleiCell nucleusIn cell biology, the nucleus is a membrane-enclosed organelle found in eukaryotic cells. It contains most of the cell's genetic material, organized as multiple long linear DNA molecules in complex with a large variety of proteins, such as histones, to form chromosomes. The genes within these...
with chromosomes that contain DNA with noncoding regionsNoncoding DNAIn genetics, noncoding DNA describes components of an organism's DNA sequences that do not encode for protein sequences. In many eukaryotes, a large percentage of an organism's total genome size is noncoding DNA, although the amount of noncoding DNA, and the proportion of coding versus noncoding...
called intronIntronAn intron is any nucleotide sequence within a gene that is removed by RNA splicing to generate the final mature RNA product of a gene. The term intron refers to both the DNA sequence within a gene, and the corresponding sequence in RNA transcripts. Sequences that are joined together in the final...
s and coding regions called exons. In addition, fungi possess membrane-bound cytoplasmic organelles such as mitochondria, sterolSterolSterols, also known as steroid alcohols, are a subgroup of the steroids and an important class of organic molecules. They occur naturally in plants, animals, and fungi, with the most familiar type of animal sterol being cholesterol...
-containing membranes, and ribosomes of the 80S80S80S are ribosomes present in eukaryotes. Their small subunit is 40S and the large subunit is 60S. Ribosomes present in eukaryotes differ from those found in prokaryote in many ways: they are larger, contain larger proteins as well as a larger number of proteins, and have four molecules of RNA....
type. They have a characteristic range of soluble carbohydrates and storage compounds, including sugar alcoholSugar alcoholA sugar alcohol is a hydrogenated form of carbohydrate, whose carbonyl group has been reduced to a primary or secondary hydroxyl group . Sugar alcohols have the general formula Hn+1H, whereas sugars have HnHCO...
s (e.g., mannitolMannitolMannitol is a white, crystalline organic compound with the formula . This polyol is used as an osmotic diuretic agent and a weak renal vasodilator...
), disaccharideDisaccharideA disaccharide or biose is the carbohydrate formed when two monosaccharides undergo a condensation reaction which involves the elimination of a small molecule, such as water, from the functional groups only. Like monosaccharides, disaccharides form an aqueous solution when dissolved in water...
s, (e.g., trehaloseTrehaloseTrehalose, also known as mycose or tremalose, is a natural alpha-linked disaccharide formed by an α,α-1,1-glucoside bond between two α-glucose units. In 1832, H.A.L. Wiggers discovered trehalose in an ergot of rye, and in 1859 Marcellin Berthelot isolated it from trehala manna, a substance made...
), and polysaccharidePolysaccharidePolysaccharides are long carbohydrate molecules, of repeated monomer units joined together by glycosidic bonds. They range in structure from linear to highly branched. Polysaccharides are often quite heterogeneous, containing slight modifications of the repeating unit. Depending on the structure,...
s (e.g., glycogenGlycogenGlycogen is a molecule that serves as the secondary long-term energy storage in animal and fungal cells, with the primary energy stores being held in adipose tissue...
, which is also found in animalsDeacon, pp. 128–29.). - With animals: Fungi lack chloroplastChloroplastChloroplasts are organelles found in plant cells and other eukaryotic organisms that conduct photosynthesis. Chloroplasts capture light energy to conserve free energy in the form of ATP and reduce NADP to NADPH through a complex set of processes called photosynthesis.Chloroplasts are green...
s and are heterotrophHeterotrophA heterotroph is an organism that cannot fix carbon and uses organic carbon for growth. This contrasts with autotrophs, such as plants and algae, which can use energy from sunlight or inorganic compounds to produce organic compounds such as carbohydrates, fats, and proteins from inorganic carbon...
ic organisms, requiring preformed organic compoundOrganic compoundAn organic compound is any member of a large class of gaseous, liquid, or solid chemical compounds whose molecules contain carbon. For historical reasons discussed below, a few types of carbon-containing compounds such as carbides, carbonates, simple oxides of carbon, and cyanides, as well as the...
s as energy sources. - With plants: Fungi possess a cell wall and vacuoleVacuoleA vacuole is a membrane-bound organelle which is present in all plant and fungal cells and some protist, animal and bacterial cells. Vacuoles are essentially enclosed compartments which are filled with water containing inorganic and organic molecules including enzymes in solution, though in certain...
s. They reproduce by both sexual and asexual means, and like basal plant groups (such as fernFernA fern is any one of a group of about 12,000 species of plants belonging to the botanical group known as Pteridophyta. Unlike mosses, they have xylem and phloem . They have stems, leaves, and roots like other vascular plants...
s and mossMossMosses are small, soft plants that are typically 1–10 cm tall, though some species are much larger. They commonly grow close together in clumps or mats in damp or shady locations. They do not have flowers or seeds, and their simple leaves cover the thin wiry stems...
es) produce sporeSporeIn biology, a spore is a reproductive structure that is adapted for dispersal and surviving for extended periods of time in unfavorable conditions. Spores form part of the life cycles of many bacteria, plants, algae, fungi and some protozoa. According to scientist Dr...
s. Similar to mosses and algae, fungi typically have haploid nuclei.Deacon, p. 58. - With euglenoids and bacteria: Higher fungi, euglenoids, and some bacteria produce the amino acidAmino acidAmino acids are molecules containing an amine group, a carboxylic acid group and a side-chain that varies between different amino acids. The key elements of an amino acid are carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen...
L-lysine in specific biosynthesisBiosynthesisBiosynthesis is an enzyme-catalyzed process in cells of living organisms by which substrates are converted to more complex products. The biosynthesis process often consists of several enzymatic steps in which the product of one step is used as substrate in the following step...
steps, called the α-aminoadipate pathway. - The cells of most fungi grow as tubular, elongated, and thread-like (filamentous) structures and are called hyphae, which may contain multiple nuclei and extend at their tips. Each tip contains a set of aggregated vesiclesVesicle (biology)A vesicle is a bubble of liquid within another liquid, a supramolecular assembly made up of many different molecules. More technically, a vesicle is a small membrane-enclosed sack that can store or transport substances. Vesicles can form naturally because of the properties of lipid membranes , or...
—cellular structures consisting of proteinProteinProteins are biochemical compounds consisting of one or more polypeptides typically folded into a globular or fibrous form, facilitating a biological function. A polypeptide is a single linear polymer chain of amino acids bonded together by peptide bonds between the carboxyl and amino groups of...
s, lipidLipidLipids constitute a broad group of naturally occurring molecules that include fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins , monoglycerides, diglycerides, triglycerides, phospholipids, and others...
s, and other organic molecules—called SpitzenkörperSpitzenkörperThe Spitzenkörper is a structure found in fungal hyphae which is the organizing center for hyphal growth and morphogenesis. It consists of many small vesicles and is present in growing hyphal tips, during spore germination and where branch formation occurs. Its position in the hyphal tip correlates...
. Both fungi and oomycetes grow as filamentous hyphal cells. In contrast, similar-looking organisms, such as filamentous green algaeGreen algaeThe green algae are the large group of algae from which the embryophytes emerged. As such, they form a paraphyletic group, although the group including both green algae and embryophytes is monophyletic...
, grow by repeated cell division within a chain of cells. - In common with some plant and animal species, more than 60 fungal species display the phenomenon of bioluminescenceBioluminescenceBioluminescence is the production and emission of light by a living organism. Its name is a hybrid word, originating from the Greek bios for "living" and the Latin lumen "light". Bioluminescence is a naturally occurring form of chemiluminescence where energy is released by a chemical reaction in...
.
Unique features:
- Some species grow as single-celled yeasts that reproduce by buddingBuddingBudding is a form of asexual reproduction in which a new organism grows on another one. The new organism remains attached as it grows, separating from the parent organism only when it is mature. Since the reproduction is asexual, the newly created organism is a clone and is genetically identical...
or binary fission. Dimorphic fungiDimorphic fungiDimorphic fungi are fungi which can exist as mold/hyphal/filamentous form or as yeast. An example is Penicillium marneffei:* At room temperature, it grows as a mold.* At body temperature, it grows as a yeast....
can switch between a yeast phase and a hyphal phase in response to environmental conditions.Alexopoulos et al., p. 30. - The fungal cell wall is composed of glucanGlucanA glucan molecule is a polysaccharide of D-glucose monomers linked by glycosidic bonds.Many beta-glucans are medically important.-Types:The following are glucans:-Alpha:...
s and chitinChitinChitin n is a long-chain polymer of a N-acetylglucosamine, a derivative of glucose, and is found in many places throughout the natural world...
; while the former compounds are also found in plants and the latter in the exoskeletonExoskeletonAn exoskeleton is the external skeleton that supports and protects an animal's body, in contrast to the internal skeleton of, for example, a human. In popular usage, some of the larger kinds of exoskeletons are known as "shells". Examples of exoskeleton animals include insects such as grasshoppers...
of arthropods, fungi are the only organisms that combine these two structural molecules in their cell wall. In contrast to plants and the oomycetes, fungal cell walls do not contain cellulose.

Xylem
Xylem is one of the two types of transport tissue in vascular plants. . The word xylem is derived from the Classical Greek word ξυλον , meaning "wood"; the best-known xylem tissue is wood, though it is found throughout the plant...
and phloem
Phloem
In vascular plants, phloem is the living tissue that carries organic nutrients , in particular, glucose, a sugar, to all parts of the plant where needed. In trees, the phloem is the innermost layer of the bark, hence the name, derived from the Greek word "bark"...
in many plants. To overcome these limitations, some fungi, such as Armillaria, form rhizomorphs
Mycelial cord
Mycelial cords are linear aggregations of parallel-oriented hyphae. The mature cords are composed of wide, empty vessel hyphae surrounded by narrower sheathing hyphae...
, that resemble and perform functions similar to the root
Root
In vascular plants, the root is the organ of a plant that typically lies below the surface of the soil. This is not always the case, however, since a root can also be aerial or aerating . Furthermore, a stem normally occurring below ground is not exceptional either...
s of plants. Another characteristic shared with plants includes a biosynthetic pathway for producing terpene
Terpene
Terpenes are a large and diverse class of organic compounds, produced by a variety of plants, particularly conifers, though also by some insects such as termites or swallowtail butterflies, which emit terpenes from their osmeterium. They are often strong smelling and thus may have had a protective...
s that uses mevalonic acid
Mevalonic acid
Mevalonic acid is a key organic compound in biochemistry. The anion of mevalonic acid, the predominant form in biological media, is known as mevalonate. This compound is of major pharmaceutical importance...
and pyrophosphate
Pyrophosphate
In chemistry, the anion, the salts, and the esters of pyrophosphoric acid are called pyrophosphates. Any salt or ester containing two phosphate groups is called a diphosphate. As a food additive, diphosphates are known as E450.- Chemistry :...
as chemical building blocks
Precursor (chemistry)
In chemistry, a precursor is a compound that participates in the chemical reaction that produces another compound. In biochemistry, the term "precursor" is used more specifically to refer to a chemical compound preceding another in a metabolic pathway....
. However, plants have an additional terpene pathway in their chloroplasts, a structure fungi do not possess. Fungi produce several secondary metabolite
Secondary metabolite
Secondary metabolites are organic compounds that are not directly involved in the normal growth, development, or reproduction of an organism. Unlike primary metabolites, absence of secondary metabolities does not result in immediate death, but rather in long-term impairment of the organism's...
s that are similar or identical in structure to those made by plants. Many of the plant and fungal enzymes that make these compounds differ from each other in sequence
Peptide sequence
Peptide sequence or amino acid sequence is the order in which amino acid residues, connected by peptide bonds, lie in the chain in peptides and proteins. The sequence is generally reported from the N-terminal end containing free amino group to the C-terminal end containing free carboxyl group...
and other characteristics, which indicates separate origins and evolution of these enzymes in the fungi and plants.
Diversity
Fungi have a worldwide distribution, and grow in a wide range of habitats, including extreme environments such as desertsDesert fungi
A variety of terricolous fungi inhabit the biological soil crust of arid regions. Those exposed to the sun typically contain melanin and are resistant to high temperatures, dryness and low nutrition. Species that are common elsewhere do not thrive in these conditions. Producing large dark...
or areas with high salt concentrations or ionizing radiation
Ionizing radiation
Ionizing radiation is radiation composed of particles that individually have sufficient energy to remove an electron from an atom or molecule. This ionization produces free radicals, which are atoms or molecules containing unpaired electrons...
, as well as in deep sea
Deep sea
The deep sea, or deep layer, is the lowest layer in the ocean, existing below the thermocline and above the seabed, at a depth of 1000 fathoms or more. Little or no light penetrates this part of the ocean and most of the organisms that live there rely for subsistence on falling organic matter...
sediments. Some can survive the intense UV and cosmic radiation encountered during space travel. Most grow in terrestrial environments, though several species live partly or solely in aquatic habitats, such as the chytrid fungus Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis
Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis
Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis is a chytrid fungus that causes the disease chytridiomycosis. In the decade after it was first discovered in amphibians in 1998, the disease devastated amphibian populations around the world, in a global decline towards multiple extinctions, part of the Holocene...
, a parasite that has been responsible for a worldwide decline in amphibian
Amphibian
Amphibians , are a class of vertebrate animals including animals such as toads, frogs, caecilians, and salamanders. They are characterized as non-amniote ectothermic tetrapods...
populations. This organism spends part of its life cycle as a motile zoospore
Zoospore
A zoospore is a motile asexual spore that uses a flagellum for locomotion. Also called a swarm spore, these spores are created by some algae, bacteria and fungi to propagate themselves.-Flagella:...
, enabling it to propel itself through water and enter its amphibian host. Other examples of aquatic fungi include those living in hydrothermal areas of the ocean.
Around 100,000 species of fungi have been formally described by taxonomists
Taxonomy
Taxonomy is the science of identifying and naming species, and arranging them into a classification. The field of taxonomy, sometimes referred to as "biological taxonomy", revolves around the description and use of taxonomic units, known as taxa...
, but the global biodiversity of the fungus kingdom is not fully understood. On the basis of observations of the ratio of the number of fungal species to the number of plant species in selected environments, the fungal kingdom has been estimated to contain about 1.5 million species; a recent (2011) estimate suggests there may be over 5 million species. In mycology, species
Species
In biology, a species is one of the basic units of biological classification and a taxonomic rank. A species is often defined as a group of organisms capable of interbreeding and producing fertile offspring. While in many cases this definition is adequate, more precise or differing measures are...
have historically been distinguished by a variety of methods and concepts. Classification based on morphological
Morphology (biology)
In biology, morphology is a branch of bioscience dealing with the study of the form and structure of organisms and their specific structural features....
characteristics, such as the size and shape of spores or fruiting structures, has traditionally dominated fungal taxonomy.Kirk et al., p. 489. Species may also be distinguished by their biochemical
Biochemistry
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes in living organisms, including, but not limited to, living matter. Biochemistry governs all living organisms and living processes...
and physiological
Physiology
Physiology is the science of the function of living systems. This includes how organisms, organ systems, organs, cells, and bio-molecules carry out the chemical or physical functions that exist in a living system. The highest honor awarded in physiology is the Nobel Prize in Physiology or...
characteristics, such as their ability to metabolize certain biochemicals, or their reaction to chemical tests
Chemical tests in mushroom identification
Chemical tests in mushroom identification are methods that aid in determining the variety of some fungi. The most useful tests are Melzer's reagent and potassium hydroxide.- Ammonia :Household ammonia can be used. A couple of drops are placed on the flesh...
. The biological species concept discriminates species based on their ability to mate
Mating in fungi
Mating in fungi is a complex process governed by mating types. Research on fungal mating has focused on only a few model species. Since not all of the fungi reproduce sexually and many that do are isogamous, the terms male and female do not apply to this kingdom...
. The application of molecular
Molecular biology
Molecular biology is the branch of biology that deals with the molecular basis of biological activity. This field overlaps with other areas of biology and chemistry, particularly genetics and biochemistry...
tools, such as DNA sequencing
DNA sequencing
DNA sequencing includes several methods and technologies that are used for determining the order of the nucleotide bases—adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine—in a molecule of DNA....
and phylogenetic analysis, to study diversity has greatly enhanced the resolution and added robustness to estimates of genetic diversity
Genetic diversity
Genetic diversity, the level of biodiversity, refers to the total number of genetic characteristics in the genetic makeup of a species. It is distinguished from genetic variability, which describes the tendency of genetic characteristics to vary....
within various taxonomic groups.
Microscopic structures
Most fungi grow as hyphaHypha
A hypha is a long, branching filamentous structure of a fungus, and also of unrelated Actinobacteria. In most fungi, hyphae are the main mode of vegetative growth, and are collectively called a mycelium; yeasts are unicellular fungi that do not grow as hyphae.-Structure:A hypha consists of one or...
e, which are cylindrical, thread-like structures 2–10 µm in diameter and up to several centimeters in length. Hyphae grow at their tips (apices); new hyphae are typically formed by emergence of new tips along existing hyphae by a process called branching, or occasionally growing hyphal tips bifurcate (fork) giving rise to two parallel-growing hyphae. The combination of apical growth and branching/forking leads to the development of a mycelium
Mycelium
thumb|right|Fungal myceliaMycelium is the vegetative part of a fungus, consisting of a mass of branching, thread-like hyphae. The mass of hyphae is sometimes called shiro, especially within the fairy ring fungi. Fungal colonies composed of mycelia are found in soil and on or within many other...
, an interconnected network of hyphae. Hyphae can be either septate or coenocytic: septate hyphae are divided into compartments separated by cross walls (internal cell walls, called septa, that are formed at right angle
Right angle
In geometry and trigonometry, a right angle is an angle that bisects the angle formed by two halves of a straight line. More precisely, if a ray is placed so that its endpoint is on a line and the adjacent angles are equal, then they are right angles...
s to the cell wall giving the hypha its shape), with each compartment containing one or more nuclei; coenocytic hyphae are not compartmentalized. Septa have pores that allow cytoplasm
Cytoplasm
The cytoplasm is a small gel-like substance residing between the cell membrane holding all the cell's internal sub-structures , except for the nucleus. All the contents of the cells of prokaryote organisms are contained within the cytoplasm...
, organelle
Organelle
In cell biology, an organelle is a specialized subunit within a cell that has a specific function, and is usually separately enclosed within its own lipid bilayer....
s, and sometimes nuclei to pass through; an example is the dolipore septum in the fungi of the phylum Basidiomycota. Coenocytic hyphae are essentially multinucleate
Multinucleate
Multinucleate cells have more than one nucleus per cell, which is the result of nuclear division not being followed by cytokinesis. As a consequence, multiple nuclei share one common cytoplasm. This can be the consequence of a disturbed cell cycle control Multinucleate (also multinucleated,...
supercells.
Many species have developed specialized hyphal structures for nutrient uptake from living hosts; examples include haustoria in plant-parasitic species of most fungal phyla, and arbuscules
Arbuscular mycorrhiza
An arbuscular mycorrhiza is a type of mycorrhiza in which the fungus penetrates the cortical cells of the roots of a vascular plant....
of several mycorrhiza
Mycorrhiza
A mycorrhiza is a symbiotic association between a fungus and the roots of a vascular plant....
l fungi, which penetrate into the host cells to consume nutrients.
Although fungi are opisthokont
Opisthokont
The opisthokonts or "Fungi/Metazoa group" are a broad group of eukaryotes, including both the animal and fungus kingdoms, together with the eukaryotic microorganisms that are sometimes grouped in the paraphyletic phylum Choanozoa...
s—a grouping of evolutionarily related organisms broadly characterized by a single posterior flagellum
Flagellum
A flagellum is a tail-like projection that protrudes from the cell body of certain prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, and plays the dual role of locomotion and sense organ, being sensitive to chemicals and temperatures outside the cell. There are some notable differences between prokaryotic and...
—all phyla except for the chytrids have lost their posterior flagella. Fungi are unusual among the eukaryotes in having a cell wall that, in addition to glucan
Glucan
A glucan molecule is a polysaccharide of D-glucose monomers linked by glycosidic bonds.Many beta-glucans are medically important.-Types:The following are glucans:-Alpha:...
s (e.g., β-1,3-glucan) and other typical components, also contains the biopolymer
Biopolymer
Biopolymers are polymers produced by living organisms. Since they are polymers, Biopolymers contain monomeric units that are covalently bonded to form larger structures. There are three main classes of biopolymers based on the differing monomeric units used and the structure of the biopolymer formed...
chitin.
Macroscopic structures
Fungal mycelia can become visible to the naked eye, for example, on various surfaces and substrates, such as damp walls and on spoiled food, where they are commonly called moldMold
Molds are fungi that grow in the form of multicellular filaments called hyphae. Molds are not considered to be microbes but microscopic fungi that grow as single cells called yeasts...
s. Mycelia grown on solid agar
Agar
Agar or agar-agar is a gelatinous substance derived from a polysaccharide that accumulates in the cell walls of agarophyte red algae. Throughout history into modern times, agar has been chiefly used as an ingredient in desserts throughout Asia and also as a solid substrate to contain culture medium...
media in laboratory petri dish
Petri dish
A Petri dish is a shallow glass or plastic cylindrical lidded dish that biologists use to culture cells or small moss plants. It was named after German bacteriologist Julius Richard Petri, who invented it when working as an assistant to Robert Koch...
es are usually referred to as colonies
Colony (biology)
In biology, a colony reference to several individual organisms of the same species living closely together, usually for mutual benefit, such as stronger defense or the ability to attack bigger prey. Some insects live only in colonies...
. These colonies can exhibit growth shapes and colors (due to spores or pigment
Pigment
A pigment is a material that changes the color of reflected or transmitted light as the result of wavelength-selective absorption. This physical process differs from fluorescence, phosphorescence, and other forms of luminescence, in which a material emits light.Many materials selectively absorb...
ation) that can be used as diagnostic features in the identification of species or groups. Some individual fungal colonies can reach extraordinary dimensions and ages as in the case of a clonal
Clone (cell biology)
A clone is a group of identical cells that share a common ancestry, meaning they are derived from the same mother cell.Clonality implies the state of a cell or a substance being derived from one source or the other...
colony of Armillaria solidipes, which extends over an area of more than 900 ha
Hectare
The hectare is a metric unit of area defined as 10,000 square metres , and primarily used in the measurement of land. In 1795, when the metric system was introduced, the are was defined as being 100 square metres and the hectare was thus 100 ares or 1/100 km2...
(3.5 square miles), with an estimated age of nearly 9,000 years.
The apothecium—a specialized structure important in sexual reproduction
Sexual reproduction
Sexual reproduction is the creation of a new organism by combining the genetic material of two organisms. There are two main processes during sexual reproduction; they are: meiosis, involving the halving of the number of chromosomes; and fertilization, involving the fusion of two gametes and the...
in the ascomycetes—is a cup-shaped fruiting body that holds the hymenium
Hymenium
The hymenium is the tissue layer on the hymenophore of a fungal fruiting body where the cells develop into basidia or asci, which produce spores. In some species all of the cells of the hymenium develop into basidia or asci, while in others some cells develop into sterile cells called cystidia or...
, a layer of tissue containing the spore-bearing cells. The fruiting bodies of the basidiomycetes (basidiocarp
Basidiocarp
In fungi, a basidiocarp, basidiome or basidioma , is the sporocarp of a basidiomycete, the multicellular structure on which the spore-producing hymenium is borne. Basidiocarps are characteristic of the hymenomycetes; rusts and smuts do not produce such structures...
s) and some ascomycetes can sometimes grow very large, and many are well-known as mushroom
Mushroom
A mushroom is the fleshy, spore-bearing fruiting body of a fungus, typically produced above ground on soil or on its food source. The standard for the name "mushroom" is the cultivated white button mushroom, Agaricus bisporus; hence the word "mushroom" is most often applied to those fungi that...
s.
Growth and physiology

Surface area to volume ratio
The surface-area-to-volume ratio also called the surface-to-volume ratio and variously denoted sa/vol or SA:V, is the amount of surface area per unit volume of an object or collection of objects. The surface-area-to-volume ratio is measured in units of inverse distance. A cube with sides of...
s. Hyphae are specifically adapted for growth on solid surfaces, and to invade substrates
Substrate (biology)
In biology a substrate is the surface a plant or animal lives upon and grows on. A substrate can include biotic or abiotic materials and animals. For example, encrusting algae that lives on a rock can be substrate for another animal that lives on top of the algae. See also substrate .-External...
and tissues. They can exert large penetrative mechanical forces; for example, the plant pathogen Magnaporthe grisea
Magnaporthe grisea
Magnaporthe grisea, also known as rice blast fungus, rice rotten neck, rice seedling blight, blast of rice, oval leaf spot of graminea, pitting disease, ryegrass blast, and Johnson spot, is a plant-pathogenic fungus that causes an important disease affecting rice. It is now known that M...
forms a structure called an appressorium
Appressorium
An appressorium is a flattened, hyphal "pressing" organ, from which a minute infection peg grows and enters the host, using turgor pressure capable of punching through even Mylar....
that evolved to puncture plant tissues. The pressure generated by the appressorium, directed against the plant epidermis
Epidermis (botany)
The epidermis is a single-layered group of cells that covers plants' leaves, flowers, roots and stems. It forms a boundary between the plant and the external environment. The epidermis serves several functions, it protects against water loss, regulates gas exchange, secretes metabolic compounds,...
, can exceed 8 megapascals (1,160.3 psi). The filamentous fungus Paecilomyces lilacinus uses a similar structure to penetrate the eggs of nematode
Nematode
The nematodes or roundworms are the most diverse phylum of pseudocoelomates, and one of the most diverse of all animals. Nematode species are very difficult to distinguish; over 28,000 have been described, of which over 16,000 are parasitic. It has been estimated that the total number of nematode...
s.
The mechanical pressure exerted by the appressorium is generated from physiological processes that increase intracellular turgor by producing osmolyte
Osmolyte
Osmolytes are compounds affecting osmosis. They are soluble in the solution within a cell, or in the surrounding fluid, e.g. as plasma osmolytes. They play a role in maintaining cell volume and fluid balance. For example, when a cell swells due to external osmotic pressure, membrane channels open...
s such as glycerol
Glycerol
Glycerol is a simple polyol compound. It is a colorless, odorless, viscous liquid that is widely used in pharmaceutical formulations. Glycerol has three hydroxyl groups that are responsible for its solubility in water and its hygroscopic nature. The glycerol backbone is central to all lipids...
. Morphological adaptations such as these are complemented by hydrolytic enzymes
Cellulase
400px|thumb|right|alt = Colored dice with checkered background|Ribbon representation of the Streptomyces lividans beta-1,4-endoglucanase catalytic domain - an example from the family 12 glycoside hydrolases...
secreted into the environment to digest large organic molecules—such as polysaccharide
Polysaccharide
Polysaccharides are long carbohydrate molecules, of repeated monomer units joined together by glycosidic bonds. They range in structure from linear to highly branched. Polysaccharides are often quite heterogeneous, containing slight modifications of the repeating unit. Depending on the structure,...
s, protein
Protein
Proteins are biochemical compounds consisting of one or more polypeptides typically folded into a globular or fibrous form, facilitating a biological function. A polypeptide is a single linear polymer chain of amino acids bonded together by peptide bonds between the carboxyl and amino groups of...
s, lipid
Lipid
Lipids constitute a broad group of naturally occurring molecules that include fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins , monoglycerides, diglycerides, triglycerides, phospholipids, and others...
s, and other organic substrates—into smaller molecules that may then be absorbed as nutrients. The vast majority of filamentous fungi grow in a polar fashion—i.e., by extension into one direction—by elongation at the tip (apex) of the hypha. Alternative forms of fungal growth include intercalary extension (i.e., by longitudinal expansion of hyphal compartments that are below the apex) as in the case of some endophytic
Endophyte
An endophyte is an endosymbiont, often a bacterium or fungus, that lives within a plant for at least part of its life without causing apparent disease. Endophytes are ubiquitous and have been found in all the species of plants studied to date; however, most of these endophyte/plant relationships...
fungi, or growth by volume expansion during the development of mushroom stipes and other large organs. Growth of fungi as multicellular structures consisting of somatic
Somatic
The term somatic means 'of the body',, relating to the body. In medicine, somatic illness is bodily, not mental, illness. The term is often used in biology to refer to the cells of the body in contrast to the germ line cells which usually give rise to the gametes...
and reproductive cells—a feature independently evolved in animals and plants—has several functions, including the development of fruiting bodies for dissemination of sexual spores (see above) and biofilm
Biofilm
A biofilm is an aggregate of microorganisms in which cells adhere to each other on a surface. These adherent cells are frequently embedded within a self-produced matrix of extracellular polymeric substance...
s for substrate colonization and intercellular communication.
Traditionally, the fungi are considered heterotroph
Heterotroph
A heterotroph is an organism that cannot fix carbon and uses organic carbon for growth. This contrasts with autotrophs, such as plants and algae, which can use energy from sunlight or inorganic compounds to produce organic compounds such as carbohydrates, fats, and proteins from inorganic carbon...
s, organisms that rely solely on carbon fixed
Carbon fixation
In biology, carbon fixation is the reduction of carbon dioxide to organic compounds by living organisms. The obvious example is photosynthesis. Carbon fixation requires both a source of energy such as sunlight, and an electron donor such as water. All life depends on fixed carbon. Organisms that...
by other organisms for metabolism
Metabolism
Metabolism is the set of chemical reactions that happen in the cells of living organisms to sustain life. These processes allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to their environments. Metabolism is usually divided into two categories...
. Fungi have evolved
Evolution
Evolution is any change across successive generations in the heritable characteristics of biological populations. Evolutionary processes give rise to diversity at every level of biological organisation, including species, individual organisms and molecules such as DNA and proteins.Life on Earth...
a high degree of metabolic versatility that allows them to use a diverse range of organic substrates for growth, including simple compounds such as nitrate
Nitrate
The nitrate ion is a polyatomic ion with the molecular formula NO and a molecular mass of 62.0049 g/mol. It is the conjugate base of nitric acid, consisting of one central nitrogen atom surrounded by three identically-bonded oxygen atoms in a trigonal planar arrangement. The nitrate ion carries a...
, ammonia
Ammonia
Ammonia is a compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the formula . It is a colourless gas with a characteristic pungent odour. Ammonia contributes significantly to the nutritional needs of terrestrial organisms by serving as a precursor to food and fertilizers. Ammonia, either directly or...
, acetate
Acetate
An acetate is a derivative of acetic acid. This term includes salts and esters, as well as the anion found in solution. Most of the approximately 5 billion kilograms of acetic acid produced annually in industry are used in the production of acetates, which usually take the form of polymers. In...
, or ethanol
Ethanol
Ethanol, also called ethyl alcohol, pure alcohol, grain alcohol, or drinking alcohol, is a volatile, flammable, colorless liquid. It is a psychoactive drug and one of the oldest recreational drugs. Best known as the type of alcohol found in alcoholic beverages, it is also used in thermometers, as a...
. For some species it has been shown that the pigment melanin
Melanin
Melanin is a pigment that is ubiquitous in nature, being found in most organisms . In animals melanin pigments are derivatives of the amino acid tyrosine. The most common form of biological melanin is eumelanin, a brown-black polymer of dihydroxyindole carboxylic acids, and their reduced forms...
may play a role in extracting energy from ionizing radiation
Ionizing radiation
Ionizing radiation is radiation composed of particles that individually have sufficient energy to remove an electron from an atom or molecule. This ionization produces free radicals, which are atoms or molecules containing unpaired electrons...
, such as gamma radiation; however, this form of "radiotrophic"
Radiotrophic fungus
Radiotrophic fungi are fungi which appear to use the pigment melanin to convert gamma radiation into chemical energy for growth. This proposed mechanism may be similar to anabolic pathways for the synthesis of reduced organic carbon in phototrophic organisms, which capture photons from visible...
growth has only been described for a few species, the effects on growth rates are small, and the underlying biophysical
Biophysics
Biophysics is an interdisciplinary science that uses the methods of physical science to study biological systems. Studies included under the branches of biophysics span all levels of biological organization, from the molecular scale to whole organisms and ecosystems...
and biochemical processes are not known. The authors speculate that this process might bear similarity to CO2 fixation
Carbon fixation
In biology, carbon fixation is the reduction of carbon dioxide to organic compounds by living organisms. The obvious example is photosynthesis. Carbon fixation requires both a source of energy such as sunlight, and an electron donor such as water. All life depends on fixed carbon. Organisms that...
via visible light
Visible spectrum
The visible spectrum is the portion of the electromagnetic spectrum that is visible to the human eye. Electromagnetic radiation in this range of wavelengths is called visible light or simply light. A typical human eye will respond to wavelengths from about 390 to 750 nm. In terms of...
, but instead utilizing ionizing radiation as a source of energy.
Reproduction

Biological life cycle
A life cycle is a period involving all different generations of a species succeeding each other through means of reproduction, whether through asexual reproduction or sexual reproduction...
of a species, the teleomorph and the anamorph. Environmental conditions trigger genetically determined developmental states that lead to the creation of specialized structures for sexual or asexual reproduction. These structures aid reproduction by efficiently dispersing spores or spore-containing propagule
Propagule
In horticulture, a propagule is any plant material used for the purpose of plant propagation. In asexual reproduction, a propagule may be a woody, semi-hardwood, or softwood cutting, leaf section, or any number of other plant parts. In sexual reproduction, a propagule is a seed or spore...
s.
Asexual reproduction
Asexual reproductionAsexual reproduction
Asexual reproduction is a mode of reproduction by which offspring arise from a single parent, and inherit the genes of that parent only, it is reproduction which does not involve meiosis, ploidy reduction, or fertilization. A more stringent definition is agamogenesis which is reproduction without...
via vegetative spores (conidia
Conidium
Conidia, sometimes termed conidiospores, are asexual, non-motile spores of a fungus and are named after the greek word for dust, konia. They are also called mitospores due to the way they are generated through the cellular process of mitosis...
) or through mycelial fragmentation is common; it maintains clonal populations adapted to a specific niche
Ecological niche
In ecology, a niche is a term describing the relational position of a species or population in its ecosystem to each other; e.g. a dolphin could potentially be in another ecological niche from one that travels in a different pod if the members of these pods utilize significantly different food...
, and allows more rapid dispersal than sexual reproduction. The "Fungi imperfecti" (fungi lacking the perfect or sexual stage) or Deuteromycota comprise all the species which lack an observable sexual cycle.
Sexual reproduction
Sexual reproduction with meiosisMeiosis
Meiosis is a special type of cell division necessary for sexual reproduction. The cells produced by meiosis are gametes or spores. The animals' gametes are called sperm and egg cells....
exists in all fungal phyla (with the exception of the Glomeromycota
Glomeromycota
Glomeromycota is one of seven currently recognized phyla within the kingdom Fungi, with approximately 230 described species. Members of the Glomeromycota form arbuscular mycorrhizas with the roots or thalli of land plants. Geosiphon pyriformis forms an endocytobiotic association with Nostoc...
).
A fungus is a member of a large group of eukaryotic
Eukaryote
A eukaryote is an organism whose cells contain complex structures enclosed within membranes. Eukaryotes may more formally be referred to as the taxon Eukarya or Eukaryota. The defining membrane-bound structure that sets eukaryotic cells apart from prokaryotic cells is the nucleus, or nuclear...
organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeast
Yeast
Yeasts are eukaryotic micro-organisms classified in the kingdom Fungi, with 1,500 species currently described estimated to be only 1% of all fungal species. Most reproduce asexually by mitosis, and many do so by an asymmetric division process called budding...
s and mold
Mold
Molds are fungi that grow in the form of multicellular filaments called hyphae. Molds are not considered to be microbes but microscopic fungi that grow as single cells called yeasts...
s (British English: moulds), as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom
Kingdom (biology)
In biology, kingdom is a taxonomic rank, which is either the highest rank or in the more recent three-domain system, the rank below domain. Kingdoms are divided into smaller groups called phyla or divisions in botany...
, Fungi, which is separate from plant
Plant
Plants are living organisms belonging to the kingdom Plantae. Precise definitions of the kingdom vary, but as the term is used here, plants include familiar organisms such as trees, flowers, herbs, bushes, grasses, vines, ferns, mosses, and green algae. The group is also called green plants or...
s, animal
Animal
Animals are a major group of multicellular, eukaryotic organisms of the kingdom Animalia or Metazoa. Their body plan eventually becomes fixed as they develop, although some undergo a process of metamorphosis later on in their life. Most animals are motile, meaning they can move spontaneously and...
s, and bacteria
Bacteria
Bacteria are a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria have a wide range of shapes, ranging from spheres to rods and spirals...
. One major difference is that fungal cells have cell wall
Cell wall
The cell wall is the tough, usually flexible but sometimes fairly rigid layer that surrounds some types of cells. It is located outside the cell membrane and provides these cells with structural support and protection, and also acts as a filtering mechanism. A major function of the cell wall is to...
s that contain chitin
Chitin
Chitin n is a long-chain polymer of a N-acetylglucosamine, a derivative of glucose, and is found in many places throughout the natural world...
, unlike the cell walls of plants, which contain cellulose
Cellulose
Cellulose is an organic compound with the formula , a polysaccharide consisting of a linear chain of several hundred to over ten thousand β linked D-glucose units....
. These and other differences show that the fungi form a single group of related organisms, named the Eumycota (true fungi or Eumycetes), that share a common ancestor (a monophyletic group). This fungal group is distinct from the structurally similar myxomycetes (slime molds) and oomycetes (water molds). The discipline of biology
Biology
Biology is a natural science concerned with the study of life and living organisms, including their structure, function, growth, origin, evolution, distribution, and taxonomy. Biology is a vast subject containing many subdivisions, topics, and disciplines...
devoted to the study of fungi is known as mycology
Mycology
Mycology is the branch of biology concerned with the study of fungi, including their genetic and biochemical properties, their taxonomy and their use to humans as a source for tinder, medicinals , food and entheogens, as well as their dangers, such as poisoning or...
, which is often regarded as a branch of botany
Botany
Botany, plant science, or plant biology is a branch of biology that involves the scientific study of plant life. Traditionally, botany also included the study of fungi, algae and viruses...
, even though genetic studies have shown that fungi are more closely related to animals than to plants.
Abundant worldwide, most fungi are inconspicuous because of the small size of their structures, and their cryptic
Crypsis
In ecology, crypsis is the ability of an organism to avoid observation or detection by other organisms. It may be either a predation strategy or an antipredator adaptation, and methods include camouflage, nocturnality, subterranean lifestyle, transparency, and mimicry...
lifestyles in soil, on dead matter, and as symbionts
Symbiosis
Symbiosis is close and often long-term interaction between different biological species. In 1877 Bennett used the word symbiosis to describe the mutualistic relationship in lichens...
of plants, animals, or other fungi. They may become noticeable when fruiting
Sporocarp (fungi)
In fungi, the sporocarp is a multicellular structure on which spore-producing structures, such as basidia or asci, are borne...
, either as mushrooms or molds. Fungi perform an essential role in the decomposition of organic matter and have fundamental roles in nutrient cycling
Biogeochemical cycle
In ecology and Earth science, a biogeochemical cycle or substance turnover or cycling of substances is a pathway by which a chemical element or molecule moves through both biotic and abiotic compartments of Earth. A cycle is a series of change which comes back to the starting point and which can...
and exchange. They have long been used as a direct source of food, such as mushrooms and truffles, as a leavening agent for bread, and in fermentation
Fermentation (food)
Fermentation in food processing typically is the conversion of carbohydrates to alcohols and carbon dioxide or organic acids using yeasts, bacteria, or a combination thereof, under anaerobic conditions. Fermentation in simple terms is the chemical conversion of sugars into ethanol...
of various food products, such as wine
Wine
Wine is an alcoholic beverage, made of fermented fruit juice, usually from grapes. The natural chemical balance of grapes lets them ferment without the addition of sugars, acids, enzymes, or other nutrients. Grape wine is produced by fermenting crushed grapes using various types of yeast. Yeast...
, beer
Beer
Beer is the world's most widely consumed andprobably oldest alcoholic beverage; it is the third most popular drink overall, after water and tea. It is produced by the brewing and fermentation of sugars, mainly derived from malted cereal grains, most commonly malted barley and malted wheat...
, and soy sauce
Soy sauce
Soy sauce is a condiment produced by fermenting soybeans with Aspergillus oryzae or Aspergillus sojae molds, along with water and salt...
. Since the 1940s, fungi have been used for the production of antibiotic
Antibiotic
An antibacterial is a compound or substance that kills or slows down the growth of bacteria.The term is often used synonymously with the term antibiotic; today, however, with increased knowledge of the causative agents of various infectious diseases, antibiotic has come to denote a broader range of...
s, and, more recently, various enzyme
Enzyme
Enzymes are proteins that catalyze chemical reactions. In enzymatic reactions, the molecules at the beginning of the process, called substrates, are converted into different molecules, called products. Almost all chemical reactions in a biological cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates...
s produced by fungi are used industrially and in detergents. Fungi are also used as biological pesticides to control weeds, plant diseases and insect pests. Many species produce bioactive compounds called mycotoxin
Mycotoxin
A mycotoxin is a toxic secondary metabolite produced by organisms of the fungus kingdom, commonly known as molds. The term ‘mycotoxin’ is usually reserved for the toxic chemical products produced by fungi that readily colonize crops...
s, such as alkaloid
Alkaloid
Alkaloids are a group of naturally occurring chemical compounds that contain mostly basic nitrogen atoms. This group also includes some related compounds with neutral and even weakly acidic properties. Also some synthetic compounds of similar structure are attributed to alkaloids...
s and polyketide
Polyketide
Polyketides are secondary metabolites from bacteria, fungi, plants, and animals. Polyketides are usually biosynthesized through the decarboxylative condensation of malonyl-CoA derived extender units in a similar process to fatty acid synthesis...
s, that are toxic to animals including humans. The fruiting structures of a few species contain psychotropic compounds and are consumed recreationally
Recreational drug use
Recreational drug use is the use of a drug, usually psychoactive, with the intention of creating or enhancing recreational experience. Such use is controversial, however, often being considered to be also drug abuse, and it is often illegal...
or in traditional spiritual ceremonies. Fungi can break down manufactured materials and buildings, and become significant pathogen
Pathogenic fungi
Pathogenic fungi are fungi that cause disease in humans or other organisms. The study of pathogenic fungi is referred to as medical mycology. Although fungi are eukaryotic organisms many pathogenic fungi are also microorganisms.-Candida:...
s of humans and other animals. Losses of crops due to fungal diseases (e.g. rice blast disease) or food spoilage can have a large impact on human food supplies
Food security
Food security refers to the availability of food and one's access to it. A household is considered food-secure when its occupants do not live in hunger or fear of starvation. According to the World Resources Institute, global per capita food production has been increasing substantially for the past...
and local economies.
The fungus kingdom encompasses an enormous diversity of taxa
Taxon
|thumb|270px|[[African elephants]] form a widely-accepted taxon, the [[genus]] LoxodontaA taxon is a group of organisms, which a taxonomist adjudges to be a unit. Usually a taxon is given a name and a rank, although neither is a requirement...
with varied ecologies, life cycle
Biological life cycle
A life cycle is a period involving all different generations of a species succeeding each other through means of reproduction, whether through asexual reproduction or sexual reproduction...
strategies, and morphologies
Morphology (biology)
In biology, morphology is a branch of bioscience dealing with the study of the form and structure of organisms and their specific structural features....
ranging from single-celled aquatic chytrids to large mushrooms. However, little is known of the true biodiversity
Biodiversity
Biodiversity is the degree of variation of life forms within a given ecosystem, biome, or an entire planet. Biodiversity is a measure of the health of ecosystems. Biodiversity is in part a function of climate. In terrestrial habitats, tropical regions are typically rich whereas polar regions...
of Kingdom Fungi, which has been estimated at around 1.5 million species, with about 5% of these having been formally classified. Ever since the pioneering 18th and 19th century taxonomical
Taxonomy
Taxonomy is the science of identifying and naming species, and arranging them into a classification. The field of taxonomy, sometimes referred to as "biological taxonomy", revolves around the description and use of taxonomic units, known as taxa...
works of Carl Linnaeus, Christian Hendrik Persoon
Christian Hendrik Persoon
Christiaan Hendrik Persoon was a mycologist who made additions to Linnaeus' mushroom taxonomy.-Early life:...
, and Elias Magnus Fries
Elias Magnus Fries
-External links:*, Authors of fungal names, Mushroom, the Journal of Wild Mushrooming.*...
, fungi have been classified
Biological classification
Biological classification, or scientific classification in biology, is a method to group and categorize organisms by biological type, such as genus or species. Biological classification is part of scientific taxonomy....
according to their morphology (e.g., characteristics such as spore color or microscopic features) or physiology
Physiology
Physiology is the science of the function of living systems. This includes how organisms, organ systems, organs, cells, and bio-molecules carry out the chemical or physical functions that exist in a living system. The highest honor awarded in physiology is the Nobel Prize in Physiology or...
. Advances in molecular genetics
Molecular genetics
Molecular genetics is the field of biology and genetics that studies the structure and function of genes at a molecular level. The field studies how the genes are transferred from generation to generation. Molecular genetics employs the methods of genetics and molecular biology...
have opened the way for DNA analysis
DNA sequencing
DNA sequencing includes several methods and technologies that are used for determining the order of the nucleotide bases—adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine—in a molecule of DNA....
to be incorporated into taxonomy, which has sometimes challenged the historical groupings based on morphology and other traits. Phylogenetic studies published in the last decade have helped reshape the classification of Kingdom Fungi, which is divided into one subkingdom
Taxonomic rank
In biological classification, rank is the level in a taxonomic hierarchy. Examples of taxonomic ranks are species, genus, family, and class. Each rank subsumes under it a number of less general categories...
, seven phyla
Phylum
In biology, a phylum The term was coined by Georges Cuvier from Greek φῦλον phylon, "race, stock," related to φυλή phyle, "tribe, clan." is a taxonomic rank below kingdom and above class. "Phylum" is equivalent to the botanical term division....
, and ten subphyla.
Etymology
The English word fungus is directly adopted from the LatinLatin
Latin is an Italic language originally spoken in Latium and Ancient Rome. It, along with most European languages, is a descendant of the ancient Proto-Indo-European language. Although it is considered a dead language, a number of scholars and members of the Christian clergy speak it fluently, and...
fungus (mushroom), used in the writings of Horace
Horace
Quintus Horatius Flaccus , known in the English-speaking world as Horace, was the leading Roman lyric poet during the time of Augustus.-Life:...
and Pliny
Pliny the Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus , better known as Pliny the Elder, was a Roman author, naturalist, and natural philosopher, as well as naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and personal friend of the emperor Vespasian...
. This in turn is derived from the Greek
Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek is the stage of the Greek language in the periods spanning the times c. 9th–6th centuries BC, , c. 5th–4th centuries BC , and the c. 3rd century BC – 6th century AD of ancient Greece and the ancient world; being predated in the 2nd millennium BC by Mycenaean Greek...
word sphongos/σφογγος ("sponge"), which refers to the macroscopic
Macroscopic
The macroscopic scale is the length scale on which objects or processes are of a size which is measurable and observable by the naked eye.When applied to phenomena and abstract objects, the macroscopic scale describes existence in the world as we perceive it, often in contrast to experiences or...
structures and morphology of mushrooms and molds; the root is also used in other languages, such as the German Schwamm ("sponge") and Schimmel ("mold"). The use of the word mycology, which is derived from the Greek mykes/μύκης (mushroom) and logos/λόγος (discourse), to denote the scientific study of fungi is thought to have originated in 1836 with English naturalist Miles Joseph Berkeley
Miles Joseph Berkeley
Miles Joseph Berkeley was an English cryptogamist and clergyman, and one of the founders of the science of plant pathology....
's publication The English Flora of Sir James Edward Smith, Vol. 5.Ainsworth, p. 2.
Characteristics
Before the introduction of molecular methods for phylogenetic analysis, taxonomistsTaxonomy
Taxonomy is the science of identifying and naming species, and arranging them into a classification. The field of taxonomy, sometimes referred to as "biological taxonomy", revolves around the description and use of taxonomic units, known as taxa...
considered fungi to be members of the Plant Kingdom
Plant
Plants are living organisms belonging to the kingdom Plantae. Precise definitions of the kingdom vary, but as the term is used here, plants include familiar organisms such as trees, flowers, herbs, bushes, grasses, vines, ferns, mosses, and green algae. The group is also called green plants or...
because of similarities in lifestyle: both fungi and plants are mainly immobile
Sessility (zoology)
In zoology, sessility is a characteristic of animals which are not able to move about. They are usually permanently attached to a solid substrate of some kind, such as a part of a plant or dead tree trunk, a rock, or the hull of a ship in the case of barnacles. Corals lay down their own...
, and have similarities in general morphology and growth habitat. Like plants, fungi often grow in soil, and in the case of mushroom
Mushroom
A mushroom is the fleshy, spore-bearing fruiting body of a fungus, typically produced above ground on soil or on its food source. The standard for the name "mushroom" is the cultivated white button mushroom, Agaricus bisporus; hence the word "mushroom" is most often applied to those fungi that...
s form conspicuous fruiting bodies, which sometimes bear resemblance to plants such as mosses. The fungi are now considered a separate kingdom, distinct from both plants and animals, from which they appear to have diverged around one billion years ago. Some morphological, biochemical, and genetic features are shared with other organisms, while others are unique to the fungi, clearly separating them from the other kingdoms:
Shared features:
- With other eukaryoteEukaryoteA eukaryote is an organism whose cells contain complex structures enclosed within membranes. Eukaryotes may more formally be referred to as the taxon Eukarya or Eukaryota. The defining membrane-bound structure that sets eukaryotic cells apart from prokaryotic cells is the nucleus, or nuclear...
s: As other eukaryotes, fungal cells contain membrane-bound nucleiCell nucleusIn cell biology, the nucleus is a membrane-enclosed organelle found in eukaryotic cells. It contains most of the cell's genetic material, organized as multiple long linear DNA molecules in complex with a large variety of proteins, such as histones, to form chromosomes. The genes within these...
with chromosomes that contain DNA with noncoding regionsNoncoding DNAIn genetics, noncoding DNA describes components of an organism's DNA sequences that do not encode for protein sequences. In many eukaryotes, a large percentage of an organism's total genome size is noncoding DNA, although the amount of noncoding DNA, and the proportion of coding versus noncoding...
called intronIntronAn intron is any nucleotide sequence within a gene that is removed by RNA splicing to generate the final mature RNA product of a gene. The term intron refers to both the DNA sequence within a gene, and the corresponding sequence in RNA transcripts. Sequences that are joined together in the final...
s and coding regions called exons. In addition, fungi possess membrane-bound cytoplasmic organelles such as mitochondria, sterolSterolSterols, also known as steroid alcohols, are a subgroup of the steroids and an important class of organic molecules. They occur naturally in plants, animals, and fungi, with the most familiar type of animal sterol being cholesterol...
-containing membranes, and ribosomes of the 80S80S80S are ribosomes present in eukaryotes. Their small subunit is 40S and the large subunit is 60S. Ribosomes present in eukaryotes differ from those found in prokaryote in many ways: they are larger, contain larger proteins as well as a larger number of proteins, and have four molecules of RNA....
type. They have a characteristic range of soluble carbohydrates and storage compounds, including sugar alcoholSugar alcoholA sugar alcohol is a hydrogenated form of carbohydrate, whose carbonyl group has been reduced to a primary or secondary hydroxyl group . Sugar alcohols have the general formula Hn+1H, whereas sugars have HnHCO...
s (e.g., mannitolMannitolMannitol is a white, crystalline organic compound with the formula . This polyol is used as an osmotic diuretic agent and a weak renal vasodilator...
), disaccharideDisaccharideA disaccharide or biose is the carbohydrate formed when two monosaccharides undergo a condensation reaction which involves the elimination of a small molecule, such as water, from the functional groups only. Like monosaccharides, disaccharides form an aqueous solution when dissolved in water...
s, (e.g., trehaloseTrehaloseTrehalose, also known as mycose or tremalose, is a natural alpha-linked disaccharide formed by an α,α-1,1-glucoside bond between two α-glucose units. In 1832, H.A.L. Wiggers discovered trehalose in an ergot of rye, and in 1859 Marcellin Berthelot isolated it from trehala manna, a substance made...
), and polysaccharidePolysaccharidePolysaccharides are long carbohydrate molecules, of repeated monomer units joined together by glycosidic bonds. They range in structure from linear to highly branched. Polysaccharides are often quite heterogeneous, containing slight modifications of the repeating unit. Depending on the structure,...
s (e.g., glycogenGlycogenGlycogen is a molecule that serves as the secondary long-term energy storage in animal and fungal cells, with the primary energy stores being held in adipose tissue...
, which is also found in animalsDeacon, pp. 128–29.). - With animals: Fungi lack chloroplastChloroplastChloroplasts are organelles found in plant cells and other eukaryotic organisms that conduct photosynthesis. Chloroplasts capture light energy to conserve free energy in the form of ATP and reduce NADP to NADPH through a complex set of processes called photosynthesis.Chloroplasts are green...
s and are heterotrophHeterotrophA heterotroph is an organism that cannot fix carbon and uses organic carbon for growth. This contrasts with autotrophs, such as plants and algae, which can use energy from sunlight or inorganic compounds to produce organic compounds such as carbohydrates, fats, and proteins from inorganic carbon...
ic organisms, requiring preformed organic compoundOrganic compoundAn organic compound is any member of a large class of gaseous, liquid, or solid chemical compounds whose molecules contain carbon. For historical reasons discussed below, a few types of carbon-containing compounds such as carbides, carbonates, simple oxides of carbon, and cyanides, as well as the...
s as energy sources. - With plants: Fungi possess a cell wall and vacuoleVacuoleA vacuole is a membrane-bound organelle which is present in all plant and fungal cells and some protist, animal and bacterial cells. Vacuoles are essentially enclosed compartments which are filled with water containing inorganic and organic molecules including enzymes in solution, though in certain...
s. They reproduce by both sexual and asexual means, and like basal plant groups (such as fernFernA fern is any one of a group of about 12,000 species of plants belonging to the botanical group known as Pteridophyta. Unlike mosses, they have xylem and phloem . They have stems, leaves, and roots like other vascular plants...
s and mossMossMosses are small, soft plants that are typically 1–10 cm tall, though some species are much larger. They commonly grow close together in clumps or mats in damp or shady locations. They do not have flowers or seeds, and their simple leaves cover the thin wiry stems...
es) produce sporeSporeIn biology, a spore is a reproductive structure that is adapted for dispersal and surviving for extended periods of time in unfavorable conditions. Spores form part of the life cycles of many bacteria, plants, algae, fungi and some protozoa. According to scientist Dr...
s. Similar to mosses and algae, fungi typically have haploid nuclei.Deacon, p. 58. - With euglenoids and bacteria: Higher fungi, euglenoids, and some bacteria produce the amino acidAmino acidAmino acids are molecules containing an amine group, a carboxylic acid group and a side-chain that varies between different amino acids. The key elements of an amino acid are carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen...
L-lysine in specific biosynthesisBiosynthesisBiosynthesis is an enzyme-catalyzed process in cells of living organisms by which substrates are converted to more complex products. The biosynthesis process often consists of several enzymatic steps in which the product of one step is used as substrate in the following step...
steps, called the α-aminoadipate pathway. - The cells of most fungi grow as tubular, elongated, and thread-like (filamentous) structures and are called hyphae, which may contain multiple nuclei and extend at their tips. Each tip contains a set of aggregated vesiclesVesicle (biology)A vesicle is a bubble of liquid within another liquid, a supramolecular assembly made up of many different molecules. More technically, a vesicle is a small membrane-enclosed sack that can store or transport substances. Vesicles can form naturally because of the properties of lipid membranes , or...
—cellular structures consisting of proteinProteinProteins are biochemical compounds consisting of one or more polypeptides typically folded into a globular or fibrous form, facilitating a biological function. A polypeptide is a single linear polymer chain of amino acids bonded together by peptide bonds between the carboxyl and amino groups of...
s, lipidLipidLipids constitute a broad group of naturally occurring molecules that include fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins , monoglycerides, diglycerides, triglycerides, phospholipids, and others...
s, and other organic molecules—called SpitzenkörperSpitzenkörperThe Spitzenkörper is a structure found in fungal hyphae which is the organizing center for hyphal growth and morphogenesis. It consists of many small vesicles and is present in growing hyphal tips, during spore germination and where branch formation occurs. Its position in the hyphal tip correlates...
. Both fungi and oomycetes grow as filamentous hyphal cells. In contrast, similar-looking organisms, such as filamentous green algaeGreen algaeThe green algae are the large group of algae from which the embryophytes emerged. As such, they form a paraphyletic group, although the group including both green algae and embryophytes is monophyletic...
, grow by repeated cell division within a chain of cells. - In common with some plant and animal species, more than 60 fungal species display the phenomenon of bioluminescenceBioluminescenceBioluminescence is the production and emission of light by a living organism. Its name is a hybrid word, originating from the Greek bios for "living" and the Latin lumen "light". Bioluminescence is a naturally occurring form of chemiluminescence where energy is released by a chemical reaction in...
.
Unique features:
- Some species grow as single-celled yeasts that reproduce by buddingBuddingBudding is a form of asexual reproduction in which a new organism grows on another one. The new organism remains attached as it grows, separating from the parent organism only when it is mature. Since the reproduction is asexual, the newly created organism is a clone and is genetically identical...
or binary fission. Dimorphic fungiDimorphic fungiDimorphic fungi are fungi which can exist as mold/hyphal/filamentous form or as yeast. An example is Penicillium marneffei:* At room temperature, it grows as a mold.* At body temperature, it grows as a yeast....
can switch between a yeast phase and a hyphal phase in response to environmental conditions.Alexopoulos et al., p. 30. - The fungal cell wall is composed of glucanGlucanA glucan molecule is a polysaccharide of D-glucose monomers linked by glycosidic bonds.Many beta-glucans are medically important.-Types:The following are glucans:-Alpha:...
s and chitinChitinChitin n is a long-chain polymer of a N-acetylglucosamine, a derivative of glucose, and is found in many places throughout the natural world...
; while the former compounds are also found in plants and the latter in the exoskeletonExoskeletonAn exoskeleton is the external skeleton that supports and protects an animal's body, in contrast to the internal skeleton of, for example, a human. In popular usage, some of the larger kinds of exoskeletons are known as "shells". Examples of exoskeleton animals include insects such as grasshoppers...
of arthropods, fungi are the only organisms that combine these two structural molecules in their cell wall. In contrast to plants and the oomycetes, fungal cell walls do not contain cellulose.

Xylem
Xylem is one of the two types of transport tissue in vascular plants. . The word xylem is derived from the Classical Greek word ξυλον , meaning "wood"; the best-known xylem tissue is wood, though it is found throughout the plant...
and phloem
Phloem
In vascular plants, phloem is the living tissue that carries organic nutrients , in particular, glucose, a sugar, to all parts of the plant where needed. In trees, the phloem is the innermost layer of the bark, hence the name, derived from the Greek word "bark"...
in many plants. To overcome these limitations, some fungi, such as Armillaria, form rhizomorphs
Mycelial cord
Mycelial cords are linear aggregations of parallel-oriented hyphae. The mature cords are composed of wide, empty vessel hyphae surrounded by narrower sheathing hyphae...
, that resemble and perform functions similar to the root
Root
In vascular plants, the root is the organ of a plant that typically lies below the surface of the soil. This is not always the case, however, since a root can also be aerial or aerating . Furthermore, a stem normally occurring below ground is not exceptional either...
s of plants. Another characteristic shared with plants includes a biosynthetic pathway for producing terpene
Terpene
Terpenes are a large and diverse class of organic compounds, produced by a variety of plants, particularly conifers, though also by some insects such as termites or swallowtail butterflies, which emit terpenes from their osmeterium. They are often strong smelling and thus may have had a protective...
s that uses mevalonic acid
Mevalonic acid
Mevalonic acid is a key organic compound in biochemistry. The anion of mevalonic acid, the predominant form in biological media, is known as mevalonate. This compound is of major pharmaceutical importance...
and pyrophosphate
Pyrophosphate
In chemistry, the anion, the salts, and the esters of pyrophosphoric acid are called pyrophosphates. Any salt or ester containing two phosphate groups is called a diphosphate. As a food additive, diphosphates are known as E450.- Chemistry :...
as chemical building blocks
Precursor (chemistry)
In chemistry, a precursor is a compound that participates in the chemical reaction that produces another compound. In biochemistry, the term "precursor" is used more specifically to refer to a chemical compound preceding another in a metabolic pathway....
. However, plants have an additional terpene pathway in their chloroplasts, a structure fungi do not possess. Fungi produce several secondary metabolite
Secondary metabolite
Secondary metabolites are organic compounds that are not directly involved in the normal growth, development, or reproduction of an organism. Unlike primary metabolites, absence of secondary metabolities does not result in immediate death, but rather in long-term impairment of the organism's...
s that are similar or identical in structure to those made by plants. Many of the plant and fungal enzymes that make these compounds differ from each other in sequence
Peptide sequence
Peptide sequence or amino acid sequence is the order in which amino acid residues, connected by peptide bonds, lie in the chain in peptides and proteins. The sequence is generally reported from the N-terminal end containing free amino group to the C-terminal end containing free carboxyl group...
and other characteristics, which indicates separate origins and evolution of these enzymes in the fungi and plants.
Diversity
Fungi have a worldwide distribution, and grow in a wide range of habitats, including extreme environments such as desertsDesert fungi
A variety of terricolous fungi inhabit the biological soil crust of arid regions. Those exposed to the sun typically contain melanin and are resistant to high temperatures, dryness and low nutrition. Species that are common elsewhere do not thrive in these conditions. Producing large dark...
or areas with high salt concentrations or ionizing radiation
Ionizing radiation
Ionizing radiation is radiation composed of particles that individually have sufficient energy to remove an electron from an atom or molecule. This ionization produces free radicals, which are atoms or molecules containing unpaired electrons...
, as well as in deep sea
Deep sea
The deep sea, or deep layer, is the lowest layer in the ocean, existing below the thermocline and above the seabed, at a depth of 1000 fathoms or more. Little or no light penetrates this part of the ocean and most of the organisms that live there rely for subsistence on falling organic matter...
sediments. Some can survive the intense UV and cosmic radiation encountered during space travel. Most grow in terrestrial environments, though several species live partly or solely in aquatic habitats, such as the chytrid fungus Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis
Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis
Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis is a chytrid fungus that causes the disease chytridiomycosis. In the decade after it was first discovered in amphibians in 1998, the disease devastated amphibian populations around the world, in a global decline towards multiple extinctions, part of the Holocene...
, a parasite that has been responsible for a worldwide decline in amphibian
Amphibian
Amphibians , are a class of vertebrate animals including animals such as toads, frogs, caecilians, and salamanders. They are characterized as non-amniote ectothermic tetrapods...
populations. This organism spends part of its life cycle as a motile zoospore
Zoospore
A zoospore is a motile asexual spore that uses a flagellum for locomotion. Also called a swarm spore, these spores are created by some algae, bacteria and fungi to propagate themselves.-Flagella:...
, enabling it to propel itself through water and enter its amphibian host. Other examples of aquatic fungi include those living in hydrothermal areas of the ocean.
Around 100,000 species of fungi have been formally described by taxonomists
Taxonomy
Taxonomy is the science of identifying and naming species, and arranging them into a classification. The field of taxonomy, sometimes referred to as "biological taxonomy", revolves around the description and use of taxonomic units, known as taxa...
, but the global biodiversity of the fungus kingdom is not fully understood. On the basis of observations of the ratio of the number of fungal species to the number of plant species in selected environments, the fungal kingdom has been estimated to contain about 1.5 million species; a recent (2011) estimate suggests there may be over 5 million species. In mycology, species
Species
In biology, a species is one of the basic units of biological classification and a taxonomic rank. A species is often defined as a group of organisms capable of interbreeding and producing fertile offspring. While in many cases this definition is adequate, more precise or differing measures are...
have historically been distinguished by a variety of methods and concepts. Classification based on morphological
Morphology (biology)
In biology, morphology is a branch of bioscience dealing with the study of the form and structure of organisms and their specific structural features....
characteristics, such as the size and shape of spores or fruiting structures, has traditionally dominated fungal taxonomy.Kirk et al., p. 489. Species may also be distinguished by their biochemical
Biochemistry
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes in living organisms, including, but not limited to, living matter. Biochemistry governs all living organisms and living processes...
and physiological
Physiology
Physiology is the science of the function of living systems. This includes how organisms, organ systems, organs, cells, and bio-molecules carry out the chemical or physical functions that exist in a living system. The highest honor awarded in physiology is the Nobel Prize in Physiology or...
characteristics, such as their ability to metabolize certain biochemicals, or their reaction to chemical tests
Chemical tests in mushroom identification
Chemical tests in mushroom identification are methods that aid in determining the variety of some fungi. The most useful tests are Melzer's reagent and potassium hydroxide.- Ammonia :Household ammonia can be used. A couple of drops are placed on the flesh...
. The biological species concept discriminates species based on their ability to mate
Mating in fungi
Mating in fungi is a complex process governed by mating types. Research on fungal mating has focused on only a few model species. Since not all of the fungi reproduce sexually and many that do are isogamous, the terms male and female do not apply to this kingdom...
. The application of molecular
Molecular biology
Molecular biology is the branch of biology that deals with the molecular basis of biological activity. This field overlaps with other areas of biology and chemistry, particularly genetics and biochemistry...
tools, such as DNA sequencing
DNA sequencing
DNA sequencing includes several methods and technologies that are used for determining the order of the nucleotide bases—adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine—in a molecule of DNA....
and phylogenetic analysis, to study diversity has greatly enhanced the resolution and added robustness to estimates of genetic diversity
Genetic diversity
Genetic diversity, the level of biodiversity, refers to the total number of genetic characteristics in the genetic makeup of a species. It is distinguished from genetic variability, which describes the tendency of genetic characteristics to vary....
within various taxonomic groups.
Microscopic structures
Most fungi grow as hyphaHypha
A hypha is a long, branching filamentous structure of a fungus, and also of unrelated Actinobacteria. In most fungi, hyphae are the main mode of vegetative growth, and are collectively called a mycelium; yeasts are unicellular fungi that do not grow as hyphae.-Structure:A hypha consists of one or...
e, which are cylindrical, thread-like structures 2–10 µm in diameter and up to several centimeters in length. Hyphae grow at their tips (apices); new hyphae are typically formed by emergence of new tips along existing hyphae by a process called branching, or occasionally growing hyphal tips bifurcate (fork) giving rise to two parallel-growing hyphae. The combination of apical growth and branching/forking leads to the development of a mycelium
Mycelium
thumb|right|Fungal myceliaMycelium is the vegetative part of a fungus, consisting of a mass of branching, thread-like hyphae. The mass of hyphae is sometimes called shiro, especially within the fairy ring fungi. Fungal colonies composed of mycelia are found in soil and on or within many other...
, an interconnected network of hyphae. Hyphae can be either septate or coenocytic: septate hyphae are divided into compartments separated by cross walls (internal cell walls, called septa, that are formed at right angle
Right angle
In geometry and trigonometry, a right angle is an angle that bisects the angle formed by two halves of a straight line. More precisely, if a ray is placed so that its endpoint is on a line and the adjacent angles are equal, then they are right angles...
s to the cell wall giving the hypha its shape), with each compartment containing one or more nuclei; coenocytic hyphae are not compartmentalized. Septa have pores that allow cytoplasm
Cytoplasm
The cytoplasm is a small gel-like substance residing between the cell membrane holding all the cell's internal sub-structures , except for the nucleus. All the contents of the cells of prokaryote organisms are contained within the cytoplasm...
, organelle
Organelle
In cell biology, an organelle is a specialized subunit within a cell that has a specific function, and is usually separately enclosed within its own lipid bilayer....
s, and sometimes nuclei to pass through; an example is the dolipore septum in the fungi of the phylum Basidiomycota. Coenocytic hyphae are essentially multinucleate
Multinucleate
Multinucleate cells have more than one nucleus per cell, which is the result of nuclear division not being followed by cytokinesis. As a consequence, multiple nuclei share one common cytoplasm. This can be the consequence of a disturbed cell cycle control Multinucleate (also multinucleated,...
supercells.
Many species have developed specialized hyphal structures for nutrient uptake from living hosts; examples include haustoria in plant-parasitic species of most fungal phyla, and arbuscules
Arbuscular mycorrhiza
An arbuscular mycorrhiza is a type of mycorrhiza in which the fungus penetrates the cortical cells of the roots of a vascular plant....
of several mycorrhiza
Mycorrhiza
A mycorrhiza is a symbiotic association between a fungus and the roots of a vascular plant....
l fungi, which penetrate into the host cells to consume nutrients.
Although fungi are opisthokont
Opisthokont
The opisthokonts or "Fungi/Metazoa group" are a broad group of eukaryotes, including both the animal and fungus kingdoms, together with the eukaryotic microorganisms that are sometimes grouped in the paraphyletic phylum Choanozoa...
s—a grouping of evolutionarily related organisms broadly characterized by a single posterior flagellum
Flagellum
A flagellum is a tail-like projection that protrudes from the cell body of certain prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, and plays the dual role of locomotion and sense organ, being sensitive to chemicals and temperatures outside the cell. There are some notable differences between prokaryotic and...
—all phyla except for the chytrids have lost their posterior flagella. Fungi are unusual among the eukaryotes in having a cell wall that, in addition to glucan
Glucan
A glucan molecule is a polysaccharide of D-glucose monomers linked by glycosidic bonds.Many beta-glucans are medically important.-Types:The following are glucans:-Alpha:...
s (e.g., β-1,3-glucan) and other typical components, also contains the biopolymer
Biopolymer
Biopolymers are polymers produced by living organisms. Since they are polymers, Biopolymers contain monomeric units that are covalently bonded to form larger structures. There are three main classes of biopolymers based on the differing monomeric units used and the structure of the biopolymer formed...
chitin.
Macroscopic structures
Fungal mycelia can become visible to the naked eye, for example, on various surfaces and substrates, such as damp walls and on spoiled food, where they are commonly called moldMold
Molds are fungi that grow in the form of multicellular filaments called hyphae. Molds are not considered to be microbes but microscopic fungi that grow as single cells called yeasts...
s. Mycelia grown on solid agar
Agar
Agar or agar-agar is a gelatinous substance derived from a polysaccharide that accumulates in the cell walls of agarophyte red algae. Throughout history into modern times, agar has been chiefly used as an ingredient in desserts throughout Asia and also as a solid substrate to contain culture medium...
media in laboratory petri dish
Petri dish
A Petri dish is a shallow glass or plastic cylindrical lidded dish that biologists use to culture cells or small moss plants. It was named after German bacteriologist Julius Richard Petri, who invented it when working as an assistant to Robert Koch...
es are usually referred to as colonies
Colony (biology)
In biology, a colony reference to several individual organisms of the same species living closely together, usually for mutual benefit, such as stronger defense or the ability to attack bigger prey. Some insects live only in colonies...
. These colonies can exhibit growth shapes and colors (due to spores or pigment
Pigment
A pigment is a material that changes the color of reflected or transmitted light as the result of wavelength-selective absorption. This physical process differs from fluorescence, phosphorescence, and other forms of luminescence, in which a material emits light.Many materials selectively absorb...
ation) that can be used as diagnostic features in the identification of species or groups. Some individual fungal colonies can reach extraordinary dimensions and ages as in the case of a clonal
Clone (cell biology)
A clone is a group of identical cells that share a common ancestry, meaning they are derived from the same mother cell.Clonality implies the state of a cell or a substance being derived from one source or the other...
colony of Armillaria solidipes, which extends over an area of more than 900 ha
Hectare
The hectare is a metric unit of area defined as 10,000 square metres , and primarily used in the measurement of land. In 1795, when the metric system was introduced, the are was defined as being 100 square metres and the hectare was thus 100 ares or 1/100 km2...
(3.5 square miles), with an estimated age of nearly 9,000 years.
The apothecium—a specialized structure important in sexual reproduction
Sexual reproduction
Sexual reproduction is the creation of a new organism by combining the genetic material of two organisms. There are two main processes during sexual reproduction; they are: meiosis, involving the halving of the number of chromosomes; and fertilization, involving the fusion of two gametes and the...
in the ascomycetes—is a cup-shaped fruiting body that holds the hymenium
Hymenium
The hymenium is the tissue layer on the hymenophore of a fungal fruiting body where the cells develop into basidia or asci, which produce spores. In some species all of the cells of the hymenium develop into basidia or asci, while in others some cells develop into sterile cells called cystidia or...
, a layer of tissue containing the spore-bearing cells. The fruiting bodies of the basidiomycetes (basidiocarp
Basidiocarp
In fungi, a basidiocarp, basidiome or basidioma , is the sporocarp of a basidiomycete, the multicellular structure on which the spore-producing hymenium is borne. Basidiocarps are characteristic of the hymenomycetes; rusts and smuts do not produce such structures...
s) and some ascomycetes can sometimes grow very large, and many are well-known as mushroom
Mushroom
A mushroom is the fleshy, spore-bearing fruiting body of a fungus, typically produced above ground on soil or on its food source. The standard for the name "mushroom" is the cultivated white button mushroom, Agaricus bisporus; hence the word "mushroom" is most often applied to those fungi that...
s.
Growth and physiology

Surface area to volume ratio
The surface-area-to-volume ratio also called the surface-to-volume ratio and variously denoted sa/vol or SA:V, is the amount of surface area per unit volume of an object or collection of objects. The surface-area-to-volume ratio is measured in units of inverse distance. A cube with sides of...
s. Hyphae are specifically adapted for growth on solid surfaces, and to invade substrates
Substrate (biology)
In biology a substrate is the surface a plant or animal lives upon and grows on. A substrate can include biotic or abiotic materials and animals. For example, encrusting algae that lives on a rock can be substrate for another animal that lives on top of the algae. See also substrate .-External...
and tissues. They can exert large penetrative mechanical forces; for example, the plant pathogen Magnaporthe grisea
Magnaporthe grisea
Magnaporthe grisea, also known as rice blast fungus, rice rotten neck, rice seedling blight, blast of rice, oval leaf spot of graminea, pitting disease, ryegrass blast, and Johnson spot, is a plant-pathogenic fungus that causes an important disease affecting rice. It is now known that M...
forms a structure called an appressorium
Appressorium
An appressorium is a flattened, hyphal "pressing" organ, from which a minute infection peg grows and enters the host, using turgor pressure capable of punching through even Mylar....
that evolved to puncture plant tissues. The pressure generated by the appressorium, directed against the plant epidermis
Epidermis (botany)
The epidermis is a single-layered group of cells that covers plants' leaves, flowers, roots and stems. It forms a boundary between the plant and the external environment. The epidermis serves several functions, it protects against water loss, regulates gas exchange, secretes metabolic compounds,...
, can exceed 8 megapascals (1,160.3 psi). The filamentous fungus Paecilomyces lilacinus uses a similar structure to penetrate the eggs of nematode
Nematode
The nematodes or roundworms are the most diverse phylum of pseudocoelomates, and one of the most diverse of all animals. Nematode species are very difficult to distinguish; over 28,000 have been described, of which over 16,000 are parasitic. It has been estimated that the total number of nematode...
s.
The mechanical pressure exerted by the appressorium is generated from physiological processes that increase intracellular turgor by producing osmolyte
Osmolyte
Osmolytes are compounds affecting osmosis. They are soluble in the solution within a cell, or in the surrounding fluid, e.g. as plasma osmolytes. They play a role in maintaining cell volume and fluid balance. For example, when a cell swells due to external osmotic pressure, membrane channels open...
s such as glycerol
Glycerol
Glycerol is a simple polyol compound. It is a colorless, odorless, viscous liquid that is widely used in pharmaceutical formulations. Glycerol has three hydroxyl groups that are responsible for its solubility in water and its hygroscopic nature. The glycerol backbone is central to all lipids...
. Morphological adaptations such as these are complemented by hydrolytic enzymes
Cellulase
400px|thumb|right|alt = Colored dice with checkered background|Ribbon representation of the Streptomyces lividans beta-1,4-endoglucanase catalytic domain - an example from the family 12 glycoside hydrolases...
secreted into the environment to digest large organic molecules—such as polysaccharide
Polysaccharide
Polysaccharides are long carbohydrate molecules, of repeated monomer units joined together by glycosidic bonds. They range in structure from linear to highly branched. Polysaccharides are often quite heterogeneous, containing slight modifications of the repeating unit. Depending on the structure,...
s, protein
Protein
Proteins are biochemical compounds consisting of one or more polypeptides typically folded into a globular or fibrous form, facilitating a biological function. A polypeptide is a single linear polymer chain of amino acids bonded together by peptide bonds between the carboxyl and amino groups of...
s, lipid
Lipid
Lipids constitute a broad group of naturally occurring molecules that include fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins , monoglycerides, diglycerides, triglycerides, phospholipids, and others...
s, and other organic substrates—into smaller molecules that may then be absorbed as nutrients. The vast majority of filamentous fungi grow in a polar fashion—i.e., by extension into one direction—by elongation at the tip (apex) of the hypha. Alternative forms of fungal growth include intercalary extension (i.e., by longitudinal expansion of hyphal compartments that are below the apex) as in the case of some endophytic
Endophyte
An endophyte is an endosymbiont, often a bacterium or fungus, that lives within a plant for at least part of its life without causing apparent disease. Endophytes are ubiquitous and have been found in all the species of plants studied to date; however, most of these endophyte/plant relationships...
fungi, or growth by volume expansion during the development of mushroom stipes and other large organs. Growth of fungi as multicellular structures consisting of somatic
Somatic
The term somatic means 'of the body',, relating to the body. In medicine, somatic illness is bodily, not mental, illness. The term is often used in biology to refer to the cells of the body in contrast to the germ line cells which usually give rise to the gametes...
and reproductive cells—a feature independently evolved in animals and plants—has several functions, including the development of fruiting bodies for dissemination of sexual spores (see above) and biofilm
Biofilm
A biofilm is an aggregate of microorganisms in which cells adhere to each other on a surface. These adherent cells are frequently embedded within a self-produced matrix of extracellular polymeric substance...
s for substrate colonization and intercellular communication.
Traditionally, the fungi are considered heterotroph
Heterotroph
A heterotroph is an organism that cannot fix carbon and uses organic carbon for growth. This contrasts with autotrophs, such as plants and algae, which can use energy from sunlight or inorganic compounds to produce organic compounds such as carbohydrates, fats, and proteins from inorganic carbon...
s, organisms that rely solely on carbon fixed
Carbon fixation
In biology, carbon fixation is the reduction of carbon dioxide to organic compounds by living organisms. The obvious example is photosynthesis. Carbon fixation requires both a source of energy such as sunlight, and an electron donor such as water. All life depends on fixed carbon. Organisms that...
by other organisms for metabolism
Metabolism
Metabolism is the set of chemical reactions that happen in the cells of living organisms to sustain life. These processes allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to their environments. Metabolism is usually divided into two categories...
. Fungi have evolved
Evolution
Evolution is any change across successive generations in the heritable characteristics of biological populations. Evolutionary processes give rise to diversity at every level of biological organisation, including species, individual organisms and molecules such as DNA and proteins.Life on Earth...
a high degree of metabolic versatility that allows them to use a diverse range of organic substrates for growth, including simple compounds such as nitrate
Nitrate
The nitrate ion is a polyatomic ion with the molecular formula NO and a molecular mass of 62.0049 g/mol. It is the conjugate base of nitric acid, consisting of one central nitrogen atom surrounded by three identically-bonded oxygen atoms in a trigonal planar arrangement. The nitrate ion carries a...
, ammonia
Ammonia
Ammonia is a compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the formula . It is a colourless gas with a characteristic pungent odour. Ammonia contributes significantly to the nutritional needs of terrestrial organisms by serving as a precursor to food and fertilizers. Ammonia, either directly or...
, acetate
Acetate
An acetate is a derivative of acetic acid. This term includes salts and esters, as well as the anion found in solution. Most of the approximately 5 billion kilograms of acetic acid produced annually in industry are used in the production of acetates, which usually take the form of polymers. In...
, or ethanol
Ethanol
Ethanol, also called ethyl alcohol, pure alcohol, grain alcohol, or drinking alcohol, is a volatile, flammable, colorless liquid. It is a psychoactive drug and one of the oldest recreational drugs. Best known as the type of alcohol found in alcoholic beverages, it is also used in thermometers, as a...
. For some species it has been shown that the pigment melanin
Melanin
Melanin is a pigment that is ubiquitous in nature, being found in most organisms . In animals melanin pigments are derivatives of the amino acid tyrosine. The most common form of biological melanin is eumelanin, a brown-black polymer of dihydroxyindole carboxylic acids, and their reduced forms...
may play a role in extracting energy from ionizing radiation
Ionizing radiation
Ionizing radiation is radiation composed of particles that individually have sufficient energy to remove an electron from an atom or molecule. This ionization produces free radicals, which are atoms or molecules containing unpaired electrons...
, such as gamma radiation; however, this form of "radiotrophic"
Radiotrophic fungus
Radiotrophic fungi are fungi which appear to use the pigment melanin to convert gamma radiation into chemical energy for growth. This proposed mechanism may be similar to anabolic pathways for the synthesis of reduced organic carbon in phototrophic organisms, which capture photons from visible...
growth has only been described for a few species, the effects on growth rates are small, and the underlying biophysical
Biophysics
Biophysics is an interdisciplinary science that uses the methods of physical science to study biological systems. Studies included under the branches of biophysics span all levels of biological organization, from the molecular scale to whole organisms and ecosystems...
and biochemical processes are not known. The authors speculate that this process might bear similarity to CO2 fixation
Carbon fixation
In biology, carbon fixation is the reduction of carbon dioxide to organic compounds by living organisms. The obvious example is photosynthesis. Carbon fixation requires both a source of energy such as sunlight, and an electron donor such as water. All life depends on fixed carbon. Organisms that...
via visible light
Visible spectrum
The visible spectrum is the portion of the electromagnetic spectrum that is visible to the human eye. Electromagnetic radiation in this range of wavelengths is called visible light or simply light. A typical human eye will respond to wavelengths from about 390 to 750 nm. In terms of...
, but instead utilizing ionizing radiation as a source of energy.
Reproduction

Biological life cycle
A life cycle is a period involving all different generations of a species succeeding each other through means of reproduction, whether through asexual reproduction or sexual reproduction...
of a species, the teleomorph and the anamorph. Environmental conditions trigger genetically determined developmental states that lead to the creation of specialized structures for sexual or asexual reproduction. These structures aid reproduction by efficiently dispersing spores or spore-containing propagule
Propagule
In horticulture, a propagule is any plant material used for the purpose of plant propagation. In asexual reproduction, a propagule may be a woody, semi-hardwood, or softwood cutting, leaf section, or any number of other plant parts. In sexual reproduction, a propagule is a seed or spore...
s.
Asexual reproduction
Asexual reproductionAsexual reproduction
Asexual reproduction is a mode of reproduction by which offspring arise from a single parent, and inherit the genes of that parent only, it is reproduction which does not involve meiosis, ploidy reduction, or fertilization. A more stringent definition is agamogenesis which is reproduction without...
via vegetative spores (conidia
Conidium
Conidia, sometimes termed conidiospores, are asexual, non-motile spores of a fungus and are named after the greek word for dust, konia. They are also called mitospores due to the way they are generated through the cellular process of mitosis...
) or through mycelial fragmentation is common; it maintains clonal populations adapted to a specific niche
Ecological niche
In ecology, a niche is a term describing the relational position of a species or population in its ecosystem to each other; e.g. a dolphin could potentially be in another ecological niche from one that travels in a different pod if the members of these pods utilize significantly different food...
, and allows more rapid dispersal than sexual reproduction. The "Fungi imperfecti" (fungi lacking the perfect or sexual stage) or Deuteromycota comprise all the species which lack an observable sexual cycle.
Sexual reproduction
Sexual reproduction with meiosisMeiosis
Meiosis is a special type of cell division necessary for sexual reproduction. The cells produced by meiosis are gametes or spores. The animals' gametes are called sperm and egg cells....
exists in all fungal phyla (with the exception of the Glomeromycota
Glomeromycota
Glomeromycota is one of seven currently recognized phyla within the kingdom Fungi, with approximately 230 described species. Members of the Glomeromycota form arbuscular mycorrhizas with the roots or thalli of land plants. Geosiphon pyriformis forms an endocytobiotic association with Nostoc...
). It differs in many aspects from sexual reproduction in animals or plants. Differences also exist between fungal groups and can be used to discriminate species by morphological differences in sexual structures and reproductive strategies. Mating
Mating in fungi
Mating in fungi is a complex process governed by mating types. Research on fungal mating has focused on only a few model species. Since not all of the fungi reproduce sexually and many that do are isogamous, the terms male and female do not apply to this kingdom...
experiments between fungal isolates may identify species on the basis of biological species concepts. The major fungal groupings have initially been delineated based on the morphology of their sexual structures and spores; for example, the spore-containing structures, asci
Ascus
An ascus is the sexual spore-bearing cell produced in ascomycete fungi. On average, asci normally contain eight ascospores, produced by a meiotic cell division followed, in most species, by a mitotic cell division. However, asci in some genera or species can number one , two, four, or multiples...
and basidia
Basidium
thumb|right|500px|Schematic showing a basidiomycete mushroom, gill structure, and spore-bearing basidia on the gill margins.A basidium is a microscopic, spore-producing structure found on the hymenophore of fruiting bodies of basidiomycete fungi. The presence of basidia is one of the main...
, can be used in the identification of ascomycetes and basidiomycetes, respectively. Some species may allow mating only between individuals of opposite mating type
Mating type
Mating types occur in eukaryotes that undergo sexual reproduction via isogamy. Since the gametes of different mating types look alike, they are often referred to by numbers, letters, or simply "+" and "-" instead of "male" and "female." Mating can only take place between different mating...
, while others can mate and sexually reproduce with any other individual or itself. Species of the former mating system
Mating system
A mating system is a way in which a group is structured in relation to sexual behaviour. The precise meaning depends upon the context. With respect to higher animals, it specifies which males mate with which females, under which circumstances; recognised animal mating systems include monogamy,...
are called heterothallic
Heterothallic
Heterothallic species have sexes that reside in different individuals....
, and of the latter homothallic
Homothallic
Homothallic refers to the possession, within a single organism, of the resources to reproduce sexually.It can be contrasted to heterothallic.It is often used to categorize fungi. In yeast, heterothallic cells have mating types a and α...
.
Most fungi have both an haploid and diploid stage in their life cycles. In sexually reproducing fungi, compatible individuals may combine by fusing their hyphae together into an interconnected network; this process, anastomosis
Anastomosis
An anastomosis is the reconnection of two streams that previously branched out, such as blood vessels or leaf veins. The term is used in medicine, biology, mycology and geology....
, is required for the initiation of the sexual cycle. Ascomycetes and basidiomycetes go through a dikaryotic stage, in which the nuclei inherited from the two parents do not combine immediately after cell fusion, but remain separate in the hyphal cells (see heterokaryosis
Heterokaryosis
Heterokaryosis is a term used in biology meaning to have two or more genetically different nuclei within the same mycelium of a fungus or other life form. This is a special type of syncytium.A heterokaryon is a cell with more than one nucleus of differing genetic origin...
).

Hymenium
The hymenium is the tissue layer on the hymenophore of a fungal fruiting body where the cells develop into basidia or asci, which produce spores. In some species all of the cells of the hymenium develop into basidia or asci, while in others some cells develop into sterile cells called cystidia or...
(the spore-bearing tissue layer) form a characteristic hook at the hyphal septum. During cell division
Cell division
Cell division is the process by which a parent cell divides into two or more daughter cells . Cell division is usually a small segment of a larger cell cycle. This type of cell division in eukaryotes is known as mitosis, and leaves the daughter cell capable of dividing again. The corresponding sort...
, formation of the hook ensures proper distribution of the newly divided nuclei into the apical and basal hyphal compartments. An ascus (plural asci) is then formed, in which karyogamy
Karyogamy
Karyogamy is the fusion of pronuclei of two cells, as part of syngamy, fertilization, or true bacterial conjugation.It is one of the two major modes of reproduction in fungi...
(nuclear fusion) occurs. Asci are embedded in an ascocarp
Ascocarp
An ascocarp, or ascoma , is the fruiting body of an ascomycete fungus. It consists of very tightly interwoven hyphae and may contain millions of asci, each of which typically contains eight ascospores...
, or fruiting body. Karyogamy in the asci is followed immediately by meiosis and the production of ascospore
Ascospore
An ascospore is a spore contained in an ascus or that was produced inside an ascus. This kind of spore is specific to fungi classified as ascomycetes ....
s. After dispersal, the ascospores may germinate and form a new haploid mycelium.
Sexual reproduction in basidiomycetes is similar to that of the ascomycetes. Compatible haploid hyphae fuse to produce a dikaryotic mycelium. However, the dikaryotic phase is more extensive in the basidiomycetes, often also present in the vegetatively growing mycelium. A specialized anatomical structure, called a clamp connection
Clamp connection
A clamp connection is a structure formed by growing hyphal cells of certain fungi. It is created to ensure each septum, or segment of hypha separated by crossed walls, receives a set of differing nuclei, which are obtained through mating of hyphae of differing sexual types...
, is formed at each hyphal septum. As with the structurally similar hook in the ascomycetes, the clamp connection in the basidiomycetes is required for controlled transfer of nuclei during cell division, to maintain the dikaryotic stage with two genetically different nuclei in each hyphal compartment. A basidiocarp
Basidiocarp
In fungi, a basidiocarp, basidiome or basidioma , is the sporocarp of a basidiomycete, the multicellular structure on which the spore-producing hymenium is borne. Basidiocarps are characteristic of the hymenomycetes; rusts and smuts do not produce such structures...
is formed in which club-like structures known as basidia generate haploid basidiospores after karyogamy and meiosis. The most commonly known basidiocarps are mushrooms, but they may also take other forms (see Morphology section).
In glomeromycetes (formerly zygomycetes), haploid hyphae of two individuals fuse, forming a gametangium, a specialized cell structure that becomes a fertile gamete
Gamete
A gamete is a cell that fuses with another cell during fertilization in organisms that reproduce sexually...
-producing cell. The gametangium develops into a zygospore
Zygospore
A zygospore is a diploid reproductive stage in the life cycle of many fungi and protists. Zygospores are created by the nuclear fusion of haploid cells. In fungi, zygospores are termed chlamydospores and are formed after the fusion of hyphae of different mating types...
, a thick-walled spore formed by the union of gametes. When the zygospore germinates, it undergoes meiosis
Meiosis
Meiosis is a special type of cell division necessary for sexual reproduction. The cells produced by meiosis are gametes or spores. The animals' gametes are called sperm and egg cells....
, generating new haploid hyphae, which may then form asexual sporangiospores. These sporangiospores allow the fungus to rapidly disperse and germinate into new genetically identical haploid fungal mycelia.
Spore dispersal
Both asexual and sexual spores or sporangiospores are often actively dispersed by forcible ejection from their reproductive structures. This ejection ensures exit of the spores from the reproductive structures as well as travelling through the air over long distances.
Hydrophobin
Hydrophobins are a class of small, cysteine rich proteins that are expressed only by filamentous fungi. They are known for their capability of forming a hydrophobic coating on a surface of an object. They were first discovered and separated in Schizophyllum commune in 1991...
s), enable efficient spore ejection. For example, the structure of the spore-bearing cells
Ascus
An ascus is the sexual spore-bearing cell produced in ascomycete fungi. On average, asci normally contain eight ascospores, produced by a meiotic cell division followed, in most species, by a mitotic cell division. However, asci in some genera or species can number one , two, four, or multiples...
in some ascomycete species is such that the buildup of substances
Osmolyte
Osmolytes are compounds affecting osmosis. They are soluble in the solution within a cell, or in the surrounding fluid, e.g. as plasma osmolytes. They play a role in maintaining cell volume and fluid balance. For example, when a cell swells due to external osmotic pressure, membrane channels open...
affecting cell volume and fluid balance enables the explosive discharge of spores into the air. The forcible discharge of single spores termed ballistospores involves formation of a small drop of water (Buller's drop), which upon contact with the spore leads to its projectile release with an initial acceleration of more than 10,000 g
G-force
The g-force associated with an object is its acceleration relative to free-fall. This acceleration experienced by an object is due to the vector sum of non-gravitational forces acting on an object free to move. The accelerations that are not produced by gravity are termed proper accelerations, and...
; the net result is that the spore is ejected 0.01–0.02 cm, sufficient distance for it to fall through the gills or pores into the air below. Other fungi, like the puffballs, rely on alternative mechanisms for spore release, such as external mechanical forces. The bird's nest fungi
Nidulariaceae
The Nidulariaceae are a family of fungi in the order Nidulariales. Commonly known as the bird's nest fungi, their fruiting bodies resemble tiny egg-filled birds' nests...
use the force of falling water drops to liberate the spores from cup-shaped fruiting bodies. Another strategy is seen in the stinkhorns, a group of fungi with lively colors and putrid odor that attract insects to disperse their spores.
Other sexual processes
Besides regular sexual reproduction with meiosis, certain fungi, such as those in the genera PenicilliumPenicillium
Penicillium is a genus of ascomycetous fungi of major importance in the natural environment as well as food and drug production. Members of the genus produce penicillin, a molecule that is used as an antibiotic, which kills or stops the growth of certain kinds of bacteria inside the body...
and Aspergillus
Aspergillus
Aspergillus is a genus consisting of several hundred mold species found in various climates worldwide. Aspergillus was first catalogued in 1729 by the Italian priest and biologist Pier Antonio Micheli...
, may exchange genetic material via parasexual processes, initiated by anastomosis between hyphae and plasmogamy
Plasmogamy
Plasmogamy is a stage in the sexual reproduction of fungi. In this stage, the cytoplasm of two parent mycelia fuse together without the fusion of nuclei, as occurs in higher terrestrial fungi. After plasmogamy occurs, the secondary mycelium forms. The secondary mycelium consists of dikaryotic...
of fungal cells. The frequency and relative importance of parasexual events is unclear and may be lower than other sexual processes. It is known to play a role in intraspecific hybridization and is likely required for hybridization between species, which has been associated with major events in fungal evolution.
Evolution
In contrast to plantsEvolutionary history of plants
The evolution of plants has resulted in increasing levels of complexity, from the earliest algal mats, through bryophytes, lycopods, ferns to the complex gymnosperms and angiosperms of today...
and animals
Evolutionary history of life
The evolutionary history of life on Earth traces the processes by which living and fossil organisms have evolved since life on Earth first originated until the present day. Earth formed about 4.5 Ga and life appeared on its surface within one billion years...
, the early fossil record of the fungi is meager. Factors that likely contribute to the under-representation of fungal species among fossils include the nature of fungal fruiting bodies
Sporocarp (fungi)
In fungi, the sporocarp is a multicellular structure on which spore-producing structures, such as basidia or asci, are borne...
, which are soft, fleshy, and easily degradable tissues and the microscopic dimensions of most fungal structures, which therefore are not readily evident. Fungal fossils are difficult to distinguish from those of other microbes, and are most easily identified when they resemble extant fungi. Often recovered from a permineralized
Permineralization
Permineralization is a process of fossilization in which mineral deposits form internal casts of organisms. Carried by water, these minerals fill the spaces within organic tissue...
plant or animal host, these samples are typically studied by making thin-section preparations that can be examined with light microscopy
Optical microscope
The optical microscope, often referred to as the "light microscope", is a type of microscope which uses visible light and a system of lenses to magnify images of small samples. Optical microscopes are the oldest design of microscope and were possibly designed in their present compound form in the...
or transmission electron microscopy
Transmission electron microscopy
Transmission electron microscopy is a microscopy technique whereby a beam of electrons is transmitted through an ultra thin specimen, interacting with the specimen as it passes through...
. Compression fossil
Compression fossil
A compression fossil is a fossil preserved in sedimentary rock that has undergone physical compression. While it is uncommon to find animals preserved as good compression fossils, it is very common to find plants preserved this way...
s are studied by dissolving the surrounding matrix with acid and then using light or scanning electron microscopy to examine surface details.
The earliest fossils possessing features typical of fungi date to the Proterozoic
Proterozoic
The Proterozoic is a geological eon representing a period before the first abundant complex life on Earth. The name Proterozoic comes from the Greek "earlier life"...
eon, some (Ma); these multicellular benthic organisms had filamentous structures with septa, and were capable of anastomosis. More recent studies (2009) estimate the arrival of fungal organisms at about 760–1060 Ma on the basis of comparisons of the rate of evolution in closely related groups. For much of the Paleozoic
Paleozoic
The Paleozoic era is the earliest of three geologic eras of the Phanerozoic eon, spanning from roughly...
Era (542–251 Ma), the fungi appear to have been aquatic and consisted of organisms similar to the extant chytrids in having flagellum-bearing spores. The evolutionary adaptation from an aquatic to a terrestrial lifestyle necessitated a diversification of ecological strategies for obtaining nutrients, including parasitism
Parasitism
Parasitism is a type of symbiotic relationship between organisms of different species where one organism, the parasite, benefits at the expense of the other, the host. Traditionally parasite referred to organisms with lifestages that needed more than one host . These are now called macroparasites...
, saprobism, and the development of mutualistic relationships such as mycorrhiza
Mycorrhiza
A mycorrhiza is a symbiotic association between a fungus and the roots of a vascular plant....
and lichenization. Recent (2009) studies suggest that the ancestral ecological state of the Ascomycota
Ascomycota
The Ascomycota are a Division/Phylum of the kingdom Fungi, and subkingdom Dikarya. Its members are commonly known as the Sac fungi. They are the largest phylum of Fungi, with over 64,000 species...
was saprobism, and that independent lichen
Lichen
Lichens are composite organisms consisting of a symbiotic organism composed of a fungus with a photosynthetic partner , usually either a green alga or cyanobacterium...
ization events have occurred multiple times.
The fungi probably colonized the land during the Cambrian
Cambrian
The Cambrian is the first geological period of the Paleozoic Era, lasting from Mya ; it is succeeded by the Ordovician. Its subdivisions, and indeed its base, are somewhat in flux. The period was established by Adam Sedgwick, who named it after Cambria, the Latin name for Wales, where Britain's...
(542–488.3 Ma), long before land plants. Fossilized hyphae and spores recovered from the Ordovician
Ordovician
The Ordovician is a geologic period and system, the second of six of the Paleozoic Era, and covers the time between 488.3±1.7 to 443.7±1.5 million years ago . It follows the Cambrian Period and is followed by the Silurian Period...
of Wisconsin (460 Ma) resemble modern-day Glomerales
Glomerales
Glomerales is an order of symbiotic fungi within the phylum Glomeromycota.- Biology :These Fungi are all biotrophic mutualists. Most employ the arbuscular mycorrhizal method of nutrient exchange with plants...
, and existed at a time when the land flora likely consisted of only non-vascular bryophyte
Bryophyte
Bryophyte is a traditional name used to refer to all embryophytes that do not have true vascular tissue and are therefore called 'non-vascular plants'. Some bryophytes do have specialized tissues for the transport of water; however since these do not contain lignin, they are not considered to be...
-like plants. Prototaxites
Prototaxites
The genus Prototaxites describes terrestrial organisms known only from fossils dating from the Silu-Devonian, approximately 420 to 370 million years ago. Prototaxites formed large trunk-like structures up to wide, reaching in height, made up of interwoven tubes just in diameter...
, which was probably a fungus or lichen, would have been the tallest organism of the late Silurian
Silurian
The Silurian is a geologic period and system that extends from the end of the Ordovician Period, about 443.7 ± 1.5 Mya , to the beginning of the Devonian Period, about 416.0 ± 2.8 Mya . As with other geologic periods, the rock beds that define the period's start and end are well identified, but the...
. Fungal fossils do not become common and uncontroversial until the early Devonian
Devonian
The Devonian is a geologic period and system of the Paleozoic Era spanning from the end of the Silurian Period, about 416.0 ± 2.8 Mya , to the beginning of the Carboniferous Period, about 359.2 ± 2.5 Mya...
(416–359.2 Ma), when they are abundant in the Rhynie chert
Rhynie chert
The Rhynie chert is an Early Devonian sedimentary deposit exhibiting extraordinary fossil detail or completeness . It is exposed near the village of Rhynie, Aberdeenshire, Scotland; a second unit, the Windyfield chert, is located some 700 m away...
, mostly as Zygomycota
Zygomycota
Zygomycota, or zygote fungi, is a phylum of fungi. The name comes from zygosporangia, where resistant spherical spores are formed during sexual reproduction. Approximately 1060 species are known. They are mostly terrestrial in habitat, living in soil or on decaying plant or animal material...
and Chytridiomycota
Chytridiomycota
Chytridiomycota is a division of the Fungi kingdom. The name is derived from the Greek chytridion, meaning "little pot", describing the structure containing unreleased spores. In older classifications, chytrids were placed in the Class Phycomycetes under the subdivision Myxomycophyta of the...
. At about this same time, approximately 400 Ma, the Ascomycota and Basidiomycota diverged, and all modern classes
Class (biology)
In biological classification, class is* a taxonomic rank. Other well-known ranks are life, domain, kingdom, phylum, order, family, genus, and species, with class fitting between phylum and order...
of fungi were present by the Late Carboniferous
Carboniferous
The Carboniferous is a geologic period and system that extends from the end of the Devonian Period, about 359.2 ± 2.5 Mya , to the beginning of the Permian Period, about 299.0 ± 0.8 Mya . The name is derived from the Latin word for coal, carbo. Carboniferous means "coal-bearing"...
(Pennsylvanian
Pennsylvanian
The Pennsylvanian is, in the ICS geologic timescale, the younger of two subperiods of the Carboniferous Period. It lasted from roughly . As with most other geochronologic units, the rock beds that define the Pennsylvanian are well identified, but the exact date of the start and end are uncertain...
, 318.1–299 Ma).
Lichen
Lichen
Lichens are composite organisms consisting of a symbiotic organism composed of a fungus with a photosynthetic partner , usually either a green alga or cyanobacterium...
-like fossils have been found in the Doushantuo Formation
Doushantuo Formation
The Doushantuo Formation is a Lagerstätte in Guizhou Province, China that is notable for being one of the oldest fossil beds to contain highly preserved fossils...
in southern China dating back to 635–551 Ma. Lichens were a component of the early terrestrial ecosystems, and the estimated age of the oldest terrestrial lichen fossil is 400 Ma; this date corresponds to the age of the oldest known sporocarp
Sporocarp (fungi)
In fungi, the sporocarp is a multicellular structure on which spore-producing structures, such as basidia or asci, are borne...
fossil, a Paleopyrenomycites species found in the Rhynie Chert. The oldest fossil with microscopic features resembling modern-day basidiomycetes is Palaeoancistrus, found permineralized with a fern
Fern
A fern is any one of a group of about 12,000 species of plants belonging to the botanical group known as Pteridophyta. Unlike mosses, they have xylem and phloem . They have stems, leaves, and roots like other vascular plants...
from the Pennsylvanian. Rare in the fossil record are the Homobasidiomycetes (a taxon
Taxon
|thumb|270px|[[African elephants]] form a widely-accepted taxon, the [[genus]] LoxodontaA taxon is a group of organisms, which a taxonomist adjudges to be a unit. Usually a taxon is given a name and a rank, although neither is a requirement...
roughly equivalent to the mushroom-producing species of the Agaricomycetes
Agaricomycetes
Agaricomycetes is a class of fungi. The taxon is roughly identical to that defined for the Homobasidiomycetes by Hibbett & Thorn, with the inclusion of Auriculariales and Sebacinales. It includes not only mushrooms but also most species placed in the deprecated taxa Gasteromycetes and...
). Two amber
Amber
Amber is fossilized tree resin , which has been appreciated for its color and natural beauty since Neolithic times. Amber is used as an ingredient in perfumes, as a healing agent in folk medicine, and as jewelry. There are five classes of amber, defined on the basis of their chemical constituents...
-preserved specimens provide evidence that the earliest known mushroom-forming fungi (the extinct species Archaeomarasmius leggetti) appeared during the mid-Cretaceous
Cretaceous
The Cretaceous , derived from the Latin "creta" , usually abbreviated K for its German translation Kreide , is a geologic period and system from circa to million years ago. In the geologic timescale, the Cretaceous follows the Jurassic period and is followed by the Paleogene period of the...
, 90 Ma.
Some time after the Permian–Triassic extinction event (251.4 Ma), a fungal spike (originally thought to be an extraordinary abundance of fungal spores in sediment
Sediment
Sediment is naturally occurring material that is broken down by processes of weathering and erosion, and is subsequently transported by the action of fluids such as wind, water, or ice, and/or by the force of gravity acting on the particle itself....
s) formed, suggesting that fungi were the dominant life form at this time, representing nearly 100% of the available fossil record for this period. However, the relative proportion of fungal spores relative to spores formed by algal
Algae
Algae are a large and diverse group of simple, typically autotrophic organisms, ranging from unicellular to multicellular forms, such as the giant kelps that grow to 65 meters in length. They are photosynthetic like plants, and "simple" because their tissues are not organized into the many...
species is difficult to assess, the spike did not appear worldwide, and in many places it did not fall on the Permian–Triassic boundary.
Taxonomy
Although commonly included in botany curricula and textbooks, fungi are more closely related to animalAnimal
Animals are a major group of multicellular, eukaryotic organisms of the kingdom Animalia or Metazoa. Their body plan eventually becomes fixed as they develop, although some undergo a process of metamorphosis later on in their life. Most animals are motile, meaning they can move spontaneously and...
s than to plants and are placed with the animals in the monophyletic group of opisthokont
Opisthokont
The opisthokonts or "Fungi/Metazoa group" are a broad group of eukaryotes, including both the animal and fungus kingdoms, together with the eukaryotic microorganisms that are sometimes grouped in the paraphyletic phylum Choanozoa...
s. Analyses using molecular phylogenetics support a monophyletic origin of the Fungi. The taxonomy
Taxonomy
Taxonomy is the science of identifying and naming species, and arranging them into a classification. The field of taxonomy, sometimes referred to as "biological taxonomy", revolves around the description and use of taxonomic units, known as taxa...
of the Fungi is in a state of constant flux, especially due to recent research based on DNA comparisons. These current phylogenetic analyses often overturn classifications based on older and sometimes less discriminative methods based on morphological features and biological species concepts obtained from experimental mating
Mating
In biology, mating is the pairing of opposite-sex or hermaphroditic organisms for copulation. In social animals, it also includes the raising of their offspring. Copulation is the union of the sex organs of two sexually reproducing animals for insemination and subsequent internal fertilization...
s.
There is no unique generally accepted system at the higher taxonomic levels and there are frequent name changes at every level, from species upwards. Efforts among researchers are now underway to establish and encourage usage of a unified and more consistent nomenclature
Botanical nomenclature
Botanical nomenclature is the formal, scientific naming of plants. It is related to, but distinct from taxonomy. Plant taxonomy is concerned with grouping and classifying plants; botanical nomenclature then provides names for the results of this process. The starting point for modern botanical...
. Fungal species can also have multiple scientific names depending on their life cycle and mode (sexual or asexual) of reproduction. Web sites such as Index Fungorum
Index Fungorum
Index Fungorum, an international project to index all formal names in the Fungi Kingdom. Somewhat comparable to the IPNI, but with more contributing institutions....
and ITIS
Integrated Taxonomic Information System
The Integrated Taxonomic Information System is a partnership designed to provide consistent and reliable information on the taxonomy of biological species. ITIS was originally formed in 1996 as an interagency group within the U.S...
list current names of fungal species (with cross-references to older synonyms).
The 2007 classification of Kingdom Fungi is the result of a large-scale collaborative research effort involving dozens of mycologists and other scientists working on fungal taxonomy. It recognizes seven phyla
Phylum
In biology, a phylum The term was coined by Georges Cuvier from Greek φῦλον phylon, "race, stock," related to φυλή phyle, "tribe, clan." is a taxonomic rank below kingdom and above class. "Phylum" is equivalent to the botanical term division....
, two of which—the Ascomycota and the Basidiomycota—are contained within a branch representing subkingdom Dikarya. The below cladogram
Cladogram
A cladogram is a diagram used in cladistics which shows ancestral relations between organisms, to represent the evolutionary tree of life. Although traditionally such cladograms were generated largely on the basis of morphological characters, DNA and RNA sequencing data and computational...
depicts the major fungal taxa
Taxon
|thumb|270px|[[African elephants]] form a widely-accepted taxon, the [[genus]] LoxodontaA taxon is a group of organisms, which a taxonomist adjudges to be a unit. Usually a taxon is given a name and a rank, although neither is a requirement...
and their relationship to opisthokont and unikont organisms. The lengths of the branches in this tree are not proportional to evolutionary distances.
Taxonomic groups
The major phylaPhylum
In biology, a phylum The term was coined by Georges Cuvier from Greek φῦλον phylon, "race, stock," related to φυλή phyle, "tribe, clan." is a taxonomic rank below kingdom and above class. "Phylum" is equivalent to the botanical term division....
(sometimes called divisions) of fungi have been classified mainly on the basis of characteristics of their sexual reproductive structures. Currently, seven phyla are proposed: Microsporidia, Chytridiomycota, Blastocladiomycota, Neocallimastigomycota, Glomeromycota, Ascomycota, and Basidiomycota.
Phylogenetic analysis has demonstrated that the Microsporidia
Microsporidia
The microsporidia constitute a phylum of spore-forming unicellular parasites. They were once thought to be protists but are now known to be fungi. Loosely 1500 of the probably more than one million species are named now. Microsporidia are restricted to animal hosts, and all major groups of animals...
, unicellular parasites of animals and protists, are fairly recent and highly derived endobiotic fungi (living within the tissue of another species). One 2006 study concludes that the Microsporidia are a sister group to the true fungi, that is, they are each other's closest evolutionary relative. Hibbett and colleagues suggest that this analysis does not clash with their classification of the Fungi, and although the Microsporidia are elevated to phylum status, it is acknowledged that further analysis is required to clarify evolutionary relationships within this group.
The Chytridiomycota
Chytridiomycota
Chytridiomycota is a division of the Fungi kingdom. The name is derived from the Greek chytridion, meaning "little pot", describing the structure containing unreleased spores. In older classifications, chytrids were placed in the Class Phycomycetes under the subdivision Myxomycophyta of the...
are commonly known as chytrids. These fungi are distributed worldwide. Chytrids produce zoospore
Zoospore
A zoospore is a motile asexual spore that uses a flagellum for locomotion. Also called a swarm spore, these spores are created by some algae, bacteria and fungi to propagate themselves.-Flagella:...
s that are capable of active movement through aqueous phases with a single flagellum
Flagellum
A flagellum is a tail-like projection that protrudes from the cell body of certain prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, and plays the dual role of locomotion and sense organ, being sensitive to chemicals and temperatures outside the cell. There are some notable differences between prokaryotic and...
, leading early taxonomists to classify them as protist
Protist
Protists are a diverse group of eukaryotic microorganisms. Historically, protists were treated as the kingdom Protista, which includes mostly unicellular organisms that do not fit into the other kingdoms, but this group is contested in modern taxonomy...
s. Molecular phylogenies, inferred from rRNA sequences in ribosome
Ribosome
A ribosome is a component of cells that assembles the twenty specific amino acid molecules to form the particular protein molecule determined by the nucleotide sequence of an RNA molecule....
s, suggest that the Chytrids are a basal
Basal (phylogenetics)
In phylogenetics, a basal clade is the earliest clade to branch in a larger clade; it appears at the base of a cladogram.A basal group forms an outgroup to the rest of the clade, such as in the following example:...
group divergent from the other fungal phyla, consisting of four major clade
Clade
A clade is a group consisting of a species and all its descendants. In the terms of biological systematics, a clade is a single "branch" on the "tree of life". The idea that such a "natural group" of organisms should be grouped together and given a taxonomic name is central to biological...
s with suggestive evidence for paraphyly
Paraphyly
A group of taxa is said to be paraphyletic if the group consists of all the descendants of a hypothetical closest common ancestor minus one or more monophyletic groups of descendants...
or possibly polyphyly
Polyphyly
A polyphyletic group is one whose members' last common ancestor is not a member of the group.For example, the group consisting of warm-blooded animals is polyphyletic, because it contains both mammals and birds, but the most recent common ancestor of mammals and birds was cold-blooded...
.
The Blastocladiomycota
Blastocladiomycota
Blastocladiomycota is one of eight currently recognized phyla within the kingdom Fungi. These zoosporic fungi are found in soil and fresh water habitats and are mostly detritivores, subsisting on decaying organic matter....
were previously considered a taxonomic clade within the Chytridiomycota. Recent molecular data and ultrastructural
Ultrastructure
Ultrastructure is the detailed structure of a biological specimen, such as a cell, tissue, or organ, that can be observed by electron microscopy...
characteristics, however, place the Blastocladiomycota as a sister clade to the Zygomycota, Glomeromycota, and Dikarya (Ascomycota and Basidiomycota). The blastocladiomycetes are saprotrophs
Saprotrophic nutrition
Saprotrophic nutrition is a process of chemoheterotrophic extra-cellular digestion involved in the processing of dead or decayed organic matter that occurs in saprotrophs or heterotrophs, and is most often associated with fungi, for example Mucor and Rhizopus...
, feeding on decomposing organic matter, and they are parasites of all eukaryotic groups. Unlike their close relatives, the chytrids, which mostly exhibit zygotic meiosis, the blastocladiomycetes undergo sporic meiosis.
The Neocallimastigomycota
Neocallimastigomycota
Neocallimastigomycota is a phylum of anaerobic fungi, found in the digestive tracts of herbivores. It encompasses only one family.-Discovery:...
were earlier placed in the phylum Chytridomycota. Members of this small phylum are anaerobic organism
Anaerobic organism
An anaerobic organism or anaerobe is any organism that does not require oxygen for growth. It could possibly react negatively and may even die if oxygen is present...
s, living in the digestive system of larger herbivorous mammals and possibly in other terrestrial and aquatic environments. They lack mitochondria but contain hydrogenosome
Hydrogenosome
A hydrogenosome is a membrane-enclosed organelle of some anaerobic ciliates, trichomonads and fungi. The hydrogenosomes of trichomonads produce molecular hydrogen, acetate, carbon dioxide and ATP by the combined actions of pyruvate:ferredoxin oxido-reductase, hydrogenase, acetate:succinate CoA...
s of mitochondrial origin. As the related chrytrids, neocallimastigomycetes form zoospores that are posteriorly uniflagellate or polyflagellate.
Members of the Glomeromycota
Glomeromycota
Glomeromycota is one of seven currently recognized phyla within the kingdom Fungi, with approximately 230 described species. Members of the Glomeromycota form arbuscular mycorrhizas with the roots or thalli of land plants. Geosiphon pyriformis forms an endocytobiotic association with Nostoc...
form arbuscular mycorrhizae, a form of symbiosis
Symbiosis
Symbiosis is close and often long-term interaction between different biological species. In 1877 Bennett used the word symbiosis to describe the mutualistic relationship in lichens...
where fungal hyphae invade plant root cells and both species benefit from the resulting increased supply of nutrients. All known Glomeromycota species reproduce asexually. The symbiotic association between the Glomeromycota and plants is ancient, with evidence dating to 400 million years ago. Formerly part of the Zygomycota
Zygomycota
Zygomycota, or zygote fungi, is a phylum of fungi. The name comes from zygosporangia, where resistant spherical spores are formed during sexual reproduction. Approximately 1060 species are known. They are mostly terrestrial in habitat, living in soil or on decaying plant or animal material...
(commonly known as 'sugar' and 'pin' molds), the Glomeromycota were elevated to phylum status in 2001 and now replace the older phylum Zygomycota. Fungi that were placed in the Zygomycota are now being reassigned to the Glomeromycota, or the subphyla incertae sedis
Incertae sedis
, is a term used to define a taxonomic group where its broader relationships are unknown or undefined. Uncertainty at specific taxonomic levels is attributed by , , and similar terms.-Examples:*The fossil plant Paradinandra suecica could not be assigned to any...
Mucoromycotina
Mucoromycotina
Mucoromycotina is a subdivision of Fungi of uncertain affinities. It contains 3 orders, 61 genera, and 325 species.It includes the orders Endogonales, Mucorales, and Mortierellales....
, Kickxellomycotina
Kickxellomycotina
Kickxellomycotina is a fungus grouping.The name was changed from "Harpellomycotina", because "Kickxellomycotina" had an older stem.Orders include Asellariales, Kickxellales, Dimargaritales, and Harpellales.-External links:...
, the Zoopagomycotina
Zoopagomycotina
Zoopagomycotina is subphylum of Fungi that includes the order Zoopagales.-External links:* http://www.uniprot.org/taxonomy/451827* http://agclass.canr.msu.edu/mtwdk.exe?w=125844&k=default&s=5&t=2&n=1&l=60...
and the Entomophthoromycotina
Entomophthoromycotina
Entomophthoromycotina is a fungus subphylum.It includes the order Entomophthorales....
. Some well-known examples of fungi formerly in the Zygomycota include black bread mold (Rhizopus stolonifer), and Pilobolus
Pilobolus
Pilobolus is a genus of fungi that commonly grows on herbivore dung.-Life cycle:The life cycle of Pilobolus begins with a black sporangium that has been discharged onto a plant substrate such as grass. A herbivorous animal such as a horse then eats the substrate, unknowingly consuming the...
species, capable of ejecting spore
Spore
In biology, a spore is a reproductive structure that is adapted for dispersal and surviving for extended periods of time in unfavorable conditions. Spores form part of the life cycles of many bacteria, plants, algae, fungi and some protozoa. According to scientist Dr...
s several meters through the air. Medically relevant genera include Mucor
Mucor
Mucor is a microbial genus of about 3000 species of moulds commonly found in soil, digestive systems, plant surfaces, and rotten vegetable matter.-Description:...
, Rhizomucor
Rhizomucor
Rhizomucor is a genus of fungi in the Mucoraceae family. The widespread genus contains six species. Rhizomucor parasiticus, the species originally selected as the type, is now considered synonymous with Rhizomucor pusillus....
, and Rhizopus
Rhizopus
Rhizopus is a genus of common saprobic fungi on plants and specialized parasites on animals. They are found on a wide variety of organic substrates, including "mature fruits and vegetables", faeces, jellies, syrups, leather, bread, peanuts and tobacco. Some Rhizopus species are opportunistic agents...
.

Ascomycota
The Ascomycota are a Division/Phylum of the kingdom Fungi, and subkingdom Dikarya. Its members are commonly known as the Sac fungi. They are the largest phylum of Fungi, with over 64,000 species...
, commonly known as sac fungi or ascomycetes, constitute the largest taxonomic group within the Eumycota. These fungi form meiotic spores called ascospore
Ascospore
An ascospore is a spore contained in an ascus or that was produced inside an ascus. This kind of spore is specific to fungi classified as ascomycetes ....
s, which are enclosed in a special sac-like structure called an ascus
Ascus
An ascus is the sexual spore-bearing cell produced in ascomycete fungi. On average, asci normally contain eight ascospores, produced by a meiotic cell division followed, in most species, by a mitotic cell division. However, asci in some genera or species can number one , two, four, or multiples...
. This phylum includes morel
Morel
Morchella, the true morels, is a genus of edible mushrooms closely related to anatomically simpler cup fungi. These distinctive mushrooms appear honeycomb-like in that the upper portion is composed of a network of ridges with pits between them....
s, a few mushroom
Mushroom
A mushroom is the fleshy, spore-bearing fruiting body of a fungus, typically produced above ground on soil or on its food source. The standard for the name "mushroom" is the cultivated white button mushroom, Agaricus bisporus; hence the word "mushroom" is most often applied to those fungi that...
s and truffles, single-celled yeast
Yeast
Yeasts are eukaryotic micro-organisms classified in the kingdom Fungi, with 1,500 species currently described estimated to be only 1% of all fungal species. Most reproduce asexually by mitosis, and many do so by an asymmetric division process called budding...
s (e.g., of the genera Saccharomyces
Saccharomyces
Saccharomyces is a genus in the kingdom of fungi that includes many species of yeast. Saccharomyces is from Greek σάκχαρ and μύκης and means sugar fungus. Many members of this genus are considered very important in food production. One example is Saccharomyces cerevisiae, which is used in making...
, Kluyveromyces
Kluyveromyces
Kluyveromyces is a genus of ascomycetous yeasts in the family Saccharomycetaceae. Some of the species, such as K. marxianus, are the teleomorphs of Candida species....
, Pichia
Pichia
Pichia is a genus of yeasts in the family Saccharomycetaceae with spherical, elliptical or oblong acuminate cells. Pichia is a teleomorph, and forms during sexual reproduction hat-shaped, hemispherical or round ascospores. The anamorphs of some Pichia species are Candida species...
, and Candida
Candida (genus)
Candida is a genus of yeasts. Many species are harmless commensals or endosymbionts of animal hosts including humans, but other species, or harmless species in the wrong location, can cause disease. Candida albicans can cause infections in humans and other animals, especially in immunocompromised...
), and many filamentous fungi living as saprotrophs, parasites, and mutualistic symbionts. Prominent and important genera of filamentous ascomycetes include Aspergillus
Aspergillus
Aspergillus is a genus consisting of several hundred mold species found in various climates worldwide. Aspergillus was first catalogued in 1729 by the Italian priest and biologist Pier Antonio Micheli...
, Penicillium
Penicillium
Penicillium is a genus of ascomycetous fungi of major importance in the natural environment as well as food and drug production. Members of the genus produce penicillin, a molecule that is used as an antibiotic, which kills or stops the growth of certain kinds of bacteria inside the body...
, Fusarium
Fusarium
Fusarium is a large genus of filamentous fungi widely distributed in soil and in association with plants. Most species are harmless saprobes, and are relatively abundant members of the soil microbial community. Some species produce mycotoxins in cereal crops that can affect human and animal health...
, and Claviceps. Many ascomycete species have only been observed undergoing asexual reproduction (called anamorphic species), but analysis of molecular data has often been able to identify their closest teleomorphs in the Ascomycota. Because the products of meiosis are retained within the sac-like ascus, ascomycetes have been used for elucidating principles of genetics and heredity (e.g. Neurospora crassa
Neurospora crassa
Neurospora crassa is a type of red bread mold of the phylum Ascomycota. The genus name, meaning "nerve spore" refers to the characteristic striations on the spores. The first published account of this fungus was from an infestation of French bakeries in 1843. N...
).
Members of the Basidiomycota
Basidiomycota
Basidiomycota is one of two large phyla that, together with the Ascomycota, comprise the subkingdom Dikarya within the Kingdom Fungi...
, commonly known as the club fungi or basidiomycetes, produce meiospores called basidiospore
Basidiospore
A basidiospore is a reproductive spore produced by Basidiomycete fungi. Basidiospores typically each contain one haploid nucleus that is the product of meiosis, and they are produced by specialized fungal cells called basidia. In grills under a cap of one common species in the phylum of...
s on club-like stalks called basidia
Basidium
thumb|right|500px|Schematic showing a basidiomycete mushroom, gill structure, and spore-bearing basidia on the gill margins.A basidium is a microscopic, spore-producing structure found on the hymenophore of fruiting bodies of basidiomycete fungi. The presence of basidia is one of the main...
. Most common mushrooms belong to this group, as well as rust
Rust (fungus)
Rusts are plant diseases caused by pathogenic fungi of the order Pucciniales. About 7800 species are known. Rusts can affect a variety of plants; leaves, stems, fruits and seeds. Rust is most commonly seen as coloured powder, composed off tiny aeciospores which land on vegetation producing...
and smut fungi
Smut (fungus)
The smuts are multicellular fungi, that are characterized by their large numbers of teliospores. The smuts get their name from a Germanic word for dirt because of their dark, thick-walled and dust-like teliospores. They are mostly Ustilaginomycetes and can cause plant disease...
, which are major pathogens of grains. Other important basidiomycetes include the maize
Maize
Maize known in many English-speaking countries as corn or mielie/mealie, is a grain domesticated by indigenous peoples in Mesoamerica in prehistoric times. The leafy stalk produces ears which contain seeds called kernels. Though technically a grain, maize kernels are used in cooking as a vegetable...
pathogen Ustilago maydis, human commensal
Commensalism
In ecology, commensalism is a class of relationship between two organisms where one organism benefits but the other is neutral...
species of the genus Malassezia, and the opportunistic
Opportunistic infection
An opportunistic infection is an infection caused by pathogens, particularly opportunistic pathogens—those that take advantage of certain situations—such as bacterial, viral, fungal or protozoan infections that usually do not cause disease in a healthy host, one with a healthy immune system...
human pathogen, Cryptococcus neoformans
Cryptococcus neoformans
Cryptococcus neoformans is an encapsulated yeast that can live in both plants and animals. Its teleomorph is Filobasidiella neoformans, a filamentous fungus belonging to the class Tremellomycetes. It is often found in pigeon excrement....
.
Fungus-like organisms
Because of similarities in morphology and lifestyle, the slime molds (myxomycetes) and water molds (oomycetes) were formerly classified in the kingdom Fungi. Unlike true fungi the cell walls of these organisms contain cellulose and lack chitin. Myxomycetes are unikontUnikont
Unikonts are members of the Unikonta, a taxonomic group proposed by Thomas Cavalier-Smith.It includes amoebozoa, opisthokonts, and Apusozoa.-Clade:...
s like fungi, but are grouped in the Amoebozoa
Amoebozoa
The Amoebozoa are a major group of amoeboid protozoa, including the majority that move by means ofinternal cytoplasmic flow. Their pseudopodia are characteristically blunt and finger-like,...
. Oomycetes are diploid bikont
Bikont
A Bikont is a eukaryotic cell with two flagella, as its name suggests. It is a division of eukaryotes.-Enzymes:Another shared trait of bikonts is the fusion of two genes into a single unit: the genes for thymidylate synthase and dihydrofolate reductase encode a singleprotein with two...
s, grouped in the Chromalveolate
Chromalveolate
Chromalveolata is a eukaryote supergroup first proposed by Thomas Cavalier-Smith as a refinement of his kingdom Chromista, which was first put forward in 1981. Chromalveolata was proposed to represent the result of a single secondary endosymbiosis between a line descending from a bikont and a red...
kingdom. Neither water molds nor slime molds are closely related to the true fungi, and, therefore, taxonomists no longer group them in the kingdom Fungi. Nonetheless, studies of the oomycetes and myxomycetes are still often included in mycology
Mycology
Mycology is the branch of biology concerned with the study of fungi, including their genetic and biochemical properties, their taxonomy and their use to humans as a source for tinder, medicinals , food and entheogens, as well as their dangers, such as poisoning or...
textbooks and primary research literature.
The Rozellida
Rozellida
Cryptomycota , or Rozellida are a clade of micro-organisms which are either fungi or a sister group to fungi. They differ from classical fungi in that they lack chitinous cell walls....
clade, including the "chytrid" Rozella
Rozella
Rozella is a genus of fungi. Considered one of the earliest diverging lineages of fungi, the widespread genus contains 22 species. Rozella was circumscribed by French mycologist Marie Maxime Cornu in 1872.-Species:* Rozella achlyae...
, is a genetically disparate group known mostly from environmental DNA sequences which is a sister group to fungi. Members of the group which have been isolated lack the chitinous cell wall which is characteristic of fungi.
The nucleariid
Nucleariid
The nucleariids are a group of amoebae with filose pseudopods, known mostly from soils and freshwater. They are distinguished from the similar vampyrellids mainly by having mitochondria with discoid cristae.-Classification:...
s, currently grouped in the Choanozoa
Choanozoa
Choanozoa is the name of a phylum of protists that belongs to the line of opisthokonts....
, may be the next sister group to the eumycete clade, and as such could be included in an expanded fungal kingdom.
Ecology
Although often inconspicuous, fungi occur in every environment on EarthEarth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun, and the densest and fifth-largest of the eight planets in the Solar System. It is also the largest of the Solar System's four terrestrial planets...
and play very important roles in most ecosystems. Along with bacteria, fungi are the major decomposers in most terrestrial (and some aquatic) ecosystems, and therefore play a critical role in biogeochemical cycles and in many food webs. As decomposers, they play an essential role in nutrient cycling, especially as saprotrophs and symbionts, degrading organic matter
Organic matter
Organic matter is matter that has come from a once-living organism; is capable of decay, or the product of decay; or is composed of organic compounds...
to inorganic molecules, which can then re-enter anabolic metabolic pathways in plants or other organisms.
Symbiosis
Many fungi have important symbiotic relationships with organisms from most if not all KingdomKingdom (biology)
In biology, kingdom is a taxonomic rank, which is either the highest rank or in the more recent three-domain system, the rank below domain. Kingdoms are divided into smaller groups called phyla or divisions in botany...
s. These interactions can be mutualistic or antagonistic in nature, or in the case of commensal fungi are of no apparent benefit or detriment to the host.
With plants
MycorrhizaMycorrhiza
A mycorrhiza is a symbiotic association between a fungus and the roots of a vascular plant....
l symbiosis between plants and fungi is one of the most well-known plant–fungus associations and is of significant importance for plant growth and persistence in many ecosystems; over 90% of all plant species engage in mycorrhizal relationships with fungi and are dependent upon this relationship for survival.

Nitrate
The nitrate ion is a polyatomic ion with the molecular formula NO and a molecular mass of 62.0049 g/mol. It is the conjugate base of nitric acid, consisting of one central nitrogen atom surrounded by three identically-bonded oxygen atoms in a trigonal planar arrangement. The nitrate ion carries a...
and phosphate
Phosphate
A phosphate, an inorganic chemical, is a salt of phosphoric acid. In organic chemistry, a phosphate, or organophosphate, is an ester of phosphoric acid. Organic phosphates are important in biochemistry and biogeochemistry or ecology. Inorganic phosphates are mined to obtain phosphorus for use in...
from soils having low concentrations of these key plant nutrients. The fungal partners may also mediate plant-to-plant transfer of carbohydrates and other nutrients. Such mycorrhizal communities are called "common mycorrhizal networks". A special case of mycorrhiza is myco-heterotrophy, whereby the plant parasitizes the fungus, obtaining all of its nutrients from its fungal symbiont. Some fungal species inhabit the tissues inside roots, stems, and leaves, in which case they are called endophytes. Similar to mycorrhiza, endophytic colonization by fungi may benefit both symbionts; for example, endophytes of grasses impart to their host increased resistance to herbivores and other environmental stresses and receive food and shelter from the plant in return.
With algae and cyanobacteria

Algae
Algae are a large and diverse group of simple, typically autotrophic organisms, ranging from unicellular to multicellular forms, such as the giant kelps that grow to 65 meters in length. They are photosynthetic like plants, and "simple" because their tissues are not organized into the many...
or cyanobacteria (referred to in lichen terminology as "photobionts") and fungi (mostly various species of ascomycetes and a few basidiomycetes), in which individual photobiont cells are embedded in a tissue formed by the fungus. Lichens occur in every ecosystem on all continents, play a key role in soil formation and the initiation of biological succession
Ecological succession
Ecological succession, is the phenomenon or process by which a community progressively transforms itself until a stable community is formed. It is a fundamental concept in ecology, and refers to more or less predictable and orderly changes in the composition or structure of an ecological community...
, and are the dominating life forms in extreme environments, including polar
Polar region
Earth's polar regions are the areas of the globe surrounding the poles also known as frigid zones. The North Pole and South Pole being the centers, these regions are dominated by the polar ice caps, resting respectively on the Arctic Ocean and the continent of Antarctica...
, alpine
Alpine climate
Alpine climate is the average weather for a region above the tree line. This climate is also referred to as mountain climate or highland climate....
, and semiarid desert regions. They are able to grow on inhospitable surfaces, including bare soil, rocks, tree bark
Bark
Bark is the outermost layers of stems and roots of woody plants. Plants with bark include trees, woody vines and shrubs. Bark refers to all the tissues outside of the vascular cambium and is a nontechnical term. It overlays the wood and consists of the inner bark and the outer bark. The inner...
, wood, shells, barnacles and leaves. As in mycorrhiza
Mycorrhiza
A mycorrhiza is a symbiotic association between a fungus and the roots of a vascular plant....
s, the photobiont provides sugars and other carbohydrates via photosynthesis
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a chemical process that converts carbon dioxide into organic compounds, especially sugars, using the energy from sunlight. Photosynthesis occurs in plants, algae, and many species of bacteria, but not in archaea. Photosynthetic organisms are called photoautotrophs, since they can...
, while the fungus provides minerals and water. The functions of both symbiotic organisms are so closely intertwined that they function almost as a single organism; in most cases the resulting organism differs greatly from the individual components. Lichenization is a common mode of nutrition; around 20% of fungi—between 17,500 and 20,000 described species—are lichenized. Characteristics common to most lichens include obtaining organic carbon by photosynthesis, slow growth, small size, long life, long-lasting (seasonal) vegetative reproductive
Vegetative reproduction
Vegetative reproduction is a form of asexual reproduction in plants. It is a process by which new individuals arise without production of seeds or spores...
structures, mineral nutrition obtained largely from airborne sources, and greater tolerance of desiccation
Desiccation
Desiccation is the state of extreme dryness, or the process of extreme drying. A desiccant is a hygroscopic substance that induces or sustains such a state in its local vicinity in a moderately sealed container.-Science:...
than most other photosynthetic organisms in the same habitat.
With insects
Many insects also engage in mutualistic relationshipsAnt-fungus mutualism
Ant-fungus mutualism is a symbiosis seen in certain ant and fungal species, where ants actively cultivate fungus much like humans farm crops as a food source. In some species, the ants and fungi are dependent on each other for survival. The leafcutter ant is a well known example of this symbiosis...
with fungi. Several groups of ants cultivate fungi in the order Agaricales
Agaricales
The fungal order Agaricales, also known as gilled mushrooms , or euagarics, contains some of the most familiar types of mushrooms. The order has 33 extant families, 413 genera, and over 13000 described species, along with five extinct genera known only from the fossil record...
as their primary food source, while ambrosia beetles cultivate various species of fungi in the bark of trees that they infest. Similarly, females of several wood wasp
Wood wasp
The term wood wasp is a colloquial name applied to various unrelated families of Symphyta, whose only shared feature is that the larvae are found in wood. The name is thus applied to "wood wasps" , "parasitic wood wasps" , "cedar wood wasps" , or, at times, to "horntails"...
species (genus Sirex
Sirex
Sirex is a genus of wood wasp in the Siricidae family....
) inject their eggs together with spores of the wood-rotting fungus Amylostereum areolatum into the sapwood of pine
Pine
Pines are trees in the genus Pinus ,in the family Pinaceae. They make up the monotypic subfamily Pinoideae. There are about 115 species of pine, although different authorities accept between 105 and 125 species.-Etymology:...
trees; the growth of the fungus provides ideal nutritional conditions for the development of the wasp larvae. Termites on the African savannah
Savannah
Savannah or savanna is a type of grassland.It can also mean:-People:* Savannah King, a Canadian freestyle swimmer* Savannah Outen, a singer who gained popularity on You Tube...
are also known to cultivate fungi, and yeasts of the genera Candida
Candida (genus)
Candida is a genus of yeasts. Many species are harmless commensals or endosymbionts of animal hosts including humans, but other species, or harmless species in the wrong location, can cause disease. Candida albicans can cause infections in humans and other animals, especially in immunocompromised...
and Lachancea inhabit the gut
Gastrointestinal tract
The human gastrointestinal tract refers to the stomach and intestine, and sometimes to all the structures from the mouth to the anus. ....
of a wide range of insects, including neuroptera
Neuroptera
The insect order Neuroptera, or net-winged insects, includes the lacewings, mantidflies, antlions, and their relatives. The order contains some 6,010 species...
ns, beetle
Beetle
Coleoptera is an order of insects commonly called beetles. The word "coleoptera" is from the Greek , koleos, "sheath"; and , pteron, "wing", thus "sheathed wing". Coleoptera contains more species than any other order, constituting almost 25% of all known life-forms...
s, and cockroach
Cockroach
Cockroaches are insects of the order Blattaria or Blattodea, of which about 30 species out of 4,500 total are associated with human habitations...
es; it is not known whether these fungi benefit their hosts.
As pathogens and parasites

Ophiostoma ulmi
Ophiostoma ulmi is a species of fungus in the Ophiostomataceae family. It is one of the causative agents of Dutch elm disease. It was first described under the name Graphium ulmi, and later transferred to the genus Ophiostoma....
and Ophiostoma novo-ulmi causing Dutch elm disease
Dutch elm disease
Dutch elm disease is a disease caused by a member of the sac fungi category, affecting elm trees which is spread by the elm bark beetle. Although believed to be originally native to Asia, the disease has been accidentally introduced into America and Europe, where it has devastated native...
, and Cryphonectria parasitica responsible for chestnut blight
Chestnut blight
The pathogenic fungus Cryphonectria parasitica is a member of the ascomycota category, and is the main cause of chestnut blight, a devastating disease of the American chestnut tree that caused a mass extinction in the early 1900s of this once plentiful tree from its historic range in the eastern...
, and plant pathogens in the genera Fusarium
Fusarium
Fusarium is a large genus of filamentous fungi widely distributed in soil and in association with plants. Most species are harmless saprobes, and are relatively abundant members of the soil microbial community. Some species produce mycotoxins in cereal crops that can affect human and animal health...
, Ustilago
Ustilago
Ustilago is a genus of approximately 200 smut fungi parasitic on grasses.There is a large research community that works on Ustilago maydis including researchers at the University of Georgia, Philipps-Universität Marburg, University of British Columbia and others...
, Alternaria
Alternaria
Alternaria is a genus of ascomycete fungi. Alternaria species are known as major plant pathogens. They are also common allergens in humans, growing indoors and causing hay fever or hypersensitivity reactions that sometimes lead to asthma...
, and Cochliobolus
Cochliobolus
The fungal genus Cochliobolus includes 55 species , including the following plant pathogenic species: C. carbonum, C. heterostrophus, C. miyabeanus, C. sativus and C...
. Some carnivorous fungi, like Paecilomyces lilacinus, are predators
Nematophagous fungus
Nematophagous fungi are carnivorous fungi specialized in trapping and digesting nematodes. Around 160 species are known. There exist both species that live inside the nematodes from the beginning and others that catch them mostly with glue traps or in rings, some of which constrict on contact. Some...
of nematodes, which they capture using an array of specialized structures such as constricting rings or adhesive nets.
Some fungi can cause serious diseases in humans, several of which may be fatal if untreated. These include aspergilloses
Aspergillosis
Aspergillosis is the name given to a wide variety of diseases caused by fungi of the genus Aspergillus. The most common forms are allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis, pulmonary aspergilloma and invasive aspergillosis. Most humans inhale Aspergillus spores every day...
, candidoses, coccidioidomycosis
Coccidioidomycosis
Coccidioidomycosis is a fungal disease caused by Coccidioides immitis or C. posadasii. It is endemic in certain parts of Arizona, California, Nevada, New Mexico, Texas, Utah and northwestern Mexico.C...
, cryptococcosis
Cryptococcosis
Cryptococcosis, or cryptococcal disease, is a potentially fatal fungal disease. It is caused by one of two species; Cryptococcus neoformans and Cryptococcus gattii. These were all previously thought to be subspecies of C...
, histoplasmosis
Histoplasmosis
Histoplasmosis is a disease caused by the fungus Histoplasma capsulatum. Symptoms of this infection vary greatly, but the disease primarily affects the lungs...
, mycetomas
Eumycetoma
Eumycetoma is a chronic, specific, granulomatous, fungal disease. It mainly affects the foot; and Mycetoma pedis is also known as Madura foot. This infection is endemic in Africa, India, and Central and South America.-Causes and presentation:...
, and paracoccidioidomycosis
Paracoccidioidomycosis
Paracoccidioidomycosis is a mycosis caused by the fungus Paracoccidioides brasiliensis...
. Furthermore, persons with immuno-deficiencies
Immunodeficiency
Immunodeficiency is a state in which the immune system's ability to fight infectious disease is compromised or entirely absent. Immunodeficiency may also decrease cancer immunosurveillance. Most cases of immunodeficiency are acquired but some people are born with defects in their immune system,...
are particularly susceptible to disease by genera such as Aspergillus
Aspergillus
Aspergillus is a genus consisting of several hundred mold species found in various climates worldwide. Aspergillus was first catalogued in 1729 by the Italian priest and biologist Pier Antonio Micheli...
, Candida
Candida (genus)
Candida is a genus of yeasts. Many species are harmless commensals or endosymbionts of animal hosts including humans, but other species, or harmless species in the wrong location, can cause disease. Candida albicans can cause infections in humans and other animals, especially in immunocompromised...
, Cryptoccocus
Cryptococcus neoformans
Cryptococcus neoformans is an encapsulated yeast that can live in both plants and animals. Its teleomorph is Filobasidiella neoformans, a filamentous fungus belonging to the class Tremellomycetes. It is often found in pigeon excrement....
, Histoplasma
Histoplasma
Histoplasma is a genus of dimorphic fungi commonly found in bird and bat fecal material. Histoplasma contains a few species, including—H. capsulatum—the causative agent of histoplasmosis; and Histoplasma capsulatum var. farciminosum , causing epizootic lymphangitis in horses...
, and Pneumocystis. Other fungi can attack eyes, nails, hair, and especially skin, the so-called dermatophytic
Dermatophyte
Dermatophytes are a common label for a group of three types of fungus that commonly causes skin disease in animals and humans. These anamorphic genera are: Microsporum, Epidermophyton and Trichophyton. There are about 40 species in these three genera...
and keratinophilic fungi, and cause local infections such as ringworm and athlete’s foot. Fungal spores are also a cause of allergies, and fungi from different taxonomic groups can evoke allergic reactions.
Human use

Ethnomycology
Ethnomycology is the study of the historical uses and sociological impact of fungi , and can be considered a subfield of ethnobotany or ethnobiology...
. Because of the capacity of this group to produce an enormous range of natural products with antimicrobial
Antimicrobial
An anti-microbial is a substance that kills or inhibits the growth of microorganisms such as bacteria, fungi, or protozoans. Antimicrobial drugs either kill microbes or prevent the growth of microbes...
or other biological activities, many species have long been used or are being developed for industrial production of antibiotics
Production of antibiotics
The production of antibiotics has been widespread since the pioneering efforts of Florey and Chain in 1938. The importance of antibiotics to medicine has led to much research into their discovery and production.- Identifying useful antibiotics :...
, vitamins, and anti-cancer and cholesterol-lowering
Lovastatin
Lovastatin is a member of the drug class of statins, used for lowering cholesterol in those with hypercholesterolemia and so preventing cardiovascular disease...
drugs. More recently, methods have been developed for genetic engineering
Genetic engineering
Genetic engineering, also called genetic modification, is the direct human manipulation of an organism's genome using modern DNA technology. It involves the introduction of foreign DNA or synthetic genes into the organism of interest...
of fungi, enabling metabolic engineering
Metabolic engineering
Metabolic engineering is the practice of optimizing genetic and regulatory processes within cells to increase the cells' production of a certain substance. These processes are chemical networks that use a series of biochemical reactions and enzymes that allow cells to convert raw materials into...
of fungal species. For example, genetic modification of yeast species—which are easy to grow at fast rates in large fermentation vessels—has opened up ways of pharmaceutical production that are potentially more efficient than production by the original source organisms.
Drugs
Many species produce metabolites that are major sources of pharmacologicallyPharmacology
Pharmacology is the branch of medicine and biology concerned with the study of drug action. More specifically, it is the study of the interactions that occur between a living organism and chemicals that affect normal or abnormal biochemical function...
active drugs. Particularly important are the antibiotics, including the penicillin
Penicillin
Penicillin is a group of antibiotics derived from Penicillium fungi. They include penicillin G, procaine penicillin, benzathine penicillin, and penicillin V....
s, a structurally related group of β-lactam antibiotics that are synthesized from small peptide
Peptide
Peptides are short polymers of amino acid monomers linked by peptide bonds. They are distinguished from proteins on the basis of size, typically containing less than 50 monomer units. The shortest peptides are dipeptides, consisting of two amino acids joined by a single peptide bond...
s. Although naturally occurring penicillins such as penicillin G (produced by Penicillium chrysogenum
Penicillium chrysogenum
Penicillium chrysogenum is common in temperate and subtropical regions and can be found on salted food products, but it is mostly found in indoor environments, especially in damp or waterdamaged buildings. It was previously known as Penicillium notatum. It has rarely been reported as a cause of...
) have a relatively narrow spectrum of biological activity, a wide range of other penicillins can be produced by chemical modification
Chemical synthesis
In chemistry, chemical synthesis is purposeful execution of chemical reactions to get a product, or several products. This happens by physical and chemical manipulations usually involving one or more reactions...
of the natural penicillins. Modern penicillins are semisynthetic compounds, obtained initially from fermentation
Fermentation (biochemistry)
Fermentation is the process of extracting energy from the oxidation of organic compounds, such as carbohydrates, using an endogenous electron acceptor, which is usually an organic compound. In contrast, respiration is where electrons are donated to an exogenous electron acceptor, such as oxygen,...
cultures, but then structurally altered for specific desirable properties. Other antibiotics produced by fungi include: ciclosporin
Ciclosporin
Ciclosporin , cyclosporine , cyclosporin , or cyclosporin A is an immunosuppressant drug widely used in post-allogeneic organ transplant to reduce the activity of the immune system, and therefore the risk of organ rejection...
, commonly used as an immunosuppressant
Immunosuppressant
An immunosuppressant is any substance that performs immunosuppression of the immune system. They may be either exogenous, as immunosuppressive drugs, or endogenous, as ,e. g., testosterone...
during transplant surgery
Organ transplant
Organ transplantation is the moving of an organ from one body to another or from a donor site on the patient's own body, for the purpose of replacing the recipient's damaged or absent organ. The emerging field of regenerative medicine is allowing scientists and engineers to create organs to be...
; and fusidic acid
Fusidic acid
Fusidic acid is a bacteriostatic antibiotic that is often used topically in creams and eyedrops, but may also be given systemically as tablets or injections...
, used to help control infection from methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus is a bacterium responsible for several difficult-to-treat infections in humans. It is also called multidrug-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and oxacillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus...
bacteria. Widespread use of these antibiotics for the treatment of bacterial diseases, such as tuberculosis
Tuberculosis
Tuberculosis, MTB, or TB is a common, and in many cases lethal, infectious disease caused by various strains of mycobacteria, usually Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Tuberculosis usually attacks the lungs but can also affect other parts of the body...
, syphilis
Syphilis
Syphilis is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the spirochete bacterium Treponema pallidum subspecies pallidum. The primary route of transmission is through sexual contact; however, it may also be transmitted from mother to fetus during pregnancy or at birth, resulting in congenital syphilis...
, leprosy
Leprosy
Leprosy or Hansen's disease is a chronic disease caused by the bacteria Mycobacterium leprae and Mycobacterium lepromatosis. Named after physician Gerhard Armauer Hansen, leprosy is primarily a granulomatous disease of the peripheral nerves and mucosa of the upper respiratory tract; skin lesions...
, and many others began in the early 20th century and continues to play a major part in anti-bacterial
Antiseptic
Antiseptics are antimicrobial substances that are applied to living tissue/skin to reduce the possibility of infection, sepsis, or putrefaction...
chemotherapy
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy is the treatment of cancer with an antineoplastic drug or with a combination of such drugs into a standardized treatment regimen....
. In nature, antibiotics of fungal or bacterial origin appear to play a dual role: at high concentrations they act as chemical defense against competition with other microorganisms in species-rich environments, such as the rhizosphere
Rhizosphere (ecology)
The rhizosphere is the narrow region of soil that is directly influenced by root secretions and associated soil microorganisms. Soil which is not part of the rhizosphere is known as bulk soil. The rhizosphere contains many bacteria that feed on sloughed-off plant cells, termed rhizodeposition, and...
, and at low concentrations as quorum-sensing
Quorum sensing
Quorum sensing is a system of stimulus and response correlated to population density. Many species of bacteria use quorum sensing to coordinate gene expression according to the density of their local population. In similar fashion, some social insects use quorum sensing to determine where to nest...
molecules for intra- or interspecies signaling.
Other drugs produced by fungi include griseofulvin
Griseofulvin
Griseofulvin is an antifungal drug that is administered orally. It is used both in animals and in humans, to treat fungal infections of the skin and nails...
isolated from Penicillium griseofulvum, used to treat fungal infections, and statin
Statin
Statins are a class of drugs used to lower cholesterol levels by inhibiting the enzyme HMG-CoA reductase, which plays a central role in the production of cholesterol in the liver. Increased cholesterol levels have been associated with cardiovascular diseases, and statins are therefore used in the...
s (HMG-CoA reductase
HMG-CoA reductase
HMG-CoA reductase is the rate-controlling enzyme of the mevalonate pathway, the metabolic pathway that produces cholesterol and other isoprenoids...
inhibitors), used to inhibit cholesterol synthesis. Examples of statins found in fungi include mevastatin
Mevastatin
Mevastatin, compactin, ML-236B is a hypolipidemic agent that belongs to the statins class.It was isolated from the mold Penicillium citrinum by Akira Endo in the 1970s and he identified it as a HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor, i.e.; a statin...
from Penicillium citrinum and lovastatin
Lovastatin
Lovastatin is a member of the drug class of statins, used for lowering cholesterol in those with hypercholesterolemia and so preventing cardiovascular disease...
from Aspergillus terreus
Aspergillus terreus
Aspergillus terreus is a fungus commonly used in industry to produce important organic acids, such as itaconic acid and cis-aconitic acid. It was also the initial source for the drug mevinolin , a drug for lowering serum cholesterol. A. terreus may cause opportunistic infection in people with...
and the oyster mushroom.
Cultured foods
Baker's yeastBaker's yeast
Baker's yeast is the common name for the strains of yeast commonly used as a leavening agent in baking bread and bakery products, where it converts the fermentable sugars present in the dough into carbon dioxide and ethanol...
or Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Saccharomyces cerevisiae is a species of yeast. It is perhaps the most useful yeast, having been instrumental to baking and brewing since ancient times. It is believed that it was originally isolated from the skin of grapes...
, a single-celled fungus, is used to make bread
Bread
Bread is a staple food prepared by cooking a dough of flour and water and often additional ingredients. Doughs are usually baked, but in some cuisines breads are steamed , fried , or baked on an unoiled frying pan . It may be leavened or unleavened...
and other wheat-based products, such as pizza
Pizza
Pizza is an oven-baked, flat, disc-shaped bread typically topped with a tomato sauce, cheese and various toppings.Originating in Italy, from the Neapolitan cuisine, the dish has become popular in many parts of the world. An establishment that makes and sells pizzas is called a "pizzeria"...
dough and dumpling
Dumpling
Dumplings are cooked balls of dough. They are based on flour, potatoes or bread, and may include meat, fish, vegetables, or sweets. They may be cooked by boiling, steaming, simmering, frying, or baking. They may have a filling, or there may be other ingredients mixed into the dough. Dumplings may...
s. Yeast species of the genus Saccharomyces
Saccharomyces
Saccharomyces is a genus in the kingdom of fungi that includes many species of yeast. Saccharomyces is from Greek σάκχαρ and μύκης and means sugar fungus. Many members of this genus are considered very important in food production. One example is Saccharomyces cerevisiae, which is used in making...
are also used to produce alcoholic beverage
Alcoholic beverage
An alcoholic beverage is a drink containing ethanol, commonly known as alcohol. Alcoholic beverages are divided into three general classes: beers, wines, and spirits. They are legally consumed in most countries, and over 100 countries have laws regulating their production, sale, and consumption...
s through fermentation. Shoyu koji mold (Aspergillus oryzae
Aspergillus oryzae
Aspergillus oryzae is a filamentous fungus . It is used in Chinese and Japanese cuisine to ferment soybeans. It is also used to saccharify rice, other grains, and potatoes in the making of alcoholic beverages such as huangjiu, sake, and shōchū...
) is an essential ingredient in brewing Shoyu (soy sauce
Soy sauce
Soy sauce is a condiment produced by fermenting soybeans with Aspergillus oryzae or Aspergillus sojae molds, along with water and salt...
) and sake, and the preparation of miso
Miso
is a traditional Japanese seasoning produced by fermenting rice, barley and/or soybeans, with salt and the fungus , the most typical miso being made with soy. The result is a thick paste used for sauces and spreads, pickling vegetables or meats, and mixing with dashi soup stock to serve as miso...
, while Rhizopus
Rhizopus
Rhizopus is a genus of common saprobic fungi on plants and specialized parasites on animals. They are found on a wide variety of organic substrates, including "mature fruits and vegetables", faeces, jellies, syrups, leather, bread, peanuts and tobacco. Some Rhizopus species are opportunistic agents...
species are used for making tempeh
Tempeh
Tempeh , or tempe , is a traditional soy product originally from Indonesia. It is made by a natural culturing and controlled fermentation process that binds soybeans into a cake form, similar to a very firm vegetarian burger patty...
. Several of these fungi are domesticated
Domestication
Domestication or taming is the process whereby a population of animals or plants, through a process of selection, becomes accustomed to human provision and control. In the Convention on Biological Diversity a domesticated species is defined as a 'species in which the evolutionary process has been...
species that were bred
Breeding program
Breeding programs help animals to breed and can be good for animals as well as the agricultural economy.A breeding program is the planned breeding of a group of animals or plants, usually involving at least several individuals and extending over several generations...
or selected according to their capacity to ferment food without producing harmful mycotoxins (see below), which are produced by very closely related Aspergilli
Aspergillus flavus
Aspergillus flavus is a fungus. It is a common mold in the environment, and can cause storage problems in stored grains. It can also be a human pathogen, associated with aspergillosis of the lungs and sometimes causing corneal, otomycotic, and nasoorbital infections. Many strains produce...
. Quorn
Quorn
Quorn is the leading brand of mycoprotein food product in the UK and Ireland. The mycoprotein used to produce Quorn is extracted from a fungus, Fusarium venenatum, which is grown in large vats....
, a meat substitute
Meat analogue
A meat analogue, also called a meat substitute, mock meat, faux meat, or imitation meat, approximates the aesthetic qualities and/or chemical characteristics of specific types of meat...
, is made from Fusarium venenatum
Fusarium venenatum
Fusarium venenatum is a microfungus of the genus Fusarium that has a high protein content. One of its strains is used commercially for the production of the single cell protein mycoprotein....
.
Medicinal use
Certain mushrooms enjoy usage as therapeutics in folk medicineFolk medicine
-Description:Refers to healing practices and ideas of body physiology and health preservation known to a limited segment of the population in a culture, transmitted informally as general knowledge, and practiced or applied by anyone in the culture having prior experience.All cultures and societies...
s, such as Traditional Chinese medicine
Traditional Chinese medicine
Traditional Chinese Medicine refers to a broad range of medicine practices sharing common theoretical concepts which have been developed in China and are based on a tradition of more than 2,000 years, including various forms of herbal medicine, acupuncture, massage , exercise , and dietary therapy...
. Notable medicinal mushrooms with a well-documented history of use include Agaricus subrufescens, Ganoderma lucidum, and Ophiocordyceps sinensis. Research has identified compounds produced by these and other fungi that have inhibitory biological effects against virus
Virus
A virus is a small infectious agent that can replicate only inside the living cells of organisms. Viruses infect all types of organisms, from animals and plants to bacteria and archaea...
es and cancer cells. Specific metabolites, such as polysaccharide-K
Polysaccharide-K
Polysaccharide-K is a protein-bound polysaccharide, which is used as an immune system boosting agent in the treatment of cancer in some countries in Europe as well as China and Japan. In Japan, PSK is approved as an adjuvant for cancer therapy and is covered by government health insurance...
, ergotamine, and β-lactam antibiotics
Beta-lactam antibiotic
β-Lactam antibiotics are a broad class of antibiotics, consisting of all antibiotic agents that contains a β-lactam nucleus in its molecular structure. This includes penicillin derivatives , cephalosporins , monobactams, and carbapenems...
, are routinely used in clinical medicine. The shiitake
Shiitake
The Shiitake is an edible mushroom native to East Asia, which is cultivated and consumed in many Asian countries, as well as being dried and exported to many countries around the world. It is a feature of many Asian cuisines including Vietnamese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean and Thai...
mushroom is a source of lentinan
Lentinan
Lentinan is a beta-glucan with a glycosidic β-1,3:β-1,6 linkage. It is an anti-tumor polysaccharide from the shiitake mushroom. Lentinan is a polysaccharide that has a molecular weight of approximately 500,000 Da...
, a clinical drug approved for use in cancer treatments in several countries, including Japan
Japan
Japan is an island nation in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean, it lies to the east of the Sea of Japan, China, North Korea, South Korea and Russia, stretching from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea and Taiwan in the south...
. In Europe
Europe
Europe is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting...
and Japan
Japan
Japan is an island nation in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean, it lies to the east of the Sea of Japan, China, North Korea, South Korea and Russia, stretching from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea and Taiwan in the south...
, polysaccharide-K
Polysaccharide-K
Polysaccharide-K is a protein-bound polysaccharide, which is used as an immune system boosting agent in the treatment of cancer in some countries in Europe as well as China and Japan. In Japan, PSK is approved as an adjuvant for cancer therapy and is covered by government health insurance...
(brand name Krestin), a chemical derived from Trametes versicolor
Trametes versicolor
Trametes versicolor — formerly known as Coriolus versicolor and Polyporus versicolor — is an extremely common polypore mushroom which can be found throughout the world. Versicolor means 'of several colours' and it is true that this mushroom is found in a wide variety of different colours. T...
, is an approved adjuvant
Adjuvant
An adjuvant is a pharmacological or immunological agent that modifies the effect of other agents, such as a drug or vaccine, while having few if any direct effects when given by itself...
for cancer therapy.
Edible and poisonous species

Edible mushroom
Edible mushrooms are the fleshy and edible fruiting bodies of several species of fungi. Mushrooms belong to the macrofungi, because their fruiting structures are large enough to be seen with the naked eye. They can appear either below ground or above ground where they may be picked by hand...
s are well-known examples of fungi. Many are commercially raised, but others must be harvested from the wild. Agaricus bisporus, sold as button mushrooms when small or Portobello mushrooms when larger, is a commonly eaten species, used in salads, soups, and many other dishes. Many Asian fungi are commercially grown and have increased in popularity in the West. They are often available fresh in grocery store
Grocery store
A grocery store is a store that retails food. A grocer, the owner of a grocery store, stocks different kinds of foods from assorted places and cultures, and sells these "groceries" to customers. Large grocery stores that stock products other than food, such as clothing or household items, are...
s and markets, including straw mushrooms (Volvariella volvacea
Volvariella volvacea
Volvariella volvacea is a species of edible mushroom cultivated throughout East and Southeast Asia and used extensively in Asian cuisines. In Chinese, they are called cǎogū Volvariella volvacea (also known as straw mushroom or paddy straw mushroom; syn. Volvaria volvacea, Agaricus volvaceus,...
), oyster mushrooms (Pleurotus ostreatus), shiitakes (Lentinula edodes), and enokitake
Enokitake
Enokitake , also Enokidake or Enoki are long, thin white mushrooms used in East Asian cuisine . These mushrooms are cultivars of Flammulina velutipes also called golden needle mushroom...
(Flammulina
Flammulina
Flammulina is a genus of fungi in the Physalacriaceae family. The genus, widespread in temperate regions, has been estimated to contain 10 species.-List of species:* Flammulina callistosporioides* Flammulina elastica* Flammulina fennae...
spp.).
There are many more mushroom species that are harvested from the wild
Mushroom hunting
Mushroom hunting, mushrooming, mushroom picking, and similar terms describe the activity of gathering mushrooms in the wild, typically for eating...
for personal consumption or commercial sale. Milk mushrooms
Lactarius deliciosus
Lactarius deliciosus, commonly known as the Saffron milk cap, Red pine mushroom, is one of the best known members of the large milk-cap genus Lactarius in the order Russulales...
, morel
Morel
Morchella, the true morels, is a genus of edible mushrooms closely related to anatomically simpler cup fungi. These distinctive mushrooms appear honeycomb-like in that the upper portion is composed of a network of ridges with pits between them....
s, chanterelle
Chanterelle
Cantharellus cibarius, commonly known as the chanterelle, golden chanterelle or girolle, is a fungus. It is probably the best known species of the genus Cantharellus, if not the entire family of Cantharellaceae. It is orange or yellow, meaty and funnel-shaped...
s, truffles, black trumpets
Craterellus
Craterellus is a genus of generally edible fungi similar to the closely related chanterelles, with some species recently reassigned to this genus. They are distinguished by their lack of gill-like structures on the underside of their caps....
, and porcini mushrooms (Boletus edulis
Boletus edulis
Boletus edulis, commonly known as penny bun, porcino or cep, is a basidiomycete fungus, and the type species of the genus Boletus. Widely distributed in the Northern Hemisphere across Europe, Asia, and North America, it does not occur naturally in the Southern Hemisphere, although it has been...
) (also known as king boletes) demand a high price on the market. They are often used in gourmet dishes.
Certain types of cheeses require inoculation of milk curds with fungal species that impart a unique flavor and texture to the cheese. Examples include the blue
Blue cheese
Blue cheese is a general classification of cow's milk, sheep's milk, or goat's milk cheeses that have had cultures of the mold Penicillium added so that the final product is spotted or veined throughout with blue, blue-gray or blue-green mold, and carries a distinct smell, either from that or...
color in cheeses such as Stilton or Roquefort, which are made by inoculation with Penicillium roqueforti
Penicillium roqueforti
Penicillium roqueforti is a common saprotrophic fungus from the family Trichocomaceae. Widespread in nature, it can be isolated from soil, decaying organic matter, and plants. The major industrial use of this fungus is the production of blue cheeses, flavouring agents, antifungals, polysaccharides,...
. Molds used in cheese production are non-toxic and are thus safe for human consumption; however, mycotoxins (e.g., aflatoxins, roquefortine C
Roquefortine C
Roquefortin C is a mycotoxin produced by various fungi, particularly species from the Penicillium genus. It was first isolated from a strain of Penicillium roqueforti, a species commercially used to make Roquefort cheese.-References:*...
, patulin, or others) may accumulate because of growth of other fungi during cheese ripening or storage.

Mushroom poisoning
Mushroom poisoning refers to harmful effects from ingestion of toxic substances present in a mushroom. These symptoms can vary from slight gastrointestinal discomfort to death. The toxins present are secondary metabolites produced in specific biochemical pathways in the fungal cells...
to humans, with toxicities ranging from slight digestive problems or allergic
Allergy
An Allergy is a hypersensitivity disorder of the immune system. Allergic reactions occur when a person's immune system reacts to normally harmless substances in the environment. A substance that causes a reaction is called an allergen. These reactions are acquired, predictable, and rapid...
reactions as well as hallucination
Hallucination
A hallucination, in the broadest sense of the word, is a perception in the absence of a stimulus. In a stricter sense, hallucinations are defined as perceptions in a conscious and awake state in the absence of external stimuli which have qualities of real perception, in that they are vivid,...
s to severe organ failures and death. Genera with mushrooms containing deadly toxins include Conocybe
Conocybe
The genus Conocybe is a genus of mushrooms consisting of Conocybe tenera and at least 243 other species, with at least 50 species in North America....
, Galerina
Galerina
Galerina is a genus of small brown-spored saprobic mushrooms, with over 300 species found throughout the world, from the far north to remote Macquarie Island in the Southern Ocean. Species are typically small and hygrophanous, with a slender and brittle stem. They are often found growing on wood,...
, Lepiota
Lepiota
Lepiota is a genus of gilled mushrooms in the family Agaricaceae. All Lepiota species are ground-dwelling saprotrophs with a preference for rich, calcareous soils. Basidiocarps are agaricoid with whitish spores, typically with scaly caps and a ring on the stem. Around 400 species of Lepiota are...
, and most infamously, Amanita
Amanita
The genus Amanita contains about 600 species of agarics including some of the most toxic known mushrooms found worldwide. This genus is responsible for approximately 95% of the fatalities resulting from mushroom poisoning, with the death cap accounting for about 50% on its own...
. The latter genus includes the destroying angel (A. virosa
Amanita virosa
Amanita virosa, commonly known as the European destroying angel, is a deadly poisonous basidiomycete fungus, one of many in the genus Amanita. Occurring in Europe, A. virosa associates with various deciduous and coniferous trees...
) and the death cap (A. phalloides), the most common cause of deadly mushroom poisoning. The false morel (Gyromitra esculenta) is occasionally considered a delicacy when cooked, yet can be highly toxic when eaten raw. Tricholoma equestre
Tricholoma equestre
Tricholoma equestre or Tricholoma flavovirens, also known as Man on horseback or Yellow knight is a formerly widely eaten but hazardous fungus of the Tricholoma genus that forms ectomycorrhiza with pine trees....
was considered edible until being implicated in serious poisonings causing rhabdomyolysis
Rhabdomyolysis
Rhabdomyolysis is a condition in which damaged skeletal muscle tissue breaks down rapidly. Breakdown products of damaged muscle cells are released into the bloodstream; some of these, such as the protein myoglobin, are harmful to the kidneys and may lead to kidney failure...
. Fly agaric
Amanita muscaria
Amanita muscaria, commonly known as the fly agaric or fly amanita , is a poisonous and psychoactive basidiomycete fungus, one of many in the genus Amanita...
mushrooms (Amanita muscaria) also cause occasional non-fatal poisonings, mostly as a result of ingestion for use as a recreational
Recreational drug use
Recreational drug use is the use of a drug, usually psychoactive, with the intention of creating or enhancing recreational experience. Such use is controversial, however, often being considered to be also drug abuse, and it is often illegal...
drug for its hallucinogenic
Psychedelics, dissociatives and deliriants
This general group of pharmacological agents can be divided into three broad categories: psychedelics, dissociatives, and deliriants. These classes of psychoactive drugs have in common that they can cause subjective changes in perception, thought, emotion and consciousness...
properties. Historically, fly agaric was used by different peoples in Europe and Asia and its present usage for religious or shamanic
Shamanism
Shamanism is an anthropological term referencing a range of beliefs and practices regarding communication with the spiritual world. To quote Eliade: "A first definition of this complex phenomenon, and perhaps the least hazardous, will be: shamanism = technique of ecstasy." Shamanism encompasses the...
purposes is reported from some ethnic groups such as the Koryak people
Koryaks
Koryaks are an indigenous people of Kamchatka Krai in the Russian Far East, who inhabit the coastlands of the Bering Sea to the south of the Anadyr basin and the country to the immediate north of the Kamchatka Peninsula, the southernmost limit of their range being Tigilsk. They are akin to the...
of north-eastern Siberia
Siberia
Siberia is an extensive region constituting almost all of Northern Asia. Comprising the central and eastern portion of the Russian Federation, it was part of the Soviet Union from its beginning, as its predecessor states, the Tsardom of Russia and the Russian Empire, conquered it during the 16th...
.
As it is difficult to accurately identify a safe mushroom without proper training and knowledge, it is often advised to assume that a wild mushroom is poisonous and not to consume it.
Pest control

Pathogen
A pathogen gignomai "I give birth to") or infectious agent — colloquially, a germ — is a microbe or microorganism such as a virus, bacterium, prion, or fungus that causes disease in its animal or plant host...
ic microorganisms such as bacteria or other fungi via the competitive exclusion principle
Competitive exclusion principle
In ecology, the competitive exclusion principle, sometimes referred to as Gause's law of competitive exclusion or just Gause's law, is a proposition which states that two species competing for the same resources cannot coexist if other ecological factors are constant...
, or if they are parasites
Parasitism
Parasitism is a type of symbiotic relationship between organisms of different species where one organism, the parasite, benefits at the expense of the other, the host. Traditionally parasite referred to organisms with lifestages that needed more than one host . These are now called macroparasites...
of these pathogens. For example, certain species may be used to eliminate or suppress the growth of harmful plant pathogens, such as insects, mites
MITES
MITES, or Minority Introduction to Engineering and Science, is a highly selective six-week summer program for rising high school seniors held at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology. Its purpose is to expose students from minority, or otherwise disadvantaged backgrounds, to the fields of...
, weed
Weed
A weed in a general sense is a plant that is considered by the user of the term to be a nuisance, and normally applied to unwanted plants in human-controlled settings, especially farm fields and gardens, but also lawns, parks, woods, and other areas. More specifically, the term is often used to...
s, nematodes and other fungi that cause diseases of important crop
Crop
Crop may refer to:* Crop, a plant grown and harvested for agricultural use* Crop , part of the alimentary tract of some animals* Crop , a modified whip used in horseback riding or disciplining humans...
plants. This has generated strong interest in practical applications that use these fungi in the biological control of these agricultural pests. Entomopathogenic fungi can be used as biopesticides, as they actively kill insects. Examples that have been used as biological insecticides are Beauveria bassiana
Beauveria bassiana
Beauveria bassiana is a fungus that grows naturally in soils throughout the world and acts as a parasite on various arthropod species, causing white muscardine disease; it thus belongs to the entomopathogenic fungi. It is being used as a biological insecticide to control a number of pests such as...
, Metarhizium
Metarhizium
Metarhizium is a genus of entomopathogenic fungi in the Clavicipitaceae family. With the advent of genetic profiling, it has now become possible to place these fungi in proper taxa. Most turn out to be the asexual forms of fungi in the phylum Ascomycota.- Species :Nine distinct species have now...
spp, Hirsutella
Hirsutella
Hirsutella is a genus of asexually reproducing fungi in the Ophiocordycipitaceae family. Originally described by French mycologist Narcisse Théophile Patouillard in 1892, this genus includes species that are pathogens of insects, mites and nematodes; there is interest in the use of these fungi as...
spp, Paecilomyces
Paecilomyces
Paecilomyces is a genus of nematophagous fungus which kills harmful nematodes by pathogenesis, causing disease in the nematodes. Therefore the fungus can be used as a bio-nematicide to control nematodes by applying it to soil.-Species:...
(Isaria) spp, and Lecanicillium lecanii
Lecanicillium lecanii
Lecanicillium lecanii is now an approved name of an entomopathogenic fungus species, that was previously widely known as Verticillium lecanii Viegas), but is now understood to be an anamorphic form in the Cordyceps group of genera in the Clavicipitaceae . It now appears that isolates formerly...
. Endophytic fungi of grasses of the genus Neotyphodium
Neotyphodium
Neotyphodium is a form genus containing species of endophytic fungi. These endophytes are asexual, seed-borne symbionts of cool-season grasses, and grow intercellularly throughout the aerial tissues of their hosts, including shoot apical meristems, leaf sheaths and blades, inflorescences, seeds and...
, such as N. coenophialum
Neotyphodium coenophialum
Neotyphodium coenophialum is a systemic and seed-transmissible symbiont of Schedonorus arundinaceus , a grass endemic to Eurasia and North Africa, but widely naturalized in North America, Australia and New Zealand / Aotearoa...
, produce alkaloids that are toxic to a range of invertebrate and vertebrate herbivores. These alkaloids protect grass plants from herbivory, but several endophyte alkaloids can poison grazing animals, such as cattle and sheep. Infecting cultivars of pasture
Pasture
Pasture is land used for grazing. Pasture lands in the narrow sense are enclosed tracts of farmland, grazed by domesticated livestock, such as horses, cattle, sheep or swine. The vegetation of tended pasture, forage, consists mainly of grasses, with an interspersion of legumes and other forbs...
or forage
Forage
Forage is plant material eaten by grazing livestock.Historically the term forage has meant only plants eaten by the animals directly as pasture, crop residue, or immature cereal crops, but it is also used more loosely to include similar plants cut for fodder and carried to the animals, especially...
grasses with Neotyphodium endophytes is one approach being used in grass breeding
Plant breeding
Plant breeding is the art and science of changing the genetics of plants in order to produce desired characteristics. Plant breeding can be accomplished through many different techniques ranging from simply selecting plants with desirable characteristics for propagation, to more complex molecular...
programs; the fungal strains are selected for producing only alkaloids that increase resistance to herbivores such as insects, while being non-toxic to livestock.
Bioremediation
Certain fungi, in particular "white rot" fungi, can degrade insecticideInsecticide
An insecticide is a pesticide used against insects. They include ovicides and larvicides used against the eggs and larvae of insects respectively. Insecticides are used in agriculture, medicine, industry and the household. The use of insecticides is believed to be one of the major factors behind...
s, herbicide
Herbicide
Herbicides, also commonly known as weedkillers, are pesticides used to kill unwanted plants. Selective herbicides kill specific targets while leaving the desired crop relatively unharmed. Some of these act by interfering with the growth of the weed and are often synthetic "imitations" of plant...
s, pentachlorophenol
Pentachlorophenol
Pentachlorophenol is an organochlorine compound used as a pesticide and a disinfectant. First produced in the 1930s, it is marketed under many trade names...
, creosote
Creosote
Creosote is the portion of chemical products obtained by the distillation of a tar that remains heavier than water, notably useful for its anti-septic and preservative properties...
, coal tar
Coal tar
Coal tar is a brown or black liquid of extremely high viscosity, which smells of naphthalene and aromatic hydrocarbons. Coal tar is among the by-products when coal iscarbonized to make coke or gasified to make coal gas...
s, and heavy fuels and turn them into carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a naturally occurring chemical compound composed of two oxygen atoms covalently bonded to a single carbon atom...
, water, and basic elements. Fungi have been shown to biomineralize uranium
Uranium
Uranium is a silvery-white metallic chemical element in the actinide series of the periodic table, with atomic number 92. It is assigned the chemical symbol U. A uranium atom has 92 protons and 92 electrons, of which 6 are valence electrons...
oxide
Oxide
An oxide is a chemical compound that contains at least one oxygen atom in its chemical formula. Metal oxides typically contain an anion of oxygen in the oxidation state of −2....
s, suggesting they may have application in the bioremediation of radioactively polluted sites.
Model organisms
Several pivotal discoveries in biology were made by researchers using fungi as model organisms, that is, fungi that grow and sexually reproduce rapidly in the laboratory. For example, the one gene-one enzyme hypothesisOne gene-one enzyme hypothesis
The one gene-one enzyme hypothesis is the idea that genes act through the production of enzymes, with each gene responsible for producing a single enzyme that in turn affects a single step in a metabolic pathway...
was formulated by scientists who used the bread mold Neurospora crassa
Neurospora crassa
Neurospora crassa is a type of red bread mold of the phylum Ascomycota. The genus name, meaning "nerve spore" refers to the characteristic striations on the spores. The first published account of this fungus was from an infestation of French bakeries in 1843. N...
to test their biochemical theories. Other important model fungi are Aspergillus nidulans
Aspergillus nidulans
Aspergillus nidulans is one of many species of filamentous fungi in the phylum Ascomycota...
and the yeasts, Saccaromyces cerevisiae and Schizosaccharomyces pombe
Schizosaccharomyces pombe
Schizosaccharomyces pombe, also called "fission yeast", is a species of yeast. It is used as a model organism in molecular and cell biology. It is a unicellular eukaryote, whose cells are rod-shaped. Cells typically measure 3 to 4 micrometres in diameter and 7 to 14 micrometres in length...
, each of which has a long history of use to investigate issues in eukaryotic cell biology
Cell biology
Cell biology is a scientific discipline that studies cells – their physiological properties, their structure, the organelles they contain, interactions with their environment, their life cycle, division and death. This is done both on a microscopic and molecular level...
and genetics
Genetics
Genetics , a discipline of biology, is the science of genes, heredity, and variation in living organisms....
, such as cell cycle
Cell cycle
The cell cycle, or cell-division cycle, is the series of events that takes place in a cell leading to its division and duplication . In cells without a nucleus , the cell cycle occurs via a process termed binary fission...
regulation, chromatin
Chromatin
Chromatin is the combination of DNA and proteins that make up the contents of the nucleus of a cell. The primary functions of chromatin are; to package DNA into a smaller volume to fit in the cell, to strengthen the DNA to allow mitosis and meiosis and prevent DNA damage, and to control gene...
structure, and gene regulation. Other fungal models have more recently emerged that each address specific biological questions relevant to medicine
Medicine
Medicine is the science and art of healing. It encompasses a variety of health care practices evolved to maintain and restore health by the prevention and treatment of illness....
, plant pathology, and industrial uses; examples include Candida albicans
Candida albicans
Candida albicans is a diploid fungus that grows both as yeast and filamentous cells and a causal agent of opportunistic oral and genital infections in humans. Systemic fungal infections including those by C...
, a dimorphic, opportunistic human pathogen, Magnaporthe grisea
Magnaporthe grisea
Magnaporthe grisea, also known as rice blast fungus, rice rotten neck, rice seedling blight, blast of rice, oval leaf spot of graminea, pitting disease, ryegrass blast, and Johnson spot, is a plant-pathogenic fungus that causes an important disease affecting rice. It is now known that M...
, a plant pathogen, and Pichia pastoris
Pichia pastoris
Pichia pastoris is a species of methylotrophic yeast. Pichia is widely used for protein expression using recombinant DNA techniques. Hence it is used in biochemical and genetic research in academia and the biotechnical industry....
, a yeast widely used for eukaryotic protein expression
Protein expression
Protein expression is a subcomponent of gene expression. It consists of the stages after DNA has been translated into polypeptide chains, which are ultimately folded into proteins...
.
Others
Fungi are used extensively to produce industrial chemicals like citricCitric acid
Citric acid is a weak organic acid. It is a natural preservative/conservative and is also used to add an acidic, or sour, taste to foods and soft drinks...
, gluconic
Gluconic acid
Gluconic acid is an organic compound with molecular formula C6H12O7 and condensed structural formula HOCH24COOH. It is one of the 16 stereoisomers of 2,3,4,5,6-pentahydroxyhexanoic acid....
, lactic
Lactic acid
Lactic acid, also known as milk acid, is a chemical compound that plays a role in various biochemical processes and was first isolated in 1780 by the Swedish chemist Carl Wilhelm Scheele. Lactic acid is a carboxylic acid with the chemical formula C3H6O3...
, and malic
Malic acid
Malic acid is an organic compound with the formula HO2CCH2CHOHCO2H. It is a dicarboxylic acid which is made by all living organisms, contributes to the pleasantly sour taste of fruits, and is used as a food additive. Malic acid has two stereoisomeric forms , though only the L-isomer exists...
acids, and industrial enzymes, such as lipase
Lipase
A lipase is an enzyme that catalyzes the formation or cleavage of fats . Lipases are a subclass of the esterases.Lipases perform essential roles in the digestion, transport and processing of dietary lipids in most, if not all, living organisms...
s used in biological detergent
Biological detergent
A biological detergent is a laundry detergent that contains enzymes harvested from micro-organisms such as bacteria adapted to live in hot springs. The description is commonly used in the United Kingdom, where other washing detergents are described as "non-biological"...
s, cellulase
Cellulase
400px|thumb|right|alt = Colored dice with checkered background|Ribbon representation of the Streptomyces lividans beta-1,4-endoglucanase catalytic domain - an example from the family 12 glycoside hydrolases...
s used in making cellulosic ethanol
Cellulosic ethanol
Cellulosic ethanol is a biofuel produced from wood, grasses, or the non-edible parts of plants.It is a type of biofuel produced from lignocellulose, a structural material that comprises much of the mass of plants. Lignocellulose is composed mainly of cellulose, hemicellulose and lignin...
and stonewashed jeans, and amylase
Amylase
Amylase is an enzyme that catalyses the breakdown of starch into sugars. Amylase is present in human saliva, where it begins the chemical process of digestion. Food that contains much starch but little sugar, such as rice and potato, taste slightly sweet as they are chewed because amylase turns...
s, invertase
Invertase
Invertase is an enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of sucrose . The resulting mixture of fructose and glucose is called inverted sugar syrup. Related to invertases are sucrases. Invertases and sucrases hydrolyze sucrose to give the same mixture of glucose and fructose...
s, protease
Protease
A protease is any enzyme that conducts proteolysis, that is, begins protein catabolism by hydrolysis of the peptide bonds that link amino acids together in the polypeptide chain forming the protein....
s and xylanase
Xylanase
Xylanase is the name given to a class of enzymes which degrade the linear polysaccharide beta-1,4-xylan into xylose, thus breaking down hemicellulose, one of the major components of plant cell walls....
s. Several species, most notably Psilocybin mushroom
Psilocybin mushroom
Psilocybin mushrooms are fungi that contain the psychoactive compounds psilocybin and psilocin. There are multiple colloquial terms for psilocybin mushrooms, the most common being shrooms or magic mushrooms....
s (colloquially known as magic mushrooms), are ingested for their psychedelic
Psychedelic drug
A psychedelic substance is a psychoactive drug whose primary action is to alter cognition and perception. Psychedelics are part of a wider class of psychoactive drugs known as hallucinogens, a class that also includes related substances such as dissociatives and deliriants...
properties, both recreationally and religiously.
Mycotoxins

Biological activity
In pharmacology, biological activity or pharmacological activity describes the beneficial or adverse effects of a drug on living matter. When a drug is a complex chemical mixture, this activity is exerted by the substance's active ingredient or pharmacophore but can be modified by the other...
compounds, several of which are toxic
Toxin
A toxin is a poisonous substance produced within living cells or organisms; man-made substances created by artificial processes are thus excluded...
to animals or plants and are therefore called mycotoxins. Of particular relevance to humans are mycotoxins produced by molds causing food spoilage, and poisonous mushrooms (see above). Particularly infamous are the lethal amatoxin
Amatoxin
Amatoxins are a subgroup of at least eight toxic compounds found in several genera of poisonous mushrooms, most notably Amanita phalloides and several other members of the genus Amanita, as well as some Conocybe, Galerina and Lepiota mushroom species.-Structure:The compounds have a similar...
s in some Amanita
Amanita
The genus Amanita contains about 600 species of agarics including some of the most toxic known mushrooms found worldwide. This genus is responsible for approximately 95% of the fatalities resulting from mushroom poisoning, with the death cap accounting for about 50% on its own...
mushrooms, and ergot alkaloids, which have a long history of causing serious epidemics of ergotism
Ergotism
Ergotism is the effect of long-term ergot poisoning, traditionally due to the ingestion of the alkaloids produced by the Claviceps purpurea fungus which infects rye and other cereals, and more recently by the action of a number of ergoline-based drugs. It is also known as ergotoxicosis, ergot...
(St Anthony's Fire) in people consuming rye
Rye
Rye is a grass grown extensively as a grain and as a forage crop. It is a member of the wheat tribe and is closely related to barley and wheat. Rye grain is used for flour, rye bread, rye beer, some whiskeys, some vodkas, and animal fodder...
or related cereal
Cereal
Cereals are grasses cultivated for the edible components of their grain , composed of the endosperm, germ, and bran...
s contaminated with sclerotia of the ergot fungus, Claviceps purpurea
Claviceps purpurea
Claviceps purpurea is a fungus that grows on the ears of rye and related cereal and forage plants. Consumption of grains or seeds contaminated with the fruiting structure of this fungus, the ergot sclerotium, can cause ergotism in humans and other mammals.. C...
. Other notable mycotoxins include the aflatoxin
Aflatoxin
Aflatoxins are naturally occurring mycotoxins that are produced by many species of Aspergillus, a fungus, the most notable ones being Aspergillus flavus and Aspergillus parasiticus. Aflatoxins are toxic and among the most carcinogenic substances known...
s, which are insidious liver toxins
Hepatotoxicity
Hepatotoxicity implies chemical-driven liver damage.The liver plays a central role in transforming and clearing chemicals and is susceptible to the toxicity from these agents. Certain medicinal agents, when taken in overdoses and sometimes even when introduced within therapeutic ranges, may injure...
and highly carcinogenic metabolites produced by certain Aspergillus
Aspergillus
Aspergillus is a genus consisting of several hundred mold species found in various climates worldwide. Aspergillus was first catalogued in 1729 by the Italian priest and biologist Pier Antonio Micheli...
species often growing in or on grains and nuts consumed by humans, ochratoxin
Ochratoxin
Ochratoxins are a group of mycotoxins produced by some Aspergillus species and Penicillium species including Aspergillus ochraceus and Penicillium viridicatum...
s, patulin
Patulin
Patulin is a mycotoxin produced by a variety of molds, in particular, Aspergillus and Penicillium. It is commonly found in rotting apples, and the amount of patulin in apple products is generally viewed as a measure of the quality of the apples used in production...
, and trichothecene
Trichothecene
Trichothecenes are a very large family of chemically related mycotoxins produced by various species of Fusarium, Myrothecium, Trichoderma, Trichothecium, Cephalosporium, Verticimonosporium, and Stachybotrys...
s (e.g., T-2 mycotoxin
T-2 mycotoxin
T-2 is a trichothecene mycotoxin. It is a naturally occurring mold byproduct of Fusarium spp fungus which is toxic to humans and animals...
) and fumonisins, which have significant impact on human food supplies or animal livestock
Livestock
Livestock refers to one or more domesticated animals raised in an agricultural setting to produce commodities such as food, fiber and labor. The term "livestock" as used in this article does not include poultry or farmed fish; however the inclusion of these, especially poultry, within the meaning...
.
Mycotoxins are secondary metabolites (or natural product
Natural product
A natural product is a chemical compound or substance produced by a living organism - found in nature that usually has a pharmacological or biological activity for use in pharmaceutical drug discovery and drug design...
s), and research has established the existence of biochemical pathways solely for the purpose of producing mycotoxins and other natural products in fungi. Mycotoxins may provide fitness
Fitness (biology)
Fitness is a central idea in evolutionary theory. It can be defined either with respect to a genotype or to a phenotype in a given environment...
benefits in terms of physiological adaptation, competition with other microbes and fungi, and protection from consumption (fungivory
Fungivore
A fungivore or mycophage is any animal that primarily or solely feeds upon living members of the fungus kingdom. Fungivory is a type of predation, and is an important part of the soil food web...
).
Mycology
MycologyMycology
Mycology is the branch of biology concerned with the study of fungi, including their genetic and biochemical properties, their taxonomy and their use to humans as a source for tinder, medicinals , food and entheogens, as well as their dangers, such as poisoning or...
is the branch of biology
Biology
Biology is a natural science concerned with the study of life and living organisms, including their structure, function, growth, origin, evolution, distribution, and taxonomy. Biology is a vast subject containing many subdivisions, topics, and disciplines...
concerned with the systematic study of fungi, including their genetic and biochemical properties, their taxonomy, and their use to humans as a source of medicine, food, and psychotropic substances
Entheogen
An entheogen , in the strict sense, is a psychoactive substance used in a religious, shamanic, or spiritual context. Historically, entheogens were mostly derived from plant sources and have been used in a variety of traditional religious contexts...
consumed for religious purposes, as well as their dangers, such as poisoning or infection. The field of phytopathology
Phytopathology
Plant pathology is the scientific study of plant diseases caused by pathogens and environmental conditions . Organisms that cause infectious disease include fungi, oomycetes, bacteria, viruses, viroids, virus-like organisms, phytoplasmas, protozoa, nematodes and parasitic plants...
, the study of plant diseases, is closely related because many plant pathogens are fungi.
Use of fungi by humans dates back to prehistory; Ötzi the Iceman
Ötzi the Iceman
Ötzi the Iceman , Similaun Man, and Man from Hauslabjoch are modern names for a well-preserved natural mummy of a man who lived about 5,300 years ago. The mummy was found in September 1991 in the Ötztal Alps, near Hauslabjoch on the border between Austria and Italy. The nickname comes from the...
, a well-preserved mummy of a 5,300 year old Neolithic
Neolithic
The Neolithic Age, Era, or Period, or New Stone Age, was a period in the development of human technology, beginning about 9500 BC in some parts of the Middle East, and later in other parts of the world. It is traditionally considered as the last part of the Stone Age...
man found frozen in the Austrian Alps, carried two species of polypore
Polypore
Polypores are a group of tough, leathery poroid mushrooms similar to boletes, but typically lacking a distinct stalk. The technical distinction between the two types of mushrooms is that polypores do not have the spore-bearing tissue continuous along the entire underside of the mushroom. Many...
mushrooms that may have been used as tinder
Tinder
Tinder is easily combustible material used to ignite fires by rudimentary methods. A small fire consisting of tinder is then used to ignite kindling. Anything that can be ignited by a match can be considered tinder; or by more rigorous definition, anything that begins to glow under a shower of...
(Fomes fomentarius
Fomes fomentarius
Fomes fomentarius is a species of fungal plant pathogen found in Europe, Asia, Africa and North America...
), or for medicinal purposes (Piptoporus betulinus). Ancient peoples have used fungi as food sources–often unknowingly–for millennia, in the preparation of leavened bread and fermented juices. Some of the oldest written records contain references to the destruction of crops that were probably caused by pathogenic fungi.
History
Mycology is a relatively new science that became systematic after the development of the microscopeMicroscope
A microscope is an instrument used to see objects that are too small for the naked eye. The science of investigating small objects using such an instrument is called microscopy...
in the 16th century. Although fungal spores were first observed by Giambattista della Porta
Giambattista della Porta
Giambattista della Porta , also known as Giovanni Battista Della Porta and John Baptist Porta, was an Italian scholar, polymath and playwright who lived in Naples at the time of the Scientific Revolution and Reformation....
in 1588, the seminal work in the development of mycology is considered to be the publication of Pier Antonio Micheli
Pier Antonio Micheli
Pier Antonio Micheli was a noted Italian botanist, professor of botany in Pisa, curator of the Orto Botanico di Firenze, author of Nova plantarum genera iuxta Tournefortii methodum disposita...
's 1729 work Nova plantarum genera. Micheli not only observed spores, but showed that under the proper conditions, they could be induced into growing into the same species of fungi from which they originated. Extending the use of the binomial system of nomenclature introduced by Carl Linnaeus in his Species plantarum
Species Plantarum
Species Plantarum was first published in 1753, as a two-volume work by Carl Linnaeus. Its prime importance is perhaps that it is the primary starting point of plant nomenclature as it exists today. This means that the first names to be considered validly published in botany are those that appear...
(1753), the Dutch Christian Hendrik Persoon
Christian Hendrik Persoon
Christiaan Hendrik Persoon was a mycologist who made additions to Linnaeus' mushroom taxonomy.-Early life:...
(1761–1836) established the first classification of mushrooms with such skill so as to be considered a founder of modern mycology. Later, Elias Magnus Fries
Elias Magnus Fries
-External links:*, Authors of fungal names, Mushroom, the Journal of Wild Mushrooming.*...
(1794–1878) further elaborated the classification
Biological classification
Biological classification, or scientific classification in biology, is a method to group and categorize organisms by biological type, such as genus or species. Biological classification is part of scientific taxonomy....
of fungi, using spore color and various microscopic characteristics, methods still used by taxonomists today. Other notable early contributors to mycology in the 17th–19th and early 20th centuries include Miles Joseph Berkeley
Miles Joseph Berkeley
Miles Joseph Berkeley was an English cryptogamist and clergyman, and one of the founders of the science of plant pathology....
, August Carl Joseph Corda
August Carl Joseph Corda
August Carl Joseph Corda was a Czech physician and mycologist.-Early life and education:Corda was born in Reichenberg , Bohemia on November 15, 1809. Corda's father was a textile seller...
, Anton de Bary
Anton de Bary
Heinrich Anton de Bary was a German surgeon, botanist, microbiologist, and mycologist ....
, the brothers Louis René
Louis René Tulasne
Louis René Tulasne, aka Edmond Tulasne was a French botanist and mycologist who was born in Azay-le-Rideau. He originally studied law at Poitiers, but his interest later turned to botany. As a young man he accompanied botanist Auguste de Saint-Hilaire to South America to study the flora of Brazil...
and Charles Tulasne
Charles Tulasne
Charles Tulasne was a French physician and mycologist who was born in Langeais in the département of Indre-et-Loire. He received his medical doctorate in 1840 and practiced medicine in Paris until 1854. Afterwards he worked with his older brother Louis René Tulasne in the field of mycology...
, Arthur H. R. Buller
Arthur Henry Reginald Buller
Arthur Henry Reginald Buller was a British-Canadian mycologist. He is mainly known as a researcher of fungi and wheat rust.- Academic career :...
, Curtis G. Lloyd
Curtis Gates Lloyd
Curtis Gates Lloyd was an American mycologist known for both his research on the Gasteromycetes, as well as his controversial views on naming conventions in taxonomy. He had a herbarium with over 59,000 fungal specimens, and published over a thousand new species of fungi...
, and Pier Andrea Saccardo
Pier Andrea Saccardo
Pier Andrea Saccardo was an Italian botanist and mycologist.- Life :...
. The 20th century has seen a modernization of mycology that has come from advances in biochemistry
Biochemistry
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes in living organisms, including, but not limited to, living matter. Biochemistry governs all living organisms and living processes...
, genetics
Genetics
Genetics , a discipline of biology, is the science of genes, heredity, and variation in living organisms....
, molecular biology
Molecular biology
Molecular biology is the branch of biology that deals with the molecular basis of biological activity. This field overlaps with other areas of biology and chemistry, particularly genetics and biochemistry...
, and biotechnology
Biotechnology
Biotechnology is a field of applied biology that involves the use of living organisms and bioprocesses in engineering, technology, medicine and other fields requiring bioproducts. Biotechnology also utilizes these products for manufacturing purpose...
. The use of DNA sequencing
DNA sequencing
DNA sequencing includes several methods and technologies that are used for determining the order of the nucleotide bases—adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine—in a molecule of DNA....
technologies and phylogenetic analysis has provided new insights into fungal relationships and biodiversity
Biodiversity
Biodiversity is the degree of variation of life forms within a given ecosystem, biome, or an entire planet. Biodiversity is a measure of the health of ecosystems. Biodiversity is in part a function of climate. In terrestrial habitats, tropical regions are typically rich whereas polar regions...
, and has challenged traditional morphology-based groupings in fungal taxonomy
Taxonomy
Taxonomy is the science of identifying and naming species, and arranging them into a classification. The field of taxonomy, sometimes referred to as "biological taxonomy", revolves around the description and use of taxonomic units, known as taxa...
.
See also
- Conservation of fungiConservation of fungiFungi are considered to be in urgent need of conservation by the British Mycological Society on the grounds that it is a traditionally neglected taxon which has legal protection in few countries...
- MycoBankMycoBankMycoBank is an online database, documenting new mycological names and combinations, eventually combined with descriptions and illustrations. It is run by the Centraalbureau voor Schimmelcultures fungal biodiversity center in Utrecht....
- Plant pathology
External links
- Tree of Life web project: Fungi
- Mushroom ObserverMushroom ObserverMushroom Observer is a collaborative amateur mycology website started by Nathan Wilson in 2006. Its purpose is to "record observations about mushrooms, help people identify mushrooms they aren’t familiar with, and expand the community around the scientific exploration of mushrooms".As of 2010, the...
(mushroomobserver.org), a collaborative fungus recording and identification project

