
Greater East Asia Co-Prosperity Sphere
Encyclopedia

Empire of Japan
The Empire of Japan is the name of the state of Japan that existed from the Meiji Restoration on 3 January 1868 to the enactment of the post-World War II Constitution of...
. It represented the desire to create a self-sufficient "bloc of Asian nations led by the Japanese and free of Western powers". It was announced in a radio address entitled "The International Situation and Japan's Position" by Foreign Minister Hachirō Arita
Hachiro Arita
was a Japanese politician and diplomat who served as the Minister for Foreign Affairs for three terms. He is believed to have originated the concept of the Greater East Asia Co-Prosperity Sphere.- Biography :...
on June 29, 1940.
The concept was a geographically enlarged version of the similar concept of New Order in East Asia, which was announced by Prime Minister Fumimaro Konoe on 22 December 1938 and was limited to Northeast Asia
Northeast Asia
Northeast Asia and Northeastern Asia refers to the northeastern subregion of Asia. Though the precise definition of Northeast Asia changes according to context, it always includes Japan and the Korean Peninsula, and is sometimes used to refer to these two regions exclusively.-Definitions:The...
only.
Development of concept
The original concept was an idealistic wish to free Asia from colonizing powers, but soon, nationalists saw it as a way to gain resources to keep Japan a modern power, and militarists saw the same resources as raw materials for war. Many Japanese were drawn to it as idealistic. Many of them remained convinced, throughout the war, that the Sphere was idealistic, offering slogans in a newspaper competition, praising the sphere for constructive efforts and peace.The Japanese Prime Minister Fumimaro Konoe
Fumimaro Konoe
Prince was a politician in the Empire of Japan who served as the 34th, 38th and 39th Prime Minister of Japan and founder/leader of the Taisei Yokusankai.- Early life :...
planned the Sphere in 1940 in an attempt to create a Great East Asia, comprising Japan
Japan
Japan is an island nation in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean, it lies to the east of the Sea of Japan, China, North Korea, South Korea and Russia, stretching from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea and Taiwan in the south...
, Manchukuo
Manchukuo
Manchukuo or Manshū-koku was a puppet state in Manchuria and eastern Inner Mongolia, governed under a form of constitutional monarchy. The region was the historical homeland of the Manchus, who founded the Qing Empire in China...
, China
China
Chinese civilization may refer to:* China for more general discussion of the country.* Chinese culture* Greater China, the transnational community of ethnic Chinese.* History of China* Sinosphere, the area historically affected by Chinese culture...
, and parts of Southeast Asia, that would, according to imperial propaganda, establish a new international order seeking "co prosperity" for Asian countries which would share prosperity and peace, free from Western colonialism and domination. Military goals of this expansion included naval operations in the Indian Ocean
Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third largest of the world's oceanic divisions, covering approximately 20% of the water on the Earth's surface. It is bounded on the north by the Indian Subcontinent and Arabian Peninsula ; on the west by eastern Africa; on the east by Indochina, the Sunda Islands, and...
and the isolation of Australia
Australia
Australia , officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country in the Southern Hemisphere comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands in the Indian and Pacific Oceans. It is the world's sixth-largest country by total area...
. This would enable the principle of hakkō ichiu
Hakko ichiu
was a Japanese political slogan that became popular from the Second Sino-Japanese War to World War II, and was popularized in a speech by Prime Minister of Japan Fumimaro Konoe on January 8, 1940.-Outline:...
.
This was one of a number of slogans and concepts used in the justification of Japanese aggression in East Asia in the 1930s through the end of World War II
World War II
World War II, or the Second World War , was a global conflict lasting from 1939 to 1945, involving most of the world's nations—including all of the great powers—eventually forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis...
. The term "Greater East Asia Co-Prosperity Sphere" is remembered largely as a front for the Japanese
Empire of Japan
The Empire of Japan is the name of the state of Japan that existed from the Meiji Restoration on 3 January 1868 to the enactment of the post-World War II Constitution of...
control of occupied countries during World War II, in which puppet governments manipulated local populations and economies for the benefit of Imperial Japan.
To combat the protectionist dollar and sterling zones, Japanese economic planners called for a "yen bloc."
Japan's experiment with such financial imperialism encompassed both official and semi-official colonies. In the period between 1895 (when Japan annexed Taiwan) and 1937 (the outbreak of the Second Sino-Japanese War
Second Sino-Japanese War
The Second Sino-Japanese War was a military conflict fought primarily between the Republic of China and the Empire of Japan. From 1937 to 1941, China fought Japan with some economic help from Germany , the Soviet Union and the United States...
), monetary specialists in Tokyo directed and managed programs of coordinated monetary reforms in Taiwan, Korea, Manchuria, and the peripheral Japanese-controlled islands in the Pacific. These reforms aimed to foster a network of linked political and economic relationships. These efforts foundered in the eventual debacle of the Greater East-Asia Co-Prosperity Sphere.
The negative connotations that still attach to the term "Greater East Asia" (大東亜) remain one of a number of difficulties facing the annual East Asia Summit
East Asia Summit
The East Asia Summit is a forum held annually by leaders of, initially, 16 countries in the East Asian region. Membership will expand to 18 countries including the United States and Russia at the Sixth EAS in 2011. EAS meetings are held after annual ASEAN leaders’ meetings...
s, begun in 2005 to discuss the possibility of the establishment of a stronger, more united East Asian Community
East Asian Community
East Asian Community is a proposed trade bloc for the East Asia countries that may arise out of either ASEAN Plus Three or the East Asia Summit .- Prior to the EAS :...
.
History
World War II puppet governments ran many countries occupied by Japan — manipulating local populations and economies for the benefit of Imperial Japan and backing the conception of a united Asia in the absence of (or opposed to) European influence. Propaganda claimed that they had liberated these countries for governments of their own (an effect somewhat undermined by these governments' total lack of effective power).It was an Imperial Japanese Army
Imperial Japanese Army
-Foundation:During the Meiji Restoration, the military forces loyal to the Emperor were samurai drawn primarily from the loyalist feudal domains of Satsuma and Chōshū...
concept that originated with General Hachiro Arita
Hachiro Arita
was a Japanese politician and diplomat who served as the Minister for Foreign Affairs for three terms. He is believed to have originated the concept of the Greater East Asia Co-Prosperity Sphere.- Biography :...
, an army ideologist who served as Minister for Foreign Affairs
Minister for Foreign Affairs (Japan)
The of Japan is the Cabinet member responsible for Japanese foreign policy and the chief executive of the Ministry of Foreign Affairs.Since the end of the American occupation of Japan, the position has been one of the most powerful in the Cabinet, as Japan's economic interests have long relied on...
from 1936-1940. was a Japanese term—banned during the post-war Occupation—referring to Far East
Far East
The Far East is an English term mostly describing East Asia and Southeast Asia, with South Asia sometimes also included for economic and cultural reasons.The term came into use in European geopolitical discourse in the 19th century,...
Asia. The new Japanese empire was presented as an Asian equivalent of the Monroe Doctrine
Monroe Doctrine
The Monroe Doctrine is a policy of the United States introduced on December 2, 1823. It stated that further efforts by European nations to colonize land or interfere with states in North or South America would be viewed as acts of aggression requiring U.S. intervention...
. The regions of Asia, it was argued, were as essential to Japan as Latin America was to the U.S.
The Japanese Foreign Minister
Minister for Foreign Affairs (Japan)
The of Japan is the Cabinet member responsible for Japanese foreign policy and the chief executive of the Ministry of Foreign Affairs.Since the end of the American occupation of Japan, the position has been one of the most powerful in the Cabinet, as Japan's economic interests have long relied on...
Matsuoka Yosuke formally announced the idea of the Co-Prosperity Sphere on August 1, 1940, in a press interview, but it had already existed in various forms for many years. Leaders in Japan had long had an interest in the idea, in reality to extend Japanese power and acquire an empire based on European models, though ostensibly to free Asia from imperialism
Imperialism
Imperialism, as defined by Dictionary of Human Geography, is "the creation and/or maintenance of an unequal economic, cultural, and territorial relationships, usually between states and often in the form of an empire, based on domination and subordination." The imperialism of the last 500 years,...
. The outbreak of World War II fighting in Europe had given the Japanese an opportunity to demand the withdrawal of support from China in the name of "Asia for Asians", with the European powers unable to effectively retaliate.
As part of its war drive, Japanese propaganda included phrases like "Asia for the Asians!" and talked about the perceived need to liberate Asian countries from imperialist powers. The failure to win the Second Sino-Japanese War
Second Sino-Japanese War
The Second Sino-Japanese War was a military conflict fought primarily between the Republic of China and the Empire of Japan. From 1937 to 1941, China fought Japan with some economic help from Germany , the Soviet Union and the United States...
was blamed on British and American exploitation of Southeast Asian colonies, even though the Chinese received far more assistance from the Soviet Union. In some cases local people welcomed Japanese troops when they invaded, driving out British
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
, French
France
The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
, and other governments and military forces. In general, however, the subsequent brutality and racism of the Japanese led to people of the occupied areas regarding the new Asian imperialists as equal to or (more often) much worse than Western imperialists. The Japanese government directed that local economies be managed strictly for the production of raw war materials for the Japanese, and a cabinet member declared, "There are no restrictions. They are enemy possessions. We can take them, do anything we want."
An Investigation of Global Policy with the Yamato Race as Nucleus
An Investigation of Global Policy with the Yamato Race as Nucleus
, was a secret Japanese government report created by the Ministry of Health and Welfare’s Population Problems Research Center, and completed on July 1, 1943....
— a secret document completed in 1943 for high-ranking government use — laid out that the superior position of Japan in the Greater Asia Co-Prosperity Sphere, showing the subordination of other nations was not forced by the war, but part of explicit policy. It explicitly states the superiority of the Japanese over other Asian races and suggests that the Sphere was merely propaganda intended to mask Japan's true intention of domination over Asia.
China and other Asian nations were regarded as too weak and lacking in unity to be treated as equal partners. The booklet Read This and the War is Won—for the Japanese army—presented colonialism as a tiny group of colonists living in luxury by burdening Asians; because ties of blood connect them to Japanese, and Asians had been weakened by colonialism, it was Japan's place to "make men of them again."
From the Japanese point of view, one common principal reason stood behind both forming the Greater East Asia Co-Prosperity Sphere and initiating war with the Allies: Chinese markets. Japan wanted their "paramount relations" in regard to Chinese markets acknowledged by the U.S. government. The U.S., recognizing the abundance of potential wealth in these markets, refused to let the Japanese have an advantage in selling to China. In an attempt to give Japan a formal advantage over the Chinese markets, the Japanese Imperial regime first invaded China and later launched the Greater East Asia Co-Prosperity Sphere.
According to Foreign Minister Shigenori Togo
Shigenori Togo
was Minister of Foreign Affairs for the Empire of Japan at both the start and the end of the Japanese-American conflict during World War II...
(in office 1941-1942 and 1945), should Japan be successful in creating this sphere, it would emerge as the leader of Eastern Asia, and the Greater East Asia Co-Prosperity Sphere would be another name for the Japanese Empire.
Greater East Asia Conference
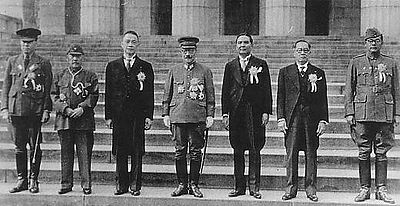
Head of State
A head of state is the individual that serves as the chief public representative of a monarchy, republic, federation, commonwealth or other kind of state. His or her role generally includes legitimizing the state and exercising the political powers, functions, and duties granted to the head of...
of various component members of the Greater East Asia Co-Prosperity Sphere. The conference was also referred to as the Tokyo Conference. The common language used by the delegates during the conference was English.
The Conference addressed few issues of any substance, but was intended by the Japanese to illustrate the Empire of Japan's commitments to the Pan-Asianism
Pan-Asianism
Pan-Asianism is an ideology or a movement that Asian nations unite and solidify and create a continental identity to defeat the designs of the Western nations to perpetuate hegemony.-Japanese Asianism:...
ideal and to emphasize its role as the "liberator" of Asia from western colonialism
Colonialism
Colonialism is the establishment, maintenance, acquisition and expansion of colonies in one territory by people from another territory. It is a process whereby the metropole claims sovereignty over the colony and the social structure, government, and economics of the colony are changed by...
.
The following dignitaries attended:
- Hideki TojoHideki TōjōHideki Tōjō was a general of the Imperial Japanese Army , the leader of the Taisei Yokusankai, and the 40th Prime Minister of Japan during most of World War II, from 17 October 1941 to 22 July 1944...
, Prime Minister of Japan - Zhang JinghuiZhang JinghuiZhāng Jǐnghuì ; 1871 – 1 November 1959) was a Chinese general and politician during the Warlord era. He is noted for his role in the Japanese puppet regime of Manchukuo in which he served as its second and final Prime Minister.-Biography:...
, Prime Minister of ManchukuoManchukuoManchukuo or Manshū-koku was a puppet state in Manchuria and eastern Inner Mongolia, governed under a form of constitutional monarchy. The region was the historical homeland of the Manchus, who founded the Qing Empire in China... - Wang JingweiWang JingweiWang Jingwei , alternate name Wang Zhaoming, was a Chinese politician. He was initially known as a member of the left wing of the Kuomintang , but later became increasingly anti-Communist after his efforts to collaborate with the CCP ended in political failure...
, President of the Nationalist Government of Republic of China in NanjingWang Jingwei GovernmentIn March 1940 a puppet government led by Wang Jingwei was established in the Republic of China under the protection of the Empire of Japan. The regime officially called itself the Republic of China and its government the Reorganized National Government of China... - Ba MawBa MawDr. Ba Maw was a Burmese political leader, active during the interwar and World War II period.-Early life and education:Ba Maw was born in Maubin. Ba Maw came from a distinguished family of mixed Mon-Burmese parentage which bred many scholars and lawyers...
, Head of State, State of BurmaState of BurmaThe State of Burma was created in 1943 under Japanese occupation.-Background:During the early stages of World War II, the Empire of Japan invaded British Burma primarily to obtain raw materials , and to close off the Burma Road, which was a primary link for aid and munitions to the Chinese... - Subhas Chandra Bose, Head of State of Provisional Government of Free India (Arzi Hukumat-e-Azad Hind)
- José P. LaurelJose P. LaurelJosé Paciano Laurel y García was the president of the Republic of the Philippines, a Japanese-sponsored administration during World War II, from 1943 to 1945...
, President of the Second Philippine RepublicSecond Philippine RepublicThe Second Philippine Republic, officially known as the Republic of the Philippines , was a state in the Philippines established on October 14, 1943 under Japanese occupation.... - Prince Wan WaithayakonWan WaithayakonWan Waithayakon , known in the West as Wan Waithayakon , was a Thai diplomat. He was elected President of the Eleventh Session of the United Nations General Assembly, while serving as Thailand's Permanent Representative to the United Nations...
, envoy from the Kingdom of ThailandThailandThailand , officially the Kingdom of Thailand , formerly known as Siam , is a country located at the centre of the Indochina peninsula and Southeast Asia. It is bordered to the north by Burma and Laos, to the east by Laos and Cambodia, to the south by the Gulf of Thailand and Malaysia, and to the...
Tojo greeted them with a speech praising the "spiritual essence" of Asia, as opposed to the "materialistic civilization" of the West. Their meeting was characterized by praise of solidarity and condemnation of Western colonism, but without practical plans for either economic development or integration.
The Conference issued a Joint Declaration promoting economic and political cooperation against the Allied countries
Allies of World War II
The Allies of World War II were the countries that opposed the Axis powers during the Second World War . Former Axis states contributing to the Allied victory are not considered Allied states...
.
Failure
The Co-Prosperity Sphere collapsed with Japan's surrenderSurrender of Japan
The surrender of Japan in 1945 brought hostilities of World War II to a close. By the end of July 1945, the Imperial Japanese Navy was incapable of conducting operations and an Allied invasion of Japan was imminent...
to the Allies in August 1945. Although Japan succeeded in stimulating anti-Westernism in Asia, the sphere never materialized into a unified Asia. Dr. Ba Maw
Ba Maw
Dr. Ba Maw was a Burmese political leader, active during the interwar and World War II period.-Early life and education:Ba Maw was born in Maubin. Ba Maw came from a distinguished family of mixed Mon-Burmese parentage which bred many scholars and lawyers...
, wartime President of Burma under the Japanese, blamed the Japanese military:
- "The militarists saw everything only in a Japanese perspective and, even worse, they insisted that all others dealing with them should do the same. For them there was only one way to do a thing, the Japanese way; only one goal and interest, the Japanese interest; only one destiny for the East Asian countries, to become so many Manchukuos or Koreas tied forever to Japan. These racial impositions... made any real understanding between the Japanese militarists and the people of our region virtually impossible."
In other words, the Greater East Asia Co-Prosperity Sphere operated not for the betterment of all the East Asia countries, but rather for Japan's own interests, and thus the Japanese failed to gather support in other East Asian countries. Nationalist movements did appear in these East Asian countries during this period and these nationalists did, to some extent, cooperate with the Japanese. However, Willard Elsbree, professor emeritus of political science
Political science
Political Science is a social science discipline concerned with the study of the state, government and politics. Aristotle defined it as the study of the state. It deals extensively with the theory and practice of politics, and the analysis of political systems and political behavior...
at Ohio University
Ohio University
Ohio University is a public university located in the Midwestern United States in Athens, Ohio, situated on an campus...
, claims that the Japanese government and these nationalist leaders never developed "a real unity of interests between the two parties, [and] there was no overwhelming despair on the part of the Asians at Japan's defeat".
The failure of Japan to understand the goals and interests of the other countries involved in the Greater East Asia Co-Prosperity Sphere led to a weak association of countries bound to Japan only in theory and not in spirit. Dr. Ba Maw argues that Japan could have engineered a very different outcome if the Japanese had only managed to act in accord with the hortatory concept of "Asia for the Asians". He argues that if Japan had proclaimed this maxim at the beginning of the war, and if the Japanese had actually acted on that idea,
- "No military defeat could then have robbed her of the trust and gratitude of half of Asia or even more, and that would have mattered a great deal in finding for her a new, great, and abiding place in a postwar world in which Asia was coming into her own."
Propaganda efforts
Pamphlets were dropped by airplane on the Philippines, Malaysia, and Indonesia, urging them to join this movement. Mutual cultural societies were founded in all conquered nations to ingratiate with the natives and try to supplant English with Japanese as the commonly used language. Multi-lingual pamphlets depicted many Asians marching or working together in happy unity, with the flags of all the nations and a map depicting the intended sphere. Others proclaimed that they had given independent governments to the countries they occupied, a claim undermined by the lack of power given these puppet governments. In Thailand, a street was built to demonstrate it, to be filled with modern buildings and shops, but of it consisted of false fronts.Projected territorial extent

Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was a state that existed from 1721 until the Russian Revolution of 1917. It was the successor to the Tsardom of Russia and the predecessor of the Soviet Union...
(South Sakhalin and the Kwantung Leased Territory
Kwantung Leased Territory
The Kwantung Leased Territory was a territory in the southern part of the Liaodong Peninsula in Inner Manchuria that existed from 1898 to 1945. It was one of the numerous territorial concessions that the Empire of China was compelled to award to foreign countries at the end of the 19th century...
), Germany
German Empire
The German Empire refers to Germany during the "Second Reich" period from the unification of Germany and proclamation of Wilhelm I as German Emperor on 18 January 1871, to 1918, when it became a federal republic after defeat in World War I and the abdication of the Emperor, Wilhelm II.The German...
(the South Pacific Mandate
South Pacific Mandate
The was the Japanese League of Nations mandate consisting of several groups of islands in the Pacific Ocean which came under the administration of Japan after the defeat of the German Empire in World War I.-Early history:Under the terms of the Anglo-Japanese Alliance, after the start of World...
) and China
Republic of China
The Republic of China , commonly known as Taiwan , is a unitary sovereign state located in East Asia. Originally based in mainland China, the Republic of China currently governs the island of Taiwan , which forms over 99% of its current territory, as well as Penghu, Kinmen, Matsu and other minor...
(Manchuria
Manchuria
Manchuria is a historical name given to a large geographic region in northeast Asia. Depending on the definition of its extent, Manchuria usually falls entirely within the People's Republic of China, or is sometimes divided between China and Russia. The region is commonly referred to as Northeast...
) would be retained, as well as Korea
Korea under Japanese rule
Korea was under Japanese rule as part of Japan's 35-year imperialist expansion . Japanese rule ended in 1945 shortly after the Japanese defeat in World War II....
(Chōsen), Taiwan
Taiwan under Japanese rule
Between 1895 and 1945, Taiwan was a dependency of the Empire of Japan. The expansion into Taiwan was a part of Imperial Japan's general policy of southward expansion during the late 19th century....
(Formosa), the recently seized
Second Sino-Japanese War
The Second Sino-Japanese War was a military conflict fought primarily between the Republic of China and the Empire of Japan. From 1937 to 1941, China fought Japan with some economic help from Germany , the Soviet Union and the United States...
additional portions of China and occupied French Indochina
French Indochina
French Indochina was part of the French colonial empire in southeast Asia. A federation of the three Vietnamese regions, Tonkin , Annam , and Cochinchina , as well as Cambodia, was formed in 1887....
.
The Land Disposal Plan
A reasonably accurate indication as to the geographic dimensions of the Co-Prosperity Sphere are elaborated on in a Japanese wartime document prepared in December 1941 by the Research Department of the Imperial Ministry of WarMinistry of War of Japan
The , more popularly known as the Ministry of War of Japan, was cabinet-level ministry in the Empire of Japan charged with the administrative affairs of the Imperial Japanese Army...
. Known as the "Land Disposal Plan in the Greater East Asia Co-Prosperity Sphere" (大東亜共栄圏における土地処分案) it was put together with the consent of and according to the directions of the Minister of War (later Prime [Minister) Hideki Tojo
Hideki Tōjō
Hideki Tōjō was a general of the Imperial Japanese Army , the leader of the Taisei Yokusankai, and the 40th Prime Minister of Japan during most of World War II, from 17 October 1941 to 22 July 1944...
. It assumed that the already established puppet governments of Manchukuo
Manchukuo
Manchukuo or Manshū-koku was a puppet state in Manchuria and eastern Inner Mongolia, governed under a form of constitutional monarchy. The region was the historical homeland of the Manchus, who founded the Qing Empire in China...
, Mengjiang
Mengjiang
Mengjiang , also known in English as Mongol Border Land, was an autonomous area in Inner Mongolia, operating under nominal Chinese sovereignty and Japanese control. It consisted of the then-Chinese provinces of Chahar and Suiyuan, corresponding to the central part of modern Inner Mongolia...
, and the Wang Jingwei
Wang Jingwei
Wang Jingwei , alternate name Wang Zhaoming, was a Chinese politician. He was initially known as a member of the left wing of the Kuomintang , but later became increasingly anti-Communist after his efforts to collaborate with the CCP ended in political failure...
regime in Japanese-occupied China would continue to function in these areas. Beyond these contemporary parts of Japan's sphere of influence
Sphere of influence
In the field of international relations, a sphere of influence is a spatial region or conceptual division over which a state or organization has significant cultural, economic, military or political influence....
it also envisaged the conquest of a vast range of territories covering virtually all of East Asia, the Pacific Ocean
Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest of the Earth's oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic in the north to the Southern Ocean in the south, bounded by Asia and Australia in the west, and the Americas in the east.At 165.2 million square kilometres in area, this largest division of the World...
, and even sizable portions of the Western Hemisphere
Western Hemisphere
The Western Hemisphere or western hemisphere is mainly used as a geographical term for the half of the Earth that lies west of the Prime Meridian and east of the Antimeridian , the other half being called the Eastern Hemisphere.In this sense, the western hemisphere consists of the western portions...
, including in locations as far removed from Japan as South America
South America
South America is a continent situated in the Western Hemisphere, mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere. The continent is also considered a subcontinent of the Americas. It is bordered on the west by the Pacific Ocean and on the north and east...
and the eastern Caribbean
Caribbean
The Caribbean is a crescent-shaped group of islands more than 2,000 miles long separating the Gulf of Mexico and the Caribbean Sea, to the west and south, from the Atlantic Ocean, to the east and north...
.
Although the projected extension of the Co-Prosperity Sphere was extremely ambitious, the Japanese goal during the "Greater East Asia War" was not to acquire all the territory designated in the plan at once, but to prepare for a future decisive war some 20 years later by conquering the Asian colonies of the defeated European powers, as well as the Philippines
Commonwealth of the Philippines
The Commonwealth of the Philippines was a designation of the Philippines from 1935 to 1946 when the country was a commonwealth of the United States. The Commonwealth was created by the Tydings-McDuffie Act, which was passed by the U.S. Congress in 1934. When Manuel L...
from the United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
. When Tojo Hideki spoke on the plan to the House of Peers
House of Peers (Japan)
The ' was the upper house of the Imperial Diet as mandated under the Constitution of the Empire of Japan ....
he was vague about the long-term prospects, but insinuated that the Philippines and Burma might be allowed independence, although vital territories such as Hong Kong
Hong Kong
Hong Kong is one of two Special Administrative Regions of the People's Republic of China , the other being Macau. A city-state situated on China's south coast and enclosed by the Pearl River Delta and South China Sea, it is renowned for its expansive skyline and deep natural harbour...
would remain under Japanese rule.
The islands north of the equator that had been seized from Germany
German Empire
The German Empire refers to Germany during the "Second Reich" period from the unification of Germany and proclamation of Wilhelm I as German Emperor on 18 January 1871, to 1918, when it became a federal republic after defeat in World War I and the abdication of the Emperor, Wilhelm II.The German...
in World War I
World War I
World War I , which was predominantly called the World War or the Great War from its occurrence until 1939, and the First World War or World War I thereafter, was a major war centred in Europe that began on 28 July 1914 and lasted until 11 November 1918...
and which were assigned to Japan as C-Class Mandates
League of Nations mandate
A League of Nations mandate was a legal status for certain territories transferred from the control of one country to another following World War I, or the legal instruments that contained the internationally agreed-upon terms for administering the territory on behalf of the League...
, namely the Marianas, Carolines, Marshall Islands
Marshall Islands
The Republic of the Marshall Islands , , is a Micronesian nation of atolls and islands in the middle of the Pacific Ocean, just west of the International Date Line and just north of the Equator. As of July 2011 the population was 67,182...
, and several others do not figure into this project. They were the subject of earlier negotiations with the Germans and were expected to be officially ceded to Japan in return for economic and monetary compensations.
The plan divided Japan's future empire into two different groups. The first group of territories were expected to become either part of Japan or otherwise be under its direct administration. Second were those territories that would fall under the control of a number of tightly-controlled pro-Japanese vassal state
Vassal state
A vassal state is any state that is subordinate to another. The vassal in these cases is the ruler, rather than the state itself. Being a vassal most commonly implies providing military assistance to the dominant state when requested to do so; it sometimes implies paying tribute, but a state which...
s based on the model of Manchukuo, as nominally "independent" members of the Greater East Asian alliance.
Japanese-governed
- Government-General of Formosa
Hong Kong
Hong Kong
Hong Kong is one of two Special Administrative Regions of the People's Republic of China , the other being Macau. A city-state situated on China's south coast and enclosed by the Pearl River Delta and South China Sea, it is renowned for its expansive skyline and deep natural harbour...
, the Philippines
Philippines
The Philippines , officially known as the Republic of the Philippines , is a country in Southeast Asia in the western Pacific Ocean. To its north across the Luzon Strait lies Taiwan. West across the South China Sea sits Vietnam...
, Macau
Macau
Macau , also spelled Macao , is, along with Hong Kong, one of the two special administrative regions of the People's Republic of China...
(to be purchased from Portugal), the Paracel Islands
Paracel Islands
The Paracel Islands, also called Xisha Islands in Chinese and Hoàng Sa Islands in Vietnamese, is a group of islands under the administration of Hainan Province, The People's Republic of China. Vietnam and the Republic of China also claim sovereignty of these islands...
, and Hainan Island (to be purchased from the Chinese puppet regime). Contrary to its name it was not intended to include the island of Formosa (Taiwan
Taiwan
Taiwan , also known, especially in the past, as Formosa , is the largest island of the same-named island group of East Asia in the western Pacific Ocean and located off the southeastern coast of mainland China. The island forms over 99% of the current territory of the Republic of China following...
)
- South Seas Government Office
Guam
Guam
Guam is an organized, unincorporated territory of the United States located in the western Pacific Ocean. It is one of five U.S. territories with an established civilian government. Guam is listed as one of 16 Non-Self-Governing Territories by the Special Committee on Decolonization of the United...
, Nauru
Nauru
Nauru , officially the Republic of Nauru and formerly known as Pleasant Island, is an island country in Micronesia in the South Pacific. Its nearest neighbour is Banaba Island in Kiribati, to the east. Nauru is the world's smallest republic, covering just...
, Ocean Island
Banaba Island
Banaba Island , an island in the Pacific Ocean, is a solitary raised coral island west of the Gilbert Island chain and 300 km east of Nauru. It is part of the Republic of Kiribati. It has an area of 6.5 km², and the highest point on the island is also the highest point in Kiribati, at 81...
, the Gilbert Islands
Gilbert Islands
The Gilbert Islands are a chain of sixteen atolls and coral islands in the Pacific Ocean. They are the main part of Republic of Kiribati and include Tarawa, the site of the country's capital and residence of almost half of the population.-Geography:The atolls and islands of the Gilbert Islands...
and Wake Island
Wake Island
Wake Island is a coral atoll having a coastline of in the North Pacific Ocean, located about two-thirds of the way from Honolulu west to Guam east. It is an unorganized, unincorporated territory of the United States, administered by the Office of Insular Affairs, U.S. Department of the Interior...
.
- Melanesian Region Government-General or South Pacific Government-General
British New Guinea, Australian New Guinea, the Admiralties, New Britain
New Britain
New Britain, or Niu Briten, is the largest island in the Bismarck Archipelago of Papua New Guinea. It is separated from the island of New Guinea by the Dampier and Vitiaz Straits and from New Ireland by St. George's Channel...
, New Ireland, the Solomon Islands
Solomon Islands
Solomon Islands is a sovereign state in Oceania, east of Papua New Guinea, consisting of nearly one thousand islands. It covers a land mass of . The capital, Honiara, is located on the island of Guadalcanal...
, the Santa Cruz Archipelago
Santa Cruz Islands
The Santa Cruz Islands are a group of islands in the Pacific Ocean, part of Temotu Province of the Solomon Islands. They lie approximately 250 miles to the southeast of the Solomon Islands Chain...
, the Ellice Islands, the Fiji Islands, the New Hebrides
New Hebrides
New Hebrides was the colonial name for an island group in the South Pacific that now forms the nation of Vanuatu. The New Hebrides were colonized by both the British and French in the 18th century shortly after Captain James Cook visited the islands...
, New Caledonia
New Caledonia
New Caledonia is a special collectivity of France located in the southwest Pacific Ocean, east of Australia and about from Metropolitan France. The archipelago, part of the Melanesia subregion, includes the main island of Grande Terre, the Loyalty Islands, the Belep archipelago, the Isle of...
, the Loyalty Islands
Loyalty Islands
The Loyalty Islands are an archipelago in the Pacific. They are part of the French territory of New Caledonia, whose mainland is away. They form the Loyalty Islands Province , one of the three provinces of New Caledonia...
, and the Chesterfield Islands
Chesterfield Islands
Chesterfield Islands is a french archipelago of New Caledonia located in the Coral Sea, 550 km northwest of Grande Terre the main island of New Caledonia. Chesterfield Islands are a 120 km long and 70 km broad structure composed with 11 islets and many reefs...
.
- Eastern Pacific Government-General
Hawaii
Hawaii
Hawaii is the newest of the 50 U.S. states , and is the only U.S. state made up entirely of islands. It is the northernmost island group in Polynesia, occupying most of an archipelago in the central Pacific Ocean, southwest of the continental United States, southeast of Japan, and northeast of...
, Howland Island
Howland Island
Howland Island is an uninhabited coral island located just north of the equator in the central Pacific Ocean, about southwest of Honolulu. The island lies almost halfway between Hawaii and Australia and is an unincorporated, unorganized territory of the United States. Geographically, it is part...
, Baker Island
Baker Island
Baker Island is an uninhabited atoll located just north of the equator in the central Pacific Ocean about southwest of Honolulu. The island lies almost halfway between Hawaii and Australia, and is a possession of the United States. Its nearest neighbor is Howland Island, to the north.Located at...
, the Phoenix Islands
Phoenix Islands
The Phoenix Islands are a group of eight atolls and two submerged coral reefs, lying in the central Pacific Ocean east of the Gilbert Islands and west of the Line Islands. They are a part of the Republic of Kiribati. During the late 1930s they became the site of the last attempted colonial...
, the Rain Islands, the Marquesas
Marquesas Islands
The Marquesas Islands enana and Te Fenua `Enata , both meaning "The Land of Men") are a group of volcanic islands in French Polynesia, an overseas collectivity of France in the southern Pacific Ocean. The Marquesas are located at 9° 00S, 139° 30W...
and Tuamotu Islands, the Society Islands
Society Islands
The Society Islands are a group of islands in the South Pacific Ocean. They are politically part of French Polynesia. The archipelago is generally believed to have been named by Captain James Cook in honor of the Royal Society, the sponsor of the first British scientific survey of the islands;...
, the Cook
Cook Islands
The Cook Islands is a self-governing parliamentary democracy in the South Pacific Ocean in free association with New Zealand...
and Austral Islands
Austral Islands
The Austral Islands are the southernmost group of islands in French Polynesia, an overseas collectivity of France in the South Pacific. Geographically, they consist of two separate archipelagos, namely in the northwest the Tubuai Islands consisting of the Îles Maria, Rimatara, Rurutu, Tubuai...
, all of the Samoan Islands
Samoan Islands
The Samoan Islands or Samoa Islands is an archipelago covering in the central South Pacific, forming part of Polynesia and the wider region of Oceania...
, and Tonga
Tonga
Tonga, officially the Kingdom of Tonga , is a state and an archipelago in the South Pacific Ocean, comprising 176 islands scattered over of ocean in the South Pacific...
. The possibility of re-establishing the defunct Kingdom of Hawaii
Kingdom of Hawaii
The Kingdom of Hawaii was established during the years 1795 to 1810 with the subjugation of the smaller independent chiefdoms of Oahu, Maui, Molokai, Lānai, Kauai and Niihau by the chiefdom of Hawaii into one unified government...
was also considered, based on the model of Manchukuo. Those favoring annexation of Hawaii (on the model of Karafuto) intended to use the local Japanese community
Japanese in Hawaii
The Japanese in Hawaii simply Japanese or “Local Japanese”, rarely Kepanī are the second largest ethnic group in Hawaii. At their height in 1920, they constituted 43% of Hawaii's population. They now number about 16.7% of the islands' population, according to the 2000 U.S...
, which had constituted 43% (c. 160,000) of Hawaii's population in the 1920s, as a leverage. Hawaii was to become self-sufficient in food production, while the Big Five
Big Five (Hawaii)
The Big Five was the name given to a group of what started as sugarcane processing corporations that wielded considerable political power in the Territory of Hawaii during the early 20th century and leaned heavily towards the Hawaii Republican Party. The Big Five were Castle & Cooke, Alexander &...
corporations of sugar and pineapple processing where to be broken up. No decision was ever reached regarding whether Hawaii would be annexed to Japan, become a puppet kingdom, or be used as a bargaining chip for leverage against the U.S.
- Australian Government-General
All of Australia
Australia
Australia , officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country in the Southern Hemisphere comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands in the Indian and Pacific Oceans. It is the world's sixth-largest country by total area...
including Tasmania
Tasmania
Tasmania is an Australian island and state. It is south of the continent, separated by Bass Strait. The state includes the island of Tasmania—the 26th largest island in the world—and the surrounding islands. The state has a population of 507,626 , of whom almost half reside in the greater Hobart...
. Australia and New Zealand were to accommodate up to two million Japanese settlers. However, there are indications that the Japanese were also looking for a separate peace with Australia, and a satellite rather than colony status similar to that of Burma and the Philippines.
- New Zealand Government-General
New Zealand
New Zealand
New Zealand is an island country in the south-western Pacific Ocean comprising two main landmasses and numerous smaller islands. The country is situated some east of Australia across the Tasman Sea, and roughly south of the Pacific island nations of New Caledonia, Fiji, and Tonga...
North
North Island
The North Island is one of the two main islands of New Zealand, separated from the much less populous South Island by Cook Strait. The island is in area, making it the world's 14th-largest island...
and South Island
South Island
The South Island is the larger of the two major islands of New Zealand, the other being the more populous North Island. It is bordered to the north by Cook Strait, to the west by the Tasman Sea, to the south and east by the Pacific Ocean...
s, Macquarie Island
Macquarie Island
Macquarie Island lies in the southwest corner of the Pacific Ocean, about half-way between New Zealand and Antarctica, at 54°30S, 158°57E. Politically, it has formed part of the Australian state of Tasmania since 1900 and became a Tasmanian State Reserve in 1978. In 1997 it became a world heritage...
, as well as the rest of the Southwest Pacific.
- Ceylon Government-General
All of India
India
India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
below a line running approximately from Portuguese Goa
Portuguese India
The Portuguese Viceroyalty of India , later the Portuguese State of India , was the aggregate of Portugal's colonial holdings in India.The government started in 1505, six years after the discovery of a sea route to India by Vasco da Gama, with the nomination of the first Viceroy Francisco de...
to the coastline of the Bay of Bengal
Bay of Bengal
The Bay of Bengal , the largest bay in the world, forms the northeastern part of the Indian Ocean. It resembles a triangle in shape, and is bordered mostly by the Eastern Coast of India, southern coast of Bangladesh and Sri Lanka to the west and Burma and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands to the...
.
- Alaska Government-General
The Alaska Territory
Alaska Territory
The Territory of Alaska was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from August 24, 1912, until January 3, 1959, when it was admitted to the Union as the State of Alaska...
, the Yukon Territory, the western portion of the Northwest Territories
Northwest Territories
The Northwest Territories is a federal territory of Canada.Located in northern Canada, the territory borders Canada's two other territories, Yukon to the west and Nunavut to the east, and three provinces: British Columbia to the southwest, and Alberta and Saskatchewan to the south...
, Alberta
Alberta
Alberta is a province of Canada. It had an estimated population of 3.7 million in 2010 making it the most populous of Canada's three prairie provinces...
, British Columbia
British Columbia
British Columbia is the westernmost of Canada's provinces and is known for its natural beauty, as reflected in its Latin motto, Splendor sine occasu . Its name was chosen by Queen Victoria in 1858...
, and Washington. There were also plans to make the American West Coast a semi-autonomous satellite state. This latter plan was not seriously considered; it depended upon a global victory of Axis forces.
- Government-General of Central America
Guatemala
Guatemala
Guatemala is a country in Central America bordered by Mexico to the north and west, the Pacific Ocean to the southwest, Belize to the northeast, the Caribbean to the east, and Honduras and El Salvador to the southeast...
, San Salvador
San Salvador
The city of San Salvador the capital and largest city of El Salvador, which has been designated a Gamma World City. Its complete name is La Ciudad de Gran San Salvador...
, Honduras
Honduras
Honduras is a republic in Central America. It was previously known as Spanish Honduras to differentiate it from British Honduras, which became the modern-day state of Belize...
, British Honduras
British Honduras
British Honduras was a British colony that is now the independent nation of Belize.First colonised by Spaniards in the 17th century, the territory on the east coast of Central America, south of Mexico, became a British crown colony from 1862 until 1964, when it became self-governing. Belize became...
, Nicaragua
Nicaragua
Nicaragua is the largest country in the Central American American isthmus, bordered by Honduras to the north and Costa Rica to the south. The country is situated between 11 and 14 degrees north of the Equator in the Northern Hemisphere, which places it entirely within the tropics. The Pacific Ocean...
, Costa Rica
Costa Rica
Costa Rica , officially the Republic of Costa Rica is a multilingual, multiethnic and multicultural country in Central America, bordered by Nicaragua to the north, Panama to the southeast, the Pacific Ocean to the west and the Caribbean Sea to the east....
, Panama
Panama
Panama , officially the Republic of Panama , is the southernmost country of Central America. Situated on the isthmus connecting North and South America, it is bordered by Costa Rica to the northwest, Colombia to the southeast, the Caribbean Sea to the north and the Pacific Ocean to the south. The...
, Colombia
Colombia
Colombia, officially the Republic of Colombia , is a unitary constitutional republic comprising thirty-two departments. The country is located in northwestern South America, bordered to the east by Venezuela and Brazil; to the south by Ecuador and Peru; to the north by the Caribbean Sea; to the...
, Maracaibo
Maracaibo
Maracaibo is a city and municipality located in northwestern Venezuela off the western coast of the Lake Maracaibo. It is the second-largest city in the country after the national capital Caracas and the capital of Zulia state...
(western) portion of Venezuela
Venezuela
Venezuela , officially called the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela , is a tropical country on the northern coast of South America. It borders Colombia to the west, Guyana to the east, and Brazil to the south...
, Ecuador
Ecuador
Ecuador , officially the Republic of Ecuador is a representative democratic republic in South America, bordered by Colombia on the north, Peru on the east and south, and by the Pacific Ocean to the west. It is one of only two countries in South America, along with Chile, that do not have a border...
, Cuba
Cuba
The Republic of Cuba is an island nation in the Caribbean. The nation of Cuba consists of the main island of Cuba, the Isla de la Juventud, and several archipelagos. Havana is the largest city in Cuba and the country's capital. Santiago de Cuba is the second largest city...
, Haiti
Haiti
Haiti , officially the Republic of Haiti , is a Caribbean country. It occupies the western, smaller portion of the island of Hispaniola, in the Greater Antillean archipelago, which it shares with the Dominican Republic. Ayiti was the indigenous Taíno or Amerindian name for the island...
, Dominica
Dominican Republic
The Dominican Republic is a nation on the island of La Hispaniola, part of the Greater Antilles archipelago in the Caribbean region. The western third of the island is occupied by the nation of Haiti, making Hispaniola one of two Caribbean islands that are shared by two countries...
, Jamaica
Jamaica
Jamaica is an island nation of the Greater Antilles, in length, up to in width and 10,990 square kilometres in area. It is situated in the Caribbean Sea, about south of Cuba, and west of Hispaniola, the island harbouring the nation-states Haiti and the Dominican Republic...
, and the Bahamas. In addition, if either Mexico
Mexico
The United Mexican States , commonly known as Mexico , is a federal constitutional republic in North America. It is bordered on the north by the United States; on the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; on the southeast by Guatemala, Belize, and the Caribbean Sea; and on the east by the Gulf of...
, Peru
Peru
Peru , officially the Republic of Peru , is a country in western South America. It is bordered on the north by Ecuador and Colombia, on the east by Brazil, on the southeast by Bolivia, on the south by Chile, and on the west by the Pacific Ocean....
or Chile
Chile
Chile ,officially the Republic of Chile , is a country in South America occupying a long, narrow coastal strip between the Andes mountains to the east and the Pacific Ocean to the west. It borders Peru to the north, Bolivia to the northeast, Argentina to the east, and the Drake Passage in the far...
were to enter the war against Japan, substantial parts of these states would also be ceded to Japan. The future of Trinidad
Trinidad
Trinidad is the larger and more populous of the two major islands and numerous landforms which make up the island nation of Trinidad and Tobago. It is the southernmost island in the Caribbean and lies just off the northeastern coast of Venezuela. With an area of it is also the fifth largest in...
, British
British Guiana
British Guiana was the name of the British colony on the northern coast of South America, now the independent nation of Guyana.The area was originally settled by the Dutch at the start of the 17th century as the colonies of Essequibo, Demerara, and Berbice...
and Dutch Guiana
Dutch Guiana
Dutch Guiana, also known as Netherlands Guyana or Dutch Guyana , is the name given to various Dutch colonies on the northern coast of South America, created by the Dutch West India Company...
, and British
British West Indies
The British West Indies was a term used to describe the islands in and around the Caribbean that were part of the British Empire The term was sometimes used to include British Honduras and British Guiana, even though these territories are not geographically part of the Caribbean...
and French
French West Indies
The term French West Indies or French Antilles refers to the seven territories currently under French sovereignty in the Antilles islands of the Caribbean: the two overseas departments of Guadeloupe and Martinique, the two overseas collectivities of Saint Martin and Saint Barthélemy, plus...
possessions in the Leeward Islands
Leeward Islands
The Leeward Islands are a group of islands in the West Indies. They are the northern islands of the Lesser Antilles chain. As a group they start east of Puerto Rico and reach southward to Dominica. They are situated where the northeastern Caribbean Sea meets the western Atlantic Ocean...
were left open for negotiations with Germany
Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany , also known as the Third Reich , but officially called German Reich from 1933 to 1943 and Greater German Reich from 26 June 1943 onward, is the name commonly used to refer to the state of Germany from 1933 to 1945, when it was a totalitarian dictatorship ruled by...
after the war.
Asian puppet states
- ManchukuoManchukuoManchukuo or Manshū-koku was a puppet state in Manchuria and eastern Inner Mongolia, governed under a form of constitutional monarchy. The region was the historical homeland of the Manchus, who founded the Qing Empire in China...
Chinese Manchuria
Manchuria
Manchuria is a historical name given to a large geographic region in northeast Asia. Depending on the definition of its extent, Manchuria usually falls entirely within the People's Republic of China, or is sometimes divided between China and Russia. The region is commonly referred to as Northeast...
.
- MengjiangMengjiangMengjiang , also known in English as Mongol Border Land, was an autonomous area in Inner Mongolia, operating under nominal Chinese sovereignty and Japanese control. It consisted of the then-Chinese provinces of Chahar and Suiyuan, corresponding to the central part of modern Inner Mongolia...
Outer Mongolia
Outer Mongolia
Outer Mongolia was a territory of the Qing Dynasty = the Manchu Empire. Its area was roughly equivalent to that of the modern state of Mongolia, which is sometimes informally called "Outer Mongolia" today...
territories west of Manchuria
Manchuria
Manchuria is a historical name given to a large geographic region in northeast Asia. Depending on the definition of its extent, Manchuria usually falls entirely within the People's Republic of China, or is sometimes divided between China and Russia. The region is commonly referred to as Northeast...
.
- Republic of China
Other parts of China occupied by Japan
Second Sino-Japanese War
The Second Sino-Japanese War was a military conflict fought primarily between the Republic of China and the Empire of Japan. From 1937 to 1941, China fought Japan with some economic help from Germany , the Soviet Union and the United States...
.
- East Indies Kingdom
Dutch East Indies
Dutch East Indies
The Dutch East Indies was a Dutch colony that became modern Indonesia following World War II. It was formed from the nationalised colonies of the Dutch East India Company, which came under the administration of the Netherlands government in 1800....
, British Borneo
British Borneo
British Borneo means the two parts of the island of Borneo presently part of the Federation of Malaysia, during the British colonial rule: Labuan and what was called British North Borneo .-Catholic missions:In 1687 Father Ventimiglia, a Theatine, was commissioned by Pope Innocent XI to...
, Labuan
Labuan
Labuan is a federal territory in East Malaysia. It is an island off the coast of the state of Sabah. Labuan's capital is Victoria and is best known as an offshore financial centre offering international financial and business services via Labuan IBFC since 1990 as well as being an offshore support...
, Sarawak
Sarawak
Sarawak is one of two Malaysian states on the island of Borneo. Known as Bumi Kenyalang , Sarawak is situated on the north-west of the island. It is the largest state in Malaysia followed by Sabah, the second largest state located to the North- East.The administrative capital is Kuching, which...
, Brunei
Brunei
Brunei , officially the State of Brunei Darussalam or the Nation of Brunei, the Abode of Peace , is a sovereign state located on the north coast of the island of Borneo, in Southeast Asia...
, the Cocos and Christmas Islands, the Andaman
Andaman Islands
The Andaman Islands are a group of Indian Ocean archipelagic islands in the Bay of Bengal between India to the west, and Burma , to the north and east...
and Nicobar Islands
Nicobar Islands
The Nicobar Islands are an archipelagic island chain in the eastern Indian Ocean...
, and Portuguese Timor
Portuguese Timor
Portuguese Timor was the name of East Timor when it was under Portuguese control. During this period, Portugal shared the island of Timor with the Netherlands East Indies, and later with Indonesia....
(to be purchased from Portugal).
- Kingdom of Burma
Burma proper, Assam
Assam
Assam , also, rarely, Assam Valley and formerly the Assam Province , is a northeastern state of India and is one of the most culturally and geographically distinct regions of the country...
(a province of the British Raj
British Raj
British Raj was the British rule in the Indian subcontinent between 1858 and 1947; The term can also refer to the period of dominion...
) and large part of Bengal.
- Kingdom of Thailand
Pre-war Thailand
Thailand
Thailand , officially the Kingdom of Thailand , formerly known as Siam , is a country located at the centre of the Indochina peninsula and Southeast Asia. It is bordered to the north by Burma and Laos, to the east by Laos and Cambodia, to the south by the Gulf of Thailand and Malaysia, and to the...
, which was also expanded with portions of British Malaya
British Malaya
British Malaya loosely described a set of states on the Malay Peninsula and the Island of Singapore that were brought under British control between the 18th and the 20th centuries...
, Burma, and French Indochina
French Indochina
French Indochina was part of the French colonial empire in southeast Asia. A federation of the three Vietnamese regions, Tonkin , Annam , and Cochinchina , as well as Cambodia, was formed in 1887....
during the war, although this wasn't included in the original plan.
- Kingdom of Malaya
Remainder of the Malay states.
- Kingdom of Cambodia
Cambodia
Cambodia
Cambodia , officially known as the Kingdom of Cambodia, is a country located in the southern portion of the Indochina Peninsula in Southeast Asia...
and French Cochinchina
Cochinchina
Cochinchina is a region encompassing the southern third of Vietnam whose principal city is Saigon. It was a French colony from 1862 to 1954. The later state of South Vietnam was created in 1954 by combining Cochinchina with southern Annam. In Vietnamese, the region is called Nam Bộ...
.
- Kingdom of Annam
Annam, Laos
Laos
Laos Lao: ສາທາລະນະລັດ ປະຊາທິປະໄຕ ປະຊາຊົນລາວ Sathalanalat Paxathipatai Paxaxon Lao, officially the Lao People's Democratic Republic, is a landlocked country in Southeast Asia, bordered by Burma and China to the northwest, Vietnam to the east, Cambodia to the south and Thailand to the west...
, and Tongking.
Soviet territories
The "Land Disposal Plan" noticeably lacked any mention of SovietSoviet Union
The Soviet Union , officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics , was a constitutionally socialist state that existed in Eurasia between 1922 and 1991....
Siberia
Siberia
Siberia is an extensive region constituting almost all of Northern Asia. Comprising the central and eastern portion of the Russian Federation, it was part of the Soviet Union from its beginning, as its predecessor states, the Tsardom of Russia and the Russian Empire, conquered it during the 16th...
n and Far Eastern
Russian Far East
Russian Far East is a term that refers to the Russian part of the Far East, i.e., extreme east parts of Russia, between Lake Baikal in Eastern Siberia and the Pacific Ocean...
lands to be taken, reflecting Japan's then-stance of non-aggression towards Russia
Soviet-Japanese Neutrality Pact
The , more extensively known as was a pact between the Empire of Japan and the Soviet Union signed on April 13, 1941, two years after the brief Soviet-Japanese Border War .- Background and history :...
while it was instead moving forward in the Pacific and South-East Asia. Nevertheless, the Imperial Army had designed military plans to be put into action in the case of a Soviet military collapse in the war against Germany. The army projected the annexation of Northern Sakhalin
Sakhalin
Sakhalin or Saghalien, is a large island in the North Pacific, lying between 45°50' and 54°24' N.It is part of Russia, and is Russia's largest island, and is administered as part of Sakhalin Oblast...
and the Kamchatka Peninsula
Kamchatka Peninsula
The Kamchatka Peninsula is a peninsula in the Russian Far East, with an area of . It lies between the Pacific Ocean to the east and the Sea of Okhotsk to the west...
and an establishment of a Japanese sphere of influence up to Lake Baikal
Lake Baikal
Lake Baikal is the world's oldest at 30 million years old and deepest lake with an average depth of 744.4 metres.Located in the south of the Russian region of Siberia, between Irkutsk Oblast to the northwest and the Buryat Republic to the southeast, it is the most voluminous freshwater lake in the...
(see Far Eastern Republic
Far Eastern Republic
The Far Eastern Republic , sometimes called the Chita Republic, was a nominally independent state that existed from April 1920 to November 1922 in the easternmost part of the Russian Far East...
). A demilitarized buffer zone between Lake Baikal and Novosibirsk
Novosibirsk
Novosibirsk is the third-largest city in Russia, after Moscow and Saint Petersburg, and the largest city of Siberia, with a population of 1,473,737 . It is the administrative center of Novosibirsk Oblast as well as of the Siberian Federal District...
was also planned.
An Axis powers conference on 18 January 1942 placed a proposed north-south running demarcation line at 70º east
70th meridian east
The meridian 70° east of Greenwich is a line of longitude that extends from the North Pole across the Arctic Ocean, Asia, the Indian Ocean, the Southern Ocean, and Antarctica to the South Pole....
longitude, going southwards through the Ob River
Ob River
The Ob River , also Obi, is a major river in western Siberia, Russia and is the world's seventh longest river. It is the westernmost of the three great Siberian rivers that flow into the Arctic Ocean .The Gulf of Ob is the world's longest estuary.-Names:The Ob is known to the Khanty people as the...
's Arctic estuary, southwards to just east of Khost
Khost
Khost or Khowst is a city in eastern Afghanistan. It is the capital of Khost province, which is a mountainous region near Afghanistan's border with Pakistan...
in Afghanistan and heading into the Indian Ocean
Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third largest of the world's oceanic divisions, covering approximately 20% of the water on the Earth's surface. It is bounded on the north by the Indian Subcontinent and Arabian Peninsula ; on the west by eastern Africa; on the east by Indochina, the Sunda Islands, and...
just west of Rajkot in India, to split the Lebensraum
Lebensraum
was one of the major political ideas of Adolf Hitler, and an important component of Nazi ideology. It served as the motivation for the expansionist policies of Nazi Germany, aiming to provide extra space for the growth of the German population, for a Greater Germany...
land holdings of Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany , also known as the Third Reich , but officially called German Reich from 1933 to 1943 and Greater German Reich from 26 June 1943 onward, is the name commonly used to refer to the state of Germany from 1933 to 1945, when it was a totalitarian dictatorship ruled by...
and the similar spazio vitale areas of Fascist Italy
Kingdom of Italy (1861–1946)
The Kingdom of Italy was a state forged in 1861 by the unification of Italy under the influence of the Kingdom of Sardinia, which was its legal predecessor state...
to the west of it, and the Empire of Japan (and the Co-Prosperity Sphere) to the east of it, after a complete defeat of the Soviet Union by the Third Reich.
Other projects
The Japanese also considered creating an enlarged Malay state in South-East Asia out of the Malay peninsulaMalay Peninsula
The Malay Peninsula or Thai-Malay Peninsula is a peninsula in Southeast Asia. The land mass runs approximately north-south and, at its terminus, is the southern-most point of the Asian mainland...
and Sumatra
Sumatra
Sumatra is an island in western Indonesia, westernmost of the Sunda Islands. It is the largest island entirely in Indonesia , and the sixth largest island in the world at 473,481 km2 with a population of 50,365,538...
, to be called Mahamalaya ("Greater Malaya").
Political parties and movements with Japanese support
- Azad Hind (IndiaIndiaIndia , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
n nationalist movement) - Indian Independence LeagueIndian Independence LeagueThe Indian Independence League was a political organisation operated from the 1920s to the 1940s to organize those living outside of India into seeking the removal of British colonial rule over India...
(Indian nationalist movement) - Indonesian Nationalist Party (IndonesiaIndonesiaIndonesia , officially the Republic of Indonesia , is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania. Indonesia is an archipelago comprising approximately 13,000 islands. It has 33 provinces with over 238 million people, and is the world's fourth most populous country. Indonesia is a republic, with an...
n nationalist movement) - Khmer IssarakKhmer IssarakThe Khmer Issarak was an anti-French, Khmer nationalist political movement formed in 1945 with the backing of the government of Thailand. It sought to expel the French colonial authorities from Cambodia, and establish an independent Khmer state....
(Cambodian-Khmer nationalist group) - Dobama Asiayone (We Burmans Association) (BurmeseBamarThe Bamar are the dominant ethnic group of Burma , constituting approximately two-thirds of the population. The Bamar live primarily in the Irrawaddy basin, and speak the Burmese language, which is also the official language of Burma. Bamar customs and identity are closely intertwined with general...
anti-British nationalist association)
See also
- Hachirō AritaHachiro Aritawas a Japanese politician and diplomat who served as the Minister for Foreign Affairs for three terms. He is believed to have originated the concept of the Greater East Asia Co-Prosperity Sphere.- Biography :...
: Army thinker who thought up the Greater East Asian concept - Satō Nobuhiro: alleged founder of the Greater East Asia concept
- East Asia Development BoardEast Asia Development BoardThe was a cabinet level agency in the Empire of Japan, created on 1938-11-18 under the first Konoe administration to coordinate the government's China policy....
- Imperialism in AsiaImperialism in AsiaImperialism in Asia traces its roots back to the late 15th century with a series of voyages that sought a sea passage to India in the hope of establishing direct trade between Europe and Asia in spices. Before 1500 European economies were largely self-sufficient, only supplemented by minor trade...
- Militarism-Socialism in Shōwa JapanStatism in Shōwa JapanStatism in Shōwa Japan was a political syncretism of Japanese right-wing political ideologies, developed over a period of time from the Meiji Restoration...
- Japanese nationalismJapanese nationalismencompasses a broad range of ideas and sentiments harbored by the Japanese people over the last two centuries regarding their native country, its cultural nature, political form and historical destiny...
- Japanese war crimesJapanese war crimesJapanese war crimes occurred during the period of Japanese imperialism, primarily during the Second Sino-Japanese War and World War II. Some of the incidents have also been described as an Asian Holocaust and Japanese war atrocities...
- Ministry of Greater East Asia (Japan)
- Greater East Asia ConferenceGreater East Asia Conferencewas an international summit held in Tokyo, Japan from 5 – 6 November 1943, in which Japan hosted the heads of state of various component members of the Greater East Asia Co-Prosperity Sphere...
(November 1943) - List of East Asian leaders in the Japanese sphere of influence (1931-1945)
- East Asia SummitEast Asia SummitThe East Asia Summit is a forum held annually by leaders of, initially, 16 countries in the East Asian region. Membership will expand to 18 countries including the United States and Russia at the Sixth EAS in 2011. EAS meetings are held after annual ASEAN leaders’ meetings...
: unrelated term in the early 21st century

