
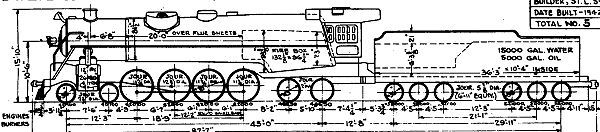
4-8-4
Encyclopedia

Whyte notation
The Whyte notation for classifying steam locomotives by wheel arrangement was devised by Frederick Methvan Whyte and came into use in the early twentieth century encouraged by an editorial in American Engineer and Railroad Journal...
classification of steam locomotive
Steam locomotive
A steam locomotive is a railway locomotive that produces its power through a steam engine. These locomotives are fueled by burning some combustible material, usually coal, wood or oil, to produce steam in a boiler, which drives the steam engine...
s, 4-8-4 represents the wheel arrangement
Wheel arrangement
In rail transport, a wheel arrangement is a system of classifying the way in which wheels are distributed beneath a locomotive.. Several notations exist to describe the wheel assemblies of a locomotive by type, position, and connections, with the adopted notations varying by country...
of four leading wheel
Leading wheel
The leading wheel or leading axle of a steam locomotive is an unpowered wheel or axle located in front of the driving wheels. The axle or axles of the leading wheels are normally located in a truck...
s on two axles (usually in a leading truck), eight powered and coupled driving wheel
Driving wheel
On a steam locomotive, a driving wheel is a powered wheel which is driven by the locomotive's pistons...
s on four axles, and four trailing wheel
Trailing wheel
On a steam locomotive, a trailing wheel or trailing axle is generally an unpowered wheel or axle located behind the driving wheels. The axle of the trailing wheels was usually located on a trailing truck...
s on two axles (usually in a trailing truck).
Other equivalent classifications are:
UIC classification
UIC classification
The UIC classification of locomotive axle arrangements describes the wheel arrangement of locomotives, multiple units and trams. It is set out in the International Union of Railways "Leaflet 650 - Standard designation of axle arrangement on locomotives and multiple-unit sets". It is used in much...
: 2D2 (also known as German classification and Italian classification)
French classification: 242 (also known as Spanish classification
Spanish classification
With the Spanish classification system for locomotive wheel arrangements, the system for steam machines.- Steam :With steam locomotives, there are three digits normally and more with articulated locomotives...
)
Turkish classification
Turkish classification
In the Turkish classification system for railway locomotives, the number of powered axles are followed by the total number of axles. It is identical to the Swiss system except that the latter places a slash between the two numbers.Thus0-6-0 becomes 33...
: 48
Swiss classification: 4/8
Russian classification: 2-4-2
The type is sometimes called Northern.
The 4-8-4 was an obvious progression from the 4-8-2
4-8-2
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, 4-8-2 represents the wheel arrangement of four leading wheels on two axles , eight powered and coupled driving wheels on four axles, and two trailing wheels on one axle...
"Mountain" and, like the 2-8-4
2-8-4
In the Whyte notation, a 2-8-4 is a railroad steam locomotive that has one unpowered leading axle followed by four powered driving axles and two unpowered trailing axles. This locomotive type is most often referred to as a Berkshire, though the Chesapeake and Ohio Railway used the name Kanawha for...
"Berkshire" and 4-6-4
4-6-4
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, 4-6-4 represents the wheel arrangement of four leading wheels on two axles , six powered and coupled driving wheels on three axles, and four trailing wheels on two axles .Other equivalent classifications are:UIC classification:...
"Hudson" types, an example of the "Super Power" concept in steam locomotive design. It combined the stability at speed of the 4-6-4 and 4-8-2 due to the 4-wheel lead truck, the greater adhesive weight
Adhesive weight
Adhesive weight is the amount of a locomotive's weight that is applied to the driving wheels and so capable of delivering traction. The more weight applied to the driving wheels, the greater the locomotive's ability to haul a load. But if the weight on the driving wheels exceeds the axle load of...
of the 2-8-4 and 4-8-2 (leading to greater traction, and allowing a larger, more powerful locomotive) and the larger firebox supported by the 4-wheel trailing truck common to 2-8-4s and 4-6-4s (allowing for freer steaming, particularly at speed).
Development in North America
Northern Pacific Railway
The Northern Pacific Railway was a railway that operated in the west along the Canadian border of the United States. Construction began in 1870 and the main line opened all the way from the Great Lakes to the Pacific when former president Ulysses S. Grant drove in the final "golden spike" in...
and the type was thereafter named "Northern". Most railroads used this name, but a number adopted different titles, including Confederation (Canadian National), Golden State (Southern Pacific), Niagara (New York Central and NdeM), Pocono (DL&W), Wyoming (Lehigh Valley Railroad
Lehigh Valley Railroad
The Lehigh Valley Railroad was one of a number of railroads built in the northeastern United States primarily to haul anthracite coal.It was authorized April 21, 1846 in the U.S. state of Pennsylvania and incorporated September 20, 1847 as the Delaware, Lehigh, Schuylkill and Susquehanna Railroad...
), Dixie (NC&StL), Big Apple (Central of Georgia Railway), Greenbrier (Chesapeake and Ohio Railway
Chesapeake and Ohio Railway
The Chesapeake and Ohio Railway was a Class I railroad formed in 1869 in Virginia from several smaller Virginia railroads begun in the 19th century. Led by industrialist Collis P...
), Western (D&RGW), Potomac (Western Maryland Railway
Western Maryland Railway
The Western Maryland Railway was an American Class I railroad which operated in Maryland, West Virginia, and Pennsylvania. It was primarily a coal hauling and freight railroad, with a small passenger train operation. The WM became part of the Chessie System in 1973 and ceased operating its lines...
) while the RF&P gave each of its three classes a separate title: General, Governor and Statesman.
Although locomotives of the 4-8-4 wheel arrangement were used in a number of countries, those developed outside the Americas included various design features which set them apart from North American practice. The United States, Canada and Mexico were the home of the American 4-8-4, and scaled down examples of the type were exported by two American builders for metre gauge lines in Brazil.
The American 4-8-4
The Northern type evolved in the United States soon after the Lima Locomotive WorksLima Locomotive Works
Lima Locomotive Works was an American firm that manufactured railroad locomotives from the 1870s through the 1950s. The company took the most distinctive part of its name from its main shops location in Lima, Ohio. The shops were located between the Baltimore & Ohio's Cincinnati-Toledo main line...
introduced the concept of "Lima Super Power" in 1925. The Northern Pacific Railway prototype was built by Alco in 1927 to Super Power principles, with a four-wheel trailing truck to carry the weight of a very large firebox designed to burn low quality lignite coal. But the potential of supporting a firebox with a 100 square feet (9.3 m²) grate on a four-wheel trailing truck was quickly seen, as given the additional weight of approximately 15000 lb (6.8 t) over the two-wheel truck, the four wheel truck could carry an additional 55000 lb (24.9 t) engine weight. So the difference of 40000 lb (18.1 t) was available for increased boiler capacity, or in other words, the power plant of the locomotive.
The Northern type came at a time when nearly all the important design improvements had been proven, such as the superheater, mechanical stoker, outside valve gear, the Delta trailing truck and the one-piece bed frame of cast steel with integral cylinders, which did so much to advance the application of roller bearings on locomotives since it gave the strength and rigidity to hold them in correct alignment. Indeed, in 1930 the Timken Company
Timken Company
The Timken Company is a global manufacturer of bearings, alloy steels, and related components and assemblies.- History :The company was founded by Henry Timken in St. Louis, Missouri in 1899 and incorporated as The Timken Roller Bearing Axle Company. A year earlier, in 1898, Timken got a patent...
used a 4-8-4 with roller bearings an all axles, which they classified Timken 1111
Timken 1111
Timken 1111, also called the Timken Four Aces, was a 4-8-4 steam locomotive built in 1930 by American Locomotive Company to serve as a demonstration unit for new roller bearings produced by the Timken Roller Bearing Company...
, to demonstrate the value of their roller bearings over nearly every main line in the United States. It was subsequently sold to the Northern Pacific Railway.
The stability of the 4-8-4 enabled it to be provided with driving wheels up to 80 inches (2 m) diameter for high speed passenger and fast freight operation, and with the latest lateral control devices, the type was flexible on curves. The increased boiler size possible with this type, together with the high axle loads permitted on main lines in North America, led to the design of some massive locomotives, with all up weights exceeding 350 tons including tender.
Builders

American Locomotive Company
The American Locomotive Company, often shortened to ALCO or Alco , was a builder of railroad locomotives in the United States.-Early history:...
, the Baldwin Locomotive Works
Baldwin Locomotive Works
The Baldwin Locomotive Works was an American builder of railroad locomotives. It was located in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, originally, and later in nearby Eddystone, Pennsylvania. Although the company was very successful as a producer of steam locomotives, its transition to the production of...
or the Lima Locomotive Works. The large fleet of CNR was built by the Montreal Locomotive Works
Montreal Locomotive Works
Montreal Locomotive Works was a Canadian railway locomotive manufacturer which existed under several names from 1883–1985, producing both steam and diesel locomotives. For a number of years it was a subsidiary of the American Locomotive Company...
, and only the Canadian Pacific Railway
Canadian Pacific Railway
The Canadian Pacific Railway , formerly also known as CP Rail between 1968 and 1996, is a historic Canadian Class I railway founded in 1881 and now operated by Canadian Pacific Railway Limited, which began operations as legal owner in a corporate restructuring in 2001...
, the N&W, the Cotton Belt
St. Louis Southwestern Railway
The St. Louis Southwestern Railway , known by its nickname of "The Cotton Belt Route" or simply Cotton Belt, was organized on January 15, 1891, although it had its origins in a series of short lines founded in Tyler, Texas, in 1870 that connected northeastern Texas to Arkansas and southeastern...
and Reading Railroad built their own.
Owning railroads
The Northern type was purchased by 36 railroads in the Americas, including 31 railroads in the United States, three in Canada, one in Mexico and two in Brazil. In all, there were less than 1,200 engines of this type, compared with approximately 2,500 Mountain types and 6,800 Pacific types built in the United States. By far the largest fleet was owned by the Canadian National RailwayCanadian National Railway
The Canadian National Railway Company is a Canadian Class I railway headquartered in Montreal, Quebec. CN's slogan is "North America's Railroad"....
and its subsidiary the Grand Trunk Western Railroad
Grand Trunk Western Railroad
The Grand Trunk Western Railroad is an important subsidiary of the Canadian National Railway , constituting the majority of CN's Chicago Division ....
, with 203 engines. Other major owners were the Chicago, Rock Island and Pacific Railroad
Chicago, Rock Island and Pacific Railroad
The Chicago, Rock Island and Pacific Railroad was a Class I railroad in the United States. It was also known as the Rock Island Line, or, in its final years, The Rock.-Incorporation:...
with 85, the Southern Pacific Railroad
Southern Pacific Railroad
The Southern Pacific Transportation Company , earlier Southern Pacific Railroad and Southern Pacific Company, and usually simply called the Southern Pacific or Espee, was an American railroad....
with 74, the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway
Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway
The Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway , often abbreviated as Santa Fe, was one of the larger railroads in the United States. The company was first chartered in February 1859...
with 65, the Delaware, Lackawanna and Western Railroad
Delaware, Lackawanna and Western Railroad
The Delaware, Lackawanna and Western Railroad Company was a railroad connecting Pennsylvania's Lackawanna Valley, rich in anthracite coal, to Hoboken, New Jersey, , Buffalo and Oswego, New York...
with 56, the Chicago, Milwaukee, St. Paul and Pacific Railroad
Chicago, Milwaukee, St. Paul and Pacific Railroad
The Milwaukee Road, officially the Chicago, Milwaukee, St. Paul and Pacific Railroad , was a Class I railroad that operated in the Midwest and Northwest of the United States from 1847 until its merger into the Soo Line Railroad on January 1, 1986. The company went through several official names...
with 53, the Union Pacific Railroad
Union Pacific Railroad
The Union Pacific Railroad , headquartered in Omaha, Nebraska, is the largest railroad network in the United States. James R. Young is president, CEO and Chairman....
with 45, the Chesapeake and Ohio Railway
Chesapeake and Ohio Railway
The Chesapeake and Ohio Railway was a Class I railroad formed in 1869 in Virginia from several smaller Virginia railroads begun in the 19th century. Led by industrialist Collis P...
and the Western Maryland Railway
Western Maryland Railway
The Western Maryland Railway was an American Class I railroad which operated in Maryland, West Virginia, and Pennsylvania. It was primarily a coal hauling and freight railroad, with a small passenger train operation. The WM became part of the Chessie System in 1973 and ceased operating its lines...
owning 12 each. The Ontario Northland own only 4 of this type, #1100-1103. The Pennsylvania Railroad
Pennsylvania Railroad
The Pennsylvania Railroad was an American Class I railroad, founded in 1846. Commonly referred to as the "Pennsy", the PRR was headquartered in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania....
did not own any 4-8-4 steam locomotives but, the Pennsy had an electric 4-8-4. This was the PRR R1
PRR R1
The Pennsylvania Railroad's class R1 comprised a single prototype electric locomotive constructed in 1934 by the Baldwin Locomotive Works of Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, USA, with the electrical equipment by Westinghouse....
electric.
| Railroad (quantity, nickname) | Class | Road numbers | Builder | Build year | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Northern Pacific Railway Northern Pacific Railway The Northern Pacific Railway was a railway that operated in the west along the Canadian border of the United States. Construction began in 1870 and the main line opened all the way from the Great Lakes to the Pacific when former president Ulysses S. Grant drove in the final "golden spike" in... (48 "Northerns") |
|
|
American Locomotive Company The American Locomotive Company, often shortened to ALCO or Alco , was a builder of railroad locomotives in the United States.-Early history:... |
|
|
| |
|
Baldwin Locomotive Works The Baldwin Locomotive Works was an American builder of railroad locomotives. It was located in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, originally, and later in nearby Eddystone, Pennsylvania. Although the company was very successful as a producer of steam locomotives, its transition to the production of... |
|
||
| |
|
|
|
||
| |
|
|
|
||
| |
|
|
|
||
| Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway The Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway , often abbreviated as Santa Fe, was one of the larger railroads in the United States. The company was first chartered in February 1859... (65 "Northerns") |
|
|
|
|
3751 is used as an excursion loco |
| |
|
|
|
||
| |
|
|
|
||
| |
|
|
|
||
| Canadian National Railway Canadian National Railway The Canadian National Railway Company is a Canadian Class I railway headquartered in Montreal, Quebec. CN's slogan is "North America's Railroad".... s (160 "Confederations") |
|
|
Canadian Locomotive Company The Canadian Locomotive Company, commonly referred to as CLC, was a Canadian manufacturer of railway locomotives located in Kingston, Ontario. Its works were located on Ontario Street and Gore Street on Kingston's waterfront.... |
|
|
| |
|
Montreal Locomotive Works Montreal Locomotive Works was a Canadian railway locomotive manufacturer which existed under several names from 1883–1985, producing both steam and diesel locomotives. For a number of years it was a subsidiary of the American Locomotive Company... |
|
||
| |
|
|
|
||
| |
|
|
|
||
| |
|
|
|
||
| |
|
|
|
||
| |
|
|
|
||
| |
|
|
|
||
| |
|
|
|
Streamlined | |
| Canadian National subsidiary Grand Trunk Western Railroad Grand Trunk Western Railroad The Grand Trunk Western Railroad is an important subsidiary of the Canadian National Railway , constituting the majority of CN's Chicago Division .... (43 "Confederations") |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
||
| |
|
Lima Locomotive Works Lima Locomotive Works was an American firm that manufactured railroad locomotives from the 1870s through the 1950s. The company took the most distinctive part of its name from its main shops location in Lima, Ohio. The shops were located between the Baltimore & Ohio's Cincinnati-Toledo main line... |
|
Streamlined | |
| Delaware, Lackawanna and Western Railroad Delaware, Lackawanna and Western Railroad The Delaware, Lackawanna and Western Railroad Company was a railroad connecting Pennsylvania's Lackawanna Valley, rich in anthracite coal, to Hoboken, New Jersey, , Buffalo and Oswego, New York... (55 "Poconos") |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
||
| |
|
|
|
||
| |
|
|
|
||
| Canadian Pacific Railway Canadian Pacific Railway The Canadian Pacific Railway , formerly also known as CP Rail between 1968 and 1996, is a historic Canadian Class I railway founded in 1881 and now operated by Canadian Pacific Railway Limited, which began operations as legal owner in a corporate restructuring in 2001... (2 "Northerns") |
|
|
|
|
|
| Chicago and North Western Railway Chicago and North Western Railway The Chicago and North Western Transportation Company was a Class I railroad in the Midwest United States. It was also known as the North Western. The railroad operated more than of track as of the turn of the 20th century, and over of track in seven states before retrenchment in the late 1970s... (35 "Northerns") |
|
|
|
|
24 rebuilt to H-1 |
| Chicago, Rock Island and Pacific Railroad Chicago, Rock Island and Pacific Railroad The Chicago, Rock Island and Pacific Railroad was a Class I railroad in the United States. It was also known as the Rock Island Line, or, in its final years, The Rock.-Incorporation:... (85 "Northerns") |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
||
| Denver and Rio Grande Western Railroad Denver and Rio Grande Western Railroad The Denver & Rio Grande Western Railroad , often shortened to Rio Grande or D&RGW, formerly the Denver & Rio Grande Railroad, is a defunct U.S. railroad company. The railroad started as a narrow gauge line running south from Denver, Colorado in 1870; however, served mainly as a transcontinental... (19 "Westerns") |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
||
| Great Northern Railway (38) | |
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
||
| Chicago, Burlington and Quincy Railroad Chicago, Burlington and Quincy Railroad The Chicago, Burlington and Quincy Railroad was a railroad that operated in the Midwestern United States. Commonly referred to as the Burlington or as the Q, the Burlington Route served a large area, including extensive trackage in the states of Colorado, Illinois, Iowa, Kentucky, Missouri,... (36) |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
||
| Milwaukee Road (52 "Northerns") | |
|
|
|
Renumbered 250 in 1938 |
| |
|
|
|
||
| |
|
|
|
||
| |
|
|
|
||
| Nashville, Chattanooga and St. Louis Railway Nashville, Chattanooga and St. Louis Railway The Nashville, Chattanooga and St. Louis Railway was a railway company operating in the southern United States in Kentucky, Tennessee, Alabama and Georgia... (25 "Dixies") |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
||
| St. Louis Southwestern Railway St. Louis Southwestern Railway The St. Louis Southwestern Railway , known by its nickname of "The Cotton Belt Route" or simply Cotton Belt, was organized on January 15, 1891, although it had its origins in a series of short lines founded in Tyler, Texas, in 1870 that connected northeastern Texas to Arkansas and southeastern... (20 "Northerns") |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
||
| Southern Pacific (70 "Golden States") | Southern Pacific class GS-1 The GS-1 was a 4-8-4 Northern type steam locomotive that served the Southern Pacific Railroad and its Texas subsidiary the Texas and New Orleans Railroad from 1930 to 1956. They were built by Baldwin Locomotive Works and were numbered 4400 through 4409... |
|
|
|
|
| Southern Pacific class GS-2 The GS-2 was a streamlined 4-8-4 Northern type steam locomotive that served the Southern Pacific Company from 1937 to 1956. They were built by Lima Locomotive Works and were numbered 4410 through 4415. GS stands for "Golden State" or "General Service."... |
|
|
|
||
| Southern Pacific class GS-3 The GS-3 was a streamlined 4-8-4 Northern type steam locomotive that served the Southern Pacific Company from 1938 to 1957. They were built by Lima Locomotive Works and were numbered 4416 through 4429. GS stands for "Golden State" or "General Service."... |
|
|
|
||
| Southern Pacific class GS-4 The GS-4 was a streamlined 4-8-4 Northern type steam locomotive that served the Southern Pacific Company from 1941 to 1958. They were built by the Lima Locomotive Works and were numbered 4430 through 4457... |
|
|
|
4449 Southern Pacific 4449 Southern Pacific 4449 is the only surviving example of Southern Pacific Railroad's GS-4 class of steam locomotives. The GS-4 is a streamlined 4-8-4 type steam locomotive... is the only surviving GS-4 and is used as an excursion loco |
|
| Southern Pacific class GS-5 The GS-5 was a streamlined 4-8-4 Northern type steam locomotive that served the Southern Pacific Company from 1942 to 1958. Only two locomotives were built by the Lima Locomotive Works and were numbered 4458 and 4459. GS stands for "Golden State" or "General Service."The GS-5s are exactly identical... |
|
|
|
||
| Southern Pacific class GS-6 The GS-6 is a semi-streamlined 4-8-4 Northern type steam locomotive that served the Southern Pacific Railroad from 1943 to 1958 and the Western Pacific Railroad from 1943 to 1953. They were built during World War II for the Southern Pacific Railroad by the Lima Locomotive Works and were numbered... |
|
|
|
||
| Southern Pacific subsidiary Texas and New Orleans Railroad Texas and New Orleans Railroad The Texas and New Orleans Railroad is a former railroad in Texas and Louisiana. At one point the company was the largest railroad in Texas, with of trackage in 1934, but by 1961 there were only remaining when it was merged with parent company Southern Pacific.... ("4 Golden States") |
Southern Pacific class GS-1 The GS-1 was a 4-8-4 Northern type steam locomotive that served the Southern Pacific Railroad and its Texas subsidiary the Texas and New Orleans Railroad from 1930 to 1956. They were built by Baldwin Locomotive Works and were numbered 4400 through 4409... |
|
|
|
|
| Timken Roller Bearing Company Timken Roller Bearing Company The Timken Roller Bearing Company was one of the first to introduce roller bearings for railroad cars. Railroad cars owned and operated by the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway were some of the first to use roller bearings rather than "oil waste journal" boxes.Also, the ATSF was the first... (demonstrator) |
|
Timken 1111 Timken 1111, also called the Timken Four Aces, was a 4-8-4 steam locomotive built in 1930 by American Locomotive Company to serve as a demonstration unit for new roller bearings produced by the Timken Roller Bearing Company... |
|
|
to NP 2626, class A-1 |
| Wabash Railroad Wabash Railroad The Wabash Railroad was a Class I railroad that operated in the mid-central United States. It served a large area, including trackage in the states of Ohio, Indiana, Illinois, Iowa, Michigan, Missouri and Ontario. Its primary connections included Chicago, Illinois, Kansas City, Missouri, Detroit,... (25 "Northerns") |
|
|
|
|
|
| Lehigh Valley Railroad Lehigh Valley Railroad The Lehigh Valley Railroad was one of a number of railroads built in the northeastern United States primarily to haul anthracite coal.It was authorized April 21, 1846 in the U.S. state of Pennsylvania and incorporated September 20, 1847 as the Delaware, Lehigh, Schuylkill and Susquehanna Railroad... (37 "Wyomings") |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
||
| |
|
|
|
||
| |
|
|
|
||
| New York Central Railroad New York Central Railroad The New York Central Railroad , known simply as the New York Central in its publicity, was a railroad operating in the Northeastern United States... ("28 Niagaras") |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
||
| |
|
|
|
||
| |
|
|
|
||
| Chesapeake and Ohio Railway Chesapeake and Ohio Railway The Chesapeake and Ohio Railway was a Class I railroad formed in 1869 in Virginia from several smaller Virginia railroads begun in the 19th century. Led by industrialist Collis P... (15 "Greenbriers") |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
||
| Ontario Northland Railway Ontario Northland Railway The Ontario Northland Railway is a Canadian railway operated by the Ontario Northland Transportation Commission, a provincial Crown agency of the government of Ontario.... (5 "Northerns") |
|
|
|
|
|
| Atlantic Coast Line Railroad Atlantic Coast Line Railroad The Atlantic Coast Line Railroad was an American railroad that existed between 1900 and 1967, when it merged with the Seaboard Air Line Railroad, its long-time rival, to form the Seaboard Coast Line Railroad... (12 "1800s") |
|
|
|
|
|
| Richmond, Fredericksburg and Potomac Railroad Richmond, Fredericksburg and Potomac Railroad The Richmond, Fredericksburg, and Potomac Railroad was a railroad connecting Richmond, Virginia, to Washington, D.C. It is now a portion of the CSX Transportation system.... (27) |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
||
| |
|
|
|
||
| Toledo, Peoria and Western Railway Toledo, Peoria and Western Railway The Toledo, Peoria and Western Railway is a short-line railroad that operates of track from Mapleton, Illinois, through Peoria across Illinois to Logansport, Indiana, and includes a branch line between Logansport to Winamac, Indiana... (6 "Northerns") |
|
|
|
|
|
| Union Pacific Railroad Union Pacific Railroad The Union Pacific Railroad , headquartered in Omaha, Nebraska, is the largest railroad network in the United States. James R. Young is president, CEO and Chairman.... (45 "Four-Eight-Fours") |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
||
| |
|
|
|
844 Union Pacific 844 Union Pacific 844 is a 4-8-4 steam locomotive owned by Union Pacific Railroad. It was the last steam locomotive delivered to Union Pacific and is unique in that it is the only steam locomotive never retired by a North American Class I railroad.... is the world's longest operating loco and is used as an excursion loco |
|
| Wisconsin Central Railway (4 "Northerns") | |
|
|
|
|
| Spokane, Portland and Seattle Railway Spokane, Portland and Seattle Railway The Spokane, Portland and Seattle Railway was a United States-based railroad incorporated in 1905. It was a joint venture by the Great Northern Railway and the Northern Pacific Railway to build a railroad along the north bank of the Columbia River.... (3 "Northerns") |
SP&S Class E-1 Spokane Portland and Seattle Railway’s E-1 class was a class of three 4-8-4 locomotives built by the Baldwin Locomotive Works in 1938-Preservation:... |
|
|
|
NP A-3 class; 700 Spokane, Portland and Seattle 700 Spokane, Portland & Seattle 700 is the only surviving example of their E-1 class 4-8-4 Northern type steam locomotive. Nearly identical to the A-3 class Northerns built for Northern Pacific Railway, but burning oil instead of coal.... survives and is used as an excursion loco |
| Missouri Pacific Railroad Missouri Pacific Railroad The Missouri Pacific Railroad , also known as the MoPac, was one of the first railroads in the United States west of the Mississippi River. MoPac was a Class I railroad growing from dozens of predecessors and mergers, including the St. Louis, Iron Mountain and Southern Railway , Texas and Pacific... (40 "Northerns") |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
||
| Norfolk and Western Railway Norfolk and Western Railway The Norfolk and Western Railway , a US class I railroad, was formed by more than 200 railroad mergers between 1838 and 1982. It had headquarters in Roanoke, Virginia for most of its 150 year existence.... (14 "J"s) |
|
|
Roanoke Shops thumb|250px|[[Norfolk Southern]] Roanoke Shops in 2004.The Roanoke Shops of the Norfolk and Western Railway in Roanoke, Virginia were founded in 1881 as the Roanoke Machine Works. It came under the control of the railroad in 1883. Locomotive production started in 1884 and 152 locomotives were... |
|
|
| Central of Georgia Railway (8 "Big Apples") | |
|
|
|
|
| Delaware and Hudson Railroad (15 "Northerns") | |
|
|
|
|
| St. Louis – San Francisco Railway (25 "Northerns") | |
|
|
|
|
| Western Pacific Railroad Western Pacific Railroad The Western Pacific Railroad was a Class I railroad in the United States. It was formed in 1903 as an attempt to break the near-monopoly the Southern Pacific Railroad had on rail service into northern California... (6 "Northerns") |
|
|
Lima | |
SP GS-6 Southern Pacific class GS-6 The GS-6 is a semi-streamlined 4-8-4 Northern type steam locomotive that served the Southern Pacific Railroad from 1943 to 1958 and the Western Pacific Railroad from 1943 to 1953. They were built during World War II for the Southern Pacific Railroad by the Lima Locomotive Works and were numbered... |
| Reading Company Reading Company The Reading Company , usually called the Reading Railroad, officially the Philadelphia and Reading Rail Road and then the Philadelphia and Reading Railway until 1924, operated in southeast Pennsylvania and neighboring states... (30 "Northerns") |
|
|
Reading | |
Converted from Class I-10a 2-8-0 locomotives |
| Ferrocarriles Nacionales de México Ferrocarriles Nacionales de México Ferrocarriles Nacionales de México, was Mexico's state owned railroad company from 1938 to 1998, and prior to 1938 a major railroad controlled by the government that linked Mexico City to the major cities of Nuevo Laredo and Ciudad Juárez on the U.S. border... (32 "Niágaras") |
|
|
Baldwin (16) |
|
|
| Western Maryland Railway Western Maryland Railway The Western Maryland Railway was an American Class I railroad which operated in Maryland, West Virginia, and Pennsylvania. It was primarily a coal hauling and freight railroad, with a small passenger train operation. The WM became part of the Chessie System in 1973 and ceased operating its lines... (12 "Potomacs") |
|
|
|
|
Route availability
The American 4-8-4 was a heavy locomotive, nearly all examples in the United States having axle loads above 30 short tons. On railroads with 130 lb/ydrail, axle loads of over 36 short tons were permitted, and exceptionally heavy Northerns were therefore introduced on the AT&SF, C&NW, C&O, MILW, NPNorthern Pacific Railway
The Northern Pacific Railway was a railway that operated in the west along the Canadian border of the United States. Construction began in 1870 and the main line opened all the way from the Great Lakes to the Pacific when former president Ulysses S. Grant drove in the final "golden spike" in...
, N&W, SP&S and WM. The preserved Spokane, Portland and Seattle 700
Spokane, Portland and Seattle 700
Spokane, Portland & Seattle 700 is the only surviving example of their E-1 class 4-8-4 Northern type steam locomotive. Nearly identical to the A-3 class Northerns built for Northern Pacific Railway, but burning oil instead of coal....
is a surviving example of the three E-1 class
SP&S Class E-1
Spokane Portland and Seattle Railway’s E-1 class was a class of three 4-8-4 locomotives built by the Baldwin Locomotive Works in 1938-Preservation:...
, which had the heaviest axle load of all at 37.1 short tons. The lightest Northerns in the United States were the six H-10 class of the Toledo, Peoria & Western with an axle load of 23 short tons.
The Canadian and Mexican 4-8-4's weighed in with axle loads between 27.3 and 31.3 short tons, as main lines in those countries were generally laid with 115 lb/yd rail.
Performance
The 4-8-4 proved itself suitable for both express passenger and fast freight service. It was not suited to heavy drag freightDrag freight
A drag freight is a slow, high-tonnage railroad train, often carrying commodities such as coal or ore. Compared to Fast freight trains, drag freight trains have a very low power-to-weight ratio, making them somewhat unpredictable on steep grades or hilly routes...
, but faster and lighter trains were well suited to the type.
The AT&SF Northerns were daily rostered to haul the Chief and the Fast Mail between La Junta and Los Angeles, a distance of 1255 miles (2,019.7 km), and also handled the Grand Canyon Limited between Los Angeles and Wellington, Kansas (1534 miles (2,468.7 km)). From 1942 they ran through from Los Angeles to Kansas City via Amarillo, a distance of 1789 miles (2,879.1 km), setting a new record for through steam locomotive rosters. The Niagaras of the NYC also accomplished long runs, handling the 12 daily New York to Chicago passenger trains including the Chicagoan and Commodore Vanderbilt; Northern Pacific 4-8-4s pulled the North Coast Limited 1008 miles (1,622.2 km) from St Paul to Livingston, Montana.
Not all railroads favored the type. The Pennsylvania Railroad
Pennsylvania Railroad
The Pennsylvania Railroad was an American Class I railroad, founded in 1846. Commonly referred to as the "Pennsy", the PRR was headquartered in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania....
owned none of the type, instead engineering their own T1
PRR T1
The Pennsylvania Railroad's 52 T1 class duplex-drive 4-4-4-4 steam locomotives, introduced in 1942 and 1946 , were their last-built steam locomotives and their most controversial. They were ambitious, technologically sophisticated, powerful, fast, and uniquely streamlined by Raymond Loewy...
4-4-4-4 "Duplex"
Duplex locomotive
A duplex locomotive is a steam locomotive that divides the driving force on its wheels by using two pairs of cylinders rigidly mounted to a single locomotive frame; it is not an articulated locomotive...
locomotives. The Canadian Pacific Railway
Canadian Pacific Railway
The Canadian Pacific Railway , formerly also known as CP Rail between 1968 and 1996, is a historic Canadian Class I railway founded in 1881 and now operated by Canadian Pacific Railway Limited, which began operations as legal owner in a corporate restructuring in 2001...
experimented with Northerns in 1928, building two K-1a class in its Angus shops, numbered 3100 and 3101. As the CPR had main lines built to high standards, they preferred to develop the 4-6-4 Hudson type for passenger work, as it gave adequate power and was cheaper to maintain. For heavy-duty work they adopted ten coupled types. Nevertheless, although CPR's Northerns were orphans, they proved their worth on Montreal–Toronto overnight passenger trains, and before retirement in 1960 worked freight trains in the prairie provinces.
Rebuilds
The AT&SF spent considerable effort in developing their Northerns. The fourteen 3751 class engines introduced in 1928 were a rather conservative design, with 73 inches (1.9 m) driving wheels, and a boiler pressure of 210 pound per square inches (1.4 MPa). In 1938 these engines were rebuilt with features including new 80 inches (2 m) Boxpok driving wheels, increased size of steam passages to and from the cylinders, boiler pressure raised to 230 pound per square inches (1.6 MPa), and roller bearings on all engine axles. This gave them a maximum drawbar power of 3600 hp at 50 mi/h. Engine 3752 was also fitted with Franklin rotary-cam poppet valves, and achieved the very low steam rate of 13.5 lb per indicated horsepower-hourHorsepower-hour
A Horsepower-hour is an outdated unit of energy, not used in the SI system of units. The unit represents an amount of work a horse is supposed capable of delivering during an hour...
(2.28 mg/J). These engines were permitted to run at 90 mi/h, but they were alleged to exceed 100 mi/h several times.
The very heavy Northerns of the C&NW were rebuilt in 1940 with lightweight rods, Boxpok driving wheels and roller bearings on all axles, and boiler pressure was raised from 250 to 275 psi (1.7 to 1.9 MPa). Some years later 24 of them underwent another rebuild which included new nickel–steel frames, new cylinders, pilot beams and air reservoirs, new fireboxes and many other minor improvements. These were reclassified as Class H-1.
In 1945–1947 a conversion was undertaken by the Reading Company
Reading Company
The Reading Company , usually called the Reading Railroad, officially the Philadelphia and Reading Rail Road and then the Philadelphia and Reading Railway until 1924, operated in southeast Pennsylvania and neighboring states...
. Thirty of their heavy I-10 class 2-8-0s were rebuilt as booster-fitted 4-8-4s with 5 in 10 in (1.78 m) driving wheels, class T1 Nos. 2100–2129. An additional ring was added at the smokebox end of the boiler, increasing the length of the tubes from 13 in 6 in (4.11 m) to 20 ft (6.1 m), and a much larger smokebox provided with distance of 111 inches (2.8 m) instead of 34 inch (0.8636 m) between the tube plate and the chimney centre line. The steam pressure was raised from 220 to 240 psi (1.5 to 1.7 MPa). Four syphons were fitted, three in the firebox proper, and one in the combustion chamber. A much larger 12-wheeled tender, containing 23.5 tons of coal and 19000 gallons (71.9 m³) of water, and weighing not less than 167 tons loaded, was attached. A new cast steel frame, with the cylinder cast integral, and roller bearings to all carrying wheels, was of course provided. Two of these engines, preserved for hauling special trains, were still in service in 1963.
Fame
During their service lives, the Northerns were workhorses that went without much public recognition. But there were a few exceptions. The Southern Pacific class GS-4Southern Pacific class GS-4
The GS-4 was a streamlined 4-8-4 Northern type steam locomotive that served the Southern Pacific Company from 1941 to 1958. They were built by the Lima Locomotive Works and were numbered 4430 through 4457...
were semi-streamlined and given one of the most striking liveries of the steam era. A real flag waver for the SP, they headed the Coast Daylight
Coast Daylight (SP)
Coast Daylight was a passenger train originally run by the Southern Pacific Railroad between the cities of Los Angeles and San Francisco, California, via SP's Coast Line...
train between Los Angeles and San Francisco, and caught the eye of Hollywood movie makers. Every episode of the TV series Superman
Superman
Superman is a fictional comic book superhero appearing in publications by DC Comics, widely considered to be an American cultural icon. Created by American writer Jerry Siegel and Canadian-born American artist Joe Shuster in 1932 while both were living in Cleveland, Ohio, and sold to Detective...
was introduced by a GS-4 as the announcer declared that the hero was "more powerful than a locomotive!"
Southern Pacific 4449
Southern Pacific 4449
Southern Pacific 4449 is the only surviving example of Southern Pacific Railroad's GS-4 class of steam locomotives. The GS-4 is a streamlined 4-8-4 type steam locomotive...
, a GS-4, has been restored and survives in operating condition.
The Canadian National U-4a Confederation locomotive
Confederation locomotive
The Confederation type was a large locomotive type with a 4-8-4 wheel arrangement used on Canadian railroads. Most were built by the Montreal Locomotive Works in Montreal, Quebec, and the Canadian Locomotive Works in Kingston, Ontario, for the Canadian National Railway . The "Confederation"...
was one of few fully streamlined 4-8-4's, and number 6400 achieved fame in 1939 by heading the Royal Train, and being exhibited at the New York World's Fair the same year.Chesepeake & Ohio J-3A Greenbrier # 614 is the last commercially built steam locomotive in the U.S and is the most modern Northern in the world
After the demise of steam however, the Northern has constantly come into the spotlight of publicity, and has been the favoured type to provide main line excursions in the United States. Indeed, UP 844 of the Union Pacific FEF Series
Union Pacific FEF Series
The FEF was a series of three types of 4-8-4 steam locomotives owned and operated by the Union Pacific Railway. The classes were: FEF-1; FEF-2; FEF-3. "FEF" was an acronym for the wheel arrangement, "four-eight-four."-Origins:...
is the only steam locomotive of a Class I railroad
Class I railroad
A Class I railroad in the United States and Mexico, or a Class I rail carrier in Canada, is a large freight railroad company, as classified based on operating revenue.Smaller railroads are classified as Class II and Class III...
never to have been retired.
Exports to Latin America
The Ferrocarriles Nacionales de MéxicoFerrocarriles Nacionales de México
Ferrocarriles Nacionales de México, was Mexico's state owned railroad company from 1938 to 1998, and prior to 1938 a major railroad controlled by the government that linked Mexico City to the major cities of Nuevo Laredo and Ciudad Juárez on the U.S. border...
placed orders with ALCO and Baldwin
Baldwin Locomotive Works
The Baldwin Locomotive Works was an American builder of railroad locomotives. It was located in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, originally, and later in nearby Eddystone, Pennsylvania. Although the company was very successful as a producer of steam locomotives, its transition to the production of...
for 60 Niagaras in 1946 for use on its principal express passenger services on upgraded lines, but the order was reduced to 32 in favour of diesel locomotives. These QR-1 class engines were used mainly on lines north of Mexico City
Mexico City
Mexico City is the Federal District , capital of Mexico and seat of the federal powers of the Mexican Union. It is a federal entity within Mexico which is not part of any one of the 31 Mexican states but belongs to the federation as a whole...
, and were nicknamed to La Maquina. All were taken out of service in the late 1960s. #3028 survives, although not in operable condition. It is stored on the deadline at the New Hope & Ivyland Railroad in New Hope, Pennsylvania
New Hope, Pennsylvania
New Hope, formerly known as Coryell's Ferry, is a borough in Bucks County, Pennsylvania, USA. The population was 2,528 at the 2010 census. The borough lies on the west bank of the Delaware River at its confluence with Aquetong Creek. A two-lane bridge carries automobile and foot traffic across the...
.
In order to meet the acute locomotive shortages in Brazil
Brazil
Brazil , officially the Federative Republic of Brazil , is the largest country in South America. It is the world's fifth largest country, both by geographical area and by population with over 192 million people...
post–World War II, 27 scaled down 4-8-4's were ordered by the Brazilian Departamento Nacional de Estradas de Ferro from ALCO (USA) in 1946, and supplied to the Viação Férrea do Rio Grande do Sul (VFRGS), which then purchased another 15 directly from ALCO in 1947. These locomotives became the 1001 class. From 1956 to 1957, some of these locomotives were sold to Bolivia.
The Baldwin Locomotive Works supplied similar metre-gauge 4-8-4's to the Rede Mineira de Viação (RMV) Nos 601–604, the Rede de Viação Paraná – Santa Catarina (RVPSC), Nos 801–806, and the Noroeste do Brasil (NOB), Nos 621–623.
Builder details:
- DNEF 1001–1027 4-8-4 (2D2-h2) ALCo-S 73767–73778 / 1945–6 for V.F.de Rio Grande do Sul.
- VFRGS 1028–1042 4-8-4 (2D2-h2) ALCo-M 74873–74887 / 1946 meter gauge.
- All locomotives—cylinder: 18 by diameter. Wheel diameter 59 inches (1.5 m). Grate 57 sq ft (5.3 m²) Evap 2054 sq ft (190.8 m²) Super 652 sq ft (60.6 m²), Ad. Weight 52 tons Engine Weight 98 tons.
The Chapelon-designed 4-8-4's supplied to Brazil are discussed under "The French 4-8-4" below.
Disadvantages
The big wheeled 4-8-4 was at home on heavy passenger trains, and quite capable of speeds over 100 mi/h, but freight was the railroad's bread and butter and in that service the Northern had limitations. On a 4-8-4 adhesive weight was limited to about 60 percent of the engine's weight, not including the dead weight of the tender. Henry Bowen, the chief mechanical engineer of the CPR (1928–1949) recognized this, and after testing the first two K-1a Northerns introduced by his predecessor, he designed a 2-10-4 using the same boiler, or in other words, the same power plant. This T-1a Selkirk locomotiveSelkirk locomotive
The Selkirk locomotives were 36 steam locomotives of the 2-10-4 wheel arrangement built for Canadian Pacific Railway by Montreal Locomotive Works, Montreal, Quebec, Canada....
had the same number of axles as the Northern, but the driving wheels were reduced from 75 to 63 in (1.9 to 1.6 m), and tractive effort increased by 27 percent. In a later variant, Bowen added a booster to the trailing truck, enabling the big Selkirk to exert nearly 50 percent more tractive effort than the K-1a, which was much the same size. A three-unit EMD F3
EMD F-unit
EMD F-units were a line of Diesel-electric locomotives produced between November 1939 and November 1960 by General Motors Electro-Motive Division and General Motors-Diesel Division. Final assembly for all F-units was at the GM-EMD plant at La Grange, Illinois and the GMDD plant in London, Ontario...
diesel electric weighing a little less than the total engine and tender of K-1a could produce nearly three times its tractive effort: this won the railroads, and super power steam locomotives a few years old were set aside as quickly as finance allowed.
Variants
Most 4-8-4's were two-cylinder locomotives, but three classes of three cylinder 4-8-4's were built, one by the Deutsche ReichsbahnDeutsche Reichsbahn
Deutsche Reichsbahn was the name of the following two companies:* Deutsche Reichsbahn, the German Imperial Railways during the Weimar Republic, the Third Reich and the immediate aftermath...
, one by the Victorian Railways
Victorian Railways
The Victorian Railways operated railways in the Australian state of Victoria from 1859 to 1983. The first railways in Victoria were private companies, but when these companies failed or defaulted, the Victorian Railways was established to take over their operations...
, and the 242A1 of the SNCF
SNCF
The SNCF , is France's national state-owned railway company. SNCF operates the country's national rail services, including the TGV, France's high-speed rail network...
in France, which also had the distinction of being (along with an experimental high pressure locomotive of the New York Central) one of the few compound 4-8-4's. These are described below.
The only four cylinder design was the large and striking duplex locomotive
Duplex locomotive
A duplex locomotive is a steam locomotive that divides the driving force on its wheels by using two pairs of cylinders rigidly mounted to a single locomotive frame; it is not an articulated locomotive...
developed by the Baldwin Locomotive Works and the Pennsylvania Railroad
Pennsylvania Railroad
The Pennsylvania Railroad was an American Class I railroad, founded in 1846. Commonly referred to as the "Pennsy", the PRR was headquartered in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania....
, which used two sets of cylinders in a rigid frame, each set driving two of the four driving axles. The 52 T1
PRR T1
The Pennsylvania Railroad's 52 T1 class duplex-drive 4-4-4-4 steam locomotives, introduced in 1942 and 1946 , were their last-built steam locomotives and their most controversial. They were ambitious, technologically sophisticated, powerful, fast, and uniquely streamlined by Raymond Loewy...
class are classified by the Whyte system as a 4-4-4-4
4-4-4-4
A 4-4-4-4 steam locomotive, in the Whyte notation for describing locomotive wheel arrangements, has a four-wheel leading truck, two sets of four driving wheels, and a four-wheel trailing truck.Other equivalent classifications are:...
type, but they had the same number of leading, driving and trailing wheels as a 4-8-4 and are generally compared with other 4-8-4's. Indeed, they were set in competition against the NYC Niagara's between New York and Chicago, and provided a brief swan song of giant high speed super power steam.
The Russian 4-8-4
Outside North America, the largest fleet of 4-8-4's was the P36 class of the SZD (Sovetskie Zheleznye Dorogi or Soviet Railways), with 251 examples built from 1949 to 1956. As the last Russian standard class steam locomotive, they shared some common components and design attributes with the earlier standard designs, the L class 2-10-0 and LV 2-10-2, plus common attributes with the P34 2-6-6-2 Mallet and P38 2-8-8-4 Mallet. For example, the P36 and LV-classes shared the same feedwater heaterFeedwater heater
A feedwater heater is a power plant component used to pre-heat water delivered to a steam generating boiler. Preheating the feedwater reduces the irreversibilities involved in steam generation and therefore improves the thermodynamic efficiency of the system...
made by the Bryansk
Bryansk
Bryansk is a city and the administrative center of Bryansk Oblast, Russia, located southwest of Moscow. Population: -History:The first written mention of Bryansk was in 1146, in the Hypatian Codex, as Debryansk...
machine factory. They were the only semi-streamlined steam locomotives built in Russia, although a trio of fully streamlined 4-6-4 locomotives were built. They were one of the best classes of passenger steam locomotives built in Soviet Union. They had boilers of 243.2 m2, worked on 15 kgf/cm2 (1.5 MPa) boiler pressure. Russian-designed roller bearings were fitted throughout, and the boilers were designed to provide continuous steaming capacity of 57 kg for each square meter of heating surface on boiler. The 1850 mm driving wheels could easily provide speeds up to 125 km/h and the 575 × 800 mm cylinders proved to be satisfactory with passenger train up to 800 tons.
Class P36 appeared at first on the Oktyabrskaya Railway
Oktyabrskaya Railway
The broad gauge Oktyabrskaya Railway or October Railway , which forms part of RZD, is the oldest railway in Russia, located in the north-west of the country. It stretches from Moscow's Leningrad Terminal in the south to Murmansk beyond the Arctic Circle in the north. The total length of the lines...
to haul principal express trains between Moscow and Leningrad
Leningrad
Leningrad is the former name of Saint Petersburg, Russia.Leningrad may also refer to:- Places :* Leningrad Oblast, a federal subject of Russia, around Saint Petersburg* Leningrad, Tajikistan, capital of Muminobod district in Khatlon Province...
. But they were very short lived on this 650 km main line. The diesels took over after only a couple of years and the P36 locomotives were transferred to other railways. At first they worked on Moscow–Kursk
Kursk
Kursk is a city and the administrative center of Kursk Oblast, Russia, located at the confluence of the Kur, Tuskar, and Seym Rivers. The area around Kursk was site of a turning point in the Russian-German struggle during World War II and the site of the largest tank battle in history...
, Moscow–Ryazan
Ryazan
Ryazan is a city and the administrative center of Ryazan Oblast, Russia. It is located on the Oka River southeast of Moscow. Population: The strategic bomber base Dyagilevo is just west of the city, and the air base of Alexandrovo is to the southeast as is the Ryazan Turlatovo Airport...
, Kalinin, October, Krasnoyarsk
Krasnoyarsk
Krasnoyarsk is a city and the administrative center of Krasnoyarsk Krai, Russia, located on the Yenisei River. It is the third largest city in Siberia, with the population of 973,891. Krasnoyarsk is an important junction of the Trans-Siberian Railway and one of Russia's largest producers of...
, Belorussian, Stalin (Melitopol
Melitopol
Melitopol is a city in the Zaporizhia Oblast of the southeastern Ukraine. It is situated on the Molochna River that flows through the eastern edge of the city and into the Molochnyi Liman, which eventually joins the Sea of Azov....
depot), Kuibyshev, and Northern (Alexandrov depot) Railways.
Later, when the electrification and dieselization expanded, many of the class P36 locomotives were transferred to work on Lvov, Far East
Far East
The Far East is an English term mostly describing East Asia and Southeast Asia, with South Asia sometimes also included for economic and cultural reasons.The term came into use in European geopolitical discourse in the 19th century,...
, Eastern Siberia, and Transbaikal
Transbaikal
Transbaikal, Trans-Baikal, Transbaikalia , or Dauria is a mountainous region to the east of or "beyond" Lake Baikal in Russia. The alternative name, Dauria, is derived from the ethnonym of the Daur people. It stretches for almost 1000 km from north to south from the Patomskoye Plateau and North...
Railways. The last were withdrawn in 1974 from regular scheduled express passenger train service. All were stored in full working order for times of extraordinary demand. It was common that at certain intervals the engines were taken out from store, steamed up and coupled to trains to haul them to test the condition of the locomotives. Only in the late 1980s were these "strategic reserves" of locomotives disbanded and the P36 locomotives were distributed for museums and for preservation. Some, without regular use for more than 15 years, which were in the worst mechanical condition, were scrapped. It was found that the roller bearings suffered most by standing unused. When the computerised new class numbers were introduced by MPS class P36 become class 1000.001 -1000.0251 with a control digit. In the 1990s, after the collapse of the Soviet Union, a number were sold to private train operators.
Builder details:
- P36-0001 Kolomna Locomotive Works 9000 / 1949 (prototype)
- P36-0002–P36-0005 Kolomna Locomotive Works ? – ? / 1953
- P36-0006 Kolomna Locomotive Works ? / 1954
- P36-0007–P36-0036 Kolomna Locomotive Works 10182–10201 / 1954
- P36-0037–P36-0161 Kolomna Locomotive Works 10205–10330 / 1955
- P36-0162–P36-0251 Kolomna Locomotive Works 10331–10420 / 1956
The South African 4-8-4

Spoornet
Transnet Freight Rail is a South African rail transport company, formerly known as Spoornet. It was part of 'South African Railways and Harbours', a state-controlled organisation that employed hundreds of thousands of people for decades from the first half of the 20th century and was widely...
introduced the first of 140 Class 25 4-8-4
South African Class 25 4-8-4
Between 1953 and 1955 the South African Railways placed ninety Class 25 condensing steam locomotives with a 4-8-4 Northern wheel arrangement in service...
's in 1953, at a time when American railroads were replacing the type with diesel-electric locomotives. These powerful engines incorporated many aspects of American 4-8-4 locomotive design, scaled down for 3 in 6 in (1,066.8 mm) narrow gauge operation. A novel feature of many of these locomotives was the use of enormous condensing tenders, designed to save water in arid areas by converting exhaust steam back to water. The condensing tenders were so big that Henschel provided their own works numbers for the tenders it built.
- Henschel 28780 - 28839 / 1953
Originally, when placed into service the class 25 with condensing tenders worked through Great Karroo from Beaufort West
Beaufort West
Beaufort West is a town in the Western Cape province in South Africa. It is the largest town in the arid Great Karoo region, and forms part of the Beaufort West Local Municipality, with 37 000 inhabitants in 2001....
to De Aar and the non-condensing locomotives, class 25NC
South African Class 25NC 4-8-4
Between 1953 and 1955 the South African Railways placed fifty Class 25NC steam locomotives with a 4-8-4 wheel arrangement in service. The Class 25NC is the non condensing version of the Class 25 condensing locomotive, of which ninety were placed in service at the same time...
, north of De Aar to Kimberley
Kimberley, Northern Cape
Kimberley is a city in South Africa, and the capital of the Northern Cape. It is located near the confluence of the Vaal and Orange Rivers. The town has considerable historical significance due its diamond mining past and siege during the Second Boer War...
and to Welverdiend near Johannesburg
Johannesburg
Johannesburg also known as Jozi, Jo'burg or Egoli, is the largest city in South Africa, by population. Johannesburg is the provincial capital of Gauteng, the wealthiest province in South Africa, having the largest economy of any metropolitan region in Sub-Saharan Africa...
. These locomotives nearly monopolised the service between Kimberley and Beaufort West (485 km) including named express trains such as the Blue Train
Blue Train (South Africa)
The Blue Train travels an approximately journey in South Africa between Pretoria and Cape Town. It is one of the most luxurious train journeys in the world...
, Orange Express and Drakensberg
Drakensberg
The Drakensberg is the highest mountain range in Southern Africa, rising to in height. In Zulu, it is referred to as uKhahlamba , and in Sesotho as Maluti...
.
This line has always been a busy one in South Africa. Up to 60 trains per day occupied the rails. The 25 class locomotives become known as "Silent Suzy". In late 1970s the need of condensing locomotives dropped dramatically when dieselization and electrification expanded. Most of the condensing class 25 locomoives, when passing through major overhaul at Salt River Works were rebuilt to non-condensing version, class 25NC. Only three remained with condensing tenders, 87 locomotives being rebuilt. These locomotives become known in Afrikaans
Afrikaans
Afrikaans is a West Germanic language, spoken natively in South Africa and Namibia. It is a daughter language of Dutch, originating in its 17th century dialects, collectively referred to as Cape Dutch .Afrikaans is a daughter language of Dutch; see , , , , , .Afrikaans was historically called Cape...
as "Worshonde" (Sausage Dog) after the shape of their rebuilt tenders.
When the teething troubles had been solved the class 25 locomotives proved to be most economical in the service, especially class 25NC locomotives. Their enormous boilers were in the 1970s still in splendid condition and needed only 600 to 800 man-hours at works during major overhauls. The major overhaul was done only after 800.000 km or nine year intervals. Intermediate repairs were carried out after 400.000 km or 54 months (4.5 years). As early as in 1960 SAR reported that ninety condensing locomotives had achieved an aggregate mileage of 30 million corresponding to a monthly average of around 5 to 6 mi (8 to 9.7 km) per locomotive over difficult terrain. They hauled heavy, but relatively slow (by European standard), trains with much time spend standing at passing points on the mainly single line railway.
In 1981, a Class 25 locomotive was rebuilt into the experimental Class 26 "Red Devil". This relatively compact locomotive (the engine unit weighed just 123 tonnes) was capable of extraordinary power (in excess of 4000 hp drawbar) yet delivered exceptional economy in coal and water use. However, like the French 242A1 4-8-4 built 35 years earlier, the 26 remained a one-off. The new leadership of SAR had decided to modernise its fleet with diesel and electric traction rather than invest further development in steam traction.
Builder details:
- 3401 - 3410 2D2-h2 24x28 60 (610x711 1524) North British Locomotive 27287 - 27296 / 1953
- 3411 2D2-h2 24x28 60 (610x711 1524) North British Locomotive 27311 / 1953
- 3412 - 3450 2D2-h2 24x28 60 (610x711 1524) Henschel 28731 - 28769 / 1953
- 3451 2D2-h2 24x28 60 (610x711 1524) Henschel 28730 / 1953
- 3452 - 3540 2D2-h2 24x28 60 (610x711 1524) North British Locomotive 27312 - 27400 / 1953
The 4-8-4 in New Zealand

New Zealand Railways Department
The New Zealand Railways Department, NZR or NZGR and often known as the "Railways", was a government department charged with owning and maintaining New Zealand's railway infrastructure and operating the railway system. The Department was created in 1880 and was reformed in 1981 into the New...
had the largest fleet of 4-8-4's outside North America, with 71 similar locomotives in the K
NZR K class (1932)
The NZR K class of 1932 was a class of mixed traffic 4-8-4 steam locomotives that operated on New Zealand's railway network. The locomotives were developed following the failure of the G class Garratts...
, KA
NZR Ka class
The NZR KA class of 1939 was a class of mixed traffic 4-8-4 steam locomotives that operated on New Zealand's railway network. They were built after the success of the K class to meet the increasing traffic demands of the New Zealand Railways Department...
and KBclasses
NZR Kb class
The NZR KB class of 1939 was a class of mixed traffic steam locomotives that operated on New Zealand's railway network. They were built by the New Zealand Railways Department after the success of the K class to meet the increasing traffic demands on the Midland Line in the South Island...
.
The small South Pacific nation of New Zealand adopted the narrow gauge of 3 in 6 in (1,066.8 mm) to minimise railway construction costs, and due to the mountainous terrain the structure gauge
Structure gauge
The structure gauge, also called the minimum clearance outline, is the minimum height and width of tunnels and bridges as well as the minimum height and width of the doors that allow a rail siding access into a warehouse...
was restricted to a maximum height of 11 in 6 in (3.51 m) and width of 8 in 6 in (2.59 m) – one of the most restrictive structure gauges in the world. No doubt this reduced the cost of building the 200 odd tunnels on the railway system, but it posed major problems for locomotive designers, which were exacerbated by an axle load limit of 14 tons.
The remarkable K class 4-8-4 was designed by R.J.Gard to the requirements of Locomotive Superintendent (later Chief Mechanical Engineer) P.R. Angus. and was built locally at the NZR Hutt Workshops, the first being outshopped during the depths of the Depression in 1932. The 47 sq ft (4.4 m²) grate and comparatively large boiler was slung low on narrow frames to keep within the height restrictions, and width restrictions were avoided by sloped cab sides and the mounting of two single stage air compressors in front of the smokebox.
After construction of 30 K class locomotives, the NZR further developed the design to strengthen the frames, and introduce improvements such as roller bearings on all axles and ACFI feedwater heaters. Introduced from 1939, they were built in NZR workshops, most of them with streamlined casing to cover external pipe work. Thirty five were classed Ka, and worked North Island mainlines with the older K class, but six others were built for service on the steeply graded Midland line in the South Island, and were given trailing truck boosters, which lifted their tractive effort by 6000 lb (2,721.6 kg).
The streamlining of the Ka and Kb was removed in the late 1940s as the ACFI feedwater heaters were replaced with exhaust steam injectors. These 4-8-4's recorded speeds up to 75 mi/h on occasion. The last of them was set aside in 1968 due to dieselisation
Dieselisation
Dieselisation or dieselization is a term generally used for the increasingly common use of diesel fuel in vehicles, as opposed to gasoline or steam engines.-Water Transport:...
.
Seven examples have been preserved, including three each of the K class [900, 911 and 917] and KA class [935, 942, 945] respectively, and one Kb [968].
The French 4-8-4
Although only one 4-8-4 was designed and built for the SNCF, a class of 24 distinctively French 4-8-4's was built for metre gauge railways in Brazil. As the hand of Andre ChapelonAndré Chapelon
André Chapelon was a noted French mechanical engineer and designer of advanced steam locomotives. Engineer of Ecole Centrale Paris, he was one of very few locomotive designers who brought a rigorous scientific method to their design, and he sought to apply up-to-date knowledge and theories in...
is evident in all these locomotives, they are considered together.
SNCF 242A1
The lone SNCF 242A1 prototype, rebuilt from an unsuccessful Etat three-cylinder 4-8-2 simple expansion locomotive 241.101 into a 4-8-4 compound locomotiveCompound locomotive
A compound engine unit is a type of steam engine where steam is expanded in two or more stages.A typical arrangement for a compound engine is that the steam is first expanded in a high-pressure cylinder, then having given up heat and losing pressure, it exhausts directly into one or more larger...
. This remarkable locomotive achieved both extraordinary power outputs and efficiencies in coal and water use, but no further examples were built as SNCF focused on electric traction for its future motive power development. 242A1 was trialed on many test runs which showed that this locomotive was equal in power output as the (then) existed SNCF electric locomotives. Here, for the first time in Europe, was a steam locomotive with a 20-ton axle load which not only was at least as powerful as the most powerful high-speed electric locomotive but which could repeatedly develop its maximum power without any mechanical trouble. Developing 5300 ihp[vague] in the cylinders and with 65679 lbf (292.2 kN) of peak tractive effort, 46225 lbf (205.6 kN) mean tractive effort—nothing in Europe could touch it.
While Nr.242A1 being tested the electrical engineers were designing the locomotives for 512 km (318.1 mi) Paris - Lyon
Lyon
Lyon , is a city in east-central France in the Rhône-Alpes region, situated between Paris and Marseille. Lyon is located at from Paris, from Marseille, from Geneva, from Turin, and from Barcelona. The residents of the city are called Lyonnais....
line, which was to be electrified. An electric locomotive slightly more powerful than the successful Paris - Orléans
Orléans
-Prehistory and Roman:Cenabum was a Gallic stronghold, one of the principal towns of the Carnutes tribe where the Druids held their annual assembly. It was conquered and destroyed by Julius Caesar in 52 BC, then rebuilt under the Roman Empire...
2-D-2 type electric locomotive was contemplated. But when the test results of the test of 242A1 become known, the design was hurriedly changed to incorporate the maximum capacity possible within a 23-ton axle load, and then the 144-ton 9100 class http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/Category:SNCF_Class_2D2_9100 was produced with over 1 hp more than the originally designed. Thus the performances of the Mistral and other heavy passenger express trains would not have been so outstanding if 242A1 had not existed.
Therefore Andre Chapelon indirectly influenced French electric locomotive design. In addition 242A1 demonstrated the suitability of the Sauvage-Smith system of compounding for French conditions and the designs for future French steam locomotives, prepared but unfortunately stopped, were of Sauvage-Smith compounding system.
In ordinary service 242A1 was allocated at Le Mans
Le Mans
Le Mans is a city in France, located on the Sarthe River. Traditionally the capital of the province of Maine, it is now the capital of the Sarthe department and the seat of the Roman Catholic diocese of Le Mans. Le Mans is a part of the Pays de la Loire region.Its inhabitants are called Manceaux...
depot (SNCF Region-3 Ouest and hauled express trains in 1950 - 1960 between Le Mans and Brest
Brest, France
Brest is a city in the Finistère department in Brittany in northwestern France. Located in a sheltered position not far from the western tip of the Breton peninsula, and the western extremity of metropolitan France, Brest is an important harbour and the second French military port after Toulon...
411 km. Nr. 242A1 did not last long, it was withdrawn from service and hurriedly scrapped in 1960.
Builder details:
- SNCF 242A1 2D2-h3v (1)600x720 (HP) / (2)680x760 (LP) 1950 148 tons Marine Homecourt 339 / 1945 (rebuilt from 2D1-h3 Fives Lille 4800 / 1932) Written off from books 10 / 1960.
Brazil's 242F
French engineer André Chapelon was chief designer of 24 metre gauge 4-8-4's built by GELSAGelsa
Gelsa is a municipality located in the province of Zaragoza, comarca of Ribera Baja del Ebro, Aragon, Spain. According to the 2004 census , the municipality has a population of 1,216 inhabitants....
, - Groupement d´Exportation de Locomotives en Sud-Amerique -, a job he took after retirement from SNCF where he had designed the 242A1. On October 27, 1949, a contract was signed between the D.N.E.F. (Brazil) and the GELSA for the construction 24 locomotives of the 4-8-4 type with a 13 ton axle load. The order included 66 2-8-4's and all were delivered by January 1953. The Federal DNEF - Departamento Nacional de Estradas de Ferro allocated the locomotives to four of Brazil's state railways. The specification was for a maximum speed of 80 km/h, a Tractive Effort @ 85% pressure of 29,120 lbs, and the ability to negotiate curves with a minimum radius of 80 metres. This last point proved to be a source of contention, as it was later discovered that in some places the curves were less than 50 metres. Consequently the 242F was involved in a number of derailments.
These modern, - perhaps too modern - locomotives for Brazilian railway conditions were not liked by local staff, and were not used as much as had been hoped. Their maximum axle load of 13 tons restricted their use, as did their long tenders. In some places turntables were too short to turn the engines and they had to be turned on triangles.
The 242s were built by Batignolles Chatillon. They were two cylinder simple expansion locomotives designed to burn local low calorific thermal value coal, with driving wheels of 1525 mm (60 in) / 5 ft) diameter and grate area of 58 sq ft (5.4 m²) to burn the poor quality coal. They were coupled to big tenders which carried 18 tons of coal. The Belpaire firebox
Belpaire firebox
The Belpaire firebox is a type of firebox used on steam locomotives. It was invented by Alfred Belpaire of Belgium. It has a greater surface area at the top of the firebox, improving heat transfer and steam production...
included a combustion chamber and the boiler pressure was a high 18 kg (atm) /sq cm. One member of class 242F1 - 242F24 locomotive was tested on metre gauge Reseau Breton
Réseau Breton
The Réseau Breton is a standard gauge, and former metre gauge railway in Finistère, France, with a few kilometres of line in Côtes du Nord, Ille-et-Vilaine and Morbihan. The hub of the system was Carhaix...
line before shipment to Brazil.
In the late 1960s they were relegated down from first class passenger trains. Some locomotives, allocated to Southern Brazilia, were even tried in Bolivia
Bolivia
Bolivia officially known as Plurinational State of Bolivia , is a landlocked country in central South America. It is the poorest country in South America...
.
Builder details:
- 2D2-h2 Batignolles - Chatillon 850 - 861 / 1951 DNEF 242F1 - 242F12
- 2D2-h2 Batignolles - Chatillon 862 - 873 / 1952 DNEF 242F13 - 242F24
Note: These Nantes-St.Joseph works plates are not confirmed.
The British 4-8-4 for China

Shanghai
Shanghai is the largest city by population in China and the largest city proper in the world. It is one of the four province-level municipalities in the People's Republic of China, with a total population of over 23 million as of 2010...
-Nanking Railway. These Chinese Government Railways Class KF1 were designed by Colonel Kenneth Cantlie and No 607 is preserved by the National Railway Museum
National Railway Museum
The National Railway Museum is a museum in York forming part of the British National Museum of Science and Industry and telling the story of rail transport in Britain and its impact on society. It has won many awards, including the European Museum of the Year Award in 2001...
, UK.
Originally idented for 303 km Shanghai-Nanking Railway, these big 2D2-h2 locomotives worked on this railway only up to Japan - China Incident, their roster included also the famous Shanghai Express (Named after the Hollywood classic film Shangai Express
Shanghai Express (film)
Shanghai Express is a 1932 American film directed by Josef von Sternberg. The pre-Code picture stars Marlene Dietrich, Clive Brook, Anna May Wong, and Warner Oland. It was written by Jules Furthman, based on a story by Harry Hervey. It was the fourth of seven teamings of Sternberg and Dietrich.The...
).
When the whole 706 km Changsha - Canton
Guangzhou
Guangzhou , known historically as Canton or Kwangchow, is the capital and largest city of the Guangdong province in the People's Republic of China. Located in southern China on the Pearl River, about north-northwest of Hong Kong, Guangzhou is a key national transportation hub and trading port...
Railway was finally completed in October 1936,
the class KF 1 - 24 locomotives were transferred to operate over northern section between Hankow and Changsha on this new main line, combining Tientsin and Peking with Kanton, over vast distance of 2428 and 2290 km (1,508.7 and 1,422.9 mi).
Most of the class KF survived the 1937 - 1945 Sino-Japanese war
Second Sino-Japanese War
The Second Sino-Japanese War was a military conflict fought primarily between the Republic of China and the Empire of Japan. From 1937 to 1941, China fought Japan with some economic help from Germany , the Soviet Union and the United States...
. They retained their old classification and continued in service up to early 1970s. One was presented by the Chinese Government
Government of the People's Republic of China
All power within the government of the People's Republic of China is divided among three bodies: the People's Republic of China, State Council, and the People's Liberation Army . This article is concerned with the formal structure of the state, its departments and their responsibilities...
, as a goodwill return gesture to the British, representing what is commonly thought to be the biggest and heaviest non-articulated British-built exported steam locomotive; in fact several other classes, including the South African 4-8-4 in condensing form (see above) and South Australian 500 class (below), were larger in at least one dimension.
Builder details:
- KF 1-16 2D2-h2 520x725 1752 Vulcan FoundryVulcan FoundryVulcan Foundry was a British locomotive builder sited at Newton-le-Willows, Lancashire .-History:It was originally opened in 1832 as Charles Tayleur and Company to produce girders for bridges, switches and crossings, and other ironwork following the opening of the Liverpool and Manchester Railway...
4668 - 4683 / 1935 Renumbered to 'KF' 601 - 616 - KF 17-24 2D2-h2 520x725 1752 Vulcan Foundry 4696 - 4703 / 1936 Renumbered to 'KF' 617 - 624
Edit: -
The 'South Australian 500 class (below) (from above) is actually a locally (Australian made) 520 class light lines 4-8-4, not a 500 class 4-8-2 (later converted to 4-8-4, locally).
The South Australian Railways 500 class 4-8-2 (later 500B 4-8-4), built by Armstrong-Whitworth, in 1926, would have been substantially heavier than Col. Cantlie's Chinese essays.
The 4-8-4 in Australia
A total of 21 4-8-4's operated in Australia, built to three distinct designs.South Australian Railways
The South Australian RailwaysSouth Australian Railways
South Australian Railways built and operated railways in South Australia from 1854 to the incorporation of its non-urban railways into the Australian National Railways Commission in 1975, together with the former Commonwealth Railways and the former Tasmanian Government Railways...
500 class of 1926, originally a 4-8-2 design, was modified in 1929 into the 4-8-4 500B class by the replacement of the trailing axle with a booster-equipped four-wheel trailing truck. These engines were built by Armstrong Whitworth and were the largest non-articulated locomotives built in Great Britain. The design was based on ALCO drawings modified by AW and SAR engineers.
In 1943 the first of twelve streamlined South Australian Railways 520 class were outshopped from the Islington Workshops in Adelaide. They were designed to run on lightly constructed 30 kg/m (60 lb/yd) track by virtue of the engine unit's weight being spread over eight axles. Their streamlining bears a strong resemblance to that of the PRR T1
PRR T1
The Pennsylvania Railroad's 52 T1 class duplex-drive 4-4-4-4 steam locomotives, introduced in 1942 and 1946 , were their last-built steam locomotives and their most controversial. They were ambitious, technologically sophisticated, powerful, fast, and uniquely streamlined by Raymond Loewy...
locomotive introduced on the Pennsylvania Railroad
Pennsylvania Railroad
The Pennsylvania Railroad was an American Class I railroad, founded in 1846. Commonly referred to as the "Pennsy", the PRR was headquartered in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania....
the preceding year.
Victorian Railways
The Victorian RailwaysVictorian Railways
The Victorian Railways operated railways in the Australian state of Victoria from 1859 to 1983. The first railways in Victoria were private companies, but when these companies failed or defaulted, the Victorian Railways was established to take over their operations...
H class
Victorian Railways H class
The H class was an express passenger steam locomotive that ran on Victorian Railways from 1941 to 1958. Intended to eliminate the use of double heading A2 class locomotives on Overland services on the steeply graded Western line to Adelaide, wartime restrictions led to only one locomotive being built...
three-cylinder 4-8-4 of 1941 was designed for heavy passenger work on the Melbourne
Melbourne
Melbourne is the capital and most populous city in the state of Victoria, and the second most populous city in Australia. The Melbourne City Centre is the hub of the greater metropolitan area and the Census statistical division—of which "Melbourne" is the common name. As of June 2009, the greater...
-Adelaide
Adelaide
Adelaide is the capital city of South Australia and the fifth-largest city in Australia. Adelaide has an estimated population of more than 1.2 million...
line. It was the largest and most powerful locomotive built in Australia. Due to the necessary upgrades to the Adelaide line being deferred, the H class operated only on the Melbourne-Albury
Albury, New South Wales
Albury is a major regional city in New South Wales, Australia, located on the Hume Highway on the northern side of the Murray River. It is located wholly within the boundaries of the City of Albury Local Government Area...
line, achieving success as a fast freight locomotive.
The 4-8-4 in Chile
In 1935 the German builder Henschel & SonHenschel & Son
Henschel & Son was a German company, situated in Kassel, best known during the 20th century as a maker of transportation equipment, including locomotives, trucks, buses and trolleybuses, and armoured fighting vehicles and weapons....
supplied ten 4-8-4s of the 5’6" gauge to the FdE, Ferrocarriles del Estado (State Railways), of Chile
Chile
Chile ,officially the Republic of Chile , is a country in South America occupying a long, narrow coastal strip between the Andes mountains to the east and the Pacific Ocean to the west. It borders Peru to the north, Bolivia to the northeast, Argentina to the east, and the Drake Passage in the far...
, which became their 100 class. They were called "Super Montañas" (Super Mountains) as they followed the 80 class 4-8-2 introduced six years previously. They were equipped with mechanical stokers, and Vanderbilt tenders, and weighed 185 tonnes. On test they produced 2,355 Indicated Horse Power, at a coal consumption of 34 kg/km and water consumption of 274 l/km. The design was not repeated however, and the FdE returned to the 4-8-2. The 100 class were used on the Almeda to Talca
Talca
Talca is a city and commune in Chile located about south of Santiago, and is the capital of both Talca Province and Maule Region . As of the 2002 census, the city had a population of 193,755....
line, and were replaced by diesels in 1970. No 1009 is preserved in the Santiago Railway Museum.
The 4-8-4 in Spain
Ten express passenger 4-8-4's were designed by the RENFERENFE
Renfe Operadora is the state-owned company which operates freight and passenger trains on the 1668-mm "Iberian gauge" and 1435-mm "European gauge" networks of the Spanish national railway infrastructure company ADIF .- History :The name RENFE is derived from that of the former Spanish National...
in 1955, and were remarkably well-proportioned. Developed from a preceding 4-8-2 type, they had improved steam passages and developed 30 to 40 per cent more power at medium cut-offs and high speed. These engines, Nos.242F2001 - 242F2010 were built by La Maquinista Terrestre y Maritima SA, Barcelona
Barcelona
Barcelona is the second largest city in Spain after Madrid, and the capital of Catalonia, with a population of 1,621,537 within its administrative limits on a land area of...
to burn fuel oil and had Witte type smoke deflectors. They were fitted with a double Kylchap
Kylchap
The Kylchap steam locomotive steam locomotive exhaust system was designed and patented by the famous French steam engineer André Chapelon, using a second-stage nozzle designed by the Finnish engineer Kyösti Kylälä and known as the Kylälä spreader; thus the name KylChap for this design.The Kylchap...
(Kylälä-Chapelon) blast-pipe, a Worthington feedwater heater and the T.I.A. (Traitement Integral Armand) water-softening device. The plate frames, 1.25 inches (31.8 mm) thick were substantially braced by a cast-steel coffer between the cylinders, transverse plates between the cylinders and the first coupled axle, by front and back buffer beams by six groups of transverse cross-ties, those joining the lower parts of the frames near the firebox being of heavy design in order to counteract any tendency of the frames to distort. The main journals were 10.25 inches (260.4 mm) in diameter, the journals of the coupled axles, 9.5 inches (241.3 mm). All axles had SKF
SKF
SKF, Svenska Kullagerfabriken AB , later AB SKF, is a Swedish bearing company founded in 1907, supplying bearings, seals, lubrication and lubrication systems, maintenance products, mechatronics products, power transmission products and related services globally.-History:The company was founded on...
roller-bearing axle-boxes and the coupled axles were provided with Franklin automatic wedges. All the rotating weights and 33 per cent of the alternating weights were balanced. The weight per coupled axle was reduced to 19 tons, with driving wheels of 6 foot in diameter (later replaced with 1900 mm diameter wheels). The spokes of the coupled wheels were of U section and both sides of the wheels were braked. The four-wheeled pony truck was provided with Isothermos axle boxes as well as the tender bogies. To increase the comfort of the locomotive crew, the cabs of these oil-fired 4-8-4s had a wooden floor mounted on springs, and the seats of the driver and fireman were also provided with springs, a very welcome improvement for long runs on poor tracks. These locomotives were painted green when turned out from the builder's works at Barcelona.
The 4-8-4 was a very swift machine, and when tested on the line from Barcelona to Tarragona
Tarragona
Tarragona is a city located in the south of Catalonia on the north-east of Spain, by the Mediterranean. It is the capital of the Spanish province of the same name and the capital of the Catalan comarca Tarragonès. In the medieval and modern times it was the capital of the Vegueria of Tarragona...
between Villanueva y Geltru and San Vincente, over 10.4 miles (16.7 km) of practically level and straight line a speed exceeding 84 miles per hour (135.2 km/h) was sustained twice, firstly with 430 tons and then with 480 tons behind the tender. High-capacity tests took place between Madrid
Madrid
Madrid is the capital and largest city of Spain. The population of the city is roughly 3.3 million and the entire population of the Madrid metropolitan area is calculated to be 6.271 million. It is the third largest city in the European Union, after London and Berlin, and its metropolitan...
and Ávila. A train weighing 426 tons, including a dynamometer car, was hauled at sustained speeds of 70.3 miles per hour (113.1 km/h) up a gradient of 3.5 pro mille (1 in 286), 57.2 miles per hour (92.1 km/h) up 10.5 pro mille (1 in 95) and 39.1 miles per hour (62.9 km/h) up 22.8 pro mille (1 in 44.5). The gross hp figures recorded with the dynamometer car were 1.790, 2.350, and 2.320, and the calculated hp at the rim of driving wheels being 2.600, 3.400 and 3.580. The latter output indicates about 4 ihp.
With these engines there was some anxiety about water. The capacity of the tender was limited at only 6.200 gallons and, with only few water cranes in service, the full capacity of the locomotive was not always used for fear of running short of this essential supply in the half-arid Spanish landscape. As example, for the 163.3 km (101.5 mi) between Medina del Campo
Medina del Campo
Medina del Campo is a town located in the middle of the Spanish Meseta Central, in the province of Valladolid, Castile-Leon autonomous region, 45 km from Valladolid. It is the capital of a farming area, far away from the great economic centres.-History:...
and Burgos
Burgos
Burgos is a city of northern Spain, historic capital of Castile. It is situated at the edge of the central plateau, with about 178,966 inhabitants in the city proper and another 20,000 in its suburbs. It is the capital of the province of Burgos, in the autonomous community of Castile and León...
, rising 131 metres with an uphill start, three intermediate stops, one slack and some shunting movements to couple extra coaches in the train, the amount of water consumed was about 7.300 gallons.
All ten were allocated to Miranda de Ebro
Miranda de Ebro
Miranda de Ebro is a city on the Ebro river in the province of Burgos in the autonomous community of Castile and León, Spain. It is located in the north-eastern part of the province, on the border with the province of Álava and the autonomous community of La Rioja...
shed to haul principal heavy express trains. They were called generally Los Verdes. In the 1960s they were a familiar sight at the head of the best express trains, but in 1971 they were transferred entirely to semifast passenger trains and even to the haulage of heavy seasonal fruit trains between Castejon
Castejón
Castejón is a town and municipality located in the province and autonomous community of Navarre, northern Spain.Castejón is home to Spain's largest photovoltaic power plant , which opened in 2006 .-External links:*...
and Alasua from October to January. One, 242F.2009, is preserved at the Railway Museum (Madrid)
Railway Museum (Madrid)
The Museo del Ferrocarril in Madrid, Spain, is one of the largest historic railroad collections in Europe. Located in the Las Delicias Station, just south of Atocha in the barrio of Delicias, it was built in 1880 by Gustave Eiffel....
.
Builder details:
- 242F.2001 2D2-h2 1672 640x710 1900 142.3 tons La Maquinista 695 - 704 / 1955-1956
RENFE 242F.2001 was completed in October 1955, 242F.2002 - 242F.2010 in 1956.
The German 4-8-4
In 1939 the Deutsche Reichsbahn placed in service two prototype three cylinder DRB Class 06 heavy express locomotives, with a maximum speed of 140 km/h (87 mph). Due to World War II no further examples were produced, and 06 002 was bombed during the hostilities. The 06 001 survived until 1951, when it was set aside. With large 2000 mm (6'6¾") driving wheels, a high 280 psi (1,930,532 Pa) boiler pressure and tractive effort of 14566 lbf (64.8 kN), they could haul a 650 tonne train at 120 km/h. Many parts such as the boiler were standardised with the DRG Class 45DRG Class 45
German Class 45 steam locomotives were standard locomotives designed by the Deutsche Reichsbahn for hauling goods trains.- History :...
heavy freight locomotive. Both were scrapped in the 1950s.
- DRBDeutsche ReichsbahnDeutsche Reichsbahn was the name of the following two companies:* Deutsche Reichsbahn, the German Imperial Railways during the Weimar Republic, the Third Reich and the immediate aftermath...
06.001 - 06.002 2D2-h3 3x520 x 720 2000 129.9 tons KruppKruppThe Krupp family , a prominent 400-year-old German dynasty from Essen, have become famous for their steel production and for their manufacture of ammunition and armaments. The family business, known as Friedrich Krupp AG Hoesch-Krupp, was the largest company in Europe at the beginning of the 20th...
2000 -2001 / 1938 + 14.11.1951
Preservation
The 4-8-4 was a late development of the steam locomotive, and was often 'name' passenger power at the time of steam's demise. Many were therefore earmarked for preservation, either plinthed or in museums, with a few in running condition.Of the 205 original Canadian Northerns only eight have been preserved, six CNR Northerns and both 3100 and 3101 Canadian Pacific Railway (CPR) Northerns.
Some of the more notable of this type are:



- Atchison, Topeka & Santa Fe 2903 - Illinois Railway Museum Union, IllinoisUnion, IllinoisUnion is a village in McHenry County, Illinois, United States. The population was 580 at the 2010 census, up from 576 at the 2000 census.-Geography:Union is located at ....
. - Atchison, Topeka & Santa Fe 2912 - On static display in Pueblo, ColoradoPueblo, ColoradoPueblo is a Home Rule Municipality that is the county seat and the most populous city of Pueblo County, Colorado, United States. The population was 106,595 in 2010 census, making it the 246th most populous city in the United States....
, currently awaiting restoration - Atchison, Topeka & Santa Fe 2913Santa Fe 2913Santa Fe 2913 is a 4-8-4 locomotive. It was built in the 1940s and is currently on display in a park in Fort Madison, Iowa, having been donated to the town upon retirement. It is currently undergoing cosmetic restoration....
- On static display in Fort Madison, IowaFort Madison, IowaFort Madison, situated on the Mississippi River, is a city in and one of the county seats of Lee County, Iowa, United States. The other county seat is Keokuk. The population was 10,715 at the 2000 census... - Atchison, Topeka & Santa Fe 2921 - Beard Brook Park Modesto, CaliforniaModesto, CaliforniaModesto is a city in, and is the county seat of, Stanislaus County, California. With a population of approximately 201,165 at the 2010 census, Modesto ranks as the 18th largest city in the state of California....
. - Atchison, Topeka & Santa Fe 2925 - California State Railroad Museum Sacramento, CaliforniaSacramento, CaliforniaSacramento is the capital city of the U.S. state of California and the county seat of Sacramento County. It is located at the confluence of the Sacramento River and the American River in the northern portion of California's expansive Central Valley. With a population of 466,488 at the 2010 census,...
. - Atchison, Topeka & Santa Fe 2926Santa Fe 2926Santa Fe 2926 is a former Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway 4-8-4 steam locomotive originally built in 1944 by Baldwin. This locomotive was part of the last group of steam locomotives, and one of the largest 4-8-4 types that was ever built, purchased new by the Santa Fe...
- Currently under restoration in Albuquerque at a site leased from the GSA near 8th Street and Haynes Avenue, due to be completed in 2013 and now available for tour and close inspection. More information at New Mexico Steam Locomotive and Railroad Historical Society. - Atchison, Topeka & Santa Fe 3751Santa Fe 3751Santa Fe 3751 is a restored 4-8-4 steam locomotive that was originally owned and operated by the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway. It is located in the Central City East neighborhood of Los Angeles, California and is listed on the National Register of Historic Places.- History :Built in 1927...
- Restored in 1991, owned by the San Bernardino Railroad Historical Society - Atchison, Topeka & Santa Fe 3759Santa Fe 3759Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway 3759 is a standard gauge 4-8-4, Northern type, steam railway locomotive built by Baldwin in 1928 for the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway. It is on display in Locomotive Park, located between Andy Devine Avenue and Beale Street in Kingman, Arizona...
- On Display in Kingman, Arizona. - Atchison, Topeka & Santa Fe 3768 - Great Plains Transportation Museum Wichita, KansasWichita, KansasWichita is the largest city in the U.S. state of Kansas.As of the 2010 census, the city population was 382,368. Located in south-central Kansas on the Arkansas River, Wichita is the county seat of Sedgwick County and the principal city of the Wichita metropolitan area...
. - Canadian National RailwayCanadian National RailwayThe Canadian National Railway Company is a Canadian Class I railway headquartered in Montreal, Quebec. CN's slogan is "North America's Railroad"....
6153 - On static display at the Canadian Railway MuseumCanadian Railway MuseumThe Canadian Railway Museum Musée Ferrovaire Canadien) is a rail transport museum in Delson/Saint-Constant, Quebec south of Montreal.-Collection:...
in Delson, QuebecDelson, QuebecDelson is an off-island suburb of Montreal, Quebec, Canada. It is situated 8 mi/13 km SSE of Montreal within the regional county municipality of Roussillion in the administrative region of Montérégie. The population as of the Canada 2006 Census was 7,322.On its small territory, Delson is crossed... - Canadian National Railway 6167 - On static display in downtown GuelphGuelphGuelph is a city in Ontario, Canada.Guelph may also refer to:* Guelph , consisting of the City of Guelph, Ontario* Guelph , as the above* University of Guelph, in the same city...
, OntarioOntarioOntario is a province of Canada, located in east-central Canada. It is Canada's most populous province and second largest in total area. It is home to the nation's most populous city, Toronto, and the nation's capital, Ottawa.... - Canadian National Railway 6200 - Canadian Science & Technology Museum Ottawa,Ontario
- Canadian National Railways 6213CN 6213The CNR 6213 is a preserved 4-8-4 steam locomotive. It was a member of the Canadian National Railway's massive fleet of U-2-g “Northerns”. The 6213 is on static display in Toronto, Ontario. There are possible options of restoring the U-2-g to operating condition...
- On static display in downtown TorontoTorontoToronto is the provincial capital of Ontario and the largest city in Canada. It is located in Southern Ontario on the northwestern shore of Lake Ontario. A relatively modern city, Toronto's history dates back to the late-18th century, when its land was first purchased by the British monarchy from...
, OntarioOntarioOntario is a province of Canada, located in east-central Canada. It is Canada's most populous province and second largest in total area. It is home to the nation's most populous city, Toronto, and the nation's capital, Ottawa....
, at the Toronto Railway Heritage CentreToronto Railway Heritage CentreThe Toronto Railway Heritage Centre is a museum being developed by the Toronto Railway Historical Association in partnership with the City of Toronto in Ontario, Canada.-Mission:The mission of the Toronto Railway Heritage Centre is to:...
. - Canadian National Railway 6218 - Fort Erie Railroad Museum Fort Erie, OntarioFort Erie, OntarioFort Erie is a town on the Niagara River in the Niagara Region, Ontario, Canada. It is located directly across the river from Buffalo, New York....
- Canadian National Railway 6400 - Canadian Science & Technology Museum Ottawa,Ontario
- Canadian Pacific Railroad 3100 - Canadian Science & Technology Museum Ottawa,Ontario
- Canadian Pacific Railroad 3101 - Display at IPSCO Steel Regina,Saskatchawan
- Chesapeake & Ohio 614Chesapeake & Ohio 614Chesapeake & Ohio 614 is a 4-8-4 steam locomotive built by the Lima Locomotive Works in Lima, Ohio, in June 1948 for the Chesapeake and Ohio Railway .-Background:...
- Restored in 1980 and again in 1995, owned by Iron Horse Enterprise
Clifton Forge, Virginia
Clifton Forge, Virginia
Clifton Forge is a town in Alleghany County, Virginia, United States which is part of the Roanoke Region. The population was 3,884 at the 2010 census. The Jackson River flows through the town, which as a result was once known as Jackson's River Station....
- Chicago, Burlington and Quincy Railroad 5614 Patee Park St. Joseph, Missouri
- Chicago, Burlington and Quincy Railroad 5629 Colorado Railroad Museum Golden, ColoradoGolden, ColoradoThe City of Golden is a home rule municipality that is the county seat of Jefferson County, Colorado, United States. Golden lies along Clear Creek at the edge of the foothills of the Front Range of the Rocky Mountains. Founded during the Pike's Peak Gold Rush on 16 June 1859, the mining camp was...
- Chicago, Burlington and Quincy Railroad 5631 Rotary Park Sheridan, WyomingSheridan, WyomingSheridan is a city in Sheridan County, Wyoming, United States. The 2010 census put the population at 17,444 and a Micropolitan Statistical Area of 29,116...
- Chicago, Burlington and Quincy Railroad 5633 Douglas Railroad Interpretive Center Douglass, Wyoming
- Ferrocarriles Nacionales de México 3027 Guadalajara, JaliscoGuadalajara, JaliscoGuadalajara is the capital of the Mexican state of Jalisco, and the seat of the municipality of Guadalajara. The city is located in the central region of Jalisco in the western-pacific area of Mexico. With a population of 1,564,514 it is Mexico's second most populous municipality...
- Ferrocarriles Nacionales de México 3028 - Retired in 1966, acquired by the Great North Eastern Railroad Foundation and displayed at the Altamont, New York, fairgrounds until 1983. Currently on lease to and being restored by the New Hope and Ivyland RailroadNew Hope and Ivyland RailroadThe New Hope and Ivyland Railroad is a shortline railroad in Pennsylvania. It also operates a heritage railroad, offering passenger excursions....
. Eleven other N de M Niagara QR-1 class locomotives are preserved in various locations in Mexico; one (in PueblaPueblaPuebla officially Estado Libre y Soberano de Puebla is one of the 31 states which, with the Federal District, comprise the 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided in 217 municipalities and its capital city is Puebla....
) is operational. - Ferrocarriles Nacionales de México 3030 Zacatecas, ZacatecasZacatecas, ZacatecasZacatecas is a city and municipality in Mexico and the capital of the state of Zacatecas. It is located in the north central part of the country. The city had its start as a Spanish mining camp in the mid 16th century. Prior to this, the area's rich deposits in silver and other minerals were known...
- Ferrocarriles Nacionales de México 3031 Huehuetoca, Mexico
- Ferrocarriles Nacionales de México 3033 Pachuca, Hidalgo
- Ferrocarriles Nacionales de México 3034 Puebla Puebla
- Ferrocarriles Nacionales de México 3035 Aguascalientes, AguascalientesAguascalientes, AguascalientesThe city of Aguascalientes is the capital of the state of Aguascalientes in western central Mexico. It stands on the banks of the Río Aguascalientes, 1880 meters above sea level, at...
- Ferrocarriles Nacionales de México 3036 Leon, GuanajuatoLeón, GuanajuatoThe city of León, formally León de los Aldama is the sixth most populous city in Mexico and the first in the state of Guanajuato. It is also the seat of the municipality of León...
- Ferrocarriles Nacionales de México 3038 Mexico, Mexico, D. F.
- Ferrocarriles Nacionales de México 3039 Monterrey, Nuevo Leon
- Ferrocarriles Nacionales de México 3040 Oriental, Puebla
- Ferrocarriles Nacionales de México 3056 Tequisuiapan, Queretaro
- Grand Trunk Western 6323 - Currently on display at the Illinois Railway MuseumIllinois Railway MuseumThe Illinois Railway Museum is the largest railroad museum in the United States and is located in Union, Illinois, northwest of Chicago...
in Union, IllinoisUnion, IllinoisUnion is a village in McHenry County, Illinois, United States. The population was 580 at the 2010 census, up from 576 at the 2000 census.-Geography:Union is located at ....
. - Grand Trunk Western 6325Grand Trunk Western 6325Grand Trunk Western 6325 is one of two survivng examples of the Grand Trunk Western Railroad U-3-b class of steam locomotives. The U-3-b class is a 4-8-4 type steam locomotive.- History :...
- Restored in 2001 by the Ohio Central Railroad to Age of Steam Roundhouse Sugar Creek, Ohio - Great Northern Railway S-2 No.2584, on display at the Havre, MontanaHavre, MontanaHavre is a city in, and the county seat of, Hill County, Montana, United States. It is said to be named after the city of Le Havre in France. The population was 9,621 at the 2000 census.-History:...
depot. - Milwaukee Road 261Milwaukee Road 261The Milwaukee Road 261 is a 4-8-4, steam-powered locomotive owned and maintained by a Minnesota-based nonprofit organization known as the Friends of the 261, which runs seasonal train excursions...
- Restored in 1993, owned, maintained, and operated by the Friends of the 261 in Minneapolis, MinnesotaMinneapolis, MinnesotaMinneapolis , nicknamed "City of Lakes" and the "Mill City," is the county seat of Hennepin County, the largest city in the U.S. state of Minnesota, and the 48th largest in the United States... - Milwaukee Road 265 - Illinois Railway MuseumIllinois Railway MuseumThe Illinois Railway Museum is the largest railroad museum in the United States and is located in Union, Illinois, northwest of Chicago...
in Union, IllinoisUnion, IllinoisUnion is a village in McHenry County, Illinois, United States. The population was 580 at the 2010 census, up from 576 at the 2000 census.-Geography:Union is located at ....
.
Nashville, Chattanooga, & St. Louis 576 Centennial Park Nashville, Tennessee
Nashville, Tennessee
Nashville is the capital of the U.S. state of Tennessee and the county seat of Davidson County. It is located on the Cumberland River in Davidson County, in the north-central part of the state. The city is a center for the health care, publishing, banking and transportation industries, and is home...
- New Zealand Government Railways
- K 900 - on static display at MOTAT in Auckland next to NZR DA classNZR DA classThe NZR Da diesel-electric mainline locomotive class ran on the New Zealand railway system between 1955 and 1989. With 146 locomotives, it was the most numerous class to operate in New Zealand, just five more than the AB class steam locomotive....
No: 1400 - K 911 - under overhaul at Mainline Steam, Plimmerton, Wellington.
- K 917 - stored missing many parts Steam Incorporated, Paekakariki, Wellington
- KA 935 - awaiting overhaul at the Silver Stream RailwaySilver Stream RailwayThe Silver Stream Railway is a heritage railway at Silverstream in the Hutt Valley near Wellington, New Zealand. It regularly operates preserved New Zealand Railways Department locomotives along a restored section of the Hutt Valley Line before a deviation was built in 1954.- History :The...
, near WellingtonWellingtonWellington is the capital city and third most populous urban area of New Zealand, although it is likely to have surpassed Christchurch due to the exodus following the Canterbury Earthquake. It is at the southwestern tip of the North Island, between Cook Strait and the Rimutaka Range...
, New Zealand. - KA 942 - in service at Mainline Steam, Plimmerton, Wellington, used on mainline excursions
- KA 945 - stored in dismantled condition at Steam Incorporated, WellingtonWellingtonWellington is the capital city and third most populous urban area of New Zealand, although it is likely to have surpassed Christchurch due to the exodus following the Canterbury Earthquake. It is at the southwestern tip of the North Island, between Cook Strait and the Rimutaka Range...
- KB 968 - owned by Canterbury Railway Society, leased to Mainline Steam. Under overhaul at Mainline Steam, ChristchurchChristchurchChristchurch is the largest city in the South Island of New Zealand, and the country's second-largest urban area after Auckland. It lies one third of the way down the South Island's east coast, just north of Banks Peninsula which itself, since 2006, lies within the formal limits of...
- Norfolk & Western 611 - Ran frequent excursions in the 1980s and early 1990s, on display in the Virginia Museum of Transportation Roanoke, VirginiaRoanoke, VirginiaRoanoke is an independent city in the Mid-Atlantic U.S. state of Virginia and is the tenth-largest city in the Commonwealth. It is located in the Roanoke Valley of the Roanoke Region of Virginia. The population within the city limits was 97,032 as of 2010...
. - Reading 2100 - Restored in 1988, and 1998, converted to burn oil in the Early 2000s. Stored in Richland, WashingtonRichland, WashingtonRichland is a city in Benton County in the southeastern part of the U.S. state of Washington, at the confluence of the Yakima and the Columbia Rivers. As of the 2010 census, the city population was 48,058. April 1, 2011 estimates from the Washington State Office of Financial Management put the...
. - Reading 2101 - B&O Railroad Museum Baltimore, Maryland.
- Reading 2102 - Reading & Norhtern Railroad Port Clinton, PennsylvaniaPort Clinton, PennsylvaniaPort Clinton is a borough in Schuylkill County, Pennsylvania, United States. The population was 288 at the 2000 census.-Geography:Port Clinton is located at ....
. - Reading 2124 - Used on the "Reading Rambles" in the late 1950s and 1960s. On static display at Steamtown National Historic SiteSteamtown National Historic SiteSteamtown National Historic Site is a railroad museum and heritage railroad located on in downtown Scranton, Pennsylvania, at the site of the former Scranton yards of the Delaware, Lackawanna and Western Railroad . The museum is built around a working replica turntable and a roundhouse that is...
in Scranton, PennsylvaniaScranton, PennsylvaniaScranton is a city in the northeastern part of Pennsylvania, United States. It is the county seat of Lackawanna County and the largest principal city in the Scranton/Wilkes-Barre metropolitan area. Scranton had a population of 76,089 in 2010, according to the U.S...
. - St. Louis Southwestern 819St. Louis Southwestern 819The St. Louis Southwestern #819 is a 4-8-4 steam locomotive. It was completed in 1943 and was the last engine built by the railway affectionately known as the "Cotton Belt Route". It was also the last locomotive built in Arkansas to date...
- Built in 1943, it was the last locomotive build by the Cotton BeltSt. Louis Southwestern RailwayThe St. Louis Southwestern Railway , known by its nickname of "The Cotton Belt Route" or simply Cotton Belt, was organized on January 15, 1891, although it had its origins in a series of short lines founded in Tyler, Texas, in 1870 that connected northeastern Texas to Arkansas and southeastern...
. Restored to service in 1986 and housed at the Arkansas Railroad Museum in Pine Bluff, ArkansasPine Bluff, ArkansasPine Bluff is the largest city and county seat of Jefferson County, Arkansas, United States. It is also the principal city of the Pine Bluff Metropolitan Statistical Area and part of the Little Rock-North Little Rock-Pine Bluff, Arkansas Combined Statistical Area...
. - St. Louis-San Francisco RailwaySt. Louis-San Francisco RailwayThe St. Louis – San Francisco Railway , also known as the Frisco, was a railroad that operated in the Midwest and South Central U.S. from 1876 to 1980.-History:...
4500 - As the Frisco Meteor, ran overnight passenger service between St. Louis, Tulsa and Oklahoma City. Cosmeticaly restored and relocated to Route 66 Station Park in Tulsa, OK in 2011. - St. Louis-San Francisco RailwaySt. Louis-San Francisco RailwayThe St. Louis – San Francisco Railway , also known as the Frisco, was a railroad that operated in the Midwest and South Central U.S. from 1876 to 1980.-History:...
4501 - Built in 1942, ran overnight passenger service as the Frisco Meteor between St. Louis, Tulsa, and Oklahoma City. Donated to the Dallas Museum of the American RailroadMuseum of the American RailroadThe Museum of the American Railroad, formerly known as the Age of Steam Railroad Museum, is located at 1105 Washington Street in Fair Park, Dallas, Texas. The museum has a large collection of steam, diesel and passenger railroad equipment...
in September 1964 - St. Louis-San Francisco RailwaySt. Louis-San Francisco RailwayThe St. Louis – San Francisco Railway , also known as the Frisco, was a railroad that operated in the Midwest and South Central U.S. from 1876 to 1980.-History:...
4516 - Missouri State Fairgrounds Sedalia, MissouriSedalia, MissouriSedalia is a city located about south of the Missouri River in Pettis County, Missouri. U.S. Highway 50 and U.S. Highway 65 intersect in the city. As of 2006, the city had a total population of 20,669. It is the county seat of Pettis County. The Sedalia Micropolitan Statistical Area consists of...
. - St. Louis-San Francisco RailwaySt. Louis-San Francisco RailwayThe St. Louis – San Francisco Railway , also known as the Frisco, was a railroad that operated in the Midwest and South Central U.S. from 1876 to 1980.-History:...
4524 - Grant Beach Park Springfield, MissouriSpringfield, MissouriSpringfield is the third largest city in the U.S. state of Missouri and the county seat of Greene County. According to the 2010 census data, the population was 159,498, an increase of 5.2% since the 2000 census. The Springfield Metropolitan Area, population 436,712, includes the counties of...
. - Spokane, Portland and Seattle 700Spokane, Portland and Seattle 700Spokane, Portland & Seattle 700 is the only surviving example of their E-1 class 4-8-4 Northern type steam locomotive. Nearly identical to the A-3 class Northerns built for Northern Pacific Railway, but burning oil instead of coal....
- South Australian RailwaysSouth Australian RailwaysSouth Australian Railways built and operated railways in South Australia from 1854 to the incorporation of its non-urban railways into the Australian National Railways Commission in 1975, together with the former Commonwealth Railways and the former Tasmanian Government Railways...
504 - in static preservation at the National Railway MuseumNational Railway MuseumThe National Railway Museum is a museum in York forming part of the British National Museum of Science and Industry and telling the story of rail transport in Britain and its impact on society. It has won many awards, including the European Museum of the Year Award in 2001...
in Port AdelaidePort AdelaidePort Adelaide is a suburb of Adelaide lying about 14 kilometres northwest of the City of Adelaide. It lies within the City of Port Adelaide Enfield and is the main port for the city of Adelaide...
. - South Australian Railways 520 - Restored to service in 1972, operating the SteamrangerSteamRangerSteamRanger is an historic train society in South Australia running trains on the Victor Harbor railway line. They are the only group regularly running broad gauge steam locomotives in South Australia...
tourist railway between Mount BarkerMount Barker, South AustraliaMount Barker is an expanding city, home to 10 258 residents that is 33 kilometres up the South Eastern Freeway, east of Adelaide, in South Australia. It is the seat of the District Council of Mount Barker, is the largest town in the Adelaide Hills, and is one of the fastest growing areas in the...
and Victor Harbor - Southern Pacific 4449Southern Pacific 4449Southern Pacific 4449 is the only surviving example of Southern Pacific Railroad's GS-4 class of steam locomotives. The GS-4 is a streamlined 4-8-4 type steam locomotive...
- still in operation, served as the locomotive for the Bicentennial American Freedom TrainAmerican Freedom TrainThe United States has seen two national 'Freedom Trains'. The 1947–1949 Freedom Train was a special exhibit train that toured the United States in the later half of the 1940s. A similar train called the American Freedom Train toured the country for the United States Bicentennial celebration in... - Southern Pacific 4460Southern Pacific 4460Southern Pacific 4460 is the only surviving GS-6 Class steam locomotive. The GS-6 is a semi-streamlined 4-8-4 Northern type steam locomotive. GS stands for "Golden State" or "General Service." The locomotive was built by the Lima Locomotive Works for the Southern Pacific Railroad in 1943...
- on static display at the Museum of TransportationMuseum of TransportationThe Museum of Transportation of the St. Louis County, Missouri, United States Parks Department is a museum located in the Greater St. Louis area. It was first founded in 1944 by a group of individuals dedicated to preserving the past and has a wide variety of vehicles from American history...
in St. Louis, MissouriSt. Louis, MissouriSt. Louis is an independent city on the eastern border of Missouri, United States. With a population of 319,294, it was the 58th-largest U.S. city at the 2010 U.S. Census. The Greater St...
. This was the last steam locomotive used in revenue service by the SP. - Union Pacific 814 - Rock Island Depot Museum Council Bluffs, IowaCouncil Bluffs, IowaCouncil Bluffs, known until 1852 as Kanesville, Iowathe historic starting point of the Mormon Trail and eventual northernmost anchor town of the other emigrant trailsis a city in and the county seat of Pottawattamie County, Iowa, United States and is on the east bank of the Missouri River across...
- Union Pacific 833 - Utah State Railroad Museum Ogden, UtahOgden, UtahOgden is a city in Weber County, Utah, United States. Ogden serves as the county seat of Weber County. The population was 82,825 according to the 2010 Census. The city served as a major railway hub through much of its history, and still handles a great deal of freight rail traffic which makes it a...
- Union Pacific 838 - Union Pacific Railroad Cheyenne, WyomingCheyenne, WyomingCheyenne is the capital and most populous city of the U.S. state of Wyoming and the county seat of Laramie County. It is the principal city of the Cheyenne, Wyoming, Metropolitan Statistical Area which encompasses all of Laramie County. The population is 59,466 at the 2010 census. Cheyenne is the...
. - Union Pacific 844Union Pacific 844Union Pacific 844 is a 4-8-4 steam locomotive owned by Union Pacific Railroad. It was the last steam locomotive delivered to Union Pacific and is unique in that it is the only steam locomotive never retired by a North American Class I railroad....
- the last steam locomotive built for Union Pacific Railroad (12/1944). Part of UP heritage fleet, often used for running in excursion service, and on occasion revenue service. Never retired, longest continuously operating steam engine on a Class 1 Railroad. Kept at Cheyenne, WyomingCheyenne, WyomingCheyenne is the capital and most populous city of the U.S. state of Wyoming and the county seat of Laramie County. It is the principal city of the Cheyenne, Wyoming, Metropolitan Statistical Area which encompasses all of Laramie County. The population is 59,466 at the 2010 census. Cheyenne is the...
when not on excursion. - P36-0001 - Lebyazhe store (TsMZhT)
- P36-0027 - Babaevo (TsMOZhD)
- P36-0031 - ZlatoustZlatoustZlatoust is a city in Chelyabinsk Oblast, Russia, located on the Ay River , west of Chelyabinsk. Population: 181,000 ; 161,000 ; 99,000 ; 48,000 ; 21,000 ....
(Intertrack a/o) - P36-0032 - the only private steam locomotive operated in Russia. Owned by GW Travel.
- P36-0050 - KorostenKorostenKorosten is a historic city and a large railway node in the Zhytomyr Oblast of northern Ukraine. Serving as the administrative center of the Korosten Raion , the city itself is also designated as a separate raion within the oblast, and is located on the Uzh River.The city was founded over a...
depot (Belarus Railways) - P36-0058 - Zlatoust (Intertrack a/o)
- P36-0062 - Sibirtsevo Station
- P36-0064 - BrestBrest, BelarusBrest , formerly also Brest-on-the-Bug and Brest-Litovsk , is a city in Belarus at the border with Poland opposite the city of Terespol, where the Bug River and Mukhavets rivers meet...
(Belarus Railways) - P36-0071 - Zlatoust (Intertrack a/o and Steam Traction)
- P36-0086 - Zlatoust (Intertrack a/o)
- P36-0091 - Skovorodino station
- P36-0094 - Belogorsk station
- P36-0097 - Zlatoust (Intertrack a/o)
- P36-0107 - Park near IrkutskIrkutskIrkutsk is a city and the administrative center of Irkutsk Oblast, Russia, one of the largest cities in Siberia. Population: .-History:In 1652, Ivan Pokhabov built a zimovye near the site of Irkutsk for gold trading and for the collection of fur taxes from the Buryats. In 1661, Yakov Pokhabov...
- P36-0110 - Mogzhon station
- P36-0111 - OrshaOrshaOrsha is a city in Belarus in Vitebsk voblast on the fork of the Dnieper and Arshytsa rivers.-Facts:*Location: *Population: 125,000 *Phone code: +375 216*Postal codes: 211030, 211381–211394, 211396–211398-History:...
station, BelarusBelarusBelarus , officially the Republic of Belarus, is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe, bordered clockwise by Russia to the northeast, Ukraine to the south, Poland to the west, and Lithuania and Latvia to the northwest. Its capital is Minsk; other major cities include Brest, Grodno , Gomel ,... - P36-0120 - named after Ilicha depot, Moscow
- P36-0123 - Shushary Railway Museum, St.Petersburg (TsMOZhD)
- P36-0124 - Chernyshevsk depot
- P36-0147 - Sharja station
- P36-0164 - Zlatoust (Intertrack a/o)
- P36-0182 - Zlatoust (Intertrack a/o)
- P36-0192 - Taiga station
- P36-0218 - Tihoretsk depot, Northern Caucasus, (Veltour s/p)
- P36-0228 - Uulan Baatar Railway Museum, MongoliaMongoliaMongolia is a landlocked country in East and Central Asia. It is bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south, east and west. Although Mongolia does not share a border with Kazakhstan, its western-most point is only from Kazakhstan's eastern tip. Ulan Bator, the capital and largest...
- P36-0232 - Zlatoust (Intertrack a/o)
- P36-0249 - Babaevo (TsMZhT)
- P36-0250 - TashkentTashkentTashkent is the capital of Uzbekistan and of the Tashkent Province. The officially registered population of the city in 2008 was about 2.2 million. Unofficial sources estimate the actual population may be as much as 4.45 million.-Early Islamic History:...
Railway Museum, UzbekistanUzbekistanUzbekistan , officially the Republic of Uzbekistan is a doubly landlocked country in Central Asia and one of the six independent Turkic states. It shares borders with Kazakhstan to the west and to the north, Kyrgyzstan and Tajikistan to the east, and Afghanistan and Turkmenistan to the south.... - P36-0251 - Shushary Railway Museum, St. Petersburg
RENFE242F-2009. Retired in 1973,restored in 1989 and another time in 2005. Altougth she is in running order, usually is in static display at Museo Nacional Feroviario from Madrid-Delicias

