
New Zealand–United States relations
Encyclopedia


New Zealand
New Zealand is an island country in the south-western Pacific Ocean comprising two main landmasses and numerous smaller islands. The country is situated some east of Australia across the Tasman Sea, and roughly south of the Pacific island nations of New Caledonia, Fiji, and Tonga...
and the United States of America
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
. According to the U.S. State Department, relations as of August 2011 are "the best they have been in decades."
After U.S. president Barack Obama
Barack Obama
Barack Hussein Obama II is the 44th and current President of the United States. He is the first African American to hold the office. Obama previously served as a United States Senator from Illinois, from January 2005 until he resigned following his victory in the 2008 presidential election.Born in...
and New Zealand prime minister John Key
John Key
John Phillip Key is the 38th Prime Minister of New Zealand, in office since 2008. He has led the New Zealand National Party since 2006....
's first conversation, Obama acknowledged a very strong relationship between the two countries but said he wanted that relationship to be even better. New Zealand is a major non-NATO ally
Major non-NATO ally
Major non-NATO ally is a designation given by the United States government to close allies who have strategic working relationships with US armed forces but are not members of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization...
of the United States.
Both the United States and New Zealand share some common ancestry and history (having both been British colonies. Both countries had native peoples who were at times dispossessed of their land by the process of colonisation. Both have been part of the Western alliance of nations in various wars. The two countries are both developed economies with democratically-elected governments.
History

The United States established consular representation in New Zealand in 1838 to represent and protect American shipping and whaling interests, appointing James Reddy Clendon
James Reddy Clendon
James Reddy Clendon was an early European settler in New Zealand, the first United States Consul to New Zealand, and a witness to the Treaty of Waitangi.-Early life:...
as Consul, resident in Russell. In 1840, New Zealand became part of the British Empire
British Empire
The British Empire comprised the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom. It originated with the overseas colonies and trading posts established by England in the late 16th and early 17th centuries. At its height, it was the...
with the signing of the Treaty of Waitangi
Treaty of Waitangi
The Treaty of Waitangi is a treaty first signed on 6 February 1840 by representatives of the British Crown and various Māori chiefs from the North Island of New Zealand....
. Although it gradually grew more independent, for its first hundred years, New Zealand followed the United Kingdom
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
's lead on foreign policy. In declaring war on Germany
Germany
Germany , officially the Federal Republic of Germany , is a federal parliamentary republic in Europe. The country consists of 16 states while the capital and largest city is Berlin. Germany covers an area of 357,021 km2 and has a largely temperate seasonal climate...
on 3 September 1939, Prime Minister Michael Joseph Savage
Michael Joseph Savage
Michael Joseph Savage was the first Labour Prime Minister of New Zealand.- Early life :Born in Tatong, Victoria, Australia, Savage first became involved in politics while working in that state. He emigrated to New Zealand in 1907. There he worked in a variety of jobs, as a miner, flax-cutter and...
proclaimed, "Where she goes, we go; where she stands, we stand".
Guadalcanal, Tarawa, Iwo Jima and beyond

Battle of Tarawa
The Battle of Tarawa, code named Operation Galvanic, was a battle in the Pacific Theater of World War II, largely fought from November 20 to November 23, 1943. It was the first American offensive in the critical central Pacific region....
, Guadacanal
Guadalcanal campaign
The Guadalcanal Campaign, also known as the Battle of Guadalcanal and codenamed Operation Watchtower by Allied forces, was a military campaign fought between August 7, 1942 and February 9, 1943 on and around the island of Guadalcanal in the Pacific theatre of World War II...
, Saipan
Battle of Saipan
The Battle of Saipan was a battle of the Pacific campaign of World War II, fought on the island of Saipan in the Mariana Islands from 15 June-9 July 1944. The Allied invasion fleet embarking the expeditionary forces left Pearl Harbor on 5 June 1944, the day before Operation Overlord in Europe was...
and Iwo Jima
Battle of Iwo Jima
The Battle of Iwo Jima , or Operation Detachment, was a major battle in which the United States fought for and captured the island of Iwo Jima from the Empire of Japan. The U.S...
exerted an increased influence on culture, and the New Zealand people gained a clearer sense of national identity
National identity
National identity is the person's identity and sense of belonging to one state or to one nation, a feeling one shares with a group of people, regardless of one's citizenship status....
.

After the war, New Zealand joined with Australia
Australia
Australia , officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country in the Southern Hemisphere comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands in the Indian and Pacific Oceans. It is the world's sixth-largest country by total area...
and the United States in the ANZUS security treaty in 1951, and later fought alongside the United States in both the Korean
Korean War
The Korean War was a conventional war between South Korea, supported by the United Nations, and North Korea, supported by the People's Republic of China , with military material aid from the Soviet Union...
and Vietnam War
Vietnam War
The Vietnam War was a Cold War-era military conflict that occurred in Vietnam, Laos, and Cambodia from 1 November 1955 to the fall of Saigon on 30 April 1975. This war followed the First Indochina War and was fought between North Vietnam, supported by its communist allies, and the government of...
, plus the Gulf War
Gulf War
The Persian Gulf War , commonly referred to as simply the Gulf War, was a war waged by a U.N.-authorized coalition force from 34 nations led by the United States, against Iraq in response to Iraq's invasion and annexation of Kuwait.The war is also known under other names, such as the First Gulf...
and the current Afghanistan conflict
War in Afghanistan (2001–present)
The War in Afghanistan began on October 7, 2001, as the armed forces of the United States of America, the United Kingdom, Australia, and the Afghan United Front launched Operation Enduring Freedom...
.
ANZUS Treaty
The Australia, New Zealand, United States Security Treaty (ANZUS or ANZUS Treaty) is the military alliance which binds Australia and New Zealand and, separately, Australia and the United States to cooperate on defence matters in the Pacific OceanPacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest of the Earth's oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic in the north to the Southern Ocean in the south, bounded by Asia and Australia in the west, and the Americas in the east.At 165.2 million square kilometres in area, this largest division of the World...
area, though today the treaty is understood to relate to defence operations. While the ANZUS Treaty was once fully mutual between Australia, New Zealand and the United States, this is no longer the case due to New Zealand's ban of nuclear warships and the US's consequent suspension of treaty obligations to New Zealand.
Ultimately New Zealand has fought alongside the United States in multiple conflicts, including in the Second World War
World War II
World War II, or the Second World War , was a global conflict lasting from 1939 to 1945, involving most of the world's nations—including all of the great powers—eventually forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis...
, the Korean War
Korean War
The Korean War was a conventional war between South Korea, supported by the United Nations, and North Korea, supported by the People's Republic of China , with military material aid from the Soviet Union...
, the Vietnam War
Vietnam War
The Vietnam War was a Cold War-era military conflict that occurred in Vietnam, Laos, and Cambodia from 1 November 1955 to the fall of Saigon on 30 April 1975. This war followed the First Indochina War and was fought between North Vietnam, supported by its communist allies, and the government of...
, the Gulf War
Gulf War
The Persian Gulf War , commonly referred to as simply the Gulf War, was a war waged by a U.N.-authorized coalition force from 34 nations led by the United States, against Iraq in response to Iraq's invasion and annexation of Kuwait.The war is also known under other names, such as the First Gulf...
, and Afghanistan
War in Afghanistan (2001–present)
The War in Afghanistan began on October 7, 2001, as the armed forces of the United States of America, the United Kingdom, Australia, and the Afghan United Front launched Operation Enduring Freedom...
.
Post ANZUS thawing of military ties with the US
In May 2006, US Assistant Secretary of State for East Asian and Pacific AffairsAssistant Secretary of State for East Asian and Pacific Affairs
The Assistant Secretary of State for East Asian and Pacific Affairs is the head of the Bureau of East Asian and Pacific Affairs within the United States Department of State. The Assistant Secretary guides operation of the U.S...
, Christopher R. Hill
Christopher R. Hill
Christopher Robert Hill is an American diplomat who served as the U.S. Ambassador to Iraq.On July 1, 2010, Hill was chosen to be the dean of the Josef Korbel School of International Studies at the University of Denver...
, described the New Zealand anti-nuclear issue as "a relic", and signalled that the US wanted a closer defence relationship with New Zealand. He also praised New Zealand's involvement in Afghanistan
Afghanistan
Afghanistan , officially the Islamic Republic of Afghanistan, is a landlocked country located in the centre of Asia, forming South Asia, Central Asia and the Middle East. With a population of about 29 million, it has an area of , making it the 42nd most populous and 41st largest nation in the world...
and reconstruction in Iraq
Iraq
Iraq ; officially the Republic of Iraq is a country in Western Asia spanning most of the northwestern end of the Zagros mountain range, the eastern part of the Syrian Desert and the northern part of the Arabian Desert....
. "Rather than trying to change each other's minds on the nuclear issue, which is a bit of a relic, I think we should focus on things we can make work"
While there have been signs of the nuclear dispute between the United States and New Zealand thawing out, pressure from the United States increased in 2006 with US trade officials linking the repeal of the ban of American nuclear ships from New Zealand's ports to a potential free trade agreement between the two countries.
On an official visit to New Zealand in July 2008, when questioned on the issue of New Zealand Nuclear-free policy Secretary of State
United States Secretary of State
The United States Secretary of State is the head of the United States Department of State, concerned with foreign affairs. The Secretary is a member of the Cabinet and the highest-ranking cabinet secretary both in line of succession and order of precedence...
Condoleezza Rice
Condoleezza Rice
Condoleezza Rice is an American political scientist and diplomat. She served as the 66th United States Secretary of State, and was the second person to hold that office in the administration of President George W. Bush...
stated that "US and New Zealand have moved on. If there are remaining issues to be addressed then we should address them". She went on to say that: "New Zealand and the United States, Kiwis and Americans, have a long history of partnership. It is one that is grounded in common interests, but it is elevated by common ideals. And it is always defined by the warmth and the respect of two nations, but more importantly, of two peoples who are bound together by countless ties of friendship and family and shared experience."
Conflicts fought alongside the United States
New Zealand has fought in a number of conflicts on the same side as the United States, including World War IWorld War I
World War I , which was predominantly called the World War or the Great War from its occurrence until 1939, and the First World War or World War I thereafter, was a major war centred in Europe that began on 28 July 1914 and lasted until 11 November 1918...
, World War II
World War II
World War II, or the Second World War , was a global conflict lasting from 1939 to 1945, involving most of the world's nations—including all of the great powers—eventually forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis...
, the Korean War
Korean War
The Korean War was a conventional war between South Korea, supported by the United Nations, and North Korea, supported by the People's Republic of China , with military material aid from the Soviet Union...
, the Vietnam War
Vietnam War
The Vietnam War was a Cold War-era military conflict that occurred in Vietnam, Laos, and Cambodia from 1 November 1955 to the fall of Saigon on 30 April 1975. This war followed the First Indochina War and was fought between North Vietnam, supported by its communist allies, and the government of...
, the Gulf War
Gulf War
The Persian Gulf War , commonly referred to as simply the Gulf War, was a war waged by a U.N.-authorized coalition force from 34 nations led by the United States, against Iraq in response to Iraq's invasion and annexation of Kuwait.The war is also known under other names, such as the First Gulf...
and the Afghanistan War
War in Afghanistan (2001–present)
The War in Afghanistan began on October 7, 2001, as the armed forces of the United States of America, the United Kingdom, Australia, and the Afghan United Front launched Operation Enduring Freedom...
; it has also sent a unit of army engineers to help rebuild Iraqi infrastructure for one year during the Iraq War. As of 2009, New Zealand forces are still active in Afghanistan.
Korean War 1950–1953
New Zealand was among those who responded to the United NationsUnited Nations
The United Nations is an international organization whose stated aims are facilitating cooperation in international law, international security, economic development, social progress, human rights, and achievement of world peace...
call for help. New Zealand joined 15 other nations including the United Kingdom and the United States in the anti-communist war. But the Korean War was also significant, as it marked New Zealand's first move towards association with the United States in supporting that country's stand against communism.
New Zealand contributed six frigates, several smaller craft and a 1044 strong volunteer force (known as K-FORCE) to the Korean War
Korean War
The Korean War was a conventional war between South Korea, supported by the United Nations, and North Korea, supported by the People's Republic of China , with military material aid from the Soviet Union...
. The ships were under the command of a British flag officer and formed part of the US Navy
United States Navy
The United States Navy is the naval warfare service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the seven uniformed services of the United States. The U.S. Navy is the largest in the world; its battle fleet tonnage is greater than that of the next 13 largest navies combined. The U.S...
screening force during the Battle of Inchon
Battle of Inchon
The Battle of Inchon was an amphibious invasion and battle of the Korean War that resulted in a decisive victory and strategic reversal in favor of the United Nations . The operation involved some 75,000 troops and 261 naval vessels, and led to the recapture of the South Korean capital Seoul two...
, performing shore raids and inland bombardment. The last New Zealand soldiers did not leave until 1957 and a single liaison officer remained until 1971. A total of 3,794 New Zealand
New Zealand
New Zealand is an island country in the south-western Pacific Ocean comprising two main landmasses and numerous smaller islands. The country is situated some east of Australia across the Tasman Sea, and roughly south of the Pacific island nations of New Caledonia, Fiji, and Tonga...
soldiers served in K-FORCE and 1300 in the Navy
Royal New Zealand Navy
The Royal New Zealand Navy is the maritime arm of the New Zealand Defence Force...
deployment. 33 were killed in action, 79 wounded and one soldier was taken prisoner. That prisoner was held in North Korea for eighteen months and repatriated after the armistices.



Vietnam War
New Zealand's involvement in the Vietnam WarVietnam War
The Vietnam War was a Cold War-era military conflict that occurred in Vietnam, Laos, and Cambodia from 1 November 1955 to the fall of Saigon on 30 April 1975. This war followed the First Indochina War and was fought between North Vietnam, supported by its communist allies, and the government of...
was highly controversial, sparking widespread protest at home from anti-Vietnam War movements modelled on their American counterparts. This conflict was also the first in which New Zealand did not fight alongside the United Kingdom, instead following the loyalties of the ANZUS Pact.
New Zealand's initial response was carefully considered and characterised by Prime Minister Keith Holyoake
Keith Holyoake
Sir Keith Jacka Holyoake, KG, GCMG, CH, QSO, KStJ was a New Zealand politician. The only person to have been both Prime Minister and Governor-General of New Zealand, Holyoake was National Party Prime Minister from 20 September 1957 to 12 December 1957, then again from 12 December 1960 to 7...
's cautiousness towards the entire Vietnam question. New Zealand non-military economic assistance would continue from 1966 onwards and averaged at US$347,500 annually. This funding went to several mobile health teams to support refugee camps, the training of village vocational experts, to medical and teaching equipment for Hue University
Hue University
Huế University is a university located in Huế, the former imperial capital of Vietnam; this university is one of the important regional universities of Vietnam...
, equipment for a technical high school and a contribution toward the construction of a science building at the University of Saigon. Private civilian funding was also donated for 80 Vietnamese students to take scholarships in New Zealand.
The government preferred minimal involvement, with other South East Asian deployments already having a strain on the New Zealand armed forces. From 1961, New Zealand came under pressure from the United States to contribute military and economic assistance to South Vietnam, but refused.

Indonesia
Indonesia , officially the Republic of Indonesia , is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania. Indonesia is an archipelago comprising approximately 13,000 islands. It has 33 provinces with over 238 million people, and is the world's fourth most populous country. Indonesia is a republic, with an...
-Malaysian Confrontation, but eventually the government decided to contribute. It was seen as in the nation's best interests to do so—failure to contribute even a token force to the effort in Vietnam would have undermined New Zealand's position in ANZUS and could have had an adverse effect on the alliance itself. New Zealand had also established its post-Second World War security agenda around countering communism in South-East Asia and of sustaining a strategy of forward defence, and so needed to be seen to be acting upon these principles. On 27 May 1965 Holyoake, announced the government's decision to send 161 Battery, Royal New Zealand Artillery to South Vietnam
South Vietnam
South Vietnam was a state which governed southern Vietnam until 1975. It received international recognition in 1950 as the "State of Vietnam" and later as the "Republic of Vietnam" . Its capital was Saigon...
in a combat role. The Engineers were replaced by the Battery in July 1965.
In 1966, when Confrontation came to an end and Australia decided to expand the 1st Australian Task Force
1st Australian Task Force
The 1st Australian Task Force commanded the Australian and New Zealand Army units deployed to South Vietnam between 1966 and 1972. 1 ATF was based at Nui Dat in Phuoc Tuy Province...
, New Zealand came under pressure to increase its commitment and did so.
In March 1968 they were integrated—forming the 2RAR/NZ (ANZAC) Battalion, with New Zealand personnel assuming various positions in the battalion, including that of second in command. The rifle companies were deployed on infantry operations in Phuoc Tuy Province and were replaced several times, usually after a 12-month tour of duty. Two more RNZAF pilots joined No. 9 Squadron
No. 9 Squadron RAAF
No. 9 Squadron was a unit of the Royal Australian Air Force. The Squadron saw active service in World War II and the Vietnam War before being disbanded in 1989.-Fleet co-operation:...
in 1968 and from December 1968 two forward air controllers served with the Seventh Air Force
Seventh Air Force
The Seventh Air Force is a numbered air force of the United States Air Force Pacific Air Forces . It is headquartered at Osan Air Base, Republic of Korea....
, United States Air Force
United States Air Force
The United States Air Force is the aerial warfare service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the American uniformed services. Initially part of the United States Army, the USAF was formed as a separate branch of the military on September 18, 1947 under the National Security Act of...
.
As American focus shifted to President Richard Nixon
Richard Nixon
Richard Milhous Nixon was the 37th President of the United States, serving from 1969 to 1974. The only president to resign the office, Nixon had previously served as a US representative and senator from California and as the 36th Vice President of the United States from 1953 to 1961 under...
's 'Vietnamization
Vietnamization
Vietnamization was a policy of the Richard M. Nixon administration during the Vietnam War, as a result of the Viet Cong's Tet Offensive, to "expand, equip, and train South Vietnam's forces and assign to them an ever-increasing combat role, at the same time steadily reducing the number of U.S....
'—a policy of slow disengagement from the war, by gradually building up the Army of the Republic of Vietnam
Army of the Republic of Vietnam
The Army of the Republic of Viet Nam , sometimes parsimoniously referred to as the South Vietnamese Army , was the land-based military forces of the Republic of Vietnam , which existed from October 26, 1955 until the fall of Saigon on April 30, 1975...
so that it could fight the war on its own, New Zealand dispatched the 2nd New Zealand Army
New Zealand Army
The New Zealand Army , is the land component of the New Zealand Defence Force and comprises around 4,500 Regular Force personnel, 2,000 Territorial Force personnel and 500 civilians. Formerly the New Zealand Military Forces, the current name was adopted around 1946...
Training Team Vietnam
Vietnam
Vietnam – sometimes spelled Viet Nam , officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam – is the easternmost country on the Indochina Peninsula in Southeast Asia. It is bordered by China to the north, Laos to the northwest, Cambodia to the southwest, and the South China Sea –...
in January 1971. Numbering 25 men, it assisted the United States Army
United States Army
The United States Army is the main branch of the United States Armed Forces responsible for land-based military operations. It is the largest and oldest established branch of the U.S. military, and is one of seven U.S. uniformed services...
Training Team in Chi Lang. In February 1972 a second training team, 18 strong (including two Royal New Zealand Navy
Royal New Zealand Navy
The Royal New Zealand Navy is the maritime arm of the New Zealand Defence Force...
personnel), was deployed to Vietnam and was based at Dong Ba Thin, near Cam Ranh Bay. It assisted with the training of Cambodia
Cambodia
Cambodia , officially known as the Kingdom of Cambodia, is a country located in the southern portion of the Indochina Peninsula in Southeast Asia...
n infantry battalions. This team also provided first aid instruction and specialist medical instruction at Dong Ba Thin's 50-bed hospital.
Vietnam War and 'Agent Orange'
Like veterans from many of the other allied nations, as well as Vietnamese civilians, New Zealand veterans of the Vietnam WarVietnam War
The Vietnam War was a Cold War-era military conflict that occurred in Vietnam, Laos, and Cambodia from 1 November 1955 to the fall of Saigon on 30 April 1975. This war followed the First Indochina War and was fought between North Vietnam, supported by its communist allies, and the government of...
claimed that they (as well as their children and grandchildren) had suffered serious harm as a result of exposure to Agent Orange
Agent Orange
Agent Orange is the code name for one of the herbicides and defoliants used by the U.S. military as part of its herbicidal warfare program, Operation Ranch Hand, during the Vietnam War from 1961 to 1971. Vietnam estimates 400,000 people were killed or maimed, and 500,000 children born with birth...
– the code name for a powerful herbicide and defoliant used by the U.S. military in its Herbicidal Warfare
Herbicidal warfare
Herbicidal warfare is a form of Chemical warfare in which the objective is to destroy the plant-based ecosystem of an area. In contrast to other forms, its use is not prohibited by international agreement...
program during the conflict. In 1984, Agent Orange manufacturers paid New Zealand, Australian and Canadian
Canada
Canada is a North American country consisting of ten provinces and three territories. Located in the northern part of the continent, it extends from the Atlantic Ocean in the east to the Pacific Ocean in the west, and northward into the Arctic Ocean...
veterans in an out-of-court settlement , and in 2004 Prime Minister Helen Clark
Helen Clark
Helen Elizabeth Clark, ONZ is a New Zealand political figure who was the 37th Prime Minister of New Zealand for three consecutive terms from 1999 to 2008...
's government apologised to Vietnam War veterans who were exposed to Agent Orange or other toxic defoliants, following a health select committee's inquiry into the use of Agent Orange on New Zealand servicemen and its effects. In 2005, the New Zealand government confirmed that it supplied Agent Orange chemicals to the United States military during the conflict. Since the early 1960s, and up until 1987, it manufactured the 2,4,5T herbicide at a plant in New Plymouth
New Plymouth
New Plymouth is the major city of the Taranaki Region on the west coast of the North Island of New Zealand. It is named after Plymouth, Devon, England, from where the first English settlers migrated....
which was then shipped to U.S. military bases in South East Asia
The Middle East (1982–present)

United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
in many of their military activities in the Middle East
Middle East
The Middle East is a region that encompasses Western Asia and Northern Africa. It is often used as a synonym for Near East, in opposition to Far East...
. However New Zealand forces have fought only in Afghanistan; in other countries New Zealand support has been in the form of support and engineering. During the Iran–Iraq War two New Zealand frigates joined the Royal Navy
Royal Navy
The Royal Navy is the naval warfare service branch of the British Armed Forces. Founded in the 16th century, it is the oldest service branch and is known as the Senior Service...
in monitoring merchant shipping in the Persian Gulf
Persian Gulf
The Persian Gulf, in Southwest Asia, is an extension of the Indian Ocean located between Iran and the Arabian Peninsula.The Persian Gulf was the focus of the 1980–1988 Iran-Iraq War, in which each side attacked the other's oil tankers...
. and in 1991, New Zealand contributed three transport aircraft and a medical team to assist coalition forces in the Gulf War
Gulf War
The Persian Gulf War , commonly referred to as simply the Gulf War, was a war waged by a U.N.-authorized coalition force from 34 nations led by the United States, against Iraq in response to Iraq's invasion and annexation of Kuwait.The war is also known under other names, such as the First Gulf...
.
New Zealand's heaviest military involvement in the Middle East in recent decades has been in Afghanistan following the United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
-led invasion of that country after the September 11, 2001 attacks
September 11, 2001 attacks
The September 11 attacks The September 11 attacks The September 11 attacks (also referred to as September 11, September 11th or 9/119/11 is pronounced "nine eleven". The slash is not part of the pronunciation...
. Fifty Special Air Service of New Zealand
Special Air Service of New Zealand
The New Zealand Special Air Service was formed on 7 July 1955 and is a special forces unit of the New Zealand Army modelled on the British Special Air Service . The New Zealand Government states that NZ SAS is the "premier combat unit of the New Zealand Defence Force". Its key roles are to...
(SAS) units were dispatched, and in March 2002 they took part in Operation Anaconda
Operation Anaconda
Operation Anaconda took place in early March 2002 in which the United States military and CIA Paramilitary Officers, working with allied Afghan military forces, and other North Atlantic Treaty Organization and non NATO forces attempted to destroy al-Qaeda and Taliban forces in the Shahi-Kot...
against about 500 to 1000 al-Qaeda
Al-Qaeda
Al-Qaeda is a global broad-based militant Islamist terrorist organization founded by Osama bin Laden sometime between August 1988 and late 1989. It operates as a network comprising both a multinational, stateless army and a radical Sunni Muslim movement calling for global Jihad...
and Taliban forces in the Shahi-Kot Valley and Arma Mountains southeast of Zorma, Afghanistan. New Zealand has also supplied two transport aircraft and a 122-strong tri-service Provincial Reconstruction Team, which has been located in Bamyan Province since 2003.
Afghanistan (2001–present)
Starting in late 2001, the SAS began operations assisting in the War on TerrorismWar on Terrorism
The War on Terror is a term commonly applied to an international military campaign led by the United States and the United Kingdom with the support of other North Atlantic Treaty Organisation as well as non-NATO countries...
in Afghanistan. Three six-month rotations of between 40 and 65 soldiers from the Special Air Service of New Zealand served in Afghanistan during Operation Enduring Freedom before the unit was withdrawn in November 2005.[1] On 17 June 2004, two SAS soldiers were wounded in a predawn gun-battle in central Afghanistan.
Secrecy still surrounds most of the operations in Afghanistan of the Special Air Service of New Zealand, although a Radio New Zealand news piece claimed the service had maintained a mission success rate of 100%.


There were "casualties on both sides" during gun battles, but no New Zealanders were killed.
In December 2004, the United States Navy
United States Navy
The United States Navy is the naval warfare service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the seven uniformed services of the United States. The U.S. Navy is the largest in the world; its battle fleet tonnage is greater than that of the next 13 largest navies combined. The U.S...
Presidential Unit Citation was awarded to those units that comprised the Combined Joint Special Operations Task Force-SOUTH/Task Force K-BAR between 17 October 2001 and 30 March 2002 for "extraordinary heroism" in action. One of these units was the Special Air Service of New Zealand
Special Air Service of New Zealand
The New Zealand Special Air Service was formed on 7 July 1955 and is a special forces unit of the New Zealand Army modelled on the British Special Air Service . The New Zealand Government states that NZ SAS is the "premier combat unit of the New Zealand Defence Force". Its key roles are to...
.
The citation said SAS units helped "neutralise" Taliban and al-Qaeda in "extremely high risk missions, including search and rescue, special reconnaissance, sensitive site exploitation, direct action missions, destruction of multiple cave and tunnel complexes, identification and destruction of several known al-Qaeda training camps, explosions of thousands of pounds of enemy ordnance."
"They established benchmark standards of professionalism, tenacity, courage, tactical brilliance and operational excellence while demonstrating superb esprit de corps and maintaining the highest measures of combat readiness."
In August 2009, the John Key
Fifth National Government of New Zealand
The Fifth National Government of New Zealand is the current government of New Zealand. It is led by Prime Minister John Key.After the 2008 general election the National Party and its allies were able to form a government, taking over from Helen Clark's Fifth Labour Government. The National party...
government decided that NZSAS forces would be sent back to Afghanistan.
Iraq (2003–present)
In accordance with United Nations Security CouncilUnited Nations Security Council
The United Nations Security Council is one of the principal organs of the United Nations and is charged with the maintenance of international peace and security. Its powers, outlined in the United Nations Charter, include the establishment of peacekeeping operations, the establishment of...
Resolution 1483 New Zealand contributed a small engineering and support force to assist in post-war reconstruction and provision of humanitarian aid. The engineers returned home in October, 2004 and New Zealand is still represented in Iraq
Iraq
Iraq ; officially the Republic of Iraq is a country in Western Asia spanning most of the northwestern end of the Zagros mountain range, the eastern part of the Syrian Desert and the northern part of the Arabian Desert....
by liaison and staff officers working with coalition forces.
Hurricane Katrina
On August 30, 2005 NZSTTime in New Zealand
New Zealand has two time zones. The main islands use New Zealand Standard Time , 12 hours in advance of Coordinated Universal Time , while the outlying Chatham Islands use Chatham Standard Time , 12 hours 45 minutes in advance of UTC.During summer daylight saving time is observed and clocks are...
(August 29 UTC-6/-5
Central time
Central time can refer to:*North American Central Time Zone*Central European Time*Central Standard Time Australia...
) Prime Minister
Prime Minister of New Zealand
The Prime Minister of New Zealand is New Zealand's head of government consequent on being the leader of the party or coalition with majority support in the Parliament of New Zealand...
Helen Clark
Helen Clark
Helen Elizabeth Clark, ONZ is a New Zealand political figure who was the 37th Prime Minister of New Zealand for three consecutive terms from 1999 to 2008...
sent condolences by phone and in a letter with an offer of help to United States President George W. Bush
George W. Bush
George Walker Bush is an American politician who served as the 43rd President of the United States, from 2001 to 2009. Before that, he was the 46th Governor of Texas, having served from 1995 to 2000....
and Foreign Affairs Minister Phil Goff
Phil Goff
Philip Bruce Goff is the current Leader of the Opposition and the Leader of the New Zealand Labour Party. During the Fifth Labour Government, he served in a number of ministerial portfolios, including Minister of Defence of New Zealand, Minister of Corrections, Minister of Foreign Affairs and...
also sent a message of sympathy to Secretary of State
Secretary of State
Secretary of State or State Secretary is a commonly used title for a senior or mid-level post in governments around the world. The role varies between countries, and in some cases there are multiple Secretaries of State in the Government....
Condoleezza Rice
Condoleezza Rice
Condoleezza Rice is an American political scientist and diplomat. She served as the 66th United States Secretary of State, and was the second person to hold that office in the administration of President George W. Bush...
. This offer included an official pledge by the New Zealand Government to the Red Cross of $2 million for aid and disaster relief.
After the New Zealand
New Zealand
New Zealand is an island country in the south-western Pacific Ocean comprising two main landmasses and numerous smaller islands. The country is situated some east of Australia across the Tasman Sea, and roughly south of the Pacific island nations of New Caledonia, Fiji, and Tonga...
government's initial pledge of money, they offered further contributions to the recovery effort including Urban Search and Rescue Teams, a Disaster Victim Identification team and post disaster recovery personnel. Those offers were gratefully received by the United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
. A senior member of the Ministry of Civil Defence and Emergency Management, John Titmus went to Denton, Texas
Denton, Texas
The city of Denton is the county seat of Denton County, Texas in the United States. Its population was 119,454 according to the 2010 U.S. Census, making it the eleventh largest city in the Dallas/Fort Worth Metroplex...
to lead an official UN Disaster Assessment and Coordination (UNDAC) team to assess the damage from Hurricane Katrina
Hurricane Katrina
Hurricane Katrina of the 2005 Atlantic hurricane season was a powerful Atlantic hurricane. It is the costliest natural disaster, as well as one of the five deadliest hurricanes, in the history of the United States. Among recorded Atlantic hurricanes, it was the sixth strongest overall...
. The US Embassy in Wellington
Wellington
Wellington is the capital city and third most populous urban area of New Zealand, although it is likely to have surpassed Christchurch due to the exodus following the Canterbury Earthquake. It is at the southwestern tip of the North Island, between Cook Strait and the Rimutaka Range...
said it deeply appreciated the $2 million donation and gratefully acknowledged the offer of disaster management personnel.
New Zealand and United States relations today


President of the United States
The President of the United States of America is the head of state and head of government of the United States. The president leads the executive branch of the federal government and is the commander-in-chief of the United States Armed Forces....
George W. Bush
George W. Bush
George Walker Bush is an American politician who served as the 43rd President of the United States, from 2001 to 2009. Before that, he was the 46th Governor of Texas, having served from 1995 to 2000....
and Prime Minister of New Zealand
Prime Minister of New Zealand
The Prime Minister of New Zealand is New Zealand's head of government consequent on being the leader of the party or coalition with majority support in the Parliament of New Zealand...
Helen Clark
Helen Clark
Helen Elizabeth Clark, ONZ is a New Zealand political figure who was the 37th Prime Minister of New Zealand for three consecutive terms from 1999 to 2008...
have been able to improve the two nations relations and work around New Zealand's anti-nuclear
Anti-nuclear
The anti-nuclear movement is a social movement that opposes the use of nuclear technologies. Many direct action groups, environmental groups, and professional organisations have identified themselves with the movement at the local, national, and international level...
policy and focus on working together on more important issues, although the United States is still interested in changing New Zealand's anti-nuclear policy.
After Helen Clark's visit to Washington and talks with President Bush, The New Zealand Herald reported, on March 23, 2007, that the United States "no longer seeks to change" New Zealand's anti-nuclear policy, and that this constituted "a turning point in the US-NZ relationship".

Condoleezza Rice
Condoleezza Rice is an American political scientist and diplomat. She served as the 66th United States Secretary of State, and was the second person to hold that office in the administration of President George W. Bush...
, the United States Secretary of State
United States Secretary of State
The United States Secretary of State is the head of the United States Department of State, concerned with foreign affairs. The Secretary is a member of the Cabinet and the highest-ranking cabinet secretary both in line of succession and order of precedence...
, visited New Zealand, which she referred to as "a friend and an ally". The New Zealand Herald reported that the use of the word "ally" was unexpected, as United States officials had avoided it since the ANZUS crisis. Rice stated that the relationship between the two countries was a "deepening" one, "by no means [...] harnessed to or constrained by the past", which prompted the Herald to write of a "thaw in US-NZ relations".
Proposed Free Trade Agreement
The government of New Zealand had indicated its strong desire to pursue a free trade agreement (FTA) between the United States and New Zealand. Such an agreement would presumably be pursued alongside, or together with, an FTA between the United States and Australia since New Zealand and Australia have had their own FTA for almost twenty years and their economies are by now closely integrated. Fifty House members wrote to President Bush in January 2003 advocating the initiation of negotiations, as did 19 Senators in March 2003. However, Administration officials had enumerated several political and security impediments to a potential FTA, including New Zealand’s longstanding refusal to allow nuclear powered ships into its harbors and its refusal to support the United States in the Iraq war.New Zealand is very small compared with the United States, so the economic impact of an FTA would be quite modest for the United States and considerably larger for New Zealand. However, US merchandise exports to New Zealand would rise by about 25 percent and virtually every US sector would benefit. The inclusion of Australia would increase the magnitude of these results substantially; US exports would rise by about $3 billion. The adjustment costs for the United States would be minimal: production in the most impacted sector, dairy products, would decline by only 0.5 percent and any adverse effect on jobs would be very small. It would also contribute toward the accomplishment of APEC
Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation
Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation is a forum for 21 Pacific Rim countries that seeks to promote free trade and economic cooperation throughout the Asia-Pacific region...
's goals of achieving “free and open trade and investment in the (Asia Pacific) region by 2010,”
On February 4, 2008, U.S. Trade Representative Susan Schwab
Susan Schwab
Susan C. Schwab is an American politician, who served as United States Trade Representative from June, 2006 to January, 2009....
announced that the United States will join negotiations 4 Asia
Asia
Asia is the world's largest and most populous continent, located primarily in the eastern and northern hemispheres. It covers 8.7% of the Earth's total surface area and with approximately 3.879 billion people, it hosts 60% of the world's current human population...
-Pacific countries: Brunei
Brunei
Brunei , officially the State of Brunei Darussalam or the Nation of Brunei, the Abode of Peace , is a sovereign state located on the north coast of the island of Borneo, in Southeast Asia...
, Chile
Chile
Chile ,officially the Republic of Chile , is a country in South America occupying a long, narrow coastal strip between the Andes mountains to the east and the Pacific Ocean to the west. It borders Peru to the north, Bolivia to the northeast, Argentina to the east, and the Drake Passage in the far...
, New Zealand
New Zealand
New Zealand is an island country in the south-western Pacific Ocean comprising two main landmasses and numerous smaller islands. The country is situated some east of Australia across the Tasman Sea, and roughly south of the Pacific island nations of New Caledonia, Fiji, and Tonga...
& Singapore
Singapore
Singapore , officially the Republic of Singapore, is a Southeast Asian city-state off the southern tip of the Malay Peninsula, north of the equator. An island country made up of 63 islands, it is separated from Malaysia by the Straits of Johor to its north and from Indonesia's Riau Islands by the...
to be known as the "P-4". These nations already have an FTA called the Trans-Pacific Strategic Economic Partnership
Trans-Pacific Strategic Economic Partnership
The Trans-Pacific Partnership , also known as the Trans-Pacific Strategic Economic Partnership Agreement, is a multilateral free trade agreement that aims to further liberalise the economies of the Asia-Pacific region; specifically, Article 1.1.3 notes: “The Parties seek to support the wider...
and the United States will be looking to become involved in the "vitally important emerging Asia-Pacific region" A number of U.S. organizations support the negotiations including, but not limited to: the United States Chamber of Commerce
United States Chamber of Commerce
The United States Chamber of Commerce is an American lobbying group representing the interests of many businesses and trade associations. It is not an agency of the United States government....
, National Association of Manufacturers
National Association of Manufacturers
The National Association of Manufacturers is an advocacy group headquartered in Washington, D.C. with 10 additional offices across the country...
, National Foreign Trade Council
National Foreign Trade Council
Founded in 1914, the National Foreign Trade Council is the oldest and largest trade association advocating an open, rules-based international trade system. It serves hundreds of member companies in activities encompassing international trade policy, international tax policy, human resources, and...
, Emergency Committee for American Trade and Coalition of Service Industries.
On September 23, 2008, an official announcement was made from Washington, D.C.
Washington, D.C.
Washington, D.C., formally the District of Columbia and commonly referred to as Washington, "the District", or simply D.C., is the capital of the United States. On July 16, 1790, the United States Congress approved the creation of a permanent national capital as permitted by the U.S. Constitution....
that the United States was to begin negotiations with the P-4 countries ASAP, with the first round of talks scheduled for March 2009 with New Zealand Prime Minister
Prime Minister of New Zealand
The Prime Minister of New Zealand is New Zealand's head of government consequent on being the leader of the party or coalition with majority support in the Parliament of New Zealand...
Helen Clark
Helen Clark
Helen Elizabeth Clark, ONZ is a New Zealand political figure who was the 37th Prime Minister of New Zealand for three consecutive terms from 1999 to 2008...
stating "I think the value to New Zealand of the United States coming into a transpacific agreement as a partner would be of the same value as we would hope to get from a bilateral FTA.... It's very, very big news." Although the outcome of the FTA could become largely dependent on the results of the 2008 United States Presidential election
United States presidential election, 2008
The United States presidential election of 2008 was the 56th quadrennial presidential election. It was held on November 4, 2008. Democrat Barack Obama, then the junior United States Senator from Illinois, defeated Republican John McCain, the senior U.S. Senator from Arizona. Obama received 365...
as it is believed the Democratic Party
Democratic Party (United States)
The Democratic Party is one of two major contemporary political parties in the United States, along with the Republican Party. The party's socially liberal and progressive platform is largely considered center-left in the U.S. political spectrum. The party has the lengthiest record of continuous...
are less friendly towards free trade than their Republican counterparts, despite this, Helen Clark said "I believe that to Democrats, New Zealand offers very few problems because we are very keen on environment and labour agreements as part of an overall approach to an FTA".
Since the inauguration of Barack Obama, talks about an FTA between the two nations have been postponed since Obama is yet to appoint a US Trade Representative as his nominee, Ron Kirk
Ron Kirk
Ronald "Ron" Kirk is the 16th United States Trade Representative, serving in the Obama administration. He served as mayor of Dallas, Texas from 1995 to 2002; he also ran for the United States Senate in 2002.-Early life and career:...
, has not been approved by the Senate. "The government is deeply disappointed" that the United States is postponing trade talks involving New Zealand that were scheduled to get underway at the end of the month, Prime Minister John Key says and that "New Zealand will continue to advocate very strongly for a trade deal."
At the APEC meeting in Singapore in 2009, President Barack Obama
Barack Obama
Barack Hussein Obama II is the 44th and current President of the United States. He is the first African American to hold the office. Obama previously served as a United States Senator from Illinois, from January 2005 until he resigned following his victory in the 2008 presidential election.Born in...
announced a free trade deal with New Zealand would go ahead.
Congressional support
The Friends of New Zealand Congressional Caucus Member numbers now stand at 62.Congressional support is vital for the US free trade agenda. New Zealand already enjoys strong support in the United States Congress
United States Congress
The United States Congress is the bicameral legislature of the federal government of the United States, consisting of the Senate and the House of Representatives. The Congress meets in the United States Capitol in Washington, D.C....
- both in the House of Representatives
United States House of Representatives
The United States House of Representatives is one of the two Houses of the United States Congress, the bicameral legislature which also includes the Senate.The composition and powers of the House are established in Article One of the Constitution...
and the Senate
United States Senate
The United States Senate is the upper house of the bicameral legislature of the United States, and together with the United States House of Representatives comprises the United States Congress. The composition and powers of the Senate are established in Article One of the U.S. Constitution. Each...
:
- Several letters to the PresidentPresident of the United StatesThe President of the United States of America is the head of state and head of government of the United States. The president leads the executive branch of the federal government and is the commander-in-chief of the United States Armed Forces....
signed by Congressmen and women from both sides of the House – have recommended negotiations with New Zealand
- Leading Senators Baucus, Grassley and, most recently, Senator and former presidential nominee John McCainJohn McCainJohn Sidney McCain III is the senior United States Senator from Arizona. He was the Republican nominee for president in the 2008 United States election....
have also advocated a negotiation with New Zealand
- Friends of New Zealand Caucus was established in the Congress in February 2005 led by Representatives Kolbe (R-Arizona) and Tauscher (D-California).
- Congressional support is enhanced by the absence of any difficulty New Zealand might pose in terms of non trade issues such as environment or labour.
Wellington Declaration
On 4 November 2010, US Secretary of State Hillary Clinton began her three-day visit to New Zealand and at 4:23 pm, she co-signed the Wellington Declaration with New Zealand Foreign Minister Murray McCullyMurray McCully
Murray Stuart McCully is a New Zealand politician. He is a member of the National Party, and Minister of Foreign Affairs, Minister for Sport and Recreation, and Minister for the Rugby World Cup.-Early life:...
. The agreement signals closer relations between New Zealand and the United States, with an increase in the strategic partnership between the two nations. In doing so, the agreement stresses the continued pledge for the United States and New Zealand to work together, explicitly saying that: "The United States-New Zealand strategic partnership is to have two fundamental elements: a new focus on practical cooperation in the Pacific region; and enhanced political and subject-matter dialogue - including regular Foreign Ministers' meetings and political-military discussions." The agreement also stresses the continued need for New Zealand and the United States to work together on issues like nuclear proliferation, climate change and terrorism.
Controversies
- In 2003, New Zealand Prime Minister Helen Clark caused controversy by claiming that the Iraq War would not have occurred had the Democratic nominee, Al GoreAl GoreAlbert Arnold "Al" Gore, Jr. served as the 45th Vice President of the United States , under President Bill Clinton. He was the Democratic Party's nominee for President in the 2000 U.S. presidential election....
, won the 2000 US Presidential Election. She later apologised for her remark.
- In an interview with Newsweek magazine, DemocraticDemocratic Party (United States)The Democratic Party is one of two major contemporary political parties in the United States, along with the Republican Party. The party's socially liberal and progressive platform is largely considered center-left in the U.S. political spectrum. The party has the lengthiest record of continuous...
Presidential HopefulUnited States presidential election, 2008The United States presidential election of 2008 was the 56th quadrennial presidential election. It was held on November 4, 2008. Democrat Barack Obama, then the junior United States Senator from Illinois, defeated Republican John McCain, the senior U.S. Senator from Arizona. Obama received 365...
Hillary Clinton described Helen ClarkHelen ClarkHelen Elizabeth Clark, ONZ is a New Zealand political figure who was the 37th Prime Minister of New Zealand for three consecutive terms from 1999 to 2008...
as a "former" prime minister of New ZealandPrime Minister of New ZealandThe Prime Minister of New Zealand is New Zealand's head of government consequent on being the leader of the party or coalition with majority support in the Parliament of New Zealand...
. The comment came during an interview with magazine when Mrs Clinton was asked to tell a joke.
"Here's a good one," she said. "Helen Clark, former prime minister of New Zealand: her opponents have observed that in the event of a nuclear war
Nuclear warfare
Nuclear warfare, or atomic warfare, is a military conflict or political strategy in which nuclear weaponry is detonated on an opponent. Compared to conventional warfare, nuclear warfare can be vastly more destructive in range and extent of damage...
, the two things that will emerge from the rubble are the cockroach
Cockroach
Cockroaches are insects of the order Blattaria or Blattodea, of which about 30 species out of 4,500 total are associated with human habitations...
es and Helen Clark."
The Dominion Post reported today that Helen Clark found the anecdote amusing and suggested Mrs Clinton should talk to her husband, former US president Bill Clinton
Bill Clinton
William Jefferson "Bill" Clinton is an American politician who served as the 42nd President of the United States from 1993 to 2001. Inaugurated at age 46, he was the third-youngest president. He took office at the end of the Cold War, and was the first president of the baby boomer generation...
.
"As a current prime minister I spoke with him as a former US president in London
London
London is the capital city of :England and the :United Kingdom, the largest metropolitan area in the United Kingdom, and the largest urban zone in the European Union by most measures. Located on the River Thames, London has been a major settlement for two millennia, its history going back to its...
only two weeks ago."
Shared history
The two countries share much in common:- Both New Zealand and the United States are former colonies of the British EmpireBritish EmpireThe British Empire comprised the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom. It originated with the overseas colonies and trading posts established by England in the late 16th and early 17th centuries. At its height, it was the...
.
- Apart from their common language and status as fully developed new world economies, both countries soldiers have fought together in the two world wars and New Zealand supported US interests in every regional conflict in the 20th century and lately in the war against terrorism.
- Their cultures are relatively aligned and they continue to stand together on many of the same issues, such as the need to spread democracy and human rights around the globe, and the advantages of freer trade and the rule of international trade law.
- During WW2, 400,000 US soldiers were billeted in Auckland and Wellington prior to being sent into action in the likes of Tarawa, Iwo Jima, Leyte Gulf and Guadalcanal. Many of these leathernecks and doughboys remember this experience fondly.
- New Zealand and the US were also closely related when they worked almost exclusively for the formation of the United NationsUnited NationsThe United Nations is an international organization whose stated aims are facilitating cooperation in international law, international security, economic development, social progress, human rights, and achievement of world peace...
.
- Even though ANZUS is no longer a strong link between the two countries, they worked very closely in SEATOSoutheast Asia Treaty OrganizationThe Southeast Asia Treaty Organization was an international organization for collective defense in Southeast Asia created by the Southeast Asia Collective Defense Treaty, or Manila Pact, signed in September 1954 in Manila, Philippines. The formal institution of SEATO was established on 19 February...
during 1954-77.
- Both of them are close allies in the WTO and committed to the goal of free tradeFree tradeUnder a free trade policy, prices emerge from supply and demand, and are the sole determinant of resource allocation. 'Free' trade differs from other forms of trade policy where the allocation of goods and services among trading countries are determined by price strategies that may differ from...
and investment in the APEC region by 2010.
Sports

Rugby
New Zealand and the United States have historically had little connection over sports. Sport in New Zealand largely reflects its BritishGreat Britain
Great Britain or Britain is an island situated to the northwest of Continental Europe. It is the ninth largest island in the world, and the largest European island, as well as the largest of the British Isles...
colonial
Colonialism
Colonialism is the establishment, maintenance, acquisition and expansion of colonies in one territory by people from another territory. It is a process whereby the metropole claims sovereignty over the colony and the social structure, government, and economics of the colony are changed by...
heritage. Some of the most popular sports in New Zealand, namely rugby
Rugby football
Rugby football is a style of football named after Rugby School in the United Kingdom. It is seen most prominently in two current sports, rugby league and rugby union.-History:...
, cricket
Cricket
Cricket is a bat-and-ball game played between two teams of 11 players on an oval-shaped field, at the centre of which is a rectangular 22-yard long pitch. One team bats, trying to score as many runs as possible while the other team bowls and fields, trying to dismiss the batsmen and thus limit the...
and netball
Netball
Netball is a ball sport played between two teams of seven players. Its development, derived from early versions of basketball, began in England in the 1890s. By 1960 international playing rules had been standardised for the game, and the International Federation of Netball and Women's Basketball ...
, are primarily played in Commonwealth countries
Commonwealth of Nations
The Commonwealth of Nations, normally referred to as the Commonwealth and formerly known as the British Commonwealth, is an intergovernmental organisation of fifty-four independent member states...
, whereas America is predominantly stronger in Baseball
Baseball
Baseball is a bat-and-ball sport played between two teams of nine players each. The aim is to score runs by hitting a thrown ball with a bat and touching a series of four bases arranged at the corners of a ninety-foot diamond...
, Basketball
Basketball
Basketball is a team sport in which two teams of five players try to score points by throwing or "shooting" a ball through the top of a basketball hoop while following a set of rules...
and American Football
American football
American football is a sport played between two teams of eleven with the objective of scoring points by advancing the ball into the opposing team's end zone. Known in the United States simply as football, it may also be referred to informally as gridiron football. The ball can be advanced by...
. But in recent years there has been much more cooperation in the area of sports between both countries, particularly in Rugby and Soccer. In January 2008 during the New Zealand Stage
2008 Wellington Sevens
The Emirates Airline Wellington Sevens is played annually as part of the IRB Sevens World Series for international rugby sevens...
of the 2007-08 IRB Sevens World Series
2007-08 IRB Sevens World Series
The 2007–08 IRB Sevens World Series was the ninth of an annual series of rugby union sevens tournaments for full national sides run by the International Rugby Board since 1999–2000...
the United States national team
United States national rugby union team (sevens)
The United States National Rugby Union Sevens team competes in the IRB Sevens World Series, Rugby World Cup Sevens, World Games, and Pan American Games. The Team will also represent the United States in the Summer Olympics beginning in 2016. Under current head coach Al Caravelli the Eagles have...
participated in the finals of the knockout round, beating Kenya to win the shield and New Zealand beating Samoa in the finals to win the Cup.
Soccer
Soccer is still a smaller sport in both New Zealand and the United StatesSoccer in the United States
Soccer, fully known as association football,See the articles Football and Names for association football#North America for more detailed explanations of the differing names for soccer. has long been a popular sport in the United States...
and is far less publicised in both nations, but ties to teams in both countries have been growing, particularly when on December 1, 2007, Wellington Phoenix played a friendly match against United States MLS
Major League Soccer
Major League Soccer is a professional soccer league based in the United States and sanctioned by the United States Soccer Federation . The league is composed of 19 teams — 16 in the U.S. and 3 in Canada...
club Los Angeles Galaxy
Los Angeles Galaxy
The Los Angeles Galaxy are an American professional soccer team, based in the Los Angeles suburb of Carson, California, which competes in Major League Soccer , the top professional soccer league in the United States and Canada. It is one of the ten charter clubs of MLS, and the league's second...
. In the contract to secure the friendly, David Beckham
David Beckham
David Robert Joseph Beckham, OBE is an English footballer who plays midfield for Los Angeles Galaxy in Major League Soccer, having previously played for Manchester United, Preston North End, Real Madrid, and A.C...
will play a minimum of 55 minutes on the pitch. Wellington was beaten by a 1-4 scoreline. David Beckham played the entire match and scored from the penalty spot in the second half. The attendance of 31,853 was a record for any football match in New Zealand. David Beckham played the full 90 minutes with a broken rib which he sustained in a tackle in the previous match.
Basketball
Probably the most well-known former New Zealand Tall Black player in the National Basketball AssociationNational Basketball Association
The National Basketball Association is the pre-eminent men's professional basketball league in North America. It consists of thirty franchised member clubs, of which twenty-nine are located in the United States and one in Canada...
is New Orleans Hornets forward Sean Marks
Sean Marks
Sean Andrew Marks is a New Zealand-American professional basketball player. He is the first native New Zealander to play in the NBA.-Basketball career:...
, who is in his tenth NBA season. Another New Zealand player, former University of Wisconsin–Madison
University of Wisconsin–Madison
The University of Wisconsin–Madison is a public research university located in Madison, Wisconsin, United States. Founded in 1848, UW–Madison is the flagship campus of the University of Wisconsin System. It became a land-grant institution in 1866...
star Kirk Penney
Kirk Penney
Kirk Samuel Penney is a New Zealander professional basketball player.-University of Wisconsin :...
, signed in 2005 with two-time defending Euroleague
Euroleague
Euroleague Basketball, commonly known as the Euroleague, is the highest level tier and most important professional club basketball competition in Europe, with teams from up to 18 different countries, members of FIBA Europe. For sponsorship reasons, for five seasons starting with 2010–2011, it is...
champions Maccabi Tel Aviv and in 2010 signed with the Sioux Falls Skyforce
Sioux Falls Skyforce
The Sioux Falls Skyforce is a professional basketball team that plays in the NBA Development League. They are based in Sioux Falls, South Dakota, United States. The team plays at the Sioux Falls Arena. The Skyforce began in the CBA in 1989...
in the NBA Development League.
Golf
The 2005 U.S. Open Golf Championship2005 U.S. Open Golf Championship
The 2005 United States Open Championship was the 105th U.S. Open, played from June 13 to June 19 at Pinehurst Resort course No. 2. The U.S. Open returned to Pinehurst No. 2 for the first time since 1999 when Payne Stewart won his second U.S. Open four months before his death. Six years was the...
was the second major win by a New Zealand golfer and earned winner Michael Campbell
Michael Campbell
Michael Shane Campbell, CNZM is a New Zealand golfer who is best known for having won the 2005 U.S. Open and the richest prize in golf, the £1,000,000 HSBC World Match Play Championship, in the same year. He is a member of the European Tour.Ethnically, he is predominantly Māori, from the Ngati...
much recogniton in his sport for beating out golfing legend Tiger Woods
Tiger Woods
Eldrick Tont "Tiger" Woods is an American professional golfer whose achievements to date rank him among the most successful golfers of all time. Formerly the World No...
to win the $1.17 million prize in the final round.
Motor racing

Indianapolis 500
The Indianapolis 500-Mile Race, also known as the Indianapolis 500, the 500 Miles at Indianapolis, the Indy 500 or The 500, is an American automobile race, held annually, typically on the last weekend in May at the Indianapolis Motor Speedway in Speedway, Indiana...
-Mile Race was run on Sunday, 25 May 2008 at the Indianapolis Motor Speedway
Indianapolis Motor Speedway
The Indianapolis Motor Speedway, located in Speedway, Indiana in the United States, is the home of the Indianapolis 500-Mile Race and the Brickyard 400....
in Speedway, Indiana
Speedway, Indiana
Speedway is a town in Wayne Township, Marion County, Indiana, United States. The population was 12,881 at the 2000 census. Speedway is the home of the Indianapolis Motor Speedway, from which the town derives its name, and is a complete enclave of Indianapolis....
. It was won by Scott Dixon
Scott Dixon
Scott Ronald Dixon, MNZM is a New Zealand motor racer who became the most successful all-time driver in the Indy Racing League championship in the United States when he won the Honda Indy 200 at Mid-Ohio in August 2009. This took his total to 21 wins...
of New Zealand, the first kiwi ever to do so.
| UKUSA Community |
|---|
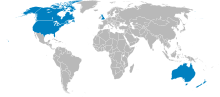  Australia Australia
 Canada Canada
 New Zealand New Zealand
 United Kingdom United Kingdom
 United States United States
|
New Zealand and the UKUSA Community
New Zealand is one of five countries who share intelligence under the UKUSA agreement. New Zealand has two (known) listening posts run by the Government Communications Security BureauGovernment Communications Security Bureau
The Government Communications Security Bureau is an intelligence agency of the New Zealand government.The mission statement is given as:To contribute to the national security of New Zealand through:...
(GCSB) as part of the ECHELON spy network. The partnership gives "a direct line into the inner circles of power in London and Washington," gives New Zealand a distinct partnership with the United States not just on economic policies but domestic security agreements and operations as well, and is a familiar platform for further deals involving both countries.
UKUSA military exercises
On March 10, 2008 (NZT
Time in New Zealand
New Zealand has two time zones. The main islands use New Zealand Standard Time , 12 hours in advance of Coordinated Universal Time , while the outlying Chatham Islands use Chatham Standard Time , 12 hours 45 minutes in advance of UTC.During summer daylight saving time is observed and clocks are...
) New Zealand, Canada
Canada
Canada is a North American country consisting of ten provinces and three territories. Located in the northern part of the continent, it extends from the Atlantic Ocean in the east to the Pacific Ocean in the west, and northward into the Arctic Ocean...
, Australia
Australia
Australia , officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country in the Southern Hemisphere comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands in the Indian and Pacific Oceans. It is the world's sixth-largest country by total area...
, the United States and the United Kingdom
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
took part in a massive multinational war game
Military simulation
Military simulations, also known informally as war games, are simulations in which theories of warfare can be tested and refined without the need for actual hostilities. Many professional contemporary analysts object to the term wargames as this is generally taken to be referring to the civilian...
that simulated a terrorist attack on "strategic networks" like power grids, financial centres and telecommunications focusing mainly on cyber-terrorism
Cyber-terrorism
Cyberterrorism is the use of Internet based attacks in terrorist activities, including acts of deliberate, large-scale disruption of computer networks, especially of personal computers attached to the Internet, by the means of tools such as computer viruses....
. The exercise was named Cyber Storm 2 and was co-ordinated by the United States Department of Homeland Security
United States Department of Homeland Security
The United States Department of Homeland Security is a cabinet department of the United States federal government, created in response to the September 11 attacks, and with the primary responsibilities of protecting the territory of the United States and protectorates from and responding to...
and the New Zealand Government Communications Security Bureau
Government Communications Security Bureau
The Government Communications Security Bureau is an intelligence agency of the New Zealand government.The mission statement is given as:To contribute to the national security of New Zealand through:...
. It was used to identify policies & issues that affect cyber response & recovery by government agencies.
The exercise encompassed:
- 8 government departments and 3 government agencies
- The states of: MichiganMichiganMichigan is a U.S. state located in the Great Lakes Region of the United States of America. The name Michigan is the French form of the Ojibwa word mishigamaa, meaning "large water" or "large lake"....
, MontanaMontanaMontana is a state in the Western United States. The western third of Montana contains numerous mountain ranges. Smaller, "island ranges" are found in the central third of the state, for a total of 77 named ranges of the Rocky Mountains. This geographical fact is reflected in the state's name,...
, New YorkNew YorkNew York is a state in the Northeastern region of the United States. It is the nation's third most populous state. New York is bordered by New Jersey and Pennsylvania to the south, and by Connecticut, Massachusetts and Vermont to the east...
, Washington - 9 major IT firms
- 6 electric utility firms (generation, transmission & grid operations)
- 2 major air carriers
and focused on information technology
Information technology
Information technology is the acquisition, processing, storage and dissemination of vocal, pictorial, textual and numerical information by a microelectronics-based combination of computing and telecommunications...
, energy
Energy
In physics, energy is an indirectly observed quantity. It is often understood as the ability a physical system has to do work on other physical systems...
, finance
Finance
"Finance" is often defined simply as the management of money or “funds” management Modern finance, however, is a family of business activity that includes the origination, marketing, and management of cash and money surrogates through a variety of capital accounts, instruments, and markets created...
.
After the exercise the NZ 'CCIP' (Centre for Critical Infrastructure Protection) said in a statement.
"The New Zealand component of the exercise was successful in testing information sharing and response coordination across both public and private sectors and national and international cooperation,"
A report on the overall results will be published at some stage ahead of Cyber Storm III scheduled for 2010.
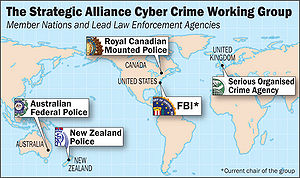
Strategic Alliance Cyber Crime Working Group
The Strategic Alliance Cyber Crime Working Group is a new initiative by Australia, Canada, New Zealand, the United Kingdom and headed by the United States as a "formal partnership between these nations dedicated to tackling larger global crime issues, particularly organized crime". The cooperation consists of "five countries from three continents banding together to fight cyber crime in a synergistic way by sharing intelligence, swapping tools and best practices, and strengthening and even synchronizing their respective laws." This means that there will be increased information sharing between the New Zealand PoliceNew Zealand Police
The New Zealand Police is the national police force of New Zealand, responsible for enforcing criminal law, enhancing public safety, maintaining order and keeping the peace throughout New Zealand...
and the Federal Bureau of Investigation
Federal Bureau of Investigation
The Federal Bureau of Investigation is an agency of the United States Department of Justice that serves as both a federal criminal investigative body and an internal intelligence agency . The FBI has investigative jurisdiction over violations of more than 200 categories of federal crime...
on matters relating to serious fraud or cyber crime.
Bilateral representation
There are many official contacts between New Zealand and the United States, which provide the opportunity for high-level discussions and the continued development of bilateral relations. Many ministers meet with their US counterparts at international meetings and events.American tours by New Zealand delegates and ministers
New Zealand Ministerial Visits to the United States| Dates | Minister/Delegate | Cities visited | Reason |
|---|---|---|---|
| July 2007 | Gerry Brownlee and Shane Jones, chairman and deputy chairman of the New Zealand United States Parliamentary Friendship Group | Washington D.C. | Visited Washington for a series of meetings, including calls on their counterparts, co-chairs of the Friends of New Zealand Congressional Caucus, Representatives Ellen Tauscher and Kevin Brady amongst others. They were accompanied by NZUS Council Executive Director Stephen Jacobi who stayed on in Washington to further plan for the upcoming Partnership Forum. |
| May 2007 | Minister of Trade, Defence Minister of Defence (New Zealand) The Minister of Defence is a minister in the government of New Zealand with responsibility for the New Zealand armed forces and the Ministry of Defence.The present Minister is Dr... , and Disarmament Disarmament Disarmament is the act of reducing, limiting, or abolishing weapons. Disarmament generally refers to a country's military or specific type of weaponry. Disarmament is often taken to mean total elimination of weapons of mass destruction, such as nuclear arms... and Arms Control Arms control Arms control is an umbrella term for restrictions upon the development, production, stockpiling, proliferation, and usage of weapons, especially weapons of mass destruction... , Phil Goff Phil Goff Philip Bruce Goff is the current Leader of the Opposition and the Leader of the New Zealand Labour Party. During the Fifth Labour Government, he served in a number of ministerial portfolios, including Minister of Defence of New Zealand, Minister of Corrections, Minister of Foreign Affairs and... |
Washington D.C. | Mr Goff met with senior Administration officials including USTR Susan Schwab; Secretary of Defense Robert Gates; National Security Advisor Stephen Hadley; Agriculture Secretary Mike Johanns; Interior Secretary Dirk Kempthorne; then Under Secretary of Commerce for International Trade, Frank Lavin; and Assistant Secretary of State for East Asian and Pacific Affairs, Chris Hill. |
| May 2007 | Minister of Trade, Defence Minister of Defence (New Zealand) The Minister of Defence is a minister in the government of New Zealand with responsibility for the New Zealand armed forces and the Ministry of Defence.The present Minister is Dr... , and Disarmament Disarmament Disarmament is the act of reducing, limiting, or abolishing weapons. Disarmament generally refers to a country's military or specific type of weaponry. Disarmament is often taken to mean total elimination of weapons of mass destruction, such as nuclear arms... and Arms Control Arms control Arms control is an umbrella term for restrictions upon the development, production, stockpiling, proliferation, and usage of weapons, especially weapons of mass destruction... , Phil Goff Phil Goff Philip Bruce Goff is the current Leader of the Opposition and the Leader of the New Zealand Labour Party. During the Fifth Labour Government, he served in a number of ministerial portfolios, including Minister of Defence of New Zealand, Minister of Corrections, Minister of Foreign Affairs and... |
Washington D.C. | The Minister delivered an address on the outlook for the Doha Round at a well attended US Chamber/US NZ Council luncheon. The Minister also witnessed the signing of an agreement for New Zealand's third contribution to the G8 Global Partnership for the disposal of Weapons of Mass Destruction. |
| May 2007 | Economic Development Economic development Economic development generally refers to the sustained, concerted actions of policymakers and communities that promote the standard of living and economic health of a specific area... Minister, Trevor Mallard Trevor Mallard Trevor Colin Mallard is a New Zealand politician. He was a Cabinet Minister in the Fifth Labour Government of New Zealand holding portfolios including Environment, Labour, Broadcasting, State Owned Enterprises, Rugby World Cup and Education. He was also Associate Minister of Finance.-Early... |
Boston Boston Boston is the capital of and largest city in Massachusetts, and is one of the oldest cities in the United States. The largest city in New England, Boston is regarded as the unofficial "Capital of New England" for its economic and cultural impact on the entire New England region. The city proper had... |
To attend BIO 2007 which was attended by more than 40 New Zealand biotechnology companies |
| May 2007 | Economic Development Economic development Economic development generally refers to the sustained, concerted actions of policymakers and communities that promote the standard of living and economic health of a specific area... Minister, Trevor Mallard Trevor Mallard Trevor Colin Mallard is a New Zealand politician. He was a Cabinet Minister in the Fifth Labour Government of New Zealand holding portfolios including Environment, Labour, Broadcasting, State Owned Enterprises, Rugby World Cup and Education. He was also Associate Minister of Finance.-Early... |
Boston Boston Boston is the capital of and largest city in Massachusetts, and is one of the oldest cities in the United States. The largest city in New England, Boston is regarded as the unofficial "Capital of New England" for its economic and cultural impact on the entire New England region. The city proper had... and New York New York New York is a state in the Northeastern region of the United States. It is the nation's third most populous state. New York is bordered by New Jersey and Pennsylvania to the south, and by Connecticut, Massachusetts and Vermont to the east... |
To promote New Zealand to US financial and investment contacts and to discuss international economic trends. |
| 19–24 March 2007 | The Prime Minister Prime Minister of New Zealand The Prime Minister of New Zealand is New Zealand's head of government consequent on being the leader of the party or coalition with majority support in the Parliament of New Zealand... , Helen Clark Helen Clark Helen Elizabeth Clark, ONZ is a New Zealand political figure who was the 37th Prime Minister of New Zealand for three consecutive terms from 1999 to 2008... |
Washington, D.C. Washington, D.C. Washington, D.C., formally the District of Columbia and commonly referred to as Washington, "the District", or simply D.C., is the capital of the United States. On July 16, 1790, the United States Congress approved the creation of a permanent national capital as permitted by the U.S. Constitution.... , Chicago Chicago Chicago is the largest city in the US state of Illinois. With nearly 2.7 million residents, it is the most populous city in the Midwestern United States and the third most populous in the US, after New York City and Los Angeles... and Seattle |
Her two-day visit to Washington D.C. included a meeting and lunch at the White House with President George W Bush (as well as other senior Bush Administration officials), and meetings with the Secretary of State, Condoleezza Rice, the Secretary of Defense, Robert Gates, the US Trade Representative, Susan Schwab, and the Director of National Intelligence, Admiral Mike McConnell. She also made calls on the Speaker of the House of Representatives, Nancy Pelosi, and Senator Barbara Boxer, Chair of the Senate Foreign Relations Subcommittee on East Asian and Pacific Affairs. |
| January 2007 | Prime Minister Prime Minister of New Zealand The Prime Minister of New Zealand is New Zealand's head of government consequent on being the leader of the party or coalition with majority support in the Parliament of New Zealand... and Sir Edmund Hillary |
Antarctica | To celebrate 50 years of Antarctica cooperation between New Zealand and the United States. |
| Early January 2007 | Hon Chris Carter Chris Carter (politician) Christopher Joseph Carter was an independent Member of Parliament in New Zealand, and a former member of the New Zealand Labour Party until his expulsion. Carter was a senior Cabinet Minister in the Fifth Labour Government of New Zealand, serving lastly as Minister of Education, Minister... , Minister of Conservation New Zealand Parliamentary Caucuses and MPs' responsibilities The 2005 New Zealand general election took place on 17 September 2005 and determined the composition of the 48th New Zealand Parliament. The table below lists all the political parties and the members of parliaments in the New Zealand Parliament, 48th New Zealand Parliament... |
Washington, D.C. Washington, D.C. Washington, D.C., formally the District of Columbia and commonly referred to as Washington, "the District", or simply D.C., is the capital of the United States. On July 16, 1790, the United States Congress approved the creation of a permanent national capital as permitted by the U.S. Constitution.... |
Represented New Zealand at the funeral of former President President of the United States The President of the United States of America is the head of state and head of government of the United States. The president leads the executive branch of the federal government and is the commander-in-chief of the United States Armed Forces.... Gerald Ford Gerald Ford Gerald Rudolph "Jerry" Ford, Jr. was the 38th President of the United States, serving from 1974 to 1977, and the 40th Vice President of the United States serving from 1973 to 1974... |
| October 2006 | Minister of Civil Defence New Zealand Parliamentary Caucuses and MPs' responsibilities The 2005 New Zealand general election took place on 17 September 2005 and determined the composition of the 48th New Zealand Parliament. The table below lists all the political parties and the members of parliaments in the New Zealand Parliament, 48th New Zealand Parliament... and Emergency Emergency An emergency is a situation that poses an immediate risk to health, life, property or environment. Most emergencies require urgent intervention to prevent a worsening of the situation, although in some situations, mitigation may not be possible and agencies may only be able to offer palliative... Management, Hon Rick Barker Rick Barker Richard John Barker is a New Zealand politician. He is a member of the Labour Party, and was a middle-ranking Cabinet minister in the Fifth Labour Government of New Zealand.-Early life:... |
Boston Boston Boston is the capital of and largest city in Massachusetts, and is one of the oldest cities in the United States. The largest city in New England, Boston is regarded as the unofficial "Capital of New England" for its economic and cultural impact on the entire New England region. The city proper had... and Washington, D.C. Washington, D.C. Washington, D.C., formally the District of Columbia and commonly referred to as Washington, "the District", or simply D.C., is the capital of the United States. On July 16, 1790, the United States Congress approved the creation of a permanent national capital as permitted by the U.S. Constitution.... |
Official Visit |
| July 2006 | Minister of Foreign Affairs Minister of Foreign Affairs (New Zealand) The Minister of Foreign Affairs is a major ministerial portfolio in the government of New Zealand.The current Minister of Foreign Affairs is Murray McCully, who was National Party Spokeperson of Foreign Affairs and Shadow Minister of Foreign Affairs. There are also Associate Minister roles... Rt Hon Winston Peters Winston Peters Winston Raymond Peters is a New Zealand politician and leader of New Zealand First, a political party he founded in 1993. Peters has had a turbulent political career since entering Parliament in 1978. He served as Minister of Maori Affairs in the Bolger National Party Government before being... |
Washington DC | Official visit |
| April 2006 | Minister of Defence Minister of Defence (New Zealand) The Minister of Defence is a minister in the government of New Zealand with responsibility for the New Zealand armed forces and the Ministry of Defence.The present Minister is Dr... and Minister of Trade New Zealand Parliamentary Caucuses and MPs' responsibilities The 2005 New Zealand general election took place on 17 September 2005 and determined the composition of the 48th New Zealand Parliament. The table below lists all the political parties and the members of parliaments in the New Zealand Parliament, 48th New Zealand Parliament... , Hon Phil Goff Phil Goff Philip Bruce Goff is the current Leader of the Opposition and the Leader of the New Zealand Labour Party. During the Fifth Labour Government, he served in a number of ministerial portfolios, including Minister of Defence of New Zealand, Minister of Corrections, Minister of Foreign Affairs and... , and Minister of Immigration New Zealand Parliamentary Caucuses and MPs' responsibilities The 2005 New Zealand general election took place on 17 September 2005 and determined the composition of the 48th New Zealand Parliament. The table below lists all the political parties and the members of parliaments in the New Zealand Parliament, 48th New Zealand Parliament... Hon David Cunliffe David Cunliffe David Richard Cunliffe is a New Zealand politician. He is a member of the Labour Party, and the sitting member of parliament for New Lynn, West Auckland. He served as the Minister of Health and Minister for Communications and Information Technology for the Fifth Labour Government of New Zealand... |
Washington, D.C. Washington, D.C. Washington, D.C., formally the District of Columbia and commonly referred to as Washington, "the District", or simply D.C., is the capital of the United States. On July 16, 1790, the United States Congress approved the creation of a permanent national capital as permitted by the U.S. Constitution.... |
Official visit |
| January and March 2006 | Minister Phil Goff Phil Goff Philip Bruce Goff is the current Leader of the Opposition and the Leader of the New Zealand Labour Party. During the Fifth Labour Government, he served in a number of ministerial portfolios, including Minister of Defence of New Zealand, Minister of Corrections, Minister of Foreign Affairs and... and Economic Development Minister Mallard Trevor Mallard Trevor Colin Mallard is a New Zealand politician. He was a Cabinet Minister in the Fifth Labour Government of New Zealand holding portfolios including Environment, Labour, Broadcasting, State Owned Enterprises, Rugby World Cup and Education. He was also Associate Minister of Finance.-Early... |
California California California is a state located on the West Coast of the United States. It is by far the most populous U.S. state, and the third-largest by land area... |
Official visit |
| May 2005 | Foreign Affairs and Trade Minister Minister of Foreign Affairs (New Zealand) The Minister of Foreign Affairs is a major ministerial portfolio in the government of New Zealand.The current Minister of Foreign Affairs is Murray McCully, who was National Party Spokeperson of Foreign Affairs and Shadow Minister of Foreign Affairs. There are also Associate Minister roles... Goff Phil Goff Philip Bruce Goff is the current Leader of the Opposition and the Leader of the New Zealand Labour Party. During the Fifth Labour Government, he served in a number of ministerial portfolios, including Minister of Defence of New Zealand, Minister of Corrections, Minister of Foreign Affairs and... , Customs Minister Barker and Economic Development and Forestry Minister Anderton |
Various | Separate official visits |
| April 2005 | Speaker of the House of Representatives Speaker of the New Zealand House of Representatives In New Zealand the Speaker of the House of Representatives is the individual who chairs the country's legislative body, the New Zealand House of Representatives... , Hon Margaret Wilson Margaret Wilson Dame Margaret Wilson DCNZM is a New Zealand academic and former politician. She was Speaker of the New Zealand House of Representatives during the Fifth Labour Government of New Zealand. She is a member of the Labour Party.-Early life:... |
Washington, D.C. Washington, D.C. Washington, D.C., formally the District of Columbia and commonly referred to as Washington, "the District", or simply D.C., is the capital of the United States. On July 16, 1790, the United States Congress approved the creation of a permanent national capital as permitted by the U.S. Constitution.... and Philadelphia |
Led a parliamentary delegation to the US |
| April 2005 | Associate Minister of Finance New Zealand Parliamentary Caucuses and MPs' responsibilities The 2005 New Zealand general election took place on 17 September 2005 and determined the composition of the 48th New Zealand Parliament. The table below lists all the political parties and the members of parliaments in the New Zealand Parliament, 48th New Zealand Parliament... , Hon Trevor Mallard Trevor Mallard Trevor Colin Mallard is a New Zealand politician. He was a Cabinet Minister in the Fifth Labour Government of New Zealand holding portfolios including Environment, Labour, Broadcasting, State Owned Enterprises, Rugby World Cup and Education. He was also Associate Minister of Finance.-Early... |
Washington, D.C. Washington, D.C. Washington, D.C., formally the District of Columbia and commonly referred to as Washington, "the District", or simply D.C., is the capital of the United States. On July 16, 1790, the United States Congress approved the creation of a permanent national capital as permitted by the U.S. Constitution.... |
International Monetary Fund International Monetary Fund The International Monetary Fund is an organization of 187 countries, working to foster global monetary cooperation, secure financial stability, facilitate international trade, promote high employment and sustainable economic growth, and reduce poverty around the world... /World Bank World Bank The World Bank is an international financial institution that provides loans to developing countries for capital programmes.The World Bank's official goal is the reduction of poverty... Spring Meetings |
| September 2004 | Deputy Prime Minister Deputy Prime Minister of New Zealand The Deputy Prime Minister of New Zealand is second most senior officer in the Government of New Zealand, although this seniority does not necessarily translate into power.... and Minister of Finance New Zealand Parliamentary Caucuses and MPs' responsibilities The 2005 New Zealand general election took place on 17 September 2005 and determined the composition of the 48th New Zealand Parliament. The table below lists all the political parties and the members of parliaments in the New Zealand Parliament, 48th New Zealand Parliament... , Michael Cullen |
Washington, D.C. Washington, D.C. Washington, D.C., formally the District of Columbia and commonly referred to as Washington, "the District", or simply D.C., is the capital of the United States. On July 16, 1790, the United States Congress approved the creation of a permanent national capital as permitted by the U.S. Constitution.... |
Official Visit |
| Other Ministerial visits in 2004 | Minister of Health New Zealand Parliamentary Caucuses and MPs' responsibilities The 2005 New Zealand general election took place on 17 September 2005 and determined the composition of the 48th New Zealand Parliament. The table below lists all the political parties and the members of parliaments in the New Zealand Parliament, 48th New Zealand Parliament... , Hon Annette King Annette King Annette Faye King is a New Zealand politician. She is the current Deputy Leader of the Opposition in the New Zealand. She was a Cabinet Minister in the Fifth Labour Government of New Zealand.-Early life:... ; Minister for Trade Negotiations New Zealand Parliamentary Caucuses and MPs' responsibilities The 2005 New Zealand general election took place on 17 September 2005 and determined the composition of the 48th New Zealand Parliament. The table below lists all the political parties and the members of parliaments in the New Zealand Parliament, 48th New Zealand Parliament... , Hon Jim Sutton Jim Sutton James Robert Sutton, CNZM , generally known as Jim Sutton, was a New Zealand politician from 1984–1990 and from 1993–2006. He has held a range of ministerial portfolios including Agriculture, Forestry, Rural Affairs, Biosecurity, and Trade Negotiations.-Biography:Sutton was born in... ; Minister of Energy New Zealand Parliamentary Caucuses and MPs' responsibilities The 2005 New Zealand general election took place on 17 September 2005 and determined the composition of the 48th New Zealand Parliament. The table below lists all the political parties and the members of parliaments in the New Zealand Parliament, 48th New Zealand Parliament... , Hon Pete Hodgson Pete Hodgson Peter Colin Hodgson is a New Zealand politician. He is a member of the Labour Party.Hodgson was born in Whangarei, and received a Bachelor's degree in veterinary science from Massey University... ; and Minister of Foreign Affairs and Trade Minister of Foreign Affairs (New Zealand) The Minister of Foreign Affairs is a major ministerial portfolio in the government of New Zealand.The current Minister of Foreign Affairs is Murray McCully, who was National Party Spokeperson of Foreign Affairs and Shadow Minister of Foreign Affairs. There are also Associate Minister roles... , Hon Phil Goff Phil Goff Philip Bruce Goff is the current Leader of the Opposition and the Leader of the New Zealand Labour Party. During the Fifth Labour Government, he served in a number of ministerial portfolios, including Minister of Defence of New Zealand, Minister of Corrections, Minister of Foreign Affairs and... . |
Various | Separate Official Visits |
| Visits in 2003 | Minister of Police New Zealand Police The New Zealand Police is the national police force of New Zealand, responsible for enforcing criminal law, enhancing public safety, maintaining order and keeping the peace throughout New Zealand... , George Warren Hawkins George Warren Hawkins George Warren Hawkins is a New Zealand politician. He is a member of the Labour Party.-Early life:Hawkins was born in 1946 in the Auckland suburb of Mt Eden. He attended Dominion Road Primary School, Mount Albert Grammar School and then Auckland Teachers' College.-Papakura:Hawkins was a... ; Associate Minister of Agriculture New Zealand Parliamentary Caucuses and MPs' responsibilities The 2005 New Zealand general election took place on 17 September 2005 and determined the composition of the 48th New Zealand Parliament. The table below lists all the political parties and the members of parliaments in the New Zealand Parliament, 48th New Zealand Parliament... , Damien O'Connor Damien O'Connor Damien Peter O'Connor is a New Zealand politician from the West Coast of the South Island. He is a member of the Labour Party and a Member of Parliament.-Early years:... ; Minister of State New Zealand Parliamentary Caucuses and MPs' responsibilities The 2005 New Zealand general election took place on 17 September 2005 and determined the composition of the 48th New Zealand Parliament. The table below lists all the political parties and the members of parliaments in the New Zealand Parliament, 48th New Zealand Parliament... , David Cunliffe David Cunliffe David Richard Cunliffe is a New Zealand politician. He is a member of the Labour Party, and the sitting member of parliament for New Lynn, West Auckland. He served as the Minister of Health and Minister for Communications and Information Technology for the Fifth Labour Government of New Zealand... ; The Minister of Education New Zealand Parliamentary Caucuses and MPs' responsibilities The 2005 New Zealand general election took place on 17 September 2005 and determined the composition of the 48th New Zealand Parliament. The table below lists all the political parties and the members of parliaments in the New Zealand Parliament, 48th New Zealand Parliament... and Associate Minister of Finance, Trevor Mallard Trevor Mallard Trevor Colin Mallard is a New Zealand politician. He was a Cabinet Minister in the Fifth Labour Government of New Zealand holding portfolios including Environment, Labour, Broadcasting, State Owned Enterprises, Rugby World Cup and Education. He was also Associate Minister of Finance.-Early... ; Minister for Research, Science and Technology New Zealand Parliamentary Caucuses and MPs' responsibilities The 2005 New Zealand general election took place on 17 September 2005 and determined the composition of the 48th New Zealand Parliament. The table below lists all the political parties and the members of parliaments in the New Zealand Parliament, 48th New Zealand Parliament... , Pete Hodgson Pete Hodgson Peter Colin Hodgson is a New Zealand politician. He is a member of the Labour Party.Hodgson was born in Whangarei, and received a Bachelor's degree in veterinary science from Massey University... and The Minister of Health New Zealand Parliamentary Caucuses and MPs' responsibilities The 2005 New Zealand general election took place on 17 September 2005 and determined the composition of the 48th New Zealand Parliament. The table below lists all the political parties and the members of parliaments in the New Zealand Parliament, 48th New Zealand Parliament... , Annette King Annette King Annette Faye King is a New Zealand politician. She is the current Deputy Leader of the Opposition in the New Zealand. She was a Cabinet Minister in the Fifth Labour Government of New Zealand.-Early life:... . |
Various | Various |
| Visits in 2002 | Prime Minister Prime Minister of New Zealand The Prime Minister of New Zealand is New Zealand's head of government consequent on being the leader of the party or coalition with majority support in the Parliament of New Zealand... , Helen Clark Helen Clark Helen Elizabeth Clark, ONZ is a New Zealand political figure who was the 37th Prime Minister of New Zealand for three consecutive terms from 1999 to 2008... |
Various | Made two official visits to the United States in 2002 |
| 2002 | Other Ministerial visits included Deputy Prime Minister Dr Michael Cullen, Minister for Foreign Affairs Minister of Foreign Affairs (New Zealand) The Minister of Foreign Affairs is a major ministerial portfolio in the government of New Zealand.The current Minister of Foreign Affairs is Murray McCully, who was National Party Spokeperson of Foreign Affairs and Shadow Minister of Foreign Affairs. There are also Associate Minister roles... Phil Goff Phil Goff Philip Bruce Goff is the current Leader of the Opposition and the Leader of the New Zealand Labour Party. During the Fifth Labour Government, he served in a number of ministerial portfolios, including Minister of Defence of New Zealand, Minister of Corrections, Minister of Foreign Affairs and... and Minister for Trade Negotiations Jim Sutton Jim Sutton James Robert Sutton, CNZM , generally known as Jim Sutton, was a New Zealand politician from 1984–1990 and from 1993–2006. He has held a range of ministerial portfolios including Agriculture, Forestry, Rural Affairs, Biosecurity, and Trade Negotiations.-Biography:Sutton was born in... . |
Various | Official Visits |
New Zealand tours by United States delegates
United States delegations to New Zealand| Dates | Minister/Delegate | Cities visited | Reason |
|---|---|---|---|
| November 2010 | Secretary of State United States Secretary of State The United States Secretary of State is the head of the United States Department of State, concerned with foreign affairs. The Secretary is a member of the Cabinet and the highest-ranking cabinet secretary both in line of succession and order of precedence... Hillary Clinton |
Wellington Wellington Wellington is the capital city and third most populous urban area of New Zealand, although it is likely to have surpassed Christchurch due to the exodus following the Canterbury Earthquake. It is at the southwestern tip of the North Island, between Cook Strait and the Rimutaka Range... |
Official Visit to meet with Prime Minister Prime Minister of New Zealand The Prime Minister of New Zealand is New Zealand's head of government consequent on being the leader of the party or coalition with majority support in the Parliament of New Zealand... John Key John Key John Phillip Key is the 38th Prime Minister of New Zealand, in office since 2008. He has led the New Zealand National Party since 2006.... . |
| July 2008 | Secretary of State United States Secretary of State The United States Secretary of State is the head of the United States Department of State, concerned with foreign affairs. The Secretary is a member of the Cabinet and the highest-ranking cabinet secretary both in line of succession and order of precedence... Condoleezza Rice Condoleezza Rice Condoleezza Rice is an American political scientist and diplomat. She served as the 66th United States Secretary of State, and was the second person to hold that office in the administration of President George W. Bush... |
Government House Government House, Auckland The site of the present day Government House, Auckland was first built upon in the 1880s or 1890s, although some of the trees are slightly older, dating from the 1870s... , Auckland Auckland The Auckland metropolitan area , in the North Island of New Zealand, is the largest and most populous urban area in the country with residents, percent of the country's population. Auckland also has the largest Polynesian population of any city in the world... |
Official Visit to meet with Minister of Foreign Affairs Minister of Foreign Affairs (New Zealand) The Minister of Foreign Affairs is a major ministerial portfolio in the government of New Zealand.The current Minister of Foreign Affairs is Murray McCully, who was National Party Spokeperson of Foreign Affairs and Shadow Minister of Foreign Affairs. There are also Associate Minister roles... Winston Peters Winston Peters Winston Raymond Peters is a New Zealand politician and leader of New Zealand First, a political party he founded in 1993. Peters has had a turbulent political career since entering Parliament in 1978. He served as Minister of Maori Affairs in the Bolger National Party Government before being... and Prime Minister Prime Minister of New Zealand The Prime Minister of New Zealand is New Zealand's head of government consequent on being the leader of the party or coalition with majority support in the Parliament of New Zealand... Helen Clark Helen Clark Helen Elizabeth Clark, ONZ is a New Zealand political figure who was the 37th Prime Minister of New Zealand for three consecutive terms from 1999 to 2008... . Held a joint press conference with the Prime Minister. |
| August 2006 | Deputy Assistant Secretary of State for East Asia and Pacific Affairs Assistant Secretary of State for East Asian and Pacific Affairs The Assistant Secretary of State for East Asian and Pacific Affairs is the head of the Bureau of East Asian and Pacific Affairs within the United States Department of State. The Assistant Secretary guides operation of the U.S... Glyn Davies |
Wellington Wellington Wellington is the capital city and third most populous urban area of New Zealand, although it is likely to have surpassed Christchurch due to the exodus following the Canterbury Earthquake. It is at the southwestern tip of the North Island, between Cook Strait and the Rimutaka Range... |
Official Visit |
| May 2006 | Washington State Governor Christine Gregoire Christine Gregoire Christine O'Grady "Chris" Gregoire is the 22nd and current Governor of the state of Washington, and a member of the Democratic Party. Gregoire defeated Republican candidate Dino Rossi in 2004, and again in 2008. She is the second female governor of Washington... |
Auckland Auckland The Auckland metropolitan area , in the North Island of New Zealand, is the largest and most populous urban area in the country with residents, percent of the country's population. Auckland also has the largest Polynesian population of any city in the world... |
Official Visit |
| April 2006 | Secretary of Veterans Affairs Jim Nicholson Jim Nicholson (U.S. politician) Robert James "Jim" Nicholson is an attorney, real estate developer, and a former Republican Party chairman. He was the United States Secretary of Veterans Affairs from January 26, 2005 until October 1, 2007.-Personal life:... |
Auckland Auckland The Auckland metropolitan area , in the North Island of New Zealand, is the largest and most populous urban area in the country with residents, percent of the country's population. Auckland also has the largest Polynesian population of any city in the world... |
Official Visit |
| March 2006 | Assistant Secretary of State for East Asian and Pacific Affairs Assistant Secretary of State for East Asian and Pacific Affairs The Assistant Secretary of State for East Asian and Pacific Affairs is the head of the Bureau of East Asian and Pacific Affairs within the United States Department of State. The Assistant Secretary guides operation of the U.S... Christopher R. Hill Christopher R. Hill Christopher Robert Hill is an American diplomat who served as the U.S. Ambassador to Iraq.On July 1, 2010, Hill was chosen to be the dean of the Josef Korbel School of International Studies at the University of Denver... |
Wellington Wellington Wellington is the capital city and third most populous urban area of New Zealand, although it is likely to have surpassed Christchurch due to the exodus following the Canterbury Earthquake. It is at the southwestern tip of the North Island, between Cook Strait and the Rimutaka Range... |
Official Visit |
| January 2006 | General General A general officer is an officer of high military rank, usually in the army, and in some nations, the air force. The term is widely used by many nations of the world, and when a country uses a different term, there is an equivalent title given.... John Abizaid John Abizaid John Philip Abizaid, AO is a retired General in the United States Army and former Commander of the United States Central Command , overseeing American military operations in a 27-country region, from the Horn of Africa, the Arabian Peninsula, to South and Central Asia, covering much of the Middle... , Commander Commander Commander is a naval rank which is also sometimes used as a military title depending on the individual customs of a given military service. Commander is also used as a rank or title in some organizations outside of the armed forces, particularly in police and law enforcement.-Commander as a naval... US Central Command United States Central Command The United States Central Command is a theater-level Unified Combatant Command unit of the U.S. armed forces, established in 1983 under the operational control of the U.S. Secretary of Defense... & William J. Fallon William J. Fallon William Joseph Fallon is a retired United States Navy four-star admiral who retired after serving for over 41 years. His last military assignment was as Commander, U.S. Central Command from March 2007 to March 2008. ADM Fallon was the first Navy officer to hold that position. His other four-star... , Commander, US Pacific Command United States Pacific Command The United States Pacific Command is a Unified Combatant Command of the United States armed forces responsible for the Pacific Ocean area. It is led by the Commander, Pacific Command , who is the supreme military authority for the various branches of the Armed Forces of the United States serving... |
Various | Official Visit |
| January 2006 | Senator United States Senate The United States Senate is the upper house of the bicameral legislature of the United States, and together with the United States House of Representatives comprises the United States Congress. The composition and powers of the Senate are established in Article One of the U.S. Constitution. Each... s John McCain John McCain John Sidney McCain III is the senior United States Senator from Arizona. He was the Republican nominee for president in the 2008 United States election.... (R-Arizona Arizona Arizona ; is a state located in the southwestern region of the United States. It is also part of the western United States and the mountain west. The capital and largest city is Phoenix... ), Chairman of the Senate Armed Services Committee, Susan Collins Susan Collins Susan Margaret Collins is the junior United States Senator from Maine and a member of the Republican Party. First elected to the Senate in 1996, she is the ranking member of the Senate Committee on Homeland Security and Governmental Affairs... (R-Maine Maine Maine is a state in the New England region of the northeastern United States, bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the east and south, New Hampshire to the west, and the Canadian provinces of Quebec to the northwest and New Brunswick to the northeast. Maine is both the northernmost and easternmost... ), and John E. Sununu John E. Sununu John Edward Sununu is a former Republican United States Senator from New Hampshire, of Lebanese and Palestinian Christian ancestry. Sununu was the youngest member of the Senate for his entire six year term. He is the son of former New Hampshire Governor John H... (R-New Hampshire New Hampshire New Hampshire is a state in the New England region of the northeastern United States of America. The state was named after the southern English county of Hampshire. It is bordered by Massachusetts to the south, Vermont to the west, Maine and the Atlantic Ocean to the east, and the Canadian... ) |
Various | Official Visit |
| January 2006 | Congressman United States Congress The United States Congress is the bicameral legislature of the federal government of the United States, consisting of the Senate and the House of Representatives. The Congress meets in the United States Capitol in Washington, D.C.... Sherwood Boehlert Sherwood Boehlert Sherwood "Sherry" Louis Boehlert is a retired American politician from New York. He represented upstate New York in the United States House of Representatives from 1983 until 2007. Boehlert, a Republican, was considered to be a member of the party's moderate wing. In 2003, Utica Union Station was... (R-New York New York New York is a state in the Northeastern region of the United States. It is the nation's third most populous state. New York is bordered by New Jersey and Pennsylvania to the south, and by Connecticut, Massachusetts and Vermont to the east... ) |
Various | Led a House Science Committee delegation –The delegation included: Lincoln Davis Lincoln Davis Lincoln Edward Davis is the former U.S. Representative for . He is a member of the Democratic Party.-Early life, education and career:... (D-Tennessee Tennessee Tennessee is a U.S. state located in the Southeastern United States. It has a population of 6,346,105, making it the nation's 17th-largest state by population, and covers , making it the 36th-largest by total land area... ), Bob Inglis Bob Inglis Robert Durden "Bob" Inglis, Sr. is a former U.S. Representative for , serving from 1993 to 1999, and then again from 2005 until 2011. He is a member of the Republican Party... (R-North Carolina North Carolina North Carolina is a state located in the southeastern United States. The state borders South Carolina and Georgia to the south, Tennessee to the west and Virginia to the north. North Carolina contains 100 counties. Its capital is Raleigh, and its largest city is Charlotte... ), Brad Miller Brad Miller (congressman) Ralph Bradley "Brad" Miller is the U.S. Representative for , serving since 2003. District 13 includes all of Caswell and Person counties, and parts of Alamance, Granville, Guilford, Rockingham and Wake counties... (D-North Carolina North Carolina North Carolina is a state located in the southeastern United States. The state borders South Carolina and Georgia to the south, Tennessee to the west and Virginia to the north. North Carolina contains 100 counties. Its capital is Raleigh, and its largest city is Charlotte... ), Ben Chandler Ben Chandler Albert Benjamin "Ben" Chandler III is the U.S. Representative for , serving since a special election in 2004. He is a member of the Democratic Party.-Early life, education and career:... (D-Kentucky Kentucky The Commonwealth of Kentucky is a state located in the East Central United States of America. As classified by the United States Census Bureau, Kentucky is a Southern state, more specifically in the East South Central region. Kentucky is one of four U.S. states constituted as a commonwealth... ), R (Bud) Cramer (D-Alabama Alabama Alabama is a state located in the southeastern region of the United States. It is bordered by Tennessee to the north, Georgia to the east, Florida and the Gulf of Mexico to the south, and Mississippi to the west. Alabama ranks 30th in total land area and ranks second in the size of its inland... ), Phil Gingery (R-Georgia Georgia (U.S. state) Georgia is a state located in the southeastern United States. It was established in 1732, the last of the original Thirteen Colonies. The state is named after King George II of Great Britain. Georgia was the fourth state to ratify the United States Constitution, on January 2, 1788... ), Darlene Hooley Darlene Hooley Darlene Kay Olson Hooley is a former Democratic member of the U.S. House of Representatives from Oregon who represented the state's . A native of North Dakota, she spent eight years teaching high school before entering politics when she was elected to the West Linn, Oregon city council in 1975... (D-Oregon Oregon Oregon is a state in the Pacific Northwest region of the United States. It is located on the Pacific coast, with Washington to the north, California to the south, Nevada on the southeast and Idaho to the east. The Columbia and Snake rivers delineate much of Oregon's northern and eastern... ), Jim Costa Jim Costa James Manuel "Jim" Costa is the U.S. Representative for , serving since his initial election in 2004. He is a member of the Democratic Party. The district takes in large and predominantly Latino portions of Fresno and Bakersfield in the Central Valley.-Early life and education:Born in Fresno,... (D-California California California is a state located on the West Coast of the United States. It is by far the most populous U.S. state, and the third-largest by land area... ), and Roscoe Bartlett Roscoe Bartlett Roscoe Gardner Bartlett, Ph.D. is the U.S. Representative for , serving since 1993. He is a member of the Republican Party, and a member of the Tea Party Caucus... (R-Maryland Maryland Maryland is a U.S. state located in the Mid Atlantic region of the United States, bordering Virginia, West Virginia, and the District of Columbia to its south and west; Pennsylvania to its north; and Delaware to its east... ) |
| September 2005 | Secretary of Agriculture Mike Johanns Mike Johanns Michael Owen "Mike" Johanns is an American Republican politician who has been the junior United States Senator from Nebraska since 2009. Previously he was the 38th Governor of Nebraska from 1999 to 2005 and was U.S. Secretary of Agriculture from 2005 to 2007, becoming the fourth Nebraskan to hold... |
Various | Official Visit |
| 2005 | Congressman Jim Kolbe Jim Kolbe James Thomas "Jim" Kolbe is a former Republican member of the United States House of Representatives for Arizona's 8th congressional district, serving 11 terms from 1985 to 2007.-Early life:... (Republican Republican Party (United States) The Republican Party is one of the two major contemporary political parties in the United States, along with the Democratic Party. Founded by anti-slavery expansion activists in 1854, it is often called the GOP . The party's platform generally reflects American conservatism in the U.S... , Arizona Arizona Arizona ; is a state located in the southwestern region of the United States. It is also part of the western United States and the mountain west. The capital and largest city is Phoenix... ) |
Various | Is the co-Chair of the Friends of New Zealand Caucus in the United States House of Representatives United States House of Representatives The United States House of Representatives is one of the two Houses of the United States Congress, the bicameral legislature which also includes the Senate.The composition and powers of the House are established in Article One of the Constitution... |
| December 2004 | US Senator Tom Harkin Tom Harkin Thomas Richard "Tom" Harkin is the junior United States Senator from Iowa and a member of the Democratic Party. He previously served in the United States House of Representatives .... (D-Iowa Iowa Iowa is a state located in the Midwestern United States, an area often referred to as the "American Heartland". It derives its name from the Ioway people, one of the many American Indian tribes that occupied the state at the time of European exploration. Iowa was a part of the French colony of New... ) and Congressman Dennis Kucinich Dennis Kucinich Dennis John Kucinich is the U.S. Representative for , serving since 1997. He was furthermore a candidate for the Democratic nomination for President of the United States in the 2004 and 2008 presidential elections.... (D-Ohio Ohio Ohio is a Midwestern state in the United States. The 34th largest state by area in the U.S.,it is the 7th‑most populous with over 11.5 million residents, containing several major American cities and seven metropolitan areas with populations of 500,000 or more.The state's capital is Columbus... ) |
Wellington Wellington Wellington is the capital city and third most populous urban area of New Zealand, although it is likely to have surpassed Christchurch due to the exodus following the Canterbury Earthquake. It is at the southwestern tip of the North Island, between Cook Strait and the Rimutaka Range... |
High-level visits to attend Parliamentarians for Global Action Conference |
| November 2004 | US Senator Max Baucus Max Baucus Max Sieben Baucus is the senior United States Senator from Montana and a member of the Democratic Party. First elected to the Senate in 1978, as of 2010 he is the longest-serving Senator from Montana, and the fifth longest-serving U.S... (D-Montana Montana Montana is a state in the Western United States. The western third of Montana contains numerous mountain ranges. Smaller, "island ranges" are found in the central third of the state, for a total of 77 named ranges of the Rocky Mountains. This geographical fact is reflected in the state's name,... ) |
Various | Led a business delegation from Montana Montana Montana is a state in the Western United States. The western third of Montana contains numerous mountain ranges. Smaller, "island ranges" are found in the central third of the state, for a total of 77 named ranges of the Rocky Mountains. This geographical fact is reflected in the state's name,... |
| November 2004 | Delegation of Californian State Senators United States Congressional Delegations from California These are tables of congressional delegations from California in the United States Senate and United States House of Representatives.-United States Senate:- Mid-term changes :-United States House of Representatives:... |
Various | Official Visit |
| August 2004 | US Senator Richard Shelby Richard Shelby Richard Craig Shelby is the senior U.S. Senator from Alabama. First elected to the Senate in 1986, he is the ranking member of the United States Senate Committee on Banking, Housing, and Urban Affairs and was its chairman from 2003 to 2007.... (R-Alabama Alabama Alabama is a state located in the southeastern region of the United States. It is bordered by Tennessee to the north, Georgia to the east, Florida and the Gulf of Mexico to the south, and Mississippi to the west. Alabama ranks 30th in total land area and ranks second in the size of its inland... ) and Congressman Robert E. Cramer (D-Alabama Alabama Alabama is a state located in the southeastern region of the United States. It is bordered by Tennessee to the north, Georgia to the east, Florida and the Gulf of Mexico to the south, and Mississippi to the west. Alabama ranks 30th in total land area and ranks second in the size of its inland... ) |
Various | Official Visit |
| March 2004 | Governor of Iowa, Thomas Vilsack | Various | Led a biotechnology trade delegation from his state to New Zealand. |
| January 2004 | Led by Senator Don Nickles Don Nickles Donald Lee Nickles is an American businessman and politician who was a Republican United States Senator from Oklahoma from 1981 until 2005. He was a fiscal and social conservative.-Early life:... (R-Oklahoma Oklahoma Oklahoma is a state located in the South Central region of the United States of America. With an estimated 3,751,351 residents as of the 2010 census and a land area of 68,667 square miles , Oklahoma is the 28th most populous and 20th-largest state... ) |
Various | A Congressional Delegation of six Republican Senators |
| Visits in 2003 | Under-Secretary for Regulatory Programs, Bill Hawks Bill Hawks William T. Hawks is an American politician and civil servant, and a businessman active in agriculture.... , Under-Secretary for Commerce Grant Aldonas and Under-Secretary of State for International Security and Arms Control, John R. Bolton John R. Bolton John Robert Bolton is an American lawyer and diplomat who has served in several Republican presidential administrations. He served as the U.S. Permanent Representative to the United Nations from August 2005 until December 2006 on a recess appointment... . |
Auckland Auckland The Auckland metropolitan area , in the North Island of New Zealand, is the largest and most populous urban area in the country with residents, percent of the country's population. Auckland also has the largest Polynesian population of any city in the world... |
US delegation also visited Auckland Auckland The Auckland metropolitan area , in the North Island of New Zealand, is the largest and most populous urban area in the country with residents, percent of the country's population. Auckland also has the largest Polynesian population of any city in the world... for the 34th Pacific Islands Forum Pacific Islands Forum The Pacific Islands Forum is an inter-governmental organization that aims to enhance cooperation between the independent countries of the Pacific Ocean. It was founded in 1971 as the South Pacific Forum... , where the US was a dialogue partner. |
United States – New Zealand Council
Dating back to 1986, the United States – New Zealand CouncilUnited States – New Zealand Council
The United States – New Zealand Council is an independent non-profit, non-partisan organisation dedicated to promoting a strong bilateral relationship between the United States and New Zealand...
has played a prominent role in US-NZ bilateral relations. The Council provides information on a range of economic, political, and security issues affecting the two countries and on their increasing collaboration, historical links and shared values, outlooks, and approaches on economic, political, and legal systems.
As well as working with the New Zealand United States Council to organise the widely lauded Partnership Forums, the US-NZ Council periodically honours distinguished individuals with the Torchbearer Award for promoting bilateral exchanges. Past recipients have included Assistant Secretary of State for East Asian and Pacific Affairs, Christopher Hill; Three-term NZ Prime Minister and Ambassador to the United States, Jim Bolger; California Congressman, Calvin Dooley; NZ Prime Minister and Director of WTO, Mike Moore; Agriculture Secretary and US Trade Representative, Clayton Yeutter.
Currently the Council's efforts are focused on the Trans-Pacific Partnership agreement, which the United States has signaled they will engage in discussion. The Asia-Pacific region is important for both the United States and New Zealand, the Council spreads awareness of its importance both in the business community and on the Hill.
The United States – New Zealand Council is a non-profit, nonpartisan, organisation.
New Zealand United States Council

The Council works closely with its counterpart in Washington, D.C.
Washington, D.C.
Washington, D.C., formally the District of Columbia and commonly referred to as Washington, "the District", or simply D.C., is the capital of the United States. On July 16, 1790, the United States Congress approved the creation of a permanent national capital as permitted by the U.S. Constitution....
, the US NZ Council, with business groups in New Zealand and with government agencies, especially the Ministry of Foreign Affairs and Trade and the New Zealand Embassy in Washington.
The council has been working tirelessly towards an improvement in NZ-US relations with New Zealand MPs (Members of Parliament) and their American counterparts in Congress. Such things as verbal and face-to-face discussions about political and domestic issues involving either countries. Their work has not been in vain: United States Secretary of State
United States Secretary of State
The United States Secretary of State is the head of the United States Department of State, concerned with foreign affairs. The Secretary is a member of the Cabinet and the highest-ranking cabinet secretary both in line of succession and order of precedence...
Condoleezza Rice
Condoleezza Rice
Condoleezza Rice is an American political scientist and diplomat. She served as the 66th United States Secretary of State, and was the second person to hold that office in the administration of President George W. Bush...
has begun regular communication with New Zealand's Foreign Affairs Minister
Minister of Foreign Affairs (New Zealand)
The Minister of Foreign Affairs is a major ministerial portfolio in the government of New Zealand.The current Minister of Foreign Affairs is Murray McCully, who was National Party Spokeperson of Foreign Affairs and Shadow Minister of Foreign Affairs. There are also Associate Minister roles...
Winston Peters
Winston Peters
Winston Raymond Peters is a New Zealand politician and leader of New Zealand First, a political party he founded in 1993. Peters has had a turbulent political career since entering Parliament in 1978. He served as Minister of Maori Affairs in the Bolger National Party Government before being...
about issues such as nuclear tests in North Korea
North Korea
The Democratic People’s Republic of Korea , , is a country in East Asia, occupying the northern half of the Korean Peninsula. Its capital and largest city is Pyongyang. The Korean Demilitarized Zone serves as the buffer zone between North Korea and South Korea...
, and other issues of politics, trade and business affairs of both New Zealand and the United States.
See also
- Embassy of the United States in WellingtonEmbassy of the United States in WellingtonThe Embassy of the United States in Wellington, New Zealand along with the consulate general in Auckland provides assistance to American citizens and issues travel visas to foreign nationals who wish to visit the United States....
- Foreign relations of New ZealandForeign relations of New ZealandThe foreign relations of New Zealand are oriented chiefly toward developed democratic nations and emerging Pacific economies. The country’s major political parties have generally agreed on the broad outlines of foreign policy, and the current coalition government has been active in promoting free...
- Foreign relations of the United StatesForeign relations of the United StatesThe United States has formal diplomatic relations with most nations. The United States federal statutes relating to foreign relations can be found in Title 22 of the United States Code.-Pacific:-Americas:-Caribbean:...
- Military history of New ZealandMilitary history of New ZealandThe military history of New Zealand is an aspect of the history of New Zealand that spans several hundred years. When first settled by Māori almost a millennium ago, there was much land and resources, but war began to break out as the country's carrying capacity was approached...
- Military history of the United StatesMilitary history of the United StatesThe military history of the United States spans a period of over two centuries. During the course of those years, the United States evolved from a new nation fighting the British Empire for independence without a professional military , through a monumental American Civil War to the world's sole...
- USS Glacier (AGB-4)USS Glacier (AGB-4)USS Glacier is the historic Glacier class icebreaker which served in the first through fifteenth Operation Deep Freeze expeditions. Glacier was first icebreaker to make her way through the frozen Bellingshausen Sea, and most of the topography in the area is named for her crewmembers...
External links
- History of New Zealand - U.S. relations
- New Zealand Government Official Site
- United States Government Official Site
- United States - New Zealand Council The United States - New Zealand Council, an independent non-profit organization dedicated to strengthening United States-New Zealand relations through enhanced communications between the two nations.
- New Zealand Embassy in Washington Official Site
- United States of America Embassy in Wellington Official Site
- "Rice hints at thaw in US-NZ relations", New Zealand Herald, July 26, 2008

