
Territorial evolution of the Caribbean
Encyclopedia

The region covered is the Caribbean, its islands (most of which enclose the sea), and the surrounding coasts. Also included is southern part of the Gulf of Mexico
Gulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico is a partially landlocked ocean basin largely surrounded by the North American continent and the island of Cuba. It is bounded on the northeast, north and northwest by the Gulf Coast of the United States, on the southwest and south by Mexico, and on the southeast by Cuba. In...
, Florida
Florida
Florida is a state in the southeastern United States, located on the nation's Atlantic and Gulf coasts. It is bordered to the west by the Gulf of Mexico, to the north by Alabama and Georgia and to the east by the Atlantic Ocean. With a population of 18,801,310 as measured by the 2010 census, it...
, Central America
Central America
Central America is the central geographic region of the Americas. It is the southernmost, isthmian portion of the North American continent, which connects with South America on the southeast. When considered part of the unified continental model, it is considered a subcontinent...
, and the northern region of South America.
The political evolution of the land surrounding the Caribbean reveals the significant role the region played in the colonial struggles of the European powers since Christopher Columbus
Christopher Columbus
Christopher Columbus was an explorer, colonizer, and navigator, born in the Republic of Genoa, in northwestern Italy. Under the auspices of the Catholic Monarchs of Spain, he completed four voyages across the Atlantic Ocean that led to general European awareness of the American continents in the...
arrived in 1492. In the 20th century the Caribbean was again important during World War II, in the decolonization
Decolonization
Decolonization refers to the undoing of colonialism, the unequal relation of polities whereby one people or nation establishes and maintains dependent Territory over another...
wave in the post-war period, and in the tension between Communist Cuba
Cuba
The Republic of Cuba is an island nation in the Caribbean. The nation of Cuba consists of the main island of Cuba, the Isla de la Juventud, and several archipelagos. Havana is the largest city in Cuba and the country's capital. Santiago de Cuba is the second largest city...
and the United States (U.S.). Genocide, slavery, immigration and rivalry between world powers have given Caribbean history an impact disproportionate to the size of this small region.
At the time of the European
European colonization of the Americas
The start of the European colonization of the Americas is typically dated to 1492. The first Europeans to reach the Americas were the Vikings during the 11th century, who established several colonies in Greenland and one short-lived settlement in present day Newfoundland...
discovery of most of the islands of the Caribbean, three major Amerindian indigenous peoples
Indigenous peoples
Indigenous peoples are ethnic groups that are defined as indigenous according to one of the various definitions of the term, there is no universally accepted definition but most of which carry connotations of being the "original inhabitants" of a territory....
lived on the islands: the Taíno
Taíno people
The Taínos were pre-Columbian inhabitants of the Bahamas, Greater Antilles, and the northern Lesser Antilles. It is thought that the seafaring Taínos are relatives of the Arawak people of South America...
in the Greater Antilles
Greater Antilles
The Greater Antilles are one of three island groups in the Caribbean. Comprising Cuba, Jamaica, Hispaniola , and Puerto Rico, the Greater Antilles constitute almost 90% of the land mass of the entire West Indies.-Greater Antilles in context :The islands of the Caribbean Sea, collectively known as...
, The Bahamas and the Leeward Islands; the Island Caribs and Galibi in the Windward Islands
Windward Islands
The Windward Islands are the southern islands of the Lesser Antilles, within the West Indies.-Name and geography:The Windward Islands are called such because they were more windward to sailing ships arriving in the New World than the Leeward Islands, given that the prevailing trade winds in the...
; and the Ciboney
Ciboney
The Ciboney were pre-Columbian indigenous inhabitants of the Greater Antilles in the Caribbean Sea. The name Ciboney derives from the indigenous Taíno people which means Cave Dwellers; evidence has shown that a number of the Ciboney people have lived in caves at some time. Over the years, many...
in western Cuba
Cuba
The Republic of Cuba is an island nation in the Caribbean. The nation of Cuba consists of the main island of Cuba, the Isla de la Juventud, and several archipelagos. Havana is the largest city in Cuba and the country's capital. Santiago de Cuba is the second largest city...
. The Taínos are subdivided into Classic Taínos, who occupied Hispaniola and Puerto Rico, Western Taínos, who occupied Cuba, Jamaica, and the Bahamian archipelago, and the Eastern Taínos, who occupied the Leeward Islands. Trinidad
Trinidad
Trinidad is the larger and more populous of the two major islands and numerous landforms which make up the island nation of Trinidad and Tobago. It is the southernmost island in the Caribbean and lies just off the northeastern coast of Venezuela. With an area of it is also the fifth largest in...
was inhabited by both Carib speaking
Carib language
Carib, also known as Caribe, Cariña, Galibi, Galibí, Kali'na, Kalihna, Kalinya, Galibi Carib, Maraworno and Marworno, is an Amerindian language in the Cariban language family....
and Arawak-speaking
Arawak language
Arawak is the eponymous language of the Arawakan language family. The term is often used to cover the closely related Taino language of the Caribbean islands. The ethnonym Lokono may be used more specifically....
groups.
1700

Kingdom of England
who controlled:- Mosquito CoastMosquito CoastThe Caribbean Mosquito Coast historically consisted of an area along the Atlantic coast of present-day Nicaragua and Honduras, and part of the Western Caribbean Zone. It was named after the local Miskito Indians and long dominated by British interests...
- The Mosquito Coast or eastern portion of what is now NicaraguaNicaraguaNicaragua is the largest country in the Central American American isthmus, bordered by Honduras to the north and Costa Rica to the south. The country is situated between 11 and 14 degrees north of the Equator in the Northern Hemisphere, which places it entirely within the tropics. The Pacific Ocean...
was declared to be under the protection of the English crown in 1687. - AnguillaAnguillaAnguilla is a British overseas territory and overseas territory of the European Union in the Caribbean. It is one of the most northerly of the Leeward Islands in the Lesser Antilles, lying east of Puerto Rico and the Virgin Islands and directly north of Saint Martin...
- In 1650, English settlers arrived from St Kitts and colonized Anguilla. In 1656 Indians from a neighboring island came and destroyed the settlement. The French temporarily overtook the island in 1666 but under the Treaty of Breda it was returned to English control. - Antigua and BarbudaAntigua and BarbudaAntigua and Barbuda is a twin-island nation lying between the Caribbean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean. It consists of two major inhabited islands, Antigua and Barbuda, and a number of smaller islands...
- As part of the Treaty of Breda France formally ends its claim of Antigua in 1667 giving control to the British. In 1685 the plantation owner Christopher CodringtonChristopher CodringtonChristopher Codrington , British soldier, bibliophile and colonial governor, was born on the island of Barbados, West Indies, in 1668...
, a sugar planter from Barbados leases the island of Barbuda from the British crown. - Bahamas - In 1670 King Charles IICharles II of EnglandCharles II was monarch of the three kingdoms of England, Scotland, and Ireland.Charles II's father, King Charles I, was executed at Whitehall on 30 January 1649, at the climax of the English Civil War...
granted the islands to the Earl of Craven a Lord Proprietor of the Carolinas, who rented the islands from the king with rights of trading, tax, appointing governors, and administering the country. - BarbadosBarbadosBarbados is an island country in the Lesser Antilles. It is in length and as much as in width, amounting to . It is situated in the western area of the North Atlantic and 100 kilometres east of the Windward Islands and the Caribbean Sea; therein, it is about east of the islands of Saint...
- British sailors who landed on Barbados in 1625 arrived at the site of present-day HoletownHoletownHoletown , is a small town located in the Caribbean island nation of Barbados. Holetown is located in the parish of Saint James on the sheltered west coast of the island.-History:...
. From the arrival of the first British settlers in 1627–1628 until independence in 1966, Barbados was under uninterrupted British control. - British Honduras (Belize)BelizeBelize is a constitutional monarchy and the northernmost country in Central America. Belize has a diverse society, comprising many cultures and languages. Even though Kriol and Spanish are spoken among the population, Belize is the only country in Central America where English is the official...
" English buccaneerBuccaneerThe buccaneers were privateers who attacked Spanish shipping in the Caribbean Sea during the late 17th century.The term buccaneer is now used generally as a synonym for pirate...
s began cutting logwood (Haematoxylum campechianum), which was used in the production of a textile dyeDyeA dye is a colored substance that has an affinity to the substrate to which it is being applied. The dye is generally applied in an aqueous solution, and requires a mordant to improve the fastness of the dye on the fiber....
. English buccaneers began using the coastline as a base from which to attack Spanish ships. Buccaneers stopped plundering Spanish logwood ships and started cutting their own wood in the 1650s and 1660s. Logwood extraction then became the main reason for the English settlement for more than a century. A 1667 treaty, in which the European powers agreed to suppress piracy, encouraged the shift from buccaneering to cutting logwood and led to more permanent settlement. - British Virgin IslandsBritish Virgin IslandsThe Virgin Islands, often called the British Virgin Islands , is a British overseas territory and overseas territory of the European Union, located in the Caribbean to the east of Puerto Rico. The islands make up part of the Virgin Islands archipelago, the remaining islands constituting the U.S...
- During the 1698 negotiations between the Netherlands and the British over the ownership of the islands an order from the King become known. The King in 1694 issued an order to prevent foreign settlement in the Virgin Islands. In February 1698 Governor Christopher CodringtonChristopher CodringtonChristopher Codrington , British soldier, bibliophile and colonial governor, was born on the island of Barbados, West Indies, in 1668...
was told to regard the earlier 1694 orders as final, and the British entertained no further claims to the islands. - Cayman IslandsCayman IslandsThe Cayman Islands is a British Overseas Territory and overseas territory of the European Union located in the western Caribbean Sea. The territory comprises the three islands of Grand Cayman, Cayman Brac, and Little Cayman, located south of Cuba and northwest of Jamaica...
- The islands were captured, then ceded to England in 1670 under the Treaty of MadridTreaty of Madrid (1670)The Treaty of Madrid adopted in 1670 was a treaty between England and Spain. Under the terms of the treaty, Spain recognized English possessions in the Caribbean Sea: "all those lands, islands, colonies and places whatsoever situated in the West Indies." England took formal control of Jamaica and...
. - JamaicaJamaicaJamaica is an island nation of the Greater Antilles, in length, up to in width and 10,990 square kilometres in area. It is situated in the Caribbean Sea, about south of Cuba, and west of Hispaniola, the island harbouring the nation-states Haiti and the Dominican Republic...
- Jamaica was captured, then ceded to England in 1670 under the Treaty of MadridTreaty of Madrid (1670)The Treaty of Madrid adopted in 1670 was a treaty between England and Spain. Under the terms of the treaty, Spain recognized English possessions in the Caribbean Sea: "all those lands, islands, colonies and places whatsoever situated in the West Indies." England took formal control of Jamaica and... - MontserratMontserratMontserrat is a British overseas territory located in the Leeward Islands, part of the chain of islands called the Lesser Antilles in the West Indies. This island measures approximately long and wide, giving of coastline...
- Fell under English control in 1632. - Saint Kitts and NevisSaint Kitts and NevisThe Federation of Saint Kitts and Nevis , located in the Leeward Islands, is a federal two-island nation in the West Indies. It is the smallest sovereign state in the Americas, in both area and population....
- After the Kalinago Genocide of 1626Kalinago Genocide of 1626The Kalinago Genocide of 1626 occurred in the West Indian island of St. Kitts at Bloody Point. The Caribs realized that many more Europeans would come and settle in St.Kitts. The Caribs decided that the European settlers had to be destroyed. Large numbers of Caribs from Dominica and other...
, Saint KittsSaint KittsSaint Kitts Saint Kitts Saint Kitts (also known more formally as Saint Christopher Island (Saint-Christophe in French) is an island in the West Indies. The west side of the island borders the Caribbean Sea, and the eastern coast faces the Atlantic Ocean...
was partitioned between the British and French, with the French gaining the ends, Capisterre in the North and Basseterre in the south, and the British gaining the centre. In 1689, during the War of the Grand Alliance, France re-occupied the entire island, and decimated the British farms. English retaliation by General Codrington defeated the French forces and deported them to Martinique. The Treaty of Rijswijk in 1697 restored pre-war conditions. NevisNevisNevis is an island in the Caribbean Sea, located near the northern end of the Lesser Antilles archipelago, about 350 km east-southeast of Puerto Rico and 80 km west of Antigua. The 93 km² island is part of the inner arc of the Leeward Islands chain of the West Indies...
was ruled by the British - Saint LuciaSaint LuciaSaint Lucia is an island country in the eastern Caribbean Sea on the boundary with the Atlantic Ocean. Part of the Lesser Antilles, it is located north/northeast of the island of Saint Vincent, northwest of Barbados and south of Martinique. It covers a land area of 620 km2 and has an...
- In 1664, Thomas Warner (son of the governor of St Kitts) claimed Saint Lucia for England. He brought 1,000 men there to defend it from the French, but after two years there were only 89 left, mostly due to disease. - Turks and Caicos IslandsTurks and Caicos IslandsThe Turks and Caicos Islands are a British Overseas Territory and overseas territory of the European Union consisting of two groups of tropical islands in the Caribbean, the larger Caicos Islands and the smaller Turks Islands, known for tourism and as an offshore financial centre.The Turks and...
- Bermudians claimed the islands for Britain and came to Turks & Caicos to rake the salt and take it back to Bermuda. Salt was a precious commodity back then as it was used not only for flavoring food but for preserving it as well. They held the islands until 1706
Dutch Republic
The Dutch RepublicDutch Republic
The Dutch Republic — officially known as the Republic of the Seven United Netherlands , the Republic of the United Netherlands, or the Republic of the Seven United Provinces — was a republic in Europe existing from 1581 to 1795, preceding the Batavian Republic and ultimately...
controlled:
- ArubaArubaAruba is a 33 km-long island of the Lesser Antilles in the southern Caribbean Sea, located 27 km north of the coast of Venezuela and 130 km east of Guajira Peninsula...
- Acquired in 1636 by the Dutch and remained under their control for nearly two centuries. - Netherlands AntillesNetherlands AntillesThe Netherlands Antilles , also referred to informally as the Dutch Antilles, was an autonomous Caribbean country within the Kingdom of the Netherlands, consisting of two groups of islands in the Lesser Antilles: Aruba, Bonaire and Curaçao , in Leeward Antilles just off the Venezuelan coast; and Sint...
- In the 17th century, the islands were conquered by the Dutch West India Company and were used as military outposts and trade bases, most prominent the slave trade. - GuyanaGuyanaGuyana , officially the Co-operative Republic of Guyana, previously the colony of British Guiana, is a sovereign state on the northern coast of South America that is culturally part of the Anglophone Caribbean. Guyana was a former colony of the Dutch and of the British...
- The Dutch West India Company, which administered most of the colony from 1621 to 1792, granted early Dutch and then British settlers ownership over 100-hectare tracts of land.
Kingdom of France
At the year 1700 Louis XIVLouis XIV of France
Louis XIV , known as Louis the Great or the Sun King , was a Bourbon monarch who ruled as King of France and Navarre. His reign, from 1643 to his death in 1715, began at the age of four and lasted seventy-two years, three months, and eighteen days...
ruled as King of France and of Navarre. In the new world he controlled:
- DominicaDominicaDominica , officially the Commonwealth of Dominica, is an island nation in the Lesser Antilles region of the Caribbean Sea, south-southeast of Guadeloupe and northwest of Martinique. Its size is and the highest point in the country is Morne Diablotins, which has an elevation of . The Commonwealth...
- The first permanent settlers on the Island were French smallholders fom Martinique who arrived in 1715. The island would stay French until the Treaty of Aix-la-ChapelleTreaty of Aix-la-Chapelle (1748)The Treaty of Aix-la-Chapelle of 1748 ended the War of the Austrian Succession following a congress assembled at the Imperial Free City of Aachen—Aix-la-Chapelle in French—in the west of the Holy Roman Empire, on 24 April 1748...
in 1748 when it was decided between, Great Britain and France to treat the island as neutral ground and leave it to the Caribs. - HaitiHaitiHaiti , officially the Republic of Haiti , is a Caribbean country. It occupies the western, smaller portion of the island of Hispaniola, in the Greater Antillean archipelago, which it shares with the Dominican Republic. Ayiti was the indigenous Taíno or Amerindian name for the island...
- The first official settlement on Tortuga was established in 1659 under the commission of King Louis XIVLouis XIV of FranceLouis XIV , known as Louis the Great or the Sun King , was a Bourbon monarch who ruled as King of France and Navarre. His reign, from 1643 to his death in 1715, began at the age of four and lasted seventy-two years, three months, and eighteen days...
. France established the first permanent French settlement on the mainland of Hispaniola, Cap François (later Cap Français, now Cap-HaïtienCap-HaïtienCap-Haïtien is a city of about 190,000 people on the north coast of Haiti and capital of the Department of Nord...
) in 1670. Under the 1697 Treaty of RyswickTreaty of RyswickThe Treaty of Ryswick or Ryswyck was signed on 20 September 1697 and named after Ryswick in the Dutch Republic. The treaty settled the Nine Years' War, which pitted France against the Grand Alliance of England, Spain, the Holy Roman Empire and the United Provinces.Negotiations started in May...
, Spain officially ceded the western third of HispaniolaHispaniolaHispaniola is a major island in the Caribbean, containing the two sovereign states of the Dominican Republic and Haiti. The island is located between the islands of Cuba to the west and Puerto Rico to the east, within the hurricane belt...
to France. - GrenadaGrenadaGrenada is an island country and Commonwealth Realm consisting of the island of Grenada and six smaller islands at the southern end of the Grenadines in the southeastern Caribbean Sea...
- On 17 March 1649 a French expedition of 203 men from MartiniqueMartiniqueMartinique is an island in the eastern Caribbean Sea, with a land area of . Like Guadeloupe, it is an overseas region of France, consisting of a single overseas department. To the northwest lies Dominica, to the south St Lucia, and to the southeast Barbados...
, led by Jacques Dyel du Parquet who had been the Governor of Martinique on behalf of the Compagnie des Iles de l'AmeriqueCompagnie des Îles de l'AmériqueThe Compagnie des Îles de l'Amérique, French for Company of the American Islands, was a French chartered company that in 1635 took over the administration of the French portion Saint-Christophe island from Compagnie de Saint-Christophe which was the only French settlement in the Caribbean at that...
(Company of the Isles of America) since 1637, landed at St. Georges Harbour and constructed a fortified settlement, which they named Fort Annunciation. - GuadeloupeGuadeloupeGuadeloupe is an archipelago located in the Leeward Islands, in the Lesser Antilles, with a land area of 1,628 square kilometres and a population of 400,000. It is the first overseas region of France, consisting of a single overseas department. As with the other overseas departments, Guadeloupe...
- The island was first settled by the French in 1635. Along with the rest of the French Caribbean it became a crown colony of France in 1674. - MartiniqueMartiniqueMartinique is an island in the eastern Caribbean Sea, with a land area of . Like Guadeloupe, it is an overseas region of France, consisting of a single overseas department. To the northwest lies Dominica, to the south St Lucia, and to the southeast Barbados...
- The island was first settled by France in 1635 and evolved into a plantation society. - Saint BarthélemySaint BarthélemySaint Barthélemy , officially the Territorial collectivity of Saint Barthélemy , is an overseas collectivity of France. Often abbreviated to Saint-Barth in French, or St. Barts in English, the indigenous people called the island Ouanalao...
- From 1651 to 1673 Saint Barthélemy was under the control of the Knights of MaltaKnights HospitallerThe Sovereign Military Hospitaller Order of Saint John of Jerusalem of Rhodes and of Malta , also known as the Sovereign Military Order of Malta , Order of Malta or Knights of Malta, is a Roman Catholic lay religious order, traditionally of military, chivalrous, noble nature. It is the world's...
After 1673 it was returned to France. - St. VincentSaint Vincent (island)Saint Vincent is a volcanic island in the Caribbean. It is the largest island of the chain called Saint Vincent and the Grenadines. It is located in the Caribbean Sea, between Saint Lucia and Grenada. It is composed of partially submerged volcanic mountains...
- While the English were the first to lay claim to St. Vincent in 1627, the French would be the first European settlers on the island when they established their first colony at Barrouallie on the Leeward side of St. Vincent shortly before 1700. - Saint Kitts and NevisSaint Kitts and NevisThe Federation of Saint Kitts and Nevis , located in the Leeward Islands, is a federal two-island nation in the West Indies. It is the smallest sovereign state in the Americas, in both area and population....
- After the Kalinago Genocide of 1626Kalinago Genocide of 1626The Kalinago Genocide of 1626 occurred in the West Indian island of St. Kitts at Bloody Point. The Caribs realized that many more Europeans would come and settle in St.Kitts. The Caribs decided that the European settlers had to be destroyed. Large numbers of Caribs from Dominica and other...
, Saint KittsSaint KittsSaint Kitts Saint Kitts Saint Kitts (also known more formally as Saint Christopher Island (Saint-Christophe in French) is an island in the West Indies. The west side of the island borders the Caribbean Sea, and the eastern coast faces the Atlantic Ocean...
was partitioned between the British and French, with the French gaining the ends, Capisterre in the North and Basseterre in the south, and the British gaining the centre. In 1689, during the War of the Grand Alliance, France re-occupied the entire island, and decimated the British farms. English retaliation by General Codrington defeated the French forces and deported them to Martinique. The Treaty of Rijswijk in 1697 restored pre-war coniditons.
Denmark
Denmark controlled what is now the:- United States Virgin IslandsUnited States Virgin IslandsThe Virgin Islands of the United States are a group of islands in the Caribbean that are an insular area of the United States. The islands are geographically part of the Virgin Islands archipelago and are located in the Leeward Islands of the Lesser Antilles.The U.S...
- The Danish West India CompanyDanish West IndiesThe Danish West Indies or "Danish Antilles", were a colony of Denmark-Norway and later Denmark in the Caribbean. They were sold to the United States in 1916 in the Treaty of the Danish West Indies and became the United States Virgin Islands in 1917...
settled on Saint Thomas in 1672, on Saint John in 1694, and purchased Saint Croix from France in 1733.
1702
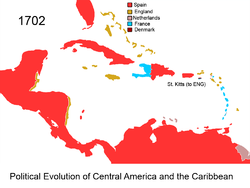
Saint Kitts and Nevis
The Federation of Saint Kitts and Nevis , located in the Leeward Islands, is a federal two-island nation in the West Indies. It is the smallest sovereign state in the Americas, in both area and population....
.
1706
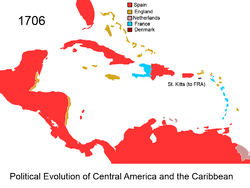
Saint Kitts and Nevis
The Federation of Saint Kitts and Nevis , located in the Leeward Islands, is a federal two-island nation in the West Indies. It is the smallest sovereign state in the Americas, in both area and population....
the French made one more major attack on British troops in 1706 during the War of the Spanish Succession
War of the Spanish Succession
The War of the Spanish Succession was fought among several European powers, including a divided Spain, over the possible unification of the Kingdoms of Spain and France under one Bourbon monarch. As France and Spain were among the most powerful states of Europe, such a unification would have...
taking the whole of the island.
1706

Turks and Caicos Islands
The Turks and Caicos Islands are a British Overseas Territory and overseas territory of the European Union consisting of two groups of tropical islands in the Caribbean, the larger Caicos Islands and the smaller Turks Islands, known for tourism and as an offshore financial centre.The Turks and...
in 1706.
1710

Bermuda
Bermuda is a British overseas territory in the North Atlantic Ocean. Located off the east coast of the United States, its nearest landmass is Cape Hatteras, North Carolina, about to the west-northwest. It is about south of Halifax, Nova Scotia, Canada, and northeast of Miami, Florida...
's only independent military operation.
1713
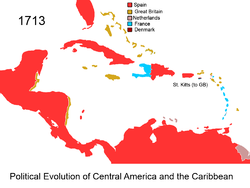
Saint Kitts and Nevis
The Federation of Saint Kitts and Nevis , located in the Leeward Islands, is a federal two-island nation in the West Indies. It is the smallest sovereign state in the Americas, in both area and population....
for 8 years (1713) until the Treaty of Utrecht
Treaty of Utrecht
The Treaty of Utrecht, which established the Peace of Utrecht, comprises a series of individual peace treaties, rather than a single document, signed by the belligerents in the War of Spanish Succession, in the Dutch city of Utrecht in March and April 1713...
was signed. The treaty ceded the entire island of St. Kitts to the British.
1723

Saint Lucia
Saint Lucia is an island country in the eastern Caribbean Sea on the boundary with the Atlantic Ocean. Part of the Lesser Antilles, it is located north/northeast of the island of Saint Vincent, northwest of Barbados and south of Martinique. It covers a land area of 620 km2 and has an...
becomes Neutral territory (agreed by Britain and France in the Treaty of Choc Island)
1733

1744

Saint Lucia
Saint Lucia is an island country in the eastern Caribbean Sea on the boundary with the Atlantic Ocean. Part of the Lesser Antilles, it is located north/northeast of the island of Saint Vincent, northwest of Barbados and south of Martinique. It covers a land area of 620 km2 and has an...
becomes French colony (Sainte Lucie).

