
Megalith
Encyclopedia


Rock (geology)
In geology, rock or stone is a naturally occurring solid aggregate of minerals and/or mineraloids.The Earth's outer solid layer, the lithosphere, is made of rock. In general rocks are of three types, namely, igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic...
that has been used to construct a structure or monument, either alone or together with other stones. Megalithic describes structures made of such large stones, utilizing an interlocking system without the use of mortar or cement.
The word 'megalith' comes from the Ancient Greek
Greek language
Greek is an independent branch of the Indo-European family of languages. Native to the southern Balkans, it has the longest documented history of any Indo-European language, spanning 34 centuries of written records. Its writing system has been the Greek alphabet for the majority of its history;...
megas meaning great, and lithos meaning stone. Megalith also denotes an item consisting of rock(s) hewn in definite shapes for special purposes. It has been used to describe buildings built by people from many parts of the world living in many different periods. A variety of large stones are seen as megaliths, with the most widely known megaliths not being sepulchral. The construction of these structures took place mainly in the Neolithic
Neolithic
The Neolithic Age, Era, or Period, or New Stone Age, was a period in the development of human technology, beginning about 9500 BC in some parts of the Middle East, and later in other parts of the world. It is traditionally considered as the last part of the Stone Age...
(though earlier Mesolithic
Mesolithic
The Mesolithic is an archaeological concept used to refer to certain groups of archaeological cultures defined as falling between the Paleolithic and the Neolithic....
examples are known) and continued into the Chalcolithic and Bronze Age
Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a period characterized by the use of copper and its alloy bronze as the chief hard materials in the manufacture of some implements and weapons. Chronologically, it stands between the Stone Age and Iron Age...
.
Early stone complexes in eastern Turkey

Turkey
Turkey , known officially as the Republic of Turkey , is a Eurasian country located in Western Asia and in East Thrace in Southeastern Europe...
, large ceremonial complexes from the 9th millennium BC
9th millennium BC
The 9th millennium BC marks the beginning of the Neolithic period.Agriculture spread throughout the Fertile Crescent and use of pottery became more widespread. Larger settlements like Jericho arose along salt and flint trade routes. Northern Eurasia was resettled as the glaciers of the last glacial...
have been discovered. They belong to the incipient phases of agriculture
Agriculture
Agriculture is the cultivation of animals, plants, fungi and other life forms for food, fiber, and other products used to sustain life. Agriculture was the key implement in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that nurtured the...
and animal husbandry
Animal husbandry
Animal husbandry is the agricultural practice of breeding and raising livestock.- History :Animal husbandry has been practiced for thousands of years, since the first domestication of animals....
. Large circular structures involving carved megalithic orthostats are a typical feature, e.g. at Nevali Cori
Nevali Cori
Nevalı Çori was an early Neolithic settlement on the middle Euphrates, in the province of Şanlıurfa , eastern Turkey. The site is famous for having revealed some of the world's most ancient known temples and monumental sculpture...
and Göbekli Tepe
Göbekli Tepe
Göbekli Tepe [ɡøbe̞kli te̞pɛ] is a hilltop sanctuary erected on the highest point of an elongated mountain ridge in southeastern Turkey, some northeast of the town of Şanlıurfa . It is the oldest human-made religious structure yet discovered...
. Although these structures are the most ancient megalithic structures known so far, it is not clear that any of the European Megalithic traditions (see below) are actually derived from them. At Göbekli Tepe four stone circles have been excavated from an estimated 20. Some measure up to 30 metres across. The stones carry carved reliefs of boars, foxes, lions, birds, snakes and scorpions.
European megaliths

Portugal
Portugal , officially the Portuguese Republic is a country situated in southwestern Europe on the Iberian Peninsula. Portugal is the westernmost country of Europe, and is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the West and South and by Spain to the North and East. The Atlantic archipelagos of the...
, stazzone in Sardinia
Sardinia
Sardinia is the second-largest island in the Mediterranean Sea . It is an autonomous region of Italy, and the nearest land masses are the French island of Corsica, the Italian Peninsula, Sicily, Tunisia and the Spanish Balearic Islands.The name Sardinia is from the pre-Roman noun *sard[],...
, hunebed in the Netherlands
Netherlands
The Netherlands is a constituent country of the Kingdom of the Netherlands, located mainly in North-West Europe and with several islands in the Caribbean. Mainland Netherlands borders the North Sea to the north and west, Belgium to the south, and Germany to the east, and shares maritime borders...
, Hünengrab in Germany
Germany
Germany , officially the Federal Republic of Germany , is a federal parliamentary republic in Europe. The country consists of 16 states while the capital and largest city is Berlin. Germany covers an area of 357,021 km2 and has a largely temperate seasonal climate...
, dysse in Denmark
Denmark
Denmark is a Scandinavian country in Northern Europe. The countries of Denmark and Greenland, as well as the Faroe Islands, constitute the Kingdom of Denmark . It is the southernmost of the Nordic countries, southwest of Sweden and south of Norway, and bordered to the south by Germany. Denmark...
, and cromlech in Wales
Wales
Wales is a country that is part of the United Kingdom and the island of Great Britain, bordered by England to its east and the Atlantic Ocean and Irish Sea to its west. It has a population of three million, and a total area of 20,779 km²...
. It is assumed that most portal tombs were originally covered by earthen mounds.
The second-most-common tomb type is the passage grave
Passage grave
thumb|250px|right|A simple passage tomb in [[Carrowmore]] near [[Sligo]] in IrelandA passage grave or passage tomb consists of a narrow passage made of large stones and one or multiple burial chambers covered in earth or stone. Megaliths are usually used in the construction of passage tombs, which...
. It normally consists of a square, circular, or cruciform chamber with a slabbed or corbelled roof, accessed by a long, straight passageway, with the whole structure covered by a circular mound of earth. Sometimes it is also surrounded by an external stone kerb. Prominent examples include the sites of Brú na Bóinne
Brú na Bóinne
is a World Heritage Site in County Meath, Ireland and is the largest and one of the most important prehistoric megalithic sites in Europe.-The site:...
and Carrowmore
Carrowmore
Carrowmore, County Sligo is one of the four major passage tomb cemeteries in Ireland. It is located at the centre of a prehistoric ritual landscape on the Cúil Irra Peninsula in County Sligo in Ireland....
in Ireland
Ireland
Ireland is an island to the northwest of continental Europe. It is the third-largest island in Europe and the twentieth-largest island on Earth...
, Maes Howe in Orkney, and Gavrinis
Gavrinis
Gavrinis is a small island, situated in the Gulf of Morbihan in Brittany, France. It contains the Gavrinis tomb, a megalithic monument notable for its abundance of megalithic art in the European Neolithic. Administratively, it is part of the commune of Larmor-Baden.-Geography:Reachable by boat...
in France
France
The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
.
The third tomb type is a diverse group known as gallery grave
Gallery grave
A Gallery grave is a form of Megalithic tomb where there is no size difference between the burial chamber itself and the entrance passage. Two parallel walls of stone slabs were erected to form a corridor and covered with a line of capstones. The rectangular tomb was covered with a barrow or a cairn...
s. These are axially arranged chambers placed under elongated mounds. The Irish court tombs, British long barrow
Long barrow
A long barrow is a prehistoric monument dating to the early Neolithic period. They are rectangular or trapezoidal tumuli or earth mounds traditionally interpreted as collective tombs...
s, and German Steinkisten belong to this group.
Another type of megalithic monument is the single standing stone, or menhir
Menhir
A menhir is a large upright standing stone. Menhirs may be found singly as monoliths, or as part of a group of similar stones. Their size can vary considerably; but their shape is generally uneven and squared, often tapering towards the top...
. Some of these are thought to have an astronomical function as a marker or foresight, and, in some areas, long and complex alignments of such stones exist, for example, at Carnac
Carnac
Carnac is a commune beside the Gulf of Morbihan on the south coast of Brittany in the Morbihan department in north-western France.Its inhabitants are called Carnacois...
in Brittany
Brittany
Brittany is a cultural and administrative region in the north-west of France. Previously a kingdom and then a duchy, Brittany was united to the Kingdom of France in 1532 as a province. Brittany has also been referred to as Less, Lesser or Little Britain...
.
In parts of Britain
Great Britain
Great Britain or Britain is an island situated to the northwest of Continental Europe. It is the ninth largest island in the world, and the largest European island, as well as the largest of the British Isles...
and Ireland
Ireland
Ireland is an island to the northwest of continental Europe. It is the third-largest island in Europe and the twentieth-largest island on Earth...
the best-known type of megalithic construction is the stone circle
Stone circle
A stone circle is a monument of standing stones arranged in a circle. Such monuments have been constructed across the world throughout history for many different reasons....
, of which examples include Stonehenge
Stonehenge
Stonehenge is a prehistoric monument located in the English county of Wiltshire, about west of Amesbury and north of Salisbury. One of the most famous sites in the world, Stonehenge is composed of a circular setting of large standing stones set within earthworks...
, Avebury
Avebury
Avebury is a Neolithic henge monument containing three stone circles which is located around the village of Avebury in Wiltshire, south west England. Unique amongst megalithic monuments, Avebury contains the largest stone circle in Europe, and is one of the best known prehistoric sites in Britain...
, Ring of Brodgar
Ring of Brodgar
The Ring of Brodgar is a Neolithic henge and stone circle on the Mainland, the largest island in Orkney, Scotland...
, and Beltany
Beltany
Beltany is a neolithic stone circle just south of Raphoe town in County Donegal, Ireland. It dates from around 1400-800 BC and comprises 64 stones around a low earth platform or tumulus, situated at the summit of Tops Hill. One stone is decorated with cup marks and many of the stones stand at...
. These, too, display evidence of astronomical alignments, both solar and lunar. Stonehenge, for example, is famous for its solstice
Solstice
A solstice is an astronomical event that happens twice each year when the Sun's apparent position in the sky, as viewed from Earth, reaches its northernmost or southernmost extremes...
alignment. Examples of stone circles are also found in the rest of Europe. They are assumed to be of later date than the tombs, straddling the Neolithic
Neolithic
The Neolithic Age, Era, or Period, or New Stone Age, was a period in the development of human technology, beginning about 9500 BC in some parts of the Middle East, and later in other parts of the world. It is traditionally considered as the last part of the Stone Age...
and the Bronze Age
Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a period characterized by the use of copper and its alloy bronze as the chief hard materials in the manufacture of some implements and weapons. Chronologically, it stands between the Stone Age and Iron Age...
s.
Tombs

Chamber tomb
A chamber tomb is a tomb for burial used in many different cultures. In the case of individual burials, the chamber is thought to signify a higher status for the interree than a simple grave. Built from rock or sometimes wood, the chambers could also serve as places for storage of the dead from one...
, and the term is used to describe the structures built across Atlantic Europe
Atlantic Europe
Atlantic Europe is a geographical and anthropological term for the western portion of Europe which borders the Atlantic Ocean. The term may refer to the idea of Atlantic Europe as a cultural unit and/or as an biogeographical region....
, the Mediterranean, and neighbouring regions, mostly during the Neolithic
Neolithic
The Neolithic Age, Era, or Period, or New Stone Age, was a period in the development of human technology, beginning about 9500 BC in some parts of the Middle East, and later in other parts of the world. It is traditionally considered as the last part of the Stone Age...
period, by Neolithic farming communities. They differ from the contemporary long barrow
Long barrow
A long barrow is a prehistoric monument dating to the early Neolithic period. They are rectangular or trapezoidal tumuli or earth mounds traditionally interpreted as collective tombs...
s through their structural use of stone.
There is a huge variety of megalithic tombs. The free-standing single chamber dolmen
Dolmen
A dolmen—also known as a portal tomb, portal grave, dolmain , cromlech , anta , Hünengrab/Hünenbett , Adamra , Ispun , Hunebed , dös , goindol or quoit—is a type of single-chamber megalithic tomb, usually consisting of...
s and portal dolmens found in Brittany
Brittany
Brittany is a cultural and administrative region in the north-west of France. Previously a kingdom and then a duchy, Brittany was united to the Kingdom of France in 1532 as a province. Brittany has also been referred to as Less, Lesser or Little Britain...
, Denmark
Denmark
Denmark is a Scandinavian country in Northern Europe. The countries of Denmark and Greenland, as well as the Faroe Islands, constitute the Kingdom of Denmark . It is the southernmost of the Nordic countries, southwest of Sweden and south of Norway, and bordered to the south by Germany. Denmark...
, Germany
Germany
Germany , officially the Federal Republic of Germany , is a federal parliamentary republic in Europe. The country consists of 16 states while the capital and largest city is Berlin. Germany covers an area of 357,021 km2 and has a largely temperate seasonal climate...
, Ireland
Ireland
Ireland is an island to the northwest of continental Europe. It is the third-largest island in Europe and the twentieth-largest island on Earth...
, Netherlands
Netherlands
The Netherlands is a constituent country of the Kingdom of the Netherlands, located mainly in North-West Europe and with several islands in the Caribbean. Mainland Netherlands borders the North Sea to the north and west, Belgium to the south, and Germany to the east, and shares maritime borders...
, Sweden
Sweden
Sweden , officially the Kingdom of Sweden , is a Nordic country on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. Sweden borders with Norway and Finland and is connected to Denmark by a bridge-tunnel across the Öresund....
, Wales
Wales
Wales is a country that is part of the United Kingdom and the island of Great Britain, bordered by England to its east and the Atlantic Ocean and Irish Sea to its west. It has a population of three million, and a total area of 20,779 km²...
, and elsewhere consist of a large flat stone supported by three, four, or more standing stones. They were covered by a stone cairn
Cairn
Cairn is a term used mainly in the English-speaking world for a man-made pile of stones. It comes from the or . Cairns are found all over the world in uplands, on moorland, on mountaintops, near waterways and on sea cliffs, and also in barren desert and tundra areas...
or earth barrow
Tumulus
A tumulus is a mound of earth and stones raised over a grave or graves. Tumuli are also known as barrows, burial mounds, Hügelgrab or kurgans, and can be found throughout much of the world. A tumulus composed largely or entirely of stones is usually referred to as a cairn...
.
Examples with outer areas, not used for burial, are also known. The Court Cairn
Court cairn
The court cairn or court tomb is a megalithic type of chamber tomb and gallery grave, specifically a variant of the chambered cairn, found in western and northern Ireland, and in mostly southwest Scotland...
s of southwest Scotland
Scotland
Scotland is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Occupying the northern third of the island of Great Britain, it shares a border with England to the south and is bounded by the North Sea to the east, the Atlantic Ocean to the north and west, and the North Channel and Irish Sea to the...
and northern Ireland
Ireland
Ireland is an island to the northwest of continental Europe. It is the third-largest island in Europe and the twentieth-largest island on Earth...
, the Severn-Cotswold tomb
Severn-Cotswold tomb
Severn-Cotswold is a name given to a type of Megalithic chamber tomb built by Neolithic peoples in Wales and South West England around 3500 BC.-Description:...
s of southwest England
England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Scotland to the north and Wales to the west; the Irish Sea is to the north west, the Celtic Sea to the south west, with the North Sea to the east and the English Channel to the south separating it from continental...
and the Transepted gallery grave
Transepted gallery grave
Transepted gallery grave is a term used to describe a number of similar megalithic chamber tombs built across Atlantic Europe during the Neolithic period.It refers to burial monuments with side rooms extending laterally from a central chamber...
s of the Loire
Loire
Loire is an administrative department in the east-central part of France occupying the River Loire's upper reaches.-History:Loire was created in 1793 when after just 3½ years the young Rhône-et-Loire department was split into two. This was a response to counter-Revolutionary activities in Lyon...
region in France
France
The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
share many internal features, although the links between them are not yet fully understood. That they often have antechambers or forecourts is thought to imply a desire on the part of the builders to emphasize a special ritual
Ritual
A ritual is a set of actions, performed mainly for their symbolic value. It may be prescribed by a religion or by the traditions of a community. The term usually excludes actions which are arbitrarily chosen by the performers....
or physical separation of the dead from the living.
The Passage grave
Passage grave
thumb|250px|right|A simple passage tomb in [[Carrowmore]] near [[Sligo]] in IrelandA passage grave or passage tomb consists of a narrow passage made of large stones and one or multiple burial chambers covered in earth or stone. Megaliths are usually used in the construction of passage tombs, which...
s of Orkney, Ireland's Boyne
Boyne
Several terms incorporating the word "Boyne" include:* Boann, the Irish goddess after whom the river is named* Boyne River * Boyne Falls, Michigan,* Boyne Resorts, a ski resort company in Michigan...
Valley, and north Wales are even more complex and impressive, with cross-shaped arrangements of chambers and passages. The workmanship on the stone blocks at Maeshowe
Maeshowe
Maeshowe is a Neolithic chambered cairn and passage grave situated on Mainland, Orkney, Scotland. The monuments around Maeshowe, including Skara Brae, were designated a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1999. It gives its name to the Maeshowe type of chambered cairn, which is limited to Orkney...
for example is unknown elsewhere in northwest Europe at the time.
Megalithic tombs appear to have been used by communities for the long-term deposition of the remains of their dead, and some seem to have undergone alteration and enlargement. The organization and effort required to erect these large stones suggest that the societies concerned placed great emphasis on the proper treatment of their dead. The ritual
Ritual
A ritual is a set of actions, performed mainly for their symbolic value. It may be prescribed by a religion or by the traditions of a community. The term usually excludes actions which are arbitrarily chosen by the performers....
significance of the tombs is supported by the presence of megalithic art
Pre-historic art
In the history of art, prehistoric art is all art produced in preliterate, prehistorical cultures beginning somewhere in very late geological history, and generally continuing until that culture either develops writing or other methods of record-keeping, or it makes significant contact with another...
carved into the stones at some sites. Hearths and deposits of pottery and animal bone found by archaeologists around some tombs also implies that some form of burial feast or sacrificial rites took place there.

Midhowe Chambered Cairn
Midhowe is a large Neolithic chambered cairn located on the south shore of the island of Rousay, Orkney, Scotland. The name "Midhowe" comes from the spectacular Bronze Age broch that lies just west of the tomb...
in Orkney and the passage grave at Bryn Celli Ddu
Bryn Celli Ddu
Bryn Celli Ddu is a prehistoric site on the Welsh island of Anglesey located near Llanddaniel Fab. Its name means 'the mound in the dark grove'. It was plundered in 1699 and archaeologically excavated between 1928 and 1929....
on Anglesey
Anglesey
Anglesey , also known by its Welsh name Ynys Môn , is an island and, as Isle of Anglesey, a county off the north west coast of Wales...
. Despite its name, the Stone Tomb in Ukraine
Ukraine
Ukraine is a country in Eastern Europe. It has an area of 603,628 km², making it the second largest contiguous country on the European continent, after Russia...
was not a tomb but rather a sanctuary.
Other structures
Associated with the megalithic constructions across Europe, there are often large earthworksEarthworks (archaeology)
In archaeology, earthwork is a general term to describe artificial changes in land level. Earthworks are often known colloquially as 'lumps and bumps'. Earthworks can themselves be archaeological features or they can show features beneath the surface...
of various designs – ditches and banks, broad terraces, circular enclosures known as henges, and frequently artificial mounds such as Silbury Hill
Silbury Hill
Silbury Hill is a prehistoric artificial chalk mound near Avebury in the English county of Wiltshire. It is part of the Stonehenge, Avebury and Associated Sites UNESCO World Heritage Site, and lies at ....
in England
England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Scotland to the north and Wales to the west; the Irish Sea is to the north west, the Celtic Sea to the south west, with the North Sea to the east and the English Channel to the south separating it from continental...
and Monte d’Accoddi
Sassari
Sassari is an Italian city. It is the second-largest city of Sardinia in terms of population with about 130,000 inhabitants, or about 300,000 including the greater metropolitan area...
in Sardinia. Sometimes, as at Glastonbury Tor
Glastonbury Tor
Glastonbury Tor is a hill at Glastonbury, Somerset, England, which features the roofless St. Michael's Tower. The site is managed by the National Trust. It has been designated as a Scheduled Ancient Monument ....
in England, it is suggested that a natural hill has been artificially sculpted to form a maze or spiral pattern in the turf.
It seems that spirals were an important motif for the megalith builders, and have been found carved into megalithic structures all over Europe – along with other symbols such as lozenges, eye-patterns, zigzags in various configurations, and cup and ring mark
Cup and ring mark
Cup and ring marks or cup marks are a form of prehistoric art found mainly in Atlantic Europe and Mediterranean Europe although similar forms are also found throughout the world including Mexico, Brazil, Greece, and India, where...
s. While not a written script in the modern sense of the term, these symbols are considered to have conveyed meaning to their creators, and are remarkably consistent across the whole of Western Europe.
Spread of megalithic architecture in Europe
In Western Europe and the Mediterranean, megaliths are, in general, constructions erected during the NeolithicNeolithic
The Neolithic Age, Era, or Period, or New Stone Age, was a period in the development of human technology, beginning about 9500 BC in some parts of the Middle East, and later in other parts of the world. It is traditionally considered as the last part of the Stone Age...
or late stone age and Chalcolithic or Copper Age (4500-1500 BC). Perhaps the most famous megalithic structure is Stonehenge
Stonehenge
Stonehenge is a prehistoric monument located in the English county of Wiltshire, about west of Amesbury and north of Salisbury. One of the most famous sites in the world, Stonehenge is composed of a circular setting of large standing stones set within earthworks...
in England, although many others are known throughout the world. The French Comte de Caylus was the first to describe the Carnac stones
Carnac stones
The Carnac stones are an exceptionally dense collection of megalithic sites around the French village of Carnac, in Brittany, consisting of alignments, dolmens, tumuli and single menhirs. The more than 3,000 prehistoric standing stones were hewn from local rock and erected by the pre-Celtic people...
. Legrand d'Aussy introduced the terms menhir
Menhir
A menhir is a large upright standing stone. Menhirs may be found singly as monoliths, or as part of a group of similar stones. Their size can vary considerably; but their shape is generally uneven and squared, often tapering towards the top...
and dolmen
Dolmen
A dolmen—also known as a portal tomb, portal grave, dolmain , cromlech , anta , Hünengrab/Hünenbett , Adamra , Ispun , Hunebed , dös , goindol or quoit—is a type of single-chamber megalithic tomb, usually consisting of...
, both taken from the Breton language
Breton language
Breton is a Celtic language spoken in Brittany , France. Breton is a Brythonic language, descended from the Celtic British language brought from Great Britain to Armorica by migrating Britons during the Early Middle Ages. Like the other Brythonic languages, Welsh and Cornish, it is classified as...
, into antiquarian terminology. He interpreted megaliths as gallic tombs. In Britain, the antiquarian
Antiquarian
An antiquarian or antiquary is an aficionado or student of antiquities or things of the past. More specifically, the term is used for those who study history with particular attention to ancient objects of art or science, archaeological and historic sites, or historic archives and manuscripts...
s Aubrey
John Aubrey
John Aubrey FRS, was an English antiquary, natural philosopher and writer. He is perhaps best known as the author of the collection of short biographical pieces usually referred to as Brief Lives...
and Stukeley
William Stukeley
William Stukeley FRS, FRCP, FSA was an English antiquarian who pioneered the archaeological investigation of the prehistoric monuments of Stonehenge and Avebury, work for which he has been remembered as "probably... the most important of the early forerunners of the discipline of archaeology"...
conducted early research into megaliths. In 1805, Jacques Cambry
Jacques Cambry
Jacques Cambry was a Breton writer and expert in Celtic France. An early proponent of what came to be called Celtomania, he was the founder of the Celtic Academy, the forerunner of the Societé des Antiquaires de France...
published a book called Monuments celtiques, ou recherches sur le culte des Pierres, précédées d'une notice sur les Celtes et sur les Druides, et suivies d'Etymologie celtiques, where he proposed a Celt
Celt
The Celts were a diverse group of tribal societies in Iron Age and Roman-era Europe who spoke Celtic languages.The earliest archaeological culture commonly accepted as Celtic, or rather Proto-Celtic, was the central European Hallstatt culture , named for the rich grave finds in Hallstatt, Austria....
ic stone cult. This completely unfounded connection between druids and megaliths has haunted the public imagination ever since. In Belgium
Belgium
Belgium , officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a federal state in Western Europe. It is a founding member of the European Union and hosts the EU's headquarters, and those of several other major international organisations such as NATO.Belgium is also a member of, or affiliated to, many...
, there is a megalithic site at Wéris, a little town situated in the Ardennes
Ardennes
The Ardennes is a region of extensive forests, rolling hills and ridges formed within the Givetian Ardennes mountain range, primarily in Belgium and Luxembourg, but stretching into France , and geologically into the Eifel...
. In the Netherlands, megalithic structures can be found in the northeast of the country, mostly in the province of Drenthe
Drenthe
Drenthe is a province of the Netherlands, located in the north-east of the country. The capital city is Assen. It is bordered by Overijssel to the south, Friesland to the west, Groningen to the north, and Germany to the east.-History:Drenthe, unlike many other parts of the Netherlands, has been a...
. Knowth
Knowth
Knowth is a Neolithic passage grave and an ancient monument of Brú na Bóinne in the valley of the River Boyne in Ireland.Knowth is the largest of all passage graves situated within the Brú na Bóinne complex. The site consists of one large mound and 17 smaller satellite tombs...
is a passage grave
Passage grave
thumb|250px|right|A simple passage tomb in [[Carrowmore]] near [[Sligo]] in IrelandA passage grave or passage tomb consists of a narrow passage made of large stones and one or multiple burial chambers covered in earth or stone. Megaliths are usually used in the construction of passage tombs, which...
of the Brú na Bóinne
Brú na Bóinne
is a World Heritage Site in County Meath, Ireland and is the largest and one of the most important prehistoric megalithic sites in Europe.-The site:...
neolithic complex in Ireland, dating from c.3500-3000 BC. It contains more than a third of the total number of examples of megalithic art
Megalithic art
Megalithic art refers to the use of large stones as an artistic medium. Although some modern artists and sculptors make use of large stones in their work, the term is more generally used to describe art carved onto megaliths in prehistoric Europe....
in all Western Europe, with over 200 decorated stones found during excavations.
Timeline of megalithic construction
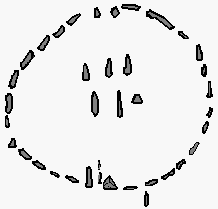
Mesolithic
Excavation of some Megalithic monuments (in Britain, Ireland, Scandinavia, and France) has revealed evidence of ritual activity, sometimes involving architecture, from the MesolithicMesolithic
The Mesolithic is an archaeological concept used to refer to certain groups of archaeological cultures defined as falling between the Paleolithic and the Neolithic....
, i.e., predating the Neolithic monuments by centuries or millennia. Caveats apply: In some cases, they are so far removed in time from their successors that continuity is unlikely; in other cases, the early dates, or the exact character of activity, are controversial.
Neolithic
- Circa 5000 BC: Constructions in PortugalPortugalPortugal , officially the Portuguese Republic is a country situated in southwestern Europe on the Iberian Peninsula. Portugal is the westernmost country of Europe, and is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the West and South and by Spain to the North and East. The Atlantic archipelagos of the...
(ÉvoraAlmendres CromlechThe Cromlech of the Almendres megalithic complex , located near Guadalupe, in the civil parish of Nossa Senhora de Guadalupe, municipality of Évora, is the largest existing group of structured menhirs in the Iberian Peninsula, and one of the largest in Europe...
). Emergence of the Atlantic NeolithicNeolithicThe Neolithic Age, Era, or Period, or New Stone Age, was a period in the development of human technology, beginning about 9500 BC in some parts of the Middle East, and later in other parts of the world. It is traditionally considered as the last part of the Stone Age...
period, the age of agriculture along the western shores of EuropeEuropeEurope is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting...
during the sixth millenium B.C. culture of La AlmagraLa AlmagraLa Almagra is a red pottery found in a number of archaeological sites of the Neolithic period in Spain. It is not known how it relates to other pottery of the Neolithic period....
near by, perhaps procedent from Africa.
- Circa 4800 BC: Constructions in BrittanyBrittanyBrittany is a cultural and administrative region in the north-west of France. Previously a kingdom and then a duchy, Brittany was united to the Kingdom of France in 1532 as a province. Brittany has also been referred to as Less, Lesser or Little Britain...
(BarnenezBarnenezThe Cairn of Barnenez is a Neolithic monument located near Plouezoc'h, on the Kernéléhen peninsula in northern Finistère, Brittany...
) and PoitouPoitouPoitou was a province of west-central France whose capital city was Poitiers.The region of Poitou was called Thifalia in the sixth century....
(BougonTumulus of BougonThe Tumulus of Bougon or Necropolis of Bougon is a group of five Neolithic monuments located in Bougon near La-Mothe-Saint-Héray, between Exoudon and Pamproux in Poitou-Charentes, France. Their discovery in 1840 raised great scientific interest...
).
- Circa 4400 BC: Constructions in MaltaMaltaMalta , officially known as the Republic of Malta , is a Southern European country consisting of an archipelago situated in the centre of the Mediterranean, south of Sicily, east of Tunisia and north of Libya, with Gibraltar to the west and Alexandria to the east.Malta covers just over in...
(Skorba temples).
- Circa 4000 BC: Constructions in Brittany (CarnacCarnacCarnac is a commune beside the Gulf of Morbihan on the south coast of Brittany in the Morbihan department in north-western France.Its inhabitants are called Carnacois...
), Portugal (LisbonLisbonLisbon is the capital city and largest city of Portugal with a population of 545,245 within its administrative limits on a land area of . The urban area of Lisbon extends beyond the administrative city limits with a population of 3 million on an area of , making it the 9th most populous urban...
), FranceFranceThe French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
(central and southern), CorsicaCorsicaCorsica is an island in the Mediterranean Sea. It is located west of Italy, southeast of the French mainland, and north of the island of Sardinia....
, England and WalesWalesWales is a country that is part of the United Kingdom and the island of Great Britain, bordered by England to its east and the Atlantic Ocean and Irish Sea to its west. It has a population of three million, and a total area of 20,779 km²...
.
- Circa 3700 BC: Constructions in Ireland (Knockiveagh and elsewhere).
- Circa 3600 BC: Constructions in England (Maumbury RingsMaumbury RingsMaumbury Rings is a Neolithic henge in the south of Dorchester town in Dorset, England. It is a large circular earthwork, 85 metres in diameter, with a single bank and internal ditch and an entrance to the north east. The ditch was created by digging a series of funnel-shaped shafts, each 10...
and GodmanchesterGodmanchesterGodmanchester is a small town and civil parish within the Huntingdonshire district of Cambridgeshire, in England. It lies on the south bank of the River Great Ouse, south of the larger town of Huntingdon, and on the A14 road....
), and MaltaMaltaMalta , officially known as the Republic of Malta , is a Southern European country consisting of an archipelago situated in the centre of the Mediterranean, south of Sicily, east of Tunisia and north of Libya, with Gibraltar to the west and Alexandria to the east.Malta covers just over in...
(ĠgantijaGgantijaĠgantija is a Neolithic, megalithic temple complex on the Mediterranean island of Gozo. The Ġgantija temples are the earliest of a series of megalithic temples in Malta. Their makers erected the two Ġgantija temples during the Neolithic Age , which makes these temples more than 5500 years old and...
and MnajdraMnajdraMnajdra is a megalithic temple complex found on the southern coast of the Mediterranean island of Malta. Mnajdra is approximately 500 metres from the Ħaġar Qim megalithic complex...
temples).
- Circa 3500 BC: Constructions in SpainSpainSpain , officially the Kingdom of Spain languages]] under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, Spain's official name is as follows:;;;;;;), is a country and member state of the European Union located in southwestern Europe on the Iberian Peninsula...
(MálagaMálagaMálaga is a city and a municipality in the Autonomous Community of Andalusia, Spain. With a population of 568,507 in 2010, it is the second most populous city of Andalusia and the sixth largest in Spain. This is the southernmost large city in Europe...
and GuadianaGuadianaThe Guadiana , or Odiana, is an international river located on the Portuguese–Spanish border, separating Extremadura and Andalucia from Alentejo and Algarve...
), Ireland (south-west), France (ArlesArlesArles is a city and commune in the south of France, in the Bouches-du-Rhône department, of which it is a subprefecture, in the former province of Provence....
and the north), SardiniaSardiniaSardinia is the second-largest island in the Mediterranean Sea . It is an autonomous region of Italy, and the nearest land masses are the French island of Corsica, the Italian Peninsula, Sicily, Tunisia and the Spanish Balearic Islands.The name Sardinia is from the pre-Roman noun *sard[],...
, SicilySicilySicily is a region of Italy, and is the largest island in the Mediterranean Sea. Along with the surrounding minor islands, it constitutes an autonomous region of Italy, the Regione Autonoma Siciliana Sicily has a rich and unique culture, especially with regard to the arts, music, literature,...
, Malta (and elsewhere in the Mediterranean), BelgiumBelgiumBelgium , officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a federal state in Western Europe. It is a founding member of the European Union and hosts the EU's headquarters, and those of several other major international organisations such as NATO.Belgium is also a member of, or affiliated to, many...
(north-east) and GermanyGermanyGermany , officially the Federal Republic of Germany , is a federal parliamentary republic in Europe. The country consists of 16 states while the capital and largest city is Berlin. Germany covers an area of 357,021 km2 and has a largely temperate seasonal climate...
(central and south-west).
- Circa 3400 BC: Constructions in Ireland (NewgrangeNewgrangeNewgrange is a prehistoric monument located in County Meath, on the eastern side of Ireland, about one kilometre north of the River Boyne. It was built around 3200 BC , during the Neolithic period...
), NetherlandsNetherlandsThe Netherlands is a constituent country of the Kingdom of the Netherlands, located mainly in North-West Europe and with several islands in the Caribbean. Mainland Netherlands borders the North Sea to the north and west, Belgium to the south, and Germany to the east, and shares maritime borders...
(north-east), Germany (northern and central) SwedenSwedenSweden , officially the Kingdom of Sweden , is a Nordic country on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. Sweden borders with Norway and Finland and is connected to Denmark by a bridge-tunnel across the Öresund....
and DenmarkDenmarkDenmark is a Scandinavian country in Northern Europe. The countries of Denmark and Greenland, as well as the Faroe Islands, constitute the Kingdom of Denmark . It is the southernmost of the Nordic countries, southwest of Sweden and south of Norway, and bordered to the south by Germany. Denmark...
.
- Circa 3300 BC: Constructions in France (Carnac stonesCarnac stonesThe Carnac stones are an exceptionally dense collection of megalithic sites around the French village of Carnac, in Brittany, consisting of alignments, dolmens, tumuli and single menhirs. The more than 3,000 prehistoric standing stones were hewn from local rock and erected by the pre-Celtic people...
)
- Circa 3200 BC: Constructions in Malta (Ħaġar Qim and TarxienTarxien-Etymology:Ħal Tarxien is a small village in the south east of Malta. The etymology of the village may be a corruption of Tirix, meaning a large stone, similar to those used for the village's noted temples. The village motto is Tyrii Genure Coloni .-Population:Today, the village is inhabited by...
).
- Circa 3000 BC: Constructions in France (SaumurSaumurSaumur is a commune in the Maine-et-Loire department in western France.The historic town is located between the Loire and Thouet rivers, and is surrounded by the vineyards of Saumur itself, Chinon, Bourgueil, Coteaux du Layon, etc...
, DordogneDordogneDordogne is a départment in south-west France. The départment is located in the region of Aquitaine, between the Loire valley and the High Pyrénées named after the great river Dordogne that runs through it...
, LanguedocLanguedocLanguedoc is a former province of France, now continued in the modern-day régions of Languedoc-Roussillon and Midi-Pyrénées in the south of France, and whose capital city was Toulouse, now in Midi-Pyrénées. It had an area of approximately 42,700 km² .-Geographical Extent:The traditional...
, BiscayBiscayBiscay is a province of Spain and a historical territory of the Basque Country, heir of the ancient Lord of Biscay. Its capital city is Bilbao...
, and the Mediterranean coast), Spain (Los MillaresLos MillaresLos Millares is the name of a Chalcolithic occupation site 17 km north of Almería, in the municipality of Santa Fe de Mondújar, Andalusia, Spain. The complex was in use from the end of the fourth millennium to the end of the second millennium BC and probably supported somewhere around 1000...
), Sicily, Belgium (ArdennesArdennesThe Ardennes is a region of extensive forests, rolling hills and ridges formed within the Givetian Ardennes mountain range, primarily in Belgium and Luxembourg, but stretching into France , and geologically into the Eifel...
), and Orkney, as well as the first hengeHengeThere are three related types of Neolithic earthwork which are all sometimes loosely called henges. The essential characteristic of all three types is that they feature a ring bank and ditch but with the ditch inside the bank rather than outside...
s (circular earthworks) in BritainGreat BritainGreat Britain or Britain is an island situated to the northwest of Continental Europe. It is the ninth largest island in the world, and the largest European island, as well as the largest of the British Isles...
.
Chalcolithic
- Circa 2500 BC: Constructions in Brittany (Le MenecLa Trinité-sur-MerLa Trinité-sur-Mer , is a commune in the Morbihan department in Brittany, in north-western France.It is located east of Carnac. The town is primarily a port, with a seaside quay dotted by numerous seafood restaurants...
, Kermario and elsewhere), ItalyItalyItaly , officially the Italian Republic languages]] under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, Italy's official name is as follows:;;;;;;;;), is a unitary parliamentary republic in South-Central Europe. To the north it borders France, Switzerland, Austria and...
(OtrantoOtrantoOtranto is a town and comune in the province of Lecce , in a fertile region once famous for its breed of horses.It is located on the east coast of the Salento peninsula. The Strait of Otranto, to which the city gives its name, connects the Adriatic Sea with the Ionian Sea and Italy with Albania...
), Sardinia, and ScotlandScotlandScotland is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Occupying the northern third of the island of Great Britain, it shares a border with England to the south and is bounded by the North Sea to the east, the Atlantic Ocean to the north and west, and the North Channel and Irish Sea to the...
(northeast), plus the climax of the megalithic Bell-beaker cultureBeaker cultureThe Bell-Beaker culture , ca. 2400 – 1800 BC, is the term for a widely scattered cultural phenomenon of prehistoric western Europe starting in the late Neolithic or Chalcolithic running into the early Bronze Age...
in IberiaIberian PeninsulaThe Iberian Peninsula , sometimes called Iberia, is located in the extreme southwest of Europe and includes the modern-day sovereign states of Spain, Portugal and Andorra, as well as the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar...
, Germany, and the British IslesBritish IslesThe British Isles are a group of islands off the northwest coast of continental Europe that include the islands of Great Britain and Ireland and over six thousand smaller isles. There are two sovereign states located on the islands: the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland and...
(stone circle at Stonehenge). With the bell-beakers, the Neolithic period gave way to the Chalcolithic, the age of copper.
- Circa 2400 BC: The Bell-beaker culture was dominant in Britain, and hundreds of smaller stone circles were built in the British Isles at this time.
Bronze Age
- Circa 2000 BC: Constructions in Brittany (Er GrahLocmariaquerLocmariaquer is a commune in the Morbihan department in Brittany in north-western France.It lies south of Auray by road.-Coat of arms:This coat of arms was created 30 years ago by the local artist Jean-Baptiste Corlobé...
), Italy (BariBariBari is the capital city of the province of Bari and of the Apulia region, on the Adriatic Sea, in Italy. It is the second most important economic centre of mainland Southern Italy after Naples, and is well known as a port and university city, as well as the city of Saint Nicholas...
), Sardinia (northern), and Scotland (CallanishCallanishCallanish is a village on the West Side of the Isle of Lewis, in the Outer Hebrides , Scotland. A linear settlement with a jetty, it is situated on a headland jutting into Loch Roag, a sea loch...
). The Chalcolithic period gave way to the Bronze AgeBronze AgeThe Bronze Age is a period characterized by the use of copper and its alloy bronze as the chief hard materials in the manufacture of some implements and weapons. Chronologically, it stands between the Stone Age and Iron Age...
in western and northern Europe.
- Circa 1800 BC: Constructions in Italy (GiovinazzoGiovinazzoGiovinazzo is a port city situated on the Adriatic coast in the region of Apulia, southern Italy. Giovinazzo lies 18 km WNW of the provincial capital of Bari, and is adjacent to the city ofMolfetta.-History:...
).
- Circa 1500 BC: Constructions in Portugal (Alter PedrosoAlter do ChãoAlter do Chão is a municipality in Portugal with a total area of 362.0 km² and a total population of 3,666 inhabitants.The municipality is composed of 4 parishes, and is located in the District of Portalegre....
and MourelaPeneda-Gerês National ParkThe Peneda-Gerês National Park , also known simply as Gerês, is the only national park in Portugal...
).
- Circa 1400 BC: Burial of the Egtved GirlEgtved GirlThe Egtved Girl was a Nordic Bronze Age girl whose well-preserved remains were found at Egtved , Denmark in 1921. Aged 16–18 at death, she was slim, 160 cm tall , had short, blonde hair and well-trimmed nails. Her burial has been dated by dendrochronology to 1370 BCE...
in Denmark, whose body is today one of the most well-preserved examples of its kind.
- Circa 1200 BC: Last vestiges of the megalithic tradition in the Mediterranean and elsewhere come to an end during the general population upheaval known to ancient history as the Invasions of the Sea PeoplesSea PeoplesThe Sea Peoples were a confederacy of seafaring raiders of the second millennium BC who sailed into the eastern Mediterranean, caused political unrest, and attempted to enter or control Egyptian territory during the late 19th dynasty and especially during year 8 of Ramesses III of the 20th Dynasty...
.
Nabta Playa
Nabta Playa
Nabta Playa was once a large basin in the Nubian Desert, located approximately 800 kilometers south of modern day Cairo or about 100 kilometers west of Abu Simbel in southern Egypt, 22° 32' north, 30° 42' east...
at the southwest corner of the western Egyptian desert was once a large lake in the Nubia
Nubia
Nubia is a region along the Nile river, which is located in northern Sudan and southern Egypt.There were a number of small Nubian kingdoms throughout the Middle Ages, the last of which collapsed in 1504, when Nubia became divided between Egypt and the Sennar sultanate resulting in the Arabization...
n Desert, located 500 miles south of modern-day Cairo
Cairo
Cairo , is the capital of Egypt and the largest city in the Arab world and Africa, and the 16th largest metropolitan area in the world. Nicknamed "The City of a Thousand Minarets" for its preponderance of Islamic architecture, Cairo has long been a centre of the region's political and cultural life...
. By the 5th millennium BC, the peoples in Nabta Playa had fashioned the world's earliest known astronomical
Astronomy
Astronomy is a natural science that deals with the study of celestial objects and phenomena that originate outside the atmosphere of Earth...
device, 1000 years older than, but comparable to, Stonehenge
Stonehenge
Stonehenge is a prehistoric monument located in the English county of Wiltshire, about west of Amesbury and north of Salisbury. One of the most famous sites in the world, Stonehenge is composed of a circular setting of large standing stones set within earthworks...
. Research shows it to be a prehistoric calendar
Calendar
A calendar is a system of organizing days for social, religious, commercial, or administrative purposes. This is done by giving names to periods of time, typically days, weeks, months, and years. The name given to each day is known as a date. Periods in a calendar are usually, though not...
that accurately marks the summer
Summer
Summer is the warmest of the four temperate seasons, between spring and autumn. At the summer solstice, the days are longest and the nights are shortest, with day-length decreasing as the season progresses after the solstice...
solstice
Solstice
A solstice is an astronomical event that happens twice each year when the Sun's apparent position in the sky, as viewed from Earth, reaches its northernmost or southernmost extremes...
. Findings indicate that the region was occupied only seasonally, likely only in the summer
Summer
Summer is the warmest of the four temperate seasons, between spring and autumn. At the summer solstice, the days are longest and the nights are shortest, with day-length decreasing as the season progresses after the solstice...
when the local lake filled with water for grazing cattle
Cattle
Cattle are the most common type of large domesticated ungulates. They are a prominent modern member of the subfamily Bovinae, are the most widespread species of the genus Bos, and are most commonly classified collectively as Bos primigenius...
. There are other megalithic stone circles in the southwestern desert.
Middle Eastern megaliths
Dolmens and standing stones have been found in large areas of the Middle EastMiddle East
The Middle East is a region that encompasses Western Asia and Northern Africa. It is often used as a synonym for Near East, in opposition to Far East...
starting at the Turkish
Turkey
Turkey , known officially as the Republic of Turkey , is a Eurasian country located in Western Asia and in East Thrace in Southeastern Europe...
border in the north of Syria
Syria
Syria , officially the Syrian Arab Republic , is a country in Western Asia, bordering Lebanon and the Mediterranean Sea to the West, Turkey to the north, Iraq to the east, Jordan to the south, and Israel to the southwest....
close to Aleppo
Aleppo
Aleppo is the largest city in Syria and the capital of Aleppo Governorate, the most populous Syrian governorate. With an official population of 2,301,570 , expanding to over 2.5 million in the metropolitan area, it is also one of the largest cities in the Levant...
, southwards down to Yemen
Yemen
The Republic of Yemen , commonly known as Yemen , is a country located in the Middle East, occupying the southwestern to southern end of the Arabian Peninsula. It is bordered by Saudi Arabia to the north, the Red Sea to the west, and Oman to the east....
. They can be encountered in northern Lebanon
Lebanon
Lebanon , officially the Republic of LebanonRepublic of Lebanon is the most common term used by Lebanese government agencies. The term Lebanese Republic, a literal translation of the official Arabic and French names that is not used in today's world. Arabic is the most common language spoken among...
, southern Syria, Israel
Israel
The State of Israel is a parliamentary republic located in the Middle East, along the eastern shore of the Mediterranean Sea...
, Jordan
Jordan
Jordan , officially the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan , Al-Mamlaka al-Urduniyya al-Hashemiyya) is a kingdom on the East Bank of the River Jordan. The country borders Saudi Arabia to the east and south-east, Iraq to the north-east, Syria to the north and the West Bank and Israel to the west, sharing...
, and Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia
The Kingdom of Saudi Arabia , commonly known in British English as Saudi Arabia and in Arabic as as-Sa‘ūdiyyah , is the largest state in Western Asia by land area, constituting the bulk of the Arabian Peninsula, and the second-largest in the Arab World...
. The most concentrated occurrence of dolmen in particular is in a large area on both sides of the Great Rift Valley
Great Rift Valley
The Great Rift Valley is a name given in the late 19th century by British explorer John Walter Gregory to the continuous geographic trench, approximately in length, that runs from northern Syria in Southwest Asia to central Mozambique in South East Africa...
, with greater predominance on the eastern side. They occur first and foremost on the Golan Heights, the Hauran
Hauran
Hauran, , also spelled Hawran or Houran, is a volcanic plateau, a geographic area and a people located in southwestern Syria and extending into the northwestern corner of Jordan. It gets its name from the Aramaic Hawran, meaning "cave land." In geographic and geomorphic terms, its boundaries...
, and in Jordan, which probably has the largest concentration of dolmen in the Middle East. In Saudi Arabia, only very few dolmen have been identified so far in the Hejaz
Hejaz
al-Hejaz, also Hijaz is a region in the west of present-day Saudi Arabia. Defined primarily by its western border on the Red Sea, it extends from Haql on the Gulf of Aqaba to Jizan. Its main city is Jeddah, but it is probably better known for the Islamic holy cities of Mecca and Medina...
. They seem, however, to re-emerge in Yemen in small numbers, and thus could indicate a continuous tradition related to those of Somalia
Somalia
Somalia , officially the Somali Republic and formerly known as the Somali Democratic Republic under Socialist rule, is a country located in the Horn of Africa. Since the outbreak of the Somali Civil War in 1991 there has been no central government control over most of the country's territory...
and Ethiopia
Ethiopia
Ethiopia , officially known as the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a country located in the Horn of Africa. It is the second-most populous nation in Africa, with over 82 million inhabitants, and the tenth-largest by area, occupying 1,100,000 km2...
.
The standing stone has a very ancient tradition in the Middle East, dating back from Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia is a toponym for the area of the Tigris–Euphrates river system, largely corresponding to modern-day Iraq, northeastern Syria, southeastern Turkey and southwestern Iran.Widely considered to be the cradle of civilization, Bronze Age Mesopotamia included Sumer and the...
n times. Although not always 'megalithic' in the true sense, they occur throughout the Orient
Orient
The Orient means "the East." It is a traditional designation for anything that belongs to the Eastern world or the Far East, in relation to Europe. In English it is a metonym that means various parts of Asia.- Derivation :...
, and can reach 5 metres or more in some cases (such as Ader
Al Karak
Karak is a city in Jordan that is known for the famous crusader castle Kerak. The castle is one of the three largest castles in the region, the other two being in Syria...
in Jordan). This phenomenon can also be traced through many passages from the Old Testament
Old Testament
The Old Testament, of which Christians hold different views, is a Christian term for the religious writings of ancient Israel held sacred and inspired by Christians which overlaps with the 24-book canon of the Masoretic Text of Judaism...
, such as those related to Jacob
Jacob
Jacob "heel" or "leg-puller"), also later known as Israel , as described in the Hebrew Bible, the Talmud, the New Testament and the Qur'an was the third patriarch of the Hebrew people with whom God made a covenant, and ancestor of the tribes of Israel, which were named after his descendants.In the...
, the grandson of Abraham
Abraham
Abraham , whose birth name was Abram, is the eponym of the Abrahamic religions, among which are Judaism, Christianity and Islam...
, who poured oil over a stone that he erected after his famous dream in which angels climbed to heaven (Genesis 28:10-22). Jacob is also described as putting up stones at other occasions, whereas Moses
Moses
Moses was, according to the Hebrew Bible and Qur'an, a religious leader, lawgiver and prophet, to whom the authorship of the Torah is traditionally attributed...
erected twelve pillars symbolizing the tribes of Israel. The tradition of venerating (standing) stones continued in Nabatean times and is reflected in, e.g., the Islamic rituals surrounding the Kaaba
Kaaba
The Kaaba is a cuboid-shaped building in Mecca, Saudi Arabia, and is the most sacred site in Islam. The Qur'an states that the Kaaba was constructed by Abraham, or Ibraheem, in Arabic, and his son Ishmael, or Ismaeel, as said in Arabic, after he had settled in Arabia. The building has a mosque...
and nearby pillars.
Related phenomena, such as cupholes, rock-cut tombs and circles also occur in the Middle East.
Asian megaliths

Korean Peninsula
The Korean Peninsula is a peninsula in East Asia. It extends southwards for about 684 miles from continental Asia into the Pacific Ocean and is surrounded by the Sea of Japan to the south, and the Yellow Sea to the west, the Korea Strait connecting the first two bodies of water.Until the end of...
. They are also found in the Liaoning
Liaoning
' is a province of the People's Republic of China, located in the northeast of the country. Its one-character abbreviation is "辽" , a name taken from the Liao River that flows through the province. "Níng" means "peace"...
, Shandong
Shandong
' is a Province located on the eastern coast of the People's Republic of China. Shandong has played a major role in Chinese history from the beginning of Chinese civilization along the lower reaches of the Yellow River and served as a pivotal cultural and religious site for Taoism, Chinese...
, and Zhejiang
Zhejiang
Zhejiang is an eastern coastal province of the People's Republic of China. The word Zhejiang was the old name of the Qiantang River, which passes through Hangzhou, the provincial capital...
in China
China
Chinese civilization may refer to:* China for more general discussion of the country.* Chinese culture* Greater China, the transnational community of ethnic Chinese.* History of China* Sinosphere, the area historically affected by Chinese culture...
, Kyūshū
Kyushu
is the third largest island of Japan and most southwesterly of its four main islands. Its alternate ancient names include , , and . The historical regional name is referred to Kyushu and its surrounding islands....
and Shikoku
Shikoku
is the smallest and least populous of the four main islands of Japan, located south of Honshū and east of the island of Kyūshū. Its ancient names include Iyo-no-futana-shima , Iyo-shima , and Futana-shima...
in Japan
Japan
Japan is an island nation in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean, it lies to the east of the Sea of Japan, China, North Korea, South Korea and Russia, stretching from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea and Taiwan in the south...
, Dong Nai province in Vietnam
Vietnam
Vietnam – sometimes spelled Viet Nam , officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam – is the easternmost country on the Indochina Peninsula in Southeast Asia. It is bordered by China to the north, Laos to the northwest, Cambodia to the southwest, and the South China Sea –...
and parts of Pakistan
Pakistan
Pakistan , officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan is a sovereign state in South Asia. It has a coastline along the Arabian Sea and the Gulf of Oman in the south and is bordered by Afghanistan and Iran in the west, India in the east and China in the far northeast. In the north, Tajikistan...
and India
India
India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
. Some living megalithic traditions is found on the island of Sumba
Sumba
Sumba is an island in eastern Indonesia, is one of the Lesser Sunda Islands, and is in the province of East Nusa Tenggara. Sumba has an area of 11,153 km², and the population was officially at 611,422 in 2005...
and Nias
Nias
Nīas is an island off the western coast of Sumatra, Indonesia. Nias is also the name of the archipelago, containing the Hinako archipelago....
in Indonesia
Indonesia
Indonesia , officially the Republic of Indonesia , is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania. Indonesia is an archipelago comprising approximately 13,000 islands. It has 33 provinces with over 238 million people, and is the world's fourth most populous country. Indonesia is a republic, with an...
. The greatest concentration of megalithic burials is in Korea. Archaeologists estimate that there are 15,000 to 100,000 southern megaliths in the Korean Peninsula. Typical estimates hover around the 30,000 mark for the entire peninsula, which in itself constitutes some 40% of all dolmens worldwide (see Dolmen).
Northern style
Northeast Asian megalithic traditions originated in ManchuriaManchuria
Manchuria is a historical name given to a large geographic region in northeast Asia. Depending on the definition of its extent, Manchuria usually falls entirely within the People's Republic of China, or is sometimes divided between China and Russia. The region is commonly referred to as Northeast...
, in particular the Liao River
Liao River
The Liao River is the principal river in northeast China . The province of Liaoning and the Liaodong Peninsula derive their names from the river....
basin. The practice of erecting megalithic burials spread quickly from the Liao River Basin and into the Korean Peninsula, where the structure of megaliths is geographically and chronologically distinct. The earliest megalithic burials are called "northern" or "table-style" because they feature an above-ground burial chamber formed by heavy stone slabs that form a rectangular cist. An oversized capstone is placed over the stone slab burial chamber, giving the appearance of a table-top. These megalithic burials date to the early part of the Mumun Pottery Period
Mumun pottery period
The Mumun pottery period is an archaeological era in Korean prehistory that dates to approximately 1500-300 BC This period is named after the Korean name for undecorated or plain cooking and storage vessels that form a large part of the pottery assemblage over the entire length of the period, but...
(c. 1500-850 BC) and are distributed, with a few exceptions, north of the Han River
Han River (Korea)
The Han River is a major river in South Korea and the fourth longest river on the Korean peninsula after the Amnok, Duman, and Nakdong rivers. It is formed by the confluence of the Namhan River , which originates in Mount Daedeok, and the Bukhan River , which originates on the slopes of Mount...
. Few northern-style megaliths in Manchuria contain grave goods
Grave goods
Grave goods, in archaeology and anthropology, are the items buried along with the body.They are usually personal possessions, supplies to smooth the deceased's journey into the afterlife or offerings to the gods. Grave goods are a type of votive deposit...
such as Liaoning bronze daggers
Liaoning bronze dagger culture
The Liaoning bronze dagger culture is an archeological complex of the late Bronze Age in Korea and China. Artifacts from the culture are found primarily in the Liaoning area of Manchuria and in the Korean peninsula. Various other bronze artifacts, including ornaments and weapons, are associated...
, prompting some archaeologists to interpret the burials as the graves of chiefs or preeminent individuals. However, whether a result of grave-robbery or intentional mortuary behaviour, most northern megaliths contain no grave goods.
Southern style
Southern-style megalithic burials are distributed in the southern Korean PeninsulaKorean Peninsula
The Korean Peninsula is a peninsula in East Asia. It extends southwards for about 684 miles from continental Asia into the Pacific Ocean and is surrounded by the Sea of Japan to the south, and the Yellow Sea to the west, the Korea Strait connecting the first two bodies of water.Until the end of...
. It is thought that most of them date to the latter part of the Early Mumun or to the Middle Mumun Period. Southern-style megaliths are typically smaller in scale than northern megaliths. The interment area of southern megaliths has an underground burial chamber made of earth or lined with thin stone slabs. A massive capstone is placed over the interment area and is supported by smaller propping stones. Most of the megalithic burials on the Korean Peninsula
Korean Peninsula
The Korean Peninsula is a peninsula in East Asia. It extends southwards for about 684 miles from continental Asia into the Pacific Ocean and is surrounded by the Sea of Japan to the south, and the Yellow Sea to the west, the Korea Strait connecting the first two bodies of water.Until the end of...
are of the southern type.
Capstone-style
These megaliths are distinguished from other types by the presence of a burial shaft, sometimes up to 4 m in depth, which is lined with large cobbles. A large capstone is placed over the burial shaft without propping stones. Capstone-style megaliths are the most monumental type in the Korean PeninsulaKorean Peninsula
The Korean Peninsula is a peninsula in East Asia. It extends southwards for about 684 miles from continental Asia into the Pacific Ocean and is surrounded by the Sea of Japan to the south, and the Yellow Sea to the west, the Korea Strait connecting the first two bodies of water.Until the end of...
, and they are primarily distributed near or on the south coast of Korea. It seems that most of these burials date to the latter part of the Middle Mumun (c. 700-550 BC), and they may have been built into the early part of the Late Mumun. An example is found near modern Changwon
Changwon
Changwon is a city in and the capital of Gyeongsangnam-do in South Korea. Changwon city is 8th most populous city in South Korea, with a 2010 established population of 1,089,039. It encompasses a land area of on southeastern of South Korea. The population of Southeastern part of Korea, that...
at Deokcheon-ni, where a small cemetery contained a capstone burial (No. 1) with a massive, rectangularly shaped, stone and earthen platform. Archaeologists were not able to recover the entire feature, but the low platform was at least 56 X 18 m in size.
Living megalith culture of Indonesia
Indonesian archipelago is the host of AustronesianAustronesian people
The Austronesian-speaking peoples are various populations in Oceania and Southeast Asia that speak languages of the Austronesian family. They include Taiwanese aborigines; the majority ethnic groups of East Timor, Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines, Brunei, Madagascar, Micronesia, and Polynesia,...
megalith cultures in past and present. Living megalith culture can be found in Nias
Nias
Nīas is an island off the western coast of Sumatra, Indonesia. Nias is also the name of the archipelago, containing the Hinako archipelago....
, an isolated island offcoast western North Sumatra
North Sumatra
North Sumatra is a province of Indonesia on the Sumatra island. Its capital is Medan. It is the most populous Indonesian province outside of Java. It is slightly larger than Sri Lanka in area.- Geography and population :...
, Batak
Batak (Indonesia)
Batak is a collective term used to identify a number of ethnic groups predominantly found in North Sumatra, Indonesia. The term is used to include the Toba, Karo, Pakpak, Simalungun, Angkola and Mandailing, each of which are distinct but related groups with distinct, albeit related, languages and...
culture in interior North Sumatra, Sumba
Sumba
Sumba is an island in eastern Indonesia, is one of the Lesser Sunda Islands, and is in the province of East Nusa Tenggara. Sumba has an area of 11,153 km², and the population was officially at 611,422 in 2005...
island in East Nusa Tenggara
East Nusa Tenggara
East Nusa Tenggara is a province of Indonesia, located in the eastern portion of the Lesser Sunda Islands, including West Timor. The provincial capital is Kupang, located on West Timor...
, also Toraja
Toraja
The Toraja are an ethnic group indigenous to a mountainous region of South Sulawesi, Indonesia. Their population is approximately 650,000, of which 450,000 still live in the regency of Tana Toraja . Most of the population is Christian, and others are Muslim or have local animist beliefs known as aluk...
culture in interior South Sulawesi
South Sulawesi
South Sulawesi is a province of Indonesia, located on the western southern peninsula of Sulawesi Island. The province is bordered by Central Sulawesi province to the north, South East Sulawesi province to the east and West Sulawesi province to the west...
. These megalith cultures remain preserved, isolated and undisturbed well until late 19th century.
Several megalith sites and structures also found across Indonesia. Menhirs, dolmens, stone tables, ancestral stone statues, and step pyramid
Step pyramid
Step pyramids are structures which characterized several cultures throughout history, in several locations throughout the world. These pyramids typically are large and made of several layers of stone...
s structure called Punden Berundak were discovered in various sites in Java
Java
Java is an island of Indonesia. With a population of 135 million , it is the world's most populous island, and one of the most densely populated regions in the world. It is home to 60% of Indonesia's population. The Indonesian capital city, Jakarta, is in west Java...
, Sumatra
Sumatra
Sumatra is an island in western Indonesia, westernmost of the Sunda Islands. It is the largest island entirely in Indonesia , and the sixth largest island in the world at 473,481 km2 with a population of 50,365,538...
, Sulawesi
Sulawesi
Sulawesi is one of the four larger Sunda Islands of Indonesia and is situated between Borneo and the Maluku Islands. In Indonesia, only Sumatra, Borneo, and Papua are larger in territory, and only Java and Sumatra have larger Indonesian populations.- Etymology :The Portuguese were the first to...
, and Lesser Sunda Islands
Lesser Sunda Islands
The Lesser Sunda Islands or Nusa Tenggara are a group of islands in the southern Maritime Southeast Asia, north of Australia. Together with the Greater Sunda Islands to the west they make up the Sunda Islands...
.
Punden step pyramid and menhir can be found in Pagguyangan Cisolok and Gunung Padang, West Java
West Java
West Java , with a population of over 43 million, is the most populous and most densely populated province of Indonesia. Located on the island of Java, it is slightly smaller in area than densely populated Taiwan, but with nearly double the population...
. Cipari megalith site also in West Java displayed monolith, stone terraces, and sarcophagus. The Punden step pyramid is believed to be the predecessor and basic design of later Hindu-Buddhist temples
Candi of Indonesia
Candi are the Hindu and Buddhist temples and sanctuaries of Indonesia, mostly built during the 8th to 15th centuries...
structure in Java after the adoption of Hinduism and Buddhism by native population. The 8th century Borobudur
Borobudur
Borobudur, or Barabudur, is a 9th-century Mahayana Buddhist monument near Magelang, Central Java, Indonesia. The monument comprises six square platforms topped by three circular platforms, and is decorated with 2,672 relief panels and 504 Buddha statues...
and 15th-century Candi Sukuh
Candi Sukuh
Sukuh is a 15th century Javanese-Hindu temple that is located on the western slope of Mount Lawu on the border between Central and East Java provinces....
featured the step-pyramid structure.
Lore Lindu National Park
Lore Lindu National Park
Lore Lindu National Park is a forested protected area on the Indonesian island of Sulawesi, in the province of Central Sulawesi. The area of the national park is 2,180 km² covering both lowland and montane forests. It provides habitat to numerous rare species, including 77 bird species...
in Central Sulawesi
Central Sulawesi
Central Sulawesi is a province of Indonesia located in the centre of Sulawesi. It was established on 13 April 1964....
houses ancient megalith relics such as ancestral stone statues. Mostly located in the Bada, Besoa and Napu valleys.
Madia Gonds of Maharashtra, India
A study mentions living megalithic practices amongst the Madia GondMadia Gond
Madia Gonds or Madia or Maria are one of the endogamous Gond tribes living in Chandrapur District and Gadchiroli District of Maharashtra State, and Bastar division of Chhattisgad State India. They have been granted the status of a Primitive Tribe by the Government of Maharashtra under its...
s. The Madia Gonds live in Bhamragad Taluka of Gadchiroli District
Gadchiroli District
Gadchiroli district is an administrative district in Maharashtra, India. The town of Gadchiroli is the administrative headquarters of the district....
of Maharashtra
Maharashtra
Maharashtra is a state located in India. It is the second most populous after Uttar Pradesh and third largest state by area in India...
, India
India
India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
.
Analysis and evaluation
Megaliths were used for a variety of purposes. The purpose of megaliths ranged from serving as boundary markers of territory, to a reminder of past events, to being part of the society's religion. Common motifs including crooks and axes seem to be symbols of political power, much like the crook was a symbol of Egyptian pharaohs. Amongst the indigenous peoplesIndigenous peoples
Indigenous peoples are ethnic groups that are defined as indigenous according to one of the various definitions of the term, there is no universally accepted definition but most of which carry connotations of being the "original inhabitants" of a territory....
of India
India
India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
, Malaysia, Polynesia
Polynesia
Polynesia is a subregion of Oceania, made up of over 1,000 islands scattered over the central and southern Pacific Ocean. The indigenous people who inhabit the islands of Polynesia are termed Polynesians and they share many similar traits including language, culture and beliefs...
, North Africa
North Africa
North Africa or Northern Africa is the northernmost region of the African continent, linked by the Sahara to Sub-Saharan Africa. Geopolitically, the United Nations definition of Northern Africa includes eight countries or territories; Algeria, Egypt, Libya, Morocco, South Sudan, Sudan, Tunisia, and...
, North America
North America
North America is a continent wholly within the Northern Hemisphere and almost wholly within the Western Hemisphere. It is also considered a northern subcontinent of the Americas...
, and South America
South America
South America is a continent situated in the Western Hemisphere, mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere. The continent is also considered a subcontinent of the Americas. It is bordered on the west by the Pacific Ocean and on the north and east...
, the worship of these stones, or the use of these stones to symbolize a spirit or deity, is a possibility. In the early 20th century, some scholars believed that all megaliths belonged to one global "Megalithic culture" (hyperdiffusionism, e. g. 'the Manchester school', by Grafton Elliot Smith
Grafton Elliot Smith
Sir Grafton Elliot Smith, FRS FRCP was an Australian anatomist and a proponent of the hyperdiffusionist view of prehistory.-Professional career:Smith was born in Grafton, New South Wales...
and William James Perry
William James Perry
William James Perry , usually known as W. J. Perry, was a leader in cultural anthropology at University College, London.Megalith culture, according to him, was transmitted to the rest of the world from Egypt....
), but this has long been disproved by modern dating methods. Nor is it believed any longer that there was a European megalithic culture, although regional cultures existed, even within such a small areas as the British Isles. The archaeologist Euan Mackie wrote "Likewise it cannot be doubted that important regional cultures existed in the Neolithic period and can be defined by different kinds of stone circles and local pottery styles (Ruggles & Barclay 2000: figure 1). No-one has ever been rash enough to claim a nation-wide unity of all aspects of Neolithic archaeology!"
Types of megalithic structures
The types of megalithic structures can be divided into two categories, the "Polylithic type" and the "Monolithic type". Different megalithic structures include:Polylithic type
|
Monolithic type
|
See also
- List of megalithic sites
- Megalithic monuments in Europe
- Irish Megalithic TombsIrish Megalithic TombsIreland has a wealth of impressive historical monuments. In Ireland there are four types of megalithic tombs: court cairns, passage tombs, wedge tombs and portal dolmens.-Court tombs:...
- Megaliths in the UralsMegaliths in the UralsDuring the last years a lot of megaliths have been discovered in the Urals: dolmens, menhirs and a large megalithic cultic complex of the Vera Island.-Dolmens of the Middle Urals:At present time more than 200 dolmens have been discovered in the Sverdlovsk Oblast...
- Plain of JarsPlain of JarsThe Plain of Jars is a megalithic archaeological landscape in Laos. Scattered in the landscape of the Xieng Khouang plateau Xieng Khouang, Lao PDR, are thousands of megalithic jars...
ranging from the Khorat Plateau in Thailand in the south, through Laos and to Dima Hasao of northerneastern India. - Standing stoneStanding stoneStanding stones, orthostats, liths, or more commonly megaliths are solitary stones set vertically in the ground and come in many different varieties....
- Stone circleStone circleA stone circle is a monument of standing stones arranged in a circle. Such monuments have been constructed across the world throughout history for many different reasons....
- Nature worshipNature worshipNature worship describes a variety of religious, spiritual and devotional practices that focus on natural phenomenon. A nature deity can be in charge of nature, the biosphere, the cosmos or the universe. Nature worship can be found in panentheism, pantheism, deism, polytheism, animism, totemism,...
- Bilger's rocksBilger's rocksBilger's Rocks is a site in Clearfield County, Pennsylvania, near the town of Grampian in Bloom Township. The surrounding area is intricately laced with hills, mountains, and river valleys that generally follow the Appalachian mountain range in a northwest to southeast direction...
External links
- MegalithicIreland.com
- New Geology - solved mysteries of cart ruts & megaliths
- Dolmens, Menhirs & Stones-Circles in the South of France
- Megaliths in Charente-Maritime, France
- Dolmen Path - Russian Megaliths
- The Megalithic Portal and Megalith Map
- Index of Megalithic monuments in Ireland
- The Modern Antiquarian
- Pretanic World - Megaliths and Monuments
- Modern Megalith-Building

