
Standard electrode potential (data page)
Encyclopedia
The values of standard electrode potentials are given in the table below in volt
s relative to the standard hydrogen electrode
and are assembled from references
The values are for the following conditions:
Legend: (s) – solid; (l) – liquid; (g) – gas; (aq) – aqueous (default for all charged species); (Hg) – amalgam
.
The following values are calculated for pH
7, which is more biologically realistic, but makes the values incompatible with the values in the table above with standard criteria.
Volt
The volt is the SI derived unit for electric potential, electric potential difference, and electromotive force. The volt is named in honor of the Italian physicist Alessandro Volta , who invented the voltaic pile, possibly the first chemical battery.- Definition :A single volt is defined as the...
s relative to the standard hydrogen electrode
Standard hydrogen electrode
The standard hydrogen electrode , is a redox electrode which forms the basis of the thermodynamic scale of oxidation-reduction potentials...
and are assembled from references
The values are for the following conditions:
- the temperature of 298.15 K (25 °C);
- the effective concentrationActivity (chemistry)In chemical thermodynamics, activity is a measure of the “effective concentration” of a species in a mixture, meaning that the species' chemical potential depends on the activity of a real solution in the same way that it would depend on concentration for an ideal solution.By convention, activity...
of 1 mol/L for each aqueous species or a species in a mercury amalgamAmalgam (chemistry)An amalgam is a substance formed by the reaction of mercury with another metal. Almost all metals can form amalgams with mercury, notable exceptions being iron and platinum. Silver-mercury amalgams are important in dentistry, and gold-mercury amalgam is used in the extraction of gold from ore.The...
; - the partial pressureFugacityIn chemical thermodynamics, the fugacity of a real gas is an effective pressure which replaces the true mechanical pressure in accurate chemical equilibrium calculations. It is equal to the pressure of an ideal gas which has the same chemical potential as the real gas. For example, nitrogen gas ...
of 101.325 kPaPascal (unit)The pascal is the SI derived unit of pressure, internal pressure, stress, Young's modulus and tensile strength, named after the French mathematician, physicist, inventor, writer, and philosopher Blaise Pascal. It is a measure of force per unit area, defined as one newton per square metre...
(absolute) (1 atmAtmosphere (unit)The standard atmosphere is an international reference pressure defined as 101325 Pa and formerly used as unit of pressure. For practical purposes it has been replaced by the bar which is 105 Pa...
, 1.01325 barBar (unit)The bar is a unit of pressure equal to 100 kilopascals, and roughly equal to the atmospheric pressure on Earth at sea level. Other units derived from the bar are the megabar , kilobar , decibar , centibar , and millibar...
) for each gaseous reagent. This pressure is used because most literature data are still given for this value rather than for the current standard of 100 kPa. - the activityActivity (chemistry)In chemical thermodynamics, activity is a measure of the “effective concentration” of a species in a mixture, meaning that the species' chemical potential depends on the activity of a real solution in the same way that it would depend on concentration for an ideal solution.By convention, activity...
of unity for each pure solid, pure liquid, or for water (solvent).
Legend: (s) – solid; (l) – liquid; (g) – gas; (aq) – aqueous (default for all charged species); (Hg) – amalgam
Amalgam (chemistry)
An amalgam is a substance formed by the reaction of mercury with another metal. Almost all metals can form amalgams with mercury, notable exceptions being iron and platinum. Silver-mercury amalgams are important in dentistry, and gold-mercury amalgam is used in the extraction of gold from ore.The...
.
| Half-reaction Half-reaction A half reaction is either the oxidation or reduction reaction component of a redox reaction. A half reaction is obtained by considering the change in oxidation states of individual substances involved in the redox reaction.-Example:... |
E° (V) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|
| 3⁄2N2 Nitrogen Nitrogen is a chemical element that has the symbol N, atomic number of 7 and atomic mass 14.00674 u. Elemental nitrogen is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, and mostly inert diatomic gas at standard conditions, constituting 78.08% by volume of Earth's atmosphere... (g) + + HN3(aq) |
||
| Li Lithium Lithium is a soft, silver-white metal that belongs to the alkali metal group of chemical elements. It is represented by the symbol Li, and it has the atomic number 3. Under standard conditions it is the lightest metal and the least dense solid element. Like all alkali metals, lithium is highly... + Li(s) |
||
| N2(g) + 4 + 2 2NH2OH Hydroxylamine Hydroxylamine is an inorganic compound with the formula NH2OH. The pure material is a white, unstable crystalline, hygroscopic compound. However, hydroxylamine is almost always provided and used as an aqueous solution. It is used to prepare oximes, an important functional group. It is also an... (aq) + 2 |
||
| Cs + Cs(s) | ||
| Rb Rubidium Rubidium is a chemical element with the symbol Rb and atomic number 37. Rubidium is a soft, silvery-white metallic element of the alkali metal group. Its atomic mass is 85.4678. Elemental rubidium is highly reactive, with properties similar to those of other elements in group 1, such as very rapid... + Rb(s) |
||
| K Potassium Potassium is the chemical element with the symbol K and atomic number 19. Elemental potassium is a soft silvery-white alkali metal that oxidizes rapidly in air and is very reactive with water, generating sufficient heat to ignite the hydrogen emitted in the reaction.Potassium and sodium are... + K(s) |
||
| Ba Barium Barium is a chemical element with the symbol Ba and atomic number 56. It is the fifth element in Group 2, a soft silvery metallic alkaline earth metal. Barium is never found in nature in its pure form due to its reactivity with air. Its oxide is historically known as baryta but it reacts with... 2+ + 2 Ba(s) |
||
| La Lanthanum Lanthanum is a chemical element with the symbol La and atomic number 57.Lanthanum is a silvery white metallic element that belongs to group 3 of the periodic table and is the first element of the lanthanide series. It is found in some rare-earth minerals, usually in combination with cerium and... (OH)3(s) + 3 La(s) + 3 |
||
| Sr Strontium Strontium is a chemical element with the symbol Sr and the atomic number 38. An alkaline earth metal, strontium is a soft silver-white or yellowish metallic element that is highly reactive chemically. The metal turns yellow when exposed to air. It occurs naturally in the minerals celestine and... 2+ + 2 Sr(s) |
||
| Ca Calcium Calcium is the chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. It has an atomic mass of 40.078 amu. Calcium is a soft gray alkaline earth metal, and is the fifth-most-abundant element by mass in the Earth's crust... 2+ + 2 Ca(s) |
||
| Eu Europium Europium is a chemical element with the symbol Eu and atomic number 63. It is named after the continent of Europe. It is a moderately hard silvery metal which readily oxidizes in air and water... 2+ + 2 Eu(s) |
||
| Ra Radium Radium is a chemical element with atomic number 88, represented by the symbol Ra. Radium is an almost pure-white alkaline earth metal, but it readily oxidizes on exposure to air, becoming black in color. All isotopes of radium are highly radioactive, with the most stable isotope being radium-226,... 2+ + 2 Ra(s) |
||
| Na Sodium Sodium is a chemical element with the symbol Na and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal and is a member of the alkali metals; its only stable isotope is 23Na. It is an abundant element that exists in numerous minerals, most commonly as sodium chloride... + Na(s) |
||
| La Lanthanum Lanthanum is a chemical element with the symbol La and atomic number 57.Lanthanum is a silvery white metallic element that belongs to group 3 of the periodic table and is the first element of the lanthanide series. It is found in some rare-earth minerals, usually in combination with cerium and... 3+ + 3 La(s) |
||
| Y Yttrium Yttrium is a chemical element with symbol Y and atomic number 39. It is a silvery-metallic transition metal chemically similar to the lanthanides and it has often been classified as a "rare earth element". Yttrium is almost always found combined with the lanthanides in rare earth minerals and is... 3+ + 3 Y(s) |
||
| Mg Magnesium Magnesium is a chemical element with the symbol Mg, atomic number 12, and common oxidation number +2. It is an alkaline earth metal and the eighth most abundant element in the Earth's crust and ninth in the known universe as a whole... 2+ + 2 Mg(s) |
||
| ZrO(OH)2(s) + + 4 Zr(s) + 4 | ||
| Al(OH)4− + 3 Al(s) + 4 | ||
| Al(OH)3(s) + 3 Al(s) + 3 | ||
| H2 Hydrogen Hydrogen is the chemical element with atomic number 1. It is represented by the symbol H. With an average atomic weight of , hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant chemical element, constituting roughly 75% of the Universe's chemical elemental mass. Stars in the main sequence are mainly... (g) + 2 2H− |
||
| Ac Actinium Actinium is a radioactive chemical element with the symbol Ac and atomic number 89, which was discovered in 1899. It was the first non-primordial radioactive element to be isolated. Polonium, radium and radon were observed before actinium, but they were not isolated until 1902... 3+ + 3 Ac(s) |
||
| Be Beryllium Beryllium is the chemical element with the symbol Be and atomic number 4. It is a divalent element which occurs naturally only in combination with other elements in minerals. Notable gemstones which contain beryllium include beryl and chrysoberyl... 2+ + 2 Be(s) |
||
| U Uranium Uranium is a silvery-white metallic chemical element in the actinide series of the periodic table, with atomic number 92. It is assigned the chemical symbol U. A uranium atom has 92 protons and 92 electrons, of which 6 are valence electrons... 3+ + 3 U(s) |
||
| Al Aluminium Aluminium or aluminum is a silvery white member of the boron group of chemical elements. It has the symbol Al, and its atomic number is 13. It is not soluble in water under normal circumstances.... 3+ + 3 Al(s) |
||
| Ti Titanium Titanium is a chemical element with the symbol Ti and atomic number 22. It has a low density and is a strong, lustrous, corrosion-resistant transition metal with a silver color.... 2+ + 2 Ti(s) |
||
| ZrO2 Zirconium dioxide Zirconium dioxide , sometimes known as zirconia , is a white crystalline oxide of zirconium. Its most naturally occurring form, with a monoclinic crystalline structure, is the rare mineral baddeleyite. The high temperature cubic crystalline form is rarely found in nature as mineral tazheranite O2... (s) + 4 + 4 Zr(s) + 2 |
||
| Zr4+ Zirconium Zirconium is a chemical element with the symbol Zr and atomic number 40. The name of zirconium is taken from the mineral zircon. Its atomic mass is 91.224. It is a lustrous, grey-white, strong transition metal that resembles titanium... + 4 Zr(s) |
||
| Ti3+ + 3 Ti(s) | ||
| TiO Titanium(II) oxide Titanium oxide is an inorganic chemical compound of titanium and oxygen. It can be prepared from titanium dioxide and titanium metal at 1500°C. It is non-stoichiometric in a range TiO0.7 to TiO1.3 and this is caused by vacancies of either Ti or O in the defect rock salt structure . In pure TiO... (s) + 2 + 2 Ti(s) + |
||
| Ti2O3 Titanium(III) oxide Titanium oxide is a chemical compound of titanium and oxygen. It is prepared by reacting titanium dioxide with titanium metal at 1600°C.... (s) + 2 + 2 2TiO(s) + |
||
| Zn(OH)42− + 2 Zn(s) + 4 | ||
| Mn Manganese Manganese is a chemical element, designated by the symbol Mn. It has the atomic number 25. It is found as a free element in nature , and in many minerals... 2+ + 2 Mn(s) |
||
| Fe Iron Iron is a chemical element with the symbol Fe and atomic number 26. It is a metal in the first transition series. It is the most common element forming the planet Earth as a whole, forming much of Earth's outer and inner core. It is the fourth most common element in the Earth's crust... (CN)64− + 6 + 2 Fe(s) + 4HCN(aq) |
||
| Te(s) + 2 Te2− | ||
| V Vanadium Vanadium is a chemical element with the symbol V and atomic number 23. It is a hard, silvery gray, ductile and malleable transition metal. The formation of an oxide layer stabilizes the metal against oxidation. The element is found only in chemically combined form in nature... 2+ + 2 V(s) |
||
| Nb Niobium Niobium or columbium , is a chemical element with the symbol Nb and atomic number 41. It's a soft, grey, ductile transition metal, which is often found in the pyrochlore mineral, the main commercial source for niobium, and columbite... 3+ + 3 Nb(s) |
||
| Sn Tin Tin is a chemical element with the symbol Sn and atomic number 50. It is a main group metal in group 14 of the periodic table. Tin shows chemical similarity to both neighboring group 14 elements, germanium and lead and has two possible oxidation states, +2 and the slightly more stable +4... (s) + 4 + 4 SnH4(g) |
||
| SiO Silicon dioxide The chemical compound silicon dioxide, also known as silica , is an oxide of silicon with the chemical formula '. It has been known for its hardness since antiquity... 2(s) + 4 + 4 Si(s) + 2 |
||
| B(OH) Boric acid Boric acid, also called hydrogen borate or boracic acid or orthoboric acid or acidum boricum, is a weak acid of boron often used as an antiseptic, insecticide, flame retardant, as a neutron absorber, and as a precursor of other chemical compounds. It exists in the form of colorless crystals or a... 3(aq) + 3 + 3 B(s) + 3 |
||
| Fe(OH)2(s) + 2 Fe(s) + 2 | ||
| Fe2O3(s) + 3 + 2 2Fe(OH)2(s) + 2 | ||
| TiO2+ + 2 + 4 Ti(s) + | ||
| 2 Water Water is a chemical substance with the chemical formula H2O. A water molecule contains one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms connected by covalent bonds. Water is a liquid at ambient conditions, but it often co-exists on Earth with its solid state, ice, and gaseous state . Water also exists in a... + 2 H2(g) + 2 |
||
| Bi Bismuth Bismuth is a chemical element with symbol Bi and atomic number 83. Bismuth, a trivalent poor metal, chemically resembles arsenic and antimony. Elemental bismuth may occur naturally uncombined, although its sulfide and oxide form important commercial ores. The free element is 86% as dense as lead... (s) + 3 + 3 BiH3 Bismuthine Bismuthine is the chemical compound with the formula BiH3. As the heaviest analogue of ammonia, BiH3 is unstable, decomposing to bismuth metal well below 0 °C... |
||
| Zn Zinc Zinc , or spelter , is a metallic chemical element; it has the symbol Zn and atomic number 30. It is the first element in group 12 of the periodic table. Zinc is, in some respects, chemically similar to magnesium, because its ion is of similar size and its only common oxidation state is +2... 2+ + 2 Zn(Hg) |
||
| Zn Zinc Zinc , or spelter , is a metallic chemical element; it has the symbol Zn and atomic number 30. It is the first element in group 12 of the periodic table. Zinc is, in some respects, chemically similar to magnesium, because its ion is of similar size and its only common oxidation state is +2... 2+ + 2 Zn(s) |
||
| Ta2O5(s) + 10 + 10 2Ta Tantalum Tantalum is a chemical element with the symbol Ta and atomic number 73. Previously known as tantalium, the name comes from Tantalus, a character in Greek mythology. Tantalum is a rare, hard, blue-gray, lustrous transition metal that is highly corrosion resistant. It is part of the refractory... (s) + 5 |
||
| Cr Chromium Chromium is a chemical element which has the symbol Cr and atomic number 24. It is the first element in Group 6. It is a steely-gray, lustrous, hard metal that takes a high polish and has a high melting point. It is also odorless, tasteless, and malleable... 3+ + 3 Cr(s) |
||
| [Au(CN)2]− + Au Gold Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au and an atomic number of 79. Gold is a dense, soft, shiny, malleable and ductile metal. Pure gold has a bright yellow color and luster traditionally considered attractive, which it maintains without oxidizing in air or water. Chemically, gold is a... (s) + 2CN− |
||
| Ta3+ + 3 Ta(s) | ||
| PbO(s) + + 2 Pb(s) + 2 | ||
| 2TiO2(s) + 2 + 2 Ti2O3(s) + | ||
| Ga Gallium Gallium is a chemical element that has the symbol Ga and atomic number 31. Elemental gallium does not occur in nature, but as the gallium salt in trace amounts in bauxite and zinc ores. A soft silvery metallic poor metal, elemental gallium is a brittle solid at low temperatures. As it liquefies... 3+ + 3 Ga(s) |
||
| U4+ + U3+ | ||
| H3PO2 Hypophosphorous acid Hypophosphorous acid is a phosphorus oxoacid and a powerful reducing agent with molecular formula H3PO2. Inorganic chemists refer to the free acid by this name , or the acceptable name of phosphinic acid. It is a colorless low-melting compound, which is soluble in water, dioxane, and alcohols... (aq) + + P(white) + 2 |
||
| H3PO3(aq) + 2 + 2 H3PO2(aq) + | ||
| H3PO3 Phosphorous acid Phosphorous acid is the compound described by the formula H3PO3. This acid is diprotic , not triprotic as might be suggested by this formula. Phosphorous acid is as an intermediate in the preparation of other phosphorus compounds.-Nomenclature and tautomerism:H3PO3 is more clearly described with... (aq) + 3 + 3 P(red) + 3 |
||
| Fe Iron Iron is a chemical element with the symbol Fe and atomic number 26. It is a metal in the first transition series. It is the most common element forming the planet Earth as a whole, forming much of Earth's outer and inner core. It is the fourth most common element in the Earth's crust... 2+ + 2 Fe(s) |
||
| 2CO2 Carbon dioxide Carbon dioxide is a naturally occurring chemical compound composed of two oxygen atoms covalently bonded to a single carbon atom... (g) + 2 + 2 HOOCCOOH Oxalic acid Oxalic acid is an organic compound with the formula H2C2O4. This colourless solid is a dicarboxylic acid. In terms of acid strength, it is about 3,000 times stronger than acetic acid. Oxalic acid is a reducing agent and its conjugate base, known as oxalate , is a chelating agent for metal cations... (aq) |
||
| Cr3+ + Cr2+ | ||
| Cd Cadmium Cadmium is a chemical element with the symbol Cd and atomic number 48. This soft, bluish-white metal is chemically similar to the two other stable metals in group 12, zinc and mercury. Similar to zinc, it prefers oxidation state +2 in most of its compounds and similar to mercury it shows a low... 2+ + 2 Cd(s) |
||
| GeO2 Germanium dioxide Germanium dioxide, also called germanium oxide and germania, is an inorganic compound, an oxide of germanium. Its chemical formula is GeO2. Other names include germanic acid, G-15, and ACC10380... (s) + 2 + 2 GeO(s) + |
||
| Cu2O Copper(I) oxide Copper oxide or cuprous oxide is the inorganic compound with the formula Cu2O. It is one of the principal oxides of copper. This red-coloured solid is a component of some antifouling paints. The compound can appear either yellow or red, depending on the size of the particles, but both forms... (s) + + 2 2Cu(s) + 2 |
||
| PbSO4 Lead(II) sulfate Lead sulfate is a white crystal or powder. It is also known as fast white, milk white, sulfuric acid lead salt or anglesite.... (s) + 2 Pb Lead Lead is a main-group element in the carbon group with the symbol Pb and atomic number 82. Lead is a soft, malleable poor metal. It is also counted as one of the heavy metals. Metallic lead has a bluish-white color after being freshly cut, but it soon tarnishes to a dull grayish color when exposed... (s) + SO42− |
||
| PbSO4(s) + 2 Pb(Hg) + SO42− | ||
| Eu3+ Europium Europium is a chemical element with the symbol Eu and atomic number 63. It is named after the continent of Europe. It is a moderately hard silvery metal which readily oxidizes in air and water... + Eu2+ |
||
| In Indium Indium is a chemical element with the symbol In and atomic number 49. This rare, very soft, malleable and easily fusible post-transition metal is chemically similar to gallium and thallium, and shows the intermediate properties between these two... 3+ + 3 In(s) |
||
| Tl Thallium Thallium is a chemical element with the symbol Tl and atomic number 81. This soft gray poor metal resembles tin but discolors when exposed to air. The two chemists William Crookes and Claude-Auguste Lamy discovered thallium independently in 1861 by the newly developed method of flame spectroscopy... + Tl(s) |
||
| Ge Germanium Germanium is a chemical element with the symbol Ge and atomic number 32. It is a lustrous, hard, grayish-white metalloid in the carbon group, chemically similar to its group neighbors tin and silicon. The isolated element is a semiconductor, with an appearance most similar to elemental silicon.... (s) + 4 + 4 GeH4(g) |
||
| Co Cobalt Cobalt is a chemical element with symbol Co and atomic number 27. It is found naturally only in chemically combined form. The free element, produced by reductive smelting, is a hard, lustrous, silver-gray metal.... 2+ + 2 Co(s) |
||
| H3PO4 Phosphoric acid Phosphoric acid, also known as orthophosphoric acid or phosphoric acid, is a mineral acid having the chemical formula H3PO4. Orthophosphoric acid molecules can combine with themselves to form a variety of compounds which are also referred to as phosphoric acids, but in a more general way... (aq) + 2 + 2 H3PO3(aq) + |
||
| V3+ + V2+ | ||
| Ni Nickel Nickel is a chemical element with the chemical symbol Ni and atomic number 28. It is a silvery-white lustrous metal with a slight golden tinge. Nickel belongs to the transition metals and is hard and ductile... 2+ + 2 Ni(s) |
||
| As Arsenic Arsenic is a chemical element with the symbol As, atomic number 33 and relative atomic mass 74.92. Arsenic occurs in many minerals, usually in conjunction with sulfur and metals, and also as a pure elemental crystal. It was first documented by Albertus Magnus in 1250.Arsenic is a metalloid... (s) + 3 + 3 AsH3 Arsine Arsine is the chemical compound with the formula AsH3. This flammable, pyrophoric, and highly toxic gas is one of the simplest compounds of arsenic... (g) |
||
| AgI Silver iodide Silver iodide is a yellow, inorganic, photosensitive iodide of silver used in photography, in medicine as an antiseptic, and in rainmaking for cloud seeding.-Crystal structure:... (s) + Ag(s) + I− |
||
| MoO Molybdenum dioxide Molybdenum dioxide is the chemical compound with the formula MoO2. It is a violet-colored solid and is a metallic conductor. It crystallizes in a monoclinic cell, and has a distorted rutile, crystal structure. In TiO2 the oxide anions are close packed and titanium atoms occupy half of the... 2(s) + 4 + 4 Mo(s) + 2 |
||
| Si Silicon Silicon is a chemical element with the symbol Si and atomic number 14. A tetravalent metalloid, it is less reactive than its chemical analog carbon, the nonmetal directly above it in the periodic table, but more reactive than germanium, the metalloid directly below it in the table... (s) + 4 + 4 SiH4(g) |
||
| Sn2+ + 2 Sn(s) | ||
| O Oxygen Oxygen is the element with atomic number 8 and represented by the symbol O. Its name derives from the Greek roots ὀξύς and -γενής , because at the time of naming, it was mistakenly thought that all acids required oxygen in their composition... 2(g) + + HO2•(aq) |
||
| Pb Lead Lead is a main-group element in the carbon group with the symbol Pb and atomic number 82. Lead is a soft, malleable poor metal. It is also counted as one of the heavy metals. Metallic lead has a bluish-white color after being freshly cut, but it soon tarnishes to a dull grayish color when exposed... 2+ + 2 Pb(s) |
||
| WO2 Tungsten(IV) oxide Tungsten dioxide is the chemical compound with the formula WO2. The bronze-colored solid crystallizes in a monoclinic cell. The rutile-like structure features distorted octahedral WO6 centers with alternate short W–W bonds... (s) + 4 + 4 W Tungsten Tungsten , also known as wolfram , is a chemical element with the chemical symbol W and atomic number 74.A hard, rare metal under standard conditions when uncombined, tungsten is found naturally on Earth only in chemical compounds. It was identified as a new element in 1781, and first isolated as... (s) + 2 |
||
| P Phosphorus Phosphorus is the chemical element that has the symbol P and atomic number 15. A multivalent nonmetal of the nitrogen group, phosphorus as a mineral is almost always present in its maximally oxidized state, as inorganic phosphate rocks... (red) + 3 + 3 PH3 Phosphine Phosphine is the compound with the chemical formula PH3. It is a colorless, flammable, toxic gas. Pure phosphine is odourless, but technical grade samples have a highly unpleasant odor like garlic or rotting fish, due to the presence of substituted phosphine and diphosphine... (g) |
||
| CO2(g) + 2 + 2 HCOOH(aq) | ||
| Se Selenium Selenium is a chemical element with atomic number 34, chemical symbol Se, and an atomic mass of 78.96. It is a nonmetal, whose properties are intermediate between those of adjacent chalcogen elements sulfur and tellurium... (s) + 2 + 2 H2Se(g) |
||
| CO2(g) + 2 + 2 CO(g) + | ||
| SnO Tin(II) oxide Tin oxide is a compound of tin and oxygen where tin has the oxidation state of +2. There are two forms, a stable blue-black form and a metastable red form.-Preparation and reactions:... (s) + 2 + 2 Sn(s) + |
||
| SnO2 Tin dioxide Tin dioxide is the inorganic compound with the formula SnO2. The mineral form of SnO2 is called cassiterite, and this is the main ore of tin. With many other names , this oxide of tin is the most important raw material in tin chemistry... (s) + 2 + 2 SnO(s) + |
||
| WO3(aq) + 6 + 6 W(s) + 3 | ||
| P Phosphorus Phosphorus is the chemical element that has the symbol P and atomic number 15. A multivalent nonmetal of the nitrogen group, phosphorus as a mineral is almost always present in its maximally oxidized state, as inorganic phosphate rocks... (white) + 3 + 3 PH3 Phosphine Phosphine is the compound with the chemical formula PH3. It is a colorless, flammable, toxic gas. Pure phosphine is odourless, but technical grade samples have a highly unpleasant odor like garlic or rotting fish, due to the presence of substituted phosphine and diphosphine... (g) |
||
| Fe3+ + 3 Fe(s) | ||
| HCOOH Formic acid Formic acid is the simplest carboxylic acid. Its chemical formula is HCOOH or HCO2H. It is an important intermediate in chemical synthesis and occurs naturally, most notably in the venom of bee and ant stings. In fact, its name comes from the Latin word for ant, formica, referring to its early... (aq) + 2 + 2 HCHO(aq) + |
||
| 2 + 2 H2(g) | 0.0000 | ≡ 0 |
| AgBr Silver bromide Silver bromide , a soft, pale-yellow, water insoluble salt well known for its unusual sensitivity to light. This property has allowed silver halides to become the basis of modern photographic materials. AgBr is widely used in photographic films and is believed by some to have been used for making... (s) + Ag(s) + Br− |
+0.07133 | |
| S4O62− Tetrathionate The tetrathionate anion, S4O62−, is a sulfur oxoanion derived from the compound tetrathionic acid, H2S4O6. Two of the sulfur atoms present in the ion are in oxidation state 0 and two are in oxidation state +5. Alternatively, the compound can be viewed as the adduct resulting from the binding of... + 2 2S2O32− Thiosulfate Thiosulfate is an oxyanion of sulfur. The prefix thio indicates that thiosulfate ion is a sulfate ion with one oxygen replaced by a sulfur. Thiosulfate occurs naturally and is produced by certain biochemical processes... |
+0.08 | |
| Fe3O4 Magnetite Magnetite is a ferrimagnetic mineral with chemical formula Fe3O4, one of several iron oxides and a member of the spinel group. The chemical IUPAC name is iron oxide and the common chemical name is ferrous-ferric oxide. The formula for magnetite may also be written as FeO·Fe2O3, which is one part... (s) + 8 + 8 3Fe(s) + 4 |
+0.085 | |
| N2 Nitrogen Nitrogen is a chemical element that has the symbol N, atomic number of 7 and atomic mass 14.00674 u. Elemental nitrogen is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, and mostly inert diatomic gas at standard conditions, constituting 78.08% by volume of Earth's atmosphere... (g) + 2 + 6 + 6 2NH4OH Ammonium hydroxide Ammonia solution, also known as ammonium hydroxide, ammonia water, ammonical liquor, ammonia liquor, aqua ammonia, aqueous ammonia, or simply ammonia, is a solution of ammonia in water. It can be denoted by the symbols NH3... (aq) |
+0.092 | |
| HgO Mercury(II) oxide Mercury oxide, also called mercuric oxide or simply mercury oxide, has a formula of HgO. It has a red or orange color. Mercury oxide is a solid at room temperature and pressure... (s) + + 2 Hg(l) + 2 |
+0.0977 | |
| Cu(NH3)42+ + Cu(NH3)2 + 2NH3 | +0.10 | |
| Ru(NH3)63+ Ruthenium Ruthenium is a chemical element with symbol Ru and atomic number 44. It is a rare transition metal belonging to the platinum group of the periodic table. Like the other metals of the platinum group, ruthenium is inert to most chemicals. The Russian scientist Karl Ernst Claus discovered the element... + Ru(NH3)62+ |
+0.10 | |
| N2H4 Hydrazine Hydrazine is an inorganic compound with the formula N2H4. It is a colourless flammable liquid with an ammonia-like odor. Hydrazine is highly toxic and dangerously unstable unless handled in solution. Approximately 260,000 tons are manufactured annually... (aq) + 4 + 2 2NH4 + 4 |
+0.11 | |
| H2MoO4 Molybdic acid Molybdic acid refrs to solid, hydrated forms of molybdenum trioxide and species in aqueous solution.The simplest solid form, the monohydrate, is MoO3·H2O, though the dihydrate is also known. The solid state structure of MoO3·H2O consists of layers of octahedrally coordinated MoO5· units where 4... (aq) + 6 + 6 Mo(s) + 4 |
+0.11 | |
| Ge4+ + 4 Ge(s) | +0.12 | |
| C Carbon Carbon is the chemical element with symbol C and atomic number 6. As a member of group 14 on the periodic table, it is nonmetallic and tetravalent—making four electrons available to form covalent chemical bonds... (s) + 4 + 4 CH4 Methane Methane is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is the simplest alkane, the principal component of natural gas, and probably the most abundant organic compound on earth. The relative abundance of methane makes it an attractive fuel... (g) |
+0.13 | |
| HCHO Formaldehyde Formaldehyde is an organic compound with the formula CH2O. It is the simplest aldehyde, hence its systematic name methanal.Formaldehyde is a colorless gas with a characteristic pungent odor. It is an important precursor to many other chemical compounds, especially for polymers... (aq) + 2 + 2 CH3OH Methanol Methanol, also known as methyl alcohol, wood alcohol, wood naphtha or wood spirits, is a chemical with the formula CH3OH . It is the simplest alcohol, and is a light, volatile, colorless, flammable liquid with a distinctive odor very similar to, but slightly sweeter than, ethanol... (aq) |
+0.13 | |
| S Sulfur Sulfur or sulphur is the chemical element with atomic number 16. In the periodic table it is represented by the symbol S. It is an abundant, multivalent non-metal. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms form cyclic octatomic molecules with chemical formula S8. Elemental sulfur is a bright yellow... (s) + 2 + 2 H2S(g) |
+0.14 | |
| Sn4+ + 2 Sn2+ | +0.15 | |
| Cu Copper Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu and atomic number 29. It is a ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. Pure copper is soft and malleable; an exposed surface has a reddish-orange tarnish... 2+ + Cu |
+0.159 | |
| HSO4− + 3 + 2 SO2(aq) + 2 | +0.16 | |
| UO22+ Uranyl The uranyl ion is an oxycation of uranium in the oxidation state +6, with the chemical formula [UO2]2+. It has a linear structure with short U-O bonds, indicative of the presence of multiple bonds between uranium and oxygen. Four or more ligands are bound to the uranyl ion in an equatorial plane... + UO2 |
+0.163 | |
| SO42− + 4 + 2 SO2(aq) + 2 | +0.17 | |
| TiO2+ + 2 + Ti3+ + | +0.19 | |
| SbO + 2 + 3 Sb(s) + | +0.20 | |
| AgCl Silver chloride Silver chloride is a chemical compound with the chemical formula AgCl. This white crystalline solid is well known for its low solubility in water . Upon illumination or heating, silver chloride converts to silver , which is signalled by greyish or purplish coloration to some samples... (s) + Ag(s) + Cl− |
+0.22233 | |
| H3AsO3(aq) + 3 + 3 As(s) + 3 | +0.24 | |
| GeO(s) + 2 + 2 Ge(s) + | +0.26 | |
| UO2 + 4 + U4+ + 2 | +0.273 | |
| Re Rhenium Rhenium is a chemical element with the symbol Re and atomic number 75. It is a silvery-white, heavy, third-row transition metal in group 7 of the periodic table. With an average concentration of 1 part per billion , rhenium is one of the rarest elements in the Earth's crust. The free element has... 3+ + 3 Re(s) |
+0.300 | |
| Bi3+ + 3 Bi(s) | +0.308 | |
| VO2+ + 2 + V3+ + | +0.34 | |
| Cu2+ + 2 Cu(s) | +0.340 | |
| [Fe(CN)6]3− + [Fe(CN)6]4− | +0.36 | |
| O2(g) + 2 + 4 4(aq) | +0.40 | |
| H2MoO4 + 6 + 3 Mo3+ + 2 | +0.43 | |
| CH3OH(aq) + 2 + 2 CH4(g) + | +0.50 | |
| SO2(aq) + 4 + 4 S(s) + 2 | +0.50 | |
| Cu + Cu(s) | +0.520 | |
| CO Carbon monoxide Carbon monoxide , also called carbonous oxide, is a colorless, odorless, and tasteless gas that is slightly lighter than air. It is highly toxic to humans and animals in higher quantities, although it is also produced in normal animal metabolism in low quantities, and is thought to have some normal... (g) + 2 + 2 C(s) + |
+0.52 | |
| I3− + 2 3I− | +0.53 | |
| I Iodine Iodine is a chemical element with the symbol I and atomic number 53. The name is pronounced , , or . The name is from the , meaning violet or purple, due to the color of elemental iodine vapor.... 2(s) + 2 2I− |
+0.54 | |
| [AuI4]− + 3 Au(s) + 4I− | +0.56 | |
| H3AsO4(aq) + 2 + 2 H3AsO3(aq) + | +0.56 | |
| [AuI2]− + Au(s) + 2I− | +0.58 | |
| MnO4− + 2 + 3 MnO2(s) + 4 | +0.59 | |
| S2O32− + 6 + 4 2S(s) + 3 | +0.60 | |
| Fc Ferrocene Ferrocene is an organometallic compound with the formula Fe2. It is the prototypical metallocene, a type of organometallic chemical compound consisting of two cyclopentadienyl rings bound on opposite sides of a central metal atom. Such organometallic compounds are also known as sandwich compounds... + Fc(s) |
+0.641 | |
| H2MoO4(aq) + 2 + 2 MoO2(s) + 2 | +0.65 | |
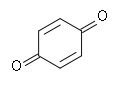 |
+0.6992 | |
| O2(g) + 2 + 2 2(aq) | +0.70 | |
| Tl3+ + 3 Tl(s) | +0.72 | |
| PtCl62− + 2 PtCl42− + 2Cl− | +0.726 | |
| H2SeO3(aq) + 4 + 4 Se(s) + 3 | +0.74 | |
| PtCl42− + 2 Pt(s) + 4Cl− | +0.758 | |
| Fe3+ + Fe2+ | +0.77 | |
| Ag Silver Silver is a metallic chemical element with the chemical symbol Ag and atomic number 47. A soft, white, lustrous transition metal, it has the highest electrical conductivity of any element and the highest thermal conductivity of any metal... + Ag(s) |
+0.7996 | |
| Hg Mercury (element) Mercury is a chemical element with the symbol Hg and atomic number 80. It is also known as quicksilver or hydrargyrum... 2+ + 2 Hg(l) |
+0.80 | |
| NO3− Nitrate The nitrate ion is a polyatomic ion with the molecular formula NO and a molecular mass of 62.0049 g/mol. It is the conjugate base of nitric acid, consisting of one central nitrogen atom surrounded by three identically-bonded oxygen atoms in a trigonal planar arrangement. The nitrate ion carries a... (aq) + 2 + NO2 Nitrogen dioxide Nitrogen dioxide is the chemical compound with the formula it is one of several nitrogen oxides. is an intermediate in the industrial synthesis of nitric acid, millions of tons of which are produced each year. This reddish-brown toxic gas has a characteristic sharp, biting odor and is a prominent... (g) + |
+0.80 | |
| FeO42− Ferrate In chemistry, ferrate refers either to the anion , in which iron is in the +6 oxidation state, or to a salt containing this anion. The term ferrate is often used to mean ferrate, although according to IUPAC naming conventions, it may also refer to other iron-containing oxyanions, such as ferrate... + 5 + 6 Fe2O3(s) + 10 |
+0.81 | |
| [AuBr4]− + 3 Au(s) + 4Br− | +0.85 | |
| Hg2+ + 2 Hg(l) | +0.85 | |
| MnO4− + + HMnO4− | +0.90 | |
| 2Hg2+ + 2 Hg22+ | +0.91 | |
| Pd2+ Palladium Palladium is a chemical element with the chemical symbol Pd and an atomic number of 46. It is a rare and lustrous silvery-white metal discovered in 1803 by William Hyde Wollaston. He named it after the asteroid Pallas, which was itself named after the epithet of the Greek goddess Athena, acquired... + 2 Pd(s) |
+0.915 | |
| [AuCl4]− + 3 Au(s) + 4Cl− | +0.93 | |
| MnO2(s) + 4 + Mn3+ + 2 | +0.95 | |
| [AuBr2]− + Au(s) + 2Br− | +0.96 | |
| [HXeO6]3− + 2 + 2 + [HXeO4]− + 4 | +0.99 | |
| H6TeO6 Telluric acid Telluric acid is a chemical compound with the formula Te6. It is a white solid made up of octahedral Te6 molecules which persist in aqueous solution... (aq) + 2 + 2 TeO2(s) + 4 |
+1.02 | |
| Br2(l) + 2 2Br− | +1.066 | |
| Br2(aq) + 2 2Br− | +1.0873 | |
| IO3− + 5 + 4 HIO(aq) + 2 | +1.13 | |
| [AuCl2]− + Au(s) + 2Cl− | +1.15 | |
| HSeO4− + 3 + 2 H2SeO3(aq) + | +1.15 | |
| Ag2O(s) + 2 + 2 2Ag(s) + | +1.17 | |
| ClO3− + 2 + ClO2(g) + | +1.18 | |
| [HXeO6]3− + 5 + 8 Xe(g) + 11 | +1.18 | |
| Pt2+ Platinum Platinum is a chemical element with the chemical symbol Pt and an atomic number of 78. Its name is derived from the Spanish term platina del Pinto, which is literally translated into "little silver of the Pinto River." It is a dense, malleable, ductile, precious, gray-white transition metal... + 2 Pt(s) |
+1.188 | |
| ClO2(g) + + HClO2(aq) | +1.19 | |
| 2IO3− + 12 + 10 I2(s) + 6 | +1.20 | |
| ClO4− + 2 + 2 ClO3− + | +1.20 | |
| O2(g) + 4 + 4 2 | +1.229 | |
| MnO2(s) + 4 + 2 Mn2+ + 2 | +1.23 | |
| [HXeO4]− + 3 + 6 Xe(g) + 7 | +1.24 | |
| Tl3+ + 2 Tl | +1.25 | |
| Cr2O72− + 14 + 6 2Cr3+ + 7 | +1.33 | |
| Cl2(g) + 2 2Cl− | +1.36 | |
| CoO2(s) + 4 + Co3+ + 2 | +1.42 | |
| 2NH3O Hydroxylamine Hydroxylamine is an inorganic compound with the formula NH2OH. The pure material is a white, unstable crystalline, hygroscopic compound. However, hydroxylamine is almost always provided and used as an aqueous solution. It is used to prepare oximes, an important functional group. It is also an... + + 2 N2H5 Hydrazine Hydrazine is an inorganic compound with the formula N2H4. It is a colourless flammable liquid with an ammonia-like odor. Hydrazine is highly toxic and dangerously unstable unless handled in solution. Approximately 260,000 tons are manufactured annually... + 2 |
+1.42 | |
| 2HIO(aq) + 2 + 2 I2(s) + 2 | +1.44 | |
| Ce4+ + Ce3+ | +1.44 | |
| BrO3− + 5 + 4 HBrO(aq) + 2 | +1.45 | |
| β-PbO2(s) + 4 + 2 Pb2+ + 2 | +1.460 | |
| α-PbO2(s) + 4 + 2 Pb2+ + 2 | +1.468 | |
| 2BrO3− + 12 + 10 Br2(l) + 6 | +1.48 | |
| 2ClO3− + 12 + 10 Cl2(g) + 6 | +1.49 | |
| MnO4− + 8 + 5 Mn2+ + 4 | +1.51 | |
| HO2• + + 2(aq) | +1.51 | |
| Au3+ + 3 Au(s) | +1.52 | |
| NiO2(s) + 4 + 2 Ni2+ + 2 | +1.59 | |
| 2HClO(aq) + 2 + 2 Cl2(g) + 2 | +1.63 | |
| Ag2O3(s) + 6 + 4 2Ag + 3 | +1.67 | |
| HClO2(aq) + 2 + 2 HClO(aq) + | +1.67 | |
| Pb4+ + 2 Pb2+ | +1.69 | |
| MnO4− Permanganate A permanganate is the general name for a chemical compound containing the manganate ion, . Because manganese is in the +7 oxidation state, the permanganate ion is a strong oxidizing agent. The ion has tetrahedral geometry... + 4 + 3 MnO2 Manganese(IV) oxide Manganese oxide is the inorganic compound with the formula . This blackish or brown solid occurs naturally as the mineral pyrolusite, which is the main ore of manganese and a component of manganese nodules. The principal use for MnO2 is for dry-cell batteries, such as the alkaline battery and the... (s) + 2 |
+1.70 | |
| AgO(s) + 2 + Ag + | +1.77 | |
| 2(aq) + 2 + 2 2 | +1.78 | |
| Co3+ + Co2+ | +1.82 | |
| Au + Au(s) | +1.83 | |
| BrO4− + 2 + 2 BrO3− + | +1.85 | |
| Ag2+ + Ag | +1.98 | |
| S2O82− Peroxodisulfate The peroxodisulfate ion, S2O82−, is a sulfur oxoanion. It is commonly referred to as the persulfate ion, but this term also refers to the peroxomonosulfate ion, SO52−.-Compounds containing peroxodisulfate:* Na2S2O8* K2S2O8* 2S2O8... + 2 2SO42− Sulfate In inorganic chemistry, a sulfate is a salt of sulfuric acid.-Chemical properties:... |
+2.010 | |
| O3 Ozone Ozone , or trioxygen, is a triatomic molecule, consisting of three oxygen atoms. It is an allotrope of oxygen that is much less stable than the diatomic allotrope... (g) + 2 + 2 O2(g) + |
+2.075 | |
| HMnO4− + 3 + 2 MnO2(s) + 2 | +2.09 | |
| XeO3(aq) + 6 + 6 Xe(g) + 3 | +2.12 | |
| H4XeO6(aq) + 8 + 8 Xe(g) + 6 | +2.18 | |
| FeO42− + 3 + 8 Fe3+ + 4 | +2.20 | |
| XeF2(aq) + 2 + 2 Xe(g) + 2HF(aq) | +2.32 | |
| H4XeO6(aq) + 2 + 2 XeO3(aq) + | +2.42 | |
| F Fluorine Fluorine is the chemical element with atomic number 9, represented by the symbol F. It is the lightest element of the halogen column of the periodic table and has a single stable isotope, fluorine-19. At standard pressure and temperature, fluorine is a pale yellow gas composed of diatomic... 2(g) + 2 2F− |
+2.87 | |
| F2(g) + 2 + 2 2HF(aq) | +3.05 |
In oxidative phosphorylation
Oxidative phosphorylation is the means by which organism generate energy, and is driven by differences in electrode potential between intermediaries in a chain of reactions.The following values are calculated for pH
PH
In chemistry, pH is a measure of the acidity or basicity of an aqueous solution. Pure water is said to be neutral, with a pH close to 7.0 at . Solutions with a pH less than 7 are said to be acidic and solutions with a pH greater than 7 are basic or alkaline...
7, which is more biologically realistic, but makes the values incompatible with the values in the table above with standard criteria.
| Respiratory enzyme | Redox pair Redox Redox reactions describe all chemical reactions in which atoms have their oxidation state changed.... |
Midpoint potential (Volts) |
|---|---|---|
| NADH dehydrogenase NADH dehydrogenase NADH dehydrogenase is an enzyme located in the inner mitochondrial membrane that catalyzes the transfer of electrons from NADH to coenzyme Q... |
NAD Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, abbreviated NAD, is a coenzyme found in all living cells. The compound is a dinucleotide, since it consists of two nucleotides joined through their phosphate groups. One nucleotide contains an adenine base and the other nicotinamide.In metabolism, NAD is involved... / NADH Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, abbreviated NAD, is a coenzyme found in all living cells. The compound is a dinucleotide, since it consists of two nucleotides joined through their phosphate groups. One nucleotide contains an adenine base and the other nicotinamide.In metabolism, NAD is involved... |
−0.32 |
| Succinate dehydrogenase | FMN Flavin mononucleotide Flavin mononucleotide , or riboflavin-5′-phosphate, is a biomolecule produced from riboflavin by the enzyme riboflavin kinase and functions as prosthetic group of various oxidoreductases including NADH dehydrogenase as well as cofactor in biological blue-light photo receptors... or FAD FAD In biochemistry, flavin adenine dinucleotide is a redox cofactor involved in several important reactions in metabolism. FAD can exist in two different redox states, which it converts between by accepting or donating electrons. The molecule consists of a riboflavin moiety bound to the phosphate... / FMNH2 or FADH2 |
−0.20 |
| Cytochrome bc1 complex Coenzyme Q - cytochrome c reductase In enzymology, a ubiquinol—cytochrome-c reductase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reactionThus, the two substrates of this enzyme are dihydroquinone and ferri- cytochrome c, whereas its 3 products are quinone , ferro- cytochrome c, and H+.This enzyme belongs to the family of... |
Coenzyme Q10ox / Coenzyme Q10red | +0.06 |
| Cytochrome bc1 complex | Cytochrome b Cytochrome b Cytochrome b/b6 is the main subunit of transmembrane cytochrome bc1 and b6f complexes. In addition, it commonly refers to a region of mtDNA used for population genetics and phylogenetics.- Function :... ox / Cytochrome bred |
+0.12 |
| Complex IV Cytochrome c oxidase The enzyme cytochrome c oxidase or Complex IV is a large transmembrane protein complex found in bacteria and the mitochondrion.It is the last enzyme in the respiratory electron transport chain of mitochondria located in the mitochondrial membrane... |
Cytochrome c Cytochrome c The Cytochrome complex, or cyt c is a small heme protein found loosely associated with the inner membrane of the mitochondrion. It belongs to the cytochrome c family of proteins. Cytochrome c is a highly soluble protein, unlike other cytochromes, with a solubility of about 100 g/L and is an... ox / Cytochrome cred |
+0.22 |
| Complex IV | Cytochrome aox / Cytochrome ared | +0.29 |
| Complex IV | O2 / HO− | +0.82 |
See also
- Galvanic seriesGalvanic seriesThe galvanic series determines the nobility of metals and semi-metals. When two metals are submerged in an electrolyte, while electrically connected, the less noble will experience galvanic corrosion. The rate of corrosion is determined by the electrolyte and the difference in nobility...
- biochemically relevant redox potentialsTable of standard reduction potentials for half-reactions important in biochemistryThe values below are standard reduction potentials for half-reactions measured at 25°C, 1 atmosphere and a pH of 7 in aqueous solution....
- Standard electrode potentialStandard electrode potentialIn electrochemistry, the standard electrode potential, abbreviated E° or E , is the measure of individual potential of a reversible electrode at standard state, which is with solutes at an effective concentration of 1 mol dm−3, and gases at a pressure of 1 atm...

