
Geological history of Earth
Encyclopedia
The geological history of Earth follows the major events in Earth's past based on the geologic time scale
, a system of chronological measurement based on the study of the planet's rock layers (stratigraphy
). Earth formed about 4.54 billion years ago
by accretion from the solar nebula
, a disk-shaped mass of dust and gas left over from the formation of the Sun, which also created the rest of the Solar System
.
Earth was initially molten due to extreme volcanism
and frequent collisions with other bodies. Eventually, the outer layer of the planet cooled to form a solid crust
when water began accumulating in the atmosphere. The Moon
formed soon afterwards, possibly as the result of a Mars
-sized object with about 10% of the Earth's mass impacting the planet
in a glancing blow. Some of this object's mass merged with the Earth, significantly altering its internal composition, and a portion was ejected into space. Some of the material survived to form an orbiting moon. Outgassing and volcanic
activity produced the primordial atmosphere. Condensing water vapor
, augmented by ice delivered from comet
s, produced the oceans.
As the surface continually reshaped itself over hundreds of millions of years, continents formed and broke apart. They migrated across the surface
, occasionally combining to form a supercontinent
. Roughly 750 Ma (million years ago), the earliest-known supercontinent Rodinia
, began to break apart. The continents later recombined to form Pannotia
, 600–540 Ma, then finally Pangaea
, which broke apart 180 Ma.
The present pattern of ice age
s began about 40 Ma, then intensified during the Pleistocene
about 3 Ma. The polar regions have since undergone repeated cycles of glaciation and thaw, repeating every 40,000–100,000 years. The last glacial period of the current ice age ended about 10,000 years ago.
See the Table of Contents below for an overview of the major divisions that constitute the geologic time scale.
It includes three eons, the Hadean, Archean, and Proterozoic Eons.
 During Hadean
During Hadean
time (4.6–3.8 Ga), the Solar System
was forming, probably within a large cloud of gas and dust around the sun, called an accretion disc
. The Hadean Eon is not formally recognized, but it essentially marks the era before there were any rocks. The oldest dated zircons date from about 4400 Ma (million years ago) – very close to the hypothesized time of the Earth's formation.
During the Hadean period the Late Heavy Bombardment
occurred (approximately 3800 to 4100 Ma) during which a large number of impact craters are believed to have formed on the Moon
, and by inference on Earth
, Mercury
, Venus
and Mars
as well.
(3,800-2,500 Ma) may have had a different tectonic style. During this time, the Earth's crust
cooled enough that rocks and continental plates began to form. Some scientists think because the Earth was hotter, that plate tectonic activity was more vigorous than it is today, resulting in a much greater rate of recycling of crustal material. This may have prevented cratonisation and continent formation until the mantle
cooled and convection slowed down. Others argue that the subcontinental lithospheric mantle is too buoyant to subduct
and that the lack of Archean rocks is a function of erosion
and subsequent tectonic events.
In contrast to the Proterozoic
, Archean rocks are often heavily metamorphized deep-water sediments, such as graywackes, mudstone
s, volcanic sediments and banded iron formation
s. Greenstone belt
s are typical Archean formations, consisting of alternating high- and low-grade metamorphic rocks. The high-grade rocks were derived from volcanic island arc
s, while the low-grade metamorphic rocks represent deep-sea sediments eroded from the neighboring island arcs and deposited in a forearc basin
. In short, greenstone belts represent sutured protocontinents.
By 3.5 billion years ago, the Earth's magnetic field
was established. The solar wind
flux was about 100 times the value of the modern Sun
, so the presence of the magnetic field helped prevent the planet's atmosphere from being stripped away, which is what likely happened to the atmosphere of Mars
. However, the field strength was lower than at present and the magnetosphere
was about half the modern radius.
. In contrast to the deep-water deposits of the Archean, the Proterozoic features many strata
that were laid down in extensive shallow epicontinental seas
; furthermore, many of these rocks are less metamorphosed
than Archean-age ones, and plenty are unaltered. Study of these rocks show that the eon featured massive, rapid continent
al accretion (unique to the Proterozoic), supercontinent cycle
s, and wholly modern orogenic
activity.
The first-known glaciations occurred during the Proterozoic, one began shortly after the beginning of the eon, while there were at least four during the Neoproterozoic, climaxing with the Snowball Earth
of the Varangian glaciation.
The Phanerozoic is divided into three eras — the Paleozoic
, the Mesozoic
and the Cenozoic
.
, Ordovician
, Silurian
, Devonian, Carboniferous
and Permian
. Geologically, the Paleozoic
starts shortly after the breakup of a supercontinent called Pannotia
and at the end of a global ice age. Throughout the early Paleozoic, the Earth's landmass was broken up into a substantial number of relatively small continents. Toward the end of the era the continents gathered together into a supercontinent called Pangaea
, which included most of the Earth's land area.
continents are thought to have resulted from the breakup of a Neoproterozoic
supercontinent called Pannotia. The waters of the Cambrian period appear to have been widespread and shallow. Continental drift rates may have been anomalously high. Laurentia
, Baltica
and Siberia
remained independent continents following the break-up of the supercontinent of Pannotia. Gondwana
started to drift toward the South Pole. Panthalassa
covered most of the southern hemisphere, and minor oceans included the Proto-Tethys Ocean
, Iapetus Ocean
and Khanty Ocean
.
some time about 488.3 ± 1.7 Ma. During the Ordovician
the southern continents were collected into a single continent called Gondwana. Gondwana started the period in the equatorial latitudes and, as the period progressed, drifted toward the South Pole. Early in the Ordovician the continents Laurentia, Siberia and Baltica were still independent continents (since the break-up of the supercontinent Pannotia earlier), but Baltica
began to move toward Laurentia later in the period, causing the Iapetus Ocean to shrink between them. Also, Avalonia
broke free from Gondwana and began to head north toward Laurentia. The Rheic Ocean
was formed as a result of this. By the end of the period, Gondwana had neared or approached the pole and was largely glaciated.
The Ordovician came to a close in a series of extinction event
s that, taken together, comprise the second-largest of the five major extinction events in Earth's history
in terms of percentage of genera
that went extinct. The only larger one was the Permian-Triassic extinction event. The extinctions occurred approximately 444-447 Ma and mark the boundary between the Ordovician and the following Silurian
Period.
The most-commonly accepted theory is that these events were triggered by the onset of an ice age
, in the Hirnantian faunal stage that ended the long, stable greenhouse
conditions typical of the Ordovician. The ice age was probably not as long-lasting as once thought; study of oxygen isotopes in fossil brachiopods shows that it was probably no longer than 0.5 to 1.5 million years. The event was preceded by a fall in atmospheric carbon dioxide (from 7000ppm to 4400ppm) which selectively affected the shallow seas where most organisms lived. As the southern supercontinent Gondwana
drifted over the South Pole, ice caps formed on it. Evidence of these ice caps have been detected in Upper Ordovician rock strata of North Africa
and then-adjacent northeastern South America, which were south-polar locations at the time.
, Gondwana continued a slow southward drift to high southern latitudes, but there is evidence that the Silurian ice caps were less extensive than those of the late Ordovician glaciation. The melting of ice caps and glaciers contributed to a rise in sea level
s, recognizable from the fact that Silurian sediments overlie eroded Ordovician sediments, forming an unconformity
. Other craton
s and continent fragments drifted together near the equator, starting the formation of a second supercontinent known as Euramerica
. The vast ocean of Panthalassa covered most of the northern hemisphere. Other minor oceans include Proto-Tethys, Paleo-Tethys, Rheic Ocean, a seaway of Iapetus Ocean (now in between Avalonia and Laurentia), and newly formed Ural Ocean
.
and Gondwanaland drew closer together. The continent Euramerica (or Laurussia) was created in the early Devonian by the collision of Laurentia and Baltica, which rotated into the natural dry zone along the Tropic of Capricorn
. In these near-deserts, the Old Red Sandstone
sedimentary beds formed, made red by the oxidized iron (hematite
) characteristic of drought conditions. Near the equator Pangaea began to consolidate from the plates containing North America and Europe, further raising the northern Appalachian Mountains
and forming the Caledonian Mountains in Great Britain
and Scandinavia
. The southern continents remained tied together in the supercontinent of Gondwana
. The remainder of modern Eurasia lay in the Northern Hemisphere. Sea levels were high worldwide, and much of the land lay submerged under shallow seas. The deep, enormous Panthalassa (the "universal ocean") covered the rest of the planet. Other minor oceans were Paleo-Tethys, Proto-Tethys, Rheic Ocean and Ural Ocean (which was closed during the collision with Siberia and Baltica).
A global drop in sea level at the end of the Devonian reversed early in the Carboniferous
; this created the widespread epicontinental seas and carbonate deposition of the Mississippian. There was also a drop in south polar temperatures; southern Gondwanaland was glaciated throughout the period, though it is uncertain if the ice sheets were a holdover from the Devonian or not. These conditions apparently had little effect in the deep tropics, where lush coal
swamps flourished within 30 degrees of the northernmost glaciers. A mid-Carboniferous drop in sea-level precipitated a major marine extinction, one that hit crinoid
s and ammonite
s especially hard. This sea-level drop and the associated unconformity in North America separate the Mississippian Period from the Pennsylvanian period.
The Carboniferous was a time of active mountain building, as the supercontinent Pangea came together. The southern continents remained tied together in the supercontinent Gondwana, which collided with North America-Europe (Laurussia) along the present line of eastern North America
. This continental collision resulted in the Hercynian orogeny in Europe, and the Alleghenian orogeny
in North America; it also extended the newly uplifted Appalachians southwestward as the Ouachita Mountains
. In the same time frame, much of present eastern Eurasian
plate welded itself to Europe along the line of the Ural mountains
. There were two major oceans in the Carboniferous the Panthalassa and Paleo-Tethys. Other minor oceans were shrinking and eventually closed the Rheic Ocean
(closed by the assembly of South and North America), the small, shallow Ural Ocean
(which was closed by the collision of Baltica
, and Siberia
continents, creating the Ural Mountains) and Proto-Tethys Ocean.
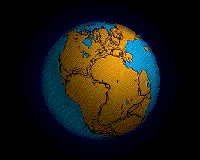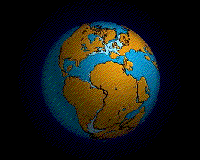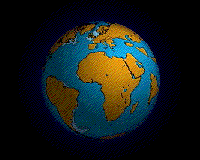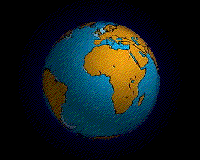
During the Permian
all the Earth's major land masses, except portions of East Asia, were collected into a single supercontinent known as Pangaea
. Pangaea straddled the equator and extended toward the poles, with a corresponding effect on ocean currents in the single great ocean (Panthalassa
, the universal sea), and the Paleo-Tethys Ocean
, a large ocean that was between Asia and Gondwana. The Cimmeria continent rifted away from Gondwana and drifted north to Laurasia, causing the Paleo-Tethys to shrink. A new ocean was growing on its southern end, the Tethys Ocean, an ocean that would dominate much of the Mesozoic Era. Large continental landmasses create climates with extreme variations of heat and cold ("continental climate") and monsoon conditions with highly seasonal rainfall patterns. Desert
s seem to have been widespread on Pangaea.
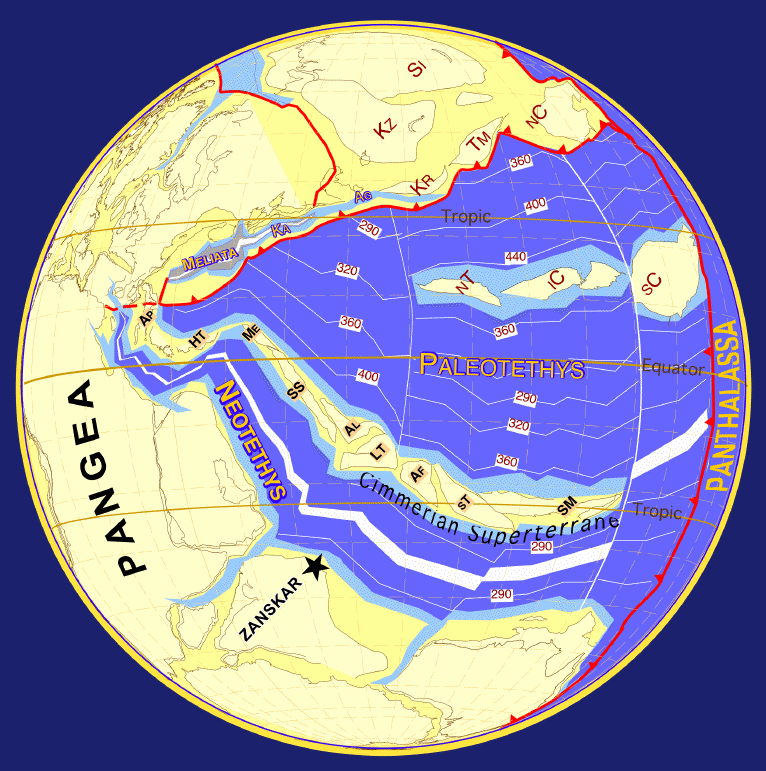
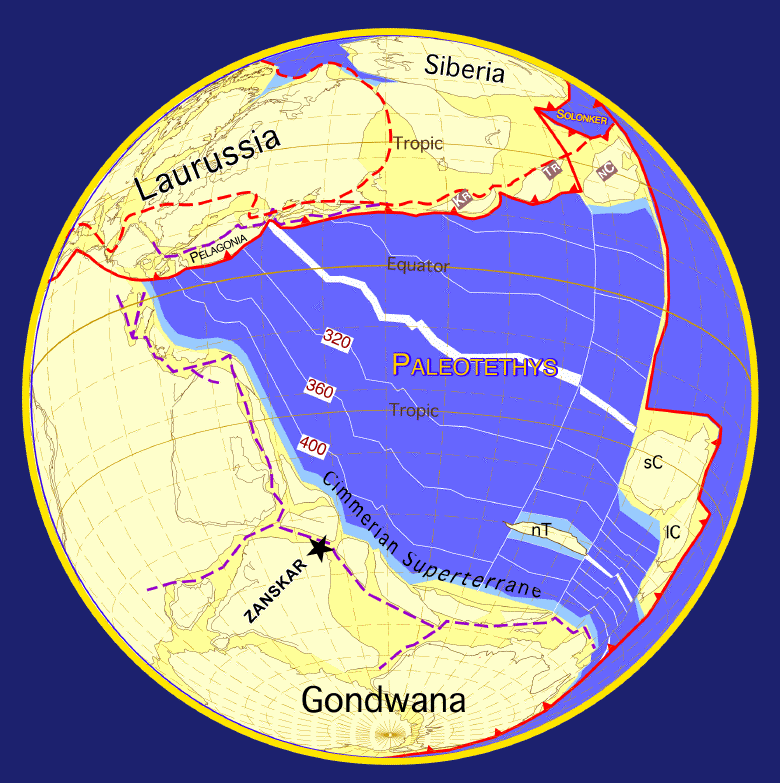 The Mesozoic extended roughly from 251 Ma to 65 Ma.
The Mesozoic extended roughly from 251 Ma to 65 Ma.
After the vigorous convergent plate mountain-building of the late Paleozoic
, Mesozoic
tectonic deformation was comparatively mild. Nevertheless, the era featured the dramatic rifting of the supercontinent Pangaea
. Pangaea gradually split into a northern continent, Laurasia
, and a southern continent, Gondwana
. This created the passive continental margin that characterizes most of the Atlantic coastline (such as along the U.S. East Coast) today.
, almost all the Earth's land mass was concentrated into a single supercontinent
centered more or less on the equator, called Pangaea
("all the land"). This took the form of a giant "Pac-Man
" with an east-facing "mouth" constituting the Tethys sea
, a vast gulf that opened farther westward in the mid-Triassic, at the expense of the shrinking Paleo-Tethys Ocean
, an ocean that existed during the Paleozoic
.
The remainder was the world-ocean known as Panthalassa
("all the sea"). All the deep-ocean sediments laid down during the Triassic have disappeared through subduction
of oceanic plates; thus, very little is known of the Triassic open ocean. The supercontinent Pangaea was rifting during the Triassic—especially late in the period—but had not yet separated. The first nonmarine sediments in the rift
that marks the initial break-up of Pangea—which separated New Jersey
from Morocco
—are of Late Triassic age; in the U.S., these thick sediments comprise the Newark Supergroup.
Because of the limited shoreline of one super-continental mass, Triassic marine deposits are globally relatively rare; despite their prominence in Western Europe
, where the Triassic was first studied. In North America
, for example, marine deposits are limited to a few exposures in the west. Thus Triassic stratigraphy
is mostly based on organisms living in lagoons and hypersaline environments, such as Estheria crustaceans and terrestrial vertebrates.
During the early Jurassic
, the supercontinent Pangaea
broke up into the northern supercontinent Laurasia
and the southern supercontinent Gondwana
; the Gulf of Mexico
opened in the new rift between North America and what is now Mexico
's Yucatan Peninsula
. The Jurassic North Atlantic Ocean
was relatively narrow, while the South Atlantic did not open until the following Cretaceous Period, when Gondwana itself rifted apart.
The Tethys Sea
closed, and the Neotethys
basin appeared. Climates were warm, with no evidence of glaciation
. As in the Triassic, there was apparently no land near either pole, and no extensive ice caps existed. The Jurassic geological record is good in western Europe
, where extensive marine sequences indicate a time when much of the continent was submerged under shallow tropical seas; famous locales include the Jurassic Coast
World Heritage Site
and the renowned late Jurassic lagerstätte
n of Holzmaden
and Solnhofen
.
In contrast, the North American Jurassic record is the poorest of the Mesozoic, with few outcrops at the surface. Though the epicontinental
Sundance Sea
left marine deposits in parts of the northern plains of the United States
and Canada
during the late Jurassic, most exposed sediments from this period are continental, such as the alluvial
deposits of the Morrison Formation
. The first of several massive batholith
s were emplaced in the northern Cordillera
beginning in the mid-Jurassic, marking the Nevadan orogeny
. Important Jurassic exposures are also found in Russia
, India
, South America
, Japan
, Australasia
and the United Kingdom
.
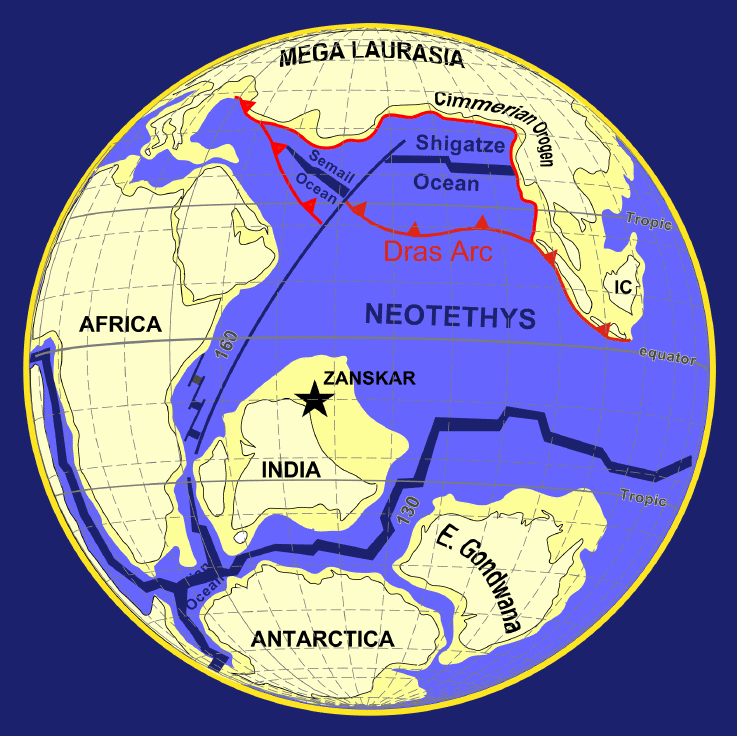 The Cretaceous Period extends from about 145.5 ± 4.0 Ma to about 65.5 ± 0.3 Ma.
The Cretaceous Period extends from about 145.5 ± 4.0 Ma to about 65.5 ± 0.3 Ma.
During the Cretaceous
, the late Paleozoic
-early Mesozoic supercontinent
of Pangaea
completed its breakup into present day continent
s, although their positions were substantially different at the time. As the Atlantic Ocean
widened, the convergent-margin orogenies
that had begun during the Jurassic continued in the North American Cordillera
, as the Nevadan orogeny
was followed by the Sevier
and Laramide orogenies
. Though Gondwana was still intact in the beginning of the Cretaceous, Gondwana
itself broke up as South America
, Antarctica and Australia
rifted away from Africa
(though India
and Madagascar
remained attached to each other); thus, the South Atlantic and Indian Ocean
s were newly formed. Such active rifting lifted great undersea mountain chains along the welts, raising eustatic sea levels
worldwide.
To the north of Africa the Tethys Sea continued to narrow. Broad shallow seas advanced across central North America
(the Western Interior Seaway
) and Europe, then receded late in the period, leaving thick marine deposits sandwiched between coal
beds. At the peak of the Cretaceous transgression
, one-third of Earth's present land area was submerged. The Cretaceous is justly famous for its chalk
; indeed, more chalk formed in the Cretaceous than in any other period in the Phanerozoic
. Mid-ocean ridge
activity—or rather, the circulation of seawater through the enlarged ridges—enriched the oceans in calcium; this made the oceans more saturated, as well as increased the bioavailability of the element for calcareous nanoplankton. These widespread carbonate
s and other sedimentary deposits
make the Cretaceous rock record especially fine. Famous formations
from North America include the rich marine fossils of Kansas
's Smoky Hill Chalk Member
and the terrestrial fauna of the late Cretaceous Hell Creek Formation
. Other important Cretaceous exposures occur in Europe
and China
. In the area that is now India, massive lava
beds called the Deccan Traps
were laid down in the very late Cretaceous and early Paleocene.
up to and including the present day. By the end of the Mesozoic
era, the continents had rifted into nearly their present form. Laurasia
became North America
and Eurasia
, while Gondwana
split into South America
, Africa
, Australia
, Antarctica and the Indian subcontinent
, which collided with the Asian plate. This impact gave rise to the Himalayas. The Tethys Sea, which had separated the northern continents from Africa and India, began to close up, forming the Mediterranean sea
.
Era. This period consists of the Paleocene
, Eocene
and Oligocene
Epochs.
The Paleocene, lasted from 65.5 ± 0.3 Ma to 55.8 ± 0.2 Ma.
In many ways, the Paleocene
continued processes that had begun during the late Cretaceous Period. During the Paleocene, the continent
s continued to drift toward their present positions. Supercontinent Laurasia
had not yet separated into three continents. Europe
and Greenland
were still connected. North America
and Asia
were still intermittently joined by a land bridge, while Greenland and North America were beginning to separate. The Laramide orogeny
of the late Cretaceous continued to uplift the Rocky Mountains
in the American west, which ended in the succeeding epoch. South and North America remained separated by equatorial seas (they joined during the Neogene
); the components of the former southern supercontinent Gondwanaland continued to split apart, with Africa
, South America, Antarctica and Australia
pulling away from each other. Africa was heading north toward Europe
, slowly closing the Tethys Ocean
, and India
began its migration to Asia that would lead to a tectonic collision and the formation of the Himalayas
.
During the Eocene
(55.8 ± 0.2 - 33.9 ± 0.1 Ma), the continents continued to drift toward their present positions. At the beginning of the period, Australia and Antarctica remained connected, and warm equator
ial currents mixed with colder Antarctic waters, distributing the heat around the world and keeping global temperatures high. But when Australia split from the southern continent around 45 Ma, the warm equatorial currents were deflected away from Antarctica, and an isolated cold water channel developed between the two continents. The Antarctic region cooled down, and the ocean surrounding Antarctica began to freeze, sending cold water and ice floes north, reinforcing the cooling. The northern supercontinent
of Laurasia
began to break up, as Europe
, Greenland
and North America
drifted apart. In western North America, mountain building
started in the Eocene, and huge lakes formed in the high flat basins among uplifts. In Europe, the Tethys Sea finally vanished, while the uplift of the Alps
isolated its final remnant, the Mediterranean
, and created another shallow sea with island archipelago
s to the north. Though the North Atlantic
was opening, a land connection appears to have remained between North America and Europe since the faunas of the two regions are very similar. India
continued its journey away from Africa
and began its collision with Asia
, creating the Himalayan orogeny.
The Oligocene Epoch extends from about 34 Ma to 23 Ma. During the Oligocene
the continents continued to drift toward their present positions.
Antarctica continued to become more isolated and finally developed a permanent ice cap
. Mountain building
in western North America
continued, and the Alps
started to rise in Europe
as the African plate
continued to push north into the Eurasian plate
, isolating the remnants of Tethys Sea. A brief marine incursion marks the early Oligocene in Europe. There appears to have been a land bridge in the early Oligocene between North America
and Europe
since the faunas of the two regions are very similar. During the Oligocene, South America
was finally detached from Antarctica and drifted north toward North America
. It also allowed the Antarctic Circumpolar Current
to flow, rapidly cooling the continent.
Period. Under the current proposal of the International Commission on Stratigraphy
(ICS), the Neogene would consist of the Miocene
, Pliocene
, Pleistocene
and Holocene
epochs and continue until the present.
The Miocene extends from about 23.03 to 5.332 Ma.
During the Miocene
continents continued to drift toward their present positions. Of the modern geologic features, only the land bridge between South America
and North America
was absent, the subduction zone along the Pacific Ocean
margin of South America caused the rise of the Andes
and the southward extension of the Meso-American peninsula. India
continued to collide with Asia
. The Tethys Seaway continued to shrink and then disappeared as Africa
collided with Eurasia
in the Turkish
-Arabian region between 19 and 12 Ma (ICS
2004). Subsequent uplift of mountains in the western Mediterranean region and a global fall in sea levels combined to cause a temporary drying up of the Mediterranean Sea resulting in the Messinian salinity crisis
near the end of the Miocene.
The Pliocene extends from 5.332 Ma to 2.588 Ma. During the Pliocene
continents continued to drift toward their present positions, moving from positions possibly as far as 250 kilometres (155 mi) from their present locations to positions only 70 km from their current locations.
South America became linked to North America through the Isthmus of Panama
during the Pliocene, bringing a nearly complete end to South America's distinctive marsupial faunas. The formation of the Isthmus had major consequences on global temperatures, since warm equatorial ocean currents were cut off and an Atlantic cooling cycle began, with cold Arctic and Antarctic waters dropping temperatures in the now-isolated Atlantic Ocean. Africa
's collision with Europe
formed the Mediterranean Sea
, cutting off the remnants of the Tethys Ocean
. Sea level changes exposed the land-bridge between Alaska
and Asia. Near the end of the Pliocene, about 2.58 Ma (the start the of the Quaternary
Period), the current ice age
began.
The Pleistocene extends from 2.588 million to 11,700 years before present. The modern continent
s were essentially at their present positions during the Pleistocene
, the plates upon which they sit probably having moved no more than 100 kilometres (62 mi) relative to each other since the beginning of the period.
The Holocene Epoch began approximately 11,550 calendar years before present and continues to the present. During the Holocene
, continental motions have been less than a kilometer.
However, ice melt caused world sea levels to rise about 35 metres (115 ft) in the early part of the Holocene. In addition, many areas above about 40 degrees north
latitude had been depressed by the weight of the Pleistocene glacier
s and rose as much as 180 metres (591 ft) over the late Pleistocene and Holocene, and are still rising today. The sea level rise and temporary land depression allowed temporary marine incursions into areas that are now far from the sea. Holocene marine fossils are known from Vermont
, Quebec
, Ontario
and Michigan
. Other than higher latitude temporary marine incursions associated with glacial depression, Holocene fossils are found primarily in lakebed, floodplain and cave deposits. Holocene marine deposits along low-latitude coastlines are rare because the rise in sea levels during the period exceeds any likely upthrusting of non-glacial origin. Post-glacial rebound
in Scandinavia
resulted in the emergence of coastal areas around the Baltic Sea
, including much of Finland
. The region continues to rise, still causing weak earthquake
s across Northern Europe
. The equivalent event in North America was the rebound of Hudson Bay
, as it shrank from its larger, immediate post-glacial Tyrrell Sea
phase, to near its present boundaries.
Geologic time scale
The geologic time scale provides a system of chronologic measurement relating stratigraphy to time that is used by geologists, paleontologists and other earth scientists to describe the timing and relationships between events that have occurred during the history of the Earth...
, a system of chronological measurement based on the study of the planet's rock layers (stratigraphy
Stratigraphy
Stratigraphy, a branch of geology, studies rock layers and layering . It is primarily used in the study of sedimentary and layered volcanic rocks....
). Earth formed about 4.54 billion years ago
Age of the Earth
The age of the Earth is 4.54 billion years This age is based on evidence from radiometric age dating of meteorite material and is consistent with the ages of the oldest-known terrestrial and lunar samples...
by accretion from the solar nebula
Solar nebula
In cosmogony, the nebular hypothesis is the most widely accepted model explaining the formation and evolution of the Solar System. There is evidence that it was first proposed in 1734 by Emanuel Swedenborg. Originally applied only to our own Solar System, this method of planetary system formation...
, a disk-shaped mass of dust and gas left over from the formation of the Sun, which also created the rest of the Solar System
Solar System
The Solar System consists of the Sun and the astronomical objects gravitationally bound in orbit around it, all of which formed from the collapse of a giant molecular cloud approximately 4.6 billion years ago. The vast majority of the system's mass is in the Sun...
.
Earth was initially molten due to extreme volcanism
Volcanism
Volcanism is the phenomenon connected with volcanoes and volcanic activity. It includes all phenomena resulting from and causing magma within the crust or mantle of a planet to rise through the crust and form volcanic rocks on the surface....
and frequent collisions with other bodies. Eventually, the outer layer of the planet cooled to form a solid crust
Crust (geology)
In geology, the crust is the outermost solid shell of a rocky planet or natural satellite, which is chemically distinct from the underlying mantle...
when water began accumulating in the atmosphere. The Moon
Moon
The Moon is Earth's only known natural satellite,There are a number of near-Earth asteroids including 3753 Cruithne that are co-orbital with Earth: their orbits bring them close to Earth for periods of time but then alter in the long term . These are quasi-satellites and not true moons. For more...
formed soon afterwards, possibly as the result of a Mars
Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun in the Solar System. The planet is named after the Roman god of war, Mars. It is often described as the "Red Planet", as the iron oxide prevalent on its surface gives it a reddish appearance...
-sized object with about 10% of the Earth's mass impacting the planet
Giant impact hypothesis
The giant impact hypothesis states that the Moon was created out of the debris left over from a collision between the young Earth and a Mars-sized body. The colliding body is sometimes called Theia for the mythical Greek Titan who was the mother of Selene, the goddess of the moon.The giant impact...
in a glancing blow. Some of this object's mass merged with the Earth, significantly altering its internal composition, and a portion was ejected into space. Some of the material survived to form an orbiting moon. Outgassing and volcanic
Volcano
2. Bedrock3. Conduit 4. Base5. Sill6. Dike7. Layers of ash emitted by the volcano8. Flank| 9. Layers of lava emitted by the volcano10. Throat11. Parasitic cone12. Lava flow13. Vent14. Crater15...
activity produced the primordial atmosphere. Condensing water vapor
Water vapor
Water vapor or water vapour , also aqueous vapor, is the gas phase of water. It is one state of water within the hydrosphere. Water vapor can be produced from the evaporation or boiling of liquid water or from the sublimation of ice. Under typical atmospheric conditions, water vapor is continuously...
, augmented by ice delivered from comet
Comet
A comet is an icy small Solar System body that, when close enough to the Sun, displays a visible coma and sometimes also a tail. These phenomena are both due to the effects of solar radiation and the solar wind upon the nucleus of the comet...
s, produced the oceans.
As the surface continually reshaped itself over hundreds of millions of years, continents formed and broke apart. They migrated across the surface
Plate tectonics
Plate tectonics is a scientific theory that describes the large scale motions of Earth's lithosphere...
, occasionally combining to form a supercontinent
Supercontinent
In geology, a supercontinent is a landmass comprising more than one continental core, or craton. The assembly of cratons and accreted terranes that form Eurasia qualifies as a supercontinent today.-History:...
. Roughly 750 Ma (million years ago), the earliest-known supercontinent Rodinia
Rodinia
In geology, Rodinia is the name of a supercontinent, a continent which contained most or all of Earth's landmass. According to plate tectonic reconstructions, Rodinia existed between 1.1 billion and 750 million years ago, in the Neoproterozoic era...
, began to break apart. The continents later recombined to form Pannotia
Pannotia
Pannotia, first described by Ian W. D. Dalziel in 1997, is a hypothetical supercontinent that existed from the Pan-African orogeny about six hundred million years ago to the end of the Precambrian about five hundred and fifty million years ago. It is also known as the Vendian supercontinent...
, 600–540 Ma, then finally Pangaea
Pangaea
Pangaea, Pangæa, or Pangea is hypothesized as a supercontinent that existed during the Paleozoic and Mesozoic eras about 250 million years ago, before the component continents were separated into their current configuration....
, which broke apart 180 Ma.
The present pattern of ice age
Ice age
An ice age or, more precisely, glacial age, is a generic geological period of long-term reduction in the temperature of the Earth's surface and atmosphere, resulting in the presence or expansion of continental ice sheets, polar ice sheets and alpine glaciers...
s began about 40 Ma, then intensified during the Pleistocene
Pleistocene
The Pleistocene is the epoch from 2,588,000 to 11,700 years BP that spans the world's recent period of repeated glaciations. The name pleistocene is derived from the Greek and ....
about 3 Ma. The polar regions have since undergone repeated cycles of glaciation and thaw, repeating every 40,000–100,000 years. The last glacial period of the current ice age ended about 10,000 years ago.
See the Table of Contents below for an overview of the major divisions that constitute the geologic time scale.
Precambrian
Precambrian includes approximately 90% of geologic time. It extends from 4.6 billion years ago to the beginning of the Cambrian Period (about 570 Ma).It includes three eons, the Hadean, Archean, and Proterozoic Eons.
Hadean Eon

Hadean
The Hadean is the geologic eon before the Archean. It started with the formation of the Earth about 4.7 Ga and ended roughly 3.8 Ga, though the latter date varies according to different sources. The name "Hadean" derives from Hades, Greek for "Underworld", referring to the "hellish"...
time (4.6–3.8 Ga), the Solar System
Solar System
The Solar System consists of the Sun and the astronomical objects gravitationally bound in orbit around it, all of which formed from the collapse of a giant molecular cloud approximately 4.6 billion years ago. The vast majority of the system's mass is in the Sun...
was forming, probably within a large cloud of gas and dust around the sun, called an accretion disc
Accretion disc
An accretion disc is a structure formed by diffuse material in orbital motion around a central body. The central body is typically a star. Gravity causes material in the disc to spiral inward towards the central body. Gravitational forces compress the material causing the emission of...
. The Hadean Eon is not formally recognized, but it essentially marks the era before there were any rocks. The oldest dated zircons date from about 4400 Ma (million years ago) – very close to the hypothesized time of the Earth's formation.
During the Hadean period the Late Heavy Bombardment
Late Heavy Bombardment
The Late Heavy Bombardment is a period of time approximately 4.1 to 3.8 billion years ago during which a large number of impact craters are believed to have formed on the Moon, and by inference on Earth, Mercury, Venus, and Mars as well...
occurred (approximately 3800 to 4100 Ma) during which a large number of impact craters are believed to have formed on the Moon
Moon
The Moon is Earth's only known natural satellite,There are a number of near-Earth asteroids including 3753 Cruithne that are co-orbital with Earth: their orbits bring them close to Earth for periods of time but then alter in the long term . These are quasi-satellites and not true moons. For more...
, and by inference on Earth
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun, and the densest and fifth-largest of the eight planets in the Solar System. It is also the largest of the Solar System's four terrestrial planets...
, Mercury
Mercury (planet)
Mercury is the innermost and smallest planet in the Solar System, orbiting the Sun once every 87.969 Earth days. The orbit of Mercury has the highest eccentricity of all the Solar System planets, and it has the smallest axial tilt. It completes three rotations about its axis for every two orbits...
, Venus
Venus
Venus is the second planet from the Sun, orbiting it every 224.7 Earth days. The planet is named after Venus, the Roman goddess of love and beauty. After the Moon, it is the brightest natural object in the night sky, reaching an apparent magnitude of −4.6, bright enough to cast shadows...
and Mars
Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun in the Solar System. The planet is named after the Roman god of war, Mars. It is often described as the "Red Planet", as the iron oxide prevalent on its surface gives it a reddish appearance...
as well.
Archean Eon
The Earth of the early ArcheanArchean
The Archean , also spelled Archeozoic or Archæozoic) is a geologic eon before the Paleoproterozoic Era of the Proterozoic Eon, before 2.5 Ga ago. Instead of being based on stratigraphy, this date is defined chronometrically...
(3,800-2,500 Ma) may have had a different tectonic style. During this time, the Earth's crust
Crust (geology)
In geology, the crust is the outermost solid shell of a rocky planet or natural satellite, which is chemically distinct from the underlying mantle...
cooled enough that rocks and continental plates began to form. Some scientists think because the Earth was hotter, that plate tectonic activity was more vigorous than it is today, resulting in a much greater rate of recycling of crustal material. This may have prevented cratonisation and continent formation until the mantle
Mantle (geology)
The mantle is a part of a terrestrial planet or other rocky body large enough to have differentiation by density. The interior of the Earth, similar to the other terrestrial planets, is chemically divided into layers. The mantle is a highly viscous layer between the crust and the outer core....
cooled and convection slowed down. Others argue that the subcontinental lithospheric mantle is too buoyant to subduct
Subduction
In geology, subduction is the process that takes place at convergent boundaries by which one tectonic plate moves under another tectonic plate, sinking into the Earth's mantle, as the plates converge. These 3D regions of mantle downwellings are known as "Subduction Zones"...
and that the lack of Archean rocks is a function of erosion
Erosion
Erosion is when materials are removed from the surface and changed into something else. It only works by hydraulic actions and transport of solids in the natural environment, and leads to the deposition of these materials elsewhere...
and subsequent tectonic events.
In contrast to the Proterozoic
Proterozoic
The Proterozoic is a geological eon representing a period before the first abundant complex life on Earth. The name Proterozoic comes from the Greek "earlier life"...
, Archean rocks are often heavily metamorphized deep-water sediments, such as graywackes, mudstone
Mudstone
Mudstone is a fine grained sedimentary rock whose original constituents were clays or muds. Grain size is up to 0.0625 mm with individual grains too small to be distinguished without a microscope. With increased pressure over time the platey clay minerals may become aligned, with the...
s, volcanic sediments and banded iron formation
Banded iron formation
Banded iron formations are distinctive units of sedimentary rock that are almost always of Precambrian age. A typical BIF consists of repeated, thin layers of iron oxides, either magnetite or hematite , alternating with bands of iron-poor shale and chert...
s. Greenstone belt
Greenstone belt
Greenstone belts are zones of variably metamorphosed mafic to ultramafic volcanic sequences with associated sedimentary rocks that occur within Archaean and Proterozoic cratons between granite and gneiss bodies....
s are typical Archean formations, consisting of alternating high- and low-grade metamorphic rocks. The high-grade rocks were derived from volcanic island arc
Island arc
An island arc is a type of archipelago composed of a chain of volcanoes which alignment is arc-shaped, and which are situated parallel and close to a boundary between two converging tectonic plates....
s, while the low-grade metamorphic rocks represent deep-sea sediments eroded from the neighboring island arcs and deposited in a forearc basin
Forearc
A forearc or forarc, also called arc-trench gap is a depression in the sea floor located between a subduction zone and an associated volcanic arc. It is typically filled with sediments from the adjacent landmass and the island arc in addition to trapped oceanic crustal material...
. In short, greenstone belts represent sutured protocontinents.
By 3.5 billion years ago, the Earth's magnetic field
Magnetic field
A magnetic field is a mathematical description of the magnetic influence of electric currents and magnetic materials. The magnetic field at any given point is specified by both a direction and a magnitude ; as such it is a vector field.Technically, a magnetic field is a pseudo vector;...
was established. The solar wind
Solar wind
The solar wind is a stream of charged particles ejected from the upper atmosphere of the Sun. It mostly consists of electrons and protons with energies usually between 1.5 and 10 keV. The stream of particles varies in temperature and speed over time...
flux was about 100 times the value of the modern Sun
Sun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is almost perfectly spherical and consists of hot plasma interwoven with magnetic fields...
, so the presence of the magnetic field helped prevent the planet's atmosphere from being stripped away, which is what likely happened to the atmosphere of Mars
Atmosphere of Mars
The atmosphere of Mars is relatively thin and is composed mostly of carbon dioxide . There has been interest in studying its composition since the detection of trace amounts of methane, which may indicate the presence of life on Mars, but may also be produced by a geochemical process, volcanic or...
. However, the field strength was lower than at present and the magnetosphere
Magnetosphere
A magnetosphere is formed when a stream of charged particles, such as the solar wind, interacts with and is deflected by the intrinsic magnetic field of a planet or similar body. Earth is surrounded by a magnetosphere, as are the other planets with intrinsic magnetic fields: Mercury, Jupiter,...
was about half the modern radius.
Proterozoic Eon
The geologic record of the Proterozoic (2,500-570 Ma) is much better than that for the preceding ArcheanArchean
The Archean , also spelled Archeozoic or Archæozoic) is a geologic eon before the Paleoproterozoic Era of the Proterozoic Eon, before 2.5 Ga ago. Instead of being based on stratigraphy, this date is defined chronometrically...
. In contrast to the deep-water deposits of the Archean, the Proterozoic features many strata
Stratum
In geology and related fields, a stratum is a layer of sedimentary rock or soil with internally consistent characteristics that distinguish it from other layers...
that were laid down in extensive shallow epicontinental seas
Epeiric Sea
An epeiric sea is a shallow sea that extends over part of a continent.Epeiric seas are usually associated with the marine transgressions of the geologic past, which have variously been due to either global eustatic sea level changes, local tectonic deformation, or both, and are occasionally...
; furthermore, many of these rocks are less metamorphosed
Metamorphic rock
Metamorphic rock is the transformation of an existing rock type, the protolith, in a process called metamorphism, which means "change in form". The protolith is subjected to heat and pressure causing profound physical and/or chemical change...
than Archean-age ones, and plenty are unaltered. Study of these rocks show that the eon featured massive, rapid continent
Continent
A continent is one of several very large landmasses on Earth. They are generally identified by convention rather than any strict criteria, with seven regions commonly regarded as continents—they are : Asia, Africa, North America, South America, Antarctica, Europe, and Australia.Plate tectonics is...
al accretion (unique to the Proterozoic), supercontinent cycle
Supercontinent cycle
The supercontinent cycle describes the quasi-periodic aggregation and dispersal of Earth's continental crust. There are varying opinions as to whether the amount of continental crust is increasing, decreasing, or staying about the same, but it is agreed that the Earth's crust is constantly being...
s, and wholly modern orogenic
Orogeny
Orogeny refers to forces and events leading to a severe structural deformation of the Earth's crust due to the engagement of tectonic plates. Response to such engagement results in the formation of long tracts of highly deformed rock called orogens or orogenic belts...
activity.
The first-known glaciations occurred during the Proterozoic, one began shortly after the beginning of the eon, while there were at least four during the Neoproterozoic, climaxing with the Snowball Earth
Snowball Earth
The Snowball Earth hypothesis posits that the Earth's surface became entirely or nearly entirely frozen at least once, some time earlier than 650 Ma . Proponents of the hypothesis argue that it best explains sedimentary deposits generally regarded as of glacial origin at tropical...
of the Varangian glaciation.
Phanerozoic Eon
The Phanerozoic Eon is the current eon in the geologic timescale. It covers roughly 545 million years. During this period continents drifted about, eventually collected into a single landmass known as Pangea and then split up into the current continental landmasses.The Phanerozoic is divided into three eras — the Paleozoic
Paleozoic
The Paleozoic era is the earliest of three geologic eras of the Phanerozoic eon, spanning from roughly...
, the Mesozoic
Mesozoic
The Mesozoic era is an interval of geological time from about 250 million years ago to about 65 million years ago. It is often referred to as the age of reptiles because reptiles, namely dinosaurs, were the dominant terrestrial and marine vertebrates of the time...
and the Cenozoic
Cenozoic
The Cenozoic era is the current and most recent of the three Phanerozoic geological eras and covers the period from 65.5 mya to the present. The era began in the wake of the Cretaceous–Tertiary extinction event at the end of the Cretaceous that saw the demise of the last non-avian dinosaurs and...
.
Paleozoic Era
The Paleozoic spanned from roughly 542 Ma to roughly 251 Ma, and is subdivided into six geologic periods; from oldest to youngest they are the CambrianCambrian
The Cambrian is the first geological period of the Paleozoic Era, lasting from Mya ; it is succeeded by the Ordovician. Its subdivisions, and indeed its base, are somewhat in flux. The period was established by Adam Sedgwick, who named it after Cambria, the Latin name for Wales, where Britain's...
, Ordovician
Ordovician
The Ordovician is a geologic period and system, the second of six of the Paleozoic Era, and covers the time between 488.3±1.7 to 443.7±1.5 million years ago . It follows the Cambrian Period and is followed by the Silurian Period...
, Silurian
Silurian
The Silurian is a geologic period and system that extends from the end of the Ordovician Period, about 443.7 ± 1.5 Mya , to the beginning of the Devonian Period, about 416.0 ± 2.8 Mya . As with other geologic periods, the rock beds that define the period's start and end are well identified, but the...
, Devonian, Carboniferous
Carboniferous
The Carboniferous is a geologic period and system that extends from the end of the Devonian Period, about 359.2 ± 2.5 Mya , to the beginning of the Permian Period, about 299.0 ± 0.8 Mya . The name is derived from the Latin word for coal, carbo. Carboniferous means "coal-bearing"...
and Permian
Permian
The PermianThe term "Permian" was introduced into geology in 1841 by Sir Sir R. I. Murchison, president of the Geological Society of London, who identified typical strata in extensive Russian explorations undertaken with Edouard de Verneuil; Murchison asserted in 1841 that he named his "Permian...
. Geologically, the Paleozoic
Paleozoic
The Paleozoic era is the earliest of three geologic eras of the Phanerozoic eon, spanning from roughly...
starts shortly after the breakup of a supercontinent called Pannotia
Pannotia
Pannotia, first described by Ian W. D. Dalziel in 1997, is a hypothetical supercontinent that existed from the Pan-African orogeny about six hundred million years ago to the end of the Precambrian about five hundred and fifty million years ago. It is also known as the Vendian supercontinent...
and at the end of a global ice age. Throughout the early Paleozoic, the Earth's landmass was broken up into a substantial number of relatively small continents. Toward the end of the era the continents gathered together into a supercontinent called Pangaea
Pangaea
Pangaea, Pangæa, or Pangea is hypothesized as a supercontinent that existed during the Paleozoic and Mesozoic eras about 250 million years ago, before the component continents were separated into their current configuration....
, which included most of the Earth's land area.
Cambrian Period
The Cambrian is a major division of the geologic timescale that begins about 542 ± 1.0 Ma. CambrianCambrian
The Cambrian is the first geological period of the Paleozoic Era, lasting from Mya ; it is succeeded by the Ordovician. Its subdivisions, and indeed its base, are somewhat in flux. The period was established by Adam Sedgwick, who named it after Cambria, the Latin name for Wales, where Britain's...
continents are thought to have resulted from the breakup of a Neoproterozoic
Neoproterozoic
The Neoproterozoic Era is the unit of geologic time from 1,000 to 542.0 ± 1.0 million years ago. The terminal Era of the formal Proterozoic Eon , it is further subdivided into the Tonian, Cryogenian, and Ediacaran Periods...
supercontinent called Pannotia. The waters of the Cambrian period appear to have been widespread and shallow. Continental drift rates may have been anomalously high. Laurentia
Laurentia
Laurentia is a large area of continental craton, which forms the ancient geological core of the North American continent...
, Baltica
Baltica
Baltica is a name applied by geologists to a late-Proterozoic, early-Palaeozoic continent that now includes the East European craton of northwestern Eurasia. Baltica was created as an entity not earlier than 1.8 billion years ago. Before this time, the three segments/continents that now comprise...
and Siberia
Siberia
Siberia is an extensive region constituting almost all of Northern Asia. Comprising the central and eastern portion of the Russian Federation, it was part of the Soviet Union from its beginning, as its predecessor states, the Tsardom of Russia and the Russian Empire, conquered it during the 16th...
remained independent continents following the break-up of the supercontinent of Pannotia. Gondwana
Gondwana
In paleogeography, Gondwana , originally Gondwanaland, was the southernmost of two supercontinents that later became parts of the Pangaea supercontinent. It existed from approximately 510 to 180 million years ago . Gondwana is believed to have sutured between ca. 570 and 510 Mya,...
started to drift toward the South Pole. Panthalassa
Panthalassa
Panthalassa , also known as the Panthalassic Ocean, was the vast global ocean that surrounded the supercontinent Pangaea, during the late Paleozoic and the early Mesozoic years. It included the Pacific Ocean to the west and north and the Tethys Ocean to the southeast...
covered most of the southern hemisphere, and minor oceans included the Proto-Tethys Ocean
Proto-Tethys Ocean
The Proto-Tethys Ocean was an ancient ocean that existed from the latest Ediacaran to the Carboniferous . It was an ocean predecessor of the later Paleo-Tethys Ocean. The ocean formed when Pannotia disintegrated, Proto-Laurasia rifted away from a supercontinent that would become Gondwana...
, Iapetus Ocean
Iapetus Ocean
The Iapetus Ocean was an ocean that existed in the Neoproterozoic and Paleozoic eras of the geologic timescale . The Iapetus Ocean was situated in the southern hemisphere, between the paleocontinents of Laurentia, Baltica and Avalonia...
and Khanty Ocean
Khanty Ocean
Khanty Ocean was an ancient, small ocean that existed near the end of the Precambrian time to the Silurian. It was between Baltica and the Siberian continent, with the bordering oceans of Panthalassa to the north, Proto-Tethys to the northeast, and Paleo-Tethys to the south and east...
.
Ordovician Period
The Ordovician Period started at a major extinction event called the Cambrian-Ordovician extinction eventsCambrian-Ordovician extinction events
The Cambrian–Ordovician extinction event occurred approximately 488 million years ago . This early Phanerozoic Eon extinction event eliminated many brachiopods and conodonts, and severely reduced the number of trilobite species....
some time about 488.3 ± 1.7 Ma. During the Ordovician
Ordovician
The Ordovician is a geologic period and system, the second of six of the Paleozoic Era, and covers the time between 488.3±1.7 to 443.7±1.5 million years ago . It follows the Cambrian Period and is followed by the Silurian Period...
the southern continents were collected into a single continent called Gondwana. Gondwana started the period in the equatorial latitudes and, as the period progressed, drifted toward the South Pole. Early in the Ordovician the continents Laurentia, Siberia and Baltica were still independent continents (since the break-up of the supercontinent Pannotia earlier), but Baltica
Baltica
Baltica is a name applied by geologists to a late-Proterozoic, early-Palaeozoic continent that now includes the East European craton of northwestern Eurasia. Baltica was created as an entity not earlier than 1.8 billion years ago. Before this time, the three segments/continents that now comprise...
began to move toward Laurentia later in the period, causing the Iapetus Ocean to shrink between them. Also, Avalonia
Avalonia
Avalonia was a microcontinent in the Paleozoic era. Crustal fragments of this former microcontinent underlie south-west Great Britain, and the eastern coast of North America. It is the source of many of the older rocks of Western Europe, Atlantic Canada, and parts of the coastal United States...
broke free from Gondwana and began to head north toward Laurentia. The Rheic Ocean
Rheic Ocean
The Rheic Ocean was a Paleozoic ocean between the large continent Gondwana to the south and the microcontinents Avalonia and others to the north...
was formed as a result of this. By the end of the period, Gondwana had neared or approached the pole and was largely glaciated.
The Ordovician came to a close in a series of extinction event
Extinction event
An extinction event is a sharp decrease in the diversity and abundance of macroscopic life. They occur when the rate of extinction increases with respect to the rate of speciation...
s that, taken together, comprise the second-largest of the five major extinction events in Earth's history
History of Earth
The history of the Earth describes the most important events and fundamental stages in the development of the planet Earth from its formation 4.578 billion years ago to the present day. Nearly all branches of natural science have contributed to the understanding of the main events of the Earth's...
in terms of percentage of genera
Genus
In biology, a genus is a low-level taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms, which is an example of definition by genus and differentia...
that went extinct. The only larger one was the Permian-Triassic extinction event. The extinctions occurred approximately 444-447 Ma and mark the boundary between the Ordovician and the following Silurian
Silurian
The Silurian is a geologic period and system that extends from the end of the Ordovician Period, about 443.7 ± 1.5 Mya , to the beginning of the Devonian Period, about 416.0 ± 2.8 Mya . As with other geologic periods, the rock beds that define the period's start and end are well identified, but the...
Period.
The most-commonly accepted theory is that these events were triggered by the onset of an ice age
Ice age
An ice age or, more precisely, glacial age, is a generic geological period of long-term reduction in the temperature of the Earth's surface and atmosphere, resulting in the presence or expansion of continental ice sheets, polar ice sheets and alpine glaciers...
, in the Hirnantian faunal stage that ended the long, stable greenhouse
Greenhouse
A greenhouse is a building in which plants are grown. These structures range in size from small sheds to very large buildings...
conditions typical of the Ordovician. The ice age was probably not as long-lasting as once thought; study of oxygen isotopes in fossil brachiopods shows that it was probably no longer than 0.5 to 1.5 million years. The event was preceded by a fall in atmospheric carbon dioxide (from 7000ppm to 4400ppm) which selectively affected the shallow seas where most organisms lived. As the southern supercontinent Gondwana
Gondwana
In paleogeography, Gondwana , originally Gondwanaland, was the southernmost of two supercontinents that later became parts of the Pangaea supercontinent. It existed from approximately 510 to 180 million years ago . Gondwana is believed to have sutured between ca. 570 and 510 Mya,...
drifted over the South Pole, ice caps formed on it. Evidence of these ice caps have been detected in Upper Ordovician rock strata of North Africa
North Africa
North Africa or Northern Africa is the northernmost region of the African continent, linked by the Sahara to Sub-Saharan Africa. Geopolitically, the United Nations definition of Northern Africa includes eight countries or territories; Algeria, Egypt, Libya, Morocco, South Sudan, Sudan, Tunisia, and...
and then-adjacent northeastern South America, which were south-polar locations at the time.
Siluronian Period
The Silurian is a major division of the geologic timescale that started about 443.7 ± 1.5 Ma. During the SilurianSilurian
The Silurian is a geologic period and system that extends from the end of the Ordovician Period, about 443.7 ± 1.5 Mya , to the beginning of the Devonian Period, about 416.0 ± 2.8 Mya . As with other geologic periods, the rock beds that define the period's start and end are well identified, but the...
, Gondwana continued a slow southward drift to high southern latitudes, but there is evidence that the Silurian ice caps were less extensive than those of the late Ordovician glaciation. The melting of ice caps and glaciers contributed to a rise in sea level
Sea level
Mean sea level is a measure of the average height of the ocean's surface ; used as a standard in reckoning land elevation...
s, recognizable from the fact that Silurian sediments overlie eroded Ordovician sediments, forming an unconformity
Unconformity
An unconformity is a buried erosion surface separating two rock masses or strata of different ages, indicating that sediment deposition was not continuous. In general, the older layer was exposed to erosion for an interval of time before deposition of the younger, but the term is used to describe...
. Other craton
Craton
A craton is an old and stable part of the continental lithosphere. Having often survived cycles of merging and rifting of continents, cratons are generally found in the interiors of tectonic plates. They are characteristically composed of ancient crystalline basement rock, which may be covered by...
s and continent fragments drifted together near the equator, starting the formation of a second supercontinent known as Euramerica
Euramerica
Euramerica was a minor supercontinent created in the Devonian as the result of a collision between the Laurentian, Baltica, and Avalonia cratons .300 million years ago in the Late Carboniferous tropical rainforests lay over the equator of Euramerica...
. The vast ocean of Panthalassa covered most of the northern hemisphere. Other minor oceans include Proto-Tethys, Paleo-Tethys, Rheic Ocean, a seaway of Iapetus Ocean (now in between Avalonia and Laurentia), and newly formed Ural Ocean
Ural Ocean
The Ural Ocean was a small, ancient ocean that was situated between Siberia and Baltica. The ocean formed in the Late Ordovician epoch, when large islands from Siberia collided with Baltica, which was now part of a minor supercontinent of Euramerica. The islands also caused Ural Ocean's precursor,...
.
Devonian Period
The Devonian spanned roughly from 416 to 359 Ma. The period was a time of great tectonic activity, as LaurasiaLaurasia
In paleogeography, Laurasia was the northernmost of two supercontinents that formed part of the Pangaea supercontinent from approximately...
and Gondwanaland drew closer together. The continent Euramerica (or Laurussia) was created in the early Devonian by the collision of Laurentia and Baltica, which rotated into the natural dry zone along the Tropic of Capricorn
Tropic of Capricorn
The Tropic of Capricorn, or Southern tropic, marks the most southerly latitude on the Earth at which the Sun can be directly overhead. This event occurs at the December solstice, when the southern hemisphere is tilted towards the Sun to its maximum extent.Tropic of Capricorn is one of the five...
. In these near-deserts, the Old Red Sandstone
Old Red Sandstone
The Old Red Sandstone is a British rock formation of considerable importance to early paleontology. For convenience the short version of the term, 'ORS' is often used in literature on the subject.-Sedimentology:...
sedimentary beds formed, made red by the oxidized iron (hematite
Hematite
Hematite, also spelled as haematite, is the mineral form of iron oxide , one of several iron oxides. Hematite crystallizes in the rhombohedral system, and it has the same crystal structure as ilmenite and corundum...
) characteristic of drought conditions. Near the equator Pangaea began to consolidate from the plates containing North America and Europe, further raising the northern Appalachian Mountains
Appalachian Mountains
The Appalachian Mountains #Whether the stressed vowel is or ,#Whether the "ch" is pronounced as a fricative or an affricate , and#Whether the final vowel is the monophthong or the diphthong .), often called the Appalachians, are a system of mountains in eastern North America. The Appalachians...
and forming the Caledonian Mountains in Great Britain
Great Britain
Great Britain or Britain is an island situated to the northwest of Continental Europe. It is the ninth largest island in the world, and the largest European island, as well as the largest of the British Isles...
and Scandinavia
Scandinavia
Scandinavia is a cultural, historical and ethno-linguistic region in northern Europe that includes the three kingdoms of Denmark, Norway and Sweden, characterized by their common ethno-cultural heritage and language. Modern Norway and Sweden proper are situated on the Scandinavian Peninsula,...
. The southern continents remained tied together in the supercontinent of Gondwana
Gondwana
In paleogeography, Gondwana , originally Gondwanaland, was the southernmost of two supercontinents that later became parts of the Pangaea supercontinent. It existed from approximately 510 to 180 million years ago . Gondwana is believed to have sutured between ca. 570 and 510 Mya,...
. The remainder of modern Eurasia lay in the Northern Hemisphere. Sea levels were high worldwide, and much of the land lay submerged under shallow seas. The deep, enormous Panthalassa (the "universal ocean") covered the rest of the planet. Other minor oceans were Paleo-Tethys, Proto-Tethys, Rheic Ocean and Ural Ocean (which was closed during the collision with Siberia and Baltica).
Carboniferous Period
The Carboniferous extends from about 359.2 ± 2.5 Ma to about 299.0 ± 0.8 Ma.A global drop in sea level at the end of the Devonian reversed early in the Carboniferous
Carboniferous
The Carboniferous is a geologic period and system that extends from the end of the Devonian Period, about 359.2 ± 2.5 Mya , to the beginning of the Permian Period, about 299.0 ± 0.8 Mya . The name is derived from the Latin word for coal, carbo. Carboniferous means "coal-bearing"...
; this created the widespread epicontinental seas and carbonate deposition of the Mississippian. There was also a drop in south polar temperatures; southern Gondwanaland was glaciated throughout the period, though it is uncertain if the ice sheets were a holdover from the Devonian or not. These conditions apparently had little effect in the deep tropics, where lush coal
Coal
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock usually occurring in rock strata in layers or veins called coal beds or coal seams. The harder forms, such as anthracite coal, can be regarded as metamorphic rock because of later exposure to elevated temperature and pressure...
swamps flourished within 30 degrees of the northernmost glaciers. A mid-Carboniferous drop in sea-level precipitated a major marine extinction, one that hit crinoid
Crinoid
Crinoids are marine animals that make up the class Crinoidea of the echinoderms . Crinoidea comes from the Greek word krinon, "a lily", and eidos, "form". They live both in shallow water and in depths as great as 6,000 meters. Sea lilies refer to the crinoids which, in their adult form, are...
s and ammonite
Ammonite
Ammonite, as a zoological or paleontological term, refers to any member of the Ammonoidea an extinct subclass within the Molluscan class Cephalopoda which are more closely related to living coleoids Ammonite, as a zoological or paleontological term, refers to any member of the Ammonoidea an extinct...
s especially hard. This sea-level drop and the associated unconformity in North America separate the Mississippian Period from the Pennsylvanian period.
The Carboniferous was a time of active mountain building, as the supercontinent Pangea came together. The southern continents remained tied together in the supercontinent Gondwana, which collided with North America-Europe (Laurussia) along the present line of eastern North America
North America
North America is a continent wholly within the Northern Hemisphere and almost wholly within the Western Hemisphere. It is also considered a northern subcontinent of the Americas...
. This continental collision resulted in the Hercynian orogeny in Europe, and the Alleghenian orogeny
Alleghenian orogeny
The Alleghenian orogeny or Appalachian orogeny is one of the geological mountain-forming events that formed the Appalachian Mountains and Allegheny Mountains. The term and spelling Alleghany orogeny was originally proposed by H.P. Woodward in 1957....
in North America; it also extended the newly uplifted Appalachians southwestward as the Ouachita Mountains
Ouachita Mountains
The Ouachita Mountains are a mountain range in west central Arkansas and southeastern Oklahoma. The range's subterranean roots may extend as far as central Texas, or beyond it to the current location of the Marathon Uplift. Along with the Ozark Mountains, the Ouachita Mountains form the U.S...
. In the same time frame, much of present eastern Eurasian
Eurasian Plate
The Eurasian Plate is a tectonic plate which includes most of the continent of Eurasia , with the notable exceptions of the Indian subcontinent, the Arabian subcontinent, and the area east of the Chersky Range in East Siberia...
plate welded itself to Europe along the line of the Ural mountains
Ural Mountains
The Ural Mountains , or simply the Urals, are a mountain range that runs approximately from north to south through western Russia, from the coast of the Arctic Ocean to the Ural River and northwestern Kazakhstan. Their eastern side is usually considered the natural boundary between Europe and Asia...
. There were two major oceans in the Carboniferous the Panthalassa and Paleo-Tethys. Other minor oceans were shrinking and eventually closed the Rheic Ocean
Rheic Ocean
The Rheic Ocean was a Paleozoic ocean between the large continent Gondwana to the south and the microcontinents Avalonia and others to the north...
(closed by the assembly of South and North America), the small, shallow Ural Ocean
Ural Ocean
The Ural Ocean was a small, ancient ocean that was situated between Siberia and Baltica. The ocean formed in the Late Ordovician epoch, when large islands from Siberia collided with Baltica, which was now part of a minor supercontinent of Euramerica. The islands also caused Ural Ocean's precursor,...
(which was closed by the collision of Baltica
Baltica
Baltica is a name applied by geologists to a late-Proterozoic, early-Palaeozoic continent that now includes the East European craton of northwestern Eurasia. Baltica was created as an entity not earlier than 1.8 billion years ago. Before this time, the three segments/continents that now comprise...
, and Siberia
Siberia (continent)
Siberia is the craton located in the heart of the region of Siberia. Siberia or "Angaraland" is today the Central Siberian Plateau...
continents, creating the Ural Mountains) and Proto-Tethys Ocean.

Permian Period
The Permian extends from about 299.0 ± 0.8 Ma to 251.0 ± 0.4 Ma.During the Permian
Permian
The PermianThe term "Permian" was introduced into geology in 1841 by Sir Sir R. I. Murchison, president of the Geological Society of London, who identified typical strata in extensive Russian explorations undertaken with Edouard de Verneuil; Murchison asserted in 1841 that he named his "Permian...
all the Earth's major land masses, except portions of East Asia, were collected into a single supercontinent known as Pangaea
Pangaea
Pangaea, Pangæa, or Pangea is hypothesized as a supercontinent that existed during the Paleozoic and Mesozoic eras about 250 million years ago, before the component continents were separated into their current configuration....
. Pangaea straddled the equator and extended toward the poles, with a corresponding effect on ocean currents in the single great ocean (Panthalassa
Panthalassa
Panthalassa , also known as the Panthalassic Ocean, was the vast global ocean that surrounded the supercontinent Pangaea, during the late Paleozoic and the early Mesozoic years. It included the Pacific Ocean to the west and north and the Tethys Ocean to the southeast...
, the universal sea), and the Paleo-Tethys Ocean
Paleo-Tethys Ocean
The Paleo-Tethys Ocean was an ancient Paleozoic ocean. It was located between the paleocontinent Gondwana and the so called Hunic terranes. These are divided into the European Hunic and Asiatic Hunic...
, a large ocean that was between Asia and Gondwana. The Cimmeria continent rifted away from Gondwana and drifted north to Laurasia, causing the Paleo-Tethys to shrink. A new ocean was growing on its southern end, the Tethys Ocean, an ocean that would dominate much of the Mesozoic Era. Large continental landmasses create climates with extreme variations of heat and cold ("continental climate") and monsoon conditions with highly seasonal rainfall patterns. Desert
Desert
A desert is a landscape or region that receives an extremely low amount of precipitation, less than enough to support growth of most plants. Most deserts have an average annual precipitation of less than...
s seem to have been widespread on Pangaea.
Mesozoic Era


After the vigorous convergent plate mountain-building of the late Paleozoic
Paleozoic
The Paleozoic era is the earliest of three geologic eras of the Phanerozoic eon, spanning from roughly...
, Mesozoic
Mesozoic
The Mesozoic era is an interval of geological time from about 250 million years ago to about 65 million years ago. It is often referred to as the age of reptiles because reptiles, namely dinosaurs, were the dominant terrestrial and marine vertebrates of the time...
tectonic deformation was comparatively mild. Nevertheless, the era featured the dramatic rifting of the supercontinent Pangaea
Pangaea
Pangaea, Pangæa, or Pangea is hypothesized as a supercontinent that existed during the Paleozoic and Mesozoic eras about 250 million years ago, before the component continents were separated into their current configuration....
. Pangaea gradually split into a northern continent, Laurasia
Laurasia
In paleogeography, Laurasia was the northernmost of two supercontinents that formed part of the Pangaea supercontinent from approximately...
, and a southern continent, Gondwana
Gondwana
In paleogeography, Gondwana , originally Gondwanaland, was the southernmost of two supercontinents that later became parts of the Pangaea supercontinent. It existed from approximately 510 to 180 million years ago . Gondwana is believed to have sutured between ca. 570 and 510 Mya,...
. This created the passive continental margin that characterizes most of the Atlantic coastline (such as along the U.S. East Coast) today.
Triassic Period
The Triassic Period extends from about 251 ± 0.4 to 199.6 ± 0.6 Ma. During the TriassicTriassic
The Triassic is a geologic period and system that extends from about 250 to 200 Mya . As the first period of the Mesozoic Era, the Triassic follows the Permian and is followed by the Jurassic. Both the start and end of the Triassic are marked by major extinction events...
, almost all the Earth's land mass was concentrated into a single supercontinent
Supercontinent
In geology, a supercontinent is a landmass comprising more than one continental core, or craton. The assembly of cratons and accreted terranes that form Eurasia qualifies as a supercontinent today.-History:...
centered more or less on the equator, called Pangaea
Pangaea
Pangaea, Pangæa, or Pangea is hypothesized as a supercontinent that existed during the Paleozoic and Mesozoic eras about 250 million years ago, before the component continents were separated into their current configuration....
("all the land"). This took the form of a giant "Pac-Man
Pac-Man
is an arcade game developed by Namco and licensed for distribution in the United States by Midway, first released in Japan on May 22, 1980. Immensely popular from its original release to the present day, Pac-Man is considered one of the classics of the medium, virtually synonymous with video games,...
" with an east-facing "mouth" constituting the Tethys sea
Tethys Ocean
The Tethys Ocean was an ocean that existed between the continents of Gondwana and Laurasia during the Mesozoic era before the opening of the Indian Ocean.-Modern theory:...
, a vast gulf that opened farther westward in the mid-Triassic, at the expense of the shrinking Paleo-Tethys Ocean
Paleo-Tethys Ocean
The Paleo-Tethys Ocean was an ancient Paleozoic ocean. It was located between the paleocontinent Gondwana and the so called Hunic terranes. These are divided into the European Hunic and Asiatic Hunic...
, an ocean that existed during the Paleozoic
Paleozoic
The Paleozoic era is the earliest of three geologic eras of the Phanerozoic eon, spanning from roughly...
.
The remainder was the world-ocean known as Panthalassa
Panthalassa
Panthalassa , also known as the Panthalassic Ocean, was the vast global ocean that surrounded the supercontinent Pangaea, during the late Paleozoic and the early Mesozoic years. It included the Pacific Ocean to the west and north and the Tethys Ocean to the southeast...
("all the sea"). All the deep-ocean sediments laid down during the Triassic have disappeared through subduction
Subduction
In geology, subduction is the process that takes place at convergent boundaries by which one tectonic plate moves under another tectonic plate, sinking into the Earth's mantle, as the plates converge. These 3D regions of mantle downwellings are known as "Subduction Zones"...
of oceanic plates; thus, very little is known of the Triassic open ocean. The supercontinent Pangaea was rifting during the Triassic—especially late in the period—but had not yet separated. The first nonmarine sediments in the rift
Rift
In geology, a rift or chasm is a place where the Earth's crust and lithosphere are being pulled apart and is an example of extensional tectonics....
that marks the initial break-up of Pangea—which separated New Jersey
New Jersey
New Jersey is a state in the Northeastern and Middle Atlantic regions of the United States. , its population was 8,791,894. It is bordered on the north and east by the state of New York, on the southeast and south by the Atlantic Ocean, on the west by Pennsylvania and on the southwest by Delaware...
from Morocco
Morocco
Morocco , officially the Kingdom of Morocco , is a country located in North Africa. It has a population of more than 32 million and an area of 710,850 km², and also primarily administers the disputed region of the Western Sahara...
—are of Late Triassic age; in the U.S., these thick sediments comprise the Newark Supergroup.
Because of the limited shoreline of one super-continental mass, Triassic marine deposits are globally relatively rare; despite their prominence in Western Europe
Western Europe
Western Europe is a loose term for the collection of countries in the western most region of the European continents, though this definition is context-dependent and carries cultural and political connotations. One definition describes Western Europe as a geographic entity—the region lying in the...
, where the Triassic was first studied. In North America
North America
North America is a continent wholly within the Northern Hemisphere and almost wholly within the Western Hemisphere. It is also considered a northern subcontinent of the Americas...
, for example, marine deposits are limited to a few exposures in the west. Thus Triassic stratigraphy
Stratigraphy
Stratigraphy, a branch of geology, studies rock layers and layering . It is primarily used in the study of sedimentary and layered volcanic rocks....
is mostly based on organisms living in lagoons and hypersaline environments, such as Estheria crustaceans and terrestrial vertebrates.
Jurassic Period
The Jurassic Period extends from about 199.6 ± 0.6 Ma to 145.4 ± 4.0 Ma.During the early Jurassic
Jurassic
The Jurassic is a geologic period and system that extends from about Mya to Mya, that is, from the end of the Triassic to the beginning of the Cretaceous. The Jurassic constitutes the middle period of the Mesozoic era, also known as the age of reptiles. The start of the period is marked by...
, the supercontinent Pangaea
Pangaea
Pangaea, Pangæa, or Pangea is hypothesized as a supercontinent that existed during the Paleozoic and Mesozoic eras about 250 million years ago, before the component continents were separated into their current configuration....
broke up into the northern supercontinent Laurasia
Laurasia
In paleogeography, Laurasia was the northernmost of two supercontinents that formed part of the Pangaea supercontinent from approximately...
and the southern supercontinent Gondwana
Gondwana
In paleogeography, Gondwana , originally Gondwanaland, was the southernmost of two supercontinents that later became parts of the Pangaea supercontinent. It existed from approximately 510 to 180 million years ago . Gondwana is believed to have sutured between ca. 570 and 510 Mya,...
; the Gulf of Mexico
Gulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico is a partially landlocked ocean basin largely surrounded by the North American continent and the island of Cuba. It is bounded on the northeast, north and northwest by the Gulf Coast of the United States, on the southwest and south by Mexico, and on the southeast by Cuba. In...
opened in the new rift between North America and what is now Mexico
Mexico
The United Mexican States , commonly known as Mexico , is a federal constitutional republic in North America. It is bordered on the north by the United States; on the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; on the southeast by Guatemala, Belize, and the Caribbean Sea; and on the east by the Gulf of...
's Yucatan Peninsula
Yucatán Peninsula
The Yucatán Peninsula, in southeastern Mexico, separates the Caribbean Sea from the Gulf of Mexico, with the northern coastline on the Yucatán Channel...
. The Jurassic North Atlantic Ocean
Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's oceanic divisions. With a total area of about , it covers approximately 20% of the Earth's surface and about 26% of its water surface area...
was relatively narrow, while the South Atlantic did not open until the following Cretaceous Period, when Gondwana itself rifted apart.
The Tethys Sea
Tethys Ocean
The Tethys Ocean was an ocean that existed between the continents of Gondwana and Laurasia during the Mesozoic era before the opening of the Indian Ocean.-Modern theory:...
closed, and the Neotethys
Mediterranean Basin
In biogeography, the Mediterranean Basin refers to the lands around the Mediterranean Sea that have a Mediterranean climate, with mild, rainy winters and hot, dry summers, which supports characteristic Mediterranean forests, woodlands, and scrub vegetation...
basin appeared. Climates were warm, with no evidence of glaciation
Glacier
A glacier is a large persistent body of ice that forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its ablation over many years, often centuries. At least 0.1 km² in area and 50 m thick, but often much larger, a glacier slowly deforms and flows due to stresses induced by its weight...
. As in the Triassic, there was apparently no land near either pole, and no extensive ice caps existed. The Jurassic geological record is good in western Europe
Europe
Europe is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting...
, where extensive marine sequences indicate a time when much of the continent was submerged under shallow tropical seas; famous locales include the Jurassic Coast
Jurassic Coast
The Jurassic Coast is a World Heritage Site on the English Channel coast of southern England. The site stretches from Orcombe Point near Exmouth in East Devon to Old Harry Rocks near Swanage in East Dorset, a distance of ....
World Heritage Site
World Heritage Site
A UNESCO World Heritage Site is a place that is listed by the UNESCO as of special cultural or physical significance...
and the renowned late Jurassic lagerstätte
Lagerstätte
A Lagerstätte is a sedimentary deposit that exhibits extraordinary fossil richness or completeness.Palaeontologists distinguish two kinds....
n of Holzmaden
Holzmaden
Holzmaden is a town in Baden-Württemberg, Germany that lies between Stuttgart and Ulm.The ground in and around the city contains rich layers of well preserved fossils of the Jurassic period. The fossils are found in the 160 million year old Posidonia Shale and displayed in the local Museum Hauff...
and Solnhofen
Solnhofen limestone
The Solnhofen Plattenkalk is a Jurassic Konservat-Lagerstätte that preserves a rare assemblage of fossilized organisms, including highly detailed imprints of soft bodied organisms such as sea jellies...
.
In contrast, the North American Jurassic record is the poorest of the Mesozoic, with few outcrops at the surface. Though the epicontinental
Epeiric Sea
An epeiric sea is a shallow sea that extends over part of a continent.Epeiric seas are usually associated with the marine transgressions of the geologic past, which have variously been due to either global eustatic sea level changes, local tectonic deformation, or both, and are occasionally...
Sundance Sea
Sundance Sea
The Sundance Sea was an epeiric sea that existed in North America during the mid to late Jurassic Period of the Mesozoic Era. It was an arm of what is now the Arctic Ocean, and extended through what is now western Canada into the central western United States...
left marine deposits in parts of the northern plains of the United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
and Canada
Canada
Canada is a North American country consisting of ten provinces and three territories. Located in the northern part of the continent, it extends from the Atlantic Ocean in the east to the Pacific Ocean in the west, and northward into the Arctic Ocean...
during the late Jurassic, most exposed sediments from this period are continental, such as the alluvial
Alluvium
Alluvium is loose, unconsolidated soil or sediments, eroded, deposited, and reshaped by water in some form in a non-marine setting. Alluvium is typically made up of a variety of materials, including fine particles of silt and clay and larger particles of sand and gravel...
deposits of the Morrison Formation
Morrison Formation
The Morrison Formation is a distinctive sequence of Late Jurassic sedimentary rock that is found in the western United States, which has been the most fertile source of dinosaur fossils in North America. It is composed of mudstone, sandstone, siltstone and limestone and is light grey, greenish...
. The first of several massive batholith
Batholith
A batholith is a large emplacement of igneous intrusive rock that forms from cooled magma deep in the Earth's crust...
s were emplaced in the northern Cordillera
American cordillera
The American Cordillera is a cordillera that consists of an essentially continuous sequence of mountain ranges that form the western "backbone" of North America, Central America, South America and Antarctica. From north to south, this sequence of overlapping and parallel ranges begins with the...
beginning in the mid-Jurassic, marking the Nevadan orogeny
Nevadan orogeny
The Nevadan Orogeny was a major mountain building event that took place along the western edge of ancient North America between the Mid to Late Jurassic...
. Important Jurassic exposures are also found in Russia
Russia
Russia or , officially known as both Russia and the Russian Federation , is a country in northern Eurasia. It is a federal semi-presidential republic, comprising 83 federal subjects...
, India
India
India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
, South America
South America
South America is a continent situated in the Western Hemisphere, mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere. The continent is also considered a subcontinent of the Americas. It is bordered on the west by the Pacific Ocean and on the north and east...
, Japan
Japan
Japan is an island nation in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean, it lies to the east of the Sea of Japan, China, North Korea, South Korea and Russia, stretching from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea and Taiwan in the south...
, Australasia
Australasia
Australasia is a region of Oceania comprising Australia, New Zealand, the island of New Guinea, and neighbouring islands in the Pacific Ocean. The term was coined by Charles de Brosses in Histoire des navigations aux terres australes...
and the United Kingdom
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
.
Cretaceous Period

During the Cretaceous
Cretaceous
The Cretaceous , derived from the Latin "creta" , usually abbreviated K for its German translation Kreide , is a geologic period and system from circa to million years ago. In the geologic timescale, the Cretaceous follows the Jurassic period and is followed by the Paleogene period of the...
, the late Paleozoic
Paleozoic
The Paleozoic era is the earliest of three geologic eras of the Phanerozoic eon, spanning from roughly...
-early Mesozoic supercontinent
Supercontinent
In geology, a supercontinent is a landmass comprising more than one continental core, or craton. The assembly of cratons and accreted terranes that form Eurasia qualifies as a supercontinent today.-History:...
of Pangaea
Pangaea
Pangaea, Pangæa, or Pangea is hypothesized as a supercontinent that existed during the Paleozoic and Mesozoic eras about 250 million years ago, before the component continents were separated into their current configuration....
completed its breakup into present day continent
Continent
A continent is one of several very large landmasses on Earth. They are generally identified by convention rather than any strict criteria, with seven regions commonly regarded as continents—they are : Asia, Africa, North America, South America, Antarctica, Europe, and Australia.Plate tectonics is...
s, although their positions were substantially different at the time. As the Atlantic Ocean
Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's oceanic divisions. With a total area of about , it covers approximately 20% of the Earth's surface and about 26% of its water surface area...
widened, the convergent-margin orogenies
Orogeny
Orogeny refers to forces and events leading to a severe structural deformation of the Earth's crust due to the engagement of tectonic plates. Response to such engagement results in the formation of long tracts of highly deformed rock called orogens or orogenic belts...
that had begun during the Jurassic continued in the North American Cordillera
American cordillera
The American Cordillera is a cordillera that consists of an essentially continuous sequence of mountain ranges that form the western "backbone" of North America, Central America, South America and Antarctica. From north to south, this sequence of overlapping and parallel ranges begins with the...
, as the Nevadan orogeny
Nevadan orogeny
The Nevadan Orogeny was a major mountain building event that took place along the western edge of ancient North America between the Mid to Late Jurassic...
was followed by the Sevier
Sevier orogeny
The Sevier orogeny was a mountain-building event that affected western North America from Canada to the north to Mexico to the south. This orogeny was the result of convergent boundary tectonic activity between approximately 140 million years ago and 50 Ma. The Sevier River area of central Utah...
and Laramide orogenies
Laramide orogeny
The Laramide orogeny was a period of mountain building in western North America, which started in the Late Cretaceous, 70 to 80 million years ago, and ended 35 to 55 million years ago. The exact duration and ages of beginning and end of the orogeny are in dispute, as is the cause. The Laramide...
. Though Gondwana was still intact in the beginning of the Cretaceous, Gondwana
Gondwana
In paleogeography, Gondwana , originally Gondwanaland, was the southernmost of two supercontinents that later became parts of the Pangaea supercontinent. It existed from approximately 510 to 180 million years ago . Gondwana is believed to have sutured between ca. 570 and 510 Mya,...
itself broke up as South America
South America
South America is a continent situated in the Western Hemisphere, mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere. The continent is also considered a subcontinent of the Americas. It is bordered on the west by the Pacific Ocean and on the north and east...
, Antarctica and Australia
Australia
Australia , officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country in the Southern Hemisphere comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands in the Indian and Pacific Oceans. It is the world's sixth-largest country by total area...
rifted away from Africa
Africa
Africa is the world's second largest and second most populous continent, after Asia. At about 30.2 million km² including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of the Earth's total surface area and 20.4% of the total land area...
(though India
India
India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
and Madagascar
Madagascar
The Republic of Madagascar is an island country located in the Indian Ocean off the southeastern coast of Africa...
remained attached to each other); thus, the South Atlantic and Indian Ocean
Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third largest of the world's oceanic divisions, covering approximately 20% of the water on the Earth's surface. It is bounded on the north by the Indian Subcontinent and Arabian Peninsula ; on the west by eastern Africa; on the east by Indochina, the Sunda Islands, and...
s were newly formed. Such active rifting lifted great undersea mountain chains along the welts, raising eustatic sea levels
Sea level
Mean sea level is a measure of the average height of the ocean's surface ; used as a standard in reckoning land elevation...
worldwide.
To the north of Africa the Tethys Sea continued to narrow. Broad shallow seas advanced across central North America
North America
North America is a continent wholly within the Northern Hemisphere and almost wholly within the Western Hemisphere. It is also considered a northern subcontinent of the Americas...
(the Western Interior Seaway
Western Interior Seaway
The Western Interior Seaway, also called the Cretaceous Seaway, the Niobraran Sea, and the North American Inland Sea, was a huge inland sea that split the continent of North America into two halves, Laramidia and Appalachia, during most of the mid- and late-Cretaceous Period...
) and Europe, then receded late in the period, leaving thick marine deposits sandwiched between coal
Coal
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock usually occurring in rock strata in layers or veins called coal beds or coal seams. The harder forms, such as anthracite coal, can be regarded as metamorphic rock because of later exposure to elevated temperature and pressure...
beds. At the peak of the Cretaceous transgression
Transgression (geology)
A marine transgression is a geologic event during which sea level rises relative to the land and the shoreline moves toward higher ground, resulting in flooding. Transgressions can be caused either by the land sinking or the ocean basins filling with water...
, one-third of Earth's present land area was submerged. The Cretaceous is justly famous for its chalk
Chalk
Chalk is a soft, white, porous sedimentary rock, a form of limestone composed of the mineral calcite. Calcite is calcium carbonate or CaCO3. It forms under reasonably deep marine conditions from the gradual accumulation of minute calcite plates shed from micro-organisms called coccolithophores....
; indeed, more chalk formed in the Cretaceous than in any other period in the Phanerozoic
Phanerozoic
The Phanerozoic Eon is the current eon in the geologic timescale, and the one during which abundant animal life has existed. It covers roughly 542 million years and goes back to the time when diverse hard-shelled animals first appeared...
. Mid-ocean ridge
Mid-ocean ridge
A mid-ocean ridge is a general term for an underwater mountain system that consists of various mountain ranges , typically having a valley known as a rift running along its spine, formed by plate tectonics. This type of oceanic ridge is characteristic of what is known as an oceanic spreading...
activity—or rather, the circulation of seawater through the enlarged ridges—enriched the oceans in calcium; this made the oceans more saturated, as well as increased the bioavailability of the element for calcareous nanoplankton. These widespread carbonate
Carbonate
In chemistry, a carbonate is a salt of carbonic acid, characterized by the presence of the carbonate ion, . The name may also mean an ester of carbonic acid, an organic compound containing the carbonate group C2....
s and other sedimentary deposits
Sedimentary rock
Sedimentary rock are types of rock that are formed by the deposition of material at the Earth's surface and within bodies of water. Sedimentation is the collective name for processes that cause mineral and/or organic particles to settle and accumulate or minerals to precipitate from a solution....
make the Cretaceous rock record especially fine. Famous formations
Geologic formation
A formation or geological formation is the fundamental unit of lithostratigraphy. A formation consists of a certain number of rock strata that have a comparable lithology, facies or other similar properties...
from North America include the rich marine fossils of Kansas
Kansas
Kansas is a US state located in the Midwestern United States. It is named after the Kansas River which flows through it, which in turn was named after the Kansa Native American tribe, which inhabited the area. The tribe's name is often said to mean "people of the wind" or "people of the south...
's Smoky Hill Chalk Member
Smoky Hill Chalk
The Smoky Hill Chalk Member of the Niobrara Chalk formation is a Cretaceous conservation Lagerstätte, or fossil rich geological formation, known primarily for its exceptionally well-preserved marine reptiles. The Smoky Hill Chalk Member is the uppermost of the two structural units of the Niobrara...
and the terrestrial fauna of the late Cretaceous Hell Creek Formation
Hell Creek Formation
The Hell Creek Formation is an intensely-studied division of Upper Cretaceous to lower Paleocene rocks in North America, named for exposures studied along Hell Creek, near Jordan, Montana...
. Other important Cretaceous exposures occur in Europe
Europe
Europe is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting...
and China
China
Chinese civilization may refer to:* China for more general discussion of the country.* Chinese culture* Greater China, the transnational community of ethnic Chinese.* History of China* Sinosphere, the area historically affected by Chinese culture...
. In the area that is now India, massive lava
Lava
Lava refers both to molten rock expelled by a volcano during an eruption and the resulting rock after solidification and cooling. This molten rock is formed in the interior of some planets, including Earth, and some of their satellites. When first erupted from a volcanic vent, lava is a liquid at...
beds called the Deccan Traps
Deccan Traps
The Deccan Traps are a large igneous province located on the Deccan Plateau of west-central India and one of the largest volcanic features on Earth. They consist of multiple layers of solidified flood basalt that together are more than thick and cover an area of and a volume of...
were laid down in the very late Cretaceous and early Paleocene.
Cenozoic Era
The Cenozoic Era covers the 65.5 million years since the Cretaceous-Tertiary extinction eventCretaceous-Tertiary extinction event
The Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event, formerly named and still commonly referred to as the Cretaceous-Tertiary extinction event, occurred approximately 65.5 million years ago at the end of the Maastrichtian age of the Cretaceous period. It was a large-scale mass extinction of animal and plant...
up to and including the present day. By the end of the Mesozoic
Mesozoic
The Mesozoic era is an interval of geological time from about 250 million years ago to about 65 million years ago. It is often referred to as the age of reptiles because reptiles, namely dinosaurs, were the dominant terrestrial and marine vertebrates of the time...
era, the continents had rifted into nearly their present form. Laurasia
Laurasia
In paleogeography, Laurasia was the northernmost of two supercontinents that formed part of the Pangaea supercontinent from approximately...
became North America
North America
North America is a continent wholly within the Northern Hemisphere and almost wholly within the Western Hemisphere. It is also considered a northern subcontinent of the Americas...
and Eurasia
Eurasia
Eurasia is a continent or supercontinent comprising the traditional continents of Europe and Asia ; covering about 52,990,000 km2 or about 10.6% of the Earth's surface located primarily in the eastern and northern hemispheres...
, while Gondwana
Gondwana
In paleogeography, Gondwana , originally Gondwanaland, was the southernmost of two supercontinents that later became parts of the Pangaea supercontinent. It existed from approximately 510 to 180 million years ago . Gondwana is believed to have sutured between ca. 570 and 510 Mya,...
split into South America
South America
South America is a continent situated in the Western Hemisphere, mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere. The continent is also considered a subcontinent of the Americas. It is bordered on the west by the Pacific Ocean and on the north and east...
, Africa
Africa
Africa is the world's second largest and second most populous continent, after Asia. At about 30.2 million km² including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of the Earth's total surface area and 20.4% of the total land area...
, Australia
Australia
Australia , officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country in the Southern Hemisphere comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands in the Indian and Pacific Oceans. It is the world's sixth-largest country by total area...
, Antarctica and the Indian subcontinent
Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent, also Indian Subcontinent, Indo-Pak Subcontinent or South Asian Subcontinent is a region of the Asian continent on the Indian tectonic plate from the Hindu Kush or Hindu Koh, Himalayas and including the Kuen Lun and Karakoram ranges, forming a land mass which extends...
, which collided with the Asian plate. This impact gave rise to the Himalayas. The Tethys Sea, which had separated the northern continents from Africa and India, began to close up, forming the Mediterranean sea
Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean surrounded by the Mediterranean region and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Anatolia and Europe, on the south by North Africa, and on the east by the Levant...
.
Paleogene Period
The Paleogene (alternatively Palaeogene) Period is a unit of geologic time that began 65.5 ± 0.3 and ended 23.03 ± 0.05 Ma and comprises the first part of the CenozoicCenozoic
The Cenozoic era is the current and most recent of the three Phanerozoic geological eras and covers the period from 65.5 mya to the present. The era began in the wake of the Cretaceous–Tertiary extinction event at the end of the Cretaceous that saw the demise of the last non-avian dinosaurs and...
Era. This period consists of the Paleocene
Paleocene
The Paleocene or Palaeocene, the "early recent", is a geologic epoch that lasted from about . It is the first epoch of the Palaeogene Period in the modern Cenozoic Era...
, Eocene
Eocene
The Eocene Epoch, lasting from about 56 to 34 million years ago , is a major division of the geologic timescale and the second epoch of the Paleogene Period in the Cenozoic Era. The Eocene spans the time from the end of the Palaeocene Epoch to the beginning of the Oligocene Epoch. The start of the...
and Oligocene
Oligocene
The Oligocene is a geologic epoch of the Paleogene Period and extends from about 34 million to 23 million years before the present . As with other older geologic periods, the rock beds that define the period are well identified but the exact dates of the start and end of the period are slightly...
Epochs.
Paleocene Epoch
The Paleocene, lasted from 65.5 ± 0.3 Ma to 55.8 ± 0.2 Ma.
In many ways, the Paleocene
Paleocene
The Paleocene or Palaeocene, the "early recent", is a geologic epoch that lasted from about . It is the first epoch of the Palaeogene Period in the modern Cenozoic Era...
continued processes that had begun during the late Cretaceous Period. During the Paleocene, the continent
Continent
A continent is one of several very large landmasses on Earth. They are generally identified by convention rather than any strict criteria, with seven regions commonly regarded as continents—they are : Asia, Africa, North America, South America, Antarctica, Europe, and Australia.Plate tectonics is...
s continued to drift toward their present positions. Supercontinent Laurasia
Laurasia
In paleogeography, Laurasia was the northernmost of two supercontinents that formed part of the Pangaea supercontinent from approximately...
had not yet separated into three continents. Europe
Europe
Europe is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting...
and Greenland
Greenland
Greenland is an autonomous country within the Kingdom of Denmark, located between the Arctic and Atlantic Oceans, east of the Canadian Arctic Archipelago. Though physiographically a part of the continent of North America, Greenland has been politically and culturally associated with Europe for...
were still connected. North America
North America
North America is a continent wholly within the Northern Hemisphere and almost wholly within the Western Hemisphere. It is also considered a northern subcontinent of the Americas...
and Asia
Asia
Asia is the world's largest and most populous continent, located primarily in the eastern and northern hemispheres. It covers 8.7% of the Earth's total surface area and with approximately 3.879 billion people, it hosts 60% of the world's current human population...
were still intermittently joined by a land bridge, while Greenland and North America were beginning to separate. The Laramide orogeny
Laramide orogeny
The Laramide orogeny was a period of mountain building in western North America, which started in the Late Cretaceous, 70 to 80 million years ago, and ended 35 to 55 million years ago. The exact duration and ages of beginning and end of the orogeny are in dispute, as is the cause. The Laramide...
of the late Cretaceous continued to uplift the Rocky Mountains
Rocky Mountains
The Rocky Mountains are a major mountain range in western North America. The Rocky Mountains stretch more than from the northernmost part of British Columbia, in western Canada, to New Mexico, in the southwestern United States...
in the American west, which ended in the succeeding epoch. South and North America remained separated by equatorial seas (they joined during the Neogene
Neogene
The Neogene is a geologic period and system in the International Commission on Stratigraphy Geologic Timescale starting 23.03 ± 0.05 million years ago and ending 2.588 million years ago...
); the components of the former southern supercontinent Gondwanaland continued to split apart, with Africa
Africa
Africa is the world's second largest and second most populous continent, after Asia. At about 30.2 million km² including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of the Earth's total surface area and 20.4% of the total land area...
, South America, Antarctica and Australia
Australia
Australia , officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country in the Southern Hemisphere comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands in the Indian and Pacific Oceans. It is the world's sixth-largest country by total area...
pulling away from each other. Africa was heading north toward Europe
Europe
Europe is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting...
, slowly closing the Tethys Ocean
Tethys Ocean
The Tethys Ocean was an ocean that existed between the continents of Gondwana and Laurasia during the Mesozoic era before the opening of the Indian Ocean.-Modern theory:...
, and India
India
India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
began its migration to Asia that would lead to a tectonic collision and the formation of the Himalayas
Himalayas
The Himalaya Range or Himalaya Mountains Sanskrit: Devanagari: हिमालय, literally "abode of snow"), usually called the Himalayas or Himalaya for short, is a mountain range in Asia, separating the Indian subcontinent from the Tibetan Plateau...
.
Eocene Epoch
During the Eocene
Eocene
The Eocene Epoch, lasting from about 56 to 34 million years ago , is a major division of the geologic timescale and the second epoch of the Paleogene Period in the Cenozoic Era. The Eocene spans the time from the end of the Palaeocene Epoch to the beginning of the Oligocene Epoch. The start of the...
(55.8 ± 0.2 - 33.9 ± 0.1 Ma), the continents continued to drift toward their present positions. At the beginning of the period, Australia and Antarctica remained connected, and warm equator
Equator
An equator is the intersection of a sphere's surface with the plane perpendicular to the sphere's axis of rotation and containing the sphere's center of mass....
ial currents mixed with colder Antarctic waters, distributing the heat around the world and keeping global temperatures high. But when Australia split from the southern continent around 45 Ma, the warm equatorial currents were deflected away from Antarctica, and an isolated cold water channel developed between the two continents. The Antarctic region cooled down, and the ocean surrounding Antarctica began to freeze, sending cold water and ice floes north, reinforcing the cooling. The northern supercontinent
Supercontinent
In geology, a supercontinent is a landmass comprising more than one continental core, or craton. The assembly of cratons and accreted terranes that form Eurasia qualifies as a supercontinent today.-History:...
of Laurasia
Laurasia
In paleogeography, Laurasia was the northernmost of two supercontinents that formed part of the Pangaea supercontinent from approximately...
began to break up, as Europe
Europe
Europe is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting...
, Greenland
Greenland
Greenland is an autonomous country within the Kingdom of Denmark, located between the Arctic and Atlantic Oceans, east of the Canadian Arctic Archipelago. Though physiographically a part of the continent of North America, Greenland has been politically and culturally associated with Europe for...
and North America
North America
North America is a continent wholly within the Northern Hemisphere and almost wholly within the Western Hemisphere. It is also considered a northern subcontinent of the Americas...
drifted apart. In western North America, mountain building
Orogeny
Orogeny refers to forces and events leading to a severe structural deformation of the Earth's crust due to the engagement of tectonic plates. Response to such engagement results in the formation of long tracts of highly deformed rock called orogens or orogenic belts...
started in the Eocene, and huge lakes formed in the high flat basins among uplifts. In Europe, the Tethys Sea finally vanished, while the uplift of the Alps
Alps
The Alps is one of the great mountain range systems of Europe, stretching from Austria and Slovenia in the east through Italy, Switzerland, Liechtenstein and Germany to France in the west....
isolated its final remnant, the Mediterranean
Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean surrounded by the Mediterranean region and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Anatolia and Europe, on the south by North Africa, and on the east by the Levant...
, and created another shallow sea with island archipelago
Archipelago
An archipelago , sometimes called an island group, is a chain or cluster of islands. The word archipelago is derived from the Greek ἄρχι- – arkhi- and πέλαγος – pélagos through the Italian arcipelago...
s to the north. Though the North Atlantic
Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's oceanic divisions. With a total area of about , it covers approximately 20% of the Earth's surface and about 26% of its water surface area...
was opening, a land connection appears to have remained between North America and Europe since the faunas of the two regions are very similar. India
India
India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
continued its journey away from Africa
Africa
Africa is the world's second largest and second most populous continent, after Asia. At about 30.2 million km² including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of the Earth's total surface area and 20.4% of the total land area...
and began its collision with Asia
Asia
Asia is the world's largest and most populous continent, located primarily in the eastern and northern hemispheres. It covers 8.7% of the Earth's total surface area and with approximately 3.879 billion people, it hosts 60% of the world's current human population...
, creating the Himalayan orogeny.
Oligocene Epoch
The Oligocene Epoch extends from about 34 Ma to 23 Ma. During the Oligocene
Oligocene
The Oligocene is a geologic epoch of the Paleogene Period and extends from about 34 million to 23 million years before the present . As with other older geologic periods, the rock beds that define the period are well identified but the exact dates of the start and end of the period are slightly...
the continents continued to drift toward their present positions.
Antarctica continued to become more isolated and finally developed a permanent ice cap
Ice cap
An ice cap is an ice mass that covers less than 50 000 km² of land area . Masses of ice covering more than 50 000 km² are termed an ice sheet....
. Mountain building
Orogeny
Orogeny refers to forces and events leading to a severe structural deformation of the Earth's crust due to the engagement of tectonic plates. Response to such engagement results in the formation of long tracts of highly deformed rock called orogens or orogenic belts...
in western North America
North America
North America is a continent wholly within the Northern Hemisphere and almost wholly within the Western Hemisphere. It is also considered a northern subcontinent of the Americas...
continued, and the Alps
Alps
The Alps is one of the great mountain range systems of Europe, stretching from Austria and Slovenia in the east through Italy, Switzerland, Liechtenstein and Germany to France in the west....
started to rise in Europe
Europe
Europe is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting...
as the African plate
African Plate
The African Plate is a tectonic plate which includes the continent of Africa, as well as oceanic crust which lies between the continent and various surrounding ocean ridges.-Boundaries:...
continued to push north into the Eurasian plate
Eurasian Plate
The Eurasian Plate is a tectonic plate which includes most of the continent of Eurasia , with the notable exceptions of the Indian subcontinent, the Arabian subcontinent, and the area east of the Chersky Range in East Siberia...
, isolating the remnants of Tethys Sea. A brief marine incursion marks the early Oligocene in Europe. There appears to have been a land bridge in the early Oligocene between North America
North America
North America is a continent wholly within the Northern Hemisphere and almost wholly within the Western Hemisphere. It is also considered a northern subcontinent of the Americas...
and Europe
Europe
Europe is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting...
since the faunas of the two regions are very similar. During the Oligocene, South America
South America
South America is a continent situated in the Western Hemisphere, mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere. The continent is also considered a subcontinent of the Americas. It is bordered on the west by the Pacific Ocean and on the north and east...
was finally detached from Antarctica and drifted north toward North America
North America
North America is a continent wholly within the Northern Hemisphere and almost wholly within the Western Hemisphere. It is also considered a northern subcontinent of the Americas...
. It also allowed the Antarctic Circumpolar Current
Antarctic Circumpolar Current
The Antarctic Circumpolar Current is an ocean current that flows from west to east around Antarctica. An alternative name for the ACC is the West Wind Drift. The ACC is the dominant circulation feature of the Southern Ocean and, at approximately 125 Sverdrups, the largest ocean current...
to flow, rapidly cooling the continent.
Neogene Period
Neogene Period is a unit of geologic time starting 23.03 ± 0.05 Ma. The Neogene Period follows the PaleogenePaleogene
The Paleogene is a geologic period and system that began 65.5 ± 0.3 and ended 23.03 ± 0.05 million years ago and comprises the first part of the Cenozoic Era...
Period. Under the current proposal of the International Commission on Stratigraphy
International Commission on Stratigraphy
The International Commission on Stratigraphy , sometimes referred to by the unofficial "International Stratigraphic Commission" is a daughter or major subcommittee grade scientific daughter organization that concerns itself with stratigraphy, geological, and geochronological matters on a global...
(ICS), the Neogene would consist of the Miocene
Miocene
The Miocene is a geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about . The Miocene was named by Sir Charles Lyell. Its name comes from the Greek words and and means "less recent" because it has 18% fewer modern sea invertebrates than the Pliocene. The Miocene follows the Oligocene...
, Pliocene
Pliocene
The Pliocene Epoch is the period in the geologic timescale that extends from 5.332 million to 2.588 million years before present. It is the second and youngest epoch of the Neogene Period in the Cenozoic Era. The Pliocene follows the Miocene Epoch and is followed by the Pleistocene Epoch...
, Pleistocene
Pleistocene
The Pleistocene is the epoch from 2,588,000 to 11,700 years BP that spans the world's recent period of repeated glaciations. The name pleistocene is derived from the Greek and ....
and Holocene
Holocene
The Holocene is a geological epoch which began at the end of the Pleistocene and continues to the present. The Holocene is part of the Quaternary period. Its name comes from the Greek words and , meaning "entirely recent"...
epochs and continue until the present.
Miocene Epoch
The Miocene extends from about 23.03 to 5.332 Ma.
During the Miocene
Miocene
The Miocene is a geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about . The Miocene was named by Sir Charles Lyell. Its name comes from the Greek words and and means "less recent" because it has 18% fewer modern sea invertebrates than the Pliocene. The Miocene follows the Oligocene...
continents continued to drift toward their present positions. Of the modern geologic features, only the land bridge between South America
South America
South America is a continent situated in the Western Hemisphere, mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere. The continent is also considered a subcontinent of the Americas. It is bordered on the west by the Pacific Ocean and on the north and east...
and North America
North America
North America is a continent wholly within the Northern Hemisphere and almost wholly within the Western Hemisphere. It is also considered a northern subcontinent of the Americas...
was absent, the subduction zone along the Pacific Ocean
Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest of the Earth's oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic in the north to the Southern Ocean in the south, bounded by Asia and Australia in the west, and the Americas in the east.At 165.2 million square kilometres in area, this largest division of the World...
margin of South America caused the rise of the Andes
Andes
The Andes is the world's longest continental mountain range. It is a continual range of highlands along the western coast of South America. This range is about long, about to wide , and of an average height of about .Along its length, the Andes is split into several ranges, which are separated...
and the southward extension of the Meso-American peninsula. India
India
India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
continued to collide with Asia
Asia
Asia is the world's largest and most populous continent, located primarily in the eastern and northern hemispheres. It covers 8.7% of the Earth's total surface area and with approximately 3.879 billion people, it hosts 60% of the world's current human population...
. The Tethys Seaway continued to shrink and then disappeared as Africa
Africa
Africa is the world's second largest and second most populous continent, after Asia. At about 30.2 million km² including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of the Earth's total surface area and 20.4% of the total land area...
collided with Eurasia
Eurasia
Eurasia is a continent or supercontinent comprising the traditional continents of Europe and Asia ; covering about 52,990,000 km2 or about 10.6% of the Earth's surface located primarily in the eastern and northern hemispheres...
in the Turkish
Turkey
Turkey , known officially as the Republic of Turkey , is a Eurasian country located in Western Asia and in East Thrace in Southeastern Europe...
-Arabian region between 19 and 12 Ma (ICS
International Commission on Stratigraphy
The International Commission on Stratigraphy , sometimes referred to by the unofficial "International Stratigraphic Commission" is a daughter or major subcommittee grade scientific daughter organization that concerns itself with stratigraphy, geological, and geochronological matters on a global...
2004). Subsequent uplift of mountains in the western Mediterranean region and a global fall in sea levels combined to cause a temporary drying up of the Mediterranean Sea resulting in the Messinian salinity crisis
Messinian salinity crisis
The Messinian Salinity Crisis, also referred to as the Messinian Event, and in its latest stage as the Lago Mare event, was a geological event during which the Mediterranean Sea went into a cycle of partly or nearly complete desiccation throughout the latter part of the Messinian age of the Miocene...
near the end of the Miocene.
Pliocene Epoch
The Pliocene extends from 5.332 Ma to 2.588 Ma. During the Pliocene
Pliocene
The Pliocene Epoch is the period in the geologic timescale that extends from 5.332 million to 2.588 million years before present. It is the second and youngest epoch of the Neogene Period in the Cenozoic Era. The Pliocene follows the Miocene Epoch and is followed by the Pleistocene Epoch...
continents continued to drift toward their present positions, moving from positions possibly as far as 250 kilometres (155 mi) from their present locations to positions only 70 km from their current locations.
South America became linked to North America through the Isthmus of Panama
Isthmus of Panama
The Isthmus of Panama, also historically known as the Isthmus of Darien, is the narrow strip of land that lies between the Caribbean Sea and the Pacific Ocean, linking North and South America. It contains the country of Panama and the Panama Canal...
during the Pliocene, bringing a nearly complete end to South America's distinctive marsupial faunas. The formation of the Isthmus had major consequences on global temperatures, since warm equatorial ocean currents were cut off and an Atlantic cooling cycle began, with cold Arctic and Antarctic waters dropping temperatures in the now-isolated Atlantic Ocean. Africa
Africa
Africa is the world's second largest and second most populous continent, after Asia. At about 30.2 million km² including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of the Earth's total surface area and 20.4% of the total land area...
's collision with Europe
Europe
Europe is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting...
formed the Mediterranean Sea
Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean surrounded by the Mediterranean region and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Anatolia and Europe, on the south by North Africa, and on the east by the Levant...
, cutting off the remnants of the Tethys Ocean
Tethys Ocean
The Tethys Ocean was an ocean that existed between the continents of Gondwana and Laurasia during the Mesozoic era before the opening of the Indian Ocean.-Modern theory:...
. Sea level changes exposed the land-bridge between Alaska
Alaska
Alaska is the largest state in the United States by area. It is situated in the northwest extremity of the North American continent, with Canada to the east, the Arctic Ocean to the north, and the Pacific Ocean to the west and south, with Russia further west across the Bering Strait...
and Asia. Near the end of the Pliocene, about 2.58 Ma (the start the of the Quaternary
Quaternary
The Quaternary Period is the most recent of the three periods of the Cenozoic Era in the geologic time scale of the ICS. It follows the Neogene Period, spanning 2.588 ± 0.005 million years ago to the present...
Period), the current ice age
Quaternary glaciation
Quaternary glaciation, also known as the Pleistocene glaciation, the current ice age or simply the ice age, refers to the period of the last few million years in which permanent ice sheets were established in Antarctica and perhaps Greenland, and fluctuating ice sheets have occurred elsewhere...
began.
Pleistocene Epoch
The Pleistocene extends from 2.588 million to 11,700 years before present. The modern continent
Continent
A continent is one of several very large landmasses on Earth. They are generally identified by convention rather than any strict criteria, with seven regions commonly regarded as continents—they are : Asia, Africa, North America, South America, Antarctica, Europe, and Australia.Plate tectonics is...
s were essentially at their present positions during the Pleistocene
Pleistocene
The Pleistocene is the epoch from 2,588,000 to 11,700 years BP that spans the world's recent period of repeated glaciations. The name pleistocene is derived from the Greek and ....
, the plates upon which they sit probably having moved no more than 100 kilometres (62 mi) relative to each other since the beginning of the period.
Holocene Epoch
The Holocene Epoch began approximately 11,550 calendar years before present and continues to the present. During the Holocene
Holocene
The Holocene is a geological epoch which began at the end of the Pleistocene and continues to the present. The Holocene is part of the Quaternary period. Its name comes from the Greek words and , meaning "entirely recent"...
, continental motions have been less than a kilometer.
However, ice melt caused world sea levels to rise about 35 metres (115 ft) in the early part of the Holocene. In addition, many areas above about 40 degrees north
40th parallel north
The 40th parallel north is a circle of latitude that is 40 degrees north of the Earth's equatorial plane. It crosses Europe, the Mediterranean Sea, Asia, the Pacific Ocean, North America, and the Atlantic Ocean....
latitude had been depressed by the weight of the Pleistocene glacier
Glacier
A glacier is a large persistent body of ice that forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its ablation over many years, often centuries. At least 0.1 km² in area and 50 m thick, but often much larger, a glacier slowly deforms and flows due to stresses induced by its weight...
s and rose as much as 180 metres (591 ft) over the late Pleistocene and Holocene, and are still rising today. The sea level rise and temporary land depression allowed temporary marine incursions into areas that are now far from the sea. Holocene marine fossils are known from Vermont
Vermont
Vermont is a state in the New England region of the northeastern United States of America. The state ranks 43rd in land area, , and 45th in total area. Its population according to the 2010 census, 630,337, is the second smallest in the country, larger only than Wyoming. It is the only New England...
, Quebec
Quebec
Quebec or is a province in east-central Canada. It is the only Canadian province with a predominantly French-speaking population and the only one whose sole official language is French at the provincial level....
, Ontario
Ontario
Ontario is a province of Canada, located in east-central Canada. It is Canada's most populous province and second largest in total area. It is home to the nation's most populous city, Toronto, and the nation's capital, Ottawa....
and Michigan
Michigan
Michigan is a U.S. state located in the Great Lakes Region of the United States of America. The name Michigan is the French form of the Ojibwa word mishigamaa, meaning "large water" or "large lake"....
. Other than higher latitude temporary marine incursions associated with glacial depression, Holocene fossils are found primarily in lakebed, floodplain and cave deposits. Holocene marine deposits along low-latitude coastlines are rare because the rise in sea levels during the period exceeds any likely upthrusting of non-glacial origin. Post-glacial rebound
Post-glacial rebound
Post-glacial rebound is the rise of land masses that were depressed by the huge weight of ice sheets during the last glacial period, through a process known as isostasy...
in Scandinavia
Scandinavia
Scandinavia is a cultural, historical and ethno-linguistic region in northern Europe that includes the three kingdoms of Denmark, Norway and Sweden, characterized by their common ethno-cultural heritage and language. Modern Norway and Sweden proper are situated on the Scandinavian Peninsula,...
resulted in the emergence of coastal areas around the Baltic Sea
Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is a brackish mediterranean sea located in Northern Europe, from 53°N to 66°N latitude and from 20°E to 26°E longitude. It is bounded by the Scandinavian Peninsula, the mainland of Europe, and the Danish islands. It drains into the Kattegat by way of the Øresund, the Great Belt and...
, including much of Finland
Finland
Finland , officially the Republic of Finland, is a Nordic country situated in the Fennoscandian region of Northern Europe. It is bordered by Sweden in the west, Norway in the north and Russia in the east, while Estonia lies to its south across the Gulf of Finland.Around 5.4 million people reside...
. The region continues to rise, still causing weak earthquake
Earthquake
An earthquake is the result of a sudden release of energy in the Earth's crust that creates seismic waves. The seismicity, seismism or seismic activity of an area refers to the frequency, type and size of earthquakes experienced over a period of time...
s across Northern Europe
Northern Europe
Northern Europe is the northern part or region of Europe. Northern Europe typically refers to the seven countries in the northern part of the European subcontinent which includes Denmark, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Norway, Finland and Sweden...
. The equivalent event in North America was the rebound of Hudson Bay
Hudson Bay
Hudson Bay , sometimes called Hudson's Bay, is a large body of saltwater in northeastern Canada. It drains a very large area, about , that includes parts of Ontario, Quebec, Saskatchewan, Alberta, most of Manitoba, southeastern Nunavut, as well as parts of North Dakota, South Dakota, Minnesota,...
, as it shrank from its larger, immediate post-glacial Tyrrell Sea
Tyrrell Sea
The Tyrrell Sea, named for Canadian geologist Joseph Tyrrell, is another name for prehistoric Hudson Bay, namely as it existed during the retreat of the Laurentide Ice Sheet....
phase, to near its present boundaries.
See also
- Timeline of natural historyTimeline of natural historyThis timeline of natural history summarizes significant cosmological, geological and biological events from the formation of the Universe to the beginning of the Stone Age.-Formation of the Universe:...
- Future of the EarthFuture of the EarthThe biological and geological future of the Earth can be extrapolated based upon the estimated effects of several long-term influences. These include the chemistry at the Earth's surface, the rate of cooling of the planet's interior, the gravitational interactions with other objects in the Solar...
- Plate reconstructionPlate reconstructionPlate reconstruction is the process of reconstructing the positions of tectonic plates relative to each other or to other reference frames, such as the earth's magnetic field or groups of hotspots, in the geological past...
- Plate tectonicsPlate tectonicsPlate tectonics is a scientific theory that describes the large scale motions of Earth's lithosphere...
External links
- Cosmic Evolution — a detailed look at events from the origin of the universe to the present
- Valley, John W. “A Cool Early Earth?” Scientific AmericanScientific AmericanScientific American is a popular science magazine. It is notable for its long history of presenting science monthly to an educated but not necessarily scientific public, through its careful attention to the clarity of its text as well as the quality of its specially commissioned color graphics...
. 2005 Oct:58–65. – discusses the timing of the formation of the oceans and other major events in Earth’s early history. - Davies, PaulPaul DaviesPaul Charles William Davies, AM is an English physicist, writer and broadcaster, currently a professor at Arizona State University as well as the Director of BEYOND: Center for Fundamental Concepts in Science...
. “Quantum leap of life”. The GuardianThe GuardianThe Guardian, formerly known as The Manchester Guardian , is a British national daily newspaper in the Berliner format...
. 2005 Dec 20. – discusses speculation into the role of quantum systems in the origin of life - Evolution timeline (uses Shockwave). Animated story of life since about 13,700,000,000 shows everything from the big bang to the formation of the earth and the development of bacteria and other organisms to the ascent of man.
- Scientific American Magazine (October 2005 Issue) A Cool Early Earth?
- Artist's Conception of Cold Early Earth
- Theory of the Earth
- Theory of the Earth & Abstract of the Theory of the Earth
- Paleomaps Since 600 Ma (Mollweide Projection, Longitude 0)
- Paleomaps Since 600 Ma (Mollweide Projection, Longitude 180)

