
History of Connecticut
Encyclopedia
The U.S. state of Connecticut
began as three distinct settlements, referred to at the time as "Colonies" or "Plantations". These ventures were eventually combined under a single royal charter in 1662.
tribes inhabited the area prior to European settlement. The Dutch were the first Europeans in Connecticut. In 1614 Adriaen Block
explored the coast of Long Island Sound
, and sailed up the Connecticut River
at least as far as the confluence of the Park River
, site of modern Hartford, Connecticut
. By 1623, the new Dutch West India Company
regularly traded for furs there and ten years later they fortified it for protection from the Pequot
Indians
as well as from the expanding English colonies. They fortified the site, which was named "House of Hope" (also identified as "Fort Hoop
", "Good Hope" and "Hope"), but encroaching English colonists made them agree to withdraw in the 1650 Treaty of Hartford
, and by 1654 they were gone.
The first English colonists came from the Bay Colony
and Plymouth Colony
in Massachusetts
. They settled at Windsor
in 1633, Wethersfield
in 1634, and Hartford
in 1636. Thomas Hooker
led the Hartford group.
In 1631, the Earl of Warwick
granted a patent to a company of investors headed by William Fiennes, 1st Viscount Saye and Sele
and Robert Greville, 2nd Baron Brooke
. They funded the establishment of the Saybrook Colony
(named for the two lords) at the mouth of the Connecticut River, where Fort Saybrook
, was erected in 1636. Another Puritan group left Massachusetts and started the New Haven Colony
farther west on the northern shore of Long Island Sound in 1637. The Massachusetts colonies did not seek to govern their progeny in Connecticut and Rhode Island
. Communication and travel were too difficult, and it was also convenient to have a place for nonconformists to go.
The English settlement and trading post at Windsor especially threatened the Dutch trade, since it was upriver and more accessible to Native people from the interior. That fall and winter the Dutch sent a party upriver as far as modern Springfield, Massachusetts
spreading gifts to convince the indigenous inhabitants in the area to bring their trade to the Dutch post at Hartford. Unfortunately, they also spread smallpox
and, by the end of the 1633–34 winter, the Native population of the entire valley was reduced from over 8,000 to less than 2,000. Europeans took advantage of this decimation by further settling the fertile valley.
 The Pequot War was the first serious armed conflict between the indigenous peoples and the European settlers in New England. The ravages of disease, coupled with trade pressures, invited the Pequots to tighten their hold on the river tribes. Additional incidents began to involve the colonists in the area in 1635, and next spring their raid on Wethersfield prompted the three towns to meet. Following the raid on Wethersfield, the war climaxed when 300 Pequot men, women, and children were burned out of their village, hunted down and massacred
The Pequot War was the first serious armed conflict between the indigenous peoples and the European settlers in New England. The ravages of disease, coupled with trade pressures, invited the Pequots to tighten their hold on the river tribes. Additional incidents began to involve the colonists in the area in 1635, and next spring their raid on Wethersfield prompted the three towns to meet. Following the raid on Wethersfield, the war climaxed when 300 Pequot men, women, and children were burned out of their village, hunted down and massacred
.
On May 1, 1637, leaders of Connecticut Colony's river towns each sent delegates to the first General Court held at the meeting house in Hartford. This was the start of self-government in Connecticut. They pooled their militia under the command of John Mason
of Windsor, and declared war on the Pequots. When the war was over, the Pequots had been destroyed as a tribe. In the Treaty of Hartford
in 1638, the various New England colonies and their Native allies divided the lands of the Pequots amongst themselves.
On April 22, 1662, the Connecticut Colony
succeeded in gaining a Royal Charter that embodied and confirmed the self-government that they had created with the Fundamental Orders. The only significant change was that it called for a single Connecticut government with a southern limit at Long Island Sound
, and a western limit of the Pacific ocean, which meant that this charter was still in conflict with the New Netherland
colony.
Since 1638, the New Haven Colony
had been independent of the river towns, but there other factors added to the Charter. New Haven Colony lost its strongest governor, Theophilus Eaton
, and suffered economically after losing its only ocean going ship. Furthermore, in the early 1660s the colony harbored several of the regicide judges who had sentenced King Charles I
to death. The colony was absorbed by the Connecticut Colony partly as royal punishment by King Charles II
for harboring the regicide judges. When the English took New Netherland
in the 1660s the new government of the Province of New York
claimed the New Haven settlements on Long Island. By January 1665, the merger of the two colonies was completed.
Indian pressures were relieved for some time by the severity and ferocity of the Pequot War. King Philip's War
(1675–1676) brought renewed fighting to Connecticut. Although primarily a war affecting Massachusetts, Connecticut provided men and supplies. This war effectively removed any remaining warlike Native American influences in Connecticut.
was commissioned as the Royal Governor of the Dominion of New England
. Andros maintained that his commission superseded Connecticut's 1662 charter. At first, Connecticut ignored this situation. But in late October 1687, Andros arrived with troops and naval support. Governor Robert Treat
had no choice but to convene the assembly. Andros met with the governor and General Court on the evening of October 31, 1687.
 Governor Andros praised their industry and government, but after he read them his commission, he demanded their charter. As they placed it on the table, people blew out all the candles. When the light was restored, the charter was missing. According to legend, it was hidden in the Charter Oak
Governor Andros praised their industry and government, but after he read them his commission, he demanded their charter. As they placed it on the table, people blew out all the candles. When the light was restored, the charter was missing. According to legend, it was hidden in the Charter Oak
. Sir Edmund named four members to his Council for the Government of New England and proceeded to his capital at Boston.
Since Andros viewed New York and Massachusetts as the important parts of his Dominion, he mostly ignored Connecticut. Aside from some taxes demanded and sent to Boston, Connecticut also mostly ignored the new government. When word arrived that the Glorious Revolution
had placed William and Mary
on the throne, the citizens of Boston arrested Andros
and sent him back to England in chains. The Connecticut court met and voted on May 9, 1689 to restore the old charter. They also reelected Robert Treat as governor each year until 1698.
, the western boundary of Connecticut ran north from the west side of Greenwich Bay
"provided the said line come not within 10 miles (16.1 km) of Hudson River." On the other hand, Connecticut's original charter in 1662 granted it all the land to the "South Sea" (i.e. the Pacific Ocean
).
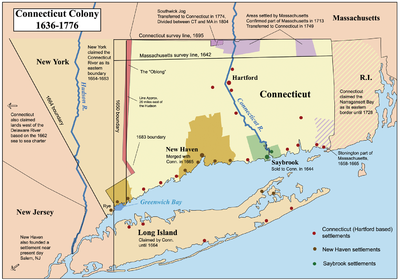 Needless to say, this brought it into territorial conflict with those states which then lay between Connecticut and the Pacific. A patent
Needless to say, this brought it into territorial conflict with those states which then lay between Connecticut and the Pacific. A patent
issued on March 12, 1664, granted the Duke of York
"all the land from the west side of Connecticut River to the east side of Delaware Bay." In October, 1664, Connecticut and New York agreed to grant Long Island
to New York, and establish the boundary between Connecticut and New York as a line from the Mamaroneck River "north-northwest to the line of the Massachusetts", crossing the Hudson River
near Peekskill and the boundary of Massachusetts near the northwest corner of the current Ulster County, New York
. This agreement was never really accepted, however, and boundary disputes continued. The Governor of New York issued arrest warrants for residents of Greenwich, Rye, and Stamford, and founded a settlement north of Tarrytown
in what Connecticut considered part of its territory in May 1682. Finally, on November 28, 1683, the states negotiated a new agreement establishing the border as 20 miles (32.2 km) east of the Hudson River
, north to Massachusetts. In recognition of the wishes of the residents, the 61660 acres (249.5 km²) east of the Byram River
making up the Connecticut Panhandle
were granted to Connecticut. In exchange, Rye was granted to New York, along with a 1.81 miles (2.9 km) wide strip of land running north from Ridgefield
to Massachusetts alongside Dutchess, Putnam, and Westchester Counties, New York, known as the "Oblong".
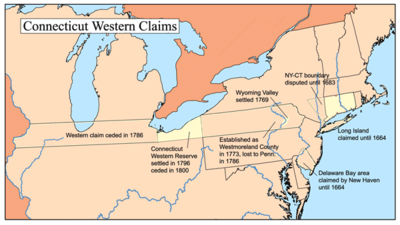 In the 1750s, the western frontier remained on the other side of New York. In 1754 the Susquehannah Company of Windham, Connecticut
In the 1750s, the western frontier remained on the other side of New York. In 1754 the Susquehannah Company of Windham, Connecticut
obtained from a group of Native Americans a deed to a tract of land along the Susquehanna River
which covered about one-third of present-day Pennsylvania. This venture met with the disapproval of not only Pennsylvania, but also of many in Connecticut including the Deputy Governor, who opposed Governor Jonathan Trumbull
's support for the company, fearing that pressing these claims would endanger the charter of the colony. In 1769, Wilkes-Barre
was founded by John Durkee and a group of 240 Connecticut settlers. The British government finally ruled "that no Connecticut settlements could be made until the royal pleasure was known". In 1773 the issue was settled in favor of Connecticut and Westmoreland, Connecticut
was established as a town and later a county.
Pennsylvania did not accede to the ruling, however, and open warfare broke out between them and Connecticut, ending with an attack in July 1778, which killed approximately 150 of the settlers and forced thousands to flee. While they periodically attempted to regain their land, they were continuously repulsed, until, in December 1783, a commission ruled in favor of Pennsylvania. After complex litigation, in 1786, Connecticut dropped its claims by a deed of cession to Congress, in exchange for freedom for war debt and confirmation of the rights to land further west in present-day Ohio
, which became known as the Western Reserve. Pennsylvania granted the individual settlers from Connecticut the titles to their land claims. Although the region had been called Westmoreland County, Connecticut, it has no relationship with the current Westmoreland County, Pennsylvania
.
The Western Reserve, which Connecticut received in recompense for giving up all claims to any Pennsylvania land in 1786, constituted a strip of land in what is currently northeast Ohio, 120 miles (193.1 km) wide from east to west bordering Lake Erie
and Pennsylvania. Connecticut owned this territory until selling it to the Connecticut Land Company
in 1795 for $1,200,000, which resold parcels of land to settlers. In 1796, the first settlers, led by Moses Cleaveland
, began a community which was to become Cleveland, Ohio
; in a short time, the area became known as "New Connecticut".
An area 25 miles (40.2 km) wide at the western end of the Western Reserve, set aside by Connecticut in 1792 to compensate those from Danbury, New Haven, Fairfield, Norwalk, and New London who had suffered heavy losses when they were burnt out by fires set by British raids during the War of Independence, became known as the Firelands
. By this time, however, most of those granted the relief by the state were either dead or too old to actually move there. The Firelands now constitutes Erie and Huron Counties, as well as part of Ashland County, Ohio.
 Connecticut was the only one of the 13 colonies involved in the American Revolution
Connecticut was the only one of the 13 colonies involved in the American Revolution
that did not have an internal revolution of its own. It had been largely self-governing since its beginnings. Governor Jonathan Trumbull
was elected every year from 1769 to 1784. Connecticut's government continued unchanged even after the revolution, until the United States Constitution
was adopted in 1789. A Connecticut privateer
was the Guilford, formerly the Loyalist privateer Mars.
Several significant events during the American Revolution occurred in Connecticut. Notably, the landing of a British invasion force in Westport, Connecticut
which subsequently marched to and burnt the city of Danbury, Connecticut
for safeguarding Patriot
supplies and was engaged by General David Wooster
and General Benedict Arnold
on their return in the Battle of Ridgefield
in 1777, which would deter future strategic landing attempts by the British for the remainder of the war. The state was also the launching site for a number of raids against Long Island orchestrated by Samuel Holden Parsons
and Benjamin Tallmadge
, and provided men and material for the war effort, especially to Washington's army outside New York City. General William Tryon
raided the Connecticut coast
in July 1779, focusing on New Haven, Norwalk, and Fairfield. The French General the Comte de Rochambeau
celebrated the first Catholic Mass in Connecticut at Lebanon
in summer 1781 while marching through the state from Rhode Island
to rendezvous with General George Washington
in Dobbs Ferry, New York
. New London and Groton Heights were raided
in September 1781 by Connecticut native and turncoat Benedict Arnold
.
. One historian explains how well organized it was in Connecticut:
Given the power of the Federalists, the Democratic-Republicans had to work harder to win. In 1806, the state leadership sent town leaders instructions for the forthcoming elections. Every town manager was told by state leaders "to appoint a district manager in each district or section of his town, obtaining from each an assurance that he will faithfully do his duty." Then, the town manager was instructed to compile lists and total up the number of taxpayers, the number of eligible voters, how many were "decided republicans," "decided federalists," or "doubtful," and finally to count the number of supporters who were not currently eligible to vote but who might qualify (by age or taxes) at the next election. These highly detailed returns were to be sent to the county manager. They, in turn, were to compile county-wide statistics and send it on to the state manager. Using the newly compiled lists of potential voters, the managers were told to get all the eligibles to the town meetings, and help the young men qualify to vote. At the annual official town meeting, the managers were told to, "notice what republicans are present, and see that each stays and votes till the whole business is ended. And each District-Manager shall report to the Town-Manager the names of all republicans absent, and the cause of absence, if known to him." Of utmost importance, the managers had to nominate candidates for local elections, and to print and distribute the party ticket. The state manager was responsible for supplying party newspapers to each town for distribution by town and district managers. This highly coordinated "get-out-the-vote" drive would be familiar to modern political campaigners, but was the first of its kind in world history.
Connecticut prospered during the era, as the seaports were busy and the first textile factories were built. The American Embargo and the British blockade during the War of 1812
severely hurt the export business, but did help promote the rapid growth of industry. Eli Whitney
of New Haven was one of many engineers and inventors who made the state a world leader in machine tools and industrial technology generally. The state was known for its political conservatism, typified by its Federalist party and the Yale College of Timothy Dwight
. The foremost intellectuals were Dwight and Noah Webster
, who compiled his great dictionary in New Haven. Religious tensions polarized the state, as the established Congregational Church, in alliance with the Federalists, tried to maintain its grip on power. The failure of the Hartford Convention
in 1814 wounded the Federalists, who were finally upended by the Republicans in 1817.
Connecticut started off with the raw materials of abundant running water and navigable waterways, and using the Yankee work ethic quickly became an industrial leader. Between the birth of the U.S. patent
system in 1790 and 1930, Connecticut had more patents issued per capita than any other state; in the 1800s, when the U.S. as a whole was issued one patent per three thousand population, Connecticut inventors were issued one patent for every 700–1000 residents. Connecticut's first recorded invention was a lapidary
machine, by Abel Buell
of Killingworth
, in 1765.
and Navy
with weapons, ammunition, and military materiel
during the Civil War
. A number of Connecticut residents were generals in the Federal service and Gideon Welles
was the United States Secretary of the Navy
and a confidant of President Abraham Lincoln
.
Starting in the 1830s, and accelerating when Connecticut abolished slavery entirely in 1848, African Americans from in- and out-of-state began relocating to urban centers for employment and opportunity, forming new neighborhoods such as Bridgeport's Little Liberia.
, New Haven
, Waterbury
and Hartford
were magnets for European immigrants. The largest groups comprised Italian American
, and Polish American
, and other Eastern Europe
ans. They brought much needed unskilled labor and Catholicism
to a historically Protestant state. A significant number of Jewish immigrants also arrived in this period due to an 1843 change in the law. Connecticut's population was almost 30% immigrant by 1910.
 In World War I
In World War I
(1917–1918), munitions were the most prosperous business in Connecticut, and would remain so until the Great Depression
.
Not everyone welcomed the new immigrants and the change in the state's ethnic and religious makeup. The Ku Klux Klan
had a following among some in Connecticut after it was reorganized in Georgia
in 1915. It preached a doctrine of Protestant control of America and wanted to keep down blacks, Jews and Catholics. The Klan enjoyed only a brief period of popularity in the state, but it had a peak of 15,000 members in 1925. The group was most active in New Haven
, New Britain
and Stamford
, which all had large Catholic populations. By 1926, the Klan leadership was divided, and it lost strength, although it continued to maintain small, local branches for years afterward in Stamford
, Bridgeport
, Darien
, Greenwich
and Norwalk
. The Klan has since disappeared from the state.
 With rising unemployment in both urban and rural areas, Connecticut Democrats
With rising unemployment in both urban and rural areas, Connecticut Democrats
saw their chance to return to power. The hero of the movement was Yale
English professor Governor Wilbur Lucius Cross
(1931–1939), who emulated much of Franklin D. Roosevelt
's New Deal
policies by creating new public services and instituted a minimum wage. The Merritt Parkway
was constructed in this period.
However, in 1938, the Democratic Party was wracked by controversy, which quickly allowed the Republicans to gain control once again, with Governor Raymond E. Baldwin
. Connecticut became a highly competitive, two-party state.
The lingering Depression soon gave way to unparalleled opportunity with the United States involvement in World War II
(1941–1945). Roosevelt's call for America to be the Arsenal of Democracy
led to remarkable growth in munition-related inductries, such as airplane engines, radio, radar, proximity fuzes, rifles, and a thousand other products. Pratt and Whitney made airplane engines, Cheney sewed silk parachutes, and Electric Boat
built submarines. This was coupled with traditional manufacturing including guns, ships, uniforms, munitions, and artillery. Ken Burns
focused on Waterbury
's munitions production in his 2007 miniseries The War
. Although most munitions production ended in 1945, high tech electronics and airplane parts continued.
years, Connecticut's suburbs thrived while its cities struggled. Connecticut built the first nuclear-powered submarine, the and other essential weapons for The Pentagon
. The increased job market gave the state the highest per capita income at the beginning of the 1960s. The increased standard of living could be seen in the various suburban neighborhoods that began to develop outside major cities. Construction of major highways such as the Connecticut Turnpike
caused former small towns to become locations for large-scale development, a trend that continues to this day.
However, all of these developments also led to the economic downfall of many of Connecticut's cities, many of which remain dotted with abandoned mills and other broken-down buildings. During this time, Connecticut's cities saw major growth in the African American
and Latino
populations. African Americans and Latinos inherited urban spaces that were no longer a high priority for the state or private industry, and by the 1980s crime and urban blight
were major issues. In fact, the poor conditions that many inhabited were cause for militant movements that pushed for the gentrification of ghettos and the desegregation of the school system. In 1987, Hartford
, became the first American city to elect an African-American woman as mayor, Carrie Saxon Perry.
Connecticut business thrived until the end of the 1980s, with many well-known corporations moving to Fairfield County
, including General Electric
, American Brands, and Union Carbide
. The state also benefited from the defense buildup initiated by Ronald Reagan
, due to such major employers as Electric Boat
shipyards, Sikorsky
helicopters, and Pratt & Whitney
jet engines.
. The resulting budget crisis helped elect Lowell Weicker as Governor on a third party ticket in 1990. Weicker's remedy, a state income tax, proved effective in balancing the budget but politically unpopular, as Weicker retired after a single term.
With newly "reconquered" land, the Pequots initiated plans for the construction of a multi-million dollar casino complex to be built on reservation land. The Foxwoods Casino
was completed in 1992 and the enormous revenue it received made the Mashantucket Pequot Reservation one of the wealthiest in the country. With the newfound money, great educational and cultural initiatives were carried out, including the construction of the Mashantucket Pequot Museum and Research Center. The Mohegan
Reservation gained political recognition shortly thereafter and, in 1994, opened another successful casino (Mohegan Sun
) near the town of Uncasville
. The success of casino gambling helped shift the state's economy away from manufacturing
to entertainment, such as ESPN
, financial services, including hedge funds and pharmaceutical firms such as Pfizer
.
residents who were working in the World Trade Center
. Greenwich
lost 12 residents, Stamford
and Norwalk
each lost nine and Darien
lost six. A state memorial was later set up at Sherwood Island State Park in Westport
. The New York City skyline can be seen from the park.
A number of political scandals rocked Connecticut in the early 21st century. These included the 2003 removal from office of the mayors of Bridgeport
, Joseph P. Ganim
on 16 corruption charges, as well as Waterbury
mayor Philip A. Giordano, whom was charged with 18 counts of sexual abuse of two girls.
In 2004, Governor John G. Rowland
resigned during a corruption investigation. Rowland later plead guilty to federal charges, and his successor M. Jodi Rell
, focused her administration on reforms in the wake of the Rowland scandal.
In April 2005, Connecticut passed a law which grants all rights of marriage to same-sex couples
. However, the law required that such unions be called "civil unions", and that the title of marriage be limited to those unions whose parties are of the opposite sex. The state was the first to pass a law permitting civil unions without a prior court proceeding. In October 2008, the Supreme Court of Connecticut ordered same-sex marriage legalized.
In July 2009, the Connecticut legislature overrode a veto by Governor M. Jodi Rell
to pass SustiNet
, the first significant public-option health care reform legislation in the nation.
The state's criminal justice system also dealt with the first execution in the state since 1960, the 2005 execution of serial killer Michael Ross and was rocked by the July 2007 home invasion
murders in Cheshire
. As the accused perpetrators of the Petit murders were out on parole
, Governor M. Jodi Rell
promised a full investigation into the state's criminal justice policies.
Connecticut
Connecticut is a state in the New England region of the northeastern United States. It is bordered by Rhode Island to the east, Massachusetts to the north, and the state of New York to the west and the south .Connecticut is named for the Connecticut River, the major U.S. river that approximately...
began as three distinct settlements, referred to at the time as "Colonies" or "Plantations". These ventures were eventually combined under a single royal charter in 1662.
Colonies in Connecticut
Various AlgonquianAlgonquian peoples
The Algonquian are one of the most populous and widespread North American native language groups, with tribes originally numbering in the hundreds. Today hundreds of thousands of individuals identify with various Algonquian peoples...
tribes inhabited the area prior to European settlement. The Dutch were the first Europeans in Connecticut. In 1614 Adriaen Block
Adriaen Block
Adriaen Block was a Dutch private trader and navigator who is best known for exploring the coastal and river valley areas between present-day New Jersey and Massachusetts during four voyages from 1611 to 1614, following the 1609 expedition by Henry Hudson...
explored the coast of Long Island Sound
Long Island Sound
Long Island Sound is an estuary of the Atlantic Ocean, located in the United States between Connecticut to the north and Long Island, New York to the south. The mouth of the Connecticut River at Old Saybrook, Connecticut, empties into the sound. On its western end the sound is bounded by the Bronx...
, and sailed up the Connecticut River
Connecticut River
The Connecticut River is the largest and longest river in New England, and also an American Heritage River. It flows roughly south, starting from the Fourth Connecticut Lake in New Hampshire. After flowing through the remaining Connecticut Lakes and Lake Francis, it defines the border between the...
at least as far as the confluence of the Park River
Park River (Connecticut)
The Park River, sometimes called the Hog River, is a subterranean urban river that flows through and under the city of Hartford, Connecticut. It was diverted underground by the Army Corps of Engineers in 1940. The stated reason for this was to reduce the risk of spring seasonal floods which had...
, site of modern Hartford, Connecticut
Hartford, Connecticut
Hartford is the capital of the U.S. state of Connecticut. The seat of Hartford County until Connecticut disbanded county government in 1960, it is the second most populous city on New England's largest river, the Connecticut River. As of the 2010 Census, Hartford's population was 124,775, making...
. By 1623, the new Dutch West India Company
Dutch West India Company
Dutch West India Company was a chartered company of Dutch merchants. Among its founding fathers was Willem Usselincx...
regularly traded for furs there and ten years later they fortified it for protection from the Pequot
Pequot
Pequot people are a tribe of Native Americans who, in the 17th century, inhabited much of what is now Connecticut. They were of the Algonquian language family. The Pequot War and Mystic massacre reduced the Pequot's sociopolitical influence in southern New England...
Indians
Native Americans in the United States
Native Americans in the United States are the indigenous peoples in North America within the boundaries of the present-day continental United States, parts of Alaska, and the island state of Hawaii. They are composed of numerous, distinct tribes, states, and ethnic groups, many of which survive as...
as well as from the expanding English colonies. They fortified the site, which was named "House of Hope" (also identified as "Fort Hoop
Fort Hoop
Fort Hoop was a settlement in the seventeenth century colonial province of New Netherland that eventually developed into Hartford, Connecticut.-History:...
", "Good Hope" and "Hope"), but encroaching English colonists made them agree to withdraw in the 1650 Treaty of Hartford
Treaty of Hartford
The term Treaty of Hartford applies to three historic agreements negotiated at Hartford, Connecticut. The 1638 treaty divided the spoils of the Pequot War. The 1650 treaty defined a border between the Dutch Nieuw Amsterdam and English settlers in Connecticut...
, and by 1654 they were gone.
The first English colonists came from the Bay Colony
Massachusetts Bay Colony
The Massachusetts Bay Colony was an English settlement on the east coast of North America in the 17th century, in New England, situated around the present-day cities of Salem and Boston. The territory administered by the colony included much of present-day central New England, including portions...
and Plymouth Colony
Plymouth Colony
Plymouth Colony was an English colonial venture in North America from 1620 to 1691. The first settlement of the Plymouth Colony was at New Plymouth, a location previously surveyed and named by Captain John Smith. The settlement, which served as the capital of the colony, is today the modern town...
in Massachusetts
Massachusetts
The Commonwealth of Massachusetts is a state in the New England region of the northeastern United States of America. It is bordered by Rhode Island and Connecticut to the south, New York to the west, and Vermont and New Hampshire to the north; at its east lies the Atlantic Ocean. As of the 2010...
. They settled at Windsor
Windsor, Connecticut
Windsor is a town in Hartford County, Connecticut, United States, and was the first English settlement in the state. It lies on the northern border of Connecticut's capital, Hartford. The population was estimated at 28,778 in 2005....
in 1633, Wethersfield
Wethersfield, Connecticut
Wethersfield is a town in Hartford County, Connecticut, United States. Many records from colonial times spell the name Weathersfield, while Native Americans called it Pyquag...
in 1634, and Hartford
Hartford, Connecticut
Hartford is the capital of the U.S. state of Connecticut. The seat of Hartford County until Connecticut disbanded county government in 1960, it is the second most populous city on New England's largest river, the Connecticut River. As of the 2010 Census, Hartford's population was 124,775, making...
in 1636. Thomas Hooker
Thomas Hooker
Thomas Hooker was a prominent Puritan colonial leader, who founded the Colony of Connecticut after dissenting with Puritan leaders in Massachusetts...
led the Hartford group.
In 1631, the Earl of Warwick
Robert Rich, 2nd Earl of Warwick
Robert Rich, 2nd Earl of Warwick was an English colonial administrator, admiral, and puritan.Rich was the eldest son of Robert Rich, 1st Earl of Warwick and his wife Penelope Devereux, Lady Rich, and succeeded to his father's title in 1619...
granted a patent to a company of investors headed by William Fiennes, 1st Viscount Saye and Sele
William Fiennes, 1st Viscount Saye and Sele
William Fiennes, 1st Viscount Saye and Sele was born at the family home of Broughton Castle near Banbury, in Oxfordshire. He was the only son of Richard Fiennes, seventh Baron Saye and Sele...
and Robert Greville, 2nd Baron Brooke
Robert Greville, 2nd Baron Brooke
Robert Greville, 2nd Baron Brooke was an English Civil War Roundhead General.Greville was the cousin and adopted son of Fulke Greville, 1st Baron Brooke, and thus became 2nd Lord Brooke, and owner of Warwick Castle. He was born in 1607, and entered parliament for Warwickshire in 1628...
. They funded the establishment of the Saybrook Colony
Saybrook Colony
The Saybrook Colony was established in late 1635 at the mouth of the Connecticut River in present day Old Saybrook, Connecticut by John Winthrop, the Younger, son of John Winthrop, the Governor of Massachusetts. The former was designated Governor by the original settlers which included Colonel...
(named for the two lords) at the mouth of the Connecticut River, where Fort Saybrook
Old Saybrook, Connecticut
Old Saybrook is a town in Middlesex County, Connecticut, United States. The population was 10,367 at the 2000 census. It contains the incorporated borough of Fenwick, as well as the census-designated places of Old Saybrook Center and Saybrook Manor.-History:...
, was erected in 1636. Another Puritan group left Massachusetts and started the New Haven Colony
New Haven Colony
The New Haven Colony was an English colonial venture in present-day Connecticut in North America from 1637 to 1662.- Quinnipiac Colony :A Puritan minister named John Davenport led his flock from exile in the Netherlands back to England and finally to America in the spring of 1637...
farther west on the northern shore of Long Island Sound in 1637. The Massachusetts colonies did not seek to govern their progeny in Connecticut and Rhode Island
Rhode Island
The state of Rhode Island and Providence Plantations, more commonly referred to as Rhode Island , is a state in the New England region of the United States. It is the smallest U.S. state by area...
. Communication and travel were too difficult, and it was also convenient to have a place for nonconformists to go.
The English settlement and trading post at Windsor especially threatened the Dutch trade, since it was upriver and more accessible to Native people from the interior. That fall and winter the Dutch sent a party upriver as far as modern Springfield, Massachusetts
Springfield, Massachusetts
Springfield is the most populous city in Western New England, and the seat of Hampden County, Massachusetts, United States. Springfield sits on the eastern bank of the Connecticut River near its confluence with three rivers; the western Westfield River, the eastern Chicopee River, and the eastern...
spreading gifts to convince the indigenous inhabitants in the area to bring their trade to the Dutch post at Hartford. Unfortunately, they also spread smallpox
Smallpox
Smallpox was an infectious disease unique to humans, caused by either of two virus variants, Variola major and Variola minor. The disease is also known by the Latin names Variola or Variola vera, which is a derivative of the Latin varius, meaning "spotted", or varus, meaning "pimple"...
and, by the end of the 1633–34 winter, the Native population of the entire valley was reduced from over 8,000 to less than 2,000. Europeans took advantage of this decimation by further settling the fertile valley.
The Pequot War

Mystic Massacre
The Mystic massacre took place on May 26, 1637, during the Pequot War, when English settlers under Captain John Mason, and Narragansett and Mohegan allies set fire to a fortified Pequot village near the Mystic River...
.
On May 1, 1637, leaders of Connecticut Colony's river towns each sent delegates to the first General Court held at the meeting house in Hartford. This was the start of self-government in Connecticut. They pooled their militia under the command of John Mason
John Mason (c.1600-1672)
John Mason was an English Army Major who immigrated to New England in 1632. Within five years he had joined those moving west from the Massachusetts Bay Colony to the nascent settlements along the Connecticut River that would become the Connecticut Colony...
of Windsor, and declared war on the Pequots. When the war was over, the Pequots had been destroyed as a tribe. In the Treaty of Hartford
Treaty of Hartford
The term Treaty of Hartford applies to three historic agreements negotiated at Hartford, Connecticut. The 1638 treaty divided the spoils of the Pequot War. The 1650 treaty defined a border between the Dutch Nieuw Amsterdam and English settlers in Connecticut...
in 1638, the various New England colonies and their Native allies divided the lands of the Pequots amongst themselves.
Under the Fundamental Orders
The River Towns had created a general government when faced with the demands of a war. In 1639, they took the unprecedented step of documenting the source and form of that government. They enumerated individual rights and concluded that a free people were the only source of government's authority. Rapid growth and expansion grew under this new regime.On April 22, 1662, the Connecticut Colony
Connecticut Colony
The Connecticut Colony or Colony of Connecticut was an English colony located in British America that became the U.S. state of Connecticut. Originally known as the River Colony, it was organized on March 3, 1636 as a haven for Puritan noblemen. After early struggles with the Dutch, the English...
succeeded in gaining a Royal Charter that embodied and confirmed the self-government that they had created with the Fundamental Orders. The only significant change was that it called for a single Connecticut government with a southern limit at Long Island Sound
Long Island Sound
Long Island Sound is an estuary of the Atlantic Ocean, located in the United States between Connecticut to the north and Long Island, New York to the south. The mouth of the Connecticut River at Old Saybrook, Connecticut, empties into the sound. On its western end the sound is bounded by the Bronx...
, and a western limit of the Pacific ocean, which meant that this charter was still in conflict with the New Netherland
New Netherland
New Netherland, or Nieuw-Nederland in Dutch, was the 17th-century colonial province of the Republic of the Seven United Netherlands on the East Coast of North America. The claimed territories were the lands from the Delmarva Peninsula to extreme southwestern Cape Cod...
colony.
Since 1638, the New Haven Colony
New Haven Colony
The New Haven Colony was an English colonial venture in present-day Connecticut in North America from 1637 to 1662.- Quinnipiac Colony :A Puritan minister named John Davenport led his flock from exile in the Netherlands back to England and finally to America in the spring of 1637...
had been independent of the river towns, but there other factors added to the Charter. New Haven Colony lost its strongest governor, Theophilus Eaton
Theophilus Eaton
Theophilus Eaton was a merchant, farmer, and Puritan colonial leader who was the co-founder and first governor of New Haven Colony, Connecticut.-Early life and first marriage:...
, and suffered economically after losing its only ocean going ship. Furthermore, in the early 1660s the colony harbored several of the regicide judges who had sentenced King Charles I
Charles I of England
Charles I was King of England, King of Scotland, and King of Ireland from 27 March 1625 until his execution in 1649. Charles engaged in a struggle for power with the Parliament of England, attempting to obtain royal revenue whilst Parliament sought to curb his Royal prerogative which Charles...
to death. The colony was absorbed by the Connecticut Colony partly as royal punishment by King Charles II
Charles II of England
Charles II was monarch of the three kingdoms of England, Scotland, and Ireland.Charles II's father, King Charles I, was executed at Whitehall on 30 January 1649, at the climax of the English Civil War...
for harboring the regicide judges. When the English took New Netherland
New Netherland
New Netherland, or Nieuw-Nederland in Dutch, was the 17th-century colonial province of the Republic of the Seven United Netherlands on the East Coast of North America. The claimed territories were the lands from the Delmarva Peninsula to extreme southwestern Cape Cod...
in the 1660s the new government of the Province of New York
Province of New York
The Province of New York was an English and later British crown territory that originally included all of the present U.S. states of New York, New Jersey, Delaware and Vermont, along with inland portions of Connecticut, Massachusetts, and Maine, as well as eastern Pennsylvania...
claimed the New Haven settlements on Long Island. By January 1665, the merger of the two colonies was completed.
Indian pressures were relieved for some time by the severity and ferocity of the Pequot War. King Philip's War
King Philip's War
King Philip's War, sometimes called Metacom's War, Metacomet's War, or Metacom's Rebellion, was an armed conflict between Native American inhabitants of present-day southern New England and English colonists and their Native American allies in 1675–76. The war is named after the main leader of the...
(1675–1676) brought renewed fighting to Connecticut. Although primarily a war affecting Massachusetts, Connecticut provided men and supplies. This war effectively removed any remaining warlike Native American influences in Connecticut.
The Dominion of New England
In 1686, Sir Edmund AndrosEdmund Andros
Sir Edmund Andros was an English colonial administrator in North America. Andros was known most notably for his governorship of the Dominion of New England during most of its three-year existence. He also governed at various times the provinces of New York, East and West Jersey, Virginia, and...
was commissioned as the Royal Governor of the Dominion of New England
Dominion of New England
The Dominion of New England in America was an administrative union of English colonies in the New England region of North America. The dominion was ultimately a failure because the area it encompassed was too large for a single governor to manage...
. Andros maintained that his commission superseded Connecticut's 1662 charter. At first, Connecticut ignored this situation. But in late October 1687, Andros arrived with troops and naval support. Governor Robert Treat
Robert Treat
Robert Treat was an American colonial leader, militia officer and governor of Connecticut between 1683 and 1698....
had no choice but to convene the assembly. Andros met with the governor and General Court on the evening of October 31, 1687.

Charter Oak
The Charter Oak was an unusually large white oak tree growing, from around the 12th or 13th century until 1856, on what the English colonists named Wyllys Hyll, in Hartford, Connecticut, USA...
. Sir Edmund named four members to his Council for the Government of New England and proceeded to his capital at Boston.
Since Andros viewed New York and Massachusetts as the important parts of his Dominion, he mostly ignored Connecticut. Aside from some taxes demanded and sent to Boston, Connecticut also mostly ignored the new government. When word arrived that the Glorious Revolution
Glorious Revolution
The Glorious Revolution, also called the Revolution of 1688, is the overthrow of King James II of England by a union of English Parliamentarians with the Dutch stadtholder William III of Orange-Nassau...
had placed William and Mary
William III of England
William III & II was a sovereign Prince of Orange of the House of Orange-Nassau by birth. From 1672 he governed as Stadtholder William III of Orange over Holland, Zeeland, Utrecht, Guelders, and Overijssel of the Dutch Republic. From 1689 he reigned as William III over England and Ireland...
on the throne, the citizens of Boston arrested Andros
1689 Boston revolt
The 1689 Boston revolt was a popular uprising on April 18, 1689, against the rule of Sir Edmund Andros, the governor of the Dominion of New England. A well-organized "mob" of provincial militia and citizens formed in the city and arrested dominion officials...
and sent him back to England in chains. The Connecticut court met and voted on May 9, 1689 to restore the old charter. They also reelected Robert Treat as governor each year until 1698.
Territorial disputes
According to the 1650 Treaty of Hartford with the DutchNetherlands
The Netherlands is a constituent country of the Kingdom of the Netherlands, located mainly in North-West Europe and with several islands in the Caribbean. Mainland Netherlands borders the North Sea to the north and west, Belgium to the south, and Germany to the east, and shares maritime borders...
, the western boundary of Connecticut ran north from the west side of Greenwich Bay
Greenwich Bay (Rhode Island)
Greenwich Bay, is a bay on the coast of Rhode Island in the United States near East Greenwich, Rhode Island off of Narragansett Bay.The United States Navy seaplane tender USS Greenwich Bay, in commission from 1945 to 1966, was named for the bay....
"provided the said line come not within 10 miles (16.1 km) of Hudson River." On the other hand, Connecticut's original charter in 1662 granted it all the land to the "South Sea" (i.e. the Pacific Ocean
Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest of the Earth's oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic in the north to the Southern Ocean in the south, bounded by Asia and Australia in the west, and the Americas in the east.At 165.2 million square kilometres in area, this largest division of the World...
).
- ALL that parte of our dominions in Newe England in America bounded on the East by Norrogancett River, commonly called Norrogancett Bay, where the said River falleth into the Sea, and on the North by the lyne of the Massachusetts Plantacon, and on the south by the Sea, and in longitude as the lyne of the Massachusetts Colony, runinge from East to West, (that is to say) from the Said Norrogancett Bay on the East to the South Sea on the West parte, with the Islands thervnto adioyneinge, Together with all firme lands ... TO HAVE AND TO HOLD ... for ever....
Dispute with New York

Land grant
A land grant is a gift of real estate – land or its privileges – made by a government or other authority as a reward for services to an individual, especially in return for military service...
issued on March 12, 1664, granted the Duke of York
Duke of York
The Duke of York is a title of nobility in the British peerage. Since the 15th century, it has, when granted, usually been given to the second son of the British monarch. The title has been created a remarkable eleven times, eight as "Duke of York" and three as the double-barreled "Duke of York and...
"all the land from the west side of Connecticut River to the east side of Delaware Bay." In October, 1664, Connecticut and New York agreed to grant Long Island
Long Island
Long Island is an island located in the southeast part of the U.S. state of New York, just east of Manhattan. Stretching northeast into the Atlantic Ocean, Long Island contains four counties, two of which are boroughs of New York City , and two of which are mainly suburban...
to New York, and establish the boundary between Connecticut and New York as a line from the Mamaroneck River "north-northwest to the line of the Massachusetts", crossing the Hudson River
Hudson River
The Hudson is a river that flows from north to south through eastern New York. The highest official source is at Lake Tear of the Clouds, on the slopes of Mount Marcy in the Adirondack Mountains. The river itself officially begins in Henderson Lake in Newcomb, New York...
near Peekskill and the boundary of Massachusetts near the northwest corner of the current Ulster County, New York
Ulster County, New York
Ulster County is a county located in the state of New York, USA. It sits in the state's Mid-Hudson Region of the Hudson Valley. As of the 2010 census, the population was 182,493. Recent population estimates completed by the United States Census Bureau for the 12-month period ending July 1 are at...
. This agreement was never really accepted, however, and boundary disputes continued. The Governor of New York issued arrest warrants for residents of Greenwich, Rye, and Stamford, and founded a settlement north of Tarrytown
Tarrytown, New York
Tarrytown is a village in the town of Greenburgh in Westchester County, New York, United States. It is located on the eastern bank of the Hudson River, about north of midtown Manhattan in New York City, and is served by a stop on the Metro-North Hudson Line...
in what Connecticut considered part of its territory in May 1682. Finally, on November 28, 1683, the states negotiated a new agreement establishing the border as 20 miles (32.2 km) east of the Hudson River
Hudson River
The Hudson is a river that flows from north to south through eastern New York. The highest official source is at Lake Tear of the Clouds, on the slopes of Mount Marcy in the Adirondack Mountains. The river itself officially begins in Henderson Lake in Newcomb, New York...
, north to Massachusetts. In recognition of the wishes of the residents, the 61660 acres (249.5 km²) east of the Byram River
Byram River
The Byram River is a river approximately in length, in southeast New York and southwestern Connecticut in the United States.The river has an elevation of at its headwaters at Byram Lake in Westchester County, New York, and flows in a southward direction, crossing the New York-Connecticut border...
making up the Connecticut Panhandle
Connecticut Panhandle
The Connecticut Panhandle, informally known to locals as the Tail, is in southwestern Connecticut, where it abuts New York State. It is contained entirely in Fairfield County and includes all of Greenwich, Stamford, New Canaan, and Darien, as well as part of Norwalk and containing some of the most...
were granted to Connecticut. In exchange, Rye was granted to New York, along with a 1.81 miles (2.9 km) wide strip of land running north from Ridgefield
Ridgefield, Connecticut
Ridgefield is a town in Fairfield County, Connecticut, United States. Situated in the foothills of the Berkshire Mountains, the 300-year-old community had a population of 24,638 at the 2010 census. The town center, which was formerly a borough, is defined by the U.S...
to Massachusetts alongside Dutchess, Putnam, and Westchester Counties, New York, known as the "Oblong".
Dispute with Pennsylvania

Windham, Connecticut
Windham is a town in Windham County, Connecticut, United States. It contains the city of Willimantic and the villages of Windham Center, North Windham, and South Windham. The city of Willimantic was consolidated with the town in 1983...
obtained from a group of Native Americans a deed to a tract of land along the Susquehanna River
Susquehanna River
The Susquehanna River is a river located in the northeastern United States. At long, it is the longest river on the American east coast that drains into the Atlantic Ocean, and with its watershed it is the 16th largest river in the United States, and the longest river in the continental United...
which covered about one-third of present-day Pennsylvania. This venture met with the disapproval of not only Pennsylvania, but also of many in Connecticut including the Deputy Governor, who opposed Governor Jonathan Trumbull
Jonathan Trumbull
Jonathan Trumbull, Sr. was one of the few Americans who served as governor in both a pre-Revolutionary colony and a post-Revolutionary state...
's support for the company, fearing that pressing these claims would endanger the charter of the colony. In 1769, Wilkes-Barre
Wilkes-Barre, Pennsylvania
Wilkes-Barre is a city in the U.S. state of Pennsylvania, the county seat of Luzerne County. It is at the center of the Wyoming Valley area and is one of the principal cities in the Scranton/Wilkes-Barre metropolitan area, which had a population of 563,631 as of the 2010 Census...
was founded by John Durkee and a group of 240 Connecticut settlers. The British government finally ruled "that no Connecticut settlements could be made until the royal pleasure was known". In 1773 the issue was settled in favor of Connecticut and Westmoreland, Connecticut
Westmoreland County, Connecticut
Westmoreland County, Connecticut was a county established by the State of Connecticut in the present day area of Wyoming Valley, Pennsylvania, until it was ceded to Pennsylvania in 1784, of which it now forms the northeastern corner. It briefly seceded to become the State of Westmoreland...
was established as a town and later a county.
Pennsylvania did not accede to the ruling, however, and open warfare broke out between them and Connecticut, ending with an attack in July 1778, which killed approximately 150 of the settlers and forced thousands to flee. While they periodically attempted to regain their land, they were continuously repulsed, until, in December 1783, a commission ruled in favor of Pennsylvania. After complex litigation, in 1786, Connecticut dropped its claims by a deed of cession to Congress, in exchange for freedom for war debt and confirmation of the rights to land further west in present-day Ohio
Ohio
Ohio is a Midwestern state in the United States. The 34th largest state by area in the U.S.,it is the 7th‑most populous with over 11.5 million residents, containing several major American cities and seven metropolitan areas with populations of 500,000 or more.The state's capital is Columbus...
, which became known as the Western Reserve. Pennsylvania granted the individual settlers from Connecticut the titles to their land claims. Although the region had been called Westmoreland County, Connecticut, it has no relationship with the current Westmoreland County, Pennsylvania
Westmoreland County, Pennsylvania
-Demographics:As of the census of 2000, there were 369,993 people, 149,813 households, and 104,569 families residing in the county. The population density was 361 people per square mile . There were 161,058 housing units at an average density of 157 per square mile...
.
The Western Reserve, which Connecticut received in recompense for giving up all claims to any Pennsylvania land in 1786, constituted a strip of land in what is currently northeast Ohio, 120 miles (193.1 km) wide from east to west bordering Lake Erie
Lake Erie
Lake Erie is the fourth largest lake of the five Great Lakes in North America, and the tenth largest globally. It is the southernmost, shallowest, and smallest by volume of the Great Lakes and therefore also has the shortest average water residence time. It is bounded on the north by the...
and Pennsylvania. Connecticut owned this territory until selling it to the Connecticut Land Company
Connecticut Land Company
The Connecticut Land Company was formed in the late eighteenth century to survey and encourage settlement in the Connecticut Western Reserve, part of the Old Northwest Territory. The Western Reserve is located in Northeast Ohio with its hub being Cleveland. In 1795, the Connecticut Land Company...
in 1795 for $1,200,000, which resold parcels of land to settlers. In 1796, the first settlers, led by Moses Cleaveland
Moses Cleaveland
Moses Cleaveland was a lawyer, politician, soldier, and surveyor from Connecticut who founded the U.S. city of Cleveland, Ohio, while surveying the Western Reserve in 1796.-Early life:...
, began a community which was to become Cleveland, Ohio
Cleveland, Ohio
Cleveland is a city in the U.S. state of Ohio and is the county seat of Cuyahoga County, the most populous county in the state. The city is located in northeastern Ohio on the southern shore of Lake Erie, approximately west of the Pennsylvania border...
; in a short time, the area became known as "New Connecticut".
An area 25 miles (40.2 km) wide at the western end of the Western Reserve, set aside by Connecticut in 1792 to compensate those from Danbury, New Haven, Fairfield, Norwalk, and New London who had suffered heavy losses when they were burnt out by fires set by British raids during the War of Independence, became known as the Firelands
Firelands
The Firelands or Sufferers' Lands tract was located at the western end of the Connecticut Western Reserve in what is now the U.S. state of Ohio...
. By this time, however, most of those granted the relief by the state were either dead or too old to actually move there. The Firelands now constitutes Erie and Huron Counties, as well as part of Ashland County, Ohio.
The American Revolution (1775–1789)

American Revolution
The American Revolution was the political upheaval during the last half of the 18th century in which thirteen colonies in North America joined together to break free from the British Empire, combining to become the United States of America...
that did not have an internal revolution of its own. It had been largely self-governing since its beginnings. Governor Jonathan Trumbull
Jonathan Trumbull
Jonathan Trumbull, Sr. was one of the few Americans who served as governor in both a pre-Revolutionary colony and a post-Revolutionary state...
was elected every year from 1769 to 1784. Connecticut's government continued unchanged even after the revolution, until the United States Constitution
United States Constitution
The Constitution of the United States is the supreme law of the United States of America. It is the framework for the organization of the United States government and for the relationship of the federal government with the states, citizens, and all people within the United States.The first three...
was adopted in 1789. A Connecticut privateer
Privateer
A privateer is a private person or ship authorized by a government by letters of marque to attack foreign shipping during wartime. Privateering was a way of mobilizing armed ships and sailors without having to spend public money or commit naval officers...
was the Guilford, formerly the Loyalist privateer Mars.
Several significant events during the American Revolution occurred in Connecticut. Notably, the landing of a British invasion force in Westport, Connecticut
Westport, Connecticut
-Neighborhoods:* Saugatuck – around the Westport railroad station near the southwestern corner of the town – a built-up area with some restaurants, stores and offices....
which subsequently marched to and burnt the city of Danbury, Connecticut
Danbury, Connecticut
Danbury is a city in northern Fairfield County, Connecticut, United States. It had population at the 2010 census of 80,893. Danbury is the fourth largest city in Fairfield County and is the seventh largest city in Connecticut....
for safeguarding Patriot
Patriot (American Revolution)
Patriots is a name often used to describe the colonists of the British Thirteen United Colonies who rebelled against British control during the American Revolution. It was their leading figures who, in July 1776, declared the United States of America an independent nation...
supplies and was engaged by General David Wooster
David Wooster
David Wooster was an American general who served in the French and Indian War and in the American Revolutionary War. He died of wounds sustained during the Battle of Ridgefield, Connecticut. Cities, schools, and public places were named after him...
and General Benedict Arnold
Benedict Arnold
Benedict Arnold V was a general during the American Revolutionary War. He began the war in the Continental Army but later defected to the British Army. While a general on the American side, he obtained command of the fort at West Point, New York, and plotted to surrender it to the British forces...
on their return in the Battle of Ridgefield
Battle of Ridgefield
The Battle of Ridgefield was a battle and a series of skirmishes between American and British forces during the American Revolutionary War. The main battle was fought in the village of Ridgefield, Connecticut on April 27, 1777 and more skirmishing occurred the next day between Ridgefield and the...
in 1777, which would deter future strategic landing attempts by the British for the remainder of the war. The state was also the launching site for a number of raids against Long Island orchestrated by Samuel Holden Parsons
Samuel Holden Parsons
Samuel Holden Parsons was an American lawyer, jurist, and military leader.Parsons was born in Lyme, Connecticut, the son of Jonathan Parsons and Phoebe Parsons...
and Benjamin Tallmadge
Benjamin Tallmadge
Benjamin Tallmadge was a member of the United States House of Representatives. His birth date is alternately listed as February 25, 1754....
, and provided men and material for the war effort, especially to Washington's army outside New York City. General William Tryon
William Tryon
William Tryon was a British soldier and colonial administrator who served as governor of the Province of North Carolina and the Province of New York .-Early life and career:...
raided the Connecticut coast
Tryon's raid
In July 1779, British Major General William Tryon and 2,600 men embarked onto a Royal Navy fleet led by Admiral George Collier, and raided the Connecticut ports of New Haven, Fairfield, and Norwalk. Military and public stores, supply houses, and ships were destroyed, as were private homes,...
in July 1779, focusing on New Haven, Norwalk, and Fairfield. The French General the Comte de Rochambeau
Jean-Baptiste Donatien de Vimeur, comte de Rochambeau
Marshal of France Jean-Baptiste Donatien de Vimeur, comte de Rochambeau was a French nobleman and general who participated in the American Revolutionary War as the commander-in-chief of the French Expeditionary Force which came to help the American Continental Army...
celebrated the first Catholic Mass in Connecticut at Lebanon
Lebanon, Connecticut
Lebanon is a town in New London County, Connecticut, United States. The population was 6,907 at the 2000 census. The town lies just to the northwest of Norwich, north of New London, and east of Hartford...
in summer 1781 while marching through the state from Rhode Island
Rhode Island
The state of Rhode Island and Providence Plantations, more commonly referred to as Rhode Island , is a state in the New England region of the United States. It is the smallest U.S. state by area...
to rendezvous with General George Washington
George Washington
George Washington was the dominant military and political leader of the new United States of America from 1775 to 1799. He led the American victory over Great Britain in the American Revolutionary War as commander-in-chief of the Continental Army from 1775 to 1783, and presided over the writing of...
in Dobbs Ferry, New York
Dobbs Ferry, New York
Dobbs Ferry is a village in Westchester County, New York, United States. The population was 10,875 at the 2010 census.The Village of Dobbs Ferry is located in, and is a part of, the town of Greenburgh...
. New London and Groton Heights were raided
Battle of Groton Heights
The Battle of Groton Heights was a battle of the American Revolutionary War fought on September 6, 1781 between a small Connecticut militia force led by Lieutenant Colonel William Ledyard and the more numerous British forces led by Brigadier General Benedict Arnold and Lieutenant...
in September 1781 by Connecticut native and turncoat Benedict Arnold
Benedict Arnold
Benedict Arnold V was a general during the American Revolutionary War. He began the war in the Continental Army but later defected to the British Army. While a general on the American side, he obtained command of the fort at West Point, New York, and plotted to surrender it to the British forces...
.
Early National Period (1789–1818)
New England was the stronghold of the Federalist partyFederalist Party (United States)
The Federalist Party was the first American political party, from the early 1790s to 1816, the era of the First Party System, with remnants lasting into the 1820s. The Federalists controlled the federal government until 1801...
. One historian explains how well organized it was in Connecticut:
- It was only necessary to perfect the working methods of the organized body of office-holders who made up the nucleus of the party. There were the state officers, the assistants, and a large majority of the Assembly. In every county there was a sheriff with his deputies. All of the state, county, and town judges were potential and generally active workers. Every town had several justices of the peace, school directors and, in Federalist towns, all the town officers who were ready to carry on the party's work. Every parish had a "standing agent," whose anathemas were said to convince at least ten voting deacons. Militia officers, state's attorneys, lawyers, professors and schoolteachers were in the van of this "conscript army." In all, about a thousand or eleven hundred dependent officer-holders were described as the inner ring which could always be depended upon for their own and enough more votes within their control to decide an election. This was the Federalist machine.
Given the power of the Federalists, the Democratic-Republicans had to work harder to win. In 1806, the state leadership sent town leaders instructions for the forthcoming elections. Every town manager was told by state leaders "to appoint a district manager in each district or section of his town, obtaining from each an assurance that he will faithfully do his duty." Then, the town manager was instructed to compile lists and total up the number of taxpayers, the number of eligible voters, how many were "decided republicans," "decided federalists," or "doubtful," and finally to count the number of supporters who were not currently eligible to vote but who might qualify (by age or taxes) at the next election. These highly detailed returns were to be sent to the county manager. They, in turn, were to compile county-wide statistics and send it on to the state manager. Using the newly compiled lists of potential voters, the managers were told to get all the eligibles to the town meetings, and help the young men qualify to vote. At the annual official town meeting, the managers were told to, "notice what republicans are present, and see that each stays and votes till the whole business is ended. And each District-Manager shall report to the Town-Manager the names of all republicans absent, and the cause of absence, if known to him." Of utmost importance, the managers had to nominate candidates for local elections, and to print and distribute the party ticket. The state manager was responsible for supplying party newspapers to each town for distribution by town and district managers. This highly coordinated "get-out-the-vote" drive would be familiar to modern political campaigners, but was the first of its kind in world history.
Connecticut prospered during the era, as the seaports were busy and the first textile factories were built. The American Embargo and the British blockade during the War of 1812
War of 1812
The War of 1812 was a military conflict fought between the forces of the United States of America and those of the British Empire. The Americans declared war in 1812 for several reasons, including trade restrictions because of Britain's ongoing war with France, impressment of American merchant...
severely hurt the export business, but did help promote the rapid growth of industry. Eli Whitney
Eli Whitney
Eli Whitney was an American inventor best known for inventing the cotton gin. This was one of the key inventions of the Industrial Revolution and shaped the economy of the Antebellum South...
of New Haven was one of many engineers and inventors who made the state a world leader in machine tools and industrial technology generally. The state was known for its political conservatism, typified by its Federalist party and the Yale College of Timothy Dwight
Timothy Dwight IV
Timothy Dwight was an American academic and educator, a Congregationalist minister, theologian, and author...
. The foremost intellectuals were Dwight and Noah Webster
Noah Webster
Noah Webster was an American educator, lexicographer, textbook pioneer, English spelling reformer, political writer, editor, and prolific author...
, who compiled his great dictionary in New Haven. Religious tensions polarized the state, as the established Congregational Church, in alliance with the Federalists, tried to maintain its grip on power. The failure of the Hartford Convention
Hartford Convention
The Hartford Convention was an event spanning from December 15, 1814–January 4, 1815 in the United States during the War of 1812 in which New England's opposition to the war reached the point where secession from the United States was discussed...
in 1814 wounded the Federalists, who were finally upended by the Republicans in 1817.
Modernization and industry
Up until this time, Connecticut had adhered to the 1662 Charter, and with the independence of the American colonies over forty years prior, much of what the Charter stood for was no longer relevant. In 1818, a new constitution was adopted that was the first piece of written legislation to separate church and state in Connecticut, and give equality all religions. Gubernatorial powers were also expanded as well as increased independence for courts by allowing their judges to serve life terms.Connecticut started off with the raw materials of abundant running water and navigable waterways, and using the Yankee work ethic quickly became an industrial leader. Between the birth of the U.S. patent
Patent
A patent is a form of intellectual property. It consists of a set of exclusive rights granted by a sovereign state to an inventor or their assignee for a limited period of time in exchange for the public disclosure of an invention....
system in 1790 and 1930, Connecticut had more patents issued per capita than any other state; in the 1800s, when the U.S. as a whole was issued one patent per three thousand population, Connecticut inventors were issued one patent for every 700–1000 residents. Connecticut's first recorded invention was a lapidary
Lapidary
A lapidary is an artist or artisan who forms stone, mineral, gemstones, and other suitably durable materials into decorative items such as engraved gems, including cameos, or cabochons, and faceted designs...
machine, by Abel Buell
Abel Buell
Abel Buell , born in Killingworth, Connecticut, was a goldsmith, silversmith, jewelry designer, engraver, surveyor, type manufacturer, mint master, textile miller, and counterfeiter in the American colonies...
of Killingworth
Killingworth, Connecticut
Killingworth is a town in Middlesex County, Connecticut, United States. The town's name can easily be confused with another Connecticut town, Killingly; or a Vermont ski area, Killington. The population was 6,018 at the 2000 census.-History:...
, in 1765.
Civil War era
As a result of the industrialization of the state and New England as a region, Connecticut manufacturers played a prominent role in supplying the Union ArmyUnion Army
The Union Army was the land force that fought for the Union during the American Civil War. It was also known as the Federal Army, the U.S. Army, the Northern Army and the National Army...
and Navy
Union Navy
The Union Navy is the label applied to the United States Navy during the American Civil War, to contrast it from its direct opponent, the Confederate States Navy...
with weapons, ammunition, and military materiel
Materiel
Materiel is a term used in English to refer to the equipment and supplies in military and commercial supply chain management....
during the Civil War
American Civil War
The American Civil War was a civil war fought in the United States of America. In response to the election of Abraham Lincoln as President of the United States, 11 southern slave states declared their secession from the United States and formed the Confederate States of America ; the other 25...
. A number of Connecticut residents were generals in the Federal service and Gideon Welles
Gideon Welles
Gideon Welles was the United States Secretary of the Navy from 1861 to 1869. His buildup of the Navy to successfully execute blockades of Southern ports was a key component of Northern victory of the Civil War...
was the United States Secretary of the Navy
United States Secretary of the Navy
The Secretary of the Navy of the United States of America is the head of the Department of the Navy, a component organization of the Department of Defense...
and a confidant of President Abraham Lincoln
Abraham Lincoln
Abraham Lincoln was the 16th President of the United States, serving from March 1861 until his assassination in April 1865. He successfully led his country through a great constitutional, military and moral crisis – the American Civil War – preserving the Union, while ending slavery, and...
.
Starting in the 1830s, and accelerating when Connecticut abolished slavery entirely in 1848, African Americans from in- and out-of-state began relocating to urban centers for employment and opportunity, forming new neighborhoods such as Bridgeport's Little Liberia.
Immigration
Connecticut factories in BridgeportBridgeport, Connecticut
Bridgeport is the most populous city in the U.S. state of Connecticut. Located in Fairfield County, the city had an estimated population of 144,229 at the 2010 United States Census and is the core of the Greater Bridgeport area...
, New Haven
New Haven, Connecticut
New Haven is the second-largest city in Connecticut and the sixth-largest in New England. According to the 2010 Census, New Haven's population increased by 5.0% between 2000 and 2010, a rate higher than that of the State of Connecticut, and higher than that of the state's five largest cities, and...
, Waterbury
Waterbury, Connecticut
Waterbury is a city in New Haven County, Connecticut, on the Naugatuck River, 33 miles southwest of Hartford and 77 miles northeast of New York City...
and Hartford
Hartford, Connecticut
Hartford is the capital of the U.S. state of Connecticut. The seat of Hartford County until Connecticut disbanded county government in 1960, it is the second most populous city on New England's largest river, the Connecticut River. As of the 2010 Census, Hartford's population was 124,775, making...
were magnets for European immigrants. The largest groups comprised Italian American
Italian American
An Italian American , is an American of Italian ancestry. The designation may also refer to someone possessing Italian and American dual citizenship...
, and Polish American
Polish American
A Polish American , is a citizen of the United States of Polish descent. There are an estimated 10 million Polish Americans, representing about 3.2% of the population of the United States...
, and other Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is the eastern part of Europe. The term has widely disparate geopolitical, geographical, cultural and socioeconomic readings, which makes it highly context-dependent and even volatile, and there are "almost as many definitions of Eastern Europe as there are scholars of the region"...
ans. They brought much needed unskilled labor and Catholicism
Catholicism
Catholicism is a broad term for the body of the Catholic faith, its theologies and doctrines, its liturgical, ethical, spiritual, and behavioral characteristics, as well as a religious people as a whole....
to a historically Protestant state. A significant number of Jewish immigrants also arrived in this period due to an 1843 change in the law. Connecticut's population was almost 30% immigrant by 1910.

World War I
World War I , which was predominantly called the World War or the Great War from its occurrence until 1939, and the First World War or World War I thereafter, was a major war centred in Europe that began on 28 July 1914 and lasted until 11 November 1918...
(1917–1918), munitions were the most prosperous business in Connecticut, and would remain so until the Great Depression
Great Depression
The Great Depression was a severe worldwide economic depression in the decade preceding World War II. The timing of the Great Depression varied across nations, but in most countries it started in about 1929 and lasted until the late 1930s or early 1940s...
.
Not everyone welcomed the new immigrants and the change in the state's ethnic and religious makeup. The Ku Klux Klan
Ku Klux Klan
Ku Klux Klan, often abbreviated KKK and informally known as the Klan, is the name of three distinct past and present far-right organizations in the United States, which have advocated extremist reactionary currents such as white supremacy, white nationalism, and anti-immigration, historically...
had a following among some in Connecticut after it was reorganized in Georgia
Georgia (U.S. state)
Georgia is a state located in the southeastern United States. It was established in 1732, the last of the original Thirteen Colonies. The state is named after King George II of Great Britain. Georgia was the fourth state to ratify the United States Constitution, on January 2, 1788...
in 1915. It preached a doctrine of Protestant control of America and wanted to keep down blacks, Jews and Catholics. The Klan enjoyed only a brief period of popularity in the state, but it had a peak of 15,000 members in 1925. The group was most active in New Haven
New Haven, Connecticut
New Haven is the second-largest city in Connecticut and the sixth-largest in New England. According to the 2010 Census, New Haven's population increased by 5.0% between 2000 and 2010, a rate higher than that of the State of Connecticut, and higher than that of the state's five largest cities, and...
, New Britain
New Britain, Connecticut
New Britain is a city in Hartford County, Connecticut, United States. It is located approximately 9 miles southwest of Hartford. According to 2006 Census Bureau estimates, the population of the city is 71,254....
and Stamford
Stamford, Connecticut
Stamford is a city in Fairfield County, Connecticut, United States. According to the 2010 census, the population of the city is 122,643, making it the fourth largest city in the state and the eighth largest city in New England...
, which all had large Catholic populations. By 1926, the Klan leadership was divided, and it lost strength, although it continued to maintain small, local branches for years afterward in Stamford
Stamford, Connecticut
Stamford is a city in Fairfield County, Connecticut, United States. According to the 2010 census, the population of the city is 122,643, making it the fourth largest city in the state and the eighth largest city in New England...
, Bridgeport
Bridgeport, Connecticut
Bridgeport is the most populous city in the U.S. state of Connecticut. Located in Fairfield County, the city had an estimated population of 144,229 at the 2010 United States Census and is the core of the Greater Bridgeport area...
, Darien
Darien, Connecticut
Darien is a town in Fairfield County, Connecticut, United States. A relatively small community on Connecticut's "Gold Coast", the population was 20,732 at the 2010 census. Darien was listed at #9 at CNN Money's list of "top-earning towns" in the United States as of 2011...
, Greenwich
Greenwich, Connecticut
Greenwich is a town in Fairfield County, Connecticut, United States. As of the 2010 census, the town had a total population of 61,171. It is home to many hedge funds and other financial service companies. Greenwich is the southernmost and westernmost municipality in Connecticut and is 38+ minutes ...
and Norwalk
Norwalk, Connecticut
Norwalk is a city in Fairfield County, Connecticut, United States. According to the 2010 U.S. Census, the population of the city is 85,603, making Norwalk sixth in population in Connecticut, and third in Fairfield County...
. The Klan has since disappeared from the state.
Depression and War Years

Democratic Party (United States)
The Democratic Party is one of two major contemporary political parties in the United States, along with the Republican Party. The party's socially liberal and progressive platform is largely considered center-left in the U.S. political spectrum. The party has the lengthiest record of continuous...
saw their chance to return to power. The hero of the movement was Yale
Yale University
Yale University is a private, Ivy League university located in New Haven, Connecticut, United States. Founded in 1701 in the Colony of Connecticut, the university is the third-oldest institution of higher education in the United States...
English professor Governor Wilbur Lucius Cross
Wilbur Lucius Cross
Wilbur Lucius Cross, Ph. D. was an American educator and political figure who was the 71st Governor of Connecticut for eight years.-Biography:Born in 1862 in Mansfield, Connecticut, Cross graduated from Yale University Wilbur Lucius Cross, Ph. D. (April 10, 1862 – October 5, 1948) was an American...
(1931–1939), who emulated much of Franklin D. Roosevelt
Franklin D. Roosevelt
Franklin Delano Roosevelt , also known by his initials, FDR, was the 32nd President of the United States and a central figure in world events during the mid-20th century, leading the United States during a time of worldwide economic crisis and world war...
's New Deal
New Deal
The New Deal was a series of economic programs implemented in the United States between 1933 and 1936. They were passed by the U.S. Congress during the first term of President Franklin D. Roosevelt. The programs were Roosevelt's responses to the Great Depression, and focused on what historians call...
policies by creating new public services and instituted a minimum wage. The Merritt Parkway
Merritt Parkway
The Merritt Parkway is a historic limited-access parkway in Fairfield County, Connecticut. The parkway is known for its scenic layout, its uniquely styled signage, and the architecturally elaborate overpasses along the route. It is designated as a National Scenic Byway and is also listed in the...
was constructed in this period.
However, in 1938, the Democratic Party was wracked by controversy, which quickly allowed the Republicans to gain control once again, with Governor Raymond E. Baldwin
Raymond E. Baldwin
Raymond Earl Baldwin was a United States Senator, the 72nd and 74th Governor of Connecticut.-Biography:Born in Rye, New York, he moved to Middletown, Connecticut in 1903 and attended the public schools. He graduated from Wesleyan University in Middletown in 1916, and entered Yale University...
. Connecticut became a highly competitive, two-party state.
The lingering Depression soon gave way to unparalleled opportunity with the United States involvement in World War II
World War II
World War II, or the Second World War , was a global conflict lasting from 1939 to 1945, involving most of the world's nations—including all of the great powers—eventually forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis...
(1941–1945). Roosevelt's call for America to be the Arsenal of Democracy
Arsenal of Democracy
"The Arsenal of Democracy" was a propaganda slogan coined by U.S. President Franklin D. Roosevelt, in a radio broadcast delivered on December 29, 1940. Roosevelt promised to help the United Kingdom fight Nazi Germany by giving them military supplies while the United States stayed out of the actual...
led to remarkable growth in munition-related inductries, such as airplane engines, radio, radar, proximity fuzes, rifles, and a thousand other products. Pratt and Whitney made airplane engines, Cheney sewed silk parachutes, and Electric Boat
Electric Boat Corporation
The General Dynamics Electric Boat is a division of General Dynamics Corporation. It has been the primary builder of submarines for the United States Navy for over 100 years....
built submarines. This was coupled with traditional manufacturing including guns, ships, uniforms, munitions, and artillery. Ken Burns
Ken Burns
Kenneth Lauren "Ken" Burns is an American director and producer of documentary films, known for his style of using archival footage and photographs...
focused on Waterbury
Waterbury
Waterbury is a city in Connecticut in the United States.Waterbury may also refer to any one of the following:-Places:United States*Waterbury, Nebraska*Waterbury, Vermont*Waterbury , Vermont,a village within the town of Waterbury, Vermont....
's munitions production in his 2007 miniseries The War
The War (documentary)
The War is a 2007 American seven-part documentary television mini-series about World War II from the perspective of the United States that premiered on September 23, 2007...
. Although most munitions production ended in 1945, high tech electronics and airplane parts continued.
Cold War Years
In the Cold WarCold War
The Cold War was the continuing state from roughly 1946 to 1991 of political conflict, military tension, proxy wars, and economic competition between the Communist World—primarily the Soviet Union and its satellite states and allies—and the powers of the Western world, primarily the United States...
years, Connecticut's suburbs thrived while its cities struggled. Connecticut built the first nuclear-powered submarine, the and other essential weapons for The Pentagon
The Pentagon
The Pentagon is the headquarters of the United States Department of Defense, located in Arlington County, Virginia. As a symbol of the U.S. military, "the Pentagon" is often used metonymically to refer to the Department of Defense rather than the building itself.Designed by the American architect...
. The increased job market gave the state the highest per capita income at the beginning of the 1960s. The increased standard of living could be seen in the various suburban neighborhoods that began to develop outside major cities. Construction of major highways such as the Connecticut Turnpike
Connecticut Turnpike
The Connecticut Turnpike, known now as the Governor John Davis Lodge Turnpike, is a freeway in Connecticut that runs from Greenwich to Killingly. It is signed as Interstate 95 from the New York state line at Greenwich to East Lyme, and then as Interstate 395 from East Lyme to Plainfield...
caused former small towns to become locations for large-scale development, a trend that continues to this day.
However, all of these developments also led to the economic downfall of many of Connecticut's cities, many of which remain dotted with abandoned mills and other broken-down buildings. During this time, Connecticut's cities saw major growth in the African American
African American
African Americans are citizens or residents of the United States who have at least partial ancestry from any of the native populations of Sub-Saharan Africa and are the direct descendants of enslaved Africans within the boundaries of the present United States...
and Latino
Hispanic and Latino Americans
Hispanic or Latino Americans are Americans with origins in the Hispanic countries of Latin America or in Spain, and in general all persons in the United States who self-identify as Hispanic or Latino.1990 Census of Population and Housing: A self-designated classification for people whose origins...
populations. African Americans and Latinos inherited urban spaces that were no longer a high priority for the state or private industry, and by the 1980s crime and urban blight
Urban decay
Urban decay is the process whereby a previously functioning city, or part of a city, falls into disrepair and decrepitude...
were major issues. In fact, the poor conditions that many inhabited were cause for militant movements that pushed for the gentrification of ghettos and the desegregation of the school system. In 1987, Hartford
Hartford, Connecticut
Hartford is the capital of the U.S. state of Connecticut. The seat of Hartford County until Connecticut disbanded county government in 1960, it is the second most populous city on New England's largest river, the Connecticut River. As of the 2010 Census, Hartford's population was 124,775, making...
, became the first American city to elect an African-American woman as mayor, Carrie Saxon Perry.
Connecticut business thrived until the end of the 1980s, with many well-known corporations moving to Fairfield County
Fairfield County, Connecticut
Fairfield County is a county located in the southwestern corner of the U.S. state of Connecticut. The county population is 916,829 according to the 2010 Census. There are currently 1,465 people per square mile in the county. It is the most populous county in the State of Connecticut and contains...
, including General Electric
General Electric
General Electric Company , or GE, is an American multinational conglomerate corporation incorporated in Schenectady, New York and headquartered in Fairfield, Connecticut, United States...
, American Brands, and Union Carbide
Union Carbide
Union Carbide Corporation is a wholly owned subsidiary of The Dow Chemical Company. It currently employs more than 2,400 people. Union Carbide primarily produces chemicals and polymers that undergo one or more further conversions by customers before reaching consumers. Some are high-volume...
. The state also benefited from the defense buildup initiated by Ronald Reagan
Ronald Reagan
Ronald Wilson Reagan was the 40th President of the United States , the 33rd Governor of California and, prior to that, a radio, film and television actor....
, due to such major employers as Electric Boat
Electric boat
While a significant majority of water vessels are powered by diesel engines, with sail power and gasoline engines also remaining popular, boats powered by electricity have been used for over 120 years. Electric boats were very popular from the 1880s until the 1920s, when the internal combustion...
shipyards, Sikorsky
Sikorsky Aircraft
The Sikorsky Aircraft Corporation is an American aircraft manufacturer based in Stratford, Connecticut. Its parent company is United Technologies Corporation.-History:...
helicopters, and Pratt & Whitney
Pratt & Whitney
Pratt & Whitney is a U.S.-based aerospace manufacturer with global service operations. It is a subsidiary of United Technologies Corporation . Pratt & Whitney's aircraft engines are widely used in both civil aviation and military aviation. Its headquarters are in East Hartford, Connecticut, USA...
jet engines.
The late 20th century
Connecticut's dependence on the defense industry posed an economic challenge at the end of the Cold WarCold War
The Cold War was the continuing state from roughly 1946 to 1991 of political conflict, military tension, proxy wars, and economic competition between the Communist World—primarily the Soviet Union and its satellite states and allies—and the powers of the Western world, primarily the United States...
. The resulting budget crisis helped elect Lowell Weicker as Governor on a third party ticket in 1990. Weicker's remedy, a state income tax, proved effective in balancing the budget but politically unpopular, as Weicker retired after a single term.
With newly "reconquered" land, the Pequots initiated plans for the construction of a multi-million dollar casino complex to be built on reservation land. The Foxwoods Casino
Foxwoods Resort Casino
Foxwoods Resort Casino is a hotel-casino in Mashantucket, Connecticut, United States. Together with the MGM Grand at Foxwoods, it is one of the largest casino complexes in the world in terms of floor space for gaming. The entire resort comprises of space. The casino has over 380 gaming tables...
was completed in 1992 and the enormous revenue it received made the Mashantucket Pequot Reservation one of the wealthiest in the country. With the newfound money, great educational and cultural initiatives were carried out, including the construction of the Mashantucket Pequot Museum and Research Center. The Mohegan
Mohegan
The Mohegan tribe is an Algonquian-speaking tribe that lives in the eastern upper Thames River valley of Connecticut. Mohegan translates to "People of the Wolf". At the time of European contact, the Mohegan and Pequot were one people, historically living in the lower Connecticut region...
Reservation gained political recognition shortly thereafter and, in 1994, opened another successful casino (Mohegan Sun
Mohegan Sun
Mohegan Sun, located in Uncasville, Connecticut, is the second largest casino in the United States with of gaming space. It is located on along the banks of the Thames River. It is at the heart of the scenic foothills of southeastern Connecticut, where 60 percent of the state's tourism is...
) near the town of Uncasville
Uncasville, Connecticut
Uncasville is an area in the town of Montville, Connecticut. The area traditionally known as Uncasville is a village in southeastern Montville, at the mouth of the Oxoboxo River...
. The success of casino gambling helped shift the state's economy away from manufacturing
Manufacturing
Manufacturing is the use of machines, tools and labor to produce goods for use or sale. The term may refer to a range of human activity, from handicraft to high tech, but is most commonly applied to industrial production, in which raw materials are transformed into finished goods on a large scale...
to entertainment, such as ESPN
ESPN
Entertainment and Sports Programming Network, commonly known as ESPN, is an American global cable television network focusing on sports-related programming including live and pre-taped event telecasts, sports talk shows, and other original programming....
, financial services, including hedge funds and pharmaceutical firms such as Pfizer
Pfizer
Pfizer, Inc. is an American multinational pharmaceutical corporation. The company is based in New York City, New York with its research headquarters in Groton, Connecticut, United States...
.
21st century
In the terrorist attacks of September 11, 2001, 65 state residents were killed. The vast majority were Fairfield CountyFairfield County, Connecticut
Fairfield County is a county located in the southwestern corner of the U.S. state of Connecticut. The county population is 916,829 according to the 2010 Census. There are currently 1,465 people per square mile in the county. It is the most populous county in the State of Connecticut and contains...
residents who were working in the World Trade Center
World Trade Center
The original World Trade Center was a complex with seven buildings featuring landmark twin towers in Lower Manhattan, New York City, United States. The complex opened on April 4, 1973, and was destroyed in 2001 during the September 11 attacks. The site is currently being rebuilt with five new...
. Greenwich
Greenwich, Connecticut
Greenwich is a town in Fairfield County, Connecticut, United States. As of the 2010 census, the town had a total population of 61,171. It is home to many hedge funds and other financial service companies. Greenwich is the southernmost and westernmost municipality in Connecticut and is 38+ minutes ...
lost 12 residents, Stamford
Stamford, Connecticut
Stamford is a city in Fairfield County, Connecticut, United States. According to the 2010 census, the population of the city is 122,643, making it the fourth largest city in the state and the eighth largest city in New England...
and Norwalk
Norwalk, Connecticut
Norwalk is a city in Fairfield County, Connecticut, United States. According to the 2010 U.S. Census, the population of the city is 85,603, making Norwalk sixth in population in Connecticut, and third in Fairfield County...
each lost nine and Darien
Darien, Connecticut
Darien is a town in Fairfield County, Connecticut, United States. A relatively small community on Connecticut's "Gold Coast", the population was 20,732 at the 2010 census. Darien was listed at #9 at CNN Money's list of "top-earning towns" in the United States as of 2011...
lost six. A state memorial was later set up at Sherwood Island State Park in Westport
Westport, Connecticut
-Neighborhoods:* Saugatuck – around the Westport railroad station near the southwestern corner of the town – a built-up area with some restaurants, stores and offices....
. The New York City skyline can be seen from the park.
A number of political scandals rocked Connecticut in the early 21st century. These included the 2003 removal from office of the mayors of Bridgeport
Bridgeport
Bridgeport is the most populous city in the U.S. state of Connecticut.Bridgeport may also refer to:-Places:In Canada:* Bridgeport, Nova ScotiaIn the United States:* Bridgeport, Alabama* Bridgeport, California, in Mono County...
, Joseph P. Ganim
Joseph P. Ganim
Joseph P. Ganim is a former mayor of Bridgeport, Connecticut, succeeded by John M. Fabrizi. He is also a member of the U.S. Democratic Party. He was also a Presidential Elector for Connecticut in 1992 and a delegate to the Democratic National Convention from Connecticut in 1996.-Mayor of...
on 16 corruption charges, as well as Waterbury
Waterbury
Waterbury is a city in Connecticut in the United States.Waterbury may also refer to any one of the following:-Places:United States*Waterbury, Nebraska*Waterbury, Vermont*Waterbury , Vermont,a village within the town of Waterbury, Vermont....
mayor Philip A. Giordano, whom was charged with 18 counts of sexual abuse of two girls.
In 2004, Governor John G. Rowland
John G. Rowland
John Grosvenor Rowland was the 86th Governor of Connecticut from 1995 to 2004; he is a member of the Republican Party. He is married to Patty Rowland, his second wife, and the couple have five children between them...
resigned during a corruption investigation. Rowland later plead guilty to federal charges, and his successor M. Jodi Rell
M. Jodi Rell
Mary Jodi Rell is a Republican politician and was the 87th Governor of the U.S. state of Connecticut from 2004 until 2011. She was the Lieutenant Governor of Connecticut under Governor John G. Rowland, who resigned during a corruption investigation. Rell is Connecticut's second female Governor,...
, focused her administration on reforms in the wake of the Rowland scandal.
In April 2005, Connecticut passed a law which grants all rights of marriage to same-sex couples
Same-sex marriage
Same-sex marriage is marriage between two persons of the same biological sex or social gender. Supporters of legal recognition for same-sex marriage typically refer to such recognition as marriage equality....
. However, the law required that such unions be called "civil unions", and that the title of marriage be limited to those unions whose parties are of the opposite sex. The state was the first to pass a law permitting civil unions without a prior court proceeding. In October 2008, the Supreme Court of Connecticut ordered same-sex marriage legalized.
In July 2009, the Connecticut legislature overrode a veto by Governor M. Jodi Rell
M. Jodi Rell
Mary Jodi Rell is a Republican politician and was the 87th Governor of the U.S. state of Connecticut from 2004 until 2011. She was the Lieutenant Governor of Connecticut under Governor John G. Rowland, who resigned during a corruption investigation. Rell is Connecticut's second female Governor,...
to pass SustiNet
SustiNet
SustiNet is a Connecticut health care plan passed into law in July, 2009. Its goal is to provide affordable health care coverage to 98% of Connecticut residents by 2014.-Provisions of the legislation:...
, the first significant public-option health care reform legislation in the nation.
The state's criminal justice system also dealt with the first execution in the state since 1960, the 2005 execution of serial killer Michael Ross and was rocked by the July 2007 home invasion
Home invasion
Home invasion is the act of illegally burgling or entering a private and occupied dwelling for the purpose of committing a crime Home invasion is the act of illegally burgling or entering a private and occupied dwelling for the purpose of committing a crime Home invasion is the act of illegally...
murders in Cheshire
Steven Hayes (criminal)
The Cheshire, Connecticut, home invasion murders occurred on July 23, 2007, when a mother and her two daughters were murdered during a home invasion in Cheshire, Connecticut. The Hartford Courant referred to the case as "possibly the most widely publicized crime in the state's history". In 2010,...
. As the accused perpetrators of the Petit murders were out on parole
Parole
Parole may have different meanings depending on the field and judiciary system. All of the meanings originated from the French parole . Following its use in late-resurrected Anglo-French chivalric practice, the term became associated with the release of prisoners based on prisoners giving their...
, Governor M. Jodi Rell
M. Jodi Rell
Mary Jodi Rell is a Republican politician and was the 87th Governor of the U.S. state of Connecticut from 2004 until 2011. She was the Lieutenant Governor of Connecticut under Governor John G. Rowland, who resigned during a corruption investigation. Rell is Connecticut's second female Governor,...
promised a full investigation into the state's criminal justice policies.
See also
- History of the Connecticut Constitution
- List of newspapers in Connecticut in the 18th-century
External links
- Benjamin TrumbullBenjamin TrumbullBenjamin Trumbull was a historian. He was graduated at Yale in 1759, and received his theological education under Rev...
. History of Connecticut. 1898. - Changing Connecticut, 1634 – 1980
- THE CONVENTION TROOPS IN CONNECTICUT
- Constitutional History of Connecticut
- Slavery in Connecticut
- The Tories of Connecticut
- Connecticut town histories
- Connecticut Radio History
- Brief historical geography of Connecticut towns
- Connecticut's "Susquehannah Settlers"
- Firelands Museum and Research Center
- The Firelands
- Research Guide to Connecticut's "Western Lands" or "Western Reserve"
- The Western Reserve Historical Society
- U.S. Census Bureau. "Census Regions and Divisions of the United States" (PDF). Retrieved May 11, 2005.
- "History of Connecticut's Towns"

