
Islamic contributions to Medieval Europe
Encyclopedia

Islamic art
Islamic art encompasses the visual arts produced from the 7th century onwards by people who lived within the territory that was inhabited by or ruled by culturally Islamic populations...
, architecture
Islamic architecture
Islamic architecture encompasses a wide range of both secular and religious styles from the foundation of Islam to the present day, influencing the design and construction of buildings and structures in Islamic culture....
, medicine
Islamic medicine
In the history of medicine, Islamic medicine, Arabic medicine or Arabian medicine refers to medicine developed in the Islamic Golden Age, and written in Arabic, the lingua franca of Islamic civilization....
, agriculture
Muslim Agricultural Revolution
The Arab Agricultural Revolution is a term coined by the historian Andrew Watson in his influential 1974 paper postulating a fundamental transformation in agriculture from the 8th century to the 13th century in the Muslim...
, music
Islamic music
Islamic music is Muslim religious music, as sung or played in public services or private devotions. The classic heartland of Islam is the Middle East, North Africa, Iran, Central Asia, Horn of Africa and South Asia. Due to Islam being a multi-ethnic religion, the musical expression of its adherents...
, language
Influence of Arabic on other languages
Arabic has had a great influence on other languages, especially in vocabulary. The influence of Arabic has been most profound in those countries dominated by Islam or Islamic power...
, and technology
Inventions in the Islamic world
A number of inventions were developed in the medieval Islamic world, a geopolitical region that has at various times extended from Spain and Africa in the west to the Indian subcontinent in the east. The inventions listed here were developed during the medieval Islamic world, which covers the...
. From the 11th to 13th centuries, Europe absorbed knowledge from the Islamic civilization
Islamic Golden Age
During the Islamic Golden Age philosophers, scientists and engineers of the Islamic world contributed enormously to technology and culture, both by preserving earlier traditions and by adding their own inventions and innovations...
. Of particular importance was the rediscovery of the ancient classic texts, most notably the work of the Greek natural philosopher
Greek philosophy
Ancient Greek philosophy arose in the 6th century BCE and continued through the Hellenistic period, at which point Ancient Greece was incorporated in the Roman Empire...
Aristotle
Aristotle
Aristotle was a Greek philosopher and polymath, a student of Plato and teacher of Alexander the Great. His writings cover many subjects, including physics, metaphysics, poetry, theater, music, logic, rhetoric, linguistics, politics, government, ethics, biology, and zoology...
, through retranslations from Arabic.
Transmission routes
Sicily
Sicily is a region of Italy, and is the largest island in the Mediterranean Sea. Along with the surrounding minor islands, it constitutes an autonomous region of Italy, the Regione Autonoma Siciliana Sicily has a rich and unique culture, especially with regard to the arts, music, literature,...
, and in Spain
Spain
Spain , officially the Kingdom of Spain languages]] under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, Spain's official name is as follows:;;;;;;), is a country and member state of the European Union located in southwestern Europe on the Iberian Peninsula...
, particularly in Toledo
Toledo, Spain
Toledo's Alcázar became renowned in the 19th and 20th centuries as a military academy. At the outbreak of the Spanish Civil War in 1936 its garrison was famously besieged by Republican forces.-Economy:...
(with Gerard of Cremone, 1114–1187, following the conquest of the city by the Spanish Christians in 1085). In Sicily, following the Islamic conquest of the island
History of Islam in southern Italy
The history of Islam in southern Italy begins with the Islamic conquest and subsequent rule of Sicily and Malta, a process that started in the 9th century. Islamic rule over Sicily was effective from 902, and the complete rule of the island lasted from 965 until 1061...
in 965 and its reconquest by the Normans
Normans
The Normans were the people who gave their name to Normandy, a region in northern France. They were descended from Norse Viking conquerors of the territory and the native population of Frankish and Gallo-Roman stock...
in 1091, an intense Arab-Norman culture developed, exemplified by rulers such as Roger II
Roger II of Sicily
Roger II was King of Sicily, son of Roger I of Sicily and successor to his brother Simon. He began his rule as Count of Sicily in 1105, later became Duke of Apulia and Calabria , then King of Sicily...
, who had Islamic soldiers, poets and scientists at his court. The Moroccan
Morocco
Morocco , officially the Kingdom of Morocco , is a country located in North Africa. It has a population of more than 32 million and an area of 710,850 km², and also primarily administers the disputed region of the Western Sahara...
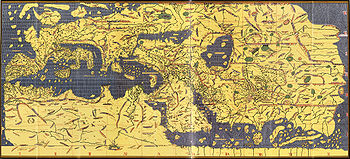
Muhammad al-Idrisi
Muhammad al-Idrisi
Abu Abd Allah Muhammad al-Idrisi al-Qurtubi al-Hasani al-Sabti or simply Al Idrisi was a Moroccan Muslim geographer, cartographer, Egyptologist and traveller who lived in Sicily, at the court of King Roger II. Muhammed al-Idrisi was born in Ceuta then belonging to the Almoravid Empire and died in...
wrote "The Book of Pleasant Journeys into Faraway Lands" or Tabula Rogeriana
Tabula Rogeriana
The Nuzhat al-mushtaq fi'khtiraq al-afaq lit. "the book of pleasant journeys into faraway lands", most often known as the Tabula Rogeriana , is a description of the world and world map created by the Arab geographer, Muhammad al-Idrisi, in 1154...
, one of the greatest geographical treatises of the Middle Ages, for Roger.
The Crusades
Crusades
The Crusades were a series of religious wars, blessed by the Pope and the Catholic Church with the main goal of restoring Christian access to the holy places in and near Jerusalem...
also intensified exchanges between Europe and the Levant
Levant
The Levant or ) is the geographic region and culture zone of the "eastern Mediterranean littoral between Anatolia and Egypt" . The Levant includes most of modern Lebanon, Syria, Jordan, Israel, the Palestinian territories, and sometimes parts of Turkey and Iraq, and corresponds roughly to the...
, with the Italian maritime republics taking a great role in these exchanges. In the Levant, such cities as Antioch
Antioch
Antioch on the Orontes was an ancient city on the eastern side of the Orontes River. It is near the modern city of Antakya, Turkey.Founded near the end of the 4th century BC by Seleucus I Nicator, one of Alexander the Great's generals, Antioch eventually rivaled Alexandria as the chief city of the...
, Arab and Latin cultures intermixed intensively.
Classical knowledge
Following the fall of the Roman EmpireRoman Empire
The Roman Empire was the post-Republican period of the ancient Roman civilization, characterised by an autocratic form of government and large territorial holdings in Europe and around the Mediterranean....
and the dawn of the Middle Ages
Middle Ages
The Middle Ages is a periodization of European history from the 5th century to the 15th century. The Middle Ages follows the fall of the Western Roman Empire in 476 and precedes the Early Modern Era. It is the middle period of a three-period division of Western history: Classic, Medieval and Modern...
, many texts from Classical Antiquity
Classical antiquity
Classical antiquity is a broad term for a long period of cultural history centered on the Mediterranean Sea, comprising the interlocking civilizations of ancient Greece and ancient Rome, collectively known as the Greco-Roman world...
had been unavailable to the Europeans. However, in the Middle East
Middle East
The Middle East is a region that encompasses Western Asia and Northern Africa. It is often used as a synonym for Near East, in opposition to Far East...
many of these Greek texts (such as Aristotle
Aristotle
Aristotle was a Greek philosopher and polymath, a student of Plato and teacher of Alexander the Great. His writings cover many subjects, including physics, metaphysics, poetry, theater, music, logic, rhetoric, linguistics, politics, government, ethics, biology, and zoology...
) were translated from Greek
Greek language
Greek is an independent branch of the Indo-European family of languages. Native to the southern Balkans, it has the longest documented history of any Indo-European language, spanning 34 centuries of written records. Its writing system has been the Greek alphabet for the majority of its history;...
into Syriac
Syriac language
Syriac is a dialect of Middle Aramaic that was once spoken across much of the Fertile Crescent. Having first appeared as a script in the 1st century AD after being spoken as an unwritten language for five centuries, Classical Syriac became a major literary language throughout the Middle East from...
during the 6th and 7th centuries by Nestorian
Nestorianism
Nestorianism is a Christological doctrine advanced by Nestorius, Patriarch of Constantinople from 428–431. The doctrine, which was informed by Nestorius's studies under Theodore of Mopsuestia at the School of Antioch, emphasizes the disunion between the human and divine natures of Jesus...
, Melkite
Melkite
The term Melkite, also written Melchite, refers to various Byzantine Rite Christian churches and their members originating in the Middle East. The word comes from the Syriac word malkāyā , and the Arabic word Malakī...
or Jacobite
West Syrian Rite
The West Syrian Rite, also known as the Syrian Rite or the Syro-Antiochene Rite, is a Christian liturgical rite chiefly practiced in the Syriac Orthodox Church and churches related to or descended from it. It is part of the liturgical family known as the Antiochene Rite, which originated in the...
monks living in Palestine
Palestine
Palestine is a conventional name, among others, used to describe the geographic region between the Mediterranean Sea and the Jordan River, and various adjoining lands....
, or by Greek exiles from Athens
Athens
Athens , is the capital and largest city of Greece. Athens dominates the Attica region and is one of the world's oldest cities, as its recorded history spans around 3,400 years. Classical Athens was a powerful city-state...
or Edessa
Edessa, Mesopotamia
Edessa is the Greek name of an Aramaic town in northern Mesopotamia, as refounded by Seleucus I Nicator. For the modern history of the city, see Şanlıurfa.-Names:...
who visited Islamic Universities. Many of these texts however were then kept, translated, and developed upon by the Islamic world, especially in centers of learning such as Baghdad
Baghdad
Baghdad is the capital of Iraq, as well as the coterminous Baghdad Governorate. The population of Baghdad in 2011 is approximately 7,216,040...
, where a “House of Wisdom
House of Wisdom
The House of Wisdom was a library and translation institute established in Abbassid-era Baghdad, Iraq. It was a key institution in the Translation Movement and considered to have been a major intellectual centre during the Islamic Golden Age...
”, with thousands of manuscripts existed as soon as 832. These texts were translated again into European languages during the Middle Ages. Eastern Christians played an important role in exploiting this knowledge, especially through the Christian Aristotelician School of Baghdad in the 11th and 12th centuries.
These texts were translated back into Latin in multiple ways. The main points of transmission of Islamic knowledge to Europe were in Sicily
Sicily
Sicily is a region of Italy, and is the largest island in the Mediterranean Sea. Along with the surrounding minor islands, it constitutes an autonomous region of Italy, the Regione Autonoma Siciliana Sicily has a rich and unique culture, especially with regard to the arts, music, literature,...
and Toledo, Spain
Toledo, Spain
Toledo's Alcázar became renowned in the 19th and 20th centuries as a military academy. At the outbreak of the Spanish Civil War in 1936 its garrison was famously besieged by Republican forces.-Economy:...
(with Gerard of Cremona
Gerard of Cremona
Gerard of Cremona was an Italian translator of Arabic scientific works found in the abandoned Arab libraries of Toledo, Spain....
, 1114–1187). Burgundio of Pisa (died in 1193) discovered in Antioch lost texts of Aristotle
Aristotle
Aristotle was a Greek philosopher and polymath, a student of Plato and teacher of Alexander the Great. His writings cover many subjects, including physics, metaphysics, poetry, theater, music, logic, rhetoric, linguistics, politics, government, ethics, biology, and zoology...
and translated them into Latin.
Islamic sciences

Algebra
Algebra is the branch of mathematics concerning the study of the rules of operations and relations, and the constructions and concepts arising from them, including terms, polynomials, equations and algebraic structures...
, chemistry, geology
Geology
Geology is the science comprising the study of solid Earth, the rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which it evolves. Geology gives insight into the history of the Earth, as it provides the primary evidence for plate tectonics, the evolutionary history of life, and past climates...
, spherical trigonometry
Spherical trigonometry
Spherical trigonometry is a branch of spherical geometry which deals with polygons on the sphere and the relationships between the sides and the angles...
, etc. which were later also transmitted to the West.
Stefan of Pise translated into Latin around 1127 an Arab manual of medical theory. The method of algorism
Algorism
Algorism is the technique of performing basic arithmetic by writing numbers in place value form and applying a set of memorized rules and facts to the digits. One who practices algorism is known as an algorist...
for performing arithmetic with Indian-Arabic numerals
Arabic numerals
Arabic numerals or Hindu numerals or Hindu-Arabic numerals or Indo-Arabic numerals are the ten digits . They are descended from the Hindu-Arabic numeral system developed by Indian mathematicians, in which a sequence of digits such as "975" is read as a numeral...
was developed by al-Khwarizmi (hence the word “Algorithm
Algorithm
In mathematics and computer science, an algorithm is an effective method expressed as a finite list of well-defined instructions for calculating a function. Algorithms are used for calculation, data processing, and automated reasoning...
”) in the 9th century, and introduced in Europe by Leonardo Fibonacci (1170–1250). A translation by Robert of Chester
Robert of Chester
Robert of Chester was an English arabist of the 12th century. He translated several historically important books from Arabic to Latin, by authors such as Abu Musa Jabir Ibn Hayyan and Al-Khwarizmi including:...
of the Algebra
The Compendious Book on Calculation by Completion and Balancing
, also known under a shorter name spelled as Hisab al-jabr w’al-muqabala, Kitab al-Jabr wa-l-Muqabala and other transliterations) is a mathematical book written in Arabic in approximately AD 820 by the Persian (Arabic for "The Compendious Book on Calculation by Completion and Balancing", in...
by al-Kharizmi is known as early as 1145. Ibn al-Haytham (Alhazen, 980–1037) compiled treatises on optical sciences, which were used as references by Newton
Isaac Newton
Sir Isaac Newton PRS was an English physicist, mathematician, astronomer, natural philosopher, alchemist, and theologian, who has been "considered by many to be the greatest and most influential scientist who ever lived."...
and Descartes. Medical sciences were also highly developed in Islam as testified by the Crusaders, who relied on Arab doctors on numerous occasions. Joinville
Jean de Joinville
Jean de Joinville was one of the great chroniclers of medieval France.Son of Simon de Joinville and Beatrice d'Auxonne, he belonged to a noble family from Champagne. He received an education befitting a young noble at the court of Theobald IV, count of Champagne: reading, writing, and the...
reports he was saved in 1250 by a “Saracen
Saracen
Saracen was a term used by the ancient Romans to refer to a people who lived in desert areas in and around the Roman province of Arabia, and who were distinguished from Arabs. In Europe during the Middle Ages the term was expanded to include Arabs, and then all who professed the religion of Islam...
” doctor.
Contributing to the growth of European science was the major search by European scholars for new learning. They were interested in ancient Greek philosophical and scientific texts such as the Almagest
Almagest
The Almagest is a 2nd-century mathematical and astronomical treatise on the apparent motions of the stars and planetary paths. Written in Greek by Claudius Ptolemy, a Roman era scholar of Egypt,...
, which were not obtainable in Latin in Western Europe, but which had survived and been translated into Arabic in the Muslim world. They were also interested in commentaries and advances which the Arabs had made on these works. Islamic Spain
Al-Andalus
Al-Andalus was the Arabic name given to a nation and territorial region also commonly referred to as Moorish Iberia. The name describes parts of the Iberian Peninsula and Septimania governed by Muslims , at various times in the period between 711 and 1492, although the territorial boundaries...
and Sicily
History of Islam in southern Italy
The history of Islam in southern Italy begins with the Islamic conquest and subsequent rule of Sicily and Malta, a process that started in the 9th century. Islamic rule over Sicily was effective from 902, and the complete rule of the island lasted from 965 until 1061...
were particularly productive areas because of the proximity of multi-lingual scholars. These scholars translated many scientific and philosophical texts from Arabic
Arabic language
Arabic is a name applied to the descendants of the Classical Arabic language of the 6th century AD, used most prominently in the Quran, the Islamic Holy Book...
into Latin
Latin
Latin is an Italic language originally spoken in Latium and Ancient Rome. It, along with most European languages, is a descendant of the ancient Proto-Indo-European language. Although it is considered a dead language, a number of scholars and members of the Christian clergy speak it fluently, and...
.
One of the most productive translators in Spain was Gerard of Cremona
Gerard of Cremona
Gerard of Cremona was an Italian translator of Arabic scientific works found in the abandoned Arab libraries of Toledo, Spain....
, who translated 87 books from Arabic to Latin,
including Muhammad ibn Mūsā al-Khwārizmī
Muhammad ibn Musa al-Khwarizmi
'There is some confusion in the literature on whether al-Khwārizmī's full name is ' or '. Ibn Khaldun notes in his encyclopedic work: "The first who wrote upon this branch was Abu ʿAbdallah al-Khowarizmi, after whom came Abu Kamil Shojaʿ ibn Aslam." . 'There is some confusion in the literature on...
's On Algebra and Almucabala
The Compendious Book on Calculation by Completion and Balancing
, also known under a shorter name spelled as Hisab al-jabr w’al-muqabala, Kitab al-Jabr wa-l-Muqabala and other transliterations) is a mathematical book written in Arabic in approximately AD 820 by the Persian (Arabic for "The Compendious Book on Calculation by Completion and Balancing", in...
, Jabir ibn Aflah
Jabir ibn Aflah
Abū Muḥammad Jābir ibn Aflaḥ was a Muslim astronomer and mathematician from Seville, who was active in 12th century Andalusia. His work Iṣlāḥ al-Majisṭi influenced Islamic, Jewish and Christian astronomers....
's Elementa astronomica,
al-Kindi
Al-Kindi
' , known as "the Philosopher of the Arabs", was a Muslim Arab philosopher, mathematician, physician, and musician. Al-Kindi was the first of the Muslim peripatetic philosophers, and is unanimously hailed as the "father of Islamic or Arabic philosophy" for his synthesis, adaptation and promotion...
's On Optics, Ahmad ibn Muhammad ibn Kathīr al-Farghānī's On Elements of Astronomy on the Celestial Motions, al-Farabi
Al-Farabi
' known in the West as Alpharabius , was a scientist and philosopher of the Islamic world...
's On the Classification of the Sciences,
the chemical and medical
Islamic medicine
In the history of medicine, Islamic medicine, Arabic medicine or Arabian medicine refers to medicine developed in the Islamic Golden Age, and written in Arabic, the lingua franca of Islamic civilization....
works of Rhazes,
the works of Thabit ibn Qurra
Thabit ibn Qurra
' was a mathematician, physician, astronomer and translator of the Islamic Golden Age.Ibn Qurra made important discoveries in algebra, geometry and astronomy...
and Hunayn ibn Ishaq
Hunayn ibn Ishaq
Hunayn ibn Ishaq was a famous and influential Assyrian Nestorian Christian scholar, physician, and scientist, known for his work in translating Greek scientific and medical works into Arabic and Syriac during the heyday of the Islamic Abbasid Caliphate.Ḥunayn ibn Isḥaq was the most productive...
,
and the works of Arzachel
Arzachel
', Al-Zarqali, Ibn Zarqala , Latinized as Arzachel, was an instrument maker and one of the leading theoretical and practical astronomers of his time. Although his name is conventionally given as al-Zarqālī, it is probable that the correct form was al-Zarqālluh. He lived in Toledo in Castile,...
, Jabir ibn Aflah
Jabir ibn Aflah
Abū Muḥammad Jābir ibn Aflaḥ was a Muslim astronomer and mathematician from Seville, who was active in 12th century Andalusia. His work Iṣlāḥ al-Majisṭi influenced Islamic, Jewish and Christian astronomers....
, the Banū Mūsā
Banu Musa
The Banū Mūsā brothers , namely Abū Jaʿfar Muḥammad ibn Mūsā ibn Shākir , Abū al‐Qāsim Aḥmad ibn Mūsā ibn Shākir and Al-Ḥasan ibn Mūsā ibn Shākir , were three 9th-century Persian scholars of Baghdad who are known for their Book of Ingenious Devices on automata and mechanical devices...
, Abū Kāmil Shujā ibn Aslam, Abu al-Qasim
Abu al-Qasim
Abu al-Qasim Khalaf ibn al-Abbas Al-Zahrawi , also known in the West as Abulcasis, was an Arab physician who lived in Al-Andalus. He is considered the greatest medieval surgeon to have appeared from the Islamic World, and has been described by some as the father of modern surgery...
, and Ibn al-Haytham (including the Book of Optics
Book of Optics
The Book of Optics ; ; Latin: De Aspectibus or Opticae Thesaurus: Alhazeni Arabis; Italian: Deli Aspecti) is a seven-volume treatise on optics and other fields of study composed by the medieval Muslim scholar Alhazen .-See also:* Science in medieval Islam...
).
Alchemy
The Latin alchemicalAlchemy
Alchemy is an influential philosophical tradition whose early practitioners’ claims to profound powers were known from antiquity. The defining objectives of alchemy are varied; these include the creation of the fabled philosopher's stone possessing powers including the capability of turning base...
works of "Geber" were standard texts for European alchemists. The exact attribution of these works remains a matter of some controversy. Some are undoubtedly translations from Arabic from works attributed to Jābir ibn Hayyān, including the Kitab al-Kimya (titled Book of the Composition of Alchemy in Europe), translated by Robert of Chester
Robert of Chester
Robert of Chester was an English arabist of the 12th century. He translated several historically important books from Arabic to Latin, by authors such as Abu Musa Jabir Ibn Hayyan and Al-Khwarizmi including:...
(1144); and the Kitab al-Sab'een, translated by Gerard of Cremona
Gerard of Cremona
Gerard of Cremona was an Italian translator of Arabic scientific works found in the abandoned Arab libraries of Toledo, Spain....
(before 1187). Whether these were actually written by one man (or whether indeed Jābir was a real historical figure) is disputed, but there is no doubting the influence on medieval European alchemy of the translated Arabic works. (A few of the Latin works are now attributed to a Pseudo-Geber
Pseudo-Geber
Pseudo-Geber is the name assigned by modern scholars to an anonymous European alchemist born in the 13th century, sometimes identified with Paul of Taranto, who wrote books on alchemy and metallurgy, in Latin, under the pen name of "Geber". "Geber" is the shortened and Latinised form of the name...
, as although attributed to "Geber", they have no identified Arabic source and appear to have been composed in Latin in the 13th century).
Marcelin Berthelot translated some of the Jabirian works under the fanciful titles Book of the Kingdom, Book of the Balances, and Book of Eastern Mercury. Several technical Arabic terms
Influence of Arabic on other languages
Arabic has had a great influence on other languages, especially in vocabulary. The influence of Arabic has been most profound in those countries dominated by Islam or Islamic power...
introduced in Jabir's works, such as alkali
Alkali
In chemistry, an alkali is a basic, ionic salt of an alkali metal or alkaline earth metal element. Some authors also define an alkali as a base that dissolves in water. A solution of a soluble base has a pH greater than 7. The adjective alkaline is commonly used in English as a synonym for base,...
, have found their way into various European languages and have become part of scientific vocabulary.
The alchemical works of Muhammad ibn Zakarīya Rāzi (Rhazes) were also translated into Latin around the 12th century.
Astronomy and mathematics

Muhammad ibn Musa al-Khwarizmi
'There is some confusion in the literature on whether al-Khwārizmī's full name is ' or '. Ibn Khaldun notes in his encyclopedic work: "The first who wrote upon this branch was Abu ʿAbdallah al-Khowarizmi, after whom came Abu Kamil Shojaʿ ibn Aslam." . 'There is some confusion in the literature on...
's work greatly influenced mathematics in Europe. As Professor Victor J. Katz writes: "Most early algebra works in Europe in fact recognized that the first algebra works in that continent were translations of the work of al-Khwärizmï and other Islamic authors. There was also some awareness that much of plane and spherical trigonometry could be attributed to Islamic authors". The words algorithm
Algorithm
In mathematics and computer science, an algorithm is an effective method expressed as a finite list of well-defined instructions for calculating a function. Algorithms are used for calculation, data processing, and automated reasoning...
, deriving from Al-Khwarizmi's Latinized name Algorismi, and algebra
Algebra
Algebra is the branch of mathematics concerning the study of the rules of operations and relations, and the constructions and concepts arising from them, including terms, polynomials, equations and algebraic structures...
, deriving from the title of his AD 820 book Hisab al-jabr w’al-muqabala, Kitab al-Jabr wa-l-Muqabala
The Compendious Book on Calculation by Completion and Balancing
, also known under a shorter name spelled as Hisab al-jabr w’al-muqabala, Kitab al-Jabr wa-l-Muqabala and other transliterations) is a mathematical book written in Arabic in approximately AD 820 by the Persian (Arabic for "The Compendious Book on Calculation by Completion and Balancing", in...
("The Compendious Book on Calculation by Completion and Balancing") are themselves Arabic loanwords. This and other Arabic astronomical and mathematical works, such as those by al-Battani and Muhammad al-Fazari
Muhammad al-Fazari
Abu abdallah Muhammad ibn Ibrahim al-Fazari was a Muslim philosopher, mathematician and astronomer. He is not to be confused with his father Ibrāhīm al-Fazārī, also an astronomer and mathematician....
's Great Sindhind (based on the Surya Siddhanta
Surya Siddhanta
The Surya Siddhanta is one of the earliest siddhanta in archeo-astronomy of the Hindus by an unknown author. It describes the archeo-astronomy theories, principles and methods of the ancient Hindus. This siddhanta is supposed to be the knowledge that the Sun god gave to an Asura called Maya. Asuras...
and the works of Brahmagupta
Brahmagupta
Brahmagupta was an Indian mathematician and astronomer who wrote many important works on mathematics and astronomy. His best known work is the Brāhmasphuṭasiddhānta , written in 628 in Bhinmal...
). were translated into Latin during the 12th century.
Al-Khazini
Al-Khazini
Abu al-Fath Abd al-Rahman Mansour al-Khāzini or simply Abu al-Fath Khāzini was a Muslim astronomer of Greek ethnicity from Merv, then in the Khorasan province of Persia .-References:...
's Zij
Zij
Zīj is the generic name applied to Islamic astronomical books that tabulate parameters used for astronomical calculations of the positions of the Sun, Moon, stars, and planets. The name is derived from the Middle Persian term zih or zīg, meaning cord...
as-Sanjari (1115–1116) was translated into Greek
Greek language
Greek is an independent branch of the Indo-European family of languages. Native to the southern Balkans, it has the longest documented history of any Indo-European language, spanning 34 centuries of written records. Its writing system has been the Greek alphabet for the majority of its history;...
by Gregory Choniades
Gregory Choniades
Gregory Choniades was a Byzantine Greek astronomer. He travelled to Persia where he learnt Persian mathematical and astronomical science which he introduced into Byzantium upon return from Persia and founded an astronomical academy at Trebizond...
in the 13th century and was studied in the Byzantine Empire
Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire was the Eastern Roman Empire during the periods of Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, centred on the capital of Constantinople. Known simply as the Roman Empire or Romania to its inhabitants and neighbours, the Empire was the direct continuation of the Ancient Roman State...
. The astronomical modifications to the Ptolemaic model made by al-Battani
Al-Battani
Abū ʿAbd Allāh Muḥammad ibn Jābir ibn Sinān al-Raqqī al-Ḥarrānī al-Ṣābiʾ al-Battānī was a Muslim astronomer, astrologer, and mathematician...
and Averroes
Averroes
' , better known just as Ibn Rushd , and in European literature as Averroes , was a Muslim polymath; a master of Aristotelian philosophy, Islamic philosophy, Islamic theology, Maliki law and jurisprudence, logic, psychology, politics, Arabic music theory, and the sciences of medicine, astronomy,...
led to non-Ptolemaic models produced by Mo'ayyeduddin Urdi
Mo'ayyeduddin Urdi
Mu’ayyad al-Din al-’Urdi was an Kurdish Muslim astronomer, mathematician, architect and engineer working at the Maragheh observatory...
(Urdi lemma), Nasīr al-Dīn al-Tūsī
Nasir al-Din al-Tusi
Khawaja Muḥammad ibn Muḥammad ibn Ḥasan Ṭūsī , better known as Naṣīr al-Dīn al-Ṭūsī , was a Persian polymath and prolific writer: an astronomer, biologist, chemist, mathematician, philosopher, physician, physicist, scientist, theologian and Marja Taqleed...
(Tusi-couple
Tusi-couple
The Tusi-couple is a mathematical device in which a small circle rotates inside a larger circle twice the diameter of the smaller circle. Rotations of the circles cause a point on the circumference of the smaller circle to oscillate back and forth in linear motion along a diameter of the larger...
) and Ibn al-Shatir
Ibn al-Shatir
Ala Al-Din Abu'l-Hasan Ali Ibn Ibrahim Ibn al-Shatir was an Arab Muslim astronomer, mathematician, engineer and inventor who worked as muwaqqit at the Umayyad Mosque in Damascus, Syria.-Astronomy:...
, which were later adapted into the Copernican heliocentric
Copernican heliocentrism
Copernican heliocentrism is the name given to the astronomical model developed by Nicolaus Copernicus and published in 1543. It positioned the Sun near the center of the Universe, motionless, with Earth and the other planets rotating around it in circular paths modified by epicycles and at uniform...
model. Abū al-Rayhān al-Bīrūnī's Ta'rikh al-Hind and Kitab al-qanun al-Mas’udi were translated into Latin as Indica and Canon Mas’udicus respectively.
Fibonacci
Fibonacci
Leonardo Pisano Bigollo also known as Leonardo of Pisa, Leonardo Pisano, Leonardo Bonacci, Leonardo Fibonacci, or, most commonly, simply Fibonacci, was an Italian mathematician, considered by some "the most talented western mathematician of the Middle Ages."Fibonacci is best known to the modern...
presented the first complete European account of the Hindu-Arabic numeral system
Hindu-Arabic numeral system
The Hindu–Arabic numeral system or Hindu numeral system is a positional decimal numeral system developed between the 1st and 5th centuries by Indian mathematicians, adopted by Persian and Arab mathematicians , and spread to the western world...
from Arabic sources
Arabic numerals
Arabic numerals or Hindu numerals or Hindu-Arabic numerals or Indo-Arabic numerals are the ten digits . They are descended from the Hindu-Arabic numeral system developed by Indian mathematicians, in which a sequence of digits such as "975" is read as a numeral...
in his Liber Abaci
Liber Abaci
Liber Abaci is a historic book on arithmetic by Leonardo of Pisa, known later by his nickname Fibonacci...
(1202).
Al-Jayyani
Al-Jayyani
Abū ʿAbd Allāh Muḥammad ibn Muʿādh al-Jayyānī was a mathematician, Islamic scholar, and Qadi from Al-Andalus...
's The book of unknown arcs of a sphere (a treatise on spherical trigonometry
Spherical trigonometry
Spherical trigonometry is a branch of spherical geometry which deals with polygons on the sphere and the relationships between the sides and the angles...
) had a "strong influence on European mathematics". Regiomantus' On Triangles (c. 1463) certainly took his material on spherical trigonometry (without acknowledgement) from Arab sources. Much of the material was taken from the twelfth-century work of Jabir ibn Aflah
Jabir ibn Aflah
Abū Muḥammad Jābir ibn Aflaḥ was a Muslim astronomer and mathematician from Seville, who was active in 12th century Andalusia. His work Iṣlāḥ al-Majisṭi influenced Islamic, Jewish and Christian astronomers....
(otherwise known as Geber), as noted in the sixteenth century by Gerolamo Cardano
Gerolamo Cardano
Gerolamo Cardano was an Italian Renaissance mathematician, physician, astrologer and gambler...
.
A short verse used by Fulbert of Chartres
Fulbert of Chartres
Fulbert of Chartres –10 April 1028) was the bishop of the Cathedral of Chartres from 1006 till 1028. He was a teacher at the Cathedral school there, he was responsible for the advancement of the celebration of the Feast day of “Nativity of the Virgin”, and he was responsible for one of the...
(952-970 –1028) to help remember some of the brightest stars in the sky gives us the earliest known use of Arabic loanwords in a Latin text: "Aldebaran stands out in Taurus, Menke and Rigel in Gemini, and Frons and bright Calbalazet in Leo. Scorpio, you have Galbalagrab; and you, Capricorn, Deneb. You, Batanalhaut, are alone enough for Pisces."
Medicine

Avicenna
Abū ʿAlī al-Ḥusayn ibn ʿAbd Allāh ibn Sīnā , commonly known as Ibn Sīnā or by his Latinized name Avicenna, was a Persian polymath, who wrote almost 450 treatises on a wide range of subjects, of which around 240 have survived...
's The Canon of Medicine
The Canon of Medicine
The Canon of Medicine is an encyclopedia of Galenic medicine in five books compiled by Ibn Sīnā and completed in 1025. It presents a clear and organized summary of all the medical knowledge of the time...
(1025), which was translated into Latin and then disseminated in manuscript and printed form throughout Europe. It remained a standard medical textbook in Europe until the early modern period, and during the 15th and 16th centuries alone, The Canon of Medicine was published more than thirty-five times. Avicenna noted the contagious nature of some infectious disease
Infectious disease
Infectious diseases, also known as communicable diseases, contagious diseases or transmissible diseases comprise clinically evident illness resulting from the infection, presence and growth of pathogenic biological agents in an individual host organism...
s (which he attributed to "traces" left in the air by a sick person), and discussed how to effectively test new medicines. He also wrote The Book of Healing
The Book of Healing
The Book of Healing is a scientific and philosophical encyclopedia written by Abū Alī ibn Sīnā from Asfahana, near Bukhara in Greater Persia. Despite its English title, it is not in fact concerned with medicine...
, a more general encyclopedia of science and philosophy, which became another popular textbook in Europe. Muhammad ibn Zakarīya Rāzi (al-Razi) wrote the Comprehensive Book of Medicine, with its careful description of and distinction between measles
Measles
Measles, also known as rubeola or morbilli, is an infection of the respiratory system caused by a virus, specifically a paramyxovirus of the genus Morbillivirus. Morbilliviruses, like other paramyxoviruses, are enveloped, single-stranded, negative-sense RNA viruses...
and smallpox
Smallpox
Smallpox was an infectious disease unique to humans, caused by either of two virus variants, Variola major and Variola minor. The disease is also known by the Latin names Variola or Variola vera, which is a derivative of the Latin varius, meaning "spotted", or varus, meaning "pimple"...
, which was also influential in Europe. Abu al-Qasim al-Zahrawi (also known as Albucasis) wrote Kitab al-Tasrif
Al-Tasrif
The Kitab al-Tasrif was an Arabic encyclopedia on medicine and surgery, written near the year 1000 by Abu al-Qasim al-Zahrawi...
, an encyclopedia of medicine which was particularly famed for its section on surgery. It included descriptions and diagrams of over 200 surgical instruments, many of which he developed. The surgery section was translated into Latin by Gerard of Cremona
Gerard of Cremona
Gerard of Cremona was an Italian translator of Arabic scientific works found in the abandoned Arab libraries of Toledo, Spain....
in the 1100s, and used in European medical school
Medical school
A medical school is a tertiary educational institution—or part of such an institution—that teaches medicine. Degree programs offered at medical schools often include Doctor of Osteopathic Medicine, Bachelor/Doctor of Medicine, Doctor of Philosophy, master's degree, or other post-secondary...
s for centuries, still being reprinted in the 1770s.
Physics
One of the most important scientific works to be translated was Ibn al-Haytham (Alhazen)'s Book of OpticsBook of Optics
The Book of Optics ; ; Latin: De Aspectibus or Opticae Thesaurus: Alhazeni Arabis; Italian: Deli Aspecti) is a seven-volume treatise on optics and other fields of study composed by the medieval Muslim scholar Alhazen .-See also:* Science in medieval Islam...
(1021). Alhazen's book was notable for his early use of an experiment based scientific method
Scientific method
Scientific method refers to a body of techniques for investigating phenomena, acquiring new knowledge, or correcting and integrating previous knowledge. To be termed scientific, a method of inquiry must be based on gathering empirical and measurable evidence subject to specific principles of...
, in which he developed a theory of vision and light which built on the work of the Roman writer Ptolemy
Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy , was a Roman citizen of Egypt who wrote in Greek. He was a mathematician, astronomer, geographer, astrologer, and poet of a single epigram in the Greek Anthology. He lived in Egypt under Roman rule, and is believed to have been born in the town of Ptolemais Hermiou in the...
(but which rejected Ptolemy's theory that light was emitted by the eye
Emission theory (vision)
Emission theory or extramission theory is the proposal that visual perception is accomplished by rays of light emitted by the eyes. This theory has been replaced by intromission theory, which states that visual perception comes from something representative of the object entering the eyes...
, insisting instead that light rays entered the eye), and was the most significant advance in this field until Kepler. The Book of Optics was an important stepping stone in the history of the scientific method and history of optics
History of optics
Optics began with the development of lenses by the ancient Egyptians and Mesopotamians, followed by theories on light and vision developed by ancient Greek and Indian philosophers, and the development of geometrical optics in the Greco-Roman world. The word optics is derived from the Greek term τα...
. The Latin translation of the Book of Optics influenced the works of many later European scientists, including Roger Bacon
Roger Bacon
Roger Bacon, O.F.M. , also known as Doctor Mirabilis , was an English philosopher and Franciscan friar who placed considerable emphasis on the study of nature through empirical methods...
and Johannes Kepler
Johannes Kepler
Johannes Kepler was a German mathematician, astronomer and astrologer. A key figure in the 17th century scientific revolution, he is best known for his eponymous laws of planetary motion, codified by later astronomers, based on his works Astronomia nova, Harmonices Mundi, and Epitome of Copernican...
. The book also influenced other aspects of European culture. In religion
Religion
Religion is a collection of cultural systems, belief systems, and worldviews that establishes symbols that relate humanity to spirituality and, sometimes, to moral values. Many religions have narratives, symbols, traditions and sacred histories that are intended to give meaning to life or to...
, for example, John Wycliffe
John Wycliffe
John Wycliffe was an English Scholastic philosopher, theologian, lay preacher, translator, reformer and university teacher who was known as an early dissident in the Roman Catholic Church during the 14th century. His followers were known as Lollards, a somewhat rebellious movement, which preached...
, the intellectual progenitor of the Protestant Reformation
Protestant Reformation
The Protestant Reformation was a 16th-century split within Western Christianity initiated by Martin Luther, John Calvin and other early Protestants. The efforts of the self-described "reformers", who objected to the doctrines, rituals and ecclesiastical structure of the Roman Catholic Church, led...
, referred to Alhazen in discussing the seven deadly sin
Sin
In religion, sin is the violation or deviation of an eternal divine law or standard. The term sin may also refer to the state of having committed such a violation. Christians believe the moral code of conduct is decreed by God In religion, sin (also called peccancy) is the violation or deviation...
s in terms of the distortions in the seven types of mirror
Mirror
A mirror is an object that reflects light or sound in a way that preserves much of its original quality prior to its contact with the mirror. Some mirrors also filter out some wavelengths, while preserving other wavelengths in the reflection...
s analyzed in De aspectibus. In literature
Literature
Literature is the art of written works, and is not bound to published sources...
, Alhazen's Book of Optics is praised in Guillaume de Lorris
Guillaume de Lorris
Guillaume de Lorris was a French scholar and poet from Lorris. He was the author of the first section of the Roman de la Rose. Little is known about him, other than that he wrote the earlier section of the poem around 1230, and that the work was completed forty years later by Jean de Meun.-...
' Roman de la Rose
Roman de la Rose
The Roman de la rose, , is a medieval French poem styled as an allegorical dream vision. It is a notable instance of courtly literature. The work's stated purpose is to both entertain and to teach others about the Art of Love. At various times in the poem, the "Rose" of the title is seen as the...
. In art
Art
Art is the product or process of deliberately arranging items in a way that influences and affects one or more of the senses, emotions, and intellect....
, the Book of Optics laid the foundations for the linear perspective
Perspective (graphical)
Perspective in the graphic arts, such as drawing, is an approximate representation, on a flat surface , of an image as it is seen by the eye...
technique and may have influenced the use of optical aids in Renaissance
Renaissance
The Renaissance was a cultural movement that spanned roughly the 14th to the 17th century, beginning in Italy in the Late Middle Ages and later spreading to the rest of Europe. The term is also used more loosely to refer to the historical era, but since the changes of the Renaissance were not...
art (see Hockney-Falco thesis
Hockney-Falco thesis
The Hockney–Falco thesis is a controversial theory of art history, advanced by artist David Hockney and physicist Charles M. Falco, suggesting that advances in realism and accuracy in the history of Western art since the Renaissance were primarily the result of optical aids such as the camera...
). These same techniques were then employed in European geographical
Geography
Geography is the science that studies the lands, features, inhabitants, and phenomena of Earth. A literal translation would be "to describe or write about the Earth". The first person to use the word "geography" was Eratosthenes...
maps made by cartographers such as Paolo Toscanelli during the Age of Exploration.
The theory of motion developed by Avicenna
Avicenna
Abū ʿAlī al-Ḥusayn ibn ʿAbd Allāh ibn Sīnā , commonly known as Ibn Sīnā or by his Latinized name Avicenna, was a Persian polymath, who wrote almost 450 treatises on a wide range of subjects, of which around 240 have survived...
from Aristotelian physics
Aristotelian physics
Aristotelian Physics the natural sciences, are described in the works of the Greek philosopher Aristotle . In the Physics, Aristotle established general principles of change that govern all natural bodies; both living and inanimate, celestial and terrestrial—including all motion, change in respect...
may have influenced Jean Buridan
Jean Buridan
Jean Buridan was a French priest who sowed the seeds of the Copernican revolution in Europe. Although he was one of the most famous and influential philosophers of the late Middle Ages, he is today among the least well known...
's theory of impetus
Theory of impetus
The theory of impetus was an auxiliary or secondary theory of Aristotelian dynamics, put forth initially to explain projectile motion against gravity...
(the ancestor of the inertia
Inertia
Inertia is the resistance of any physical object to a change in its state of motion or rest, or the tendency of an object to resist any change in its motion. It is proportional to an object's mass. The principle of inertia is one of the fundamental principles of classical physics which are used to...
and momentum
Momentum
In classical mechanics, linear momentum or translational momentum is the product of the mass and velocity of an object...
concepts). The work of Galileo Galilei
Galileo Galilei
Galileo Galilei , was an Italian physicist, mathematician, astronomer, and philosopher who played a major role in the Scientific Revolution. His achievements include improvements to the telescope and consequent astronomical observations and support for Copernicanism...
on classical mechanics
Classical mechanics
In physics, classical mechanics is one of the two major sub-fields of mechanics, which is concerned with the set of physical laws describing the motion of bodies under the action of a system of forces...
(superseding Aristotelian physics) was also influenced by earlier medieval physics writers, including Avempace.
Other works
Other Arabic works translated into Latin during the medieval period include the works of Razi and AvicennaAvicenna
Abū ʿAlī al-Ḥusayn ibn ʿAbd Allāh ibn Sīnā , commonly known as Ibn Sīnā or by his Latinized name Avicenna, was a Persian polymath, who wrote almost 450 treatises on a wide range of subjects, of which around 240 have survived...
(including The Book of Healing
The Book of Healing
The Book of Healing is a scientific and philosophical encyclopedia written by Abū Alī ibn Sīnā from Asfahana, near Bukhara in Greater Persia. Despite its English title, it is not in fact concerned with medicine...
and The Canon of Medicine
The Canon of Medicine
The Canon of Medicine is an encyclopedia of Galenic medicine in five books compiled by Ibn Sīnā and completed in 1025. It presents a clear and organized summary of all the medical knowledge of the time...
),
the works of Averroes
Averroes
' , better known just as Ibn Rushd , and in European literature as Averroes , was a Muslim polymath; a master of Aristotelian philosophy, Islamic philosophy, Islamic theology, Maliki law and jurisprudence, logic, psychology, politics, Arabic music theory, and the sciences of medicine, astronomy,...
,
the works of Nur Ed-Din Al Betrugi
Nur Ed-Din Al Betrugi
Nur ad-Din al-Bitruji was an astronomer and a Qadi from Al-Andalus...
, including On the Motions of the Heavens,
Ali ibn Abbas al-Majusi
Ali ibn Abbas al-Majusi
Ali ibn al-'Abbas al-Majusi , also known as Masoudi, or Latinized as Haly Abbas, was a Persian physician and psychologist most famous for the Kitab al-Maliki or Complete Book of the Medical Art, his textbook on medicine and psychology.-Biography:He was born in Ahvaz, southwestern Persia, and...
's medical encyclopedia, The Complete Book of the Medical Art,
Abu Mashar's Introduction to Astrology,
Abū Kāmil Shujā ibn Aslam's Algebra,
and the De Proprietatibus Elementorum, an Arabic work on geology
Islamic geography
Geography and cartography in medieval Islam refers to the advancement of geography, cartography and the earth sciences in the medieval Islamic civilization....
written by a pseudo-Aristotle
Pseudo-Aristotle
Pseudo-Aristotle is a general cognomen for authors of philosophical or medical treatises who attributed their work to the Greek philosopher Aristotle, or whose work was later attributed to him by others....
. By the beginning of the 13th century Mark of Toledo
Mark of Toledo
Mark of Toledo was a Spanish physician and a canon of Toledo.He produced one of the earliest translations of the Qur'an into Latin while working at the Toledo School of Translators...
had translated the Qur'an
Qur'an
The Quran , also transliterated Qur'an, Koran, Alcoran, Qur’ān, Coran, Kuran, and al-Qur’ān, is the central religious text of Islam, which Muslims consider the verbatim word of God . It is regarded widely as the finest piece of literature in the Arabic language...
and various medical works
Islamic medicine
In the history of medicine, Islamic medicine, Arabic medicine or Arabian medicine refers to medicine developed in the Islamic Golden Age, and written in Arabic, the lingua franca of Islamic civilization....
.
Islamic techniques
In the 12th century, various unknown fruits were introduced to Europe via the Middle East and North Africa: the artichokeArtichoke
-Plants:* Globe artichoke, a partially edible perennial thistle originating in southern Europe around the Mediterranean* Jerusalem artichoke, a species of sunflower with an edible tuber...
, spinach
Spinach
Spinach is an edible flowering plant in the family of Amaranthaceae. It is native to central and southwestern Asia. It is an annual plant , which grows to a height of up to 30 cm. Spinach may survive over winter in temperate regions...
s, aubergines, peach
Peach
The peach tree is a deciduous tree growing to tall and 6 in. in diameter, belonging to the subfamily Prunoideae of the family Rosaceae. It bears an edible juicy fruit called a peach...
es, apricots.
Numerous new techniques in clothing, as well as new materials were also introduced, such as muslin
Muslin
Muslin |sewing patterns]], such as for clothing, curtains, or upholstery. Because air moves easily through muslin, muslin clothing is suitable for hot, dry climates.- Etymology and history :...
, taffeta
Taffeta
Taffeta is a crisp, smooth plain woven fabric made from silk or synthetic fibers. The word is Persian in origin, and means "twisted woven." It is considered to be a "high end" fabric, suitable for use in ball gowns, wedding dresses, and in interiors for curtains or wallcovering. There are two...
s, and satin
Satin
Satin is a weave that typically has a glossy surface and a dull back. It is a warp-dominated weaving technique that forms a minimum number of interlacings in a fabric. If a fabric is formed with a satin weave using filament fibres such as silk, nylon, or polyester, the corresponding fabric is...
.

Arts
Islamic decorative arts were highly valued imports to Europe throughout the Middle Ages; largely because of accidents of survival the majority of surviving examples are those that were in the possession of the church. In the early period textiles were especially important, used for church vestments, shrouds, hangings and clothing for the elite. Islamic pottery of everyday quality was still preferred to European wares. Because decoration was mostly ornamental, or small hunting scenes and the like, and inscriptions were not understood, Islamic objects did not offend Christian sensibilities. Medieval art in Sicily is interesting stylistically because of the mixture of Norman, Arab and Byzantine influences in areas such as mosaicMosaic
Mosaic is the art of creating images with an assemblage of small pieces of colored glass, stone, or other materials. It may be a technique of decorative art, an aspect of interior decoration, or of cultural and spiritual significance as in a cathedral...
s and metal inlays, sculpture
Sculpture
Sculpture is three-dimensional artwork created by shaping or combining hard materials—typically stone such as marble—or metal, glass, or wood. Softer materials can also be used, such as clay, textiles, plastics, polymers and softer metals...
, and bronzeworking.
Writing: Western imitations of Arabic script

Kufic
Kufic is the oldest calligraphic form of the various Arabic scripts and consists of a modified form of the old Nabataean script. Its name is derived from the city of Kufa, Iraq, although it was known in Mesopotamia at least 100 years before the foundation of Kufa. At the time of the emergence of...
script was often imitated for decorative effect in the West during the Middle Ages and the Renaissance, to produce what is known as pseudo-Kufic
Pseudo-Kufic
Pseudo-Kufic, or Kufesque, also sometimes Pseudo-Arabic, refers to imitations of the Arabic Kufic script, or sometimes Arabic cursive script, made in a non-Arabic context, during the Middle-Ages or the Renaissance: "Imitations of Arabic in European art are often described as pseudo-Kufic, borrowing...
: "Imitations of Arabic in European art are often described as pseudo-Kufic, borrowing the term for an Arabic script that emphasizes straight and angular strokes, and is most commonly used in Islamic architectural decoration". Numerous cases of pseudo-Kufic are known from European art from around the 10th to the 15th century; usually the characters are meaningless, though sometimes a text has been copied. Pseudo-Kufic would be used as writing or as decorative elements in textiles, religious halos
Halo (religious iconography)
A halo is a ring of light that surrounds a person in art. They have been used in the iconography of many religions to indicate holy or sacred figures, and have at various periods also been used in images of rulers or heroes...
or frames. Many are visible in the paintings of Giotto. The exact reason for the incorporation of pseudo-Kufic in early Renaissance painting is unclear. It seems that Westerners mistakenly associated 13–14th century Middle-Eastern scripts as being identical with the scripts current during Jesus
Jesus
Jesus of Nazareth , commonly referred to as Jesus Christ or simply as Jesus or Christ, is the central figure of Christianity...
's time, and thus found natural to represent early Christians in association with them: "In Renaissance art, pseudo-Kufic script was used to decorate the costumes of Old Testament
Old Testament
The Old Testament, of which Christians hold different views, is a Christian term for the religious writings of ancient Israel held sacred and inspired by Christians which overlaps with the 24-book canon of the Masoretic Text of Judaism...
heroes like David". Another reason might be that artist wished to express a cultural universality for the Christian faith, by blending together various written languages, at a time when the church had strong international ambitions.
Painting: Islamic carpets in European painting
Islamic carpetCarpet
A carpet is a textile floor covering consisting of an upper layer of "pile" attached to a backing. The pile is generally either made from wool or a manmade fibre such as polypropylene,nylon or polyester and usually consists of twisted tufts which are often heat-treated to maintain their...
s of Middle-Eastern origin, either from the Ottoman Empire
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman EmpireIt was usually referred to as the "Ottoman Empire", the "Turkish Empire", the "Ottoman Caliphate" or more commonly "Turkey" by its contemporaries...
, the Levant
Levant
The Levant or ) is the geographic region and culture zone of the "eastern Mediterranean littoral between Anatolia and Egypt" . The Levant includes most of modern Lebanon, Syria, Jordan, Israel, the Palestinian territories, and sometimes parts of Turkey and Iraq, and corresponds roughly to the...
or the Mamluk
Mamluk
A Mamluk was a soldier of slave origin, who were predominantly Cumans/Kipchaks The "mamluk phenomenon", as David Ayalon dubbed the creation of the specific warrior...
state of Egypt
Egypt
Egypt , officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, Arabic: , is a country mainly in North Africa, with the Sinai Peninsula forming a land bridge in Southwest Asia. Egypt is thus a transcontinental country, and a major power in Africa, the Mediterranean Basin, the Middle East and the Muslim world...
or Northern Africa, were used as important decorative features in paintings from the 13th century onwards, starting from the Medieval period and continuing into the Renaissance period. Such carpets were often integrated into Christian imagery as symbols of luxury and status of Middle-Eastern origin, and together with Pseudo-Kufic
Pseudo-Kufic
Pseudo-Kufic, or Kufesque, also sometimes Pseudo-Arabic, refers to imitations of the Arabic Kufic script, or sometimes Arabic cursive script, made in a non-Arabic context, during the Middle-Ages or the Renaissance: "Imitations of Arabic in European art are often described as pseudo-Kufic, borrowing...
script offer an interesting example of the integration of Eastern elements into European painting.
Music

Musical instrument
A musical instrument is a device created or adapted for the purpose of making musical sounds. In principle, any object that produces sound can serve as a musical instrument—it is through purpose that the object becomes a musical instrument. The history of musical instruments dates back to the...
s used in European music were influenced by Arabic musical instruments, including the rebec
Rebec
The rebecha is a bowed string musical instrument. In its most common form, it has a narrow boat-shaped body and 1-5 strings and is played on the arm or under the chin, like a violin.- Origins :The rebec dates back to the Middle Ages and was particularly popular in the 15th and 16th centuries...
(ancestor of violin
Violin
The violin is a string instrument, usually with four strings tuned in perfect fifths. It is the smallest, highest-pitched member of the violin family of string instruments, which includes the viola and cello....
) from the rebab
Rebab
The rebab , also rebap, rabab, rebeb, rababah, or al-rababa) is a type of string instrument so named no later than the 8th century and spread via Islamic trading routes over much of North Africa, the Middle East, parts of Europe, and the Far East...
, the guitar
Guitar
The guitar is a plucked string instrument, usually played with fingers or a pick. The guitar consists of a body with a rigid neck to which the strings, generally six in number, are attached. Guitars are traditionally constructed of various woods and strung with animal gut or, more recently, with...
from qitara, the naker
Naker
A naker or nakir is a small drum, of Arabic origin, and the forebear of the European timpani .The nakers were imported into Europe during the Crusades of the 13th century....
from naqareh
Naqareh
The naqqāra is a drum with a rounded back and a hide head. It is thus a membranophone.The term naqqāra , also naqqarat, naqqarah, naqqåre, nakkare, nagora comes from the Arabic verb naqr- that means "to strike, beat".-Construction:The rounded section of a naqqara is made of baked clay, while the...
and the shawm
Shawm
The shawm was a medieval and Renaissance musical instrument of the woodwind family made in Europe from the 12th century until the 17th century. It was developed from the oriental zurna and is the predecessor of the modern oboe. The body of the shawm was usually turned from a single piece of wood,...
and dulzaina
Dulzaina
The dulzaina or dolçaina is a Spanish double reed instrument in the oboe family. It has a conical shape and is the equivalent of the Breton bombarde....
from the reed instruments
Reed (instrument)
A reed is a thin strip of material which vibrates to produce a sound on a musical instrument. The reeds of most Woodwind instruments are made from Arundo donax or synthetic material; tuned reeds are made of metal or synthetics.-Single reeds:Single reeds are used on the mouthpieces of clarinets...
zamr and al-zurna
Zurna
The zurna , is a multinational outdoor wind instrument, usually accompanied by a davul in Anatolian folk music. The name is from Turkish zurna, itself derived from Persian سرنای surnāy, composed of sūr “banquet, feast” and nāy “reed, pipe”...
.
There are many different theories regarding the origins of the troubadour
Troubadour
A troubadour was a composer and performer of Old Occitan lyric poetry during the High Middle Ages . Since the word "troubadour" is etymologically masculine, a female troubadour is usually called a trobairitz....
tradition; one of the most commonly-held theories is that it had Arabic origins. William of Aquitaine, the first troubadour whose work survives, had extensive contact with the Islamic world in the Crusade of 1101
Crusade of 1101
The Crusade of 1101 was a minor crusade of three separate movements, organized in 1100 and 1101 in the successful aftermath of the First Crusade. It is also called the Crusade of the Faint-Hearted due to the number of participants who joined this crusade after having turned back from the First...
and in the Reconquista
Reconquista
The Reconquista was a period of almost 800 years in the Middle Ages during which several Christian kingdoms succeeded in retaking the Muslim-controlled areas of the Iberian Peninsula broadly known as Al-Andalus...
in Spain (where he was given a rock crystal vase
Rock crystal vase
A rock crystal vase is a vase made of rock crystal, a type of hardstone carving.Some such vases were rare expensive items, decorated with gold and jewels, used by royalty in Europe....
by a Muslim ally). In his study, Lévi-Provençal
Évariste Lévi-Provençal
Évariste Lévi-Provençal was a French medievalist, orientalist, Arabist, and historian of Islam.Born 4 January 1894 in Constantine, French Algeria, as Makhlóuf Evariste Levi, his name already revealing Gallicized tendencies in his North-African Jewish family...
is said to have found four Arabo-Hispanic verses nearly or completely recopied in William's manuscript. According to historic sources, William VIII
William VIII of Aquitaine
William VIII , born Guy-Geoffrey , was duke of Gascony , and then duke of Aquitaine and count of Poitiers between 1058 and 1086, succeeding his brother William VII ....
, the father of William IX, brought to Poitiers hundreds of Muslim prisoners. The hypothesis that the troubadour tradition was created, more or less, by William after his experience of Moorish arts while fighting with the Reconquista
Reconquista
The Reconquista was a period of almost 800 years in the Middle Ages during which several Christian kingdoms succeeded in retaking the Muslim-controlled areas of the Iberian Peninsula broadly known as Al-Andalus...
in Spain was championed by Ramón Menéndez Pidal
Ramón Menéndez Pidal
Ramón Menéndez Pidal was a Spanish philologist and historian. He worked extensively on the history of the Spanish language and Spanish folklore and folk poetry. One of his main topics was the history and legend of The Cid....
in the early 20th-century, but its origins go back as far as Giammaria Barbieri in the 16th century. Certainly "a body of song of comparable intensity, profanity and eroticism [existed] in Arabic from the second half of the 9th century onwards."
The standard theory on the origins of the Western solfège
Solfege
In music, solfège is a pedagogical solmization technique for the teaching of sight-singing in which each note of the score is sung to a special syllable, called a solfège syllable...
musical notation is that is arose in Italy in the 11th century, but some scholars have argued that the solfège syllables (do, re, mi, fa, sol, la, ti) may have been derived from the syllables of the Arabic solmization
Solmization
Solmization is a system of attributing a distinct syllable to each note in a musical scale. Various forms of solmization are in use and have been used throughout the world.In Europe and North America, solfège is the convention used most often...
system Durr-i-Mufassal ("Separated Pearls") (dal, ra, mim, fa, sad, lam). This origin theory was first proposed by Meninski in his Thesaurus Linguarum Orientalum (1680) and then by Laborde in his Essai sur la Musique Ancienne et Moderne (1780). No documentary evidence has been found to prove this theory however.
Technology
A number of technologies in the Islamic world were adopted in European medieval technologyMedieval technology
Medieval technology refers to the technology used in medieval Europe under Christian rule. After the Renaissance of the 12th century, medieval Europe saw a radical change in the rate of new inventions, innovations in the ways of managing traditional means of production, and economic growth...
. These included various crops; various astronomical instruments, including the Greek astrolabe
Astrolabe
An astrolabe is an elaborate inclinometer, historically used by astronomers, navigators, and astrologers. Its many uses include locating and predicting the positions of the Sun, Moon, planets, and stars, determining local time given local latitude and longitude, surveying, triangulation, and to...
which Arab astronomers developed and refined into such instruments as the Quadrans Vetus, a universal horary quadrant which could be used for any latitude
Latitude
In geography, the latitude of a location on the Earth is the angular distance of that location south or north of the Equator. The latitude is an angle, and is usually measured in degrees . The equator has a latitude of 0°, the North pole has a latitude of 90° north , and the South pole has a...
, and the Saphaea, a universal astrolabe invented by Abū Ishāq Ibrāhīm al-Zarqālī; the astronomical sextant
Sextant (astronomical)
Sextants for astronomical observations were used primarily for measuring the positions of stars. They are little used today, having been replaced over time by transit telescopes, astrometry techniques, and satellites such as Hipparcos....
; various surgical instruments, including refinements on older forms and completely new inventions; and advanced gearing in waterclocks and automata. Distillation
Distillation
Distillation is a method of separating mixtures based on differences in volatilities of components in a boiling liquid mixture. Distillation is a unit operation, or a physical separation process, and not a chemical reaction....
was known to the Greeks and Romans, but was rediscovered in medieval Europe through the Arabs. The words alcohol
Alcohol
In chemistry, an alcohol is an organic compound in which the hydroxy functional group is bound to a carbon atom. In particular, this carbon center should be saturated, having single bonds to three other atoms....
(to describe the liquid produced by distillation) and alembic
Alembic
An alembic is an alchemical still consisting of two vessels connected by a tube...
(via the Greek Ambix) both come from Arab terms. Islamic examples of complex water clocks and automata are believed to have strongly influenced the European craftsmen who produced the first mechanical clocks in the 13th century.
The importation of both the ancient and new technology from the Middle East and the Orient
Orient
The Orient means "the East." It is a traditional designation for anything that belongs to the Eastern world or the Far East, in relation to Europe. In English it is a metonym that means various parts of Asia.- Derivation :...
to Renaissance Europe represented “one of the largest technology transfers in world history.”
In an influential 1974 paper, historian Andrew Watson suggested that there had been an Arab Agricultural Revolution between 700 and 1100, which had diffused a large number of crops and technologies from Spain into medieval Europe, where farming was mostly restricted to wheat strains obtained much earlier via central Asia. Watson listed eighteen crops, including sorghum from Africa, citrus fruits from China, and numerous crops from India such as mangos, rice, cotton and sugar cane, which were distributed throughout Islamic lands that, according to Watson, had previously not grown them. Watson argued that these introductions, along with an increased mechanization of agriculture, led to major changes in economy, population distribution, vegetation cover, agricultural production and income, population levels, urban growth, the distribution of the labour force, linked industries, cooking, diet and clothing in the Islamic world. Also transmitted via Muslim influence, a silk industry flourished, flax was cultivated and linen exported, and esparto
Esparto
Esparto, or esparto grass, also known as "halfah grass" or "needle grass", Macrochloa tenacissima and Stipa tenacissima, is a perennial grass grown in northwest Africa and the southern part of the Iberian Peninsula employed for crafts .-Esparto paper:It is also used for fiber production for paper...
grass, which grew wild in the more arid parts, was collected and turned into various articles. However Michael Decker has challenged significant parts of Watson's thesis, including whether all these crops were introduced to Europe during this period. Decker used literary and archaeological evidence to suggest that four of the listed crops (i.e. durum wheat, Asiatic rice, sorghum and cotton) were common centuries before the Islamic period, that the crops which were new were not as important as Watson had suggested, and generally arguing that Islamic agricultural practices in areas such as irrigation were more of an evolution from those of the ancient world than the revolution suggested by Watson.
The production of sugar
Sugar
Sugar is a class of edible crystalline carbohydrates, mainly sucrose, lactose, and fructose, characterized by a sweet flavor.Sucrose in its refined form primarily comes from sugar cane and sugar beet...
from sugar cane, water clocks
Water clock
A water clock or clepsydra is any timepiece in which time is measured by the regulated flow of liquid into or out from a vessel where the amount is then measured.Water clocks, along with sundials, are likely to be the oldest time-measuring instruments, with the only exceptions...
, pulp
Pulp (paper)
Pulp is a lignocellulosic fibrous material prepared by chemically or mechanically separating cellulose fibres from wood, fibre crops or waste paper. Wood pulp is the most common raw material in papermaking.-History:...
and paper
Paper
Paper is a thin material mainly used for writing upon, printing upon, drawing or for packaging. It is produced by pressing together moist fibers, typically cellulose pulp derived from wood, rags or grasses, and drying them into flexible sheets....
, silk
Silk
Silk is a natural protein fiber, some forms of which can be woven into textiles. The best-known type of silk is obtained from the cocoons of the larvae of the mulberry silkworm Bombyx mori reared in captivity...
, and various advances in making perfume
Perfume
Perfume is a mixture of fragrant essential oils and/or aroma compounds, fixatives, and solvents used to give the human body, animals, objects, and living spaces "a pleasant scent"...
, were transferred from the Islamic world to medieval Europe. Fulling
Fulling
Fulling or tucking or walking is a step in woolen clothmaking which involves the cleansing of cloth to eliminate oils, dirt, and other impurities, and making it thicker. The worker who does the job is a fuller, tucker, or walker...
mills and advances in mill technology may have also been transmitted from the Islamic world to medieval Europe, along with the large scale use of inventions like the suction
Suction
Suction is the flow of a fluid into a partial vacuum, or region of low pressure. The pressure gradient between this region and the ambient pressure will propel matter toward the low pressure area. Suction is popularly thought of as an attractive effect, which is incorrect since vacuums do not...
pump
Pump
A pump is a device used to move fluids, such as liquids, gases or slurries.A pump displaces a volume by physical or mechanical action. Pumps fall into three major groups: direct lift, displacement, and gravity pumps...
, noria
Noria
A noria is a machine for lifting water into a small aqueduct, either for the purpose of irrigation or, in at least one known instance, to feed seawater into a saltern....
and chain pumps for irrigation purposes. According to Watson, "The Islamic contribution was less in the invention of new devices than in the application on a much wider scale of devices which in pre-Islamic times had been used only over limited areas and to a limited extent." These innovations made it possible for some industrial operations that were previously served by manual labour or draught animals to be driven by machinery in medieval Europe.
Coinage

Ancient Rome
Ancient Rome was a thriving civilization that grew on the Italian Peninsula as early as the 8th century BC. Located along the Mediterranean Sea and centered on the city of Rome, it expanded to one of the largest empires in the ancient world....
had widely-circulated currency, Islamic coinage had some influence on Medieval European minting. The 8th century English king Offa of Mercia
Offa of Mercia
Offa was the King of Mercia from 757 until his death in July 796. The son of Thingfrith and a descendant of Eowa, Offa came to the throne after a period of civil war following the assassination of Æthelbald after defeating the other claimant Beornred. In the early years of Offa's reign it is likely...
minted a near-copy of Abbasid dinars struck in 774 by Caliph Al-Mansur
Al-Mansur
Al-Mansur, Almanzor or Abu Ja'far Abdallah ibn Muhammad al-Mansur was the second Abbasid Caliph from 136 AH to 158 AH .-Biography:...
with "Offa Rex" centered on the reverse. The moneyer visibly had little understanding of Arabic
Arabic language
Arabic is a name applied to the descendants of the Classical Arabic language of the 6th century AD, used most prominently in the Quran, the Islamic Holy Book...
as the Arabic text contains a number of errors.

Sicily
Sicily is a region of Italy, and is the largest island in the Mediterranean Sea. Along with the surrounding minor islands, it constitutes an autonomous region of Italy, the Regione Autonoma Siciliana Sicily has a rich and unique culture, especially with regard to the arts, music, literature,...
, Malta
Malta
Malta , officially known as the Republic of Malta , is a Southern European country consisting of an archipelago situated in the centre of the Mediterranean, south of Sicily, east of Tunisia and north of Libya, with Gibraltar to the west and Alexandria to the east.Malta covers just over in...
and South Italy
South Italy
South Italy is one of the five official statistical regions of Italy used by the National Institute of Statistics , a first level NUTS region and a European Parliament constituency. South Italy encompasses six of the country's 20 regions:*Abruzzo...
from about 913 tarì
Tarì
A tarì was the Christian designation of a type of gold coin of Islamic origin minted in Sicily, Malta and South Italy from about 913 to 1859.-History:...
gold coins of Islamic origin were minted in great number by the Normans
Normans
The Normans were the people who gave their name to Normandy, a region in northern France. They were descended from Norse Viking conquerors of the territory and the native population of Frankish and Gallo-Roman stock...
, Hohenstaufen
Hohenstaufen
The House of Hohenstaufen was a dynasty of German kings in the High Middle Ages, lasting from 1138 to 1254. Three of these kings were also crowned Holy Roman Emperor. In 1194 the Hohenstaufens also became Kings of Sicily...
s and the early Angevins
Capetian House of Anjou
The Capetian House of Anjou, also known as the House of Anjou-Sicily and House of Anjou-Naples, was a royal house and cadet branch of the direct House of Capet. Founded by Charles I of Sicily, a son of Louis VIII of France, the Capetian king first ruled the Kingdom of Sicily during the 13th century...
rulers. When the Normans invaded Sicily in the 12th century, they issued tarì coins bearing legends in Arabic and Latin
Latin
Latin is an Italic language originally spoken in Latium and Ancient Rome. It, along with most European languages, is a descendant of the ancient Proto-Indo-European language. Although it is considered a dead language, a number of scholars and members of the Christian clergy speak it fluently, and...
. The tarìs were so widespread that imitations were made in southern Italy (Amalfi
Amalfi
Amalfi is a town and comune in the province of Salerno, in the region of Campania, Italy, on the Gulf of Salerno, c. 35 km southeast of Naples. It lies at the mouth of a deep ravine, at the foot of Monte Cerreto , surrounded by dramatic cliffs and coastal scenery...
and Salerno
Salerno
Salerno is a city and comune in Campania and is the capital of the province of the same name. It is located on the Gulf of Salerno on the Tyrrhenian Sea....
) which only used illegible "pseudo-Kufic" imitations of Arabic.
According to Janet Abu-Lughod
Janet Abu-Lughod
Janet L. Abu-Lughod, née Lippman is an American sociologist with major contributions to World-systems theory and Urban sociology.-Family:She was married in 1951–1991 to Ibrahim Abu-Lughod...
:
The preferred specie for international transactions before the thirteenth century, in Europe as well as the Middle East and even India, were the gold coins struck by ByzantiumByzantiumByzantium was an ancient Greek city, founded by Greek colonists from Megara in 667 BC and named after their king Byzas . The name Byzantium is a Latinization of the original name Byzantion...
and then EgyptEgyptEgypt , officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, Arabic: , is a country mainly in North Africa, with the Sinai Peninsula forming a land bridge in Southwest Asia. Egypt is thus a transcontinental country, and a major power in Africa, the Mediterranean Basin, the Middle East and the Muslim world...
. It was not until after the thirtheenth century that some Italian cities (FlorenceFlorenceFlorence is the capital city of the Italian region of Tuscany and of the province of Florence. It is the most populous city in Tuscany, with approximately 370,000 inhabitants, expanding to over 1.5 million in the metropolitan area....
and GenoaGenoaGenoa |Ligurian]] Zena ; Latin and, archaically, English Genua) is a city and an important seaport in northern Italy, the capital of the Province of Genoa and of the region of Liguria....
) began to mint their own gold coins, but these were used to supplement rather than supplant the Middle Eastern coins already in circulation.
Literature
It was first suggested by Miguel Asín PalaciosMiguel Asin Y Palacios
Miguel Asín Palacios was a Spanish scholar of Islamic studies and the Arabic language, and a Roman Catholic priest. He is primarily known for suggesting Muslim sources for ideas and motifs present in Dante's Divine Comedy, which he discusses in his book La Escatología musulmana en la Divina Comedia...
in 1919 that Dante Alighieri
Dante Alighieri
Durante degli Alighieri, mononymously referred to as Dante , was an Italian poet, prose writer, literary theorist, moral philosopher, and political thinker. He is best known for the monumental epic poem La commedia, later named La divina commedia ...
's Divine Comedy, considered the greatest epic of Italian literature
Italian literature
Italian literature is literature written in the Italian language, particularly within Italy. It may also refer to literature written by Italians or in Italy in other languages spoken in Italy, often languages that are closely related to modern Italian....
, derived many features of and episodes about the hereafter directly or indirectly from Arabic works on Islamic eschatology
Islamic eschatology
Islamic eschatology is concerned with the al-Qiyāmah . Like the other Abrahamic religions, Islam teaches the bodily resurrection of the dead, the fulfillment of a divine plan for creation, and the judgement of the soul; the righteous are rewarded with the pleasures of Jannah while the unrighteous...
, such as the Hadith
Hadith
The term Hadīth is used to denote a saying or an act or tacit approval or criticism ascribed either validly or invalidly to the Islamic prophet Muhammad....
and the spiritual writings of Ibn Arabi
Ibn Arabi
Ibn ʿArabī was an Andalusian Moorish Sufi mystic and philosopher. His full name was Abū 'Abdillāh Muḥammad ibn 'Alī ibn Muḥammad ibn `Arabī .-Biography:...
. The Kitab al-Miraj, concerning Muhammad
Muhammad
Muhammad |ligature]] at U+FDF4 ;Arabic pronunciation varies regionally; the first vowel ranges from ~~; the second and the last vowel: ~~~. There are dialects which have no stress. In Egypt, it is pronounced not in religious contexts...
's ascension to Heaven, was translated into Latin in 1264 or shortly before as Liber Scale Machometi, "The Book of Muhammad's Ladder". Dante was certainly aware of Muslim philosophy, naming Avicenna
Avicenna
Abū ʿAlī al-Ḥusayn ibn ʿAbd Allāh ibn Sīnā , commonly known as Ibn Sīnā or by his Latinized name Avicenna, was a Persian polymath, who wrote almost 450 treatises on a wide range of subjects, of which around 240 have survived...
and Averroes
Averroes
' , better known just as Ibn Rushd , and in European literature as Averroes , was a Muslim polymath; a master of Aristotelian philosophy, Islamic philosophy, Islamic theology, Maliki law and jurisprudence, logic, psychology, politics, Arabic music theory, and the sciences of medicine, astronomy,...
last in his list of non-Christian philosophers in Limbo, alongside the great Greek and Latin philosophers. How strong the similarities are to Kitab al-Miraj remains a matter of scholarly debate however, with no clear evidence that Dante was in fact influenced. Francesco Gabrieli described it as "at least possible, if not probable" that Dante may have taken certain images and concepts from Muslim eschatology.
Philosophy
From Islamic SpainAl-Andalus
Al-Andalus was the Arabic name given to a nation and territorial region also commonly referred to as Moorish Iberia. The name describes parts of the Iberian Peninsula and Septimania governed by Muslims , at various times in the period between 711 and 1492, although the territorial boundaries...
, the Arabic philosophical literature
Early Islamic philosophy
Early Islamic philosophy or classical Islamic philosophy is a period of intense philosophical development beginning in the 2nd century AH of the Islamic calendar and lasting until the 6th century AH...
was translated into Hebrew
Hebrew language
Hebrew is a Semitic language of the Afroasiatic language family. Culturally, is it considered by Jews and other religious groups as the language of the Jewish people, though other Jewish languages had originated among diaspora Jews, and the Hebrew language is also used by non-Jewish groups, such...
, Latin
Latin
Latin is an Italic language originally spoken in Latium and Ancient Rome. It, along with most European languages, is a descendant of the ancient Proto-Indo-European language. Although it is considered a dead language, a number of scholars and members of the Christian clergy speak it fluently, and...
, and Ladino, contributing to the development of modern European philosophy. The Jewish philosopher Moses Maimonides, Muslim sociologist-historian Ibn Khaldun
Ibn Khaldun
Ibn Khaldūn or Ibn Khaldoun was an Arab Tunisian historiographer and historian who is often viewed as one of the forerunners of modern historiography, sociology and economics...
, Carthage
Carthage
Carthage , implying it was a 'new Tyre') is a major urban centre that has existed for nearly 3,000 years on the Gulf of Tunis, developing from a Phoenician colony of the 1st millennium BC...
citizen Constantine the African
Constantine the African
Constantine the African was a Tunisian doctor of the eleventh century. The first part of his life was spent in Tunisia and the rest in Italy. In Salerno, Italy, he became a professor of medicine and his work attracted widespread attention...
who translated Greek
Greek language
Greek is an independent branch of the Indo-European family of languages. Native to the southern Balkans, it has the longest documented history of any Indo-European language, spanning 34 centuries of written records. Its writing system has been the Greek alphabet for the majority of its history;...
medical texts, and the Muslim Al-Khwarizmi's collation of mathematical techniques were important figures of the Golden Age.

Avicenna
Abū ʿAlī al-Ḥusayn ibn ʿAbd Allāh ibn Sīnā , commonly known as Ibn Sīnā or by his Latinized name Avicenna, was a Persian polymath, who wrote almost 450 treatises on a wide range of subjects, of which around 240 have survived...
founded the Avicennism school of philosophy, which was influential in both Islamic and Christian lands. He was an important commentator on the works of Aristotle
Aristotle
Aristotle was a Greek philosopher and polymath, a student of Plato and teacher of Alexander the Great. His writings cover many subjects, including physics, metaphysics, poetry, theater, music, logic, rhetoric, linguistics, politics, government, ethics, biology, and zoology...
, modifying it with his own original thinking in some areas, notably logic. The main significance of Latin
Latin
Latin is an Italic language originally spoken in Latium and Ancient Rome. It, along with most European languages, is a descendant of the ancient Proto-Indo-European language. Although it is considered a dead language, a number of scholars and members of the Christian clergy speak it fluently, and...
Avicennism lies in the interpretation of Avicennian doctrines such as the nature of the soul
Soul
A soul in certain spiritual, philosophical, and psychological traditions is the incorporeal essence of a person or living thing or object. Many philosophical and spiritual systems teach that humans have souls, and others teach that all living things and even inanimate objects have souls. The...
and his existence
Existence
In common usage, existence is the world we are aware of through our senses, and that persists independently without them. In academic philosophy the word has a more specialized meaning, being contrasted with essence, which specifies different forms of existence as well as different identity...
-essence
Essence
In philosophy, essence is the attribute or set of attributes that make an object or substance what it fundamentally is, and which it has by necessity, and without which it loses its identity. Essence is contrasted with accident: a property that the object or substance has contingently, without...
distinction, along with the debates and censure that they raised in scholastic Europe
Scholasticism
Scholasticism is a method of critical thought which dominated teaching by the academics of medieval universities in Europe from about 1100–1500, and a program of employing that method in articulating and defending orthodoxy in an increasingly pluralistic context...
. This was particularly the case in Paris
Paris
Paris is the capital and largest city in France, situated on the river Seine, in northern France, at the heart of the Île-de-France region...
, where Avicennism was later proscribed in 1210, though the influence of his psychology and theory of knowledge upon William of Auvergne
William of Auvergne
William of Auvergne may refer to:* William of Auvergne, Bishop of Paris * William IV of Auvergne * William V of Auvergne...
and Albertus Magnus
Albertus Magnus
Albertus Magnus, O.P. , also known as Albert the Great and Albert of Cologne, is a Catholic saint. He was a German Dominican friar and a bishop, who achieved fame for his comprehensive knowledge of and advocacy for the peaceful coexistence of science and religion. Those such as James A. Weisheipl...
have been noted. The effects of Avicennism in Christianity
Christianity
Christianity is a monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus as presented in canonical gospels and other New Testament writings...
, however, was later submerged by Averroism
Averroism
Averroism is the term applied to either of two philosophical trends among scholastics in the late 13th century: the Arab philosopher Averroës or Ibn Rushd's interpretations of Aristotle and his reconciliation of Aristotelianism with Islamic faith; and the application of these ideas in the Latin...
, a school of philosophy founded by Averroes
Averroes
' , better known just as Ibn Rushd , and in European literature as Averroes , was a Muslim polymath; a master of Aristotelian philosophy, Islamic philosophy, Islamic theology, Maliki law and jurisprudence, logic, psychology, politics, Arabic music theory, and the sciences of medicine, astronomy,...
, one of the most influential Muslim philosophers in the West. Averroes disagreed with Avicenna's interpretations of Aristotle in areas such as the unity of the intellect, and it was his interpretation of Aristotle which had the most influence in medieval Europe. Dante Aligheri argues along Averroist lines for a secularist theory of the state in De Monarchia. Averroes also developed the concept of "existence precedes essence
Existence precedes essence
The proposition that existence precedes essence is a central claim of existentialism, which reverses the traditional philosophical view that the essence or nature of a thing is more fundamental and immutable than its existence...
".
Al-Ghazali
Al-Ghazali
Abu Hāmed Mohammad ibn Mohammad al-Ghazzālī , known as Algazel to the western medieval world, born and died in Tus, in the Khorasan province of Persia was a Persian Muslim theologian, jurist, philosopher, and mystic....
also had an important influence on Christian
Christian
A Christian is a person who adheres to Christianity, an Abrahamic, monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth as recorded in the Canonical gospels and the letters of the New Testament...
medieval philosophers
Medieval philosophy
Medieval philosophy is the philosophy in the era now known as medieval or the Middle Ages, the period roughly extending from the fall of the Western Roman Empire in the fifth century AD to the Renaissance in the sixteenth century...
along with Jewish thinkers like Maimonides
Maimonides
Moses ben-Maimon, called Maimonides and also known as Mūsā ibn Maymūn in Arabic, or Rambam , was a preeminent medieval Jewish philosopher and one of the greatest Torah scholars and physicians of the Middle Ages...
. According to Margaret Smith
Margaret Smith (author)
Margaret Smith was a scholar writing on early Christian and Muslim mysticism, presenting a view from an open-minded Christian perspective...
, "There can be no doubt that Ghazali’s works would be among the first to attract the attention of these European scholars" and "The greatest of these Christian writers who was influenced by Al-Ghazali was St. Thomas Aquinas
Thomas Aquinas
Thomas Aquinas, O.P. , also Thomas of Aquin or Aquino, was an Italian Dominican priest of the Catholic Church, and an immensely influential philosopher and theologian in the tradition of scholasticism, known as Doctor Angelicus, Doctor Communis, or Doctor Universalis...
(1225–1274), who made a study of the Islamic writers and admitted his indebtedness to them. He studied at the University of Naples where the influence of Islamic literature and culture was predominant at the time."

Renaissance humanism
Renaissance humanism was an activity of cultural and educational reform engaged by scholars, writers, and civic leaders who are today known as Renaissance humanists. It developed during the fourteenth and the beginning of the fifteenth centuries, and was a response to the challenge of Mediæval...
have their roots in the medieval Islamic world
Islamic Golden Age
During the Islamic Golden Age philosophers, scientists and engineers of the Islamic world contributed enormously to technology and culture, both by preserving earlier traditions and by adding their own inventions and innovations...
, the "art of dictation
Dictation (exercise)
Dictation is the transcription of spoken text: one person who is "dictating" speaks and another who is "taking dictation" writes down the words as they are spoken.-La dictée:...
, called in Latin
Latin
Latin is an Italic language originally spoken in Latium and Ancient Rome. It, along with most European languages, is a descendant of the ancient Proto-Indo-European language. Although it is considered a dead language, a number of scholars and members of the Christian clergy speak it fluently, and...
, ars dictaminis
Ars dictaminis
The ars dictaminis was the medieval description of the art of prose composition, and more specifically of the writing of letters . It is closely linked to the ars dictandi, covering the composition of documents other than letters. The standing assumption was that these writings would be composed in...
,"
and "the humanist attitude toward classical language
Classical language
A classical language is a language with a literature that is classical. According to UC Berkeley linguist George L. Hart, it should be ancient, it should be an independent tradition that arose mostly on its own, not as an offshoot of another tradition, and it must have a large and extremely rich...
". He notes that dictation was a necessary part of Arabic scholarship (where the vowel sounds need to be added correctly based on the spoken word), and argues that the medieval Italian use of the term "ars dictaminis" makes best sense in this context. He also believes that the medieval humanist favouring of classical Latin over medieval Latin makes most sense in the context of a reaction to Arabic scholarship, with its study of the classical Arabic of the Koran in preference to medieval Arabic.
Vocabulary
The adoption of the techniques and materials from the Islamic world is reflected in the origin of many of the Arabic words now in use in the Western world.- AdmiralAdmiralAdmiral is the rank, or part of the name of the ranks, of the highest naval officers. It is usually considered a full admiral and above vice admiral and below admiral of the fleet . It is usually abbreviated to "Adm" or "ADM"...
, from amir al-bahr امير البحر (“Prince of the sea”) - AlchemyAlchemyAlchemy is an influential philosophical tradition whose early practitioners’ claims to profound powers were known from antiquity. The defining objectives of alchemy are varied; these include the creation of the fabled philosopher's stone possessing powers including the capability of turning base...
/ ChemistryChemistryChemistry is the science of matter, especially its chemical reactions, but also its composition, structure and properties. Chemistry is concerned with atoms and their interactions with other atoms, and particularly with the properties of chemical bonds....
, from al kemiya (الكيمياء) - AlgebraAlgebraAlgebra is the branch of mathematics concerning the study of the rules of operations and relations, and the constructions and concepts arising from them, including terms, polynomials, equations and algebraic structures...
, which comes from al-djabr (الجبر) - AlgorithmAlgorithmIn mathematics and computer science, an algorithm is an effective method expressed as a finite list of well-defined instructions for calculating a function. Algorithms are used for calculation, data processing, and automated reasoning...
, from the name of the scientist al-Khwarizmi (الخوارزمي) - AlmanacAlmanacAn almanac is an annual publication that includes information such as weather forecasts, farmers' planting dates, and tide tables, containing tabular information in a particular field or fields often arranged according to the calendar etc...
, from al-manakh (المناخ) (timetables) - AmberAmberAmber is fossilized tree resin , which has been appreciated for its color and natural beauty since Neolithic times. Amber is used as an ingredient in perfumes, as a healing agent in folk medicine, and as jewelry. There are five classes of amber, defined on the basis of their chemical constituents...
, from Anbar (عنبر) - ArtichokeArtichoke-Plants:* Globe artichoke, a partially edible perennial thistle originating in southern Europe around the Mediterranean* Jerusalem artichoke, a species of sunflower with an edible tuber...
, from ard-i-choke (أرضِ شوكي) - Avarie (French for "ship damage"), from awar (عَوَر) ("damage")
- Baldaquin, from a tissue material made in Baghdad
- CamphorCamphorCamphor is a waxy, white or transparent solid with a strong, aromatic odor. It is a terpenoid with the chemical formula C10H16O. It is found in wood of the camphor laurel , a large evergreen tree found in Asia and also of Dryobalanops aromatica, a giant of the Bornean forests...
, from kafur - Carat (unit), from qīrāṭ (قيراط) ("mass")
- CoffeeCoffeeCoffee is a brewed beverage with a dark,init brooo acidic flavor prepared from the roasted seeds of the coffee plant, colloquially called coffee beans. The beans are found in coffee cherries, which grow on trees cultivated in over 70 countries, primarily in equatorial Latin America, Southeast Asia,...
, from Kahwa (قهوة) - CottonCottonCotton is a soft, fluffy staple fiber that grows in a boll, or protective capsule, around the seeds of cotton plants of the genus Gossypium. The fiber is almost pure cellulose. The botanical purpose of cotton fiber is to aid in seed dispersal....
, from koton (قطن) - GauzeGauzeGauze is a thin, translucent fabric with a loose open weave.-Uses and types:Gauze was originally made of silk and was used for clothing. It is now used for many different things, including gauze sponges for medical purposes. When used as a medical dressing, gauze is generally made of cotton...
, from qazz (قز) ("raw silk") - HazardHazardA hazard is a situation that poses a level of threat to life, health, property, or environment. Most hazards are dormant or potential, with only a theoretical risk of harm; however, once a hazard becomes "active", it can create an emergency situation. A hazard does not exist when it is not...
, from az-zahr (الزهر) (game of dice) - LacquerLacquerIn a general sense, lacquer is a somewhat imprecise term for a clear or coloured varnish that dries by solvent evaporation and often a curing process as well that produces a hard, durable finish, in any sheen level from ultra matte to high gloss and that can be further polished as required...
, from lakk - LuteLuteLute can refer generally to any plucked string instrument with a neck and a deep round back, or more specifically to an instrument from the family of European lutes....
, from al-ud (العود) - MagazineMagazineMagazines, periodicals, glossies or serials are publications, generally published on a regular schedule, containing a variety of articles. They are generally financed by advertising, by a purchase price, by pre-paid magazine subscriptions, or all three...
, from makhâzin (مخازن) - MateCheckmateCheckmate is a situation in chess in which one player's king is threatened with capture and there is no way to meet that threat. Or, simply put, the king is under direct attack and cannot avoid being captured...
(as in "Checkmate"), from mât (مات) ("Death") - OrangeOrange (word)The word orange is both a noun and an adjective in the English language. In both cases, it refers primarily to the orange fruit and the colour orange, but has many other derivative meanings....
, from nârandj (نارنج) - RacketRacketRacket may refer to:*Racket , a systematised element of organized crime*Rackets , a ball game*Racquet, a piece of equipment used to play tennis*Racket with Michele Placido, Tanya Roberts and Franco Interlenghi...
, from râhat (راحات) (palm of the hand) - Sorbet, from sharab (شراب \ شربة)
- SugarSugarSugar is a class of edible crystalline carbohydrates, mainly sucrose, lactose, and fructose, characterized by a sweet flavor.Sucrose in its refined form primarily comes from sugar cane and sugar beet...
, from soukkar (سكّر) - Zero, from Greek zephyrus which comes from şifr (صفر) ("zero")
External links
- Islamic Contributions to the West by Rachida El Diwani, Professor of Comparative Literature.
- "How Greek Science Passed to the Arabs" by De Lacy O'Leary
- Islamic Contributions to Civilization by Stanwood CobbStanwood CobbStanwood Cobb was an American educator, author and prominent Bahá'í of the 20th century.He was born in Newton, Massachusetts to Darius Cobb - a Civil War soldier, artist and descendent of Elder Henry Cobb of the second voyage of the Mayflower - and Eunice Hale - founding president of the Ladies...
(1963)

