
American philosophy
Encyclopedia

United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
and abroad. The Internet Encyclopedia of Philosophy
Internet Encyclopedia of Philosophy
The Internet Encyclopedia of Philosophy is a free online encyclopedia on philosophical topics and philosophers founded by James Fieser in 1995. The current general editors are James Fieser and Bradley Dowden...
notes that while American philosophy lacks a "core of defining features, American Philosophy can nevertheless be seen as both reflecting and shaping collective American identity over the history of the nation."
17th century
The American philosophical tradition began at the time of the European colonizationEuropean colonization of the Americas
The start of the European colonization of the Americas is typically dated to 1492. The first Europeans to reach the Americas were the Vikings during the 11th century, who established several colonies in Greenland and one short-lived settlement in present day Newfoundland...
of the New World
New World
The New World is one of the names used for the Western Hemisphere, specifically America and sometimes Oceania . The term originated in the late 15th century, when America had been recently discovered by European explorers, expanding the geographical horizon of the people of the European middle...
. The Puritan
Puritan
The Puritans were a significant grouping of English Protestants in the 16th and 17th centuries. Puritanism in this sense was founded by some Marian exiles from the clergy shortly after the accession of Elizabeth I of England in 1558, as an activist movement within the Church of England...
arrival in New York
New York
New York is a state in the Northeastern region of the United States. It is the nation's third most populous state. New York is bordered by New Jersey and Pennsylvania to the south, and by Connecticut, Massachusetts and Vermont to the east...
set the earliest American philosophy into the religious tradition, and there was also an emphasis on the relationship between the individual and the community. This is evident by the early colonial documents such as the Fundamental Orders of Connecticut
Fundamental Orders of Connecticut
The Fundamental Orders were adopted by the Connecticut Colony council on January 14, 1638/39 OS . The orders describe the government set up by the Connecticut River towns, setting its structure and powers....
(1639) and the Massachusetts Body of Liberties
Massachusetts Body of Liberties
The Massachusetts Body of Liberties was the first legal code established by European colonists in New England. Compiled by the Puritan minister Nathaniel Ward, the laws were established by the Massachusetts General Court in 1641...
(1641).
Thinkers such as John Winthrop
John Winthrop
John Winthrop was a wealthy English Puritan lawyer, and one of the leading figures in the founding of the Massachusetts Bay Colony, the first major settlement in New England after Plymouth Colony. Winthrop led the first large wave of migrants from England in 1630, and served as governor for 12 of...
emphasized the public life over the private, holding that the former takes precedence over the latter, while other writers, such as Roger Williams
Roger Williams (theologian)
Roger Williams was an English Protestant theologian who was an early proponent of religious freedom and the separation of church and state. In 1636, he began the colony of Providence Plantation, which provided a refuge for religious minorities. Williams started the first Baptist church in America,...
(co-founder of Rhode Island
Rhode Island
The state of Rhode Island and Providence Plantations, more commonly referred to as Rhode Island , is a state in the New England region of the United States. It is the smallest U.S. state by area...
) held that religious tolerance was more integral than trying to achieve religious homogeneity in a community.
18th century
18th century American philosophy is often broken into two halves, the earlier half being marked by Puritan CalvinismCalvinism
Calvinism is a Protestant theological system and an approach to the Christian life...
, and the latter characterized by the American incarnation of the European Enlightenment that is associated with the political thought of the Founding Fathers.
Calvinism
Jonathan Edwards is considered to be "America's most important and original philosophical theologian." Noted for his energetic sermons, such as "Sinners in the Hands of an Angry GodSinners in the Hands of an Angry God
"Sinners in the Hands of an Angry God" is a sermon written by American Christian theologian Jonathan Edwards, preached on July 8, 1741 in Enfield, Connecticut. Like Edwards' other sermons and writings, it combines vivid imagery of Hell with observations of the world and citations of scripture...
" (which is said to have begun the First Great Awakening
First Great Awakening
The First Awakening was a Christian revitalization movement that swept Protestant Europe and British America, and especially the American colonies in the 1730s and 1740s, leaving a permanent impact on American religion. It resulted from powerful preaching that gave listeners a sense of personal...
), Edwards emphasized "the absolute sovereignty of God and the beauty of God's holiness." Working to unite Christian Platonism
Platonism
Platonism is the philosophy of Plato or the name of other philosophical systems considered closely derived from it. In a narrower sense the term might indicate the doctrine of Platonic realism...
with an empiricist epistemology, with the aid of Newtonian physics, Edwards was deeply influenced by George Berkeley
George Berkeley
George Berkeley , also known as Bishop Berkeley , was an Irish philosopher whose primary achievement was the advancement of a theory he called "immaterialism"...
, himself an empiricist, and Edwards derived his importance of the immaterial for the creation human experience from Bishop Berkeley.
The non-material mind consists of understanding and will, and it is understanding, interpreted in a Newtonian framework, that leads to Edwards' fundamental metaphysical category of Resistance. Whatever features an object may have, it has these properties because the object resists. Resistance itself is the exertion of God's power, and it can be seen in Newton's laws of motion
Newton's laws of motion
Newton's laws of motion are three physical laws that form the basis for classical mechanics. They describe the relationship between the forces acting on a body and its motion due to those forces...
, where an object is "unwilling" to change its current state of motion; an object at rest will remain at rest and an object in motion will remain in motion.
As a Calvinist and hard determinist, Jonathan Edwards also rejected the freedom of the will
Free will
"To make my own decisions whether I am successful or not due to uncontrollable forces" -Troy MorrisonA pragmatic definition of free willFree will is the ability of agents to make choices free from certain kinds of constraints. The existence of free will and its exact nature and definition have long...
, saying that "we can do as we please, but we cannot please as we please." According to Edwards, neither good works nor self-originating faith lead to salvation, but rather it is the unconditional grace of God which stands as the sole arbiter of human fortune.
The Age of Enlightenment
While the early 18th century American philosophical tradition was decidedly marked by religious themes, the latter half saw a reliance on reasonReason
Reason is a term that refers to the capacity human beings have to make sense of things, to establish and verify facts, and to change or justify practices, institutions, and beliefs. It is closely associated with such characteristically human activities as philosophy, science, language, ...
and science
Science
Science is a systematic enterprise that builds and organizes knowledge in the form of testable explanations and predictions about the universe...
, and, in step with the thought of the Age of Enlightenment
Age of Enlightenment
The Age of Enlightenment was an elite cultural movement of intellectuals in 18th century Europe that sought to mobilize the power of reason in order to reform society and advance knowledge. It promoted intellectual interchange and opposed intolerance and abuses in church and state...
, a belief in the perfectibility of human beings, laissez-faire
Laissez-faire
In economics, laissez-faire describes an environment in which transactions between private parties are free from state intervention, including restrictive regulations, taxes, tariffs and enforced monopolies....
economics
Economics
Economics is the social science that analyzes the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services. The term economics comes from the Ancient Greek from + , hence "rules of the house"...
, and a general focus on political matters.
Four of the Founding Fathers
Founding Fathers of the United States
The Founding Fathers of the United States of America were political leaders and statesmen who participated in the American Revolution by signing the United States Declaration of Independence, taking part in the American Revolutionary War, establishing the United States Constitution, or by some...
, John Adams
John Adams
John Adams was an American lawyer, statesman, diplomat and political theorist. A leading champion of independence in 1776, he was the second President of the United States...
, Thomas Jefferson
Thomas Jefferson
Thomas Jefferson was the principal author of the United States Declaration of Independence and the Statute of Virginia for Religious Freedom , the third President of the United States and founder of the University of Virginia...
, Benjamin Franklin
Benjamin Franklin
Dr. Benjamin Franklin was one of the Founding Fathers of the United States. A noted polymath, Franklin was a leading author, printer, political theorist, politician, postmaster, scientist, musician, inventor, satirist, civic activist, statesman, and diplomat...
, and James Madison
James Madison
James Madison, Jr. was an American statesman and political theorist. He was the fourth President of the United States and is hailed as the “Father of the Constitution” for being the primary author of the United States Constitution and at first an opponent of, and then a key author of the United...
, wrote extensively on political issues. In continuing with the chief concerns of the Puritans in the 17th century, the Founding Fathers debated the relationship between the individual and the state, as well as the nature of the state, importantly concerning the state's relationship to God and religion. It was at this time that the United States Declaration of Independence
United States Declaration of Independence
The Declaration of Independence was a statement adopted by the Continental Congress on July 4, 1776, which announced that the thirteen American colonies then at war with Great Britain regarded themselves as independent states, and no longer a part of the British Empire. John Adams put forth a...
and United States Constitution
United States Constitution
The Constitution of the United States is the supreme law of the United States of America. It is the framework for the organization of the United States government and for the relationship of the federal government with the states, citizens, and all people within the United States.The first three...
were written, and they are the result of debate and compromise.
The Constitution sets forth a federated republic
Republic
A republic is a form of government in which the people, or some significant portion of them, have supreme control over the government and where offices of state are elected or chosen by elected people. In modern times, a common simplified definition of a republic is a government where the head of...
an form of government
Government
Government refers to the legislators, administrators, and arbitrators in the administrative bureaucracy who control a state at a given time, and to the system of government by which they are organized...
that is marked by a balance of powers accompanied by a checks and balances system between the three branches of government: a judicial branch, an executive branch led by the President
President of the United States
The President of the United States of America is the head of state and head of government of the United States. The president leads the executive branch of the federal government and is the commander-in-chief of the United States Armed Forces....
, and a legislative branch composed of a bicameral legislature where the House of Representatives
United States House of Representatives
The United States House of Representatives is one of the two Houses of the United States Congress, the bicameral legislature which also includes the Senate.The composition and powers of the House are established in Article One of the Constitution...
is the lower house
Lower house
A lower house is one of two chambers of a bicameral legislature, the other chamber being the upper house.Despite its official position "below" the upper house, in many legislatures worldwide the lower house has come to wield more power...
and the Senate
United States Senate
The United States Senate is the upper house of the bicameral legislature of the United States, and together with the United States House of Representatives comprises the United States Congress. The composition and powers of the Senate are established in Article One of the U.S. Constitution. Each...
is the upper house
Upper house
An upper house, often called a senate, is one of two chambers of a bicameral legislature, the other chamber being the lower house; a legislature composed of only one house is described as unicameral.- Possible specific characteristics :...
.
While the Declaration of Independence does contain within it references to the Creator, the Founding Fathers were decidedly not exclusively theistic
Theism
Theism, in the broadest sense, is the belief that at least one deity exists.In a more specific sense, theism refers to a doctrine concerning the nature of a monotheistic God and God's relationship to the universe....
, some openly professing personal concepts of deism
Deism
Deism in religious philosophy is the belief that reason and observation of the natural world, without the need for organized religion, can determine that the universe is the product of an all-powerful creator. According to deists, the creator does not intervene in human affairs or suspend the...
, as was characteristic of other European Enlightenment thinkers, such as Maximilien Robespierre
Maximilien Robespierre
Maximilien François Marie Isidore de Robespierre is one of the best-known and most influential figures of the French Revolution. He largely dominated the Committee of Public Safety and was instrumental in the period of the Revolution commonly known as the Reign of Terror, which ended with his...
, François-Marie Arouet (better known by his pen name
Pen name
A pen name, nom de plume, or literary double, is a pseudonym adopted by an author. A pen name may be used to make the author's name more distinctive, to disguise his or her gender, to distance an author from some or all of his or her works, to protect the author from retribution for his or her...
, Voltaire
Voltaire
François-Marie Arouet , better known by the pen name Voltaire , was a French Enlightenment writer, historian and philosopher famous for his wit and for his advocacy of civil liberties, including freedom of religion, free trade and separation of church and state...
), and Rousseau. The most notably and self-consciously Christian of the Founding Fathers was John Adams. However, the 1796 Treaty of Tripoli, signed by John Adams, states that "the government of the United States of America is not in any sense founded on the Christian Religion".
Thomas Paine
Thomas Paine
Thomas "Tom" Paine was an English author, pamphleteer, radical, inventor, intellectual, revolutionary, and one of the Founding Fathers of the United States...
, the intellectual
Intellectual
An intellectual is a person who uses intelligence and critical or analytical reasoning in either a professional or a personal capacity.- Terminology and endeavours :"Intellectual" can denote four types of persons:...
, pamphleteer
Pamphleteer
A pamphleteer is a historical term for someone who creates or distributes pamphlets. Pamphlets were used to broadcast the writer's opinions on an issue, for example, in order to get people to vote for their favorite politician or to articulate a particular political ideology.A famous pamphleteer...
, and revolutionary
Revolutionary
A revolutionary is a person who either actively participates in, or advocates revolution. Also, when used as an adjective, the term revolutionary refers to something that has a major, sudden impact on society or on some aspect of human endeavor.-Definition:...
who wrote Common Sense
Common Sense (pamphlet)
Common Sense is a pamphlet written by Thomas Paine. It was first published anonymously on January 10, 1776, during the American Revolution. Common Sense, signed "Written by an Englishman", became an immediate success. In relation to the population of the Colonies at that time, it had the largest...
and Rights of Man
Rights of Man
Rights of Man , a book by Thomas Paine, posits that popular political revolution is permissible when a government does not safeguard its people, their natural rights, and their national interests. Using these points as a base it defends the French Revolution against Edmund Burke's attack in...
was an influential Enlightenment thinker and American Founding Father. Common Sense, which has been described as “the most incendiary and popular pamphlet of the entire revolutionary era" provides justification for the American revolution and independence from the British Crown.
19th century
The 19th century saw the rise of RomanticismRomanticism
Romanticism was an artistic, literary and intellectual movement that originated in the second half of the 18th century in Europe, and gained strength in reaction to the Industrial Revolution...
in America. The American incarnation of Romanticism was transcendentalism
Transcendentalism
Transcendentalism is a philosophical movement that developed in the 1830s and 1840s in the New England region of the United States as a protest against the general state of culture and society, and in particular, the state of intellectualism at Harvard University and the doctrine of the Unitarian...
and it stands as a major American innovation. The 19th century also saw the rise of the school of pragmatism, along with a smaller, Hegelian philosophical movement led by George Holmes Howison
George Holmes Howison
George Holmes Howison was an American philosopher who established the philosophy department at the University of California, Berkeley and held the position there of Mills Professor of Intellectual and Moral Philosophy and Civil Polity. He also founded the Philosophical Union, one of the oldest...
that was focused in St. Louis, though the influence of American pragmatism far outstripped that of the small Hegelian movement.
Other reactions to materialism included the "Objective idealism
Objective idealism
Objective idealism is an idealistic metaphysics that postulates that there is in an important sense only one perceiver, and that this perceiver is one with that which is perceived. One important advocate of such a metaphysics, Josiah Royce, wrote that he was indifferent "whether anybody calls all...
" of Josiah Royce
Josiah Royce
Josiah Royce was an American objective idealist philosopher.-Life:Royce, born in Grass Valley, California, grew up in pioneer California very soon after the California Gold Rush. He received the B.A...
, and the "Personalism
Personalism
Personalism is a philosophical school of thought searching to describe the uniqueness of a human person in the world of nature, specifically in relation to animals...
," sometimes called "Boston personalism," of Borden Parker Bowne
Borden Parker Bowne
Borden Parker Bowne was an American Christian philosopher and theologian in the Methodist tradition. In 1876 he became a professor of philosophy at Boston University, where he taught for more than thirty years. He later served as dean of the graduate school. Bowne was an acute critic of positivism...
.
Transcendentalism


Transcendentalism
Transcendentalism is a philosophical movement that developed in the 1830s and 1840s in the New England region of the United States as a protest against the general state of culture and society, and in particular, the state of intellectualism at Harvard University and the doctrine of the Unitarian...
in the United States was marked by an emphasis on subjective experience, and can be viewed as a reaction against modernism
Modernism
Modernism, in its broadest definition, is modern thought, character, or practice. More specifically, the term describes the modernist movement, its set of cultural tendencies and array of associated cultural movements, originally arising from wide-scale and far-reaching changes to Western society...
and intellectualism
Intellectualism
Intellectualism denotes the use and development of the intellect, the practice of being an intellectual, and of holding intellectual pursuits in great regard. Moreover, in philosophy, “intellectualism” occasionally is synonymous with “rationalism”, i.e. knowledge derived mostly from reason and...
in general and the mechanistic, reductionistic
Reductionism
Reductionism can mean either an approach to understanding the nature of complex things by reducing them to the interactions of their parts, or to simpler or more fundamental things or a philosophical position that a complex system is nothing but the sum of its parts, and that an account of it can...
worldview in particular. Transcendentalism is marked by the holistic
Holism
Holism is the idea that all the properties of a given system cannot be determined or explained by its component parts alone...
belief in an ideal spiritual state that 'transcends' the physical and empirical, and this perfect state can only be attained by one's own intuition and personal reflection, as opposed to either industrial progress and scientific advancement or the principles and prescriptions of traditional, organized religion. The most notable transcendentalist writers include Ralph Waldo Emerson
Ralph Waldo Emerson
Ralph Waldo Emerson was an American essayist, lecturer, and poet, who led the Transcendentalist movement of the mid-19th century...
, Henry David Thoreau
Henry David Thoreau
Henry David Thoreau was an American author, poet, philosopher, abolitionist, naturalist, tax resister, development critic, surveyor, historian, and leading transcendentalist...
, and Margaret Fuller
Margaret Fuller
Sarah Margaret Fuller Ossoli, commonly known as Margaret Fuller, was an American journalist, critic, and women's rights advocate associated with the American transcendentalism movement. She was the first full-time American female book reviewer in journalism...
.
The transcendentalist writers all desired a deep return to nature
Nature
Nature, in the broadest sense, is equivalent to the natural world, physical world, or material world. "Nature" refers to the phenomena of the physical world, and also to life in general...
, and believed that real, true knowledge is intuitive and personal and arises out of personal immersion and reflection in nature, as opposed to scientific knowledge that is the result of empirical sense experience.
Things such as scientific tools, political institutions, and the conventional rules of morality as dictated by traditional religion need to be transcended. This is found in Henry David Thoreau
Henry David Thoreau
Henry David Thoreau was an American author, poet, philosopher, abolitionist, naturalist, tax resister, development critic, surveyor, historian, and leading transcendentalist...
's Walden; or, Life in the Woods where transcendence is achieved through immersion in nature and the distancing of oneself from society.
Darwinism in America
The release of Charles DarwinCharles Darwin
Charles Robert Darwin FRS was an English naturalist. He established that all species of life have descended over time from common ancestry, and proposed the scientific theory that this branching pattern of evolution resulted from a process that he called natural selection.He published his theory...
's evolutionary theory in his 1859 publication of On the Origin of Species had a strong impact on American philosophy. John Fiske and Chauncey Wright
Chauncey Wright
Chauncey Wright , American philosopher and mathematician, was born at Northampton, Massachusetts.In 1852 he graduated at Harvard, and became computer to the American Ephemeris and Nautical Almanac. He made his name by contributions on mathematical and physical subjects in the Mathematical Monthly...
both wrote about and argued for the re-conceiving of philosophy through an evolutionary lens. They both wanted to understand morality
Morality
Morality is the differentiation among intentions, decisions, and actions between those that are good and bad . A moral code is a system of morality and a moral is any one practice or teaching within a moral code...
and the mind
Mind
The concept of mind is understood in many different ways by many different traditions, ranging from panpsychism and animism to traditional and organized religious views, as well as secular and materialist philosophies. Most agree that minds are constituted by conscious experience and intelligent...
in Darwinian terms, setting a precedent for evolutionary psychology
Evolutionary psychology
Evolutionary psychology is an approach in the social and natural sciences that examines psychological traits such as memory, perception, and language from a modern evolutionary perspective. It seeks to identify which human psychological traits are evolved adaptations, that is, the functional...
and evolutionary ethics
Evolutionary ethics
Evolutionary ethics could be either a form of descriptive ethics or normative ethics.Descriptive evolutionary ethics consists of biological approaches to ethics based on the role of evolution in shaping human psychology and behavior...
.
Darwin's biological theory was also integrated into the social and political philosophies of English
English people
The English are a nation and ethnic group native to England, who speak English. The English identity is of early mediaeval origin, when they were known in Old English as the Anglecynn. England is now a country of the United Kingdom, and the majority of English people in England are British Citizens...
thinker Herbert Spencer
Herbert Spencer
Herbert Spencer was an English philosopher, biologist, sociologist, and prominent classical liberal political theorist of the Victorian era....
and American philosopher William Graham Sumner
William Graham Sumner
William Graham Sumner was an American academic and "held the first professorship in sociology" at Yale College. For many years he had a reputation as one of the most influential teachers there. He was a polymath with numerous books and essays on American history, economic history, political...
. Herbert Spencer, who coined the oft-misattributed term "survival of the fittest
Survival of the fittest
"Survival of the fittest" is a phrase originating in evolutionary theory, as an alternative description of Natural selection. The phrase is today commonly used in contexts that are incompatible with the original meaning as intended by its first two proponents: British polymath philosopher Herbert...
," believed that societies were in a struggle for survival, and that groups within society are where they are because of some level of fitness. This struggle is beneficial to human kind, as in the long run the weak will be weeded out and only the strong will survive. This position is often referred to as Social Darwinism
Social Darwinism
Social Darwinism is a term commonly used for theories of society that emerged in England and the United States in the 1870s, seeking to apply the principles of Darwinian evolution to sociology and politics...
.
Sumner, much influenced by Spencer, believed along with the industrialist Andrew Carnegie
Andrew Carnegie
Andrew Carnegie was a Scottish-American industrialist, businessman, and entrepreneur who led the enormous expansion of the American steel industry in the late 19th century...
that the social implication of the fact of the struggle for survival is that laissez-faire capitalism is the natural political-economic system and is the one that will lead to the greatest amount of well-being. William Sumner, in addition to his advocacy of free markets, also espoused anti-imperialism
Anti-imperialism
Anti-imperialism, strictly speaking, is a term that may be applied to a movement opposed to any form of colonialism or imperialism. Anti-imperialism includes opposition to wars of conquest, particularly of non-contiguous territory or people with a different language or culture; it also includes...
(having been credited with coining the term "ethnocentrism
Ethnocentrism
Ethnocentrism is the tendency to believe that one's ethnic or cultural group is centrally important, and that all other groups are measured in relation to one's own. The ethnocentric individual will judge other groups relative to his or her own particular ethnic group or culture, especially with...
"), and advocated for the gold standard
Gold standard
The gold standard is a monetary system in which the standard economic unit of account is a fixed mass of gold. There are distinct kinds of gold standard...
.
Pragmatism
Perhaps the most influential school of thought that is uniquely American is pragmatismPragmatism
Pragmatism is a philosophical tradition centered on the linking of practice and theory. It describes a process where theory is extracted from practice, and applied back to practice to form what is called intelligent practice...
. It began in the late nineteenth century in the United States with Charles Sanders Peirce, William James
William James
William James was a pioneering American psychologist and philosopher who was trained as a physician. He wrote influential books on the young science of psychology, educational psychology, psychology of religious experience and mysticism, and on the philosophy of pragmatism...
, and John Dewey
John Dewey
John Dewey was an American philosopher, psychologist and educational reformer whose ideas have been influential in education and social reform. Dewey was an important early developer of the philosophy of pragmatism and one of the founders of functional psychology...
. Pragmatism begins with the idea that belief is that upon which one is willing to act. It holds that a proposition's meaning is the consequent form of conduct or practice that would be implied by accepting the proposition as true.
Charles Sanders Peirce

Polymath
A polymath is a person whose expertise spans a significant number of different subject areas. In less formal terms, a polymath may simply be someone who is very knowledgeable...
, logician, mathematician
Mathematician
A mathematician is a person whose primary area of study is the field of mathematics. Mathematicians are concerned with quantity, structure, space, and change....
, philosopher, and scientist
Scientist
A scientist in a broad sense is one engaging in a systematic activity to acquire knowledge. In a more restricted sense, a scientist is an individual who uses the scientific method. The person may be an expert in one or more areas of science. This article focuses on the more restricted use of the word...
Charles Sanders Peirce (icon like "purse"; 1839–1914) coined the term "pragmatism" in the 1870s. He was a member of The Metaphysical Club
The Metaphysical Club
The Metaphysical Club was a conversational philosophical club that future Supreme Court Justice Oliver Wendell Holmes, Jr., psychologist William James, and polymath Charles Sanders Peirce formed in January 1872 in Cambridge, Massachusetts and dissolved in December 1872. Upon Peirce's arrival at...
, which was a conversational club of intellectuals that also included Chauncey Wright
Chauncey Wright
Chauncey Wright , American philosopher and mathematician, was born at Northampton, Massachusetts.In 1852 he graduated at Harvard, and became computer to the American Ephemeris and Nautical Almanac. He made his name by contributions on mathematical and physical subjects in the Mathematical Monthly...
, future Supreme Court
Supreme Court of the United States
The Supreme Court of the United States is the highest court in the United States. It has ultimate appellate jurisdiction over all state and federal courts, and original jurisdiction over a small range of cases...
Justice Oliver Wendell Holmes, Jr.
Oliver Wendell Holmes, Jr.
Oliver Wendell Holmes, Jr. was an American jurist who served as an Associate Justice of the Supreme Court of the United States from 1902 to 1932...
, and another early figure of pragmatism, William James
William James
William James was a pioneering American psychologist and philosopher who was trained as a physician. He wrote influential books on the young science of psychology, educational psychology, psychology of religious experience and mysticism, and on the philosophy of pragmatism...
. In addition to making profound contributions to semiotics
Semiotics
Semiotics, also called semiotic studies or semiology, is the study of signs and sign processes , indication, designation, likeness, analogy, metaphor, symbolism, signification, and communication...
, logic, and mathematics, Peirce wrote what are considered to be the founding documents of pragmatism, "The Fixation of Belief" (1877) and "How to Make Our Ideas Clear" (1878).
In "The Fixation of Belief" Peirce argues for the superiority of the scientific method
Scientific method
Scientific method refers to a body of techniques for investigating phenomena, acquiring new knowledge, or correcting and integrating previous knowledge. To be termed scientific, a method of inquiry must be based on gathering empirical and measurable evidence subject to specific principles of...
in settling belief on theoretical questions. In "How to Make Our Ideas Clear" Peirce argued for pragmatism as summed up in that which he later called the pragmatic maxim
Pragmatic maxim
The pragmatic maxim, also known as the maxim of pragmatism or the maxim of pragmaticism, is a maxim of logic formulated by Charles Sanders Peirce...
: "Consider what effects, that might conceivably have practical bearings, we conceive the object of our conception to have. Then, our conception of these effects is the whole of our conception of the object". Peirce emphasized that a conception is general, such that its meaning is not a set of actual, definite effects themselves. Instead the conception of an object is equated to a conception of that object's effects to a general extent of their conceivable implications for informed practice. Those conceivable practical implications are the conception's meaning.
The maxim is intended to help fruitfully clarify confusions caused, for example, by distinctions that make formal but not practical differences. Traditionally one analyzes an idea into parts (his example: a definition of truth as a sign's correspondence to its object). To that needful but confined step, the maxim adds a further and practice-oriented step (his example: a definition of truth as sufficient investigation's destined end).
It is the heart of his pragmatism as a method of experimentational mental reflection arriving at conceptions in terms of conceivable confirmatory and disconfirmatory circumstances — a method hospitable to the formation of explanatory hypotheses, and conducive to the use and improvement of verification. Typical of Peirce is his concern with inference to explanatory hypotheses as outside the usual foundational alternative between deductivist rationalism and inductivist empiricism, though he himself was a mathematician of logic and a founder of statistics
Founders of statistics
Statistics is the theory and application of mathematics to the scientific method including hypothesis generation, experimental design, sampling, data collection, data summarization, estimation, prediction and inference from those results to the population from which the experimental sample was drawn...
.
Peirce's philosophy includes a pervasive three-category system
Categories (Peirce)
On May 14, 1867, the 27-year-old Charles Sanders Peirce, who eventually founded Pragmatism, presented a paper entitled "On a New List of Categories" to the American Academy of Arts and Sciences. Among other things, this paper outlined a theory of predication involving three universal categories...
, both fallibilism
Fallibilism
Fallibilism is the philosophical principle that human beings could be wrong about their beliefs, expectations, or their understanding of the world...
and anti-skeptical belief that truth is discoverable and immutable, logic as formal semiotic (including semiotic elements and classes of signs
Semiotic elements and classes of signs (Peirce)
Logician, mathematician, philosopher, and scientist Charles Sanders Peirce began writing on semeiotic, semiotics, or the theory of sign relations in the 1860s, around the time that he devised his system of three categories...
, modes of inference, and methods of inquiry along with pragmatism and critical common-sensism), Scholastic realism
Philosophical realism
Contemporary philosophical realism is the belief that our reality, or some aspect of it, is ontologically independent of our conceptual schemes, linguistic practices, beliefs, etc....
, theism, objective idealism
Objective idealism
Objective idealism is an idealistic metaphysics that postulates that there is in an important sense only one perceiver, and that this perceiver is one with that which is perceived. One important advocate of such a metaphysics, Josiah Royce, wrote that he was indifferent "whether anybody calls all...
, and belief in the reality of continuity
Synechism
Synechism , a philosophical term proposed by C. S. Peirce to express the tendency to regard things such as space, time, and law as continuous:His synechism holds that the essential feature in philosophic speculation is continuity...
of space, time, and law, and in the reality of chance
Tychism
Tychism is a thesis proposed by the American philosopher Charles Sanders Peirce that holds that absolute chance, or indeterminism, is a real factor operative in the universe. This doctrine forms a central part of Peirce's comprehensive evolutionary cosmology...
, mechanical necessity, and creative love
Agapism
Agapism is belief in selfless, charitable, non-erotic love, spiritual love, love of the soul. It can mean belief that such love should be the sole ultimate value and that all other values are derived from it, or that the sole moral imperative is to love. Theological agapism holds that our love...
as principles operative in the cosmos and as modes of its evolution.
William James
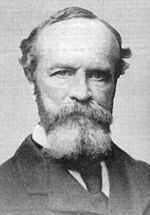
William James
William James was a pioneering American psychologist and philosopher who was trained as a physician. He wrote influential books on the young science of psychology, educational psychology, psychology of religious experience and mysticism, and on the philosophy of pragmatism...
(1842–1910) was "an original thinker in and between the disciplines of physiology, psychology and philosophy." He is famous as the author of The Varieties of Religious Experience
The Varieties of Religious Experience
The Varieties of Religious Experience: A Study in Human Nature is a book by the Harvard University psychologist and philosopher William James that comprises his edited Gifford Lectures on "Natural Theology" delivered at the University of Edinburgh in Scotland between 1901 and 1902.These lectures...
, his monumental tome Principles of Psychology
Principles of Psychology
The Principles of Psychology is a monumental text in the history of psychology, written by William James and published in 1890.There were four methods in James' psychology: analysis , introspection , experiment The Principles of Psychology is a monumental text in the history of psychology, written...
, and his lecture "The Will to Believe."
James, along with Peirce, saw pragmatism as embodying familiar attitudes elaborated into a radical new philosophical method of thinking and resolving dilemmas. In his 1910 Pragmatism: A New Name for Some Old Ways of Thinking he wrote:
James is also known for his radical empiricism
Radical empiricism
Radical empiricism is a pragmatist doctrine put forth by William James. It asserts that experience includes both particulars and relations between those particulars, and that therefore both deserve a place in our explanations...
which holds that relations between objects are as real as the objects themselves. James was also a pluralist in that he believed that there may actually be multiple correct accounts of truth. He rejected the correspondence theory of truth
Correspondence theory of truth
The correspondence theory of truth states that the truth or falsity of a statement is determined only by how it relates to the world, and whether it accurately describes that world...
and instead held that truth involves a belief, facts about the world, other background beliefs, and future consequences of those beliefs. Later in his life James would also come to adopt neutral monism
Neutral monism
Neutral monism, in philosophy, is the metaphysical view that the mental and the physical are two ways of organizing or describing the same elements, which are themselves "neutral," that is, neither physical nor mental. This view denies that the mental and the physical are two fundamentally...
, the view that the ultimate reality
Reality
In philosophy, reality is the state of things as they actually exist, rather than as they may appear or might be imagined. In a wider definition, reality includes everything that is and has been, whether or not it is observable or comprehensible...
is of one kind, and is neither mental
Mental substance
Mental substance refers to the concept held by dualists and idealists, that minds are made-up of non-physical substance. This substance is often referred to as consciousness....
nor physical
Physical property
A physical property is any property that is measurable whose value describes a physical system's state. The changes in the physical properties of a system can be used to describe its transformations ....
.
John Dewey
John DeweyJohn Dewey
John Dewey was an American philosopher, psychologist and educational reformer whose ideas have been influential in education and social reform. Dewey was an important early developer of the philosophy of pragmatism and one of the founders of functional psychology...
(1859–1952), while still engaging in the lofty academic philosophical work of James and Peirce before him, also wrote extensively on political and social matters, and his presence in the public sphere was much greater than his pragmatist predecessors. In addition to being one of the founding members of pragmatism, John Dewey was one of the founders of functional psychology
Functional psychology
Functional psychology or functionalism refers to a general psychological philosophy that considers mental life and behavior in terms of active adaptation to the person's environment. As such, it provides the general basis for developing psychological theories not readily testable by controlled...
and was a leading figure of the progressive movement in U.S. schooling during the first half of the 20th century.
Dewey argued against the individualism of classical liberalism, asserting that social institutions are not "means for obtaining something for individuals. They are means for creating individuals." He held that individuals are not things that should be accommodated by social institutions, instead, social institutions are prior to and shape the individuals. These social arrangements are a means of creating individuals and promoting individual freedom.
Dewey is well known for his work in the applied philosophy of the philosophy of education
Philosophy of education
Philosophy of education can refer to either the academic field of applied philosophy or to one of any educational philosophies that promote a specific type or vision of education, and/or which examine the definition, goals and meaning of education....
. Dewey's philosophy of education is one where children learn by doing. Dewey believed that schooling was unnecessarily long and formal, and that children would be better suited to learn by engaging in real-life activities. For example, in math, students could learn by figuring out proportions in cooking or seeing how long it would take to travel distances with certain modes of transportation.
20th century

Theory of relativity
The theory of relativity, or simply relativity, encompasses two theories of Albert Einstein: special relativity and general relativity. However, the word relativity is sometimes used in reference to Galilean invariance....
. The middle of the 20th century was witness to the increase in popularity of the philosophy of language
Philosophy of language
Philosophy of language is the reasoned inquiry into the nature, origins, and usage of language. As a topic, the philosophy of language for analytic philosophers is concerned with four central problems: the nature of meaning, language use, language cognition, and the relationship between language...
and analytic philosophy in America. Existentialism
Existentialism
Existentialism is a term applied to a school of 19th- and 20th-century philosophers who, despite profound doctrinal differences, shared the belief that philosophical thinking begins with the human subject—not merely the thinking subject, but the acting, feeling, living human individual...
and phenomenology, while very popular in Europe in the 20th century, never achieved the level of popularity in America as they did in continental Europe.
Rejection of idealism
Pragmatism continued its influence into the 20th century, and Spanish-born philosopher George SantayanaGeorge Santayana
George Santayana was a philosopher, essayist, poet, and novelist. A lifelong Spanish citizen, Santayana was raised and educated in the United States and identified himself as an American. He wrote in English and is generally considered an American man of letters...
was one of the leading proponents of pragmatism in this period. He held that idealism
Idealism
In philosophy, idealism is the family of views which assert that reality, or reality as we can know it, is fundamentally mental, mentally constructed, or otherwise immaterial. Epistemologically, idealism manifests as a skepticism about the possibility of knowing any mind-independent thing...
was an outright contradiction and rejection of common sense
Common sense
Common sense is defined by Merriam-Webster as, "sound and prudent judgment based on a simple perception of the situation or facts." Thus, "common sense" equates to the knowledge and experience which most people already have, or which the person using the term believes that they do or should have...
. He held that, if something must be certain in order to be knowledge, then it seems no knowledge may be possible, and the result will be skepticism
Skepticism
Skepticism has many definitions, but generally refers to any questioning attitude towards knowledge, facts, or opinions/beliefs stated as facts, or doubt regarding claims that are taken for granted elsewhere...
. According to Santayana, knowledge involved a sort of faith, which he termed "animal faith."
In his book Scepticism and Animal Faith he asserts that knowledge is not the result of reasoning. Instead, knowledge is what is required to order to act and successfully engage with the world. As a naturalist, Santayana was a harsh critic of epistemological foundationalism
Foundationalism
Foundationalism is any theory in epistemology that holds that beliefs are justified based on what are called basic beliefs . This position is intended to resolve the infinite regress problem in epistemology...
. The explanation of events in the natural world is within the realm of science, while the meaning and value of this action should be studied by philosophers. Santayana was accompanied in the intellectual climate of 'common sense' philosophy by the thinkers of the New Realism
New realism
Nouveau réalisme refers to an artistic movement founded in 1960 by the art critic Pierre Restany and the painter Yves Klein during the first collective exposition in the Apollinaire gallery in Milan...
movement, such as Ralph Barton Perry
Ralph Barton Perry
Ralph Barton Perry was an American philosopher.-Career:...
.
Process philosophy
Process philosophyProcess philosophy
Process philosophy identifies metaphysical reality with change and dynamism. Since the time of Plato and Aristotle, philosophers have posited true reality as "timeless", based on permanent substances, whilst processes are denied or subordinated to timeless substances...
embraces the Einsteinian world-view, and its main proponents include Alfred North Whitehead
Alfred North Whitehead
Alfred North Whitehead, OM FRS was an English mathematician who became a philosopher. He wrote on algebra, logic, foundations of mathematics, philosophy of science, physics, metaphysics, and education...
and Charles Hartshorne
Charles Hartshorne
Charles Hartshorne was a prominent American philosopher who concentrated primarily on the philosophy of religion and metaphysics. He developed the neoclassical idea of God and produced a modal proof of the existence of God that was a development of St. Anselm's Ontological Argument...
. The core belief of process philosophy is the claim that events and processes are principle ontological categories. Whitehead asserted in his book The Concept of Nature that the things in nature, what he referred to as "concresences" are a conjunction of events that maintain a permanence of character. Process philosophy is Heraclitan in the sense that a fundamental ontological category is change. Charles Hartshorne was also responsible for developing the process philosophy of Whitehead into process theology
Process theology
Process theology is a school of thought influenced by the metaphysical process philosophy of Alfred North Whitehead and further developed by Charles Hartshorne . While there are process theologies that are similar, but unrelated to the work of Whitehead the term is generally applied to the...
.
Analytic philosophy

Analytic philosophy
Analytic philosophy is a generic term for a style of philosophy that came to dominate English-speaking countries in the 20th century...
in America. Analytic philosophy, prior to its arrival in America, had begun in Europe with the work of Gottlob Frege
Gottlob Frege
Friedrich Ludwig Gottlob Frege was a German mathematician, logician and philosopher. He is considered to be one of the founders of modern logic, and made major contributions to the foundations of mathematics. He is generally considered to be the father of analytic philosophy, for his writings on...
, Bertrand Russell
Bertrand Russell
Bertrand Arthur William Russell, 3rd Earl Russell, OM, FRS was a British philosopher, logician, mathematician, historian, and social critic. At various points in his life he considered himself a liberal, a socialist, and a pacifist, but he also admitted that he had never been any of these things...
, Ludwig Wittgenstein
Ludwig Wittgenstein
Ludwig Josef Johann Wittgenstein was an Austrian philosopher who worked primarily in logic, the philosophy of mathematics, the philosophy of mind, and the philosophy of language. He was professor in philosophy at the University of Cambridge from 1939 until 1947...
, and the logical positivists. According to logical positivism, the truths of logic and mathematics are tautologies
Tautology (logic)
In logic, a tautology is a formula which is true in every possible interpretation. Philosopher Ludwig Wittgenstein first applied the term to redundancies of propositional logic in 1921; it had been used earlier to refer to rhetorical tautologies, and continues to be used in that alternate sense...
, and those of science are empirically verifiable. Any other claim, including the claims of ethics, aesthetics, theology, metaphysics, and ontology, are meaningless (this theory is called verificationism). With the rise of Adolf Hitler
Adolf Hitler
Adolf Hitler was an Austrian-born German politician and the leader of the National Socialist German Workers Party , commonly referred to as the Nazi Party). He was Chancellor of Germany from 1933 to 1945, and head of state from 1934 to 1945...
and the Nazi Party, many positivists fled Germany
Germany
Germany , officially the Federal Republic of Germany , is a federal parliamentary republic in Europe. The country consists of 16 states while the capital and largest city is Berlin. Germany covers an area of 357,021 km2 and has a largely temperate seasonal climate...
to Britain
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
and America, and this helped reinforce the dominance of analytic philosophy in the United States in subsequent years.
W.V.O. Quine, while not a logical positivist, shared their view that philosophy should stand shoulder to shoulder with science in its pursuit of intellectual clarity and understanding of the world. He criticized the logical positivists and the analytic/synthetic distinction of knowledge in his essay "Two Dogmas of Empiricism
Two Dogmas of Empiricism
W. V. Quine's paper Two Dogmas of Empiricism, published in 1951, is one of the most celebrated papers of twentieth century philosophy in the analytic tradition. According to Harvard professor of philosophy Peter Godfrey-Smith, this "paper [is] sometimes regarded as the most important in all of...
" and advocated for his "web of belief," which is a coherentist
Coherentism
There are two distinct types of coherentism. One refers to the coherence theory of truth. The other refers to the coherence theory of justification. The coherentist theory of justification characterizes epistemic justification as a property of a belief only if that belief is a member of a coherent...
theory of justificiation. In Quine's epistemology, since no experiences occur in isolation, there is actually a holistic approach to knowledge where every belief or experience is intertwined with the whole. Quine is also famous for inventing the term "gavagai" as part of his theory of the indeterminacy of translation
Indeterminacy of translation
The indeterminacy of translation is a thesis propounded by 20th century analytic philosopher W. V. Quine. The classic statement of this thesis can be found in his 1960 book Word and Object, which gathered together and refined much of Quine's previous work on subjects other than formal logic and set...
.

Saul Kripke
Saul Aaron Kripke is an American philosopher and logician. He is a professor emeritus at Princeton and teaches as a Distinguished Professor of Philosophy at the CUNY Graduate Center...
, a student of Quine at Harvard, has profoundly influenced analytic philosophy. Kripke was ranked among the top ten most important philosophers of the past 200 years in a poll conducted by Brian Leiter
Brian Leiter
Brian Leiter is an American philosopher and legal scholar who is currently John Wilson Professor of Law at the University of Chicago Law School, and founder and Director of Chicago's new Center for Law, Philosophy, and Human Values and the editor of the Philosophical Gourmet Report. He taught from...
(Leiter Reports: a Philosophy Blog; open access poll) Kripke is best known for four contributions to philosophy: (1) Kripke semantics
Kripke semantics
Kripke semantics is a formal semantics for non-classical logic systems created in the late 1950s and early 1960s by Saul Kripke. It was first made for modal logics, and later adapted to intuitionistic logic and other non-classical systems...
for modal
Modal logic
Modal logic is a type of formal logic that extends classical propositional and predicate logic to include operators expressing modality. Modals — words that express modalities — qualify a statement. For example, the statement "John is happy" might be qualified by saying that John is...
and related logics, published in several essays beginning while he was still in his teens. (2) His 1970 Princeton lectures Naming and Necessity
Naming and Necessity
Naming and Necessity is a book by the philosopher Saul Kripke that was first published in 1980 and deals with the debates of proper nouns in the philosophy of language. The book is based on a transcript of three lectures given at Princeton University in 1970...
(published in 1972 and 1980), that significantly restructured the philosophy of language
Philosophy of language
Philosophy of language is the reasoned inquiry into the nature, origins, and usage of language. As a topic, the philosophy of language for analytic philosophers is concerned with four central problems: the nature of meaning, language use, language cognition, and the relationship between language...
and, as some have put it, "made metaphysics respectable again". (3) His interpretation of the philosophy of Wittgenstein. (4) His theory of truth
Truth
Truth has a variety of meanings, such as the state of being in accord with fact or reality. It can also mean having fidelity to an original or to a standard or ideal. In a common usage, it also means constancy or sincerity in action or character...
. He has also made important contributions to set theory
Set theory
Set theory is the branch of mathematics that studies sets, which are collections of objects. Although any type of object can be collected into a set, set theory is applied most often to objects that are relevant to mathematics...
(see admissible ordinal
Admissible ordinal
In set theory, an ordinal number α is an admissible ordinal if Lα is an admissible set ; in other words, α is admissible when α is a limit ordinal and Lα⊧Σ0-collection....
and Kripke-Platek set theory)
David Kellogg Lewis
David Kellogg Lewis
David Kellogg Lewis was an American philosopher. Lewis taught briefly at UCLA and then at Princeton from 1970 until his death. He is also closely associated with Australia, whose philosophical community he visited almost annually for more than thirty years...
, another student of Quine at Harvard, was ranked as one of the greatest philosophers of the 20th century in a poll conducted by Brian Leiter
Brian Leiter
Brian Leiter is an American philosopher and legal scholar who is currently John Wilson Professor of Law at the University of Chicago Law School, and founder and Director of Chicago's new Center for Law, Philosophy, and Human Values and the editor of the Philosophical Gourmet Report. He taught from...
(open access poll). He is well known for his controversial advocacy of modal realism
Modal realism
Modal realism is the view, notably propounded by David Kellogg Lewis, that all possible worlds are as real as the actual world. It is based on the following tenets: possible worlds exist; possible worlds are not different in kind from the actual world; possible worlds are irreducible entities; the...
, the position which holds that there is an infinite number of concrete and causally isolated possible worlds
Possible world
In philosophy and logic, the concept of a possible world is used to express modal claims. The concept of possible worlds is common in contemporary philosophical discourse and has also been disputed.- Possibility, necessity, and contingency :...
, of which ours is one. These possible worlds arise in the field of modal logic
Modal logic
Modal logic is a type of formal logic that extends classical propositional and predicate logic to include operators expressing modality. Modals — words that express modalities — qualify a statement. For example, the statement "John is happy" might be qualified by saying that John is...
.
Thomas Kuhn
Thomas Kuhn
Thomas Samuel Kuhn was an American historian and philosopher of science whose controversial 1962 book The Structure of Scientific Revolutions was deeply influential in both academic and popular circles, introducing the term "paradigm shift," which has since become an English-language staple.Kuhn...
was an important philosopher and writer who worked extensively in the fields of the history of science
History of science
The history of science is the study of the historical development of human understandings of the natural world and the domains of the social sciences....
and the philosophy of science
Philosophy of science
The philosophy of science is concerned with the assumptions, foundations, methods and implications of science. It is also concerned with the use and merit of science and sometimes overlaps metaphysics and epistemology by exploring whether scientific results are actually a study of truth...
. He is famous for writing The Structure of Scientific Revolutions
The Structure of Scientific Revolutions
The Structure of Scientific Revolutions , by Thomas Kuhn, is an analysis of the history of science. Its publication was a landmark event in the history, philosophy, and sociology of scientific knowledge and it triggered an ongoing worldwide assessment and reaction in — and beyond — those scholarly...
, one of the most cited academic works of all time. The book argues that science proceeds through different paradigms as scientists find new puzzles to solve. There follows a widespread struggle to find answers to questions, and a shift in world views occurs, which is referred to by Kuhn as a paradigm shift
Paradigm shift
A Paradigm shift is, according to Thomas Kuhn in his influential book The Structure of Scientific Revolutions , a change in the basic assumptions, or paradigms, within the ruling theory of science...
. The work is considered a milestone in the sociology of knowledge
Sociology of knowledge
The Sociology of knowledge is the study of the relationship between human thought and the social context within which it arises, and of the effects prevailing ideas have on societies...
.
Return to political philosophy
The analytic philosophers troubled themselves with the abstract and the conceptual, and American philosophy did not fully return to social and political concerns (that dominated American philosophy at the time of the founding of the United States) until the 1970s. The return to political and social concerns included the popularity of works of Ayn RandAyn Rand
Ayn Rand was a Russian-American novelist, philosopher, playwright, and screenwriter. She is known for her two best-selling novels The Fountainhead and Atlas Shrugged and for developing a philosophical system she called Objectivism....
, who promoted Ethical egoism
Ethical egoism
Ethical egoism is the normative ethical position that moral agents ought to do what is in their own self-interest. It differs from psychological egoism, which claims that people can only act in their self-interest. Ethical egoism also differs from rational egoism, which holds merely that it is...
(which she called Objectivism
Objectivism (Ayn Rand)
Objectivism is a philosophy created by the Russian-American philosopher and novelist Ayn Rand . Objectivism holds that reality exists independent of consciousness, that human beings have direct contact with reality through sense perception, that one can attain objective knowledge from perception...
) in her novels, The Fountainhead
The Fountainhead
The Fountainhead is a 1943 novel by Ayn Rand. It was Rand's first major literary success and brought her fame and financial success. More than 6.5 million copies of the book have been sold worldwide....
in 1943 and Atlas Shrugged
Atlas Shrugged
Atlas Shrugged is a novel by Ayn Rand, first published in 1957 in the United States. Rand's fourth and last novel, it was also her longest, and the one she considered to be her magnum opus in the realm of fiction writing...
in 1957.
These two novels gave birth to the Objectivist movement
Objectivist movement
The Objectivist movement is a movement to study and advance the philosophy of Objectivism. It was founded by novelist and philosopher Ayn Rand. The movement began informally in the 1950s and consisted of students who were brought together by their mutual interest in Rand’s novel, The Fountainhead...
, one which started as a small group of students called The Collective, one of whom was a young Alan Greenspan
Alan Greenspan
Alan Greenspan is an American economist who served as Chairman of the Federal Reserve of the United States from 1987 to 2006. He currently works as a private advisor and provides consulting for firms through his company, Greenspan Associates LLC...
, the well-known libertarian Chairman of the Federal Reserve
Chairman of the Federal Reserve
The Chairman of the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System is the head of the central banking system of the United States. Known colloquially as "Chairman of the Fed," or in market circles "Fed Chairman" or "Fed Chief"...
. Objectivism holds that there is an objective external reality that can be known with reason, that human beings should act in accordance with their own rational self-interest
Ethical egoism
Ethical egoism is the normative ethical position that moral agents ought to do what is in their own self-interest. It differs from psychological egoism, which claims that people can only act in their self-interest. Ethical egoism also differs from rational egoism, which holds merely that it is...
, and that the proper form of economic organization is laissez-faire
Laissez-faire
In economics, laissez-faire describes an environment in which transactions between private parties are free from state intervention, including restrictive regulations, taxes, tariffs and enforced monopolies....
capitalism. Academic philosophers have been highly critical of the quality and intellectual rigor of Rand's work, but she remains a popular, albeit controversial, figure within the American libertarian movement.
In 1971 John Rawls
John Rawls
John Bordley Rawls was an American philosopher and a leading figure in moral and political philosophy. He held the James Bryant Conant University Professorship at Harvard University....
published his book A Theory of Justice
A Theory of Justice
A Theory of Justice is a book of political philosophy and ethics by John Rawls. It was originally published in 1971 and revised in both 1975 and 1999. In A Theory of Justice, Rawls attempts to solve the problem of distributive justice by utilising a variant of the familiar device of the social...
. The book puts forth Rawls' view of justice as fairness
Justice as Fairness
Justice as Fairness is the political philosopher John Rawls' conception of justice. It comprises two main principles of Liberty and Equality; the second is subdivided into Fair Equality of Opportunity and the Difference Principle....
, one which is based on a form of social contract
Social contract
The social contract is an intellectual device intended to explain the appropriate relationship between individuals and their governments. Social contract arguments assert that individuals unite into political societies by a process of mutual consent, agreeing to abide by common rules and accept...
theory. Rawls employs the use of a conceptual mechanism called the veil of ignorance to outline his idea of the original position
Original position
The original position is a hypothetical situation developed by American philosopher John Rawls as a thought experiment to replace the imagery of a savage state of nature of prior political philosophers like Thomas Hobbes. In it, the parties select principles that will determine the basic structure...
.
In Rawls' philosophy, the original position is the correlate to the Hobbesian
Thomas Hobbes
Thomas Hobbes of Malmesbury , in some older texts Thomas Hobbs of Malmsbury, was an English philosopher, best known today for his work on political philosophy...
state of nature
State of nature
State of nature is a term in political philosophy used in social contract theories to describe the hypothetical condition that preceded governments...
. While in the original position, persons are said to be behind the veil of ignorance, which makes these persons unaware of their individual characteristics and their place in society, such as their race, religion, wealth, etc. The principles of justice are chosen by rational persons while in this original position. The two principles of justice are the equal liberty principle and the principle which governs the distribution of social and economic inequalities. From this, Rawls argues for a system of distributive justice
Distributive justice
Distributive justice concerns what some consider to be socially just allocation of goods in a society. A society in which incidental inequalities in outcome do not arise would be considered a society guided by the principles of distributive justice...
in accordance with the Difference Principle, which says that all social and economic inequalities must be to the greatest benefit of the least advantaged.
Viewing Rawls as promoting excessive government control and rights violations, libertarian
Libertarianism
Libertarianism, in the strictest sense, is the political philosophy that holds individual liberty as the basic moral principle of society. In the broadest sense, it is any political philosophy which approximates this view...
Robert Nozick
Robert Nozick
Robert Nozick was an American political philosopher, most prominent in the 1970s and 1980s. He was a professor at Harvard University. He is best known for his book Anarchy, State, and Utopia , a right-libertarian answer to John Rawls's A Theory of Justice...
published Anarchy, State, and Utopia
Anarchy, State, and Utopia
Anarchy, State, and Utopia is a work of political philosophy written by Robert Nozick in 1974. This minarchist book was the winner of the 1975 National Book Award...
in 1974. The book advocates for a minimal state and defends the liberty of the individual. He argues that the role of government should be limited to "police protection, national defense, and the administration of courts of law, with all other tasks commonly performed by modern governments – education, social insurance, welfare, and so forth – taken over by religious bodies, charities, and other private institutions operating in a free market."
Nozick asserts his view of the entitlement theory
Entitlement Theory
Entitlement theory is a theory of distributive justice and private property created by Robert Nozick in his book Anarchy, State, and Utopia...
of justice, which says that if everyone in society has acquired their holdings in accordance with the principles of acquisition, transfer, and rectification, then any pattern of allocation, no matter how unequal the distribution may be, is just. The entitlement theory of justice holds that the "justice of a distribution is indeed determined by certain historical circumstances (contrary to end-state theories), but it has nothing to do with fitting any pattern guaranteeing that those who worked the hardest or are most deserving have the most shares."
Alasdair MacIntyre
Alasdair MacIntyre
Alasdair Chalmers MacIntyre is a British philosopher primarily known for his contribution to moral and political philosophy but known also for his work in history of philosophy and theology...
, while he was born and educated in the United Kingdom
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
, has spent around forty years living and working in the United States. He is responsible for the resurgence of interest in virtue ethics
Virtue ethics
Virtue ethics describes the character of a moral agent as a driving force for ethical behavior, rather than rules , consequentialism , or social context .The difference between these four approaches to morality tends to lie more in the way moral dilemmas are...
, a moral theory
Ethics
Ethics, also known as moral philosophy, is a branch of philosophy that addresses questions about morality—that is, concepts such as good and evil, right and wrong, virtue and vice, justice and crime, etc.Major branches of ethics include:...
first propounded by the ancient Greek philosopher
Greek philosophy
Ancient Greek philosophy arose in the 6th century BCE and continued through the Hellenistic period, at which point Ancient Greece was incorporated in the Roman Empire...
Aristotle
Aristotle
Aristotle was a Greek philosopher and polymath, a student of Plato and teacher of Alexander the Great. His writings cover many subjects, including physics, metaphysics, poetry, theater, music, logic, rhetoric, linguistics, politics, government, ethics, biology, and zoology...
. He is considered the preeminent Thomist
Thomism
Thomism is the philosophical school that arose as a legacy of the work and thought of St. Thomas Aquinas, philosopher, theologian, and Doctor of the Church. In philosophy, his commentaries on Aristotle are his most lasting contribution...
political philosopher. He holds that "modern philosophy and modern life are characterized by the absence of any coherent moral code, and that the vast majority of individuals living in this world lack a meaningful sense of purpose in their lives and also lack any genuine community". He recommends a return to genuine political communities where individuals can properly acquire their virtues.
Outside academic philosophy, political and social concerns took center stage with the Civil Rights Movement
Civil rights movement
The civil rights movement was a worldwide political movement for equality before the law occurring between approximately 1950 and 1980. In many situations it took the form of campaigns of civil resistance aimed at achieving change by nonviolent forms of resistance. In some situations it was...
and the writings of Martin Luther King, Jr.
Martin Luther King, Jr.
Martin Luther King, Jr. was an American clergyman, activist, and prominent leader in the African-American Civil Rights Movement. He is best known for being an iconic figure in the advancement of civil rights in the United States and around the world, using nonviolent methods following the...
Feminism

Sarah Grimké
Sarah Moore Grimké was an American abolitionist, writer, and suffragist.-Early life:Sarah Grimké was born in South Carolina. She was sixth of fourteen children and the second daughter of Mary and John Faucheraud Grimké, a rich plantation owner who was also an attorney and a judge in South Carolina...
, Charlotte Perkins Gilman
Charlotte Perkins Gilman
Charlotte Perkins Gilman was a prominent American sociologist, novelist, writer of short stories, poetry, and nonfiction, and a lecturer for social reform...
, Elizabeth Cady Stanton
Elizabeth Cady Stanton
Elizabeth Cady Stanton was an American social activist, abolitionist, and leading figure of the early woman's movement...
, and Anne Hutchinson
Anne Hutchinson
Anne Hutchinson was one of the most prominent women in colonial America, noted for her strong religious convictions, and for her stand against the staunch religious orthodoxy of 17th century Massachusetts...
, the feminist movement of the 1960s and 1970s, also known as second-wave feminism
Second-wave feminism
The Feminist Movement, or the Women's Liberation Movement in the United States refers to a period of feminist activity which began during the early 1960s and lasted through the early 1990s....
, is notable for its impact in philosophy.
The popular mind was taken with Betty Friedan
Betty Friedan
Betty Friedan was an American writer, activist, and feminist.A leading figure in the Women's Movement in the United States, her 1963 book The Feminine Mystique is often credited with sparking the "second wave" of American feminism in the twentieth century...
's The Feminine Mystique
The Feminine Mystique
The Feminine Mystique, published February 19, 1963, by W.W. Norton and Co., is a nonfiction book written by Betty Friedan. It is widely credited with sparking the beginning of second-wave feminism in the United States....
. This was accompanied by other feminist philosophers, such as Adrienne Rich
Adrienne Rich
Adrienne Cecile Rich is an American poet, essayist and feminist. She has been called "one of the most widely read and influential poets of the second half of the 20th century."-Early life:...
. These philosophers critiqued basic assumptions and values of philosophy, such as objectivity and what they believe to be masculine approaches to ethics, for example, rights-based political theories. They wrote that there is no such thing as a value-neutral inquiry and they sought to analyze the social dimensions of philosophical issues.
Contemporary philosophy

Hilary Putnam
Hilary Whitehall Putnam is an American philosopher, mathematician and computer scientist, who has been a central figure in analytic philosophy since the 1960s, especially in philosophy of mind, philosophy of language, philosophy of mathematics, and philosophy of science...
and Richard Rorty
Richard Rorty
Richard McKay Rorty was an American philosopher. He had a long and diverse academic career, including positions as Stuart Professor of Philosophy at Princeton, Kenan Professor of Humanities at the University of Virginia, and Professor of Comparative Literature at Stanford University...
. Rorty is famous as the author of Philosophy and the Mirror of Nature
Philosophy and the Mirror of Nature
Philosophy and the Mirror of Nature is a famous book by American philosopher Richard Rorty. In it, Rorty attempts to dissolve so-called philosophical problems instead of solving them by exposing them as pseudo-problems that only exist in the language-game of Analytic philosophy...
and Philosophy and Social Hope
Philosophy and Social Hope
Philosophy and Social Hope is a 1999 book written by philosopher Richard Rorty and published by Penguin. The book is a collection of cultural and political essays intended to reach a wider audience and, like his previous books, it presents Rorty's own version of pragmatism...
. Hilary Putnam is well known for his quasi-empiricism in mathematics
Quasi-empiricism in mathematics
Quasi-empiricism in mathematics is the attempt in the philosophy of mathematics to direct philosophers' attention to mathematical practice, in particular, relations with physics, social sciences, and computational mathematics, rather than solely to issues in the foundations of mathematics...
, his challenge of the brain in a vat
Brain in a vat
In philosophy, the brain in a vat is an element used in a variety of thought experiments intended to draw out certain features of our ideas of knowledge, reality, truth, mind, and meaning...
thought experiment
Thought experiment
A thought experiment or Gedankenexperiment considers some hypothesis, theory, or principle for the purpose of thinking through its consequences...
, and his other work in philosophy of mind
Philosophy of mind
Philosophy of mind is a branch of philosophy that studies the nature of the mind, mental events, mental functions, mental properties, consciousness and their relationship to the physical body, particularly the brain. The mind-body problem, i.e...
, philosophy of language
Philosophy of language
Philosophy of language is the reasoned inquiry into the nature, origins, and usage of language. As a topic, the philosophy of language for analytic philosophers is concerned with four central problems: the nature of meaning, language use, language cognition, and the relationship between language...
, and philosophy of science
Philosophy of science
The philosophy of science is concerned with the assumptions, foundations, methods and implications of science. It is also concerned with the use and merit of science and sometimes overlaps metaphysics and epistemology by exploring whether scientific results are actually a study of truth...
.
The debates that occur within the philosophy of mind
Philosophy of mind
Philosophy of mind is a branch of philosophy that studies the nature of the mind, mental events, mental functions, mental properties, consciousness and their relationship to the physical body, particularly the brain. The mind-body problem, i.e...
have taken center stage. American philosophers such as Hilary Putnam, Donald Davidson
Donald Davidson (philosopher)
Donald Herbert Davidson was an American philosopher born in Springfield, Massachusetts, who served as Slusser Professor of Philosophy at the University of California, Berkeley from 1981 to 2003 after having also held teaching appointments at Stanford University, Rockefeller University, Princeton...
, Daniel Dennett
Daniel Dennett
Daniel Clement Dennett is an American philosopher, writer and cognitive scientist whose research centers on the philosophy of mind, philosophy of science and philosophy of biology, particularly as those fields relate to evolutionary biology and cognitive science. He is currently the Co-director of...
, Douglas Hofstadter
Douglas Hofstadter
Douglas Richard Hofstadter is an American academic whose research focuses on consciousness, analogy-making, artistic creation, literary translation, and discovery in mathematics and physics...
, John Searle
John Searle
John Rogers Searle is an American philosopher and currently the Slusser Professor of Philosophy at the University of California, Berkeley.-Biography:...
, as well as Patricia
Patricia Churchland
Patricia Smith Churchland is a Canadian-American philosopher noted for her contributions to neurophilosophy and the philosophy of mind. She has been a Professor at the University of California, San Diego since 1984...
and Paul Churchland
Paul Churchland
Paul Churchland is a philosopher noted for his studies in neurophilosophy and the philosophy of mind. He is currently a Professor at the University of California, San Diego, where he holds the Valtz Chair of Philosophy. Churchland holds a joint appointment with the Cognitive Science Faculty and...
continue the discussion of such issues as the nature of mind
Mind
The concept of mind is understood in many different ways by many different traditions, ranging from panpsychism and animism to traditional and organized religious views, as well as secular and materialist philosophies. Most agree that minds are constituted by conscious experience and intelligent...
and the hard problem of consciousness
Hard problem of consciousness
The hard problem of consciousness is the problem of explaining how and why we have qualitative phenomenal experiences. David Chalmers contrasts this with the "easy problems" of explaining the ability to discriminate, integrate information, report mental states, focus attention, etc...
, a philosophical problem indicated by the Australian philosopher David Chalmers
David Chalmers
David John Chalmers is an Australian philosopher specializing in the area of philosophy of mind and philosophy of language, whose recent work concerns verbal disputes. He is Professor of Philosophy and Director of the Centre for Consciousness at the Australian National University...
.
Noted American legal philosophers Ronald Dworkin
Ronald Dworkin
Ronald Myles Dworkin, QC, FBA is an American philosopher and scholar of constitutional law. He is Frank Henry Sommer Professor of Law and Philosophy at New York University and Emeritus Professor of Jurisprudence at University College London, and has taught previously at Yale Law School and the...
and Richard Posner
Richard Posner
Richard Allen Posner is an American jurist, legal theorist, and economist who is currently a judge on the United States Court of Appeals for the Seventh Circuit in Chicago and a Senior Lecturer at the University of Chicago Law School...
work in the fields of political philosophy and jurisprudence
Jurisprudence
Jurisprudence is the theory and philosophy of law. Scholars of jurisprudence, or legal theorists , hope to obtain a deeper understanding of the nature of law, of legal reasoning, legal systems and of legal institutions...
. Posner is famous for his economic analysis of law, a theory which uses microeconomics to understand legal rules and institutions. Dworkin is famous for his theory of law as integrity
Law as integrity
In philosophy of law, law as integrity is a theory of law put forward by the legal philosopher Ronald Dworkin.- External links :*http://law.queensu.ca/facultyAndStaff/facultyDirectory/walters/legalHumanismAndLawAsIntegrityPublishedEd.pdf...
and legal interpretivism.
African-American philosopher Cornel West
Cornel West
Cornel Ronald West is an American philosopher, author, critic, actor, civil rights activist and prominent member of the Democratic Socialists of America....
is known for his analysis of American cultural life with regards to race, gender
Gender
Gender is a range of characteristics used to distinguish between males and females, particularly in the cases of men and women and the masculine and feminine attributes assigned to them. Depending on the context, the discriminating characteristics vary from sex to social role to gender identity...
, and class
Social class
Social classes are economic or cultural arrangements of groups in society. Class is an essential object of analysis for sociologists, political scientists, economists, anthropologists and social historians. In the social sciences, social class is often discussed in terms of 'social stratification'...
issues, as well as his associations with pragmatism
Pragmatism
Pragmatism is a philosophical tradition centered on the linking of practice and theory. It describes a process where theory is extracted from practice, and applied back to practice to form what is called intelligent practice...
and transcendentalism
Transcendentalism
Transcendentalism is a philosophical movement that developed in the 1830s and 1840s in the New England region of the United States as a protest against the general state of culture and society, and in particular, the state of intellectualism at Harvard University and the doctrine of the Unitarian...
.
Alvin Plantinga
Alvin Plantinga
Alvin Carl Plantinga is an American analytic philosopher and the emeritus John A. O'Brien Professor of Philosophy at the University of Notre Dame. He is known for his work in philosophy of religion, epistemology, metaphysics, and Christian apologetics...
is a Christian
Christian
A Christian is a person who adheres to Christianity, an Abrahamic, monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth as recorded in the Canonical gospels and the letters of the New Testament...
thinker known for his evolutionary argument against naturalism
Evolutionary argument against naturalism
The evolutionary argument against naturalism is a philosophical argument regarding a perceived tension between biological evolutionary theory and philosophical naturalism — the belief that there are no supernatural entities or processes...
, his assertion that one can know God as a properly basic belief
Basic belief
Under the epistemological view called foundationalism, basic beliefs are the axioms of a belief system.Foundationalism holds that all beliefs must be justified in order to be believed...
, and his modal
Modal logic
Modal logic is a type of formal logic that extends classical propositional and predicate logic to include operators expressing modality. Modals — words that express modalities — qualify a statement. For example, the statement "John is happy" might be qualified by saying that John is...
version of the ontological argument
Ontological argument
The ontological argument for the existence of God is an a priori argument for the existence of God. The ontological argument was first proposed by the eleventh-century monk Anselm of Canterbury, who defined God as the greatest possible being we can conceive...
for the existence of God. Michael C. Rea
Michael C. Rea
Michael C. Rea is an analytic philosopher, who is currently working as a professor of philosophy at the University of Notre Dame. He specializes in metaphysics and philosophy of religion and has competence in epistemology and applied ethics as well....
has developed Plantinga's thought by claiming that both naturalism and supernaturalism are research programmes that have to be adopted as a basis for research.
See also
- History of philosophyHistory of philosophyThe history of philosophy is the study of philosophical ideas and concepts through time. Issues specifically related to history of philosophy might include : How can changes in philosophy be accounted for historically? What drives the development of thought in its historical context? To what...
Lists:
- List of American philosophers
- List of African American philosophers
- List of Jewish American philosophers
Organizations:
- American Philosophical AssociationAmerican Philosophical AssociationThe American Philosophical Association is the main professional organization for philosophers in the United States. Founded in 1900, its mission is to promote the exchange of ideas among philosophers, to encourage creative and scholarly activity in philosophy, to facilitate the professional work...
- American Society for Political and Legal PhilosophyAmerican Society for Political and Legal PhilosophyThe American Society for Political and Legal Philosophy, or ASPLP, is a learned society founded in 1955 by political theorist Carl Friedrich. The ASPLP's annual thematic conferences form the foundation for the Nomos series. The ASPLP operates according to a distinctive three-discipline structure...
- American Philosophical SocietyAmerican Philosophical SocietyThe American Philosophical Society, founded in 1743, and located in Philadelphia, Pa., is an eminent scholarly organization of international reputation, that promotes useful knowledge in the sciences and humanities through excellence in scholarly research, professional meetings, publications,...

