
Surface area to volume ratio
Encyclopedia
The surface-area-to-volume ratio also called the surface-to-volume ratio and variously denoted sa/vol or SA:V, is the amount of surface area
per unit volume of an object or collection of objects. The surface-area-to-volume ratio is measured in units of inverse distance. A cube
with sides of length a will have a surface area of 6a2 and a volume of a3. The surface to volume ratio for a cube is thus shown as
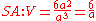 .
.
For a given shape, SA:V is inversely proportional to size. A cube 2 m on a side has a ratio of 3 m−1, half that of a cube 1 m on a side. On the converse, preserving SA:V as size increases requires changing to a less compact
shape.
to volume
ratios (e.g., very small diameter, or very porous
or otherwise not compact
) react at much faster rates than monolithic materials, because more surface is available to react. Examples include grain dust; while grain is not typically flammable, grain dust is explosive. Finely ground salt dissolves much more quickly than coarse salt. It is same-case-applicable to a multiparticulate system or any system that has a surface coating, a very important parameter to be consider while performing coating for pharmaceutical solid oral-dosage form.
High surface-area-to-volume ratio provides a strong "driving force" to speed up thermodynamic processes that minimize thermodynamic free energy
.
The ratio between the surface area and volume of cells and organisms has an enormous impact on their biology. For example, many aquatic microorganisms have increased surface area to increase their drag in the water. This reduces their rate of sink and allows them to remain near the surface with less energy expenditure. Humans and other large animals cannot rely on diffusion for absorption and rejection of respiratory gases for their whole body; however, animals such as flatworms and leeches can, as they have more surface area per unit volume. For similar reasons, surface to volume ratio places a maximum limit on the size of a cell.
An increased surface area to volume ratio also means increased exposure to the environment. The many tentacles of jellyfish and anemones provide increased surface area for the acquisition of food. Greater surface area allows more of the surrounding water to be sifted for nutrients.
Individual organs in animals are often shaped by requirements of surface area to volume ratio. The numerous internal branchings of the lung increase the surface area through which oxygen is passed into the blood and carbon dioxide is released from the blood. The intestine has a finely wrinkled internal surface, increasing the area through which nutrients are absorbed by the body.
Smaller single celled organisms need to have a high surface area to volume ratio in order to survive. This is because they rely on oxygen diffusing into the cell. The higher the SA:Volume ratio they have, the more efficient this process can be.
A wide and thin cell, such as a nerve cell
, or one with membrane protrusions such as microvilli has a greater surface-area-to-volume ratio than a spheroidal one.
Increased surface area can also lead to biological problems. More contact with the environment through the surface of a cell or an organ (relative to its volume) increases loss of water and dissolved substances. High surface-area-to-volume ratios also present problems of temperature control in unfavorable environments.
Surface area
Surface area is the measure of how much exposed area a solid object has, expressed in square units. Mathematical description of the surface area is considerably more involved than the definition of arc length of a curve. For polyhedra the surface area is the sum of the areas of its faces...
per unit volume of an object or collection of objects. The surface-area-to-volume ratio is measured in units of inverse distance. A cube
Cube
In geometry, a cube is a three-dimensional solid object bounded by six square faces, facets or sides, with three meeting at each vertex. The cube can also be called a regular hexahedron and is one of the five Platonic solids. It is a special kind of square prism, of rectangular parallelepiped and...
with sides of length a will have a surface area of 6a2 and a volume of a3. The surface to volume ratio for a cube is thus shown as
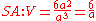 .
.For a given shape, SA:V is inversely proportional to size. A cube 2 m on a side has a ratio of 3 m−1, half that of a cube 1 m on a side. On the converse, preserving SA:V as size increases requires changing to a less compact
Compactness measure of a shape
The compactness measure of a shape, sometimes called the shape factor, is a numerical quantity representing the degree to which a shape is compact. The meaning of "compact" here is not related to the topological notion of compact space. Various compactness measures are used...
shape.
Physical chemistry
In involving a solid material, the surface-area-to-volume ratio is an important factor for the reactivity, that is, the rate at which the chemical reaction will proceed. Materials with large surface areaSurface area
Surface area is the measure of how much exposed area a solid object has, expressed in square units. Mathematical description of the surface area is considerably more involved than the definition of arc length of a curve. For polyhedra the surface area is the sum of the areas of its faces...
to volume
Volume
Volume is the quantity of three-dimensional space enclosed by some closed boundary, for example, the space that a substance or shape occupies or contains....
ratios (e.g., very small diameter, or very porous
Porosity
Porosity or void fraction is a measure of the void spaces in a material, and is a fraction of the volume of voids over the total volume, between 0–1, or as a percentage between 0–100%...
or otherwise not compact
Compactness measure of a shape
The compactness measure of a shape, sometimes called the shape factor, is a numerical quantity representing the degree to which a shape is compact. The meaning of "compact" here is not related to the topological notion of compact space. Various compactness measures are used...
) react at much faster rates than monolithic materials, because more surface is available to react. Examples include grain dust; while grain is not typically flammable, grain dust is explosive. Finely ground salt dissolves much more quickly than coarse salt. It is same-case-applicable to a multiparticulate system or any system that has a surface coating, a very important parameter to be consider while performing coating for pharmaceutical solid oral-dosage form.
High surface-area-to-volume ratio provides a strong "driving force" to speed up thermodynamic processes that minimize thermodynamic free energy
Thermodynamic free energy
The thermodynamic free energy is the amount of work that a thermodynamic system can perform. The concept is useful in the thermodynamics of chemical or thermal processes in engineering and science. The free energy is the internal energy of a system less the amount of energy that cannot be used to...
.
Biology
The ratio between the surface area and volume of cells and organisms has an enormous impact on their biology. For example, many aquatic microorganisms have increased surface area to increase their drag in the water. This reduces their rate of sink and allows them to remain near the surface with less energy expenditure. Humans and other large animals cannot rely on diffusion for absorption and rejection of respiratory gases for their whole body; however, animals such as flatworms and leeches can, as they have more surface area per unit volume. For similar reasons, surface to volume ratio places a maximum limit on the size of a cell.
An increased surface area to volume ratio also means increased exposure to the environment. The many tentacles of jellyfish and anemones provide increased surface area for the acquisition of food. Greater surface area allows more of the surrounding water to be sifted for nutrients.
Individual organs in animals are often shaped by requirements of surface area to volume ratio. The numerous internal branchings of the lung increase the surface area through which oxygen is passed into the blood and carbon dioxide is released from the blood. The intestine has a finely wrinkled internal surface, increasing the area through which nutrients are absorbed by the body.
Smaller single celled organisms need to have a high surface area to volume ratio in order to survive. This is because they rely on oxygen diffusing into the cell. The higher the SA:Volume ratio they have, the more efficient this process can be.
A wide and thin cell, such as a nerve cell
Neuron
A neuron is an electrically excitable cell that processes and transmits information by electrical and chemical signaling. Chemical signaling occurs via synapses, specialized connections with other cells. Neurons connect to each other to form networks. Neurons are the core components of the nervous...
, or one with membrane protrusions such as microvilli has a greater surface-area-to-volume ratio than a spheroidal one.
Increased surface area can also lead to biological problems. More contact with the environment through the surface of a cell or an organ (relative to its volume) increases loss of water and dissolved substances. High surface-area-to-volume ratios also present problems of temperature control in unfavorable environments.
Examples
| Shape | Length  |
Area | Volume | SA/V ratio | SA/V ratio for unit volume | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tetrahedron Tetrahedron In geometry, a tetrahedron is a polyhedron composed of four triangular faces, three of which meet at each vertex. A regular tetrahedron is one in which the four triangles are regular, or "equilateral", and is one of the Platonic solids... |
 |
side | 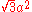 |
 |
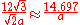 |
7.21 |
| Cube Cube In geometry, a cube is a three-dimensional solid object bounded by six square faces, facets or sides, with three meeting at each vertex. The cube can also be called a regular hexahedron and is one of the five Platonic solids. It is a special kind of square prism, of rectangular parallelepiped and... |
 |
side |  |
 |
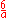 |
6 |
| Octahedron Octahedron In geometry, an octahedron is a polyhedron with eight faces. A regular octahedron is a Platonic solid composed of eight equilateral triangles, four of which meet at each vertex.... |
 |
side |  |
 |
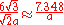 |
5.72 |
| Dodecahedron |  |
side |  |
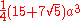 |
 |
5.31 |
| Icosahedron Icosahedron In geometry, an icosahedron is a regular polyhedron with 20 identical equilateral triangular faces, 30 edges and 12 vertices. It is one of the five Platonic solids.... |
 |
side |  |
 |
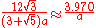 |
5.148 |
| Sphere Sphere A sphere is a perfectly round geometrical object in three-dimensional space, such as the shape of a round ball. Like a circle in two dimensions, a perfect sphere is completely symmetrical around its center, with all points on the surface lying the same distance r from the center point... |
 |
radius |  |
 |
 |
4.836 |
See also
- Sphericity
- Compactness measure of a shapeCompactness measure of a shapeThe compactness measure of a shape, sometimes called the shape factor, is a numerical quantity representing the degree to which a shape is compact. The meaning of "compact" here is not related to the topological notion of compact space. Various compactness measures are used...
- Bergmann's ruleBergmann's RuleBergmann's rule is an ecogeographic principle that states that within a broadly distributed genus, species of larger size are found in colder environments, and species of smaller size are found in warmer regions. Although originally formulated in terms of species within a genus, it has often been...
- Specific surface areaSpecific surface areaSpecific surface area is a material property of solids which measures the total surface area per unit of mass, solid or bulk volume, or cross-sectional area...

