Iraq Resolution
Encyclopedia

Joint resolution
In the United States Congress, a joint resolution is a legislative measure that requires approval by the Senate and the House and is presented to the President for his/her approval or disapproval, in exactly the same case as a bill....
passed by the United States Congress
United States Congress
The United States Congress is the bicameral legislature of the federal government of the United States, consisting of the Senate and the House of Representatives. The Congress meets in the United States Capitol in Washington, D.C....
in October 2002 as Public Law
Public law
Public law is a theory of law governing the relationship between individuals and the state. Under this theory, constitutional law, administrative law and criminal law are sub-divisions of public law...
No: 107-243, authorizing military action against Iraq.
Contents
The resolution cited many factors to justify the use of military force against Iraq:- Iraq's noncompliance with the conditions of the 1991 ceasefire agreementUnited Nations Security Council Resolution 687United Nations Security Council Resolution 687, adopted on April 3, 1991, after reaffirming resolutions 660, 661, 662, 664, 665, 666, 667, 669, 670, 674, 677, 678 and 686 , the Council set the terms, in a comprehensive resolution, with which Iraq was to comply after losing the Gulf War.The...
, including interference with U.N. weapons inspectorsUnited Nations Special CommissionUnited Nations Special Commission was an inspection regime created by the United Nations to ensure Iraq's compliance with policies concerning Iraqi production and use of weapons of mass destruction after the Gulf War...
. - Iraq's alleged weapons of mass destructionWeapons of mass destructionA weapon of mass destruction is a weapon that can kill and bring significant harm to a large number of humans and/or cause great damage to man-made structures , natural structures , or the biosphere in general...
, and programs to develop such weapons, posed a "threat to the national security of the United States and international peace and security in the Persian GulfPersian GulfThe Persian Gulf, in Southwest Asia, is an extension of the Indian Ocean located between Iran and the Arabian Peninsula.The Persian Gulf was the focus of the 1980–1988 Iran-Iraq War, in which each side attacked the other's oil tankers...
region." - Iraq's "brutal repression of its civilian population."
- Iraq's "capability and willingness to use weapons of mass destruction against other nations and its own peopleAl-Anfal CampaignThe al-Anfal Campaign , also known as Operation Anfal or simply Anfal, was a genocidal campaign against the Kurdish people in Northern Iraq, led by the Iraqi regime of Saddam Hussein and headed by Ali Hassan al-Majid in the final stages of Iran-Iraq War...
". - Iraq's hostility towards the United States as demonstrated by the 1993 assassination attempt on former President George H. W. BushGeorge H. W. BushGeorge Herbert Walker Bush is an American politician who served as the 41st President of the United States . He had previously served as the 43rd Vice President of the United States , a congressman, an ambassador, and Director of Central Intelligence.Bush was born in Milton, Massachusetts, to...
and firing on coalition aircraft enforcing the no-fly zonesIraqi no-fly zonesThe Iraqi no-fly zones were a set of two separate no-fly zones , and were proclaimed by the United States, United Kingdom and France after the Gulf War of 1991 to protect the Kurdish people in northern Iraq and Shiite Muslims in the south. Iraqi aircraft were forbidden from flying inside the zones...
following the 1991 Gulf War. - Members of al-QaedaAl-QaedaAl-Qaeda is a global broad-based militant Islamist terrorist organization founded by Osama bin Laden sometime between August 1988 and late 1989. It operates as a network comprising both a multinational, stateless army and a radical Sunni Muslim movement calling for global Jihad...
, an organization bearing responsibility for attacks on the United States, its citizens, and interests, including the attacks that occurred on September 11, 2001, are known to be in Iraq. - Iraq's "continu[ing] to aid and harbor other international terroristTerrorismTerrorism is the systematic use of terror, especially as a means of coercion. In the international community, however, terrorism has no universally agreed, legally binding, criminal law definition...
organizations," including anti-United States terrorist organizations. - Iraq paid bountyBounty (reward)A bounty is a payment or reward often offered by a group as an incentive for the accomplishment of a task by someone usually not associated with the group. Bounties are most commonly issued for the capture or retrieval of a person or object. They are typically in the form of money...
to families of suicide bombersSuicide attackA suicide attack is a type of attack in which the attacker expects or intends to die in the process.- Historical :...
. - The efforts by the Congress and the President to fight terroristsAuthorization for Use of Military Force Against TerroristsThe Authorization for Use of Military Force Against Terrorists , one of two resolutions commonly known as "AUMF" , was a joint resolution passed by the United States Congress on September 14, 2001, authorizing the use of United States Armed Forces against those responsible for the attacks on...
, and those who aided or harbored them. - The authorization by the ConstitutionUnited States ConstitutionThe Constitution of the United States is the supreme law of the United States of America. It is the framework for the organization of the United States government and for the relationship of the federal government with the states, citizens, and all people within the United States.The first three...
and the CongressUnited States CongressThe United States Congress is the bicameral legislature of the federal government of the United States, consisting of the Senate and the House of Representatives. The Congress meets in the United States Capitol in Washington, D.C....
for the PresidentPresident of the United StatesThe President of the United States of America is the head of state and head of government of the United States. The president leads the executive branch of the federal government and is the commander-in-chief of the United States Armed Forces....
to fight anti-United States terrorism. - The governments in TurkeyTurkeyTurkey , known officially as the Republic of Turkey , is a Eurasian country located in Western Asia and in East Thrace in Southeastern Europe...
, KuwaitKuwaitThe State of Kuwait is a sovereign Arab state situated in the north-east of the Arabian Peninsula in Western Asia. It is bordered by Saudi Arabia to the south at Khafji, and Iraq to the north at Basra. It lies on the north-western shore of the Persian Gulf. The name Kuwait is derived from the...
, and Saudi ArabiaSaudi ArabiaThe Kingdom of Saudi Arabia , commonly known in British English as Saudi Arabia and in Arabic as as-Sa‘ūdiyyah , is the largest state in Western Asia by land area, constituting the bulk of the Arabian Peninsula, and the second-largest in the Arab World...
feared Saddam and wanted him removed from power. - Citing the Iraq Liberation Act of 1998, the resolution reiterated that it should be the policy of the United States to remove the Saddam HusseinSaddam HusseinSaddam Hussein Abd al-Majid al-Tikriti was the fifth President of Iraq, serving in this capacity from 16 July 1979 until 9 April 2003...
regime and promote a democraticDemocracyDemocracy is generally defined as a form of government in which all adult citizens have an equal say in the decisions that affect their lives. Ideally, this includes equal participation in the proposal, development and passage of legislation into law...
replacement.
The resolution "supported" and "encouraged" diplomatic efforts by President George W. Bush
George W. Bush
George Walker Bush is an American politician who served as the 43rd President of the United States, from 2001 to 2009. Before that, he was the 46th Governor of Texas, having served from 1995 to 2000....
to "strictly enforce through the U.N. Security Council all relevant Security Council resolutions regarding Iraq" and "obtain prompt and decisive action by the Security Council to ensure that Iraq abandons its strategy of delay, evasion, and noncompliance and promptly and strictly complies with all relevant Security Council resolutions regarding Iraq."
The resolution authorized President Bush to use the Armed Forces of the United States
Military of the United States
The United States Armed Forces are the military forces of the United States. They consist of the Army, Navy, Marine Corps, Air Force, and Coast Guard.The United States has a strong tradition of civilian control of the military...
"as he determines to be necessary and appropriate" in order to "defend the national security
National security
National security is the requirement to maintain the survival of the state through the use of economic, diplomacy, power projection and political power. The concept developed mostly in the United States of America after World War II...
of the United States against the continuing threat posed by Iraq; and enforce all relevant United Nations Security Council Resolutions regarding Iraq."
Passage
An authorization by Congress was sought by President George W. BushGeorge W. Bush
George Walker Bush is an American politician who served as the 43rd President of the United States, from 2001 to 2009. Before that, he was the 46th Governor of Texas, having served from 1995 to 2000....
soon after his September 12, 2002, statement before the U.N. General Assembly asking for quick action by the Security Council in enforcing the resolutions against Iraq.
Of the legislation introduced by Congress in response to President Bush's requests, sponsored by Sen. Daschle
Tom Daschle
Thomas Andrew "Tom" Daschle is a former U.S. Senator from South Dakota and former U.S. Senate Majority Leader. He is a member of the Democratic Party....
& Sen. Lott
Trent Lott
Chester Trent Lott, Sr. , is a former United States Senator from Mississippi and has served in numerous leadership positions in the House of Representatives and the Senate....
was based on the original White House proposal authorizing the use of force in Iraq, sponsored by Rep. Hastert
Dennis Hastert
John Dennis "Denny" Hastert was the 59th Speaker of the House serving from 1999 to 2007. He represented as a Republican for twenty years, 1987 to 2007.He is the longest-serving Republican Speaker in history...
& Rep. Gephardt
Dick Gephardt
Richard Andrew "Dick" Gephardt is a lobbyist and former prominent American politician of the Democratic Party. Gephardt served as a U.S. Representative from Missouri from January 3, 1977, until January 3, 2005, serving as House Majority Leader from 1989 to 1995, and as Minority Leader from 1995 to...
and the substantially similar sponsored by Sen. Lieberman
Joe Lieberman
Joseph Isadore "Joe" Lieberman is the senior United States Senator from Connecticut. A former member of the Democratic Party, he was the party's nominee for Vice President in the 2000 election. Currently an independent, he remains closely affiliated with the party.Born in Stamford, Connecticut,...
were modified proposals. sponsored by Rep. Hastings
Alcee Hastings
Alcee Lamar Hastings is the U.S. Representative for , serving since 1993. He is a member of the Democratic Party.-Early life, education and career:...
was a separate proposal never considered on the floor. Eventually, the Hastert-Gephardt proposal became the legislation Congress focused on.
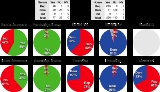
Introduced in Congress on October 2, 2002, in conjunction with the Administration's proposals, passed the House of Representatives
United States House of Representatives
The United States House of Representatives is one of the two Houses of the United States Congress, the bicameral legislature which also includes the Senate.The composition and powers of the House are established in Article One of the Constitution...
on Thursday afternoon at 3:05 p.m. EDT on October 10, 2002, by a vote of 296-133, and passed the Senate
United States Senate
The United States Senate is the upper house of the bicameral legislature of the United States, and together with the United States House of Representatives comprises the United States Congress. The composition and powers of the Senate are established in Article One of the U.S. Constitution. Each...
after midnight early Friday morning, at 12:50 a.m. EDT on October 11, 2002, by a vote of 77-23. It was signed into law as by President Bush on October 16, 2002.
United States House of Representatives
{| class="wikitable"
|-
! Party
! Ayes
! Nays
! PRES
! No Vote
|-
| Republican
| 215
| 6
| 0
| 2
|-
| Democratic
| 82
| 126
| 0
| 1
|-
|Independent
| 0
| 1
| 0
| 0
|-
|TOTALS
| 297
| 133
| 0
| 3
|}
- 126 (61%) of 208 Democratic Representatives voted against the resolution.
- 6 (<3%) of 223 Republican Representatives voted against the resolution: Reps. Duncan (RRepublican Party (United States)The Republican Party is one of the two major contemporary political parties in the United States, along with the Democratic Party. Founded by anti-slavery expansion activists in 1854, it is often called the GOP . The party's platform generally reflects American conservatism in the U.S...
-TNTennesseeTennessee is a U.S. state located in the Southeastern United States. It has a population of 6,346,105, making it the nation's 17th-largest state by population, and covers , making it the 36th-largest by total land area...
), HostettlerJohn HostettlerJohn Nathan Hostettler , was a Republican candidate for the open U.S. Senate seat in the state of Indiana held by retiring Senator Evan Bayh. On December 3, 2009, Hostettler announced his candidacy for the U.S. Senate, but lost to former Senator Dan Coats.Hostettler served in the U.S...
(RRepublican Party (United States)The Republican Party is one of the two major contemporary political parties in the United States, along with the Democratic Party. Founded by anti-slavery expansion activists in 1854, it is often called the GOP . The party's platform generally reflects American conservatism in the U.S...
-INIndianaIndiana is a US state, admitted to the United States as the 19th on December 11, 1816. It is located in the Midwestern United States and Great Lakes Region. With 6,483,802 residents, the state is ranked 15th in population and 16th in population density. Indiana is ranked 38th in land area and is...
), HoughtonAmo HoughtonAmory "Amo" Houghton Jr. is a politician from the state of New York, a retired member of the House of Representatives, and member of one of upstate New York's most prominent families in business, the Houghton family.-Early life:...
(RRepublican Party (United States)The Republican Party is one of the two major contemporary political parties in the United States, along with the Democratic Party. Founded by anti-slavery expansion activists in 1854, it is often called the GOP . The party's platform generally reflects American conservatism in the U.S...
-NYNew YorkNew York is a state in the Northeastern region of the United States. It is the nation's third most populous state. New York is bordered by New Jersey and Pennsylvania to the south, and by Connecticut, Massachusetts and Vermont to the east...
), LeachJim LeachJames Albert Smith "Jim" Leach is a former member of the U.S. House of Representatives from Iowa. In August 2009, he became Chairman of the National Endowment for the Humanities ....
(RRepublican Party (United States)The Republican Party is one of the two major contemporary political parties in the United States, along with the Democratic Party. Founded by anti-slavery expansion activists in 1854, it is often called the GOP . The party's platform generally reflects American conservatism in the U.S...
-IAIowaIowa is a state located in the Midwestern United States, an area often referred to as the "American Heartland". It derives its name from the Ioway people, one of the many American Indian tribes that occupied the state at the time of European exploration. Iowa was a part of the French colony of New...
), MorellaConnie MorellaConstance Albanese "Connie" Morella is a Republican United States politician who represented in the United States House of Representatives from 1987 to 2003. She also served as Permanent Representative to the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development from 2003 to 2007. She...
(RRepublican Party (United States)The Republican Party is one of the two major contemporary political parties in the United States, along with the Democratic Party. Founded by anti-slavery expansion activists in 1854, it is often called the GOP . The party's platform generally reflects American conservatism in the U.S...
-MDMarylandMaryland is a U.S. state located in the Mid Atlantic region of the United States, bordering Virginia, West Virginia, and the District of Columbia to its south and west; Pennsylvania to its north; and Delaware to its east...
), PaulRon PaulRonald Ernest "Ron" Paul is an American physician, author and United States Congressman who is seeking to be the Republican Party candidate in the 2012 presidential election. Paul represents Texas's 14th congressional district, which covers an area south and southwest of Houston that includes...
(RRepublican Party (United States)The Republican Party is one of the two major contemporary political parties in the United States, along with the Democratic Party. Founded by anti-slavery expansion activists in 1854, it is often called the GOP . The party's platform generally reflects American conservatism in the U.S...
-TXTexasTexas is the second largest U.S. state by both area and population, and the largest state by area in the contiguous United States.The name, based on the Caddo word "Tejas" meaning "friends" or "allies", was applied by the Spanish to the Caddo themselves and to the region of their settlement in...
). - The only Independent Representative voted against the resolution: Rep. SandersBernie SandersBernard "Bernie" Sanders is the junior United States Senator from Vermont. He previously represented Vermont's at-large district in the United States House of Representatives...
(IIndependent (politician)In politics, an independent or non-party politician is an individual not affiliated to any political party. Independents may hold a centrist viewpoint between those of major political parties, a viewpoint more extreme than any major party, or they may have a viewpoint based on issues that they do...
-VTVermontVermont is a state in the New England region of the northeastern United States of America. The state ranks 43rd in land area, , and 45th in total area. Its population according to the 2010 census, 630,337, is the second smallest in the country, larger only than Wyoming. It is the only New England...
)- Reps. OrtizSolomon P. OrtizSolomon Porfirio Ortiz is the former U.S. Representative for , serving from 1983 until 2011. He is a member of the Democratic Party. The district is based in Corpus Christi...
(DDemocratic Party (United States)The Democratic Party is one of two major contemporary political parties in the United States, along with the Republican Party. The party's socially liberal and progressive platform is largely considered center-left in the U.S. political spectrum. The party has the lengthiest record of continuous...
-TXTexasTexas is the second largest U.S. state by both area and population, and the largest state by area in the contiguous United States.The name, based on the Caddo word "Tejas" meaning "friends" or "allies", was applied by the Spanish to the Caddo themselves and to the region of their settlement in...
), RoukemaMarge RoukemaMargaret Scafati "Marge" Roukema represented New Jersey in the U.S. House of Representatives for twenty-two years as a Republican. No woman has served in Congress from New Jersey since Roukema left office....
(RRepublican Party (United States)The Republican Party is one of the two major contemporary political parties in the United States, along with the Democratic Party. Founded by anti-slavery expansion activists in 1854, it is often called the GOP . The party's platform generally reflects American conservatism in the U.S...
-NJNew JerseyNew Jersey is a state in the Northeastern and Middle Atlantic regions of the United States. , its population was 8,791,894. It is bordered on the north and east by the state of New York, on the southeast and south by the Atlantic Ocean, on the west by Pennsylvania and on the southwest by Delaware...
), and StumpBob StumpRobert Lee "Bob" Stump was a U.S. Congressman from Arizona.-Early life and career:Stump was born in Phoenix, and was a U.S. Navy World War II combat veteran, where he served on the USS Tulagi from 1943 to 1946. He graduated from Tolleson High School in 1947, and Arizona State University in 1951...
(RRepublican Party (United States)The Republican Party is one of the two major contemporary political parties in the United States, along with the Democratic Party. Founded by anti-slavery expansion activists in 1854, it is often called the GOP . The party's platform generally reflects American conservatism in the U.S...
-AZArizonaArizona ; is a state located in the southwestern region of the United States. It is also part of the western United States and the mountain west. The capital and largest city is Phoenix...
) did not vote on the resolution.
- Reps. Ortiz
United States Senate
| Party | Ayes | Nays | No Vote |
|---|---|---|---|
| Republican | 48 | 1 | 0 |
| Democratic | 29 | 21 | 0 |
| Independent | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| TOTALS | 77 | 23 | 0 |
- 21 (42%) of 50 Democratic senators voted against the resolution: Sens. AkakaDaniel AkakaDaniel Kahikina Akaka is the junior U.S. Senator from Hawaii and a member of the Democratic Party. He is the first U.S. Senator of Native Hawaiian ancestry and is currently the only member of the Senate who has Chinese ancestry....
(D-HIHawaiiHawaii is the newest of the 50 U.S. states , and is the only U.S. state made up entirely of islands. It is the northernmost island group in Polynesia, occupying most of an archipelago in the central Pacific Ocean, southwest of the continental United States, southeast of Japan, and northeast of...
), BingamanJeff BingamanJesse Francis "Jeff" Bingaman, Jr. , is the senior U.S. Senator from New Mexico and a member of the Democratic Party...
(D-NMNew MexicoNew Mexico is a state located in the southwest and western regions of the United States. New Mexico is also usually considered one of the Mountain States. With a population density of 16 per square mile, New Mexico is the sixth-most sparsely inhabited U.S...
), BoxerBarbara BoxerBarbara Levy Boxer is the junior United States Senator from California . A member of the Democratic Party, she previously served in the U.S. House of Representatives ....
(D-CACaliforniaCalifornia is a state located on the West Coast of the United States. It is by far the most populous U.S. state, and the third-largest by land area...
), ByrdRobert ByrdRobert Carlyle Byrd was a United States Senator from West Virginia. A member of the Democratic Party, Byrd served as a U.S. Representative from 1953 until 1959 and as a U.S. Senator from 1959 to 2010...
(D-WVWest VirginiaWest Virginia is a state in the Appalachian and Southeastern regions of the United States, bordered by Virginia to the southeast, Kentucky to the southwest, Ohio to the northwest, Pennsylvania to the northeast and Maryland to the east...
), ConradKent ConradKent Conrad is the senior United States Senator from North Dakota. He is a member of the North Dakota Democratic-NPL Party, the North Dakota affiliate of the Democratic Party...
(D-NDNorth DakotaNorth Dakota is a state located in the Midwestern region of the United States of America, along the Canadian border. The state is bordered by Canada to the north, Minnesota to the east, South Dakota to the south and Montana to the west. North Dakota is the 19th-largest state by area in the U.S....
), CorzineJon CorzineJon Stevens Corzine is the former CEO of Goldman Sachs and of MF Global, and a one time American politician, who served as the 54th Governor of New Jersey from 2006 to 2010. A Democrat, Corzine served five years of a six-year U.S. Senate term representing New Jersey before being elected Governor...
(D-NJNew JerseyNew Jersey is a state in the Northeastern and Middle Atlantic regions of the United States. , its population was 8,791,894. It is bordered on the north and east by the state of New York, on the southeast and south by the Atlantic Ocean, on the west by Pennsylvania and on the southwest by Delaware...
), DaytonMark DaytonMark Brandt Dayton is an American politician, the 40th and current Governor of the state of Minnesota. Dayton previously served as United States Senator from Minnesota from 2001 to 2007 in the 107th, 108th, and 109th Congresses...
(D-MNMinnesotaMinnesota is a U.S. state located in the Midwestern United States. The twelfth largest state of the U.S., it is the twenty-first most populous, with 5.3 million residents. Minnesota was carved out of the eastern half of the Minnesota Territory and admitted to the Union as the thirty-second state...
), Durbin (D-ILIllinoisIllinois is the fifth-most populous state of the United States of America, and is often noted for being a microcosm of the entire country. With Chicago in the northeast, small industrial cities and great agricultural productivity in central and northern Illinois, and natural resources like coal,...
), FeingoldRuss FeingoldRussell Dana "Russ" Feingold is an American politician from the U.S. state of Wisconsin. He served as a Democratic party member of the U.S. Senate from 1993 to 2011. From 1983 to 1993, Feingold was a Wisconsin State Senator representing the 27th District.He is a recipient of the John F...
(D-WIWisconsinWisconsin is a U.S. state located in the north-central United States and is part of the Midwest. It is bordered by Minnesota to the west, Iowa to the southwest, Illinois to the south, Lake Michigan to the east, Michigan to the northeast, and Lake Superior to the north. Wisconsin's capital is...
), GrahamBob GrahamDaniel Robert "Bob" Graham is an American politician. He was the 38th Governor of Florida from 1979 to 1987 and a United States Senator from that state from 1987 to 2005...
(D-FLFloridaFlorida is a state in the southeastern United States, located on the nation's Atlantic and Gulf coasts. It is bordered to the west by the Gulf of Mexico, to the north by Alabama and Georgia and to the east by the Atlantic Ocean. With a population of 18,801,310 as measured by the 2010 census, it...
), InouyeDaniel InouyeDaniel Ken "Dan" Inouye is the senior United States Senator from Hawaii, a member of the Democratic Party, and the President pro tempore of the United States Senate making him the highest-ranking Asian American politician in American history. Inouye is the chairman of the United States Senate...
(D-HIHawaiiHawaii is the newest of the 50 U.S. states , and is the only U.S. state made up entirely of islands. It is the northernmost island group in Polynesia, occupying most of an archipelago in the central Pacific Ocean, southwest of the continental United States, southeast of Japan, and northeast of...
), KennedyTed KennedyEdward Moore "Ted" Kennedy was a United States Senator from Massachusetts and a member of the Democratic Party. Serving almost 47 years, he was the second most senior member of the Senate when he died and is the fourth-longest-serving senator in United States history...
(D-MAMassachusettsThe Commonwealth of Massachusetts is a state in the New England region of the northeastern United States of America. It is bordered by Rhode Island and Connecticut to the south, New York to the west, and Vermont and New Hampshire to the north; at its east lies the Atlantic Ocean. As of the 2010...
), LeahyPatrick LeahyPatrick Joseph Leahy is the senior United States Senator from Vermont and member of the Democratic Party. He is the first and only elected Democratic United States Senator in Vermont's history. He is the chairman of the Senate Judiciary Committee. Leahy is the second most senior U.S. Senator,...
(D-VTVermontVermont is a state in the New England region of the northeastern United States of America. The state ranks 43rd in land area, , and 45th in total area. Its population according to the 2010 census, 630,337, is the second smallest in the country, larger only than Wyoming. It is the only New England...
), LevinCarl LevinCarl Milton Levin is a Jewish-American United States Senator from Michigan, serving since 1979. He is the Chairman of the Senate Committee on Armed Services. He is a member of the Democratic Party....
(D-MIMichiganMichigan is a U.S. state located in the Great Lakes Region of the United States of America. The name Michigan is the French form of the Ojibwa word mishigamaa, meaning "large water" or "large lake"....
), MikulskiBarbara MikulskiBarbara Ann Mikulski is the senior United States Senator from Maryland and a member of the Democratic Party. Mikulski, a former U.S. Representative, is the longest-serving female senator in U.S...
(D-MDMarylandMaryland is a U.S. state located in the Mid Atlantic region of the United States, bordering Virginia, West Virginia, and the District of Columbia to its south and west; Pennsylvania to its north; and Delaware to its east...
), MurrayPatty MurrayPatricia Lynn "Patty" Murray is the senior United States Senator from Washington and a member of the Democratic Party. Murray was first elected to the Senate in 1992, becoming Washington's first female senator...
(D-WA), Reed (D-RIRhode IslandThe state of Rhode Island and Providence Plantations, more commonly referred to as Rhode Island , is a state in the New England region of the United States. It is the smallest U.S. state by area...
), SarbanesPaul SarbanesPaul Spyros Sarbanes , a Democrat, is a former United States Senator who represented the state of Maryland. Sarbanes was the longest-serving senator in Maryland history, having served from 1977 until 2007. He did not seek re-election in 2006, when he was succeeded by fellow Democrat Ben Cardin...
(D-MDMarylandMaryland is a U.S. state located in the Mid Atlantic region of the United States, bordering Virginia, West Virginia, and the District of Columbia to its south and west; Pennsylvania to its north; and Delaware to its east...
), StabenowDebbie StabenowDeborah Ann Greer "Debbie" Stabenow is the junior United States Senator from Michigan and a member of the Democratic Party. Before her election to the U.S. Senate, she was a member of the United States House of Representatives, representing Michigan's 8th congressional district from 1997 to 2001...
(D-MIMichiganMichigan is a U.S. state located in the Great Lakes Region of the United States of America. The name Michigan is the French form of the Ojibwa word mishigamaa, meaning "large water" or "large lake"....
), WellstonePaul WellstonePaul David Wellstone was a two-term U.S. Senator from the state of Minnesota and member of the Democratic-Farmer-Labor Party, which is affiliated with the national Democratic Party. Before being elected to the Senate in 1990, he was a professor of political science at Carleton College...
(D-MNMinnesotaMinnesota is a U.S. state located in the Midwestern United States. The twelfth largest state of the U.S., it is the twenty-first most populous, with 5.3 million residents. Minnesota was carved out of the eastern half of the Minnesota Territory and admitted to the Union as the thirty-second state...
), and WydenRon WydenRonald Lee "Ron" Wyden is the senior U.S. Senator for Oregon, serving since 1996, and a member of the Democratic Party. He previously served in the United States House of Representatives from 1981 to 1996....
(D-OROregonOregon is a state in the Pacific Northwest region of the United States. It is located on the Pacific coast, with Washington to the north, California to the south, Nevada on the southeast and Idaho to the east. The Columbia and Snake rivers delineate much of Oregon's northern and eastern...
). - 1 (2%) of 49 Republican senators voted against the resolution: Sen. ChafeeLincoln ChafeeLincoln Davenport Chafee is an American politician who has been the 74th Governor of Rhode Island since January 2011. Prior to his election as governor, Chafee served in the United States Senate as a Republican from 1999 until losing his Senate re-election bid in 2006 to Democrat Sheldon...
(RRepublican Party (United States)The Republican Party is one of the two major contemporary political parties in the United States, along with the Democratic Party. Founded by anti-slavery expansion activists in 1854, it is often called the GOP . The party's platform generally reflects American conservatism in the U.S...
-RIRhode IslandThe state of Rhode Island and Providence Plantations, more commonly referred to as Rhode Island , is a state in the New England region of the United States. It is the smallest U.S. state by area...
). - The only Independent senator voted against the resolution: Sen. JeffordsJim JeffordsJames Merrill "Jim" Jeffords is a former U.S. Senator from Vermont. He served as a Republican until 2001, when he left the party to become an independent. He retired from the Senate in 2006.-Background:...
(IIndependent (politician)In politics, an independent or non-party politician is an individual not affiliated to any political party. Independents may hold a centrist viewpoint between those of major political parties, a viewpoint more extreme than any major party, or they may have a viewpoint based on issues that they do...
-VTVermontVermont is a state in the New England region of the northeastern United States of America. The state ranks 43rd in land area, , and 45th in total area. Its population according to the 2010 census, 630,337, is the second smallest in the country, larger only than Wyoming. It is the only New England...
)

The Lee Amendment
- Amendment in the nature of a substitute sought to have the United States work through the United Nations to seek to resolve the matter of ensuring that Iraq is not developing weapons of mass destruction, through mechanisms such as the resumption of weapons inspections, negotiation, enquiry, mediation, regional arrangements, and other peaceful means.
- Sponsored by Rep. Barbara LeeBarbara LeeBarbara Jean Lee is the U.S. Representative for , serving since 1998. She is a member of the Democratic Party. She is the first woman to represent that district. Lee was the Chair of the Congressional Black Caucus and was the Co-Chair of the Congressional Progressive Caucus...
(D-CA).
- Sponsored by Rep. Barbara Lee
-
-
- Failed by the Yeas and Nays: 72 - 355
-
The Spratt Amendment
- Amendment in the nature of a substitute sought to authorize the use of U.S. armed forces to support any new U.N. Security Council resolution that mandated the elimination, by force if necessary, of all Iraqi weapons of mass destruction, long-range ballistic missiles, and the means of producing such weapons and missiles. Requested that the President should seek authorization from Congress to use the armed forces of the U.S. in the absence of a U.N. Security Council resolution sufficient to eliminate, by force if necessary, all Iraqi weapons of mass destruction, long-range ballistic missiles, and the means of producing such weapons and missiles. Provided expedited consideration for authorization in the latter case.
- Sponsored by Rep. John Spratt (D-SC-5).
-
-
- Failed by the Yeas and Nays: 155 - 270
-
The House Rules Amendment
- An amendment considered as adopted pursuant to the provisions of
-
- Sponsored by House Rules.
-
-
- Resolution (H.RES.574) agreed to by voice vote
-
The Byrd Amendments
- To provide statutory construction that constitutional authorities remain unaffected and that no additional grant of authority is made to the President not directly related to the existing threat posed by Iraq.
-
- Sponsored by Sen. Robert ByrdRobert ByrdRobert Carlyle Byrd was a United States Senator from West Virginia. A member of the Democratic Party, Byrd served as a U.S. Representative from 1953 until 1959 and as a U.S. Senator from 1959 to 2010...
(D-WV).
- Sponsored by Sen. Robert Byrd
-
-
- Amendment SA 4868 not agreed to by Yea-Nay Vote: 14 - 86
-
- To provide a termination date for the authorization of the use of the Armed Forces of the United States, together with procedures for the extension of such date unless Congress disapproves the extension.
- Sponsored by Sen. Robert ByrdRobert ByrdRobert Carlyle Byrd was a United States Senator from West Virginia. A member of the Democratic Party, Byrd served as a U.S. Representative from 1953 until 1959 and as a U.S. Senator from 1959 to 2010...
(D-WV).
- Sponsored by Sen. Robert Byrd
-
-
- Amendment SA 4869 not agreed to by Yea-Nay Vote: 31 - 66
-
The Levin Amendment
- To authorize the use of the United States Armed Forces, pursuant to a new resolution of the United Nations Security Council, to destroy, remove, or render harmless Iraq's weapons of mass destruction, nuclear weapons-usable material, long-range ballistic missiles, and related facilities, and for other purposes.
- Sponsored by Sen. Carl LevinCarl LevinCarl Milton Levin is a Jewish-American United States Senator from Michigan, serving since 1979. He is the Chairman of the Senate Committee on Armed Services. He is a member of the Democratic Party....
(D-MI).
- Sponsored by Sen. Carl Levin
-
-
- Amendment SA 4862 not agreed to by Yea-Nay Vote: 24 - 75
-
The Durbin Amendment
- To amend the authorization for the use of the Armed Forces to cover an imminent threat posed by Iraq's weapons of mass destruction rather than the continuing threat posed by Iraq.
- Sponsored by Sen. Dick Durbin (D-IL).
-
-
- Amendment SA 4865 not agreed to by Yea-Nay Vote: 30 - 70
-
Weapons of mass destruction and Al-Qaeda

A 2007 report by the Inspector General of the Department of Defense, declassified and released at the request of Senator Carl M. Levin (D-Mich), asserted that the claims of an operational working relationship between Iraq and al Qaeda, as put forth by a key Pentagon office in the lead up to the invasion of Iraq, were based on dubious or unconfirmed reports. President Bush has, since the invasion of Iraq, explicitly stated that Iraq was not involved in 9-11, which has also been concluded by subsequent reports, and al-Qaeda were operating in areas outside of Saddam Hussein's control. Also, the day before she voted on the resolution, Senator Hillary Rodham Clinton
Hillary Rodham Clinton
Hillary Diane Rodham Clinton is the 67th United States Secretary of State, serving in the administration of President Barack Obama. She was a United States Senator for New York from 2001 to 2009. As the wife of the 42nd President of the United States, Bill Clinton, she was the First Lady of the...
said during a speech on the Senate floor that there was no dispute that Hussein was not involved in the September 11th attacks. Nevertheless, BBC News
BBC News
BBC News is the department of the British Broadcasting Corporation responsible for the gathering and broadcasting of news and current affairs. The department is the world's largest broadcast news organisation and generates about 120 hours of radio and television output each day, as well as online...
, The Christian Science Monitor, the New York Times, the Washington Post, the Institute for Public Accuracy
Institute for Public Accuracy
The Institute for Public Accuracy is a Washington, D.C.-based organization that encourages mainstream news media to interview alternative sources. It was founded in 1997 by Norman Solomon, who serves as executive director; its communications director is Sam Husseini....
, and Media Matters for America
Media Matters for America
Media Matters for America is a politically progressive media watchdog group which says it is "dedicated to comprehensively monitoring, analyzing, and correcting conservative misinformation in the U.S. media." Set up as a 501 non-profit organization, MMfA was founded in 2004 by journalist and...
contend that members of the administration repeatedly over the years made suggestive statements with the implied message there was a link between Saddam Hussein and the attacks.
The Bush administration initially suggested the discrepancy between the allegations and the subsequent findings was due to failure by the intelligence community. However, it became apparent that, prior to the invasion, these allegations had already been widely disputed, which had purportedly been reported to the U.S. administration. An in-depth investigation into the nature of these discrepancies by the Senate Intelligence Committee was frustrated, according to the New York Times. The Robb-Silberman Commission stated that the President's Daily Brief
President's Daily Brief
The President's Daily Brief , sometimes incorrectly referred to as the President's Daily Briefing or the President's Daily Bulletin, is a top-secret document produced each morning for the President of the United States...
s from the intelligence community tended to repeat information in a misleading way. The National Intelligence Estimate
National Intelligence Estimate
National Intelligence Estimates are United States federal government documents that are the authoritative assessment of the Director of National Intelligence on intelligence related to a particular national security issue...
(NIE) provided to Congress was more "nuanced" and less "alarmist" than information given to the President. However, the vast majority of Senators did not read the NIE and relied on briefings by the administration. Among those who have stated they did not read the NIE and voted positively for the Iraq Resolution are the former Senator
United States Senate
The United States Senate is the upper house of the bicameral legislature of the United States, and together with the United States House of Representatives comprises the United States Congress. The composition and powers of the Senate are established in Article One of the U.S. Constitution. Each...
and current United States Secretary of State
United States Secretary of State
The United States Secretary of State is the head of the United States Department of State, concerned with foreign affairs. The Secretary is a member of the Cabinet and the highest-ranking cabinet secretary both in line of succession and order of precedence...
Hillary Clinton, Senator
United States Senate
The United States Senate is the upper house of the bicameral legislature of the United States, and together with the United States House of Representatives comprises the United States Congress. The composition and powers of the Senate are established in Article One of the U.S. Constitution. Each...
John McCain
John McCain
John Sidney McCain III is the senior United States Senator from Arizona. He was the Republican nominee for president in the 2008 United States election....
, and former Senator
United States Senate
The United States Senate is the upper house of the bicameral legislature of the United States, and together with the United States House of Representatives comprises the United States Congress. The composition and powers of the Senate are established in Article One of the U.S. Constitution. Each...
John Edwards
John Edwards
Johnny Reid "John" Edwards is an American politician, who served as a U.S. Senator from North Carolina. He was the Democratic nominee for Vice President in 2004, and was a candidate for the Democratic presidential nomination in 2004 and 2008.He defeated incumbent Republican Lauch Faircloth in...
.
The assertion such weapons posed a threat towards the U.S. was not supported by the available evidence at the time, according to an editorial in the New York Times. The Bush administration asserted that two small trailers that had been found in Iraq were "weapons factories," despite the fact that U.S. intelligence officials possessed evidence to the contrary at that time. Weapon inspectors were given access to the alleged weapon factories, despite statements to the contrary by the Bush administration. Continuing these inspections was made impossible by the U.S.-led invasion of Iraq which forced the U.N. inspectors out, ignoring their requests for more time.
Skeptics argue that the administration knowingly distorted intelligence reports or ignored contrary information in constructing their case for the war. The Downing Street memo
Downing Street memo
The "Downing Street memo" , sometimes described by critics of the Iraq War as the "smoking gun memo", is the note of a secret 23 July 2002, meeting of senior British Labour government, defence and intelligence figures discussing the build-up to the war, which included direct reference to classified...
and the Bush-Blair memo
Bush-Blair memo
The Bush–Blair 2003 Iraq memo or Manning memo was a secret memo of a meeting between American President George W. Bush and British Prime Minister Tony Blair that took place on January 31, 2003 in the White House...
are used to substantiate that allegation. Congressional Democrats sponsored both a request for documents and a resolution of inquiry.
International law
Debate about the legality of the 2003 invasion of Iraq under international law, centers around ambiguous language in parts of UN Resolution 1441 (2002). The UN Charter prohibits any war unless it is out of self-defense or when it is sanctioned by the UN security council. If these requirements are not met international law describes it a war of aggressionWar of aggression
A war of aggression, sometimes also war of conquest, is a military conflict waged without the justification of self-defense usually for territorial gain and subjugation. The phrase is distinctly modern and diametrically opposed to the prior legal international standard of "might makes right", under...
.
The position of the US and UK is that the invasion was authorized by a series of UN resolutions dating back to 1990. Resolution 1441 declared that Iraq was in "material breach" of the cease-fire under UN Resolution 687
United Nations Security Council Resolution 687
United Nations Security Council Resolution 687, adopted on April 3, 1991, after reaffirming resolutions 660, 661, 662, 664, 665, 666, 667, 669, 670, 674, 677, 678 and 686 , the Council set the terms, in a comprehensive resolution, with which Iraq was to comply after losing the Gulf War.The...
(1991), which required cooperation with weapons inspectors. The Vienna Convention on the Law of Treaties
Vienna Convention on the Law of Treaties
The Vienna Convention on the Law of Treaties is a treaty concerning the international law on treaties between states. It was adopted on 22 May 1969 and opened for signature on 23 May 1969. The Convention entered into force on 27 January 1980. The VCLT has been ratified by 111 states as of November...
states that under certain conditions, a party may invoke a "material breach" to suspend a multilateral treaty. Thus, the US and UK claim that they used their right to suspend the cease-fire in Resolution 687 and to continue hostilities against Iraq under the authority of UN Resolution 678 (1990), which originally authorized the use of force after Iraq invaded Kuwait. This is the same argument that was used for Operation Desert Fox
Operation Desert Fox
The December 1998 bombing of Iraq was a major four-day bombing campaign on Iraqi targets from December 16–19, 1998 by the United States and United Kingdom...
in 1998. They also contend that, while Resolution 1441 required the UNSC to assemble and assess reports from the weapons inspectors, it was not necessary for the UNSC to reach an agreement on the course of action. If, at that time, it was determined that Iraq breached Resolution 1441, the resolution did not "constrain any member state from acting to defend itself against the threat posed by Iraq".
It remains unclear whether any party other than the Security Council can make the determination that Iraq breached Resolution 1441, as UN members commented that it is not up to one member state to interpret and enforce UN resolutions for the entire council. In addition, other nations have stated that a second resolution was required to initiate hostilities. John Conyers
John Conyers
John Conyers, Jr. is the U.S. Representative for , serving since 1965 . He is a member of the Democratic Party...
, Robert Parry
Robert Parry
Robert Parry is an American investigative journalist. He was awarded the George Polk Award for National Reporting in 1984 for his work with the Associated Press on the Iran-Contra story and uncovered Oliver North's involvement in it as a Washington-based correspondent for Newsweek. In 1995, he...
and Marjorie Cohn
Marjorie Cohn
Marjorie Cohn is a professor of law at the Thomas Jefferson School of Law, San Diego, California, and a former president of the National Lawyers Guild.In 1978 Cohn received a job in the International Association of Democratic Lawyers...
assert that the Iraq war was a violation of the U.N. Charter
United Nations Charter
The Charter of the United Nations is the foundational treaty of the international organization called the United Nations. It was signed at the San Francisco War Memorial and Performing Arts Center in San Francisco, United States, on 26 June 1945, by 50 of the 51 original member countries...
and as such a war of aggression (a crime against peace
Crime against peace
A crime against peace, in international law, refers to "planning, preparation, initiation, or waging of wars of aggression, or a war in violation of international treaties, agreements or assurances, or participation in a common plan or conspiracy for the accomplishment of any of the foregoing"...
) and therefore a war crime
War crime
War crimes are serious violations of the laws applicable in armed conflict giving rise to individual criminal responsibility...
. Kofi Annan
Kofi Annan
Kofi Atta Annan is a Ghanaian diplomat who served as the seventh Secretary-General of the UN from 1 January 1997 to 31 December 2006...
too has said the war in Iraq is an "illegal act that contravened the UN charter." Some scholars, including Cornell law professor Michael Dorf, have argued that treaties are binding on the U.S. under international law.
U.S. law
In early 2003, the Iraq Resolution was challenged in court to stop the invasion from happening. The plaintiffs argued that the President does not have the authority to declare war. The final decision came from a three-judge panel from the US Court of Appeals for the First Circuit which dismissed the case. Judge LynchSandra Lea Lynch
Sandra Lea Lynch is the chief judge of the United States Court of Appeals for the First Circuit. She is the first woman to have served on that Court, and on June 16, 2008, became its first female chief judge.-Federal Judicial Service:...
wrote in the opinion that the Judiciary cannot intervene unless there is a fully developed conflict between the President and Congress or if Congress gave the President "absolute discretion" to declare war.
See also
- 2003 invasion of Iraq2003 invasion of IraqThe 2003 invasion of Iraq , was the start of the conflict known as the Iraq War, or Operation Iraqi Freedom, in which a combined force of troops from the United States, the United Kingdom, Australia and Poland invaded Iraq and toppled the regime of Saddam Hussein in 21 days of major combat operations...
- Authorization for Use of Military ForceAuthorization for Use of Military ForceAuthorization for Use of Military Force may refer to:*Authorization for Use of Military Force Against Iraq Resolution of 1991 authorizing the Persian Gulf War, also known as Operation Desert Storm: H.R.J. Res...
- Command responsibilityCommand responsibilityCommand responsibility, sometimes referred to as the Yamashita standard or the Medina standard, and also known as superior responsibility, is the doctrine of hierarchical accountability in cases of war crimes....
- Jus ad bellumJus ad bellumJus ad bellum is a set of criteria that are to be consulted before engaging in war, in order to determine whether entering into war is permissible; that is, whether it is a just war....
- Iraq War
- Legality of the Iraq WarLegality of the Iraq WarThe legality of the invasion and occupation of Iraq has been widely debated since the United States, United Kingdom, and a coalition of other countries launched the 2003 invasion of Iraq...
- Legitimacy of the 2003 invasion of IraqLegitimacy of the 2003 invasion of IraqA dispute exists over the "legitimacy" of the 2003 invasion of Iraq. The debate centers around the question whether the invasion was an unprovoked assault on an independent country that may have breached international law, or if the United Nations Security Council authorized the invasion A dispute...
- Rationale for the Iraq WarRationale for the Iraq WarThe rationale for the Iraq War has been a contentious issue since the Bush administration began actively pressing for military intervention in Iraq in late 2001. The primary rationalization for the Iraq War was articulated by a joint resolution of the U.S. Congress known as the Iraq Resolution.The...
- United NationsUnited NationsThe United Nations is an international organization whose stated aims are facilitating cooperation in international law, international security, economic development, social progress, human rights, and achievement of world peace...
- United Nations CharterUnited Nations CharterThe Charter of the United Nations is the foundational treaty of the international organization called the United Nations. It was signed at the San Francisco War Memorial and Performing Arts Center in San Francisco, United States, on 26 June 1945, by 50 of the 51 original member countries...
- Views on the 2003 invasion of IraqViews on the 2003 invasion of IraqThe events surrounding the 2003 invasion of Iraq have led to numerous expressions of opinion with respect to the war. This page contains links to several topics relating to views on the invasion, and the subsequent occupation of Iraq.American views...
- War of aggressionWar of aggressionA war of aggression, sometimes also war of conquest, is a military conflict waged without the justification of self-defense usually for territorial gain and subjugation. The phrase is distinctly modern and diametrically opposed to the prior legal international standard of "might makes right", under...
- War on TerrorWar on TerrorThe War on Terror is a term commonly applied to an international military campaign led by the United States and the United Kingdom with the support of other North Atlantic Treaty Organisation as well as non-NATO countries...
External links
- Iraq War Resolution, Roll Call Vote - House (clerk.house.gov)
- Iraq War Resolution, Roll Call Vote - Senate (senate.gov)
- Text of Joint Resolution (gpo.gov)
- Bill status and summary (thomas.loc.gov)
- President Signs Iraq Resolution, East Room Remarks
- Statement by President George W. Bush on his signing the resolution into law
- October 16, 2002 Press Briefing by Ari Fleischer
- Floor speeches
- Floor Speech of Sen Hillary Clinton (earthhopenetwork.net)
- Floor Speech of Sen Russ Feingold (feingold.senate.gov)
- Floor Speech of Sen Jay Rockefeller (rockefeller.senate.gov)
- Floor Speech of Rep Ron Paul (www.house.gov/paul)
- Floor Speech of Rep Pete Stark
- Floor Speech of Rep Dennis Kucinich
- Congressional Records related to the Congress' consent to the Authorization of the Use of Military Force in Iraq

