
Latgalians
Encyclopedia
The term Latgalians
The term Latgalians (Latgalian
: latgalīši, latgali, (also spelt Latgallians and sometimes known as Lettigalls, Latgolans, or Lettigallians) can refer to the inhabitants of the Latgale
region in eastern Latvia
in general, the ethnic Latvians
of Latgale (especially those who speak the Latgalian language
), or to the ancient Baltic
tribe. In English, the more archaic Lettigallians usually refers to the tribe.
In Latvian, latgaļi refers to the ancient tribe, latgalieši refers to the ethnic Latvians of Latgale, which developed separately from the rest of ethnic Latvia in 1621-1917, whilst, though the terms are confused in colloquial Latvian.
, or "Latgalians" (i.e. inhabitants of the primal Latgale, – this ancient Central-Baltic term derives very likely from *Lætgale = "The Lettland"; compare with *Zemgale
= "The lower-land"), were a Central Baltic
tribe of little-known origin, which dwell in the 5th-6th centuries only in the Eastern part of present-day Vidzeme
(westwards from Aiviekste River
), and later on – in nearly all the territory of that region. In written sources, they are mentioned from the 11th century. In the first two decades of the 13th century, the (Western) Latgalians allied with German (mainly Saxon) crusaders and their lands were incorporated in unclear circumstances into Livonia
. In the 13th-14th centuries, they assimilated in present-day Latgale an unknown East-Baltic tribe, the latter in this way becoming a part of today's ethnic Latvians
(It's striking that the Latvian term latgalieši ("Latgalians"), in the sense of "Eastern Latvians", dates only to the early 20th century).
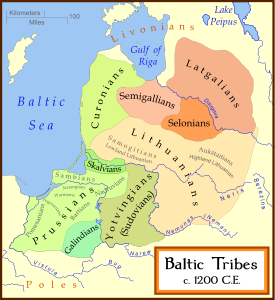
. In the lands of the Western and the Eastern Latgalians, about 80 flat cemeteries of Western Latgalian origin have been excavated, with more than 2000 burials uncovered. The first large scale excavations took place in Ludza Odukalns Cemetery in Latgale (1890-1891), where 339 Late Iron Age burials were uncovered. In the excavations at Pildas Nukši Cemetery (in Latgale, 1947-1948), 218 burials were uncovered, dated to 9th-12th century, while at Zvirgzdenes Kivti Cemetery (in Latgale; 1948, 1955-1958) 175 burials from the 7th-12th century were excavated. 315 burials were found at Aglonas Kristapiņi Cemetery (in Latgale; 1928, 1938, 1977-1980, 1984-1987, 1999-2000), in use from the late 8th to 12th century. Ērgļu Jaunāķēni Cemetery was totally excavated in 1971-1972, when 89 burials were found. At Koknese
Cemetery 102 burials from the Late Iron Age were uncovered (1986-1989). In the area of Gauja
's Latgallians two cemeteries, Drabešu Liepiņas and Priekuļu Ģūģeri are well excavated too.
Archaeological excavations have also been carried out on the hillforts of Ķente, Koknese
, Sārumkalns, Tanīskalns, as well as on other Latgalian sites. Only a few (Western) Latgalian settlements have been excavated; large scale excavations (1960s-1970s) and reconstruction has been done at the Āraiši lake dwelling site
(9th century).
In Latgale, dating from the 6th-7th centuries, there were flat cemeteries as well as barrow cemeteries, but in the 9th-10th century the transition started from flat graves to barrows. There are about 15 excavated Eastern Latgalian barrow cemeteries, but usually only a small number of barrows were investigated.
Archaeologically identified dwelling-sites in Latgale
include hill forts, settlements and lake dwellings. Among hillforts, well researched is Jersika
Hillfort (excavated in 1939 and from 1990 onwards), forming complex together with Dignāja Hillfort, on the opposite bank of Daugava. Jersika was occupied in the 10th-14th century, probably after the decline of Dignāja, which had been inhabited since the 6th century.
It is possible that ancestors of the so-called Eastern Latgalians migrated to the territory of present-day Latgale in the 7th and 10th-11th centuries, pushed from their previously inhabited territory by Slavic migration; some archaeologists also believe, that the Eastern Latgalians formed from the most ancient East-Baltic inhabitants of Latvia, who lived in central
and Eastern parts of Latvia
just in the "Roman" Iron age
(1st-4th centuries).
, the terms latgalīši and latgali have been traditionally used as synonyms describing both the ancient and contemporary Latgalians as a part of the same continuum. The term latgalīši (in both meanings) prevailed in Latgalian literature and mass media during the first decades of the 20th century, whereas the term latgali has been consistently used (also in both meanings) in Latgalian literature and media published during the 1920s and 1930s in Latvia and from 1940 to 1988 in exile. Since the cultural revival of Latgalians in 1988, there is a tendency in Latgalian literature and media to follow Latvians in their use of both names.
The term Latgalians (Latgalian
Latgalian language
Latgalian language can mean one of the following:#It was a language spoken by Latgalians in a great part of the area which is now Latvia. Latgalian was a member of the Baltic group of the Indo-European language family. Historically the Latvian language is derived from Latgalian Latgalian language...
: latgalīši, latgali, (also spelt Latgallians and sometimes known as Lettigalls, Latgolans, or Lettigallians) can refer to the inhabitants of the Latgale
Latgale
Latgale is one of the four historical and cultural regions of Latvia recognised in the Constitution of the Latvian Republic. It is the easternmost region north of the Daugava River...
region in eastern Latvia
Latvia
Latvia , officially the Republic of Latvia , is a country in the Baltic region of Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by Estonia , to the south by Lithuania , to the east by the Russian Federation , to the southeast by Belarus and shares maritime borders to the west with Sweden...
in general, the ethnic Latvians
Latvians
Latvians or Letts are the indigenous Baltic people of Latvia.-History:Latvians occasionally refer to themselves by the ancient name of Latvji, which may have originated from the word Latve which is a name of the river that presumably flowed through what is now eastern Latvia...
of Latgale (especially those who speak the Latgalian language
Latgalian language
Latgalian language can mean one of the following:#It was a language spoken by Latgalians in a great part of the area which is now Latvia. Latgalian was a member of the Baltic group of the Indo-European language family. Historically the Latvian language is derived from Latgalian Latgalian language...
), or to the ancient Baltic
Balts
The Balts or Baltic peoples , defined as speakers of one of the Baltic languages, a branch of the Indo-European language family, are descended from a group of Indo-European tribes who settled the area between the Jutland peninsula in the west and Moscow, Oka and Volga rivers basins in the east...
tribe. In English, the more archaic Lettigallians usually refers to the tribe.
In Latvian, latgaļi refers to the ancient tribe, latgalieši refers to the ethnic Latvians of Latgale, which developed separately from the rest of ethnic Latvia in 1621-1917, whilst, though the terms are confused in colloquial Latvian.
The ancient Latgalians
The ancient LettsLetts
Letts may refer to the following people:*Arthur Letts, English-born millionaire developer of Holmby Hills, Los Angeles, California*Barry Letts , British actor, television director and producer...
, or "Latgalians" (i.e. inhabitants of the primal Latgale, – this ancient Central-Baltic term derives very likely from *Lætgale = "The Lettland"; compare with *Zemgale
Semigalia
Zemgale, also known under Latinized names Semigalia or Semigallia is a historical region of Latvia, sometimes also including a part of Lithuania. It lies in the middle of the southern part of the Republic of Latvia, and borders historical regions of Selonia, Samogitia, Courland and Livland. The...
= "The lower-land"), were a Central Baltic
Balts
The Balts or Baltic peoples , defined as speakers of one of the Baltic languages, a branch of the Indo-European language family, are descended from a group of Indo-European tribes who settled the area between the Jutland peninsula in the west and Moscow, Oka and Volga rivers basins in the east...
tribe of little-known origin, which dwell in the 5th-6th centuries only in the Eastern part of present-day Vidzeme
Vidzeme
Vidzeme is one of the historical and cultural regions of Latvia. Literally meaning "the Middle Land" it is situated in north-central Latvia north of the Daugava River...
(westwards from Aiviekste River
Aiviekste River
The Aiviekste is a river in Latvia. It begins at Lake Lubāns and drains into the Daugava . The Aiviekste is the largest tributary of the Daugava in Latvia. The Aiviekste, along with the Pededze River, forms the border between Vidzeme and Latgale.-Tributaries:*Pededze River*Balupe River...
), and later on – in nearly all the territory of that region. In written sources, they are mentioned from the 11th century. In the first two decades of the 13th century, the (Western) Latgalians allied with German (mainly Saxon) crusaders and their lands were incorporated in unclear circumstances into Livonia
Livonia
Livonia is a historic region along the eastern shores of the Baltic Sea. It was once the land of the Finnic Livonians inhabiting the principal ancient Livonian County Metsepole with its center at Turaida...
. In the 13th-14th centuries, they assimilated in present-day Latgale an unknown East-Baltic tribe, the latter in this way becoming a part of today's ethnic Latvians
Latvians
Latvians or Letts are the indigenous Baltic people of Latvia.-History:Latvians occasionally refer to themselves by the ancient name of Latvji, which may have originated from the word Latve which is a name of the river that presumably flowed through what is now eastern Latvia...
(It's striking that the Latvian term latgalieši ("Latgalians"), in the sense of "Eastern Latvians", dates only to the early 20th century).

Archaeological data
The most accurate source of information about the ancient (Western) Latgalians comes from archaeologyArchaeology
Archaeology, or archeology , is the study of human society, primarily through the recovery and analysis of the material culture and environmental data that they have left behind, which includes artifacts, architecture, biofacts and cultural landscapes...
. In the lands of the Western and the Eastern Latgalians, about 80 flat cemeteries of Western Latgalian origin have been excavated, with more than 2000 burials uncovered. The first large scale excavations took place in Ludza Odukalns Cemetery in Latgale (1890-1891), where 339 Late Iron Age burials were uncovered. In the excavations at Pildas Nukši Cemetery (in Latgale, 1947-1948), 218 burials were uncovered, dated to 9th-12th century, while at Zvirgzdenes Kivti Cemetery (in Latgale; 1948, 1955-1958) 175 burials from the 7th-12th century were excavated. 315 burials were found at Aglonas Kristapiņi Cemetery (in Latgale; 1928, 1938, 1977-1980, 1984-1987, 1999-2000), in use from the late 8th to 12th century. Ērgļu Jaunāķēni Cemetery was totally excavated in 1971-1972, when 89 burials were found. At Koknese
Koknese
Koknese is a historic town in Latvia, the administrative centre of Koknese municipality on the right bank of the Daugava River. It has a population of nearly 3,000.-History:...
Cemetery 102 burials from the Late Iron Age were uncovered (1986-1989). In the area of Gauja
Gauja
The Gauja is one of the longest rivers in Latvia, with a length of and a catchment area of . Its source is in the hills southeast of Cēsis. It first flows east and north and forms the border with Estonia for about . South of Valga and Valka, it turns west towards Valmiera, continuing southwest...
's Latgallians two cemeteries, Drabešu Liepiņas and Priekuļu Ģūģeri are well excavated too.
Archaeological excavations have also been carried out on the hillforts of Ķente, Koknese
Koknese
Koknese is a historic town in Latvia, the administrative centre of Koknese municipality on the right bank of the Daugava River. It has a population of nearly 3,000.-History:...
, Sārumkalns, Tanīskalns, as well as on other Latgalian sites. Only a few (Western) Latgalian settlements have been excavated; large scale excavations (1960s-1970s) and reconstruction has been done at the Āraiši lake dwelling site
Araiši lake dwelling site
Āraiši lake dwelling site is a popular tourist location with original and reconstructed remnants of Latvian prehistory. It is a unique nationally important archaeological site: remains of the 9th–10th centuries Latgalian settlement on the island of Āraiši lake....
(9th century).
In Latgale, dating from the 6th-7th centuries, there were flat cemeteries as well as barrow cemeteries, but in the 9th-10th century the transition started from flat graves to barrows. There are about 15 excavated Eastern Latgalian barrow cemeteries, but usually only a small number of barrows were investigated.
Archaeologically identified dwelling-sites in Latgale
Latgale
Latgale is one of the four historical and cultural regions of Latvia recognised in the Constitution of the Latvian Republic. It is the easternmost region north of the Daugava River...
include hill forts, settlements and lake dwellings. Among hillforts, well researched is Jersika
Jersika
The principality of Jersika was an early medieval principality in eastern modern Latvia. The capital of Jersika was located on a hill fort southeast of Riga.- History :...
Hillfort (excavated in 1939 and from 1990 onwards), forming complex together with Dignāja Hillfort, on the opposite bank of Daugava. Jersika was occupied in the 10th-14th century, probably after the decline of Dignāja, which had been inhabited since the 6th century.
It is possible that ancestors of the so-called Eastern Latgalians migrated to the territory of present-day Latgale in the 7th and 10th-11th centuries, pushed from their previously inhabited territory by Slavic migration; some archaeologists also believe, that the Eastern Latgalians formed from the most ancient East-Baltic inhabitants of Latvia, who lived in central
Vidzeme
Vidzeme is one of the historical and cultural regions of Latvia. Literally meaning "the Middle Land" it is situated in north-central Latvia north of the Daugava River...
and Eastern parts of Latvia
Latgale
Latgale is one of the four historical and cultural regions of Latvia recognised in the Constitution of the Latvian Republic. It is the easternmost region north of the Daugava River...
just in the "Roman" Iron age
Iron Age
The Iron Age is the archaeological period generally occurring after the Bronze Age, marked by the prevalent use of iron. The early period of the age is characterized by the widespread use of iron or steel. The adoption of such material coincided with other changes in society, including differing...
(1st-4th centuries).
Latgalīši
In LatgalianLatgalian language
Latgalian language can mean one of the following:#It was a language spoken by Latgalians in a great part of the area which is now Latvia. Latgalian was a member of the Baltic group of the Indo-European language family. Historically the Latvian language is derived from Latgalian Latgalian language...
, the terms latgalīši and latgali have been traditionally used as synonyms describing both the ancient and contemporary Latgalians as a part of the same continuum. The term latgalīši (in both meanings) prevailed in Latgalian literature and mass media during the first decades of the 20th century, whereas the term latgali has been consistently used (also in both meanings) in Latgalian literature and media published during the 1920s and 1930s in Latvia and from 1940 to 1988 in exile. Since the cultural revival of Latgalians in 1988, there is a tendency in Latgalian literature and media to follow Latvians in their use of both names.

