Tibetan language
Overview
Tibeto-Burman languages
The Tibeto-Burman languages are the non-Chinese members of the Sino-Tibetan language family, over 400 of which are spoken thoughout the highlands of southeast Asia, as well as lowland areas in Burma ....
spoken primarily by Tibetan people
Tibetan people
The Tibetan people are an ethnic group that is native to Tibet, which is mostly in the People's Republic of China. They number 5.4 million and are the 10th largest ethnic group in the country. Significant Tibetan minorities also live in India, Nepal, and Bhutan...
s who live across a wide area of eastern Central Asia bordering the Indian subcontinent
Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent, also Indian Subcontinent, Indo-Pak Subcontinent or South Asian Subcontinent is a region of the Asian continent on the Indian tectonic plate from the Hindu Kush or Hindu Koh, Himalayas and including the Kuen Lun and Karakoram ranges, forming a land mass which extends...
, including the Tibetan Plateau
Tibetan Plateau
The Tibetan Plateau , also known as the Qinghai–Tibetan Plateau is a vast, elevated plateau in Central Asia covering most of the Tibet Autonomous Region and Qinghai, in addition to smaller portions of western Sichuan, southwestern Gansu, and northern Yunnan in Western China and Ladakh in...
and the northern Indian subcontinent in Baltistan
Baltistan
Baltistan , also known as بلتیول བལིུལ་ in the Balti language, is a region in northern Pakistan which forms Gilgit-Baltistan, bordering the Xinjiang Autonomous Region of China. In addition, a part of Baltistan also falls into Jammu and Kashmir of India. It is situated in the Karakoram mountains...
, Ladakh
Ladakh
Ladakh is a region of Jammu and Kashmir, the northernmost state of the Republic of India. It lies between the Kunlun mountain range in the north and the main Great Himalayas to the south, inhabited by people of Indo-Aryan and Tibetan descent...
, Nepal
Nepal
Nepal , officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal, is a landlocked sovereign state located in South Asia. It is located in the Himalayas and bordered to the north by the People's Republic of China, and to the south, east, and west by the Republic of India...
, Sikkim
Sikkim
Sikkim is a landlocked Indian state nestled in the Himalayan mountains...
, and Bhutan
Bhutan
Bhutan , officially the Kingdom of Bhutan, is a landlocked state in South Asia, located at the eastern end of the Himalayas and bordered to the south, east and west by the Republic of India and to the north by the People's Republic of China...
. The classical written form
Classical Tibetan
Classical Tibetan refers to the language of any text written in Tibetan after the Old Tibetan period and before the modern period, but in particular refers to the language of early canonical texts translated from other languages, especially Sanskrit...
is a major regional literary language, particularly for its use in Buddhist
Buddhism
Buddhism is a religion and philosophy encompassing a variety of traditions, beliefs and practices, largely based on teachings attributed to Siddhartha Gautama, commonly known as the Buddha . The Buddha lived and taught in the northeastern Indian subcontinent some time between the 6th and 4th...
literature.
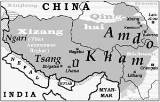
For political reasons, the dialects of central Tibet (including Lhasa
Lhasa
Lhasa is the administrative capital of the Tibet Autonomous Region in the People's Republic of China and the second most populous city on the Tibetan Plateau, after Xining. At an altitude of , Lhasa is one of the highest cities in the world...
), Kham
Kham
Kham , is a historical region covering a land area largely divided between present-day Tibetan Autonomous Region and Sichuan province, with smaller portions located within Qinghai, Gansu and Yunnan provinces of China. During the Republic of China's rule over mainland China , most of the region was...
s, and Amdo
Amdo
Amdo is one of the three traditional regions of Tibet, the other two being Ü-Tsang and Kham; it is also the birth place of the 14th Dalai Lama. Amdo encompasses a large area from the Machu River to the Drichu river . While culturally and ethnically a Tibetan area, Amdo has been administered by a...
in China
China
Chinese civilization may refer to:* China for more general discussion of the country.* Chinese culture* Greater China, the transnational community of ethnic Chinese.* History of China* Sinosphere, the area historically affected by Chinese culture...
are considered dialects of a single Tibetan language, while Dzongkha, Sikkimese, Sherpa
Sherpa language
Sherpa is a language spoken in parts of Nepal and Sikkim mainly by the Sherpa community. About 130,000 speakers live in Nepal , some 20,000 in India , and some 800 in Tibet ....
, and Ladakhi
Ladakhi language
The Ladakhi language , now also called Bhoti, and by linguists more generally called Western Archaic Tibetan when the Balti and Burig or Purig or Purki dialects are included, is the predominant language in the Ladakh region of the Jammu and Kashmir state of India, and is also spoken in Baltistan...
are generally considered to be separate languages, although their speakers may consider themselves to be ethnically Tibetan.
Unanswered Questions

