
Geology of England
Encyclopedia

Sedimentary rock
Sedimentary rock are types of rock that are formed by the deposition of material at the Earth's surface and within bodies of water. Sedimentation is the collective name for processes that cause mineral and/or organic particles to settle and accumulate or minerals to precipitate from a solution....
. The youngest rocks are in the south east around London
Geology of London
The geology of London comprises various differing layers of sedimentary rock upon which London, England is built.-Oldest rocks:The oldest rocks proved through boreholes to exist below London are the old, hard rocks of the Palaeozoic. These consist of Silurian mudstones and sandstones, generally...
, progressing in age in a north westerly direction. The Tees-Exe line
Tees-Exe line
The Tees-Exe line is an imaginary line that can be drawn on a map of Great Britain which roughly divides the lowland and upland regions of the country....
marks the division between younger, softer and low-lying rocks in the south east and older, harder, and generally a higher relief in north west of the line. The geology
Geology
Geology is the science comprising the study of solid Earth, the rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which it evolves. Geology gives insight into the history of the Earth, as it provides the primary evidence for plate tectonics, the evolutionary history of life, and past climates...
of England
England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Scotland to the north and Wales to the west; the Irish Sea is to the north west, the Celtic Sea to the south west, with the North Sea to the east and the English Channel to the south separating it from continental...
is recognisable in the landscape of its counties
Counties of England
Counties of England are areas used for the purposes of administrative, geographical and political demarcation. For administrative purposes, England outside Greater London and the Isles of Scilly is divided into 83 counties. The counties may consist of a single district or be divided into several...
, the building materials of its town
Town
A town is a human settlement larger than a village but smaller than a city. The size a settlement must be in order to be called a "town" varies considerably in different parts of the world, so that, for example, many American "small towns" seem to British people to be no more than villages, while...
s and its regional extractive industries.
Bedrock
The bedrockBedrock
In stratigraphy, bedrock is the native consolidated rock underlying the surface of a terrestrial planet, usually the Earth. Above the bedrock is usually an area of broken and weathered unconsolidated rock in the basal subsoil...
consists of many layers formed over vast periods of time. These were laid down in various climate
Climate
Climate encompasses the statistics of temperature, humidity, atmospheric pressure, wind, rainfall, atmospheric particle count and other meteorological elemental measurements in a given region over long periods...
s as the global climate changed, the landmasses moved due to continental drift
Continental drift
Continental drift is the movement of the Earth's continents relative to each other. The hypothesis that continents 'drift' was first put forward by Abraham Ortelius in 1596 and was fully developed by Alfred Wegener in 1912...
, and the land and sea levels rose or fell. From time to time horizontal forces caused the rock to undergo considerable deformation, folding the layers of rock to form mountains which have since been eroded
Erosion
Erosion is when materials are removed from the surface and changed into something else. It only works by hydraulic actions and transport of solids in the natural environment, and leads to the deposition of these materials elsewhere...
and overlain with other layers. To further complicate the geology, the land has also been subject to periods of earthquake
Earthquake
An earthquake is the result of a sudden release of energy in the Earth's crust that creates seismic waves. The seismicity, seismism or seismic activity of an area refers to the frequency, type and size of earthquakes experienced over a period of time...
s and volcanic
Vulcanism
Vulcanism may refer to* Volcanism or volcanic activity.* Plutonism, a scientific theory of the Earth....
activity.
Deposits by glaciers
Overprinted on this bedrockBedrock
In stratigraphy, bedrock is the native consolidated rock underlying the surface of a terrestrial planet, usually the Earth. Above the bedrock is usually an area of broken and weathered unconsolidated rock in the basal subsoil...
geology ("solid geology" in the terminology of the maps) is a somewhat variable distribution of soils and fragmental material deposited by glaciers (boulder clay
Boulder clay
Boulder clay, in geology, is a deposit of clay, often full of boulders, which is formed in and beneath glaciers and ice-sheets wherever they are found, but is in a special sense the typical deposit of the Glacial Period in northern Europe and North America...
, and other forms of glacial drift in the recent past. Maps showing the distribution of this "drift" geology are frequently produced as either separate maps, or as literal overprints on the solid geology maps. When ordering maps, this distinction should be kept in mind. Catalogues often distinguish them as "S", "D" or "S+D" maps. "Drift" geology is often more important than "solid" geology when considering building works, drainage, siting water boreholes, soil fertility, and many other issues.
Glaciation and the resulting glacial and fluvio-glacial deposition has had a vast impact on the geology of England covering many areas with a veneer of glacial till in the lower lying areas north of a line running from Bristol
Bristol
Bristol is a city, unitary authority area and ceremonial county in South West England, with an estimated population of 433,100 for the unitary authority in 2009, and a surrounding Larger Urban Zone with an estimated 1,070,000 residents in 2007...
to London
London
London is the capital city of :England and the :United Kingdom, the largest metropolitan area in the United Kingdom, and the largest urban zone in the European Union by most measures. Located on the River Thames, London has been a major settlement for two millennia, its history going back to its...
. In the Ribble
River Ribble
The River Ribble is a river that runs through North Yorkshire and Lancashire, in northern England. The river's drainage basin also includes parts of Greater Manchester around Wigan.-Geography:...
valley, Lancashire
Lancashire
Lancashire is a non-metropolitan county of historic origin in the North West of England. It takes its name from the city of Lancaster, and is sometimes known as the County of Lancaster. Although Lancaster is still considered to be the county town, Lancashire County Council is based in Preston...
in north west England
England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Scotland to the north and Wales to the west; the Irish Sea is to the north west, the Celtic Sea to the south west, with the North Sea to the east and the English Channel to the south separating it from continental...
the resulting drumlins are clearly visible. Cromer Ridge
Cromer Ridge
Cromer Ridge is a ridge of old glacial moraines that stands next to the coast above Cromer, Norfolk, England. Cromer Ridge seems to have been the front line of the ice sheet for some time at the last glaciation, which is shown by the large size of the feature...
in East Anglia
East Anglia
East Anglia is a traditional name for a region of eastern England, named after an ancient Anglo-Saxon kingdom, the Kingdom of the East Angles. The Angles took their name from their homeland Angeln, in northern Germany. East Anglia initially consisted of Norfolk and Suffolk, but upon the marriage of...
is terminal moraine
Terminal moraine
A terminal moraine, also called end moraine, is a moraine that forms at the end of the glacier called the snout.Terminal moraines mark the maximum advance of the glacier. An end moraine is at the present boundary of the glacier....
. Indeed most of East Anglia
East Anglia
East Anglia is a traditional name for a region of eastern England, named after an ancient Anglo-Saxon kingdom, the Kingdom of the East Angles. The Angles took their name from their homeland Angeln, in northern Germany. East Anglia initially consisted of Norfolk and Suffolk, but upon the marriage of...
is covered with glacial till which has produced its rich loam
Loam
Loam is soil composed of sand, silt, and clay in relatively even concentration . Loam soils generally contain more nutrients and humus than sandy soils, have better infiltration and drainage than silty soils, and are easier to till than clay soils...
y soils. This unconsolidated material (it is not stuck tightly together) is very easily eroded hence the rapid rate of retreat of the coastline.

Yorkshire
Yorkshire is a historic county of northern England and the largest in the United Kingdom. Because of its great size in comparison to other English counties, functions have been increasingly undertaken over time by its subdivisions, which have also been subject to periodic reform...
in the Holderness
Holderness
Holderness is an area of the East Riding of Yorkshire, on the east coast of England. An area of rich agricultural land, Holderness was marshland until it was drained in the Middle Ages. Topographically, Holderness has more in common with the Netherlands than other parts of Yorkshire...
region. The chalk outcrop at Flamborough Head
Flamborough Head
Flamborough Head is a promontory of on the Yorkshire coast of England, between the Filey and Bridlington bays of the North Sea. It is a chalk headland, and the resistance it offers to coastal erosion may be contrasted with the low coast of Holderness to the south...
in the north produces a headland resistant to coastal erosion whilst the coastline south of this at such places as Mappleton and Hornsea
Hornsea
Hornsea is a small seaside resort, town and civil parish in the East Riding of Yorkshire, England at the eastern end of the Trans Pennine Trail.-Overview:According to the 2001 UK Census, Hornsea parish had a population of 8,243....
with their soft glacial deposits are vulnerable.
Former ice caps did not reach south of the line running from Bristol
Bristol
Bristol is a city, unitary authority area and ceremonial county in South West England, with an estimated population of 433,100 for the unitary authority in 2009, and a surrounding Larger Urban Zone with an estimated 1,070,000 residents in 2007...
to London
London
London is the capital city of :England and the :United Kingdom, the largest metropolitan area in the United Kingdom, and the largest urban zone in the European Union by most measures. Located on the River Thames, London has been a major settlement for two millennia, its history going back to its...
, so this area has only been impacted by fluvio-glacial deposition which is represented in gravel beds around rivers such as the Thames
River Thames
The River Thames flows through southern England. It is the longest river entirely in England and the second longest in the United Kingdom. While it is best known because its lower reaches flow through central London, the river flows alongside several other towns and cities, including Oxford,...
. As the ice caps retreated northwards, more fluvio-glacial deposition occurred for example in the Vale of York
Vale of York
The Vale of York is an area of flat land in the north-east of England. The vale is a major agricultural area and serves as the main north-south transport corridor for northern England....
Proterozoic Era
ProterozoicProterozoic
The Proterozoic is a geological eon representing a period before the first abundant complex life on Earth. The name Proterozoic comes from the Greek "earlier life"...
(2,500-542 Ma). The early geological development of the Avalonia terrane
Avalonia
Avalonia was a microcontinent in the Paleozoic era. Crustal fragments of this former microcontinent underlie south-west Great Britain, and the eastern coast of North America. It is the source of many of the older rocks of Western Europe, Atlantic Canada, and parts of the coastal United States...
, including England, is believed to have been in volcanic arc
Volcanic arc
A volcanic arc is a chain of volcanoes positioned in an arc shape as seen from above. Offshore volcanoes form islands, resulting in a volcanic island arc. Generally they result from the subduction of an oceanic tectonic plate under another tectonic plate, and often parallel an oceanic trench...
s near a subduction zone on the margin of the Gondwana
Gondwana
In paleogeography, Gondwana , originally Gondwanaland, was the southernmost of two supercontinents that later became parts of the Pangaea supercontinent. It existed from approximately 510 to 180 million years ago . Gondwana is believed to have sutured between ca. 570 and 510 Mya,...
continent. Some material may have accreted from volcanic island arcs which formed further out in the ocean and later collided with Gondwana as a result of plate tectonic
Plate tectonics
Plate tectonics is a scientific theory that describes the large scale motions of Earth's lithosphere...
movements. The igneous activity had started by 730 million years ago and continued until around 570 million years ago, resulting in a region of volcanic islands within a shallow sea. The remains of these islands underlie much of central England with small outcrops visible in various places.
Around 600 million years ago, the Cadomian Orogeny
Cadomian Orogeny
The Cadomian Orogeny was a tectonic event or series of events in the late Neoproterozoic, about 650-550 Ma, which probably included the formation of mountains. This occurred on the margin of the Gondwana continent, involving one or more collisions of island arcs and accretion of other material at a...
(mountain building period) caused the English landscape to be transformed into a mountainous region, along with much of north west Europe
Europe
Europe is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting...
.
Paleozoic Era
PaleozoicPaleozoic
The Paleozoic era is the earliest of three geologic eras of the Phanerozoic eon, spanning from roughly...
(542–251 Ma). In the early Cambrian
Cambrian
The Cambrian is the first geological period of the Paleozoic Era, lasting from Mya ; it is succeeded by the Ordovician. Its subdivisions, and indeed its base, are somewhat in flux. The period was established by Adam Sedgwick, who named it after Cambria, the Latin name for Wales, where Britain's...
period the volcano
Volcano
2. Bedrock3. Conduit 4. Base5. Sill6. Dike7. Layers of ash emitted by the volcano8. Flank| 9. Layers of lava emitted by the volcano10. Throat11. Parasitic cone12. Lava flow13. Vent14. Crater15...
es and mountain
Mountain
Image:Himalaya_annotated.jpg|thumb|right|The Himalayan mountain range with Mount Everestrect 58 14 160 49 Chomo Lonzorect 200 28 335 52 Makalurect 378 24 566 45 Mount Everestrect 188 581 920 656 Tibetan Plateaurect 250 406 340 427 Rong River...
s of England
England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Scotland to the north and Wales to the west; the Irish Sea is to the north west, the Celtic Sea to the south west, with the North Sea to the east and the English Channel to the south separating it from continental...
were eroded as the land became flooded by a rise in sea level, and new layers of sediment were laid down. Cambrian shales laid down in a shallow sea are exposed in the Midlands at Nuneaton
Nuneaton
Nuneaton is the largest town in the Borough of Nuneaton and Bedworth and in the English county of Warwickshire.Nuneaton is most famous for its associations with the 19th century author George Eliot, who was born on a farm on the Arbury Estate just outside Nuneaton in 1819 and lived in the town for...
. Much of central England formed a stable block of crust which has remained largely undeformed ever since.
dec2004.jpg)
Ordovician
The Ordovician is a geologic period and system, the second of six of the Paleozoic Era, and covers the time between 488.3±1.7 to 443.7±1.5 million years ago . It follows the Cambrian Period and is followed by the Silurian Period...
period, southern Britain, the east coast of North America
North America
North America is a continent wholly within the Northern Hemisphere and almost wholly within the Western Hemisphere. It is also considered a northern subcontinent of the Americas...
and south-east Newfoundland broke away from Gondwanaland to form the continent of Avalonia
Avalonia
Avalonia was a microcontinent in the Paleozoic era. Crustal fragments of this former microcontinent underlie south-west Great Britain, and the eastern coast of North America. It is the source of many of the older rocks of Western Europe, Atlantic Canada, and parts of the coastal United States...
. The Skiddaw
Skiddaw
Skiddaw is a mountain in the Lake District National Park in England. With a summit at 931 m above sea level it is the fourth highest mountain in England. It lies just north of the town of Keswick, Cumbria, and dominates the skyline in this part of the northern lakes...
Slate
Slate
Slate is a fine-grained, foliated, homogeneous metamorphic rock derived from an original shale-type sedimentary rock composed of clay or volcanic ash through low-grade regional metamorphism. The result is a foliated rock in which the foliation may not correspond to the original sedimentary layering...
s of the Lake District
Lake District
The Lake District, also commonly known as The Lakes or Lakeland, is a mountainous region in North West England. A popular holiday destination, it is famous not only for its lakes and its mountains but also for its associations with the early 19th century poetry and writings of William Wordsworth...
consist of metamorphosed marine sediments laid down on the northern margin of Avalonia
Avalonia
Avalonia was a microcontinent in the Paleozoic era. Crustal fragments of this former microcontinent underlie south-west Great Britain, and the eastern coast of North America. It is the source of many of the older rocks of Western Europe, Atlantic Canada, and parts of the coastal United States...
.
Large quantities of volcanic lava
Lava
Lava refers both to molten rock expelled by a volcano during an eruption and the resulting rock after solidification and cooling. This molten rock is formed in the interior of some planets, including Earth, and some of their satellites. When first erupted from a volcanic vent, lava is a liquid at...
and ash known as the Borrowdale Volcanics
Borrowdale Volcanics
The Borrowdale Volcanic Group is a group of igneous rock formations named after the Borrowdale area of the Lake District, in England. They are late Ordovician in age . It is thought that they represent the remains of a volcanic island arc, approximately similar to the island arcs of the west...
covered the Lake District
Lake District
The Lake District, also commonly known as The Lakes or Lakeland, is a mountainous region in North West England. A popular holiday destination, it is famous not only for its lakes and its mountains but also for its associations with the early 19th century poetry and writings of William Wordsworth...
, still seen in the form of mountains such as Helvellyn
Helvellyn
Helvellyn is a mountain in the English Lake District, the apex of the Eastern Fells. At above sea level, it is the third highest peak in both the Lake District and England...
and Scafell Pike
Scafell Pike
Scafell Pike is the highest mountain in England at . It is located in Lake District National Park sometimes confused with the neighbouring Sca Fell, to which it is connected by the col of Mickledore...
.
In the Silurian
Silurian
The Silurian is a geologic period and system that extends from the end of the Ordovician Period, about 443.7 ± 1.5 Mya , to the beginning of the Devonian Period, about 416.0 ± 2.8 Mya . As with other geologic periods, the rock beds that define the period's start and end are well identified, but the...
period, sandstones and mudstones were deposited in some parts of England. Volcanic ashes and lavas deposited during the period are still found in the Mendip Hills
Mendip Hills
The Mendip Hills is a range of limestone hills to the south of Bristol and Bath in Somerset, England. Running east to west between Weston-super-Mare and Frome, the hills overlook the Somerset Levels to the south and the Avon Valley to the north...
.
Avalonia had now joined with the continent of Baltica
Baltica
Baltica is a name applied by geologists to a late-Proterozoic, early-Palaeozoic continent that now includes the East European craton of northwestern Eurasia. Baltica was created as an entity not earlier than 1.8 billion years ago. Before this time, the three segments/continents that now comprise...
, and the combined landmass collided with Laurentia
Laurentia
Laurentia is a large area of continental craton, which forms the ancient geological core of the North American continent...
around 425 million years ago, joining the southern and northern halves of the British Isles
British Isles
The British Isles are a group of islands off the northwest coast of continental Europe that include the islands of Great Britain and Ireland and over six thousand smaller isles. There are two sovereign states located on the islands: the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland and...
together. The resulting Caledonian Orogeny
Caledonian orogeny
The Caledonian orogeny is a mountain building era recorded in the northern parts of the British Isles, the Scandinavian Mountains, Svalbard, eastern Greenland and parts of north-central Europe. The Caledonian orogeny encompasses events that occurred from the Ordovician to Early Devonian, roughly...
produced an Alpine
Alps
The Alps is one of the great mountain range systems of Europe, stretching from Austria and Slovenia in the east through Italy, Switzerland, Liechtenstein and Germany to France in the west....
-style mountain range. England lay on the southern fringe of this range.
In the Devonian
Devonian
The Devonian is a geologic period and system of the Paleozoic Era spanning from the end of the Silurian Period, about 416.0 ± 2.8 Mya , to the beginning of the Carboniferous Period, about 359.2 ± 2.5 Mya...
period, northern England was a region uplifted by the Caledonian Orogeny. The uplifted regions were gradually eroded down, resulting in the deposition of numerous sedimentary rock layers in lowlands and seas. The Old Red Sandstone
Old Red Sandstone
The Old Red Sandstone is a British rock formation of considerable importance to early paleontology. For convenience the short version of the term, 'ORS' is often used in literature on the subject.-Sedimentology:...
was deposited across much of central and southern England. Sea levels varied considerably at this time with the coastline advancing and retreating from north to south across England. The Old Red Sandstone of Devon
Devon
Devon is a large county in southwestern England. The county is sometimes referred to as Devonshire, although the term is rarely used inside the county itself as the county has never been officially "shired", it often indicates a traditional or historical context.The county shares borders with...
gave the period its name.

Carboniferous
The Carboniferous is a geologic period and system that extends from the end of the Devonian Period, about 359.2 ± 2.5 Mya , to the beginning of the Permian Period, about 299.0 ± 0.8 Mya . The name is derived from the Latin word for coal, carbo. Carboniferous means "coal-bearing"...
period, England was lying at the equator, covered by the warm shallow waters of the Rheic Ocean
Rheic Ocean
The Rheic Ocean was a Paleozoic ocean between the large continent Gondwana to the south and the microcontinents Avalonia and others to the north...
. During this time carboniferous limestone
Carboniferous limestone
Carboniferous Limestone is a term used to describe a variety of different types of limestone occurring widely across Great Britain and Ireland which were deposited during the Dinantian epoch of the Carboniferous period. They were formed between 363 and 325 million years ago...
was deposited, as found in the Mendip Hills
Mendip Hills
The Mendip Hills is a range of limestone hills to the south of Bristol and Bath in Somerset, England. Running east to west between Weston-super-Mare and Frome, the hills overlook the Somerset Levels to the south and the Avon Valley to the north...
, in the Peak District
Peak District
The Peak District is an upland area in central and northern England, lying mainly in northern Derbyshire, but also covering parts of Cheshire, Greater Manchester, Staffordshire, and South and West Yorkshire....
of Derbyshire
Derbyshire
Derbyshire is a county in the East Midlands of England. A substantial portion of the Peak District National Park lies within Derbyshire. The northern part of Derbyshire overlaps with the Pennines, a famous chain of hills and mountains. The county contains within its boundary of approx...
, north Lancashire
Lancashire
Lancashire is a non-metropolitan county of historic origin in the North West of England. It takes its name from the city of Lancaster, and is sometimes known as the County of Lancaster. Although Lancaster is still considered to be the county town, Lancashire County Council is based in Preston...
and the northern Pennines
Pennines
The Pennines are a low-rising mountain range, separating the North West of England from Yorkshire and the North East.Often described as the "backbone of England", they form a more-or-less continuous range stretching from the Peak District in Derbyshire, around the northern and eastern edges of...
. The erosion of this landscape by carbonation
Carbonation
Carbonation is the process of dissolving carbon dioxide in water. The process usually involves carbon dioxide under high pressure. When the pressure is reduced, the carbon dioxide is released from the solution as small bubbles, which cause the solution to "fizz." This effect is seen in carbonated...
has led to very distinctive scenery. Particularly notable is the area around Malham
Malham
Malham is a village and civil parish in the Craven district of North Yorkshire, England. Situated in the Yorkshire Dales with a population of approximately 150. The surrounding countryside is well known for its limestone pavements and other examples of limestone scenery...
in the Yorkshire Dales
Yorkshire Dales
The Yorkshire Dales is the name given to an upland area in Northern England.The area lies within the historic county boundaries of Yorkshire, though it spans the ceremonial counties of North Yorkshire, West Yorkshire and Cumbria...
with its limestone pavement
Limestone pavement
A limestone pavement is a natural karst landform consisting of a flat, incised surface of exposed limestone that resembles an artificial pavement. The term is mainly used in the UK where many of these landforms have developed distinctive surface patterning resembling block of paving...
s, sink holes and shake holes. Gaping Gill
Gaping Gill
Gaping Gill is a natural cave in North Yorkshire, England. It is one of the unmistakable landmarks on the southern slopes of Ingleborough – a deep pothole with the stream Fell Beck flowing into it...
is a waterfall disappearing underground into the carboniferous limestone.
The formation of carboniferous limestone
Carboniferous limestone
Carboniferous Limestone is a term used to describe a variety of different types of limestone occurring widely across Great Britain and Ireland which were deposited during the Dinantian epoch of the Carboniferous period. They were formed between 363 and 325 million years ago...
was followed by the deposition of dark marine shale
Shale
Shale is a fine-grained, clastic sedimentary rock composed of mud that is a mix of flakes of clay minerals and tiny fragments of other minerals, especially quartz and calcite. The ratio of clay to other minerals is variable. Shale is characterized by breaks along thin laminae or parallel layering...
s, siltstones and coarse sandstone
Sandstone
Sandstone is a sedimentary rock composed mainly of sand-sized minerals or rock grains.Most sandstone is composed of quartz and/or feldspar because these are the most common minerals in the Earth's crust. Like sand, sandstone may be any colour, but the most common colours are tan, brown, yellow,...
s of the Millstone Grit
Millstone Grit
Millstone Grit is the name given to any of a number of coarse-grained sandstones of Carboniferous age which occur in the Northern England. The name derives from its use in earlier times as a source of millstones for use principally in watermills...
, notably in the area later uplifted to form the Pennine anticline
Anticline
In structural geology, an anticline is a fold that is convex up and has its oldest beds at its core. The term is not to be confused with antiform, which is a purely descriptive term for any fold that is convex up. Therefore if age relationships In structural geology, an anticline is a fold that is...
. This sequence can be seen in the Yorkshire Dales
Yorkshire Dales
The Yorkshire Dales is the name given to an upland area in Northern England.The area lies within the historic county boundaries of Yorkshire, though it spans the ceremonial counties of North Yorkshire, West Yorkshire and Cumbria...
with Ingleborough
Ingleborough
Ingleborough is the second highest mountain in the Yorkshire Dales. It is one of the Yorkshire Three Peaks, the other two being Whernside and Pen-y-ghent. Ingleborough is frequently climbed as part of the Yorkshire Three Peaks Challenge, which is a 24-mile circular challenge walk starting and...
protruding up above the carboniferous limestone landscape below.
Later, river delta
River delta
A delta is a landform that is formed at the mouth of a river where that river flows into an ocean, sea, estuary, lake, reservoir, flat arid area, or another river. Deltas are formed from the deposition of the sediment carried by the river as the flow leaves the mouth of the river...
s formed and the sediments deposited were colonised by swamp
Swamp
A swamp is a wetland with some flooding of large areas of land by shallow bodies of water. A swamp generally has a large number of hammocks, or dry-land protrusions, covered by aquatic vegetation, or vegetation that tolerates periodical inundation. The two main types of swamp are "true" or swamp...
s and rain forest. It was in this environment that the cyclic
Cyclic sediments
Cyclic sediments are sequences of sedimentary rocks that are characterised by repetitive patterns of different rock types within the sequence. Cyclic sediments can be identified as either autocyclic or allocyclic, and can be hundreds or even thousands of metres thick...
coal measures
Coal Measures
The Coal Measures is a lithostratigraphical term for the coal-bearing part of the Upper Carboniferous System. It represents the remains of fluvio-deltaic sediment, and consists mainly of clastic rocks interstratified with the beds of coal...
were formed. Coal
Coal
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock usually occurring in rock strata in layers or veins called coal beds or coal seams. The harder forms, such as anthracite coal, can be regarded as metamorphic rock because of later exposure to elevated temperature and pressure...
can be found as far south as Kent
Kent
Kent is a county in southeast England, and is one of the home counties. It borders East Sussex, Surrey and Greater London and has a defined boundary with Essex in the middle of the Thames Estuary. The ceremonial county boundaries of Kent include the shire county of Kent and the unitary borough of...
with deposits stretching northwards to Tyne and Wear
Tyne and Wear
Tyne and Wear is a metropolitan county in north east England around the mouths of the Rivers Tyne and Wear. It came into existence as a metropolitan county in 1974 after the passage of the Local Government Act 1972...
; though coal has largely been mined in the Midlands
English Midlands
The Midlands, or the English Midlands, is the traditional name for the area comprising central England that broadly corresponds to the early medieval Kingdom of Mercia. It borders Southern England, Northern England, East Anglia and Wales. Its largest city is Birmingham, and it was an important...
and northern England. One of the best exposures of the Coal Measures
Coal Measures
The Coal Measures is a lithostratigraphical term for the coal-bearing part of the Upper Carboniferous System. It represents the remains of fluvio-deltaic sediment, and consists mainly of clastic rocks interstratified with the beds of coal...
is on the north east coast between Whitley Bay
Whitley Bay
Whitley Bay is a town in North Tyneside, in Tyne and Wear, England. It is on the North Sea coast and has a fine stretch of golden sandy beach forming a bay stretching from St. Mary's Island in the north to Cullercoats in the south...
and Seaton Sluice
Seaton Sluice
Seaton Sluice is a village in Northumberland. It lies on the coast at the mouth of the Seaton Burn, midway between Whitley Bay and Blyth. It has a population of about 3,000 people.- Early history :...
.

Variscan orogeny
The Variscan orogeny is a geologic mountain-building event caused by Late Paleozoic continental collision between Euramerica and Gondwana to form the supercontinent of Pangaea.-Naming:...
(mountain building period) caused major deformation in south west England. The general region of Variscan folding was south of an east-west line roughly from Avon
Avon (county)
Avon was, from 1974 to 1996, a non-metropolitan and ceremonial county in the west of England.The county was named after the River Avon, which runs through the area. It was formed from parts of the historic counties of Gloucestershire and Somerset, together with the City of Bristol...
to Kent
Kent
Kent is a county in southeast England, and is one of the home counties. It borders East Sussex, Surrey and Greater London and has a defined boundary with Essex in the middle of the Thames Estuary. The ceremonial county boundaries of Kent include the shire county of Kent and the unitary borough of...
, though lesser folding took place as far north as Derbyshire
Derbyshire
Derbyshire is a county in the East Midlands of England. A substantial portion of the Peak District National Park lies within Derbyshire. The northern part of Derbyshire overlaps with the Pennines, a famous chain of hills and mountains. The county contains within its boundary of approx...
and Berwick-upon-Tweed
Berwick-upon-Tweed
Berwick-upon-Tweed or simply Berwick is a town in the county of Northumberland and is the northernmost town in England, on the east coast at the mouth of the River Tweed. It is situated 2.5 miles south of the Scottish border....
. The main tectonic pressure was from the south or south-east.
Towards the end of the orogeny the emplacement of a large batholith
Cornubian batholith
The Cornubian batholith refers to the group of associated granite intrusions which underlie the south-western peninsula of Great Britain. The main exposed masses of the batholith are seen at Dartmoor, Bodmin Moor, St Austell, Carnmenellis, Land's End and the Isles of Scilly. It formed during the...
of granite
Granite
Granite is a common and widely occurring type of intrusive, felsic, igneous rock. Granite usually has a medium- to coarse-grained texture. Occasionally some individual crystals are larger than the groundmass, in which case the texture is known as porphyritic. A granitic rock with a porphyritic...
occurred below what is now Devon
Devon
Devon is a large county in southwestern England. The county is sometimes referred to as Devonshire, although the term is rarely used inside the county itself as the county has never been officially "shired", it often indicates a traditional or historical context.The county shares borders with...
and Cornwall
Cornwall
Cornwall is a unitary authority and ceremonial county of England, within the United Kingdom. It is bordered to the north and west by the Celtic Sea, to the south by the English Channel, and to the east by the county of Devon, over the River Tamar. Cornwall has a population of , and covers an area of...
. This granite is now exposed as Dartmoor
Dartmoor
Dartmoor is an area of moorland in south Devon, England. Protected by National Park status, it covers .The granite upland dates from the Carboniferous period of geological history. The moorland is capped with many exposed granite hilltops known as tors, providing habitats for Dartmoor wildlife. The...
, Bodmin Moor
Bodmin Moor
Bodmin Moor is a granite moorland in northeastern Cornwall, England, United Kingdom. It is in size, and originally dates from the Carboniferous period of geological history....
and several other exposures in Cornwall, including the Isles of Scilly
Isles of Scilly
The Isles of Scilly form an archipelago off the southwestern tip of the Cornish peninsula of Great Britain. The islands have had a unitary authority council since 1890, and are separate from the Cornwall unitary authority, but some services are combined with Cornwall and the islands are still part...
. Granite tors form important elements in the landscape in these areas. Metamorphism of the country rocks
Country rock (geology)
Country rock is a geological term meaning the rock native to an area. It is similar and in many cases interchangeable with the terms basement and wall rocks....
and hydrothermal circulation
Hydrothermal circulation
Hydrothermal circulation in its most general sense is the circulation of hot water; 'hydros' in the Greek meaning water and 'thermos' meaning heat. Hydrothermal circulation occurs most often in the vicinity of sources of heat within the Earth's crust...
of metal-rich fluids in the cooling rock provided the source of the extensive metalliferous deposits of the region (primarily copper and tin). Later weathering
Weathering
Weathering is the breaking down of rocks, soils and minerals as well as artificial materials through contact with the Earth's atmosphere, biota and waters...
of the granite led to deposits of kaolin which has been excavated as it is an important source of china clay and ball clay
Ball clay
Ball clays are kaolinitic sedimentary clays, that commonly consist of 20-80% kaolinite, 10-25% mica, 6-65% quartz. Localized seams in the same deposit have variations in composition, including the quantity of the major minerals, accessory minerals and carbonaceous materials such as lignite...
used in the production of such products as porcelain
Porcelain
Porcelain is a ceramic material made by heating raw materials, generally including clay in the form of kaolin, in a kiln to temperatures between and...
and shiny printing paper.
By the end of the period, England had a hot arid desert
Desert
A desert is a landscape or region that receives an extremely low amount of precipitation, less than enough to support growth of most plants. Most deserts have an average annual precipitation of less than...
climate, with frequent flash floods leaving deposits that formed red beds, somewhat similar to the later, Triassic
Triassic
The Triassic is a geologic period and system that extends from about 250 to 200 Mya . As the first period of the Mesozoic Era, the Triassic follows the Permian and is followed by the Jurassic. Both the start and end of the Triassic are marked by major extinction events...
New Red Sandstone
New Red Sandstone
The New Red Sandstone is a chiefly British geological term for the beds of red sandstone and associated rocks laid down throughout the Permian to the beginning of the Triassic that underlie the Jurassic Lias; the term distinguishes it from the Old Red Sandstone which is largely Devonian in...
.
After the end of the Carboniferous period, an intrusion of quartz dolerite formed the Whin Sill
Whin Sill
The Whin Sill or Great Whin Sill is a tabular layer of the igneous rock dolerite in County Durham and Northumberland in the northeast of England. It lies partly in the North Pennines Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty and partly in Northumberland National Park and stretches from Teesdale northwards...
. The river Tees
River Tees
The River Tees is in Northern England. It rises on the eastern slope of Cross Fell in the North Pennines, and flows eastwards for 85 miles to reach the North Sea between Hartlepool and Redcar.-Geography:...
flows over this at High Force
High Force
High Force is a waterfall on the River Tees, near Middleton-in-Teesdale, Teesdale, County Durham, England. The waterfall is within the North Pennines Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty and European Geopark....
on the Alston Block
Alston Block
The Alston Block is a term used by geologists to describe the geological structure of the North Pennines of northern England and which forms a part of the Pennine Block & Basin Province which originated during the Carboniferous period. It is defined by the Stublick and Ninety Fathom Faults to the...
. Whin Sill
Whin Sill
The Whin Sill or Great Whin Sill is a tabular layer of the igneous rock dolerite in County Durham and Northumberland in the northeast of England. It lies partly in the North Pennines Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty and partly in Northumberland National Park and stretches from Teesdale northwards...
is also seen again at Hadrian's Wall
Hadrian's Wall
Hadrian's Wall was a defensive fortification in Roman Britain. Begun in AD 122, during the rule of emperor Hadrian, it was the first of two fortifications built across Great Britain, the second being the Antonine Wall, lesser known of the two because its physical remains are less evident today.The...
. The country rock is Lower Carboniferous limestone and shales.
The Permian
Permian
The PermianThe term "Permian" was introduced into geology in 1841 by Sir Sir R. I. Murchison, president of the Geological Society of London, who identified typical strata in extensive Russian explorations undertaken with Edouard de Verneuil; Murchison asserted in 1841 that he named his "Permian...
period was characterised for 30 million years by arid desert
Desert
A desert is a landscape or region that receives an extremely low amount of precipitation, less than enough to support growth of most plants. Most deserts have an average annual precipitation of less than...
and erosion of the areas uplifted in the Variscan Orogeny
Variscan orogeny
The Variscan orogeny is a geologic mountain-building event caused by Late Paleozoic continental collision between Euramerica and Gondwana to form the supercontinent of Pangaea.-Naming:...
(southwest England and adjacent areas in the present-day English Channel). Later, much of England was submerged in shallow waters as the polar ice sheets melted and the Tethys Ocean
Tethys Ocean
The Tethys Ocean was an ocean that existed between the continents of Gondwana and Laurasia during the Mesozoic era before the opening of the Indian Ocean.-Modern theory:...
and Zechstein Sea formed, depositing shale
Shale
Shale is a fine-grained, clastic sedimentary rock composed of mud that is a mix of flakes of clay minerals and tiny fragments of other minerals, especially quartz and calcite. The ratio of clay to other minerals is variable. Shale is characterized by breaks along thin laminae or parallel layering...
, limestone
Limestone
Limestone is a sedimentary rock composed largely of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of calcium carbonate . Many limestones are composed from skeletal fragments of marine organisms such as coral or foraminifera....
, gravel
Gravel
Gravel is composed of unconsolidated rock fragments that have a general particle size range and include size classes from granule- to boulder-sized fragments. Gravel can be sub-categorized into granule and cobble...
, and marl
Marl
Marl or marlstone is a calcium carbonate or lime-rich mud or mudstone which contains variable amounts of clays and aragonite. Marl was originally an old term loosely applied to a variety of materials, most of which occur as loose, earthy deposits consisting chiefly of an intimate mixture of clay...
, before finally receding to leave a flat desert with salt pan
Dry lake
Dry lakes are ephemeral lakebeds, or a remnant of an endorheic lake. Such flats consist of fine-grained sediments infused with alkali salts. Dry lakes are also referred to as alkali flats, sabkhas, playas or mud flats...
s.
Mesozoic Era
MesozoicMesozoic
The Mesozoic era is an interval of geological time from about 250 million years ago to about 65 million years ago. It is often referred to as the age of reptiles because reptiles, namely dinosaurs, were the dominant terrestrial and marine vertebrates of the time...
(251–65 Ma). As Pangaea drifted during the Triassic
Triassic
The Triassic is a geologic period and system that extends from about 250 to 200 Mya . As the first period of the Mesozoic Era, the Triassic follows the Permian and is followed by the Jurassic. Both the start and end of the Triassic are marked by major extinction events...
period, England moved away from the equator until they were between 20° and 30° north. Red beds, including sandstones and red mudstone
Mudstone
Mudstone is a fine grained sedimentary rock whose original constituents were clays or muds. Grain size is up to 0.0625 mm with individual grains too small to be distinguished without a microscope. With increased pressure over time the platey clay minerals may become aligned, with the...
s form the main sediments of the New Red Sandstone
New Red Sandstone
The New Red Sandstone is a chiefly British geological term for the beds of red sandstone and associated rocks laid down throughout the Permian to the beginning of the Triassic that underlie the Jurassic Lias; the term distinguishes it from the Old Red Sandstone which is largely Devonian in...
. The remnants of the Variscan uplands in France
France
The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
to the south were eroded down, resulting in layers of the New Red Sandstone being deposited across central England, and in faulted basins in Cheshire
Cheshire
Cheshire is a ceremonial county in North West England. Cheshire's county town is the city of Chester, although its largest town is Warrington. Other major towns include Widnes, Congleton, Crewe, Ellesmere Port, Runcorn, Macclesfield, Winsford, Northwich, and Wilmslow...
. A basin developed in the Hampshire
Hampshire
Hampshire is a county on the southern coast of England in the United Kingdom. The county town of Hampshire is Winchester, a historic cathedral city that was once the capital of England. Hampshire is notable for housing the original birthplaces of the Royal Navy, British Army, and Royal Air Force...
region around this time. Rift
Rift
In geology, a rift or chasm is a place where the Earth's crust and lithosphere are being pulled apart and is an example of extensional tectonics....
ing occurred within and around England, prior to the breakup of the super-continent in the Jurassic period.
Rock fragments found near Bristol
Bristol
Bristol is a city, unitary authority area and ceremonial county in South West England, with an estimated population of 433,100 for the unitary authority in 2009, and a surrounding Larger Urban Zone with an estimated 1,070,000 residents in 2007...
appear to indicate that in 214 million years ago England was showered with a fine layer of debris from an asteroid impact
Impact event
An impact event is the collision of a large meteorite, asteroid, comet, or other celestial object with the Earth or another planet. Throughout recorded history, hundreds of minor impact events have been reported, with some occurrences causing deaths, injuries, property damage or other significant...
at the Manicouagan Impact Crater in Canada
Canada
Canada is a North American country consisting of ten provinces and three territories. Located in the northern part of the continent, it extends from the Atlantic Ocean in the east to the Pacific Ocean in the west, and northward into the Arctic Ocean...
, although this is still being debated.

Jurassic
The Jurassic is a geologic period and system that extends from about Mya to Mya, that is, from the end of the Triassic to the beginning of the Cretaceous. The Jurassic constitutes the middle period of the Mesozoic era, also known as the age of reptiles. The start of the period is marked by...
period started, Pangaea
Pangaea
Pangaea, Pangæa, or Pangea is hypothesized as a supercontinent that existed during the Paleozoic and Mesozoic eras about 250 million years ago, before the component continents were separated into their current configuration....
began to break up and sea levels rose, as England drifted on the Eurasian Plate
Eurasian Plate
The Eurasian Plate is a tectonic plate which includes most of the continent of Eurasia , with the notable exceptions of the Indian subcontinent, the Arabian subcontinent, and the area east of the Chersky Range in East Siberia...
to between 30° and 40° north. With much of England under water again, sedimentary rock
Sedimentary rock
Sedimentary rock are types of rock that are formed by the deposition of material at the Earth's surface and within bodies of water. Sedimentation is the collective name for processes that cause mineral and/or organic particles to settle and accumulate or minerals to precipitate from a solution....
s were deposited and can now be found underlying much of southern England from the Cleveland Hills
Cleveland Hills
The Cleveland Hills are a range of hills on the north-west edge of the North York Moors in North Yorkshire, England, overlooking Cleveland and Teesside. They lie entirely within the boundaries of the North York Moors National Park. Part of the long Cleveland Way National Trail runs along the...
of Yorkshire
Yorkshire
Yorkshire is a historic county of northern England and the largest in the United Kingdom. Because of its great size in comparison to other English counties, functions have been increasingly undertaken over time by its subdivisions, which have also been subject to periodic reform...
to the Jurassic Coast
Jurassic Coast
The Jurassic Coast is a World Heritage Site on the English Channel coast of southern England. The site stretches from Orcombe Point near Exmouth in East Devon to Old Harry Rocks near Swanage in East Dorset, a distance of ....
in Dorset
Geology of Dorset
Dorset, England, rests on a variety of different rock types which give the county its interesting landscapes and habitats. Dorset is particularly noted for its coastline, the Jurassic Coast, which in 2001 was designated a World Heritage Site because of the variety of landforms and fossils...
, including clay
Clay
Clay is a general term including many combinations of one or more clay minerals with traces of metal oxides and organic matter. Geologic clay deposits are mostly composed of phyllosilicate minerals containing variable amounts of water trapped in the mineral structure.- Formation :Clay minerals...
s, sandstone
Sandstone
Sandstone is a sedimentary rock composed mainly of sand-sized minerals or rock grains.Most sandstone is composed of quartz and/or feldspar because these are the most common minerals in the Earth's crust. Like sand, sandstone may be any colour, but the most common colours are tan, brown, yellow,...
s, greensand
Greensand
Greensand or Green sand is either a sand or sandstone, which has a greenish color. This term is specifically applied to shallow marine sediment, that contains noticeable quantities of rounded greenish grains. These grains are called glauconies and consist of a mixture of mixed-layer clay...
s, oolitic
Oolite
Oolite is a sedimentary rock formed from ooids, spherical grains composed of concentric layers. The name derives from the Hellenic word òoion for egg. Strictly, oolites consist of ooids of diameter 0.25–2 mm; rocks composed of ooids larger than 2 mm are called pisolites...
limestone
Limestone
Limestone is a sedimentary rock composed largely of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of calcium carbonate . Many limestones are composed from skeletal fragments of marine organisms such as coral or foraminifera....
of the Cotswold Hills, corallian limestone
Corallian Limestone
Corallian Limestone is a coralliferous sedimentary rock, laid down in Jurassic times. It is a hard variety of "coral rag". Building stones from this geological structure tend to be irregular in shape. It is often found close to seams of Portland Limestone...
of the Vale of White Horse
Vale of White Horse
The Vale of White Horse is a local government district of Oxfordshire in England. The main town is Abingdon, other places include Faringdon and Wantage. There are 68 parishes within the district...
and the Isle of Portland. A particularly interesting Jurassic
Jurassic
The Jurassic is a geologic period and system that extends from about Mya to Mya, that is, from the end of the Triassic to the beginning of the Cretaceous. The Jurassic constitutes the middle period of the Mesozoic era, also known as the age of reptiles. The start of the period is marked by...
site is on the North Yorkshire
Yorkshire
Yorkshire is a historic county of northern England and the largest in the United Kingdom. Because of its great size in comparison to other English counties, functions have been increasingly undertaken over time by its subdivisions, which have also been subject to periodic reform...
coast between Staithes and Port Mulgrave
Hinderwell
Hinderwell is a village and civil parish in the Scarboroughdistrict of North Yorkshire, England.Hinderwell lies about a mile from the coast on the A174 road between the towns of Loftus and Whitby. It may also be visited by the Cleveland Way footpath...
.
The burial of algae
Algae
Algae are a large and diverse group of simple, typically autotrophic organisms, ranging from unicellular to multicellular forms, such as the giant kelps that grow to 65 meters in length. They are photosynthetic like plants, and "simple" because their tissues are not organized into the many...
and bacteria below the mud of the sea floor during this time resulted in the formation of North Sea oil
North Sea oil
North Sea oil is a mixture of hydrocarbons, comprising liquid oil and natural gas, produced from oil reservoirs beneath the North Sea.In the oil industry, the term "North Sea" often includes areas such as the Norwegian Sea and the area known as "West of Shetland", "the Atlantic Frontier" or "the...
and natural gas
Natural gas
Natural gas is a naturally occurring gas mixture consisting primarily of methane, typically with 0–20% higher hydrocarbons . It is found associated with other hydrocarbon fuel, in coal beds, as methane clathrates, and is an important fuel source and a major feedstock for fertilizers.Most natural...
, much of it trapped in overlying sandstone by salt
Salt
In chemistry, salts are ionic compounds that result from the neutralization reaction of an acid and a base. They are composed of cations and anions so that the product is electrically neutral...
deposits formed as the seas fell to form the swamps and salty lakes and lagoons that were home to dinosaur
Dinosaur
Dinosaurs are a diverse group of animals of the clade and superorder Dinosauria. They were the dominant terrestrial vertebrates for over 160 million years, from the late Triassic period until the end of the Cretaceous , when the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event led to the extinction of...
s.
After 20 million years during the Cretaceous
Cretaceous
The Cretaceous , derived from the Latin "creta" , usually abbreviated K for its German translation Kreide , is a geologic period and system from circa to million years ago. In the geologic timescale, the Cretaceous follows the Jurassic period and is followed by the Paleogene period of the...
period, the seas started to flood the land again until much of England was again below the sea, though sea levels frequently changed. Chalk
Chalk
Chalk is a soft, white, porous sedimentary rock, a form of limestone composed of the mineral calcite. Calcite is calcium carbonate or CaCO3. It forms under reasonably deep marine conditions from the gradual accumulation of minute calcite plates shed from micro-organisms called coccolithophores....
and flint
Flint
Flint is a hard, sedimentary cryptocrystalline form of the mineral quartz, categorized as a variety of chert. It occurs chiefly as nodules and masses in sedimentary rocks, such as chalks and limestones. Inside the nodule, flint is usually dark grey, black, green, white, or brown in colour, and...
s were deposited over much of England, now notably exposed at the White Cliffs of Dover
White cliffs of Dover
The White Cliffs of Dover are cliffs which form part of the British coastline facing the Strait of Dover and France. The cliffs are part of the North Downs formation. The cliff face, which reaches up to , owes its striking façade to its composition of chalk accentuated by streaks of black flint...
and the Seven Sisters
Seven Sisters, Sussex
The Seven Sisters are a series of chalk cliffs by the English Channel. They form part of the South Downs in East Sussex, between the towns of Seaford and Eastbourne in southern England. They are within the Seven Sisters Country Park...
, and also forming Salisbury Plain
Salisbury Plain
Salisbury Plain is a chalk plateau in central southern England covering . It is part of the Southern England Chalk Formation and largely lies within the county of Wiltshire, with a little in Hampshire. The plain is famous for its rich archaeology, including Stonehenge, one of England's best known...
. The high sea levels left only small areas of land exposed. This caused the general lack of land-origin sand, mud or clay sediments around this time - some of the late Cretaceous strata are almost pure chalk.
Cenozoic Era

Cenozoic
The Cenozoic era is the current and most recent of the three Phanerozoic geological eras and covers the period from 65.5 mya to the present. The era began in the wake of the Cretaceous–Tertiary extinction event at the end of the Cretaceous that saw the demise of the last non-avian dinosaurs and...
(65 Ma–present). In the early Paleogene
Paleogene
The Paleogene is a geologic period and system that began 65.5 ± 0.3 and ended 23.03 ± 0.05 million years ago and comprises the first part of the Cenozoic Era...
period between 63 and 52 million years ago, the last volcanic rocks in England were formed. The volcanic Lundy Island in the Bristol Channel
Bristol Channel
The Bristol Channel is a major inlet in the island of Great Britain, separating South Wales from Devon and Somerset in South West England. It extends from the lower estuary of the River Severn to the North Atlantic Ocean...
dates from this period.
The Alpine Orogeny
Alpine orogeny
The Alpine orogeny is an orogenic phase in the Late Mesozoic and Tertiary that formed the mountain ranges of the Alpide belt...
that took place about 50 million years ago was responsible for the shaping of the London Basin
London Basin
The London Basin is an elongated, roughly triangular sedimentary basin approximately long which underlies London and a large area of south east England, south eastern East Anglia and the adjacent North Sea...
syncline
Syncline
In structural geology, a syncline is a fold, with younger layers closer to the center of the structure. A synclinorium is a large syncline with superimposed smaller folds. Synclines are typically a downward fold, termed a synformal syncline In structural geology, a syncline is a fold, with younger...
and the Weald
Weald
The Weald is the name given to an area in South East England situated between the parallel chalk escarpments of the North and the South Downs. It should be regarded as three separate parts: the sandstone "High Weald" in the centre; the clay "Low Weald" periphery; and the Greensand Ridge which...
anticline
Anticline
In structural geology, an anticline is a fold that is convex up and has its oldest beds at its core. The term is not to be confused with antiform, which is a purely descriptive term for any fold that is convex up. Therefore if age relationships In structural geology, an anticline is a fold that is...
to the south. This orogeny also led to the development of the North Downs
North Downs
The North Downs are a ridge of chalk hills in south east England that stretch from Farnham in Surrey to the White Cliffs of Dover in Kent. The North Downs lie within two Areas of Outstanding Natural Beauty , the Surrey Hills and the Kent Downs...
, South Downs
South Downs
The South Downs is a range of chalk hills that extends for about across the south-eastern coastal counties of England from the Itchen Valley of Hampshire in the west to Beachy Head, near Eastbourne, East Sussex, in the east. It is bounded on its northern side by a steep escarpment, from whose...
and Chiltern Hills
Chiltern Hills
The Chiltern Hills form a chalk escarpment in South East England. They are known locally as "the Chilterns". A large portion of the hills was designated officially as an Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty in 1965.-Location:...
escarpment
Escarpment
An escarpment is a steep slope or long cliff that occurs from erosion or faulting and separates two relatively level areas of differing elevations.-Description and variants:...
s, and the near-vertical folds in south Dorset
Dorset
Dorset , is a county in South West England on the English Channel coast. The county town is Dorchester which is situated in the south. The Hampshire towns of Bournemouth and Christchurch joined the county with the reorganisation of local government in 1974...
and the Isle of Wight
Isle of Wight
The Isle of Wight is a county and the largest island of England, located in the English Channel, on average about 2–4 miles off the south coast of the county of Hampshire, separated from the mainland by a strait called the Solent...
.
During the period England was uplifted
Tectonic uplift
Tectonic uplift is a geological process most often caused by plate tectonics which increases elevation. The opposite of uplift is subsidence, which results in a decrease in elevation. Uplift may be orogenic or isostatic.-Orogenic uplift:...
. Some of this uplift was along old lines of weakness from the Caledonian
Caledonian orogeny
The Caledonian orogeny is a mountain building era recorded in the northern parts of the British Isles, the Scandinavian Mountains, Svalbard, eastern Greenland and parts of north-central Europe. The Caledonian orogeny encompasses events that occurred from the Ordovician to Early Devonian, roughly...
and Variscan Orogenies
Variscan orogeny
The Variscan orogeny is a geologic mountain-building event caused by Late Paleozoic continental collision between Euramerica and Gondwana to form the supercontinent of Pangaea.-Naming:...
long before. The uplifted areas were then eroded, and further sediments were deposited over southern England, including the London Clay
London Clay
The London Clay Formation is a marine geological formation of Ypresian age which crops out in the southeast of England. The London Clay is well known for the fossils it contains. The fossils from the Lower Eocene indicate a moderately warm climate, the flora being tropical or subtropical...
, while the English Channel
English Channel
The English Channel , often referred to simply as the Channel, is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that separates southern England from northern France, and joins the North Sea to the Atlantic. It is about long and varies in width from at its widest to in the Strait of Dover...
consisted of mud flats and river deposited sand
Sand
Sand is a naturally occurring granular material composed of finely divided rock and mineral particles.The composition of sand is highly variable, depending on the local rock sources and conditions, but the most common constituent of sand in inland continental settings and non-tropical coastal...
s. Much of the midlands and north of England may have been covered by Jurassic
Jurassic
The Jurassic is a geologic period and system that extends from about Mya to Mya, that is, from the end of the Triassic to the beginning of the Cretaceous. The Jurassic constitutes the middle period of the Mesozoic era, also known as the age of reptiles. The start of the period is marked by...
and Cretaceous
Cretaceous
The Cretaceous , derived from the Latin "creta" , usually abbreviated K for its German translation Kreide , is a geologic period and system from circa to million years ago. In the geologic timescale, the Cretaceous follows the Jurassic period and is followed by the Paleogene period of the...
deposits at the start of the Paleogene
Paleogene
The Paleogene is a geologic period and system that began 65.5 ± 0.3 and ended 23.03 ± 0.05 million years ago and comprises the first part of the Cenozoic Era...
, but lost them through erosion. By 35 million years ago, the landscape included beech
Beech
Beech is a genus of ten species of deciduous trees in the family Fagaceae, native to temperate Europe, Asia and North America.-Habit:...
, oak
Oak
An oak is a tree or shrub in the genus Quercus , of which about 600 species exist. "Oak" may also appear in the names of species in related genera, notably Lithocarpus...
, redwood
Cupressaceae
The Cupressaceae or cypress family is a conifer family with worldwide distribution. The family includes 27 to 30 genera , which include the junipers and redwoods, with about 130-140 species in total. They are monoecious, subdioecious or dioecious trees and shrubs from 1-116 m tall...
and palm
Arecaceae
Arecaceae or Palmae , are a family of flowering plants, the only family in the monocot order Arecales. There are roughly 202 currently known genera with around 2600 species, most of which are restricted to tropical, subtropical, and warm temperate climates...
trees, along with grass
Grass
Grasses, or more technically graminoids, are monocotyledonous, usually herbaceous plants with narrow leaves growing from the base. They include the "true grasses", of the Poaceae family, as well as the sedges and the rushes . The true grasses include cereals, bamboo and the grasses of lawns ...
land.
In the Miocene
Miocene
The Miocene is a geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about . The Miocene was named by Sir Charles Lyell. Its name comes from the Greek words and and means "less recent" because it has 18% fewer modern sea invertebrates than the Pliocene. The Miocene follows the Oligocene...
and Pliocene
Pliocene
The Pliocene Epoch is the period in the geologic timescale that extends from 5.332 million to 2.588 million years before present. It is the second and youngest epoch of the Neogene Period in the Cenozoic Era. The Pliocene follows the Miocene Epoch and is followed by the Pleistocene Epoch...
epochs of the Neogene
Neogene
The Neogene is a geologic period and system in the International Commission on Stratigraphy Geologic Timescale starting 23.03 ± 0.05 million years ago and ending 2.588 million years ago...
period, further uplift and erosion occurred, particularly in the Pennines. Plant and animal types developed into their modern forms, and by about 2 million years ago the landscape would have been broadly recognisable today.

Pleistocene
The Pleistocene is the epoch from 2,588,000 to 11,700 years BP that spans the world's recent period of repeated glaciations. The name pleistocene is derived from the Greek and ....
epoch have been brought about by several recent ice age
Ice age
An ice age or, more precisely, glacial age, is a generic geological period of long-term reduction in the temperature of the Earth's surface and atmosphere, resulting in the presence or expansion of continental ice sheets, polar ice sheets and alpine glaciers...
s. The most severe was the Anglian Stage, with ice up to 1,000 m (3300 ft) thick that reached as far south as London
London
London is the capital city of :England and the :United Kingdom, the largest metropolitan area in the United Kingdom, and the largest urban zone in the European Union by most measures. Located on the River Thames, London has been a major settlement for two millennia, its history going back to its...
and Bristol
Bristol
Bristol is a city, unitary authority area and ceremonial county in South West England, with an estimated population of 433,100 for the unitary authority in 2009, and a surrounding Larger Urban Zone with an estimated 1,070,000 residents in 2007...
, took place between about 500,000 to 400,000 years ago, and was responsible for the diversion of the River Thames
River Thames
The River Thames flows through southern England. It is the longest river entirely in England and the second longest in the United Kingdom. While it is best known because its lower reaches flow through central London, the river flows alongside several other towns and cities, including Oxford,...
onto its present course.
There is extensive evidence in the form of stone tools that southern England was colonised by human
Human
Humans are the only living species in the Homo genus...
populations during the warm Hoxnian Stage period that followed the glaciation of the Anglian Stage. It is possible that the English Channel
English Channel
The English Channel , often referred to simply as the Channel, is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that separates southern England from northern France, and joins the North Sea to the Atlantic. It is about long and varies in width from at its widest to in the Strait of Dover...
repeatedly opened and closed during this period, causing Britain to become an island from time to time. The oldest human fossil
Fossil
Fossils are the preserved remains or traces of animals , plants, and other organisms from the remote past...
s in the Isles also date from this time, including the skull of Swanscombe Man from 250,000 years ago, and the earlier Clactonian Man.
Multiple glaciations occurred during Wolstonian Stage, between about 352,000 to 132,000 years ago. It thought to have peaked around 150,000 years ago, was named after the town of Wolston
Wolston
Wolston is a village and civil parish in the Rugby borough of Warwickshire, England. The village is located roughly halfway between Rugby and Coventry, and has a population of about 2,300. It is close to the A45 road and the Roman road the Fosse Way....
south of Birmingham
Birmingham
Birmingham is a city and metropolitan borough in the West Midlands of England. It is the most populous British city outside the capital London, with a population of 1,036,900 , and lies at the heart of the West Midlands conurbation, the second most populous urban area in the United Kingdom with a...
which is thought to mark the southern limit of the ice.
The Wolstonian Stage was followed by interglacial climate of the Ipswichian Stage, during which hippopotamus
Hippopotamus
The hippopotamus , or hippo, from the ancient Greek for "river horse" , is a large, mostly herbivorous mammal in sub-Saharan Africa, and one of only two extant species in the family Hippopotamidae After the elephant and rhinoceros, the hippopotamus is the third largest land mammal and the heaviest...
are known to have lived as far north as Leeds
Leeds
Leeds is a city and metropolitan borough in West Yorkshire, England. In 2001 Leeds' main urban subdivision had a population of 443,247, while the entire city has a population of 798,800 , making it the 30th-most populous city in the European Union.Leeds is the cultural, financial and commercial...
.
The most recent glaciations occurred during the Devensian Stage, which is thought to have started around 75,000 years ago, peaked around 20,000 years ago and ended a mere 10,000 years ago, the Usk valley
River Usk
The River Usk rises on the northern slopes of the Black Mountain of mid-Wales, in the easternmost part of the Brecon Beacons National Park. Initially it flows north into Usk Reservoir, then east by Sennybridge to Brecon before turning southeast to flow by Talybont-on-Usk, Crickhowell and...
and Wye valley
River Wye
The River Wye is the fifth-longest river in the UK and for parts of its length forms part of the border between England and Wales. It is important for nature conservation and recreation.-Description:...
were eroded by glacier
Glacier
A glacier is a large persistent body of ice that forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its ablation over many years, often centuries. At least 0.1 km² in area and 50 m thick, but often much larger, a glacier slowly deforms and flows due to stresses induced by its weight...
s, with the ice sheet itself reaching south to Birmingham
Birmingham
Birmingham is a city and metropolitan borough in the West Midlands of England. It is the most populous British city outside the capital London, with a population of 1,036,900 , and lies at the heart of the West Midlands conurbation, the second most populous urban area in the United Kingdom with a...
. It is thought that the country was eventually abandoned as the ice sheet reached its peak, being recolonised as it retreated. By 5,000 years ago it is thought that the British Isles were warmer than they are at present.
Among the features left behind by the ice the glaciated U-shaped valleys of the Lake District
Lake District
The Lake District, also commonly known as The Lakes or Lakeland, is a mountainous region in North West England. A popular holiday destination, it is famous not only for its lakes and its mountains but also for its associations with the early 19th century poetry and writings of William Wordsworth...
and erratics
Glacial erratic
A glacial erratic is a piece of rock that differs from the size and type of rock native to the area in which it rests. "Erratics" take their name from the Latin word errare, and are carried by glacial ice, often over distances of hundreds of kilometres...
(blocks of rock) that have been transported from the Oslo
Oslo
Oslo is a municipality, as well as the capital and most populous city in Norway. As a municipality , it was established on 1 January 1838. Founded around 1048 by King Harald III of Norway, the city was largely destroyed by fire in 1624. The city was moved under the reign of Denmark–Norway's King...
region of Norway
Norway
Norway , officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic unitary constitutional monarchy whose territory comprises the western portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula, Jan Mayen, and the Arctic archipelago of Svalbard and Bouvet Island. Norway has a total area of and a population of about 4.9 million...
and deposited on the coast of Yorkshire
Yorkshire
Yorkshire is a historic county of northern England and the largest in the United Kingdom. Because of its great size in comparison to other English counties, functions have been increasingly undertaken over time by its subdivisions, which have also been subject to periodic reform...
.

Holocene
The Holocene is a geological epoch which began at the end of the Pleistocene and continues to the present. The Holocene is part of the Quaternary period. Its name comes from the Greek words and , meaning "entirely recent"...
epoch the most significant new geological features have been the deposits of peat
Peat
Peat is an accumulation of partially decayed vegetation matter or histosol. Peat forms in wetland bogs, moors, muskegs, pocosins, mires, and peat swamp forests. Peat is harvested as an important source of fuel in certain parts of the world...
in Ireland
Ireland
Ireland is an island to the northwest of continental Europe. It is the third-largest island in Europe and the twentieth-largest island on Earth...
and Scotland
Scotland
Scotland is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Occupying the northern third of the island of Great Britain, it shares a border with England to the south and is bounded by the North Sea to the east, the Atlantic Ocean to the north and west, and the North Channel and Irish Sea to the...
, as well as in coastal areas that have recently been artificially drained such as the Somerset Levels
Somerset Levels
The Somerset Levels, or the Somerset Levels and Moors as they are less commonly but more correctly known, is a sparsely populated coastal plain and wetland area of central Somerset, South West England, between the Quantock and Mendip Hills...
, The Fens
The Fens
The Fens, also known as the , are a naturally marshy region in eastern England. Most of the fens were drained several centuries ago, resulting in a flat, damp, low-lying agricultural region....
and Romney Marsh
Romney Marsh
Romney Marsh is a sparsely populated wetland area in the counties of Kent and East Sussex in the south-east of England. It covers about 100 mi ² .-Quotations:*“As Egypt was the gift of the Nile, this level tract .....
in England.
Since humans began clearing the forest during the new stone age
Neolithic
The Neolithic Age, Era, or Period, or New Stone Age, was a period in the development of human technology, beginning about 9500 BC in some parts of the Middle East, and later in other parts of the world. It is traditionally considered as the last part of the Stone Age...
, most of the land has now been deforested, speeding the natural processes of erosion
Erosion
Erosion is when materials are removed from the surface and changed into something else. It only works by hydraulic actions and transport of solids in the natural environment, and leads to the deposition of these materials elsewhere...
. Large quantities of stone, gravel and clay are extracted each year, and by 2000 11% of England was covered by road
Road
A road is a thoroughfare, route, or way on land between two places, which typically has been paved or otherwise improved to allow travel by some conveyance, including a horse, cart, or motor vehicle. Roads consist of one, or sometimes two, roadways each with one or more lanes and also any...
s or building
Building
In architecture, construction, engineering, real estate development and technology the word building may refer to one of the following:...
s.
At the present time, due to Scotland's continuing to rise as a result of the weight of Devensian ice being lifted, England is sinking. This is generally estimated at 1 mm (1/25 inch) per year, with the London area sinking at double the speed partly due to the continuing compression of the recent clay deposits. A contributary factor is the draining of many stretchs of land.
In addition, rises in sea level thought to be due to global warming
Global warming
Global warming refers to the rising average temperature of Earth's atmosphere and oceans and its projected continuation. In the last 100 years, Earth's average surface temperature increased by about with about two thirds of the increase occurring over just the last three decades...
appear likely to make low lying areas of land increasingly susceptible to flooding, while in some areas the coastline continues to erode at a geologically rapid rate.
Recent flooding events leave geological evidence such as the Bristol Channel floods
Bristol Channel floods, 1607
The Bristol Channel floods, which occurred on 30 January 1607 , resulted in the drowning of a large number of people and the destruction of a large amount of farmland and livestock...
in 1607.
The British Isles continue to be subject to several very minor earthquake
Earthquake
An earthquake is the result of a sudden release of energy in the Earth's crust that creates seismic waves. The seismicity, seismism or seismic activity of an area refers to the frequency, type and size of earthquakes experienced over a period of time...
s each month, and occasional light to moderate ones. During the 20th century 25 earthquakes with a magnitude of 4.5 to 6.1 on the Richter scale
Richter magnitude scale
The expression Richter magnitude scale refers to a number of ways to assign a single number to quantify the energy contained in an earthquake....
were felt, many of them originating within England itself. Notable was the Colchester earthquake
1884 Colchester earthquake
The Colchester earthquake, also known as the Great English Earthquake, occurred on 22 April 1884. It caused considerable damage in Colchester and the surrounding villages in Essex...
in 1884 and the 2002 Dudley earthquake
2002 Dudley earthquake
The 2002 Dudley earthquake was an earthquake registering 4.7 on the Richter scale that struck the Midlands of England, on 22 September 2002 23:53 UTC and lasted approximately 20 seconds....
.
Tectonics of Avalonia
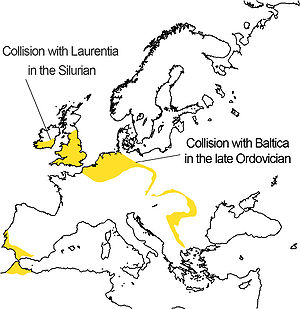
Avalonia
Avalonia was a microcontinent in the Paleozoic era. Crustal fragments of this former microcontinent underlie south-west Great Britain, and the eastern coast of North America. It is the source of many of the older rocks of Western Europe, Atlantic Canada, and parts of the coastal United States...
was an ancient microcontinent or terrane
Terrane
A terrane in geology is short-hand term for a tectonostratigraphic terrane, which is a fragment of crustal material formed on, or broken off from, one tectonic plate and accreted or "sutured" to crust lying on another plate...
whose history formed much of the older rocks of Western Europe. The name is derived from the Avalon Peninsula
Avalon Peninsula
The Avalon Peninsula is a large peninsula that makes up the southeast portion of the island of Newfoundland.The peninsula is home to 257,223 people, which is approximately 51% of Newfoundland's population in 2009, and is the location of the provincial capital, St. John's. It is connected to the...
in Newfoundland. England was entirely contained within the Avalonian block, as shown in the map, and thus shares its geolocation chronology.
In the early Cambrian
Cambrian
The Cambrian is the first geological period of the Paleozoic Era, lasting from Mya ; it is succeeded by the Ordovician. Its subdivisions, and indeed its base, are somewhat in flux. The period was established by Adam Sedgwick, who named it after Cambria, the Latin name for Wales, where Britain's...
, the supercontinent
Supercontinent
In geology, a supercontinent is a landmass comprising more than one continental core, or craton. The assembly of cratons and accreted terranes that form Eurasia qualifies as a supercontinent today.-History:...
Pannotia
Pannotia
Pannotia, first described by Ian W. D. Dalziel in 1997, is a hypothetical supercontinent that existed from the Pan-African orogeny about six hundred million years ago to the end of the Precambrian about five hundred and fifty million years ago. It is also known as the Vendian supercontinent...
broke up and Avalonia drifted off northwards from Gondwana
Gondwana
In paleogeography, Gondwana , originally Gondwanaland, was the southernmost of two supercontinents that later became parts of the Pangaea supercontinent. It existed from approximately 510 to 180 million years ago . Gondwana is believed to have sutured between ca. 570 and 510 Mya,...
. This independent movement of Avalonia started from a latitude of about 60° South. The eastern end of Avalonia collided with Baltica
Baltica
Baltica is a name applied by geologists to a late-Proterozoic, early-Palaeozoic continent that now includes the East European craton of northwestern Eurasia. Baltica was created as an entity not earlier than 1.8 billion years ago. Before this time, the three segments/continents that now comprise...
, a continental plate occupying the latitudes from about 30°S to 55°S, as the latter slowly rotated anticlockwise towards it. This happened at the end of the Ordovician
Ordovician
The Ordovician is a geologic period and system, the second of six of the Paleozoic Era, and covers the time between 488.3±1.7 to 443.7±1.5 million years ago . It follows the Cambrian Period and is followed by the Silurian Period...
and during the early Silurian
Silurian
The Silurian is a geologic period and system that extends from the end of the Ordovician Period, about 443.7 ± 1.5 Mya , to the beginning of the Devonian Period, about 416.0 ± 2.8 Mya . As with other geologic periods, the rock beds that define the period's start and end are well identified, but the...
.
In the late Silurian
Silurian
The Silurian is a geologic period and system that extends from the end of the Ordovician Period, about 443.7 ± 1.5 Mya , to the beginning of the Devonian Period, about 416.0 ± 2.8 Mya . As with other geologic periods, the rock beds that define the period's start and end are well identified, but the...
and lower Devonian
Devonian
The Devonian is a geologic period and system of the Paleozoic Era spanning from the end of the Silurian Period, about 416.0 ± 2.8 Mya , to the beginning of the Carboniferous Period, about 359.2 ± 2.5 Mya...
, the combined Baltica and Avalonia collided progressively, with Laurentia
Laurentia
Laurentia is a large area of continental craton, which forms the ancient geological core of the North American continent...
, beginning with the long extremity of Avalonia which is now attached to America. The result of this was the formation of Euramerica
Euramerica
Euramerica was a minor supercontinent created in the Devonian as the result of a collision between the Laurentian, Baltica, and Avalonia cratons .300 million years ago in the Late Carboniferous tropical rainforests lay over the equator of Euramerica...
. At the completion of this stage, the site of Britain was at 30°S and Nova Scotia
Nova Scotia
Nova Scotia is one of Canada's three Maritime provinces and is the most populous province in Atlantic Canada. The name of the province is Latin for "New Scotland," but "Nova Scotia" is the recognized, English-language name of the province. The provincial capital is Halifax. Nova Scotia is the...
at about 45°S. This collision is represented by the Caledonian
Caledonian orogeny
The Caledonian orogeny is a mountain building era recorded in the northern parts of the British Isles, the Scandinavian Mountains, Svalbard, eastern Greenland and parts of north-central Europe. The Caledonian orogeny encompasses events that occurred from the Ordovician to Early Devonian, roughly...
folding or in North America as an early phase in the Acadian orogeny
Acadian orogeny
The Taconic, Acadian and Alleghenian orogenies are the three tectonic phases responsible for the formation of the present Appalachian Mountains. The Acadian orogeny is a middle Paleozoic mountain building episode dating back 325-400 million years which should not be regarded as a single event but...
.
In the Permian
Permian
The PermianThe term "Permian" was introduced into geology in 1841 by Sir Sir R. I. Murchison, president of the Geological Society of London, who identified typical strata in extensive Russian explorations undertaken with Edouard de Verneuil; Murchison asserted in 1841 that he named his "Permian...
, the new continent and another terrane, Armorica
Armorican terrane
The Armorican terrane, Armorican terrane assemblage, or simply Armorica, refers to a microcontinent or group of continental fragments that rifted away from Gondwana towards the end of the Silurian and collided with Laurussia towards the end of the Carboniferous during the Variscan orogeny...
which included Iberia, drifted in from Gondwana, trapping Avalonia between it and the continent so adding Iberia/Armorica to Euramerica. This was followed up by the arrival of Gondwana. The effects of these collisions are seen in Europe as the Variscan
Variscan orogeny
The Variscan orogeny is a geologic mountain-building event caused by Late Paleozoic continental collision between Euramerica and Gondwana to form the supercontinent of Pangaea.-Naming:...
folding. In North America it shows as later phases of the Acadian orogeny. This was happening at around the Equator during the later Carboniferous
Carboniferous
The Carboniferous is a geologic period and system that extends from the end of the Devonian Period, about 359.2 ± 2.5 Mya , to the beginning of the Permian Period, about 299.0 ± 0.8 Mya . The name is derived from the Latin word for coal, carbo. Carboniferous means "coal-bearing"...
, forming Pangaea
Pangaea
Pangaea, Pangæa, or Pangea is hypothesized as a supercontinent that existed during the Paleozoic and Mesozoic eras about 250 million years ago, before the component continents were separated into their current configuration....
in such a way that Avalonia was near its centre but partially flooded by shallow sea.
In the Jurassic
Jurassic
The Jurassic is a geologic period and system that extends from about Mya to Mya, that is, from the end of the Triassic to the beginning of the Cretaceous. The Jurassic constitutes the middle period of the Mesozoic era, also known as the age of reptiles. The start of the period is marked by...
, Pangaea split into Laurasia
Laurasia
In paleogeography, Laurasia was the northernmost of two supercontinents that formed part of the Pangaea supercontinent from approximately...
and Gondwana, with Avalonia as part of Laurasia. In the Cretaceous
Cretaceous
The Cretaceous , derived from the Latin "creta" , usually abbreviated K for its German translation Kreide , is a geologic period and system from circa to million years ago. In the geologic timescale, the Cretaceous follows the Jurassic period and is followed by the Paleogene period of the...
, Laurasia broke up into North America
North America
North America is a continent wholly within the Northern Hemisphere and almost wholly within the Western Hemisphere. It is also considered a northern subcontinent of the Americas...
and Eurasia
Eurasia
Eurasia is a continent or supercontinent comprising the traditional continents of Europe and Asia ; covering about 52,990,000 km2 or about 10.6% of the Earth's surface located primarily in the eastern and northern hemispheres...
with Avalonia split between them.
See also
- Geology of Great Britain
- Geology of ScotlandGeology of ScotlandThe geology of Scotland is unusually varied for a country of its size, with a large number of differing geological features. There are three main geographical sub-divisions: the Highlands and Islands is a diverse area which lies to the north and west of the Highland Boundary Fault; the Central...
- Geology of WalesGeology of WalesWales is a peninsula in the south-west of the island of Great Britain. The entire area of Wales is about . It is about north-south and east-west. Wales is bordered by England to the east and by sea in the other three directions: the Bristol Channel to the south, St George's Channel to the west,...
- Geology of Scotland
- Geology of Ireland
- List of geology of English counties
- British Geological SurveyBritish Geological SurveyThe British Geological Survey is a partly publicly funded body which aims to advance geoscientific knowledge of the United Kingdom landmass and its continental shelf by means of systematic surveying, monitoring and research. The BGS headquarters are in Keyworth, Nottinghamshire, but other centres...
- Stone
- Geologic timescale
- Coal MeasuresCoal MeasuresThe Coal Measures is a lithostratigraphical term for the coal-bearing part of the Upper Carboniferous System. It represents the remains of fluvio-deltaic sediment, and consists mainly of clastic rocks interstratified with the beds of coal...
- Coal Seams of the South Yorkshire CoalfieldCoal Seams of the South Yorkshire CoalfieldThe coal seams worked in the South Yorkshire coalfield lie mainly in the middle coal measures. These are a series of mudstones, shales, sandstones, and coal seams laid down during the Carboniferous period about 350 million years ago...
- Chalk FormationChalk FormationThe Chalk Group is a lithostratigraphic unit in the northwestern part of Europe. It is characterised by thick deposits of chalk, a soft porous white limestone, deposited in a marine environment during the Upper Cretaceous period.Chalk is a limestone that consists of coccolith biomicrite...
- London ClayLondon ClayThe London Clay Formation is a marine geological formation of Ypresian age which crops out in the southeast of England. The London Clay is well known for the fossils it contains. The fossils from the Lower Eocene indicate a moderately warm climate, the flora being tropical or subtropical...
- Gault ClayGault ClayGault is a clay formation of stiff blue clay deposited in a calm, fairly deep water marine environment during the Lower Cretaceous Period...
- Old Red SandstoneOld Red SandstoneThe Old Red Sandstone is a British rock formation of considerable importance to early paleontology. For convenience the short version of the term, 'ORS' is often used in literature on the subject.-Sedimentology:...
- New Red SandstoneNew Red SandstoneThe New Red Sandstone is a chiefly British geological term for the beds of red sandstone and associated rocks laid down throughout the Permian to the beginning of the Triassic that underlie the Jurassic Lias; the term distinguishes it from the Old Red Sandstone which is largely Devonian in...
- Geology of Alderley EdgeGeology of Alderley EdgeAlderley Edge in Cheshire is one of the classic locations for the study of Triassic sandstones in the United Kingdom. Numerous scientists from the early 19th century up to the present day have studied the area and it is a popular field site for universities around the UK. As time progresses, new...
- Lizard complex
- Woolwich-and-Reading Beds
- Jurassic CoastJurassic CoastThe Jurassic Coast is a World Heritage Site on the English Channel coast of southern England. The site stretches from Orcombe Point near Exmouth in East Devon to Old Harry Rocks near Swanage in East Dorset, a distance of ....
- London BasinLondon BasinThe London Basin is an elongated, roughly triangular sedimentary basin approximately long which underlies London and a large area of south east England, south eastern East Anglia and the adjacent North Sea...

