
Poverty in Mexico
Encyclopedia
| Poverty in Mexico | |
|---|---|
| Poverty by Numbers: | |
| Population: | 112,322,757 (2010 Census) |
| Population below Poverty Line: | 44.2% (49,646,658) |
| Population in Moderate Poverty: | 33.7% (37,852,769) |
| Population in Extreme Poverty: | 10.5% (11,793,889) |
| Population without Access to Health Care: | 43.9 million (39.5%) |
| Poorest State: | Chiapas Chiapas Chiapas officially Estado Libre y Soberano de Chiapas is one of the 31 states that, with the Federal District, comprise the 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided in 118 municipalities and its capital city is Tuxtla Gutierrez. Other important cites in Chiapas include San Cristóbal de las... (76.7% below poverty line) |
| Richest State: | Baja California Sur Baja California Sur Baja California Sur , is one of the 31 states which, with the Federal District, comprise the 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. Before becoming a state on October 8, 1974, the area was known as the South Territory of Baja California. It has an area of , or 3.57% of the land mass of Mexico and comprises... (21.1% below poverty line) |
| National School Dropout Rate: | 21.7% |
| Highest Minimum Daily Wage: | US$4.45 (2010) |
| Source: | |
Poverty in Mexico is characterized as the lack of access of its citizens to basic human needs such as nutrition
Nutrition
Nutrition is the provision, to cells and organisms, of the materials necessary to support life. Many common health problems can be prevented or alleviated with a healthy diet....
, clean water
Drinking water
Drinking water or potable water is water pure enough to be consumed or used with low risk of immediate or long term harm. In most developed countries, the water supplied to households, commerce and industry is all of drinking water standard, even though only a very small proportion is actually...
, and shelter
Home
A home is a place of residence or refuge. When it refers to a building, it is usually a place in which an individual or a family can rest and store personal property. Most modern-day households contain sanitary facilities and a means of preparing food. Animals have their own homes as well, either...
; it extends to the overall infrastructure of its society to include education
Education
Education in its broadest, general sense is the means through which the aims and habits of a group of people lives on from one generation to the next. Generally, it occurs through any experience that has a formative effect on the way one thinks, feels, or acts...
, health care
Health care
Health care is the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of disease, illness, injury, and other physical and mental impairments in humans. Health care is delivered by practitioners in medicine, chiropractic, dentistry, nursing, pharmacy, allied health, and other care providers...
, social security
Social security
Social security is primarily a social insurance program providing social protection or protection against socially recognized conditions, including poverty, old age, disability, unemployment and others. Social security may refer to:...
, quality and basic services
Public utility
A public utility is an organization that maintains the infrastructure for a public service . Public utilities are subject to forms of public control and regulation ranging from local community-based groups to state-wide government monopolies...
in the household, income
Employment
Employment is a contract between two parties, one being the employer and the other being the employee. An employee may be defined as:- Employee :...
and social cohesion
Social cohesion
Social cohesion is a term used in social policy, sociology and political science to describe the bonds or "glue" that bring people together in society, particularly in the context of cultural diversity. Social cohesion is a multi-faceted notion covering many different kinds of social phenomena...
as defined by social development laws in the country.
The government currently uses a multidimensional system to measure the poverty threshold
Poverty threshold
The poverty threshold, or poverty line, is the minimum level of income deemed necessary to achieve an adequate standard of living in a given country...
in the country: extreme poverty
Extreme poverty
Extreme poverty, as defined in 1996 by Joseph Wresinski, the founder of ATD Fourth World, is:"The lack of basic security connotes the absence of one or more factors enabling individuals and families to assume basic responsibilities and to enjoy fundamental rights. The situation may become...
, moderate poverty, and overall poverty. The first measures the minimum amount of monetary means required to afford nutrition, also known as the basic goods basket, for all members of the household. The second combined with the first, measures the minimum required to afford basic health care and education as well. The latter adds to the first two, the minimum required to afford a dwelling, transportation, and overall basic expenses in the household.
Current figures indicate that as much as 44.2 percent of the Mexican population
Demographics of Mexico
With a population 112,336,538 in 2010, Mexico is the most populous Spanish-speaking country in the world, the second-most populous country in Latin America after Portuguese-speaking Brazil, and the second in North America, after the United States. Throughout most of the twentieth century Mexico's...
(over 49 million) lives below the poverty line as defined by the country's National Council of Social Development Policy Evaluation (Spanish
Spanish language
Spanish , also known as Castilian , is a Romance language in the Ibero-Romance group that evolved from several languages and dialects in central-northern Iberia around the 9th century and gradually spread with the expansion of the Kingdom of Castile into central and southern Iberia during the...
: Consejo Nacional de Evaluación de la Política de Desarrollo Social, CONEVAL). In 2008, 33.7% of the population lived in moderate poverty and at least 10.5% suffered from extreme poverty.
Historically, Mexico
Mexico
The United Mexican States , commonly known as Mexico , is a federal constitutional republic in North America. It is bordered on the north by the United States; on the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; on the southeast by Guatemala, Belize, and the Caribbean Sea; and on the east by the Gulf of...
's development has fallen behind of other developed nations and this restrain has been linked to tardiness in establishing social development as a national priority along with inadequate production models set by the Mexican government, bias politics, and corruption. In modern times, Mexico's heavy dependency on foreign influences, particularly its northern neighbor the United States and foreign trade policies that do not favor the common citizen have been cited as contributors to poverty. In general, decades of neglect have led to social enigmas like a high percentage of the population lacking formal education, unemployment
Unemployment
Unemployment , as defined by the International Labour Organization, occurs when people are without jobs and they have actively sought work within the past four weeks...
, and an overall uneven distribution
Economic inequality
Economic inequality comprises all disparities in the distribution of economic assets and income. The term typically refers to inequality among individuals and groups within a society, but can also refer to inequality among countries. The issue of economic inequality is related to the ideas of...
of opportunities. Only in recent years, after various economic setbacks, has Mexico recovered to a level where the middle class
Middle class
The middle class is any class of people in the middle of a societal hierarchy. In Weberian socio-economic terms, the middle class is the broad group of people in contemporary society who fall socio-economically between the working class and upper class....
, once virtually nonexistent, is beginning to flourish.
Mexico's positive potential and the result of millions in poverty is always a topic of discussion among opinion-makers. Some economists have speculated that in four more decades of continuous economic growth, despite common trends in Mexico such as emigration and violence
Crime in Mexico
Crime is among the most urgent concerns facing Mexico, as Mexican drug trafficking rings play a major role in the flow of cocaine, heroin, and marijuana transiting between Latin America and the United States. Drug trafficking has led to corruption, which has had a deleterious effect on Mexico's...
, Mexico will be among the five biggest economies in the world, along with the China
Economy of the People's Republic of China
The People's Republic of China ranks since 2010 as the world's second largest economy after the United States. It has been the world's fastest-growing major economy, with consistent growth rates of around 10% over the past 30 years. China is also the largest exporter and second largest importer of...
, the United States
Economy of the United States
The economy of the United States is the world's largest national economy. Its nominal GDP was estimated to be nearly $14.5 trillion in 2010, approximately a quarter of nominal global GDP. The European Union has a larger collective economy, but is not a single nation...
, Japan
Economy of Japan
The economy of Japan, a free market economy, is the third largest in the world after the United States and the People's Republic of China, and ahead of Germany at 4th...
, and India
Economy of India
The Economy of India is the ninth largest in the world by nominal GDP and the fourth largest by purchasing power parity . The country is a part of the G-20 major economies and the BRICS, in addition to being partners of the ASEAN. India has a per capita GDP of $3,608 as per 2010 figures, making it...
.
In recent times, extensive changes in government economic policy and attempts at reducing government interference through privatization of several sectors, for better or worst, has allowed Mexico to historically remain the biggest economy in Latin America, until 2005 when it became the second-largest; and a so-called "trillion dollar club
Trillion dollar club
The Trillion dollar club is an unofficial classification of the world's major economies with a gross domestic product of more than USD 1 trillion per year....
" member. Despite theses changes, Mexico continues to suffer great social inequality and lack of opportunities. The current administration
Felipe Calderón
Felipe de Jesús Calderón Hinojosa is the current President of Mexico. He assumed office on December 1, 2006, and was elected for a single six-year term through 2012...
has made an approach at reducing poverty in the country, to provide more opportunities to its citizens such as jobs, education and health care.
Background
Social stratificationSocial stratification
In sociology the social stratification is a concept of class, involving the "classification of persons into groups based on shared socio-economic conditions ... a relational set of inequalities with economic, social, political and ideological dimensions."...
is still highly present in Mexico can be traced back to the country's origin
History of Mexico
The history of Mexico, a country located in the southern portion of North America, covers a period of more than two millennia. First populated more than 13,000 years ago, the country produced complex indigenous civilizations before being conquered by the Spanish in the 16th Century.Since the...
. In the Colonial Period
New Spain
New Spain, formally called the Viceroyalty of New Spain , was a viceroyalty of the Spanish colonial empire, comprising primarily territories in what was known then as 'América Septentrional' or North America. Its capital was Mexico City, formerly Tenochtitlan, capital of the Aztec Empire...
, before its independence, the upper class was composed of those who owned the land and the lower class was made of those who worked the land. After the Mexican Revolution
Mexican Revolution
The Mexican Revolution was a major armed struggle that started in 1910, with an uprising led by Francisco I. Madero against longtime autocrat Porfirio Díaz. The Revolution was characterized by several socialist, liberal, anarchist, populist, and agrarianist movements. Over time the Revolution...
, the government ceded an estimated 50 percent of the land to the general population, covering a small portion of the gap between the wealthy and the poor. Land ownership continued to be main source of wealth for Mexicans and has dictated the hierarchy of wealth distribution amongst the population. After the country entered its economic industrial transformation
Mexican miracle
The Mexican miracle refers to the country's inward-looking development strategy that produced sustained economic growth of 3 to 4 percent and modest 3 percent inflation annually from the 1940s until the 1970s.-Background:...
, industrialists, businessmen, and politicians have controlled the direction of wealth in Mexico and have remained among the wealthy.
The average individual gross annual income in Mexico in 2002 was US$6,879.37 (2010 dollars). 12.3 percent of the Mexican labor force earns the daily minimum wage
Minimum wage
A minimum wage is the lowest hourly, daily or monthly remuneration that employers may legally pay to workers. Equivalently, it is the lowest wage at which workers may sell their labour. Although minimum wage laws are in effect in a great many jurisdictions, there are differences of opinion about...
or MX$
Mexican peso
The peso is the currency of Mexico. Modern peso and dollar currencies have a common origin in the 15th–19th century Spanish dollar, most continuing to use its sign, "$". The Mexican peso is the 12th most traded currency in the world, the third most traded in the Americas, and by far the most...
1,343.28 per month (approx. US$111.94 November 2010 exchange rates). 20.5 of the labor force earns twice the minimum wage and 21.4 percent earns up to three times the daily minimum wage while 18.6 earn no more than five daily minimum wages. Only 11.8 percent of the working population earn wages equal or above MX$6,716.40 (US$559.70) per month. Poverty line guidelines set the minimum cost of living at MX$1,586.54 (approx. UD$132.21, November 2010 exchange rates) per month, per member of the household. This means, a family of four must have monthly funds of at least MX$6,346.16 (US$528.84) to remain above the poverty line; far from the reality of millions of Mexican families whose earnings make them unable to manage their homes and maintain basic necessaries such as food and clothes for their families and the opportunity to send their children to school.
Government involvement
Social development begin to take place in the form of written policy in the early 1900s. The Mexican ConstitutionConstitution of Mexico
The Political Constitution of the United Mexican States is the current constitution of Mexico. It was drafted in Santiago de Querétaro, in the State of Querétaro, by a constitutional convention, during the Mexican Revolution. It was approved by the Constitutional Congress on February 5, 1917...
, approved in 1917, outlined the basic social protections citizens are entitled to, including the right to property
Property
Property is any physical or intangible entity that is owned by a person or jointly by a group of people or a legal entity like a corporation...
, education, health care, and employment; and it establishes the federal government responsible for the execution and enforcement of these protections.
Great Depression
The Great Depression was a severe worldwide economic depression in the decade preceding World War II. The timing of the Great Depression varied across nations, but in most countries it started in about 1929 and lasted until the late 1930s or early 1940s...
slowed down any possibility of social development in the country. Between the 1920s and the 1940s, poverty levels remained between 53 to 48 percent while illiteracy levels range between 61.5 to 58 percent. Between the 1930s and 1940s, the government focused on establishing social protection institutions. By the late 1950s, 59 percent of the population knew how to read and write. By the 1960s, individual involvement of some states to increase social development, along with the country's economic growth, as well as employment opportunities and greater income, and the migration of people from the rural states to the urban areas, helped reduced poverty nationwide. The 1970s and 1980s saw the transformation of government and economic policies. The government gave way to flexible foreign trade, deregulation and privatization of several sectors. After the economic crisis of the 1990s
1994 economic crisis in Mexico
The 1994 Economic Crisis in Mexico, widely known as the Mexican peso crisis, was caused by the sudden devaluation of the Mexican peso in December 1994....
, Mexico recovered to become an emerging economic power; however, the amount of poor nationwide has remained constant even with the country's overall growth.
Regional segregation
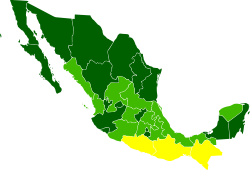
As reforms have taken place, the southern states have remained forgotten. These states have taken little part in establishing their infrastructure. The country's government has not focused on providing an even level of development and growth throughout the country. As citizens of the least fortunate states have noticed growth and improvements in others states, many have simply left seeking better opportunities. Historically, southern states like ChiapasChiapas
Chiapas officially Estado Libre y Soberano de Chiapas is one of the 31 states that, with the Federal District, comprise the 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided in 118 municipalities and its capital city is Tuxtla Gutierrez. Other important cites in Chiapas include San Cristóbal de las...
, Oaxaca
Oaxaca
Oaxaca , , officially Estado Libre y Soberano de Oaxaca is one of the 31 states which, along with the Federal District, comprise the 32 federative entities of Mexico. It is divided into 571 municipalities; of which 418 are governed by the system of customs and traditions...
, and Guerrero
Guerrero
Guerrero officially Estado Libre y Soberano de Guerrero is one of the 31 states which, with the Federal District, comprise the 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided in 81 municipalities and its capital city is Chilpancingo....
have remained segregated from the rest of the country. Their implementation of infrastructure, social development, education, and economic growth has been poorly accounted for. These states hold the highest levels of illiterates, unemployment, lack of basic services such as running water and sanitation, overall urban infrastructure, and government establishment.
Causes of poverty
The reasons for poverty in Mexico are complex and widely extensive. There is a consensual agreement that a combination of uneven distribution of wealth and resources sponsored by economic and political agendas to favor the rich and powerful is a major contributor to the millions left behind.Individual condition
In the economic sense, access to insufficient monetary means to afford goods and services becomes the immediate reason to be poor. Because a person's personal income dictates what he or she can afford and what he or she will remain deprived of, the first common cause of poverty is the individual condition. This means, a person's individual circumstances and possibilities create their opportunity for access to goods and services. This condition is triggered by a person's income, education, training or work experience, social network, age, health, and other socio-economic factors:- Lack of and unavailability of education
As population has grown, the number of students enrolled in schools throughout the country has grown tremendously since the 1950s. At the same time, government efforts to accommodate the growing student population, improving the quality of instruction and promoting prevalent school attendance has not been enough and therefore education
Education in Mexico
Education in Mexico is regulated by the Secretariat of Public Education . Education standards are set by this Ministry at all levels except in "autonomous" universities chartered by the government...
has not remained among priorities for families who must struggle with poverty. 700,000 students grades 1-9 dropped out of school in 2009 in all of Mexico. 7.9 percent (almost 9 million) of the population is illiterate. 73% of Mexican households have at least one member without education or education below the 7th grade. 40 percent of people in the states of Chiapas
Chiapas
Chiapas officially Estado Libre y Soberano de Chiapas is one of the 31 states that, with the Federal District, comprise the 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided in 118 municipalities and its capital city is Tuxtla Gutierrez. Other important cites in Chiapas include San Cristóbal de las...
, Veracruz
Veracruz
Veracruz, formally Veracruz de Ignacio de la Llave officially Estado Libre y Soberano de Veracruz de Ignacio de la Llave , is one of the 31 states that, along with the Federal District, comprise the 32 federative entities of Mexico. It is divided in 212 municipalities and its capital city is...
, Hidalgo, Oaxaca
Oaxaca
Oaxaca , , officially Estado Libre y Soberano de Oaxaca is one of the 31 states which, along with the Federal District, comprise the 32 federative entities of Mexico. It is divided into 571 municipalities; of which 418 are governed by the system of customs and traditions...
and Guerrero
Guerrero
Guerrero officially Estado Libre y Soberano de Guerrero is one of the 31 states which, with the Federal District, comprise the 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided in 81 municipalities and its capital city is Chilpancingo....
have education below the 7th grade. There are virtually no opportunities for people without education in Mexico. With daily minimum wages so low, individuals without the training or education beyond high school are unable to compete in an economy where even the educated struggle with laborer-scale wages, unable to afford a minimum standard of living.
- Underemployment
Getting an education does not immediately translate to landing better paying jobs
Underemployment
Underemployment refers to an employment situation that is insufficient in some important way for the worker, relative to a standard. Examples include holding a part-time job despite desiring full-time work, and overqualification, where the employee has education, experience, or skills beyond the...
or overcoming unemployment in Mexico. As compared to other countries, such as the United States where a college degree can be the difference between a minimum wage position and a higher-paying job because higher education
Higher education
Higher, post-secondary, tertiary, or third level education refers to the stage of learning that occurs at universities, academies, colleges, seminaries, and institutes of technology...
is required or appreciated. There are only a few better paying jobs in Mexico for university and other well-educated graduates. In fact, many college degrees holders find themselves earning wages too low to support themselves and their families. Situations like this have cause the standard of living among the urban middle class to deteriorate and as a consequence brings on emigration from this sector to other countries, mainly the United States and Canada
Canada
Canada is a North American country consisting of ten provinces and three territories. Located in the northern part of the continent, it extends from the Atlantic Ocean in the east to the Pacific Ocean in the west, and northward into the Arctic Ocean...
.
- Other challenges
Mexico does not promote equal opportunity employment
Equal Opportunity Employment
Title VII of the Civil Rights Act of 1964 was the first federal law designed to protect most U.S. employees from employment discrimination based upon that employee's race, color, religion, sex, or national origin . The Title also established the U.S...
despite established laws forbidding most socially-recognized forms of discrimination. The government doesn't become sufficiently involved to promote opportunities to all citizens; including reducing discrimination against middle-age and elder citizens. Over a million of the unemployed face age discrimination and 55% of all unemployed face some form of discrimination when seeking employment. There are virtually no opportunities for individuals with special requirements such as the disabled. As job seekers become older, it is harder for them to get employed as employers tend to seek candidates within the "younger than 35 range". Social security (IMSS) is insufficient and there is a huge gap in proportion to the entire population (50% covered), the work force (30% covered), and the retired (33% covered). There is no unemployment insurance in Mexico.
Insufficient infrastructure
Mexico is a country where investment on infrastructure has remained as unequally distributed as income, specially in rural areas and in the southern states. The government did not make significant efforts to invest in overall infrastructure of the entire country up until the 1990s. Communities often face a combination of unpaved roads, lack of electricity and potable water, improper sanitation, poorly maintained schools, vandalism and crime, and lack of social development programs. The government did not begin to focus on improving and modernizing the federal highway system up until two decades ago when it was composed of two-lane roads; often deathtraps and the scenarios of head-on collusions between truckers and families on vacation. A tour of any major city in Mexico is sufficient to see the uneven distribution of resources and public investment. City and state governments often face challenges providing every community and citizen with the basic services of urbanized life. Often citizens must provide for the development of their own neighborhoods as there is no clearly visible government agency in charge of providing regular city management and maintenance services, including tax collection and/or distribution of funds to places of most need. Because of this, higher income communities will invest in the development of their own communities while lower income communities will be deprived of the basics such as running water and drainage.- Geography and poverty
The concentration of poverty and distribution of wealth and opportunities is clearly visible from a geographic perspective. The northern region of the country offers higher development while the southern states are the most impoverished. This is clearly the result of states equipped with better infrastructure that others. The states of Chiapas, Oaxaca, and Guerrero are among the least developed in the country. These states hold the highest numbers of indigenous population. As a result, 75 percent of the indigenous population lives below the poverty line and 39 percent under extreme poverty. Their infrastructure is broken to the basics such as lack of roads, access to education, health services, and employment sources.
Unemployment
Unemployment in Mexico has been continuous. In 2009, the unemployment rate was estimated at 5.5 percent (over 2.5 million). In spite of splendid macroeconomic indicators that currently exist: continuing low levels of inflationInflation
In economics, inflation is a rise in the general level of prices of goods and services in an economy over a period of time.When the general price level rises, each unit of currency buys fewer goods and services. Consequently, inflation also reflects an erosion in the purchasing power of money – a...
and stability in the nation’s currency exchange rate
Exchange rate
In finance, an exchange rate between two currencies is the rate at which one currency will be exchanged for another. It is also regarded as the value of one country’s currency in terms of another currency...
; a sufficient number of formal jobs- at least one million every year to keep up with the growing population- have not been created in over ten years. With the abundance of natural resources in the country- as well as its petroleum wealth, these benefits don't seem to reach many of the people of Mexico who lack job opportunities and the means to raise their standards of living out of poverty and marginalization.
In order to improve present day employment opportunities in Mexico, existing laws and regulations must be replaced for efficient instruments with greater legal certainty; encourage private investment; increase the collection of taxes; stimulate the productivity of businesses and the training of workers; and create more and better jobs.
- Inequitable distribution of income
Mexico’s inequitable distribution of wealth is among the highest in the world. Eighty-five percent of the national wealth is concentrated in a few families of entrepreneurs, corporate magnates, and politicians. Carlos Slim, the richest man in Mexico and in the world has a personal fortune equal to 4 to 6 percent of the country's GDP. In spite of efforts by government officials during the past three administrations; transition to globalization
Globalization
Globalization refers to the increasingly global relationships of culture, people and economic activity. Most often, it refers to economics: the global distribution of the production of goods and services, through reduction of barriers to international trade such as tariffs, export fees, and import...
, the NAFTA agreement; Mexico has been unable to create efficient public policies in order to compensate for the distortion of its market and the poor distribution of national income.
- Obsolete regulatory framework
The absence of basic agreements among Mexico’s main political parties for more than ten years has caused a serious backwardness in needed legislation in a number of areas. As a result of structural reform failures on labor, fiscal, energy and legal matters, Mexico has fallen behind reducing poverty and encouraging development comparable to Latin American countries like Chile
Chile
Chile ,officially the Republic of Chile , is a country in South America occupying a long, narrow coastal strip between the Andes mountains to the east and the Pacific Ocean to the west. It borders Peru to the north, Bolivia to the northeast, Argentina to the east, and the Drake Passage in the far...
, Argentina
Argentina
Argentina , officially the Argentine Republic , is the second largest country in South America by land area, after Brazil. It is constituted as a federation of 23 provinces and an autonomous city, Buenos Aires...
, Brazil and Costa Rica
Costa Rica
Costa Rica , officially the Republic of Costa Rica is a multilingual, multiethnic and multicultural country in Central America, bordered by Nicaragua to the north, Panama to the southeast, the Pacific Ocean to the west and the Caribbean Sea to the east....
. The current economic framework needs adjustment on virtually all levels including business development opportunities, fair competition, tax collection and tax law; commerce, trade and finance regulations.
- Absent competitive principles
The Mexican economy does not support unprivileged businesses, considering its current standards regarding monopolies, both in the public and private sectors. By law, there are public monopolies: government-owned companies controlling oil and gas, electricity, water, etc. Private sector monopolies are found in the media, television, telecommunications, and raw materials. There have been a lot of loop holes in Mexican antitrust laws and only recently has the Mexican congress taken action. For this reason, clear principles of competitiveness that offer incentives to private investment, both national and foreign, are needed in order for jobs to be created.
Government and politics
Mexico's rampant poverty, lagged social development and general public welfare is strongly tied to its politics. Historically, the political system of MexicoPolitics of Mexico
The politics of Mexico take place in a framework of a federal presidential representative democratic republic whose government is based on a congressional system, whereby the president of Mexico is both head of state and head of government, and of a multi-party system...
has not favored the general population, mainly because it focused to become and be a single-party system of government, largely dubbed "institutionalized" where those in charge had a one-voice, unquestionable plan of action mainly focused to favor the few elite while ignoring the welfare of the rest of population. From the 1800s to the end of the 20th century, as presidential administration came and went, the forms of government has been described as authoritarian, semi-democracy, centralized government, untouchable presidencies, mass-controlling, corporatist and elite-controlled. As each administration took turn, some changes have occurred, sometimes as to contribute to the welfare of the least fortunates but, overall, the political framework behind the economic and social structure of the country continues to be the greatest contributor to inequality.
- Foreign Trade Policies and Foreign Dependence
While the NAFTA agreement proved effective in increasing Mexico's economic performance, foreign trade policies have been heavily criticized by activists such as Micheal Moore (in Awful Truth
The Awful Truth (TV series)
The Awful Truth was a satirical television show that was directed, written, and hosted by filmmaker Michael Moore, and funded by the British broadcaster Channel 4.-Format:...
) as not doing enough to promote social advancement and reducing poverty. To remain competitive in the international market, Mexico has had to offer low wages to its workers while allowing high returns and generous concessions to international corporations. The words "palancas" and "favores" are part of Mexican economic culture where high-ranking policy makers and private entrepreneurs are accused of promoting their own bottom line while ignoring the necessaries of the working class.
Current recessionary trends in the United States have an even greater impact on Mexico because of the great economic dependence on the northern neighbor. After crude oil export sales, remittances sent home by Mexicans working in the United States are Mexico’s second largest source of foreign income.
- Government Efforts and Economic Policies
Administration after administration, economic policies and social development programs have been targeted at decreasing poverty and increasing development in the country. Even with the best of intentions, friction between the "special interests" of decision-makers and the general public welfare, makes it difficult for clear goals in the benefit of the public to be accomplished.
Cancun
Cancún
Cancún is a city of international tourism development certified by the UNWTO . Located on the northeast coast of Quintana Roo in southern Mexico, more than 1,700 km from Mexico City, the Project began operations in 1974 as Integrally Planned Center, a pioneer of FONATUR Cancún is a city of...
is an excellent example of where the government failed to promote general welfare. While known for its crispy white beaches, fancy hotels of international renown, and spring break
Spring break
Spring break – also known as March break, Study week or Reading week in the United Kingdom and some parts of Canada – is a recess in early spring at universities and schools in the United States, Canada, mainland China, Korea, Japan, Taiwan, Mexico, the Dominican Republic, the United...
; Cancun is a faraway reality for most Mexicans. One only needs to step away from the exclusive hotel strip to discover how even in one of the most touristic destinations in the world, an uneven distribution of wealth and development remains. As many other projects in Mexico, Cancun was envisioned to promote economic growth but while it contributes significantly to the Mexican economy, it falls short to boost social development and reduce poverty either regionally or nationwide.
- Transparency and Corruption
The lack of political transparency in Mexico has led to bureaucratic corruption and market inefficiencies, and as explained below, income inequalities. The ability to exercise civil rights has been increasingly displaced by the control of official authorities, including access to vital information that can capture the misappropriation and mis-allocation of funds, and public participation in state and municipal-level decision-making. This opens up a channel for corruption. Evidence of this can be derived from the Corruption Perception Index 2010: Mexico received a low score of 3.1, on a scale of 0 to 10 (lower scores represent higher levels of corruption). The result is a diffusion of corruption, from the state to the municipal level, and even right down to local security.
While it can be difficult to quantify the costs of corruption with pinpoint accuracy, a report from the UN estimates that the cost is about 15 percent of Mexico’s GNP, and 9 percent of its GDP. Such higher costs have adversely affected the growth of the economy, for instance deterring foreign investments due to uncertainty and risk. A study by Pricewaterhouse Coopers reveals that Mexico had lost $8.5 billion in foreign direct investments in 1999 due to corruption. Business companies admit to spend as much as 10 percent of their revenue in bureaucratic bribes. 39 percent is spent on bribing high-ranking policy makers and 61 percent on lower-ranking bureaucratic-administrative office holders. At least 30 percent of all public spending ends up in the pockets of the corrupt.
Even the domestic impact of corruption is no less severe, incurring additional expenses on firms and households. A family on average pays 109.50 pesos as bribes to authorities; households have also reported paying up to 6.9 percent of their income as bribes. In total, the cost of corruption in terms of GDP was estimated to be about $550bn in 2000.
The situation is still problematic in spite of recent initiatives by the state to become more transparent to the public. Over the years, there has been an effort by the government to reduce opacity, but even so, these initiatives often do not realize their full potential. In June 2003, under Vincente Fox’s presidency, the implementation of the Federal Law of Transparency and Access to Public Government Information (IFAI) offered civic organizations and members of the public to acquire previously undisclosed information. This reform has led to the exposure of previous under-the-radar activities, such as the government’s misappropriation of 200 million pesos that was intended to combat AIDS. And yet, censorship is still prevalent: in 2008, changes were proposed to increase the subjugation of IFAI’s decisions to state control, so that the distribution of information would become more centralized. A number of vertical subversions were also carried out at the time, including the merging of offices that handled information requests with less important agencies. This violated the earlier progressive changes to the constitution, including Article 6, so that transparency was threatened.
Opacity is therefore a major player as a determinant of inequality, especially in effecting the welfare of lower-class households. When resources are misallocated and official funds pocketed by illegitimate parties, the true quality of public services such as healthcare tend to be lower than expected; similarly, the secrecy of the government’s budget allocation prevents public scrutiny, so it is difficult to establish financial accountability. As well, from a broader perspective, vital infrastructure from projects, especially those aimed at facilitating social mobility, will also have to deal with the potential impediments caused by the overpricing effect and unnecessary risks of corruption, thereby reducing the accessibility of infrastructure for the poor, especially in rural areas where such infrastructure is less established than in urban areas.
Reducing poverty
Poverty aid organizations and social development groups have remained active in Mexico. Despite foreign and national aid programs in the country, the overall level of poverty in the country prevails.Government approach
- In 1997, the Mexican government launched PROGRESA (Spanish: Programa de Educación, Salud y Alimentación), an integrated approach to poverty alleviation through the development of human capital.
- In 2002, the Social Development Secretary (SEDESOL) replaced PROGRESA with Oportunidades (English: Opportunities); extending coverage to the urban poor and aiding high school students.
Transparency Collective
The Transparency Collective, or El Colectivo por la Transparencia in Spanish, is a non-governmental collective organization that advocates transparency in Mexico. It was first formed by six civil society organizations in 2002 to demand for greater transparency from state agencies, and the right to access information. Currently, it consists of eleven civil society groups with the common goal of strengthening democracy and raising accountability and the transparency of the state. The Transparency Collective offers an avenue for locals to seek help in obtaining the right to information by offering manuals and online tutorials teaching the locals how to file a request for information. It also discusses topics like human rights, the legislature and government budgets so that locals will be more informed and aware of their rights. For example, Fundar, an NGO which specializes in government budget analysis, runs workshops to educate the public on disseminating information released by government agencies.The Transparency Collective has also been working with IFAI (Federal Institute of Access to Information). The civil society was productively engaged in the reform of the constitution. For example, CIDE, an academic focusing on public policy, worked at state level helping states comply with the reform. Fundar also focused on evaluating government responses to information requests, the appeals process and on training groups to analyze information released by the government.
Despite the organizational size of the Transparency Collective, collectivization has nonetheless been an important factor in its effectiveness. The collective call for greater transparency was one of the reasons for the comprehensive reform of Article 6 of the Mexican constitution in 2007, which heralded a new level of progression for Mexico's right-to-know movement. The reforms guaranteed the public's rights to non-confidential information at all levels of the government. State transparency laws also had to be standardized around certain basic principles within a year, and states had to implement electronic information systems.
However, in spite of this, there is still a considerable way to go to achieve full transparency. The 2008 constitutional amendments, and interference of the judiciary branch with the demanded disclosure of tax information, threatened the FOI laws that were previously established. Nevertheless, this movement has been met with fierce protests from civil society groups, and the Collective continues to appeal to the government to allow for more civil participation.
Demographics
- Mexico's wealth is unevenly distributed among its people where 10 percent of nation's wealthiest have 42.2 percent of all income and 10 percent of the nation's poorest have 1.3 of the remaining income.
- 53.4 percent of the rural population and 36.2 percent of the urban population has education below the 7th grade. 18.9 percent of the rural population and 8.9 percent of the urban population lacks any form of formal education.
- Current figures estimate that at least 44.2 percent of the population lives under poverty. Of those, 33.7 live under a moderate state of poverty and at least 10.5 percent live under extreme poverty.
- States with highest human development: Baja California Norte, Baja California SurBaja California SurBaja California Sur , is one of the 31 states which, with the Federal District, comprise the 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. Before becoming a state on October 8, 1974, the area was known as the South Territory of Baja California. It has an area of , or 3.57% of the land mass of Mexico and comprises...
, Chihuahua, CoahuilaCoahuilaCoahuila, formally Coahuila de Zaragoza , officially Estado Libre y Soberano de Coahuila de Zaragoza is one of the 31 states which, with the Federal District, comprise the 32 Federal Entities of Mexico...
, ColimaColimaColima is one of the 31 states which, with the Federal District, make up the 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. It shares its name with its capital and main city, Colima....
, Federal District, Nuevo LeónNuevo LeónNuevo León It is located in Northeastern Mexico. It is bordered by the states of Tamaulipas to the north and east, San Luis Potosí to the south, and Coahuila to the west. To the north, Nuevo León has a 15 kilometer stretch of the U.S.-Mexico border adjacent to the U.S...
, Quintana RooQuintana RooQuintana Roo officially Estado Libre y Soberano de Quintana Roo is one of the 31 states which, with the Federal District, comprise the 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided in 10 municipalities and its capital city is Chetumal....
, SinaloaSinaloaSinaloa officially Estado Libre y Soberano de Sinaloa is one of the 31 states which, with the Federal District, comprise the 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided in 18 municipalities and its capital city is Culiacán Rosales....
, SonoraSonoraSonora officially Estado Libre y Soberano de Sonora is one of the 31 states which, with the Federal District, comprise the 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided into 72 municipalities; the capital city is Hermosillo....
, and TamaulipasTamaulipasTamaulipas officially Estado Libre y Soberano de Tamaulipas is one of the 31 states which, with the Federal District, comprise the 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided in 43 municipalities and its capital city is Ciudad Victoria. The capital city was named after Guadalupe Victoria, the...
.
- States with lowest human development: Chiapas, Guerrero, Hidalgo, MichoacánMichoacánMichoacán officially Estado Libre y Soberano de Michoacán de Ocampo is one of the 31 states which, with the Federal District, comprise the 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided in 113 municipalities and its capital city is Morelia...
, Oaxaca, PueblaPueblaPuebla officially Estado Libre y Soberano de Puebla is one of the 31 states which, with the Federal District, comprise the 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided in 217 municipalities and its capital city is Puebla....
, TabascoTabascoTabasco officially Estado Libre y Soberano de Tabasco is one of the 31 states which, with the Federal District, comprise the 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided in 17 municipalities and its capital city is Villahermosa....
, TlaxcalaTlaxcalaTlaxcala officially Estado Libre y Soberano de Tlaxcala is one of the 31 states which along with the Federal District comprise the 32 federative entities of Mexico. It is divided into 60 municipalities and its capital city is Tlaxcala....
, Veracruz, and ZacatecasZacatecasZacatecas officially Estado Libre y Soberano de Zacatecas is one of the 31 states which, with the Federal District, comprise the 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided in 58 municipalities and its capital city is Zacatecas....
.
World comparison
- Mexico is the second richest country in Latin America, after BrazilBrazilBrazil , officially the Federative Republic of Brazil , is the largest country in South America. It is the world's fifth largest country, both by geographical area and by population with over 192 million people...
; and the second Latin American country with most number of poor, after Brazil as well; given Mexico's population is about 80 million less than Brazil.
- Mexico has the 11th to 13th richest economy in the world and ranks 4th with most number of poor among richest economies.
- Mexico is the 10th to 13th country with the most number of poor in the world.
- Of the ten countries with greater population, Mexico ranks 8th as nation with most number of poor behind the People's Republic of ChinaPeople's Republic of ChinaChina , officially the People's Republic of China , is the most populous country in the world, with over 1.3 billion citizens. Located in East Asia, the country covers approximately 9.6 million square kilometres...
, IndiaIndiaIndia , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
, IndonesiaIndonesiaIndonesia , officially the Republic of Indonesia , is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania. Indonesia is an archipelago comprising approximately 13,000 islands. It has 33 provinces with over 238 million people, and is the world's fourth most populous country. Indonesia is a republic, with an...
, Brazil, PakistanPakistanPakistan , officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan is a sovereign state in South Asia. It has a coastline along the Arabian Sea and the Gulf of Oman in the south and is bordered by Afghanistan and Iran in the west, India in the east and China in the far northeast. In the north, Tajikistan...
, NigeriaNigeriaNigeria , officially the Federal Republic of Nigeria, is a federal constitutional republic comprising 36 states and its Federal Capital Territory, Abuja. The country is located in West Africa and shares land borders with the Republic of Benin in the west, Chad and Cameroon in the east, and Niger in...
, and BangladeshBangladeshBangladesh , officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh is a sovereign state located in South Asia. It is bordered by India on all sides except for a small border with Burma to the far southeast and by the Bay of Bengal to the south...
.
- Of 169 United NationsUnited NationsThe United Nations is an international organization whose stated aims are facilitating cooperation in international law, international security, economic development, social progress, human rights, and achievement of world peace...
members, at least 113 nations show higher levels of poverty and decreased social development and at least 55 other nations have less poverty and higher social development.
- Mexico ranks 56th among most developed of the world's nations. It ranks 4th as most developed of Latin American countries, behind ChileChileChile ,officially the Republic of Chile , is a country in South America occupying a long, narrow coastal strip between the Andes mountains to the east and the Pacific Ocean to the west. It borders Peru to the north, Bolivia to the northeast, Argentina to the east, and the Drake Passage in the far...
, ArgentinaArgentinaArgentina , officially the Argentine Republic , is the second largest country in South America by land area, after Brazil. It is constituted as a federation of 23 provinces and an autonomous city, Buenos Aires...
, and UruguayUruguayUruguay ,officially the Oriental Republic of Uruguay,sometimes the Eastern Republic of Uruguay; ) is a country in the southeastern part of South America. It is home to some 3.5 million people, of whom 1.8 million live in the capital Montevideo and its metropolitan area...
.
Further reading
- Kevin J. Middlebrook and Eduardo Zepeda (2003), Confronting Development, Stanford University PressStanford University PressThe Stanford University Press is the publishing house of Stanford University. In 1892, an independent publishing company was established at the university. The first use of the name "Stanford University Press" in a book's imprinting occurred in 1895...
- Assessing Mexico’s Economic and Social Policy Challenges. - Daniel Hernández Franco, Cristina Barberena Rioseco, José Ángel Camacho Prudente, Hadid Vera Llamas (2003) Desnutrición Infantil y Pobreza en México, Secretariat of Social DevelopmentSecretariat of Social DevelopmentThe Secretariat of Social Development is the government department in charge of social development efforts in Mexico...
(SEDESOL) - Study on child malnutrition and poverty in Mexico. - Gordon H. Hanson (2005), Globalization, Labor Income, and Poverty in Mexico, National Bureau of Economic ResearchNational Bureau of Economic ResearchThe National Bureau of Economic Research is an American private nonprofit research organization "committed to undertaking and disseminating unbiased economic research among public policymakers, business professionals, and the academic community." The NBER is well known for providing start and end...
- Study on globalization and how it affected income and poverty in Mexico. - Luis Vega Martínez (2005), La Pobreza en México, UNAMUnamUNAM or UNaM may refer to:* National University of Misiones, a National University in Posadas, Argentina*National Autonomous University of Mexico , the large public autonomous university based in Mexico City...
- University professor's views and thoughts on poverty in Mexico. - Gabriela Pérez Yarahuán (2007), Social Development Policy, Expenditures and Electoral Incentives in Mexico, Universidad Iberoamericana-Ciudad de MéxicoUniversidad IberoamericanaThe Ibero-American University is a Mexican private institution of higher education sponsored by the Society of Jesus...
- Discussions and theories on social development policy in Mexico from 1990s and onward. - Francis Fukuyama (2008), Falling Behind: Explaining the Development Gap Between Latin America and the United States, Oxford University PressOxford University PressOxford University Press is the largest university press in the world. It is a department of the University of Oxford and is governed by a group of 15 academics appointed by the Vice-Chancellor known as the Delegates of the Press. They are headed by the Secretary to the Delegates, who serves as...
- Collection of essays discussing reasons for development gap between the United States and Latin America.
External links
- CONEVAL- Government Agency in charge of Social Development Studies
- United Nations Development Programme in Mexico
- Transparency International in the Americas
- Fondo España-PNUD in Latin America and Caribbean - attempts to promote social development policies.

