
Chemical plant
Encyclopedia

Industry
Industry refers to the production of an economic good or service within an economy.-Industrial sectors:There are four key industrial economic sectors: the primary sector, largely raw material extraction industries such as mining and farming; the secondary sector, involving refining, construction,...
process
Industrial process
Industrial processes are procedures involving chemical or mechanical steps to aid in the manufacture of an item or items, usually carried out on a very large scale. Industrial processes are the key components of heavy industry....
plant
Factory
A factory or manufacturing plant is an industrial building where laborers manufacture goods or supervise machines processing one product into another. Most modern factories have large warehouses or warehouse-like facilities that contain heavy equipment used for assembly line production...
that manufactures (or otherwise processes) chemicals, usually on a large scale. The general objective of a chemical plant is to create new material wealth via the chemical or biological transformation and or separation of materials. Chemical plants use special equipment, units, and technology in the processes. Other kinds of plants, such as polymer, pharmaceutical, food, and some beverage production facilities, power plants, oil refineries
Oil refinery
An oil refinery or petroleum refinery is an industrial process plant where crude oil is processed and refined into more useful petroleum products, such as gasoline, diesel fuel, asphalt base, heating oil, kerosene, and liquefied petroleum gas...
or other refineries
Refinery
A refinery is a production facility composed of a group of chemical engineering unit processes and unit operations refining certain materials or converting raw material into products of value.-Types of refineries:Different types of refineries are as follows:...
, natural gas processing
Natural gas processing
Natural-gas processing is a complex industrial process designed to clean raw natural gas by separating impurities and various non-methane hydrocarbons and fluids to produce what is known as pipeline quality dry natural gas.-Background:...
and biochemical plants, water
Water
Water is a chemical substance with the chemical formula H2O. A water molecule contains one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms connected by covalent bonds. Water is a liquid at ambient conditions, but it often co-exists on Earth with its solid state, ice, and gaseous state . Water also exists in a...
and wastewater
Wastewater
Wastewater is any water that has been adversely affected in quality by anthropogenic influence. It comprises liquid waste discharged by domestic residences, commercial properties, industry, and/or agriculture and can encompass a wide range of potential contaminants and concentrations...
treatment, and pollution
Pollution
Pollution is the introduction of contaminants into a natural environment that causes instability, disorder, harm or discomfort to the ecosystem i.e. physical systems or living organisms. Pollution can take the form of chemical substances or energy, such as noise, heat or light...
control equipment use many technologies that have similarities to chemical plant technology such as fluid systems. Some would consider an oil refinery or a pharmaceutical or polymer manufacturer to be effectively a chemical plant.
Petrochemical
Petrochemical
Petrochemicals are chemical products derived from petroleum. Some chemical compounds made from petroleum are also obtained from other fossil fuels, such as coal or natural gas, or renewable sources such as corn or sugar cane....
plants (plants using petroleum as a raw material) are usually located adjacent to an oil refinery
Oil refinery
An oil refinery or petroleum refinery is an industrial process plant where crude oil is processed and refined into more useful petroleum products, such as gasoline, diesel fuel, asphalt base, heating oil, kerosene, and liquefied petroleum gas...
to minimize
Optimization (mathematics)
In mathematics, computational science, or management science, mathematical optimization refers to the selection of a best element from some set of available alternatives....
transport
Transport
Transport or transportation is the movement of people, cattle, animals and goods from one location to another. Modes of transport include air, rail, road, water, cable, pipeline, and space. The field can be divided into infrastructure, vehicles, and operations...
ation costs for the feedstocks produced by the refinery. Specialty chemical plants are usually much smaller and not as sensitive to location.
Chemical processes
Chemical plants typically use chemical processChemical process
In a "scientific" sense, a chemical process is a method or means of somehow changing one or more chemicals or chemical compounds. Such a chemical process can occur by itself or be caused by somebody. Such a chemical process commonly involves a chemical reaction of some sort...
es, which are detailed industrial-scale methods, to produce the chemicals. The same chemical process can be used at more than one chemical plant, with possibly differently scaled capacities at each plant. Also, a chemical plant at a site may be constructed to utilize more than one chemical process.
A chemical plant commonly has usually large vessels or sections called units that are interconnected by piping
Piping
Within industry, piping is a system of pipes used to convey fluids from one location to another. The engineering discipline of piping design studies the efficient transport of fluid....
or other material-moving equipment which can carry streams of material. Such material streams can include fluid
Fluid
In physics, a fluid is a substance that continually deforms under an applied shear stress. Fluids are a subset of the phases of matter and include liquids, gases, plasmas and, to some extent, plastic solids....
s (gas
Gas
Gas is one of the three classical states of matter . Near absolute zero, a substance exists as a solid. As heat is added to this substance it melts into a liquid at its melting point , boils into a gas at its boiling point, and if heated high enough would enter a plasma state in which the electrons...
or liquid
Liquid
Liquid is one of the three classical states of matter . Like a gas, a liquid is able to flow and take the shape of a container. Some liquids resist compression, while others can be compressed. Unlike a gas, a liquid does not disperse to fill every space of a container, and maintains a fairly...
carried in piping) or sometimes solid
Solid
Solid is one of the three classical states of matter . It is characterized by structural rigidity and resistance to changes of shape or volume. Unlike a liquid, a solid object does not flow to take on the shape of its container, nor does it expand to fill the entire volume available to it like a...
s or mixtures such as slurries
Slurry
A slurry is, in general, a thick suspension of solids in a liquid.-Examples of slurries:Examples of slurries include:* Lahars* A mixture of water and cement to form concrete* A mixture of water, gelling agent, and oxidizers used as an explosive...
. An overall chemical process is commonly made up of steps called unit operation
Unit operation
In chemical engineering and related fields, a unit operation is a basic step in a process.Unit operation involves bringing a physical change such as separation, crystallization, evaporation, filtration etc.. For example in milk processing, homogenization, pasteurization, chilling, and packaging are...
s which occur in the individual units. A raw material going into a chemical process or plant as input to be converted into a product is commonly called a feedstock, or simply feed. In addition to feedstocks for the plant as a whole, an input stream of material to be processed in a particular unit can similarly be considered feed for that unit. Output streams from the plant as a whole are final products and output streams from individual units may be considered intermediate products for their units. However, final products from one plant may be intermediate chemicals used as feedstock in another plant for further processing. For example, some products from an oil refinery may used as feedstock in petrochemical plants.
Either the feedstock(s), the product(s), or both may be individual compounds
Chemical compound
A chemical compound is a pure chemical substance consisting of two or more different chemical elements that can be separated into simpler substances by chemical reactions. Chemical compounds have a unique and defined chemical structure; they consist of a fixed ratio of atoms that are held together...
or mixtures. It is often not worthwhile separating the components in these mixtures completely based on product requirements and economics.
Continuous and batch operation
Chemical processes may be run in continuous or batch operation. In batch operation, production occurs in time-sequential steps in batches. A batch of feedstock(s) is fed into a process or unit, then the chemical process takes place, then the product(s) and any other outputs are removed. Such batch production may be repeated over again and again with new batches of feedstock. Batch operation is commonly used in smaller scale plants such as pharmaceutical or specialty chemicals production.In continuous operation, all steps are ongoing continuously in time. During usual continuous operation, the feeding and product removal are ongoing streams of moving material, which together with the process itself, all take place simultaneously and continuously. Chemical plants or units in continuous operation are usually in a steady state
Steady state
A system in a steady state has numerous properties that are unchanging in time. This implies that for any property p of the system, the partial derivative with respect to time is zero:...
or approximate steady state. Steady state means that quantities related to the process do not change as time passes during operation. Such constant quantities include stream flow rates, heating or cooling rates, temperature
Temperature
Temperature is a physical property of matter that quantitatively expresses the common notions of hot and cold. Objects of low temperature are cold, while various degrees of higher temperatures are referred to as warm or hot...
s, pressure
Pressure
Pressure is the force per unit area applied in a direction perpendicular to the surface of an object. Gauge pressure is the pressure relative to the local atmospheric or ambient pressure.- Definition :...
s, and chemical compositions at every point (location). Continuous operation is more efficient in many large scale operations like petroleum refineries. It is possible for some units to operate continuously and others be in batch operation in a chemical plant; for example, see Continuous distillation
Continuous distillation
Continuous distillation, a form of distillation, is an ongoing separation in which a mixture is continuously fed into the process and separated fractions are removed continuously as output streams. A distillation is the separation or partial separation of a liquid feed mixture into components or...
and Batch distillation
Batch distillation
Batch distillation refers to the use of distillation in batches, meaning that a mixture is distilled to separate it into its component fractions before the distillation still is again charged with more mixture and the process is repeated...
. The amount of primary feedstock or product per unit of time which a plant or unit can process is referred to as the capacity of that plant or unit. For examples: the capacity of an oil refinery may be given in terms of barrel
Barrel
A barrel or cask is a hollow cylindrical container, traditionally made of vertical wooden staves and bound by wooden or metal hoops. Traditionally, the barrel was a standard size of measure referring to a set capacity or weight of a given commodity. A small barrel is called a keg.For example, a...
s of crude oil refined per day; alternatively chemical plant capacity may be given in ton
Ton
The ton is a unit of measure. It has a long history and has acquired a number of meanings and uses over the years. It is used principally as a unit of weight, and as a unit of volume. It can also be used as a measure of energy, for truck classification, or as a colloquial term.It is derived from...
s of product produced per day. In actual daily operation, a plant (or unit) will operate at a percentage of its full capacity.
Units and fluid systems
Various kinds of unit operationUnit operation
In chemical engineering and related fields, a unit operation is a basic step in a process.Unit operation involves bringing a physical change such as separation, crystallization, evaporation, filtration etc.. For example in milk processing, homogenization, pasteurization, chilling, and packaging are...
s are conducted in various kinds of units. Although some units may operate at ambient temperature or pressure, many units operate at higher or lower temperatures or pressures. Vessels in chemical plants are often cylindrical
Cylinder (geometry)
A cylinder is one of the most basic curvilinear geometric shapes, the surface formed by the points at a fixed distance from a given line segment, the axis of the cylinder. The solid enclosed by this surface and by two planes perpendicular to the axis is also called a cylinder...
with rounded ends, a shape which can be suited to hold either high pressure or vacuum
Vacuum
In everyday usage, vacuum is a volume of space that is essentially empty of matter, such that its gaseous pressure is much less than atmospheric pressure. The word comes from the Latin term for "empty". A perfect vacuum would be one with no particles in it at all, which is impossible to achieve in...
. Chemical reaction
Chemical reaction
A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Chemical reactions can be either spontaneous, requiring no input of energy, or non-spontaneous, typically following the input of some type of energy, such as heat, light or electricity...
s can convert certain kinds of compounds
Chemical compound
A chemical compound is a pure chemical substance consisting of two or more different chemical elements that can be separated into simpler substances by chemical reactions. Chemical compounds have a unique and defined chemical structure; they consist of a fixed ratio of atoms that are held together...
into other compounds in chemical reactor
Chemical reactor
In chemical engineering, chemical reactors are vessels designed to contain chemical reactions. The design of a chemical reactor deals with multiple aspects of chemical engineering. Chemical engineers design reactors to maximize net present value for the given reaction...
s. Chemical reactors may be packed bed
Packed bed
In chemical processing, a packed bed is a hollow tube, pipe, or other vessel that is filled with a packing material. The packing can be randomly filled with small objects like Raschig rings or else it can be a specifically designed structured packing...
s and may have solid heterogeneous catalysts which stay in the reactors as fluids move through. Since the surface of solid heterogeneous catalysts may sometimes become poisoned from deposits such as coke
Coke (fuel)
Coke is the solid carbonaceous material derived from destructive distillation of low-ash, low-sulfur bituminous coal. Cokes from coal are grey, hard, and porous. While coke can be formed naturally, the commonly used form is man-made.- History :...
, regeneration of catalysts may be necessary. Fluidized bed
Fluidized bed
A fluidized bed is formed when a quantity of a solid particulate substance is placed under appropriate conditions to cause the solid/fluid mixture to behave as a fluid. This is usually achieved by the introduction of pressurized fluid through the particulate medium...
s may also be used in some cases. There can also be units (or subunits) for mixing
Mixing (process engineering)
In industrial process engineering, mixing is a unit operation that involves manipulating a heterogeneous physical system, with the intent to make it more homogeneous...
(including dissolving), separation
Separation process
In chemistry and chemical engineering, a separation process, or simply a separation, is any mass transfer process used to convert a mixture of substances into two or more distinct product mixtures, at least one of which is enriched in one or more of the mixture's constituents. In some cases, a...
, heating, cooling, or some combination of these. For example, chemical reactors often have stirring for mixing and heating or cooling going on in them. When designing plants on a large scale, heat produced or absorbed by chemical reactions should be considered. Some plants may have units with organism cultures for biochemical processes such as fermentation
Industrial fermentation
Industrial fermentation is the intentional use of fermentation by microorganisms such as bacteria and fungi to make products useful to humans. Fermented products have applications as food as well as in general industry.- Food fermentation :...
or enzyme
Enzyme
Enzymes are proteins that catalyze chemical reactions. In enzymatic reactions, the molecules at the beginning of the process, called substrates, are converted into different molecules, called products. Almost all chemical reactions in a biological cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates...
production.

Filtration
Filtration is commonly the mechanical or physical operation which is used for the separation of solids from fluids by interposing a medium through which only the fluid can pass...
, settling
Settling
Settling is the process by which particulates settle to the bottom of a liquid and form a sediment. Particles that experience a force, either due to gravity or due to centrifugal motion will tend to move in a uniform manner in the direction exerted by that force...
(sedimentation), extraction
Liquid-liquid extraction
Liquid–liquid extraction, also known as solvent extraction and partitioning, is a method to separate compounds based on their relative solubilities in two different immiscible liquids, usually water and an organic solvent. It is an extraction of a substance from one liquid phase into another liquid...
or leaching, distillation
Distillation
Distillation is a method of separating mixtures based on differences in volatilities of components in a boiling liquid mixture. Distillation is a unit operation, or a physical separation process, and not a chemical reaction....
, recrystallization
Recrystallization (chemistry)
-Chemistry:In chemistry, recrystallization is a procedure for purifying compounds. The most typical situation is that a desired "compound A" is contaminated by a small amount of "impurity B". There are various methods of purification that may be attempted , which includes recrystallization...
or precipitation
Precipitation (chemistry)
Precipitation is the formation of a solid in a solution or inside anothersolid during a chemical reaction or by diffusion in a solid. When the reaction occurs in a liquid, the solid formed is called the precipitate, or when compacted by a centrifuge, a pellet. The liquid remaining above the solid...
(followed by filtration or settling), reverse osmosis
Reverse osmosis
Reverse osmosis is a membrane technical filtration method that removes many types of large molecules and ions from solutions by applying pressure to the solution when it is on one side of a selective membrane. The result is that the solute is retained on the pressurized side of the membrane and...
, drying
Drying
Drying is a mass transfer process consisting of the removal of water or another solvent by evaporation from a solid, semi-solid or liquid. This process is often used as a final production step before selling or packaging products. To be considered "dried", the final product must be solid, in the...
, and adsorption
Adsorption
Adsorption is the adhesion of atoms, ions, biomolecules or molecules of gas, liquid, or dissolved solids to a surface. This process creates a film of the adsorbate on the surface of the adsorbent. It differs from absorption, in which a fluid permeates or is dissolved by a liquid or solid...
. Heat exchanger
Heat exchanger
A heat exchanger is a piece of equipment built for efficient heat transfer from one medium to another. The media may be separated by a solid wall, so that they never mix, or they may be in direct contact...
s are often used for heating or cooling, including boiling
Boiling
Boiling is the rapid vaporization of a liquid, which occurs when a liquid is heated to its boiling point, the temperature at which the vapor pressure of the liquid is equal to the pressure exerted on the liquid by the surrounding environmental pressure. While below the boiling point a liquid...
or condensation
Condensation
Condensation is the change of the physical state of matter from gaseous phase into liquid phase, and is the reverse of vaporization. When the transition happens from the gaseous phase into the solid phase directly, the change is called deposition....
, often in conjunction with other units such as distillation towers. There may also be storage tanks
Chemical tank
Chemical tanks are storage containers for chemicals. They come in a variety of sizes and shapes, and are used for static storage, mixing, and transport of both raw materials and finished chemical products.-Design:...
for storing feedstock, intermediate or final products, or waste. Storage tanks commonly have level indicators to show how full they are. There may be structures holding or supporting sometimes massive units and their associated equipment. There are often stairs, ladders, or other steps for personnel to reach points in the units for sampling, inspection, or maintenance. An area of a plant or facility with numerous storage tanks is sometimes called a tank farm
Tank farm
Tank farm may refer to the:*Alternate name for an oil depot, a facility for storage of liquid petroleum products or petrochemicals*Tank Farm, also known as 'Tuff Crater', a volcanic crater in the Auckland Volcanic Field, New Zealand...
, especially at an oil depot
Oil depot
An oil depot is an industrial facility for the storage of oil and/or petrochemical products and from which these products are usually transported to end users or further storage facilities...
.
Fluid systems for carrying liquids and gases include piping and tubing of various diameter sizes, various types of valve
Valve
A valve is a device that regulates, directs or controls the flow of a fluid by opening, closing, or partially obstructing various passageways. Valves are technically pipe fittings, but are usually discussed as a separate category...
s for controlling or stopping flow, pump
Pump
A pump is a device used to move fluids, such as liquids, gases or slurries.A pump displaces a volume by physical or mechanical action. Pumps fall into three major groups: direct lift, displacement, and gravity pumps...
s for moving or pressurizing liquid, and compressors for pressurizing or moving gases. Vessels, piping, tubing, and sometimes other equipment at high or very low temperature are commonly covered with insulation
Thermal insulation
Thermal insulation is the reduction of the effects of the various processes of heat transfer between objects in thermal contact or in range of radiative influence. Heat transfer is the transfer of thermal energy between objects of differing temperature...
for personnel safety and to maintain temperature inside. Fluid systems and units commonly have instrumentation
Instrumentation
Instrumentation is defined as the art and science of measurement and control of process variables within a production, or manufacturing area....
such as temperature and pressure sensors and flow measuring
Flow measurement
Flow measurement is the quantification of bulk fluid movement. Flow can be measured in a variety of ways.Positive-displacement flow meters acumulate a fixed volume of fluid and then count the number of times the volume is filled to measure flow...
devices at select locations in a plant. Online analyzers for chemical or physical property analysis have become more common. Solvent
Solvent
A solvent is a liquid, solid, or gas that dissolves another solid, liquid, or gaseous solute, resulting in a solution that is soluble in a certain volume of solvent at a specified temperature...
s can sometimes be used to dissolve reactants or materials such as solids for extraction or leaching, to provide a suitable medium for certain chemical reactions to run, or so they can otherwise be treated as fluids.
Chemical plant design
Design
Design as a noun informally refers to a plan or convention for the construction of an object or a system while “to design” refers to making this plan...
ing chemical plants are done by chemical engineer
Chemical engineer
In the field of engineering, a chemical engineer is the profession in which one works principally in the chemical industry to convert basic raw materials into a variety of products, and deals with the design and operation of plants and equipment to perform such work...
s, although historically this was not always the case and many chemical plants were constructed in a haphazard way before the discipline of Chemical Engineering became established. In plant design, typically less than 1% of ideas for new designs ever become commercialized. During this solution process, typically, cost studies are used as an initial screening to eliminate unprofitable designs. If a process appears profitable, then other factors are considered, such as safety, environmental constraints, controllability, etc. The general goal in plant design, is to construct or synthesize “optimum designs” in the neighborhood of the desired constraints.
Many times chemist
Chemist
A chemist is a scientist trained in the study of chemistry. Chemists study the composition of matter and its properties such as density and acidity. Chemists carefully describe the properties they study in terms of quantities, with detail on the level of molecules and their component atoms...
s research chemical reactions or other chemical principles in a laboratory
Laboratory
A laboratory is a facility that provides controlled conditions in which scientific research, experiments, and measurement may be performed. The title of laboratory is also used for certain other facilities where the processes or equipment used are similar to those in scientific laboratories...
, commonly on a small scale in a "batch-type" experiment. Chemistry information obtained is then used by chemical engineers, along with expertise of their own, to convert to a chemical process and scale up the batch size or capacity. Commonly, a small chemical plant called a pilot plant
Pilot plant
A pilot plant is a small chemical processing system which is operated to generate information about the behavior of the system for use in design of larger facilities....
is built to provide design and operating information before construction of a large plant. From data and operating experience obtained from the pilot plant, a scaled-up plant can be designed for higher or full capacity. After the fundamental aspects of a plant design are determined, mechanical or electrical engineers may become involved with mechanical or electrical details, respectively. Structural engineer
Structural engineer
Structural engineers analyze, design, plan, and research structural components and structural systems to achieve design goals and ensure the safety and comfort of users or occupants...
s may become involved in the plant design to ensure the structures can support the weight
Weight
In science and engineering, the weight of an object is the force on the object due to gravity. Its magnitude , often denoted by an italic letter W, is the product of the mass m of the object and the magnitude of the local gravitational acceleration g; thus:...
of the units, piping, and other equipment.
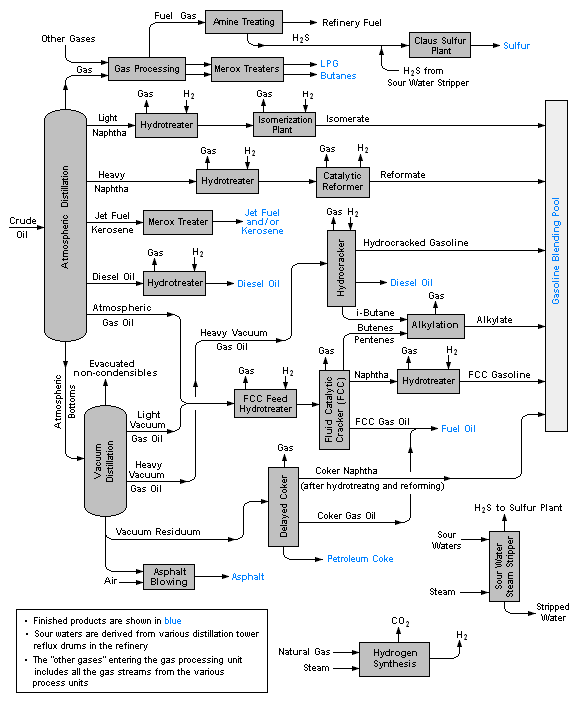
The units, streams, and fluid systems of chemical plants or processes can be represented by block flow diagrams
Block diagram
Block diagram is a diagram of a system, in which the principal parts or functions are represented by blocks connected by lines, that show the relationships of the blocks....
which are very simplified diagrams, or process flow diagram
Process Flow diagram
A process flow diagram is a diagram commonly used in engineering to indicate the general flow of plant processes and equipment.The PFD displays the relationship between major equipment of a plant facility and does not show minor details such as piping details and designations...
s which are somewhat more detailed. The streams and other piping are shown as lines with arrow heads showing usual direction of material flow. In block diagrams, units are often simply shown as blocks. Process flow diagrams may use more detailed symbols and show pumps, compressors, and major valves. Likely values or ranges of material flow rates for the various streams are determined based on desired plant capacity using material balance calculations. Energy balances are also done based on heats of reaction, heat capacities
Heat capacity
Heat capacity , or thermal capacity, is the measurable physical quantity that characterizes the amount of heat required to change a substance's temperature by a given amount...
, expected temperatures and pressures at various points to calculate amounts of heating and cooling needed in various places and to size heat exchangers. Chemical plant design can be shown in fuller detail in a piping and instrumentation diagram
Piping and instrumentation diagram
A piping and instrumentation diagram/drawing is a diagram in the process industry which shows the piping of the process flow together with the installed equipment and instrumentation.-Contents and Function:...
(P&ID) which shows all piping, tubing, valves, and instrumentation, typically with special symbols. Showing a full plant is often complicated in a P&ID, so often only individual units or specific fluid systems are shown in a single P&ID.
In the plant design, the units are sized for the maximum capacity each may have to handle. Similarly, sizes for pipes, pumps, compressors, and associated equipment are chosen for the flow capacity they have to handle. Utility systems such as electric power
Electric power
Electric power is the rate at which electric energy is transferred by an electric circuit. The SI unit of power is the watt.-Circuits:Electric power, like mechanical power, is represented by the letter P in electrical equations...
and water
Water
Water is a chemical substance with the chemical formula H2O. A water molecule contains one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms connected by covalent bonds. Water is a liquid at ambient conditions, but it often co-exists on Earth with its solid state, ice, and gaseous state . Water also exists in a...
supply should also be included in the plant design. Additional piping lines for non-routine or alternate operating procedures, such as plant or unit startups and shutdowns, may have to be included. Fluid systems design commonly includes isolation valves around various units or parts of a plant so that a section of a plant could be isolated in case of a problem such as a leak
Leak
A leak is a hole or other opening, usually unintended and therefore undesired, in a container or fluid-containing system, such as a tank or a ship's hull, through which the contents of the container can escape or outside matter can enter the container...
in a unit. If pneumatically or hydraulically actuated valves are used, a system of pressurizing lines to the actuators are needed. Any points where process samples may have to be taken should have sampling lines, valves, and access to them included in the detailed design. If necessary, provisions should be made for reducing high pressure or temperature of a sampling stream, such including a pressure reducing valve or sample cooler.
Units and fluid systems in the plant including all vessels, piping, tubing, valves, pumps, compressors, and other equipment must be rated or designed to be able to withstand the entire range of pressures, temperatures, and other conditions which they could possibly encounter, including any appropriate safety factors. All such units and equipment should also be checked for materials compatibility
Compatibility (chemical)
Chemical compatibility is a measure of how stable a substance is when mixed with another substance. If substances mix and do not change they are considered compatible. If substances mix and change or do not mix at all they are considered incompatible....
to ensure they can withstand long-term exposure to the chemicals they will come in contact with. Any closed system in a plant which has a means of pressurizing possibly beyond the rating of its equipment, such as heating, exothermic reactions, or certain pumps or compressors, should have an appropriately sized pressure relief valve
Relief valve
The relief valve is a type of valve used to control or limit the pressure in a system or vessel which can build up by a process upset, instrument or equipment failure, or fire....
included to prevent overpressurization for safety. Frequently all of these parameters (temperatures, pressures, flow, etc.) are exhaustively analyzed in combination through a Hazop
Hazop
A hazard and operability study is a structured and systematic examination of a planned or existing process or operation in order to identify and evaluate problems that may represent risks to personnel or equipment, or prevent efficientoperation....
or fault tree analysis, to ensure that the plant has no known risk of serious hazard.
Within any constraints the plant is subject to, design parameters are optimized
Process optimization
Process optimization is the discipline of adjusting a process so as to optimize some specified set of parameters without violating some constraint. The most common goals are minimizing cost, maximizing throughput, and/or efficiency...
for good economic performance while ensuring safety and welfare of personnel and the surrounding community. For flexibility, a plant may be designed to operate in a range around some optimal design parameters in case feedstock or economic conditions change and re-optimization is desirable. In more modern times, computer simulation
Computer simulation
A computer simulation, a computer model, or a computational model is a computer program, or network of computers, that attempts to simulate an abstract model of a particular system...
s or other computer calculations have been used to help in chemical plant design or optimization.
Process control
In process controlProcess control
Process control is a statistics and engineering discipline that deals with architectures, mechanisms and algorithms for maintaining the output of a specific process within a desired range...
, information gathered automatically from various sensors or other devices in the plant is used to control various equipment for running the plant, thereby controlling operation of the plant. Instruments receiving such information signals and sending out control signals to perform this function automatically are process controllers
Controller (control theory)
In control theory, a controller is a device which monitors and affects the operational conditions of a given dynamical system. The operational conditions are typically referred to as output variables of the system which can be affected by adjusting certain input variables...
. Previously, pneumatic controls were sometimes used. Electrical controls are now common. A plant often has a control room
Control room
A control room is a room serving as an operations centre where a facility or service can be monitored and controlled. Examples include:*in television production, the master control is the technical hub of a broadcast operation common among most over-the-air television stations, television networks...
with displays of parameters such as key temperatures, pressures, fluid flow rates and levels, operating positions of key valves, pumps and other equipment, etc. In addition, operators in the control room can control various aspects of the plant operation, often including overriding automatic control. Process control with a computer represents more modern technology. Based on possible changing feedstock composition, changing products requirements or economics, or other changes in constraints, operating conditions may be re-optimized to maximize profit.
Workers
As in any industrial setting, there are a variety of workers working throughout a chemical plant facility, often organized into departments, sections, or other work groups. Such workers typically include engineerEngineer
An engineer is a professional practitioner of engineering, concerned with applying scientific knowledge, mathematics and ingenuity to develop solutions for technical problems. Engineers design materials, structures, machines and systems while considering the limitations imposed by practicality,...
s, plant operator
Plant operator
A plant operator is a person who supervises the operation of an industrial plant. The term is usually applied to power plants or chemical plants such as gas extraction, petrochemical or oil refinery or other chemical processes....
s, and maintenance technicians. Other personnel at the site could include chemists, management/administration and office workers. Types of engineers involved in operations or maintenance may include chemical process engineers, mechanical engineers for maintaining mechanical equipment, and electrical/computer engineers for electrical or computer
Computer
A computer is a programmable machine designed to sequentially and automatically carry out a sequence of arithmetic or logical operations. The particular sequence of operations can be changed readily, allowing the computer to solve more than one kind of problem...
equipment.
Transport
Large quantities of fluid feedstock or product may enter or leave a plant by pipelinePipeline transport
Pipeline transport is the transportation of goods through a pipe. Most commonly, liquids and gases are sent, but pneumatic tubes that transport solid capsules using compressed air are also used....
, railroad tank car
Tank car
A tank car is a type of railroad rolling stock designed to transport liquid and gaseous commodities.-Timeline:...
, or tanker truck. For example, petroleum commonly comes to a refinery by pipeline. Pipelines can also carry petrochemical feedstock from a refinery to a nearby petrochemical plant. Natural gas
Natural gas
Natural gas is a naturally occurring gas mixture consisting primarily of methane, typically with 0–20% higher hydrocarbons . It is found associated with other hydrocarbon fuel, in coal beds, as methane clathrates, and is an important fuel source and a major feedstock for fertilizers.Most natural...
is a product which comes all the way from a natural gas processing plant to final consumers by pipeline or tubing. Large quantities of liquid feedstock are typically pumped into process units. Smaller quantities of feedstock or product may be shipped to or from a plant in drum
Drum (container)
A drum is a cylindrical container used for shipping bulk cargo. Drums can be made of steel, dense paperboard , or plastics, and are generally used for the transportation and storage of liquids and powders. Drums are often certified for shipment of dangerous goods...
s. Use of drums about 55 gallons in capacity is common for packaging industrial quantities of chemicals. Smaller batches of feedstock may be added from drums or other containers to process units by workers.
Maintenance
In addition to feeding and operating the plant, and packaging or preparing the product for shipping, plant workers are needed for taking samples for routine and troubleshooting analysis and for performing routine and non-routine maintenance. Routine maintenance can include periodic inspections and replacement of worn catalyst, analyzer reagents, various sensors, or mechanical parts. Non-routine maintenance can include investigating problems and then fixing them, such as leaks, failure to meet feed or product specifications, mechanical failures of valves, pumps, compressors, sensors, etc.Statutory and regulatory compliance
When working with chemicals, safetySafety
Safety is the state of being "safe" , the condition of being protected against physical, social, spiritual, financial, political, emotional, occupational, psychological, educational or other types or consequences of failure, damage, error, accidents, harm or any other event which could be...
is a concern. In the United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
, the law requires that employers provide workers working with chemicals with access to a Material Safety Data Sheet
Material safety data sheet
A Material Safety Data Sheet is a form with data regarding the properties of a particular substance....
(MSDS) for every kind of chemical they work with. An MSDS for a certain chemical is prepared and provided by the supplier to whoever buys the chemical. Other laws covering chemical safety, hazardous waste, and pollution must be observed, including statutes such as the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act
Resource Conservation and Recovery Act
The Resource Conservation and Recovery Act , enacted in 1976, is the principal Federal law in the United States governing the disposal of solid waste and hazardous waste.-History and Goals:...
(RCRA) and the Toxic Substances Control Act
Toxic Substances Control Act
The Toxic Substances Control Act is a United States law, passed by the United States Congress in 1976, that regulates the introduction of new or already existing chemicals. It grandfathered most existing chemicals, in contrast to the Registration, Evaluation and Authorization of Chemicals ...
(TSCA), and regulations such as the Chemical Facility Anti-Terrorism Standards
Chemical Facility Anti-Terrorism Standards
The Chemical Facility Anti-Terrorism Standards , also known as 6 CFR, Part 27, are a set of US government security regulations for high-risk chemical facilities such as chemical plants, electrical generating facilities, refineries, and universities. The US Department of Homeland Security...
in the United States. Hazmat
Hazmat
Hazmat, HazMat and similar terms can refer to:* Hazardous materials and items—see Dangerous goods** Hazchem—a system of hazardous chemical classification and firefighting modes** A hazmat suit is a type of protective clothing...
(hazardous materials) teams are trained to deal with chemical leaks or spills. Process Hazard Analysis
Process Hazard Analysis
Process Hazard Analysis is a set of organized and systematic assessments of the potential hazards associated with an industrial process. A PHA provides information intended to assist managers and employees in making decisions for improving safety and reducing the consequences of unwanted or...
(PHA) is used to assess potential hazard
Hazard
A hazard is a situation that poses a level of threat to life, health, property, or environment. Most hazards are dormant or potential, with only a theoretical risk of harm; however, once a hazard becomes "active", it can create an emergency situation. A hazard does not exist when it is not...
s in chemical plants. In 1998, the U. S. Chemical Safety and Hazard Investigation Board has become operational.
Plant facilities
The actual production or process part of a plant may be indoors, outdoors, or a combination of the two. The actual production section of a facility usually has the appearance of a rather industrial environment. Hard hats and work shoes are commonly worn. Floors and stairs are often made of metal grating, and there is practically no decoration. There may also be pollution control or waste treatmentWaste treatment
Waste treatment refers to the activities required to ensure that waste has the least practicable impact on the environment. In many countries various forms of waste treatment are required by law.-Solid waste treatment:...
facilities or equipment. Sometimes existing plants may be expanded or modified based on changing economics, feedstock, or product needs. As in other production facilities, there may be shipping
Shipping
Shipping has multiple meanings. It can be a physical process of transporting commodities and merchandise goods and cargo, by land, air, and sea. It also can describe the movement of objects by ship.Land or "ground" shipping can be by train or by truck...
and receiving, and storage facilities
Warehouse
A warehouse is a commercial building for storage of goods. Warehouses are used by manufacturers, importers, exporters, wholesalers, transport businesses, customs, etc. They are usually large plain buildings in industrial areas of cities and towns. They usually have loading docks to load and unload...
. In addition, there are usually certain other facilities, typically indoors, to support production at the site.
Although some simple sample analysis may be able to be done by operations technicians in the plant area, a chemical plant typically has a laboratory
Laboratory
A laboratory is a facility that provides controlled conditions in which scientific research, experiments, and measurement may be performed. The title of laboratory is also used for certain other facilities where the processes or equipment used are similar to those in scientific laboratories...
where chemists analyze samples taken from the plant. Such analysis can include chemical analysis or determination of physical properties. Sample analysis can include routine quality control
Quality control
Quality control, or QC for short, is a process by which entities review the quality of all factors involved in production. This approach places an emphasis on three aspects:...
on feedstock coming into the plant, intermediate and final products to ensure quality specifications are met. Non-routine samples may be taken and analyzed for investigating plant process problems also. A larger chemical company often has a research laboratory for developing and testing products and processes where there may be pilot plants, but such a laboratory may be located at a site separate from the production plants.
A plant may also have a workshop or maintenance facility for repairs or keeping maintenance equipment. There is also typically some office space for engineers, management or administration, and perhaps for receiving visitors. The decorum there is commonly more typical of an office environment.
Corrosion and use of new materials
CorrosionCorrosion
Corrosion is the disintegration of an engineered material into its constituent atoms due to chemical reactions with its surroundings. In the most common use of the word, this means electrochemical oxidation of metals in reaction with an oxidant such as oxygen...
in chemical process plants is a big issue that consumes billions of dollars yearly. Electrochemical corrosion of metals is pronounced in chemical process plants due to the presence of acid fumes and other electrolytic interactions. Recently, FRP (Fibre-reinforced plastic
Fibre-reinforced plastic
Fibre-reinforced plastic is a composite material made of a polymer matrix reinforced with fibres. The fibres are usually fibreglass, carbon, or aramid, while the polymer is usually an epoxy, vinylester or polyester thermosetting plastic...
) is used as a material of construction. The British standard specification BS4994
BS4994
BS4994 is the "specification for the design and construction of vessels and storage tanks in reinforced plastics"...
is widely used for design and construction of the vessels, tanks, etc.
See also
- Chemical industryChemical industryThe chemical industry comprises the companies that produce industrial chemicals. Central to the modern world economy, it converts raw materials into more than 70,000 different products.-Products:...
- Chemical process modelingChemical process modelingChemical process modeling is a computer modeling technique used in chemical engineering process design. It typically involves using purpose-built software to define a system of interconnected components, which are then solved so that the steady-state or dynamic behavior of the system can be...
- FRP tanks and vesselsFRP tanks and vesselsFRP is a modern composite material of construction for chemical plant equipment like tanks and vessels...
- chemical process plant equipment made of FRP - BS4994BS4994BS4994 is the "specification for the design and construction of vessels and storage tanks in reinforced plastics"...
- Electrical equipment in hazardous areasElectrical Equipment in Hazardous AreasIn electrical engineering, a hazardous location is defined as a place where concentrations of flammable gases, vapors, or dusts occur. Electrical equipment that must be installed in such locations is especially designed and tested to ensure it does not initiate an explosion, due to arcing contacts...
- Instrumentation in petrochemical industriesInstrumentation in petrochemical industriesInstrumentation in petrochemical industries are basically flowmeters, pressure transmitters, level meters, temperature instruments, and analysis instruments, etc.-Temperature Indicator:...

