
History of Southeast Asia
Encyclopedia
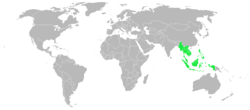
Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia, South-East Asia, South East Asia or Southeastern Asia is a subregion of Asia, consisting of the countries that are geographically south of China, east of India, west of New Guinea and north of Australia. The region lies on the intersection of geological plates, with heavy seismic...
has been characterized as interaction between regional players and foreign powers. Each country is intertwined with all the others. For instance, the Malay empires of Srivijaya
Srivijaya
Srivijaya was a powerful ancient thalassocratic Malay empire based on the island of Sumatra, modern day Indonesia, which influenced much of Southeast Asia. The earliest solid proof of its existence dates from the 7th century; a Chinese monk, I-Tsing, wrote that he visited Srivijaya in 671 for 6...
and Malacca covered modern day Indonesia, Malaysia, and Singapore while the Burmese, Thai, and Khmer peoples governed much of Indochina
Indochina
The Indochinese peninsula, is a region in Southeast Asia. It lies roughly southwest of China, and east of India. The name has its origins in the French, Indochine, as a combination of the names of "China" and "India", and was adopted when French colonizers in Vietnam began expanding their territory...
. At the same time, opportunities and threats from the east and the west shaped the direction of Southeast Asia. The history of the countries within the region only started to develop independently of each other after European colonialization
Colonialism
Colonialism is the establishment, maintenance, acquisition and expansion of colonies in one territory by people from another territory. It is a process whereby the metropole claims sovereignty over the colony and the social structure, government, and economics of the colony are changed by...
was at full steam between the 17th and the 20th century.
Introduction
The aboriginal populations of Southeast Asia are generally considered to have been members of the NegritoNegrito
The Negrito are a class of several ethnic groups who inhabit isolated parts of Southeast Asia.Their current populations include 12 Andamanese peoples of the Andaman Islands, six Semang peoples of Malaysia, the Mani of Thailand, and the Aeta, Agta, Ati, and 30 other peoples of the Philippines....
and broadly defined Austro-Melanesian
Australoid
The Australoid race is a broad racial classification. The concept originated with a typological method of racial classification. They were described as having dark skin with wavy hair, in the case of Veddoids from South Asia and Aboriginal Australians, or hair ranging from straight to kinky in the...
groups, and may have arrived as part of the hypothesized Great Coastal Migration from Africa
Africa
Africa is the world's second largest and second most populous continent, after Asia. At about 30.2 million km² including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of the Earth's total surface area and 20.4% of the total land area...
via coastal India
Coastal India
Coastal India is a geo-cultural region in the Indian Subcontinent that spans entire Coastline of India.-Region:Coastal India spans from the south west Indian coastline along the Arabian sea from the coastline of the Gulf of Kutch in its western most corner and stretches across the Gulf of Khambhat,...
. These groups now make up only a small minority of the Southeast Asian population.
Evidences suggest that the earliest non-aboriginal Southeast Asians came from southern China
China
Chinese civilization may refer to:* China for more general discussion of the country.* Chinese culture* Greater China, the transnational community of ethnic Chinese.* History of China* Sinosphere, the area historically affected by Chinese culture...
and were Austronesian speakers. Contemporary research by anthropologists, linguists (Blust, Reid, Ross, Pawley), and archaeologists (Bellwood) suggests that the inhabitants of the Maritime Southeast Asia
Maritime Southeast Asia
Maritime Southeast Asia refers to the maritime region of Southeast Asia as opposed to mainland Southeast Asia and includes the modern countries of Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines, Brunei, East Timor and Singapore....
migrated from southern China to islands of the Philippines around 2500 BCE and later spread to modern day Malaysia and Indonesia.
The earliest population of Southeast Asia was animist before Hinduism
Hinduism
Hinduism is the predominant and indigenous religious tradition of the Indian Subcontinent. Hinduism is known to its followers as , amongst many other expressions...
and Buddhism
Buddhism
Buddhism is a religion and philosophy encompassing a variety of traditions, beliefs and practices, largely based on teachings attributed to Siddhartha Gautama, commonly known as the Buddha . The Buddha lived and taught in the northeastern Indian subcontinent some time between the 6th and 4th...
were exported from the Indian subcontinent
Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent, also Indian Subcontinent, Indo-Pak Subcontinent or South Asian Subcontinent is a region of the Asian continent on the Indian tectonic plate from the Hindu Kush or Hindu Koh, Himalayas and including the Kuen Lun and Karakoram ranges, forming a land mass which extends...
. Islam
Islam
Islam . The most common are and . : Arabic pronunciation varies regionally. The first vowel ranges from ~~. The second vowel ranges from ~~~...
arrived mostly through India
India
India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
n Muslims and later dominated much of the archipelago around the 13th century while Christianity
Christianity
Christianity is a monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus as presented in canonical gospels and other New Testament writings...
came along when European colonization started around the 16th century.
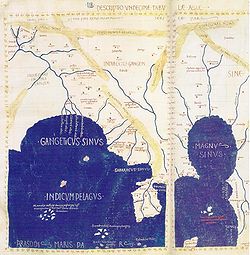
During the classical age, the existence of Southeast Asia had been known to the Greeks. The Egyptian astronomer Ptolemy
Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy , was a Roman citizen of Egypt who wrote in Greek. He was a mathematician, astronomer, geographer, astrologer, and poet of a single epigram in the Greek Anthology. He lived in Egypt under Roman rule, and is believed to have been born in the town of Ptolemais Hermiou in the...
in his Geographia named the Malay Peninsula
Malay Peninsula
The Malay Peninsula or Thai-Malay Peninsula is a peninsula in Southeast Asia. The land mass runs approximately north-south and, at its terminus, is the southern-most point of the Asian mainland...
as Aurea Chersonesus (Golden Peninsula) while Java was called Labadius. Labadius was probably a corruption of Sanskrit Yavadvipa which refers to the same island. An ancient Hindu text may have earlier referred to mainland Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia, South-East Asia, South East Asia or Southeastern Asia is a subregion of Asia, consisting of the countries that are geographically south of China, east of India, west of New Guinea and north of Australia. The region lies on the intersection of geological plates, with heavy seismic...
as Suvarnabhumi
Suwannaphum
' , , is the name of a land mentioned in many ancient sources such as the Chronicle of Sri Lanka , some stories of the Jatakas, and Milinda Panha...
which means land of gold and insular Southeast Asia as Suvarnadvipa which means island or peninsular of gold.
The region has been an important source of spices and this was one of the reasons European explorers were attracted to the Far East
Far East
The Far East is an English term mostly describing East Asia and Southeast Asia, with South Asia sometimes also included for economic and cultural reasons.The term came into use in European geopolitical discourse in the 19th century,...
. During the colonization period, states of the region became important assets to the British, the Dutch and the French. British Malaya
British Malaya
British Malaya loosely described a set of states on the Malay Peninsula and the Island of Singapore that were brought under British control between the 18th and the 20th centuries...
for instance was the world's largest producer of tin and rubber while the Dutch East Indies
Dutch East Indies
The Dutch East Indies was a Dutch colony that became modern Indonesia following World War II. It was formed from the nationalised colonies of the Dutch East India Company, which came under the administration of the Netherlands government in 1800....
was the source of Holland's wealth.
During the 1990s, Southeast Asia emerged as the fastest growing economy in the world. Its successes have caused some to call Southeast Asia an economic miracle and Singapore one of the "Four Asian Tigers". Though the Asian Financial Crisis struck in the late 1990s and left many crippled, the economy of the region has started to pick up again at a more sustainable rate as demand from the United States and People's Republic of China
People's Republic of China
China , officially the People's Republic of China , is the most populous country in the world, with over 1.3 billion citizens. Located in East Asia, the country covers approximately 9.6 million square kilometres...
soar.
Paleolithic

Stone tool
A stone tool is, in the most general sense, any tool made either partially or entirely out of stone. Although stone tool-dependent societies and cultures still exist today, most stone tools are associated with prehistoric, particularly Stone Age cultures that have become extinct...
s in Malaysia which have been dated to be 1.83 million years old.
Before the latest ice period, much of the archipelago was not under water. Sometime around the Pleistocene
Pleistocene
The Pleistocene is the epoch from 2,588,000 to 11,700 years BP that spans the world's recent period of repeated glaciations. The name pleistocene is derived from the Greek and ....
period, the Sunda Shelf
Sunda Shelf
Geologically, the Sunda Shelf is a south east extension of the continental shelf of Southeast Asia. Major landmasses on the shelf include the Malay Peninsula, Sumatra, Borneo, Java, Madura, Bali and their surrounding smaller islands. It covers an area of approximately 1.85 million km2...
was flooded as thawing occurred and thus revealing current geographical features. The area's first known human-like inhabitant some 500,000 years ago was "Java Man
Java Man
Java Man is the name given to fossils discovered in 1891 at Trinil - Ngawi Regency on the banks of the Solo River in East Java, Indonesia, one of the first known specimens of Homo erectus...
" (first classified as Pithecanthropus erectus, then subsequently named a part of the species Homo erectus
Homo erectus
Homo erectus is an extinct species of hominid that lived from the end of the Pliocene epoch to the later Pleistocene, about . The species originated in Africa and spread as far as India, China and Java. There is still disagreement on the subject of the classification, ancestry, and progeny of H...
). Recently discovered was a species of human, dubbed "Flores Man" (Homo floresiensis
Homo floresiensis
Homo floresiensis is a possible species, now extinct, in the genus Homo. The remains were discovered in 2003 on the island of Flores in Indonesia. Partial skeletons of nine individuals have been recovered, including one complete cranium...
), a miniature hominid that grew only three feet tall. Flores Man seems to have shared some islands with Java Man until only 10,000 years ago, when they became extinct.
The oldest human settlement in Malaysia has been discovered in Niah Caves
Niah Caves
Niah Caves is located within the district of Miri in Sarawak, Malaysia. Part of Niah National Park, the main cave, Niah Great Cave, is located in Gunung Subis and is made up of several voluminous, high-ceilinged chambers...
. The human remains found there have been dated back to 40,000 BC. Another remain dated back to 9000 BC dubbed the "Perak Man" and tools as old as 75,000 years have been discovered in Lenggong
Lenggong
Lenggong is a town in Perak, Malaysia. It is situated 100 km north of Ipoh.-Introduction:The Lenggong valley in Ulu Perak is one of Peninsular Malaysia's most important areas for archaeology, as excavations have revealed many traces of Malaysia's prehistory. It is the site of the oldest known place...
, Malaysia.
The oldest habitation discovered in the Philippines is located at the Tabon Caves and dates back to approximately 50,000 years; while items there found such as burial jars, earthenware, jade ornaments and other jewelry, stone tools, animal bones, and human fossils dating back to 47,000 years ago. Human remains are from approximately 24,000 years ago.
Mesolithic and early agricultural societies
AgricultureAgriculture
Agriculture is the cultivation of animals, plants, fungi and other life forms for food, fiber, and other products used to sustain life. Agriculture was the key implement in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that nurtured the...
was a development based on necessity. Before agriculture, hunting and gathering
Hunter-gatherer
A hunter-gatherer or forage society is one in which most or all food is obtained from wild plants and animals, in contrast to agricultural societies which rely mainly on domesticated species. Hunting and gathering was the ancestral subsistence mode of Homo, and all modern humans were...
sufficed to provide food. The chicken
Chicken
The chicken is a domesticated fowl, a subspecies of the Red Junglefowl. As one of the most common and widespread domestic animals, and with a population of more than 24 billion in 2003, there are more chickens in the world than any other species of bird...
and pig
Pig
A pig is any of the animals in the genus Sus, within the Suidae family of even-toed ungulates. Pigs include the domestic pig, its ancestor the wild boar, and several other wild relatives...
were domesticated here, millennia ago. So much food was available that people could gain status by giving food away in feasts and festivals, where all could eat their fill. These big men (Malay: orang kaya) would work for years, accumulating the food (wealth) needed for the festivals provided by the orang kaya. These individual acts of generosity or kindness are remembered by the people in their oral histories, which serves to provide credit in more dire times. These customs ranged throughout Southeast Asia, stretching, for example, to the island of New Guinea
New Guinea
New Guinea is the world's second largest island, after Greenland, covering a land area of 786,000 km2. Located in the southwest Pacific Ocean, it lies geographically to the east of the Malay Archipelago, with which it is sometimes included as part of a greater Indo-Australian Archipelago...
.The agricultural technology was exploited after population pressures increased to the point that systematic intensive farming was required for mere survival, say of yams
Yam (vegetable)
Yam is the common name for some species in the genus Dioscorea . These are perennial herbaceous vines cultivated for the consumption of their starchy tubers in Africa, Asia, Latin America and Oceania...
(in Papua) or rice
Rice
Rice is the seed of the monocot plants Oryza sativa or Oryza glaberrima . As a cereal grain, it is the most important staple food for a large part of the world's human population, especially in East Asia, Southeast Asia, South Asia, the Middle East, and the West Indies...
(in Indonesia). Rice paddies
Paddy field
A paddy field is a flooded parcel of arable land used for growing rice and other semiaquatic crops. Paddy fields are a typical feature of rice farming in east, south and southeast Asia. Paddies can be built into steep hillsides as terraces and adjacent to depressed or steeply sloped features such...
are well-suited for the monsoons of Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia, South-East Asia, South East Asia or Southeastern Asia is a subregion of Asia, consisting of the countries that are geographically south of China, east of India, west of New Guinea and north of Australia. The region lies on the intersection of geological plates, with heavy seismic...
. The rice paddies of Southeast Asia have existed for millennia, with evidence for their existence coeval with the rise of agriculture in other parts of the globe.
Yam cultivation in Papua, for example, consists of placing the tubers in prepared ground, heaping vegetation on them, waiting for them to propagate, and harvesting them. This work sequence is still performed by the women in the traditional societies of Southeast Asia; the men might perform the heavier duties of preparing the ground, or of fencing the area to prevent predation by pigs.
From Burma around 1500 BC, the Mon
Mon people
The Mon are an ethnic group from Burma , living mostly in Mon State, Bago Division, the Irrawaddy Delta, and along the southern Thai–Burmese border. One of the earliest peoples to reside in Southeast Asia, the Mon were responsible for the spread of Theravada Buddhism in Burma and Thailand...
and ancestors of the Khmer people
Khmer people
Khmer people are the predominant ethnic group in Cambodia, accounting for approximately 90% of the 14.8 million people in the country. They speak the Khmer language, which is part of the larger Mon–Khmer language family found throughout Southeast Asia...
started to move in into the mainland while the Tai
Tai peoples
The Tai ethnicity refers collectively to the ethnic groups of southern China and Southeast Asia, stretching from Hainan to eastern India and from southern Sichuan to Laos, Thailand, and parts of Vietnam, which speak languages in the Tai family and share similar traditions and festivals, including...
people later came from southern China to reside there in the first millennium AD.
Early Metal Phases in Southeast Asia
It was around 2500 BC that the Austronesian peopleAustronesian people
The Austronesian-speaking peoples are various populations in Oceania and Southeast Asia that speak languages of the Austronesian family. They include Taiwanese aborigines; the majority ethnic groups of East Timor, Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines, Brunei, Madagascar, Micronesia, and Polynesia,...
started to populate the archipelago and introduced primitive ironworks technology that they had mastered to the region.
By around the 5th century BC, people of the Dong Son culture
Dong Son culture
The Đông Sơn culture was a prehistoric Bronze Age age in Vietnam centered at the Red River Valley of northern Vietnam. At this time the first Vietnamese kingdoms of Văn Lang and Âu Lạc appeared...
, who lived in what is now Vietnam
Vietnam
Vietnam – sometimes spelled Viet Nam , officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam – is the easternmost country on the Indochina Peninsula in Southeast Asia. It is bordered by China to the north, Laos to the northwest, Cambodia to the southwest, and the South China Sea –...
, had mastered basic metal working. Their works are the earliest known metal object to be found by archeologists in Southeast Asia.
Ancient and classical kingdoms
Southeast AsiaSoutheast Asia
Southeast Asia, South-East Asia, South East Asia or Southeastern Asia is a subregion of Asia, consisting of the countries that are geographically south of China, east of India, west of New Guinea and north of Australia. The region lies on the intersection of geological plates, with heavy seismic...
has been inhabited since prehistoric times. The communities in the region evolved to form complex cultures with varying degrees of influence from India
India
India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
and China
China
Chinese civilization may refer to:* China for more general discussion of the country.* Chinese culture* Greater China, the transnational community of ethnic Chinese.* History of China* Sinosphere, the area historically affected by Chinese culture...
.
The ancient kingdoms can be grouped into two distinct categories. The first is agrarian kingdoms. Agrarian kingdoms had agriculture as the main economic activity. Most agrarian states were located in mainland Southeast Asia. Examples are the Ayutthaya Kingdom
Ayutthaya kingdom
Ayutthaya was a Siamese kingdom that existed from 1350 to 1767. Ayutthaya was friendly towards foreign traders, including the Chinese, Vietnamese , Indians, Japanese and Persians, and later the Portuguese, Spanish, Dutch and French, permitting them to set up villages outside the walls of the...
, based on the Chao Phraya River delta and the Khmer Empire
Khmer Empire
The Khmer Empire was one of the most powerful empires in Southeast Asia. The empire, which grew out of the former kingdom of Chenla, at times ruled over and/or vassalized parts of modern-day Laos, Thailand, Vietnam, Burma, and Malaysia. Its greatest legacy is Angkor, the site of the capital city...
on the Tonle Sap
Tonlé Sap
The Tonlé Sap is a combined lake and river system of major importance to Cambodia.The Tonlé Sap is the largest freshwater lake in South East Asia and is an ecological hot spot that was designated as a UNESCO biosphere in 1997....
. The second type is maritime
Maritime nation
A maritime nation is any nation which borders the sea and uses it for any of the following: commerce and transport, war, to define a territorial boundary, or for any maritime activity ....
states. Maritime states were dependent on sea trade. Malacca and Srivijaya
Srivijaya
Srivijaya was a powerful ancient thalassocratic Malay empire based on the island of Sumatra, modern day Indonesia, which influenced much of Southeast Asia. The earliest solid proof of its existence dates from the 7th century; a Chinese monk, I-Tsing, wrote that he visited Srivijaya in 671 for 6...
were maritime states.
A succession of trading systems dominated the trade between China and India. First, goods were shipped through Funan to the Isthmus of Kra, portaged across the narrow, and then transhipped for India and points west. Around the 6th century, CE merchants began sailing to Srivijaya where goods were transhipped directly. The limits of technology and contrary winds during parts of the year made it difficult for the ships of the time to proceed directly from the Indian Ocean to the South China Sea. The third system involved direct trade between the Indian and Chinese coasts.
Very little is known about Southeast Asian religious beliefs and practices before the advent of Indian merchants and religious influences from the 2nd century BCE onwards. Prior to the 13th century, Buddhism
Buddhism
Buddhism is a religion and philosophy encompassing a variety of traditions, beliefs and practices, largely based on teachings attributed to Siddhartha Gautama, commonly known as the Buddha . The Buddha lived and taught in the northeastern Indian subcontinent some time between the 6th and 4th...
and Hinduism
Hinduism
Hinduism is the predominant and indigenous religious tradition of the Indian Subcontinent. Hinduism is known to its followers as , amongst many other expressions...
were the main religions in Southeast Asia.
The first dominant power to arise in the archipelago was Srivijaya
Srivijaya
Srivijaya was a powerful ancient thalassocratic Malay empire based on the island of Sumatra, modern day Indonesia, which influenced much of Southeast Asia. The earliest solid proof of its existence dates from the 7th century; a Chinese monk, I-Tsing, wrote that he visited Srivijaya in 671 for 6...
in Sumatra
Sumatra
Sumatra is an island in western Indonesia, westernmost of the Sunda Islands. It is the largest island entirely in Indonesia , and the sixth largest island in the world at 473,481 km2 with a population of 50,365,538...
. From the 5th century CE, the capital, Palembang
Palembang
Palembang is the capital city of the South Sumatra province in Indonesia. Palembang is one of the oldest cities in Indonesia, and has a history of being a capital of a maritime empire. Located on the Musi River banks on the east coast of southern Sumatra island, it has an area of 400.61 square...
, became a major seaport and functioned as an entrepot
Entrepôt
An entrepôt is a trading post where merchandise can be imported and exported without paying import duties, often at a profit. This profit is possible because of trade conditions, for example, the reluctance of ships to travel the entire length of a long trading route, and selling to the entrepôt...
on the Spice Route between India and China. Srivijaya was also a notable center of Vajrayana
Vajrayana
Vajrayāna Buddhism is also known as Tantric Buddhism, Tantrayāna, Mantrayāna, Secret Mantra, Esoteric Buddhism and the Diamond Vehicle...
Buddhist learning and influence. Srivijaya's wealth and influence faded when changes in nautical technology in the 10th century CE enabled Chinese and Indian merchants to ship cargo directly between their countries and also enabled the Chola
Chola Dynasty
The Chola dynasty was a Tamil dynasty which was one of the longest-ruling in some parts of southern India. The earliest datable references to this Tamil dynasty are in inscriptions from the 3rd century BC left by Asoka, of Maurya Empire; the dynasty continued to govern over varying territory until...
state in southern India to carry out a series of destructive attacks on Srivijaya's possessions, ending Palembang's entrepot function.
In the Philippines
Philippines
The Philippines , officially known as the Republic of the Philippines , is a country in Southeast Asia in the western Pacific Ocean. To its north across the Luzon Strait lies Taiwan. West across the South China Sea sits Vietnam...
, the Laguna Copperplate Inscription
Laguna Copperplate Inscription
The Laguna Copperplate Inscription is the earliest known written document found in the Philippines. The plate was found in 1989 by a sand laborer working on Lumbang River near the outlet to Laguna de Bay, in Barangay Wawa, Lumban, in the Laguna province.The inscription on the plate was first...
dating from 900 CE relates a granted debt from a Maharlika caste nobleman named Namwaran who lived in the Manila
Manila
Manila is the capital of the Philippines. It is one of the sixteen cities forming Metro Manila.Manila is located on the eastern shores of Manila Bay and is bordered by Navotas and Caloocan to the north, Quezon City to the northeast, San Juan and Mandaluyong to the east, Makati on the southeast,...
area. This document mentions a leader of Medang in Java
Java
Java is an island of Indonesia. With a population of 135 million , it is the world's most populous island, and one of the most densely populated regions in the world. It is home to 60% of Indonesia's population. The Indonesian capital city, Jakarta, is in west Java...
.
Java was dominated by a kaleidoscope of competing agrarian kingdoms including the Sailendra
Sailendra
Sailendra is the name of an influential Indonesian dynasty that emerged in 8th century Java.The Sailendras were active promoters of Mahayana Buddhism and covered the Kedu Plain of Central Java with Buddhist monuments, including the world famous Borobudur.The Sailendras are considered to be a...
s, Mataram, Singhasari
Singhasari
Singhasari was a kingdom located in east Java between 1222 and 1292. The kingdom succeeded Kingdom of Kediri as the dominant kingdom in eastern Java.-Foundation:...
, and finally Majapahit. According to the Nagarakertagama, around the 13th century CE, Majapahit's vassal states spread throughout much of today's Indonesia, making it the largest empire ever to exist in Southeast Asia.
European colonization
European ethnic groups
The ethnic groups in Europe are the various ethnic groups that reside in the nations of Europe. European ethnology is the field of anthropology focusing on Europe....
s first came to Southeast Asia in the 16th century. It was the lure of trade that brought Europeans to Southeast Asia while missionaries also tagged along the ships as they hoped to spread Christianity
Christianity
Christianity is a monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus as presented in canonical gospels and other New Testament writings...
into the region.
Portugal
Portugal
Portugal , officially the Portuguese Republic is a country situated in southwestern Europe on the Iberian Peninsula. Portugal is the westernmost country of Europe, and is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the West and South and by Spain to the North and East. The Atlantic archipelagos of the...
was the first European power to establish a bridgehead into the lucrative Southeast Asia trade route with the conquest of the Sultanate of Malacca in 1511. The Netherlands
Netherlands
The Netherlands is a constituent country of the Kingdom of the Netherlands, located mainly in North-West Europe and with several islands in the Caribbean. Mainland Netherlands borders the North Sea to the north and west, Belgium to the south, and Germany to the east, and shares maritime borders...
and Spain
Spain
Spain , officially the Kingdom of Spain languages]] under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, Spain's official name is as follows:;;;;;;), is a country and member state of the European Union located in southwestern Europe on the Iberian Peninsula...
followed and soon superseded Portugal as the main European powers in the region. The Dutch took over Malacca
Malacca
Malacca , dubbed The Historic State or Negeri Bersejarah among locals) is the third smallest Malaysian state, after Perlis and Penang. It is located in the southern region of the Malay Peninsula, on the Straits of Malacca. It borders Negeri Sembilan to the north and the state of Johor to the south...
from the Portuguese in 1641 while Spain began to colonize the Philippines
Philippines
The Philippines , officially known as the Republic of the Philippines , is a country in Southeast Asia in the western Pacific Ocean. To its north across the Luzon Strait lies Taiwan. West across the South China Sea sits Vietnam...
(named after Philip II of Spain
Philip II of Spain
Philip II was King of Spain, Portugal, Naples, Sicily, and, while married to Mary I, King of England and Ireland. He was lord of the Seventeen Provinces from 1556 until 1581, holding various titles for the individual territories such as duke or count....
) from 1560s. Acting through the Dutch East India Company
Dutch East India Company
The Dutch East India Company was a chartered company established in 1602, when the States-General of the Netherlands granted it a 21-year monopoly to carry out colonial activities in Asia...
, the Dutch established the city of Batavia (now Jakarta
Jakarta
Jakarta is the capital and largest city of Indonesia. Officially known as the Special Capital Territory of Jakarta, it is located on the northwest coast of Java, has an area of , and a population of 9,580,000. Jakarta is the country's economic, cultural and political centre...
) as a base for trading and expansion into the other parts of Java and the surrounding territory.
Britain, in the form of the British East India Company
British East India Company
The East India Company was an early English joint-stock company that was formed initially for pursuing trade with the East Indies, but that ended up trading mainly with the Indian subcontinent and China...
, came relatively late onto the scene. Starting with Penang
Penang
Penang is a state in Malaysia and the name of its constituent island, located on the northwest coast of Peninsular Malaysia by the Strait of Malacca. It is bordered by Kedah in the north and east, and Perak in the south. Penang is the second smallest Malaysian state in area after Perlis, and the...
, the British began to expand their Southeast Asian empire. They also temporarily possessed Dutch territories during the Napoleonic Wars
Napoleonic Wars
The Napoleonic Wars were a series of wars declared against Napoleon's French Empire by opposing coalitions that ran from 1803 to 1815. As a continuation of the wars sparked by the French Revolution of 1789, they revolutionised European armies and played out on an unprecedented scale, mainly due to...
, In 1819 Stamford Raffles
Stamford Raffles
Sir Thomas Stamford Bingley Raffles, FRS was a British statesman, best known for his founding of the city of Singapore . He is often described as the "Father of Singapore"...
established Singapore
Singapore
Singapore , officially the Republic of Singapore, is a Southeast Asian city-state off the southern tip of the Malay Peninsula, north of the equator. An island country made up of 63 islands, it is separated from Malaysia by the Straits of Johor to its north and from Indonesia's Riau Islands by the...
as a key trading post for Britain in their rivalry with the Dutch. However, their rivalry cooled in 1824 when an Anglo-Dutch treaty
Anglo-Dutch Treaty
Anglo-Dutch Treaty can refer to either of the following:* Anglo-Dutch Treaty of 1814 * Anglo-Dutch Treaty of 1824...
demarcated their respective interests in Southeast Asia. From the 1850s onwards, the pace of colonization shifted to a significantly higher gear.
This phenomenon, denoted New Imperialism
New Imperialism
New Imperialism refers to the colonial expansion adopted by Europe's powers and, later, Japan and the United States, during the 19th and early 20th centuries; expansion took place from the French conquest of Algeria until World War I: approximately 1830 to 1914...
, saw the conquest of nearly all Southeast Asian territories by the colonial powers. The Dutch East India Company and British East India Company were dissolved by their respective governments, who took over the direct administration of the colonies. Only Thailand
Thailand
Thailand , officially the Kingdom of Thailand , formerly known as Siam , is a country located at the centre of the Indochina peninsula and Southeast Asia. It is bordered to the north by Burma and Laos, to the east by Laos and Cambodia, to the south by the Gulf of Thailand and Malaysia, and to the...
was spared the experience of foreign rule, although, Thailand itself was also greatly affected by the power politics of the Western powers.
By 1913, the British occupied Burma, Malaya
British Malaya
British Malaya loosely described a set of states on the Malay Peninsula and the Island of Singapore that were brought under British control between the 18th and the 20th centuries...
and the Borneo
Borneo
Borneo is the third largest island in the world and is located north of Java Island, Indonesia, at the geographic centre of Maritime Southeast Asia....
territories, the French
France
The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
controlled Indochina
Indochina
The Indochinese peninsula, is a region in Southeast Asia. It lies roughly southwest of China, and east of India. The name has its origins in the French, Indochine, as a combination of the names of "China" and "India", and was adopted when French colonizers in Vietnam began expanding their territory...
, the Dutch ruled the Netherlands East Indies while Portugal
Portugal
Portugal , officially the Portuguese Republic is a country situated in southwestern Europe on the Iberian Peninsula. Portugal is the westernmost country of Europe, and is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the West and South and by Spain to the North and East. The Atlantic archipelagos of the...
managed to hold on to Portuguese Timor
Portuguese Timor
Portuguese Timor was the name of East Timor when it was under Portuguese control. During this period, Portugal shared the island of Timor with the Netherlands East Indies, and later with Indonesia....
. In the Philippines, Filipino revolutionaries declared independence from Spain in 1898 but was handed over to the United States despite protests as a result of the Spanish-American War
Spanish-American War
The Spanish–American War was a conflict in 1898 between Spain and the United States, effectively the result of American intervention in the ongoing Cuban War of Independence...
.
Colonial rule had a profound effect on Southeast Asia. While the colonial powers profited much from the region's vast resources and large market, colonial rule did develop the region to a varying extent. Commercial agriculture, mining and an export based economy developed rapidly during this period. Increased labor demand resulted in mass immigration, especially from British India and China
China
Chinese civilization may refer to:* China for more general discussion of the country.* Chinese culture* Greater China, the transnational community of ethnic Chinese.* History of China* Sinosphere, the area historically affected by Chinese culture...
, which brought about massive demographic change. The institutions for a modern nation state like a state bureaucracy, courts of law, print media and to a smaller extent, modern education, sowed the seeds of the fledgling nationalist
Nationalism
Nationalism is a political ideology that involves a strong identification of a group of individuals with a political entity defined in national terms, i.e. a nation. In the 'modernist' image of the nation, it is nationalism that creates national identity. There are various definitions for what...
movements in the colonial territories. In the inter-war years, these nationalist movements grew and often clashed with the colonial authorities when they demanded self-determination
Self-determination
Self-determination is the principle in international law that nations have the right to freely choose their sovereignty and international political status with no external compulsion or external interference...
.
Japanese colonization
See also : Japanese Invasion of ThailandJapanese Invasion of Thailand
The Japanese invasion of Thailand occurred on December 8, 1941. It was fought between Thailand and the Empire of Japan. Despite fierce fighting in Southern Thailand, Thai resistance lasted only a few hours before ending in a ceasefire.-Background:...
, Japanese occupation of Burma
Japanese occupation of Burma
The Japanese occupation of Burma refers to the period between 1942 and 1945 during World War II, when Burma was a part of the Empire of Japan. The Japanese had assisted formation of the Burma Independence Army, and trained the Thirty Comrades, who were the founders of the modern Armed Forces...
During World War II
World War II
World War II, or the Second World War , was a global conflict lasting from 1939 to 1945, involving most of the world's nations—including all of the great powers—eventually forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis...
, the region was invaded by the Japanese Imperial Army and included in the Greater East Asia Co-Prosperity Sphere
Greater East Asia Co-Prosperity Sphere
The Greater East Asia Co-Prosperity Sphere was a concept created and promulgated during the Shōwa era by the government and military of the Empire of Japan. It represented the desire to create a self-sufficient "bloc of Asian nations led by the Japanese and free of Western powers"...
. Thailand
Thailand
Thailand , officially the Kingdom of Thailand , formerly known as Siam , is a country located at the centre of the Indochina peninsula and Southeast Asia. It is bordered to the north by Burma and Laos, to the east by Laos and Cambodia, to the south by the Gulf of Thailand and Malaysia, and to the...
was the only country to maintain a nominal independence by making a political and military alliance with the Empire of Japan
Empire of Japan
The Empire of Japan is the name of the state of Japan that existed from the Meiji Restoration on 3 January 1868 to the enactment of the post-World War II Constitution of...
.
Decolonization
With the rejuvenated nationalist movements in wait, the Europeans returned to a very different Southeast Asia after World War IIWorld War II
World War II, or the Second World War , was a global conflict lasting from 1939 to 1945, involving most of the world's nations—including all of the great powers—eventually forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis...
. Indonesia
Indonesia
Indonesia , officially the Republic of Indonesia , is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania. Indonesia is an archipelago comprising approximately 13,000 islands. It has 33 provinces with over 238 million people, and is the world's fourth most populous country. Indonesia is a republic, with an...
declared independence in 17 August 1945 and subsequently fought a bitter war against the returning Dutch; the Philippines was granted independence by the United States in 1946; Burma secured their independence from Britain in 1948, and the French
France
The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
were driven from Indochina
Indochina
The Indochinese peninsula, is a region in Southeast Asia. It lies roughly southwest of China, and east of India. The name has its origins in the French, Indochine, as a combination of the names of "China" and "India", and was adopted when French colonizers in Vietnam began expanding their territory...
in 1954 after a bitterly fought war (the Indochina War) against the Vietnamese nationalists. The newly-established United Nations
United Nations
The United Nations is an international organization whose stated aims are facilitating cooperation in international law, international security, economic development, social progress, human rights, and achievement of world peace...
provided a forum both for nationalist demands and for the newly demanded independent nations.
During the Cold War
Cold War
The Cold War was the continuing state from roughly 1946 to 1991 of political conflict, military tension, proxy wars, and economic competition between the Communist World—primarily the Soviet Union and its satellite states and allies—and the powers of the Western world, primarily the United States...
, countering the threat of communism
Communism
Communism is a social, political and economic ideology that aims at the establishment of a classless, moneyless, revolutionary and stateless socialist society structured upon common ownership of the means of production...
was a major theme in the decolonization
Decolonization
Decolonization refers to the undoing of colonialism, the unequal relation of polities whereby one people or nation establishes and maintains dependent Territory over another...
process. After suppressing the communist insurrection during the Malayan Emergency
Malayan Emergency
The Malayan Emergency was a guerrilla war fought between Commonwealth armed forces and the Malayan National Liberation Army , the military arm of the Malayan Communist Party, from 1948 to 1960....
from 1948 to 1960, Britain granted independence to Malaya
Federation of Malaya
The Federation of Malaya is the name given to a federation of 11 states that existed from 31 January 1948 until 16 September 1963. The Federation became independent on 31 August 1957...
and later, Singapore
Singapore
Singapore , officially the Republic of Singapore, is a Southeast Asian city-state off the southern tip of the Malay Peninsula, north of the equator. An island country made up of 63 islands, it is separated from Malaysia by the Straits of Johor to its north and from Indonesia's Riau Islands by the...
, Sabah
Sabah
Sabah is one of 13 member states of Malaysia. It is located on the northern portion of the island of Borneo. It is the second largest state in the country after Sarawak, which it borders on its southwest. It also shares a border with the province of East Kalimantan of Indonesia in the south...
and Sarawak
Sarawak
Sarawak is one of two Malaysian states on the island of Borneo. Known as Bumi Kenyalang , Sarawak is situated on the north-west of the island. It is the largest state in Malaysia followed by Sabah, the second largest state located to the North- East.The administrative capital is Kuching, which...
in 1957 and 1963 respectively within the framework of the Federation of Malaysia. In one of the most bloody single incidents of violence in Cold War Southeast Asia, General Suharto seized power in Indonesia in 1965 and initiated a massacre of approximately 500,000 alleged members of the Indonesian Communist Party (PKI). Recent evidence from the US National Security Archive published by George Washington University suggests this massacre was carried out with the support of the United States embassy in Jakarta, which supplied lists of names of suspected PKI members to Suharto. http://www.gwu.edu/~nsarchiv/NSAEBB/NSAEBB52/#FRUS
The United States intervention against communist forces in Indochina during a conflict commonly referred to in the United States as the Vietnam War
Vietnam War
The Vietnam War was a Cold War-era military conflict that occurred in Vietnam, Laos, and Cambodia from 1 November 1955 to the fall of Saigon on 30 April 1975. This war followed the First Indochina War and was fought between North Vietnam, supported by its communist allies, and the government of...
meant that Vietnam
Vietnam
Vietnam – sometimes spelled Viet Nam , officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam – is the easternmost country on the Indochina Peninsula in Southeast Asia. It is bordered by China to the north, Laos to the northwest, Cambodia to the southwest, and the South China Sea –...
, Laos
Laos
Laos Lao: ສາທາລະນະລັດ ປະຊາທິປະໄຕ ປະຊາຊົນລາວ Sathalanalat Paxathipatai Paxaxon Lao, officially the Lao People's Democratic Republic, is a landlocked country in Southeast Asia, bordered by Burma and China to the northwest, Vietnam to the east, Cambodia to the south and Thailand to the west...
and Cambodia
Cambodia
Cambodia , officially known as the Kingdom of Cambodia, is a country located in the southern portion of the Indochina Peninsula in Southeast Asia...
had to go through a prolonged and protracted war in their route to independence. By the war's end in 1975, all these countries were controlled by communist parties. After the communist victory, two wars between communist states — the Cambodian-Vietnamese War
Cambodian-Vietnamese War
The Cambodian–Vietnamese War was an armed conflict between the Socialist Republic of Vietnam and Democratic Kampuchea. The war began with isolated clashes along the land and maritime boundaries of Vietnam and Kampuchea between 1975 and 1977, occasionally involving division-sized military formations...
of 1975-1989 and the Sino-Vietnamese War
Sino-Vietnamese War
The Sino–Vietnamese War , also known as the Third Indochina War, known in the PRC as and in Vietnam as Chiến tranh chống bành trướng Trung Hoa , was a brief but bloody border war fought in 1979 between the People's Republic of China and the Socialist Republic of Vietnam...
of 1979 — were fought in the region.
In 1975, Portuguese rule ended in East Timor. However, independence was short-lived as Indonesia annexed the territory soon after. Finally, Britain ended its protectorate of the Sultanate of Brunei
Brunei
Brunei , officially the State of Brunei Darussalam or the Nation of Brunei, the Abode of Peace , is a sovereign state located on the north coast of the island of Borneo, in Southeast Asia...
in 1984, marking the end of European rule in Southeast Asia.
Contemporary Southeast Asia
Modern Southeast Asia has been characterized by high economic growth by most countries and closer regional integration. IndonesiaIndonesia
Indonesia , officially the Republic of Indonesia , is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania. Indonesia is an archipelago comprising approximately 13,000 islands. It has 33 provinces with over 238 million people, and is the world's fourth most populous country. Indonesia is a republic, with an...
, Malaysia, the Philippines
Philippines
The Philippines , officially known as the Republic of the Philippines , is a country in Southeast Asia in the western Pacific Ocean. To its north across the Luzon Strait lies Taiwan. West across the South China Sea sits Vietnam...
, Singapore
Singapore
Singapore , officially the Republic of Singapore, is a Southeast Asian city-state off the southern tip of the Malay Peninsula, north of the equator. An island country made up of 63 islands, it is separated from Malaysia by the Straits of Johor to its north and from Indonesia's Riau Islands by the...
and Thailand
Thailand
Thailand , officially the Kingdom of Thailand , formerly known as Siam , is a country located at the centre of the Indochina peninsula and Southeast Asia. It is bordered to the north by Burma and Laos, to the east by Laos and Cambodia, to the south by the Gulf of Thailand and Malaysia, and to the...
have traditionally experienced high growth and are commonly recognized as the more developed countries of the region. As of late, Vietnam
Vietnam
Vietnam – sometimes spelled Viet Nam , officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam – is the easternmost country on the Indochina Peninsula in Southeast Asia. It is bordered by China to the north, Laos to the northwest, Cambodia to the southwest, and the South China Sea –...
too had been experiencing an economic boom. However, Myanmar
Myanmar
Burma , officially the Republic of the Union of Myanmar , is a country in Southeast Asia. Burma is bordered by China on the northeast, Laos on the east, Thailand on the southeast, Bangladesh on the west, India on the northwest, the Bay of Bengal to the southwest, and the Andaman Sea on the south....
, Cambodia
Cambodia
Cambodia , officially known as the Kingdom of Cambodia, is a country located in the southern portion of the Indochina Peninsula in Southeast Asia...
, Laos
Laos
Laos Lao: ສາທາລະນະລັດ ປະຊາທິປະໄຕ ປະຊາຊົນລາວ Sathalanalat Paxathipatai Paxaxon Lao, officially the Lao People's Democratic Republic, is a landlocked country in Southeast Asia, bordered by Burma and China to the northwest, Vietnam to the east, Cambodia to the south and Thailand to the west...
and the newly independent East Timor
East Timor
The Democratic Republic of Timor-Leste, commonly known as East Timor , is a state in Southeast Asia. It comprises the eastern half of the island of Timor, the nearby islands of Atauro and Jaco, and Oecusse, an exclave on the northwestern side of the island, within Indonesian West Timor...
are still lagging economically.
On August 8, 1967, the Association of Southeast Asian Nations
Association of Southeast Asian Nations
The Association of Southeast Asian Nations, commonly abbreviated ASEAN rarely ), is a geo-political and economic organization of ten countries located in Southeast Asia, which was formed on 8 August 1967 by Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines, Singapore and Thailand. Since then, membership has...
(ASEAN) was founded by Thailand, Indonesia, Malaysia, Singapore, and the Philippines. Since Cambodian admission into the union in 1999, East Timor is the only Southeast Asian country that is not part of ASEAN, although plans are under way for eventual membership. The association aims to enhance cooperation among Southeast Asian community. ASEAN Free Trade Area
ASEAN Free Trade Area
ASEAN Free Trade Area is a trade bloc agreement by the Association of Southeast Asian Nations supporting local manufacturing in all ASEAN countries....
has been established to encourage greater trade among ASEAN members. ASEAN has also been a front runner in greater integration of Asia-Pacific region through East Asia Summit
East Asia Summit
The East Asia Summit is a forum held annually by leaders of, initially, 16 countries in the East Asian region. Membership will expand to 18 countries including the United States and Russia at the Sixth EAS in 2011. EAS meetings are held after annual ASEAN leaders’ meetings...
s.
See also
- Buddhism in Southeast AsiaBuddhism in Southeast AsiaBuddhism in Southeast Asia is mostly Theravadin. Vietnam however had in pre-Communist times a Mahayana majority due to Chinese influence. Indonesia was Mahayana Buddhist since the time of the Sailendra and Srivijaya empires but Mahayana Buddhism in Indonesia is now largely practiced by the Chinese...
- Hinduism in Southeast AsiaHinduism in Southeast AsiaHinduism in Southeast Asia gave birth to the former Champa civilization in southern parts of Central Vietnam, Funan in Cambodia, the Khmer Empire in Indochina, Langkasuka Kingdom, Gangga Negara and Old Kedah in the Malay Peninsular, the Srivijayan kingdom on Sumatra, the Singhasari kingdom and the...
- History of AsiaHistory of AsiaThe history of Asia can be seen as the collective history of several distinct peripheral coastal regions such as, East Asia, South Asia, and the Middle East linked by the interior mass of the Eurasian steppe....
- History of BruneiHistory of BruneiThe Sultanate of Brunei ruled during the fourteenth to the sixteenth century CE. Its territory covered the northern part of Borneo and the southern Philippines. European influence gradually brought an end to this regional power. Later, there was a brief war with Spain, in which Brunei was victorious...
- History of CambodiaHistory of Cambodia- Prehistory and early history :Carbon 14 dating of a cave at Laang Spean in northwest Cambodia reveals people who made pots were living in Cambodia as early as 4200 BCE . Further archaeological evidence indicates that other parts of the region now called Cambodia were inhabited from around...
- History of East TimorHistory of East TimorEast Timor is a small country in Southeast Asia, officially known as Democratic Republic of Timor-Leste. The country comprises the eastern half of the island of Timor and the nearby islands of Atauro and Jaco. The first inhabitants are thought to be descendant of Australoid and Melanesian peoples...
- History of IndonesiaHistory of IndonesiaThe History of Indonesia was shaped by its geographic position, its natural resources, the series of human migrations, contacts, economy and trade, conquests and politics. Indonesia is an archipelagic country of 17,508 islands stretching along the equator in South East Asia...
- History of LaosHistory of Laos-Earliest known history and the founding of Lan Xang:The earliest Laos legal document is known as "the laws of Khun Borom" , still preserved in manuscript form.This set of memoriter laws is written in a type of indigenous blank verse, and reflects the state of proto-Lao society as early...
- History of MalaysiaHistory of MalaysiaMalaysia is a country in South East Asia whose strategic sea-lane position brought trade and foreign influences that fundamentally influenced its history. Hindu and Buddhist cultures imported from India dominated early Malaysian history...
- History of MyanmarHistory of MyanmarThe history of Burma covers the period from the time of first-known human settlements 13,000 years ago to the present day. The earliest inhabitants of recorded history were the Pyu who entered the Irrawaddy valley from the north c. 2nd century BCE. By the 4th century CE, the Pyu had founded...
- History of the PhilippinesHistory of the PhilippinesThe history of the Philippines is believed to have begun with the arrival of the first humans via land bridges at least 30,000 years ago. The first recorded visit from the West is the arrival of Ferdinand Magellan, who sighted Samar on March 16, 1521 and landed on Homonhon Island southeast of Samar...
- History of SingaporeHistory of SingaporeThe history of Singapore dates to the 11th century. The island rose in importance during the 14th century under the rule of Srivijayan prince Parameswara and became an important port until it was destroyed by Acehnese raiders in 1613. The modern history of Singapore began in 1819 when Englishman...
- History of ThailandHistory of ThailandTai peoples who originally lived in southwestern China, migrated into mainland Southeast Asia over a period of many centuries. The oldest known mention of their existence in the region by the exonym Siamese is in a twelfth-century A.D. inscription at the Khmer temple complex of Angkor Wat in...
- History of VietnamHistory of VietnamThe history of Vietnam covers a period of more than 2,700 years. By far Vietnam's most important historical international relationship has been with China. Vietnam's prehistory includes a legend about a kingdom known as Van Lang that included what is now China's Guangxi Autonomous Region and...
- History of Brunei
Further reading
- Church, Peter. A Short History of South East Asia, 5th Edition ISBN 0-470-82481-6
- Heidhues,Mary Somer. "'Southeast Asia: A Concise History" ISBN 0-500-28303-6
- Osborne, Milton. Southeast Asia. An introductory history. ISBN 1-86508-390-9
- Tarling, Nicholas (ed). The Cambridge history of Southeast Asia Vol I-IV. ISBN 0-521-66369-5

