History of Latin America
Encyclopedia
Latin America
refers to countries
in the Americas
where Romance
(Latin-derived) languages are spoken. This definition, however, is not meant to include Canada
, in spite of its large French-speaking population.
Latin American countries generally lie south of the United States
. By extension, some writers and commentators, particularly in the United States, apply the term to the whole region south of the United States, including the non-Romance-speaking countries such as Suriname
, Jamaica
, and Guyana
, due to similar economic, political and social histories and present-day conditions.
Before the arrival of Europeans
in the late 15th and early 16th centuries, the region was home to many indigenous peoples, many of which had advanced civilizations, most notably, the Aztec
, Inca
and Maya
. By the end of the sixteenth century large areas of what would become Latin America were colonized by European settlers, primarily from Spain
, Portugal
and to a lesser extent, France
and the Netherlands
(in Brazil). In the early nineteenth century most of the region attained its independence, giving rise to new countries, although a few, small colonies remain.
In the early nineteenth century most of the region attained its independence, giving rise to new countries, although a few, small colonies remain.
affinity with all Romance cultures can be traced back to the 1830s, in particular in the writing of the French
Saint-Simonian
Michel Chevalier
, who postulated that this part of the Americas were inhabited by people of a "Latin race," and that it could, therefore, ally itself with "Latin Europe
" in a struggle with "Teutonic Europe
," "Anglo-Saxon America" and "Slavic Europe." The idea was later taken up by Latin American intellectuals and political leaders of the mid- and late-nineteenth century, who no longer looked to Spain or Portugal as cultural models, but rather to France. The actual term "Latin America" was coined in France under Napoleon III and played a role in his campaign to imply cultural kinship with France, transform France into a cultural and political leader of the area and install Maximilian
as emperor of Mexico.
In the mid-twentieth century, especially in the United States, there was a trend to occasionally classify all of the territory south of the United States as "Latin America," especially when the discussion focused on its contemporary political and economic relations to the rest of the world, rather than solely on its cultural aspects. Concurrently, there has been a move to avoid this oversimplification by talking about "Latin America and the Caribbean," as in the United Nations geoscheme.
Since, the concept and definitions of Latin American are very modern, going back only to the nineteenth century, it is anachronistic to talk about "a history of Latin America" before the arrival the Europeans. Nevertheless, the many and varied cultures that did exist in the pre-Columbian period had a strong and direct influence on the societies that emerged as a result of the conquest, and therefore, they cannot be overlooked. They are introduced in the next section.
. Precise dating of many of the early civilizations is difficult because there are few text sources. However, highly-developed civilizations flourished at various times and places, such as in the Andes
and Mesoamerica
.
landed in the Americas in 1492. Subsequently, the major sea powers in Europe sent expeditions to the New World
to build trade networks and colonies and to convert the native peoples to Christianity. Spain concentrated on building its empire on the central and southern parts of the Americas allotted to it by the Treaty of Tordesillas
, because of presence of large, settled societies like the Aztec
, the Inca
, the Maya
and the Chibcha
, whose human and material resources it could exploit, and large concentrations of silver
and gold
. The Portuguese built its empire in Brazil
, which fell in its sphere of influence per the Treaty of Tordesillas, by developing the land for sugar
production since there was a lack of a large, complex society or mineral resources.
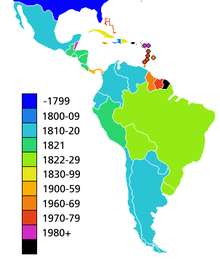 Following the model of the U.S.
Following the model of the U.S.
and French
revolutions, most of Latin America achieved its independence by 1825. Independence destroyed the old common market
that existed under the Spanish Empire after the Bourbon Reforms
and created an increased dependence on the financial investment provided by nations which had already begun to industrialize
; therefore, Western European powers, in particular Great Britain and France, and the United States began to play major roles, since the region became economically dependent on these nations. Independence also created a new, self-consciously "Latin American" ruling class and intelligentsia which at times avoided Spanish and Portuguese models in their quest to reshape their societies. This elite looked towards other Catholic European models—in particular France
—for a new Latin American culture, but did not seek input from indigenous peoples.
The failed efforts in Spanish America
to keep together most of the initial large states that emerged from independence— Gran Colombia
, the Federal Republic of Central America
and the United Provinces of South America
—resulted a number of domestic and interstate conflicts, which plagued the new countries. Brazil, in contrast to its Hispanic neighbors, remained a united monarchy and avoided the problem of civil and interstate wars. Domestic wars were often fights between federalists and centrists who ended up asserted themselves through the military repression of their opponents at the expense of civilian political life. The new nations inherited the cultural diversity of the colonial era and strived to create a new identity based around the shared European (Spanish or Portuguese) language and culture.
For the next few decades there was a long process to create a sense of nationality
. Most of the new national borders were created around the often centuries-old audiencia jurisdictions or the Bourbon intendancies
, which had become areas of political identity. In many areas the borders were unstable, since the new states fought wars with each other to gain access to resources, especially in the second half of the nineteenth century. The more important conflicts were the War of the Triple Alliance
(1864–1870) and the War of the Pacific
(1879–1884). The War of the Triple Alliance pitted Argentina, Brazil and Uruguay against Paraguay, which was utterly defeated. As a result Paraguay suffered a demographic collapse: the population went from an estimated 525,000 persons in 1864 to 221,000 in 1871 and out of this last population, only around 28,000 were men. In the War of the Pacific, Chile defeated the combined forces of Bolivia and Peru. Chile gained control of saltpeter
-rich areas, previously controlled by Peru and Bolivia, and Bolivia became a land-locked nation. By mid-century the region also confronted a growing United States, seeking to expand on the North American continent and extend its influence in the hemisphere. In Mexican–American War
(1846–1848), Mexico lost over half of its territory to the United States. In the 1860s France attempted to indirectly control Mexico
. In South America, Brazil consolidated its control of large swaths of the Amazon Basin
at the expense of its neighbors. In the 1880s the United States implemented an aggressive policy to defend and expand its political and economic interests in all of Latin America, which culminated in the creation of the Pan-American Conference
, the successful completion of the Panama Canal
and the United States intervention in the final Cuban war of independence.
The export of natural resources provided the basis of most Latin American economies in the nineteenth century, which allowed for the development of wealthy elite. The restructuring of colonial economic and political realities resulted in a sizable gap between rich and poor, with landed elites controlling the vast majority of land and resources. In Brazil
, for instance, by 1910 85% of the land belonged to 1% of the population. Gold mining and fruit growing, in particular, were monopolized by these wealthy landowners. These "Great Owners" completely controlled local activity and, furthermore, were the principal employers and the main source of wages. This led to a society of peasant
s whose connection to larger political realities remained in thrall to farming and mining magnates.
The endemic political instability and the nature of the economy resulted in the emergence of caudillos, military chiefs whose hold on power depended on their military skill and ability to dispense patronage
. The political regimes were at least in theory democratic
and took the form of either presidential
or parliamentary
governments. Both were prone to being taken over by a caudillo or an oligarchy
. The political landscape was occupied by conservatives
, who believed that the preservation of the old social hierarchies served as the best guarantee of national stability and prosperity, and liberals
, who sought to bring about progress by freeing up the economy and individual initiative. Popular insurrections were often influential and repressed: 100,000 were killed during the suppression of a Colombian revolt in 1890 during the Thousand Days War
. Some states did manage to have some of democracy: Uruguay
, and partially Argentina
, Chile
, Costa Rica
and Colombia
. The others were clearly oligarchist or authoritarian
, although these oligarchs and caudillos sometimes enjoyed support from a majority in the population. All of these regimes sought to maintain Latin America's lucrative position in the world economy as a provider of raw materials.
's Big Stick Doctrine, which modified the old Monroe Doctrine
, which had simply aimed to deter European intervention in the hemisphere. At the conclusion of the Spanish-American War
the new government of Cuba and the United States signed the Platt Amendment
in 1902, which authorized the United States to intervene in Cuban affairs when the United States deemed necessary. In Colombia
, United States sought the concession
of a territory in Panama
to build a much anticipated canal across the isthmus. The Colombian government opposed this, but a Panamanian insurrection provided the United States with an opportunity. The United States backed Panamanian independence and the new nation granted the concession. These were not the only interventions carried out in the region by the United States. In the first decades of the twentieth century, there were several military incursions into Central America and the Caribbean, mostly in defense of commercial interests, which became known as the "Banana Wars."
The greatest political upheaval in the second decade of the century took place in Mexico
. In 1908, President Porfirio Díaz
, who had been in office since 1884, promised that he would step down in 1910. Francisco I. Madero
, a moderate liberal whose aim was to modernize the country while preventing a socialist revolution, launched an election campaign in 1910. Díaz, however, changed his mind and ran for office once more. Madero was arrested on election day and Díaz declared the winner. These events provoked uprisings, which became the start of the Mexican Revolution
. Revolutionary movements were organized and some key leaders appeared: Pancho Villa
in the north, Emiliano Zapata
in the south, and Madero in Mexico City. Madero's forces defeated the federal army in early 1911, assumed temporary control of the government and won a second election later on November 6, 1911. Madero undertook moderate reforms to implement greater democracy in the political system but failed to satisfy many of the regional leaders in what had become a revolutionary situation. Madero's failure to address agrarian claims led Zapata to break with Madero and resume the revolution. On February 18, 1913 Victoriano Huerta
, a conservative general organized a coup d'état
with the support of the United States; Madero was killed four days later. Other revolutionary leaders such as Villa, Zapata, and Venustiano Carranza
continued to militarily oppose the federal government, now under Huerta's control. Allies Zapata and Villa took Mexico City in March 1914, but found themselves outside of their elements in the capital and withdrew to their respective bastions. This allowed Carranza to assume control of the central government. He then organized the repression of the rebel armies of Villa and Zapata, led in particular by General Álvaro Obregón
,. The Mexican Constitution of 1917
, still the current constitution, was proclaimed but initially little enforced. The efforts against the other revolutionary leaders continued. Zapata was assassinated on April 10, 1919. Carranza himself was assassinated on May 15, 1920, leaving Obregón in power, who was officially elected president later that year. Finally in 1923 Villa was also assassinated. With the removal of the main rivals Obregón is able to consolidate power and relative peace returned to Mexico. Under the Constitution a liberal government is implemented but some of the aspirations of the working and rural classes remained unfulfilled. (See also, Agrarian land reform in Mexico
.)
posed a great challenge to the region. The collapse of the world economy meant that the demand for raw materials drastically declined, undermining many of the economies of Latin America. Intellectuals and government leaders in Latin America turned their backs on the older economic policies and turned toward import substitution industrialization. The goal was to create self-sufficient economies, which would have their own industrial sectors and large middle classes and which would be immune to the ups and downs of the global economy. Despite the potential threats to United States commercial interests, the Roosevelt administration
(1933–1945) understood that the United States could not wholly oppose import substitution. Roosevelt implemented a Good Neighbor policy
and allowed the nationalization of some American companies in Latin America. Mexican President Lázaro Cárdenas
nationalized American oil companies
, out of which he created Pemex
. Cárdenas also oversaw the redistribution of a quantity of land, fulfilling the hopes of many since the start of the Mexican Revolution. The Platt Amendment was also repealed, freeing Cuba from legal and official interference of the United States in its politics. The Second World War
also brought the United States and most Latin American nations together.
In the postwar period, the expansion of communism
became the greatest political issue for both the United States and governments in the region. The start of the Cold War
forced governments to choose between the United States and the Soviet Union
. Several socialist
and communist insurgencies broke out in Latin America throughout the entire twentieth century, but the most successful one was in Cuba. The Cuban Revolution
was led by Fidel Castro
against the regime of Fulgencio Batista
, who since 1933 was the principal autocrat in Cuba. Since the 1860s the Cuban economy had focused on the cultivation of sugar, of which 82% was sold in the American market by the twentieth century. Despite the repeal of the Platt Amendment, the United States still had considerable influence in Cuba, both in politics and in everyday life. In fact Cuba had a reputation of being the "brothel of the United States," a place where Americans could find all sorts of licit and illicit pleasures, provided they had the cash. Despite having the socially advanced constitution of 1940
, Cuba was plagued with corruption and the interruption of constitutional rule by autocrats like Batista. Batista began his final turn as the head of the government in a 1952 coup. The coalition that formed under the revolutionaries hoped to restore the constitution, reestablish a democratic state and free Cuba from the American influence. The revolutionaries succeeded in toppling Batista on January 1, 1959. Castro, who initially declared himself as a non-socialist, initiated a program of agrarian reforms and nationalizations in May 1959, which alienated the Eisenhower administration
(1953–1961) and resulted in the United States breaking of diplomatic relations, freezing Cuban assets in the United States and placing an embargo on the nation in 1960. The Kennedy administration
(1961–1963) authorized the funding and support of an invasion of Cuba
by exiles. The invasion failed and radicalized the revolutionary government's position. Cuba officially proclaimed itself socialist and openly became an ally of the Soviet Union
. The military collaboration between Cuba and the Soviet Union, which included the placement of intercontinental ballistic missile
s in Cuba precipitated the Cuban Missile Crisis
of October 1962.
 By the 1970s, leftists had acquired a significant political influence which prompted the right-wing, ecclesiastical authorities and a large portion of each individual country's upper class to support coups d'etat to avoid what they perceived as a communist threat. This was further fueled by Cuban and United States intervention which led to a political polarization. Most South American countries were in some periods ruled by military dictatorship
By the 1970s, leftists had acquired a significant political influence which prompted the right-wing, ecclesiastical authorities and a large portion of each individual country's upper class to support coups d'etat to avoid what they perceived as a communist threat. This was further fueled by Cuban and United States intervention which led to a political polarization. Most South American countries were in some periods ruled by military dictatorship
s that were supported by the United States of America.
Around the 1970s, the regimes of the Southern Cone
collaborated in Operation Condor
killing many leftist dissidents, including some urban guerrillas.
However, by the early 90's all countries had restored their democracies.
(IMF), World Bank
, and the US Treasury Department during the 80's and 90's.
In recent years, several Latin American countries led by socialist or other left wing governments—including Argentina and Venezuela—have campaigned for (and to some degree adopted) policies contrary to the Washington Consensus set of policies. (Other Latin counties with governments of the left, including Brazil, Chile and Peru, have in practice adopted the bulk of the policies). Also critical of the policies as actually promoted by the International Monetary Fund have been some US economists, such as Joseph Stiglitz and Dani Rodrik
, who have challenged what are sometimes described as the "fundamentalist" policies of the International Monetary Fund and the US Treasury for what Stiglitz calls a "one size fits all" treatment of individual economies.
The term has become associated with neoliberal policies in general and drawn into the broader debate over the expanding role of the free market, constraints upon the state, and US influence on other countries' national sovereignty.
in Venezuela, Lula da Silva and Dilma Rousseff
in Brazil, Fernando Lugo
in Paraguay, Néstor
and Cristina Kirchner
in Argentina, Tabaré Vázquez
and José Mujica
in Uruguay, the Lagos
and Bachelet
governments in Chile, Evo Morales
in Bolivia, Daniel Ortega
in Nicaragua, Manuel Zelaya
in Honduras (although deposed by the 28 June 2009 coup d'état
), and Rafael Correa
of Ecuador are all part of this wave of left-wing politicians who also often declare themselves socialists
, Latin Americanists or anti-imperialists
.
:
Aridoamerica
:
Mesoamerica
:
South America
:
, Danish colonization of the Americas
, Dutch colonization of the Americas
, New Netherland
, French
New France
, Portuguese
, Russian
, Spanish
, New Spain
, Conquistador
, Spanish conquest of Yucatan
, Spanish conquest of Mexico
, Spanish missions in California
, Swedish
Latin America
Latin America is a region of the Americas where Romance languages – particularly Spanish and Portuguese, and variably French – are primarily spoken. Latin America has an area of approximately 21,069,500 km² , almost 3.9% of the Earth's surface or 14.1% of its land surface area...
refers to countries
Sovereign state
A sovereign state, or simply, state, is a state with a defined territory on which it exercises internal and external sovereignty, a permanent population, a government, and the capacity to enter into relations with other sovereign states. It is also normally understood to be a state which is neither...
in the Americas
Americas
The Americas, or America , are lands in the Western hemisphere, also known as the New World. In English, the plural form the Americas is often used to refer to the landmasses of North America and South America with their associated islands and regions, while the singular form America is primarily...
where Romance
Romance languages
The Romance languages are a branch of the Indo-European language family, more precisely of the Italic languages subfamily, comprising all the languages that descend from Vulgar Latin, the language of ancient Rome...
(Latin-derived) languages are spoken. This definition, however, is not meant to include Canada
Canada
Canada is a North American country consisting of ten provinces and three territories. Located in the northern part of the continent, it extends from the Atlantic Ocean in the east to the Pacific Ocean in the west, and northward into the Arctic Ocean...
, in spite of its large French-speaking population.
Latin American countries generally lie south of the United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
. By extension, some writers and commentators, particularly in the United States, apply the term to the whole region south of the United States, including the non-Romance-speaking countries such as Suriname
Suriname
Suriname , officially the Republic of Suriname , is a country in northern South America. It borders French Guiana to the east, Guyana to the west, Brazil to the south, and on the north by the Atlantic Ocean. Suriname was a former colony of the British and of the Dutch, and was previously known as...
, Jamaica
Jamaica
Jamaica is an island nation of the Greater Antilles, in length, up to in width and 10,990 square kilometres in area. It is situated in the Caribbean Sea, about south of Cuba, and west of Hispaniola, the island harbouring the nation-states Haiti and the Dominican Republic...
, and Guyana
Guyana
Guyana , officially the Co-operative Republic of Guyana, previously the colony of British Guiana, is a sovereign state on the northern coast of South America that is culturally part of the Anglophone Caribbean. Guyana was a former colony of the Dutch and of the British...
, due to similar economic, political and social histories and present-day conditions.
Before the arrival of Europeans
European colonization of the Americas
The start of the European colonization of the Americas is typically dated to 1492. The first Europeans to reach the Americas were the Vikings during the 11th century, who established several colonies in Greenland and one short-lived settlement in present day Newfoundland...
in the late 15th and early 16th centuries, the region was home to many indigenous peoples, many of which had advanced civilizations, most notably, the Aztec
Aztec
The Aztec people were certain ethnic groups of central Mexico, particularly those groups who spoke the Nahuatl language and who dominated large parts of Mesoamerica in the 14th, 15th and 16th centuries, a period referred to as the late post-classic period in Mesoamerican chronology.Aztec is the...
, Inca
Inca civilization
The Andean civilizations made up a loose patchwork of different cultures that developed from the highlands of Colombia to the Atacama Desert. The Andean civilizations are mainly based on the cultures of Ancient Peru and some others such as Tiahuanaco. The Inca Empire was the last sovereign...
and Maya
Maya civilization
The Maya is a Mesoamerican civilization, noted for the only known fully developed written language of the pre-Columbian Americas, as well as for its art, architecture, and mathematical and astronomical systems. Initially established during the Pre-Classic period The Maya is a Mesoamerican...
. By the end of the sixteenth century large areas of what would become Latin America were colonized by European settlers, primarily from Spain
Spain
Spain , officially the Kingdom of Spain languages]] under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, Spain's official name is as follows:;;;;;;), is a country and member state of the European Union located in southwestern Europe on the Iberian Peninsula...
, Portugal
Portugal
Portugal , officially the Portuguese Republic is a country situated in southwestern Europe on the Iberian Peninsula. Portugal is the westernmost country of Europe, and is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the West and South and by Spain to the North and East. The Atlantic archipelagos of the...
and to a lesser extent, France
France
The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
and the Netherlands
Netherlands
The Netherlands is a constituent country of the Kingdom of the Netherlands, located mainly in North-West Europe and with several islands in the Caribbean. Mainland Netherlands borders the North Sea to the north and west, Belgium to the south, and Germany to the east, and shares maritime borders...
(in Brazil).

Origin of the term and definition
The idea that a part of the Americas has a cultural or racialSocial interpretations of race
Social interpretations of race regard the common categorizations of people into different races, often with biologist tagging of particular "racial" attributes beyond mere anatomy, as more socially and culturally determined than based upon biology...
affinity with all Romance cultures can be traced back to the 1830s, in particular in the writing of the French
France
The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
Saint-Simonian
Saint-Simonianism
Saint-Simonianism was a French political and social movement of the first half of the 19th century, inspired by the ideas of Claude Henri de Rouvroy, comte de Saint-Simon ....
Michel Chevalier
Michel Chevalier
Michel Chevalier was a French engineer, statesman, economist and free market liberal.-Biography:Born in Limoges, Haute-Vienne, Chevalier studied at the École Polytechnique, obtaining an engineering degree at the Paris École des mines in 1829.In 1830, after the July Revolution, he became a...
, who postulated that this part of the Americas were inhabited by people of a "Latin race," and that it could, therefore, ally itself with "Latin Europe
Latin Europe
Latin Europe is a loose term for the region of Europe with an especially strong Latin cultural heritage inherited from the Roman Empire.-Application:...
" in a struggle with "Teutonic Europe
Germanic languages
The Germanic languages constitute a sub-branch of the Indo-European language family. The common ancestor of all of the languages in this branch is called Proto-Germanic , which was spoken in approximately the mid-1st millennium BC in Iron Age northern Europe...
," "Anglo-Saxon America" and "Slavic Europe." The idea was later taken up by Latin American intellectuals and political leaders of the mid- and late-nineteenth century, who no longer looked to Spain or Portugal as cultural models, but rather to France. The actual term "Latin America" was coined in France under Napoleon III and played a role in his campaign to imply cultural kinship with France, transform France into a cultural and political leader of the area and install Maximilian
Maximilian I of Mexico
Maximilian I was the only monarch of the Second Mexican Empire.After a distinguished career in the Austrian Navy, he was proclaimed Emperor of Mexico on April 10, 1864, with the backing of Napoleon III of France and a group of Mexican monarchists who sought to revive the Mexican monarchy...
as emperor of Mexico.
In the mid-twentieth century, especially in the United States, there was a trend to occasionally classify all of the territory south of the United States as "Latin America," especially when the discussion focused on its contemporary political and economic relations to the rest of the world, rather than solely on its cultural aspects. Concurrently, there has been a move to avoid this oversimplification by talking about "Latin America and the Caribbean," as in the United Nations geoscheme.
Since, the concept and definitions of Latin American are very modern, going back only to the nineteenth century, it is anachronistic to talk about "a history of Latin America" before the arrival the Europeans. Nevertheless, the many and varied cultures that did exist in the pre-Columbian period had a strong and direct influence on the societies that emerged as a result of the conquest, and therefore, they cannot be overlooked. They are introduced in the next section.
The Pre-Columbian period
What is now Latin America has been populated for several millennia, possibly for as long as 30,000 years. There are many models of migration to the New WorldModels of migration to the New World
There have been several models for the human settlement of the Americas proposed by various academic communities. The question of how, when and why humans first entered the Americas is of intense interest to archaeologists and anthropologists, and has been a subject of heated debate for centuries...
. Precise dating of many of the early civilizations is difficult because there are few text sources. However, highly-developed civilizations flourished at various times and places, such as in the Andes
Andes
The Andes is the world's longest continental mountain range. It is a continual range of highlands along the western coast of South America. This range is about long, about to wide , and of an average height of about .Along its length, the Andes is split into several ranges, which are separated...
and Mesoamerica
Mesoamerica
Mesoamerica is a region and culture area in the Americas, extending approximately from central Mexico to Belize, Guatemala, El Salvador, Honduras, Nicaragua, and Costa Rica, within which a number of pre-Columbian societies flourished before the Spanish colonization of the Americas in the 15th and...
.
Colonialism
Christopher ColumbusChristopher Columbus
Christopher Columbus was an explorer, colonizer, and navigator, born in the Republic of Genoa, in northwestern Italy. Under the auspices of the Catholic Monarchs of Spain, he completed four voyages across the Atlantic Ocean that led to general European awareness of the American continents in the...
landed in the Americas in 1492. Subsequently, the major sea powers in Europe sent expeditions to the New World
New World
The New World is one of the names used for the Western Hemisphere, specifically America and sometimes Oceania . The term originated in the late 15th century, when America had been recently discovered by European explorers, expanding the geographical horizon of the people of the European middle...
to build trade networks and colonies and to convert the native peoples to Christianity. Spain concentrated on building its empire on the central and southern parts of the Americas allotted to it by the Treaty of Tordesillas
Treaty of Tordesillas
The Treaty of Tordesillas , signed at Tordesillas , , divided the newly discovered lands outside Europe between Spain and Portugal along a meridian 370 leagueswest of the Cape Verde islands...
, because of presence of large, settled societies like the Aztec
Aztec
The Aztec people were certain ethnic groups of central Mexico, particularly those groups who spoke the Nahuatl language and who dominated large parts of Mesoamerica in the 14th, 15th and 16th centuries, a period referred to as the late post-classic period in Mesoamerican chronology.Aztec is the...
, the Inca
Inca civilization
The Andean civilizations made up a loose patchwork of different cultures that developed from the highlands of Colombia to the Atacama Desert. The Andean civilizations are mainly based on the cultures of Ancient Peru and some others such as Tiahuanaco. The Inca Empire was the last sovereign...
, the Maya
Maya peoples
The Maya people constitute a diverse range of the Native American people of southern Mexico and northern Central America. The overarching term "Maya" is a collective designation to include the peoples of the region who share some degree of cultural and linguistic heritage; however, the term...
and the Chibcha
Muisca
Muisca was the Chibcha-speaking tribe that formed the Muisca Confederation of the central highlands of present-day Colombia. They were encountered by the Spanish Empire in 1537, at the time of the conquest...
, whose human and material resources it could exploit, and large concentrations of silver
Silver
Silver is a metallic chemical element with the chemical symbol Ag and atomic number 47. A soft, white, lustrous transition metal, it has the highest electrical conductivity of any element and the highest thermal conductivity of any metal...
and gold
Gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au and an atomic number of 79. Gold is a dense, soft, shiny, malleable and ductile metal. Pure gold has a bright yellow color and luster traditionally considered attractive, which it maintains without oxidizing in air or water. Chemically, gold is a...
. The Portuguese built its empire in Brazil
Brazil
Brazil , officially the Federative Republic of Brazil , is the largest country in South America. It is the world's fifth largest country, both by geographical area and by population with over 192 million people...
, which fell in its sphere of influence per the Treaty of Tordesillas, by developing the land for sugar
Sugar
Sugar is a class of edible crystalline carbohydrates, mainly sucrose, lactose, and fructose, characterized by a sweet flavor.Sucrose in its refined form primarily comes from sugar cane and sugar beet...
production since there was a lack of a large, complex society or mineral resources.
Nineteenth-century revolutions: the postcolonial era

American Revolution
The American Revolution was the political upheaval during the last half of the 18th century in which thirteen colonies in North America joined together to break free from the British Empire, combining to become the United States of America...
and French
French Revolution
The French Revolution , sometimes distinguished as the 'Great French Revolution' , was a period of radical social and political upheaval in France and Europe. The absolute monarchy that had ruled France for centuries collapsed in three years...
revolutions, most of Latin America achieved its independence by 1825. Independence destroyed the old common market
Single market
A single market is a type of trade bloc which is composed of a free trade area with common policies on product regulation, and freedom of movement of the factors of production and of enterprise and services. The goal is that the movement of capital, labour, goods, and services between the members...
that existed under the Spanish Empire after the Bourbon Reforms
Bourbon Reforms
The Bourbon Reforms were a set of economic and political legislation introduced by the Spanish Crown under various kings of the House of Bourbon throughout the 18th century. The reforms were intended to stimulate manufacturing and technology in order to modernize Spain...
and created an increased dependence on the financial investment provided by nations which had already begun to industrialize
Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution was a period from the 18th to the 19th century where major changes in agriculture, manufacturing, mining, transportation, and technology had a profound effect on the social, economic and cultural conditions of the times...
; therefore, Western European powers, in particular Great Britain and France, and the United States began to play major roles, since the region became economically dependent on these nations. Independence also created a new, self-consciously "Latin American" ruling class and intelligentsia which at times avoided Spanish and Portuguese models in their quest to reshape their societies. This elite looked towards other Catholic European models—in particular France
France
The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
—for a new Latin American culture, but did not seek input from indigenous peoples.
The failed efforts in Spanish America
Hispanic America
Hispanic America or Spanish America is the region comprising the American countries inhabited by Spanish-speaking populations.These countries have significant commonalities with each other and with Spain, whose colonies they formerly were...
to keep together most of the initial large states that emerged from independence— Gran Colombia
Gran Colombia
Gran Colombia is a name used today for the state that encompassed much of northern South America and part of southern Central America from 1819 to 1831. This short-lived republic included the territories of present-day Colombia, Venezuela, Ecuador, Panama, northern Peru and northwest Brazil. The...
, the Federal Republic of Central America
Federal Republic of Central America
The Federal Republic of Central America, known as the United Provinces of Central America in its first year of creation, was a sovereign state in Central America, which consisted of the territories of the former Captaincy General of Guatemala of New Spain...
and the United Provinces of South America
United Provinces of South America
The United Provinces of South America was the original name of the state that emerged from the May Revolution and the early developments of the Argentine War of Independence...
—resulted a number of domestic and interstate conflicts, which plagued the new countries. Brazil, in contrast to its Hispanic neighbors, remained a united monarchy and avoided the problem of civil and interstate wars. Domestic wars were often fights between federalists and centrists who ended up asserted themselves through the military repression of their opponents at the expense of civilian political life. The new nations inherited the cultural diversity of the colonial era and strived to create a new identity based around the shared European (Spanish or Portuguese) language and culture.
For the next few decades there was a long process to create a sense of nationality
Nationalism
Nationalism is a political ideology that involves a strong identification of a group of individuals with a political entity defined in national terms, i.e. a nation. In the 'modernist' image of the nation, it is nationalism that creates national identity. There are various definitions for what...
. Most of the new national borders were created around the often centuries-old audiencia jurisdictions or the Bourbon intendancies
Intendant
The title of intendant has been used in several countries through history. Traditionally, it refers to the holder of a public administrative office...
, which had become areas of political identity. In many areas the borders were unstable, since the new states fought wars with each other to gain access to resources, especially in the second half of the nineteenth century. The more important conflicts were the War of the Triple Alliance
War of the Triple Alliance
The Paraguayan War , also known as War of the Triple Alliance , was a military conflict in South America fought from 1864 to 1870 between Paraguay and the Triple Alliance of Argentina, Brazil, and Uruguay...
(1864–1870) and the War of the Pacific
War of the Pacific
The War of the Pacific took place in western South America from 1879 through 1883. Chile fought against Bolivia and Peru. Despite cooperation among the three nations in the war against Spain, disputes soon arose over the mineral-rich Peruvian provinces of Tarapaca, Tacna, and Arica, and the...
(1879–1884). The War of the Triple Alliance pitted Argentina, Brazil and Uruguay against Paraguay, which was utterly defeated. As a result Paraguay suffered a demographic collapse: the population went from an estimated 525,000 persons in 1864 to 221,000 in 1871 and out of this last population, only around 28,000 were men. In the War of the Pacific, Chile defeated the combined forces of Bolivia and Peru. Chile gained control of saltpeter
Sodium nitrate
Sodium nitrate is the chemical compound with the formula NaNO3. This salt, also known as Chile saltpeter or Peru saltpeter to distinguish it from ordinary saltpeter, potassium nitrate, is a white solid which is very soluble in water...
-rich areas, previously controlled by Peru and Bolivia, and Bolivia became a land-locked nation. By mid-century the region also confronted a growing United States, seeking to expand on the North American continent and extend its influence in the hemisphere. In Mexican–American War
Mexican–American War
The Mexican–American War, also known as the First American Intervention, the Mexican War, or the U.S.–Mexican War, was an armed conflict between the United States and Mexico from 1846 to 1848 in the wake of the 1845 U.S...
(1846–1848), Mexico lost over half of its territory to the United States. In the 1860s France attempted to indirectly control Mexico
French intervention in Mexico
The French intervention in Mexico , also known as The Maximilian Affair, War of the French Intervention, and The Franco-Mexican War, was an invasion of Mexico by an expeditionary force sent by the Second French Empire, supported in the beginning by the United Kingdom and the Kingdom of Spain...
. In South America, Brazil consolidated its control of large swaths of the Amazon Basin
Amazon Basin
The Amazon Basin is the part of South America drained by the Amazon River and its tributaries that drains an area of about , or roughly 40 percent of South America. The basin is located in the countries of Bolivia, Brazil, Colombia, Ecuador, Guyana, Peru, and Venezuela...
at the expense of its neighbors. In the 1880s the United States implemented an aggressive policy to defend and expand its political and economic interests in all of Latin America, which culminated in the creation of the Pan-American Conference
Pan-American Conference
The Conferences of American States, commonly referred to as the Pan-American Conferences, were meetings of the Pan-American Union, an international organization for cooperation on trade and other issues. They were first introduced by James G. Blaine of Maine in order to establish closer ties...
, the successful completion of the Panama Canal
History of the Panama Canal
The history of the Panama Canal goes back almost to the earliest explorers of the Americas. The narrow land bridge between North and South America offers a unique opportunity to create a water passage between the Atlantic and Pacific oceans...
and the United States intervention in the final Cuban war of independence.
The export of natural resources provided the basis of most Latin American economies in the nineteenth century, which allowed for the development of wealthy elite. The restructuring of colonial economic and political realities resulted in a sizable gap between rich and poor, with landed elites controlling the vast majority of land and resources. In Brazil
Brazil
Brazil , officially the Federative Republic of Brazil , is the largest country in South America. It is the world's fifth largest country, both by geographical area and by population with over 192 million people...
, for instance, by 1910 85% of the land belonged to 1% of the population. Gold mining and fruit growing, in particular, were monopolized by these wealthy landowners. These "Great Owners" completely controlled local activity and, furthermore, were the principal employers and the main source of wages. This led to a society of peasant
Peasant
A peasant is an agricultural worker who generally tend to be poor and homeless-Etymology:The word is derived from 15th century French païsant meaning one from the pays, or countryside, ultimately from the Latin pagus, or outlying administrative district.- Position in society :Peasants typically...
s whose connection to larger political realities remained in thrall to farming and mining magnates.
The endemic political instability and the nature of the economy resulted in the emergence of caudillos, military chiefs whose hold on power depended on their military skill and ability to dispense patronage
Patronage
Patronage is the support, encouragement, privilege, or financial aid that an organization or individual bestows to another. In the history of art, arts patronage refers to the support that kings or popes have provided to musicians, painters, and sculptors...
. The political regimes were at least in theory democratic
Democracy
Democracy is generally defined as a form of government in which all adult citizens have an equal say in the decisions that affect their lives. Ideally, this includes equal participation in the proposal, development and passage of legislation into law...
and took the form of either presidential
Presidential system
A presidential system is a system of government where an executive branch exists and presides separately from the legislature, to which it is not responsible and which cannot, in normal circumstances, dismiss it....
or parliamentary
Parliamentary system
A parliamentary system is a system of government in which the ministers of the executive branch get their democratic legitimacy from the legislature and are accountable to that body, such that the executive and legislative branches are intertwined....
governments. Both were prone to being taken over by a caudillo or an oligarchy
Oligarchy
Oligarchy is a form of power structure in which power effectively rests with an elite class distinguished by royalty, wealth, family ties, commercial, and/or military legitimacy...
. The political landscape was occupied by conservatives
Conservatism
Conservatism is a political and social philosophy that promotes the maintenance of traditional institutions and supports, at the most, minimal and gradual change in society. Some conservatives seek to preserve things as they are, emphasizing stability and continuity, while others oppose modernism...
, who believed that the preservation of the old social hierarchies served as the best guarantee of national stability and prosperity, and liberals
Liberalism
Liberalism is the belief in the importance of liberty and equal rights. Liberals espouse a wide array of views depending on their understanding of these principles, but generally, liberals support ideas such as constitutionalism, liberal democracy, free and fair elections, human rights,...
, who sought to bring about progress by freeing up the economy and individual initiative. Popular insurrections were often influential and repressed: 100,000 were killed during the suppression of a Colombian revolt in 1890 during the Thousand Days War
Thousand Days War
The Thousand Days' War , was a civil armed conflict in the newly created Republic of Colombia, between the Conservative Party, the Liberal Party and its radical factions. In 1899 the ruling conservatives were accused of maintaining power through fraudulent elections...
. Some states did manage to have some of democracy: Uruguay
Uruguay
Uruguay ,officially the Oriental Republic of Uruguay,sometimes the Eastern Republic of Uruguay; ) is a country in the southeastern part of South America. It is home to some 3.5 million people, of whom 1.8 million live in the capital Montevideo and its metropolitan area...
, and partially Argentina
Argentina
Argentina , officially the Argentine Republic , is the second largest country in South America by land area, after Brazil. It is constituted as a federation of 23 provinces and an autonomous city, Buenos Aires...
, Chile
Chile
Chile ,officially the Republic of Chile , is a country in South America occupying a long, narrow coastal strip between the Andes mountains to the east and the Pacific Ocean to the west. It borders Peru to the north, Bolivia to the northeast, Argentina to the east, and the Drake Passage in the far...
, Costa Rica
Costa Rica
Costa Rica , officially the Republic of Costa Rica is a multilingual, multiethnic and multicultural country in Central America, bordered by Nicaragua to the north, Panama to the southeast, the Pacific Ocean to the west and the Caribbean Sea to the east....
and Colombia
Colombia
Colombia, officially the Republic of Colombia , is a unitary constitutional republic comprising thirty-two departments. The country is located in northwestern South America, bordered to the east by Venezuela and Brazil; to the south by Ecuador and Peru; to the north by the Caribbean Sea; to the...
. The others were clearly oligarchist or authoritarian
Authoritarianism
Authoritarianism is a form of social organization characterized by submission to authority. It is usually opposed to individualism and democracy...
, although these oligarchs and caudillos sometimes enjoyed support from a majority in the population. All of these regimes sought to maintain Latin America's lucrative position in the world economy as a provider of raw materials.
1900-1920
By the start of the century, the United States continued its interventionist attitude, which aimed to directly defend its interests in the region. This was officially articulated in Theodore RooseveltTheodore Roosevelt
Theodore "Teddy" Roosevelt was the 26th President of the United States . He is noted for his exuberant personality, range of interests and achievements, and his leadership of the Progressive Movement, as well as his "cowboy" persona and robust masculinity...
's Big Stick Doctrine, which modified the old Monroe Doctrine
Monroe Doctrine
The Monroe Doctrine is a policy of the United States introduced on December 2, 1823. It stated that further efforts by European nations to colonize land or interfere with states in North or South America would be viewed as acts of aggression requiring U.S. intervention...
, which had simply aimed to deter European intervention in the hemisphere. At the conclusion of the Spanish-American War
Spanish-American War
The Spanish–American War was a conflict in 1898 between Spain and the United States, effectively the result of American intervention in the ongoing Cuban War of Independence...
the new government of Cuba and the United States signed the Platt Amendment
Platt Amendment
The Platt Amendment of 1901 was a rider appended to the Army Appropriations Act presented to the U.S. Senate by Connecticut Republican Senator Orville H. Platt replacing the earlier Teller Amendment. Approved on May 22, 1903, it stipulated the conditions for the withdrawal of United States troops...
in 1902, which authorized the United States to intervene in Cuban affairs when the United States deemed necessary. In Colombia
Colombia
Colombia, officially the Republic of Colombia , is a unitary constitutional republic comprising thirty-two departments. The country is located in northwestern South America, bordered to the east by Venezuela and Brazil; to the south by Ecuador and Peru; to the north by the Caribbean Sea; to the...
, United States sought the concession
Concession (territory)
In international law, a concession is a territory within a country that is administered by an entity other than the state which holds sovereignty over it. This is usually a colonizing power, or at least mandated by one, as in the case of colonial chartered companies.Usually, it is conceded, that...
of a territory in Panama
Panama Canal Zone
The Panama Canal Zone was a unorganized U.S. territory located within the Republic of Panama, consisting of the Panama Canal and an area generally extending 5 miles on each side of the centerline, but excluding Panama City and Colón, which otherwise would have been partly within the limits of...
to build a much anticipated canal across the isthmus. The Colombian government opposed this, but a Panamanian insurrection provided the United States with an opportunity. The United States backed Panamanian independence and the new nation granted the concession. These were not the only interventions carried out in the region by the United States. In the first decades of the twentieth century, there were several military incursions into Central America and the Caribbean, mostly in defense of commercial interests, which became known as the "Banana Wars."
The greatest political upheaval in the second decade of the century took place in Mexico
Mexico
The United Mexican States , commonly known as Mexico , is a federal constitutional republic in North America. It is bordered on the north by the United States; on the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; on the southeast by Guatemala, Belize, and the Caribbean Sea; and on the east by the Gulf of...
. In 1908, President Porfirio Díaz
Porfirio Díaz
José de la Cruz Porfirio Díaz Mori was a Mexican-American War volunteer and French intervention hero, an accomplished general and the President of Mexico continuously from 1876 to 1911, with the exception of a brief term in 1876 when he left Juan N...
, who had been in office since 1884, promised that he would step down in 1910. Francisco I. Madero
Francisco I. Madero
Francisco Ignacio Madero González was a politician, writer and revolutionary who served as President of Mexico from 1911 to 1913. As a respectable upper-class politician, he supplied a center around which opposition to the dictatorship of Porfirio Díaz could coalesce...
, a moderate liberal whose aim was to modernize the country while preventing a socialist revolution, launched an election campaign in 1910. Díaz, however, changed his mind and ran for office once more. Madero was arrested on election day and Díaz declared the winner. These events provoked uprisings, which became the start of the Mexican Revolution
Mexican Revolution
The Mexican Revolution was a major armed struggle that started in 1910, with an uprising led by Francisco I. Madero against longtime autocrat Porfirio Díaz. The Revolution was characterized by several socialist, liberal, anarchist, populist, and agrarianist movements. Over time the Revolution...
. Revolutionary movements were organized and some key leaders appeared: Pancho Villa
Pancho Villa
José Doroteo Arango Arámbula – better known by his pseudonym Francisco Villa or its hypocorism Pancho Villa – was one of the most prominent Mexican Revolutionary generals....
in the north, Emiliano Zapata
Emiliano Zapata
Emiliano Zapata Salazar was a leading figure in the Mexican Revolution, which broke out in 1910, and which was initially directed against the president Porfirio Díaz. He formed and commanded an important revolutionary force, the Liberation Army of the South, during the Mexican Revolution...
in the south, and Madero in Mexico City. Madero's forces defeated the federal army in early 1911, assumed temporary control of the government and won a second election later on November 6, 1911. Madero undertook moderate reforms to implement greater democracy in the political system but failed to satisfy many of the regional leaders in what had become a revolutionary situation. Madero's failure to address agrarian claims led Zapata to break with Madero and resume the revolution. On February 18, 1913 Victoriano Huerta
Victoriano Huerta
José Victoriano Huerta Márquez was a Mexican military officer and president of Mexico. Huerta's supporters were known as Huertistas during the Mexican Revolution...
, a conservative general organized a coup d'état
Coup d'état
A coup d'état state, literally: strike/blow of state)—also known as a coup, putsch, and overthrow—is the sudden, extrajudicial deposition of a government, usually by a small group of the existing state establishment—typically the military—to replace the deposed government with another body; either...
with the support of the United States; Madero was killed four days later. Other revolutionary leaders such as Villa, Zapata, and Venustiano Carranza
Venustiano Carranza
Venustiano Carranza de la Garza, was one of the leaders of the Mexican Revolution. He ultimately became President of Mexico following the overthrow of the dictatorial Huerta regime in the summer of 1914 and during his administration the current constitution of Mexico was drafted...
continued to militarily oppose the federal government, now under Huerta's control. Allies Zapata and Villa took Mexico City in March 1914, but found themselves outside of their elements in the capital and withdrew to their respective bastions. This allowed Carranza to assume control of the central government. He then organized the repression of the rebel armies of Villa and Zapata, led in particular by General Álvaro Obregón
Álvaro Obregón
General Álvaro Obregón Salido was the President of Mexico from 1920 to 1924. He was assassinated in 1928, shortly after winning election to another presidential term....
,. The Mexican Constitution of 1917
Constitution of Mexico
The Political Constitution of the United Mexican States is the current constitution of Mexico. It was drafted in Santiago de Querétaro, in the State of Querétaro, by a constitutional convention, during the Mexican Revolution. It was approved by the Constitutional Congress on February 5, 1917...
, still the current constitution, was proclaimed but initially little enforced. The efforts against the other revolutionary leaders continued. Zapata was assassinated on April 10, 1919. Carranza himself was assassinated on May 15, 1920, leaving Obregón in power, who was officially elected president later that year. Finally in 1923 Villa was also assassinated. With the removal of the main rivals Obregón is able to consolidate power and relative peace returned to Mexico. Under the Constitution a liberal government is implemented but some of the aspirations of the working and rural classes remained unfulfilled. (See also, Agrarian land reform in Mexico
Agrarian land reform in Mexico
Before the 1910 Mexican Revolution that overthrew Porfirio Díaz, most of the land was owned by a single elite ruling class. Legally there was no slavery or serfdom; however, those with heavy debts, Indian wage workers, or peasants, were essentially debt-slaves to the landowners. A small percentage...
.)
Years 1930-1960
The Great DepressionGreat Depression
The Great Depression was a severe worldwide economic depression in the decade preceding World War II. The timing of the Great Depression varied across nations, but in most countries it started in about 1929 and lasted until the late 1930s or early 1940s...
posed a great challenge to the region. The collapse of the world economy meant that the demand for raw materials drastically declined, undermining many of the economies of Latin America. Intellectuals and government leaders in Latin America turned their backs on the older economic policies and turned toward import substitution industrialization. The goal was to create self-sufficient economies, which would have their own industrial sectors and large middle classes and which would be immune to the ups and downs of the global economy. Despite the potential threats to United States commercial interests, the Roosevelt administration
Franklin D. Roosevelt
Franklin Delano Roosevelt , also known by his initials, FDR, was the 32nd President of the United States and a central figure in world events during the mid-20th century, leading the United States during a time of worldwide economic crisis and world war...
(1933–1945) understood that the United States could not wholly oppose import substitution. Roosevelt implemented a Good Neighbor policy
Good Neighbor policy
The Good Neighbor policy was the foreign policy of the administration of United States President Franklin Roosevelt toward the countries of Latin America. Its main principle was that of non-intervention and non-interference in the domestic affairs of Latin America...
and allowed the nationalization of some American companies in Latin America. Mexican President Lázaro Cárdenas
Lázaro Cárdenas
Lázaro Cárdenas del Río was President of Mexico from 1934 to 1940.-Early life:Lázaro Cárdenas was born on May 21, 1895 in a lower-middle class family in the village of Jiquilpan, Michoacán. He supported his family from age 16 after the death of his father...
nationalized American oil companies
Petroleum industry
The petroleum industry includes the global processes of exploration, extraction, refining, transporting , and marketing petroleum products. The largest volume products of the industry are fuel oil and gasoline...
, out of which he created Pemex
Pemex
Petróleos Mexicanos or Pemex is a Mexican state-owned petroleum company. As of 2010, with a total asset worth of $415.75 billion, it is the second non-publicly listed largest company in the world by total market value, and Latin America's second largest enterprise by annual revenue as of 2009...
. Cárdenas also oversaw the redistribution of a quantity of land, fulfilling the hopes of many since the start of the Mexican Revolution. The Platt Amendment was also repealed, freeing Cuba from legal and official interference of the United States in its politics. The Second World War
World War II
World War II, or the Second World War , was a global conflict lasting from 1939 to 1945, involving most of the world's nations—including all of the great powers—eventually forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis...
also brought the United States and most Latin American nations together.
In the postwar period, the expansion of communism
Communism
Communism is a social, political and economic ideology that aims at the establishment of a classless, moneyless, revolutionary and stateless socialist society structured upon common ownership of the means of production...
became the greatest political issue for both the United States and governments in the region. The start of the Cold War
Cold War
The Cold War was the continuing state from roughly 1946 to 1991 of political conflict, military tension, proxy wars, and economic competition between the Communist World—primarily the Soviet Union and its satellite states and allies—and the powers of the Western world, primarily the United States...
forced governments to choose between the United States and the Soviet Union
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union , officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics , was a constitutionally socialist state that existed in Eurasia between 1922 and 1991....
. Several socialist
Socialism
Socialism is an economic system characterized by social ownership of the means of production and cooperative management of the economy; or a political philosophy advocating such a system. "Social ownership" may refer to any one of, or a combination of, the following: cooperative enterprises,...
and communist insurgencies broke out in Latin America throughout the entire twentieth century, but the most successful one was in Cuba. The Cuban Revolution
Cuban Revolution
The Cuban Revolution was an armed revolt by Fidel Castro's 26th of July Movement against the regime of Cuban dictator Fulgencio Batista between 1953 and 1959. Batista was finally ousted on 1 January 1959, and was replaced by a revolutionary government led by Castro...
was led by Fidel Castro
Fidel Castro
Fidel Alejandro Castro Ruz is a Cuban revolutionary and politician, having held the position of Prime Minister of Cuba from 1959 to 1976, and then President from 1976 to 2008. He also served as the First Secretary of the Communist Party of Cuba from the party's foundation in 1961 until 2011...
against the regime of Fulgencio Batista
Fulgencio Batista
Fulgencio Batista y Zaldívar was the United States-aligned Cuban President, dictator and military leader who served as the leader of Cuba from 1933 to 1944 and from 1952 to 1959, before being overthrown as a result of the Cuban Revolution....
, who since 1933 was the principal autocrat in Cuba. Since the 1860s the Cuban economy had focused on the cultivation of sugar, of which 82% was sold in the American market by the twentieth century. Despite the repeal of the Platt Amendment, the United States still had considerable influence in Cuba, both in politics and in everyday life. In fact Cuba had a reputation of being the "brothel of the United States," a place where Americans could find all sorts of licit and illicit pleasures, provided they had the cash. Despite having the socially advanced constitution of 1940
Constitution of Cuba
Since attaining its independence from Spain, Cuba has had five constitutions. The current constitution was drafted in 1976 and has since been amended.-1901 Constitution:The 1901 Constitution was Cuba's first as an independent state...
, Cuba was plagued with corruption and the interruption of constitutional rule by autocrats like Batista. Batista began his final turn as the head of the government in a 1952 coup. The coalition that formed under the revolutionaries hoped to restore the constitution, reestablish a democratic state and free Cuba from the American influence. The revolutionaries succeeded in toppling Batista on January 1, 1959. Castro, who initially declared himself as a non-socialist, initiated a program of agrarian reforms and nationalizations in May 1959, which alienated the Eisenhower administration
Dwight D. Eisenhower
Dwight David "Ike" Eisenhower was the 34th President of the United States, from 1953 until 1961. He was a five-star general in the United States Army...
(1953–1961) and resulted in the United States breaking of diplomatic relations, freezing Cuban assets in the United States and placing an embargo on the nation in 1960. The Kennedy administration
John F. Kennedy
John Fitzgerald "Jack" Kennedy , often referred to by his initials JFK, was the 35th President of the United States, serving from 1961 until his assassination in 1963....
(1961–1963) authorized the funding and support of an invasion of Cuba
Bay of Pigs Invasion
The Bay of Pigs Invasion was an unsuccessful action by a CIA-trained force of Cuban exiles to invade southern Cuba, with support and encouragement from the US government, in an attempt to overthrow the Cuban government of Fidel Castro. The invasion was launched in April 1961, less than three months...
by exiles. The invasion failed and radicalized the revolutionary government's position. Cuba officially proclaimed itself socialist and openly became an ally of the Soviet Union
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union , officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics , was a constitutionally socialist state that existed in Eurasia between 1922 and 1991....
. The military collaboration between Cuba and the Soviet Union, which included the placement of intercontinental ballistic missile
Intercontinental ballistic missile
An intercontinental ballistic missile is a ballistic missile with a long range typically designed for nuclear weapons delivery...
s in Cuba precipitated the Cuban Missile Crisis
Cuban Missile Crisis
The Cuban Missile Crisis was a confrontation among the Soviet Union, Cuba and the United States in October 1962, during the Cold War...
of October 1962.
Late 20th century military regimes and revolutions

Military dictatorship
A military dictatorship is a form of government where in the political power resides with the military. It is similar but not identical to a stratocracy, a state ruled directly by the military....
s that were supported by the United States of America.
Around the 1970s, the regimes of the Southern Cone
Southern Cone
Southern Cone is a geographic region composed of the southernmost areas of South America, south of the Tropic of Capricorn. Although geographically this includes part of Southern and Southeast of Brazil, in terms of political geography the Southern cone has traditionally comprised Argentina,...
collaborated in Operation Condor
Operation Condor
Operation Condor , was a campaign of political repression involving assassination and intelligence operations officially implemented in 1975 by the right-wing dictatorships of the Southern Cone of South America...
killing many leftist dissidents, including some urban guerrillas.
However, by the early 90's all countries had restored their democracies.
Washington Consensus
The set of specific economic policy prescriptions that were considered the "standard" reform package were promoted for crisis-wracked developing countries by Washington, DC-based institutions such as the International Monetary FundInternational Monetary Fund
The International Monetary Fund is an organization of 187 countries, working to foster global monetary cooperation, secure financial stability, facilitate international trade, promote high employment and sustainable economic growth, and reduce poverty around the world...
(IMF), World Bank
World Bank
The World Bank is an international financial institution that provides loans to developing countries for capital programmes.The World Bank's official goal is the reduction of poverty...
, and the US Treasury Department during the 80's and 90's.
In recent years, several Latin American countries led by socialist or other left wing governments—including Argentina and Venezuela—have campaigned for (and to some degree adopted) policies contrary to the Washington Consensus set of policies. (Other Latin counties with governments of the left, including Brazil, Chile and Peru, have in practice adopted the bulk of the policies). Also critical of the policies as actually promoted by the International Monetary Fund have been some US economists, such as Joseph Stiglitz and Dani Rodrik
Dani Rodrik
Dani Rodrik is a Turkish economist and Rafiq Hariri Professor of International Political Economy at the John F. Kennedy School of Government, Harvard University, teaching in the School's MPA/ID Program. He has published widely in the areas of international economics, economic development, and...
, who have challenged what are sometimes described as the "fundamentalist" policies of the International Monetary Fund and the US Treasury for what Stiglitz calls a "one size fits all" treatment of individual economies.
The term has become associated with neoliberal policies in general and drawn into the broader debate over the expanding role of the free market, constraints upon the state, and US influence on other countries' national sovereignty.
Turn to the left
Since the 2000s, or 1990s in some countries, left-wing political parties have risen to power. Hugo ChavezHugo Chávez
Hugo Rafael Chávez Frías is the 56th and current President of Venezuela, having held that position since 1999. He was formerly the leader of the Fifth Republic Movement political party from its foundation in 1997 until 2007, when he became the leader of the United Socialist Party of Venezuela...
in Venezuela, Lula da Silva and Dilma Rousseff
Dilma Rousseff
Dilma Vana Rousseff is the 36th and current President of Brazil. She is the first woman to hold the office. Prior to that, in 2005, she was also the first woman to become Chief of Staff of Brazil, appointed by then President Luiz Inácio Lula da Silva....
in Brazil, Fernando Lugo
Fernando Lugo
Fernando Armindo Lugo Méndez is the current President of Paraguay and a former Roman Catholic bishop of the Diocese of San Pedro.-Early life:...
in Paraguay, Néstor
Néstor Kirchner
Néstor Carlos Kirchner was an Argentine politician who served as the 54th President of Argentina from 25 May 2003 until 10 December 2007. Previously, he was Governor of Santa Cruz Province since 10 December 1991. He briefly served as Secretary General of the Union of South American Nations ...
and Cristina Kirchner
Cristina Fernández de Kirchner
Cristina Elisabet Fernández de Kirchner , commonly known as Cristina Fernández or Cristina Kirchner is the 55th and current President of Argentina and the widow of former President Néstor Kirchner. She is Argentina's first elected female president, and the second female president ever to serve...
in Argentina, Tabaré Vázquez
Tabaré Vázquez
Tabaré Ramón Vázquez Rosas is a former President of Uruguay. A physician by training, he is a member of the leftist Frente Amplo coalition . Vázquez was elected president on October 31, 2004, took office on March 1, 2005, and relinquished the office on March 1, 2010...
and José Mujica
José Mujica
José Alberto "Pepe" Mujica Cordano is a Uruguayan politician and former guerrilla fighter, a member of the Broad Front and current President of Uruguay....
in Uruguay, the Lagos
Ricardo Lagos
Ricardo Froilán Lagos Escobar is a lawyer, economist and social democrat politician, who served as president of Chile from 2000 to 2006. He won the 1999-2000 presidential election by a narrow margin in a runoff over Independent Democrat Union candidate Joaquín Lavín...
and Bachelet
Michelle Bachelet
Verónica Michelle Bachelet Jeria is a Social Democrat politician who was President of Chile from 11 March 2006 to 11 March 2010. She was the first woman president of her country...
governments in Chile, Evo Morales
Evo Morales
Juan Evo Morales Ayma , popularly known as Evo , is a Bolivian politician and activist, currently serving as the 80th President of Bolivia, a position that he has held since 2006. He is also the leader of both the Movement for Socialism party and the cocalero trade union...
in Bolivia, Daniel Ortega
Daniel Ortega
José Daniel Ortega Saavedra is a Nicaraguan politician and revolutionary, currently serving as the 83rd President of Nicaragua, a position that he has held since 2007. He previously served as the 79th President, between 1985 and 1990, and for much of his life, has been a leader in the Sandinista...
in Nicaragua, Manuel Zelaya
Manuel Zelaya
José Manuel Zelaya Rosales is a politician who was President of Honduras from January 27, 2006 until June 28, 2009. The eldest son of a wealthy businessman, he inherited his father's nickname "Mel," and, before entering politics, was involved in his family's logging and timber businesses.Elected...
in Honduras (although deposed by the 28 June 2009 coup d'état
2009 Honduran coup d'état
The 2009 Honduran coup d'état, part of the 2009 Honduran constitutional crisis, occurred when the Honduran Army ousted President Manuel Zelaya and sent him into exile on June 28, 2009. It was prompted by his attempts to schedule a non binding poll on holding a referendum about convening a...
), and Rafael Correa
Rafael Correa
Rafael Vicente Correa Delgado born is the President of the Republic of Ecuador and was the president pro tempore of the Union of South American Nations. An economist educated in Ecuador, Belgium and the United States, he was elected President in late 2006 and took office in January 2007...
of Ecuador are all part of this wave of left-wing politicians who also often declare themselves socialists
Socialism
Socialism is an economic system characterized by social ownership of the means of production and cooperative management of the economy; or a political philosophy advocating such a system. "Social ownership" may refer to any one of, or a combination of, the following: cooperative enterprises,...
, Latin Americanists or anti-imperialists
Anti-imperialism
Anti-imperialism, strictly speaking, is a term that may be applied to a movement opposed to any form of colonialism or imperialism. Anti-imperialism includes opposition to wars of conquest, particularly of non-contiguous territory or people with a different language or culture; it also includes...
.
Pre-Columbian
OasisamericaOasisamerica
Oasisamerica was a broad cultural area in pre-Columbian southwestern North America. It extended from modern-day Utah down to southern Chihuahua, and from the coast on the Gulf of California eastward to the Río Bravo river valley...
:
- NavajoNavajo peopleThe Navajo of the Southwestern United States are the largest single federally recognized tribe of the United States of America. The Navajo Nation has 300,048 enrolled tribal members. The Navajo Nation constitutes an independent governmental body which manages the Navajo Indian reservation in the...
- ApacheApacheApache is the collective term for several culturally related groups of Native Americans in the United States originally from the Southwest United States. These indigenous peoples of North America speak a Southern Athabaskan language, which is related linguistically to the languages of Athabaskan...
- PimaPimaThe Pima are a group of American Indians living in an area consisting of what is now central and southern Arizona. The long name, "Akimel O'odham", means "river people". They are closely related to the Tohono O'odham and the Hia C-ed O'odham...
- Cocopah
- QuechanQuechanThe Quechan are a Native American tribe who live on the Fort Yuma Indian Reservation on the lower Colorado River in Arizona and California just north of the border with Mexico...
- Puebloan peoples
- ComancheComancheThe Comanche are a Native American ethnic group whose historic range consisted of present-day eastern New Mexico, southern Colorado, northeastern Arizona, southern Kansas, all of Oklahoma, and most of northwest Texas. Historically, the Comanches were hunter-gatherers, with a typical Plains Indian...
- CoahuiltecanCoahuiltecanCoahuiltecan or Paikawa was a proposed language family in John Wesley Powell's 1891 classification of Native American languages that consisted of Coahuilteco and Cotoname. The proposal was expanded to include Comecrudo, Karankawa, and Tonkawa...
Aridoamerica
Aridoamerica
Aridoamerica, also known as the Gran Chichimeca, is a term used by Mexican archeologists to describe a region of the southwestern United States and the northern and central regions of Mexico, in contrast to Mesoamerica, which lies to the south and east...
:
- GuachichilGuachichilOf all the Chichimeca natives, the Guachichiles occupied the most extensive territory, stretching north to Saltillo in Coahuila and to the northern corners of Michoacán in the south...
- CaxcanCaxcanThe Caxcan were a partly nomadic indigenous people of Mexico. Under their leader, Francisco Tenamaztle, the Caxcan were allied with the Zacatecos against the Spaniards during the Mixtón Rebellion. During the rebellion, they were described as "the heart and the center of the Indian Rebellion". They...
- ZacatecoZacatecoThe Zacatecos were an indigenous people inhabiting part of northern Mexico, one of the peoples called Chichimecas by the Aztecs. They lived in most of what is now the state of Zacatecas and the northeastern part of Durango. They have many direct descendants, but most of their culture and...
- TecuexeTecuexeThe Tecuexe were an indigenous group found in the eastern part of present day Guadalajara, Mexico-History:It is believed that the Tecuexe derived from the dispersion of Zacateco groups from La Quemada. Like the Zacatecos, the Tecuexe were a tribe belonging to the generic "Chichimeca" peoples...
- GuamareGuamareThe Guamares were an indigenous group that were concentrated in the region of the present state of Guanajuato. They were part of the Chichimecas.The Guamares were centered in the Guanajuato Sierras, but some bands ranged as far east as Querétaro...
- OtomiOtomi peopleThe Otomi people . Smaller Otomi populations exist in the states of Puebla, Mexico, Tlaxcala, Michoacán and Guanajuato. The Otomi language belonging to the Oto-Pamean branch of the Oto-Manguean language family is spoken in many different varieties some of which are not mutually intelligible.One of...
- Chichimeca JonazChichimeca JonazThe Chichimeca Jonaz are a group of indigenous people living in Guanajuato and San Luis Potosí. In Guanajuato State the Chichimeca Jonaz people live in a community of San Luis de la Paz municipality. The settlement is 2,070 m above sea level...
- CoraCora peopleThe Cora are an indigenous ethnic group of Western Central Mexico that live in the Sierra de Nayarit and in La Mesa de Nayar in the Mexican states of Jalisco and Nayarit. They call themselves náayarite , whence the name of the present day Mexican state of Nayarit...
- Huichol
- PamePameThe Pame are an indigenous people of central Mexico living in the state of San Luis Potosí. They call themselves Xi'úi. They speak the Pame language, which belongs to the Oto-Pamean group of the Oto-Manguean language family....
- Yaquis
- MayosMayo peopleThe Mayo are a Mexican indigenous people living in the states of Sonora and Sinaloa, originally living near the Mayo River in Sonora. In their own language they call themselves Yoreme....
- O'odhamO'odhamThe O'odham peoples, including the Tohono O'odham or Papago, the Pima or Akimel O'odham, and the Hia C-ed O'odham, are an indigenous Uto-Aztecan peoples of the Sonoran desert in southern and central Arizona and northern Sonora, united by a common heritage language, the O'odham language...
- TepehuánesTepehuánThe Tepehuán are a Native American ethnic group in northwest Mexico, whose villages at the time of Spanish conquest spanned a large territory along the Sierra Madre Occidental from Chihuahua and Durango in the north to Jalisco in the south...
Mesoamerica
Mesoamerica
Mesoamerica is a region and culture area in the Americas, extending approximately from central Mexico to Belize, Guatemala, El Salvador, Honduras, Nicaragua, and Costa Rica, within which a number of pre-Columbian societies flourished before the Spanish colonization of the Americas in the 15th and...
:
- AztecHistory of the AztecsThe Aztecs were a Pre-Columbian Mesoamerican people of central Mexico in the 14th, 15th and 16th centuries. They called themselves Mexica . The Republic of Mexico and its capital, Mexico City, derive their names from the word "Mexica"....
- HuastecHuastecThe Huastec or Téenek , are an indigenous people of Mexico, historically based in the states of Hidalgo, Veracruz, San Luis Potosí and Tamaulipas concentrated along the route of the Pánuco River and along the coast of the Gulf of Mexico.There are approximately 66,000...
- MixtecMixtecThe Mixtec are indigenous Mesoamerican peoples inhabiting the Mexican states of Oaxaca, Guerrero and Puebla in a region known as La Mixteca. The Mixtecan languages form an important branch of the Otomanguean language family....
- MayaMaya civilizationThe Maya is a Mesoamerican civilization, noted for the only known fully developed written language of the pre-Columbian Americas, as well as for its art, architecture, and mathematical and astronomical systems. Initially established during the Pre-Classic period The Maya is a Mesoamerican...
- OlmecOlmecThe Olmec were the first major Pre-Columbian civilization in Mexico. They lived in the tropical lowlands of south-central Mexico, in the modern-day states of Veracruz and Tabasco....
- Pipil
- Tarascan
- TeotihuacánTeotihuacánTeotihuacan – also written Teotihuacán, with a Spanish orthographic accent on the last syllable – is an enormous archaeological site in the Basin of Mexico, just 30 miles northeast of Mexico City, containing some of the largest pyramidal structures built in the pre-Columbian Americas...
- ToltecToltecThe Toltec culture is an archaeological Mesoamerican culture that dominated a state centered in Tula, Hidalgo in the early post-classic period of Mesoamerican chronology...
- TotonacTotonacThe Totonac people resided in the eastern coastal and mountainous regions of Mexico at the time of the Spanish arrival in 1519. Today they reside in the states of Veracruz, Puebla, and Hidalgo. They are one of the possible builders of the Pre-Columbian city of El Tajín, and further maintained...
- ZapotecZapotec civilizationThe Zapotec civilization was an indigenous pre-Columbian civilization that flourished in the Valley of Oaxaca of southern Mesoamerica. Archaeological evidence shows their culture goes back at least 2500 years...
South America
South America
South America is a continent situated in the Western Hemisphere, mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere. The continent is also considered a subcontinent of the Americas. It is bordered on the west by the Pacific Ocean and on the north and east...
:
- ChavinChavín cultureThe Chavín were a civilization that developed in the northern Andean highlands of Peru from 900 BC to 200 BC. They extended their influence to other civilizations along the coast. The Chavín were located in the Mosna Valley where the Mosna and Huachecsa rivers merge...
- Chibcha
- ChimorChimorChimor was the political grouping of the Chimú culture that ruled the northern coast of Peru, beginning around 850 AD and ending around 1470 AD. Chimor was the largest kingdom in the Late Intermediate period, encompassing 1,000 km of coastline...
- ChachapoyaChachapoyas cultureThe Chachapoyas, also called the Warriors of the Clouds, were an Andean people living in the cloud forests of the Amazonas region of present-day Peru. The Incas conquered their civilization shortly before the arrival of the Spanish in Peru. When the Spanish arrived in Peru in the 16th century, the...
- Huari
- IncaHistory of the IncaThe Inca Empire was an empire centered in what is now Peru from [Anno Domini] 1400 C.E to C.E 1525. Over that period, the Inca used conquest and peaceful assimilation to incorporate in their empire a large portion of western South America, centered on the Andes mountain ranges...
- MocheMoche'The Moche civilization flourished in northern Peru from about 100 AD to 800 AD, during the Regional Development Epoch. While this issue is the subject of some debate, many scholars contend that the Moche were not politically organized as a monolithic empire or state...
- NazcaNazcaNazca is a system of valleys on the southern coast of Peru, and the name of the region's largest existing town in the Nazca Province. It is also the name applied to the Nazca culture that flourished in the area between 300 BC and AD 800...
- TiwanakuTiwanakuTiwanaku, is an important Pre-Columbian archaeological site in western Bolivia, South America. Tiwanaku is recognized by Andean scholars as one of the most important precursors to the Inca Empire, flourishing as the ritual and administrative capital of a major state power for approximately five...
- MapucheMapucheThe Mapuche are a group of indigenous inhabitants of south-central Chile and southwestern Argentina. They constitute a wide-ranging ethnicity composed of various groups who shared a common social, religious and economic structure, as well as a common linguistic heritage. Their influence extended...
- TaironaTaironaTairona was a group of chiefdoms in the region of Sierra Nevada de Santa Marta in present-day Cesar, Magdalena and La Guajira Departments of Colombia, South America, which goes back at least to the 1st century AD and had significant demographic growth around the 11th century.The Tairona people...
Colonization
British colonization of the AmericasBritish colonization of the Americas
British colonization of the Americas began in 1607 in Jamestown, Virginia and reached its peak when colonies had been established throughout the Americas...
, Danish colonization of the Americas
Danish colonization of the Americas
Denmark and the former political union of Denmark–Norway had a colonial empire from the 17th through the 20th centuries, large portions of which were found in the Americas...
, Dutch colonization of the Americas
Dutch colonization of the Americas
Dutch trading posts and plantations in the Americas precede the much wider known colonization activities of the Dutch in Asia. Whereas the first Dutch fort in Asia was built in 1600 , the first forts and settlements on the Essequibo river in Guyana and on the Amazon date from the 1590s...
, New Netherland
New Netherland
New Netherland, or Nieuw-Nederland in Dutch, was the 17th-century colonial province of the Republic of the Seven United Netherlands on the East Coast of North America. The claimed territories were the lands from the Delmarva Peninsula to extreme southwestern Cape Cod...
, French
French colonization of the Americas
The French colonization of the Americas began in the 16th century, and continued in the following centuries as France established a colonial empire in the Western Hemisphere. France founded colonies in much of eastern North America, on a number of Caribbean islands, and in South America...
New France
New France
New France was the area colonized by France in North America during a period beginning with the exploration of the Saint Lawrence River by Jacques Cartier in 1534 and ending with the cession of New France to Spain and Great Britain in 1763...
, Portuguese
Portuguese colonization of the Americas
Portugal was the leading country in the European exploration of the world in the 15th century. The Treaty of Tordesillas divided the Earth, outside Europe, in 1494 into Spanish and Portuguese global territorial hemispheres for exclusive conquest and colonization...
, Russian
Russian colonization of the Americas
The Russian colonization of the Americas covers the period, from 1732 to 1867, when the Tsarist Imperial Russian Empire laid claim to northern Pacific Coast territories in the Americas...
, Spanish
Spanish colonization of the Americas
Colonial expansion under the Spanish Empire was initiated by the Spanish conquistadores and developed by the Monarchy of Spain through its administrators and missionaries. The motivations for colonial expansion were trade and the spread of the Christian faith through indigenous conversions...
, New Spain
New Spain
New Spain, formally called the Viceroyalty of New Spain , was a viceroyalty of the Spanish colonial empire, comprising primarily territories in what was known then as 'América Septentrional' or North America. Its capital was Mexico City, formerly Tenochtitlan, capital of the Aztec Empire...
, Conquistador
Conquistador
Conquistadors were Spanish soldiers, explorers, and adventurers who brought much of the Americas under the control of Spain in the 15th to 16th centuries, following Europe's discovery of the New World by Christopher Columbus in 1492...
, Spanish conquest of Yucatan
Spanish conquest of Yucatán
The Spanish conquest of Yucatán was the campaign undertaken by the Spanish conquistadores against the Late Postclassic Maya states and polities, particularly in the northern and central Yucatán Peninsula but also involving the Maya polities of the Guatemalan highlands region...
, Spanish conquest of Mexico
Spanish conquest of Mexico
The Spanish conquest of the Aztec Empire was one of the most important campaigns in the Spanish colonization of the Americas. The invasion began in February 1519 and was acclaimed victorious on August 13, 1521, by a coalition army of Spanish conquistadors and Tlaxcalan warriors led by Hernán Cortés...
, Spanish missions in California
Spanish missions in California
The Spanish missions in California comprise a series of religious and military outposts established by Spanish Catholics of the Franciscan Order between 1769 and 1823 to spread the Christian faith among the local Native Americans. The missions represented the first major effort by Europeans to...
, Swedish
Swedish colonization of the Americas
The Swedish colonization of the Americas included a 17th-century colony on the Delaware River in what is now Delaware, New Jersey, Pennsylvania, and Maryland, as well as two possessions in the Caribbean during the 18th and 19th century....
History by country
Other topics
- Latin AmericansLatin AmericansLatin Americans are the citizens of the Latin American countries and dependencies. Latin American countries are multi-ethnic, home to people of different ethnic and national backgrounds. As a result, some Latin Americans don't take their nationality as an ethnicity, but identify themselves with...
- Latin American integrationLatin American integrationThe integration of Latin America has a history going back to Spanish American and Brazilian independence, when there was discussion of creating a regional state or confederation of Latin American nations to protect the area's newly won autonomy...
- Feminist history in Latin America
- History of the Jews in Latin AmericaHistory of the Jews in Latin AmericaThe history of the Jews in Latin America dates, according to some interpretations, back to Christopher Columbus and his first cross-Atlantic voyage on August 3, 1492, when he left Spain and eventually discovered the New World...
- Landless Workers' MovementLandless Workers' MovementLandless Workers' Movement is a social movement in Brazil; it is the second largest social movement in Latin America with an estimated 1.5 million landless members in 23 out of Brazil's 26 states. The MST states it carries out land reform in a country it sees as mired by unjust land distribution...
- Latin America – United States relations
- Latin American debt crisisLatin American debt crisisThe Latin American debt crisis was a financial crisis that occurred in the early 1980s , often known as the "lost decade", when Latin American countries reached a point where their foreign debt exceeded their earning power and they were not able to repay it.-Origins:In the 1960s and 1970s many...
- Spanish reconquest of MexicoSpanish reconquest of MexicoThe Spanish reconquest attempts in Mexico were episodes of war in Mexico that were comprised in clashes between the newly born Mexican nation and Spain, mainly covered two periods first attempts from 1821 to 1825 and the defense of territorial waters and second period divided into two stages...
- Territorial evolution of the CaribbeanTerritorial evolution of the CaribbeanThis is a timeline of the territorial evolution of Latin America and the Caribbean, listing each change to the internal and external borders of the various countries that make up Latin America and the Caribbean....

