
Hill people
Encyclopedia

Blowing horn
The blowing horn or winding horn is a sound device by and large shaped like a horn or actually a cattle or other animal horn arranged to blow from a hole in the pointed end of it...
are notable for their ability to be heard at great distances. The hill people are often divided into tribes that have a tradition of feuding among each other while resisting control by any central government. Often the hill people are minorities in their countries, and are divided by political borders.
This article gives a survey and index of hill people, with links to articles that discuss particular peoples or tribes.
Drakensberg

Drakensberg
The Drakensberg is the highest mountain range in Southern Africa, rising to in height. In Zulu, it is referred to as uKhahlamba , and in Sesotho as Maluti...
are the highest mountain range in Southern Africa
Southern Africa
Southern Africa is the southernmost region of the African continent, variably defined by geography or geopolitics. Within the region are numerous territories, including the Republic of South Africa ; nowadays, the simpler term South Africa is generally reserved for the country in English.-UN...
, rising up to 3482 metres (11,423.9 ft) in height. The people of these mountains are mostly Bantu
Bantu languages
The Bantu languages constitute a traditional sub-branch of the Niger–Congo languages. There are about 250 Bantu languages by the criterion of mutual intelligibility, though the distinction between language and dialect is often unclear, and Ethnologue counts 535 languages...
-speaking people who moved into the area from the north a thousand years ago, displacing the original Khoisan
Khoisan
Khoisan is a unifying name for two ethnic groups of Southern Africa, who share physical and putative linguistic characteristics distinct from the Bantu majority of the region. Culturally, the Khoisan are divided into the foraging San and the pastoral Khoi...
people. They include the Swazi, Xhosa and Zulu. Traditionally these people lived by cattle herding and small-scale farming, growing crops such as sorghum, maize, corn, pumpkins, beans and vegetables.
At the time the Europeans reached this part of South Africa
South Africa
The Republic of South Africa is a country in southern Africa. Located at the southern tip of Africa, it is divided into nine provinces, with of coastline on the Atlantic and Indian oceans...
(around 1830), the Zulu were temporarily in the ascendancy after a series of wars between the people of the region. The region is divided between South Africa
South Africa
The Republic of South Africa is a country in southern Africa. Located at the southern tip of Africa, it is divided into nine provinces, with of coastline on the Atlantic and Indian oceans...
, Lesotho
Lesotho
Lesotho , officially the Kingdom of Lesotho, is a landlocked country and enclave, surrounded by the Republic of South Africa. It is just over in size with a population of approximately 2,067,000. Its capital and largest city is Maseru. Lesotho is a member of the Commonwealth of Nations. The name...
and Swaziland
Swaziland
Swaziland, officially the Kingdom of Swaziland , and sometimes called Ngwane or Swatini, is a landlocked country in Southern Africa, bordered to the north, south and west by South Africa, and to the east by Mozambique...
, but the people move relatively freely between these states.
Ethiopian Highlands
EthiopiaGeography of Ethiopia
Ethiopia is located in the Horn of Africa and is bordered on the north and northeast by Eritrea, on the east by Djibouti and Somalia, on the south by Kenya, on the northwest by Sudan and on the southwest by South Sudan. The country has a high central plateau that varies from above sea level, with...
has a high central plateau that varies from 1,800 to 3,000 m (6,000 to 10,000 ft) above sea level, with the highest mountain reaching 4,533 m (14,872 ft). Near the equator but high up, the climate is temperate all year round. The heavy rains from June until mid-September feed the Blue Nile
Blue Nile
The Blue Nile is a river originating at Lake Tana in Ethiopia. With the White Nile, the river is one of the two major tributaries of the Nile...
, which waters Egypt
Egypt
Egypt , officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, Arabic: , is a country mainly in North Africa, with the Sinai Peninsula forming a land bridge in Southwest Asia. Egypt is thus a transcontinental country, and a major power in Africa, the Mediterranean Basin, the Middle East and the Muslim world...
.
The country's population is highly diverse. Most of its people speak a Semitic
Semitic languages
The Semitic languages are a group of related languages whose living representatives are spoken by more than 270 million people across much of the Middle East, North Africa and the Horn of Africa...
or Cushitic language
Cushitic languages
The Cushitic languages are a branch of the Afroasiatic language family spoken in the Horn of Africa, Tanzania, Kenya, Sudan and Egypt. They are named after the Biblical character Cush, who was identified as an ancestor of the speakers of these specific languages as early as AD 947...
. The Oromo
Oromo people
The Oromo are an ethnic group found in Ethiopia, northern Kenya, .and parts of Somalia. With 30 million members, they constitute the single largest ethnic group in Ethiopia and approximately 34.49% of the population according to the 2007 census...
, Amhara
Amhara people
Amhara are a highland people inhabiting the Northwestern highlands of Ethiopia. Numbering about 19.8 million people, they comprise 26% of the country's population, according to the 2007 national census...
, and Tigray
Tigray-Tigrinya people
Tigray-Tigrinya are an ethnic group who live in the southern, central and northern parts of Eritrea and the northern highlands of Ethiopia's Tigray province. They also live in Ethiopia's former provinces of Begemder and Wollo, which are today mostly part of Amhara Region, though a few regions...
make up more than three-quarters of the population, but there are more than 80 different ethnic groups within Ethiopia, including Somali
Somali people
Somalis are an ethnic group located in the Horn of Africa, also known as the Somali Peninsula. The overwhelming majority of Somalis speak the Somali language, which is part of the Cushitic branch of the Afro-Asiatic language family...
, Gurage
Gurage
Gurage is an ethnic group in Ethiopia. According to the 2007 national census, its population is 1,867,377 people , of whom 792,659 are urban dwellers. This is 2.53% of the total population of Ethiopia, or 7.52% of the Southern Nations, Nationalities, and People's Region...
, Sidama, Wolayta
Welayta people
Wolayta is the name of an ethnic group and its former kingdom, located in southern Ethiopia. According to the most recent census , they number 1.7 million people or 2.31 percent of the country's population, of whom 289,707 are urban inhabitants...
, Afar
Afar people
The Afar , also known as the Danakil, are an ethnic group in the Horn of Africa. They primarily live in the Afar Region of Ethiopia and in northern Djibouti, although some also inhabit the southern point of Eritrea.-Early history:...
, Hadiya
Hadiya
The Hadiya Kingdom was an ancient kingdom in located in southwestern Ethiopia, south of the Abbay River and west of Shewa. It was ruled by the Hadiya people, who spoke the Cushitic Hadiyya language. The historical Hadiya area was situated between Kembata, Gamo, and Waj, southwest of Shewa...
and Gamo. Principal crops include coffee
Coffee
Coffee is a brewed beverage with a dark,init brooo acidic flavor prepared from the roasted seeds of the coffee plant, colloquially called coffee beans. The beans are found in coffee cherries, which grow on trees cultivated in over 70 countries, primarily in equatorial Latin America, Southeast Asia,...
, pulses (e.g., beans), oilseeds, cereals, potatoes, sugarcane
Sugarcane
Sugarcane refers to any of six to 37 species of tall perennial grasses of the genus Saccharum . Native to the warm temperate to tropical regions of South Asia, they have stout, jointed, fibrous stalks that are rich in sugar, and measure two to six metres tall...
, and vegetables. Many of the people traditionally herded cattle, goat or sheep.
The Ethiopian state is ancient, dating back to at least the Aksumite Empire
Aksumite Empire
The Kingdom of Aksum or Axum, also known as the Aksumite Empire, was an important trading nation in northeastern Africa, growing from the proto-Aksumite Iron Age period ca. 4th century BC to achieve prominence by the 1st century AD...
(which officially used the name "Ethiopia" in the 4th century) and its predecessor state, D`mt (with early 1st millennium BC roots). The Twenty-fifth dynasty of Egypt
Twenty-fifth dynasty of Egypt
The twenty-fifth dynasty of Egypt, known as the Nubian Dynasty or the Kushite Empire, was the last dynasty of the Third Intermediate Period of Ancient Egypt....
(roughly 743-656 BC) was actually an Ethiopian dynasty. Despite two attempts at conquest by the Italians, the country has remained independent for almost all its history. The Coptic Christian church has a long history in Ethiopia, founded in 316 AD by a Meropius, Christian philosopher from Tyre.
Atlas and Rif

Atlas Mountains
The Atlas Mountains is a mountain range across a northern stretch of Africa extending about through Morocco, Algeria, and Tunisia. The highest peak is Toubkal, with an elevation of in southwestern Morocco. The Atlas ranges separate the Mediterranean and Atlantic coastlines from the Sahara Desert...
is a mountain range
Mountain range
A mountain range is a single, large mass consisting of a succession of mountains or narrowly spaced mountain ridges, with or without peaks, closely related in position, direction, formation, and age; a component part of a mountain system or of a mountain chain...
across a northern stretch of Africa
Africa
Africa is the world's second largest and second most populous continent, after Asia. At about 30.2 million km² including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of the Earth's total surface area and 20.4% of the total land area...
extending about 2400 km (1,491.3 mi) through Morocco
Morocco
Morocco , officially the Kingdom of Morocco , is a country located in North Africa. It has a population of more than 32 million and an area of 710,850 km², and also primarily administers the disputed region of the Western Sahara...
, Algeria
Algeria
Algeria , officially the People's Democratic Republic of Algeria , also formally referred to as the Democratic and Popular Republic of Algeria, is a country in the Maghreb region of Northwest Africa with Algiers as its capital.In terms of land area, it is the largest country in Africa and the Arab...
, and Tunisia
Tunisia
Tunisia , officially the Tunisian RepublicThe long name of Tunisia in other languages used in the country is: , is the northernmost country in Africa. It is a Maghreb country and is bordered by Algeria to the west, Libya to the southeast, and the Mediterranean Sea to the north and east. Its area...
, or the Maghreb
Maghreb
The Maghreb is the region of Northwest Africa, west of Egypt. It includes five countries: Morocco, Algeria, Tunisia, Libya, and Mauritania and the disputed territory of Western Sahara...
. The highest peak is Jbel Toubkal, with an elevation of 4167 metres (13,671 ft) in southwestern Morocco. The second highest mountain is the M'Goun
M'Goun
The M'Goun mountain, also rendered as Ighil Mgoun, Ighil n’Oumsoud, Irhil M’Goun, Ighil M’Goun, Jebel Mgoun, Jebel Ighil M’Goun and Jebel Aït M’goun, at 4,071 metres is the fourth highest peak of the Atlas Mountains . It is located in the Souss-Massa-Draâ region of Morocco....
of 4071 metres (13,356 ft).
The population of the Atlas Mountains are mainly Berber
Berber people
Berbers are the indigenous peoples of North Africa west of the Nile Valley. They are continuously distributed from the Atlantic to the Siwa oasis, in Egypt, and from the Mediterranean to the Niger River. Historically they spoke the Berber language or varieties of it, which together form a branch...
tribes, speakers of an Afro-Asiatic language
Afro-Asiatic languages
The Afroasiatic languages , also known as Hamito-Semitic, constitute one of the world's largest language families, with about 375 living languages...
, including the Kabyle
Kabyle language
Kabyle or Kabylian is a Berber language spoken by the Kabyle people north and northeast of Algeria. Estimates about the number of speakers range from 5 million to about 7 million speakers worldwide, the majority in Algeria.-Classification:The classification of Kabyle is Afro-Asiatic, Berber and...
, Chaoui
Chaoui
The Shawia people, or Chaouis are a Berber people who live mainly in the Aurès, Nememcha and Belezma Region in the Aurès Mountains, a large part of eastern Algeria known in ancient times as Numidia...
, Mozabite
Mozabite
The Mozabite people are a Berber ethnic group living in M'zab in the northern Sahara. They speak Tumzabt. Most of them are Ibadi Muslims. Nearly all of them read and write Arabic, though they use the Zenata dialect of the Berber language, for which they have no surviving written form.Mozabites...
, Riffians, Chleuh
Chleuh
The Shilha people, commonly known as the Chleuh are a Berber ethnic group. They live mainly in Morocco's Atlas Mountains and Souss Valley. The Shilha population is estimated to be approximately 8 million.They speak the Shilha language in several regional varieties...
, Sous
Sous
The Sous or Souss is a region in southern Morocco. Geologically, it is the alluvial basin of the Oued Sous , separated from the Sahara by the Anti-Atlas Mountains...
, Tuareg and Zenata
Zenata
Zenata were an ethnic group of North Africa, who were technically an Eastern Berber group and who are found in Tunisia, Algeria and Morocco....
. Although nominally subject at times to Carthage
Carthage
Carthage , implying it was a 'new Tyre') is a major urban centre that has existed for nearly 3,000 years on the Gulf of Tunis, developing from a Phoenician colony of the 1st millennium BC...
, the Roman Empire
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire was the post-Republican period of the ancient Roman civilization, characterised by an autocratic form of government and large territorial holdings in Europe and around the Mediterranean....
, the Fatimid
Fatimid
The Fatimid Islamic Caliphate or al-Fāṭimiyyūn was a Berber Shia Muslim caliphate first centered in Tunisia and later in Egypt that ruled over varying areas of the Maghreb, Sudan, Sicily, the Levant, and Hijaz from 5 January 909 to 1171.The caliphate was ruled by the Fatimids, who established the...
dynasty of Egypt
Egypt
Egypt , officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, Arabic: , is a country mainly in North Africa, with the Sinai Peninsula forming a land bridge in Southwest Asia. Egypt is thus a transcontinental country, and a major power in Africa, the Mediterranean Basin, the Middle East and the Muslim world...
(who originated in this area), the Ottoman Turks
Ottoman Turks
The Ottoman Turks were the Turkish-speaking population of the Ottoman Empire who formed the base of the state's military and ruling classes. Reliable information about the early history of Ottoman Turks is scarce, but they take their Turkish name, Osmanlı , from the house of Osman I The Ottoman...
and more recently the French
France
The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
, for most of their history the tribes of the Atlas mountains have effectively been independent.
Most Berbers are farmers, living in mountains relatively close to the Mediterranean coast, but the Tuareg and Zenaga of the southern Sahara are nomadic. The Berbers are sometimes treated as minorities in their countries, which are dominated by their Arabic-speaking relatives nearer to the coast.
Pyrenees and Galicia

Pyrenees
The Pyrenees is a range of mountains in southwest Europe that forms a natural border between France and Spain...
are a range of mountains in southwest Europe
Europe
Europe is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting...
that form a natural border between France
France
The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
and Spain
Spain
Spain , officially the Kingdom of Spain languages]] under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, Spain's official name is as follows:;;;;;;), is a country and member state of the European Union located in southwestern Europe on the Iberian Peninsula...
. Lower mountains extend to the west into Galicia. The inhabitants speak Spanish
Spanish language
Spanish , also known as Castilian , is a Romance language in the Ibero-Romance group that evolved from several languages and dialects in central-northern Iberia around the 9th century and gradually spread with the expansion of the Kingdom of Castile into central and southern Iberia during the...
, French
French language
French is a Romance language spoken as a first language in France, the Romandy region in Switzerland, Wallonia and Brussels in Belgium, Monaco, the regions of Quebec and Acadia in Canada, and by various communities elsewhere. Second-language speakers of French are distributed throughout many parts...
, Catalan
Catalan language
Catalan is a Romance language, the national and only official language of Andorra and a co-official language in the Spanish autonomous communities of Catalonia, the Balearic Islands and Valencian Community, where it is known as Valencian , as well as in the city of Alghero, on the Italian island...
(in Catalonia
Catalonia
Catalonia is an autonomous community in northeastern Spain, with the official status of a "nationality" of Spain. Catalonia comprises four provinces: Barcelona, Girona, Lleida, and Tarragona. Its capital and largest city is Barcelona. Catalonia covers an area of 32,114 km² and has an...
and Andorra
Andorra
Andorra , officially the Principality of Andorra , also called the Principality of the Valleys of Andorra, , is a small landlocked country in southwestern Europe, located in the eastern Pyrenees mountains and bordered by Spain and France. It is the sixth smallest nation in Europe having an area of...
), and the Basque language
Basque language
Basque is the ancestral language of the Basque people, who inhabit the Basque Country, a region spanning an area in northeastern Spain and southwestern France. It is spoken by 25.7% of Basques in all territories...
. A few speak the Occitan language (the Gascon
Gascon language
Gascon is usually considered as a dialect of Occitan, even though some specialists regularly consider it a separate language. Gascon is mostly spoken in Gascony and Béarn in southwestern France and in the Aran Valley of Spain...
and Languedocien
Languedocien
Languedocien or Lengadocian is an Occitan dialect spoken by some people in the part of southern France known as Languedoc, Rouergue, Quercy, Agenais and Southern Périgord....
dialects in France and the Aranese
Aranese language
Aranese is a standardized form of the Pyrenean Gascon variety of the Occitan language spoken in the Val d'Aran, in north western Catalonia on the border between Spain and France, where it is one of the three official languages besides Catalan and Spanish...
dialect in the Aran Valley), and Aragonese
Aragonese language
Aragonese is a Romance language now spoken in a number of local varieties by between 10,000 and 30,000 people over the valleys of the Aragón River, Sobrarbe and Ribagorza in Aragon, Spain...
.
It is thought that Basque people
Basque people
The Basques as an ethnic group, primarily inhabit an area traditionally known as the Basque Country , a region that is located around the western end of the Pyrenees on the coast of the Bay of Biscay and straddles parts of north-central Spain and south-western France.The Basques are known in the...
are a remnant of the early inhabitants of Western Europe. Basque tribes were already mentioned in Roman times by Strabo
Strabo
Strabo, also written Strabon was a Greek historian, geographer and philosopher.-Life:Strabo was born to an affluent family from Amaseia in Pontus , a city which he said was situated the approximate equivalent of 75 km from the Black Sea...
and Pliny
Pliny the Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus , better known as Pliny the Elder, was a Roman author, naturalist, and natural philosopher, as well as naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and personal friend of the emperor Vespasian...
, including the Vascones, the Aquitani
Aquitani
The Aquitani were a people living in what is now Aquitaine, France, in the region between the Pyrenees, the Atlantic ocean and the Garonne...
and others. Their language is quite distinct from the Indo-European
Indo-European
Indo-European may refer to:* Indo-European languages** Aryan race, a 19th century and early 20th century term for those peoples who are the native speakers of Indo-European languages...
languages spoken in most of Europe, and possibly (although there is much debate) is related to Northeast Caucasian languages
Northeast Caucasian languages
The Northeast Caucasian languages constitute a language family spoken in the Russian republics of Dagestan, Chechnya, Ingushetia, northern Azerbaijan, and in northeastern Georgia, as well as in diaspora populations in Russia, Turkey, and the Middle East...
. The Euskadi Ta Askatasuna or ETA is an illegal and armed Basque nationalist, terrorist and separatist organisation. Founded in 1959, it evolved from a group advocating traditional cultural ways to a paramilitary group demanding Basque independence.
Alps


Alps
The Alps is one of the great mountain range systems of Europe, stretching from Austria and Slovenia in the east through Italy, Switzerland, Liechtenstein and Germany to France in the west....
are one of the great mountain ranges of Europe, stretching from Austria
Austria
Austria , officially the Republic of Austria , is a landlocked country of roughly 8.4 million people in Central Europe. It is bordered by the Czech Republic and Germany to the north, Slovakia and Hungary to the east, Slovenia and Italy to the south, and Switzerland and Liechtenstein to the...
and Slovenia
Slovenia
Slovenia , officially the Republic of Slovenia , is a country in Central and Southeastern Europe touching the Alps and bordering the Mediterranean. Slovenia borders Italy to the west, Croatia to the south and east, Hungary to the northeast, and Austria to the north, and also has a small portion of...
in the east; through Italy
Italy
Italy , officially the Italian Republic languages]] under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, Italy's official name is as follows:;;;;;;;;), is a unitary parliamentary republic in South-Central Europe. To the north it borders France, Switzerland, Austria and...
, Switzerland
Switzerland
Switzerland name of one of the Swiss cantons. ; ; ; or ), in its full name the Swiss Confederation , is a federal republic consisting of 26 cantons, with Bern as the seat of the federal authorities. The country is situated in Western Europe,Or Central Europe depending on the definition....
, Liechtenstein
Liechtenstein
The Principality of Liechtenstein is a doubly landlocked alpine country in Central Europe, bordered by Switzerland to the west and south and by Austria to the east. Its area is just over , and it has an estimated population of 35,000. Its capital is Vaduz. The biggest town is Schaan...
and Germany
Germany
Germany , officially the Federal Republic of Germany , is a federal parliamentary republic in Europe. The country consists of 16 states while the capital and largest city is Berlin. Germany covers an area of 357,021 km2 and has a largely temperate seasonal climate...
; to France
France
The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
in the west. The highest mountain is Mont Blanc, at 4,808 metres (15,774 ft), on the Italian–French border. The people of the Alps speak German
German language
German is a West Germanic language, related to and classified alongside English and Dutch. With an estimated 90 – 98 million native speakers, German is one of the world's major languages and is the most widely-spoken first language in the European Union....
, French
French language
French is a Romance language spoken as a first language in France, the Romandy region in Switzerland, Wallonia and Brussels in Belgium, Monaco, the regions of Quebec and Acadia in Canada, and by various communities elsewhere. Second-language speakers of French are distributed throughout many parts...
, Italian
Italian language
Italian is a Romance language spoken mainly in Europe: Italy, Switzerland, San Marino, Vatican City, by minorities in Malta, Monaco, Croatia, Slovenia, France, Libya, Eritrea, and Somalia, and by immigrant communities in the Americas and Australia...
, and Romansh. The German spoken in the German speaking part of Switzerland is a range of Swiss dialects
Swiss German
Swiss German is any of the Alemannic dialects spoken in Switzerland and in some Alpine communities in Northern Italy. Occasionally, the Alemannic dialects spoken in other countries are grouped together with Swiss German as well, especially the dialects of Liechtenstein and Austrian Vorarlberg...
.
Early Alpine tribes included the Helvetii
Helvetii
The Helvetii were a Celtic tribe or tribal confederation occupying most of the Swiss plateau at the time of their contact with the Roman Republic in the 1st century BC...
and Alemanni. The Swiss Confederacy was an alliance among the valley communities of the central Alps founded by three cantons
Cantons of Switzerland
The 26 cantons of Switzerland are the member states of the federal state of Switzerland. Each canton was a fully sovereign state with its own borders, army and currency from the Treaty of Westphalia until the establishment of the Swiss federal state in 1848...
in 1291, later expanding to form the nucleus of modern Switzerland. Disciplined Swiss mercenaries
Swiss mercenaries
Swiss mercenaries were notable for their service in foreign armies, especially the armies of the Kings of France, throughout the Early Modern period of European history, from the Later Middle Ages into the Age of the European Enlightenment...
armed with pikes gained a formidable reputation during the perennial European wars of the Middle Ages.
In the Swiss peasant war of 1653
Swiss peasant war of 1653
The Swiss peasant war of 1653 was a popular revolt in the Old Swiss Confederacy at the time of the Ancien Régime. A devaluation of Bernese money caused a tax revolt that spread from the Entlebuch valley in the Canton of Lucerne to the Emmental valley in the Canton of Bern and then to the cantons of...
the people rose up against the nobles and authorities. Although defeated, the revolt resulted in reforms that prevented the rise of absolutism
Absolutism (European history)
Absolutism or The Age of Absolutism is a historiographical term used to describe a form of monarchical power that is unrestrained by all other institutions, such as churches, legislatures, or social elites...
as in other parts of Europe. The Swiss to this day have an unusual form of government where almost all major decisions are voted upon by the people.
The Alpine people have at times been subject in part or whole to neighboring countries, but many in the central Alps maintained the independence of their communities until 1848, when they combined into the federal state of Switzerland.
Scottish Highlands

Scottish Highlands
The Highlands is an historic region of Scotland. The area is sometimes referred to as the "Scottish Highlands". It was culturally distinguishable from the Lowlands from the later Middle Ages into the modern period, when Lowland Scots replaced Scottish Gaelic throughout most of the Lowlands...
include the rugged and mountainous regions of Scotland
Scotland
Scotland is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Occupying the northern third of the island of Great Britain, it shares a border with England to the south and is bounded by the North Sea to the east, the Atlantic Ocean to the north and west, and the North Channel and Irish Sea to the...
north and west of the Highland Boundary Fault
Highland Boundary Fault
The Highland Boundary Fault is a geological fault that traverses Scotland from Arran and Helensburgh on the west coast to Stonehaven in the east...
. They are inhabited by people of the Scottish Gaelic culture, although most now speak English
English language
English is a West Germanic language that arose in the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms of England and spread into what was to become south-east Scotland under the influence of the Anglian medieval kingdom of Northumbria...
. Traditionally the people lived by crofting
Crofting
Crofting is a form of land tenure and small-scale food production unique to the Scottish Highlands, the Islands of Scotland, and formerly on the Isle of Man....
, or small-scale farming, growing crops such as oats
OATS
OATS - Open Source Assistive Technology Software - is a source code repository or "forge" for assistive technology software. It was launched in 2006 with the goal to provide a one-stop “shop” for end users, clinicians and open-source developers to promote and develop open source assistive...
, barley
Barley
Barley is a major cereal grain, a member of the grass family. It serves as a major animal fodder, as a base malt for beer and certain distilled beverages, and as a component of various health foods...
and kale
Kale
Kale is very high in beta carotene, vitamin K, vitamin C, lutein, zeaxanthin, and reasonably rich in calcium. Kale, as with broccoli and other brassicas, contains sulforaphane , a chemical with potent anti-cancer properties. Boiling decreases the level of sulforaphane; however, steaming,...
, and supplemented their diet with fish and red deer
Red Deer
The red deer is one of the largest deer species. Depending on taxonomy, the red deer inhabits most of Europe, the Caucasus Mountains region, Asia Minor, parts of western Asia, and central Asia. It also inhabits the Atlas Mountains region between Morocco and Tunisia in northwestern Africa, being...
.
On festive occasions, the people eat haggis
Haggis
Haggis is a dish containing sheep's 'pluck' , minced with onion, oatmeal, suet, spices, and salt, mixed with stock, and traditionally simmered in the animal's stomach for approximately three hours. Most modern commercial haggis is prepared in a casing rather than an actual stomach.Haggis is a kind...
, made from a sheep's heart, liver and lungs, minced with onion, oatmeal, suet, spices, and salt, mixed with stock, and boiled in the animal's stomach for three hours. The haggis was immortalized by the lowland poet Robert Burns
Robert Burns
Robert Burns was a Scottish poet and a lyricist. He is widely regarded as the national poet of Scotland, and is celebrated worldwide...
in his Address to a Haggis
The Scottish clan
Scottish clan
Scottish clans , give a sense of identity and shared descent to people in Scotland and to their relations throughout the world, with a formal structure of Clan Chiefs recognised by the court of the Lord Lyon, King of Arms which acts as an authority concerning matters of heraldry and Coat of Arms...
s have a tradition of feuding among each other and resisting the authority of the central government based in the lowland city of Edinburgh
Edinburgh
Edinburgh is the capital city of Scotland, the second largest city in Scotland, and the eighth most populous in the United Kingdom. The City of Edinburgh Council governs one of Scotland's 32 local government council areas. The council area includes urban Edinburgh and a rural area...
. They are a martial race. The Highland regiments
Scottish regiment
A Scottish regiment is any regiment that at some time in its history has or had a name that referred to Scotland or some part, thereof, and adopted items of Scottish dress...
went to war wearing tartan
Tartan
Tartan is a pattern consisting of criss-crossed horizontal and vertical bands in multiple colours. Tartans originated in woven wool, but now they are made in many other materials. Tartan is particularly associated with Scotland. Scottish kilts almost always have tartan patterns...
kilts accompanied by bagpipe players – a sight and sound calculated to strike fear into the hearts of their enemies.
Balkans

Balkan Mountains
The Balkan mountain range is a mountain range in the eastern part of the Balkan Peninsula. The Balkan range runs 560 km from the Vrashka Chuka Peak on the border between Bulgaria and eastern Serbia eastward through central Bulgaria to Cape Emine on the Black Sea...
run 560 km from the Vrashka Chuka Peak on the border between Bulgaria
Bulgaria
Bulgaria , officially the Republic of Bulgaria , is a parliamentary democracy within a unitary constitutional republic in Southeast Europe. The country borders Romania to the north, Serbia and Macedonia to the west, Greece and Turkey to the south, as well as the Black Sea to the east...
and eastern Serbia
Serbia
Serbia , officially the Republic of Serbia , is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central and Southeast Europe, covering the southern part of the Carpathian basin and the central part of the Balkans...
eastward through central Bulgaria to Cape Emine
Cape Emine
Cape Emine is a headland located at the Bulgarian Black Sea Coast. It is located 49 miles south of Varna, 34 miles north of Burgas and 9 miles south of Obzor. It forms the tip of Stara Planina. Cape Emine is said to be Bulgaria's stormiest cape....
on the Black Sea
Black Sea
The Black Sea is bounded by Europe, Anatolia and the Caucasus and is ultimately connected to the Atlantic Ocean via the Mediterranean and the Aegean seas and various straits. The Bosphorus strait connects it to the Sea of Marmara, and the strait of the Dardanelles connects that sea to the Aegean...
. The highest peaks of the Stara planina are in central Bulgaria. The highest peak is Botev
Botev
-Places:* Botevgrad* Botev Peak, the highest peak of the Balkan mountains* Botev Point-Sports:* FC Botev Vratsa, Bulgarian soccer club* PFC Botev Plovdiv, a soccer club from Plovdiv* Botev Krivodol, Bulgarian soccer club...
(2,376 m).
Lying between Austria
Austria
Austria , officially the Republic of Austria , is a landlocked country of roughly 8.4 million people in Central Europe. It is bordered by the Czech Republic and Germany to the north, Slovakia and Hungary to the east, Slovenia and Italy to the south, and Switzerland and Liechtenstein to the...
, Italy
Italy
Italy , officially the Italian Republic languages]] under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, Italy's official name is as follows:;;;;;;;;), is a unitary parliamentary republic in South-Central Europe. To the north it borders France, Switzerland, Austria and...
, Turkey
Turkey
Turkey , known officially as the Republic of Turkey , is a Eurasian country located in Western Asia and in East Thrace in Southeastern Europe...
and the Ukraine
Ukraine
Ukraine is a country in Eastern Europe. It has an area of 603,628 km², making it the second largest contiguous country on the European continent, after Russia...
, the Balkans have had a turbulent history. At different times different parts of the Balkans were controlled by the Macedonian, Roman
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire was the post-Republican period of the ancient Roman civilization, characterised by an autocratic form of government and large territorial holdings in Europe and around the Mediterranean....
, Byzantine
Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire was the Eastern Roman Empire during the periods of Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, centred on the capital of Constantinople. Known simply as the Roman Empire or Romania to its inhabitants and neighbours, the Empire was the direct continuation of the Ancient Roman State...
, Ottoman
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman EmpireIt was usually referred to as the "Ottoman Empire", the "Turkish Empire", the "Ottoman Caliphate" or more commonly "Turkey" by its contemporaries...
and Austrian
Austrian Empire
The Austrian Empire was a modern era successor empire, which was centered on what is today's Austria and which officially lasted from 1804 to 1867. It was followed by the Empire of Austria-Hungary, whose proclamation was a diplomatic move that elevated Hungary's status within the Austrian Empire...
empires.
The Balkans are home to people speaking Slavic languages
Slavic languages
The Slavic languages , a group of closely related languages of the Slavic peoples and a subgroup of Indo-European languages, have speakers in most of Eastern Europe, in much of the Balkans, in parts of Central Europe, and in the northern part of Asia.-Branches:Scholars traditionally divide Slavic...
(Serbs
Serbs
The Serbs are a South Slavic ethnic group of the Balkans and southern Central Europe. Serbs are located mainly in Serbia, Montenegro and Bosnia and Herzegovina, and form a sizable minority in Croatia, the Republic of Macedonia and Slovenia. Likewise, Serbs are an officially recognized minority in...
, Croats
Croats
Croats are a South Slavic ethnic group mostly living in Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina and nearby countries. There are around 4 million Croats living inside Croatia and up to 4.5 million throughout the rest of the world. Responding to political, social and economic pressure, many Croats have...
, Bulgarians
Bulgarians
The Bulgarians are a South Slavic nation and ethnic group native to Bulgaria and neighbouring regions. Emigration has resulted in immigrant communities in a number of other countries.-History and ethnogenesis:...
and Macedonians
Macedonians (ethnic group)
The Macedonians also referred to as Macedonian Slavs: "... the term Slavomacedonian was introduced and was accepted by the community itself, which at the time had a much more widespread non-Greek Macedonian ethnic consciousness...
), Romanian
Romanian language
Romanian Romanian Romanian (or Daco-Romanian; obsolete spellings Rumanian, Roumanian; self-designation: română, limba română ("the Romanian language") or românește (lit. "in Romanian") is a Romance language spoken by around 24 to 28 million people, primarily in Romania and Moldova...
(related to Italian
Italian language
Italian is a Romance language spoken mainly in Europe: Italy, Switzerland, San Marino, Vatican City, by minorities in Malta, Monaco, Croatia, Slovenia, France, Libya, Eritrea, and Somalia, and by immigrant communities in the Americas and Australia...
), Turkish
Turkish language
Turkish is a language spoken as a native language by over 83 million people worldwide, making it the most commonly spoken of the Turkic languages. Its speakers are located predominantly in Turkey and Northern Cyprus with smaller groups in Iraq, Greece, Bulgaria, the Republic of Macedonia, Kosovo,...
, Greek
Greek language
Greek is an independent branch of the Indo-European family of languages. Native to the southern Balkans, it has the longest documented history of any Indo-European language, spanning 34 centuries of written records. Its writing system has been the Greek alphabet for the majority of its history;...
, Albanian
Albanian language
Albanian is an Indo-European language spoken by approximately 7.6 million people, primarily in Albania and Kosovo but also in other areas of the Balkans in which there is an Albanian population, including western Macedonia, southern Montenegro, southern Serbia and northwestern Greece...
and other languages. Through its history many other ethnic groups with their own languages lived in the area, among them Thracians
Thracians
The ancient Thracians were a group of Indo-European tribes inhabiting areas including Thrace in Southeastern Europe. They spoke the Thracian language – a scarcely attested branch of the Indo-European language family...
, Illyrians
Illyrians
The Illyrians were a group of tribes who inhabited part of the western Balkans in antiquity and the south-eastern coasts of the Italian peninsula...
, Romans
Ancient Rome
Ancient Rome was a thriving civilization that grew on the Italian Peninsula as early as the 8th century BC. Located along the Mediterranean Sea and centered on the city of Rome, it expanded to one of the largest empires in the ancient world....
, Pechenegs, Cumans
Cumans
The Cumans were Turkic nomadic people comprising the western branch of the Cuman-Kipchak confederation. After Mongol invasion , they decided to seek asylum in Hungary, and subsequently to Bulgaria...
, Avars
Eurasian Avars
The Eurasian Avars or Ancient Avars were a highly organized nomadic confederacy of mixed origins. They were ruled by a khagan, who was surrounded by a tight-knit entourage of nomad warriors, an organization characteristic of Turko-Mongol groups...
, Celts, Germans
Germans
The Germans are a Germanic ethnic group native to Central Europe. The English term Germans has referred to the German-speaking population of the Holy Roman Empire since the Late Middle Ages....
and various Germanic tribes. In addition to language, the people are divided by religion, adhering to the Roman Catholic, Greek Orthodox and Moslem religions among others.
Caucasus
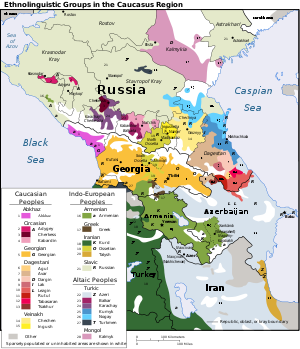
Caucasus Mountains
The Caucasus Mountains is a mountain system in Eurasia between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea in the Caucasus region .The Caucasus Mountains includes:* the Greater Caucasus Mountain Range and* the Lesser Caucasus Mountains....
is a range between the Black sea
Black Sea
The Black Sea is bounded by Europe, Anatolia and the Caucasus and is ultimately connected to the Atlantic Ocean via the Mediterranean and the Aegean seas and various straits. The Bosphorus strait connects it to the Sea of Marmara, and the strait of the Dardanelles connects that sea to the Aegean...
and the Caspian sea
Caspian Sea
The Caspian Sea is the largest enclosed body of water on Earth by area, variously classed as the world's largest lake or a full-fledged sea. The sea has a surface area of and a volume of...
. It is home to Europe's highest mountain (Mount Elbrus
Mount Elbrus
Mount Elbrus is an inactive volcano located in the western Caucasus mountain range, in Kabardino-Balkaria and Karachay-Cherkessia, Russia, near the border of Georgia. Mt. Elbrus's peak is the highest in the Caucasus, in Russia...
). Modern countries of the Caucasus are Chechnya
Chechnya
The Chechen Republic , commonly referred to as Chechnya , also spelled Chechnia or Chechenia, sometimes referred to as Ichkeria , is a federal subject of Russia . It is located in the southeastern part of Europe in the Northern Caucasus mountains. The capital of the republic is the city of Grozny...
, Ingushetia
Ingushetia
The Republic of Ingushetia is a federal subject of Russia , located in the North Caucasus region with its capital at Magas. In terms of area, the republic is the smallest of Russia's federal subjects except for the two federal cities, Moscow and Saint Petersburg...
, Dagestan, Adyghea, Kabardino-Balkaria
Kabardino-Balkaria
The Kabardino-Balkar Republic , or Kabardino-Balkaria , is a federal subject of Russia located in the North Caucasus. Population: -Geography:The republic is situated in the North Caucasus mountains, with plains in the northern part....
, Karachai-Cherkessia, North Ossetia, Krasnodar Krai
Krasnodar Krai
-External links:* **...
and Stavropol Krai
Stavropol Krai
Stavropol Krai is a federal subject of Russia . Its administrative center is the city of Stavropol. Population: -Geography:Stavropol Krai encompasses the central part of the Fore-Caucasus and most of the northern slopes of Caucasus Major...
, all parts of the Russian Federation, and the independent countries of Georgia
Georgia (country)
Georgia is a sovereign state in the Caucasus region of Eurasia. Located at the crossroads of Western Asia and Eastern Europe, it is bounded to the west by the Black Sea, to the north by Russia, to the southwest by Turkey, to the south by Armenia, and to the southeast by Azerbaijan. The capital of...
(including the disputed Abkhazia
Abkhazia
Abkhazia is a disputed political entity on the eastern coast of the Black Sea and the south-western flank of the Caucasus.Abkhazia considers itself an independent state, called the Republic of Abkhazia or Apsny...
and South Ossetia
South Ossetia
South Ossetia or Tskhinvali Region is a disputed region and partly recognized state in the South Caucasus, located in the territory of the South Ossetian Autonomous Oblast within the former Georgian Soviet Socialist Republic....
), Armenia
Armenia
Armenia , officially the Republic of Armenia , is a landlocked mountainous country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia...
, Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan , officially the Republic of Azerbaijan is the largest country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia. Located at the crossroads of Western Asia and Eastern Europe, it is bounded by the Caspian Sea to the east, Russia to the north, Georgia to the northwest, Armenia to the west, and Iran to...
and Turkey
Turkey
Turkey , known officially as the Republic of Turkey , is a Eurasian country located in Western Asia and in East Thrace in Southeastern Europe...
.
The people of these mountains have very diverse origins, with cultures influenced by periods of Turkic
Turkic peoples
The Turkic peoples are peoples residing in northern, central and western Asia, southern Siberia and northwestern China and parts of eastern Europe. They speak languages belonging to the Turkic language family. They share, to varying degrees, certain cultural traits and historical backgrounds...
, Iran
Iran
Iran , officially the Islamic Republic of Iran , is a country in Southern and Western Asia. The name "Iran" has been in use natively since the Sassanian era and came into use internationally in 1935, before which the country was known to the Western world as Persia...
ian and Russian
Russians
The Russian people are an East Slavic ethnic group native to Russia, speaking the Russian language and primarily living in Russia and neighboring countries....
control. Some, including the Georgians and Armenians, are mostly Christian, while others are Moslem in religion.
Hindu Kush and Balochistan

Hindu Kush
The Hindu Kush is an mountain range that stretches between central Afghanistan and northern Pakistan. The highest point in the Hindu Kush is Tirich Mir in the Chitral region of Khyber-Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan.It is the westernmost extension of the Pamir Mountains, the Karakoram Range, and is a...
is a mountain range located between Afghanistan
Afghanistan
Afghanistan , officially the Islamic Republic of Afghanistan, is a landlocked country located in the centre of Asia, forming South Asia, Central Asia and the Middle East. With a population of about 29 million, it has an area of , making it the 42nd most populous and 41st largest nation in the world...
and Pakistan
Pakistan
Pakistan , officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan is a sovereign state in South Asia. It has a coastline along the Arabian Sea and the Gulf of Oman in the south and is bordered by Afghanistan and Iran in the west, India in the east and China in the far northeast. In the north, Tajikistan...
. It is the westernmost extension of the Pamir Mountains
Pamir Mountains
The Pamir Mountains are a mountain range in Central Asia formed by the junction or knot of the Himalayas, Tian Shan, Karakoram, Kunlun, and Hindu Kush ranges. They are among the world’s highest mountains and since Victorian times they have been known as the "Roof of the World" a probable...
, the Karakoram Range, and is a sub-range of the Himalayas
Himalayas
The Himalaya Range or Himalaya Mountains Sanskrit: Devanagari: हिमालय, literally "abode of snow"), usually called the Himalayas or Himalaya for short, is a mountain range in Asia, separating the Indian subcontinent from the Tibetan Plateau...
. Lower mountains including the Sulaiman Range extend south to the Arabian Sea
Arabian Sea
The Arabian Sea is a region of the Indian Ocean bounded on the east by India, on the north by Pakistan and Iran, on the west by the Arabian Peninsula, on the south, approximately, by a line between Cape Guardafui in northeastern Somalia and Kanyakumari in India...
.
The people of this region are generally speak Indo-Iranian languages
Indo-Iranian languages
The Indo-Iranian language group constitutes the easternmost extant branch of the Indo-European family of languages. It consists of three language groups: the Indo-Aryan, Iranian and Nuristani...
such as Pashto
Pashto language
Pashto , known as Afghani in Persian and Pathani in Punjabi , is the native language of the indigenous Pashtun people or Afghan people who are found primarily between an area south of the Amu Darya in Afghanistan and...
, Balochi
Balochi language
Balochi is a Northwestern Iranian language. It is the principal language of the Baloch of Balochistan, Pakistan, eastern Iran and southern Afghanistan. It is also spoken as a second language by some Brahui. It is designated as one of nine official languages of Pakistan.-Vowels:The Balochi vowel...
, and languages of the Dardic
Dardic languages
The Dardic languages are a sub-group of the Indo-Aryan languages spoken in northern Pakistan, eastern Afghanistan, and the Indian region of Jammu and Kashmir...
and Nuristani
Nuristani languages
The Nuristani languages are one of the three groups within the Indo-Iranian language family, alongside the much larger Indo-Aryan and Iranian groups. They are spoken primarily in eastern Afghanistan...
groups. The Brahui people
Brahui people
The Brahui or Brohi are ethnic Baloch group of about 2.2 million people with the majority found in Kalat, Baluchistan, Pakistan, but they are also found in smaller numbers in neighboring Afghanistan and Iran. The Brahuis are almost entirely Sunni Muslims.-Origins:The ethnonym "Brahui" is a very...
speak a Dravidian language. There are many distinct tribes. The history of the region has been turbulent, lying in the path of invasions from the Persians, the Greeks
Greeks
The Greeks, also known as the Hellenes , are a nation and ethnic group native to Greece, Cyprus and neighboring regions. They also form a significant diaspora, with Greek communities established around the world....
under Alexander the Great, the Arabs, Mughals and British
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
. Given the rugged geography, central governments have generally had limited control over the tribes, a situation that persists to this day.
Pamirs
The Pamir Mountains are in Central AsiaCentral Asia
Central Asia is a core region of the Asian continent from the Caspian Sea in the west, China in the east, Afghanistan in the south, and Russia in the north...
, formed by the junction of the Tian Shan
Tian Shan
The Tian Shan , also spelled Tien Shan, is a large mountain system located in Central Asia. The highest peak in the Tian Shan is Victory Peak , ....
, Karakoram
Karakoram
The Karakoram, or Karakorum , is a large mountain range spanning the borders between Pakistan, India and China, located in the regions of Gilgit-Baltistan , Ladakh , and Xinjiang region,...
, Kunlun
Kunlun Mountains
The Kunlun Mountains are one of the longest mountain chains in Asia, extending more than 3,000 km. In the broadest sense, it forms the northern edge of the Tibetan Plateau south of the Tarim Basin and the Gansu Corridor and continues east south of the Wei River to end at the North China Plain.The...
, and Hindu Kush
Hindu Kush
The Hindu Kush is an mountain range that stretches between central Afghanistan and northern Pakistan. The highest point in the Hindu Kush is Tirich Mir in the Chitral region of Khyber-Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan.It is the westernmost extension of the Pamir Mountains, the Karakoram Range, and is a...
ranges. They are among the world’s highest mountains and in Victorian times they were known as the 'Roof of the World'. The people of this region are mostly Turkic people, and speak Pamir languages
Pamir languages
The Pamir languages are a group of the Eastern Iranian languages, spoken by numerous people in the Pamir Mountains, primarily along the Panj River and its tributaries. This includes the Badakhshan Province of northeastern Afghanistan and the Gorno-Badakhshan Autonomous Province of eastern Tajikistan...
, Tajik
Tajik language
Tajik, Tajik Persian, or Tajiki, is a variety of modern Persian spoken in Central Asia. Historically Tajiks called their language zabani farsī , meaning Persian language in English; the term zabani tajikī, or Tajik language, was introduced in the 20th century by the Soviets...
(closely related to Persian
Persian language
Persian is an Iranian language within the Indo-Iranian branch of the Indo-European languages. It is primarily spoken in Iran, Afghanistan, Tajikistan and countries which historically came under Persian influence...
), Uzbek
Uzbek language
Uzbek is a Turkic language and the official language of Uzbekistan. It has about 25.5 million native speakers, and it is spoken by the Uzbeks in Uzbekistan and elsewhere in Central Asia...
and Kyrgyz
Kyrgyz language
Kyrgyz or Kirgiz, also Kirghiz, Kyrghiz, Qyrghiz is a Turkic language and, together with Russian, an official language of Kyrgyzstan...
.
Himalayas

Himalayas
The Himalaya Range or Himalaya Mountains Sanskrit: Devanagari: हिमालय, literally "abode of snow"), usually called the Himalayas or Himalaya for short, is a mountain range in Asia, separating the Indian subcontinent from the Tibetan Plateau...
lie between the Indian subcontinent
Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent, also Indian Subcontinent, Indo-Pak Subcontinent or South Asian Subcontinent is a region of the Asian continent on the Indian tectonic plate from the Hindu Kush or Hindu Koh, Himalayas and including the Kuen Lun and Karakoram ranges, forming a land mass which extends...
and the Tibetan Plateau
Tibetan Plateau
The Tibetan Plateau , also known as the Qinghai–Tibetan Plateau is a vast, elevated plateau in Central Asia covering most of the Tibet Autonomous Region and Qinghai, in addition to smaller portions of western Sichuan, southwestern Gansu, and northern Yunnan in Western China and Ladakh in...
, thrown up by the collision of two tectonic plates
Tectonic Plates
Tectonic Plates is a 1992 independent Canadian film directed by Peter Mettler. Mettler also wrote the screenplay based on the play by Robert Lepage. The film stars Marie Gignac, Céline Bonnier and Robert Lepage.-Plot summary:...
. They include world's highest peaks including Mount Everest
Mount Everest
Mount Everest is the world's highest mountain, with a peak at above sea level. It is located in the Mahalangur section of the Himalayas. The international boundary runs across the precise summit point...
and K2
K2
K2 is the second-highest mountain on Earth, after Mount Everest...
. The Himalayas stretch across Bhutan
Bhutan
Bhutan , officially the Kingdom of Bhutan, is a landlocked state in South Asia, located at the eastern end of the Himalayas and bordered to the south, east and west by the Republic of India and to the north by the People's Republic of China...
, China
China
Chinese civilization may refer to:* China for more general discussion of the country.* Chinese culture* Greater China, the transnational community of ethnic Chinese.* History of China* Sinosphere, the area historically affected by Chinese culture...
, India
India
India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
, Nepal
Nepal
Nepal , officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal, is a landlocked sovereign state located in South Asia. It is located in the Himalayas and bordered to the north by the People's Republic of China, and to the south, east, and west by the Republic of India...
, Pakistan
Pakistan
Pakistan , officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan is a sovereign state in South Asia. It has a coastline along the Arabian Sea and the Gulf of Oman in the south and is bordered by Afghanistan and Iran in the west, India in the east and China in the far northeast. In the north, Tajikistan...
and Afghanistan
Afghanistan
Afghanistan , officially the Islamic Republic of Afghanistan, is a landlocked country located in the centre of Asia, forming South Asia, Central Asia and the Middle East. With a population of about 29 million, it has an area of , making it the 42nd most populous and 41st largest nation in the world...
.
People have filtered into the mountains from the northern plateau and from the southern plains and intermingled. They mostly speak Tibeto-Burman languages
Tibeto-Burman languages
The Tibeto-Burman languages are the non-Chinese members of the Sino-Tibetan language family, over 400 of which are spoken thoughout the highlands of southeast Asia, as well as lowland areas in Burma ....
such as Gurung
Gurung language
Gurung is spoken by the Gurung people in two dialects with limited mutual intelligibility. Total number of all Gurung speakers in Nepal is 227,918...
and Nepal Bhasa
Nepal Bhasa
Nepal Bhasa is one of the major languages of Nepal, and is also spoken in India, particularly in Sikkim where it is one of the 11 official languages. Nepal Bhasa is the mother tongue of about 3% of the people in Nepal . It is spoken mainly by the Newars, who chiefly inhabit the towns of the...
or Indo-Aryan languages
Indo-Aryan languages
The Indo-Aryan languages constitutes a branch of the Indo-Iranian languages, itself a branch of the Indo-European language family...
such as Shina
Shina language
Shina is a Dardic language spoken by a plurality of people in Gilgit-Baltistan of Pakistan and Dras in Ladakh of Indian-Administered Kashmir. The valleys in which it is spoken include Astore, Chilas, Dareil, Tangeer, Gilgit, Ghizer, and a few parts of Baltistan and Kohistan. It is also spoken in...
, Kashmiri
Kashmiri language
Kashmiri is a language from the Dardic sub-group and it is spoken primarily in the Kashmir Valley, in Jammu and Kashmir. There are approximately 5,554,496 speakers in Jammu and Kashmir, according to the Census of 2001. Most of the 105,000 speakers or so in Pakistan are émigrés from the Kashmir...
, Dogri, Pahari
Pahari languages
The Pahari languages are a geographic group of Indic languages spoken in the lower ranges of the Himalayas, from Nepal in the east to the Indian states of Uttarakhand, Himachal Pradesh and Jammu and Kashmir in the west.-Classification:The Pahari languages fall into three groups:*Eastern, consisting...
(which means "language of the mountain people"), Kumaoni, Nepali
Nepali language
Nepali or Nepalese is a language in the Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European language family.It is the official language and de facto lingua franca of Nepal and is also spoken in Bhutan, parts of India and parts of Myanmar...
and Asamiya
Assamese language
Assamese is the easternmost Indo-Aryan language. It is used mainly in the state of Assam in North-East India. It is also the official language of Assam. It is also spoken in parts of Arunachal Pradesh and other northeast Indian states. Nagamese, an Assamese-based Creole language is widely used in...
. The Gurkha
Gurkha
Gurkha are people from Nepal who take their name from the Gorkha District. Gurkhas are best known for their history in the Indian Army's Gorkha regiments, the British Army's Brigade of Gurkhas and the Nepalese Army. Gurkha units are closely associated with the kukri, a forward-curving Nepalese knife...
people of Nepal are well known for their history of bravery and strength, and still serve in foreign armies such as the British Army
British Army
The British Army is the land warfare branch of Her Majesty's Armed Forces in the United Kingdom. It came into being with the unification of the Kingdom of England and Scotland into the Kingdom of Great Britain in 1707. The new British Army incorporated Regiments that had already existed in England...
's Brigade of Gurkhas
Brigade of Gurkhas
The Brigade of Gurkhas is the collective term for units of the current British Army that are composed of Nepalese soldiers. The brigade, which is 3,640 strong, draws its heritage from Gurkha units that originally served in the British Indian Army prior to Indian independence, and prior to that of...
and the Indian Army
Indian Army
The Indian Army is the land based branch and the largest component of the Indian Armed Forces. With about 1,100,000 soldiers in active service and about 1,150,000 reserve troops, the Indian Army is the world's largest standing volunteer army...
's Gorkha regiments
Gorkha regiments (India)
The Gorkha regiments have been serving in the Indian Army ever since independence in 1947, when the Tripartite Agreement was signed. The regiments primarily consist of soldiers from India's Gorkha community and from the Gorkha tribes of Nepal...
.
Fruit, vegetables and sheep flourish in the fertile valley of Kashmir
Kashmir
Kashmir is the northwestern region of the Indian subcontinent. Until the mid-19th century, the term Kashmir geographically denoted only the valley between the Great Himalayas and the Pir Panjal mountain range...
. The people have evolved the unique and famous Kashmiri cuisine with Iranian, Indian and Turkic origins. While the stricter Hindus may restrict themselves to rice with vegetables, curd, milk and fresh fruit, the Muslims eat pilaff and mutton stuffed with spices, apricots stuffed with mutton, roast kid, fish and honey rice.
Further east, a typical Nepalese meal includes Dal, a spicy lentil soup, served over bhat (boiled rice) with tarkari (curried vegetables) together with achar (pickles) or chutni (spicy condiment made from fresh ingredients). In the hills of Nepal, people enjoy their own kind of music, playing sarangi
Sarangi
The Sārangī is a bowed, short-necked string instrument of India which is originated from Rajasthani folk instruments. It plays an important role in India's Hindustani classical music tradition...
(a string instrument), madal
Madal
The Madal , double-headed drum of Nepalese origin , used mainly for rhythm-keeping in Nepalese folk music, is the most popular and widely used hand drum in Nepal.The Madal consists of a cylindrical body with a slight bulge at its center, closed on both ends .The madal has a...
(a hand drum) and flute
Flute
The flute is a musical instrument of the woodwind family. Unlike woodwind instruments with reeds, a flute is an aerophone or reedless wind instrument that produces its sound from the flow of air across an opening...
. They also have many popular folk songs known as lok geet and lok dohari.
South-East Asia

Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia, South-East Asia, South East Asia or Southeastern Asia is a subregion of Asia, consisting of the countries that are geographically south of China, east of India, west of New Guinea and north of Australia. The region lies on the intersection of geological plates, with heavy seismic...
consists of Cambodia
Cambodia
Cambodia , officially known as the Kingdom of Cambodia, is a country located in the southern portion of the Indochina Peninsula in Southeast Asia...
, Laos
Laos
Laos Lao: ສາທາລະນະລັດ ປະຊາທິປະໄຕ ປະຊາຊົນລາວ Sathalanalat Paxathipatai Paxaxon Lao, officially the Lao People's Democratic Republic, is a landlocked country in Southeast Asia, bordered by Burma and China to the northwest, Vietnam to the east, Cambodia to the south and Thailand to the west...
, Burma, Thailand
Thailand
Thailand , officially the Kingdom of Thailand , formerly known as Siam , is a country located at the centre of the Indochina peninsula and Southeast Asia. It is bordered to the north by Burma and Laos, to the east by Laos and Cambodia, to the south by the Gulf of Thailand and Malaysia, and to the...
and Vietnam
Vietnam
Vietnam – sometimes spelled Viet Nam , officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam – is the easternmost country on the Indochina Peninsula in Southeast Asia. It is bordered by China to the north, Laos to the northwest, Cambodia to the southwest, and the South China Sea –...
, and Assam
Assam
Assam , also, rarely, Assam Valley and formerly the Assam Province , is a northeastern state of India and is one of the most culturally and geographically distinct regions of the country...
in India
India
India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
. The hills of this region include tribes of Tibeto-Burman peoples including the Akha, Bodo-Kachari
Bodo-Kachari
Bodo-Kachari is a generic term applied to a number of ethnic groups predominantly in Assam speaking Tibeto-Burman languages or claiming a common ancestry.-Origins:...
, Lahu
Lahu people
The Lahu are an ethnic group of Southeast Asia and China.They are one of the 56 ethnic groups officially recognized by the People's Republic of China, where about 450,000 live in Yunnan province. An estimated 150,000 live in Burma. In Thailand, Lahu are one of the six main hill tribes; their...
, Karen
Karen people
The Karen or Kayin people , are a Sino-Tibetan language speaking ethnic group which resides primarily in southern and southeastern Burma . The Karen make up approximately 7 percent of the total Burmese population of approximately 50 million people...
, Hmong
Hmong people
The Hmong , are an Asian ethnic group from the mountainous regions of China, Vietnam, Laos, and Thailand. Hmong are also one of the sub-groups of the Miao ethnicity in southern China...
Mien, Mizo and Lisu. It is thought that they drifted down into the area from Tibet.
Many of the tribes are spread across more than one country - the Karen people live in Burma and Thailand, the Zou people
Zou people
The Zou people is an indigenous community living along the frontier of India and Burma. In India, they live with and are similar in language and habits to the Paite and the Simte peoples, all of which are called Zomi. In Burma, Zou are counted among the Chin people...
live in Burma and India
India
India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
, and the Akha people live in small villages among the mountains of China
China
Chinese civilization may refer to:* China for more general discussion of the country.* Chinese culture* Greater China, the transnational community of ethnic Chinese.* History of China* Sinosphere, the area historically affected by Chinese culture...
, Laos, Burma, and northern Thailand. They often retain their traditional way of life but are under increasing pressure to do so. As minorities, they tend to be less well off than the majority of people in the countries where they live.
An interesting theorisation about the Hill people from this region is "Zomia". Zomia is a geographical term coined in 2002 by historian Willem van Schendel of the University of Amsterdam to refer to the huge massif of mainland Southeast Asia that has historically been beyond the control of governments based in the population centers of the lowlands. The massif arose during the Alpine orogeny, when the African, Indian and Cimmerian Plates, and smaller Asian terranes, collided with that of Eurasia. The name is from Zomi, a term for highlander common to several related Tibeto-Burman languages spoken in the India-Bangladesh-Burma border area.
The exact boundaries of Zomia differ among scholars: all would include the highlands of north Indochina (north Vietnam and all Laos,) Thailand, the Shan State of northern Burma, and the mountains of Southwest China, others extend the region as far West as Tibet, north India, Pakistan, and Afghanistan. These areas share a common elevated, rugged terrain, and have been the home of ethnic minorities that have preserved their local cultures by residing far from state control and influence. Other scholars have used the term to discuss the similar ways that Southeast Asian governments have handled minority groups.
The region covers more than 2.5 million square kilometers known as the “Southeast Asian Massif” and comprises nearly one hundred million marginal peoples. This large area is inside the fringe of nine states and at the middle of none, stretching across the standard regional designations (South Asia, East Asia, and Southeast Asia); along with its ecological diversity and its relation to states, it arouses a lot of interest. It stands for an original entity of study, a type of international Appalachia, and a different way in which to study regions. For reference, see Zomia (geography)
Zomia (geography)
Zomia is a geographical term coined in 2002 by historian Willem van Schendel of the University of Amsterdam to refer to the huge massif of mainland Southeast Asia that has historically been beyond the control of governments based in the population centers of the lowlands...
New Guinea Highlands

New Guinea
New Guinea is the world's second largest island, after Greenland, covering a land area of 786,000 km2. Located in the southwest Pacific Ocean, it lies geographically to the east of the Malay Archipelago, with which it is sometimes included as part of a greater Indo-Australian Archipelago...
, located just north of Australia
Australia
Australia , officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country in the Southern Hemisphere comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands in the Indian and Pacific Oceans. It is the world's sixth-largest country by total area...
, is the world's second-largest island. A central east-west mountain range dominates the geography of New Guinea and contains the highest mountains in Oceania
Oceania
Oceania is a region centered on the islands of the tropical Pacific Ocean. Conceptions of what constitutes Oceania range from the coral atolls and volcanic islands of the South Pacific to the entire insular region between Asia and the Americas, including Australasia and the Malay Archipelago...
, rising up to 4884 m high. The island is populated by very nearly a thousand different tribal groups and a near-equivalent number of separate languages, which makes New Guinea the most linguistically diverse area in the world. They fall into one of two groups, speakers of the Papuan languages
Papuan languages
The Papuan languages are those languages of the western Pacific which are neither Austronesian nor Australian. The term does not presuppose a genetic relationship. The concept of Papuan peoples as distinct from Melanesians was first suggested and named by Sidney Herbert Ray in 1892.-The...
and later arrivals who speak Austronesian languages
Austronesian languages
The Austronesian languages are a language family widely dispersed throughout the islands of Southeast Asia and the Pacific, with a few members spoken on continental Asia that are spoken by about 386 million people. It is on par with Indo-European, Niger-Congo, Afroasiatic and Uralic as one of the...
.
The gardens of the New Guinea Highlands
New Guinea Highlands
The New Guinea Highlands, also known as the Central Range or Central Cordillera, are a chain of mountain ranges and intermountain river valleys, many of which support thriving agricultural communities, on the large island of New Guinea, which lies to the north of Australia...
are ancient, intensive permaculture
Permaculture
Permaculture is an approach to designing human settlements and agricultural systems that is modeled on the relationships found in nature. It is based on the ecology of how things interrelate rather than on the strictly biological concerns that form the foundation of modern agriculture...
s, adapted to high population densities, very high rainfalls (as high as 10,000 mm/yr (400 in/yr)), earthquakes, hilly land, and occasional frost. The people use complex mulches, crop rotations and tillages on terraces with complex irrigation systems. Native gardeners are as or more successful than most scientific farmers in raising certain crops. Early garden crops – many of which are indigenous – included sugarcane
Sugarcane
Sugarcane refers to any of six to 37 species of tall perennial grasses of the genus Saccharum . Native to the warm temperate to tropical regions of South Asia, they have stout, jointed, fibrous stalks that are rich in sugar, and measure two to six metres tall...
, Pacific banana
Banana
Banana is the common name for herbaceous plants of the genus Musa and for the fruit they produce. Bananas come in a variety of sizes and colors when ripe, including yellow, purple, and red....
s, yams
Yam (vegetable)
Yam is the common name for some species in the genus Dioscorea . These are perennial herbaceous vines cultivated for the consumption of their starchy tubers in Africa, Asia, Latin America and Oceania...
, and taro
Taro
Taro is a common name for the corms and tubers of several plants in the family Araceae . Of these, Colocasia esculenta is the most widely cultivated, and is the subject of this article. More specifically, this article describes the 'dasheen' form of taro; another variety is called eddoe.Taro is...
, while sago
Sago
Sago is a starch extracted in the spongy center or pith, of various tropical palm stems, Metroxylon sagu. It is a major staple food for the lowland peoples of New Guinea and the Moluccas, where it is called saksak and sagu. A type of flour, called sago flour, is made from sago. The largest supply...
and pandanus
Pandanus
Pandanus is a genus of monocots with about 600 known species. They are numerous palmlike dioecious trees and shrubs native of the Old World tropics and subtropics. They are classified in the order Pandanales, family Pandanaceae.-Overview:...
were two commonly exploited native forest crops. Today's staples – sweet potato
Sweet potato
The sweet potato is a dicotyledonous plant that belongs to the family Convolvulaceae. Its large, starchy, sweet-tasting, tuberous roots are an important root vegetable. The young leaves and shoots are sometimes eaten as greens. Of the approximately 50 genera and more than 1,000 species of...
es and pig
Pig
A pig is any of the animals in the genus Sus, within the Suidae family of even-toed ungulates. Pigs include the domestic pig, its ancestor the wild boar, and several other wild relatives...
s – are later arrivals.
The people of New Guinea were traditionally warlike, with constant feuds over territory, although violence has greatly reduced in recent years.
Appalachians
The Appalachian MountainsAppalachian Mountains
The Appalachian Mountains #Whether the stressed vowel is or ,#Whether the "ch" is pronounced as a fricative or an affricate , and#Whether the final vowel is the monophthong or the diphthong .), often called the Appalachians, are a system of mountains in eastern North America. The Appalachians...
are a vast system of mountains in eastern North America
North America
North America is a continent wholly within the Northern Hemisphere and almost wholly within the Western Hemisphere. It is also considered a northern subcontinent of the Americas...
. Before the Europeans reached the area around 1650, the mountains were inhabited by Algonquian
Algonquian languages
The Algonquian languages also Algonkian) are a subfamily of Native American languages which includes most of the languages in the Algic language family. The name of the Algonquian language family is distinguished from the orthographically similar Algonquin dialect of the Ojibwe language, which is a...
people; speakers of Iroquoian languages
Iroquoian languages
The Iroquoian languages are a First Nation and Native American language family.-Family division:*Ruttenber, Edward Manning. 1992 [1872]. History of the Indian tribes of Hudson's River. Hope Farm Press....
such as the Cherokee
Cherokee
The Cherokee are a Native American people historically settled in the Southeastern United States . Linguistically, they are part of the Iroquoian language family...
; and Siouan people such as the Occaneechi
Occaneechi
The Occaneechi are Native Americans who lived primarily on a large, long Occoneechee Island and east of the confluence of the Dan and Roanoke Rivers, near current day Clarksville, Virginia in the 17th century...
, Tutelo
Tutelo
The Tutelo were Native people living above the Fall Line in present-day Virginia and West Virginia, speaking a Siouan dialect of the Tutelo language thought to be similar to that of their neighbors, the Monacan and Manahoac nations...
and Monacan. The European invaders were ruthless in their treatment of these hill people, many of whom they killed or forced to move into unfamiliar territory to the west. Many others died of diseases such as smallpox
Smallpox
Smallpox was an infectious disease unique to humans, caused by either of two virus variants, Variola major and Variola minor. The disease is also known by the Latin names Variola or Variola vera, which is a derivative of the Latin varius, meaning "spotted", or varus, meaning "pimple"...
introduced from Europe. Few of the early inhabitants remain.
Some of the people who live in the mountains today retain distinct cultural characteristics. The Hatfield-McCoy feud
Hatfield-McCoy feud
The Hatfield–McCoy feud involved two families of the West Virginia–Kentucky back country along the Tug Fork, off the Big Sandy River. The Hatfields of West Virginia were led by William Anderson "Devil Anse" Hatfield while the McCoys of Kentucky under the leadership of Randolph "Ole Ran'l" McCoy....
(1878–1891) involved two warring families of the West Virginia
West Virginia
West Virginia is a state in the Appalachian and Southeastern regions of the United States, bordered by Virginia to the southeast, Kentucky to the southwest, Ohio to the northwest, Pennsylvania to the northeast and Maryland to the east...
-Kentucky
Kentucky
The Commonwealth of Kentucky is a state located in the East Central United States of America. As classified by the United States Census Bureau, Kentucky is a Southern state, more specifically in the East South Central region. Kentucky is one of four U.S. states constituted as a commonwealth...
backcountry along the Tug Fork River
Tug Fork River
The Tug Fork is a tributary of the Big Sandy River, long, in southwestern West Virginia, southwestern Virginia, and eastern Kentucky in the United States. Via the Big Sandy and Ohio rivers, it is part of the watershed of the Mississippi River....
, off the Big Sandy River. Between 1880 and 1891, the feud claimed more than a dozen members of the two families. The 1972 film Deliverance
Deliverance
Deliverance is a 1972 American thriller film produced and directed by John Boorman. Principal cast members include Jon Voight, Burt Reynolds, Ronny Cox and Ned Beatty in his film debut. The film is based on a 1970 novel of the same name by American author James Dickey, who has a small role in the...
depicted the hill people as backward and hostile to outsiders, and the film implies some of them are inbred – a stereotype of the "Hillbilly
Hillbilly
Hillbilly is a term referring to certain people who dwell in rural, mountainous areas of the United States, primarily Appalachia but also the Ozarks. Owing to its strongly stereotypical connotations, the term is frequently considered derogatory, and so is usually offensive to those Americans of...
" culture.
Rocky Mountains

Rocky Mountains
The Rocky Mountains are a major mountain range in western North America. The Rocky Mountains stretch more than from the northernmost part of British Columbia, in western Canada, to New Mexico, in the southwestern United States...
stretch more than 4800 kilometres (2,982.6 mi) from northernmost British Columbia
British Columbia
British Columbia is the westernmost of Canada's provinces and is known for its natural beauty, as reflected in its Latin motto, Splendor sine occasu . Its name was chosen by Queen Victoria in 1858...
, in Canada
Canada
Canada is a North American country consisting of ten provinces and three territories. Located in the northern part of the continent, it extends from the Atlantic Ocean in the east to the Pacific Ocean in the west, and northward into the Arctic Ocean...
, to New Mexico
New Mexico
New Mexico is a state located in the southwest and western regions of the United States. New Mexico is also usually considered one of the Mountain States. With a population density of 16 per square mile, New Mexico is the sixth-most sparsely inhabited U.S...
, in the United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
. The range's highest peak is Mount Elbert
Mount Elbert
Mount Elbert is the highest peak in the Rocky Mountains of North America, at , the highest of the fourteeners in Colorado, and the high point of the Sawatch Range. It is located in Lake County, approximately southwest of Leadville...
in Colorado
Colorado
Colorado is a U.S. state that encompasses much of the Rocky Mountains as well as the northeastern portion of the Colorado Plateau and the western edge of the Great Plains...
at 14,440 feet (4,401 meters) above sea level.
As the Europeans continued to move west, they took most of the lands of the people who lived in the Rockies, forcing the Ute
Ute Tribe
The Ute are an American Indian people now living primarily in Utah and Colorado. There are three Ute tribal reservations: Uintah-Ouray in northeastern Utah ; Southern Ute in Colorado ; and Ute Mountain which primarily lies in Colorado, but extends to Utah and New Mexico . The name of the state of...
, Navajo
Navajo people
The Navajo of the Southwestern United States are the largest single federally recognized tribe of the United States of America. The Navajo Nation has 300,048 enrolled tribal members. The Navajo Nation constitutes an independent governmental body which manages the Navajo Indian reservation in the...
, Hopi
Hopi
The Hopi are a federally recognized tribe of indigenous Native American people, who primarily live on the Hopi Reservation in northeastern Arizona. The Hopi area according to the 2000 census has a population of 6,946 people. Their Hopi language is one of the 30 of the Uto-Aztecan language...
, Apache
Apache
Apache is the collective term for several culturally related groups of Native Americans in the United States originally from the Southwest United States. These indigenous peoples of North America speak a Southern Athabaskan language, which is related linguistically to the languages of Athabaskan...
, Yaqui and other tribes to assimilate or move onto reservations. Some adapted to farming or sheep herding, but they are the most impoverished of all ethnic groups in the USA.
The Ancient Pueblo Peoples
Ancient Pueblo Peoples
Ancient Pueblo People or Ancestral Pueblo peoples were an ancient Native American culture centered on the present-day Four Corners area of the United States, comprising southern Utah, northern Arizona, northwest New Mexico, and southern Colorado...
who lived in the present-day Four Corners area of the Southwest United States were noted for their distinctive pottery and dwelling construction styles. The cultural group is often referred to as the Anasazi. Some of their unusual cliff dwellings still stand today.
Mexican Sierras


American cordillera
The American Cordillera is a cordillera that consists of an essentially continuous sequence of mountain ranges that form the western "backbone" of North America, Central America, South America and Antarctica. From north to south, this sequence of overlapping and parallel ranges begins with the...
in Mexico includes the Sierra Madre Occidental
Sierra Madre Occidental
The Sierra Madre Occidental is a mountain range in western Mexico.-Setting:The range runs north to south, from just south of the Sonora–Arizona border southeast through eastern Sonora, western Chihuahua, Sinaloa, Durango, Zacatecas, Nayarit, Jalisco, Aguascalientes to Guanajuato, where it joins...
, Sierra Madre Oriental
Sierra Madre Oriental
The Sierra Madre Oriental is a mountain range in northeastern Mexico.-Setting:Spanning the Sierra Madre Oriental runs from Coahuila south through Nuevo León, southwest Tamaulipas, San Luis Potosí, Querétaro, and Hidalgo to northern Puebla, where it joins with the east-west running Eje Volcánico...
and Sierra Madre del Sur
Sierra Madre del Sur
The Sierra Madre del Sur is a mountain range in southern Mexico, extending from southern Michoacán east through Guerrero, to the Istmo de Tehuantepec in eastern Oaxaca.-Geography:...
. The mountain valleys have a temperate climate and fertile soil, and were the cradles of Mesoamerica
Mesoamerica
Mesoamerica is a region and culture area in the Americas, extending approximately from central Mexico to Belize, Guatemala, El Salvador, Honduras, Nicaragua, and Costa Rica, within which a number of pre-Columbian societies flourished before the Spanish colonization of the Americas in the 15th and...
n civilizations that flourished long before Europeans discovered the area, including the Olmec, Teotihuacán
Teotihuacán
Teotihuacan – also written Teotihuacán, with a Spanish orthographic accent on the last syllable – is an enormous archaeological site in the Basin of Mexico, just 30 miles northeast of Mexico City, containing some of the largest pyramidal structures built in the pre-Columbian Americas...
, Toltec
Toltec
The Toltec culture is an archaeological Mesoamerican culture that dominated a state centered in Tula, Hidalgo in the early post-classic period of Mesoamerican chronology...
, Aztec
Aztec
The Aztec people were certain ethnic groups of central Mexico, particularly those groups who spoke the Nahuatl language and who dominated large parts of Mesoamerica in the 14th, 15th and 16th centuries, a period referred to as the late post-classic period in Mesoamerican chronology.Aztec is the...
, Zapotec
Zapotec civilization
The Zapotec civilization was an indigenous pre-Columbian civilization that flourished in the Valley of Oaxaca of southern Mesoamerica. Archaeological evidence shows their culture goes back at least 2500 years...
and Mixtec
Mixtec
The Mixtec are indigenous Mesoamerican peoples inhabiting the Mexican states of Oaxaca, Guerrero and Puebla in a region known as La Mixteca. The Mixtecan languages form an important branch of the Otomanguean language family....
cultures. The bold patterns and deep saturated colors of the Mesoamerican artists are echoed in modern Mexican art
Mexican art
Mexican art consists of the various visual and plastic arts which developed over the geographical area now known as Mexico. The development of these arts roughly follow the history of Mexico, divided into the Mesoamerican era, the colonial period, with the period after the gaining of Independence...
and architecture.
After the Spanish invasion of 1519, led by Hernán Cortés
Hernán Cortés
Hernán Cortés de Monroy y Pizarro, 1st Marquis of the Valley of Oaxaca was a Spanish Conquistador who led an expedition that caused the fall of the Aztec Empire and brought large portions of mainland Mexico under the rule of the King of Castile in the early 16th century...
, most people eventually adopted the Spanish language
Spanish language
Spanish , also known as Castilian , is a Romance language in the Ibero-Romance group that evolved from several languages and dialects in central-northern Iberia around the 9th century and gradually spread with the expansion of the Kingdom of Castile into central and southern Iberia during the...
, but there remain many groups who retain their original languages and live traditional ways of life. These include the Nahuatl
Nahuatl
Nahuatl is thought to mean "a good, clear sound" This language name has several spellings, among them náhuatl , Naoatl, Nauatl, Nahuatl, Nawatl. In a back formation from the name of the language, the ethnic group of Nahuatl speakers are called Nahua...
, Zapotec, Mixtec
Mixtec
The Mixtec are indigenous Mesoamerican peoples inhabiting the Mexican states of Oaxaca, Guerrero and Puebla in a region known as La Mixteca. The Mixtecan languages form an important branch of the Otomanguean language family....
, Otomí
Otomi people
The Otomi people . Smaller Otomi populations exist in the states of Puebla, Mexico, Tlaxcala, Michoacán and Guanajuato. The Otomi language belonging to the Oto-Pamean branch of the Oto-Manguean language family is spoken in many different varieties some of which are not mutually intelligible.One of...
, Tzotzil, Tzeltal
Tzeltal people
The Tzeltal people are the largest indigenous group mostly located in the highlands or Los Altos region of the Mexican state of Chiapas. They are one of many Mayan ethnic groups and they speak a a language which belongs to the Tzeltalan subgroup of Mayan languages...
, Mazahua
Mazahua
The Mazahua are an indigenous people of Mexico, inhabiting the northwestern portion of the State of Mexico and northeastern area of Michoacán, with a presence also in the Federal District owing to recent migration...
, Mazateco, Chinantec
Chinantec
The Chinantecs are an indigenous people that live in Oaxaca and Veracruz, Mexico, especially in the districts of Cuicatlán, Ixtlán de Juárez, Tuxtepec and Choapan.The Chinantec languages belong to the Chinantecan branch of the Oto-Manguean family...
, Purépecha
P'urhépecha
The P'urhépecha, normally spelled Purépecha in Spanish and in English and traditionally referred to as Tarascans, are an indigenous people centered in the northwestern region of the Mexican state of Michoacán, principally in the area of the cities of Uruapan and Pátzcuaro...
, Mixe
Mixe
The Mixe or Mije is an indigenous group inhabiting the eastern highlands of the Mexican state of Oaxaca. They speak the Mixe languages which are classified in the Mixe–Zoque family, and are more culturally conservative than other indigenous groups of the region, maintaining their language to this...
and Tlapanec
Tlapanec people
The Tlapanec people is an ethnic group indigenous to the Mexican state of Guerrero.Their language, Me'phaa, is a part of the Oto-Manguean language family. The now extinct Subtiaba language of Nicaragua was a closely related language...
.
The traditional Mexican diet is based on Maize
Maize
Maize known in many English-speaking countries as corn or mielie/mealie, is a grain domesticated by indigenous peoples in Mesoamerica in prehistoric times. The leafy stalk produces ears which contain seeds called kernels. Though technically a grain, maize kernels are used in cooking as a vegetable...
, beans, Chili pepper
Chili pepper
Chili pepper is the fruit of plants from the genus Capsicum, members of the nightshade family, Solanaceae. The term in British English and in Australia, New Zealand, India, Malaysia and other Asian countries is just chilli without pepper.Chili peppers originated in the Americas...
s, Tomatoes, Cactus
Cactus
A cactus is a member of the plant family Cactaceae. Their distinctive appearance is a result of adaptations to conserve water in dry and/or hot environments. In most species, the stem has evolved to become photosynthetic and succulent, while the leaves have evolved into spines...
and other native plants, supplemented by iguana
Iguana
Iguana is a herbivorous genus of lizard native to tropical areas of Central America and the Caribbean. The genus was first described in 1768 by Austrian naturalist Josephus Nicolaus Laurenti in his book Specimen Medicum, Exhibens Synopsin Reptilium Emendatam cum Experimentis circa Venena...
, rattlesnake
Rattlesnake
Rattlesnakes are a group of venomous snakes of the genera Crotalus and Sistrurus of the subfamily Crotalinae . There are 32 known species of rattlesnake, with between 65-70 subspecies, all native to the Americas, ranging from southern Alberta and southern British Columbia in Canada to Central...
, fish and venison. Mexican cuisine
Mexican cuisine
Mexican cuisine, a style of food that originates in Mexico, is known for its varied flavors, colourful decoration and variety of spices and ingredients, most of which are native to the country. The cuisine of Mexico has evolved through thousands of years of blending indigenous cultures, with later...
today is one of the most rich and varied in the world. Before the Spanish came, the inhabitants of the land used drums, flutes, maracas
Maracás
Maracás is a town and municipality in the state of Bahia in the North-East region of Brazil.-References:...
, sea shells
Sea Shells
Sea Shells is a 1957 album by Peggy Lee, recorded in early 1955.The album was possibly thought by her record company to be too esoteric, hence its later release. It was her last recording for Decca Records. The album is considered one of Miss Lee's more personal records, featuring a mix of love...
and voices to make music and dances. This ancient music is still played in some parts of Mexico.
Andes

Andes
The Andes is the world's longest continental mountain range. It is a continual range of highlands along the western coast of South America. This range is about long, about to wide , and of an average height of about .Along its length, the Andes is split into several ranges, which are separated...
form the world's longest exposed mountain range, a continuous chain of highland along the western coast of South America. The range is over 7000 km (4,349.6 mi) long, 200–700 km (300 miles) wide (widest between 18° to 20°S latitude), and of an average height of about 4,000 m (13,000 ft).
Before the Spanish invasion led by Francisco Pizarro
Francisco Pizarro
Francisco Pizarro González, Marquess was a Spanish conquistador, conqueror of the Incan Empire, and founder of Lima, the modern-day capital of the Republic of Peru.-Early life:...
in 1532 the Andes were primarily inhabited by Quechua
Quechuas
Quechuas is the collective term for several indigenous ethnic groups in South America who speak a Quechua language , belonging to several ethnic groups in South America, especially in Peru, Ecuador, Bolivia, Chile, Colombia and Argentina.The Quechuas of Ecuador call themselves as well as their...
peoples such as the Inca, Chancas, Huancas and Cañaris
Cañaris
The Cañari are an indigenous ethnic group traditionally inhabiting the territory of the modern provinces of Azuay and Cañar in Ecuador; the term also refers to an independent pre-Hispanic tribal confederation of the same name, from which the modern people are descended. They are particularly noted...
in the north, and Aymaras further south. Their economy was based on the potato
Potato
The potato is a starchy, tuberous crop from the perennial Solanum tuberosum of the Solanaceae family . The word potato may refer to the plant itself as well as the edible tuber. In the region of the Andes, there are some other closely related cultivated potato species...
crop, which originated in the area, and the llama
Llama
The llama is a South American camelid, widely used as a meat and pack animal by Andean cultures since pre-Hispanic times....
and alpaca
Alpaca
An alpaca is a domesticated species of South American camelid. It resembles a small llama in appearance.Alpacas are kept in herds that graze on the level heights of the Andes of southern Peru, northern Bolivia, Ecuador, and northern Chile at an altitude of to above sea level, throughout the year...
, used for their wool and meat. Unlike most mountain people, the inhabitants of the Andes appear to have been generally unwarlike.

