
Marine habitats
Encyclopedia
This article is about the habitat
s that support marine life. Marine life depends in some way on the saltwater
that is in the sea (the term marine comes from the Latin
mare, meaning sea or ocean). A habitat is an ecological or environmental
area inhabited by one or more living species
.
Marine habitats can be divided into coastal and open ocean habitats. Coastal habitats are found in the area that extends from as far as the tide comes in on the shoreline out to the edge of the continental shelf
. Most marine life is found in coastal habitats, even though the shelf area occupies only seven percent of the total ocean area. Open ocean habitats are found in the deep ocean beyond the edge of the continental shelf.
Alternatively, marine habitats can be divided into pelagic and demersal habitats. Pelagic habitats are found near the surface or in the open water column, away from the bottom of the ocean. Demersal habitats are near or on the bottom of the ocean. An organism living in a pelagic habitat is said to be a pelagic organism, as in pelagic fish
. Similarly, an organism living in a demersal habitat is said to be a demersal organism, as in demersal fish. Pelagic habitats are intrinsically shifting and ephemeral, depending on what ocean current
s are doing.
Marine habitats can be modified by their inhabitants. Some marine organisms, like corals, kelp, mangroves and seagrasses, are ecosystem engineer
s which reshape the marine environment to the point where they create further habitat for other organisms.
 In contrast to terrestrial habitats, marine habitats are shifting and ephemeral. Swimming organisms find areas by the edge of a continental shelf
In contrast to terrestrial habitats, marine habitats are shifting and ephemeral. Swimming organisms find areas by the edge of a continental shelf
a good habitat, but only while upwelling
s bring nutrient rich water to the surface. Shellfish find habitat on sandy beaches, but storms, tides and currents mean their habitat continually reinvents itself.
What is common to all marine habitats is the presence of seawater
. Beyond that many other things determine whether a marine area makes a good habitat and the type of habitat it makes. For example:
The ocean occupies 71 percent of the world surface, averaging nearly four kilometers in depth. There are five major oceans, of which the Pacific Ocean
is nearly as large as the rest put together. Coastlines fringe the land for nearly 380,000 kilometres.
Marine habitats can be broadly divided into pelagic and demersal habitats. Pelagic habitats are the habitats of the open water column, away from the bottom of the ocean. Demersal habitats are the habitats that are near or on the bottom of the ocean. An organism living in a pelagic habitat is said to be a pelagic organism, as in pelagic fish
. Similarly, an organism living in a demersal habitat is said to be a demersal organism, as in demersal fish. Pelagic habitats are intrinsically ephemeral, depending on what ocean current
s are doing.
The land-based ecosystem
depends on topsoil and fresh water, while the marine ecosystem depends on dissolved nutrients washed down from the land.
 In marine systems, ocean current
In marine systems, ocean current
s have a key role determining which areas are effective as habitats, since ocean currents transport the basic nutrients needed to support marine life. Plankton
are the life forms that inhabit the ocean that are so small (less than 2 mm) that they cannot effectively propel themselves through the water, but must drift instead with the currents. If the current carries the right nutrients, and if it also flows at a suitably shallow depth where there is plenty of sunlight, then such a current itself can become a suitable habitat for photosynthesizing tiny algae called phytoplankton
. These tiny plants are the primary producers
in the ocean, at the start of the food chain
. In turn, as the population of drifting phytoplankton grows, the water becomes a suitable habitat for zooplankton
, which feed on the phytoplankton. While phytoplankton are tiny drifting plants, zooplankton are tiny drifting animals, such as the larvae
of fish
and marine invertebrates. If sufficient zooplankton establish themselves, the current becomes a candidate habitat for the forage fish
that feed on them. And then if sufficient forage fish move to the area, it becomes a candidate habitat for larger predatory fish
and other marine animals that feed on the forage fish. In this dynamic way, the current itself can, over time, become a moving habitat for multiple types of marine life.
 Ocean currents can be generated by differences in the density of the water. How dense water is depends on how saline or warm it is. If water contains differences in salt content or temperature, then the different densities will initiate a current. Water that is saltier or cooler will be denser, and will sink in relation to the surrounding water. Conversely, warmer and less salty water will float to the surface. Atmospheric winds and pressure differences also produces surface currents, waves and seiche
Ocean currents can be generated by differences in the density of the water. How dense water is depends on how saline or warm it is. If water contains differences in salt content or temperature, then the different densities will initiate a current. Water that is saltier or cooler will be denser, and will sink in relation to the surrounding water. Conversely, warmer and less salty water will float to the surface. Atmospheric winds and pressure differences also produces surface currents, waves and seiche
s. Ocean currents are also generated by the gravitational pull of the sun and moon (tide
s), and seismic activity (tsunami
).
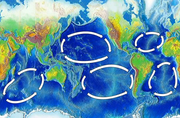
The rotation of the Earth affects the direction ocean currents take, and explains which way the large circular ocean gyres rotate in the image above left. Suppose a current at the equator is heading north. The Earth rotates eastward, so the water possesses that rotational momentum. But the further the water moves north, the slower the earth moves eastward. If the current could get to the North Pole, the earth wouldn't be moving eastward at all. To conserve its rotational momentum, the further the current travels north the faster it must move eastward. So the effect is that the current curves to the right. This is the Coriolis effect
. It is weakest at the equator and strongest at the poles. The effect is opposite south of the equator, where currents curve left.
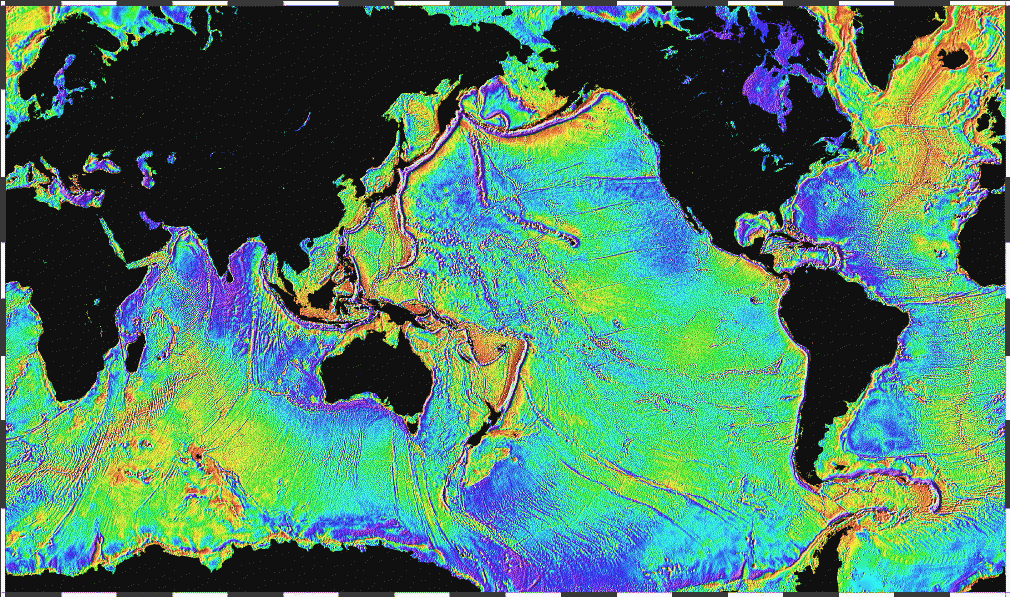 Marine topography
Marine topography
refers to the shape the land has when it interfaces with the ocean. These shapes are obvious along coastlines, but they occur also in significant ways underwater. The effectiveness of marine habitats is partially defined by these shapes, including the way they interact with and shape ocean current
s, and the way sunlight diminishes when these landforms occupy increasing depths.
Marine topographies include coastal and oceanic landforms ranging from coastal estuaries
and shorelines to continental shelves
and coral reef
s. Further out in the open ocean, they include underwater and deep sea
features such as ocean rises and seamount
s. The submerged surface has mountainous features, including a globe-spanning mid-ocean ridge
system, as well as undersea volcano
es, oceanic trench
es, submarine canyon
s, oceanic plateau
s and abyssal plain
s.
The mass of the oceans is approximately 1.35 metric tons, or about 1/4400 of the total mass of the Earth. The oceans cover an area of 3.618 km2 with a mean depth of 3,682 m, resulting in an estimated volume of 1.332 km3.
.
 Marine coasts
Marine coasts
are dynamic environments which constantly change, like the ocean which partially shape them. The Earth's natural processes, including weather
and sea level change, result in the erosion
, accretion
and resculpturing of coasts as well as the flooding and creation of continental shelves
and drowned river valleys.
The main agents responsible for deposition and erosion
along coastlines are waves, tide
s and currents
. The formation of coasts also depends on the nature of the rocks
they are made of – the harder the rocks the less likely they are to erode, so variations in rock hardness result in coastlines with different shapes.
Tide
s often determine the range over which sediment
is deposited or eroded. Areas with high tidal ranges allow waves to reach farther up the shore, and areas with lower tidal ranges produce deposition at a smaller elevation interval. The tidal range is influenced by the size and shape of the coastline. Tides do not typically cause erosion by themselves; however, tidal bore
s can erode as the waves surge up river estuaries
from the ocean.
Waves erode coastline as they break on shore releasing their energy; the larger the wave the more energy it releases and the more sediment it moves. Sediment deposited by waves comes from eroded cliff faces and is moved along the coastline by the waves. Sediment deposited by rivers is the dominant influence on the amount of sediment located on a coastline.
The sedimentologist
Francis Shepard classified coasts as primary or secondary.
 Continental coastlines usually have a continental shelf
Continental coastlines usually have a continental shelf
, a shelf of relatively shallow water, less than 200 metres deep, which extends 68 km on average beyond the coast. Worldwide, continental shelves occupy a total area of about 24 million km2 (9 million sq mi), nearly 5% of the world's total area. Since the continental shelf is usually less than 200 metres deep, it follows that coastal habitats are generally photic
, situated in the sunlit epipelagic zone. This means the conditions for photosynthetic processes so important for primary production
, are available to coastal marine habitats. Because land is nearby, there are large discharges of nutrient rich land runoff into coastal waters. Further, periodic upwelling
s from the deep ocean can provide cool and nutrient rich currents along the edge of the continental shelf.
As a result, coastal marine life is the most abundant in the world. It is found in tidal pools, fjord
s and estuaries, near sandy shores and rocky coastlines, around coral reef
s and on or above the continental shelf. Coastal fish
include small forage fish as well as the larger predator fish that feed on them. Forage fish
thrive in inshore waters where high productivity
results from upwelling
and shoreline run off of nutrients. Some are partial residents that spawn in streams, estuaries and bays, but most complete their life cycle in the zone. There can also be a mutualism between species that occupy adjacent marine habitats. For example, fringing reef
s just below low tide level have a mutually beneficial relationship with mangrove
forests at high tide level and sea grass meadows in between: the reefs protect the mangroves and seagrass from strong currents and waves that would damage them or erode
the sediments in which they are rooted, while the mangroves and seagrass protect the coral from large influxes of silt
, fresh water and pollutants
. This additional level of variety in the environment is beneficial to many types of coral reef animals, which for example may feed in the sea grass and use the reefs for protection or breeding.
Coastal habitats are the most visible marine habitats, but they are not the only important marine habitats. Coastlines run for 380,000 kilometres, and the total volume of the ocean is 1,370 million cu km. This means that for each metre of coast, there is 3.6 cu km of ocean space available somewhere for marine habitats.

s, those areas close to shore, are constantly being exposed and covered by the ocean's tides. A huge array of life lives within this zone.
Shore habitats range from the upper intertidal zones to the area where land vegetation takes prominence. It can be underwater anywhere from daily to very infrequently. Many species here are scavengers, living off of sea life that is washed up on the shore. Many land animals also make much use of the shore and intertidal habitats. A subgroup of organisms in this habitat bores and grinds exposed rock through the process of bioerosion
.
es, are coastal shorelines where sand
accumulates. Waves and currents shift the sand, continually building and eroding the shoreline. Longshore currents flow parallel to the beaches, making waves break obliquely on the sand. These currents transport large amounts of sand along coasts, forming spits
, barrier island
s and tombolo
s. Longshore currents also commonly create offshore bars, which give beaches some stability by reducing erosion.
Sandy shores are full of life, The grains of sand host diatom
s, bacteria
and other microscopic creatures. Some fish and turtles return to certain beaches and spawn
eggs in the sand. Birds habitat beaches, like gull
s, loon
s, sandpipers, tern
s and pelican
s. Aquatic mammal
s, such sea lions, recuperate on them. Clam
s, periwinkle
s, crab
s, shrimp
, starfish and sea urchin
s are found on most beaches.
Sand is a sediment
made from small grains or particles
with diameters between about 60 µm and 2 mm. Mud (see mudflats below) is a sediment made from particles finer than sand. This small particle size means that mud particles tend to stick together, whereas sand particles do not. Mud is not easily shifted by waves and currents, and when it dries out, cakes into a solid. By contrast, sand is easily shifted by waves and currents, and when sand dries out it can be blown in the wind, accumulating into shifting sand dunes. Beyond the high tide mark, if the beach is low-lying, the wind can form rolling hills of sand dunes. Small dunes shift and reshape under the influence of the wind while larger dunes stabilise the sand with vegetation.
Ocean processes grade loose sediments to particle sizes
other than sand, such as gravel
or cobble
s. Waves breaking on a beach can leave a berm
, which is a raised ridge of coarser pebbles or sand, at the high tide mark. Shingle beach
es are made of particles larger than sand, such as cobbles, or small stones. These beaches make poor habitats. Little life survives because the stones are churned and pounded together by waves and currents.
s seems to give them a permanence compared to the shifting nature of sandy shores. This apparent stability is not real over even quite short geological time scales, but it is real enough over the short life of an organism. In contrast to sandy shores, plants and animals can anchor themselves to the rocks.
Competition can develop for the rocky spaces. For example, barnacle
s can compete successfully on open intertidal rock faces to the point where the rock surface is covered with them. Barnacles resist desiccation and grip well to exposed rock faces. However, in the crevices of the same rocks, the inhabitants are different. Here mussel
s can be the successful species, secured to the rock with their byssal threads.
Rocky and sandy coasts are vulnerable because humans find them attractive and want to live near them. An increasing proportion of the humans live by the coast, putting pressure on coastal habitats.
 Mudflat
Mudflat
s are coastal wetlands that form when mud is deposited by tides or rivers. They are found in sheltered areas such as bays, bayous, lagoons, and estuaries. Mudflats may be viewed geologically as exposed layers of bay mud
, resulting from deposition of estuarine silt
s, clay
s and marine animal detritus
. Most of the sediment within a mudflat is within the intertidal zone
, and thus the flat is submerged and exposed approximately twice daily.
Mudflats are typically important regions for wildlife, supporting a large population, although levels of biodiversity are not particularly high. They are of particular importance to migratory birds. In the United Kingdom
mudflats have been classified as a Biodiversity Action Plan
priority habitat.
 Mangrove swamps and salt marsh
Mangrove swamps and salt marsh
es form important coastal habitats in topical and temperate areas respectively.
Mangroves are species of shrubs and medium size trees that grow in saline
coastal sediment habitats in the tropics
and subtropics
– mainly between latitude
s N and S. The saline conditions tolerated by various species range from brackish water
, through pure seawater
(30 to 40 ppt
), to water concentrated by evaporation
to over twice the salinity of ocean seawater (up to 90 ppt). There are many mangrove species, not all closely related. The term "mangrove" is used generally to cover all of these species, and it can be used narrowly to cover just mangrove trees of the genus Rhizophora
.
Mangroves form a distinct characteristic saline woodland
or shrubland
habitat, called a mangrove swamp or mangrove forest. Mangrove swamps are found in depositional
coastal environments, where fine sediments (often with high organic content) collect in areas protected from high-energy wave action. Mangroves dominate three quarters of tropical coastlines.
is a partly enclosed coastal body of water
with one or more river
s or stream
s flowing into it, and with a free connection to the open sea
. Estuaries form a transition zone between river environments and ocean environments and are subject to both marine influences, such as tides, waves, and the influx of saline water; and riverine influences, such as flows of fresh water and sediment. The inflow of both seawater and freshwater provide high levels of nutrients in both the water column and sediment, making estuaries among the most productive natural habitats in the world.
Most estuaries were formed by the flooding of river-eroded or glacially scoured valleys when sea level began to rise about 10,000-12,000 years ago. They are amongst the most heavily populated areas throughout the world, with about 60% of the world’s population living along estuaries and the coast. As a result, estuaries are suffering degradation by many factors, including sedimentation from soil erosion from deforestation; overgrazing and other poor farming practices; overfishing; drainage and filling of wetlands; eutrophication due to excessive nutrients from sewage and animal wastes; pollutants including heavy metals, PCBs, radionuclides and hydrocarbons from sewage inputs; and diking or damming for flood control or water diversion.
Estuaries provide habitats for a large number of organisms and support very high productivity. Estuaries provide habitats for salmon
and sea trout nurseries, as well as migratory
bird populations. Two of the main characteristics of estuarine life are the variability in salinity
and sedimentation
. Many species of fish
and invertebrate
s have various methods to control or conform to the shifts in salt concentrations and are termed osmoconformer
s and osmoregulators. Many animals also burrow to avoid predation
and to live in the more stable sedimental environment. However, large numbers of bacteria are found within the sediment which have a very high oxygen demand. This reduces the levels of oxygen within the sediment often resulting in partially anoxic conditions, which can be further exacerbated by limited water flux. Phytoplankton
are key primary producers in estuaries. They move with the water bodies and can be flushed in and out with the tide
s. Their productivity is largely dependent on the turbidity
of the water. The main phytoplankton present are diatoms and dinoflagellates which are abundant in the sediment.
 Kelp forest
Kelp forest
s are underwater areas with a high density of kelp
. They are recognized as one of the most productive and dynamic ecosystem
s on Earth. Smaller areas of anchored kelp are called kelp beds. Kelp forests occur worldwide throughout temperate
and polar
coastal oceans.
Kelp forests provide a unique three-dimensional habitat for marine organisms and are a source for understanding many ecological processes. Over the last century, they have been the focus of extensive research, particularly in trophic ecology, and continue to provoke important ideas that are relevant beyond this unique ecosystem. For example, kelp forests can influence coastal oceanographic patterns and provide many ecosystem services
.
However, humans have contributed to kelp forest degradation. Of particular concern are the effects of overfishing
nearshore ecosystems, which can release herbivores from their normal population regulation and result in the over-grazing of kelp and other algae. This can rapidly result in transitions to barren landscapes where relatively few species persist.
Frequently considered an ecosystem engineer
, kelp provides a physical substrate and habitat for kelp forest communities. In algae (Kingdom: Protista), the body of an individual organism is known as a thallus rather than as a plant (Kingdom: Plantae). The morphological structure of a kelp thallus is defined by three basic structural units:
In addition, many kelp species have pneumatocyst
s, or gas-filled bladders, usually located at the base of fronds near the stipe. These structures provide the necessary buoyancy for kelp to maintain an upright position in the water column.
The environmental factors necessary for kelp to survive include hard substrate (usually rock), high nutrients (e.g., nitrogen, phosphorus), and light (minimum annual irradiance
dose > 50 E m−2). Especially productive kelp forests tend to be associated with areas of significant oceanographic upwelling
, a process that delivers cool nutrient-rich water from depth to the ocean’s mixed surface layer
. Water flow and turbulence facilitate nutrient assimilation across kelp fronds throughout the water column. Water clarity affects the depth to which sufficient light can be transmitted. In ideal conditions, giant kelp (Macrocystis spp.) can grow as much as 30-60 centimeters vertically per day. Some species such as Nereocystis are annual
while others like Eisenia are perennial
, living for more than 20 years. In perennial kelp forests, maximum growth rates occur during upwelling months (typically spring and summer) and die-backs correspond to reduced nutrient availability, shorter photoperiods and increased storm frequency.
 Seagrass
Seagrass
es are flowering plant
s from one of four plant families which grow in marine environments. They are called seagrasses because the leaves are long and narrow and are very often green, and because the plants often grow in large meadows which look like grassland. Since seagrasses photosynthesize
and are submerged, they must grow submerged in the photic zone
, where there is enough sunlight. For this reason, most occur in shallow and sheltered coastal waters anchored in sand or mud bottoms.
Seagrasses form extensive beds or meadows, which can be either monospecific (made up of one species) or multispecific (where more than one species co-exist). Seagrass beds make highly diverse and productive ecosystem
s. They are home to phyla
such as juvenile and adult fish, epiphytic
and free-living macroalgae
and microalgae, mollusks, bristle worms, and nematode
s. Few species were originally considered to feed directly on seagrass leaves
(partly because of their low nutritional content), but scientific review
s and improved working methods have shown that seagrass herbivory
is a highly important link in the food chain, with hundreds of species feeding on seagrasses worldwide, including green turtles, dugong
s, manatee
s, fish
, geese
, swan
s, sea urchin
s and crab
s.
Seagrasses are ecosystem engineer
s in the sense that they partly create their own habitat. The leaves slow down water-currents increasing sedimentation
, and the seagrass root
s and rhizome
s stabilize the seabed. Their importance to associated species is mainly due to provision of shelter (through their three-dimensional structure in the water column), and due to their extraordinarily high rate of primary production
. As a result, seagrasses provide coastal zones with ecosystem services
, such as fishing grounds, wave protection, oxygen
production and protection against coastal erosion
. Seagrass meadows account for 15% of the ocean’s total carbon storage.
 Reef
Reef
s comprise some of the densest and most diverse habitats in the world. The best-known types of reefs are tropical coral reef
s which exist in most tropical waters; however, reefs can also exist in cold water. Reefs are built up by coral
s and other calcium
-depositing animals, usually on top of a rocky outcrop on the ocean floor. Reefs can also grow on other surfaces, which has made it possible to create artificial reef
s. Coral reefs also support a huge community of life, including the corals themselves, their symbiotic zooxanthellae, tropical fish and many other organisms.
Much attention in marine biology is focused on coral reefs and the El Niño weather phenomenon. In 1998, coral reefs experienced the most severe mass bleaching events on record, when vast expanses of reefs across the world died because sea surface temperatures rose well above normal. Some reefs are recovering, but scientists say that between 50% and 70% of the world's coral reefs are now endangered and predict that global warming
could exacerbate this trend.
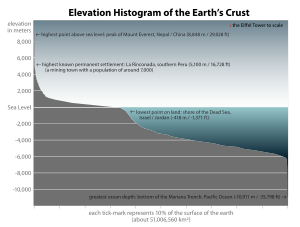 The open ocean is relatively unproductive because of a lack of nutrients, yet because it is so vast, it has more overall primary production
The open ocean is relatively unproductive because of a lack of nutrients, yet because it is so vast, it has more overall primary production
than any other marine habitat. Only about 10 percent of marine species live in the open ocean. But among them are the largest and fastest of all marine animals, as well as the animals that dive the deepest and migrate the longest. In the depths lurk animal that, to our eyes, appear hugely alien.
by phytoplankton
. The epipelagic zone is usually low in nutrients. This partially because the organic debris produced in the zone, such as excrement and dead animals, sink to the depths and are lost to the upper zone. Photosynthesis can happen only if both sunlight and nutrients are present.
In some places, like at the edge of continental shelves, nutrients can upwell
from the ocean depth, or land runoff can be distributed by storms and ocean currents. In these areas, given that both sunlight and nutrients are now present, phytoplankton can rapidly establish itself, multiplying so fast that the water turns green from the chlorophyll, resulting in an algal bloom
. These nutrient rich surface waters are among the most biologically productive in the world, supporting billions of tonnes of biomass
.
"Phytoplankton are eaten by zooplankton
- small animals which, like phytoplankton, drift in the ocean currents. The most abundant zooplankton species are copepod
s and krill
: tiny crustacean
s that are the most numerous animals on Earth. Other types of zooplankton include jelly fish and the larvae
of fish, marine worm
s, starfish, and other marine organisms". In turn, the zooplankton are eaten by filter feeding animals, including some seabird
s, small forage fish
like herrings and sardines, whale shark
s, manta ray
s, and the largest animal in the world, the blue whale
. Yet again, moving up the foodchain, the small forage fish are in turn eaten by larger predators, such as tuna, marlin, sharks, large squid, seabirds, dolphins, and toothed whale
s.
starts at the aphotic zone
, the point where sunlight loses most of its energy in the water. Many life forms that live at these depths have the ability to create their own light a unique evolution known as bio-luminescence.
In the deep ocean, the waters extend far below the epipelagic zone, and support very different types of pelagic life forms adapted to living in these deeper zones.
Much of the aphotic zone
's energy is supplied by the open ocean in the form of detritus
. In deep water, marine snow
is a continuous shower of mostly organic detritus falling from the upper layers of the water column. Its origin lies in activities within the productive photic zone
. Marine snow includes dead or dying plankton
, protist
s (diatom
s), fecal matter, sand, soot and other inorganic dust. The "snowflakes" grow over time and may reach several centimetres in diameter, travelling for weeks before reaching the ocean floor. However, most organic components of marine snow are consumed by microbes, zooplankton
and other filter-feeding animals within the first 1,000 metres of their journey, that is, within the epipelagic zone. In this way marine snow may be considered the foundation of deep-sea mesopelagic
and benthic ecosystem
s: As sunlight cannot reach them, deep-sea organisms rely heavily on marine snow as an energy source.
Some deep-sea pelagic groups, such as the lanternfish
, ridgehead
, marine hatchetfish
, and lightfish
families are sometimes termed pseudoceanic because, rather than having an even distribution in open water, they occur in significantly higher abundances around structural oases, notably seamount
s and over continental slopes. The phenomenon is explained by the likewise abundance of prey species which are also attracted to the structures.
The fish in the different pelagic and deep water benthic zones are physically structured, and behave in ways, that differ markedly from each other. Groups of coexisting species within each zone all seem to operate in similar ways, such as the small mesopelagic vertically migrating
plankton-feeders, the bathypelagic anglerfish
es, and the deep water benthic rattail
s. "
Ray finned
species, with spiny fins, are rare among deep sea fishes, which suggests that deep sea fish are ancient and so well adapted to their environment that invasions by more modern fishes have been unsuccessful. The few ray fins that do exist are mainly in the Beryciformes
and Lampriformes
, which are also ancient forms. Most deep sea pelagic fishes belong to their own orders, suggesting a long evolution in deep sea environments. In contrast, deep water benthic species, are in orders that include many related shallow water fishes.
The umbrella mouth gulper is a deep sea eel with an enormous loosely hinged mouth. It can open its mouth wide enough to swallow a fish much larger than itself, and then expand its stomach to accommodate its catch.
s along the mid-ocean ridge
spreading centers act as oases
, as do their opposites, cold seeps. Such places support unique biome
s and many new microbes and other lifeforms have been discovered at these locations.
es measure to date is the Mariana Trench
, near the Philippines
, in the Pacific Ocean
at 10,924 m (35,838 ft). At such depths, water pressure is extreme and there is no sunlight, but some life still exists. A white flatfish
, a shrimp and a jellyfish were seen by the American crew of the bathyscaphe
Trieste
when it dove to the bottom in 1960.
s that rise from the depths, where fish and other sea life congregate to spawn and feed.
Habitat
* Habitat , a place where a species lives and grows*Human habitat, a place where humans live, work or play** Space habitat, a space station intended as a permanent settlement...
s that support marine life. Marine life depends in some way on the saltwater
Seawater
Seawater is water from a sea or ocean. On average, seawater in the world's oceans has a salinity of about 3.5% . This means that every kilogram of seawater has approximately of dissolved salts . The average density of seawater at the ocean surface is 1.025 g/ml...
that is in the sea (the term marine comes from the Latin
Latin
Latin is an Italic language originally spoken in Latium and Ancient Rome. It, along with most European languages, is a descendant of the ancient Proto-Indo-European language. Although it is considered a dead language, a number of scholars and members of the Christian clergy speak it fluently, and...
mare, meaning sea or ocean). A habitat is an ecological or environmental
Natural environment
The natural environment encompasses all living and non-living things occurring naturally on Earth or some region thereof. It is an environment that encompasses the interaction of all living species....
area inhabited by one or more living species
Species
In biology, a species is one of the basic units of biological classification and a taxonomic rank. A species is often defined as a group of organisms capable of interbreeding and producing fertile offspring. While in many cases this definition is adequate, more precise or differing measures are...
.
Marine habitats can be divided into coastal and open ocean habitats. Coastal habitats are found in the area that extends from as far as the tide comes in on the shoreline out to the edge of the continental shelf
Continental shelf
The continental shelf is the extended perimeter of each continent and associated coastal plain. Much of the shelf was exposed during glacial periods, but is now submerged under relatively shallow seas and gulfs, and was similarly submerged during other interglacial periods. The continental margin,...
. Most marine life is found in coastal habitats, even though the shelf area occupies only seven percent of the total ocean area. Open ocean habitats are found in the deep ocean beyond the edge of the continental shelf.
Alternatively, marine habitats can be divided into pelagic and demersal habitats. Pelagic habitats are found near the surface or in the open water column, away from the bottom of the ocean. Demersal habitats are near or on the bottom of the ocean. An organism living in a pelagic habitat is said to be a pelagic organism, as in pelagic fish
Pelagic fish
Pelagic fish live near the surface or in the water column of coastal, ocean and lake waters, but not on the bottom of the sea or the lake. They can be contrasted with demersal fish, which do live on or near the bottom, and reef fish which are associated with coral reefs.The marine pelagic...
. Similarly, an organism living in a demersal habitat is said to be a demersal organism, as in demersal fish. Pelagic habitats are intrinsically shifting and ephemeral, depending on what ocean current
Ocean current
An ocean current is a continuous, directed movement of ocean water generated by the forces acting upon this mean flow, such as breaking waves, wind, Coriolis effect, cabbeling, temperature and salinity differences and tides caused by the gravitational pull of the Moon and the Sun...
s are doing.
Marine habitats can be modified by their inhabitants. Some marine organisms, like corals, kelp, mangroves and seagrasses, are ecosystem engineer
Ecosystem engineer
An ecosystem engineer is any organism that creates or modifies habitats. Jones et al. identified two different types of ecosystem engineers:...
s which reshape the marine environment to the point where they create further habitat for other organisms.
Overview

Continental shelf
The continental shelf is the extended perimeter of each continent and associated coastal plain. Much of the shelf was exposed during glacial periods, but is now submerged under relatively shallow seas and gulfs, and was similarly submerged during other interglacial periods. The continental margin,...
a good habitat, but only while upwelling
Upwelling
Upwelling is an oceanographic phenomenon that involves wind-driven motion of dense, cooler, and usually nutrient-rich water towards the ocean surface, replacing the warmer, usually nutrient-depleted surface water. The increased availability in upwelling regions results in high levels of primary...
s bring nutrient rich water to the surface. Shellfish find habitat on sandy beaches, but storms, tides and currents mean their habitat continually reinvents itself.
What is common to all marine habitats is the presence of seawater
Seawater
Seawater is water from a sea or ocean. On average, seawater in the world's oceans has a salinity of about 3.5% . This means that every kilogram of seawater has approximately of dissolved salts . The average density of seawater at the ocean surface is 1.025 g/ml...
. Beyond that many other things determine whether a marine area makes a good habitat and the type of habitat it makes. For example:
- temperature – is affected by geographical latitudeLatitudeIn geography, the latitude of a location on the Earth is the angular distance of that location south or north of the Equator. The latitude is an angle, and is usually measured in degrees . The equator has a latitude of 0°, the North pole has a latitude of 90° north , and the South pole has a...
, ocean currents, weatherWeatherWeather is the state of the atmosphere, to the degree that it is hot or cold, wet or dry, calm or stormy, clear or cloudy. Most weather phenomena occur in the troposphere, just below the stratosphere. Weather refers, generally, to day-to-day temperature and precipitation activity, whereas climate...
, the discharge of rivers, and by the presence of hydrothermal ventHydrothermal ventA hydrothermal vent is a fissure in a planet's surface from which geothermally heated water issues. Hydrothermal vents are commonly found near volcanically active places, areas where tectonic plates are moving apart, ocean basins, and hotspots. Hydrothermal vents exist because the earth is both...
s or cold seepCold seepA cold seep is an area of the ocean floor where hydrogen sulfide, methane and other hydrocarbon-rich fluid seepage occurs, often in the form of a brine pool...
s - sunlight – photosynthetic processes depend on how deep and turbid the water is
- nutrients – are transported by ocean currents to different marine habitats from land runoff, or by upwellings from the deep sea, or they sink though the sea as marine snowMarine snowIn the deep ocean, marine snow is a continuous shower of mostly organic detritus falling from the upper layers of the water column. It is a significant means of exporting energy from the light-rich photic zone to the aphotic zone below. The term was first coined by the explorer William Beebe as he...
- salinity – varies, particularly in estuaries or near river deltaRiver deltaA delta is a landform that is formed at the mouth of a river where that river flows into an ocean, sea, estuary, lake, reservoir, flat arid area, or another river. Deltas are formed from the deposition of the sediment carried by the river as the flow leaves the mouth of the river...
s, or by hydrothermal vents - dissolved gases – oxygen levels in particular, can be increased by wave actions and decreased during algal bloomAlgal bloomAn algal bloom is a rapid increase or accumulation in the population of algae in an aquatic system. Algal blooms may occur in freshwater as well as marine environments. Typically, only one or a small number of phytoplankton species are involved, and some blooms may be recognized by discoloration...
s - acidity – this is partly to do with dissolved gases above, since the acidity of the ocean is largely controlled by how much carbon dioxide is in the water.
- turbulence – ocean waves, fast currents and the agitation of water affect the nature of habitats
- cover – the availability of cover such as the adjacency of the sea bottomBenthic zoneThe benthic zone is the ecological region at the lowest level of a body of water such as an ocean or a lake, including the sediment surface and some sub-surface layers. Organisms living in this zone are called benthos. They generally live in close relationship with the substrate bottom; many such...
, or the presence of floating objects - the occupying organisms themselves – since organisms modify their habitats by the act of occupying them, and some, like corals, kelp, mangroves and seagrasses, create further habitats for other organisms.
| Ocean | Area million km2 |
% | Volume million cu km |
% | Mean depth km |
Max depth km |
Coastline km |
% | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pacific Ocean | 155.6 | 46.4 | 679.6 | 49.6 | 4.37 | 10.924 | 135,663 | ||
| Atlantic Ocean | 76.8 | 22.9 | 313.4 | 22.5 | 4.08 | 8.605 | 111,866 | ||
| Indian Ocean | 68.6 | 20.4 | 269.3 | 19.6 | 3.93 | 7.258 | 66,526 | ||
| Southern Ocean | 20.3 | 6.1 | 91.5 | 6.7 | 4.51 | 7.235 | 17,968 | ||
| Arctic Ocean | 14.1 | 4.2 | 17.0 | 1.2 | 1.21 | 4.665 | 45,389 | ||
| Overall | 335.3 | 1370.8 | 4.09 | 10.924 | 377,412 |
The ocean occupies 71 percent of the world surface, averaging nearly four kilometers in depth. There are five major oceans, of which the Pacific Ocean
Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest of the Earth's oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic in the north to the Southern Ocean in the south, bounded by Asia and Australia in the west, and the Americas in the east.At 165.2 million square kilometres in area, this largest division of the World...
is nearly as large as the rest put together. Coastlines fringe the land for nearly 380,000 kilometres.
Marine habitats can be broadly divided into pelagic and demersal habitats. Pelagic habitats are the habitats of the open water column, away from the bottom of the ocean. Demersal habitats are the habitats that are near or on the bottom of the ocean. An organism living in a pelagic habitat is said to be a pelagic organism, as in pelagic fish
Pelagic fish
Pelagic fish live near the surface or in the water column of coastal, ocean and lake waters, but not on the bottom of the sea or the lake. They can be contrasted with demersal fish, which do live on or near the bottom, and reef fish which are associated with coral reefs.The marine pelagic...
. Similarly, an organism living in a demersal habitat is said to be a demersal organism, as in demersal fish. Pelagic habitats are intrinsically ephemeral, depending on what ocean current
Ocean current
An ocean current is a continuous, directed movement of ocean water generated by the forces acting upon this mean flow, such as breaking waves, wind, Coriolis effect, cabbeling, temperature and salinity differences and tides caused by the gravitational pull of the Moon and the Sun...
s are doing.
The land-based ecosystem
Ecosystem
An ecosystem is a biological environment consisting of all the organisms living in a particular area, as well as all the nonliving , physical components of the environment with which the organisms interact, such as air, soil, water and sunlight....
depends on topsoil and fresh water, while the marine ecosystem depends on dissolved nutrients washed down from the land.
Ocean currents

Ocean current
An ocean current is a continuous, directed movement of ocean water generated by the forces acting upon this mean flow, such as breaking waves, wind, Coriolis effect, cabbeling, temperature and salinity differences and tides caused by the gravitational pull of the Moon and the Sun...
s have a key role determining which areas are effective as habitats, since ocean currents transport the basic nutrients needed to support marine life. Plankton
Plankton
Plankton are any drifting organisms that inhabit the pelagic zone of oceans, seas, or bodies of fresh water. That is, plankton are defined by their ecological niche rather than phylogenetic or taxonomic classification...
are the life forms that inhabit the ocean that are so small (less than 2 mm) that they cannot effectively propel themselves through the water, but must drift instead with the currents. If the current carries the right nutrients, and if it also flows at a suitably shallow depth where there is plenty of sunlight, then such a current itself can become a suitable habitat for photosynthesizing tiny algae called phytoplankton
Phytoplankton
Phytoplankton are the autotrophic component of the plankton community. The name comes from the Greek words φυτόν , meaning "plant", and πλαγκτός , meaning "wanderer" or "drifter". Most phytoplankton are too small to be individually seen with the unaided eye...
. These tiny plants are the primary producers
Primary production
400px|thumb|Global oceanic and terrestrial photoautotroph abundance, from September [[1997]] to August 2000. As an estimate of autotroph biomass, it is only a rough indicator of primary production potential, and not an actual estimate of it...
in the ocean, at the start of the food chain
Food chain
A food web depicts feeding connections in an ecological community. Ecologists can broadly lump all life forms into one of two categories called trophic levels: 1) the autotrophs, and 2) the heterotrophs...
. In turn, as the population of drifting phytoplankton grows, the water becomes a suitable habitat for zooplankton
Zooplankton
Zooplankton are heterotrophic plankton. Plankton are organisms drifting in oceans, seas, and bodies of fresh water. The word "zooplankton" is derived from the Greek zoon , meaning "animal", and , meaning "wanderer" or "drifter"...
, which feed on the phytoplankton. While phytoplankton are tiny drifting plants, zooplankton are tiny drifting animals, such as the larvae
Larvae
In Roman mythology, lemures were shades or spirits of the restless or malignant dead, and are probably cognate with an extended sense of larvae as disturbing or frightening...
of fish
Fish
Fish are a paraphyletic group of organisms that consist of all gill-bearing aquatic vertebrate animals that lack limbs with digits. Included in this definition are the living hagfish, lampreys, and cartilaginous and bony fish, as well as various extinct related groups...
and marine invertebrates. If sufficient zooplankton establish themselves, the current becomes a candidate habitat for the forage fish
Forage fish
Forage fish, also called prey fish or bait fish, are small fish which are preyed on by larger predators for food. Predators include other larger fish, seabirds and marine mammals. Typical ocean forage fish feed near the base of the food chain on plankton, often by filter feeding...
that feed on them. And then if sufficient forage fish move to the area, it becomes a candidate habitat for larger predatory fish
Predatory fish
Predatory fish are fish that predate upon other fish or animals. Some predatory fish include perch, muskie , pike, walleye, salmon.Levels of large predatory fish in the global oceans are estimated to be about 10% of their pre-industrial levels...
and other marine animals that feed on the forage fish. In this dynamic way, the current itself can, over time, become a moving habitat for multiple types of marine life.

Seiche
A seiche is a standing wave in an enclosed or partially enclosed body of water. Seiches and seiche-related phenomena have been observed on lakes, reservoirs, swimming pools, bays, harbors and seas...
s. Ocean currents are also generated by the gravitational pull of the sun and moon (tide
Tide
Tides are the rise and fall of sea levels caused by the combined effects of the gravitational forces exerted by the moon and the sun and the rotation of the Earth....
s), and seismic activity (tsunami
Tsunami
A tsunami is a series of water waves caused by the displacement of a large volume of a body of water, typically an ocean or a large lake...
).
The rotation of the Earth affects the direction ocean currents take, and explains which way the large circular ocean gyres rotate in the image above left. Suppose a current at the equator is heading north. The Earth rotates eastward, so the water possesses that rotational momentum. But the further the water moves north, the slower the earth moves eastward. If the current could get to the North Pole, the earth wouldn't be moving eastward at all. To conserve its rotational momentum, the further the current travels north the faster it must move eastward. So the effect is that the current curves to the right. This is the Coriolis effect
Coriolis effect
In physics, the Coriolis effect is a deflection of moving objects when they are viewed in a rotating reference frame. In a reference frame with clockwise rotation, the deflection is to the left of the motion of the object; in one with counter-clockwise rotation, the deflection is to the right...
. It is weakest at the equator and strongest at the poles. The effect is opposite south of the equator, where currents curve left.
Marine topography

Topography
Topography is the study of Earth's surface shape and features or those ofplanets, moons, and asteroids...
refers to the shape the land has when it interfaces with the ocean. These shapes are obvious along coastlines, but they occur also in significant ways underwater. The effectiveness of marine habitats is partially defined by these shapes, including the way they interact with and shape ocean current
Ocean current
An ocean current is a continuous, directed movement of ocean water generated by the forces acting upon this mean flow, such as breaking waves, wind, Coriolis effect, cabbeling, temperature and salinity differences and tides caused by the gravitational pull of the Moon and the Sun...
s, and the way sunlight diminishes when these landforms occupy increasing depths.
Marine topographies include coastal and oceanic landforms ranging from coastal estuaries
Estuary
An estuary is a partly enclosed coastal body of water with one or more rivers or streams flowing into it, and with a free connection to the open sea....
and shorelines to continental shelves
Continental shelf
The continental shelf is the extended perimeter of each continent and associated coastal plain. Much of the shelf was exposed during glacial periods, but is now submerged under relatively shallow seas and gulfs, and was similarly submerged during other interglacial periods. The continental margin,...
and coral reef
Coral reef
Coral reefs are underwater structures made from calcium carbonate secreted by corals. Coral reefs are colonies of tiny living animals found in marine waters that contain few nutrients. Most coral reefs are built from stony corals, which in turn consist of polyps that cluster in groups. The polyps...
s. Further out in the open ocean, they include underwater and deep sea
Deep sea
The deep sea, or deep layer, is the lowest layer in the ocean, existing below the thermocline and above the seabed, at a depth of 1000 fathoms or more. Little or no light penetrates this part of the ocean and most of the organisms that live there rely for subsistence on falling organic matter...
features such as ocean rises and seamount
Seamount
A seamount is a mountain rising from the ocean seafloor that does not reach to the water's surface , and thus is not an island. These are typically formed from extinct volcanoes, that rise abruptly and are usually found rising from a seafloor of depth. They are defined by oceanographers as...
s. The submerged surface has mountainous features, including a globe-spanning mid-ocean ridge
Mid-ocean ridge
A mid-ocean ridge is a general term for an underwater mountain system that consists of various mountain ranges , typically having a valley known as a rift running along its spine, formed by plate tectonics. This type of oceanic ridge is characteristic of what is known as an oceanic spreading...
system, as well as undersea volcano
Volcano
2. Bedrock3. Conduit 4. Base5. Sill6. Dike7. Layers of ash emitted by the volcano8. Flank| 9. Layers of lava emitted by the volcano10. Throat11. Parasitic cone12. Lava flow13. Vent14. Crater15...
es, oceanic trench
Oceanic trench
The oceanic trenches are hemispheric-scale long but narrow topographic depressions of the sea floor. They are also the deepest parts of the ocean floor....
es, submarine canyon
Submarine canyon
A submarine canyon is a steep-sided valley on the sea floor of the continental slope. Many submarine canyons are found as extensions to large rivers; however there are some that have no such association. Canyons cutting the continental slopes have been found at depths greater than 2 km below sea...
s, oceanic plateau
Oceanic plateau
An oceanic plateau is a large, relatively flat submarine region that rises well above the level of the ambient seabed. While many oceanic plateaus are composed of continental crust, and often form a step interrupting the continental slope, some plateaus are undersea remnants of large igneous...
s and abyssal plain
Abyssal plain
An abyssal plain is an underwater plain on the deep ocean floor, usually found at depths between 3000 and 6000 metres. Lying generally between the foot of a continental rise and a mid-ocean ridge, abyssal plains cover more than 50% of the Earth’s surface. They are among the flattest, smoothest...
s.
The mass of the oceans is approximately 1.35 metric tons, or about 1/4400 of the total mass of the Earth. The oceans cover an area of 3.618 km2 with a mean depth of 3,682 m, resulting in an estimated volume of 1.332 km3.
Biomass
One measure of the relative importance of different marine habitats is the rate at which they produce biomassBiomass (ecology)
Biomass, in ecology, is the mass of living biological organisms in a given area or ecosystem at a given time. Biomass can refer to species biomass, which is the mass of one or more species, or to community biomass, which is the mass of all species in the community. It can include microorganisms,...
.
| Producer | Biomass productivity (gC/m²/yr) |
Ref | Total area (million km²) |
Ref | Total production (billion tonnes C/yr) |
Comment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| swamp Swamp A swamp is a wetland with some flooding of large areas of land by shallow bodies of water. A swamp generally has a large number of hammocks, or dry-land protrusions, covered by aquatic vegetation, or vegetation that tolerates periodical inundation. The two main types of swamp are "true" or swamp... s and marsh Marsh In geography, a marsh, or morass, is a type of wetland that is subject to frequent or continuous flood. Typically the water is shallow and features grasses, rushes, reeds, typhas, sedges, other herbaceous plants, and moss.... es |
2,500 | Includes freshwater | ||||
| coral reef Coral reef Coral reefs are underwater structures made from calcium carbonate secreted by corals. Coral reefs are colonies of tiny living animals found in marine waters that contain few nutrients. Most coral reefs are built from stony corals, which in turn consist of polyps that cluster in groups. The polyps... s |
2,000 | 0.28 | 0.56 | |||
| algal bed Algae Algae are a large and diverse group of simple, typically autotrophic organisms, ranging from unicellular to multicellular forms, such as the giant kelps that grow to 65 meters in length. They are photosynthetic like plants, and "simple" because their tissues are not organized into the many... s |
2,000 | |||||
| river estuaries Estuary An estuary is a partly enclosed coastal body of water with one or more rivers or streams flowing into it, and with a free connection to the open sea.... |
1,800 | |||||
| open ocean Oceanic zone The oceanic zone begins in the area off shore where the water measures 200 meters deep or deeper.It is the region of open sea beyond the edge of the continental shelf and includes 65% of the ocean’s completely open water... |
125 | 311 | 39 |
Coastal

Coast
A coastline or seashore is the area where land meets the sea or ocean. A precise line that can be called a coastline cannot be determined due to the dynamic nature of tides. The term "coastal zone" can be used instead, which is a spatial zone where interaction of the sea and land processes occurs...
are dynamic environments which constantly change, like the ocean which partially shape them. The Earth's natural processes, including weather
Weather
Weather is the state of the atmosphere, to the degree that it is hot or cold, wet or dry, calm or stormy, clear or cloudy. Most weather phenomena occur in the troposphere, just below the stratosphere. Weather refers, generally, to day-to-day temperature and precipitation activity, whereas climate...
and sea level change, result in the erosion
Erosion
Erosion is when materials are removed from the surface and changed into something else. It only works by hydraulic actions and transport of solids in the natural environment, and leads to the deposition of these materials elsewhere...
, accretion
Accretion (geology)
Accretion is a process by which material is added to a tectonic plate or a landmass. This material may be sediment, volcanic arcs, seamounts or other igneous features.-Description:...
and resculpturing of coasts as well as the flooding and creation of continental shelves
Continental shelf
The continental shelf is the extended perimeter of each continent and associated coastal plain. Much of the shelf was exposed during glacial periods, but is now submerged under relatively shallow seas and gulfs, and was similarly submerged during other interglacial periods. The continental margin,...
and drowned river valleys.
The main agents responsible for deposition and erosion
Erosion
Erosion is when materials are removed from the surface and changed into something else. It only works by hydraulic actions and transport of solids in the natural environment, and leads to the deposition of these materials elsewhere...
along coastlines are waves, tide
Tide
Tides are the rise and fall of sea levels caused by the combined effects of the gravitational forces exerted by the moon and the sun and the rotation of the Earth....
s and currents
Ocean current
An ocean current is a continuous, directed movement of ocean water generated by the forces acting upon this mean flow, such as breaking waves, wind, Coriolis effect, cabbeling, temperature and salinity differences and tides caused by the gravitational pull of the Moon and the Sun...
. The formation of coasts also depends on the nature of the rocks
Lithology
The lithology of a rock unit is a description of its physical characteristics visible at outcrop, in hand or core samples or with low magnification microscopy, such as colour, texture, grain size, or composition. It may be either a detailed description of these characteristics or be a summary of...
they are made of – the harder the rocks the less likely they are to erode, so variations in rock hardness result in coastlines with different shapes.
Tide
Tide
Tides are the rise and fall of sea levels caused by the combined effects of the gravitational forces exerted by the moon and the sun and the rotation of the Earth....
s often determine the range over which sediment
Sediment
Sediment is naturally occurring material that is broken down by processes of weathering and erosion, and is subsequently transported by the action of fluids such as wind, water, or ice, and/or by the force of gravity acting on the particle itself....
is deposited or eroded. Areas with high tidal ranges allow waves to reach farther up the shore, and areas with lower tidal ranges produce deposition at a smaller elevation interval. The tidal range is influenced by the size and shape of the coastline. Tides do not typically cause erosion by themselves; however, tidal bore
Tidal bore
A tidal bore is a tidal phenomenon in which the leading edge of the incoming tide forms a wave of water that travel up a river or narrow bay against the direction of the river or bay's current...
s can erode as the waves surge up river estuaries
Estuary
An estuary is a partly enclosed coastal body of water with one or more rivers or streams flowing into it, and with a free connection to the open sea....
from the ocean.
Waves erode coastline as they break on shore releasing their energy; the larger the wave the more energy it releases and the more sediment it moves. Sediment deposited by waves comes from eroded cliff faces and is moved along the coastline by the waves. Sediment deposited by rivers is the dominant influence on the amount of sediment located on a coastline.
The sedimentologist
Sedimentology
Sedimentology encompasses the study of modern sediments such as sand, mud , and clay, and the processes that result in their deposition. Sedimentologists apply their understanding of modern processes to interpret geologic history through observations of sedimentary rocks and sedimentary...
Francis Shepard classified coasts as primary or secondary.
- Primary coasts are shaped by non-marine processes, by changes in the land form. If a coast is in much the same condition as it was when sea level was stabilised after the last ice age, it is called a primary coast. "Primary coasts are created by erosion (the wearing away of soil or rock), deposition (the buildup of sediment or sand) or tectonic activity (changes in the structure of the rock and soil because of earthquakes). Many of these coastlines were formed as the sea level rose during the last 18,000 years, submerging river and glacial valleys to form bays and fjords." An example of a primary coast is a river deltaRiver deltaA delta is a landform that is formed at the mouth of a river where that river flows into an ocean, sea, estuary, lake, reservoir, flat arid area, or another river. Deltas are formed from the deposition of the sediment carried by the river as the flow leaves the mouth of the river...
, which forms when a river deposits soil and other material as it enters the sea.
- Secondary coasts are produced by marine processes, such as the action of the sea or by creatures that live in it. Secondary coastlines include sea cliffs, barrier islandBarrier islandBarrier islands, a coastal landform and a type of barrier system, are relatively narrow strips of sand that parallel the mainland coast. They usually occur in chains, consisting of anything from a few islands to more than a dozen...
s, mud flats, coral reefCoral reefCoral reefs are underwater structures made from calcium carbonate secreted by corals. Coral reefs are colonies of tiny living animals found in marine waters that contain few nutrients. Most coral reefs are built from stony corals, which in turn consist of polyps that cluster in groups. The polyps...
s, mangrove swamps and salt marshSalt marshA salt marsh is an environment in the upper coastal intertidal zone between land and salt water or brackish water, it is dominated by dense stands of halophytic plants such as herbs, grasses, or low shrubs. These plants are terrestrial in origin and are essential to the stability of the salt marsh...
es.

Continental shelf
The continental shelf is the extended perimeter of each continent and associated coastal plain. Much of the shelf was exposed during glacial periods, but is now submerged under relatively shallow seas and gulfs, and was similarly submerged during other interglacial periods. The continental margin,...
, a shelf of relatively shallow water, less than 200 metres deep, which extends 68 km on average beyond the coast. Worldwide, continental shelves occupy a total area of about 24 million km2 (9 million sq mi), nearly 5% of the world's total area. Since the continental shelf is usually less than 200 metres deep, it follows that coastal habitats are generally photic
Photic zone
The photic zone or euphotic zone is the depth of the water in a lake or ocean that is exposed to sufficient sunlight for photosynthesis to occur...
, situated in the sunlit epipelagic zone. This means the conditions for photosynthetic processes so important for primary production
Primary production
400px|thumb|Global oceanic and terrestrial photoautotroph abundance, from September [[1997]] to August 2000. As an estimate of autotroph biomass, it is only a rough indicator of primary production potential, and not an actual estimate of it...
, are available to coastal marine habitats. Because land is nearby, there are large discharges of nutrient rich land runoff into coastal waters. Further, periodic upwelling
Upwelling
Upwelling is an oceanographic phenomenon that involves wind-driven motion of dense, cooler, and usually nutrient-rich water towards the ocean surface, replacing the warmer, usually nutrient-depleted surface water. The increased availability in upwelling regions results in high levels of primary...
s from the deep ocean can provide cool and nutrient rich currents along the edge of the continental shelf.
As a result, coastal marine life is the most abundant in the world. It is found in tidal pools, fjord
Fjord
Geologically, a fjord is a long, narrow inlet with steep sides or cliffs, created in a valley carved by glacial activity.-Formation:A fjord is formed when a glacier cuts a U-shaped valley by abrasion of the surrounding bedrock. Glacial melting is accompanied by rebound of Earth's crust as the ice...
s and estuaries, near sandy shores and rocky coastlines, around coral reef
Coral reef
Coral reefs are underwater structures made from calcium carbonate secreted by corals. Coral reefs are colonies of tiny living animals found in marine waters that contain few nutrients. Most coral reefs are built from stony corals, which in turn consist of polyps that cluster in groups. The polyps...
s and on or above the continental shelf. Coastal fish
Coastal fish
Coastal fish, also called offshore fish or neritic fish, are fish that inhabit the sea between the shoreline and the edge of the continental shelf. Since the continental shelf is usually less than 200 metres deep, it follows that pelagic coastal fish are generally epipelagic fish, inhabiting the...
include small forage fish as well as the larger predator fish that feed on them. Forage fish
Forage fish
Forage fish, also called prey fish or bait fish, are small fish which are preyed on by larger predators for food. Predators include other larger fish, seabirds and marine mammals. Typical ocean forage fish feed near the base of the food chain on plankton, often by filter feeding...
thrive in inshore waters where high productivity
Primary production
400px|thumb|Global oceanic and terrestrial photoautotroph abundance, from September [[1997]] to August 2000. As an estimate of autotroph biomass, it is only a rough indicator of primary production potential, and not an actual estimate of it...
results from upwelling
Upwelling
Upwelling is an oceanographic phenomenon that involves wind-driven motion of dense, cooler, and usually nutrient-rich water towards the ocean surface, replacing the warmer, usually nutrient-depleted surface water. The increased availability in upwelling regions results in high levels of primary...
and shoreline run off of nutrients. Some are partial residents that spawn in streams, estuaries and bays, but most complete their life cycle in the zone. There can also be a mutualism between species that occupy adjacent marine habitats. For example, fringing reef
Fringing reef
A fringing reef is one of the three main types of coral reefs recognized by most coral reef scientists. It is distinguished from the other two main types in that it has either an entirely shallow backreef zone or none at all...
s just below low tide level have a mutually beneficial relationship with mangrove
Mangrove
Mangroves are various kinds of trees up to medium height and shrubs that grow in saline coastal sediment habitats in the tropics and subtropics – mainly between latitudes N and S...
forests at high tide level and sea grass meadows in between: the reefs protect the mangroves and seagrass from strong currents and waves that would damage them or erode
Erosion
Erosion is when materials are removed from the surface and changed into something else. It only works by hydraulic actions and transport of solids in the natural environment, and leads to the deposition of these materials elsewhere...
the sediments in which they are rooted, while the mangroves and seagrass protect the coral from large influxes of silt
Silt
Silt is granular material of a size somewhere between sand and clay whose mineral origin is quartz and feldspar. Silt may occur as a soil or as suspended sediment in a surface water body...
, fresh water and pollutants
Pollution
Pollution is the introduction of contaminants into a natural environment that causes instability, disorder, harm or discomfort to the ecosystem i.e. physical systems or living organisms. Pollution can take the form of chemical substances or energy, such as noise, heat or light...
. This additional level of variety in the environment is beneficial to many types of coral reef animals, which for example may feed in the sea grass and use the reefs for protection or breeding.
Coastal habitats are the most visible marine habitats, but they are not the only important marine habitats. Coastlines run for 380,000 kilometres, and the total volume of the ocean is 1,370 million cu km. This means that for each metre of coast, there is 3.6 cu km of ocean space available somewhere for marine habitats.

Intertidal
Intertidal zoneIntertidal zone
The intertidal zone is the area that is above water at low tide and under water at high tide . This area can include many different types of habitats, with many types of animals like starfish, sea urchins, and some species of coral...
s, those areas close to shore, are constantly being exposed and covered by the ocean's tides. A huge array of life lives within this zone.
Shore habitats range from the upper intertidal zones to the area where land vegetation takes prominence. It can be underwater anywhere from daily to very infrequently. Many species here are scavengers, living off of sea life that is washed up on the shore. Many land animals also make much use of the shore and intertidal habitats. A subgroup of organisms in this habitat bores and grinds exposed rock through the process of bioerosion
Bioerosion
Bioerosion describes the erosion of hard ocean substrates – and less often terrestrial substrates – by living organisms. Marine bioerosion can be caused by mollusks, polychaete worms, phoronids, sponges, crustaceans, echinoids, and fish; it can occur on coastlines, on coral reefs, and...
.
Sandy shores
Sandy shores, also called beachBeach
A beach is a geological landform along the shoreline of an ocean, sea, lake or river. It usually consists of loose particles which are often composed of rock, such as sand, gravel, shingle, pebbles or cobblestones...
es, are coastal shorelines where sand
Sand
Sand is a naturally occurring granular material composed of finely divided rock and mineral particles.The composition of sand is highly variable, depending on the local rock sources and conditions, but the most common constituent of sand in inland continental settings and non-tropical coastal...
accumulates. Waves and currents shift the sand, continually building and eroding the shoreline. Longshore currents flow parallel to the beaches, making waves break obliquely on the sand. These currents transport large amounts of sand along coasts, forming spits
Spit (landform)
A spit or sandspit is a deposition landform found off coasts. At one end, spits connect to land, and extend into the sea. A spit is a type of bar or beach that develops where a re-entrant occurs, such as at cove's headlands, by the process of longshore drift...
, barrier island
Barrier island
Barrier islands, a coastal landform and a type of barrier system, are relatively narrow strips of sand that parallel the mainland coast. They usually occur in chains, consisting of anything from a few islands to more than a dozen...
s and tombolo
Tombolo
A tombolo, from the Italian tombolo, derived from the Latin tumulus, meaning 'mound,' and sometimes translated as ayre , is a deposition landform in which an island is attached to the mainland by a narrow piece of land such as a spit or bar. Once attached, the island is then known as a tied island...
s. Longshore currents also commonly create offshore bars, which give beaches some stability by reducing erosion.
Sandy shores are full of life, The grains of sand host diatom
Diatom
Diatoms are a major group of algae, and are one of the most common types of phytoplankton. Most diatoms are unicellular, although they can exist as colonies in the shape of filaments or ribbons , fans , zigzags , or stellate colonies . Diatoms are producers within the food chain...
s, bacteria
Bacteria
Bacteria are a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria have a wide range of shapes, ranging from spheres to rods and spirals...
and other microscopic creatures. Some fish and turtles return to certain beaches and spawn
Spawn (biology)
Spawn refers to the eggs and sperm released or deposited, usually into water, by aquatic animals. As a verb, spawn refers to the process of releasing the eggs and sperm, also called spawning...
eggs in the sand. Birds habitat beaches, like gull
Gull
Gulls are birds in the family Laridae. They are most closely related to the terns and only distantly related to auks, skimmers, and more distantly to the waders...
s, loon
Loon
The loons or divers are a group of aquatic birds found in many parts of North America and northern Eurasia...
s, sandpipers, tern
Tern
Terns are seabirds in the family Sternidae, previously considered a subfamily of the gull family Laridae . They form a lineage with the gulls and skimmers which in turn is related to skuas and auks...
s and pelican
Pelican
A pelican, derived from the Greek word πελεκυς pelekys is a large water bird with a large throat pouch, belonging to the bird family Pelecanidae....
s. Aquatic mammal
Aquatic mammal
Aquatic and semi-aquatic mammals are a diverse group of mammals that dwell partly or entirely in bodies of water. They include the various marine mammals who dwell in oceans, as well as various freshwater species, such as the Platypus and the European Otter.-Groups:* Order Sirenia: Sirenians**...
s, such sea lions, recuperate on them. Clam
Clam
The word "clam" can be applied to freshwater mussels, and other freshwater bivalves, as well as marine bivalves.In the United States, "clam" can be used in several different ways: one, as a general term covering all bivalve molluscs...
s, periwinkle
Littorinidae
Littorinidae is a taxonomic family of over 200 species of sea snails, marine gastropod molluscs in the clade Littorinimorpha, commonly known as periwinkles and found world-wide.-Names:...
s, crab
Crab
True crabs are decapod crustaceans of the infraorder Brachyura, which typically have a very short projecting "tail" , or where the reduced abdomen is entirely hidden under the thorax...
s, shrimp
Shrimp
Shrimp are swimming, decapod crustaceans classified in the infraorder Caridea, found widely around the world in both fresh and salt water. Adult shrimp are filter feeding benthic animals living close to the bottom. They can live in schools and can swim rapidly backwards. Shrimp are an important...
, starfish and sea urchin
Sea urchin
Sea urchins or urchins are small, spiny, globular animals which, with their close kin, such as sand dollars, constitute the class Echinoidea of the echinoderm phylum. They inhabit all oceans. Their shell, or "test", is round and spiny, typically from across. Common colors include black and dull...
s are found on most beaches.
Sand is a sediment
Sediment
Sediment is naturally occurring material that is broken down by processes of weathering and erosion, and is subsequently transported by the action of fluids such as wind, water, or ice, and/or by the force of gravity acting on the particle itself....
made from small grains or particles
Particle (ecology)
In marine and freshwater ecology, a particle is a small object. Particles can remain in suspension in the ocean or freshwater, however they eventually settle and accumulate as sediment. Some can enter the atmosphere through wave action where they can act as cloud condensation nuclei...
with diameters between about 60 µm and 2 mm. Mud (see mudflats below) is a sediment made from particles finer than sand. This small particle size means that mud particles tend to stick together, whereas sand particles do not. Mud is not easily shifted by waves and currents, and when it dries out, cakes into a solid. By contrast, sand is easily shifted by waves and currents, and when sand dries out it can be blown in the wind, accumulating into shifting sand dunes. Beyond the high tide mark, if the beach is low-lying, the wind can form rolling hills of sand dunes. Small dunes shift and reshape under the influence of the wind while larger dunes stabilise the sand with vegetation.
Ocean processes grade loose sediments to particle sizes
Particle size (grain size)
Particle size, also called grain size, refers to the diameter of individual grains of sediment, or the lithified particles in clastic rocks. The term may also be applied to other granular materials. This is different from the crystallite size, which is the size of a single crystal inside the...
other than sand, such as gravel
Gravel
Gravel is composed of unconsolidated rock fragments that have a general particle size range and include size classes from granule- to boulder-sized fragments. Gravel can be sub-categorized into granule and cobble...
or cobble
Cobble (geology)
A cobble is a clast of rock with a particle size of to based on the Krumbein phi scale of sedimentology. Cobbles are generally considered to be larger than pebbles and smaller than boulders . A rock made predominantly of cobbles is termed a conglomerate....
s. Waves breaking on a beach can leave a berm
Berm
A berm is a level space, shelf, or raised barrier separating two areas. Berm originates in the Middle Dutch and German berme and came into usage in English via French.- History :...
, which is a raised ridge of coarser pebbles or sand, at the high tide mark. Shingle beach
Shingle beach
A shingle beach is a beach which is armoured with pebbles or small- to medium-sized cobbles. Typically, the stone composition may grade from characteristic sizes ranging from two to 200 mm diameter....
es are made of particles larger than sand, such as cobbles, or small stones. These beaches make poor habitats. Little life survives because the stones are churned and pounded together by waves and currents.
Rocky shores
The relative solidity of rocky shoreRocky shore
A rocky shore is an intertidal area of seacoasts where solid rock predominates. Rocky shores are biologically rich environments, and make the ideal natural laboratory for studying intertidal ecology and other biological processes...
s seems to give them a permanence compared to the shifting nature of sandy shores. This apparent stability is not real over even quite short geological time scales, but it is real enough over the short life of an organism. In contrast to sandy shores, plants and animals can anchor themselves to the rocks.
Competition can develop for the rocky spaces. For example, barnacle
Barnacle
A barnacle is a type of arthropod belonging to infraclass Cirripedia in the subphylum Crustacea, and is hence related to crabs and lobsters. Barnacles are exclusively marine, and tend to live in shallow and tidal waters, typically in erosive settings. They are sessile suspension feeders, and have...
s can compete successfully on open intertidal rock faces to the point where the rock surface is covered with them. Barnacles resist desiccation and grip well to exposed rock faces. However, in the crevices of the same rocks, the inhabitants are different. Here mussel
Mussel
The common name mussel is used for members of several families of clams or bivalvia mollusca, from saltwater and freshwater habitats. These groups have in common a shell whose outline is elongated and asymmetrical compared with other edible clams, which are often more or less rounded or oval.The...
s can be the successful species, secured to the rock with their byssal threads.
Rocky and sandy coasts are vulnerable because humans find them attractive and want to live near them. An increasing proportion of the humans live by the coast, putting pressure on coastal habitats.
Mudflats

Mudflat
Mudflats or mud flats, also known as tidal flats, are coastal wetlands that form when mud is deposited by tides or rivers. They are found in sheltered areas such as bays, bayous, lagoons, and estuaries. Mudflats may be viewed geologically as exposed layers of bay mud, resulting from deposition of...
s are coastal wetlands that form when mud is deposited by tides or rivers. They are found in sheltered areas such as bays, bayous, lagoons, and estuaries. Mudflats may be viewed geologically as exposed layers of bay mud
Bay mud
Bay mud consists of thick deposits of soft, unconsolidated silty clay, which is saturated with water; these soil layers are situated at the bottom of certain estuaries, which are normally in temperate regions that have experienced cyclical glacial cycles...
, resulting from deposition of estuarine silt
Silt
Silt is granular material of a size somewhere between sand and clay whose mineral origin is quartz and feldspar. Silt may occur as a soil or as suspended sediment in a surface water body...
s, clay
Clay
Clay is a general term including many combinations of one or more clay minerals with traces of metal oxides and organic matter. Geologic clay deposits are mostly composed of phyllosilicate minerals containing variable amounts of water trapped in the mineral structure.- Formation :Clay minerals...
s and marine animal detritus
Detritus
Detritus is a biological term used to describe dead or waste organic material.Detritus may also refer to:* Detritus , a geological term used to describe the particles of rock produced by weathering...
. Most of the sediment within a mudflat is within the intertidal zone
Intertidal zone
The intertidal zone is the area that is above water at low tide and under water at high tide . This area can include many different types of habitats, with many types of animals like starfish, sea urchins, and some species of coral...
, and thus the flat is submerged and exposed approximately twice daily.
Mudflats are typically important regions for wildlife, supporting a large population, although levels of biodiversity are not particularly high. They are of particular importance to migratory birds. In the United Kingdom
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
mudflats have been classified as a Biodiversity Action Plan
Biodiversity Action Plan
A Biodiversity Action Plan is an internationally recognized program addressing threatened species and habitats and is designed to protect and restore biological systems. The original impetus for these plans derives from the 1992 Convention on Biological Diversity...
priority habitat.
Mangrove and salt marshes

Salt marsh
A salt marsh is an environment in the upper coastal intertidal zone between land and salt water or brackish water, it is dominated by dense stands of halophytic plants such as herbs, grasses, or low shrubs. These plants are terrestrial in origin and are essential to the stability of the salt marsh...
es form important coastal habitats in topical and temperate areas respectively.
Mangroves are species of shrubs and medium size trees that grow in saline
Saline water
Saline water is a general term for water that contains a significant concentration of dissolved salts . The concentration is usually expressed in parts per million of salt....
coastal sediment habitats in the tropics
Tropics
The tropics is a region of the Earth surrounding the Equator. It is limited in latitude by the Tropic of Cancer in the northern hemisphere at approximately N and the Tropic of Capricorn in the southern hemisphere at S; these latitudes correspond to the axial tilt of the Earth...
and subtropics
Subtropics
The subtropics are the geographical and climatical zone of the Earth immediately north and south of the tropical zone, which is bounded by the Tropic of Cancer and the Tropic of Capricorn, at latitudes 23.5°N and 23.5°S...
– mainly between latitude
Latitude
In geography, the latitude of a location on the Earth is the angular distance of that location south or north of the Equator. The latitude is an angle, and is usually measured in degrees . The equator has a latitude of 0°, the North pole has a latitude of 90° north , and the South pole has a...
s N and S. The saline conditions tolerated by various species range from brackish water
Brackish water
Brackish water is water that has more salinity than fresh water, but not as much as seawater. It may result from mixing of seawater with fresh water, as in estuaries, or it may occur in brackish fossil aquifers. The word comes from the Middle Dutch root "brak," meaning "salty"...
, through pure seawater
Seawater
Seawater is water from a sea or ocean. On average, seawater in the world's oceans has a salinity of about 3.5% . This means that every kilogram of seawater has approximately of dissolved salts . The average density of seawater at the ocean surface is 1.025 g/ml...
(30 to 40 ppt
Salinity
Salinity is the saltiness or dissolved salt content of a body of water. It is a general term used to describe the levels of different salts such as sodium chloride, magnesium and calcium sulfates, and bicarbonates...
), to water concentrated by evaporation
Evaporation
Evaporation is a type of vaporization of a liquid that occurs only on the surface of a liquid. The other type of vaporization is boiling, which, instead, occurs on the entire mass of the liquid....
to over twice the salinity of ocean seawater (up to 90 ppt). There are many mangrove species, not all closely related. The term "mangrove" is used generally to cover all of these species, and it can be used narrowly to cover just mangrove trees of the genus Rhizophora
Rhizophora
Rhizophora is a genus of tropical mangrove trees, sometimes collectively called true mangroves. The most notable species is the Red Mangrove but some other species and a few natural hybrids are known. Rhizophora species generally live in intertidal zones which are indundated daily by the ocean...
.
Mangroves form a distinct characteristic saline woodland
Woodland
Ecologically, a woodland is a low-density forest forming open habitats with plenty of sunlight and limited shade. Woodlands may support an understory of shrubs and herbaceous plants including grasses. Woodland may form a transition to shrubland under drier conditions or during early stages of...
or shrubland
Shrubland
Shrubland, scrubland, scrub or brush is a plant community characterized by vegetation dominated by shrubs, often also including grasses, herbs, and geophytes. Shrubland may either occur naturally or be the result of human activity...
habitat, called a mangrove swamp or mangrove forest. Mangrove swamps are found in depositional
Sedimentary depositional environment
In geology, sedimentary depositional environment describes the combination of physical, chemical and biological processes associated with the deposition of a particular type of sediment and, therefore, the rock types that will be formed after lithification, if the sediment is preserved in the rock...
coastal environments, where fine sediments (often with high organic content) collect in areas protected from high-energy wave action. Mangroves dominate three quarters of tropical coastlines.
Estuaries
An estuaryEstuary
An estuary is a partly enclosed coastal body of water with one or more rivers or streams flowing into it, and with a free connection to the open sea....
is a partly enclosed coastal body of water
Water
Water is a chemical substance with the chemical formula H2O. A water molecule contains one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms connected by covalent bonds. Water is a liquid at ambient conditions, but it often co-exists on Earth with its solid state, ice, and gaseous state . Water also exists in a...
with one or more river
River
A river is a natural watercourse, usually freshwater, flowing towards an ocean, a lake, a sea, or another river. In a few cases, a river simply flows into the ground or dries up completely before reaching another body of water. Small rivers may also be called by several other names, including...
s or stream
Stream
A stream is a body of water with a current, confined within a bed and stream banks. Depending on its locale or certain characteristics, a stream may be referred to as a branch, brook, beck, burn, creek, "crick", gill , kill, lick, rill, river, syke, bayou, rivulet, streamage, wash, run or...
s flowing into it, and with a free connection to the open sea
Sea
A sea generally refers to a large body of salt water, but the term is used in other contexts as well. Most commonly, it means a large expanse of saline water connected with an ocean, and is commonly used as a synonym for ocean...
. Estuaries form a transition zone between river environments and ocean environments and are subject to both marine influences, such as tides, waves, and the influx of saline water; and riverine influences, such as flows of fresh water and sediment. The inflow of both seawater and freshwater provide high levels of nutrients in both the water column and sediment, making estuaries among the most productive natural habitats in the world.
Most estuaries were formed by the flooding of river-eroded or glacially scoured valleys when sea level began to rise about 10,000-12,000 years ago. They are amongst the most heavily populated areas throughout the world, with about 60% of the world’s population living along estuaries and the coast. As a result, estuaries are suffering degradation by many factors, including sedimentation from soil erosion from deforestation; overgrazing and other poor farming practices; overfishing; drainage and filling of wetlands; eutrophication due to excessive nutrients from sewage and animal wastes; pollutants including heavy metals, PCBs, radionuclides and hydrocarbons from sewage inputs; and diking or damming for flood control or water diversion.
Estuaries provide habitats for a large number of organisms and support very high productivity. Estuaries provide habitats for salmon
Salmon
Salmon is the common name for several species of fish in the family Salmonidae. Several other fish in the same family are called trout; the difference is often said to be that salmon migrate and trout are resident, but this distinction does not strictly hold true...
and sea trout nurseries, as well as migratory
Bird migration
Bird migration is the regular seasonal journey undertaken by many species of birds. Bird movements include those made in response to changes in food availability, habitat or weather. Sometimes, journeys are not termed "true migration" because they are irregular or in only one direction...
bird populations. Two of the main characteristics of estuarine life are the variability in salinity
Salinity
Salinity is the saltiness or dissolved salt content of a body of water. It is a general term used to describe the levels of different salts such as sodium chloride, magnesium and calcium sulfates, and bicarbonates...
and sedimentation
Sedimentation
Sedimentation is the tendency for particles in suspension to settle out of the fluid in which they are entrained, and come to rest against a barrier. This is due to their motion through the fluid in response to the forces acting on them: these forces can be due to gravity, centrifugal acceleration...
. Many species of fish
Fish
Fish are a paraphyletic group of organisms that consist of all gill-bearing aquatic vertebrate animals that lack limbs with digits. Included in this definition are the living hagfish, lampreys, and cartilaginous and bony fish, as well as various extinct related groups...
and invertebrate
Invertebrate
An invertebrate is an animal without a backbone. The group includes 97% of all animal species – all animals except those in the chordate subphylum Vertebrata .Invertebrates form a paraphyletic group...
s have various methods to control or conform to the shifts in salt concentrations and are termed osmoconformer
Osmoconformer
An osmoconformer is a marine invertebrate that maintains the osmolarity of its body fluids such that it is always equal to the surrounding seawater. By maintaining their internal solute concentration the same as their environment, osmoconformers avoid water diffusing into their bodies.Marine...
s and osmoregulators. Many animals also burrow to avoid predation
Predation
In ecology, predation describes a biological interaction where a predator feeds on its prey . Predators may or may not kill their prey prior to feeding on them, but the act of predation always results in the death of its prey and the eventual absorption of the prey's tissue through consumption...
and to live in the more stable sedimental environment. However, large numbers of bacteria are found within the sediment which have a very high oxygen demand. This reduces the levels of oxygen within the sediment often resulting in partially anoxic conditions, which can be further exacerbated by limited water flux. Phytoplankton
Phytoplankton
Phytoplankton are the autotrophic component of the plankton community. The name comes from the Greek words φυτόν , meaning "plant", and πλαγκτός , meaning "wanderer" or "drifter". Most phytoplankton are too small to be individually seen with the unaided eye...
are key primary producers in estuaries. They move with the water bodies and can be flushed in and out with the tide
Tide
Tides are the rise and fall of sea levels caused by the combined effects of the gravitational forces exerted by the moon and the sun and the rotation of the Earth....
s. Their productivity is largely dependent on the turbidity
Turbidity
Turbidity is the cloudiness or haziness of a fluid caused by individual particles that are generally invisible to the naked eye, similar to smoke in air. The measurement of turbidity is a key test of water quality....
of the water. The main phytoplankton present are diatoms and dinoflagellates which are abundant in the sediment.
Kelp forests

Kelp forest
Kelp forests are underwater areas with a high density of kelp. They are recognized as one of the most productive and dynamic ecosystems on Earth. Smaller areas of anchored kelp are called kelp beds....
s are underwater areas with a high density of kelp
Kelp
Kelps are large seaweeds belonging to the brown algae in the order Laminariales. There are about 30 different genera....
. They are recognized as one of the most productive and dynamic ecosystem
Ecosystem
An ecosystem is a biological environment consisting of all the organisms living in a particular area, as well as all the nonliving , physical components of the environment with which the organisms interact, such as air, soil, water and sunlight....
s on Earth. Smaller areas of anchored kelp are called kelp beds. Kelp forests occur worldwide throughout temperate
Temperate
In geography, temperate or tepid latitudes of the globe lie between the tropics and the polar circles. The changes in these regions between summer and winter are generally relatively moderate, rather than extreme hot or cold...
and polar
Polar region
Earth's polar regions are the areas of the globe surrounding the poles also known as frigid zones. The North Pole and South Pole being the centers, these regions are dominated by the polar ice caps, resting respectively on the Arctic Ocean and the continent of Antarctica...
coastal oceans.
Kelp forests provide a unique three-dimensional habitat for marine organisms and are a source for understanding many ecological processes. Over the last century, they have been the focus of extensive research, particularly in trophic ecology, and continue to provoke important ideas that are relevant beyond this unique ecosystem. For example, kelp forests can influence coastal oceanographic patterns and provide many ecosystem services
Ecosystem services
Humankind benefits from a multitude of resources and processes that are supplied by natural ecosystems. Collectively, these benefits are known as ecosystem services and include products like clean drinking water and processes such as the decomposition of wastes...
.
However, humans have contributed to kelp forest degradation. Of particular concern are the effects of overfishing
Overfishing
Overfishing occurs when fishing activities reduce fish stocks below an acceptable level. This can occur in any body of water from a pond to the oceans....
nearshore ecosystems, which can release herbivores from their normal population regulation and result in the over-grazing of kelp and other algae. This can rapidly result in transitions to barren landscapes where relatively few species persist.
Frequently considered an ecosystem engineer
Ecosystem engineer
An ecosystem engineer is any organism that creates or modifies habitats. Jones et al. identified two different types of ecosystem engineers:...
, kelp provides a physical substrate and habitat for kelp forest communities. In algae (Kingdom: Protista), the body of an individual organism is known as a thallus rather than as a plant (Kingdom: Plantae). The morphological structure of a kelp thallus is defined by three basic structural units:
- The holdfastHoldfastA holdfast is a root-like structure that anchors aquatic sessile organisms, such as seaweed, other sessile algae, stalked crinoids, benthic cnidarians, and sponges, to the substrate. ...
is a root-like mass that anchors the thallus to the sea floor, though unlike true roots it is not responsible for absorbing and delivering nutrients to the rest of the thallus; - The stipeStipe (botany)In botany, a stipe is a stalk that supports some other structure. The precise meaning is different depending on which taxonomic group is being described....
is analogous to a plant stalk, extending vertically from the holdfast and providing a support framework for other morphological features; - The fronds are leaf- or blade-like attachments extending from the stipe, sometimes along its full length, and are the sites of nutrient uptake and photosynthetic activity.
In addition, many kelp species have pneumatocyst
Pneumatocyst
In phycology, a pneumatocyst is a large float containing gas found in brown algae. An organism may have more than one. They provide buoyancy to lift the blades toward the surface, allowing them to receive more sunlight for photosynthesis....
s, or gas-filled bladders, usually located at the base of fronds near the stipe. These structures provide the necessary buoyancy for kelp to maintain an upright position in the water column.
The environmental factors necessary for kelp to survive include hard substrate (usually rock), high nutrients (e.g., nitrogen, phosphorus), and light (minimum annual irradiance
Irradiance
Irradiance is the power of electromagnetic radiation per unit area incident on a surface. Radiant emittance or radiant exitance is the power per unit area radiated by a surface. The SI units for all of these quantities are watts per square meter , while the cgs units are ergs per square centimeter...
dose > 50 E m−2). Especially productive kelp forests tend to be associated with areas of significant oceanographic upwelling
Upwelling
Upwelling is an oceanographic phenomenon that involves wind-driven motion of dense, cooler, and usually nutrient-rich water towards the ocean surface, replacing the warmer, usually nutrient-depleted surface water. The increased availability in upwelling regions results in high levels of primary...
, a process that delivers cool nutrient-rich water from depth to the ocean’s mixed surface layer
Mixed layer
The oceanic or limnological mixed layer is a layer in which active turbulence has homogenized some range of depths. The surface mixed layer is a layer where this turbulence is generated by winds, cooling, or processes such as evaporation or sea ice formation which result in an increase in salinity...
. Water flow and turbulence facilitate nutrient assimilation across kelp fronds throughout the water column. Water clarity affects the depth to which sufficient light can be transmitted. In ideal conditions, giant kelp (Macrocystis spp.) can grow as much as 30-60 centimeters vertically per day. Some species such as Nereocystis are annual
Annual plant
An annual plant is a plant that usually germinates, flowers, and dies in a year or season. True annuals will only live longer than a year if they are prevented from setting seed...
while others like Eisenia are perennial
Perennial plant
A perennial plant or simply perennial is a plant that lives for more than two years. The term is often used to differentiate a plant from shorter lived annuals and biennials. The term is sometimes misused by commercial gardeners or horticulturalists to describe only herbaceous perennials...
, living for more than 20 years. In perennial kelp forests, maximum growth rates occur during upwelling months (typically spring and summer) and die-backs correspond to reduced nutrient availability, shorter photoperiods and increased storm frequency.
Seagrass meadows

Seagrass
Seagrasses are flowering plants from one of four plant families , all in the order Alismatales , which grow in marine, fully saline environments.-Ecology:...
es are flowering plant
Flowering plant
The flowering plants , also known as Angiospermae or Magnoliophyta, are the most diverse group of land plants. Angiosperms are seed-producing plants like the gymnosperms and can be distinguished from the gymnosperms by a series of synapomorphies...
s from one of four plant families which grow in marine environments. They are called seagrasses because the leaves are long and narrow and are very often green, and because the plants often grow in large meadows which look like grassland. Since seagrasses photosynthesize
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a chemical process that converts carbon dioxide into organic compounds, especially sugars, using the energy from sunlight. Photosynthesis occurs in plants, algae, and many species of bacteria, but not in archaea. Photosynthetic organisms are called photoautotrophs, since they can...
and are submerged, they must grow submerged in the photic zone
Photic zone
The photic zone or euphotic zone is the depth of the water in a lake or ocean that is exposed to sufficient sunlight for photosynthesis to occur...
, where there is enough sunlight. For this reason, most occur in shallow and sheltered coastal waters anchored in sand or mud bottoms.
Seagrasses form extensive beds or meadows, which can be either monospecific (made up of one species) or multispecific (where more than one species co-exist). Seagrass beds make highly diverse and productive ecosystem
Ecosystem
An ecosystem is a biological environment consisting of all the organisms living in a particular area, as well as all the nonliving , physical components of the environment with which the organisms interact, such as air, soil, water and sunlight....
s. They are home to phyla
Phylum
In biology, a phylum The term was coined by Georges Cuvier from Greek φῦλον phylon, "race, stock," related to φυλή phyle, "tribe, clan." is a taxonomic rank below kingdom and above class. "Phylum" is equivalent to the botanical term division....
such as juvenile and adult fish, epiphytic
Epiphyte
An epiphyte is a plant that grows upon another plant non-parasitically or sometimes upon some other object , derives its moisture and nutrients from the air and rain and sometimes from debris accumulating around it, and is found in the temperate zone and in the...
and free-living macroalgae
Seaweed
Seaweed is a loose, colloquial term encompassing macroscopic, multicellular, benthic marine algae. The term includes some members of the red, brown and green algae...
and microalgae, mollusks, bristle worms, and nematode
Nematode
The nematodes or roundworms are the most diverse phylum of pseudocoelomates, and one of the most diverse of all animals. Nematode species are very difficult to distinguish; over 28,000 have been described, of which over 16,000 are parasitic. It has been estimated that the total number of nematode...
s. Few species were originally considered to feed directly on seagrass leaves
Leaf
A leaf is an organ of a vascular plant, as defined in botanical terms, and in particular in plant morphology. Foliage is a mass noun that refers to leaves as a feature of plants....
(partly because of their low nutritional content), but scientific review
Review
A review is an evaluation of a publication, a product or a service, such as a movie , video game, musical composition , book ; a piece of hardware like a car, home appliance, or computer; or an event or performance, such as a live music concert, a play, musical theater show or dance show...
s and improved working methods have shown that seagrass herbivory
Herbivore
Herbivores are organisms that are anatomically and physiologically adapted to eat plant-based foods. Herbivory is a form of consumption in which an organism principally eats autotrophs such as plants, algae and photosynthesizing bacteria. More generally, organisms that feed on autotrophs in...
is a highly important link in the food chain, with hundreds of species feeding on seagrasses worldwide, including green turtles, dugong
Dugong
The dugong is a large marine mammal which, together with the manatees, is one of four living species of the order Sirenia. It is the only living representative of the once-diverse family Dugongidae; its closest modern relative, Steller's sea cow , was hunted to extinction in the 18th century...
s, manatee
Manatee
Manatees are large, fully aquatic, mostly herbivorous marine mammals sometimes known as sea cows...
s, fish
Fish
Fish are a paraphyletic group of organisms that consist of all gill-bearing aquatic vertebrate animals that lack limbs with digits. Included in this definition are the living hagfish, lampreys, and cartilaginous and bony fish, as well as various extinct related groups...
, geese
Goose
The word goose is the English name for a group of waterfowl, belonging to the family Anatidae. This family also includes swans, most of which are larger than true geese, and ducks, which are smaller....
, swan
Swan
Swans, genus Cygnus, are birds of the family Anatidae, which also includes geese and ducks. Swans are grouped with the closely related geese in the subfamily Anserinae where they form the tribe Cygnini. Sometimes, they are considered a distinct subfamily, Cygninae...
s, sea urchin
Sea urchin
Sea urchins or urchins are small, spiny, globular animals which, with their close kin, such as sand dollars, constitute the class Echinoidea of the echinoderm phylum. They inhabit all oceans. Their shell, or "test", is round and spiny, typically from across. Common colors include black and dull...
s and crab
Crab
True crabs are decapod crustaceans of the infraorder Brachyura, which typically have a very short projecting "tail" , or where the reduced abdomen is entirely hidden under the thorax...
s.
Seagrasses are ecosystem engineer
Ecosystem engineer
An ecosystem engineer is any organism that creates or modifies habitats. Jones et al. identified two different types of ecosystem engineers:...
s in the sense that they partly create their own habitat. The leaves slow down water-currents increasing sedimentation
Sedimentation
Sedimentation is the tendency for particles in suspension to settle out of the fluid in which they are entrained, and come to rest against a barrier. This is due to their motion through the fluid in response to the forces acting on them: these forces can be due to gravity, centrifugal acceleration...
, and the seagrass root
Root
In vascular plants, the root is the organ of a plant that typically lies below the surface of the soil. This is not always the case, however, since a root can also be aerial or aerating . Furthermore, a stem normally occurring below ground is not exceptional either...
s and rhizome
Rhizome
In botany and dendrology, a rhizome is a characteristically horizontal stem of a plant that is usually found underground, often sending out roots and shoots from its nodes...
s stabilize the seabed. Their importance to associated species is mainly due to provision of shelter (through their three-dimensional structure in the water column), and due to their extraordinarily high rate of primary production
Primary production
400px|thumb|Global oceanic and terrestrial photoautotroph abundance, from September [[1997]] to August 2000. As an estimate of autotroph biomass, it is only a rough indicator of primary production potential, and not an actual estimate of it...
. As a result, seagrasses provide coastal zones with ecosystem services
Ecosystem services
Humankind benefits from a multitude of resources and processes that are supplied by natural ecosystems. Collectively, these benefits are known as ecosystem services and include products like clean drinking water and processes such as the decomposition of wastes...
, such as fishing grounds, wave protection, oxygen
Oxygen
Oxygen is the element with atomic number 8 and represented by the symbol O. Its name derives from the Greek roots ὀξύς and -γενής , because at the time of naming, it was mistakenly thought that all acids required oxygen in their composition...
production and protection against coastal erosion
Erosion
Erosion is when materials are removed from the surface and changed into something else. It only works by hydraulic actions and transport of solids in the natural environment, and leads to the deposition of these materials elsewhere...
. Seagrass meadows account for 15% of the ocean’s total carbon storage.
Coral reefs

Reef
In nautical terminology, a reef is a rock, sandbar, or other feature lying beneath the surface of the water ....
s comprise some of the densest and most diverse habitats in the world. The best-known types of reefs are tropical coral reef
Coral reef
Coral reefs are underwater structures made from calcium carbonate secreted by corals. Coral reefs are colonies of tiny living animals found in marine waters that contain few nutrients. Most coral reefs are built from stony corals, which in turn consist of polyps that cluster in groups. The polyps...
s which exist in most tropical waters; however, reefs can also exist in cold water. Reefs are built up by coral
Coral
Corals are marine animals in class Anthozoa of phylum Cnidaria typically living in compact colonies of many identical individual "polyps". The group includes the important reef builders that inhabit tropical oceans and secrete calcium carbonate to form a hard skeleton.A coral "head" is a colony of...
s and other calcium
Calcium
Calcium is the chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. It has an atomic mass of 40.078 amu. Calcium is a soft gray alkaline earth metal, and is the fifth-most-abundant element by mass in the Earth's crust...
-depositing animals, usually on top of a rocky outcrop on the ocean floor. Reefs can also grow on other surfaces, which has made it possible to create artificial reef
Artificial reef
An artificial reef is a human-made underwater structure, typically built to promote marine life in areas with a generally featureless bottom, control erosion, block ship passage, or improve surfing....
s. Coral reefs also support a huge community of life, including the corals themselves, their symbiotic zooxanthellae, tropical fish and many other organisms.
Much attention in marine biology is focused on coral reefs and the El Niño weather phenomenon. In 1998, coral reefs experienced the most severe mass bleaching events on record, when vast expanses of reefs across the world died because sea surface temperatures rose well above normal. Some reefs are recovering, but scientists say that between 50% and 70% of the world's coral reefs are now endangered and predict that global warming
Global warming
Global warming refers to the rising average temperature of Earth's atmosphere and oceans and its projected continuation. In the last 100 years, Earth's average surface temperature increased by about with about two thirds of the increase occurring over just the last three decades...
could exacerbate this trend.
Open ocean

Primary production
400px|thumb|Global oceanic and terrestrial photoautotroph abundance, from September [[1997]] to August 2000. As an estimate of autotroph biomass, it is only a rough indicator of primary production potential, and not an actual estimate of it...
than any other marine habitat. Only about 10 percent of marine species live in the open ocean. But among them are the largest and fastest of all marine animals, as well as the animals that dive the deepest and migrate the longest. In the depths lurk animal that, to our eyes, appear hugely alien.
Surface waters
The surface waters are sunlit. The waters down to about 200 metres are said to be in the epipelagic zone. Enough sunlight enters the epipelagic zone to allow photosynthesisPhotosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a chemical process that converts carbon dioxide into organic compounds, especially sugars, using the energy from sunlight. Photosynthesis occurs in plants, algae, and many species of bacteria, but not in archaea. Photosynthetic organisms are called photoautotrophs, since they can...
by phytoplankton
Phytoplankton
Phytoplankton are the autotrophic component of the plankton community. The name comes from the Greek words φυτόν , meaning "plant", and πλαγκτός , meaning "wanderer" or "drifter". Most phytoplankton are too small to be individually seen with the unaided eye...
. The epipelagic zone is usually low in nutrients. This partially because the organic debris produced in the zone, such as excrement and dead animals, sink to the depths and are lost to the upper zone. Photosynthesis can happen only if both sunlight and nutrients are present.
In some places, like at the edge of continental shelves, nutrients can upwell
Upwell
Upwell is a civil parish in the English county of Norfolk.It covers an area of and had a population of 2,456 in 1,033 households as of the 2001 census.For the purposes of local government, it falls within the district of King's Lynn and West Norfolk...
from the ocean depth, or land runoff can be distributed by storms and ocean currents. In these areas, given that both sunlight and nutrients are now present, phytoplankton can rapidly establish itself, multiplying so fast that the water turns green from the chlorophyll, resulting in an algal bloom
Algal bloom
An algal bloom is a rapid increase or accumulation in the population of algae in an aquatic system. Algal blooms may occur in freshwater as well as marine environments. Typically, only one or a small number of phytoplankton species are involved, and some blooms may be recognized by discoloration...
. These nutrient rich surface waters are among the most biologically productive in the world, supporting billions of tonnes of biomass
Biomass (ecology)
Biomass, in ecology, is the mass of living biological organisms in a given area or ecosystem at a given time. Biomass can refer to species biomass, which is the mass of one or more species, or to community biomass, which is the mass of all species in the community. It can include microorganisms,...
.
"Phytoplankton are eaten by zooplankton
Zooplankton
Zooplankton are heterotrophic plankton. Plankton are organisms drifting in oceans, seas, and bodies of fresh water. The word "zooplankton" is derived from the Greek zoon , meaning "animal", and , meaning "wanderer" or "drifter"...
- small animals which, like phytoplankton, drift in the ocean currents. The most abundant zooplankton species are copepod
Copepod
Copepods are a group of small crustaceans found in the sea and nearly every freshwater habitat. Some species are planktonic , some are benthic , and some continental species may live in limno-terrestrial habitats and other wet terrestrial places, such as swamps, under leaf fall in wet forests,...
s and krill
Krill
Krill is the common name given to the order Euphausiacea of shrimp-like marine crustaceans. Also known as euphausiids, these small invertebrates are found in all oceans of the world...
: tiny crustacean
Crustacean
Crustaceans form a very large group of arthropods, usually treated as a subphylum, which includes such familiar animals as crabs, lobsters, crayfish, shrimp, krill and barnacles. The 50,000 described species range in size from Stygotantulus stocki at , to the Japanese spider crab with a leg span...
s that are the most numerous animals on Earth. Other types of zooplankton include jelly fish and the larvae
Larvae
In Roman mythology, lemures were shades or spirits of the restless or malignant dead, and are probably cognate with an extended sense of larvae as disturbing or frightening...
of fish, marine worm
Marine worm
Any worm that lives in a marine environment is considered a marine worm. Marine worms are found in several different phyla, including the Platyhelminthes, Nematoda, Annelida , Chaetognatha, Hemichordata, and Phoronida....
s, starfish, and other marine organisms". In turn, the zooplankton are eaten by filter feeding animals, including some seabird
Seabird
Seabirds are birds that have adapted to life within the marine environment. While seabirds vary greatly in lifestyle, behaviour and physiology, they often exhibit striking convergent evolution, as the same environmental problems and feeding niches have resulted in similar adaptations...
s, small forage fish
Forage fish
Forage fish, also called prey fish or bait fish, are small fish which are preyed on by larger predators for food. Predators include other larger fish, seabirds and marine mammals. Typical ocean forage fish feed near the base of the food chain on plankton, often by filter feeding...
like herrings and sardines, whale shark
Whale shark
The whale shark, Rhincodon typus, is a slow-moving filter feeding shark, the largest extant fish species. The largest confirmed individual had a length of and a weight of more than , but unconfirmed claims report considerably larger whale sharks...
s, manta ray
Manta ray
The manta ray is the largest species of the rays. The largest known specimen was more than across, with a weight of about . It ranges throughout waters of the world, typically around coral reefs...
s, and the largest animal in the world, the blue whale
Blue Whale
The blue whale is a marine mammal belonging to the suborder of baleen whales . At in length and or more in weight, it is the largest known animal to have ever existed....
. Yet again, moving up the foodchain, the small forage fish are in turn eaten by larger predators, such as tuna, marlin, sharks, large squid, seabirds, dolphins, and toothed whale
Toothed whale
The toothed whales form a suborder of the cetaceans, including sperm whales, beaked whales, dolphins, and others. As the name suggests, the suborder is characterized by the presence of teeth rather than the baleen of other whales.-Anatomy:Toothed whales have a single blowhole on the top of the head...
s.
Deep sea
The deep seaDeep sea
The deep sea, or deep layer, is the lowest layer in the ocean, existing below the thermocline and above the seabed, at a depth of 1000 fathoms or more. Little or no light penetrates this part of the ocean and most of the organisms that live there rely for subsistence on falling organic matter...
starts at the aphotic zone
Aphotic zone
The aphotic zone is the portion of a lake or ocean where there is little or no sunlight. It is formally defined as the depths beyond which less than 1% of sunlight penetrates. Consequently, bioluminescence is essentially the only light found in this zone...
, the point where sunlight loses most of its energy in the water. Many life forms that live at these depths have the ability to create their own light a unique evolution known as bio-luminescence.
In the deep ocean, the waters extend far below the epipelagic zone, and support very different types of pelagic life forms adapted to living in these deeper zones.
Much of the aphotic zone
Aphotic zone
The aphotic zone is the portion of a lake or ocean where there is little or no sunlight. It is formally defined as the depths beyond which less than 1% of sunlight penetrates. Consequently, bioluminescence is essentially the only light found in this zone...
's energy is supplied by the open ocean in the form of detritus
Detritus
Detritus is a biological term used to describe dead or waste organic material.Detritus may also refer to:* Detritus , a geological term used to describe the particles of rock produced by weathering...
. In deep water, marine snow
Marine snow
In the deep ocean, marine snow is a continuous shower of mostly organic detritus falling from the upper layers of the water column. It is a significant means of exporting energy from the light-rich photic zone to the aphotic zone below. The term was first coined by the explorer William Beebe as he...
is a continuous shower of mostly organic detritus falling from the upper layers of the water column. Its origin lies in activities within the productive photic zone
Photic zone
The photic zone or euphotic zone is the depth of the water in a lake or ocean that is exposed to sufficient sunlight for photosynthesis to occur...
. Marine snow includes dead or dying plankton
Plankton
Plankton are any drifting organisms that inhabit the pelagic zone of oceans, seas, or bodies of fresh water. That is, plankton are defined by their ecological niche rather than phylogenetic or taxonomic classification...
, protist
Protist
Protists are a diverse group of eukaryotic microorganisms. Historically, protists were treated as the kingdom Protista, which includes mostly unicellular organisms that do not fit into the other kingdoms, but this group is contested in modern taxonomy...
s (diatom
Diatom
Diatoms are a major group of algae, and are one of the most common types of phytoplankton. Most diatoms are unicellular, although they can exist as colonies in the shape of filaments or ribbons , fans , zigzags , or stellate colonies . Diatoms are producers within the food chain...
s), fecal matter, sand, soot and other inorganic dust. The "snowflakes" grow over time and may reach several centimetres in diameter, travelling for weeks before reaching the ocean floor. However, most organic components of marine snow are consumed by microbes, zooplankton
Zooplankton
Zooplankton are heterotrophic plankton. Plankton are organisms drifting in oceans, seas, and bodies of fresh water. The word "zooplankton" is derived from the Greek zoon , meaning "animal", and , meaning "wanderer" or "drifter"...
and other filter-feeding animals within the first 1,000 metres of their journey, that is, within the epipelagic zone. In this way marine snow may be considered the foundation of deep-sea mesopelagic
Mesopelagic
The mesopelagic is that part of the pelagic zone that extends from a depth of 200 to 1000 metres below the ocean surface. It lies between the photic epipelagic above and the aphotic bathypelagic below, where there is no light at all...
and benthic ecosystem
Ecosystem
An ecosystem is a biological environment consisting of all the organisms living in a particular area, as well as all the nonliving , physical components of the environment with which the organisms interact, such as air, soil, water and sunlight....
s: As sunlight cannot reach them, deep-sea organisms rely heavily on marine snow as an energy source.
Some deep-sea pelagic groups, such as the lanternfish
Lanternfish
Cooper Lanternfishes are small mesopelagic fish of the large family Myctophidae. One of two families in the order Myctophiformes, the Myctophidae are represented by 246 species in 33 genera, and are found in oceans worldwide. They are aptly named after their conspicuous use of bioluminescence...
, ridgehead
Ridgehead
Ridgeheads, also known as bigscales, are a family of small, deep-sea stephanoberyciform fish. The family contains approximately 37 species in five genera; their distribution is worldwide, but ridgeheads are absent from the Arctic Ocean and Mediterranean Sea...
, marine hatchetfish
Marine hatchetfish
Marine hatchetfishes or deep-sea hatchetfishes are small deep-sea mesopelagic ray-finned fish of the stomiiform subfamily Sternoptychinae...
, and lightfish
Phosichthyidae
Lightfishes are small stomiiform fishes in the family PhosichthyidaeThey are very small fishes found in oceans throughout the world: most species grow no longer than 10 cm, while those in the genus Vinciguerria only reach 4 cm or so....
families are sometimes termed pseudoceanic because, rather than having an even distribution in open water, they occur in significantly higher abundances around structural oases, notably seamount
Seamount
A seamount is a mountain rising from the ocean seafloor that does not reach to the water's surface , and thus is not an island. These are typically formed from extinct volcanoes, that rise abruptly and are usually found rising from a seafloor of depth. They are defined by oceanographers as...
s and over continental slopes. The phenomenon is explained by the likewise abundance of prey species which are also attracted to the structures.
The fish in the different pelagic and deep water benthic zones are physically structured, and behave in ways, that differ markedly from each other. Groups of coexisting species within each zone all seem to operate in similar ways, such as the small mesopelagic vertically migrating
Diel vertical migration
Diel vertical migration, also known as diurnal vertical migration, is a pattern of movement that some organisms living in the ocean and in lakes undertake each day. Usually organisms move up to the epipelagic zone at night and return to the mesopelagic zone of the oceans or to the hypolimnion zone...
plankton-feeders, the bathypelagic anglerfish
Anglerfish
Anglerfishes are members of the teleost order Lophiiformes . They are bony fishes named for their characteristic mode of predation, wherein a fleshy growth from the fish's head acts as a lure; this is considered analogous to angling.Some anglerfishes are pelagic , while others are benthic...
es, and the deep water benthic rattail
Rattail
Grenadiers or rattails are generally large, brown to black gadiform marine fish of the family Macrouridae...
s. "
Ray finned
Acanthopterygii
Acanthopterygii is a superorder of bony fishes in the class Actinopterygii. Members of this superorder are also known as the ray-finned fishes for the characteristic sharp, bony rays in their fins; however this name is also often given to the class Actinopterygii as a whole.Orders:* Order...
species, with spiny fins, are rare among deep sea fishes, which suggests that deep sea fish are ancient and so well adapted to their environment that invasions by more modern fishes have been unsuccessful. The few ray fins that do exist are mainly in the Beryciformes
Beryciformes
Beryciformes is an order of ray-finned fishes. This is a very poorly understood group of 16 families, 57 genera, and about 219 species. Some people believe that it is probably an artificial assemblage of unrelated taxa that are thrown together for convenience only; there are no convincing...
and Lampriformes
Lampriformes
Lampriformes is an order of ray-finned fish. They are collectively called "lamprids" or lampriforms, and unite such open-ocean and partially deep-sea Teleostei as the crestfishes, oarfish, opahs and ribbonfishes...
, which are also ancient forms. Most deep sea pelagic fishes belong to their own orders, suggesting a long evolution in deep sea environments. In contrast, deep water benthic species, are in orders that include many related shallow water fishes.
The umbrella mouth gulper is a deep sea eel with an enormous loosely hinged mouth. It can open its mouth wide enough to swallow a fish much larger than itself, and then expand its stomach to accommodate its catch.
Vents and seeps
Hydrothermal ventHydrothermal vent
A hydrothermal vent is a fissure in a planet's surface from which geothermally heated water issues. Hydrothermal vents are commonly found near volcanically active places, areas where tectonic plates are moving apart, ocean basins, and hotspots. Hydrothermal vents exist because the earth is both...
s along the mid-ocean ridge
Mid-ocean ridge
A mid-ocean ridge is a general term for an underwater mountain system that consists of various mountain ranges , typically having a valley known as a rift running along its spine, formed by plate tectonics. This type of oceanic ridge is characteristic of what is known as an oceanic spreading...
spreading centers act as oases
Oasis
In geography, an oasis or cienega is an isolated area of vegetation in a desert, typically surrounding a spring or similar water source...
, as do their opposites, cold seeps. Such places support unique biome
Biome
Biomes are climatically and geographically defined as similar climatic conditions on the Earth, such as communities of plants, animals, and soil organisms, and are often referred to as ecosystems. Some parts of the earth have more or less the same kind of abiotic and biotic factors spread over a...
s and many new microbes and other lifeforms have been discovered at these locations.
Trenches
The deepest recorded oceanic trenchOceanic trench
The oceanic trenches are hemispheric-scale long but narrow topographic depressions of the sea floor. They are also the deepest parts of the ocean floor....
es measure to date is the Mariana Trench
Mariana Trench
The Mariana Trench or Marianas Trench is the deepest part of the world's oceans. It is located in the western Pacific Ocean, to the east of the Mariana Islands. The trench is about long but has a mean width of only...
, near the Philippines
Philippines
The Philippines , officially known as the Republic of the Philippines , is a country in Southeast Asia in the western Pacific Ocean. To its north across the Luzon Strait lies Taiwan. West across the South China Sea sits Vietnam...
, in the Pacific Ocean
Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest of the Earth's oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic in the north to the Southern Ocean in the south, bounded by Asia and Australia in the west, and the Americas in the east.At 165.2 million square kilometres in area, this largest division of the World...
at 10,924 m (35,838 ft). At such depths, water pressure is extreme and there is no sunlight, but some life still exists. A white flatfish
Flatfish
The flatfish are an order of ray-finned fish, also called the Heterosomata, sometimes classified as a suborder of Perciformes. In many species, both eyes lie on one side of the head, one or the other migrating through and around the head during development...
, a shrimp and a jellyfish were seen by the American crew of the bathyscaphe
Bathyscaphe
A bathyscaphe is a free-diving self-propelled deep-sea submersible, consisting of a crew cabin similar to a bathysphere, but suspended below a float rather than from a surface cable, as in the classic bathysphere design....
Trieste
Bathyscaphe Trieste
The Trieste is a Swiss-designed, Italian-built deep-diving research bathyscaphe with a crew of two, which reached a record maximum depth of about , in the deepest known part of the Earth's oceans, the Challenger Deep, in the Mariana Trench near Guam, on January 23, 1960, crewed by Jacques Piccard ...
when it dove to the bottom in 1960.
Seamounts
Marine life also flourishes around seamountSeamount
A seamount is a mountain rising from the ocean seafloor that does not reach to the water's surface , and thus is not an island. These are typically formed from extinct volcanoes, that rise abruptly and are usually found rising from a seafloor of depth. They are defined by oceanographers as...
s that rise from the depths, where fish and other sea life congregate to spawn and feed.
External links
- Marine ecosystems Missouri Botanical Garden, 2002.

