
London Basin
Encyclopedia
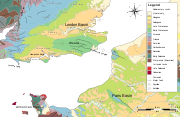
Basin (geology)
A structural basin is a large-scale structural formation of rock strata formed by tectonic warping of previously flat lying strata. Structural basins are geological depressions, and are the inverse of domes. Some elongated structural basins are also known as synclines...
approximately 250 kilometres (155.3 mi) long which underlies London and a large area of south east England, south eastern East Anglia
East Anglia
East Anglia is a traditional name for a region of eastern England, named after an ancient Anglo-Saxon kingdom, the Kingdom of the East Angles. The Angles took their name from their homeland Angeln, in northern Germany. East Anglia initially consisted of Norfolk and Suffolk, but upon the marriage of...
and the adjacent North Sea
North Sea
In the southwest, beyond the Straits of Dover, the North Sea becomes the English Channel connecting to the Atlantic Ocean. In the east, it connects to the Baltic Sea via the Skagerrak and Kattegat, narrow straits that separate Denmark from Norway and Sweden respectively...
. The basin formed as a result of extensional tectonics
Extensional tectonics
Extensional tectonics is concerned with the structures formed, and the tectonic processes associated with, the stretching of the crust or lithosphere.-Deformation styles:...
related to the Alpine orogeny
Alpine orogeny
The Alpine orogeny is an orogenic phase in the Late Mesozoic and Tertiary that formed the mountain ranges of the Alpide belt...
during the Palaeogene period and was mainly active between 60 and 40 million years ago.
Spatial boundaries
The generally accepted boundaries are the Late CretaceousLate Cretaceous
The Late Cretaceous is the younger of two epochs into which the Cretaceous period is divided in the geologic timescale. Rock strata from this epoch form the Upper Cretaceous series...
Chalk Group's escarpments of the Chilterns and Marlborough Downs to the north and the North Downs
North Downs
The North Downs are a ridge of chalk hills in south east England that stretch from Farnham in Surrey to the White Cliffs of Dover in Kent. The North Downs lie within two Areas of Outstanding Natural Beauty , the Surrey Hills and the Kent Downs...
and Berkshire Downs to the south. To the south lie the Weald
Weald
The Weald is the name given to an area in South East England situated between the parallel chalk escarpments of the North and the South Downs. It should be regarded as three separate parts: the sandstone "High Weald" in the centre; the clay "Low Weald" periphery; and the Greensand Ridge which...
and Salisbury Plain
Salisbury Plain
Salisbury Plain is a chalk plateau in central southern England covering . It is part of the Southern England Chalk Formation and largely lies within the county of Wiltshire, with a little in Hampshire. The plain is famous for its rich archaeology, including Stonehenge, one of England's best known...
and to the north is the Vale of Aylesbury. The approximate western limit is in the Marlborough area of Wiltshire
Wiltshire
Wiltshire is a ceremonial county in South West England. It is landlocked and borders the counties of Dorset, Somerset, Hampshire, Gloucestershire, Oxfordshire and Berkshire. It contains the unitary authority of Swindon and covers...
. The eastern end merges with the North Sea Basin, extending on land along the north Kent
Kent
Kent is a county in southeast England, and is one of the home counties. It borders East Sussex, Surrey and Greater London and has a defined boundary with Essex in the middle of the Thames Estuary. The ceremonial county boundaries of Kent include the shire county of Kent and the unitary borough of...
coast to Reculver
Reculver
Reculver is a hamlet and coastal resort situated about east of Herne Bay in southeast England. It is a ward of the City of Canterbury district in the county of Kent. Reculver once occupied a strategic location at the western end of the Wantsum Channel, between the Isle of Thanet and the Kent...
and up the east coast of Essex
Essex
Essex is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in the East region of England, and one of the home counties. It is located to the northeast of Greater London. It borders with Cambridgeshire and Suffolk to the north, Hertfordshire to the west, Kent to the South and London to the south west...
and into Suffolk
Suffolk
Suffolk is a non-metropolitan county of historic origin in East Anglia, England. It has borders with Norfolk to the north, Cambridgeshire to the west and Essex to the south. The North Sea lies to the east...
, where it is overlain by Pleistocene
Pleistocene
The Pleistocene is the epoch from 2,588,000 to 11,700 years BP that spans the world's recent period of repeated glaciations. The name pleistocene is derived from the Greek and ....
'Crag' deposits which cover much of eastern Suffolk
Suffolk
Suffolk is a non-metropolitan county of historic origin in East Anglia, England. It has borders with Norfolk to the north, Cambridgeshire to the west and Essex to the south. The North Sea lies to the east...
and Norfolk
Norfolk
Norfolk is a low-lying county in the East of England. It has borders with Lincolnshire to the west, Cambridgeshire to the west and southwest and Suffolk to the south. Its northern and eastern boundaries are the North Sea coast and to the north-west the county is bordered by The Wash. The county...
and are better considered as part of the North Sea Basin.
The axis of the basin runs west-east from Marlborough and Newbury
Newbury, Berkshire
Newbury is a civil parish and the principal town in the west of the county of Berkshire in England. It is situated on the River Kennet and the Kennet and Avon Canal, and has a town centre containing many 17th century buildings. Newbury is best known for its racecourse and the adjoining former USAF...
(Berkshire) to Chertsey
Chertsey
Chertsey is a town in Surrey, England, on the River Thames and its tributary rivers such as the River Bourne. It can be accessed by road from junction 11 of the M25 London orbital motorway. It shares borders with Staines, Laleham, Shepperton, Addlestone, Woking, Thorpe and Egham...
(Surrey) before swinging slightly north of east through Westminster
Westminster
Westminster is an area of central London, within the City of Westminster, England. It lies on the north bank of the River Thames, southwest of the City of London and southwest of Charing Cross...
, passing midway between Chelmsford
Chelmsford
Chelmsford is the county town of Essex, England and the principal settlement of the borough of Chelmsford. It is located in the London commuter belt, approximately northeast of Charing Cross, London, and approximately the same distance from the once provincial Roman capital at Colchester...
and Southend-on-Sea
Southend-on-Sea
Southend-on-Sea is a unitary authority area, town, and seaside resort in Essex, England. The district has Borough status, and comprises the towns of Chalkwell, Eastwood, Leigh-on-Sea, North Shoebury, Prittlewell, Shoeburyness, Southchurch, Thorpe Bay, and Westcliff-on-Sea. The district is situated...
(Essex) to the east coast between the estuaries of the Crouch
River Crouch
The River Crouch is a river that flows entirely through the English county of Essex.The distance of the Navigation between Holliwell Point which is north of Foulness Island and Battlesbridge is 17.5 Miles, i.e. 15.21 Nautical Miles.-Route:...
and the Blackwater
River Blackwater, Essex
The River Blackwater is a river in England. It rises in the northwest of Essex as the River Pant and flows to Bocking, near Braintree, from where its name changes to the Blackwater. Its course takes it near Stisted, and then via Bradwell Juxta Coggeshall and Coggeshall and near Witham where it is...
. Though north of the current mouth of the Thames, this line is well to the south of the centre-line of the basin which is asymmetric, its southern limb dipping more steeply than the northern.
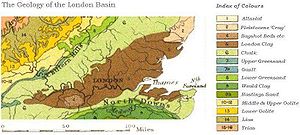
Geological boundaries
The Basin formed on top of the Late Cretaceous Chalk Group, which is exposed on the dip slopeDip slope
A dip slope is a geological formation often created by erosion of tilted strata. Dip slopes are found on homoclinal ridges with one side that is steep and irregular and another side, the dip slope, that is generally planar with a dip parallel to the bedding...
s of the Chilterns and North Downs. Within the centre of the basin the Chalk is mainly covered by Palaeocene, Eocene
Eocene
The Eocene Epoch, lasting from about 56 to 34 million years ago , is a major division of the geologic timescale and the second epoch of the Paleogene Period in the Cenozoic Era. The Eocene spans the time from the end of the Palaeocene Epoch to the beginning of the Oligocene Epoch. The start of the...
and younger rocks, though the chalk is also brought to the surface by localised ffold
Fold (geology)
The term fold is used in geology when one or a stack of originally flat and planar surfaces, such as sedimentary strata, are bent or curved as a result of permanent deformation. Synsedimentary folds are those due to slumping of sedimentary material before it is lithified. Folds in rocks vary in...
s and faults, for example at Windsor Castle
Windsor Castle
Windsor Castle is a medieval castle and royal residence in Windsor in the English county of Berkshire, notable for its long association with the British royal family and its architecture. The original castle was built after the Norman invasion by William the Conqueror. Since the time of Henry I it...
, Lewisham
Lewisham
Lewisham is a district in South London, England, located in the London Borough of Lewisham. It is situated south-east of Charing Cross. The area is identified in the London Plan as one of 35 major centres in Greater London.-History:...
and Purfleet
Purfleet
Purfleet is a place in the Thurrock unitary authority in Essex, England. It is situated south of the A13 road on the River Thames and within the easterly bounds of the M25 motorway but just outside the Greater London boundary. It was within the traditional Church of England parish of West Thurrock...
. The Chalk forms an artesian basin, with
fresh water springs emerging on the bed of the Thames. In the greater part of the basin the surface rock is Eocene London Clay
London Clay
The London Clay Formation is a marine geological formation of Ypresian age which crops out in the southeast of England. The London Clay is well known for the fossils it contains. The fossils from the Lower Eocene indicate a moderately warm climate, the flora being tropical or subtropical...
, flanked at the margins by older deposits such as the Reading Beds. In large areas towards the western end the London Clay is overlain by rather younger deposits of the Bagshot Beds
Bagshot Beds
In geology, the Bagshot Beds are a series of sands and clays of shallow-water origin, some being fresh-water, some marine. They belong to the upper Eocene formation of the London and Hampshire basins, in England and derive their name from Bagshot Heath in Surrey. They are also well developed in...
etc, forming sandy heaths.
Tectonic history
Most of the basin is underlain at depth by a block of Palaeozoic rocks known as the London Platform. This is separated by faulting from the Early CretaceousEarly Cretaceous
The Early Cretaceous or the Lower Cretaceous , is the earlier or lower of the two major divisions of the Cretaceous...
Wessex Basin (underlying the Weald
Weald
The Weald is the name given to an area in South East England situated between the parallel chalk escarpments of the North and the South Downs. It should be regarded as three separate parts: the sandstone "High Weald" in the centre; the clay "Low Weald" periphery; and the Greensand Ridge which...
and Hampshire Basin
Hampshire Basin
The Hampshire Basin is a geological basin of Paleogene age in southern England, underlying parts of Hampshire, the Isle of Wight, Dorset, and Sussex...
) to the south and the Worcester Basin to the west. Vertical movements of this block have affected both deposition and structure, with the result that many of the Mesozoic
Mesozoic
The Mesozoic era is an interval of geological time from about 250 million years ago to about 65 million years ago. It is often referred to as the age of reptiles because reptiles, namely dinosaurs, were the dominant terrestrial and marine vertebrates of the time...
rocks underlying the neighbouring Weald are not present, or are very much thinner. Rocks of Triassic
Triassic
The Triassic is a geologic period and system that extends from about 250 to 200 Mya . As the first period of the Mesozoic Era, the Triassic follows the Permian and is followed by the Jurassic. Both the start and end of the Triassic are marked by major extinction events...
age are absent under London, occurring at depth only at the western edge of the basin. Jurassic
Jurassic
The Jurassic is a geologic period and system that extends from about Mya to Mya, that is, from the end of the Triassic to the beginning of the Cretaceous. The Jurassic constitutes the middle period of the Mesozoic era, also known as the age of reptiles. The start of the period is marked by...
rocks occur over a wider area to the west and south but are also absent under London itself. During Early Cretaceous times the platform was uplifted and eroded, with the erosional material deposited to the south as the Wealden Group
Wealden Group
The Wealden Group is a group in the lithostratigraphy of southern England. The Wealden group consists of paralic to continental facies sedimentary rocks of Valanginian to Barremian age and thus forms part of the English Lower Cretaceous. It is composed of alternating sands and clays...
. Sea level rose during deposition of the Lower Greensand Group, but only completely covered the platform during deposition of the Gault Formation. The whole area remained submerged during much of the Late Cretaceous, though the Chalk contains levels indicating periods of erosion.
During the Palaeogene the south-east of England was affected by movements related to the formation of the Alps
Alps
The Alps is one of the great mountain range systems of Europe, stretching from Austria and Slovenia in the east through Italy, Switzerland, Liechtenstein and Germany to France in the west....
(the Alpine Orogeny
Alpine orogeny
The Alpine orogeny is an orogenic phase in the Late Mesozoic and Tertiary that formed the mountain ranges of the Alpide belt...
). One consequence of this was relative vertical movements, with the eastern part of the Wessex Basin being uplifted as the Weald-Artois Anticline
Weald-Artois Anticline
The Weald–Artois anticline is a large anticline, a geological structure running between the regions of the Weald in southern England and the Artois in northeastern France. The fold formed during the Alpine orogeny, from the late Oligocene to middle Miocene as an uplifted form of the Weald basin...
and the London Platform subsiding to form the London Basin. Up to 320 metres (1,049.9 ft) of Palaeocene and Eocene
Eocene
The Eocene Epoch, lasting from about 56 to 34 million years ago , is a major division of the geologic timescale and the second epoch of the Paleogene Period in the Cenozoic Era. The Eocene spans the time from the end of the Palaeocene Epoch to the beginning of the Oligocene Epoch. The start of the...
sediments were deposited in the basin. The Pleistocene
Pleistocene
The Pleistocene is the epoch from 2,588,000 to 11,700 years BP that spans the world's recent period of repeated glaciations. The name pleistocene is derived from the Greek and ....
saw the sea retreat from the basin as global sea-level fell due to accumulation of ice sheets.
Sedimentary infill and stratigraphy
The London Basin is mainly filled with Palaeogene sedimentsSedimentary rock
Sedimentary rock are types of rock that are formed by the deposition of material at the Earth's surface and within bodies of water. Sedimentation is the collective name for processes that cause mineral and/or organic particles to settle and accumulate or minerals to precipitate from a solution....
. The lowest (oldest) unit is the Thanet Sand Formation (of Thanetian
Thanetian
The Thanetian is, in the ICS' Geologic timescale, the latest age or uppermost stratigraphic stage of the Paleocene Epoch or series. It spans the time between and . The Thanetian is preceded by the Selandian age and followed by the Ypresian age...
age, 56 – 58 million years old), which rests unconformable
Unconformity
An unconformity is a buried erosion surface separating two rock masses or strata of different ages, indicating that sediment deposition was not continuous. In general, the older layer was exposed to erosion for an interval of time before deposition of the younger, but the term is used to describe...
on top of the Chalk. It is composed dominantly of shallow marine sands. On top of the Thanet Sand Formation lies the Lambeth Group
Lambeth Group
The Lambeth Group is a stratigraphic group, a set of geological rock strata in the London and Hampshire Basins of southern England. It comprises a complex of vertically and laterally varying gravels, sands, silts and clays deposited between 56-55 million years before present during the Ypresian age...
, which was deposited in a coastal plain
Coastal plain
A coastal plain is an area of flat, low-lying land adjacent to a seacoast and separated from the interior by other features. One of the world's longest coastal plains is located in eastern South America. The southwestern coastal plain of North America is notable for its species diversity...
and/or adjacent shallow sea water during the late Thanetian and early Ypresian
Ypresian
In the geologic timescale the Ypresian is the oldest age or lowest stratigraphic stage of the Eocene. It spans the time between and , is preceded by the Thanetian age and is followed by the Eocene Lutetian age....
ages. The Lambeth Group consists of the Upnor Formation, the Woolwich Formation and the Reading Formation.
The Lambeth Group is overlain by the Thames Group, which consists of two formations. From old to young these are the Harwich Formation and the Londen Clay Formation (famous for its fossils). They were deposited in shallow marine, estuarine
Estuary
An estuary is a partly enclosed coastal body of water with one or more rivers or streams flowing into it, and with a free connection to the open sea....
or coastal plain (paralic) environments and were deposited during the Ypresian age (55.8 – 48.6 million years ago).
On top of the Lambeth Group is the Bracklesham Group, which consists of the Bagshot Formation, the Windlesham Formation and the Camberley Sand Formation. The Bracklesham Group is also composed of shallow marine (near-shore) and coastal facies rocks. It can be up to 140 meter thick and is of late Ypresian to Lutetian
Lutetian
The Lutetian is, in the geologic timescale, a stage or age in the Eocene. It spans the time between and . The Lutetian is preceded by the Ypresian and is followed by the Bartonian. Together with the Bartonian it is sometimes referred to as the Middle Eocene subepoch...
age.
Drainage
The basin is mainly drained by the River ThamesRiver Thames
The River Thames flows through southern England. It is the longest river entirely in England and the second longest in the United Kingdom. While it is best known because its lower reaches flow through central London, the river flows alongside several other towns and cities, including Oxford,...
, but does not coincide with the Thames drainage basin
Drainage basin
A drainage basin is an extent or an area of land where surface water from rain and melting snow or ice converges to a single point, usually the exit of the basin, where the waters join another waterbody, such as a river, lake, reservoir, estuary, wetland, sea, or ocean...
. The upper Thames cuts through the Chilterns via the Goring Gap
Goring Gap
The Goring Gap is a British geological feature located on the River Thames approximately 8 miles upstream from Reading.Half a million years ago the River Thames flowed on its existing course through Oxfordshire, but then turned northeast to flow through Hertfordshire before eventually reaching the...
, and consequently the Thames drains parts of the Cotswolds
Cotswolds
The Cotswolds are a range of hills in west-central England, sometimes called the Heart of England, an area across and long. The area has been designated as the Cotswold Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty...
, Vale of White Horse
Vale of White Horse
The Vale of White Horse is a local government district of Oxfordshire in England. The main town is Abingdon, other places include Faringdon and Wantage. There are 68 parishes within the district...
and Vale of Aylesbury. The main headstream within the London Basin proper is the Kennet
River Kennet
The Kennet is a river in the south of England, and a tributary of the River Thames. The lower reaches of the river are navigable to river craft and are known as the Kennet Navigation, which, together with the Avon Navigation, the Kennet and Avon Canal and the Thames, links the cities of Bristol...
, which flows along the axis from the Marlborough area, joining the Thames at Reading
Reading, Berkshire
Reading is a large town and unitary authority area in England. It is located in the Thames Valley at the confluence of the River Thames and River Kennet, and on both the Great Western Main Line railway and the M4 motorway, some west of London....
.
To the south rivers such as the Mole
River Mole, Surrey
The River Mole is a tributary of the River Thames in southern England. It rises in West Sussex near Gatwick Airport and flows north west through Surrey for to the Thames near Hampton Court Palace. The river gives its name to the Surrey district of Mole Valley...
and Medway
River Medway
The River Medway, which is almost entirely in Kent, England, flows for from just inside the West Sussex border to the point where it enters the Thames Estuary....
, draining from the Weald, cut through the North Downs into the basin; these are presumed to date from before the erosion of the Weald dome.
During the Pleistocene ice age the lower Thames is believed to have been diverted well to the south of its earlier course closer to the main axis of the basin, probably by the Anglian Stage. The north eastern part of the basin is now drained to the North Sea
North Sea
In the southwest, beyond the Straits of Dover, the North Sea becomes the English Channel connecting to the Atlantic Ocean. In the east, it connects to the Baltic Sea via the Skagerrak and Kattegat, narrow straits that separate Denmark from Norway and Sweden respectively...
by rivers including the Crouch
River Crouch
The River Crouch is a river that flows entirely through the English county of Essex.The distance of the Navigation between Holliwell Point which is north of Foulness Island and Battlesbridge is 17.5 Miles, i.e. 15.21 Nautical Miles.-Route:...
, Blackwater
River Blackwater, Essex
The River Blackwater is a river in England. It rises in the northwest of Essex as the River Pant and flows to Bocking, near Braintree, from where its name changes to the Blackwater. Its course takes it near Stisted, and then via Bradwell Juxta Coggeshall and Coggeshall and near Witham where it is...
, Stour
River Stour, Suffolk
The River Stour is a river in East Anglia, England. It is 76 km long and forms most of the county boundary between Suffolk to the north, and Essex to the south. It rises in eastern Cambridgeshire, passes to the east of Haverhill, through Cavendish, Sudbury and the Dedham Vale, and joins the...
and Orwell
River Orwell
The River Orwell flows through the county of Suffolk in England. Its source river, above the tidal limit at Stoke Bridge, is known as the River Gipping. It broadens into an estuary at Ipswich where the Ipswich dock has operated since the 7th century and then flows into the North Sea at Felixstowe...
.
Settlements
Much of the basin is urbanised. Besides the whole Greater London Urban AreaGreater London Urban Area
The Greater London Urban Area is the conurbation or continuous urban area based around London, England, as defined by the Office for National Statistics. It had an estimated population of 8,505,000 in 2005 and occupied an area of at the time of the 2001 census. It includes most of Greater London,...
of over 8.5 million people, the basin contains most of the M4 Corridor
M4 corridor
The M4 corridor is the area in the United Kingdom adjacent to the M4 motorway, which runs from London to South Wales. The area is a major hub for high-technology companies...
including Newbury
Newbury, Berkshire
Newbury is a civil parish and the principal town in the west of the county of Berkshire in England. It is situated on the River Kennet and the Kennet and Avon Canal, and has a town centre containing many 17th century buildings. Newbury is best known for its racecourse and the adjoining former USAF...
, Reading
Reading, Berkshire
Reading is a large town and unitary authority area in England. It is located in the Thames Valley at the confluence of the River Thames and River Kennet, and on both the Great Western Main Line railway and the M4 motorway, some west of London....
, Bracknell
Bracknell
Bracknell is a town and civil parish in the Borough of Bracknell Forest in Berkshire, England. It lies to the south-east of Reading, southwest of Windsor and west of central London...
, Wokingham
Wokingham
Wokingham is a market town and civil parish in Berkshire in South East England about west of central London. It is about east-southeast of Reading and west of Bracknell. It spans an area of and, according to the 2001 census, has a population of 30,403...
, Finchampstead
Finchampstead
Finchampstead is a civil parish near Wokingham in the English county of Berkshire. Its northern extremity is situated south of Wokingham, west of Bracknell, south-east of Reading, and west of Central London.-Geography:...
, Maidenhead
Maidenhead
Maidenhead is a town and unparished area within the Royal Borough of Windsor and Maidenhead, in Berkshire, England. It lies on the River Thames and is situated west of Charing Cross in London.-History:...
and Slough
Slough
Slough is a borough and unitary authority within the ceremonial county of Royal Berkshire, England. The town straddles the A4 Bath Road and the Great Western Main Line, west of central London...
; the urbanised area to the south-west of London (Camberley
Camberley
Camberley is a town in Surrey, England, situated 31 miles southwest of central London, in the corridor between the M3 and M4 motorways. The town lies close to the borders of both Hampshire and Berkshire; the boundaries intersect on the western edge of the town where all three counties...
, Farnborough
Farnborough, Hampshire
-History:Name changes: Ferneberga ; Farnburghe, Farenberg ; Farnborowe, Fremborough, Fameborough .Tower Hill, Cove: There is substantial evidence...
, Aldershot
Aldershot
Aldershot is a town in the English county of Hampshire, located on heathland about southwest of London. The town is administered by Rushmoor Borough Council...
and Guildford
Guildford
Guildford is the county town of Surrey. England, as well as the seat for the borough of Guildford and the administrative headquarters of the South East England region...
); north and south Thames-side (Thurrock
Thurrock
Thurrock is a unitary authority with borough status in the English ceremonial county of Essex. It is part of the London commuter belt and an area of regeneration within the Thames Gateway redevelopment zone. The local authority is Thurrock Council....
, Tilbury
Tilbury
Tilbury is a town in the borough of Thurrock, Essex, England. As a settlement it is of relatively recent existence, although it has important historical connections, being the location of a 16th century fort and an ancient cross-river ferry...
, Basildon
Basildon
Basildon is a town located in the Basildon District of the county of Essex, England.It lies east of Central London and south of the county town of Chelmsford...
, Southend-on-Sea
Southend-on-Sea
Southend-on-Sea is a unitary authority area, town, and seaside resort in Essex, England. The district has Borough status, and comprises the towns of Chalkwell, Eastwood, Leigh-on-Sea, North Shoebury, Prittlewell, Shoeburyness, Southchurch, Thorpe Bay, and Westcliff-on-Sea. The district is situated...
, Northfleet
Northfleet
Northfleet is a town in the Borough of Gravesham in Kent, England. Its name is derived from North creek , and the settlement on the shore of the River Thames adjacent to Gravesend was known as Norfluet in the Domesday Book, and Northflet in 1201...
, Gravesend
Gravesend, Kent
Gravesend is a town in northwest Kent, England, on the south bank of the Thames, opposite Tilbury in Essex. It is the administrative town of the Borough of Gravesham and, because of its geographical position, has always had an important role to play in the history and communications of this part of...
etc); north Kent towns including Chatham, Rochester, Gillingham
Gillingham, Kent
Gillingham is a town in the unitary authority of Medway in South East England. It is part of the ceremonial county of Kent. The town includes the settlements of Brompton, Hempstead, Rainham, Rainham Mark and Twydall....
, Sittingbourne
Sittingbourne
Sittingbourne is an industrial town about eight miles east of Gillingham in England, beside the Roman Watling Street off a creek in the Swale, a channel separating the Isle of Sheppey from mainland Kent...
, Faversham
Faversham
Faversham is a market town and civil parish in the Swale borough of Kent, England. The parish of Faversham grew up around an ancient sea port on Faversham Creek and was the birthplace of the explosives industry in England.-History:...
, Whitstable
Whitstable
Whitstable is a seaside town in Northeast Kent, Southeast England. It is approximately north of the city of Canterbury and approximately west of the seaside town of Herne Bay. It is part of the City of Canterbury district and has a population of about 30,000.Whitstable is famous for its oysters,...
, Herne Bay
Herne Bay, Kent
Herne Bay is a seaside town in Kent, South East England, with a population of 35,188. On the south coast of the Thames Estuary, it is north of Canterbury and east of Whitstable. It neighbours the ancient villages of Herne and Reculver and is part of the City of Canterbury local government district...
and Canterbury
Canterbury
Canterbury is a historic English cathedral city, which lies at the heart of the City of Canterbury, a district of Kent in South East England. It lies on the River Stour....
; Essex towns including Brentwood
Brentwood, Essex
Brentwood is a town and the principal settlement of the Borough of Brentwood, in the county of Essex in the east of England. It is located in the London commuter belt, 20 miles east north-east of Charing Cross in London, and near the M25 motorway....
, Chelmsford
Chelmsford
Chelmsford is the county town of Essex, England and the principal settlement of the borough of Chelmsford. It is located in the London commuter belt, approximately northeast of Charing Cross, London, and approximately the same distance from the once provincial Roman capital at Colchester...
, Braintree
Braintree, Essex
Braintree is a town of about 42,000 people and the principal settlement of the Braintree district of Essex in the East of England. It is northeast of Chelmsford and west of Colchester on the River Blackwater, A120 road and a branch of the Great Eastern Main Line.Braintree has grown contiguous...
, Colchester
Colchester
Colchester is an historic town and the largest settlement within the borough of Colchester in Essex, England.At the time of the census in 2001, it had a population of 104,390. However, the population is rapidly increasing, and has been named as one of Britain's fastest growing towns. As the...
, Clacton-on-Sea
Clacton-on-Sea
Clacton-on-Sea is the largest town on the Tendring peninsula, in Essex, England and was founded in 1871. It is a seaside resort that attracted many tourists in the summer months between the 1950s and 1970s, but which like many other British sea-side resorts went into decline as a holiday...
and Harwich
Harwich
Harwich is a town in Essex, England and one of the Haven ports, located on the coast with the North Sea to the east. It is in the Tendring district. Nearby places include Felixstowe to the northeast, Ipswich to the northwest, Colchester to the southwest and Clacton-on-Sea to the south...
; and towns to the north and northwest of London including Bishops Stortford, Harlow
Harlow
Harlow is a new town and local government district in Essex, England. It is located in the west of the county and on the border with Hertfordshire, on the Stort Valley, The town is near the M11 motorway and forms part of the London commuter belt.The district has a current population of 78,889...
, Hertford
Hertford
Hertford is the county town of Hertfordshire, England, and is also a civil parish in the East Hertfordshire district of the county. Forming a civil parish, the 2001 census put the population of Hertford at about 24,180. Recent estimates are that it is now around 28,000...
, Stevenage
Stevenage
Stevenage is a town and borough in Hertfordshire, England. It is situated to the east of junctions 7 and 8 of the A1, and is between Letchworth Garden City to the north, and Welwyn Garden City to the south....
, Harpenden
Harpenden
Harpenden is a town in Hertfordshire, England.The town's total population is just under 30,000.-Geography and administration:There are two civil parishes: Harpenden and Harpenden Rural....
, Hatfield
Hatfield, Hertfordshire
Hatfield is a town and civil parish in Hertfordshire, England in the borough of Welwyn Hatfield. It has a population of 29,616, and is of Saxon origin. Hatfield House, the home of the Marquess of Salisbury, is the nucleus of the old town...
, Welwyn Garden City
Welwyn Garden City
-Economy:Ever since its inception as garden city, Welwyn Garden City has attracted a strong commercial base with several designated employment areas. Among the companies trading in the town are:*Air Link Systems*Baxter*British Lead Mills*Carl Zeiss...
, Potters Bar
Potters Bar
Potters Bar is a town in the Hertsmere borough of Hertfordshire, England, located north of Central London. In 2001 it had a population of 21,618....
, St Albans
St Albans
St Albans is a city in southern Hertfordshire, England, around north of central London, which forms the main urban area of the City and District of St Albans. It is a historic market town, and is now a sought-after dormitory town within the London commuter belt...
, Luton
Luton
Luton is a large town and unitary authority of Bedfordshire, England, 30 miles north of London. Luton and its near neighbours, Dunstable and Houghton Regis, form the Luton/Dunstable Urban Area with a population of about 250,000....
and High Wycombe
High Wycombe
High Wycombe , commonly known as Wycombe and formally called Chepping Wycombe or Chipping Wycombe until 1946,is a large town in Buckinghamshire, England. It is west-north-west of Charing Cross in London; this figure is engraved on the Corn Market building in the centre of the town...
.
Literature
; 2006: The geology of England and Wales, Geological Society of LondonGeological Society of London
The Geological Society of London is a learned society based in the United Kingdom with the aim of "investigating the mineral structure of the Earth"...
(2nd ed.), ISBN 1862392005.; 2004: A Geologic Time Scale 2004, Cambridge University Press
Cambridge University Press
Cambridge University Press is the publishing business of the University of Cambridge. Granted letters patent by Henry VIII in 1534, it is the world's oldest publishing house, and the second largest university press in the world...
.; 2008: Bedrock geology UK south. An explanation of the bedrock geology map of England and Wales – 1:625,000 edition, Keyworth, Nottingham, British Geological Survey
British Geological Survey
The British Geological Survey is a partly publicly funded body which aims to advance geoscientific knowledge of the United Kingdom landmass and its continental shelf by means of systematic surveying, monitoring and research. The BGS headquarters are in Keyworth, Nottinghamshire, but other centres...
, ISBN 978-085272-586-3.

