
Instrumentation
Encyclopedia
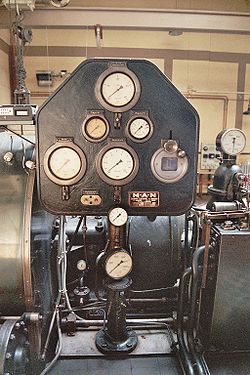
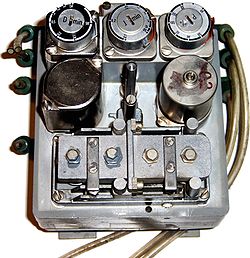
An instrument is a device that measures and/or regulates physical quantity/process variables such as flow, temperature, level, or pressure. Instruments include many varied contrivances that can be as simple as valves and transmitters
Transducer
A transducer is a device that converts one type of energy to another. Energy types include electrical, mechanical, electromagnetic , chemical, acoustic or thermal energy. While the term transducer commonly implies the use of a sensor/detector, any device which converts energy can be considered a...
, and as complex as analyzers
Analyser
An analyser, also spelt analyzer, is a person or device that analyses given data. It examines in detail the structure of the given data and tries to find patterns and relationships between parts of the data...
. Instruments often comprise control systems of varied processes such as refineries, factories, and vehicles. The control of processes is one of the main branches of applied instrumentation. Instrumentation can also refer to handheld devices that measure some desired variable. Diverse handheld instrumentation is common in laboratories, but can be found in the household as well. For example, a smoke detector
Smoke detector
A smoke detector is a device that detects smoke, typically as an indicator of fire. Commercial, industrial, and mass residential devices issue a signal to a fire alarm system, while household detectors, known as smoke alarms, generally issue a local audible and/or visual alarm from the detector...
is a common instrument found in most western homes.
Output instrumentation includes devices such as solenoid
Solenoid
A solenoid is a coil wound into a tightly packed helix. In physics, the term solenoid refers to a long, thin loop of wire, often wrapped around a metallic core, which produces a magnetic field when an electric current is passed through it. Solenoids are important because they can create...
s, valve
Valve
A valve is a device that regulates, directs or controls the flow of a fluid by opening, closing, or partially obstructing various passageways. Valves are technically pipe fittings, but are usually discussed as a separate category...
s, regulators
Regulator (automatic control)
In automatic control, a regulator is a device which has the function of maintaining a designated characteristic. It performs the activity of managing or maintaining a range of values in a machine. The measurable property of a device is managed closely by specified conditions or an advance set...
, circuit breaker
Circuit breaker
A circuit breaker is an automatically operated electrical switch designed to protect an electrical circuit from damage caused by overload or short circuit. Its basic function is to detect a fault condition and, by interrupting continuity, to immediately discontinue electrical flow...
s, and relay
Relay
A relay is an electrically operated switch. Many relays use an electromagnet to operate a switching mechanism mechanically, but other operating principles are also used. Relays are used where it is necessary to control a circuit by a low-power signal , or where several circuits must be controlled...
s. These devices control a desired output variable, and provide either remote or automated control capabilities. These are often referred to as final control elements when controlled remotely or by a control system
Control system
A control system is a device, or set of devices to manage, command, direct or regulate the behavior of other devices or system.There are two common classes of control systems, with many variations and combinations: logic or sequential controls, and feedback or linear controls...
.
Transmitters
Transducer
A transducer is a device that converts one type of energy to another. Energy types include electrical, mechanical, electromagnetic , chemical, acoustic or thermal energy. While the term transducer commonly implies the use of a sensor/detector, any device which converts energy can be considered a...
are devices that produce an output signal, often in the form of a 4–20 mA
Ampere
The ampere , often shortened to amp, is the SI unit of electric current and is one of the seven SI base units. It is named after André-Marie Ampère , French mathematician and physicist, considered the father of electrodynamics...
electrical current signal, although many other options using voltage
Voltage
Voltage, otherwise known as electrical potential difference or electric tension is the difference in electric potential between two points — or the difference in electric potential energy per unit charge between two points...
, frequency
Frequency
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit time. It is also referred to as temporal frequency.The period is the duration of one cycle in a repeating event, so the period is the reciprocal of the frequency...
, pressure
Pressure
Pressure is the force per unit area applied in a direction perpendicular to the surface of an object. Gauge pressure is the pressure relative to the local atmospheric or ambient pressure.- Definition :...
, or ethernet
Ethernet
Ethernet is a family of computer networking technologies for local area networks commercially introduced in 1980. Standardized in IEEE 802.3, Ethernet has largely replaced competing wired LAN technologies....
are possible. This signal can be used for informational purposes, or it can be sent to a PLC
Programmable logic controller
A programmable logic controller or programmable controller is a digital computer used for automation of electromechanical processes, such as control of machinery on factory assembly lines, amusement rides, or light fixtures. PLCs are used in many industries and machines...
, DCS
Distributed control system
A distributed control system refers to a control system usually of a manufacturing system, process or any kind of dynamic system, in which the controller elements are not central in location but are distributed throughout the system with each component sub-system controlled by one or more...
, SCADA
SCADA
SCADA generally refers to industrial control systems : computer systems that monitor and control industrial, infrastructure, or facility-based processes, as described below:...
system, LabView
LabVIEW
LabVIEW is a system design platform and development environment for a visual programming language from National Instruments. LabVIEW provides engineers and scientists with the tools needed to create and deploy measurement and control systems.The graphical language is named "G"...
or other type of computerized controller, where it can be interpreted into readable values and used to control other devices and processes in the system.
Control Instrumentation plays a significant role in both gathering information from the field and changing the
field parameters, and as such are a key part of control loops.
History
In the early years of process control, process indicators and control elements such as valves were monitored by an operator that walked around the unit adjusting the valves to obtain the desired temperatures, pressures, and flows. As technology evolved pneumatic controllers were invented and mounted in the field that monitored the process and controlled the valves. This reduced the amount of time process operators were needed to monitor the process. Later years the actual controllers were moved to a central room and signals were sent into the control room to monitor the process and outputs signals were sent to the final control element such as a valve to adjust the process as needed. These controllers and indicators were mounted on a wall called a control board. The operators stood in front of this board walking back and forth monitoring the process indicators. This again reduced the number and amount of time process operators were needed to walk around the units. The basic air signal used during these years was 3-15 psig.In the 1970s electronic instrumentation began to be manufactured by the instrument companies. Each instrument company came out with their own standard signal for their instrumentation, 10-50ma, 0.25-1.25Volts, 0-10Volts, 1-5volts, and 4-20ma, causing only confusion until the 4-20ma was universally used as a standard electronic instrument signal for transmitters and valves. The transformation of instrumentation from mechanical pneumatic transmitters, controllers, and valves to electronic instruments reduced maintenance costs as electronic instruments were more dependable than mechanical instruments. This also increased efficiency and production due to their increase in accuracy.
The next evolution of instrumentation came with the production of Distributed Control Systems (DCS). The pneumatic and electronic control rooms allowed control from a centralized room, DCS systems allowed control from more than one room or control stations. These stations could be next to each other or miles away. Now a process operator could sit in front of a screen and monitor thousands of points throughout a large unit or complex.
Measurement
Instrumentation is used to measure many parameters (physical values). These parameters include:- PressurePressurePressure is the force per unit area applied in a direction perpendicular to the surface of an object. Gauge pressure is the pressure relative to the local atmospheric or ambient pressure.- Definition :...
, either differential or staticStatic pressureIn fluid mechanics the term static pressure has several uses:* In the design and operation of aircraft, static pressure is the air pressure in the aircraft’s static pressure system.... - Flow
- TemperatureTemperature measurementAttempts of standardized temperature measurement have been reported as early as 170 AD by Claudius Galenus. The modern scientific field has its origins in the works by Florentine scientists in the 17th century. Early devices to measure temperature were called thermoscopes. The first sealed...
- LevelsLevel measurementLevel measurement refers to instrumentation techniques designed to measure the height of a fluid or solid within a containing vessel.- Liquid/fluid measurement techniques :*Radar*Guided radar*Electromechanical*Ultrasonic*Capacitance*Hydrostatic pressure...
of liquids etc. - DensityDensityThe mass density or density of a material is defined as its mass per unit volume. The symbol most often used for density is ρ . In some cases , density is also defined as its weight per unit volume; although, this quantity is more properly called specific weight...
- ViscosityViscosityViscosity is a measure of the resistance of a fluid which is being deformed by either shear or tensile stress. In everyday terms , viscosity is "thickness" or "internal friction". Thus, water is "thin", having a lower viscosity, while honey is "thick", having a higher viscosity...
- Other mechanical properties of materials
- Properties of ionising radiationRadiationIn physics, radiation is a process in which energetic particles or energetic waves travel through a medium or space. There are two distinct types of radiation; ionizing and non-ionizing...
- FrequencyFrequencyFrequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit time. It is also referred to as temporal frequency.The period is the duration of one cycle in a repeating event, so the period is the reciprocal of the frequency...
- Current
- VoltageVoltageVoltage, otherwise known as electrical potential difference or electric tension is the difference in electric potential between two points — or the difference in electric potential energy per unit charge between two points...
- InductanceInductanceIn electromagnetism and electronics, inductance is the ability of an inductor to store energy in a magnetic field. Inductors generate an opposing voltage proportional to the rate of change in current in a circuit...
- CapacitanceCapacitanceIn electromagnetism and electronics, capacitance is the ability of a capacitor to store energy in an electric field. Capacitance is also a measure of the amount of electric potential energy stored for a given electric potential. A common form of energy storage device is a parallel-plate capacitor...
- ResistivityResistivityElectrical resistivity is a measure of how strongly a material opposes the flow of electric current. A low resistivity indicates a material that readily allows the movement of electric charge. The SI unit of electrical resistivity is the ohm metre...
- Chemical composition
- Chemical properties
- Properties of light
- Vibration
- Weight
Control
In addition to measuring field parameters, instrumentation is also responsible for providing the ability to modify some field parameters.Instrumentation engineering
Instrumentation engineering is the engineering specialization focused on the principle and operation of measuring instruments that are used in design and configuration of automated systems in electrical, pneumatic domains etc.They typically work for industries with automated processes, such as chemical
Chemical plant
A chemical plant is an industrial process plant that manufactures chemicals, usually on a large scale. The general objective of a chemical plant is to create new material wealth via the chemical or biological transformation and or separation of materials. Chemical plants use special equipment,...
or manufacturing
Manufacturing
Manufacturing is the use of machines, tools and labor to produce goods for use or sale. The term may refer to a range of human activity, from handicraft to high tech, but is most commonly applied to industrial production, in which raw materials are transformed into finished goods on a large scale...
plants, with the goal of improving system productivity
Productivity
Productivity is a measure of the efficiency of production. Productivity is a ratio of what is produced to what is required to produce it. Usually this ratio is in the form of an average, expressing the total output divided by the total input...
, reliability, safety, optimization, and stability.
To control the parameters in a process or in a particular system, devices such as microprocessors, microcontrollers or PLCs are used, but their ultimate aim is to control the parameters of a system.
Instrumentation technologists and mechanics
Instrumentation technologists, technicians and mechanics specialize in troubleshooting and repairing and maintenance of instruments and instrumentation systems. This trade is so intertwined with electricians, pipefitters, power engineers, and engineering companies, that one can find him/herself in extremely diverse working situations.External links
- International Society of Automation, see International Society of Automation for more information.
- See Industrial Instrumentation & Controls Technology Alliance for more information.

