
Engineering
Encyclopedia

Science
Science is a systematic enterprise that builds and organizes knowledge in the form of testable explanations and predictions about the universe...
, mathematical
Mathematics
Mathematics is the study of quantity, space, structure, and change. Mathematicians seek out patterns and formulate new conjectures. Mathematicians resolve the truth or falsity of conjectures by mathematical proofs, which are arguments sufficient to convince other mathematicians of their validity...
, economic
Economics
Economics is the social science that analyzes the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services. The term economics comes from the Ancient Greek from + , hence "rules of the house"...
, social, and practical knowledge, in order to design
Design
Design as a noun informally refers to a plan or convention for the construction of an object or a system while “to design” refers to making this plan...
and build structures, machines, devices, systems, materials and processes
Process (engineering)
In engineering a process is a set of interrelated tasks that, together, transform inputs into outputs. These tasks may be carried out by people, nature, or machines using resources; so an engineering process must be considered in the context of the agents carrying out the tasks, and the resource...
that safely realize improvements to the lives of people.
The American Engineers' Council for Professional Development
American Engineers' Council for Professional Development
The American Engineers' Council for Professional Development or simply the Engineers' Council for Professional Development , established in June 1932, was an engineering professional body dedicated to the education, accreditation, regulation and professional development of the engineering...
(ECPD, the predecessor of ABET
Accreditation Board for Engineering and Technology
ABET, Inc., formerly the Accreditation Board for Engineering and Technology, is a non-profit organization that accredits post-secondary education programs in applied science, computing, engineering, and technology...
) has defined "engineering" as:
the creative application of scientific principles to design or develop structures, machines, apparatus, or manufacturing processes, or works utilizing them singly or in combination; or to construct or operate the same with full cognizance of their design; or to forecast their behavior under specific operating conditions; all as respects an intended function, economics of operation and safety to life and property.
One who practices engineering is called an engineer
Engineer
An engineer is a professional practitioner of engineering, concerned with applying scientific knowledge, mathematics and ingenuity to develop solutions for technical problems. Engineers design materials, structures, machines and systems while considering the limitations imposed by practicality,...
, and those licensed to do so may have more formal designations such as Professional Engineer
Professional Engineer
Regulation of the engineering profession is established by various jurisdictions of the world to protect the safety, well-being and other interests of the general public, and to define the licensure process through which an engineer becomes authorized to provide professional services to the...
, Chartered Engineer, Incorporated Engineer, Ingenieur or European Engineer
European Engineer
European Engineer is an international professional qualification for engineers used in over 30 European countries. The title is granted after successful application to a national member of the European Federation of National Engineering Associations which includes representation from many...
. The broad discipline of engineering encompasses a range of more specialized sub disciplines, each with a more specific emphasis on certain fields of application and particular areas of technology.
History
Engineering has existed since ancient times as humans devised fundamental inventions such as the pulley, lever, and wheel. Each of these inventions is consistent with the modern definition of engineering, exploiting basic mechanical principles to develop useful tools and objects.The term engineering itself has a much more recent etymology, deriving from the word engineer, which itself dates back to 1325, when an engine’er (literally, one who operates an engine) originally referred to “a constructor of military engines.” In this context, now obsolete, an “engine” referred to a military machine, i.e., a mechanical contraption used in war (for example, a catapult
Catapult
A catapult is a device used to throw or hurl a projectile a great distance without the aid of explosive devices—particularly various types of ancient and medieval siege engines. Although the catapult has been used since ancient times, it has proven to be one of the most effective mechanisms during...
). Notable exceptions of the obsolete usage which have survived to the present day are military engineering corps, e.g., the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers
United States Army Corps of Engineers
The United States Army Corps of Engineers is a federal agency and a major Army command made up of some 38,000 civilian and military personnel, making it the world's largest public engineering, design and construction management agency...
.
The word “engine” itself is of even older origin, ultimately deriving from the Latin
Latin
Latin is an Italic language originally spoken in Latium and Ancient Rome. It, along with most European languages, is a descendant of the ancient Proto-Indo-European language. Although it is considered a dead language, a number of scholars and members of the Christian clergy speak it fluently, and...
ingenium (c. 1250), meaning “innate quality, especially mental power, hence a clever invention.”
Later, as the design of civilian structures such as bridges and buildings matured as a technical discipline, the term civil engineering
Civil engineering
Civil engineering is a professional engineering discipline that deals with the design, construction, and maintenance of the physical and naturally built environment, including works like roads, bridges, canals, dams, and buildings...
entered the lexicon as a way to distinguish between those specializing in the construction of such non-military projects and those involved in the older discipline of military engineering.
Ancient era
The Pharos of Alexandria, the pyramidEgyptian pyramids
The Egyptian pyramids are ancient pyramid-shaped masonry structures located in Egypt.There are 138 pyramids discovered in Egypt as of 2008. Most were built as tombs for the country's Pharaohs and their consorts during the Old and Middle Kingdom periods.The earliest known Egyptian pyramids are found...
s in Egypt
Egypt
Egypt , officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, Arabic: , is a country mainly in North Africa, with the Sinai Peninsula forming a land bridge in Southwest Asia. Egypt is thus a transcontinental country, and a major power in Africa, the Mediterranean Basin, the Middle East and the Muslim world...
, the Hanging Gardens of Babylon
Hanging Gardens of Babylon
The Hanging Gardens of Babylon were considered to be one of the greatest Seven Wonders of the Ancient World, and the only one of the Wonders which may in fact have been legendary. They were purportedly built in the ancient city-state of Babylon, near present-day Al Hillah, Babil, in Iraq...
, the Acropolis
Acropolis of Athens
The Acropolis of Athens or Citadel of Athens is the best known acropolis in the world. Although there are many other acropoleis in Greece, the significance of the Acropolis of Athens is such that it is commonly known as The Acropolis without qualification...
and the Parthenon
Parthenon
The Parthenon is a temple on the Athenian Acropolis, Greece, dedicated to the Greek goddess Athena, whom the people of Athens considered their virgin patron. Its construction began in 447 BC when the Athenian Empire was at the height of its power. It was completed in 438 BC, although...
in Greece
Greece
Greece , officially the Hellenic Republic , and historically Hellas or the Republic of Greece in English, is a country in southeastern Europe....
, the Roman
Ancient Rome
Ancient Rome was a thriving civilization that grew on the Italian Peninsula as early as the 8th century BC. Located along the Mediterranean Sea and centered on the city of Rome, it expanded to one of the largest empires in the ancient world....
aqueduct
Aqueduct
An aqueduct is a water supply or navigable channel constructed to convey water. In modern engineering, the term is used for any system of pipes, ditches, canals, tunnels, and other structures used for this purpose....
s, Via Appia and the Colosseum
Colosseum
The Colosseum, or the Coliseum, originally the Flavian Amphitheatre , is an elliptical amphitheatre in the centre of the city of Rome, Italy, the largest ever built in the Roman Empire...
, Teotihuacán
Teotihuacán
Teotihuacan – also written Teotihuacán, with a Spanish orthographic accent on the last syllable – is an enormous archaeological site in the Basin of Mexico, just 30 miles northeast of Mexico City, containing some of the largest pyramidal structures built in the pre-Columbian Americas...
and the cities and pyramids of the Mayan
Maya civilization
The Maya is a Mesoamerican civilization, noted for the only known fully developed written language of the pre-Columbian Americas, as well as for its art, architecture, and mathematical and astronomical systems. Initially established during the Pre-Classic period The Maya is a Mesoamerican...
, Inca and Aztec
Aztec
The Aztec people were certain ethnic groups of central Mexico, particularly those groups who spoke the Nahuatl language and who dominated large parts of Mesoamerica in the 14th, 15th and 16th centuries, a period referred to as the late post-classic period in Mesoamerican chronology.Aztec is the...
Empires, the Great Wall of China
Great Wall of China
The Great Wall of China is a series of stone and earthen fortifications in northern China, built originally to protect the northern borders of the Chinese Empire against intrusions by various nomadic groups...
, among many others, stand as a testament to the ingenuity and skill of the ancient civil and military engineers.
The earliest civil engineer known by name is Imhotep
Imhotep
Imhotep , fl. 27th century BC was an Egyptian polymath, who served under the Third Dynasty king Djoser as chancellor to the pharaoh and high priest of the sun god Ra at Heliopolis...
. As one of the officials of the Pharaoh
Pharaoh
Pharaoh is a title used in many modern discussions of the ancient Egyptian rulers of all periods. The title originates in the term "pr-aa" which means "great house" and describes the royal palace...
, Djosèr
Djoser
Netjerikhet or Djoser is the best-known pharaoh of the Third dynasty of Egypt. He commissioned his official, Imhotep, to build the first of the pyramids, a step pyramid for him at Saqqara...
, he probably designed and supervised the construction of the Pyramid of Djoser
Pyramid of Djoser
The Pyramid of Djoser , or step pyramid is an archeological remain in the Saqqara necropolis, Egypt, northwest of the city of Memphis. It was built during the 27th century BC for the burial of Pharaoh Djoser by Imhotep, his vizier...
(the Step Pyramid
Step pyramid
Step pyramids are structures which characterized several cultures throughout history, in several locations throughout the world. These pyramids typically are large and made of several layers of stone...
) at Saqqara
Saqqara
Saqqara is a vast, ancient burial ground in Egypt, serving as the necropolis for the Ancient Egyptian capital, Memphis. Saqqara features numerous pyramids, including the world famous Step pyramid of Djoser, sometimes referred to as the Step Tomb due to its rectangular base, as well as a number of...
in Egypt
History of Ancient Egypt
The History of Ancient Egypt spans the period from the early predynastic settlements of the northern Nile Valley to the Roman conquest in 30 BC...
around 2630
27th century BC
The 27th century BC is a century which lasted from the year 2700 BC to 2601 BC.-Events:*2900 BC – 2334 BC: Mesopotamian wars of the Early Dynastic period.*2775 BC – 2650 BC: Second Dynasty wars in Egypt....
-2611 BC
27th century BC
The 27th century BC is a century which lasted from the year 2700 BC to 2601 BC.-Events:*2900 BC – 2334 BC: Mesopotamian wars of the Early Dynastic period.*2775 BC – 2650 BC: Second Dynasty wars in Egypt....
. He may also have been responsible for the first known use of column
Column
A column or pillar in architecture and structural engineering is a vertical structural element that transmits, through compression, the weight of the structure above to other structural elements below. For the purpose of wind or earthquake engineering, columns may be designed to resist lateral forces...
s in architecture
Architecture
Architecture is both the process and product of planning, designing and construction. Architectural works, in the material form of buildings, are often perceived as cultural and political symbols and as works of art...
.
Ancient Greece
Ancient Greece
Ancient Greece is a civilization belonging to a period of Greek history that lasted from the Archaic period of the 8th to 6th centuries BC to the end of antiquity. Immediately following this period was the beginning of the Early Middle Ages and the Byzantine era. Included in Ancient Greece is the...
developed machines in both the civilian and military domains. The Antikythera mechanism
Antikythera mechanism
The Antikythera mechanism is an ancient mechanical computer designed to calculate astronomical positions. It was recovered in 1900–1901 from the Antikythera wreck. Its significance and complexity were not understood until decades later. Its time of construction is now estimated between 150 and 100...
, the first known mechanical computer
Analog computer
An analog computer is a form of computer that uses the continuously-changeable aspects of physical phenomena such as electrical, mechanical, or hydraulic quantities to model the problem being solved...
, and the mechanical inventions of Archimedes
Archimedes
Archimedes of Syracuse was a Greek mathematician, physicist, engineer, inventor, and astronomer. Although few details of his life are known, he is regarded as one of the leading scientists in classical antiquity. Among his advances in physics are the foundations of hydrostatics, statics and an...
are examples of early mechanical engineering. Some of Archimedes' inventions as well as the Antikythera mechanism required sophisticated knowledge of differential gearing or epicyclic gearing
Epicyclic gearing
Epicyclic gearing or planetary gearing is a gear system consisting of one or more outer gears, or planet gears, revolving about a central, or sun gear. Typically, the planet gears are mounted on a movable arm or carrier which itself may rotate relative to the sun gear...
, two key principles in machine theory that helped design the gear train
Gear train
A gear train is formed by mounting gears on a frame so that the teeth of the gears engage. Gear teeth are designed to ensure the pitch circles of engaging gears roll on each other without slipping, this provides a smooth transmission of rotation from one gear to the next.The transmission of...
s of the Industrial revolution, and are still widely used today in diverse fields such as robotics
Robotics
Robotics is the branch of technology that deals with the design, construction, operation, structural disposition, manufacture and application of robots...
and automotive engineering
Automotive engineering
Modern automotive engineering, along with aerospace engineering and marine engineering, is a branch of vehicle engineering, incorporating elements of mechanical, electrical, electronic, software and safety engineering as applied to the design, manufacture and operation of motorcycles, automobiles,...
.
Chinese, Greek and Roman armies employed complex military machines and inventions such as artillery
Artillery
Originally applied to any group of infantry primarily armed with projectile weapons, artillery has over time become limited in meaning to refer only to those engines of war that operate by projection of munitions far beyond the range of effect of personal weapons...
which was developed by the Greeks around the 4th century B.C., the trireme
Trireme
A trireme was a type of galley, a Hellenistic-era warship that was used by the ancient maritime civilizations of the Mediterranean, especially the Phoenicians, ancient Greeks and Romans.The trireme derives its name from its three rows of oars on each side, manned with one man per oar...
, the ballista
Ballista
The ballista , plural ballistae, was an ancient missile weapon which launched a large projectile at a distant target....
and the catapult
Catapult
A catapult is a device used to throw or hurl a projectile a great distance without the aid of explosive devices—particularly various types of ancient and medieval siege engines. Although the catapult has been used since ancient times, it has proven to be one of the most effective mechanisms during...
. In the Middle Ages, the Trebuchet
Trebuchet
A trebuchet is a siege engine that was employed in the Middle Ages. It is sometimes called a "counterweight trebuchet" or "counterpoise trebuchet" in order to distinguish it from an earlier weapon that has come to be called the "traction trebuchet", the original version with pulling men instead of...
was developed.
Renaissance era
The first electrical engineer is considered to be William Gilbert, with his 1600 publication of De MagneteDe Magnete
De Magnete, Magneticisque Corporibus, et de Magno Magnete Tellure is a scientific work published in 1600 by the English physician and scientist William Gilbert and his partner Aaron Dowling...
, who was the originator of the term "electricity
Electricity
Electricity is a general term encompassing a variety of phenomena resulting from the presence and flow of electric charge. These include many easily recognizable phenomena, such as lightning, static electricity, and the flow of electrical current in an electrical wire...
".
The first steam engine
Steam engine
A steam engine is a heat engine that performs mechanical work using steam as its working fluid.Steam engines are external combustion engines, where the working fluid is separate from the combustion products. Non-combustion heat sources such as solar power, nuclear power or geothermal energy may be...
was built in 1698 by mechanical engineer Thomas Savery
Thomas Savery
Thomas Savery was an English inventor, born at Shilstone, a manor house near Modbury, Devon, England.-Career:Savery became a military engineer, rising to the rank of Captain by 1702, and spent his free time performing experiments in mechanics...
. The development of this device gave rise to the industrial revolution
Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution was a period from the 18th to the 19th century where major changes in agriculture, manufacturing, mining, transportation, and technology had a profound effect on the social, economic and cultural conditions of the times...
in the coming decades, allowing for the beginnings of mass production
Mass production
Mass production is the production of large amounts of standardized products, including and especially on assembly lines...
.
With the rise of engineering as a profession
Profession
A profession is a vocation founded upon specialized educational training, the purpose of which is to supply disinterested counsel and service to others, for a direct and definite compensation, wholly apart from expectation of other business gain....
in the eighteenth century, the term became more narrowly applied to fields in which mathematics and science were applied to these ends. Similarly, in addition to military and civil engineering the fields then known as the mechanic arts
Mechanic arts
Mechanic arts is an obsolete and archaic term. In the medieval period, the Seven Mechanical Arts were intended as a complement to the Seven Liberal Arts, and consisted of weaving, blacksmithing, war, navigation, agriculture, hunting, medicine, and the ars theatrica. In the 19th century it referred...
became incorporated into engineering.
Modern era
Electrical engineeringElectrical engineering
Electrical engineering is a field of engineering that generally deals with the study and application of electricity, electronics and electromagnetism. The field first became an identifiable occupation in the late nineteenth century after commercialization of the electric telegraph and electrical...
can trace its origins in the experiments of Alessandro Volta
Alessandro Volta
Count Alessandro Giuseppe Antonio Anastasio Gerolamo Umberto Volta was a Lombard physicist known especially for the invention of the battery in 1800.-Early life and works:...
in the 1800s, the experiments of Michael Faraday
Michael Faraday
Michael Faraday, FRS was an English chemist and physicist who contributed to the fields of electromagnetism and electrochemistry....
, Georg Ohm
Georg Ohm
Georg Simon Ohm was a German physicist. As a high school teacher, Ohm began his research with the recently-invented electrochemical cell, invented by Italian Count Alessandro Volta. Using equipment of his own creation, Ohm determined that there is a direct proportionality between the potential...
and others and the invention of the electric motor
Electric motor
An electric motor converts electrical energy into mechanical energy.Most electric motors operate through the interaction of magnetic fields and current-carrying conductors to generate force...
in 1872. The work of James Maxwell
James Clerk Maxwell
James Clerk Maxwell of Glenlair was a Scottish physicist and mathematician. His most prominent achievement was formulating classical electromagnetic theory. This united all previously unrelated observations, experiments and equations of electricity, magnetism and optics into a consistent theory...
and Heinrich Hertz in the late 19th century gave rise to the field of Electronics
Electronics
Electronics is the branch of science, engineering and technology that deals with electrical circuits involving active electrical components such as vacuum tubes, transistors, diodes and integrated circuits, and associated passive interconnection technologies...
. The later inventions of the vacuum tube
Vacuum tube
In electronics, a vacuum tube, electron tube , or thermionic valve , reduced to simply "tube" or "valve" in everyday parlance, is a device that relies on the flow of electric current through a vacuum...
and the transistor
Transistor
A transistor is a semiconductor device used to amplify and switch electronic signals and power. It is composed of a semiconductor material with at least three terminals for connection to an external circuit. A voltage or current applied to one pair of the transistor's terminals changes the current...
further accelerated the development of electronics to such an extent that electrical and electronics engineers currently outnumber their colleagues of any other Engineering specialty.
The inventions of Thomas Savery and the Scottish engineer James Watt
James Watt
James Watt, FRS, FRSE was a Scottish inventor and mechanical engineer whose improvements to the Newcomen steam engine were fundamental to the changes brought by the Industrial Revolution in both his native Great Britain and the rest of the world.While working as an instrument maker at the...
gave rise to modern Mechanical Engineering
Mechanical engineering
Mechanical engineering is a discipline of engineering that applies the principles of physics and materials science for analysis, design, manufacturing, and maintenance of mechanical systems. It is the branch of engineering that involves the production and usage of heat and mechanical power for the...
. The development of specialized machines and their maintenance tools during the industrial revolution led to the rapid growth of Mechanical Engineering both in its birthplace Britain
Great Britain
Great Britain or Britain is an island situated to the northwest of Continental Europe. It is the ninth largest island in the world, and the largest European island, as well as the largest of the British Isles...
and abroad.
Chemical Engineering
Chemical engineering
Chemical engineering is the branch of engineering that deals with physical science , and life sciences with mathematics and economics, to the process of converting raw materials or chemicals into more useful or valuable forms...
, like its counterpart Mechanical Engineering, developed in the nineteenth century during the Industrial Revolution
Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution was a period from the 18th to the 19th century where major changes in agriculture, manufacturing, mining, transportation, and technology had a profound effect on the social, economic and cultural conditions of the times...
. Industrial scale manufacturing demanded new materials and new processes and by 1880 the need for large scale production of chemicals was such that a new industry was created, dedicated to the development and large scale manufacturing of chemicals in new industrial plants. The role of the chemical engineer was the design of these chemical plants and processes.
Aeronautical Engineering deals with aircraft
Aircraft
An aircraft is a vehicle that is able to fly by gaining support from the air, or, in general, the atmosphere of a planet. An aircraft counters the force of gravity by using either static lift or by using the dynamic lift of an airfoil, or in a few cases the downward thrust from jet engines.Although...
design while Aerospace Engineering
Aerospace engineering
Aerospace engineering is the primary branch of engineering concerned with the design, construction and science of aircraft and spacecraft. It is divided into two major and overlapping branches: aeronautical engineering and astronautical engineering...
is a more modern term that expands the reach envelope of the discipline by including spacecraft
Spacecraft
A spacecraft or spaceship is a craft or machine designed for spaceflight. Spacecraft are used for a variety of purposes, including communications, earth observation, meteorology, navigation, planetary exploration and transportation of humans and cargo....
design. Its origins can be traced back to the aviation pioneers around the turn of the century from the 19th century to the 20th although the work of Sir George Cayley has recently been dated as being from the last decade of the 18th century. Early knowledge of aeronautical engineering was largely empirical with some concepts and skills imported from other branches of engineering.
The first PhD
Doctor of Philosophy
Doctor of Philosophy, abbreviated as Ph.D., PhD, D.Phil., or DPhil , in English-speaking countries, is a postgraduate academic degree awarded by universities...
in engineering (technically, applied science and engineering) awarded in the United States went to Willard Gibbs at Yale University
Yale University
Yale University is a private, Ivy League university located in New Haven, Connecticut, United States. Founded in 1701 in the Colony of Connecticut, the university is the third-oldest institution of higher education in the United States...
in 1863; it was also the second PhD awarded in science in the U.S.
Only a decade after the successful flights by the Wright brothers
Wright brothers
The Wright brothers, Orville and Wilbur , were two Americans credited with inventing and building the world's first successful airplane and making the first controlled, powered and sustained heavier-than-air human flight, on December 17, 1903...
, there was extensive development of aeronautical engineering through development of military aircraft that were used in World War I
World War I
World War I , which was predominantly called the World War or the Great War from its occurrence until 1939, and the First World War or World War I thereafter, was a major war centred in Europe that began on 28 July 1914 and lasted until 11 November 1918...
. Meanwhile, research to provide fundamental background science continued by combining theoretical physics
Theoretical physics
Theoretical physics is a branch of physics which employs mathematical models and abstractions of physics to rationalize, explain and predict natural phenomena...
with experiments.
In 1990, with the rise of computer
Computer
A computer is a programmable machine designed to sequentially and automatically carry out a sequence of arithmetic or logical operations. The particular sequence of operations can be changed readily, allowing the computer to solve more than one kind of problem...
technology, the first search engine was built by computer engineer Alan Emtage
Alan Emtage
Alan Emtage conceived and implemented the first version of Archie, a pre-Web internet search engine for locating material in public FTP archives....
.
Main branches of engineering
Engineering, much like other science, is a broad discipline which is often broken down into several sub-disciplines. These disciplines concern themselves with differing areas of engineering work. Although initially an engineer will usually be trained in a specific discipline, throughout an engineer's career the engineer may become multi-disciplined, having worked in several of the outlined areas. Engineering is often characterized as having four main branches:- Chemical engineeringChemical engineeringChemical engineering is the branch of engineering that deals with physical science , and life sciences with mathematics and economics, to the process of converting raw materials or chemicals into more useful or valuable forms...
– The exploitation of both engineering and chemical principles in order to carry out large scale chemical process. - Civil engineeringCivil engineeringCivil engineering is a professional engineering discipline that deals with the design, construction, and maintenance of the physical and naturally built environment, including works like roads, bridges, canals, dams, and buildings...
– The design and construction of public and private works, such as infrastructureInfrastructureInfrastructure is basic physical and organizational structures needed for the operation of a society or enterprise, or the services and facilities necessary for an economy to function...
(airports, roads, railways, water supply and treatment etc.), bridgeBridgeA bridge is a structure built to span physical obstacles such as a body of water, valley, or road, for the purpose of providing passage over the obstacle...
s, dams, and buildings. - Electrical engineeringElectrical engineeringElectrical engineering is a field of engineering that generally deals with the study and application of electricity, electronics and electromagnetism. The field first became an identifiable occupation in the late nineteenth century after commercialization of the electric telegraph and electrical...
– a very broad area that may encompass the design and study of various electrical and electronic systems, such as electrical circuits, generatorsElectrical generatorIn electricity generation, an electric generator is a device that converts mechanical energy to electrical energy. A generator forces electric charge to flow through an external electrical circuit. It is analogous to a water pump, which causes water to flow...
, motorsElectric motorAn electric motor converts electrical energy into mechanical energy.Most electric motors operate through the interaction of magnetic fields and current-carrying conductors to generate force...
, electromagneticElectromagnetismElectromagnetism is one of the four fundamental interactions in nature. The other three are the strong interaction, the weak interaction and gravitation...
/electromechanical devices, electronic devices, electronic circuits, optical fiberOptical fiberAn optical fiber is a flexible, transparent fiber made of a pure glass not much wider than a human hair. It functions as a waveguide, or "light pipe", to transmit light between the two ends of the fiber. The field of applied science and engineering concerned with the design and application of...
s, optoelectronic devices, computerComputerA computer is a programmable machine designed to sequentially and automatically carry out a sequence of arithmetic or logical operations. The particular sequence of operations can be changed readily, allowing the computer to solve more than one kind of problem...
systems, telecommunications, instrumentation, controls, and electronicsElectronicsElectronics is the branch of science, engineering and technology that deals with electrical circuits involving active electrical components such as vacuum tubes, transistors, diodes and integrated circuits, and associated passive interconnection technologies...
. - Mechanical engineeringMechanical engineeringMechanical engineering is a discipline of engineering that applies the principles of physics and materials science for analysis, design, manufacturing, and maintenance of mechanical systems. It is the branch of engineering that involves the production and usage of heat and mechanical power for the...
– The design of physical or mechanical systems, such as power and energyEnergyIn physics, energy is an indirectly observed quantity. It is often understood as the ability a physical system has to do work on other physical systems...
systems, aerospaceAerospaceAerospace comprises the atmosphere of Earth and surrounding space. Typically the term is used to refer to the industry that researches, designs, manufactures, operates, and maintains vehicles moving through air and space...
/aircraftAircraftAn aircraft is a vehicle that is able to fly by gaining support from the air, or, in general, the atmosphere of a planet. An aircraft counters the force of gravity by using either static lift or by using the dynamic lift of an airfoil, or in a few cases the downward thrust from jet engines.Although...
products, weapon systems, transportation products engineInternal combustion engineThe internal combustion engine is an engine in which the combustion of a fuel occurs with an oxidizer in a combustion chamber. In an internal combustion engine, the expansion of the high-temperature and high -pressure gases produced by combustion apply direct force to some component of the engine...
s, compressorsGas compressorA gas compressor is a mechanical device that increases the pressure of a gas by reducing its volume.Compressors are similar to pumps: both increase the pressure on a fluid and both can transport the fluid through a pipe. As gases are compressible, the compressor also reduces the volume of a gas...
, powertrainPowertrainIn a motor vehicle, the term powertrain or powerplant refers to the group of components that generate power and deliver it to the road surface, water, or air. This includes the engine, transmission, drive shafts, differentials, and the final drive...
s, kinematic chainKinematic chainA kinematic chain is the assembly of several kinematic pairs connecting rigid body segments. The complexity of the chain is determined by the following factors:...
s, vacuum technology, and vibration isolationVibration isolationVibration isolation is the process of isolating an object, such as a piece of equipment, from the source of vibrations.-Passive isolation:Passive vibration isolation systems consist essentially of a mass, spring and damper ....
equipment.
Beyond these four, sources vary on other main branches. Historically, naval engineering
Naval architecture
Naval architecture is an engineering discipline dealing with the design, construction, maintenance and operation of marine vessels and structures. Naval architecture involves basic and applied research, design, development, design evaluation and calculations during all stages of the life of a...
and mining engineering
Mining engineering
Mining engineering is an engineering discipline that involves the practice, the theory, the science, the technology, and application of extracting and processing minerals from a naturally occurring environment. Mining engineering also includes processing minerals for additional value.Mineral...
were major branches. Modern fields sometimes included as major branches include aerospace
Aerospace engineering
Aerospace engineering is the primary branch of engineering concerned with the design, construction and science of aircraft and spacecraft. It is divided into two major and overlapping branches: aeronautical engineering and astronautical engineering...
, architectural
Architectural engineering
Architectural engineering, also known as building engineering, is the application of engineering principles and technology to building design and construction...
, biomedical
Biomedical engineering
Biomedical Engineering is the application of engineering principles and design concepts to medicine and biology. This field seeks to close the gap between engineering and medicine: It combines the design and problem solving skills of engineering with medical and biological sciences to improve...
, industrial
Industrial engineering
Industrial engineering is a branch of engineering dealing with the optimization of complex processes or systems. It is concerned with the development, improvement, implementation and evaluation of integrated systems of people, money, knowledge, information, equipment, energy, materials, analysis...
, materials science
Materials science
Materials science is an interdisciplinary field applying the properties of matter to various areas of science and engineering. This scientific field investigates the relationship between the structure of materials at atomic or molecular scales and their macroscopic properties. It incorporates...
and nuclear engineering
Nuclear engineering
Nuclear engineering is the branch of engineering concerned with the application of the breakdown as well as the fusion of atomic nuclei and/or the application of other sub-atomic physics, based on the principles of nuclear physics...
.
New specialties sometimes combine with the traditional fields and form new branches. A new or emerging area of application will commonly be defined temporarily as a permutation or subset of existing disciplines; there is often gray area as to when a given sub-field becomes large and/or prominent enough to warrant classification as a new "branch." One key indicator of such emergence is when major universities start establishing departments and programs in the new field.
For each of these fields there exists considerable overlap, especially in the areas of the application of sciences to their disciplines such as physics, chemistry and mathematics.
Methodology

If multiple options exist, engineers weigh different design choices on their merits and choose the solution that best matches the requirements. The crucial and unique task of the engineer is to identify, understand, and interpret the constraints on a design in order to produce a successful result. It is usually not enough to build a technically successful product; it must also meet further requirements.
Constraints may include available resources, physical, imaginative or technical limitations, flexibility for future modifications and additions, and other factors, such as requirements for cost, safety
Safety engineering
Safety engineering is an applied science strongly related to systems engineering / industrial engineering and the subset System Safety Engineering...
, marketability, productibility, and serviceability
Serviceability (computer)
In software engineering and hardware engineering, serviceability is one of the -ilities or aspects...
. By understanding the constraints, engineers derive specifications for the limits within which a viable object or system may be produced and operated.
Problem solving
Engineers use their knowledge of scienceScience
Science is a systematic enterprise that builds and organizes knowledge in the form of testable explanations and predictions about the universe...
, mathematics
Mathematics
Mathematics is the study of quantity, space, structure, and change. Mathematicians seek out patterns and formulate new conjectures. Mathematicians resolve the truth or falsity of conjectures by mathematical proofs, which are arguments sufficient to convince other mathematicians of their validity...
, logic
Logic
In philosophy, Logic is the formal systematic study of the principles of valid inference and correct reasoning. Logic is used in most intellectual activities, but is studied primarily in the disciplines of philosophy, mathematics, semantics, and computer science...
, economics
Economics
Economics is the social science that analyzes the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services. The term economics comes from the Ancient Greek from + , hence "rules of the house"...
, and appropriate experience or tacit knowledge
Tacit knowledge
Tacit knowledge is knowledge that is difficult to transfer to another person by means of writing it down or verbalising it. For example, stating to someone that London is in the United Kingdom is a piece of explicit knowledge that can be written down, transmitted, and understood by a recipient...
to find suitable solutions to a problem. Creating an appropriate mathematical model
Mathematical model
A mathematical model is a description of a system using mathematical concepts and language. The process of developing a mathematical model is termed mathematical modeling. Mathematical models are used not only in the natural sciences and engineering disciplines A mathematical model is a...
of a problem allows them to analyze it (sometimes definitively), and to test potential solutions.
Usually multiple reasonable solutions exist, so engineers must evaluate the different design choice
Design choice
In engineering, a design choice is a possible solution to a problem. Given a design task and a governing set of criteria , several conceptual designs may be drafted. Each of these preliminary concepts is a potential design choice...
s on their merits and choose the solution that best meets their requirements. Genrich Altshuller
Genrich Altshuller
Genrikh Saulovich Altshuller , was a Soviet engineer, inventor, scientist, journalist and writer. He is most notable for the creation of the Theory of Inventive Problem Solving, better known by its Russia acronym TRIZ...
, after gathering statistics on a large number of patent
Patent
A patent is a form of intellectual property. It consists of a set of exclusive rights granted by a sovereign state to an inventor or their assignee for a limited period of time in exchange for the public disclosure of an invention....
s, suggested that compromise
Compromise
To compromise is to make a deal where one person gives up part of his or her demand.In arguments, compromise is a concept of finding agreement through communication, through a mutual acceptance of terms—often involving variations from an original goal or desire.Extremism is often considered as...
s are at the heart of "low-level
Level of Invention
Level of invention is a relative degree of changes to the previous system in the result of solution of inventive problem . Term was defined and introduced by TRIZ author G. S...
" engineering designs, while at a higher level the best design is one which eliminates the core contradiction causing the problem.
Engineers typically attempt to predict how well their designs will perform to their specifications prior to full-scale production. They use, among other things: prototype
Prototype
A prototype is an early sample or model built to test a concept or process or to act as a thing to be replicated or learned from.The word prototype derives from the Greek πρωτότυπον , "primitive form", neutral of πρωτότυπος , "original, primitive", from πρῶτος , "first" and τύπος ,...
s, scale model
Scale model
A scale model is a physical model, a representation or copy of an object that is larger or smaller than the actual size of the object, which seeks to maintain the relative proportions of the physical size of the original object. Very often the scale model is used as a guide to making the object in...
s, simulation
Simulation
Simulation is the imitation of some real thing available, state of affairs, or process. The act of simulating something generally entails representing certain key characteristics or behaviours of a selected physical or abstract system....
s, destructive test
Destructive testing
In destructive testing, tests are carried out to the specimen's failure, in order to understand a specimen's structural performance or material behaviour under different loads...
s, nondestructive tests
Nondestructive testing
Nondestructive testing or Non-destructive testing is a wide group of analysis techniques used in science and industry to evaluate the properties of a material, component or system without causing damage....
, and stress tests
Stress testing
Stress testing is a form of testing that is used to determine the stability of a given system or entity. It involves testing beyond normal operational capacity, often to a breaking point, in order to observe the results...
. Testing ensures that products will perform as expected.
Engineers take on the responsibility of producing designs that will perform as well as expected and will not cause unintended harm to the public at large. Engineers typically include a factor of safety
Factor of safety
Factor of safety , also known as safety factor , is a term describing the structural capacity of a system beyond the expected loads or actual loads. Essentially, how much stronger the system is than it usually needs to be for an intended load...
in their designs to reduce the risk of unexpected failure. However, the greater the safety factor, the less efficient the design may be.
The study of failed products is known as forensic engineering
Forensic engineering
Forensic engineering is the investigation of materials, products, structures or components that fail or do not operate or function as intended, causing personal injury or damage to property. The consequences of failure are dealt with by the law of product liability. The field also deals with...
, and can help the product design
Product design
-Introduction:Product design is the process of creating a new product to be sold by a business or enterprise to its customers. It is concerned with the efficient and effective generation and development of ideas through a process that leads to new products.Product designers conceptualize and...
er in evaluating his or her design in the light of real conditions. The discipline is of greatest value after disasters, such as bridge collapses, when careful analysis is needed to establish the cause or causes of the failure.
Computer use
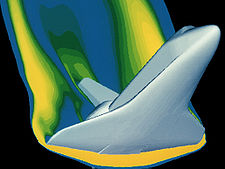
Application software
Application software, also known as an application or an "app", is computer software designed to help the user to perform specific tasks. Examples include enterprise software, accounting software, office suites, graphics software and media players. Many application programs deal principally with...
there are a number of computer aided applications (Computer-aided technologies
CAx
Computer-aided technologies is a broad term that means the use of computer technology to aid in the design, analysis, and manufacture of products....
) specifically for engineering. Computers can be used to generate models of fundamental physical processes, which can be solved using numerical methods.
One of the most widely used tools in the profession is computer-aided design
Computer-aided design
Computer-aided design , also known as computer-aided design and drafting , is the use of computer technology for the process of design and design-documentation. Computer Aided Drafting describes the process of drafting with a computer...
(CAD) software which enables engineers to create 3D models, 2D drawings, and schematics of their designs. CAD together with Digital mockup
Digital mockup
Digital MockUp or DMU is a concept that allows the description of a product, usually in 3D, for its entire life cycle. Digital Mockup is enriched by all the activities that contribute to describing the product. The product design engineers, the manufacturing engineers, and the support engineers...
(DMU) and CAE
Computer-aided engineering
Computer-aided engineering is the broad usage of computer software to aid in engineering tasks. It includes computer-aided design , computer-aided analysis , computer-integrated manufacturing , computer-aided manufacturing , material requirements planning , and computer-aided planning .- Overview...
software such as finite element method analysis
Finite element method
The finite element method is a numerical technique for finding approximate solutions of partial differential equations as well as integral equations...
or analytic element method
Analytic element method
The analytic element method is a numerical method used for the solution of partial differential equations. It was initially developed by O.D.L. Strack at the University of Minnesota...
allows engineers to create models of designs that can be analyzed without having to make expensive and time-consuming physical prototypes.
These allow products and components to be checked for flaws; assess fit and assembly; study ergonomics; and to analyze static and dynamic characteristics of systems such as stresses, temperatures, electromagnetic emissions, electrical currents and voltages, digital logic levels, fluid flows, and kinematics. Access and distribution of all this information is generally organized with the use of Product Data Management
Product Data Management
Product data management is the business function often within product lifecycle management that is responsible for the creation, management and publication of product data...
software.
There are also many tools to support specific engineering tasks such as Computer-aided manufacture (CAM) software to generate CNC machining instructions; Manufacturing Process Management
Manufacturing Process Management
Manufacturing process management is a collection of technologies and methods used to define how products are to be manufactured. MPM differs from ERP/MRP which is used to plan the ordering of materials and other resources, set manufacturing schedules, and compile cost data.A cornerstone of MPM is...
software for production engineering; EDA
Electronic design automation
Electronic design automation is a category of software tools for designing electronic systems such as printed circuit boards and integrated circuits...
for printed circuit board
Printed circuit board
A printed circuit board, or PCB, is used to mechanically support and electrically connect electronic components using conductive pathways, tracks or signal traces etched from copper sheets laminated onto a non-conductive substrate. It is also referred to as printed wiring board or etched wiring...
(PCB) and circuit schematic
Schematic
A schematic diagram represents the elements of a system using abstract, graphic symbols rather than realistic pictures. A schematic usually omits all details that are not relevant to the information the schematic is intended to convey, and may add unrealistic elements that aid comprehension...
s for electronic engineers; MRO
Maintenance, Repair and Operations
Maintenance, repair, and operations or maintenance, repair, and overhaul involves fixing any sort of mechanical or electrical device should it become out of order or broken...
applications for maintenance management; and AEC software for civil engineering.
In recent years the use of computer software to aid the development of goods has collectively come to be known as Product Lifecycle Management
Product lifecycle management
In industry, product lifecycle management is the process of managing the entire lifecycle of a product from its conception, through design and manufacture, to service and disposal...
(PLM).
Social context
Engineering is a subject that ranges from large collaborations to small individual projects. Almost all engineering projects are beholden to some sort of financing agency: a company, a set of investors, or a government. The few types of engineering that are minimally constrained by such issues are pro bonoPro bono
Pro bono publico is a Latin phrase generally used to describe professional work undertaken voluntarily and without payment or at a reduced fee as a public service. It is common in the legal profession and is increasingly seen in marketing, technology, and strategy consulting firms...
engineering and open design
Open design
Open design is the development of physical products, machines and systems through use of publicly shared design information. The process is generally facilitated by the Internet and often performed without monetary compensation...
engineering.
By its very nature engineering is bound up with society and human behavior. Every product or construction used by modern society will have been influenced by engineering design. Engineering design is a very powerful tool to make changes to environment, society and economies, and its application brings with it a great responsibility. Many engineering societies
Engineering society
An engineering society is a professional organization for engineers of various disciplines. Some are umbrella type organizations which accept many different disciplines, while others are discipline-specific. Many award professional designations, such as European Engineer, Professional Engineer,...
have established codes of practice and codes of ethics
Engineering ethics
Engineering ethics is the field of applied ethics and system of moral principles that apply to the practice of engineering. The field examines and sets the obligations by engineers to society, to their clients, and to the profession...
to guide members and inform the public at large.
Engineering projects can be subject to controversy. Examples from different engineering disciplines include the development of nuclear weapon
Nuclear weapon
A nuclear weapon is an explosive device that derives its destructive force from nuclear reactions, either fission or a combination of fission and fusion. Both reactions release vast quantities of energy from relatively small amounts of matter. The first fission bomb test released the same amount...
s, the Three Gorges Dam
Three Gorges Dam
The Three Gorges Dam is a hydroelectric dam that spans the Yangtze River by the town of Sandouping, located in the Yiling District of Yichang, in Hubei province, China...
, the design and use of Sport utility vehicle
Sport utility vehicle
A sport utility vehicle is a generic marketing term for a vehicle similar to a station wagon, but built on a light-truck chassis. It is usually equipped with four-wheel drive for on- or off-road ability, and with some pretension or ability to be used as an off-road vehicle. Not all four-wheel...
s and the extraction of oil
Fuel oil
Fuel oil is a fraction obtained from petroleum distillation, either as a distillate or a residue. Broadly speaking, fuel oil is any liquid petroleum product that is burned in a furnace or boiler for the generation of heat or used in an engine for the generation of power, except oils having a flash...
. In response, some western engineering companies have enacted serious corporate and social responsibility
Corporate social responsibility
Corporate social responsibility is a form of corporate self-regulation integrated into a business model...
policies.
Engineering is a key driver of human development. Sub-Saharan Africa in particular has a very small engineering capacity which results in many African nations being unable to develop crucial infrastructure without outside aid. The attainment of many of the Millennium Development Goals
Millennium Development Goals
The Millennium Development Goals are eight international development goals that all 193 United Nations member states and at least 23 international organizations have agreed to achieve by the year 2015...
requires the achievement of sufficient engineering capacity to develop infrastructure and sustainable technological development.
All overseas development and relief NGOs make considerable use of engineers to apply solutions in disaster and development scenarios. A number of charitable organizations aim to use engineering directly for the good of mankind:
- Engineers Without BordersEngineers Without BordersEngineers Without Borders – International is an international association of some national EWB/ISF groups, whose mission is to facilitate collaboration, exchange of information, and assistance among its member groups that have applied to become part of the association...
- Engineers Against PovertyEngineers Against PovertyEngineers Against Poverty is a specialist NGO working in the field of engineering and international development. It was established in 1998 by the UK’s leading professional Engineering Institutions, the Royal Academy of Engineering and the Department for International Development...
- Registered Engineers for Disaster Relief
- Engineers for a Sustainable WorldEngineers for a Sustainable WorldEngineers for a Sustainable World is a national not-for-profit based in Merced, California. ESW is an umbrella organization with chapters established at twenty-seven colleges and universities located primarily in the United States. ESW chapters work on technical engineering projects that have a...
- Engineering for ChangeEngineering for ChangeEngineering for Change is an online platform and international community of engineers, scientists, non-governmental organizations, local community advocates and other innovators working to solve global development problems...
Science
There exists an overlap between the sciences and engineering practice; in engineering, one applies science. Both areas of endeavor rely on accurate observation of materials and phenomena. Both use mathematics and classification criteria to analyze and communicate observations.Scientists may also have to complete engineering tasks, such as designing experimental apparatus or building prototypes. Conversely, in the process of developing technology engineers sometimes find themselves exploring new phenomena, thus becoming, for the moment, scientists.
In the book What Engineers Know and How They Know It
What Engineers Know and How They Know It
What Engineers Know and How they Know It: Analytical Studies from Aeronautical History is a historical reflection on engineering practice in US aeronautics from 1908-1953 written by an accomplished practitioner and instructor...
, Walter Vincenti asserts that engineering research has a character different from that of scientific research. First, it often deals with areas in which the basic physics
Physics
Physics is a natural science that involves the study of matter and its motion through spacetime, along with related concepts such as energy and force. More broadly, it is the general analysis of nature, conducted in order to understand how the universe behaves.Physics is one of the oldest academic...
and/or chemistry
Chemistry
Chemistry is the science of matter, especially its chemical reactions, but also its composition, structure and properties. Chemistry is concerned with atoms and their interactions with other atoms, and particularly with the properties of chemical bonds....
are well understood, but the problems themselves are too complex to solve in an exact manner.
Examples are the use of numerical approximations to the Navier-Stokes equations
Navier-Stokes equations
In physics, the Navier–Stokes equations, named after Claude-Louis Navier and George Gabriel Stokes, describe the motion of fluid substances. These equations arise from applying Newton's second law to fluid motion, together with the assumption that the fluid stress is the sum of a diffusing viscous...
to describe aerodynamic flow over an aircraft, or the use of Miner's rule
Metal Fatigue
Metal Fatigue , is a futuristic science fiction, real-time strategy computer game developed by Zono Incorporated and published by Psygnosis and TalonSoft .-Plot:...
to calculate fatigue damage. Second, engineering research employs many semi-empirical methods that are foreign to pure scientific research, one example being the method of parameter variation.
As stated by Fung et al. in the revision to the classic engineering text, Foundations of Solid Mechanics
Solid mechanics
Solid mechanics is the branch of mechanics, physics, and mathematics that concerns the behavior of solid matter under external actions . It is part of a broader study known as continuum mechanics. One of the most common practical applications of solid mechanics is the Euler-Bernoulli beam equation...
:
"Engineering is quite different from science. Scientists try to understand
nature. Engineers try to make things that do not exist in nature. Engineers
stress invention. To embody an invention the engineer must put his idea in
concrete terms, and design something that people can use. That something
can be a device, a gadget, a material, a method, a computing program, an
innovative experiment, a new solution to a problem, or an improvement on
what is existing. Since a design has to be concrete, it must have its geometry,
dimensions, and characteristic numbers. Almost all engineers working
on new designs find that they do not have all the needed information. Most
often, they are limited by insufficient scientific knowledge. Thus they study
mathematics, physics, chemistry, biology and mechanics. Often they have
to add to the sciences relevant to their profession. Thus engineering sciences
are born."
Although engineering solutions make use of scientific principles, engineers must also take into account safety, efficiency, economy, reliability and constructability or ease of fabrication, as well as legal considerations such as patent infringement or liability in the case of failure of the solution.
Medicine and biology

Medicine
Medicine is the science and art of healing. It encompasses a variety of health care practices evolved to maintain and restore health by the prevention and treatment of illness....
aims to sustain, enhance and even replace functions of the human body
Human body
The human body is the entire structure of a human organism, and consists of a head, neck, torso, two arms and two legs.By the time the human reaches adulthood, the body consists of close to 100 trillion cells, the basic unit of life...
, if necessary, through the use of technology
Technology
Technology is the making, usage, and knowledge of tools, machines, techniques, crafts, systems or methods of organization in order to solve a problem or perform a specific function. It can also refer to the collection of such tools, machinery, and procedures. The word technology comes ;...
.
Modern medicine can replace several of the body's functions through the use of artificial organs and can significantly alter the function of the human body through artificial devices such as, for example, brain implant
Brain implant
Brain implants, often referred to as neural implants, are technological devices that connect directly to a biological subject's brain - usually placed on the surface of the brain, or attached to the brain's cortex...
s and pacemaker
Artificial pacemaker
A pacemaker is a medical device that uses electrical impulses, delivered by electrodes contacting the heart muscles, to regulate the beating of the heart...
s. The fields of Bionics
Bionics
Bionics is the application of biological methods and systems found in nature to the study and design of engineering systems and modern technology.The word bionic was coined by Jack E...
and medical Bionics are dedicated to the study of synthetic implants pertaining to natural systems.
Conversely, some engineering disciplines view the human body as a biological machine worth studying, and are dedicated to emulating many of its functions by replacing biology
Biology
Biology is a natural science concerned with the study of life and living organisms, including their structure, function, growth, origin, evolution, distribution, and taxonomy. Biology is a vast subject containing many subdivisions, topics, and disciplines...
with technology. This has led to fields such as artificial intelligence
Artificial intelligence
Artificial intelligence is the intelligence of machines and the branch of computer science that aims to create it. AI textbooks define the field as "the study and design of intelligent agents" where an intelligent agent is a system that perceives its environment and takes actions that maximize its...
, neural networks
Neural Networks
Neural Networks is the official journal of the three oldest societies dedicated to research in neural networks: International Neural Network Society, European Neural Network Society and Japanese Neural Network Society, published by Elsevier...
, fuzzy logic
Fuzzy logic
Fuzzy logic is a form of many-valued logic; it deals with reasoning that is approximate rather than fixed and exact. In contrast with traditional logic theory, where binary sets have two-valued logic: true or false, fuzzy logic variables may have a truth value that ranges in degree between 0 and 1...
, and robot
Robot
A robot is a mechanical or virtual intelligent agent that can perform tasks automatically or with guidance, typically by remote control. In practice a robot is usually an electro-mechanical machine that is guided by computer and electronic programming. Robots can be autonomous, semi-autonomous or...
ics. There are also substantial interdisciplinary interactions between engineering and medicine.
Both fields provide solutions to real world problems. This often requires moving forward before phenomena are completely understood in a more rigorous scientific sense and therefore experimentation and empirical
Empirical
The word empirical denotes information gained by means of observation or experimentation. Empirical data are data produced by an experiment or observation....
knowledge is an integral part of both.
Medicine, in part, studies the function of the human body. The human body, as a biological machine, has many functions that can be modeled using Engineering methods.
The heart for example functions much like a pump, the skeleton is like a linked structure with levers, the brain produces electrical signal
Signal (electrical engineering)
In the fields of communications, signal processing, and in electrical engineering more generally, a signal is any time-varying or spatial-varying quantity....
s etc. These similarities as well as the increasing importance and application of Engineering principles in Medicine, led to the development of the field of biomedical engineering
Biomedical engineering
Biomedical Engineering is the application of engineering principles and design concepts to medicine and biology. This field seeks to close the gap between engineering and medicine: It combines the design and problem solving skills of engineering with medical and biological sciences to improve...
that uses concepts developed in both disciplines.
Newly emerging branches of science, such as Systems biology
Systems biology
Systems biology is a term used to describe a number of trends in bioscience research, and a movement which draws on those trends. Proponents describe systems biology as a biology-based inter-disciplinary study field that focuses on complex interactions in biological systems, claiming that it uses...
, are adapting analytical tools traditionally used for engineering, such as systems modeling and computational analysis, to the description of biological systems.
Art
they are direct in some fields, for example, architecture
Architecture
Architecture is both the process and product of planning, designing and construction. Architectural works, in the material form of buildings, are often perceived as cultural and political symbols and as works of art...
, landscape architecture
Landscape architecture
Landscape architecture is the design of outdoor and public spaces to achieve environmental, socio-behavioral, or aesthetic outcomes. It involves the systematic investigation of existing social, ecological, and geological conditions and processes in the landscape, and the design of interventions...
and industrial design
Industrial design
Industrial design is the use of a combination of applied art and applied science to improve the aesthetics, ergonomics, and usability of a product, but it may also be used to improve the product's marketability and production...
(even to the extent that these disciplines may sometimes be included in a University's Faculty of Engineering); and indirect in others.
The Art Institute of Chicago
Art Institute of Chicago
The School of the Art Institute of Chicago is one of America's largest accredited independent schools of art and design, located in the Loop in Chicago, Illinois. It is associated with the museum of the same name, and "The Art Institute of Chicago" or "Chicago Art Institute" often refers to either...
, for instance, held an exhibition about the art of NASA
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research...
's aerospace design. Robert Maillart
Robert Maillart
Robert Maillart was a Swiss civil engineer who revolutionized the use of structural reinforced concrete with such designs as the three-hinged arch and the deck-stiffened arch for bridges, and the beamless floor slab and mushroom ceiling for industrial buildings...
's bridge design is perceived by some to have been deliberately artistic. At the University of South Florida
University of South Florida
The University of South Florida, also known as USF, is a member institution of the State University System of Florida, one of the state's three flagship universities for public research, and is located in Tampa, Florida, USA...
, an engineering professor, through a grant with the National Science Foundation
National Science Foundation
The National Science Foundation is a United States government agency that supports fundamental research and education in all the non-medical fields of science and engineering. Its medical counterpart is the National Institutes of Health...
, has developed a course that connects art and engineering.
Among famous historical figures Leonardo Da Vinci
Leonardo da Vinci
Leonardo di ser Piero da Vinci was an Italian Renaissance polymath: painter, sculptor, architect, musician, scientist, mathematician, engineer, inventor, anatomist, geologist, cartographer, botanist and writer whose genius, perhaps more than that of any other figure, epitomized the Renaissance...
is a well known Renaissance
Renaissance
The Renaissance was a cultural movement that spanned roughly the 14th to the 17th century, beginning in Italy in the Late Middle Ages and later spreading to the rest of Europe. The term is also used more loosely to refer to the historical era, but since the changes of the Renaissance were not...
artist and engineer, and a prime example of the nexus between art and engineering.
Other fields
In Political sciencePolitical science
Political Science is a social science discipline concerned with the study of the state, government and politics. Aristotle defined it as the study of the state. It deals extensively with the theory and practice of politics, and the analysis of political systems and political behavior...
the term engineering has been borrowed for the study of the subjects of Social engineering
Social engineering (political science)
Social engineering is a discipline in political science that refers to efforts to influence popular attitudes and social behaviors on a large scale, whether by governments or private groups. In the political arena, the counterpart of social engineering is political engineering.For various reasons,...
and Political engineering
Political engineering
Political engineering is a concept in political science that deals with the designing of political institutions in a society and often involves the use of paper decrees, in the form of laws, referendums, ordinances, or otherwise, to try to achieve some desired effect within a society.The criteria...
, which deal with forming political
Political structure
Political structure is a term frequently used in political science.The term political structure, used in a general sense, refers to institutions or groups and their relations to each other, their patterns of interaction within political systems and to political regulations, laws and the norms...
and social structure
Social structure
Social structure is a term used in the social sciences to refer to patterned social arrangements in society that are both emergent from and determinant of the actions of the individuals. The usage of the term "social structure" has changed over time and may reflect the various levels of analysis...
s using engineering methodology coupled with political science
Political science
Political Science is a social science discipline concerned with the study of the state, government and politics. Aristotle defined it as the study of the state. It deals extensively with the theory and practice of politics, and the analysis of political systems and political behavior...
principles. Financial engineering has similarly borrowed the term.
See also
Lists- List of basic engineering topics
- List of engineering topics
- List of engineers
- Engineering societyEngineering societyAn engineering society is a professional organization for engineers of various disciplines. Some are umbrella type organizations which accept many different disciplines, while others are discipline-specific. Many award professional designations, such as European Engineer, Professional Engineer,...
- List of aerospace engineering topics
- List of basic chemical engineering topics
- List of electrical engineering topics
- List of genetic engineering topics
- List of mechanical engineering topics
- List of nanoengineering topics
- List of software engineering topics
Related subjects
- Controversies over the term Engineer
- DesignDesignDesign as a noun informally refers to a plan or convention for the construction of an object or a system while “to design” refers to making this plan...
- Earthquake engineeringEarthquake engineeringEarthquake engineering is the scientific field concerned with protecting society, the natural and the man-made environment from earthquakes by limiting the seismic risk to socio-economically acceptable levels...
- EngineerEngineerAn engineer is a professional practitioner of engineering, concerned with applying scientific knowledge, mathematics and ingenuity to develop solutions for technical problems. Engineers design materials, structures, machines and systems while considering the limitations imposed by practicality,...
- Engineering economics
- Engineering educationEngineering educationEngineering education is the activity of teaching knowledge and principles related to the professional practice of engineering. It includes the initial education for becoming an engineer and any advanced education and specialization that follow...
- Engineers Without BordersEngineers Without BordersEngineers Without Borders – International is an international association of some national EWB/ISF groups, whose mission is to facilitate collaboration, exchange of information, and assistance among its member groups that have applied to become part of the association...
- Forensic engineeringForensic engineeringForensic engineering is the investigation of materials, products, structures or components that fail or do not operate or function as intended, causing personal injury or damage to property. The consequences of failure are dealt with by the law of product liability. The field also deals with...
- Global Engineering EducationGlobal Engineering EducationGlobal Engineering Education is a field of study that focuses on the impact of globalization on the engineering industry.- Impact :The number of engineers coming from outside the United States has risen significantly in recent years...
- Industrial designIndustrial designIndustrial design is the use of a combination of applied art and applied science to improve the aesthetics, ergonomics, and usability of a product, but it may also be used to improve the product's marketability and production...
- InfrastructureInfrastructureInfrastructure is basic physical and organizational structures needed for the operation of a society or enterprise, or the services and facilities necessary for an economy to function...
- Open hardware
- Reverse engineeringReverse engineeringReverse engineering is the process of discovering the technological principles of a device, object, or system through analysis of its structure, function, and operation...
- Science and technologyScience and technologyScience and technology is a term of art used to encompass the relationship between science and technology. It frequently appears within titles of academic disciplines and government offices.-See also:...
- Structural failureStructural failureStructural failure refers to loss of the load-carrying capacity of a component or member within a structure or of the structure itself. Structural failure is initiated when the material is stressed to its strength limit, thus causing fracture or excessive deformations...
- Sustainable engineeringSustainable engineeringSustainable engineering is the process of using energy and resources at a rate that does not compromise the natural environment, or the ability of future generations to meet their own needs.-What engineers can do:*Water supply*Food production...
- Women in engineeringWomen in engineering-USA:The percentage of female graduate students in engineering in 2001 was 20%. Doctoral degrees awarded to women in engineering increased from 11.6% to 17.6% of total degrees awarded between 1995 and 2004...
External links
- National Society of Professional Engineers position statement on Licensure and Qualifications for Practice
- National Academy of Engineering (NAE)
- American Society for Engineering Education (ASEE)
- The US Library of Congress Engineering in History bibliography
- ICES: Institute for Complex Engineered Systems, Carnegie Mellon University, Pittsburgh, PA
- History of engineering bibliography at University of MinnesotaUniversity of MinnesotaThe University of Minnesota, Twin Cities is a public research university located in Minneapolis and St. Paul, Minnesota, United States. It is the oldest and largest part of the University of Minnesota system and has the fourth-largest main campus student body in the United States, with 52,557...

