Tethys Ocean
Encyclopedia
Ocean
An ocean is a major body of saline water, and a principal component of the hydrosphere. Approximately 71% of the Earth's surface is covered by ocean, a continuous body of water that is customarily divided into several principal oceans and smaller seas.More than half of this area is over 3,000...
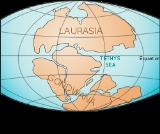
that existed between the continents of Gondwana
Gondwana
In paleogeography, Gondwana , originally Gondwanaland, was the southernmost of two supercontinents that later became parts of the Pangaea supercontinent. It existed from approximately 510 to 180 million years ago . Gondwana is believed to have sutured between ca. 570 and 510 Mya,...
and Laurasia
Laurasia
In paleogeography, Laurasia was the northernmost of two supercontinents that formed part of the Pangaea supercontinent from approximately...
during the Mesozoic
Mesozoic
The Mesozoic era is an interval of geological time from about 250 million years ago to about 65 million years ago. It is often referred to as the age of reptiles because reptiles, namely dinosaurs, were the dominant terrestrial and marine vertebrates of the time...
era before the opening of the Indian Ocean
Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third largest of the world's oceanic divisions, covering approximately 20% of the water on the Earth's surface. It is bounded on the north by the Indian Subcontinent and Arabian Peninsula ; on the west by eastern Africa; on the east by Indochina, the Sunda Islands, and...
.
Modern theory
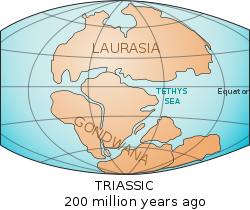
About 250 million years ago, during the TriassicTriassic
The Triassic is a geologic period and system that extends from about 250 to 200 Mya . As the first period of the Mesozoic Era, the Triassic follows the Permian and is followed by the Jurassic. Both the start and end of the Triassic are marked by major extinction events...
, a new ocean began forming in the southern end of the Paleo-Tethys Ocean
Paleo-Tethys Ocean
The Paleo-Tethys Ocean was an ancient Paleozoic ocean. It was located between the paleocontinent Gondwana and the so called Hunic terranes. These are divided into the European Hunic and Asiatic Hunic...
. A rift formed along the northern continental shelf of Southern Pangaea
Pangaea
Pangaea, Pangæa, or Pangea is hypothesized as a supercontinent that existed during the Paleozoic and Mesozoic eras about 250 million years ago, before the component continents were separated into their current configuration....
(Gondwana
Gondwana
In paleogeography, Gondwana , originally Gondwanaland, was the southernmost of two supercontinents that later became parts of the Pangaea supercontinent. It existed from approximately 510 to 180 million years ago . Gondwana is believed to have sutured between ca. 570 and 510 Mya,...
). Over the next 60 million years, that piece of shelf, known as Cimmeria
Cimmerian Plate
The Cimmerian Plate is an ancient tectonic plate that comprises parts of present-day Anatolia, Iran, Afghanistan, Tibet, Indochina and Malaya regions. The Cimmerian Plate was formerly part of the ancient supercontinent of Pangaea. Pangaea was shaped like a vast "C", facing east, and inside of the...
, traveled north, pushing the floor of the Paleo-Tethys Ocean under the eastern end of Northern Pangaea (Laurasia
Laurasia
In paleogeography, Laurasia was the northernmost of two supercontinents that formed part of the Pangaea supercontinent from approximately...
). The Tethys Ocean formed between Cimmeria and Gondwana, directly over where the Paleo-Tethys used to be.
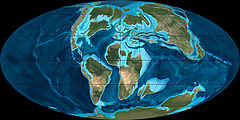
Jurassic
The Jurassic is a geologic period and system that extends from about Mya to Mya, that is, from the end of the Triassic to the beginning of the Cretaceous. The Jurassic constitutes the middle period of the Mesozoic era, also known as the age of reptiles. The start of the period is marked by...
Period (150 Ma), Cimmeria finally collided with Laurasia. There it stalled, the ocean floor behind it buckling under
Subduction
In geology, subduction is the process that takes place at convergent boundaries by which one tectonic plate moves under another tectonic plate, sinking into the Earth's mantle, as the plates converge. These 3D regions of mantle downwellings are known as "Subduction Zones"...
, forming the Tethyan Trench
Tethyan Trench
The Tethyan Trench was an ancient oceanic trench that existed in the northern part of the Tethys Ocean during the middle Mesozoic to early Cenozoic eras.-Geology:...
. Water levels rose and the western Tethys came to shallowly cover significant portions of Europe, forming the (first) Tethys Sea. Around the same time, Laurasia and Gondwana began drifting apart, opening an extension of the Tethys Sea between them that today is the part of the Atlantic Ocean
Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's oceanic divisions. With a total area of about , it covers approximately 20% of the Earth's surface and about 26% of its water surface area...
between the Mediterranean and Caribbean
Caribbean
The Caribbean is a crescent-shaped group of islands more than 2,000 miles long separating the Gulf of Mexico and the Caribbean Sea, to the west and south, from the Atlantic Ocean, to the east and north...
. As North and South America were still attached to the rest of Laurasia and Gondwana, respectively, the Tethys Ocean in its widest extension was part of a continuous oceanic belt running around the Earth between about latitude
Latitude
In geography, the latitude of a location on the Earth is the angular distance of that location south or north of the Equator. The latitude is an angle, and is usually measured in degrees . The equator has a latitude of 0°, the North pole has a latitude of 90° north , and the South pole has a...
30° N and the Equator
Equator
An equator is the intersection of a sphere's surface with the plane perpendicular to the sphere's axis of rotation and containing the sphere's center of mass....
. Thus, ocean current
Ocean current
An ocean current is a continuous, directed movement of ocean water generated by the forces acting upon this mean flow, such as breaking waves, wind, Coriolis effect, cabbeling, temperature and salinity differences and tides caused by the gravitational pull of the Moon and the Sun...
s at that time—around the Early Cretaceous
Early Cretaceous
The Early Cretaceous or the Lower Cretaceous , is the earlier or lower of the two major divisions of the Cretaceous...
—ran radically differently from the way they do today.
Between the Jurassic and the Late Cretaceous
Late Cretaceous
The Late Cretaceous is the younger of two epochs into which the Cretaceous period is divided in the geologic timescale. Rock strata from this epoch form the Upper Cretaceous series...
(which started about 100 Ma), even Gondwana began breaking up, pushing Africa
Africa
Africa is the world's second largest and second most populous continent, after Asia. At about 30.2 million km² including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of the Earth's total surface area and 20.4% of the total land area...
and India
India
India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
north, across the Tethys and opening up the Indian Ocean
Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third largest of the world's oceanic divisions, covering approximately 20% of the water on the Earth's surface. It is bounded on the north by the Indian Subcontinent and Arabian Peninsula ; on the west by eastern Africa; on the east by Indochina, the Sunda Islands, and...
. As these land masses pushed in on it from all sides, up until as recently as the Late Miocene
Miocene
The Miocene is a geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about . The Miocene was named by Sir Charles Lyell. Its name comes from the Greek words and and means "less recent" because it has 18% fewer modern sea invertebrates than the Pliocene. The Miocene follows the Oligocene...
(15 Ma), the Tethys ocean continued to shrink, becoming the Tethys Seaway or (second) Tethys Sea.
Today, India, Pakistan
Pakistan
Pakistan , officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan is a sovereign state in South Asia. It has a coastline along the Arabian Sea and the Gulf of Oman in the south and is bordered by Afghanistan and Iran in the west, India in the east and China in the far northeast. In the north, Tajikistan...
, Indonesia
Indonesia
Indonesia , officially the Republic of Indonesia , is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania. Indonesia is an archipelago comprising approximately 13,000 islands. It has 33 provinces with over 238 million people, and is the world's fourth most populous country. Indonesia is a republic, with an...
, and the Indian Ocean
Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third largest of the world's oceanic divisions, covering approximately 20% of the water on the Earth's surface. It is bounded on the north by the Indian Subcontinent and Arabian Peninsula ; on the west by eastern Africa; on the east by Indochina, the Sunda Islands, and...
cover the area once occupied by the Tethys Ocean, and Turkey
Turkey
Turkey , known officially as the Republic of Turkey , is a Eurasian country located in Western Asia and in East Thrace in Southeastern Europe...
, Iraq
Iraq
Iraq ; officially the Republic of Iraq is a country in Western Asia spanning most of the northwestern end of the Zagros mountain range, the eastern part of the Syrian Desert and the northern part of the Arabian Desert....
, and Tibet
Tibet
Tibet is a plateau region in Asia, north-east of the Himalayas. It is the traditional homeland of the Tibetan people as well as some other ethnic groups such as Monpas, Qiang, and Lhobas, and is now also inhabited by considerable numbers of Han and Hui people...
sit on Cimmeria. What was once the Tethys Sea has become the Mediterranean Sea
Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean surrounded by the Mediterranean region and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Anatolia and Europe, on the south by North Africa, and on the east by the Levant...
. Other remnants are the Black
Black Sea
The Black Sea is bounded by Europe, Anatolia and the Caucasus and is ultimately connected to the Atlantic Ocean via the Mediterranean and the Aegean seas and various straits. The Bosphorus strait connects it to the Sea of Marmara, and the strait of the Dardanelles connects that sea to the Aegean...
, Caspian
Caspian Sea
The Caspian Sea is the largest enclosed body of water on Earth by area, variously classed as the world's largest lake or a full-fledged sea. The sea has a surface area of and a volume of...
, and Aral
Aral Sea
The Aral Sea was a lake that lay between Kazakhstan in the north and Karakalpakstan, an autonomous region of Uzbekistan, in the south...
Seas (via a former inland branch known as the Paratethys
Paratethys
The Paratethys ocean, Paratethys sea or just Paratethys was a large shallow sea that stretched from the region north of the Alps over Central Europe to the Aral Sea in western Asia. The sea was formed during the Oxfordian epoch as an extension of the rift that formed the Central Atlantic Ocean and...
). Most of the floor of the Tethys Ocean disappeared under Cimmeria and Laurasia. Geologist
Geologist
A geologist is a scientist who studies the solid and liquid matter that constitutes the Earth as well as the processes and history that has shaped it. Geologists usually engage in studying geology. Geologists, studying more of an applied science than a theoretical one, must approach Geology using...
s like Suess have found fossil
Fossil
Fossils are the preserved remains or traces of animals , plants, and other organisms from the remote past...
s of ocean creatures in rocks in the Himalayas
Himalayas
The Himalaya Range or Himalaya Mountains Sanskrit: Devanagari: हिमालय, literally "abode of snow"), usually called the Himalayas or Himalaya for short, is a mountain range in Asia, separating the Indian subcontinent from the Tibetan Plateau...
, indicating that those rocks were once underwater, before the Indian continental shelf began pushing upward
Plate tectonics
Plate tectonics is a scientific theory that describes the large scale motions of Earth's lithosphere...
as it smashed into Cimmeria. We can see similar geologic evidence in the Alpine orogeny
Alpine orogeny
The Alpine orogeny is an orogenic phase in the Late Mesozoic and Tertiary that formed the mountain ranges of the Alpide belt...
of Europe
Europe
Europe is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting...
, where the movement of the African plate
African Plate
The African Plate is a tectonic plate which includes the continent of Africa, as well as oceanic crust which lies between the continent and various surrounding ocean ridges.-Boundaries:...
raised the Alps
Alps
The Alps is one of the great mountain range systems of Europe, stretching from Austria and Slovenia in the east through Italy, Switzerland, Liechtenstein and Germany to France in the west....
.
Paleontologists also find the Tethys Ocean particularly important because much of the world's sea shelves were found around its margins for such an extensive length. Marine, marsh-dwelling, and estuarian
Estuary
An estuary is a partly enclosed coastal body of water with one or more rivers or streams flowing into it, and with a free connection to the open sea....
fossils from these shelves are of considerable paleontological interest.
Historical theory
In 1893, using fossilFossil
Fossils are the preserved remains or traces of animals , plants, and other organisms from the remote past...
records from the Alps
Alps
The Alps is one of the great mountain range systems of Europe, stretching from Austria and Slovenia in the east through Italy, Switzerland, Liechtenstein and Germany to France in the west....
and Africa
Africa
Africa is the world's second largest and second most populous continent, after Asia. At about 30.2 million km² including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of the Earth's total surface area and 20.4% of the total land area...
, Eduard Suess
Eduard Suess
Eduard Suess was a geologist who was an expert on the geography of the Alps. He is responsible for hypothesising two major former geographical features, the supercontinent Gondwana and the Tethys Ocean.Born in London to a Jewish Saxon merchant, when he was three his family relocated toPrague,...
proposed the theory that an inland sea had once existed between Laurasia
Laurasia
In paleogeography, Laurasia was the northernmost of two supercontinents that formed part of the Pangaea supercontinent from approximately...
and the continents which formed Gondwana II
Gondwana
In paleogeography, Gondwana , originally Gondwanaland, was the southernmost of two supercontinents that later became parts of the Pangaea supercontinent. It existed from approximately 510 to 180 million years ago . Gondwana is believed to have sutured between ca. 570 and 510 Mya,...
. In this moment of Earth's life, however, these two continental masses were united in a unique supercontinent, known as Gondwana III or Pangaea
Pangaea
Pangaea, Pangæa, or Pangea is hypothesized as a supercontinent that existed during the Paleozoic and Mesozoic eras about 250 million years ago, before the component continents were separated into their current configuration....
. He named it the 'Tethys Sea' after the Greek
Greek mythology
Greek mythology is the body of myths and legends belonging to the ancient Greeks, concerning their gods and heroes, the nature of the world, and the origins and significance of their own cult and ritual practices. They were a part of religion in ancient Greece...
sea goddess Tethys
Tethys (mythology)
In Greek mythology, Tethys , daughter of Uranus and Gaia was an archaic Titaness and aquatic sea goddess, invoked in classical Greek poetry but not venerated in cult. Tethys was both sister and wife of Oceanus...
. When the theory of plate tectonics
Plate tectonics
Plate tectonics is a scientific theory that describes the large scale motions of Earth's lithosphere...
became established in the 1960s it became clear Suess's "sea" had in fact been an ocean
Ocean
An ocean is a major body of saline water, and a principal component of the hydrosphere. Approximately 71% of the Earth's surface is covered by ocean, a continuous body of water that is customarily divided into several principal oceans and smaller seas.More than half of this area is over 3,000...
. Plate tectonics also provided the mechanism by which the former ocean disappeared. In plate tectonic theory oceanic crust
Oceanic crust
Oceanic crust is the part of Earth's lithosphere that surfaces in the ocean basins. Oceanic crust is primarily composed of mafic rocks, or sima, which is rich in iron and magnesium...
can subduct
Subduction
In geology, subduction is the process that takes place at convergent boundaries by which one tectonic plate moves under another tectonic plate, sinking into the Earth's mantle, as the plates converge. These 3D regions of mantle downwellings are known as "Subduction Zones"...
under continental crust
Continental crust
The continental crust is the layer of igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks which form the continents and the areas of shallow seabed close to their shores, known as continental shelves. This layer is sometimes called sial due to more felsic, or granitic, bulk composition, which lies in...
.
Terminology and subdivisions
Like every science, geologyGeology
Geology is the science comprising the study of solid Earth, the rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which it evolves. Geology gives insight into the history of the Earth, as it provides the primary evidence for plate tectonics, the evolutionary history of life, and past climates...
is a continuously evolving system of theories
Theory
The English word theory was derived from a technical term in Ancient Greek philosophy. The word theoria, , meant "a looking at, viewing, beholding", and referring to contemplation or speculation, as opposed to action...
, and the terms used to describe various pre-historic formations have fluctuated as more accurate theories have emerged. For example, many internet sources use "Tethys Ocean" to refer to the "Tethys Sea" and vice versa. Some even appear to erroneously refer to the growing Atlantic Ocean
Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's oceanic divisions. With a total area of about , it covers approximately 20% of the Earth's surface and about 26% of its water surface area...
during the Jurassic
Jurassic
The Jurassic is a geologic period and system that extends from about Mya to Mya, that is, from the end of the Triassic to the beginning of the Cretaceous. The Jurassic constitutes the middle period of the Mesozoic era, also known as the age of reptiles. The start of the period is marked by...
as the Tethys Sea.
The western part of the Tethys Ocean is called Tethys Sea, Western Tethys Ocean or Alpine Tethys Ocean
Paratethys
The Paratethys ocean, Paratethys sea or just Paratethys was a large shallow sea that stretched from the region north of the Alps over Central Europe to the Aral Sea in western Asia. The sea was formed during the Oxfordian epoch as an extension of the rift that formed the Central Atlantic Ocean and...
. The Black
Black Sea
The Black Sea is bounded by Europe, Anatolia and the Caucasus and is ultimately connected to the Atlantic Ocean via the Mediterranean and the Aegean seas and various straits. The Bosphorus strait connects it to the Sea of Marmara, and the strait of the Dardanelles connects that sea to the Aegean...
, Caspian
Caspian Sea
The Caspian Sea is the largest enclosed body of water on Earth by area, variously classed as the world's largest lake or a full-fledged sea. The sea has a surface area of and a volume of...
and Aral
Aral Sea
The Aral Sea was a lake that lay between Kazakhstan in the north and Karakalpakstan, an autonomous region of Uzbekistan, in the south...
Seas are thought to be its crustal
Crust (geology)
In geology, the crust is the outermost solid shell of a rocky planet or natural satellite, which is chemically distinct from the underlying mantle...
remains (though the Black Sea may in fact be a remnant of the older Paleo-Tethys Ocean
Paleo-Tethys Ocean
The Paleo-Tethys Ocean was an ancient Paleozoic ocean. It was located between the paleocontinent Gondwana and the so called Hunic terranes. These are divided into the European Hunic and Asiatic Hunic...
. However, this "Western Tethys" was not simply a single open ocean. It covered many small plates, Cretaceous
Cretaceous
The Cretaceous , derived from the Latin "creta" , usually abbreviated K for its German translation Kreide , is a geologic period and system from circa to million years ago. In the geologic timescale, the Cretaceous follows the Jurassic period and is followed by the Paleogene period of the...
island arc
Island arc
An island arc is a type of archipelago composed of a chain of volcanoes which alignment is arc-shaped, and which are situated parallel and close to a boundary between two converging tectonic plates....
s and microcontinents. Many small oceanic basin
Basin (geology)
A structural basin is a large-scale structural formation of rock strata formed by tectonic warping of previously flat lying strata. Structural basins are geological depressions, and are the inverse of domes. Some elongated structural basins are also known as synclines...
s (Valais Ocean
Valais Ocean
The Valais Ocean is a disappeared piece of oceanic crust which was situated between the continent Europe and the microcontinent Iberia or so called Briançonnais microcontinent...
, Piemont-Liguria Ocean
Piemont-Liguria Ocean
The Piemont-Liguria basin or the Piemont-Liguria Ocean was a former piece of oceanic crust that is seen as part of the Tethys Ocean...
, Meliata ocean) were separated from each other by continental terrane
Terrane
A terrane in geology is short-hand term for a tectonostratigraphic terrane, which is a fragment of crustal material formed on, or broken off from, one tectonic plate and accreted or "sutured" to crust lying on another plate...
s on the Alboran, Iberian
Iberian plate
The microcontinent Iberia encompassed not only the Iberian Peninsula but also Corsica, Sardinia, the Balearic Islands, and the Briançonnais zone of the Penninic nappes of the Alps...
, and Apulian
Apulian Plate
The Adriatic or Apulian Plate is a small tectonic plate carrying primarily continental crust that broke away from the African plate along a large transform fault in the Cretaceous period. The name Adriatic Plate is usually used when referring to the northern part of the plate...
plates. The high sea level in the Mesozoic
Mesozoic
The Mesozoic era is an interval of geological time from about 250 million years ago to about 65 million years ago. It is often referred to as the age of reptiles because reptiles, namely dinosaurs, were the dominant terrestrial and marine vertebrates of the time...
era flooded most of these continental domains forming shallow seas.
During the Oligocene
Oligocene
The Oligocene is a geologic epoch of the Paleogene Period and extends from about 34 million to 23 million years before the present . As with other older geologic periods, the rock beds that define the period are well identified but the exact dates of the start and end of the period are slightly...
, large parts of central and eastern Europe were covered by a northern branch of the Tethys Ocean, called the Paratethys
Paratethys
The Paratethys ocean, Paratethys sea or just Paratethys was a large shallow sea that stretched from the region north of the Alps over Central Europe to the Aral Sea in western Asia. The sea was formed during the Oxfordian epoch as an extension of the rift that formed the Central Atlantic Ocean and...
. The Paratethys was separated from the Tethys by the formation of the Alps, Carpathians, Dinarides, Taurus
Taurus Mountains
Taurus Mountains are a mountain complex in southern Turkey, dividing the Mediterranean coastal region of southern Turkey from the central Anatolian Plateau. The system extends along a curve from Lake Eğirdir in the west to the upper reaches of the Euphrates and Tigris rivers in the east...
and Elburz mountains during the Alpine orogeny
Alpine orogeny
The Alpine orogeny is an orogenic phase in the Late Mesozoic and Tertiary that formed the mountain ranges of the Alpide belt...
. It gradually disappeared during the late Miocene, becoming an isolated inland sea.
The eastern part of the Tethys Ocean is likewise sometimes referred to as Eastern Tethys.
As theories have improved, scientists have extended the "Tethys" name to refer to similar oceans that preceded it. The Paleo-Tethys Ocean
Paleo-Tethys Ocean
The Paleo-Tethys Ocean was an ancient Paleozoic ocean. It was located between the paleocontinent Gondwana and the so called Hunic terranes. These are divided into the European Hunic and Asiatic Hunic...
, mentioned above, existed from the Silurian
Silurian
The Silurian is a geologic period and system that extends from the end of the Ordovician Period, about 443.7 ± 1.5 Mya , to the beginning of the Devonian Period, about 416.0 ± 2.8 Mya . As with other geologic periods, the rock beds that define the period's start and end are well identified, but the...
(440 Ma) through the Jurassic
Jurassic
The Jurassic is a geologic period and system that extends from about Mya to Mya, that is, from the end of the Triassic to the beginning of the Cretaceous. The Jurassic constitutes the middle period of the Mesozoic era, also known as the age of reptiles. The start of the period is marked by...
periods, between the Hunic terranes and Gondwana (later the Cimmerian terranes
Cimmerian Plate
The Cimmerian Plate is an ancient tectonic plate that comprises parts of present-day Anatolia, Iran, Afghanistan, Tibet, Indochina and Malaya regions. The Cimmerian Plate was formerly part of the ancient supercontinent of Pangaea. Pangaea was shaped like a vast "C", facing east, and inside of the...
). Before that, the Proto-Tethys Ocean
Proto-Tethys Ocean
The Proto-Tethys Ocean was an ancient ocean that existed from the latest Ediacaran to the Carboniferous . It was an ocean predecessor of the later Paleo-Tethys Ocean. The ocean formed when Pannotia disintegrated, Proto-Laurasia rifted away from a supercontinent that would become Gondwana...
existed from the Ediacaran
Ediacaran
The Ediacaran Period , named after the Ediacara Hills of South Australia, is the last geological period of the Neoproterozoic Era and of the Proterozoic Eon, immediately preceding the Cambrian Period, the first period of the Paleozoic Era and of the Phanerozoic Eon...
(600 Ma) into the Devonian
Devonian
The Devonian is a geologic period and system of the Paleozoic Era spanning from the end of the Silurian Period, about 416.0 ± 2.8 Mya , to the beginning of the Carboniferous Period, about 359.2 ± 2.5 Mya...
(360 Ma), and was situated between Baltica and Laurentia
Laurentia
Laurentia is a large area of continental craton, which forms the ancient geological core of the North American continent...
to the north and Gondwana
Gondwana
In paleogeography, Gondwana , originally Gondwanaland, was the southernmost of two supercontinents that later became parts of the Pangaea supercontinent. It existed from approximately 510 to 180 million years ago . Gondwana is believed to have sutured between ca. 570 and 510 Mya,...
to the south. Neither Tethys oceans should be confused with the Rheic Ocean
Rheic Ocean
The Rheic Ocean was a Paleozoic ocean between the large continent Gondwana to the south and the microcontinents Avalonia and others to the north...
, which existed to the west of them in the Silurian period.

