
Stuart period
Encyclopedia
margin-top:10px; margin-bottom:10px;"> .jpg) James I James I of England James VI and I was King of Scots as James VI from 24 July 1567 and King of England and Ireland as James I from the union of the English and Scottish crowns on 24 March 1603... Charles I Charles I of England Charles I was King of England, King of Scotland, and King of Ireland from 27 March 1625 until his execution in 1649. Charles engaged in a struggle for power with the Parliament of England, attempting to obtain royal revenue whilst Parliament sought to curb his Royal prerogative which Charles... Charles II Charles II of England Charles II was monarch of the three kingdoms of England, Scotland, and Ireland.Charles II's father, King Charles I, was executed at Whitehall on 30 January 1649, at the climax of the English Civil War...   James II James II of England James II & VII was King of England and King of Ireland as James II and King of Scotland as James VII, from 6 February 1685. He was the last Catholic monarch to reign over the Kingdoms of England, Scotland, and Ireland... Mary II Mary II of England Mary II was joint Sovereign of England, Scotland, and Ireland with her husband and first cousin, William III and II, from 1689 until her death. William and Mary, both Protestants, became king and queen regnant, respectively, following the Glorious Revolution, which resulted in the deposition of... Anne Anne of Great Britain Anne ascended the thrones of England, Scotland and Ireland on 8 March 1702. On 1 May 1707, under the Act of Union, two of her realms, England and Scotland, were united as a single sovereign state, the Kingdom of Great Britain.Anne's Catholic father, James II and VII, was deposed during the... |
|
| Preceded by | House of Tudor |
|---|---|
| Followed by | House of Hanover House of Hanover The House of Hanover is a deposed German royal dynasty which has ruled the Duchy of Brunswick-Lüneburg , the Kingdom of Hanover, the Kingdom of Great Britain, the Kingdom of Ireland and the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland... |
The Stuart period of English and British history refers to the period between 1603 and 1714, while in Scotland
Scotland
Scotland is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Occupying the northern third of the island of Great Britain, it shares a border with England to the south and is bounded by the North Sea to the east, the Atlantic Ocean to the north and west, and the North Channel and Irish Sea to the...
it begins in 1371. These dates coincide with the rule of the Scottish royal House of Stuart
House of Stuart
The House of Stuart is a European royal house. Founded by Robert II of Scotland, the Stewarts first became monarchs of the Kingdom of Scotland during the late 14th century, and subsequently held the position of the Kings of Great Britain and Ireland...
, whose first monarch to rule England
Kingdom of England
The Kingdom of England was, from 927 to 1707, a sovereign state to the northwest of continental Europe. At its height, the Kingdom of England spanned the southern two-thirds of the island of Great Britain and several smaller outlying islands; what today comprises the legal jurisdiction of England...
was James I & VI
James I of England
James VI and I was King of Scots as James VI from 24 July 1567 and King of England and Ireland as James I from the union of the English and Scottish crowns on 24 March 1603...
. The death of Queen Elizabeth I
Elizabeth I of England
Elizabeth I was queen regnant of England and Ireland from 17 November 1558 until her death. Sometimes called The Virgin Queen, Gloriana, or Good Queen Bess, Elizabeth was the fifth and last monarch of the Tudor dynasty...
, the last of the Tudors, without any descendants and without an English heir, left her two kingdoms of England and Ireland
Kingdom of Ireland
The Kingdom of Ireland refers to the country of Ireland in the period between the proclamation of Henry VIII as King of Ireland by the Crown of Ireland Act 1542 and the Act of Union in 1800. It replaced the Lordship of Ireland, which had been created in 1171...
to be ruled by Elizabeth's closest heir, the Scottish king. The regicide
Regicide
The broad definition of regicide is the deliberate killing of a monarch, or the person responsible for the killing of a monarch. In a narrower sense, in the British tradition, it refers to the judicial execution of a king after a trial...
of King Charles I
Charles I of England
Charles I was King of England, King of Scotland, and King of Ireland from 27 March 1625 until his execution in 1649. Charles engaged in a struggle for power with the Parliament of England, attempting to obtain royal revenue whilst Parliament sought to curb his Royal prerogative which Charles...
brought a temporary end to the rule of the Stuarts, when England became a Republic
Republic
A republic is a form of government in which the people, or some significant portion of them, have supreme control over the government and where offices of state are elected or chosen by elected people. In modern times, a common simplified definition of a republic is a government where the head of...
under Oliver Cromwell
Oliver Cromwell
Oliver Cromwell was an English military and political leader who overthrew the English monarchy and temporarily turned England into a republican Commonwealth, and served as Lord Protector of England, Scotland, and Ireland....
. The Stuarts were restored to the throne under Charles II
Charles II of England
Charles II was monarch of the three kingdoms of England, Scotland, and Ireland.Charles II's father, King Charles I, was executed at Whitehall on 30 January 1649, at the climax of the English Civil War...
in 1660. The Stuart period ended with the death of Queen Anne
Anne of Great Britain
Anne ascended the thrones of England, Scotland and Ireland on 8 March 1702. On 1 May 1707, under the Act of Union, two of her realms, England and Scotland, were united as a single sovereign state, the Kingdom of Great Britain.Anne's Catholic father, James II and VII, was deposed during the...
and the accession of George I
George I of Great Britain
George I was King of Great Britain and Ireland from 1 August 1714 until his death, and ruler of the Duchy and Electorate of Brunswick-Lüneburg in the Holy Roman Empire from 1698....
of the House of Hanover
House of Hanover
The House of Hanover is a deposed German royal dynasty which has ruled the Duchy of Brunswick-Lüneburg , the Kingdom of Hanover, the Kingdom of Great Britain, the Kingdom of Ireland and the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland...
.
The Stuart era experienced many changes: the Gunpowder Plot
Gunpowder Plot
The Gunpowder Plot of 1605, in earlier centuries often called the Gunpowder Treason Plot or the Jesuit Treason, was a failed assassination attempt against King James I of England and VI of Scotland by a group of provincial English Catholics led by Robert Catesby.The plan was to blow up the House of...
, civil and foreign wars, the regicide of a king, a republic, the great plague, the Great Fire of London
Great Fire of London
The Great Fire of London was a major conflagration that swept through the central parts of the English city of London, from Sunday, 2 September to Wednesday, 5 September 1666. The fire gutted the medieval City of London inside the old Roman City Wall...
and the Glorious Revolution
Glorious Revolution
The Glorious Revolution, also called the Revolution of 1688, is the overthrow of King James II of England by a union of English Parliamentarians with the Dutch stadtholder William III of Orange-Nassau...
. This was the era of Shakespeare
William Shakespeare
William Shakespeare was an English poet and playwright, widely regarded as the greatest writer in the English language and the world's pre-eminent dramatist. He is often called England's national poet and the "Bard of Avon"...
, Wren
Christopher Wren
Sir Christopher Wren FRS is one of the most highly acclaimed English architects in history.He used to be accorded responsibility for rebuilding 51 churches in the City of London after the Great Fire in 1666, including his masterpiece, St. Paul's Cathedral, on Ludgate Hill, completed in 1710...
, Galileo, Newton
Isaac Newton
Sir Isaac Newton PRS was an English physicist, mathematician, astronomer, natural philosopher, alchemist, and theologian, who has been "considered by many to be the greatest and most influential scientist who ever lived."...
and Pepys
Samuel Pepys
Samuel Pepys FRS, MP, JP, was an English naval administrator and Member of Parliament who is now most famous for the diary he kept for a decade while still a relatively young man...
, to name but a few. The era saw the settlement of the Americas
British colonization of the Americas
British colonization of the Americas began in 1607 in Jamestown, Virginia and reached its peak when colonies had been established throughout the Americas...
, trade with the Spice Islands
Maluku Islands
The Maluku Islands are an archipelago that is part of Indonesia, and part of the larger Maritime Southeast Asia region. Tectonically they are located on the Halmahera Plate within the Molucca Sea Collision Zone...
, the birth of steam engine
Steam engine
A steam engine is a heat engine that performs mechanical work using steam as its working fluid.Steam engines are external combustion engines, where the working fluid is separate from the combustion products. Non-combustion heat sources such as solar power, nuclear power or geothermal energy may be...
s, microscope
Microscope
A microscope is an instrument used to see objects that are too small for the naked eye. The science of investigating small objects using such an instrument is called microscopy...
s, coffee houses and newspaper
Newspaper
A newspaper is a scheduled publication containing news of current events, informative articles, diverse features and advertising. It usually is printed on relatively inexpensive, low-grade paper such as newsprint. By 2007, there were 6580 daily newspapers in the world selling 395 million copies a...
s.
Flags, coins and styles (1606–1707)
This James IJames I of England
James VI and I was King of Scots as James VI from 24 July 1567 and King of England and Ireland as James I from the union of the English and Scottish crowns on 24 March 1603...
proclamation of 12 April 1606 legislated an amalgamation
Amalgamation (politics)
A merger or amalgamation in a political or administrative sense is the combination of two or more political or administrative entities such as municipalities , counties, districts, etc. into a single entity. This term is used when the process occurs within a sovereign entity...
of the English
Flag of England
The Flag of England is the St George's Cross . The red cross appeared as an emblem of England during the Middle Ages and the Crusades and is one of the earliest known emblems representing England...
and Scottish
Flag of Scotland
The Flag of Scotland, , also known as Saint Andrew's Cross or the Saltire, is the national flag of Scotland. As the national flag it is the Saltire, rather than the Royal Standard of Scotland, which is the correct flag for all individuals and corporate bodies to fly in order to demonstrate both...
flags, initiating the design of the first Union Flag
Union Flag
The Union Flag, also known as the Union Jack, is the flag of the United Kingdom. It retains an official or semi-official status in some Commonwealth Realms; for example, it is known as the Royal Union Flag in Canada. It is also used as an official flag in some of the smaller British overseas...
.
.svg.png)
Great Britain
Great Britain or Britain is an island situated to the northwest of Continental Europe. It is the ninth largest island in the world, and the largest European island, as well as the largest of the British Isles...
." Non-statutory use of this style is found on heraldic
Heraldry
Heraldry is the profession, study, or art of creating, granting, and blazoning arms and ruling on questions of rank or protocol, as exercised by an officer of arms. Heraldry comes from Anglo-Norman herald, from the Germanic compound harja-waldaz, "army commander"...
and vexillogical
Vexillology
Vexillology is the scholarly study of flags. The word is a synthesis of the Latin word vexillum, meaning 'flag', and the Greek suffix -logy, meaning 'study'. The vexillum was a particular type of flag used by Roman legions during the classical era; its name is a diminutive form of the word velum...
symbolism, such as the king's Great Seals of Office, the Royal Arms, and coinage
COinS
ContextObjects in Spans, commonly abbreviated COinS, is a method to embed bibliographic metadata in the HTML code of web pages. This allows bibliographic software to publish machine-readable bibliographic items and client reference management software to retrieve bibliographic metadata. The...
. The style "King of Great Britain" (MAGNAE BRITANNIAE REX) appears on all Great Seals instead of the more formally correct "king of England and Scotland" (ANGLIAE SCOTIAE REX) in 1625–1627, 1640–1649, 1660–1689, and 1695–1707. The coins of James I and his successors used MAGNAE BRITANNIAE REX, as seen on the half crown
Half crown (British coin)
The half crown was a denomination of British money worth half of a crown, equivalent to two and a half shillings , or one-eighth of a pound. The half crown was first issued in 1549, in the reign of Edward VI...
of Charles II
Charles II of England
Charles II was monarch of the three kingdoms of England, Scotland, and Ireland.Charles II's father, King Charles I, was executed at Whitehall on 30 January 1649, at the climax of the English Civil War...
.
Social lifestyles
Many strictures were placed on society by the Puritans. Amongst other things, the Puritans banned gambling, cockfightCockfight
A cockfight is a blood sport between two roosters , held in a ring called a cockpit. Cockfighting is now illegal throughout all states in the United States, Brazil, Australia and in most of Europe. It is still legal in several U.S. territories....
s, the theatre, and even Christmas. The arrival of Charles II
Charles II of England
Charles II was monarch of the three kingdoms of England, Scotland, and Ireland.Charles II's father, King Charles I, was executed at Whitehall on 30 January 1649, at the climax of the English Civil War...
brought relief from the warlike and strict society that people had lived in for several years. The theatre returned, along with expensive fashions such as the periwig. The British Empire
British Empire
The British Empire comprised the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom. It originated with the overseas colonies and trading posts established by England in the late 16th and early 17th centuries. At its height, it was the...
had been expanding since the Elizabethian era, and along with much wealth returning to the country, expensive luxury items were appearing. Sugar and coffee from the East Indies
East Indies
East Indies is a term used by Europeans from the 16th century onwards to identify what is now known as Indian subcontinent or South Asia, Southeastern Asia, and the islands of Oceania, including the Malay Archipelago and the Philippines...
, tea from India
India
India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
and slave
Slavery
Slavery is a system under which people are treated as property to be bought and sold, and are forced to work. Slaves can be held against their will from the time of their capture, purchase or birth, and deprived of the right to leave, to refuse to work, or to demand compensation...
s from Africa
Africa
Africa is the world's second largest and second most populous continent, after Asia. At about 30.2 million km² including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of the Earth's total surface area and 20.4% of the total land area...
were all essential items forming the backbone of trade, becoming the basis of London
London
London is the capital city of :England and the :United Kingdom, the largest metropolitan area in the United Kingdom, and the largest urban zone in the European Union by most measures. Located on the River Thames, London has been a major settlement for two millennia, its history going back to its...
society. One person in nine is estimated to have lived in London near the end of the Stuart period and, as a hub of trade, expensive goods from all over accumulated there. Coffee houses were becoming the centers of business and social life. Only coffee, tea and chocolate were served (no alcohol). Here news could be had, conversation, arguments, meetings, card games, wagers made, workmen could be paid. These products can be considered as beginning the consumer society which, while it promoted trade and brought development and riches to society, helped widen the gap between rich and poor. At the beginning of the Stuart period, James I
James I of England
James VI and I was King of Scots as James VI from 24 July 1567 and King of England and Ireland as James I from the union of the English and Scottish crowns on 24 March 1603...
authorised a new translation of the Bible known as the King James Bible or Authorised Version. This was an important event in clearly separating the Anglican and Catholic
Catholic
The word catholic comes from the Greek phrase , meaning "on the whole," "according to the whole" or "in general", and is a combination of the Greek words meaning "about" and meaning "whole"...
churches, just as the Book of Common Prayer
Book of Common Prayer
The Book of Common Prayer is the short title of a number of related prayer books used in the Anglican Communion, as well as by the Continuing Anglican, "Anglican realignment" and other Anglican churches. The original book, published in 1549 , in the reign of Edward VI, was a product of the English...
had done fifty years earlier. As a standard text it was also a major influence on English literature
English literature
English literature is the literature written in the English language, including literature composed in English by writers not necessarily from England; for example, Robert Burns was Scottish, James Joyce was Irish, Joseph Conrad was Polish, Dylan Thomas was Welsh, Edgar Allan Poe was American, J....
, language and thought for centuries to come. Newspaper
Newspaper
A newspaper is a scheduled publication containing news of current events, informative articles, diverse features and advertising. It usually is printed on relatively inexpensive, low-grade paper such as newsprint. By 2007, there were 6580 daily newspapers in the world selling 395 million copies a...
s, a fairly new invention, soon became important tools of social discourse, and diarists such as Samuel Pepys
Samuel Pepys
Samuel Pepys FRS, MP, JP, was an English naval administrator and Member of Parliament who is now most famous for the diary he kept for a decade while still a relatively young man...
are some of the best sources we have of everyday life in Restoration
English Restoration
The Restoration of the English monarchy began in 1660 when the English, Scottish and Irish monarchies were all restored under Charles II after the Interregnum that followed the Wars of the Three Kingdoms...
England.
Political society
The Stuart period was plagued by political, internal and religious strife. During the Interregnum there were two types of government: the CommonwealthCommonwealth of England
The Commonwealth of England was the republic which ruled first England, and then Ireland and Scotland from 1649 to 1660. Between 1653–1659 it was known as the Commonwealth of England, Scotland and Ireland...
and the Protectorate
The Protectorate
In British history, the Protectorate was the period 1653–1659 during which the Commonwealth of England was governed by a Lord Protector.-Background:...
of Oliver Cromwell
Oliver Cromwell
Oliver Cromwell was an English military and political leader who overthrew the English monarchy and temporarily turned England into a republican Commonwealth, and served as Lord Protector of England, Scotland, and Ireland....
. Both these governments were based on the rule of the same class of gentry and wealthy merchants, who had formed the majority of the electorate to Parliament before the Civil War. The old ruling class faced challenges to their position by other sections of society. The most important of these were the Levellers
Levellers
The Levellers were a political movement during the English Civil Wars which emphasised popular sovereignty, extended suffrage, equality before the law, and religious tolerance, all of which were expressed in the manifesto "Agreement of the People". They came to prominence at the end of the First...
, who wished to "level" society, removing class
Social class
Social classes are economic or cultural arrangements of groups in society. Class is an essential object of analysis for sociologists, political scientists, economists, anthropologists and social historians. In the social sciences, social class is often discussed in terms of 'social stratification'...
distinctions to make all men equal. They wished for universal suffrage
Suffrage
Suffrage, political franchise, or simply the franchise, distinct from mere voting rights, is the civil right to vote gained through the democratic process...
for all adult male householders, regular elections and abolition of all tithe
Tithe
A tithe is a one-tenth part of something, paid as a contribution to a religious organization or compulsory tax to government. Today, tithes are normally voluntary and paid in cash, cheques, or stocks, whereas historically tithes were required and paid in kind, such as agricultural products...
s – which would break the power of the established church.
Public transport
Since 1600 public carriages for hire were a feature of London life. Travel by coach was the regular public transport, which filled the road with traffic. The discarded coaches of aristocratic families, complete with their coat of armsHeraldry
Heraldry is the profession, study, or art of creating, granting, and blazoning arms and ruling on questions of rank or protocol, as exercised by an officer of arms. Heraldry comes from Anglo-Norman herald, from the Germanic compound harja-waldaz, "army commander"...
, were among the first hackney carriage
Hackney carriage
A hackney or hackney carriage is a carriage or automobile for hire...
s to ply for hire. The first hackney-carriage licences date from 1662, and applied literally to horse-drawn carriages, later modernised as Hansom cab
Hansom cab
The hansom cab is a kind of horse-drawn cart designed and patented in 1834 by Joseph Hansom, an architect from York. The vehicle was developed and tested by Hansom in Hinckley, Leicestershire, England. Originally called the Hansom safety cab, it was designed to combine speed with safety, with a low...
s (1834), that operated as vehicles for hire. This public transport was first introduced to England by Captain Bailey, who standardised fares and issued licences for London Hackney Carriage. Road signs and the first road atlas
Road atlas
A road atlas is a map or set of maps that primarily display roads and transport links rather than geographical information.- Types :Road atlases come in many shapes, sizes and scales...
by John Ogilvy further revolutionised the transport system, and standardised the mile.
Science and technology
- The Fire OfficeFire stationA fire station is a structure or other area set aside for storage of firefighting apparatus , personal protective equipment, fire hose, fire extinguishers, and other fire extinguishing equipment...
of Nicholas BarbonNicholas BarbonNicholas If-Jesus-Christ-Had-Not-Died-For-Thee-Thou-Hadst-Been-Damned Barebon who traded as Nicholas Barbon was an English economist, physician and financial speculator. He is counted among the critics of mercantilism and was one of the first proponents of the free market...
led to the development of the first professional fire service. - The seed drillSeed drillA seed drill is a sowing device that precisely positions seeds in the soil and then covers them. Before the introduction of the seed drill, the common practice was to plant seeds by hand. Besides being wasteful, planting was very imprecise and led to a poor distribution of seeds, leading to low...
allowed Jethro TullJethro Tull (agriculturist)Jethro Tull was an English agricultural pioneer who helped bring about the British Agricultural Revolution. He perfected a horse-drawn seed drill in 1701 that economically sowed the seeds in neat rows, and later a horse-drawn hoe...
to put his revolutionary new planting techniques into practice, leading to modern agricultureAgricultureAgriculture is the cultivation of animals, plants, fungi and other life forms for food, fiber, and other products used to sustain life. Agriculture was the key implement in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that nurtured the...
. - The fountain penFountain penA fountain pen is a nib pen that, unlike its predecessor the dip pen, contains an internal reservoir of water-based liquid ink. The pen draws ink from the reservoir through a feed to the nib and deposits it on paper via a combination of gravity and capillary action...
was first mentioned in the diaries of Samuel PepysSamuel PepysSamuel Pepys FRS, MP, JP, was an English naval administrator and Member of Parliament who is now most famous for the diary he kept for a decade while still a relatively young man...
and it allowed him to write on the move. - Colourfast dyeDyeA dye is a colored substance that has an affinity to the substrate to which it is being applied. The dye is generally applied in an aqueous solution, and requires a mordant to improve the fastness of the dye on the fiber....
s were created in Britain’s first chemical works at RavenscarRavenscar, North YorkshireRavenscar is a coastal village in the Scarborough district of North Yorkshire, England, approximately north of Scarborough. It is within the civil parish of Staintondale....
when supplies of the mordant alum were cut-off. - The three-piece suit and necktieNecktieA necktie is a long piece of cloth worn for decorative purposes around the neck or shoulders, resting under the shirt collar and knotted at the throat. Variants include the ascot tie, bow tie, bolo tie, and the clip-on tie. The modern necktie, ascot, and bow tie are descended from the cravat. Neck...
were created by Charles IICharles II of EnglandCharles II was monarch of the three kingdoms of England, Scotland, and Ireland.Charles II's father, King Charles I, was executed at Whitehall on 30 January 1649, at the climax of the English Civil War...
as a political weapon in his war against FranceFranceThe French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
. - Properties of gasGasGas is one of the three classical states of matter . Near absolute zero, a substance exists as a solid. As heat is added to this substance it melts into a liquid at its melting point , boils into a gas at its boiling point, and if heated high enough would enter a plasma state in which the electrons...
es investigated by Robert BoyleRobert BoyleRobert Boyle FRS was a 17th century natural philosopher, chemist, physicist, and inventor, also noted for his writings in theology. He has been variously described as English, Irish, or Anglo-Irish, his father having come to Ireland from England during the time of the English plantations of...
and Richard TowneleyRichard TowneleyRichard Towneley was an English mathematician and astronomer from Towneley near Burnley, Lancashire. He was one of a group of seventeenth century astronomers in the north of England, which included Jeremiah Horrocks, William Crabtree and William Gascoigne, the pioneer astronomers who laid the...
led to the invention of the pressure cooker. - The steam engineSteam engineA steam engine is a heat engine that performs mechanical work using steam as its working fluid.Steam engines are external combustion engines, where the working fluid is separate from the combustion products. Non-combustion heat sources such as solar power, nuclear power or geothermal energy may be...
was invented by Thomas NewcomenThomas NewcomenThomas Newcomen was an ironmonger by trade and a Baptist lay preacher by calling. He was born in Dartmouth, Devon, England, near a part of the country noted for its tin mines. Flooding was a major problem, limiting the depth at which the mineral could be mined...
to drain water from the coalmines of the Midlands. - The pendulum clockPendulum clockA pendulum clock is a clock that uses a pendulum, a swinging weight, as its timekeeping element. The advantage of a pendulum for timekeeping is that it is a resonant device; it swings back and forth in a precise time interval dependent on its length, and resists swinging at other rates...
based on Galileo's principles was invented by Christiaan Huygens and led to the establishment of GMT. - Lunar observations of John WilkinsJohn WilkinsJohn Wilkins FRS was an English clergyman, natural philosopher and author, as well as a founder of the Invisible College and one of the founders of the Royal Society, and Bishop of Chester from 1668 until his death....
based on the previous observations of Galileo challenged long held views of the heavens. - Principia by Isaac NewtonIsaac NewtonSir Isaac Newton PRS was an English physicist, mathematician, astronomer, natural philosopher, alchemist, and theologian, who has been "considered by many to be the greatest and most influential scientist who ever lived."...
established three simple laws that revolutionised our view of the universeUniverseThe Universe is commonly defined as the totality of everything that exists, including all matter and energy, the planets, stars, galaxies, and the contents of intergalactic space. Definitions and usage vary and similar terms include the cosmos, the world and nature...
. - The microscopeMicroscopeA microscope is an instrument used to see objects that are too small for the naked eye. The science of investigating small objects using such an instrument is called microscopy...
as refined by Robert Hook and Antonie van Leeuwenhoek allowed the microscopic world to be viewed in detail. - The diving bellDiving bellA diving bell is a rigid chamber used to transport divers to depth in the ocean. The most common types are the wet bell and the closed bell....
as refined by Edmund Halley allowed the investigation of the depths of the ocean. - The micrometerMicrometerA micrometer , sometimes known as a micrometer screw gauge, is a device incorporating a calibrated screw used widely for precise measurement of small distances in mechanical engineering and machining as well as most mechanical trades, along with other metrological instruments such as dial, vernier,...
devised by William GascoigneWilliam GascoigneSir William Gascoigne Kt. was Chief Justice of England during the reign of King Henry IV. Sir William Gascoigne was born in Gawthorpe W-Riding, Yorks. In 1369, William married Elizabeth de Mowbray...
proved Johannes KeplerJohannes KeplerJohannes Kepler was a German mathematician, astronomer and astrologer. A key figure in the 17th century scientific revolution, he is best known for his eponymous laws of planetary motion, codified by later astronomers, based on his works Astronomia nova, Harmonices Mundi, and Epitome of Copernican...
’s theories of elliptical planetary motion.
Literature and art

- William ShakespeareWilliam ShakespeareWilliam Shakespeare was an English poet and playwright, widely regarded as the greatest writer in the English language and the world's pre-eminent dramatist. He is often called England's national poet and the "Bard of Avon"...
(1564–1616), English poet and playwright, is widely regarded as the greatest writer in the English language and the world's pre-eminent dramatist. He is often called England's national poet and the "Bard of Avon", producing most of his known work between 1589 and 1613. His early plays were mainly comedies and histories, genres he raised to the peak of sophistication and artistry by the end of the sixteenth century. He then wrote mainly tragedies until about 1608, including HamletHamletThe Tragical History of Hamlet, Prince of Denmark, or more simply Hamlet, is a tragedy by William Shakespeare, believed to have been written between 1599 and 1601...
, King LearKing LearKing Lear is a tragedy by William Shakespeare. The title character descends into madness after foolishly disposing of his estate between two of his three daughters based on their flattery, bringing tragic consequences for all. The play is based on the legend of Leir of Britain, a mythological...
, and MacbethMacbethThe Tragedy of Macbeth is a play by William Shakespeare about a regicide and its aftermath. It is Shakespeare's shortest tragedy and is believed to have been written sometime between 1603 and 1607...
, considered some of the finest works in the English language. - John SpeedJohn SpeedJohn Speed was an English historian and cartographer.-Life:He was born at Farndon, Cheshire, and went into his father's tailoring business where he worked until he was about 50...
(1552–1629) was a historian, best remembered as a cartographer. It was with the encouragement of William CamdenWilliam CamdenWilliam Camden was an English antiquarian, historian, topographer, and officer of arms. He wrote the first chorographical survey of the islands of Great Britain and Ireland and the first detailed historical account of the reign of Elizabeth I of England.- Early years :Camden was born in London...
that he began his Historie of Great Britaine, first published in 1611. His atlas The Theatre of the Empire of Great Britaine was published in 1610/11, and contained the first set of individual county maps of EnglandEnglandEngland is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Scotland to the north and Wales to the west; the Irish Sea is to the north west, the Celtic Sea to the south west, with the North Sea to the east and the English Channel to the south separating it from continental...
and WalesWalesWales is a country that is part of the United Kingdom and the island of Great Britain, bordered by England to its east and the Atlantic Ocean and Irish Sea to its west. It has a population of three million, and a total area of 20,779 km²...
, maps of IrelandIrelandIreland is an island to the northwest of continental Europe. It is the third-largest island in Europe and the twentieth-largest island on Earth...
, and a general map of ScotlandScotlandScotland is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Occupying the northern third of the island of Great Britain, it shares a border with England to the south and is bounded by the North Sea to the east, the Atlantic Ocean to the north and west, and the North Channel and Irish Sea to the...
. Just before his death in 1627 Speed published A Prospect of the Most Famous Parts of the World, which was the first world atlas produced by an Englishman. In 1611, he also published The genealogies recorded in the Sacred Scriptures according to every family and tribe with the line of Our Savior Jesus ChristJesusJesus of Nazareth , commonly referred to as Jesus Christ or simply as Jesus or Christ, is the central figure of Christianity...
observed from AdamAdamAdam is a figure in the Book of Genesis. According to the creation myth of Abrahamic religions, he is the first human. In the Genesis creation narratives, he was created by Yahweh-Elohim , and the first woman, Eve was formed from his rib...
to the Blessed Virgin Mary, a biblical genealogyGenealogyGenealogy is the study of families and the tracing of their lineages and history. Genealogists use oral traditions, historical records, genetic analysis, and other records to obtain information about a family and to demonstrate kinship and pedigrees of its members...
, reprinted several times during the 17th century.
Gunpowder Plot (1605)
through a practise but that morning discovered. The plot was to have blown up the King at such time as he should have been set on his Royal Throne, accompanied with all his Children, Nobility and Commoners and assisted with all Bishops, Judges and Doctors; at one instant and blast to have ruin'd the whole State and Kingdom of England.
And for the effecting of this, there was placed under the Parliament House, where the king should sit,
some 30 barrels of powder, with good store of wood, faggots, pieces and bars of iron.
Extract of a letter from Sir Edward Hoby (Gentleman of the Bedchamber
Gentleman of the Bedchamber
A Gentleman of the Bedchamber was the holder of an important office in the royal household of the Kingdom of England from the 11th century, later used also in the Kingdom of Great Britain.-Description and functions:...
) to Sir Thomas Edwards, Ambassador at Brussells [sic]
English Civil War (1629-1651)
The English Civil WarEnglish Civil War
The English Civil War was a series of armed conflicts and political machinations between Parliamentarians and Royalists...
(s), also known as the Wars of the Three Kingdoms, took place in the reign of Charles I
Charles I of England
Charles I was King of England, King of Scotland, and King of Ireland from 27 March 1625 until his execution in 1649. Charles engaged in a struggle for power with the Parliament of England, attempting to obtain royal revenue whilst Parliament sought to curb his Royal prerogative which Charles...
, the second 'British' Stuart monarch. This ended in victory for the Parliamentarians
Roundhead
"Roundhead" was the nickname given to the supporters of the Parliament during the English Civil War. Also known as Parliamentarians, they fought against King Charles I and his supporters, the Cavaliers , who claimed absolute power and the divine right of kings...
under Oliver Cromwell, when Charles I was executed in 1649.
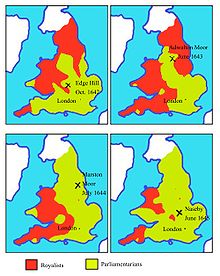
- 1629 Charles I dissolves Parliament determined to govern without one.
- 1633 Archbishop Laud translated to be Archbishop of Canterbury
- 1634-40 Ship MoneyShip moneyShip money refers to a tax that Charles I of England tried to levy without the consent of Parliament. This tax, which was only applied to coastal towns during a time of war, was intended to offset the cost of defending that part of the coast, and could be paid in actual ships or the equivalent value...
Case - 1637 Hampden's case supports Charles I's claim to collect Ship money
- 1637-40 Breakdown of Charles's government of Scotland and two attempts to impose his will by force
- 1640 Long ParliamentLong ParliamentThe Long Parliament was made on 3 November 1640, following the Bishops' Wars. It received its name from the fact that through an Act of Parliament, it could only be dissolved with the agreement of the members, and those members did not agree to its dissolution until after the English Civil War and...
summoned - 1641 Remodeling of the government in England and Scotland; abolition of conciliar courts.
- 1642 King Charles raised standard at Nottingham. The Battle of EdgehillBattle of EdgehillThe Battle of Edgehill was the first pitched battle of the First English Civil War. It was fought near Edge Hill and Kineton in southern Warwickshire on Sunday, 23 October 1642....
(Indecisive). - 1644 Battle of Marston MoorBattle of Marston MoorThe Battle of Marston Moor was fought on 2 July 1644, during the First English Civil War of 1642–1646. The combined forces of the Scottish Covenanters under the Earl of Leven and the English Parliamentarians under Lord Fairfax and the Earl of Manchester defeated the Royalists commanded by Prince...
(Parliamentary Victory) - 1645 Battle of NasebyBattle of NasebyThe Battle of Naseby was the key battle of the first English Civil War. On 14 June 1645, the main army of King Charles I was destroyed by the Parliamentarian New Model Army commanded by Sir Thomas Fairfax and Oliver Cromwell.-The Campaign:...
(Parliamentary Victory) - 1646 Charles I surrendered to Scottish Army.
- 1648 RoyalistRoyalistA royalist supports a particular monarch as head of state for a particular kingdom, or of a particular dynastic claim. In the abstract, this position is royalism. It is distinct from monarchism, which advocates a monarchical system of government, but not necessarily a particular monarch...
and Presbyterian rising suppressed by Cromwell and New Model ArmyNew Model ArmyThe New Model Army of England was formed in 1645 by the Parliamentarians in the English Civil War, and was disbanded in 1660 after the Restoration...
. - 1649 Charles I beheaded.
- 1649-50 Cromwell Invaded Ireland
- 1650 Cromwell defeated Royalists under "King Charles II" at Dunbar, Scotland.
- 1651 Battle of WorcesterBattle of WorcesterThe Battle of Worcester took place on 3 September 1651 at Worcester, England and was the final battle of the English Civil War. Oliver Cromwell and the Parliamentarians defeated the Royalist, predominantly Scottish, forces of King Charles II...
, the last battle of the Civil War, Parliamentary Victory.
After this conflict the line of Stuart monarchs was temporarily displaced by the Commonwealth of England
Commonwealth of England
The Commonwealth of England was the republic which ruled first England, and then Ireland and Scotland from 1649 to 1660. Between 1653–1659 it was known as the Commonwealth of England, Scotland and Ireland...
(1649–1660). This was ruled directly by Oliver Cromwell
Oliver Cromwell
Oliver Cromwell was an English military and political leader who overthrew the English monarchy and temporarily turned England into a republican Commonwealth, and served as Lord Protector of England, Scotland, and Ireland....
(1653–1659). After Cromwell's death the Commonwealth fell apart and the Convention Parliament welcomed Charles II
Charles II of England
Charles II was monarch of the three kingdoms of England, Scotland, and Ireland.Charles II's father, King Charles I, was executed at Whitehall on 30 January 1649, at the climax of the English Civil War...
, to return from exile to become king. This is known as the Restoration
Restoration (1660)
The term Restoration in reference to the year 1660 refers to the restoration of Charles II to his realms across the British Empire at that time.-England:...
.
Interregnum – Restoration (1651–1660)

(1652): First Anglo-Dutch War begins (ends 1654). (1653): Cromwell dissolves Rump, becomes Protector. (1655): Major-Generals appointed to supervise districts of England. Jamaica
Jamaica
Jamaica is an island nation of the Greater Antilles, in length, up to in width and 10,990 square kilometres in area. It is situated in the Caribbean Sea, about south of Cuba, and west of Hispaniola, the island harbouring the nation-states Haiti and the Dominican Republic...
seized by English. (1658): Death of Cromwell. (1660): Restoration
English Restoration
The Restoration of the English monarchy began in 1660 when the English, Scottish and Irish monarchies were all restored under Charles II after the Interregnum that followed the Wars of the Three Kingdoms...
of Charles II in Britain. (future) George I
George I of Great Britain
George I was King of Great Britain and Ireland from 1 August 1714 until his death, and ruler of the Duchy and Electorate of Brunswick-Lüneburg in the Holy Roman Empire from 1698....
born in Hanover
Hanover
Hanover or Hannover, on the river Leine, is the capital of the federal state of Lower Saxony , Germany and was once by personal union the family seat of the Hanoverian Kings of Great Britain, under their title as the dukes of Brunswick-Lüneburg...
. Royal Society
Royal Society
The Royal Society of London for Improving Natural Knowledge, known simply as the Royal Society, is a learned society for science, and is possibly the oldest such society in existence. Founded in November 1660, it was granted a Royal Charter by King Charles II as the "Royal Society of London"...
founded. (1661): "Clarendon Code" beginning of persecution of Non-conformists in England. (1664): New York
New York
New York is a state in the Northeastern region of the United States. It is the nation's third most populous state. New York is bordered by New Jersey and Pennsylvania to the south, and by Connecticut, Massachusetts and Vermont to the east...
taken by English. Second Anglo-Dutch War
Anglo-Dutch Wars
The Anglo–Dutch Wars were a series of wars fought between the English and the Dutch in the 17th and 18th centuries for control over the seas and trade routes. The first war took place during the English Interregnum, and was fought between the Commonwealth of England and the Dutch Republic...
(ends 1667). (1665): Great Plague of London
Great Plague of London
The Great Plague was a massive outbreak of disease in the Kingdom of England that killed an estimated 100,000 people, 20% of London's population. The disease is identified as bubonic plague, an infection by the bacterium Yersinia pestis, transmitted through a flea vector...
. (1666): Great Fire of London
Great Fire of London
The Great Fire of London was a major conflagration that swept through the central parts of the English city of London, from Sunday, 2 September to Wednesday, 5 September 1666. The fire gutted the medieval City of London inside the old Roman City Wall...
. Newton
Isaac Newton
Sir Isaac Newton PRS was an English physicist, mathematician, astronomer, natural philosopher, alchemist, and theologian, who has been "considered by many to be the greatest and most influential scientist who ever lived."...
discovers law of gravitation. (1667): Dutch Fleet
Anglo-Dutch Wars
The Anglo–Dutch Wars were a series of wars fought between the English and the Dutch in the 17th and 18th centuries for control over the seas and trade routes. The first war took place during the English Interregnum, and was fought between the Commonwealth of England and the Dutch Republic...
in the Medway. (1670): Secret treaty of Dover
Secret treaty of Dover
The Treaty of Dover, also known as the Secret Treaty of Dover, was a treaty between England and France signed at Dover on June 1 in 1670. It required France to assist England in the king's aim that it would rejoin the Roman Catholic Church and England to assist France in her war of conquest...
between Charles II and Louis XIV. (1672): Third Anglo-Dutch Wars
Anglo-Dutch Wars
The Anglo–Dutch Wars were a series of wars fought between the English and the Dutch in the 17th and 18th centuries for control over the seas and trade routes. The first war took place during the English Interregnum, and was fought between the Commonwealth of England and the Dutch Republic...
(ends 1674). William of Orange
William III of England
William III & II was a sovereign Prince of Orange of the House of Orange-Nassau by birth. From 1672 he governed as Stadtholder William III of Orange over Holland, Zeeland, Utrecht, Guelders, and Overijssel of the Dutch Republic. From 1689 he reigned as William III over England and Ireland...
leader of Dutch against French invasion. (1673): Test Act
Test Act
The Test Acts were a series of English penal laws that served as a religious test for public office and imposed various civil disabilities on Roman Catholics and Nonconformists...
deprives Catholic
Catholic
The word catholic comes from the Greek phrase , meaning "on the whole," "according to the whole" or "in general", and is a combination of the Greek words meaning "about" and meaning "whole"...
s and Non-conformists of public offices. (1675): Greenwich Royal Observatory founded. (1678): "Popish Plot
Popish Plot
The Popish Plot was a fictitious conspiracy concocted by Titus Oates that gripped England, Wales and Scotland in Anti-Catholic hysteria between 1678 and 1681. Oates alleged that there existed an extensive Catholic conspiracy to assassinate Charles II, accusations that led to the execution of at...
" of Titus Oates
Titus Oates
Titus Oates was an English perjurer who fabricated the "Popish Plot", a supposed Catholic conspiracy to kill King Charles II.-Early life:...
utilised by Shaftsbury and Whigs to bring pressure on Charles II. (1679): Bothwell Brig: suppression of Scottish Convenanters. Habeas Corpus
Habeas corpus
is a writ, or legal action, through which a prisoner can be released from unlawful detention. The remedy can be sought by the prisoner or by another person coming to his aid. Habeas corpus originated in the English legal system, but it is now available in many nations...
Act passed. (1681): Oxford Parliament (1681)
Oxford Parliament (1681)
An English Parliament assembled in the city of Oxford for one week from 21 March 1681 until 28 March 1681 during the reign of Charles II of England.Succeeding the Exclusion Bill Parliament, this was the fifth and last parliament of the King's reign. Both Houses of Parliament met and the King...
: Charles II overcomes opponents begins to rule without Parliament. (1683): Rye House Plot
Rye House Plot
The Rye House Plot of 1683 was a plan to assassinate King Charles II of England and his brother James, Duke of York. Historians vary in their assessment of the degree to which details of the conspiracy were finalized....
. (1685): Sedgemoor
Battle of Sedgemoor
The Battle of Sedgemoor was fought on 6 July 1685 and took place at Westonzoyland near Bridgwater in Somerset, England.It was the final battle of the Monmouth Rebellion and followed a series of skirmishes around south west England between the forces of James Scott, 1st Duke of Monmouth and the...
: Monmouths rebellion crushed by James II. Glorious revolution
Glorious Revolution
The Glorious Revolution, also called the Revolution of 1688, is the overthrow of King James II of England by a union of English Parliamentarians with the Dutch stadtholder William III of Orange-Nassau...
(1688)
Great Plague of London (1665)
The Great Plague (1665–1666) was massive outbreak of bubonic plagueBubonic plague
Plague is a deadly infectious disease that is caused by the enterobacteria Yersinia pestis, named after the French-Swiss bacteriologist Alexandre Yersin. Primarily carried by rodents and spread to humans via fleas, the disease is notorious throughout history, due to the unrivaled scale of death...
in the Kingdom of England
Kingdom of England
The Kingdom of England was, from 927 to 1707, a sovereign state to the northwest of continental Europe. At its height, the Kingdom of England spanned the southern two-thirds of the island of Great Britain and several smaller outlying islands; what today comprises the legal jurisdiction of England...
that killed an estimated 100,000 people, 20% of London
London
London is the capital city of :England and the :United Kingdom, the largest metropolitan area in the United Kingdom, and the largest urban zone in the European Union by most measures. Located on the River Thames, London has been a major settlement for two millennia, its history going back to its...
's population. In 1603, the plague killed 30,000 Londoners. In the 1636 plague 10,000 died; in 1625, some 35,000 died. The English outbreak is thought to have spread from the Netherlands
Netherlands
The Netherlands is a constituent country of the Kingdom of the Netherlands, located mainly in North-West Europe and with several islands in the Caribbean. Mainland Netherlands borders the North Sea to the north and west, Belgium to the south, and Germany to the east, and shares maritime borders...
, where the bubonic plague had occurred intermittently since 1599, with the initial contagion arriving with Dutch trading ships carrying bales of cotton
Cotton
Cotton is a soft, fluffy staple fiber that grows in a boll, or protective capsule, around the seeds of cotton plants of the genus Gossypium. The fiber is almost pure cellulose. The botanical purpose of cotton fiber is to aid in seed dispersal....
from Amsterdam
Amsterdam
Amsterdam is the largest city and the capital of the Netherlands. The current position of Amsterdam as capital city of the Kingdom of the Netherlands is governed by the constitution of August 24, 1815 and its successors. Amsterdam has a population of 783,364 within city limits, an urban population...
. Amsterdam was ravaged in 1663–1664, with a mortality given as 50,000. The dock
Dock (maritime)
A dock is a human-made structure or group of structures involved in the handling of boats or ships, usually on or close to a shore.However, the exact meaning varies among different variants of the English language...
areas outside of London, and the parish of St. Giles-in-the Fields where poor workers crowded into ill-kept structures, were the first areas struck by the plague. On 2 and 3 September 1666, the Great Fire of London
Great Fire of London
The Great Fire of London was a major conflagration that swept through the central parts of the English city of London, from Sunday, 2 September to Wednesday, 5 September 1666. The fire gutted the medieval City of London inside the old Roman City Wall...
destroyed much of the City of London. At about the same time, the plague tapered off.
Great Fire of London (1666)
Following the Great Fire of London, the notable architect Sir Christopher WrenChristopher Wren
Sir Christopher Wren FRS is one of the most highly acclaimed English architects in history.He used to be accorded responsibility for rebuilding 51 churches in the City of London after the Great Fire in 1666, including his masterpiece, St. Paul's Cathedral, on Ludgate Hill, completed in 1710...
(1632–1723), introduced Neo-classical architecture to London, and was one of the highest acclaimed English architect
Architect
An architect is a person trained in the planning, design and oversight of the construction of buildings. To practice architecture means to offer or render services in connection with the design and construction of a building, or group of buildings and the space within the site surrounding the...
s in history, responsible for rebuilding 51 churches in the City of London
City of London
The City of London is a small area within Greater London, England. It is the historic core of London around which the modern conurbation grew and has held city status since time immemorial. The City’s boundaries have remained almost unchanged since the Middle Ages, and it is now only a tiny part of...
after the Great Fire in 1666, including his masterpiece, St Paul's Cathedral
St Paul's Cathedral
St Paul's Cathedral, London, is a Church of England cathedral and seat of the Bishop of London. Its dedication to Paul the Apostle dates back to the original church on this site, founded in AD 604. St Paul's sits at the top of Ludgate Hill, the highest point in the City of London, and is the mother...
, completed in 1710.
Glorious Revolution (1688)

(1688): Seven Bishops
Seven Bishops
thumb|200px|A portrait of the Seven Bishops.The Seven Bishops of the Church of England were those imprisoned and tried for seditious libel over their opposition to the second Declaration of Indulgence issued by James II in 1688...
protest against James II's
James II of England
James II & VII was King of England and King of Ireland as James II and King of Scotland as James VII, from 6 February 1685. He was the last Catholic monarch to reign over the Kingdoms of England, Scotland, and Ireland...
policy of tolleration, and are acquitted, William of Orange
William III of England
William III & II was a sovereign Prince of Orange of the House of Orange-Nassau by birth. From 1672 he governed as Stadtholder William III of Orange over Holland, Zeeland, Utrecht, Guelders, and Overijssel of the Dutch Republic. From 1689 he reigned as William III over England and Ireland...
lands in England. Flight of James II. "Glorious Revolution
Glorious Revolution
The Glorious Revolution, also called the Revolution of 1688, is the overthrow of King James II of England by a union of English Parliamentarians with the Dutch stadtholder William III of Orange-Nassau...
". (1689): Derry
Derry
Derry or Londonderry is the second-biggest city in Northern Ireland and the fourth-biggest city on the island of Ireland. The name Derry is an anglicisation of the Irish name Doire or Doire Cholmcille meaning "oak-wood of Colmcille"...
relieved: James II fails to subdue Irish Protestants. Killiecrankie
Killiecrankie
Killiecrankie is a village in Perth and Kinross, Scotland on the River Garry. It lies at the Pass of Killiecrankie, by the A9 road. The village is home to a power station forming part of the Tummel Hydro-Electric Power Scheme...
: death of Dundee, Highland rising collapses. Bill of Rights
Bill of rights
A bill of rights is a list of the most important rights of the citizens of a country. The purpose of these bills is to protect those rights against infringement. The term "bill of rights" originates from England, where it referred to the Bill of Rights 1689. Bills of rights may be entrenched or...
defines liberties established by "Glorious Revolution." (1690): Beachy Head
Beachy Head
Beachy Head is a chalk headland on the south coast of England, close to the town of Eastbourne in the county of East Sussex, immediately east of the Seven Sisters. The cliff there is the highest chalk sea cliff in Britain, rising to 162 m above sea level. The peak allows views of the south...
: French defeat over Anglo-Dutch fleet. Boyne
Battle of the Boyne
The Battle of the Boyne was fought in 1690 between two rival claimants of the English, Scottish and Irish thronesthe Catholic King James and the Protestant King William across the River Boyne near Drogheda on the east coast of Ireland...
: William III defeats James II. (1691): Limerick
Limerick
Limerick is the third largest city in the Republic of Ireland, and the principal city of County Limerick and Ireland's Mid-West Region. It is the fifth most populous city in all of Ireland. When taking the extra-municipal suburbs into account, Limerick is the third largest conurbation in the...
capitulates: James II Irish supporters surrender. (1692): Massacre of Glencoe
Massacre of Glencoe
Early in the morning of 13 February 1692, in the aftermath of the Glorious Revolution and the Jacobite uprising of 1689 led by John Graham of Claverhouse, an infamous massacre took place in Glen Coe, in the Highlands of Scotland. This incident is referred to as the Massacre of Glencoe, or in...
: Government "lesson" to Highlander
Gàidhealtachd
The Gàidhealtachd , sometimes known as A' Ghàidhealtachd , usually refers to the Scottish highlands and islands, and especially the Scottish Gaelic culture of the area. The corresponding Irish word Gaeltacht however refers strictly to an Irish speaking area...
s. (1693): National Debt of England begun. (1694): Bank of England
Bank of England
The Bank of England is the central bank of the United Kingdom and the model on which most modern central banks have been based. Established in 1694, it is the second oldest central bank in the world...
founded. (1695): Press licensing ended: Freedom of the press
Freedom of the press
Freedom of the press or freedom of the media is the freedom of communication and expression through vehicles including various electronic media and published materials...
in England. (1700): Great Northern War
Great Northern War
The Great Northern War was a conflict in which a coalition led by the Tsardom of Russia successfully contested the supremacy of the Swedish Empire in northern Central Europe and Eastern Europe. The initial leaders of the anti-Swedish alliance were Peter I the Great of Russia, Frederick IV of...
(1700–1721) (1701): War of the Spanish Succession
War of the Spanish Succession
The War of the Spanish Succession was fought among several European powers, including a divided Spain, over the possible unification of the Kingdoms of Spain and France under one Bourbon monarch. As France and Spain were among the most powerful states of Europe, such a unification would have...
begins. Act of Settlement 1701
Act of Settlement 1701
The Act of Settlement is an act of the Parliament of England that was passed in 1701 to settle the succession to the English throne on the Electress Sophia of Hanover and her Protestant heirs. The act was later extended to Scotland, as a result of the Treaty of Union , enacted in the Acts of Union...
establishes Protestant Hanoverian
House of Hanover
The House of Hanover is a deposed German royal dynasty which has ruled the Duchy of Brunswick-Lüneburg , the Kingdom of Hanover, the Kingdom of Great Britain, the Kingdom of Ireland and the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland...
Succession
Succession (conflict)
In the conflict of laws, the subject of succession deals with all procedural matters relevant to estates containing a "foreign element" whether that element consists of the identity of the deceased, those who may inherit or the location of property...
in England. (1704): Gibraltar
Gibraltar
Gibraltar is a British overseas territory located on the southern end of the Iberian Peninsula at the entrance of the Mediterranean. A peninsula with an area of , it has a northern border with Andalusia, Spain. The Rock of Gibraltar is the major landmark of the region...
taken by Rooke
Rooke
Rooke is a surname, and may refer to :* Daphne Rooke, author* Denis Rooke* Sir George Rooke, English admiral* Hayman Rooke* Irene Rooke* Jessie Rooke* Laurence Rooke, English astronomer* Leon Rooke* Max Rooke* Jordan * Ronnie Rooke...
. Blenheim
Battle of Blenheim
The Battle of Blenheim , fought on 13 August 1704, was a major battle of the War of the Spanish Succession. Louis XIV of France sought to knock Emperor Leopold out of the war by seizing Vienna, the Habsburg capital, and gain a favourable peace settlement...
: Marlborough
John Churchill, 1st Duke of Marlborough
John Churchill, 1st Duke of Marlborough, Prince of Mindelheim, KG, PC , was an English soldier and statesman whose career spanned the reigns of five monarchs through the late 17th and early 18th centuries...
stops France from winning war. (1706): Ramillies
Battle of Ramillies
The Battle of Ramillies , fought on 23 May 1706, was a major engagement of the War of the Spanish Succession. For the Grand Alliance – Austria, England, and the Dutch Republic – the battle had followed an indecisive campaign against the Bourbon armies of King Louis XIV of France in 1705...
: Marlborough's second victory.
Acts of Union (1707)
(1707): Acts of UnionActs of Union 1707
The Acts of Union were two Parliamentary Acts - the Union with Scotland Act passed in 1706 by the Parliament of England, and the Union with England Act passed in 1707 by the Parliament of Scotland - which put into effect the terms of the Treaty of Union that had been agreed on 22 July 1706,...
ratify the 1706 Treaty of Union
Treaty of Union
The Treaty of Union is the name given to the agreement that led to the creation of the united kingdom of Great Britain, the political union of the Kingdom of England and the Kingdom of Scotland, which took effect on 1 May 1707...
, uniting the English and Scottish Parliaments and creating the Kingdom of Great Britain
Kingdom of Great Britain
The former Kingdom of Great Britain, sometimes described as the 'United Kingdom of Great Britain', That the Two Kingdoms of Scotland and England, shall upon the 1st May next ensuing the date hereof, and forever after, be United into One Kingdom by the Name of GREAT BRITAIN. was a sovereign...
. (1708): Oudenarde: Marlboroughs third great victory. (1709): Malplaquet
Battle of Malplaquet
The Battle of Malplaquet, fought on 11 September 1709, was one of the main battles of the War of the Spanish Succession, which opposed the Bourbons of France and Spain against an alliance whose major members were the Habsburg Monarchy, Great Britain, the United Provinces and the Kingdom of...
: Marlboroughs fourth great victory (at great cost in lives) (1710): Tory
Tory
Toryism is a traditionalist and conservative political philosophy which grew out of the Cavalier faction in the Wars of the Three Kingdoms. It is a prominent ideology in the politics of the United Kingdom, but also features in parts of The Commonwealth, particularly in Canada...
government in England. (1711): Dismissal of Marlborough. (1714): Death of Queen Anne
Anne of Great Britain
Anne ascended the thrones of England, Scotland and Ireland on 8 March 1702. On 1 May 1707, under the Act of Union, two of her realms, England and Scotland, were united as a single sovereign state, the Kingdom of Great Britain.Anne's Catholic father, James II and VII, was deposed during the...
. Accession of George I
George I of Great Britain
George I was King of Great Britain and Ireland from 1 August 1714 until his death, and ruler of the Duchy and Electorate of Brunswick-Lüneburg in the Holy Roman Empire from 1698....
, and Hanoverian Dynasty
House of Hanover
The House of Hanover is a deposed German royal dynasty which has ruled the Duchy of Brunswick-Lüneburg , the Kingdom of Hanover, the Kingdom of Great Britain, the Kingdom of Ireland and the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland...
. Whig oligarchy
Oligarchy
Oligarchy is a form of power structure in which power effectively rests with an elite class distinguished by royalty, wealth, family ties, commercial, and/or military legitimacy...
rules.

upon the Ist day of May next ensuing the date hereof, and for ever after,
be united into one kingdom by the name of Great Britain,
and that the ensigns armorial of the said United Kingdom be such
as Her Majesty shall appoint,
and the crosses of St. Andrew and St. George be conjoined in such manner
as Her Majesty shall think fit,
and used in all flags, banners, standards and ensigns, both at sea and land.
Stuart family Monarchs (1603–1714)
The House of StuartHouse of Stuart
The House of Stuart is a European royal house. Founded by Robert II of Scotland, the Stewarts first became monarchs of the Kingdom of Scotland during the late 14th century, and subsequently held the position of the Kings of Great Britain and Ireland...
produced six English monarchs who ruled during this period. The succession of James VI of Scotland
James I of England
James VI and I was King of Scots as James VI from 24 July 1567 and King of England and Ireland as James I from the union of the English and Scottish crowns on 24 March 1603...
to the English throne in 1603, brought both the kingdoms of England and Scotland under his rule, in what was known as the Union of Crowns. Over a century later, the Acts of Union 1707
Acts of Union 1707
The Acts of Union were two Parliamentary Acts - the Union with Scotland Act passed in 1706 by the Parliament of England, and the Union with England Act passed in 1707 by the Parliament of Scotland - which put into effect the terms of the Treaty of Union that had been agreed on 22 July 1706,...
, passed during the reign of the last Stuart monarch, Anne
Anne of Great Britain
Anne ascended the thrones of England, Scotland and Ireland on 8 March 1702. On 1 May 1707, under the Act of Union, two of her realms, England and Scotland, were united as a single sovereign state, the Kingdom of Great Britain.Anne's Catholic father, James II and VII, was deposed during the...
, amalgamated the two kingdoms, England and Scotland, into a single Kingdom of Great Britain
Kingdom of Great Britain
The former Kingdom of Great Britain, sometimes described as the 'United Kingdom of Great Britain', That the Two Kingdoms of Scotland and England, shall upon the 1st May next ensuing the date hereof, and forever after, be United into One Kingdom by the Name of GREAT BRITAIN. was a sovereign...
.
| James I James I of England James VI and I was King of Scots as James VI from 24 July 1567 and King of England and Ireland as James I from the union of the English and Scottish crowns on 24 March 1603... |
Charles I Charles I of England Charles I was King of England, King of Scotland, and King of Ireland from 27 March 1625 until his execution in 1649. Charles engaged in a struggle for power with the Parliament of England, attempting to obtain royal revenue whilst Parliament sought to curb his Royal prerogative which Charles... |
|---|---|
| Charles II Charles II of England Charles II was monarch of the three kingdoms of England, Scotland, and Ireland.Charles II's father, King Charles I, was executed at Whitehall on 30 January 1649, at the climax of the English Civil War... |
 James II of England James II & VII was King of England and King of Ireland as James II and King of Scotland as James VII, from 6 February 1685. He was the last Catholic monarch to reign over the Kingdoms of England, Scotland, and Ireland... |
 Mary II of England Mary II was joint Sovereign of England, Scotland, and Ireland with her husband and first cousin, William III and II, from 1689 until her death. William and Mary, both Protestants, became king and queen regnant, respectively, following the Glorious Revolution, which resulted in the deposition of... |
 Anne of Great Britain Anne ascended the thrones of England, Scotland and Ireland on 8 March 1702. On 1 May 1707, under the Act of Union, two of her realms, England and Scotland, were united as a single sovereign state, the Kingdom of Great Britain.Anne's Catholic father, James II and VII, was deposed during the... |
| Arms of the Stuart monarchs 1603-1707 | Commonwealth |
|---|---|
| England Arms | St. George |
| Scotland Arms | Scots saltire |
King James I
James I of England
James VI and I was King of Scots as James VI from 24 July 1567 and King of England and Ireland as James I from the union of the English and Scottish crowns on 24 March 1603...
(1603 to 1625). Son of Mary Queen of Scots and Henry Stuart, Lord Darnley
Henry Stuart, Lord Darnley
Henry Stewart or Stuart, 1st Duke of Albany , styled Lord Darnley before 1565, was king consort of Scotland and murdered at Kirk o'Field...
. King of Scotland alone, 1567–1603, until inheriting the titles King of England and Ireland, including claim to France from the extinct Tudor
Tudor dynasty
The Tudor dynasty or House of Tudor was a European royal house of Welsh origin that ruled the Kingdom of England and its realms, including the Lordship of Ireland, later the Kingdom of Ireland, from 1485 until 1603. Its first monarch was Henry Tudor, a descendant through his mother of a legitimised...
s.
King Charles I
Charles I of England
Charles I was King of England, King of Scotland, and King of Ireland from 27 March 1625 until his execution in 1649. Charles engaged in a struggle for power with the Parliament of England, attempting to obtain royal revenue whilst Parliament sought to curb his Royal prerogative which Charles...
(1625 to 1649). Son of James VI of Scotland & I of England & Ireland. After the English Civil War
English Civil War
The English Civil War was a series of armed conflicts and political machinations between Parliamentarians and Royalists...
, Charles I was executed in 1649. The country then became a Republic
Republic
A republic is a form of government in which the people, or some significant portion of them, have supreme control over the government and where offices of state are elected or chosen by elected people. In modern times, a common simplified definition of a republic is a government where the head of...
under Oliver Cromwell
Oliver Cromwell
Oliver Cromwell was an English military and political leader who overthrew the English monarchy and temporarily turned England into a republican Commonwealth, and served as Lord Protector of England, Scotland, and Ireland....
, until the restoration
English Restoration
The Restoration of the English monarchy began in 1660 when the English, Scottish and Irish monarchies were all restored under Charles II after the Interregnum that followed the Wars of the Three Kingdoms...
of Charles II in 1660.
King Charles II
Charles II of England
Charles II was monarch of the three kingdoms of England, Scotland, and Ireland.Charles II's father, King Charles I, was executed at Whitehall on 30 January 1649, at the climax of the English Civil War...
(1660 to 1685). Son of Charles I of England, Scotland & Ireland. In exile from 1649 to 1660, during a republican period of government known as the Commonwealth of England
Commonwealth of England
The Commonwealth of England was the republic which ruled first England, and then Ireland and Scotland from 1649 to 1660. Between 1653–1659 it was known as the Commonwealth of England, Scotland and Ireland...
.
King James II
James II of England
James II & VII was King of England and King of Ireland as James II and King of Scotland as James VII, from 6 February 1685. He was the last Catholic monarch to reign over the Kingdoms of England, Scotland, and Ireland...
(1685 to 1688). Brother of Charles II of England
Charles II of England
Charles II was monarch of the three kingdoms of England, Scotland, and Ireland.Charles II's father, King Charles I, was executed at Whitehall on 30 January 1649, at the climax of the English Civil War...
, Scotland & Ireland, who died with no legitimate issue. Son of Charles I. Overthrown at the Revolution
Glorious Revolution
The Glorious Revolution, also called the Revolution of 1688, is the overthrow of King James II of England by a union of English Parliamentarians with the Dutch stadtholder William III of Orange-Nassau...
of 1688.
Queen Mary II
Mary II of England
Mary II was joint Sovereign of England, Scotland, and Ireland with her husband and first cousin, William III and II, from 1689 until her death. William and Mary, both Protestants, became king and queen regnant, respectively, following the Glorious Revolution, which resulted in the deposition of...
(1689 to 1702). Daughter of James II of England
James II of England
James II & VII was King of England and King of Ireland as James II and King of Scotland as James VII, from 6 February 1685. He was the last Catholic monarch to reign over the Kingdoms of England, Scotland, and Ireland...
and Ireland & VII of Scotland, (deemed as having abdicated). Reigned with William III
William III of England
William III & II was a sovereign Prince of Orange of the House of Orange-Nassau by birth. From 1672 he governed as Stadtholder William III of Orange over Holland, Zeeland, Utrecht, Guelders, and Overijssel of the Dutch Republic. From 1689 he reigned as William III over England and Ireland...
of House of Orange-Nassau
House of Orange-Nassau
The House of Orange-Nassau , a branch of the European House of Nassau, has played a central role in the political life of the Netherlands — and at times in Europe — since William I of Orange organized the Dutch revolt against Spanish rule, which after the Eighty Years' War...
. who outlived his wife.
Queen Anne
Anne of Great Britain
Anne ascended the thrones of England, Scotland and Ireland on 8 March 1702. On 1 May 1707, under the Act of Union, two of her realms, England and Scotland, were united as a single sovereign state, the Kingdom of Great Britain.Anne's Catholic father, James II and VII, was deposed during the...
(1702 to 1714). Sister of Mary II. daughter of James II of England and Ireland & VII of Scotland. Died without surviving issue, succession
Succession (conflict)
In the conflict of laws, the subject of succession deals with all procedural matters relevant to estates containing a "foreign element" whether that element consists of the identity of the deceased, those who may inherit or the location of property...
passes to George I of the House of Hanover
House of Hanover
The House of Hanover is a deposed German royal dynasty which has ruled the Duchy of Brunswick-Lüneburg , the Kingdom of Hanover, the Kingdom of Great Britain, the Kingdom of Ireland and the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland...
.


Anne of Great Britain
Anne ascended the thrones of England, Scotland and Ireland on 8 March 1702. On 1 May 1707, under the Act of Union, two of her realms, England and Scotland, were united as a single sovereign state, the Kingdom of Great Britain.Anne's Catholic father, James II and VII, was deposed during the...
became Queen regnant of England
England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Scotland to the north and Wales to the west; the Irish Sea is to the north west, the Celtic Sea to the south west, with the North Sea to the east and the English Channel to the south separating it from continental...
, Scotland
Scotland
Scotland is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Occupying the northern third of the island of Great Britain, it shares a border with England to the south and is bounded by the North Sea to the east, the Atlantic Ocean to the north and west, and the North Channel and Irish Sea to the...
and Ireland
Ireland
Ireland is an island to the northwest of continental Europe. It is the third-largest island in Europe and the twentieth-largest island on Earth...
in 1702, succeeding William III
William III of England
William III & II was a sovereign Prince of Orange of the House of Orange-Nassau by birth. From 1672 he governed as Stadtholder William III of Orange over Holland, Zeeland, Utrecht, Guelders, and Overijssel of the Dutch Republic. From 1689 he reigned as William III over England and Ireland...
. When James II was deemed abdicated during the Glorious Revolution (1688–89), her sister and brother-in-law became joint monarchs William III and Mary II. After Mary's death in 1694, William was monarch until his death in 1702. Queen Anne's War
Queen Anne's War
Queen Anne's War , as the North American theater of the War of the Spanish Succession was known in the British colonies, was the second in a series of French and Indian Wars fought between France and England, later Great Britain, in North America for control of the continent. The War of the...
(1702–1713), between France
France
The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
and England (later Great Britain
Great Britain
Great Britain or Britain is an island situated to the northwest of Continental Europe. It is the ninth largest island in the world, and the largest European island, as well as the largest of the British Isles...
) was fought in North America
North America
North America is a continent wholly within the Northern Hemisphere and almost wholly within the Western Hemisphere. It is also considered a northern subcontinent of the Americas...
, as part of the War of the Spanish Succession
War of the Spanish Succession
The War of the Spanish Succession was fought among several European powers, including a divided Spain, over the possible unification of the Kingdoms of Spain and France under one Bourbon monarch. As France and Spain were among the most powerful states of Europe, such a unification would have...
, primarily fought in Europe
Europe
Europe is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting...
. Anne reigned until 1714; The last Stuart Queen of England and Scotland - and of this Stuart period.
See also
- House of StuartHouse of StuartThe House of Stuart is a European royal house. Founded by Robert II of Scotland, the Stewarts first became monarchs of the Kingdom of Scotland during the late 14th century, and subsequently held the position of the Kings of Great Britain and Ireland...
- Kingdom of EnglandKingdom of EnglandThe Kingdom of England was, from 927 to 1707, a sovereign state to the northwest of continental Europe. At its height, the Kingdom of England spanned the southern two-thirds of the island of Great Britain and several smaller outlying islands; what today comprises the legal jurisdiction of England...
- Kingdom of ScotlandKingdom of ScotlandThe Kingdom of Scotland was a Sovereign state in North-West Europe that existed from 843 until 1707. It occupied the northern third of the island of Great Britain and shared a land border to the south with the Kingdom of England...
- JacobitismJacobitismJacobitism was the political movement in Britain dedicated to the restoration of the Stuart kings to the thrones of England, Scotland, later the Kingdom of Great Britain, and the Kingdom of Ireland...
, for further information on the House of Stuart and their decline - The family trees of the Stuarts: Scottish branch – England and Scotland united
- Clan StuartClan StuartClan Stewart is a Highland Scottish clan. The clan is recognised by Court of the Lord Lyon, however it does not have a clan chief recognised by the Lord Lyon King of Arms...
Naval Battles (1605–1692)
James I
- 1605 Dover: Dutch fleet attacks and partly destroys a Spanish fleet of transport ships.
-
- Swally: British East India Company fleet defeats Portuguese fleet near Surat, India
- 1615 English defeat Portuguese in mainly minor skirmishes
- English vs Dutch near Jakarta+
- English defeat Portuguese
- 1622 English and Dutch defeat Portuguese near Mozambique
- English naval bombardment of Algiers
- English and Dutch defeat Portuguese+
- Swally: British East India Company fleet defeats Portuguese fleet near Surat, India
Charles I
- 1626 French with hired English and Dutch ships defeat Huguenot fleet near Rochelle
-
- English defeat Venetians/French at Scanderoon +
- 1629 Dutch under Piet Heyn defeat Dunkirkers off Scotland; Heyn is killed
- Battle of the Downs – Dutch under Tromp defeat Spanish under D'Oquendo in the English Channel
- English defeat Venetians/French at Scanderoon +
English Civil War
The English Civil War
English Civil War
The English Civil War was a series of armed conflicts and political machinations between Parliamentarians and Royalists...
(s) took place in the reign of Charles I
Charles I of England
Charles I was King of England, King of Scotland, and King of Ireland from 27 March 1625 until his execution in 1649. Charles engaged in a struggle for power with the Parliament of England, attempting to obtain royal revenue whilst Parliament sought to curb his Royal prerogative which Charles...
, the second Stuart monarch. This ended in victory for the Parliamentarians
Roundhead
"Roundhead" was the nickname given to the supporters of the Parliament during the English Civil War. Also known as Parliamentarians, they fought against King Charles I and his supporters, the Cavaliers , who claimed absolute power and the divine right of kings...
and Charles was executed in 1649.
Charles I
- 1629 Charles I dissolves Parliament determined to govern without one.
- 1633 Archbishop Laud translated to be Archbishop of Canterbury
- 1634–40 Ship Money Case
- 1637 Hampden's case supports Charles I's claim to collect Ship money
- 1637–40 Breakdown of Charles's government of Scotland and two attempts to impose his will by force
- 1640 Long Parliament summoned
- 1641 Remodeling of the government in England and Scotland; abolition of conciliar courts.
- 1642 King Charles raised standard at Nottingham. The Battle of Edgehill (Indecisive).
- 1644 Battle of Marston Moor (Parliamentary Victory)
- 1645 Battle of Naseby (Parliamentary Victory)
- 1646 Charles I surrendered to Scottish Army.
- 1648 Royalist and Presbyterian rising supressed by Cromwell and New Model Army.
- 1649 Charles I beheaded.
- 1649–50 Cromwell Invaded Ireland
- 1650 Cromwell defeated Royalists under "King Charles II" at Dunbar, Scotland.
- 1651 Battle of Worcester, the last battle of the Civil War, Parliamentary Victory.
After this conflict the line of Stuart
Stuart
-People:*House of Stuart, a royal house of Scotland and England*Clan Stuart of Bute, a Scottish clan*Stuart , people with the surname and given name Stuart-Places:Australia*Stuart, the former name for Alice Springs, Northern Territory...
monarchs was temporarily displaced by the Commonwealth of England
Commonwealth of England
The Commonwealth of England was the republic which ruled first England, and then Ireland and Scotland from 1649 to 1660. Between 1653–1659 it was known as the Commonwealth of England, Scotland and Ireland...
(1649 to 1660). This was ruled directly by Oliver Cromwell
Oliver Cromwell
Oliver Cromwell was an English military and political leader who overthrew the English monarchy and temporarily turned England into a republican Commonwealth, and served as Lord Protector of England, Scotland, and Ireland....
in the period 1653 to 1659. After Cromwell's death the Commonwealth fell apart and the Convention Parliament welcomed Charles II
Charles II of England
Charles II was monarch of the three kingdoms of England, Scotland, and Ireland.Charles II's father, King Charles I, was executed at Whitehall on 30 January 1649, at the climax of the English Civil War...
, son of Charles I to return from exile and become king. This event was known as the English Restoration
English Restoration
The Restoration of the English monarchy began in 1660 when the English, Scottish and Irish monarchies were all restored under Charles II after the Interregnum that followed the Wars of the Three Kingdoms...
.
James II
- 1689 Battle of Bantry Bay: French defeat English off SW Ireland
-
- French vs English near Casquets
- Beachy Head: (Beveziers) French defeat Anglo-Dutch fleet
- French vs English and Dutch near Madras
Mary II
- 1692 Barfleur and La Hougue Decisive defeat of French by English and Dutch in the War of the Grand Alliance
-
- French defeat English+
- Dogger Bank: French defeat Dutch
- French and English fight in Newfoundland
- Fight near San Domingo

