
History of primitive and non-Western trumpets
Encyclopedia

Trumpet
The trumpet is the musical instrument with the highest register in the brass family. Trumpets are among the oldest musical instruments, dating back to at least 1500 BCE. They are played by blowing air through closed lips, producing a "buzzing" sound which starts a standing wave vibration in the air...
of Western
Western culture
Western culture, sometimes equated with Western civilization or European civilization, refers to cultures of European origin and is used very broadly to refer to a heritage of social norms, ethical values, traditional customs, religious beliefs, political systems, and specific artifacts and...
tradition is a fairly recent invention, but primitive trumpets of one form or another have been in existence for millennia; some of the predecessors of the modern instrument are now known to date back to the Neolithic
Neolithic
The Neolithic Age, Era, or Period, or New Stone Age, was a period in the development of human technology, beginning about 9500 BC in some parts of the Middle East, and later in other parts of the world. It is traditionally considered as the last part of the Stone Age...
era. The earliest of these primordial trumpets were adapted from animal horns
Horn (anatomy)
A horn is a pointed projection of the skin on the head of various animals, consisting of a covering of horn surrounding a core of living bone. True horns are found mainly among the ruminant artiodactyls, in the families Antilocapridae and Bovidae...
and sea shells, and were common throughout Europe
Europe
Europe is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting...
, Africa
Africa
Africa is the world's second largest and second most populous continent, after Asia. At about 30.2 million km² including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of the Earth's total surface area and 20.4% of the total land area...
, India
India
India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
and, to a lesser extent, the Middle East
Middle East
The Middle East is a region that encompasses Western Asia and Northern Africa. It is often used as a synonym for Near East, in opposition to Far East...
. Primitive trumpets eventually found their way to most parts of the globe, though even today indigenous varieties are quite rare in the Americas
Americas
The Americas, or America , are lands in the Western hemisphere, also known as the New World. In English, the plural form the Americas is often used to refer to the landmasses of North America and South America with their associated islands and regions, while the singular form America is primarily...
, the Far East
Far East
The Far East is an English term mostly describing East Asia and Southeast Asia, with South Asia sometimes also included for economic and cultural reasons.The term came into use in European geopolitical discourse in the 19th century,...
and South-East Asia. Some species of primitive trumpets can still be found in remote places, where they have remained largely untouched by the passage of time.
For the most part, these primitive instruments were “natural” trumpets: that is to say, they had none of those devices (fingerholes, key
Key (instrument)
A key is a specific part of a musical instrument. The purpose and function of the part in question depends on the instrument.On instruments equipped with tuning machines, violins and guitars, for example, a key is part of a tuning machine. It is a worm gear with a key shaped end used to turn a cog,...
s, slide
Slide
-Fiction:*Slide, a fictional creature in the Sword of Truth book series-Music:*Slides , an album by Richard Harris *Slide , an album by Lisa Germano*Slide , a single by the Goo Goo Dolls...
s or valve
Valve
A valve is a device that regulates, directs or controls the flow of a fluid by opening, closing, or partially obstructing various passageways. Valves are technically pipe fittings, but are usually discussed as a separate category...
s) by which the pitch
Pitch (music)
Pitch is an auditory perceptual property that allows the ordering of sounds on a frequency-related scale.Pitches are compared as "higher" and "lower" in the sense associated with musical melodies,...
of an instrument might be altered. It is in fact quite exceptional to come across a chromatic trumpet – primitive or otherwise – which is not derived from the chromatic trumpet of Western tradition; the bãs of Madhya Pradesh
Madhya Pradesh
Madhya Pradesh , often called the Heart of India, is a state in central India. Its capital is Bhopal and Indore is the largest city....
in India, which has fingerholes bored into the side of its tube, is one such exception.
Primitive trumpets
The simplest – and presumably the earliest – type of trumpet was made from the hollowed-out hornHorn (anatomy)
A horn is a pointed projection of the skin on the head of various animals, consisting of a covering of horn surrounding a core of living bone. True horns are found mainly among the ruminant artiodactyls, in the families Antilocapridae and Bovidae...
or shell of an animal, into the end of which a hole was bored for the mouth. This “trumpet” had neither a mouthpiece
Mouthpiece (brass)
On brass instruments the mouthpiece is the part of the instrument which is placed upon the player's lips. The purpose of the mouthpiece is a resonator, which passes vibration from the lips to the column of air contained within the instrument, giving rise to the standing wave pattern of vibration in...
nor a bell, and was not so much a musical instrument as a megaphone
Megaphone
A megaphone, speaking-trumpet, bullhorn, blowhorn, or loud hailer is a portable, usually hand-held, cone-shaped horn used to amplify a person’s voice or other sounds towards a targeted direction. This is accomplished by channelling the sound through the megaphone, which also serves to match the...
into which one spoke, sang, or shouted. The intention was to distort the voice and produce a harsh, unnatural sound to ward off evil spirits or disconcert one’s enemies. Only later was the trumpet used to invoke friendly gods or to encourage one’s own warriors on the battlefield. Typically only one or two different pitches could be produced on such an instrument, though sometimes a small fingerhole was bored in the tip to provide the player with an extra pitch
Pitch (music)
Pitch is an auditory perceptual property that allows the ordering of sounds on a frequency-related scale.Pitches are compared as "higher" and "lower" in the sense associated with musical melodies,...
. Most of these early trumpets were end-blown, like the modern trumpet; side-blown varieties, however, were not unknown, and can still be found in Africa and other parts of the globe.
Primitive trumpets were mainly used in religious ceremonies and magic rituals. As they were played only by men, they probably acquired strong phallic
Phallus
A phallus is an erect penis, a penis-shaped object such as a dildo, or a mimetic image of an erect penis. Any object that symbolically resembles a penis may also be referred to as a phallus; however, such objects are more often referred to as being phallic...
overtones; among certain aboriginal tribes, for example, it was a capital offense for a woman to look at a trumpet. The tradition of playing trumpet or bugle
Bugle (instrument)
The bugle is one of the simplest brass instruments, having no valves or other pitch-altering devices. All pitch control is done by varying the player's embouchure, since the bugle has no other mechanism for controlling pitch. Consequently, the bugle is limited to notes within the harmonic series...
fanfare
Fanfare
A Fanfare is a relatively short piece of music that is typically played by trumpets and other brass instruments often accompanied by percussion...
s at sunrise (Reveille
Reveille
"Reveille" is a bugle call, trumpet call or pipes call most often associated with the military or summer camp; it is chiefly used to wake military personnel at sunrise...
), sunset (Last Post
Last Post
The "Last Post" can be either a B♭ bugle call within British Infantry regiments or an E♭ cavalry trumpet call in British Cavalry and Royal Regiment of Artillery used at Commonwealth military funerals and ceremonies commemorating those who have been killed in war.The two regimental traditions have...
), and at funerals (Taps
Taps
"Taps" is a musical piece sounded by the U.S. military nightly to indicate that it is "lights out". The tune is also sometimes known as "Butterfields Lullaby", or by the lyrics of its second verse, "Day is Done". It is also played during flag ceremonies and funerals, generally on bugle or trumpet...
), probably evolved from these ancient rituals.
The use of the trumpet as an instrument of warfare and the chase
Hunting
Hunting is the practice of pursuing any living thing, usually wildlife, for food, recreation, or trade. In present-day use, the term refers to lawful hunting, as distinguished from poaching, which is the killing, trapping or capture of the hunted species contrary to applicable law...
is probably as old. Its strident sound and animal origins must have suggested a wild or belligerent nature at a very early date, while the ritualistic uses to which it was put only served to strengthen its associations with death and male-oriented activities.
Animal-horn trumpets
Animal-horn trumpets are still employed today, especially in Africa, though they are also found in IsraelIsrael
The State of Israel is a parliamentary republic located in the Middle East, along the eastern shore of the Mediterranean Sea...
, Asia
Asia
Asia is the world's largest and most populous continent, located primarily in the eastern and northern hemispheres. It covers 8.7% of the Earth's total surface area and with approximately 3.879 billion people, it hosts 60% of the world's current human population...
and Oceania
Oceania
Oceania is a region centered on the islands of the tropical Pacific Ocean. Conceptions of what constitutes Oceania range from the coral atolls and volcanic islands of the South Pacific to the entire insular region between Asia and the Americas, including Australasia and the Malay Archipelago...
. With the exception of African varieties, most are end-blown instruments from which the tip has been removed to provide a mouthhole. In the majority of cases the player’s lips are applied directly to the mouthhole; sometimes, however, the instrument has a detachable mouthpiece
Mouthpiece (brass)
On brass instruments the mouthpiece is the part of the instrument which is placed upon the player's lips. The purpose of the mouthpiece is a resonator, which passes vibration from the lips to the column of air contained within the instrument, giving rise to the standing wave pattern of vibration in...
. Cattle, sheep, goat
Goat
The domestic goat is a subspecies of goat domesticated from the wild goat of southwest Asia and Eastern Europe. The goat is a member of the Bovidae family and is closely related to the sheep as both are in the goat-antelope subfamily Caprinae. There are over three hundred distinct breeds of...
s and antelope
Antelope
Antelope is a term referring to many even-toed ungulate species indigenous to various regions in Africa and Eurasia. Antelopes comprise a miscellaneous group within the family Bovidae, encompassing those old-world species that are neither cattle, sheep, buffalo, bison, nor goats...
s are among the animals whose horns are – or have been – most frequently used to make such trumpets. The following examples may be briefly noted:
- The SumerianSumerian languageSumerian is the language of ancient Sumer, which was spoken in southern Mesopotamia since at least the 4th millennium BC. During the 3rd millennium BC, there developed a very intimate cultural symbiosis between the Sumerians and the Akkadians, which included widespread bilingualism...
si was the ordinary word for animal horn. Literary references show that as an instrument it was played in the streets by the herald who delivered public announcements. - The JewishHistory of ancient Israel and JudahIsrael and Judah were related Iron Age kingdoms of ancient Palestine. The earliest known reference to the name Israel in archaeological records is in the Merneptah stele, an Egyptian record of c. 1209 BCE. By the 9th century BCE the Kingdom of Israel had emerged as an important local power before...
shofarShofarA shofar is a horn, traditionally that of a ram, used for Jewish religious purposes. Shofar-blowing is incorporated in synagogue services on Rosh Hashanah and Yom Kippur.Shofar come in a variety of sizes.- Bible and rabbinic literature :...
is perhaps the best-known animal-horn trumpet. It is usually made from a ram’s horn, though the horn of any kosher animal other than a cow or calf may be used. The shofar, which is still employed in Jewish religious ceremonies today, is an ancient instrument; it is mentioned frequently in the BibleBibleThe Bible refers to any one of the collections of the primary religious texts of Judaism and Christianity. There is no common version of the Bible, as the individual books , their contents and their order vary among denominations...
and rabbinic literatureRabbinic literatureRabbinic literature, in its broadest sense, can mean the entire spectrum of rabbinic writings throughout Jewish history. However, the term often refers specifically to literature from the Talmudic era, as opposed to medieval and modern rabbinic writing, and thus corresponds with the Hebrew term...
. It can generally produce only two pitchesPitch (music)Pitch is an auditory perceptual property that allows the ordering of sounds on a frequency-related scale.Pitches are compared as "higher" and "lower" in the sense associated with musical melodies,...
; theoretically, these should be a fifthPerfect fifthIn classical music from Western culture, a fifth is a musical interval encompassing five staff positions , and the perfect fifth is a fifth spanning seven semitones, or in meantone, four diatonic semitones and three chromatic semitones...
apart (being the second and third partialPartialPartial may refer to:*partial derivative, in mathematics** ∂, the partial derivative symbol, often read as "partial"*partial function, in mathematics*partial algorithm, in computer science*part score, in contract bridge...
s of the instrument’s harmonic seriesHarmonic series (music)Pitched musical instruments are often based on an approximate harmonic oscillator such as a string or a column of air, which oscillates at numerous frequencies simultaneously. At these resonant frequencies, waves travel in both directions along the string or air column, reinforcing and canceling...
); the irregular bore of the instrument, however, can reduce this to as little as a fourthPerfect fourthIn classical music from Western culture, a fourth is a musical interval encompassing four staff positions , and the perfect fourth is a fourth spanning five semitones. For example, the ascending interval from C to the next F is a perfect fourth, as the note F lies five semitones above C, and there...
or increase it to as much as a sixthMajor sixthIn classical music from Western culture, a sixth is a musical interval encompassing six staff positions , and the major sixth is one of two commonly occurring sixths. It is qualified as major because it is the largest of the two...
. These acoustical details apply to most animal-horn trumpets.

- The IndianHistory of IndiaThe history of India begins with evidence of human activity of Homo sapiens as long as 75,000 years ago, or with earlier hominids including Homo erectus from about 500,000 years ago. The Indus Valley Civilization, which spread and flourished in the northwestern part of the Indian subcontinent from...
shringa, or ṣṛnga, (SanskritSanskritSanskrit , is a historical Indo-Aryan language and the primary liturgical language of Hinduism, Jainism and Buddhism.Buddhism: besides Pali, see Buddhist Hybrid Sanskrit Today, it is listed as one of the 22 scheduled languages of India and is an official language of the state of Uttarakhand...
for “horn”) was originally made from the horn of the buffalo, though the term was later applied to almost any kind of horn or trumpet, irrespective of its origin. In the south of the country the general name of the instrument is kombu, a DravidianDravidian languagesThe Dravidian language family includes approximately 85 genetically related languages, spoken by about 217 million people. They are mainly spoken in southern India and parts of eastern and central India as well as in northeastern Sri Lanka, Pakistan, Nepal, Bangladesh, Afghanistan, Iran, and...
term which also means “horn”. The shringa is an end-blown instrument, though one particular variety – the singha of OrissaOrissaOrissa , officially Odisha since Nov 2011, is a state of India, located on the east coast of India, by the Bay of Bengal. It is the modern name of the ancient nation of Kalinga, which was invaded by the Maurya Emperor Ashoka in 261 BC. The modern state of Orissa was established on 1 April...
– is side-blown. The shringa and its close relations are known by various names in different parts of India: singe (the shringa of the BhilBhilBhils are primarily an Adivasi people of Central India. Bhils are also settled in the Tharparkar District of Sindh, Pakistan. They speak the Bhil languages, a subgroup of the Western Zone of the Indo-Aryan languages....
s), sakna (a buffalo horn of the Santals), reli'ki (the Angami’s buffalo horn, which has a bamboo mouthpieceMouthpiece (brass)On brass instruments the mouthpiece is the part of the instrument which is placed upon the player's lips. The purpose of the mouthpiece is a resonator, which passes vibration from the lips to the column of air contained within the instrument, giving rise to the standing wave pattern of vibration in...
), visan (a buffalo horn of Uttar PradeshUttar PradeshUttar Pradesh abbreviation U.P. , is a state located in the northern part of India. With a population of over 200 million people, it is India's most populous state, as well as the world's most populous sub-national entity...
), singi (a deer horn of Uttar PradeshUttar PradeshUttar Pradesh abbreviation U.P. , is a state located in the northern part of India. With a population of over 200 million people, it is India's most populous state, as well as the world's most populous sub-national entity...
), and kohuk (a horn of the Marias of Madhya PradeshMadhya PradeshMadhya Pradesh , often called the Heart of India, is a state in central India. Its capital is Bhopal and Indore is the largest city....
). India’s national epicNational epicA national epic is an epic poem or a literary work of epic scope which seeks or is believed to capture and express the essence or spirit of a particular nation; not necessarily a nation-state, but at least an ethnic or linguistic group with aspirations to independence or autonomy...
, the MahābhārataMahabharataThe Mahabharata is one of the two major Sanskrit epics of ancient India and Nepal, the other being the Ramayana. The epic is part of itihasa....
, mentions the govishanika, which is thought to have been a cow’s horn. Many species of shringa can still be found in India today. - The GreekHistory of GreeceThe history of Greece encompasses the history of the territory of the modern state of Greece, as well as that of the Greek people and the areas they ruled historically. The scope of Greek habitation and rule has varied much through the ages, and, as a result, the history of Greece is similarly...
keras (“horn”) and the Etrusco-RomanRomeRome is the capital of Italy and the country's largest and most populated city and comune, with over 2.7 million residents in . The city is located in the central-western portion of the Italian Peninsula, on the Tiber River within the Lazio region of Italy.Rome's history spans two and a half...
cornuCornu (horn)A cornu or cornum was a type of brass instrument similar to the buccina used by the Roman army of antiquity mainly for communicating orders to troops in battle. It is a Latin word literally meaning horn. The instrument was about long and took the form of a letter 'G'...
(LatinLatinLatin is an Italic language originally spoken in Latium and Ancient Rome. It, along with most European languages, is a descendant of the ancient Proto-Indo-European language. Although it is considered a dead language, a number of scholars and members of the Christian clergy speak it fluently, and...
for “horn”) were originally simple animal-horn trumpets, though both were superseded by more advanced instruments to which they lent their names. - The GermanicGermanic peoplesThe Germanic peoples are an Indo-European ethno-linguistic group of Northern European origin, identified by their use of the Indo-European Germanic languages which diversified out of Proto-Germanic during the Pre-Roman Iron Age.Originating about 1800 BCE from the Corded Ware Culture on the North...
cowhorn, or Stierhorn, which was generally made from the horn of an aurochsAurochsThe aurochs , the ancestor of domestic cattle, were a type of large wild cattle which inhabited Europe, Asia and North Africa, but is now extinct; it survived in Europe until 1627....
or buffaloWisentThe wisent , Bison bonasus, also known as the European bison or European wood bison, is a species of Eurasian bison. It is the heaviest surviving land animal in Europe; a typical wisent is about long, not counting a tail of long, and tall. Weight typically can range from , with an occasional big...
. - The rwa-dun is a TibetTibetTibet is a plateau region in Asia, north-east of the Himalayas. It is the traditional homeland of the Tibetan people as well as some other ethnic groups such as Monpas, Qiang, and Lhobas, and is now also inhabited by considerable numbers of Han and Hui people...
an ram’s-horn trumpet similar to the Jewish shofar. It has been used for centuries in BuddhistBuddhismBuddhism is a religion and philosophy encompassing a variety of traditions, beliefs and practices, largely based on teachings attributed to Siddhartha Gautama, commonly known as the Buddha . The Buddha lived and taught in the northeastern Indian subcontinent some time between the 6th and 4th...
ceremonies for the purposes of exorcismExorcismExorcism is the religious practice of evicting demons or other spiritual entities from a person or place which they are believed to have possessed...
. - The LatviaLatviaLatvia , officially the Republic of Latvia , is a country in the Baltic region of Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by Estonia , to the south by Lithuania , to the east by the Russian Federation , to the southeast by Belarus and shares maritime borders to the west with Sweden...
n āžrag was made from a goat’s horn, and was blown by young men in the summertime to announce their intention to take a wife. - The eng’ombe is a side-blown trumpet found in UgandaUgandaUganda , officially the Republic of Uganda, is a landlocked country in East Africa. Uganda is also known as the "Pearl of Africa". It is bordered on the east by Kenya, on the north by South Sudan, on the west by the Democratic Republic of the Congo, on the southwest by Rwanda, and on the south by...
; it is usually made from a cow’s horn and is blown by BugandaBugandaBuganda is a subnational kingdom within Uganda. The kingdom of the Ganda people, Buganda is the largest of the traditional kingdoms in present-day Uganda, comprising all of Uganda's Central Region, including the Ugandan capital Kampala, with the exception of the disputed eastern Kayunga District...
n huntsmen to ensure a successful hunt.
Conch-shell trumpets
ConchConch
A conch is a common name which is applied to a number of different species of medium-sized to large sea snails or their shells, generally those which are large and have a high spire and a siphonal canal....
shells have also been used as primitive instruments since Neolithic
Neolithic
The Neolithic Age, Era, or Period, or New Stone Age, was a period in the development of human technology, beginning about 9500 BC in some parts of the Middle East, and later in other parts of the world. It is traditionally considered as the last part of the Stone Age...
times, and must be numbered among the antecedents of the natural trumpet. The four shells most commonly used for this purpose are the triton
Triton (mollusk)
Triton is the common name given to a number of very large sea snails, predatory marine gastropods in the genus Charonia. The name "triton" is also often applied as part of the common name, to other, much smaller sea snails of other genera within the same family, Ranellidae.Tritons are named after...
or trumpet shell, the cassis or helmet shell, the fusus
Fusus
Fusus is a genus of sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Fasciolariidae, the spindle snails, the tulip snails and their allies. The name Fusus is a temporary name and has become invalid as a taxonomical name...
, and the strombus
Conch
A conch is a common name which is applied to a number of different species of medium-sized to large sea snails or their shells, generally those which are large and have a high spire and a siphonal canal....
or true conch, though the term “conch-shell trumpet” is generally applied to all instruments of this type. The spiral interior of the shell acts as tubing, and a mouthhole is created either by breaking off the point of the shell (end-blown conch) or by boring a small hole in the body (side-blown conch). The cassis is an end-blown shell; the other three types are usually side-blown.
Conch-shell trumpets are found in almost every part of the globe, including inland areas like Tibet
Tibet
Tibet is a plateau region in Asia, north-east of the Himalayas. It is the traditional homeland of the Tibetan people as well as some other ethnic groups such as Monpas, Qiang, and Lhobas, and is now also inhabited by considerable numbers of Han and Hui people...
, Central Europe
Central Europe
Central Europe or alternatively Middle Europe is a region of the European continent lying between the variously defined areas of Eastern and Western Europe...
and the Andes
Andes
The Andes is the world's longest continental mountain range. It is a continual range of highlands along the western coast of South America. This range is about long, about to wide , and of an average height of about .Along its length, the Andes is split into several ranges, which are separated...
. They are especially common throughout Oceania
Oceania
Oceania is a region centered on the islands of the tropical Pacific Ocean. Conceptions of what constitutes Oceania range from the coral atolls and volcanic islands of the South Pacific to the entire insular region between Asia and the Americas, including Australasia and the Malay Archipelago...
, where the conch-shell trumpet was once used on religious, ceremonial and military occasions. Today, however, the instrument is more often associated with mundane events like football matches; the Tonga
Tonga
Tonga, officially the Kingdom of Tonga , is a state and an archipelago in the South Pacific Ocean, comprising 176 islands scattered over of ocean in the South Pacific...
n football team is regularly encouraged by ensembles of up to nine kele’a! In the South Pacific
Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest of the Earth's oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic in the north to the Southern Ocean in the south, bounded by Asia and Australia in the west, and the Americas in the east.At 165.2 million square kilometres in area, this largest division of the World...
island nation
Island nation
An island country is a state whose primary territory consists of one or more islands or parts of islands. As of 2011, 47 of the 193 UN member states are island countries.-Politics:...
of Vanuatu
Vanuatu
Vanuatu , officially the Republic of Vanuatu , is an island nation located in the South Pacific Ocean. The archipelago, which is of volcanic origin, is some east of northern Australia, northeast of New Caledonia, west of Fiji, and southeast of the Solomon Islands, near New Guinea.Vanuatu was...
, local fishermen use conch-shell trumpets known as tapáe to call for assistance when they are drawing in their nets. In Fiji
Fiji
Fiji , officially the Republic of Fiji , is an island nation in Melanesia in the South Pacific Ocean about northeast of New Zealand's North Island...
, the davui conch-shell trumpet is still blown to invoke the gods.
End-blown conch-shell trumpets are still used as sacred ritual instruments in Asia. The India
India
India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
n śańkh or śańkham is blown by Brahman
Brahman
In Hinduism, Brahman is the one supreme, universal Spirit that is the origin and support of the phenomenal universe. Brahman is sometimes referred to as the Absolute or Godhead which is the Divine Ground of all being...
s in Hindu
Hindu
Hindu refers to an identity associated with the philosophical, religious and cultural systems that are indigenous to the Indian subcontinent. As used in the Constitution of India, the word "Hindu" is also attributed to all persons professing any Indian religion...
temples throughout India
India
India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
and South Asia, and is also used today as an instrument of folk music and dance; formerly it was employed as a heraldic instrument to declare war or celebrate victory. According to Hindu mythology
Hindu mythology
Hindu religious literature is the large body of traditional narratives related to Hinduism, notably as contained in Sanskrit literature, such as the Sanskrit epics and the Puranas. As such, it is a subset of Nepali and Indian culture...
the śankh will be blown by Siva
Shiva
Shiva is a major Hindu deity, and is the destroyer god or transformer among the Trimurti, the Hindu Trinity of the primary aspects of the divine. God Shiva is a yogi who has notice of everything that happens in the world and is the main aspect of life. Yet one with great power lives a life of a...
at the end of the current World Age as a sort of Last Trump
Last Judgment
The Last Judgment, Final Judgment, Day of Judgment, Judgment Day, or The Day of the Lord in Christian theology, is the final and eternal judgment by God of every nation. The concept is found in all the Canonical gospels, particularly the Gospel of Matthew. It will purportedly take place after the...
.
The conch shell is also used as a signal in Buddhist
Buddhism
Buddhism is a religion and philosophy encompassing a variety of traditions, beliefs and practices, largely based on teachings attributed to Siddhartha Gautama, commonly known as the Buddha . The Buddha lived and taught in the northeastern Indian subcontinent some time between the 6th and 4th...
ceremonies in the Far East
Far East
The Far East is an English term mostly describing East Asia and Southeast Asia, with South Asia sometimes also included for economic and cultural reasons.The term came into use in European geopolitical discourse in the 19th century,...
. In Tibet
Tibet
Tibet is a plateau region in Asia, north-east of the Himalayas. It is the traditional homeland of the Tibetan people as well as some other ethnic groups such as Monpas, Qiang, and Lhobas, and is now also inhabited by considerable numbers of Han and Hui people...
it is known as the dun-dkar, or dung-dkar
Dung-Dkar
Dung-Dkar translated from Tibetan is literally “White Conch” , and true to its name is formed from a white conch shell...
; in China
China
Chinese civilization may refer to:* China for more general discussion of the country.* Chinese culture* Greater China, the transnational community of ethnic Chinese.* History of China* Sinosphere, the area historically affected by Chinese culture...
it is the faluo or hai lo, and in Japan
Japan
Japan is an island nation in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean, it lies to the east of the Sea of Japan, China, North Korea, South Korea and Russia, stretching from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea and Taiwan in the south...
the horagai
Horagai
' are large conch shells that have been used as a trumpets in Japan for many centuries. The instrument, which has served a number of purposes throughout Japanese history, has been given a number of Japanese names depending on its function...
or hora
Hora
Hora is a type of circle dance originating in the Balkans but also found in other countries. The name is cognate to the Greek χορός : 'dance' which is cognate with the ancient Greek art form of χορεία; see Chorea. The original meaning of the Greek word χορός may have been 'circle'...
.
Early manufactured trumpets

Neolithic
The Neolithic Age, Era, or Period, or New Stone Age, was a period in the development of human technology, beginning about 9500 BC in some parts of the Middle East, and later in other parts of the world. It is traditionally considered as the last part of the Stone Age...
, and were adapted from the natural models provided by animal-horns and conch-shells. They were – and in some parts of the world are still – made from a variety of perishable and non-perishable materials, including bark
Bark
Bark is the outermost layers of stems and roots of woody plants. Plants with bark include trees, woody vines and shrubs. Bark refers to all the tissues outside of the vascular cambium and is a nontechnical term. It overlays the wood and consists of the inner bark and the outer bark. The inner...
, wood
Wood
Wood is a hard, fibrous tissue found in many trees. It has been used for hundreds of thousands of years for both fuel and as a construction material. It is an organic material, a natural composite of cellulose fibers embedded in a matrix of lignin which resists compression...
, gourd
Gourd
A gourd is a plant of the family Cucurbitaceae. Gourd is occasionally used to describe crops like cucumbers, squash, luffas, and melons. The term 'gourd' however, can more specifically, refer to the plants of the two Cucurbitaceae genera Lagenaria and Cucurbita or also to their hollow dried out shell...
s, bamboo
Bamboo
Bamboo is a group of perennial evergreens in the true grass family Poaceae, subfamily Bambusoideae, tribe Bambuseae. Giant bamboos are the largest members of the grass family....
, horn
Horn (anatomy)
A horn is a pointed projection of the skin on the head of various animals, consisting of a covering of horn surrounding a core of living bone. True horns are found mainly among the ruminant artiodactyls, in the families Antilocapridae and Bovidae...
, bone
Bone
Bones are rigid organs that constitute part of the endoskeleton of vertebrates. They support, and protect the various organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells and store minerals. Bone tissue is a type of dense connective tissue...
, ivory
Ivory
Ivory is a term for dentine, which constitutes the bulk of the teeth and tusks of animals, when used as a material for art or manufacturing. Ivory has been important since ancient times for making a range of items, from ivory carvings to false teeth, fans, dominoes, joint tubes, piano keys and...
, clay
Clay
Clay is a general term including many combinations of one or more clay minerals with traces of metal oxides and organic matter. Geologic clay deposits are mostly composed of phyllosilicate minerals containing variable amounts of water trapped in the mineral structure.- Formation :Clay minerals...
and, of course, metal
Metal
A metal , is an element, compound, or alloy that is a good conductor of both electricity and heat. Metals are usually malleable and shiny, that is they reflect most of incident light...
. Early metallic trumpets were either hammered from sheets of a suitable metal (e.g. silver
Silver
Silver is a metallic chemical element with the chemical symbol Ag and atomic number 47. A soft, white, lustrous transition metal, it has the highest electrical conductivity of any element and the highest thermal conductivity of any metal...
) or cast in bronze
Bronze
Bronze is a metal alloy consisting primarily of copper, usually with tin as the main additive. It is hard and brittle, and it was particularly significant in antiquity, so much so that the Bronze Age was named after the metal...
by the lost-wax method. Among these primitive trumpets the following may be noted:
- The ancient NordicNordic Bronze AgeThe Nordic Bronze Age is the name given by Oscar Montelius to a period and a Bronze Age culture in Scandinavian pre-history, c. 1700-500 BC, with sites that reached as far east as Estonia. Succeeding the Late Neolithic culture, its ethnic and linguistic affinities are unknown in the absence of...
lurLurA lur is a long natural blowing horn without finger holes that is played by embouchure. Lurs can be straight or curved in various shapes. The purpose of the curves was to make long instruments easier to carry A lur is a long natural blowing horn without finger holes that is played by embouchure....
was made of bronzeBronzeBronze is a metal alloy consisting primarily of copper, usually with tin as the main additive. It is hard and brittle, and it was particularly significant in antiquity, so much so that the Bronze Age was named after the metal...
and dates back to the Late Bronze AgeBronze AgeThe Bronze Age is a period characterized by the use of copper and its alloy bronze as the chief hard materials in the manufacture of some implements and weapons. Chronologically, it stands between the Stone Age and Iron Age...
(1000–500 BC). This extraordinary instrument consisted of an elaborate S-shaped conical tube, usually about 2 metres in length, with a slightly flared bell. It was an end-blown natural trumpet, and sounded rather like a modern tromboneTromboneThe trombone is a musical instrument in the brass family. Like all brass instruments, sound is produced when the player’s vibrating lips cause the air column inside the instrument to vibrate...
. To date, fifty-six lurs have been found: forty-five in DenmarkDenmarkDenmark is a Scandinavian country in Northern Europe. The countries of Denmark and Greenland, as well as the Faroe Islands, constitute the Kingdom of Denmark . It is the southernmost of the Nordic countries, southwest of Sweden and south of Norway, and bordered to the south by Germany. Denmark...
, eleven in SwedenSwedenSweden , officially the Kingdom of Sweden , is a Nordic country on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. Sweden borders with Norway and Finland and is connected to Denmark by a bridge-tunnel across the Öresund....
, four in NorwayNorwayNorway , officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic unitary constitutional monarchy whose territory comprises the western portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula, Jan Mayen, and the Arctic archipelago of Svalbard and Bouvet Island. Norway has a total area of and a population of about 4.9 million...
, five in northern GermanyGermanyGermany , officially the Federal Republic of Germany , is a federal parliamentary republic in Europe. The country consists of 16 states while the capital and largest city is Berlin. Germany covers an area of 357,021 km2 and has a largely temperate seasonal climate...
, and one in LatviaLatviaLatvia , officially the Republic of Latvia , is a country in the Baltic region of Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by Estonia , to the south by Lithuania , to the east by the Russian Federation , to the southeast by Belarus and shares maritime borders to the west with Sweden...
. They have often been discovered in matching pairs, which suggests that they were used for ceremonial or religious purposes, rather than as instruments of war. The original name of the instrument is unknown. - The CeltCeltThe Celts were a diverse group of tribal societies in Iron Age and Roman-era Europe who spoke Celtic languages.The earliest archaeological culture commonly accepted as Celtic, or rather Proto-Celtic, was the central European Hallstatt culture , named for the rich grave finds in Hallstatt, Austria....
ic carnyxCarnyxThe carnyx was a wind instrument of the Iron Age Celts, used between c. 300 BC to 200 AD. It was a type of bronze trumpet, held vertically, the mouth styled in the shape of a boar's, or other animal's, head. It was used in warfare, probably to incite troops to battle and intimidate opponents...
was also made of bronze, and was used as an instrument of war during the Iron AgeIron AgeThe Iron Age is the archaeological period generally occurring after the Bronze Age, marked by the prevalent use of iron. The early period of the age is characterized by the widespread use of iron or steel. The adoption of such material coincided with other changes in society, including differing...
(ca. 300 BC300 BCYear 300 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Corvus and Pansa...
– 200 CE). It consisted of a cylindrical tube about 2 metres long; the bell was elaborately carved to resemble a wild boar’s head, with a movable tongue and jaw; the mouthpieceMouthpiece (brass)On brass instruments the mouthpiece is the part of the instrument which is placed upon the player's lips. The purpose of the mouthpiece is a resonator, which passes vibration from the lips to the column of air contained within the instrument, giving rise to the standing wave pattern of vibration in...
was curved. The carnyx was held vertically with the bell above the player’s head. The instrument is most often associated with the CeltCeltThe Celts were a diverse group of tribal societies in Iron Age and Roman-era Europe who spoke Celtic languages.The earliest archaeological culture commonly accepted as Celtic, or rather Proto-Celtic, was the central European Hallstatt culture , named for the rich grave finds in Hallstatt, Austria....
s, but is now known to have been used also by the inhabitants of ancient DaciaDaciaIn ancient geography, especially in Roman sources, Dacia was the land inhabited by the Dacians or Getae as they were known by the Greeks—the branch of the Thracians north of the Haemus range...
. A similar S-shaped trumpet from the Iron AgeIron AgeThe Iron Age is the archaeological period generally occurring after the Bronze Age, marked by the prevalent use of iron. The early period of the age is characterized by the widespread use of iron or steel. The adoption of such material coincided with other changes in society, including differing...
has been found at Loughnashade in IrelandIrelandIreland is an island to the northwest of continental Europe. It is the third-largest island in Europe and the twentieth-largest island on Earth...
. Named the trumpa créda (archaic IrishIrish languageIrish , also known as Irish Gaelic, is a Goidelic language of the Indo-European language family, originating in Ireland and historically spoken by the Irish people. Irish is now spoken as a first language by a minority of Irish people, as well as being a second language of a larger proportion of...
for “bronze trumpet”), it consists of two curved tubes of bronze, each comprising a quarter circle, one of which is of conical bore and one of cylindrical bore, with a joint in the middle. The Loughnashade trumpet is generally displayed with the two halves joined together to make a semicircle, but it is now thought to have been played with the two parts bending in opposite directions to make an S-shaped trumpet not unlike the carnyx, to which it may have been related. - In IndiaIndiaIndia , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
the primitive shringa or kombu was adapted to make a great variety of metallic trumpets. The modern kombu is generally a C-shaped instrument made of brass or copper, with a conical bore and a detachable mouthpiece. It is still played at weddings and funerals, and during religious processions. There are two sizes of kombu: the small timiri kombu and the large bari kombu. Another type of brass kombu – known variously as turi, bānkiā, bargu, banke, ransingha, narsingha, narsĩgā and nagphani in different parts of the subcontinent – is S-shaped and looks remarkably like the trumpa créda of Ireland. Indigenous straight trumpets have been made in India since the NeolithicNeolithicThe Neolithic Age, Era, or Period, or New Stone Age, was a period in the development of human technology, beginning about 9500 BC in some parts of the Middle East, and later in other parts of the world. It is traditionally considered as the last part of the Stone Age...
and are still found today in various guises and under various names: turahi, turya, tutari, tuttoori, bhongal, kahal, kahala, and bhenr. The booraga of SanskritSanskritSanskrit , is a historical Indo-Aryan language and the primary liturgical language of Hinduism, Jainism and Buddhism.Buddhism: besides Pali, see Buddhist Hybrid Sanskrit Today, it is listed as one of the 22 scheduled languages of India and is an official language of the state of Uttarakhand...
literature was possibly also a straight trumpet made of brass or copper. - The wooden lur of medieval ScandinaviaScandinaviaScandinavia is a cultural, historical and ethno-linguistic region in northern Europe that includes the three kingdoms of Denmark, Norway and Sweden, characterized by their common ethno-cultural heritage and language. Modern Norway and Sweden proper are situated on the Scandinavian Peninsula,...
(not to be confused with the much earlier bronze instrument to which it has lent its name) is referred to in the IcelandIcelandIceland , described as the Republic of Iceland, is a Nordic and European island country in the North Atlantic Ocean, on the Mid-Atlantic Ridge. Iceland also refers to the main island of the country, which contains almost all the population and almost all the land area. The country has a population...
ic sagasSagàsSagàs is a small town and municipality located in Catalonia, in the comarca of Berguedà. It is located in the geographical area of the pre-Pyrenees.-Population:...
as an instrument of war, used to marshal troops and frighten the enemy. It is also mentioned by Saxo GrammaticusSaxo GrammaticusSaxo Grammaticus also known as Saxo cognomine Longus was a Danish historian, thought to have been a secular clerk or secretary to Absalon, Archbishop of Lund, foremost advisor to Valdemar I of Denmark. He is the author of the first full history of Denmark.- Life :The Jutland Chronicle gives...
in his Gesta DanorumGesta DanorumGesta Danorum is a patriotic work of Danish history, by the 12th century author Saxo Grammaticus . It is the most ambitious literary undertaking of medieval Denmark and is an essential source for the nation's early history...
. This particular species of lur was a straight, end-blown natural trumpet, with a cylindrical tube about 1 metre long. It was made of wood – typically by cutting a thick branch in half lengthwise and hollowing it out, and then rejoining the two halves, which are secured with tarTarTar is modified pitch produced primarily from the wood and roots of pine by destructive distillation under pyrolysis. Production and trade in tar was a major contributor in the economies of Northern Europe and Colonial America. Its main use was in preserving wooden vessels against rot. The largest...
and willowWillowWillows, sallows, and osiers form the genus Salix, around 400 species of deciduous trees and shrubs, found primarily on moist soils in cold and temperate regions of the Northern Hemisphere...
osiers. A similar instrument, but secured with birchBirchBirch is a tree or shrub of the genus Betula , in the family Betulaceae, closely related to the beech/oak family, Fagaceae. The Betula genus contains 30–60 known taxa...
, known as the birch trumpetBirch trumpetThe birch trumpet is a type of natural trumpet made of spruce covered with birch bark, native to Sweden. Even cruder and less durable versions were made of plain birch bark...
, has been used in Nordic countriesNordic countriesThe Nordic countries make up a region in Northern Europe and the North Atlantic which consists of Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Norway and Sweden and their associated territories, the Faroe Islands, Greenland and Åland...
since the Middle AgesMiddle AgesThe Middle Ages is a periodization of European history from the 5th century to the 15th century. The Middle Ages follows the fall of the Western Roman Empire in 476 and precedes the Early Modern Era. It is the middle period of a three-period division of Western history: Classic, Medieval and Modern...
as a signalling instrument and to call cattle. - The LithuaniaLithuaniaLithuania , officially the Republic of Lithuania is a country in Northern Europe, the biggest of the three Baltic states. It is situated along the southeastern shore of the Baltic Sea, whereby to the west lie Sweden and Denmark...
n daudytė is a natural wooden trumpet similar to the wooden lur of ScandinaviaScandinaviaScandinavia is a cultural, historical and ethno-linguistic region in northern Europe that includes the three kingdoms of Denmark, Norway and Sweden, characterized by their common ethno-cultural heritage and language. Modern Norway and Sweden proper are situated on the Scandinavian Peninsula,...
; its sections are held together with puttyPuttyPutty is a generic term for a plastic material similar in texture to clay or dough typically used in domestic construction and repair as a sealant or filler. Painter's Putty is typically a linseed oil based product used for filling holes, minor cracks and defacements in wood only...
and linenLinenLinen is a textile made from the fibers of the flax plant, Linum usitatissimum. Linen is labor-intensive to manufacture, but when it is made into garments, it is valued for its exceptional coolness and freshness in hot weather....
yarn. - The alphornAlphornThe alphorn or alpenhorn or alpine horn is a labrophone, consisting of a natural wooden horn of conical bore, having a wooden cup-shaped mouthpiece, used by mountain dwellers in Switzerland and elsewhere...
, or alpenhorn, is a distinctive natural wooden horn with a conical bore, upturned bell and cup-shaped mouthpieceMouthpiece (brass)On brass instruments the mouthpiece is the part of the instrument which is placed upon the player's lips. The purpose of the mouthpiece is a resonator, which passes vibration from the lips to the column of air contained within the instrument, giving rise to the standing wave pattern of vibration in...
. It has been used as a signalling instrument in the Alpine regions of Europe for about two millennia. The alphorn is generally carved from the solid softwoodSoftwoodThe term softwood is used to describe wood from trees that are known as gymnosperms.Conifers are an example. It may also be used to describe trees, which tend to be evergreen, notable exceptions being bald cypress and the larches....
of the spruceSpruceA spruce is a tree of the genus Picea , a genus of about 35 species of coniferous evergreen trees in the Family Pinaceae, found in the northern temperate and boreal regions of the earth. Spruces are large trees, from tall when mature, and can be distinguished by their whorled branches and conical...
or pinePinePines are trees in the genus Pinus ,in the family Pinaceae. They make up the monotypic subfamily Pinoideae. There are about 115 species of pine, although different authorities accept between 105 and 125 species.-Etymology:...
. In former times alphorn makers would use a tree that was already bent at the base, but today’s alphorns are pieced together from separate sections, which are secured with barkBarkBark is the outermost layers of stems and roots of woody plants. Plants with bark include trees, woody vines and shrubs. Bark refers to all the tissues outside of the vascular cambium and is a nontechnical term. It overlays the wood and consists of the inner bark and the outer bark. The inner...
or gut. The cup-shaped mouthpiece is usually carved out of a block of hardwoodHardwoodHardwood is wood from angiosperm trees . It may also be used for those trees themselves: these are usually broad-leaved; in temperate and boreal latitudes they are mostly deciduous, but in tropics and subtropics mostly evergreen.Hardwood contrasts with softwood...
. - The AustralianIndigenous AustraliansIndigenous Australians are the original inhabitants of the Australian continent and nearby islands. The Aboriginal Indigenous Australians migrated from the Indian continent around 75,000 to 100,000 years ago....
didjeriduDidgeridooThe didgeridoo is a wind instrument developed by Indigenous Australians of northern Australia around 1,500 years ago and still in widespread usage today both in Australia and around the world. It is sometimes described as a natural wooden trumpet or "drone pipe"...
is one of the best known species of primitive trumpet. A natural wooden trumpet, it has been in continuous use among the aboriginal peoples of AustraliaAustraliaAustralia , officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country in the Southern Hemisphere comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands in the Indian and Pacific Oceans. It is the world's sixth-largest country by total area...
for at least 1500 years, and possibly much longer. It is usually manufactured from the trunk of a hardwoodHardwoodHardwood is wood from angiosperm trees . It may also be used for those trees themselves: these are usually broad-leaved; in temperate and boreal latitudes they are mostly deciduous, but in tropics and subtropics mostly evergreen.Hardwood contrasts with softwood...
tree, such as the eucalyptusEucalyptusEucalyptus is a diverse genus of flowering trees in the myrtle family, Myrtaceae. Members of the genus dominate the tree flora of Australia...
, which has been suitably hollowed out by termiteTermiteTermites are a group of eusocial insects that, until recently, were classified at the taxonomic rank of order Isoptera , but are now accepted as the epifamily Termitoidae, of the cockroach order Blattodea...
s. The instrument is typically about 1 to 1.5 metres long; the boreBore (wind instruments)The bore of a wind instrument is its interior chamber that defines a flow path through which air travels and is set into vibration to produce sounds. The shape of the bore has a strong influence on the instruments' timbre.-Bore shapes:...
may be conical or cylindrical. By vibrating his lips against the mouthhole the player can produce a deep droneDrone (music)In music, a drone is a harmonic or monophonic effect or accompaniment where a note or chord is continuously sounded throughout most or all of a piece. The word drone is also used to refer to any part of a musical instrument that is just used to produce such an effect.-A musical effect:A drone...
; the note so produced may be sustained indefinitely by means of a technique called circular breathingCircular breathingCircular breathing is a technique used by players of some wind instruments to produce a continuous tone without interruption. This is accomplished by breathing in through the nose while simultaneously pushing air out through the mouth using air stored in the cheeks.It is used extensively in playing...
. Today the didjeridu is frequently played as a solo instrument for recreational purposes, though it was traditionally used to accompany dancing and singing on ceremonial occasions. - The UgandaUgandaUganda , officially the Republic of Uganda, is a landlocked country in East Africa. Uganda is also known as the "Pearl of Africa". It is bordered on the east by Kenya, on the north by South Sudan, on the west by the Democratic Republic of the Congo, on the southwest by Rwanda, and on the south by...
n arupepe is a natural wooden trumpet covered with animal hide. - The molimo is a wooden trumpet used by the MbutiMbutiMbuti or Bambuti are one of several indigenous pygmy groups in the Congo region of Africa. Their languages belong to the Central Sudanic and also to Bantu languages.-Overview:...
people of the CongoDemocratic Republic of the CongoThe Democratic Republic of the Congo is a state located in Central Africa. It is the second largest country in Africa by area and the eleventh largest in the world...
to awaken the spirit of the Ituri RainforestIturi RainforestThe Ituri Rainforest is a rainforest located in the Ituri region of eastern Democratic Republic of the Congo formerly called Zaire. The forest's name derives from the nearby Ituri River which flows through the rainforest, connecting firstly to the Aruwimi River and finally into the Congo.-...
. It is also the name of the elaborate ritual in which the instrument plays a vital role. - Bone trumpets made from human femurFemurThe femur , or thigh bone, is the most proximal bone of the leg in tetrapod vertebrates capable of walking or jumping, such as most land mammals, birds, many reptiles such as lizards, and amphibians such as frogs. In vertebrates with four legs such as dogs and horses, the femur is found only in...
s (khang ling) and tigerTigerThe tiger is the largest cat species, reaching a total body length of up to and weighing up to . Their most recognizable feature is a pattern of dark vertical stripes on reddish-orange fur with lighter underparts...
femurs (stag ling) can still be found in the Himalayas, where they are associated with BuddhistBuddhismBuddhism is a religion and philosophy encompassing a variety of traditions, beliefs and practices, largely based on teachings attributed to Siddhartha Gautama, commonly known as the Buddha . The Buddha lived and taught in the northeastern Indian subcontinent some time between the 6th and 4th...
tantraTantraTantra , anglicised tantricism or tantrism or tantram, is the name scholars give to an inter-religious spiritual movement that arose in medieval India, expressed in scriptures ....
. In TibetTibetTibet is a plateau region in Asia, north-east of the Himalayas. It is the traditional homeland of the Tibetan people as well as some other ethnic groups such as Monpas, Qiang, and Lhobas, and is now also inhabited by considerable numbers of Han and Hui people...
the human thigh-bone trumpet is called the rkan-dun (or rkang-gling) and plays an important role in the traditional shamanisticShamanismShamanism is an anthropological term referencing a range of beliefs and practices regarding communication with the spiritual world. To quote Eliade: "A first definition of this complex phenomenon, and perhaps the least hazardous, will be: shamanism = technique of ecstasy." Shamanism encompasses the...
religion known as Bön. In the Tibetan languageTibetan languageThe Tibetan languages are a cluster of mutually-unintelligible Tibeto-Burman languages spoken primarily by Tibetan peoples who live across a wide area of eastern Central Asia bordering the Indian subcontinent, including the Tibetan Plateau and the northern Indian subcontinent in Baltistan, Ladakh,...
the word dun means both “trumpet” and “bone”! Brass replicas of bone trumpets are also known in Tibet. - The borijaBorijaBorija is a village in the municipality of Kalinovik, Bosnia and Herzegovina....
, a short natural trumpet found in YugoslaviaYugoslaviaYugoslavia refers to three political entities that existed successively on the western part of the Balkans during most of the 20th century....
, is made from the spiral shavings of the willowWillowWillows, sallows, and osiers form the genus Salix, around 400 species of deciduous trees and shrubs, found primarily on moist soils in cold and temperate regions of the Northern Hemisphere...
or ashAsh treeFraxinus is a genus flowering plants in the olive and lilac family, Oleaceae. It contains 45-65 species of usually medium to large trees, mostly deciduous though a few subtropical species are evergreen. The tree's common English name, ash, goes back to the Old English æsc, while the generic name...
, bound firmly into a conical tube about 50 cm long. - The obsolete tāšu taure of LatviaLatviaLatvia , officially the Republic of Latvia , is a country in the Baltic region of Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by Estonia , to the south by Lithuania , to the east by the Russian Federation , to the southeast by Belarus and shares maritime borders to the west with Sweden...
was of similar design to the borija, but it was made from birchBirchBirch is a tree or shrub of the genus Betula , in the family Betulaceae, closely related to the beech/oak family, Fagaceae. The Betula genus contains 30–60 known taxa...
bark and could be up to 150 cm long. - In the Amazon RainforestAmazon RainforestThe Amazon Rainforest , also known in English as Amazonia or the Amazon Jungle, is a moist broadleaf forest that covers most of the Amazon Basin of South America...
giant trumpets up to four metres in length are made from tightly coiled bark; sticks are attached to one or both sides of the instruments to support them and prevent sagging. - BambooBambooBamboo is a group of perennial evergreens in the true grass family Poaceae, subfamily Bambusoideae, tribe Bambuseae. Giant bamboos are the largest members of the grass family....
trumpets can be found in many parts of AfricaAfricaAfrica is the world's second largest and second most populous continent, after Asia. At about 30.2 million km² including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of the Earth's total surface area and 20.4% of the total land area...
and South AmericaSouth AmericaSouth America is a continent situated in the Western Hemisphere, mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere. The continent is also considered a subcontinent of the Americas. It is bordered on the west by the Pacific Ocean and on the north and east...
, but are almost unheard of in the bamboo-rich regions of ChinaChinaChinese civilization may refer to:* China for more general discussion of the country.* Chinese culture* Greater China, the transnational community of ethnic Chinese.* History of China* Sinosphere, the area historically affected by Chinese culture...
and South-East Asia. A notable exception is provided by the bamboo “brass-band” tradition of SulawesiSulawesiSulawesi is one of the four larger Sunda Islands of Indonesia and is situated between Borneo and the Maluku Islands. In Indonesia, only Sumatra, Borneo, and Papua are larger in territory, and only Java and Sumatra have larger Indonesian populations.- Etymology :The Portuguese were the first to...
, which is actually quite a recent tradition. In the 19th century Dutch missionaries introduced European brass bands to the island; later, in the 1920s, local craftsmen began to make bamboo replicas of these modern instruments. Today most replicas are made of zincZincZinc , or spelter , is a metallic chemical element; it has the symbol Zn and atomic number 30. It is the first element in group 12 of the periodic table. Zinc is, in some respects, chemically similar to magnesium, because its ion is of similar size and its only common oxidation state is +2...
, though bamboo examples can still be found in isolated pockets, such as the SangirSangirSangir Besar, commonly called Sangir Island , is an island in the Sangir Islands group. Its Indonesian name literally means "Great Sangir", in reference to the fact that it is the archipelago's main island. It is part of the North Sulawesi province...
Archipelago, which lies to the north of Sulawesi. - GourdGourdA gourd is a plant of the family Cucurbitaceae. Gourd is occasionally used to describe crops like cucumbers, squash, luffas, and melons. The term 'gourd' however, can more specifically, refer to the plants of the two Cucurbitaceae genera Lagenaria and Cucurbita or also to their hollow dried out shell...
s, the hollow, dried shells of the fruitFruitIn broad terms, a fruit is a structure of a plant that contains its seeds.The term has different meanings dependent on context. In non-technical usage, such as food preparation, fruit normally means the fleshy seed-associated structures of certain plants that are sweet and edible in the raw state,...
of a member of the CucurbitaceaeCucurbitaceaeThe plant family Cucurbitaceae consists of various squashes, melons, and gourds, including crops such as cucumber, pumpkins, luffas, and watermelons...
family, can be adapted quite easily to make natural trumpets. GourdGourdA gourd is a plant of the family Cucurbitaceae. Gourd is occasionally used to describe crops like cucumbers, squash, luffas, and melons. The term 'gourd' however, can more specifically, refer to the plants of the two Cucurbitaceae genera Lagenaria and Cucurbita or also to their hollow dried out shell...
trumpets have been used in Africa for centuries, and are also to be found in Asia and the Americas; one particular variety of gourd, the calabashCalabashLagenaria siceraria , bottle gourd, opo squash or long melon is a vine grown for its fruit, which can either be harvested young and used as a vegetable, or harvested mature, dried, and used as a bottle, utensil, or pipe. For this reason, the calabash is widely known as the bottle gourd...
, is even known as the “trumpet gourd”. The gourd trumpet was also used by the AztecAztecThe Aztec people were certain ethnic groups of central Mexico, particularly those groups who spoke the Nahuatl language and who dominated large parts of Mesoamerica in the 14th, 15th and 16th centuries, a period referred to as the late post-classic period in Mesoamerican chronology.Aztec is the...
s and other indigenous peoples of Central AmericaCentral AmericaCentral America is the central geographic region of the Americas. It is the southernmost, isthmian portion of the North American continent, which connects with South America on the southeast. When considered part of the unified continental model, it is considered a subcontinent...
. One notable variety, the MayaMaya civilizationThe Maya is a Mesoamerican civilization, noted for the only known fully developed written language of the pre-Columbian Americas, as well as for its art, architecture, and mathematical and astronomical systems. Initially established during the Pre-Classic period The Maya is a Mesoamerican...
n Hom-Tah, has been compared to the Australian didjeridu. Among the gourd trumpets that are still in use today is the waza of the BertaBertaBerta is a female Germanic name or may also be a colloquial shortening of Alberta or Roberta.Berta may refer to:* Berta people, an ethnic group from western Ethiopia and eastern Sudan** Berta language, their language...
people, who live in the Blue NileBlue NileThe Blue Nile is a river originating at Lake Tana in Ethiopia. With the White Nile, the river is one of the two major tributaries of the Nile...
region of the SudanSudanSudan , officially the Republic of the Sudan , is a country in North Africa, sometimes considered part of the Middle East politically. It is bordered by Egypt to the north, the Red Sea to the northeast, Eritrea and Ethiopia to the east, South Sudan to the south, the Central African Republic to the...
.
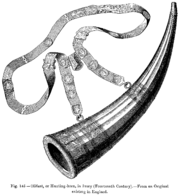
- Most trumpets fashioned from the ivoryIvoryIvory is a term for dentine, which constitutes the bulk of the teeth and tusks of animals, when used as a material for art or manufacturing. Ivory has been important since ancient times for making a range of items, from ivory carvings to false teeth, fans, dominoes, joint tubes, piano keys and...
tuskTuskTusks are elongated, continuously growing front teeth, usually but not always in pairs, that protrude well beyond the mouth of certain mammal species. They are most commonly canines, as with warthogs, wild boar, and walruses, or, in the case of elephants and narwhals, elongated incisors...
s of an elephantElephantElephants are large land mammals in two extant genera of the family Elephantidae: Elephas and Loxodonta, with the third genus Mammuthus extinct...
are of African origin; both end-blown and side-blown varieties can still be found in some parts of the continent today. The most notable exception is the medieval olifantOlifant (instrument)Olifant was the name applied in the Middle Ages to ivory hunting horns made from elephants' tusks. One of the most famous olifants belonged to the legendary Frankish knight Roland, protagonist of The Song of Roland.In The Song of Roland, Roland carries his olifant while serving on the rearguard of...
, a short, thick, end-blown trumpet carved from ivoryIvoryIvory is a term for dentine, which constitutes the bulk of the teeth and tusks of animals, when used as a material for art or manufacturing. Ivory has been important since ancient times for making a range of items, from ivory carvings to false teeth, fans, dominoes, joint tubes, piano keys and...
, which was apparently introduced to EuropeEuropeEurope is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting...
by the SaracenSaracenSaracen was a term used by the ancient Romans to refer to a people who lived in desert areas in and around the Roman province of Arabia, and who were distinguished from Arabs. In Europe during the Middle Ages the term was expanded to include Arabs, and then all who professed the religion of Islam...
s at the time of the CrusadesCrusadesThe Crusades were a series of religious wars, blessed by the Pope and the Catholic Church with the main goal of restoring Christian access to the holy places in and near Jerusalem...
; a Middle EastMiddle EastThe Middle East is a region that encompasses Western Asia and Northern Africa. It is often used as a synonym for Near East, in opposition to Far East...
ern instrument, the olifant was possibly adapted by the ArabArabArab people, also known as Arabs , are a panethnicity primarily living in the Arab world, which is located in Western Asia and North Africa. They are identified as such on one or more of genealogical, linguistic, or cultural grounds, with tribal affiliations, and intra-tribal relationships playing...
s from African models, which have a long history. - Clay trumpets can be found in South America, India, Western Europe and parts of Africa. South American varieties include imitations of conch-shell trumpets, such as the potuto of PeruPeruPeru , officially the Republic of Peru , is a country in western South America. It is bordered on the north by Ecuador and Colombia, on the east by Brazil, on the southeast by Bolivia, on the south by Chile, and on the west by the Pacific Ocean....
. The Horniman MuseumHorniman MuseumThe Horniman Museum is a museum in Forest Hill, South London, England. Commissioned in 1898, it opened in 1901 and was designed by Charles Harrison Townsend in the Arts and Crafts style....
in LondonLondonLondon is the capital city of :England and the :United Kingdom, the largest metropolitan area in the United Kingdom, and the largest urban zone in the European Union by most measures. Located on the River Thames, London has been a major settlement for two millennia, its history going back to its...
has a red-and-white-marbled clay PortuguesePortugalPortugal , officially the Portuguese Republic is a country situated in southwestern Europe on the Iberian Peninsula. Portugal is the westernmost country of Europe, and is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the West and South and by Spain to the North and East. The Atlantic archipelagos of the...
trumpet which was obviously copied from a brass instrument. Coiled clay trumpets probably derive from animal-horn or conch-shell models. Peru had long straight clay trumpets called pungacuqua or puuaqua which were up to 1.5 m long and were blown in pairs, as was the botuto from the OrinocoOrinocoThe Orinoco is one of the longest rivers in South America at . Its drainage basin, sometimes called the Orinoquia, covers , with 76.3% of it in Venezuela and the remainder in Colombia...
basin. Clay trumpets have also been found in MayaMaya civilizationThe Maya is a Mesoamerican civilization, noted for the only known fully developed written language of the pre-Columbian Americas, as well as for its art, architecture, and mathematical and astronomical systems. Initially established during the Pre-Classic period The Maya is a Mesoamerican...
n cities in Central AmericaCentral AmericaCentral America is the central geographic region of the Americas. It is the southernmost, isthmian portion of the North American continent, which connects with South America on the southeast. When considered part of the unified continental model, it is considered a subcontinent...
.
Ancient Egypt
The natural trumpet was probably first used as a military instrument in ancient EgyptHistory of Ancient Egypt
The History of Ancient Egypt spans the period from the early predynastic settlements of the northern Nile Valley to the Roman conquest in 30 BC...
. The trumpets depicted by the artists of the Eighteenth Dynasty
Eighteenth dynasty of Egypt
The eighteenth dynasty of ancient Egypt is perhaps the best known of all the dynasties of ancient Egypt...
were short straight instruments made of wood, bronze, copper or silver. The Ancient Egyptian
Egyptian language
Egyptian is the oldest known indigenous language of Egypt and a branch of the Afroasiatic language family. Written records of the Egyptian language have been dated from about 3400 BC, making it one of the oldest recorded languages known. Egyptian was spoken until the late 17th century AD in the...
name for this particular instrument was sheneb (šnb). According to the Classical writers, the Egyptian trumpet sounded like the braying of an ass.
For the most part the trumpeters depicted in Egyptian art are engaged in military activities – the sheneb was probably used on the battlefield both to encourage (and possibly also to direct) the Pharaoh
Pharaoh
Pharaoh is a title used in many modern discussions of the ancient Egyptian rulers of all periods. The title originates in the term "pr-aa" which means "great house" and describes the royal palace...
’s troops and to intimidate the enemy. In some murals from the Eighteenth Dynasty
Eighteenth dynasty of Egypt
The eighteenth dynasty of ancient Egypt is perhaps the best known of all the dynasties of ancient Egypt...
, the sheneb appears to be accompanying dancers; if this is the case, it is possibly the earliest depiction of a trumpet in a truly “musical” setting. Egyptian trumpeters are often, though not always, shown in pairs.
The oldest surviving examples of metallic trumpets are the two instruments that were discovered in the tomb of Tutankhamun
Tutankhamun
Tutankhamun , Egyptian , ; approx. 1341 BC – 1323 BC) was an Egyptian pharaoh of the 18th dynasty , during the period of Egyptian history known as the New Kingdom...
in 1922. One of these is 58.2 cm long and is made of silver
Silver
Silver is a metallic chemical element with the chemical symbol Ag and atomic number 47. A soft, white, lustrous transition metal, it has the highest electrical conductivity of any element and the highest thermal conductivity of any metal...
; it has a conical tube 1.7 to 2.6 cm in diameter, and a flaring bell 8.2 cm wide. The other instrument is 50.5 cm long and is made of copper
Copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu and atomic number 29. It is a ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. Pure copper is soft and malleable; an exposed surface has a reddish-orange tarnish...
with gold
Gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au and an atomic number of 79. Gold is a dense, soft, shiny, malleable and ductile metal. Pure gold has a bright yellow color and luster traditionally considered attractive, which it maintains without oxidizing in air or water. Chemically, gold is a...
overlay. Neither instrument has a separate mouthpiece
Mouthpiece (brass)
On brass instruments the mouthpiece is the part of the instrument which is placed upon the player's lips. The purpose of the mouthpiece is a resonator, which passes vibration from the lips to the column of air contained within the instrument, giving rise to the standing wave pattern of vibration in...
and their respective weights have not been documented. Both are inscribed with the names of gods associated with Egyptian army divisions. A third trumpet, probably dating from the Ptolemaic
Ptolemaic Kingdom
The Ptolemaic Kingdom in and around Egypt began following Alexander the Great's conquest in 332 BC and ended with the death of Cleopatra VII and the Roman conquest in 30 BC. It was founded when Ptolemy I Soter declared himself Pharaoh of Egypt, creating a powerful Hellenistic state stretching from...
era, is now preserved in the Louvre
Louvre
The Musée du Louvre – in English, the Louvre Museum or simply the Louvre – is one of the world's largest museums, the most visited art museum in the world and a historic monument. A central landmark of Paris, it is located on the Right Bank of the Seine in the 1st arrondissement...
museum in Paris
Paris
Paris is the capital and largest city in France, situated on the river Seine, in northern France, at the heart of the Île-de-France region...
.
Ancient Israel
Other trumpets are mentioned in the BibleBible
The Bible refers to any one of the collections of the primary religious texts of Judaism and Christianity. There is no common version of the Bible, as the individual books , their contents and their order vary among denominations...
besides the primitive shofar: the yowbel was the ram’s-horn trumpet whose sound made the walls of Jericho
Jericho
Jericho ; is a city located near the Jordan River in the West Bank of the Palestinian territories. It is the capital of the Jericho Governorate and has a population of more than 20,000. Situated well below sea level on an east-west route north of the Dead Sea, Jericho is the lowest permanently...
fall down (Joshua
Joshua
Joshua , is a minor figure in the Torah, being one of the spies for Israel and in few passages as Moses's assistant. He turns to be the central character in the Hebrew Bible's Book of Joshua...
6); the taqowa‘ was a Jewish military trumpet which is mentioned in Ezekiel
Ezekiel
Ezekiel , "God will strengthen" , is the central protagonist of the Book of Ezekiel in the Hebrew Bible. In Judaism, Christianity and Islam, Ezekiel is acknowledged as a Hebrew prophet...
7:14. The best known Biblical trumpet after the shofar, however, is the hasoserah. In the Book of Numbers
Book of Numbers
The Book of Numbers is the fourth book of the Hebrew Bible, and the fourth of five books of the Jewish Torah/Pentateuch....
, Moses is instructed to make two silver hasoserah:
²Make thee two trumpets of silver; of a whole piece shalt thou make them: that thou mayest use them for the calling of the assembly, and for the journeying of the camps. ³And when they shall blow with them, all the assembly shall assemble themselves to thee at the door of the tabernacle of the congregation. 4And if they blow but with one trumpet, then the princes, which are heads of the thousands of Israel, shall gather themselves unto thee. 5When ye blow an alarm, then the camps that lie on the east parts shall go forward. 6When ye blow an alarm the second time, then the camps that lie on the south side shall take their journey: they shall blow an alarm for their journeys. 7But when the congregation is to be gathered together, ye shall blow, but ye shall not sound an alarm. 8And the sons of AaronAaronIn the Hebrew Bible and the Qur'an, Aaron : Ααρών ), who is often called "'Aaron the Priest"' and once Aaron the Levite , was the older brother of Moses, and a prophet of God. He represented the priestly functions of his tribe, becoming the first High Priest of the Israelites...
, the priests, shall blow with the trumpets; and they shall be to you for an ordinance for ever throughout your generations. 9And if ye go to war in your land against the enemy that oppresseth you, then ye shall blow an alarm with the trumpets; and ye shall be remembered before the Lord your God, and ye shall be saved from your enemies. 10Also in the day of your gladness, and in your solemn days, and in the beginnings of your months, ye shall blow with the trumpets over your burnt offerings, and over the sacrifices of your peace offerings; that they may be to you for a memorial before your God.... (NumbersBook of NumbersThe Book of Numbers is the fourth book of the Hebrew Bible, and the fourth of five books of the Jewish Torah/Pentateuch....
10:2–10, King James VersionKing James Version of the BibleThe Authorized Version, commonly known as the King James Version, King James Bible or KJV, is an English translation of the Christian Bible by the Church of England begun in 1604 and completed in 1611...
.)
The hasoserah was played in two different ways: taqa‘ and teruw‘ah. The former referred to a continuous sounding of the instrument by one or two Levite
Levite
In Jewish tradition, a Levite is a member of the Hebrew tribe of Levi. When Joshua led the Israelites into the land of Canaan, the Levites were the only Israelite tribe that received cities but were not allowed to be landowners "because the Lord the God of Israel himself is their inheritance"...
s during religious ceremonies; the latter referred to the sounding of an alarm or military signal, and was always carried out by two trumpeters. In the 18th century the German music theorist Johann Ernst Altenburg
Johann Ernst Altenburg
Johann Ernst Altenburg was a German composer, organist and trumpeter.-Life:His father, Johann Kaspar Altenburg , worked from 1709 as a field trumpeter under Johann Adolf II, Duke of Saxe-Weissenfels and from 1711 as head trumpeter for the duke's brother, Duke Christian von Sachsen-Weissenfels at...
compared these two styles of playing to the two styles of trumpet playing prevalent in the Late Baroque
Baroque music
Baroque music describes a style of Western Classical music approximately extending from 1600 to 1760. This era follows the Renaissance and was followed in turn by the Classical era...
: the mellow style of the principale and the strident style of the clarino.
The military use of the natural trumpet is recorded in many passages of the Bible
Bible
The Bible refers to any one of the collections of the primary religious texts of Judaism and Christianity. There is no common version of the Bible, as the individual books , their contents and their order vary among denominations...
(e.g. Jeremiah
Book of Jeremiah
The Book of Jeremiah is the second of the Latter Prophets in the Hebrew Bible, following the book of Isaiah and preceding Ezekiel and the Book of the Twelve....
4:19, Zephaniah
Zephaniah
Zephaniah or Tzfanya is the name of several people in the Bible Old Testament and Jewish Tanakh. He is also called Sophonias as in the New Catholic Encyclopaedia and in Easton's [Bible] Dictionary....
1:16, Amos
Book of Amos
The Book of Amos is a prophetic book of the Hebrew Bible, one of the Twelve Minor Prophets. Amos, an older contemporary of Hosea and Isaiah, was active c. 750 BCE during the reign of Jeroboam II, making the Book of Amos the first biblical prophetic book written. Amos lived in the kingdom of Judah...
2:2). Other passages recount its use as a celebratory instrument (e.g. II Kings
Books of Kings
The Book of Kings presents a narrative history of ancient Israel and Judah from the death of David to the release of his successor Jehoiachin from imprisonment in Babylon, a period of some 400 years...
11:14, II Chronicles
Books of Chronicles
The Books of Chronicles are part of the Hebrew Bible. In the Masoretic Text, it appears as the first or last book of the Ketuvim . Chronicles largely parallels the Davidic narratives in the Books of Samuel and the Books of Kings...
5:12–13, Psalms 98:6).
Josephus
Josephus
Titus Flavius Josephus , also called Joseph ben Matityahu , was a 1st-century Romano-Jewish historian and hagiographer of priestly and royal ancestry who recorded Jewish history, with special emphasis on the 1st century AD and the First Jewish–Roman War, which resulted in the Destruction of...
, who credits Moses
Moses
Moses was, according to the Hebrew Bible and Qur'an, a religious leader, lawgiver and prophet, to whom the authorship of the Torah is traditionally attributed...
with the invention of the hasoserah, describes the instrument thus:
“In length it was little less than a cubitCubitThe cubit is a traditional unit of length, based on the length of the forearm. Cubits of various lengths were employed in many parts of the world in Antiquity, in the Middle Ages and into Early Modern Times....
[45.72 cm]. It was composed of a narrow tube, somewhat thicker than a flute, but with so much breadth as was sufficient for admission of the breath of a man’s mouth: it ended in the form of a bell, like common trumpets. Its sound was called in the Hebrew tongue Asosra.” (Antiquities of the JewsAntiquities of the JewsAntiquities of the Jews is a twenty volume historiographical work composed by the Jewish historian Flavius Josephus in the thirteenth year of the reign of Roman emperor Flavius Domitian which was around 93 or 94 AD. Antiquities of the Jews contains an account of history of the Jewish people,...
, 3.291)
The hasoserah is depicted on the Arch of Titus
Arch of Titus
The Arch of Titus is a 1st-century honorific arch located on the Via Sacra, Rome, just to the south-east of the Roman Forum. It was constructed in c.82 AD by the Roman Emperor Domitian shortly after the death of his older brother Titus to commemorate Titus' victories, including the Siege of...
among the spoils taken by the Romans in the sack of Jerusalem
Siege of Jerusalem (70)
The Siege of Jerusalem in the year 70 AD was the decisive event of the First Jewish-Roman War. The Roman army, led by the future Emperor Titus, with Tiberius Julius Alexander as his second-in-command, besieged and conquered the city of Jerusalem, which had been occupied by its Jewish defenders in...
in 70
70
Year 70 was a common year starting on Monday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Augustus and Vespasianus...
CE (though these particular trumpets appear to be at least a metre long).
Babylon and Assyria
A straight trumpet similar to the Egyptian sheneb was also used in ancient BabyloniaBabylonia
Babylonia was an ancient cultural region in central-southern Mesopotamia , with Babylon as its capital. Babylonia emerged as a major power when Hammurabi Babylonia was an ancient cultural region in central-southern Mesopotamia (present-day Iraq), with Babylon as its capital. Babylonia emerged as...
and Assyria
Assyria
Assyria was a Semitic Akkadian kingdom, extant as a nation state from the mid–23rd century BC to 608 BC centred on the Upper Tigris river, in northern Mesopotamia , that came to rule regional empires a number of times through history. It was named for its original capital, the ancient city of Assur...
, where it was called the qarna. On a relief
Relief
Relief is a sculptural technique. The term relief is from the Latin verb levo, to raise. To create a sculpture in relief is thus to give the impression that the sculpted material has been raised above the background plane...
from the time of Sennacherib
Sennacherib
Sennacherib |Sîn]] has replaced brothers for me"; Aramaic: ) was the son of Sargon II, whom he succeeded on the throne of Assyria .-Rise to power:...
(reigned 705 BC–681 BC) depicting the moving of a colossal bull statue, two trumpeters are standing on the statue; one is playing while the other rests. Among the descendants of the qarna are the Persian karranay and the Safavid karna. The latter, a straight metallic trumpet, can still be found in northern India
India
India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
.
Ancient Greece
The war-trumpet used by the ancient GreeksAncient Greece
Ancient Greece is a civilization belonging to a period of Greek history that lasted from the Archaic period of the 8th to 6th centuries BC to the end of antiquity. Immediately following this period was the beginning of the Early Middle Ages and the Byzantine era. Included in Ancient Greece is the...
was called the salpinx, and was probably adapted from the Egyptian sheneb. There is a fine example on display in Boston
Boston
Boston is the capital of and largest city in Massachusetts, and is one of the oldest cities in the United States. The largest city in New England, Boston is regarded as the unofficial "Capital of New England" for its economic and cultural impact on the entire New England region. The city proper had...
’s Museum of Fine Arts; the tube of this particular salpinx is 157 cm long and consists of thirteen cylindrical parts made of ivory; the instrument’s bell and mouthpiece
Mouthpiece (brass)
On brass instruments the mouthpiece is the part of the instrument which is placed upon the player's lips. The purpose of the mouthpiece is a resonator, which passes vibration from the lips to the column of air contained within the instrument, giving rise to the standing wave pattern of vibration in...
are both made of bronze, as are the rings used to hold the ivory sections together; the instrument is thought to date from the second half of the 5th century BC. The Greek playwright Aeschylus
Aeschylus
Aeschylus was the first of the three ancient Greek tragedians whose work has survived, the others being Sophocles and Euripides, and is often described as the father of tragedy. His name derives from the Greek word aiskhos , meaning "shame"...
described the sound of the salpinx as “shattering”; the word salpinx is thought to mean “thunderer”.
At the Olympic Games, contests of trumpet playing were introduced for the first time in 396 BC
396 BC
Year 396 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Tribunate of Saccus, Capitolinus, Esquilinus, Augurinus, Capitolinus and Priscus...
These contests were judged not by the participants’ musical skill but by the volume of sound they generated! Among the more famous trumpeters who participated in the games was Achias, who was awarded first prize on three occasions and in whose honour a column was erected. Another famous contestant was Herodorus of Megas, a man of immense stature, whose playing was so loud that audiences were allegedly concussed by his performances. By winning the trumpet contest at Olympia
Olympia, Greece
Olympia , a sanctuary of ancient Greece in Elis, is known for having been the site of the Olympic Games in classical times, comparable in importance to the Pythian Games held in Delphi. Both games were held every Olympiad , the Olympic Games dating back possibly further than 776 BC...
, a trumpeter was authorized to perform at the hippodrome
Hippodrome
A hippodrome was a Greek stadium for horse racing and chariot racing. The name is derived from the Greek words "hippos and "dromos"...
and to introduce the athletes for the remainder of the games.
On a painted ceramic knee guard dating from ca. 500 BC, a salpinx call is recorded using the Greek syllables TOTH TOTOTE. This is the earliest example of trumpet notation anywhere in the world.
Etruria and Ancient Rome
The use of the natural trumpet as a fully-fledged military signalling instrument is generally credited to the ancient Romans; a total of forty-three signals are said to have been used in the Roman army. Since the early days of the RepublicRoman Republic
The Roman Republic was the period of the ancient Roman civilization where the government operated as a republic. It began with the overthrow of the Roman monarchy, traditionally dated around 508 BC, and its replacement by a government headed by two consuls, elected annually by the citizens and...
, two centuria
Centuria
Centuria is a Latin substantive from the stem centum , denoting units consisting of 100 men. It also denotes a Roman unit of land area: 1 centuria = 100 heredia...
tes of troops (about 160 men) were composed entirely of trumpeters; these musicians, called aenatores, employed a variety of instruments. It is now thought that the Romans adapted these instruments, and possibly also the signals sounded on them, from Etruscan
Etruscan civilization
Etruscan civilization is the modern English name given to a civilization of ancient Italy in the area corresponding roughly to Tuscany. The ancient Romans called its creators the Tusci or Etrusci...
models. The Etruscans were expert metallurgists and keen musicians, and musical instruments were just some of the many inventions they bequeathed to their Roman conquerors. Among the trumpet-like instruments used by the Romans, the following four may be distinguished:
- The tubaRoman tubaThe tuba of ancient Rome is a military signal trumpet, quite different from the modern tuba. The tuba was produced around 500 BC. Its shape was straight, in contrast to the military buccina or cornu, which was more like the modern tuba in curving around the body. Its origin is thought to be...
was a straight trumpet played by a tubicen (pl: tubicines). It was about 117 cm long and had a conical bore of between 10 and 28 mm. It was usually made of bronze and was played with a detachable bone mouthpieceMouthpiece (brass)On brass instruments the mouthpiece is the part of the instrument which is placed upon the player's lips. The purpose of the mouthpiece is a resonator, which passes vibration from the lips to the column of air contained within the instrument, giving rise to the standing wave pattern of vibration in...
. It had a slightly flared bell. The Roman tuba was probably a direct ancestor of both the Western trumpetTrumpetThe trumpet is the musical instrument with the highest register in the brass family. Trumpets are among the oldest musical instruments, dating back to at least 1500 BCE. They are played by blowing air through closed lips, producing a "buzzing" sound which starts a standing wave vibration in the air...
and the Western hornHorn (instrument)The horn is a brass instrument consisting of about of tubing wrapped into a coil with a flared bell. A musician who plays the horn is called a horn player ....
. (The modern tuba, which shares its name with the Roman tuba, however, is a recent invention.) - The cornuCornu (horn)A cornu or cornum was a type of brass instrument similar to the buccina used by the Roman army of antiquity mainly for communicating orders to troops in battle. It is a Latin word literally meaning horn. The instrument was about long and took the form of a letter 'G'...
was a natural hornHorn (instrument)The horn is a brass instrument consisting of about of tubing wrapped into a coil with a flared bell. A musician who plays the horn is called a horn player ....
about 3 m long, with a wide, conical bore; it was made of bronze and took the form of a letter “G”. It was played with a cup-shaped mouthpieceMouthpiece (brass)On brass instruments the mouthpiece is the part of the instrument which is placed upon the player's lips. The purpose of the mouthpiece is a resonator, which passes vibration from the lips to the column of air contained within the instrument, giving rise to the standing wave pattern of vibration in...
. The large flaring bell curved over the player’s head or shoulder. The cornu was played by a trumpeter known as a cornicen (pl: cornicines). - The buccinaBuccinaA buccina or bucina , anglicized buccin or bucine, is a brass instrument used in the ancient Roman army similar to the Cornu. An aeneator who blew a buccina was called a "buccinator" or "bucinator" ....
, or bucina, was played by a buccinator (pl: buccinatores). This was of similar construction to the cornu and was also played with a cup-shaped mouthpiece, but it had a narrower, more cylindrical bore. The military buccina evolved from a primitive prototype, the buccina marina, which was a natural conch-shell trumpet; in Roman poetry the buccina marina is often called the concha. - The lituusLituusThe word lituus originally meant a curved augural staff or a curved war-trumpet in the ancient Latin language. In English it is used with several meanings.-Roman ritual wand:...
was a long J-shaped trumpet. Essentially, it was a straight trumpet, like the tuba, to which an animal-horn trumpet was attached to act as a bell; it is not unlike the Celtic carnyxCarnyxThe carnyx was a wind instrument of the Iron Age Celts, used between c. 300 BC to 200 AD. It was a type of bronze trumpet, held vertically, the mouth styled in the shape of a boar's, or other animal's, head. It was used in warfare, probably to incite troops to battle and intimidate opponents...
. The lituus was a cult instrument used in Roman rituals and does not appear to have had any military uses, though the term was later used in the Middle AgesMiddle AgesThe Middle Ages is a periodization of European history from the 5th century to the 15th century. The Middle Ages follows the fall of the Western Roman Empire in 476 and precedes the Early Modern Era. It is the middle period of a three-period division of Western history: Classic, Medieval and Modern...
to denote a military trumpet. Surviving litui are 78-140 cm long. Being the shortest of the Roman trumpets, the lituus was a higher pitched instrument, the sound of which Classical writers described as acutus (“high”). The lituus and the buccina are frequently confused.
The late Roman writer Vegetius
Vegetius
Publius Flavius Vegetius Renatus, commonly referred to simply as Vegetius, was a writer of the Later Roman Empire. Nothing is known of his life or station beyond what he tells us in his two surviving works: Epitoma rei militaris , and the lesser-known Digesta Artis Mulomedicinae, a guide to...
briefly describes the use of trumpets in the Roman legions in his treatise De Re Militari
De Re Militari
De Re Militari , also Epitoma Rei Militaris, is a treatise by the late Latin writer Vegetius about Roman warfare and military principles as a presentation of methods and practices in use during the height of Rome's power, and responsible for that power...
:
“The legion also has its tubicines, cornicines and buccinatores. The tubicen sounds the charge and the retreat. The cornicines are used only to regulate the motions of the colours; the tubicines serve when the soldiers are ordered out to any work without the colours; but in time of action, the tubicines and cornicines sound together. The classicum, which is a particular signal of the buccinatores or cornicines, is appropriated to the commander-in-chief and is used in the presence of the general, or at the execution of a soldier, as a mark of its being done by his authority. The ordinary guards and outposts are always mounted and relieved by the sound of the tubicen, who also directs the motions of the soldiers on working parties and on field days. The cornicines sound whenever the colours are to be struck or planted. These rules must be punctually observed in all exercises and reviews so that the soldiers may be ready to obey them in action without hesitation according to the general’s orders either to charge or halt, to pursue the enemy or to retire. For reason will convince us that what is necessary to be performed in the heat of action should constantly be practised in the leisure of peace.” (De Re Militari, Book II.)
Like the Greek salpinx the Roman trumpets were not regarded as musical instruments. Among the tems used to describe the tuba’s tone, for instance, were horribilis (“horrible”), terribilis (“terrible”), raucus (“raucous”), rudis (“coarse”), strepens (“noisy”) and stridulus (“shrieking”). When sounding their instruments, the tubicines sometimes girded their cheeks with the capistrum (“muzzle”) which aulos (“flute”) players used to prevent their cheeks from being puffed out unduly.
Arab and Persian
After the fall of the Western EmpireDecline of the Roman Empire
The decline of the Roman Empire refers to the gradual societal collapse of the Western Roman Empire. Many theories of causality prevail, but most concern the disintegration of political, economic, military, and other social institutions, in tandem with foreign invasions and usurpers from within the...
in 476
476
Year 476 was a leap year starting on Thursday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Basiliscus and Armatus...
, the trumpet disappeared from Europe for more than half a millennium. Elsewhere the art of bending long metal tubes was lost, for the trumpets of the succeeding era lacked the characteristic G-like curve of the cornu and buccina. The straight-tubed Roman tuba, however, continued to flourish in the Middle East
Middle East
The Middle East is a region that encompasses Western Asia and Northern Africa. It is often used as a synonym for Near East, in opposition to Far East...
among the Sassanids and their Arab
Arab
Arab people, also known as Arabs , are a panethnicity primarily living in the Arab world, which is located in Western Asia and North Africa. They are identified as such on one or more of genealogical, linguistic, or cultural grounds, with tribal affiliations, and intra-tribal relationships playing...
ic successors. The Saracen
Saracen
Saracen was a term used by the ancient Romans to refer to a people who lived in desert areas in and around the Roman province of Arabia, and who were distinguished from Arabs. In Europe during the Middle Ages the term was expanded to include Arabs, and then all who professed the religion of Islam...
s, whose long metal trumpets greatly impressed the Christian armies at the time of the Crusades, were ultimately responsible for reintroducing the instrument to Europe after a lapse of six hundred years.
During the last centuries of the Roman Empire
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire was the post-Republican period of the ancient Roman civilization, characterised by an autocratic form of government and large territorial holdings in Europe and around the Mediterranean....
the name buccina was widely used throughout the Near East
Near East
The Near East is a geographical term that covers different countries for geographers, archeologists, and historians, on the one hand, and for political scientists, economists, and journalists, on the other...
to denote a particular type of straight trumpet similar to, and probably derived from, the Roman tuba
Tuba
The tuba is the largest and lowest-pitched brass instrument. Sound is produced by vibrating or "buzzing" the lips into a large cupped mouthpiece. It is one of the most recent additions to the modern symphony orchestra, first appearing in the mid-19th century, when it largely replaced the...
. From this, undoubtedly, derives the generic term būq, which first occurs after 800
800
Year 800 was a leap year starting on Wednesday of the Julian calendar. It was around this time that the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years, so from this time on, the years began being known as 800 and onwards.- Europe :* December 25 - Pope Leo III...
; this was the name used by the Arab
Arab
Arab people, also known as Arabs , are a panethnicity primarily living in the Arab world, which is located in Western Asia and North Africa. They are identified as such on one or more of genealogical, linguistic, or cultural grounds, with tribal affiliations, and intra-tribal relationships playing...
s to describe a variety of both trumpet-like and horn-like instruments. The būq al-nafīr (“buc[cina] of war”) was a long straight metal trumpet used in the military bands of the Abbasid
Abbasid
The Abbasid Caliphate or, more simply, the Abbasids , was the third of the Islamic caliphates. It was ruled by the Abbasid dynasty of caliphs, who built their capital in Baghdad after overthrowing the Umayyad caliphate from all but the al-Andalus region....
period (750
750
Year 750 was a common year starting on Thursday of the Julian calendar. The denomination 750 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.- Asia :* Gopala is proclaimed as the first ruler of...
–1258) and thereafter; by the 14th century it could be as much as two metres long. From the 11th century, this term was used to denote any long straight trumpet.
Other Arabic words for trumpets of various sizes and shapes include qarnā and sūr; the latter is the name used in the Qur'an for the Last Trump
Last Judgment
The Last Judgment, Final Judgment, Day of Judgment, Judgment Day, or The Day of the Lord in Christian theology, is the final and eternal judgment by God of every nation. The concept is found in all the Canonical gospels, particularly the Gospel of Matthew. It will purportedly take place after the...
that will announce Judgment Day. The qarnā is thought to be a descendant of the ancient Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia is a toponym for the area of the Tigris–Euphrates river system, largely corresponding to modern-day Iraq, northeastern Syria, southeastern Turkey and southwestern Iran.Widely considered to be the cradle of civilization, Bronze Age Mesopotamia included Sumer and the...
n instrument of the same name.
The Saracen
Saracen
Saracen was a term used by the ancient Romans to refer to a people who lived in desert areas in and around the Roman province of Arabia, and who were distinguished from Arabs. In Europe during the Middle Ages the term was expanded to include Arabs, and then all who professed the religion of Islam...
s are sometimes said to be the first people to make brass trumpets from hammered sheet, though this is not at all certain.
Many of the long, straight metal trumpets that first appeared around this time were associated with the spread of Islam
Islam
Islam . The most common are and . : Arabic pronunciation varies regionally. The first vowel ranges from ~~. The second vowel ranges from ~~~...
. In Africa, for example, end-blown metal trumpets are found only in Islamic regions such as Nigeria
Nigeria
Nigeria , officially the Federal Republic of Nigeria, is a federal constitutional republic comprising 36 states and its Federal Capital Territory, Abuja. The country is located in West Africa and shares land borders with the Republic of Benin in the west, Chad and Cameroon in the east, and Niger in...
, Chad
Chad
Chad , officially known as the Republic of Chad, is a landlocked country in Central Africa. It is bordered by Libya to the north, Sudan to the east, the Central African Republic to the south, Cameroon and Nigeria to the southwest, and Niger to the west...
and central Cameroon
Cameroon
Cameroon, officially the Republic of Cameroon , is a country in west Central Africa. It is bordered by Nigeria to the west; Chad to the northeast; the Central African Republic to the east; and Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, and the Republic of the Congo to the south. Cameroon's coastline lies on the...
. Known as kakaki (among the Hausa
Hausa people
The Hausa are one of the largest ethnic groups in West Africa. They are a Sahelian people chiefly located in northern Nigeria and southeastern Niger, but having significant numbers living in regions of Cameroon, Ghana, Cote d'Ivoire, Chad and Sudan...
of Nigeria
Nigeria
Nigeria , officially the Federal Republic of Nigeria, is a federal constitutional republic comprising 36 states and its Federal Capital Territory, Abuja. The country is located in West Africa and shares land borders with the Republic of Benin in the west, Chad and Cameroon in the east, and Niger in...
) or gashi (in Chad
Chad
Chad , officially known as the Republic of Chad, is a landlocked country in Central Africa. It is bordered by Libya to the north, Sudan to the east, the Central African Republic to the south, Cameroon and Nigeria to the southwest, and Niger to the west...
), these trumpets consist of narrow cylindrical tubes, sometimes over two metres in length, with flared metal bells. The silver nafiri is one of only two trumpets found in Malaysia; its name clearly derives from the Arabic būq al-nafīr. Slightly less than one metre long, a single nafiri is present in each of the royal nobat ensembles maintained by the local sultan
Sultan
Sultan is a title with several historical meanings. Originally, it was an Arabic language abstract noun meaning "strength", "authority", "rulership", and "dictatorship", derived from the masdar سلطة , meaning "authority" or "power". Later, it came to be used as the title of certain rulers who...
s. As in Africa, these royal ensembles play on ceremonial occasions and Islamic holidays.
Asia
The dung is the long monastic trumpet of TibetTibet
Tibet is a plateau region in Asia, north-east of the Himalayas. It is the traditional homeland of the Tibetan people as well as some other ethnic groups such as Monpas, Qiang, and Lhobas, and is now also inhabited by considerable numbers of Han and Hui people...
; it is similar to, and probably derives from, straight trumpets depicted in 13th-century Arab
Arab
Arab people, also known as Arabs , are a panethnicity primarily living in the Arab world, which is located in Western Asia and North Africa. They are identified as such on one or more of genealogical, linguistic, or cultural grounds, with tribal affiliations, and intra-tribal relationships playing...
ic and Persian manuscripts. The dung is a straight, end-blown trumpet with a conical bore; it is made of copper or brass and has a separate mouthpiece
Mouthpiece (brass)
On brass instruments the mouthpiece is the part of the instrument which is placed upon the player's lips. The purpose of the mouthpiece is a resonator, which passes vibration from the lips to the column of air contained within the instrument, giving rise to the standing wave pattern of vibration in...
. It varies in length from about 60 cm (the medium-sized rag-dun) to as much as 5 m (the telescopic dung-chen). In musical ensembles, two such instruments blown in alternation provide a continuous drone, which is sustained beneath the woodwind and percussion.
The dung-chen can also be found in the northern hills of Laddakh in India
India
India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
and in Bhutan
Bhutan
Bhutan , officially the Kingdom of Bhutan, is a landlocked state in South Asia, located at the eastern end of the Himalayas and bordered to the south, east and west by the Republic of India and to the north by the People's Republic of China...
, where it is known by the name thunchen. This ceremonial instrument is used to accompany ritual dances. Nearly three metres long, it is made of copper and decorated with silver. The thunchen is generally employed in pairs; the trumpeters, known as thunchen pa, announce the commencement of ceremonies from the gamba, or temple, and also accompany ritual dances. The length and weight of thunchen make it extremely unwieldy; so the flared end is rested on the ground or a special stand, or is supported on the shoulders of another monk.
Possibly related to the Tibetan dung is the tirucinnam, a straight trumpet still found in Tamil Nadu
Tamil Nadu
Tamil Nadu is one of the 28 states of India. Its capital and largest city is Chennai. Tamil Nadu lies in the southernmost part of the Indian Peninsula and is bordered by the union territory of Pondicherry, and the states of Kerala, Karnataka, and Andhra Pradesh...
in southern India
India
India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
. Usually a pair of these long, slender instruments are blown together; until a few decades ago it was standard practice for one musician to play both of them simultaneously, which seems to have been the case also in Nepal
Nepal
Nepal , officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal, is a landlocked sovereign state located in South Asia. It is located in the Himalayas and bordered to the north by the People's Republic of China, and to the south, east, and west by the Republic of India...
. A double trumpet of this type is depicted on a relief in Chandi Jawri, Indonesia
Indonesia
Indonesia , officially the Republic of Indonesia , is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania. Indonesia is an archipelago comprising approximately 13,000 islands. It has 33 provinces with over 238 million people, and is the world's fourth most populous country. Indonesia is a republic, with an...
, dated to 1300 CE. The tirucinnam is about 75 cm long and has a wide cylindrical bore; it has a narrow conical bell but no mouthpiece (to facilitate the simultaneous blowing of two instruments).
The Chinese
China
Chinese civilization may refer to:* China for more general discussion of the country.* Chinese culture* Greater China, the transnational community of ethnic Chinese.* History of China* Sinosphere, the area historically affected by Chinese culture...
too had a long clyindrical metal trumpet known as hao t’ung (or, in Japanese
Japanese language
is a language spoken by over 130 million people in Japan and in Japanese emigrant communities. It is a member of the Japonic language family, which has a number of proposed relationships with other languages, none of which has gained wide acceptance among historical linguists .Japanese is an...
, dokaku), which may have been related to the foregoing instruments. In place of a bell, the hao t’ung had a long, broad cylinder made of wood, iron or brass, into which the rest of the instrument could be telescoped when not in use; the hao t’ung was played with the bell end resting on the ground. The ordinary Chinese trumpet was the la pa (rapa in Japanese). This came from Mongolia
Mongolia
Mongolia is a landlocked country in East and Central Asia. It is bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south, east and west. Although Mongolia does not share a border with Kazakhstan, its western-most point is only from Kazakhstan's eastern tip. Ulan Bator, the capital and largest...
, where it was called the rapal. It had a narrow, conical bore and consisted of two or three sections which telescoped into each other. (Chinese sources record the use of trumpets on the battlefield by the Huns
Huns
The Huns were a group of nomadic people who, appearing from east of the Volga River, migrated into Europe c. AD 370 and established the vast Hunnic Empire there. Since de Guignes linked them with the Xiongnu, who had been northern neighbours of China 300 years prior to the emergence of the Huns,...
, or Xiongnu
Xiongnu
The Xiongnu were ancient nomadic-based people that formed a state or confederation north of the agriculture-based empire of the Han Dynasty. Most of the information on the Xiongnu comes from Chinese sources...
, in the 3rd and 2nd centuries BC.)

