
Lovastatin
Encyclopedia
Lovastatin is a member of the drug class of statin
s, used for lowering cholesterol
(hypolipidemic agent
) in those with hypercholesterolemia
and so preventing cardiovascular disease
. Lovastatin is a naturally occurring drug found in food such as oyster mushrooms and red yeast rice.
and the prevention of cardiovascular disease
. It is recommended to be used only after other measures such as diet, exercise, and weight reduction have not improved cholesterol levels.
 Compactin and lovastatin, natural products with a powerful inhibitory effect on HMG-CoA reductase
Compactin and lovastatin, natural products with a powerful inhibitory effect on HMG-CoA reductase
, were discovered in the 1970s, and taken into clinical development as potential drugs for lowering LDL cholesterol.
In 1982, some small-scale clinical investigations of lovastatin, a polyketide-derived natural product isolated from Aspergillus terreus, in very high-risk patients were undertaken, in which dramatic reductions in LDL cholesterol were observed, with very few adverse effects. After the additional animal safety studies with lovastatin revealed no toxicity of the type thought to be associated with compactin, clinical studies continued.
Large-scale trials confirmed the effectiveness of lovastatin. Observed tolerability continued to be excellent, and lovastatin was approved by the US FDA
in 1987. It was the first statin approved by the FDA.
Lovastatin at its maximal recommended dose of 80 mg daily produced a mean reduction in LDL cholesterol of 40%, a far greater reduction than could be obtained with any of the treatments available at the time. Equally important, the drug produced very few adverse effects, was easy for patients to take, and so was rapidly accepted by prescribers and patients. The most significant adverse effect is rhabdomyolysis
; this is rare and may occur with the use of any HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor.
Lovastatin is also naturally produced by certain higher fungi
such as Pleurotus ostreatus (oyster mushroom) and closely related Pleurotus
spp. There has been extensive research into the effect of oyster mushroom and its extracts on the cholesterol levels of laboratory animals, although the effect has been demonstrated in a very limited number of human subjects.
In 1998, the FDA placed a ban on the sale of dietary supplements derived from red yeast rice, which naturally contains lovastatin, arguing that products containing prescription agents require drug approval. This ban was subsequently rescinded, in light of law that upholds that natural products are not patentable.
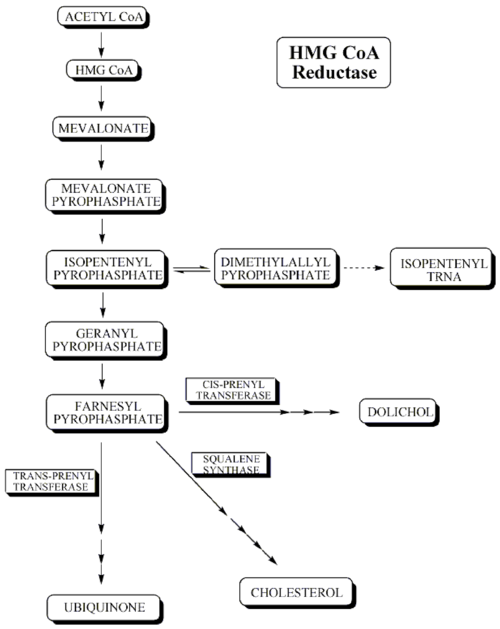
Mevalonate is a required building block for cholesterol biosynthesis and lovastatin interferes with its production by acting as a reversible competitive inhibitor for HMG-CoA, which binds to the HMG-CoA reductase. Lovastatin, being inactive in the native form, the form in which it is administered, is hydrolysed to the β-hydroxy acid form in the body; it is this form that is active.
s that are building-blocks of squalene
, the immediate precursor to sterols, which cyclizes to lanosterol (a methylated sterol) and further metabolized to cholesterol. A number of early attempts to block the synthesis of cholesterol resulted in agents that inhibited late in the biosynthetic pathway between lanosterol and cholesterol. A major rate-limiting step in the pathway is at the level of the microsomal enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of HMG CoA to mevalonic acid and that has been considered to be a prime target for pharmacologic intervention for several years.
HMG CoA reductase occurs early in the biosynthetic pathway and is among the first committed steps to cholesterol formulation. Inhibition of this enzyme could lead to accumulation of HMG CoA, a water-soluble intermediate that is, then, capable of being readily metabolized to simpler molecules. This inhibition of reductase would lead to accumulation of lipophylic intermediates with a formal sterol ring.
Lovastatin is the first specific inhibitor of HMG CoA reductase to receive approval for the treatment of hypercholesterolemia. The first breakthrough in efforts to find a potent, specific, competitive inhibitor of HMG CoA reductase occurred in 1976 when Endo et al. reported discovery of mevastatin
, a highly functionalized fungal metabolite, isolated from cultures of Penicillium citrium. Mevastatin was demonstrated to be an unusually potent inhibitor of the target enzyme and of cholesterol biosynthesis. Subsequent to the first reports describing mevastatin, efforts were initiated to search for other naturally occurring inhibitors of HMG CoA reductase. This led to the discovery of a novel fungal metabolite – lovastatin. The structure of lovastatin was determined to be different from that of mevastatin by the presence of a six alphamethyl group in the hexahydronaphthalene ring.
Key points from the study of the biosynthesis of lovastatin :-
This implies that lovastatin is a unique compound synthesized by A. terreus and that mevastatin is not an intermediate in its fornmation.

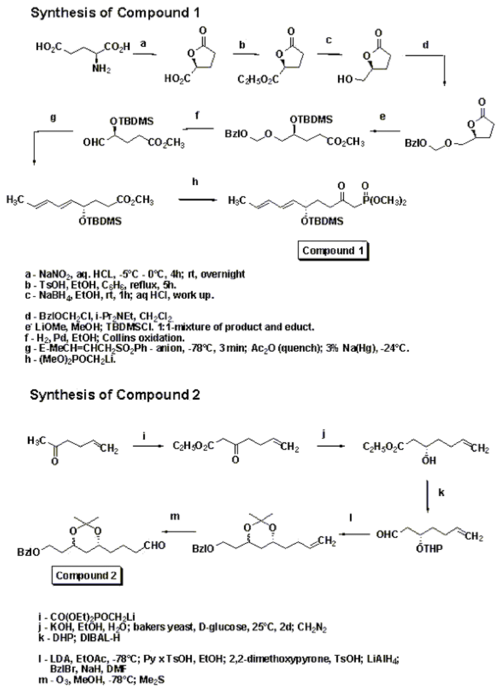
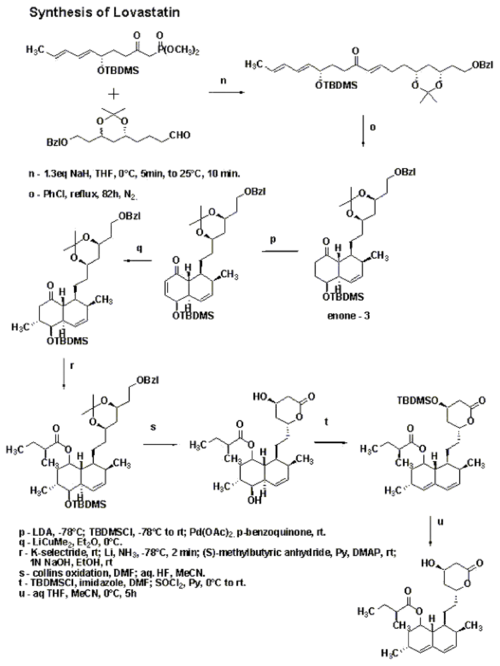
Hirama synthesized Compactin and used one of the intermediates to follow a different path to get to lovastatin. The synthetic sequence is shown in the schemes below. The γ-lactone was synthesized using Yamada methodology starting with aspartic acid. Lactone opening was done using lithium methoxide in methanol
and then silylation
to give a separable mixture of the starting lactone and the silyl ether
. The silyl ether on hydrogenolysis followed by Collins oxidation gave the aldehyde. Stereoselective preparation of (E,E)-diene was accomplished by addition of trans-crotyl phenyl sulfone anion, followed by quenching with Ac2O
and subsequent reductive elimination of sulfone acetate. Condensation of this with lithium anion of dimethyl methylphosphonate gave compound 1. Compound 2 was synthesized as shown in the scheme in the synthetic procedure. Compounds 1 and 2 were then combined together using 1.3eq sodium hydride in THF followed by reflux in chlorobenzene
for 82 hrs under nitrogen to get the enone 3.
Simple organic reactions were used to get to lovastatin as shown in the scheme.
enzyme inhibition. This enzyme is needed by the body to make cholesterol.
Lovastatin causes cholesterol to be lost from LDL, but also reduces the concentration of circulating LDL (low-density lipoprotein) particles. Apolipoprotein B concentration falls substantially during treatment with lovastatin. Lovastatin's ability to lower LDL is thought to be due to a reduction in VLDL, which is a precursor to LDL. Also, Lovastatin may increase the number of LDL receptors on the surface of cell membranes, and thus increase the breakdown of LDL.
Lovastatin can also produce slight to moderate increases in HDL, and slight to moderate decreases in triglycerides. Both of these effects are typically beneficial to a patient with a poor lipid profile.
Both lovastatin and its b-hydroxyacid metabolite are highly bound (>95%) to human plasma proteins. Animal studies demonstrated that lovastatin crosses the blood-brain and placental barriers.
Elderly patients, or those with renal insufficiency, may have higher plasma concentrations of lovastatin after administration and may require a lower dose. The usual recommended starting dose is 20 mg once a day given with the evening meal, and the dose range is 10–80 mg a day in a single dose, or divided into two doses.
Lovastatin and other statins have recently been studied for their chemopreventive and chemotherapeutic effects in certain cancers. However, based on clinical evidence such effect could not be demonstrated. In principle, independent of their hydroxymethyl glutaryl (HMG)-CoA reductase inhibition, lovastatin and other statins reduce proteasome
activity, leading to an accumulation of cyclin-dependent kinase
inhibitors p21
and p27, and G1 phase
arrest in breast cancer cell lines. For that purpose, lovastatin is also used experimentally.
or rhabdomyolysis
. This can be life-threatening if not recognised and treated in time, so any unexplained muscle pain or weakness whilst on lovastatin should be promptly mentioned to the prescribing doctor.
Lovastatin is contraindicated during pregnancy (Pregnancy Category X); it may cause skeletal deformities or learning disabilities.
, simvastatin
and other statin drugs metabolized via CYP3A4
, drinking grapefruit
juice during lovastatin therapy increases the risk of serious side-effects. Grapefruit juice inhibits CYP3A4
, thereby decreasing lovastatin's metabolism and increasing its plasma concentrations.
Lovastatin at doses higher than 20 mg per day should not be used in conjunction with gemfibrozil
or other fibrate
s, niacin
, or ciclosporin
. This is because of the significantly increased risk of rhabdomyolysis
.
Lovastatin tablets are tested for dissolution and assay as per the USP.
Limit for dissolution – Not less than 80% (Q) of the labeled amount of lovastatin is dissolved in 30 minutes.
Limit for assay – Each tablet contains not less than 90% and not more than 110% of the labeled amount of lovastatin, tested by HPLC analysis.
biosynthesis.
Lovastatin is currently in phase one of clinical trial (NCT00352599) to evaluate safety for treatment of cognitive deficits in patients with Neurofibromatosis type I
. This drug has been shown to reverse spatial deficits in mice
.
Statin
Statins are a class of drugs used to lower cholesterol levels by inhibiting the enzyme HMG-CoA reductase, which plays a central role in the production of cholesterol in the liver. Increased cholesterol levels have been associated with cardiovascular diseases, and statins are therefore used in the...
s, used for lowering cholesterol
Cholesterol
Cholesterol is a complex isoprenoid. Specifically, it is a waxy steroid of fat that is produced in the liver or intestines. It is used to produce hormones and cell membranes and is transported in the blood plasma of all mammals. It is an essential structural component of mammalian cell membranes...
(hypolipidemic agent
Hypolipidemic agent
Hypolipidemic agents, or antihyperlipidemic agents, are a diverse group of pharmaceuticals that are used in the treatment of hyperlipidemias. They are called lipid-lowering drugs or agents.- Classes of hypolipidemic drugs :...
) in those with hypercholesterolemia
Hypercholesterolemia
Hypercholesterolemia is the presence of high levels of cholesterol in the blood. It is not a disease but a metabolic derangement that can be caused by many diseases, notably cardiovascular disease...
and so preventing cardiovascular disease
Cardiovascular disease
Heart disease or cardiovascular disease are the class of diseases that involve the heart or blood vessels . While the term technically refers to any disease that affects the cardiovascular system , it is usually used to refer to those related to atherosclerosis...
. Lovastatin is a naturally occurring drug found in food such as oyster mushrooms and red yeast rice.
Medical uses
The primary uses of lovastatin is for the treatment of dyslipidemiaDyslipidemia
Dyslipidemia or dyslipidaemia is an abnormal amount of lipids in the blood. In developed countries, most dyslipidemias are hyperlipidemias; that is, an elevation of lipids in the blood, often due to diet and lifestyle. The prolonged elevation of insulin levels can lead to dyslipidemia...
and the prevention of cardiovascular disease
Cardiovascular disease
Heart disease or cardiovascular disease are the class of diseases that involve the heart or blood vessels . While the term technically refers to any disease that affects the cardiovascular system , it is usually used to refer to those related to atherosclerosis...
. It is recommended to be used only after other measures such as diet, exercise, and weight reduction have not improved cholesterol levels.
History

HMG-CoA reductase
HMG-CoA reductase is the rate-controlling enzyme of the mevalonate pathway, the metabolic pathway that produces cholesterol and other isoprenoids...
, were discovered in the 1970s, and taken into clinical development as potential drugs for lowering LDL cholesterol.
In 1982, some small-scale clinical investigations of lovastatin, a polyketide-derived natural product isolated from Aspergillus terreus, in very high-risk patients were undertaken, in which dramatic reductions in LDL cholesterol were observed, with very few adverse effects. After the additional animal safety studies with lovastatin revealed no toxicity of the type thought to be associated with compactin, clinical studies continued.
Large-scale trials confirmed the effectiveness of lovastatin. Observed tolerability continued to be excellent, and lovastatin was approved by the US FDA
Food and Drug Administration
The Food and Drug Administration is an agency of the United States Department of Health and Human Services, one of the United States federal executive departments...
in 1987. It was the first statin approved by the FDA.
Lovastatin at its maximal recommended dose of 80 mg daily produced a mean reduction in LDL cholesterol of 40%, a far greater reduction than could be obtained with any of the treatments available at the time. Equally important, the drug produced very few adverse effects, was easy for patients to take, and so was rapidly accepted by prescribers and patients. The most significant adverse effect is rhabdomyolysis
Rhabdomyolysis
Rhabdomyolysis is a condition in which damaged skeletal muscle tissue breaks down rapidly. Breakdown products of damaged muscle cells are released into the bloodstream; some of these, such as the protein myoglobin, are harmful to the kidneys and may lead to kidney failure...
; this is rare and may occur with the use of any HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor.
Lovastatin is also naturally produced by certain higher fungi
Fungus
A fungus is a member of a large group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds , as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, Fungi, which is separate from plants, animals, and bacteria...
such as Pleurotus ostreatus (oyster mushroom) and closely related Pleurotus
Pleurotus
Pleurotus is a genus of gilled mushrooms which includes one of the most widely eaten mushrooms, P. ostreatus. Species of Pleurotus may be called oyster, abalone, or tree mushrooms, and are some of the most commonly cultivated edible mushrooms in the world...
spp. There has been extensive research into the effect of oyster mushroom and its extracts on the cholesterol levels of laboratory animals, although the effect has been demonstrated in a very limited number of human subjects.
In 1998, the FDA placed a ban on the sale of dietary supplements derived from red yeast rice, which naturally contains lovastatin, arguing that products containing prescription agents require drug approval. This ban was subsequently rescinded, in light of law that upholds that natural products are not patentable.
Mechanism of action
Lovastatin is an inhibitor of 3-hydroxy-3methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase (HMG-CoA reductase), an enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of HMG-CoA to mevalonate.Mevalonate is a required building block for cholesterol biosynthesis and lovastatin interferes with its production by acting as a reversible competitive inhibitor for HMG-CoA, which binds to the HMG-CoA reductase. Lovastatin, being inactive in the native form, the form in which it is administered, is hydrolysed to the β-hydroxy acid form in the body; it is this form that is active.
Discovery, biochemistry and biology
It is now generally accepted that a major risk factor for the development of coronary heart disease is an elevated concentration of plasma cholesterol, especially low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol. The objective is to decrease excess levels of cholesterol to an amount consistent with maintenance of normal body function. Cholesterol is biosynthesized in a series of more than 25 separate enzymatic reactions that initially involves 3 successive condensations of acetyl-CoA units to form the 6-carbon compound 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A (HMG CoA). This is reduced to mevalonate and then converted in a series of reactions to the isopreneIsoprene
Isoprene , or 2-methyl-1,3-butadiene, is a common organic compound with the formula CH2=CCH=CH2. Under standard conditions it is a colorless liquid...
s that are building-blocks of squalene
Squalene
Squalene is a natural organic compound originally obtained for commercial purposes primarily from shark liver oil, though plant sources are used as well, including amaranth seed, rice bran, wheat germ, and olives. All plants and animals produce squalene, including humans...
, the immediate precursor to sterols, which cyclizes to lanosterol (a methylated sterol) and further metabolized to cholesterol. A number of early attempts to block the synthesis of cholesterol resulted in agents that inhibited late in the biosynthetic pathway between lanosterol and cholesterol. A major rate-limiting step in the pathway is at the level of the microsomal enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of HMG CoA to mevalonic acid and that has been considered to be a prime target for pharmacologic intervention for several years.
HMG CoA reductase occurs early in the biosynthetic pathway and is among the first committed steps to cholesterol formulation. Inhibition of this enzyme could lead to accumulation of HMG CoA, a water-soluble intermediate that is, then, capable of being readily metabolized to simpler molecules. This inhibition of reductase would lead to accumulation of lipophylic intermediates with a formal sterol ring.
Lovastatin is the first specific inhibitor of HMG CoA reductase to receive approval for the treatment of hypercholesterolemia. The first breakthrough in efforts to find a potent, specific, competitive inhibitor of HMG CoA reductase occurred in 1976 when Endo et al. reported discovery of mevastatin
Mevastatin
Mevastatin, compactin, ML-236B is a hypolipidemic agent that belongs to the statins class.It was isolated from the mold Penicillium citrinum by Akira Endo in the 1970s and he identified it as a HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor, i.e.; a statin...
, a highly functionalized fungal metabolite, isolated from cultures of Penicillium citrium. Mevastatin was demonstrated to be an unusually potent inhibitor of the target enzyme and of cholesterol biosynthesis. Subsequent to the first reports describing mevastatin, efforts were initiated to search for other naturally occurring inhibitors of HMG CoA reductase. This led to the discovery of a novel fungal metabolite – lovastatin. The structure of lovastatin was determined to be different from that of mevastatin by the presence of a six alphamethyl group in the hexahydronaphthalene ring.
Key points from the study of the biosynthesis of lovastatin :-
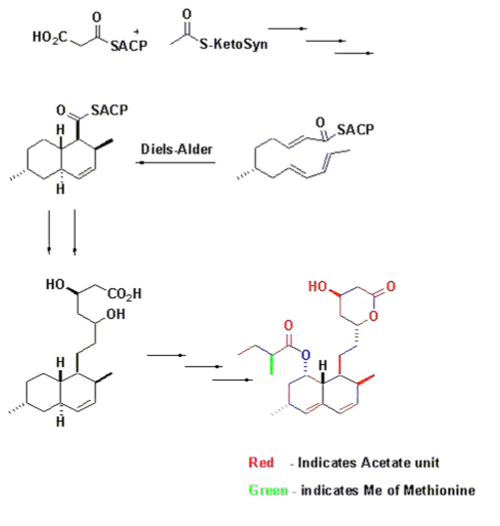
- Lovastatin is composed of two polyketide chains derived from acetate that are two and four carbons long coupled in head to tail fashion.
- six alphamethyl group and the methyl group on the four-carbon side-chain are derived from the methyl group of methionine
- six alphamethyl group is added before closure of the rings.
This implies that lovastatin is a unique compound synthesized by A. terreus and that mevastatin is not an intermediate in its fornmation.


Biosynthesis using Diels-Alder catalyzed cyclization
In vitro formation of a triketide lactone using a genetically modified protein derived from 6-deoxyerythronolide B synthase has been demonstrated. Witter and Vederas observed that "the stereochemistry of the molecule supports the intriguing idea that an enzyme-catalyzed Diels-Alder reaction may occur during assembly of the polyketide chain. It, thus, appears that biological Diels-Alder reactions may be triggered by generation of reactive triene systems on an enzyme surface."

Total synthesis
A major bulk of work in the synthesis of lovastatin was done by M. Hirama in the 1980s.Hirama synthesized Compactin and used one of the intermediates to follow a different path to get to lovastatin. The synthetic sequence is shown in the schemes below. The γ-lactone was synthesized using Yamada methodology starting with aspartic acid. Lactone opening was done using lithium methoxide in methanol
Methanol
Methanol, also known as methyl alcohol, wood alcohol, wood naphtha or wood spirits, is a chemical with the formula CH3OH . It is the simplest alcohol, and is a light, volatile, colorless, flammable liquid with a distinctive odor very similar to, but slightly sweeter than, ethanol...
and then silylation
Silylation
Silylation is the introduction of a substituted silyl group to a molecule.Nearly all functional groups which present a problem in gas chromatogaphic separation can be derivatized by silylation reagents...
to give a separable mixture of the starting lactone and the silyl ether
Silyl ether
Silyl ethers are a group of chemical compounds which contain a silicon atom covalently bonded to an alkoxy group. The general structure is R1R2R3Si−O−R4 where R4 is an alkyl group or an aryl group. Silyl ethers are usually used as protecting groups for alcohols in organic synthesis...
. The silyl ether on hydrogenolysis followed by Collins oxidation gave the aldehyde. Stereoselective preparation of (E,E)-diene was accomplished by addition of trans-crotyl phenyl sulfone anion, followed by quenching with Ac2O
Acetic anhydride
Acetic anhydride, or ethanoic anhydride, is the chemical compound with the formula 2O. Commonly abbreviated Ac2O, it is the simplest isolatable acid anhydride and is a widely used reagent in organic synthesis...
and subsequent reductive elimination of sulfone acetate. Condensation of this with lithium anion of dimethyl methylphosphonate gave compound 1. Compound 2 was synthesized as shown in the scheme in the synthetic procedure. Compounds 1 and 2 were then combined together using 1.3eq sodium hydride in THF followed by reflux in chlorobenzene
Chlorobenzene
Chlorobenzene is an aromatic organic compound with the chemical formula C6H5Cl. This colorless, flammable liquid is a common solvent and a widely used intermediate in the manufacture of other chemicals.-Uses:...
for 82 hrs under nitrogen to get the enone 3.
Simple organic reactions were used to get to lovastatin as shown in the scheme.


Pharmacology and dose
The mode of action of statins is HMG-CoA reductaseHMG-CoA reductase
HMG-CoA reductase is the rate-controlling enzyme of the mevalonate pathway, the metabolic pathway that produces cholesterol and other isoprenoids...
enzyme inhibition. This enzyme is needed by the body to make cholesterol.
Lovastatin causes cholesterol to be lost from LDL, but also reduces the concentration of circulating LDL (low-density lipoprotein) particles. Apolipoprotein B concentration falls substantially during treatment with lovastatin. Lovastatin's ability to lower LDL is thought to be due to a reduction in VLDL, which is a precursor to LDL. Also, Lovastatin may increase the number of LDL receptors on the surface of cell membranes, and thus increase the breakdown of LDL.
Lovastatin can also produce slight to moderate increases in HDL, and slight to moderate decreases in triglycerides. Both of these effects are typically beneficial to a patient with a poor lipid profile.
Both lovastatin and its b-hydroxyacid metabolite are highly bound (>95%) to human plasma proteins. Animal studies demonstrated that lovastatin crosses the blood-brain and placental barriers.
Elderly patients, or those with renal insufficiency, may have higher plasma concentrations of lovastatin after administration and may require a lower dose. The usual recommended starting dose is 20 mg once a day given with the evening meal, and the dose range is 10–80 mg a day in a single dose, or divided into two doses.
Lovastatin and other statins have recently been studied for their chemopreventive and chemotherapeutic effects in certain cancers. However, based on clinical evidence such effect could not be demonstrated. In principle, independent of their hydroxymethyl glutaryl (HMG)-CoA reductase inhibition, lovastatin and other statins reduce proteasome
Proteasome
Proteasomes are very large protein complexes inside all eukaryotes and archaea, and in some bacteria. In eukaryotes, they are located in the nucleus and the cytoplasm. The main function of the proteasome is to degrade unneeded or damaged proteins by proteolysis, a chemical reaction that breaks...
activity, leading to an accumulation of cyclin-dependent kinase
Cyclin-dependent kinase
thumb|350px|Schematic of the cell cycle. outer ring: I=[[Interphase]], M=[[Mitosis]]; inner ring: M=Mitosis; G1=[[G1 phase|Gap phase 1]]; S=[[S phase|Synthesis]]; G2=[[G2 phase|Gap phase 2]]...
inhibitors p21
P21
p21 / WAF1 also known as cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1 or CDK-interacting protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CDKN1A gene located on chromosome 6 .- Function :...
and p27, and G1 phase
G1 phase
The G1 phase is a period in the cell cycle during interphase, before the S phase. For many cells, this phase is the major period of cell growth during its lifespan. During this stage new organelles are being synthesized, so the cell requires both structural proteins and enzymes, resulting in great...
arrest in breast cancer cell lines. For that purpose, lovastatin is also used experimentally.
Side effects
Lovastatin is usually well tolerated. Lovastatin, and all statin drugs, can rarely cause myopathyMyopathy
In medicine, a myopathy is a muscular disease in which the muscle fibers do not function for any one of many reasons, resulting in muscular weakness. "Myopathy" simply means muscle disease...
or rhabdomyolysis
Rhabdomyolysis
Rhabdomyolysis is a condition in which damaged skeletal muscle tissue breaks down rapidly. Breakdown products of damaged muscle cells are released into the bloodstream; some of these, such as the protein myoglobin, are harmful to the kidneys and may lead to kidney failure...
. This can be life-threatening if not recognised and treated in time, so any unexplained muscle pain or weakness whilst on lovastatin should be promptly mentioned to the prescribing doctor.
Lovastatin is contraindicated during pregnancy (Pregnancy Category X); it may cause skeletal deformities or learning disabilities.
Drug interactions
As with atorvastatinAtorvastatin
Atorvastatin , sold by Pfizer under the trade name Lipitor, is a member of the drug class known as statins, used for lowering blood cholesterol. It also stabilizes plaque and prevents strokes through anti-inflammatory and other mechanisms...
, simvastatin
Simvastatin
Simvastatin is a hypolipidemic drug used to control elevated cholesterol, or hypercholesterolemia. Simvastatin is a member of the statin class of pharmaceuticals, is a synthetic derivate of a fermentation product of Aspergillus terreus.-Medical uses:The primary uses of simvastatin is for the...
and other statin drugs metabolized via CYP3A4
CYP3A4
Cytochrome P450 3A4 , a member of the cytochrome P450 mixed-function oxidase system, is one of the most important enzymes involved in the metabolism of xenobiotics in the body. CYP3A4 is involved in the oxidation of the largest range of substrates of all the CYPs. As a result, CYP3A4 is present in...
, drinking grapefruit
Grapefruit
The grapefruit , is a subtropical citrus tree known for its sour fruit, an 18th-century hybrid first bred in Barbados. When found, it was named the "forbidden fruit"; it has also been misidentified with the pomelo or shaddock , one of the parents of this hybrid, the other being sweet orange The...
juice during lovastatin therapy increases the risk of serious side-effects. Grapefruit juice inhibits CYP3A4
CYP3A4
Cytochrome P450 3A4 , a member of the cytochrome P450 mixed-function oxidase system, is one of the most important enzymes involved in the metabolism of xenobiotics in the body. CYP3A4 is involved in the oxidation of the largest range of substrates of all the CYPs. As a result, CYP3A4 is present in...
, thereby decreasing lovastatin's metabolism and increasing its plasma concentrations.
Lovastatin at doses higher than 20 mg per day should not be used in conjunction with gemfibrozil
Gemfibrozil
Gemfibrozil is the generic name for an oral drug used to lower lipid levels. It belongs to a group of drugs known as fibrates. It is most commonly sold as the brand name, Lopid...
or other fibrate
Fibrate
In pharmacology, the fibrates are a class of amphipathic carboxylic acids. They are used for a range of metabolic disorders, mainly hypercholesterolemia , and are therefore hypolipidemic agents.- Members :...
s, niacin
Niacin
"Niacin" redirects here. For the neo-fusion band, see Niacin .Niacin is an organic compound with the formula and, depending on the definition used, one of the forty to eighty essential human nutrients.Niacin is one of five vitamins associated with a pandemic deficiency disease: niacin deficiency...
, or ciclosporin
Ciclosporin
Ciclosporin , cyclosporine , cyclosporin , or cyclosporin A is an immunosuppressant drug widely used in post-allogeneic organ transplant to reduce the activity of the immune system, and therefore the risk of organ rejection...
. This is because of the significantly increased risk of rhabdomyolysis
Rhabdomyolysis
Rhabdomyolysis is a condition in which damaged skeletal muscle tissue breaks down rapidly. Breakdown products of damaged muscle cells are released into the bloodstream; some of these, such as the protein myoglobin, are harmful to the kidneys and may lead to kidney failure...
.
Pharmacopoeia information
Lovastatin tablets are preserved when stored in well-closed, light-resistant containers in a cool place or at controlled room temperature.Lovastatin tablets are tested for dissolution and assay as per the USP.
Limit for dissolution – Not less than 80% (Q) of the labeled amount of lovastatin is dissolved in 30 minutes.
Limit for assay – Each tablet contains not less than 90% and not more than 110% of the labeled amount of lovastatin, tested by HPLC analysis.
Brand names
- Mevacor
- Advicor (as a combination with niacinNiacin"Niacin" redirects here. For the neo-fusion band, see Niacin .Niacin is an organic compound with the formula and, depending on the definition used, one of the forty to eighty essential human nutrients.Niacin is one of five vitamins associated with a pandemic deficiency disease: niacin deficiency...
) - Altocor
- Altoprev
- Statosan (Atos Pharma)
Other applications
In plant physiology, lovastatin has occasionally been used as inhibitor of cytokininCytokinin
Cytokinins are a class of plant growth substances that promote cell division, or cytokinesis, in plant roots and shoots. They are involved primarily in cell growth and differentiation, but also affect apical dominance, axillary bud growth, and leaf senescence...
biosynthesis.
Lovastatin is currently in phase one of clinical trial (NCT00352599) to evaluate safety for treatment of cognitive deficits in patients with Neurofibromatosis type I
Neurofibromatosis type I
Neurofibromatosis type I , formerly known as von Recklinghausen disease after the researcher who first documented the disorder, is a human genetic disorder. It is possibly the most common inherited disorder caused by a single gene...
. This drug has been shown to reverse spatial deficits in mice
MICE
-Fiction:*Mice , alien species in The Hitchhiker's Guide to the Galaxy*The Mice -Acronyms:* "Meetings, Incentives, Conferencing, Exhibitions", facilities terminology for events...
.

