
Wine and health
Encyclopedia

Wine
Wine is an alcoholic beverage, made of fermented fruit juice, usually from grapes. The natural chemical balance of grapes lets them ferment without the addition of sugars, acids, enzymes, or other nutrients. Grape wine is produced by fermenting crushed grapes using various types of yeast. Yeast...
has a long history of use as an early form of medication
History of medicine
All human societies have medical beliefs that provide explanations for birth, death, and disease. Throughout history, illness has been attributed to witchcraft, demons, astral influence, or the will of the gods...
, being recommended variously as a safe alternative to drinking water
Drinking water
Drinking water or potable water is water pure enough to be consumed or used with low risk of immediate or long term harm. In most developed countries, the water supplied to households, commerce and industry is all of drinking water standard, even though only a very small proportion is actually...
, an antiseptic
Antiseptic
Antiseptics are antimicrobial substances that are applied to living tissue/skin to reduce the possibility of infection, sepsis, or putrefaction...
for treating wounds and a digestive aid
Digestion
Digestion is the mechanical and chemical breakdown of food into smaller components that are more easily absorbed into a blood stream, for instance. Digestion is a form of catabolism: a breakdown of large food molecules to smaller ones....
, as well as a cure for a wide range of ailments from lethargy and diarrhea
Diarrhea
Diarrhea , also spelled diarrhoea, is the condition of having three or more loose or liquid bowel movements per day. It is a common cause of death in developing countries and the second most common cause of infant deaths worldwide. The loss of fluids through diarrhea can cause dehydration and...
to easing the pain of child birth.
Ancient Egypt
Ancient Egypt
Ancient Egypt was an ancient civilization of Northeastern Africa, concentrated along the lower reaches of the Nile River in what is now the modern country of Egypt. Egyptian civilization coalesced around 3150 BC with the political unification of Upper and Lower Egypt under the first pharaoh...
ian Papyri and Sumer
Sumer
Sumer was a civilization and historical region in southern Mesopotamia, modern Iraq during the Chalcolithic and Early Bronze Age....
ian tablets dating back to 2200 BC detail the medicinal role of wine, making it the world's oldest documented man-made medicine. Wine continued to play a major role in medicine until the late 19th and early 20th century, when changing opinions and medical research on alcohol
Alcohol
In chemistry, an alcohol is an organic compound in which the hydroxy functional group is bound to a carbon atom. In particular, this carbon center should be saturated, having single bonds to three other atoms....
and alcoholism
Alcoholism
Alcoholism is a broad term for problems with alcohol, and is generally used to mean compulsive and uncontrolled consumption of alcoholic beverages, usually to the detriment of the drinker's health, personal relationships, and social standing...
cast doubt on the role of wine as part of a healthy lifestyle and diet.
In the late 20th and early 21st century, fueled in part by public interest in reports by the United States news broadcast 60 Minutes
60 Minutes
60 Minutes is an American television news magazine, which has run on CBS since 1968. The program was created by producer Don Hewitt who set it apart by using a unique style of reporter-centered investigation....
on the so-called "French Paradox
French paradox
The French Paradox is the observation that French people suffer a relatively low incidence of coronary heart disease, despite having a diet relatively rich in saturated fats...
", the medical establishment began to re-evaluate the role of moderate wine consumption in health. Studies have since shown positive benefits of the phenolic compound resveratrol
Resveratrol
Resveratrol is a stilbenoid, a type of natural phenol, and a phytoalexin produced naturally by several plants when under attack by pathogens such as bacteria or fungi....
with continued research attempting to better understand its functions in wine and the body.
Historical role of wine in medicine
Early medicine was intimately tied with religionReligion
Religion is a collection of cultural systems, belief systems, and worldviews that establishes symbols that relate humanity to spirituality and, sometimes, to moral values. Many religions have narratives, symbols, traditions and sacred histories that are intended to give meaning to life or to...
and the supernatural
Supernatural
The supernatural or is that which is not subject to the laws of nature, or more figuratively, that which is said to exist above and beyond nature...
, with early practitioners often being priest
Priest
A priest is a person authorized to perform the sacred rites of a religion, especially as a mediatory agent between humans and deities. They also have the authority or power to administer religious rites; in particular, rites of sacrifice to, and propitiation of, a deity or deities...
s and magicians. Wine's close association with ritual made it a logical tool for these early medical practices. Tablets from Sumerian culture and papyri from Ancient Egypt dating to 2200 BC include recipes for wine based medicines, making wine the oldest documented man made medicine.
Early history

Hippocrates
Hippocrates of Cos or Hippokrates of Kos was an ancient Greek physician of the Age of Pericles , and is considered one of the most outstanding figures in the history of medicine...
recommended wine as a part of a healthy diet
Diet (nutrition)
In nutrition, diet is the sum of food consumed by a person or other organism. Dietary habits are the habitual decisions an individual or culture makes when choosing what foods to eat. With the word diet, it is often implied the use of specific intake of nutrition for health or weight-management...
and advocated its use as a disinfectant for wounds, as well as a medium to mix other drugs in for easier consumption by the patient. He also prescribed wine as a cure for various ailments ranging from diarrhea and lethargy to pain during childbirth. The medical practices of the ancient Romans involved the use of wine in a similar manner. In his 1st century work De Medicina
De Medicina
De Medicina is a 1st-century medical treatise by Aulus Cornelius Celsus, a Roman encyclopedist and possibly a practicing physician. It is the only surviving section of a much larger encyclopedia; only small parts still survive from sections on agriculture, military science, oratory, jurisprudence...
, the Roman encyclopedist Aulus Cornelius Celsus
Aulus Cornelius Celsus
Aulus Cornelius Celsus was a Roman encyclopedist, known for his extant medical work, De Medicina, which is believed to be the only surviving section of a much larger encyclopedia. The De Medicina is a primary source on diet, pharmacy, surgery and related fields, and it is one of the best sources...
detailed a long list of Greek and Roman wines used for medicinal puropses. While treating gladiators
Gladiators
Gladiators is a British television series produced by LWT for ITV on Saturdays nights from 10 October 1992 to 1 January 2000. It is an adaptation of the United States game show American Gladiators. An Australian spin-off and a Swedish one followed...
in Asia Minor
Asia Minor
Asia Minor is a geographical location at the westernmost protrusion of Asia, also called Anatolia, and corresponds to the western two thirds of the Asian part of Turkey...
, the Roman physician Galen
Galen
Aelius Galenus or Claudius Galenus , better known as Galen of Pergamon , was a prominent Roman physician, surgeon and philosopher...
would use wine as a disinfectant for all types of wounds, even soaking exposed bowels before returning them to the body. During his four years tending to the gladiators only five deaths occurred, compared to sixty deaths under the watch of the physician before him.
Religion still played a significant role in promoting wine's use for health benefit. The Talmud
Talmud
The Talmud is a central text of mainstream Judaism. It takes the form of a record of rabbinic discussions pertaining to Jewish law, ethics, philosophy, customs and history....
noted wine to be "the foremost of all medicines: wherever wine is lacking, medicines become necessary." In his first epistle to Timothy
First Epistle to Timothy
The First Epistle of Paul to Timothy, usually referred to simply as First Timothy and often written 1 Timothy, is one of three letters in the New Testament of the Bible often grouped together as the Pastoral Epistles, the others being Second Timothy and Titus...
, Paul the Apostle recommended that his young colleague drink a little wine every now and then for the benefit of his stomach and digestion. While the Islamic Koran contained restrictions on all alcohol, Islamic doctors such as the Persian Avicenna
Avicenna
Abū ʿAlī al-Ḥusayn ibn ʿAbd Allāh ibn Sīnā , commonly known as Ibn Sīnā or by his Latinized name Avicenna, was a Persian polymath, who wrote almost 450 treatises on a wide range of subjects, of which around 240 have survived...
in the 11th century AD noted that wine was an efficient digestive aid but because of Islamic laws were limited only in using it as a disinfectant while dressing wounds. Catholic monasteries during the Middle Ages
Middle Ages
The Middle Ages is a periodization of European history from the 5th century to the 15th century. The Middle Ages follows the fall of the Western Roman Empire in 476 and precedes the Early Modern Era. It is the middle period of a three-period division of Western history: Classic, Medieval and Modern...
would also regularly use wine for various medical treatments. So closely tied was the role of wine and medicine that the first printed book on the subject of wine was written in the 14th century by a physician, Arnaldus de Villa Nova
Arnaldus de Villa Nova
Arnaldus de Villa Nova was an alchemist, astrologer and physician....
, with lengthy essays on wine's suitability for treatment of a variety of medical ailments such dementia
Dementia
Dementia is a serious loss of cognitive ability in a previously unimpaired person, beyond what might be expected from normal aging...
and sinus
Sinusitis
Sinusitis is inflammation of the paranasal sinuses, which may be due to infection, allergy, or autoimmune issues. Most cases are due to a viral infection and resolve over the course of 10 days...
problems.
Changing views highlight the risks of consumption
The lack of safe drinking waterDrinking water
Drinking water or potable water is water pure enough to be consumed or used with low risk of immediate or long term harm. In most developed countries, the water supplied to households, commerce and industry is all of drinking water standard, even though only a very small proportion is actually...
for much of history may have been one reason for wine's popularity in medicine. Wine was still being used to sterilize water as late as the Hamburg
Hamburg
-History:The first historic name for the city was, according to Claudius Ptolemy's reports, Treva.But the city takes its modern name, Hamburg, from the first permanent building on the site, a castle whose construction was ordered by the Emperor Charlemagne in AD 808...
cholera
Cholera
Cholera is an infection of the small intestine that is caused by the bacterium Vibrio cholerae. The main symptoms are profuse watery diarrhea and vomiting. Transmission occurs primarily by drinking or eating water or food that has been contaminated by the diarrhea of an infected person or the feces...
epidemic of 1892 in order to control the spread of the disease. However the late 19th century and early 20th century ushered in a period of changing views on the role of alcohol
Alcohol
In chemistry, an alcohol is an organic compound in which the hydroxy functional group is bound to a carbon atom. In particular, this carbon center should be saturated, having single bonds to three other atoms....
and (by extension) wine in health and society. The Temperance movement
Temperance movement
A temperance movement is a social movement urging reduced use of alcoholic beverages. Temperance movements may criticize excessive alcohol use, promote complete abstinence , or pressure the government to enact anti-alcohol legislation or complete prohibition of alcohol.-Temperance movement by...
began to gain steam by touting the ills of alcoholism
Alcoholism
Alcoholism is a broad term for problems with alcohol, and is generally used to mean compulsive and uncontrolled consumption of alcoholic beverages, usually to the detriment of the drinker's health, personal relationships, and social standing...
, which was eventually defined by the medical establishment as a disease
Disease Theory of Alcoholism
The modern disease theory of alcoholism states that problem drinking is sometimes caused by a disease of the brain, characterized by altered brain structure and function. The existence of alcoholism as a disease is accepted by some within the medical and scientific communities, although critics...
. Studies of the long
Long-term effects of alcohol
The long term effects of alcohol range from possible health benefits for low levels of alcohol consumption to severe detrimental effects in cases of chronic alcohol abuse...
and short-term effects of alcohol
Short-term effects of alcohol
Short-term effects of alcohol on the human body can take many forms. The drug alcohol, to be specific ethanol, is a central nervous system depressant with a range of side-effects. The amount and circumstances of consumption play a large part in determining the extent of intoxication; for example,...
caused many in the medical community to reconsider the role of wine in medicine and diet. Public opinion turned against consumption of alcohol in any form, leading to Prohibition in the United States
Prohibition in the United States
Prohibition in the United States was a national ban on the sale, manufacture, and transportation of alcohol, in place from 1920 to 1933. The ban was mandated by the Eighteenth Amendment to the Constitution, and the Volstead Act set down the rules for enforcing the ban, as well as defining which...
and other countries. In some areas wine was able to maintain a limited role, such as an exemption in the United States for "therapeutic wines" that were sold legally in drug stores. These wines were marketed for their medicinal benefits but some wineries used this measure as a loophole to sell large quantities of wine for recreational consumption. In response, the United States government issued a mandate requiring producers to include an emetic additive that would induce vomiting above the consumption of a certain dosage level.
Throughout the mid to early 20th century, health advocates pointed to the risk of alcohol consumption and the role it played in a variety of ailments such as blood disorders, high blood pressure, cancer
Cancer
Cancer , known medically as a malignant neoplasm, is a large group of different diseases, all involving unregulated cell growth. In cancer, cells divide and grow uncontrollably, forming malignant tumors, and invade nearby parts of the body. The cancer may also spread to more distant parts of the...
, infertility
Infertility
Infertility primarily refers to the biological inability of a person to contribute to conception. Infertility may also refer to the state of a woman who is unable to carry a pregnancy to full term...
, liver damage, muscle atrophy
Muscle atrophy
Muscle atrophy, or disuse atrophy, is defined as a decrease in the mass of the muscle; it can be a partial or complete wasting away of muscle. When a muscle atrophies, this leads to muscle weakness, since the ability to exert force is related to mass...
, psoriasis
Psoriasis
Psoriasis is an autoimmune disease that appears on the skin. It occurs when the immune system mistakes the skin cells as a pathogen, and sends out faulty signals that speed up the growth cycle of skin cells. Psoriasis is not contagious. However, psoriasis has been linked to an increased risk of...
, skin infections, stroke
Stroke
A stroke, previously known medically as a cerebrovascular accident , is the rapidly developing loss of brain function due to disturbance in the blood supply to the brain. This can be due to ischemia caused by blockage , or a hemorrhage...
s, and long term brain damage
Brain damage
"Brain damage" or "brain injury" is the destruction or degeneration of brain cells. Brain injuries occur due to a wide range of internal and external factors...
. Studies showed a connection between alcohol consumption among pregnant mothers and an increased risk of mental retardation
Mental retardation
Mental retardation is a generalized disorder appearing before adulthood, characterized by significantly impaired cognitive functioning and deficits in two or more adaptive behaviors...
and physical abnormalities in what became known as fetal alcohol syndrome
Fetal alcohol syndrome
Fetal alcohol syndrome is a pattern of mental and physical defects that can develop in a fetus in association with high levels of alcohol consumption during pregnancy. Current research also implicates other lifestyle choices made by the prospective mother...
, prompting the use of warning labels
Warning Labels
"Warning Labels" is the title of a song written by Kim Williams and Oscar Turman, and recorded by American country music artist Doug Stone. It was released in June 1992 as the lead single from the album From the Heart. The song reached #4 on the Billboard Hot Country Singles & Tracks chart.-Chart...
on alcohol-containing products in several countries.
1990s: French Paradox and renewed interest in the benefits of consumption
The 1990s and early 21st century saw a renewed interest in the health benefits of wine, ushered in by increasing research suggesting that moderate wine drinkers have lower mortality rates than heavy drinkers or teetotalers. In November 1991, the U.S. news program 60 Minutes aired a broadcast on the so-called "French ParadoxFrench paradox
The French Paradox is the observation that French people suffer a relatively low incidence of coronary heart disease, despite having a diet relatively rich in saturated fats...
". Featuring the research work of Bordeaux
Bordeaux
Bordeaux is a port city on the Garonne River in the Gironde department in southwestern France.The Bordeaux-Arcachon-Libourne metropolitan area, has a population of 1,010,000 and constitutes the sixth-largest urban area in France. It is the capital of the Aquitaine region, as well as the prefecture...
scientist Serge Renaud, the broadcast dealt with the seemingly paradox
Paradox
Similar to Circular reasoning, A paradox is a seemingly true statement or group of statements that lead to a contradiction or a situation which seems to defy logic or intuition...
ical relationship between the high fat/high dairy diets of French people
French people
The French are a nation that share a common French culture and speak the French language as a mother tongue. Historically, the French population are descended from peoples of Celtic, Latin and Germanic origin, and are today a mixture of several ethnic groups...
and the low occurrence of cardiovascular disease among them. The broadcast drew parallels to the American and British diets which also contained high levels of fat and dairy but which featured high incidences of heart disease. One of the theories proposed by Renaud in the broadcast was that moderate consumption of red wine was a risk-reducing factor for the French and that wine could have more positive health benefits yet to be studied. Following the 60 Minutes broadcast, sales of red wine in the United States jumped 44% over previous years.
This changing view of wine can be seen in the evolution of the language used in the U.S. Food and Drug Administration Dietary Guidelines. The 1990 edition of the guidelines contained the blanket statement that "wine has no net health benefit". By 1995, the wording had been changed to allow moderate consumption with meals providing the individual had no other alcohol-related health risk. From a research perspective, scientists began differentiating alcohol consumption among the various classes of beverages – wine, beer and spirits. This distinction allowed studies to highlight the positive medical benefits of wine apart from the mere presence of alcohol. However wine drinkers tend to share similar lifestyle habitats – better diets, regular exercise, non-smoking – that may in themselves be a factor in the supposed positive health benefits compared to drinkers of beer and spirits or those who abstain completely.
What is moderate consumption?
Nearly all research into the positive medical benefits of wine consumptions make a distinction between moderate consumption, heavy and binge drinkingBinge drinking
Binge drinking or heavy episodic drinking is the modern epithet for drinking alcoholic beverages with the primary intention of becoming intoxicated by heavy consumption of alcohol over a short period of time. It is a kind of purposeful drinking style that is popular in several countries worldwide,...
. What constitutes a moderate, healthy level of consumption will vary by individual according to age
Ageing
Ageing or aging is the accumulation of changes in a person over time. Ageing in humans refers to a multidimensional process of physical, psychological, and social change. Some dimensions of ageing grow and expand over time, while others decline...
, gender
Gender
Gender is a range of characteristics used to distinguish between males and females, particularly in the cases of men and women and the masculine and feminine attributes assigned to them. Depending on the context, the discriminating characteristics vary from sex to social role to gender identity...
, genetics
Genetics
Genetics , a discipline of biology, is the science of genes, heredity, and variation in living organisms....
, weight
Weight
In science and engineering, the weight of an object is the force on the object due to gravity. Its magnitude , often denoted by an italic letter W, is the product of the mass m of the object and the magnitude of the local gravitational acceleration g; thus:...
and body stature
Human body
The human body is the entire structure of a human organism, and consists of a head, neck, torso, two arms and two legs.By the time the human reaches adulthood, the body consists of close to 100 trillion cells, the basic unit of life...
as well as the situation-i.e. is food
Food
Food is any substance consumed to provide nutritional support for the body. It is usually of plant or animal origin, and contains essential nutrients, such as carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins, or minerals...
being consumed as well, are any other drugs currently in the individual's system, etc. Women, in general, tend to absorb alcohol quicker than men due to their lower body water
Body water
In medicine, body water is the water content of the human body. A significant fraction of the human body is water. Arthur Guyton 's Textbook of Medical Physiology states that "the total amount of water in a man of average weight is approximately 40 litres, averaging 57 percent of his total body...
content and difference in levels of stomach enzyme so their moderate levels of consumption tend to be lower than a male of equal age and weight. Some doctors define "moderate consumption" as one 5 USoz glass of wine per day for women and two glasses per day for men.
The view of consuming wine in moderation has a history almost as long as that of wine's role in medicine. The Greek poet Eubulus
Eubulus (poet)
Eubulus was an Athenian "Middle Comic" poet, victorious six times at the Lenaia, first probably in the late 370s or 360s BC According to the Suda , which dates him to the 101st Olympiad Eubulus was an Athenian "Middle Comic" poet, victorious six times at the Lenaia, first probably in the late 370s...
believed that three bowls (kylix
Kylix (drinking cup)
A kylix is a type of wine-drinking glass with a broad relatively shallow body raised on a stem from a foot and usually with two horizontal handles disposed symmetrically...
) were the ideal amount of wine to consume. The number of three bowls for moderation is a common theme throughout Greek writing; today the standard 750 mL wine bottle
Wine bottle
A wine bottle is a bottle used for holding wine, generally made of glass. Some wines are fermented in the bottle, others are bottled only after fermentation. They come in a large variety of sizes, several named for Biblical kings and other figures. The standard bottle contains 750 ml,...
contains roughly the amount of three Kylix cups (250 ml or 8 fl oz each). In his circa 375 BC play Semele or Dionysus, Eubulus has Dionysus
Dionysus
Dionysus was the god of the grape harvest, winemaking and wine, of ritual madness and ecstasy in Greek mythology. His name in Linear B tablets shows he was worshipped from c. 1500—1100 BC by Mycenean Greeks: other traces of Dionysian-type cult have been found in ancient Minoan Crete...
say:
Chemical Composition

Natural phenols and polyphenols
Although red wine contains many other chemicals which may have health benefits, resveratrolResveratrol
Resveratrol is a stilbenoid, a type of natural phenol, and a phytoalexin produced naturally by several plants when under attack by pathogens such as bacteria or fungi....
has been studied the most. Resveratrol and other such compounds mainly fall in the category of phenolics. Polyphenols play a key role in the health benefits of wine by acting as antioxidant
Antioxidant
An antioxidant is a molecule capable of inhibiting the oxidation of other molecules. Oxidation is a chemical reaction that transfers electrons or hydrogen from a substance to an oxidizing agent. Oxidation reactions can produce free radicals. In turn, these radicals can start chain reactions. When...
s that prevent cell damage, but the other possible effects of these chemicals are not yet fully understood. A recent study showed that just 100 ml of 2003 Blaufränkisch contained such levels of polyphenols that were equivalent to about four times the daily dose of rosiglitazone
Rosiglitazone
Rosiglitazone is an antidiabetic drug in the thiazolidinedione class of drugs. It works as an insulin sensitizer, by binding to the PPAR receptors in fat cells and making the cells more responsive to insulin...
, an antidiabetic drug.
Cinnamates have been shown to have more antioxidant activity when exposed in vitro to the Fenton reaction (catalytic Fe(II) with hydrogen peroxide) than the other natural phenols present in wine.
Resveratrol
Resveratrol is a non-flavonoid phenolic compound found in wine, present because of its high concentration in grape skin. It has received a lot of attention in both the mediaNews media
The news media are those elements of the mass media that focus on delivering news to the general public or a target public.These include print media , broadcast news , and more recently the Internet .-Etymology:A medium is a carrier of something...
and medical research community for its potential health benefits. Belonging to a class of compounds known as stilbenoid, resveratrol is also found outside of the Vitis
Vitis
Vitis is a genus of about 60 species of vining plants in the flowering plant family Vitaceae. The genus is made up of species predominantly from the Northern hemisphere. It is economically important as the source of grapes, both for direct consumption of the fruit and for fermentation to produce...
grapevine
Grapevine
Grapevine is the common name for plants of the genus Vitis. Other meanings include:*Grapevine , a term often used to describe a form of communication by means of gossip or rumor, as in "heard it through the grapevine"...
family in plants such as eucalyptus
Eucalyptus
Eucalyptus is a diverse genus of flowering trees in the myrtle family, Myrtaceae. Members of the genus dominate the tree flora of Australia...
and peanut
Peanut
The peanut, or groundnut , is a species in the legume or "bean" family , so it is not a nut. The peanut was probably first cultivated in the valleys of Peru. It is an annual herbaceous plant growing tall...
s. It is part of the defence mechanism in grapevines, used as a phytoalexin
Phytoalexin
Phytoalexins are antimicrobial substances synthesized de novo by plants that accumulate rapidly at areas of incompatible pathogen infection. They are broad spectrum inhibitors and are chemically diverse with different types characteristic of particular plant species...
produced in the leaves and berry skins in response to a microbial attack by fungus or grape disease. In a controlled setting, this reaction can be artificially induced by exposure to ultraviolet radiation. The build up of resveratrol slows and sometimes will stop the spreading infection.
According to NC State University researchers, Muscadines contain a unique blend of several natural antioxidants that can reduce the risk factors associated with degenerative diseases.
The production and concentration of resveratrol is not equal among all the varieties of wine grapes. Differences in clones, rootstock
Rootstock
A rootstock is a plant, and sometimes just the stump, which already has an established, healthy root system, used for grafting a cutting or budding from another plant. The tree part being grafted onto the rootstock is usually called the scion...
, Vitis species as well as climate conditions can affect the production of resveratrol. The degree of exposure to greater risk of fungal infection and grape diseases also appear to play a role. The Muscadinia family of vines, which has adapted over time through exposure to North American
North American
North American generally refers to an entity, people, group, or attribute of North America, especially of the United States and Canada together.-Culture:*North American English, a collective term used to describe American English and Canadian English...
grape diseases such as phylloxera
Phylloxera
Grape phylloxera ; originally described in France as Phylloxera vastatrix; equated to the previously described Daktulosphaira vitifoliae, Phylloxera vitifoliae; commonly just called phylloxera is a pest of commercial grapevines worldwide, originally native to eastern North America...
, has some of the highest concentrations of resveratrol among wine grapes. Among the European Vitis vinifera
Vitis vinifera
Vitis vinifera is a species of Vitis, native to the Mediterranean region, central Europe, and southwestern Asia, from Morocco and Portugal north to southern Germany and east to northern Iran....
, grapes derived from the Burgundian Pinot
Pinot
-Grape varieties:* One of several grape varieties and associated wines** Pinot blanc ** Pinot gris ** Pinot meunier** Pinot noir...
family tend to have substantially higher amounts of resveratrol than grapes derived from the Cabernet family of Bordeaux. Wine regions with cooler, wetter climates that are more prone to grape disease and fungal attacks (such as Oregon, New York) tend to produce grapes with higher concentrations of resveratrol than warmer, dry climates like California and Australia.
Red wine tends to have a significantly higher concentration of resveratrol than white wine, even though white wine grape varieties produce similar amounts in the vineyards. This is because during winemaking
Winemaking
Winemaking, or vinification, is the production of wine, starting with selection of the grapes or other produce and ending with bottling the finished wine. Although most wine is made from grapes, it may also be made from other fruit or non-toxic plant material...
white wine spends very little if any time in contact with the resveratrol-rich grape skins. This maceration
Maceration (wine)
Maceration is the winemaking process where the phenolic materials of the grape— tannins, coloring agents and flavor compounds— are leached from the grape skins, seeds and stems into the must. Maceration is the process by which the red wine receives its red color, since 99% of all grape juice is...
period not only gives red wine its color but allows for the extraction of phenolic compounds such as resveratrol into the resulting wine. Other winemaking techniques, such as the use of certain strains of yeast
Yeast
Yeasts are eukaryotic micro-organisms classified in the kingdom Fungi, with 1,500 species currently described estimated to be only 1% of all fungal species. Most reproduce asexually by mitosis, and many do so by an asymmetric division process called budding...
during fermentation
Fermentation (wine)
The process of fermentation in wine turns grape juice into an alcoholic beverage. During fermentation, yeast interact with sugars in the juice to create ethanol, commonly known as ethyl alcohol, and carbon dioxide...
or lactic acid bacteria
Lactic acid bacteria
The lactic acid bacteria comprise a clade of Gram-positive, low-GC, acid-tolerant, generally non-sporulating, non-respiring rod or cocci that are associated by their common metabolic and physiological characteristics. These bacteria, usually found in decomposing plants and lactic products, produce...
during malolactic fermentation
Malolactic fermentation
Malolactic fermentation is a process in winemaking where tart-tasting malic acid, naturally present in grape must, is converted to softer-tasting lactic acid. Malolactic fermentation tends to create a rounder, fuller mouthfeel. It has been said that malic acid tastes of green apples...
, can have an influence on the amount of resveratrol left in the resulting wines. Similarly the use of certain fining agents during the clarification and stabilization of wine
Clarification and stabilization of wine
The clarification and stabilization of wine in winemaking involves removing insoluble and suspended materials. The insoluble material causes a wine to be cloudy. These processes may include fining, filtration, centrifugation, flotation, refrigeration, barrel maturation, pasteurization and racking...
can strip the wine of some resveratrol molecules.
The prominence of resveratrol in the news and its association with positive health benefits has encouraged some wineries to highlight it in their marketing. In the early 21st century, the Oregon producer Willamette Valley Vineyards
Willamette Valley Vineyards
Willamette Valley Vineyards is a winery located in Turner, Oregon. Named after Oregon's Willamette Valley, the winery is the leading producer of Pinot Noir in Oregon, and also produces Dijon clone Chardonnay and Pinot Gris. The first planting was the Estate Vineyard, which was purchased in 1983 by...
sought approval from the Alcohol and Tobacco Tax and Trade Bureau
Alcohol and Tobacco Tax and Trade Bureau
The Alcohol and Tobacco Tax and Trade Bureau, statutorily named the Tax and Trade Bureau and frequently shortened to TTB, is a bureau of the United States Department of the Treasury....
(TTB) to state on their wine labels the resveratrol levels of their wines which ranged from 19 to 71 micromoles per liter (higher than the average 10 micromoles per liter in most red wines). The TTB gave preliminary approval to the winery, making it the first to use such information on its labels. While resveratrol is the most widely publicized, there are other components in wine that have been the focus of medical research into potential health benefits. These include the compounds catechin
Catechin
Catechin is a natural phenol antioxidant plant secondary metabolite. The term catechins is also commonly used to refer to the related family of flavonoids and the subgroup flavan-3-ols ....
and quercetin
Quercetin
Quercetin , a flavonol, is a plant-derived flavonoid found in fruits, vegetables, leaves and grains. It also may be used as an ingredient in supplements, beverages or foods.-Occurrence:...
.
To fully get the benefits of resveratrol in wines, it is recommended to sip slowly when drinking wines. Due to inactivation in the gut and liver, most of the resveratrol in imbibed red wine does not reach the blood circulation. However, when sipping slowly, absorption via the mucous membranes in the mouth can result in up to around 100 times the blood levels of resveratrol.
Bones
Heavy alcohol consumption has been shown to have a damaging effect on the cellular process that create bone tissue. Long term alcoholic consumption at high levels increases the frequency of fractureFracture
A fracture is the separation of an object or material into two, or more, pieces under the action of stress.The word fracture is often applied to bones of living creatures , or to crystals or crystalline materials, such as gemstones or metal...
s. Studies from St. Thomas' Hospital in London and the Epidimiologie de l'Ostioporose (EPIDOS) medical group in France suggest that moderate wine consumption may offer positive benefits to women, particularly elderly women, in retaining bone density
Bone density
Bone density is a medical term normally referring to the amount of mineral matter per square centimeter of bones. Bone density is used in clinical medicine as an indirect indicator of osteoporosis and fracture risk.This medical bone density is not the true physical "density" of the bone, which...
and reducing the risk of developing osteoporosis
Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a disease of bones that leads to an increased risk of fracture. In osteoporosis the bone mineral density is reduced, bone microarchitecture is deteriorating, and the amount and variety of proteins in bone is altered...
. While consuming more than three glasses of wine a day was shown to reduce bone density, the French study showed that women who drank moderately (1 to 3 glasses a day) had more overall increases in bone density over the two year study period. However, the physicians who took part in the French study noted that other factors could be in play apart from wine consumption with moderate drinkers being more likely to live active lifestyles that included physical activity which also benefits bone density.
Cancer
Alcohol is a toxinToxin
A toxin is a poisonous substance produced within living cells or organisms; man-made substances created by artificial processes are thus excluded...
and damages cells. The International Agency for Research on Cancer
International Agency for Research on Cancer
The International Agency for Research on Cancer is an intergovernmental agency forming part of the World Health Organisation of the United Nations....
of the World Health Organization
World Health Organization
The World Health Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations that acts as a coordinating authority on international public health. Established on 7 April 1948, with headquarters in Geneva, Switzerland, the agency inherited the mandate and resources of its predecessor, the Health...
has classified alcohol as a Group 1 carcinogen. Studies have linked even moderate consumption of alcohol to increase risk for a variety of cancers including breast, colon, esophageal and stomach cancer
Stomach cancer
Gastric cancer, commonly referred to as stomach cancer, can develop in any part of the stomach and may spread throughout the stomach and to other organs; particularly the esophagus, lungs, lymph nodes, and the liver...
. Focus on wine's positive benefits regarding cancer has centered on the antioxidant
Antioxidant
An antioxidant is a molecule capable of inhibiting the oxidation of other molecules. Oxidation is a chemical reaction that transfers electrons or hydrogen from a substance to an oxidizing agent. Oxidation reactions can produce free radicals. In turn, these radicals can start chain reactions. When...
properties of resveratrol, found in grapes, with some laboratory results showing a protective quality that inhibit cancerous changes in cells. The research is ongoing with no conclusive results though some studies suggest that moderate wine consumption may lower the risk for lung, ovarian and prostate cancer
Prostate cancer
Prostate cancer is a form of cancer that develops in the prostate, a gland in the male reproductive system. Most prostate cancers are slow growing; however, there are cases of aggressive prostate cancers. The cancer cells may metastasize from the prostate to other parts of the body, particularly...
.
Barrett's esophagus
Barrett's esophagus refers to an abnormal change in the cells of the inferior portion of the esophagus. A positive diagnosis generally requires observing specific macroscopic and microscopic changes...
. In one study, conducted by Kaiser Permanente
Kaiser Permanente
Kaiser Permanente is an integrated managed care consortium, based in Oakland, California, United States, founded in 1945 by industrialist Henry J. Kaiser and physician Sidney Garfield...
in California, respondents who reported drinking no more than 1 glass of wine a day had a 56% decrease in the risk for developing Barrett's esophagus-a rate lower than that of heavy and non-drinkers. While heavy alcohol consumption has been proven to increase the risk of esophageal, these studies suggest that antioxidant
Antioxidant
An antioxidant is a molecule capable of inhibiting the oxidation of other molecules. Oxidation is a chemical reaction that transfers electrons or hydrogen from a substance to an oxidizing agent. Oxidation reactions can produce free radicals. In turn, these radicals can start chain reactions. When...
s in wine may offer some benefit if consumed in moderation but there is not a conclusive link. In response to these studies, Dr Prateek Sharma, MD, of the University of Kansas
University of Kansas
The University of Kansas is a public research university and the largest university in the state of Kansas. KU campuses are located in Lawrence, Wichita, Overland Park, and Kansas City, Kansas with the main campus being located in Lawrence on Mount Oread, the highest point in Lawrence. The...
School of Medicine, notes that there may be other links such as people who drink wine leading generally healthier lifestyles with consuming less fats and eating more fruits and vegetables.
Research conducted at the Yale School of Public Health
Yale School of Public Health
The Yale School of Public Health was founded in 1915 by Charles-Edward Amory Winslow and is one of the oldest public health masters programs in the United States...
in 2009, suggest that wine may have some protective benefits against some forms of cancer. Women diagnosed with non-Hodgkin's lymphoma were questioned about their alcohol consumption patterns and followed for an 8 to 12-year period. Compared to non-drinkers, women who had drinking wine for at least 25 years prior were 33% less likely to die over the five-year period following diagnosis and 26% less likely to experience a relapse or develop a secondary cancer during that same five year period. Of all the women in the study, 75% of those who drank at least 12 glasses of wine over the course of their lifetime were alive after five years compared to 66% of the women who never drank any wine. Women who drank beer and alcohol spirits showed no differences.
While alcohol itself has been linked as increasing the risk of breast cancer in women, a 2008 study by researchers at the University of Nebraska suggest that resveratrol, which is found in grapes, may have some preventative benefits against breast cancer. Prolong exposure of breast cells to estrogen
Estrogen
Estrogens , oestrogens , or œstrogens, are a group of compounds named for their importance in the estrous cycle of humans and other animals. They are the primary female sex hormones. Natural estrogens are steroid hormones, while some synthetic ones are non-steroidal...
has long been suspected as to be a major risk factor for breast cancer. This exposure can cause toxic estrogen metabolite
Metabolite
Metabolites are the intermediates and products of metabolism. The term metabolite is usually restricted to small molecules. A primary metabolite is directly involved in normal growth, development, and reproduction. Alcohol is an example of a primary metabolite produced in large-scale by industrial...
s to appear that react with DNA
DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid is a nucleic acid that contains the genetic instructions used in the development and functioning of all known living organisms . The DNA segments that carry this genetic information are called genes, but other DNA sequences have structural purposes, or are involved in...
in the body to promote the development of tumor
Tumor
A tumor or tumour is commonly used as a synonym for a neoplasm that appears enlarged in size. Tumor is not synonymous with cancer...
s. Researchers at the University of Nebraska exposed human breast cells grown in the laboratory to low doses of resveratrol and found that it created numerous positive outcomes. The exposure to resveratrol not only decreased the production of estrogen metabolites but it also increased production of an enzyme that destroys these metabolites. It also appeared to limit interaction between these metabolites and DNA, limiting the promotion of tumor development. The amount of resveratrol used in the study was a low-dose concentration of 10 micromoles per liter. A typical glass of wine has a concentration between 9 and 28 micromoles per liter. However, this laboratory study does not suggest that consuming wine will produce the necessary concentration of resveratrol in the bloodstream to have these cancer fighting properties.
Cardiovascular system
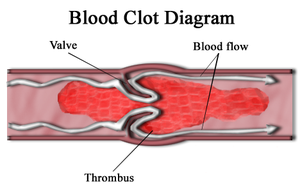
Heart disease
Heart disease, cardiac disease or cardiopathy is an umbrella term for a variety of diseases affecting the heart. , it is the leading cause of death in the United States, England, Canada and Wales, accounting for 25.4% of the total deaths in the United States.-Types:-Coronary heart disease:Coronary...
and developing potentially fatal cardiac arrhythmias. Excessive alcohol consumption can cause higher blood pressure, increase cholesterol
Cholesterol
Cholesterol is a complex isoprenoid. Specifically, it is a waxy steroid of fat that is produced in the liver or intestines. It is used to produce hormones and cell membranes and is transported in the blood plasma of all mammals. It is an essential structural component of mammalian cell membranes...
levels and weakened heart muscles. For moderate drinkers, medical research indicates moderate wine consumption may lower the mortality rate and risk of heart of disease. Studies have shown that moderate wine drinker can improve the balance of low-density lipoprotein (LDL or "bad" cholesterol) to high-density lipoprotein (HDL "good" cholesterol), which has been theorized as to clean up or remove LDL from blocking
Atheroma
In pathology, an atheroma is an accumulation and swelling in artery walls that is made up of macrophage cells, or debris, that contain lipids , calcium and a variable amount of fibrous connective tissue...
arteries. The main cause of heart attacks and the pain of angina is the lack of oxygen caused by blood clots and atheromatous plaque build up in the arteries. The alcohol in wine has anticoagulant
Anticoagulant
An anticoagulant is a substance that prevents coagulation of blood. A group of pharmaceuticals called anticoagulants can be used in vivo as a medication for thrombotic disorders. Some anticoagulants are used in medical equipment, such as test tubes, blood transfusion bags, and renal dialysis...
properties that limits blood clotting by making the platelet
Platelet
Platelets, or thrombocytes , are small,irregularly shaped clear cell fragments , 2–3 µm in diameter, which are derived from fragmentation of precursor megakaryocytes. The average lifespan of a platelet is normally just 5 to 9 days...
s in the blood less prone to stick together and reducing the levels of fibrin
Fibrin
Fibrin is a fibrous, non-globular protein involved in the clotting of blood. It is a fibrillar protein that is polymerised to form a "mesh" that forms a hemostatic plug or clot over a wound site....
protein that binds them together. However these anticoagulant properties of wine only stay in the system for a maximum of 24 hours after consumption. While having a glass of wine the night before may lower the risk of having a heart attack the next day, there is still the potential of long-term effects of alcohol
Long-term effects of alcohol
The long term effects of alcohol range from possible health benefits for low levels of alcohol consumption to severe detrimental effects in cases of chronic alcohol abuse...
. These anticoagulant properties can also be amplified adversely by binge drinking, with the individual becoming over-anticoagulated and at increase risk of a stroke or heart attack.
Additional studies have focused on the benefits of the phenolic compound resveratrol to cardiovascular health. Some studies suggest that the antioxidant
Antioxidant
An antioxidant is a molecule capable of inhibiting the oxidation of other molecules. Oxidation is a chemical reaction that transfers electrons or hydrogen from a substance to an oxidizing agent. Oxidation reactions can produce free radicals. In turn, these radicals can start chain reactions. When...
properties of resveratrol inhibits the oxidative reaction that for LDL cholesterol and decreases the "stickiness" of platelets that form blood clots.
Dementia and mental functions
One of the short-term effects of alcoholShort-term effects of alcohol
Short-term effects of alcohol on the human body can take many forms. The drug alcohol, to be specific ethanol, is a central nervous system depressant with a range of side-effects. The amount and circumstances of consumption play a large part in determining the extent of intoxication; for example,...
is impaired mental function
Mental function
Mental processes, mental functions and cognitive processes are terms often used interchangeably to mean such functions or processes as perception, introspection, memory, creativity, imagination, conception, belief, reasoning, volition, and emotion—in...
, which can cause behavioral changes and memory impairment. Long term effects of heavy drinking can inhibit new brain cell development and increase the risk for developing major depressive disorders. Studies have linked moderate alcohol consumption to lower risk of developing Alzheimer's and dementia
Dementia
Dementia is a serious loss of cognitive ability in a previously unimpaired person, beyond what might be expected from normal aging...
though wine's role in this link is not yet fully understood. A 2009 study by Wake Forest University
Wake Forest University
Wake Forest University is a private, coeducational university in the U.S. state of North Carolina, founded in 1834. The university received its name from its original location in Wake Forest, north of Raleigh, North Carolina, the state capital. The Reynolda Campus, the university's main campus, is...
School of Medicine suggest that moderate alcohol consumption may help healthy adults ward off the risks of developing dementia but can accelerate declining memory for those already suffering from cognitive impairment. The reason for the potential positive benefit of moderate consumption is not yet identified and may even be unrelated to the alcohol but rather other shared lifestyle factors of moderate drinkers (such as exercise or diets). If it is the moderate consumption, researchers theorize that it may be alcohol's role in promoting the production of "good cholesterol" which prevents blood platelets from sticking together. Another potential role of alcohol in the body may be in stimulating the release of the chemical acetylcholine
Acetylcholine
The chemical compound acetylcholine is a neurotransmitter in both the peripheral nervous system and central nervous system in many organisms including humans...
which influences brain function and memory.
Diabetes
Research has shown that moderate levels of alcohol consumed with meals does not have a substantial impact on blood sugarBlood sugar
The blood sugar concentration or blood glucose level is the amount of glucose present in the blood of a human or animal. Normally in mammals, the body maintains the blood glucose level at a reference range between about 3.6 and 5.8 mM , or 64.8 and 104.4 mg/dL...
levels. A 2005 study presented to the American Diabetes Association
American Diabetes Association
The American Diabetes Association is a United States-based association working to fight the consequences of diabetes, and to help those affected by diabetes...
suggest that moderate consumption may lower the risk of developing Type 2 diabetes.
Digestive system

Traveler's diarrhea
Traveler's diarrhea , is the most common illness affecting travelers. An estimated 10 million people—20% to 50% of international travelers—develop it annually. TD is defined as three or more unformed stools in 24 hours passed by a traveler, commonly accompanied by abdominal cramps, nausea, and...
where it was a preferred treatment to the less palatable bismuth
Bismuth
Bismuth is a chemical element with symbol Bi and atomic number 83. Bismuth, a trivalent poor metal, chemically resembles arsenic and antimony. Elemental bismuth may occur naturally uncombined, although its sulfide and oxide form important commercial ores. The free element is 86% as dense as lead...
treatments. The risk of infection from the bacterium Helicobacter pylori
Helicobacter pylori
Helicobacter pylori , previously named Campylobacter pyloridis, is a Gram-negative, microaerophilic bacterium found in the stomach. It was identified in 1982 by Barry Marshall and Robin Warren, who found that it was present in patients with chronic gastritis and gastric ulcers, conditions that were...
, strongly associated with causing gastritis
Gastritis
Gastritis is an inflammation of the lining of the stomach, and has many possible causes. The main acute causes are excessive alcohol consumption or prolonged use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs such as aspirin or ibuprofen. Sometimes gastritis develops after major surgery, traumatic...
and peptic ulcer
Peptic ulcer
A peptic ulcer, also known as PUD or peptic ulcer disease, is the most common ulcer of an area of the gastrointestinal tract that is usually acidic and thus extremely painful. It is defined as mucosal erosions equal to or greater than 0.5 cm...
s as well as being closely linked to stomach cancer, appears to lessen with moderate alcohol consumption. A German study conducted in the late 1990s showed that non-drinkers had slightly higher infection rates of Helicobacter pylori than moderate wine and beer drinkers.
Wine's positive effects on the metabolism of cholesterol
Cholesterol
Cholesterol is a complex isoprenoid. Specifically, it is a waxy steroid of fat that is produced in the liver or intestines. It is used to produce hormones and cell membranes and is transported in the blood plasma of all mammals. It is an essential structural component of mammalian cell membranes...
has been suggested as a link to lower occurrences of gallstones among moderate drinkers since cholesterol is a major component of gallstones.
Headaches
There are several potential causes of so called "red wine headaches", including histamineHistamine
Histamine is an organic nitrogen compound involved in local immune responses as well as regulating physiological function in the gut and acting as a neurotransmitter. Histamine triggers the inflammatory response. As part of an immune response to foreign pathogens, histamine is produced by...
s/tyramine
Tyramine
Tyramine is a naturally occurring monoamine compound and trace amine derived from the amino acid tyrosine. Tyramine acts as a catecholamine releasing agent...
s and the breakdown of some phenolic compounds in wine that carry the chemical messenger for serotonin
Serotonin
Serotonin or 5-hydroxytryptamine is a monoamine neurotransmitter. Biochemically derived from tryptophan, serotonin is primarily found in the gastrointestinal tract, platelets, and in the central nervous system of animals including humans...
. One culprit that is regularly dismissed by allergists as an unlikely cause of red wine headaches is sulfite
Sulfite
Sulfites are compounds that contain the sulfite ion SO. The sulfite ion is the conjugate base of bisulfite. Although the acid itself is elusive, its salts are widely used.-Structure:...
s which are used as a preservative
Preservative
A preservative is a naturally occurring or synthetically produced substance that is added to products such as foods, pharmaceuticals, paints, biological samples, wood, etc. to prevent decomposition by microbial growth or by undesirable chemical changes....
in wine. Wine, like other alcoholic beverages, is a diuretic
Diuretic
A diuretic provides a means of forced diuresis which elevates the rate of urination. There are several categories of diuretics. All diuretics increase the excretion of water from bodies, although each class does so in a distinct way.- Medical uses :...
which promotes dehydration
Dehydration
In physiology and medicine, dehydration is defined as the excessive loss of body fluid. It is literally the removal of water from an object; however, in physiological terms, it entails a deficiency of fluid within an organism...
that can lead to headaches (such as the case often experienced with hangover
Hangover
A hangover describes the sum of unpleasant physiological effects following heavy consumption of alcoholic beverages. The most commonly reported characteristics of a hangover include headache, nausea, sensitivity to light and noise, lethargy, dysphoria, diarrhea and thirst, typically after the...
s). In 2006, researchers from the University of California, Davis
University of California, Davis
The University of California, Davis is a public teaching and research university established in 1905 and located in Davis, California, USA. Spanning over , the campus is the largest within the University of California system and third largest by enrollment...
announced finding from genetic mapping that amino acid
Amino acid
Amino acids are molecules containing an amine group, a carboxylic acid group and a side-chain that varies between different amino acids. The key elements of an amino acid are carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen...
s in wine that have been slightly modified by the fermentation process may be the cause of wine related headaches. The research suggest changes in fermentation techniques may help alleviate the risk for wine drinkers sensitive to these amino acids.
Vision
The anti-oxidant and anticoagulant properties of wine may have a positive benefit in slowing the effects of macular degenerationMacular degeneration
Age-related macular degeneration is a medical condition which usually affects older adults and results in a loss of vision in the center of the visual field because of damage to the retina. It occurs in “dry” and “wet” forms. It is a major cause of blindness and visual impairment in older adults...
that causes vision
Visual perception
Visual perception is the ability to interpret information and surroundings from the effects of visible light reaching the eye. The resulting perception is also known as eyesight, sight, or vision...
to decline as people age. An American study from the late 1990s showed that vision of moderate wine drinkers suffered less macular degeneration than non-drinkers
Weight management

Arthur Agatston
Arthur Agatston is an American cardiologist best known as the developer of the South Beach Diet, but also the author of many published scholarly papers in the field of noninvasive cardiac diagnostics...
, co-creator of the South Beach diet
South Beach Diet
The South Beach Diet is a diet plan designed by cardiologist Arthur Agatston and dietician Marie Almon as an alternative to low-fat approaches such as the Ornish Diet and the Pritikin Diet advocated by the American Heart Association in the 1980s. Although the original purpose of the diet was to...
believes that wine can offer some positive benefit for weight management if it is consumed with food.
Compared to many beer
Beer
Beer is the world's most widely consumed andprobably oldest alcoholic beverage; it is the third most popular drink overall, after water and tea. It is produced by the brewing and fermentation of sugars, mainly derived from malted cereal grains, most commonly malted barley and malted wheat...
s and non-diet soda
Soft drink
A soft drink is a non-alcoholic beverage that typically contains water , a sweetener, and a flavoring agent...
s, a serving of wine has a moderate amount of calories. A standard 5 oz
Fluid ounce
A fluid ounce is a unit of volume equal to about 28.4 mL in the imperial system or about 29.6 mL in the US system. The fluid ounce is distinct from the ounce, which measures mass...
serving of red wine (based on an average alcohol content of 13%) contains approximately 106 calories and 2.51 g of carbohydrates. A similar serving of white wine contains approximately 100 calories and 1.18g of carbohydrates.
Psychological and social
Danish epidemiological studies suggest that a number of psychological health benefits are associated with drinking wine. In a study testing this idea, Mortensen et al. (2001) measured socioeconomic status, education, IQ, personality, psychiatric symptoms, and health related behaviors, which included alcohol consumption. The analysis was then broken down into groups of those who drank beer, those who drank wine, and then those who did and did not drink at all. The results showed that for both men and women drinking wine was related to higher parental social status, parental education and the social status of the subjects. When the subjects were given an IQ test, wine drinkers consistently scored higher IQs than their counterpart beer drinkers. The average difference of IQ between wine and beer drinkers was 18 points. In regards to psychological functioning, personality, and other health-related behaviors, the study found wine drinkers to operate at optimal levels while beer drinkers performed below optimal levels.Heavy metals in wine controversy
In 2008, researchers from Kingston UniversityKingston University
Kingston University is a public research university located in Kingston upon Thames, southwest London, United Kingdom. It was originally founded in 1899 as Kingston Technical Institute, a polytechnic, and became a university in 1992....
in London discovered red wine to contain high levels of toxic metals relative to other beverages in the sample. Although the metal ions, which included chromium
Chromium
Chromium is a chemical element which has the symbol Cr and atomic number 24. It is the first element in Group 6. It is a steely-gray, lustrous, hard metal that takes a high polish and has a high melting point. It is also odorless, tasteless, and malleable...
, copper
Copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu and atomic number 29. It is a ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. Pure copper is soft and malleable; an exposed surface has a reddish-orange tarnish...
, iron
Iron
Iron is a chemical element with the symbol Fe and atomic number 26. It is a metal in the first transition series. It is the most common element forming the planet Earth as a whole, forming much of Earth's outer and inner core. It is the fourth most common element in the Earth's crust...
, manganese
Manganese
Manganese is a chemical element, designated by the symbol Mn. It has the atomic number 25. It is found as a free element in nature , and in many minerals...
, nickel
Nickel
Nickel is a chemical element with the chemical symbol Ni and atomic number 28. It is a silvery-white lustrous metal with a slight golden tinge. Nickel belongs to the transition metals and is hard and ductile...
, vanadium
Vanadium
Vanadium is a chemical element with the symbol V and atomic number 23. It is a hard, silvery gray, ductile and malleable transition metal. The formation of an oxide layer stabilizes the metal against oxidation. The element is found only in chemically combined form in nature...
and zinc
Zinc
Zinc , or spelter , is a metallic chemical element; it has the symbol Zn and atomic number 30. It is the first element in group 12 of the periodic table. Zinc is, in some respects, chemically similar to magnesium, because its ion is of similar size and its only common oxidation state is +2...
, were also present in other plant-based beverages, the sample wine tested significantly higher for all metal ions, especially vanadium. Risk assessment was calculated using "target hazard quotients" (THQ), a method of quantifying health concerns associated with lifetime exposure to chemical pollutants. Developed by the Environmental Protection Agency in the US and used mainly to examine seafood
Seafood
Seafood is any form of marine life regarded as food by humans. Seafoods include fish, molluscs , crustaceans , echinoderms . Edible sea plants, such as some seaweeds and microalgae, are also seafood, and are widely eaten around the world, especially in Asia...
, a THQ of less than 1 represents no concern while, for example, mercury level
Mercury in fish
Fish and shellfish concentrate mercury in their bodies, often in the form of methylmercury, a highly toxic organic compound of mercury. Fish products have been shown to contain varying amounts of heavy metals, particularly mercury and fat-soluble pollutants from water pollution...
s in fish calculated to have THQs of between 1 and 5 would represent cause for concern.
The researchers stressed that a single glass of wine would not lead to metal poisoning, pointing out that their THQ calculations were based on the average person drinking one-third of a bottle of wine (250ml) every day between the ages of 18 and 80. However the "combined THQ values" for metal ions in the red wine they analyzed were reported to be as high as 125. A subsequent study by the same university using a meta analysis of data based on wine samples from a selection of mostly Europe
Europe
Europe is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting...
an countries found equally high levels of vanadium in many red wines, showing combined THQ values in the range of 50 to 200, with some as high as 350.
The findings sparked immediate controversy due to several issues: the study's reliance on secondary data
Secondary data
Secondary data is data collected by someone other than the user. Common sources of secondary data for social science include censuses, surveys, organizational records and data collected through qualitative methodologies or qualitative research...
; the assumption that all wines contributing to that data were representative of the countries stated; and the grouping together of poorly-understood high-concentration ions, such as vanadium, with relatively low-level, common ions such as copper and manganese. While some publications printed lists of countries showing the "worst offenders" and reported that wine from other countries did not pose a health risk, others pointed out that the lack of identifiable wines and grape varieties, specific producers or even wine regions, provided only misleading generalizations that should not be relied upon in choosing wines.
In a news bulletin following the widespread reporting of the findings, the UK's National Health Service
National Health Service
The National Health Service is the shared name of three of the four publicly funded healthcare systems in the United Kingdom. They provide a comprehensive range of health services, the vast majority of which are free at the point of use to residents of the United Kingdom...
(NHS) were also concerned that "the way the researchers added together hazards from different metals to produce a final score for individual wines may not be particularly meaningful". Commentators in the US questioned the relevance of seafood-based THQ assessments to agricultural
Agriculture
Agriculture is the cultivation of animals, plants, fungi and other life forms for food, fiber, and other products used to sustain life. Agriculture was the key implement in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that nurtured the...
produce, with the TTB
Alcohol and Tobacco Tax and Trade Bureau
The Alcohol and Tobacco Tax and Trade Bureau, statutorily named the Tax and Trade Bureau and frequently shortened to TTB, is a bureau of the United States Department of the Treasury....
, responsible for testing imports for metal ion contamination, have not detected an increased risk. George Solas, quality assessor for the Canadian Liquor Control Board of Ontario
Liquor Control Board of Ontario
The Liquor Control Board of Ontario is a provincial Crown corporation in Ontario, Canada established in 1927 by Lieutenant Governor William Donald Ross, on the advice of his Premier, Howard Ferguson, to sell liquor, wine, and beer through a chain of retail stores...
(LCBO) claimed that the levels of heavy metal contamination reported were within the permitted levels for drinking water in tested reservoir
Reservoir
A reservoir , artificial lake or dam is used to store water.Reservoirs may be created in river valleys by the construction of a dam or may be built by excavation in the ground or by conventional construction techniques such as brickwork or cast concrete.The term reservoir may also be used to...
s.
Whereas the NHS also described calls for improved wine label
Wine label
Wine labels are important sources of information for consumers since they tell the type and origin of the wine. The label is often the only resource a buyer has for evaluating the wine before purchasing it...
ing as an "extreme response" to research which provided "few solid answers", they acknowledged the authors call for further research to investigate wine production, including the influence that grape variety, soil type, geographical region, insecticide
Insecticide
An insecticide is a pesticide used against insects. They include ovicides and larvicides used against the eggs and larvae of insects respectively. Insecticides are used in agriculture, medicine, industry and the household. The use of insecticides is believed to be one of the major factors behind...
s, containment vessels and seasonal variations may have on metal ion uptake.
External links
- Dr. Philip Norrie "Chronology of wine as a medicine" The Wine Doctor
- "Red Wine Encourages Heart Health — But How?"

