
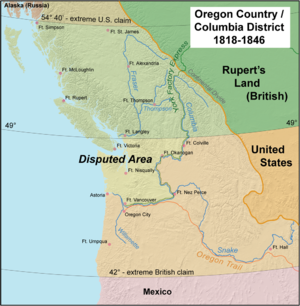
Oregon boundary dispute
Encyclopedia
United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland was the formal name of the United Kingdom during the period when what is now the Republic of Ireland formed a part of it....
and American
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
claims to the Pacific Northwest
Pacific Northwest
The Pacific Northwest is a region in northwestern North America, bounded by the Pacific Ocean to the west and, loosely, by the Rocky Mountains on the east. Definitions of the region vary and there is no commonly agreed upon boundary, even among Pacific Northwesterners. A common concept of the...
of North America
North America
North America is a continent wholly within the Northern Hemisphere and almost wholly within the Western Hemisphere. It is also considered a northern subcontinent of the Americas...
in the first half of the 19th century. Both the United Kingdom (UK) and the United States (USA) had territorial and commercial aspirations in the region as well as residual claims from treaties with Russia and Spain. The British knew the region as the Columbia District
Columbia District
The Columbia District was a fur trading district in the Pacific Northwest region of British North America in the 19th century. It was explored by the North West Company between 1793 and 1811, and established as an operating fur district around 1810...
, a fur-trading division of the Hudson's Bay Company
Hudson's Bay Company
The Hudson's Bay Company , abbreviated HBC, or "The Bay" is the oldest commercial corporation in North America and one of the oldest in the world. A fur trading business for much of its existence, today Hudson's Bay Company owns and operates retail stores throughout Canada...
(HBC), while Americans referred to it as the Oregon Country
Oregon Country
The Oregon Country was a predominantly American term referring to a disputed ownership region of the Pacific Northwest of North America. The region was occupied by British and French Canadian fur traders from before 1810, and American settlers from the mid-1830s, with its coastal areas north from...
. The broadest definition of the disputed region was defined by the following: west of the Continental Divide of the Americas, north of the 42nd parallel north
42nd parallel north
The 42nd parallel north is a circle of latitude that is 42 degrees north of the Earth's equatorial plane. It crosses Europe, the Mediterranean Sea, Asia, the Pacific Ocean, North America, and the Atlantic Ocean....
(the northern border of New Spain
New Spain
New Spain, formally called the Viceroyalty of New Spain , was a viceroyalty of the Spanish colonial empire, comprising primarily territories in what was known then as 'América Septentrional' or North America. Its capital was Mexico City, formerly Tenochtitlan, capital of the Aztec Empire...
and after 1821 of Mexico
Mexico
The United Mexican States , commonly known as Mexico , is a federal constitutional republic in North America. It is bordered on the north by the United States; on the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; on the southeast by Guatemala, Belize, and the Caribbean Sea; and on the east by the Gulf of...
), and south of the parallel 54°40′ north (the southern border of Russian America
Russian Alaska
Russian America was the name of Russian colonial possessions in the Americas from 1733 to 1867 that today is the U.S. state of Alaska and settlements farther south in California and Hawaii...
after 1825).
The Oregon Dispute became important in geopolitical diplomacy between the British Empire and the new American Republic. In 1844 the U.S. Democratic Party, appealing to expansionist
Expansionism
In general, expansionism consists of expansionist policies of governments and states. While some have linked the term to promoting economic growth , more commonly expansionism refers to the doctrine of a state expanding its territorial base usually, though not necessarily, by means of military...
sentiment and the popular theme of manifest destiny
Manifest Destiny
Manifest Destiny was the 19th century American belief that the United States was destined to expand across the continent. It was used by Democrat-Republicans in the 1840s to justify the war with Mexico; the concept was denounced by Whigs, and fell into disuse after the mid-19th century.Advocates of...
, asserted that the U.S. had a valid claim to the entire Oregon Country up to Russian America at parallel 54°40′ north. Democratic presidential candidate James K. Polk
James K. Polk
James Knox Polk was the 11th President of the United States . Polk was born in Mecklenburg County, North Carolina. He later lived in and represented Tennessee. A Democrat, Polk served as the 17th Speaker of the House of Representatives and the 12th Governor of Tennessee...
won the 1844 election, but then sought a compromise boundary along the 49th parallel
49th parallel north
The 49th parallel north is a circle of latitude that is 49 degrees north of the Earth's equatorial plane. It crosses Europe, Asia, the Pacific Ocean, North America, and the Atlantic Ocean....
, the same boundary proposed by previous U.S. administrations. Negotiations between the U.S. and the British broke down, however, and tensions grew as American expansionists like U.S. Senator Edward A. Hannegan
Edward A. Hannegan
Edward Allen Hannegan was a United States Representative and Senator from Indiana.-Early life and education:...
of Indiana
Indiana
Indiana is a US state, admitted to the United States as the 19th on December 11, 1816. It is located in the Midwestern United States and Great Lakes Region. With 6,483,802 residents, the state is ranked 15th in population and 16th in population density. Indiana is ranked 38th in land area and is...
, or Congressman Leonard Henly Sims
Leonard Henly Sims
Leonard Henley Sims was a U.S. Representative from Missouri.Born in Burke County, North Carolina, Sims received a limited schooling.He moved to Rutherford County, Tennessee, in 1830 and engaged in agricultural pursuits....
, Missouri, which urged Polk to annex the entire Oregon Country north to the parallel 54°40′ north, as the Democrats had called for in the election. The turmoil gave rise to slogans like "Fifty-four Forty or Fight
William Allen (governor)
William Allen was an Democratic Representative, Senator and 31st Governor of Ohio. He moved to the U.S. state of Ohio after his parents died, residing in Chillicothe, Ohio....
!" and the catchphrase "Manifest Destiny
Manifest Destiny
Manifest Destiny was the 19th century American belief that the United States was destined to expand across the continent. It was used by Democrat-Republicans in the 1840s to justify the war with Mexico; the concept was denounced by Whigs, and fell into disuse after the mid-19th century.Advocates of...
".
The expansionist agenda of Polk and the Democratic Party created the possibility of two different, simultaneous wars, because relations between the United States and Mexico
Mexico
The United Mexican States , commonly known as Mexico , is a federal constitutional republic in North America. It is bordered on the north by the United States; on the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; on the southeast by Guatemala, Belize, and the Caribbean Sea; and on the east by the Gulf of...
were deteriorating following the annexation of Texas. Neither Britain nor the United States really wanted to fight a third war in 70 years. Just before the outbreak of the war with Mexico, Polk returned to his earlier position on the Oregon boundary and accepted a compromise along the 49th parallel as far as the Strait of Georgia. This agreement was made official in the 1846 Oregon Treaty
Oregon Treaty
The Oregon Treaty is a treaty between the United Kingdom and the United States that was signed on June 15, 1846, in Washington, D.C. The treaty brought an end to the Oregon boundary dispute by settling competing American and British claims to the Oregon Country, which had been jointly occupied by...
, and the 49th parallel remains the boundary between the United States and Canada
Canada
Canada is a North American country consisting of ten provinces and three territories. Located in the northern part of the continent, it extends from the Atlantic Ocean in the east to the Pacific Ocean in the west, and northward into the Arctic Ocean...
west of Lake of the Woods
Lake of the Woods
Lake of the Woods is a lake occupying parts of the Canadian provinces of Ontario and Manitoba and the U.S. state of Minnesota. It separates a small land area of Minnesota from the rest of the United States. The Northwest Angle and the town of Angle Township can only be reached from the rest of...
, other than the marine boundary which curves south to the Strait of Juan de Fuca and so excludes from the United States Vancouver Island
Vancouver Island
Vancouver Island is a large island in British Columbia, Canada. It is one of several North American locations named after George Vancouver, the British Royal Navy officer who explored the Pacific Northwest coast of North America between 1791 and 1794...
and the Gulf Islands
Gulf Islands
The Gulf Islands are the islands in the Strait of Georgia , between Vancouver Island and the mainland of British Columbia, Canada....
. As a result, much of Point Roberts
Point Roberts, Washington
Point Roberts is an unincorporated community in Whatcom County, Washington, United States. It has a post office, with the ZIP code of 98281, whose ZIP Code Tabulation Area had a population of 1,314 at the 2010 census.A geopolitical oddity, Point Roberts is a part of the United States that is not...
(a small peninsula extending south into the Strait of Georgia from Canada) is an exclave of the United States.
Early British and American activity
George VancouverGeorge Vancouver
Captain George Vancouver RN was an English officer of the British Royal Navy, best known for his 1791-95 expedition, which explored and charted North America's northwestern Pacific Coast regions, including the coasts of contemporary Alaska, British Columbia, Washington and Oregon...
explored Puget Sound
Puget Sound
Puget Sound is a sound in the U.S. state of Washington. It is a complex estuarine system of interconnected marine waterways and basins, with one major and one minor connection to the Strait of Juan de Fuca and the Pacific Ocean — Admiralty Inlet being the major connection and...
in 1792. Vancouver claimed it for Great Britain on June 4, 1792, naming it for one of his officers, Lieutenant Peter Puget
Peter Puget
Peter Puget was an officer in the Royal Navy, best known for his exploration of Puget Sound.-Mr. Midshipman Puget:Puget's ancestors had fled France for Britain during Louis XIV's persecution of the Huguenots. His father, John, was a successful merchant and banker, but died in 1767, leaving Puget's...
. That year, on May 12, 1792, American merchant captain Robert Gray found the mouth of the Columbia River
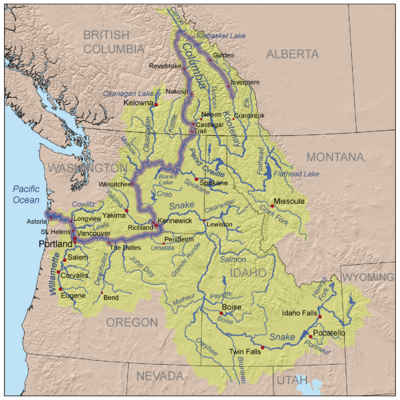
Columbia River
The Columbia River is the largest river in the Pacific Northwest region of North America. The river rises in the Rocky Mountains of British Columbia, Canada, flows northwest and then south into the U.S. state of Washington, then turns west to form most of the border between Washington and the state...
, and became the first Westerner to enter the river. He named it for his ship, the Columbia Rediviva
Columbia Rediviva
Columbia Rediviva was a privately owned ship under the command of John Kendrick, along with Captain Robert Gray, best known for going to the Pacific Northwest for the maritime fur trade. The "Rediviva" was added to her name upon a rebuilding in 1787...
.
The American overland Lewis and Clark expedition reached the mouth of the Columbia River
Columbia River
The Columbia River is the largest river in the Pacific Northwest region of North America. The river rises in the Rocky Mountains of British Columbia, Canada, flows northwest and then south into the U.S. state of Washington, then turns west to form most of the border between Washington and the state...
in 1805 and built Fort Clatsop
Fort Clatsop
Fort Clatsop was the encampment of the Lewis and Clark Expedition in the Oregon Country near the mouth of the Columbia River during the winter of 1805-1806...
, on the south side of the river, as a place to spend the winter of 1805–1806 and provision for the return trip.
North West Company
North West Company
The North West Company was a fur trading business headquartered in Montreal from 1779 to 1821. It competed with increasing success against the Hudson's Bay Company in what was to become Western Canada...
explorer David Thompson
David Thompson (explorer)
David Thompson was an English-Canadian fur trader, surveyor, and map-maker, known to some native peoples as "Koo-Koo-Sint" or "the Stargazer"...
extensively explored the Columbia River commencing in 1807. While on his 1811 voyage down the entire length of the Columbia River, Thompson camped at the junction with the Snake River
Snake River
The Snake is a major river of the greater Pacific Northwest in the United States. At long, it is the largest tributary of the Columbia River, the largest North American river that empties into the Pacific Ocean...
on July 9, 1811. He erected a pole and a notice claiming the country for the United Kingdom and stating the intention of the North West Company
North West Company
The North West Company was a fur trading business headquartered in Montreal from 1779 to 1821. It competed with increasing success against the Hudson's Bay Company in what was to become Western Canada...
to build a trading post at the site. Thompson reached a partially constructed Fort Astoria
Fort Astoria
Fort Astoria was the Pacific Fur Company's primary fur trading post in the Northwest, and was the first American-owned settlement on the Pacific coast. After a short two-year term of US ownership, the British owned and operated it for 33 years. It was the first British port on the Pacific coast...
about two months after the ill-fated Tonquin
Tonquin
The Tonquin was an American merchant ship involved with the Maritime Fur Trade of the early 19th Century. The ship was used by John Jacob Astor's Pacific Fur Company to establish fur trading outposts on the Northwest Coast of North America, including Fort Astoria at the mouth of the Columbia River...
s departure.
Fort Nez Percés
Fort Nez Percés, sometimes also spelled Fort Nez Percé , named after the Nez Perce people and later known as Fort Walla Walla, was a fortified British fur trading post on the Columbia River on the territory of modern-day Wallula, Washington...
was subsequently constructed by the North West Company. The American Pacific Fur Company
Pacific Fur Company
The Pacific Fur Company was founded June 23, 1810, in New York City. Half of the stock of the company was held by the American Fur Company, owned exclusively by John Jacob Astor, and Astor provided all of the capital for the enterprise. The other half of the stock was ascribed to working partners...
selected the more northerly Fort Okanogan
Fort Okanogan
Fort Okanogan was founded as a fur trade outpost by John Jacob Astor’s Pacific Fur Company in 1811. It was built at the confluence of the Okanogan and Columbia Rivers, in what is now Okanogan County, Washington...
as the center for their inland operations. Fort Astoria and all other Pacific Fur Company posts were sold to the North West Company. During the War of 1812
War of 1812
The War of 1812 was a military conflict fought between the forces of the United States of America and those of the British Empire. The Americans declared war in 1812 for several reasons, including trade restrictions because of Britain's ongoing war with France, impressment of American merchant...
, a rash action by the commander of HMS Racoon
HMS Racoon (1808)
HMS Racoon, sometimes spelled HMS Raccoon, was an 18-gun ship sloop of the Cormorant Class of the Royal Navy. She was built by John Preston, of Great Yarmouth, and launched on 30 March 1808.-Service:...
"captured" the fort, even though it was already under British ownership. The resulting technicality that it was returned to U.S. ownership as part of the war's settlement as a result of the Treaty of Ghent
Treaty of Ghent
The Treaty of Ghent , signed on 24 December 1814, in Ghent , was the peace treaty that ended the War of 1812 between the United States of America and the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland...
, even though no trading activity was re-commenced.
By Article III of the Anglo-American Convention of 1818
Treaty of 1818
The Convention respecting fisheries, boundary and the restoration of slaves between the United States of America and the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, also known as the London Convention, Anglo-American Convention of 1818, Convention of 1818, or simply the Treaty of 1818, was a...
the United Kingdom and the United States agreed to what has since been described as "joint occupancy," deferring on any resolution of the territorial and treaty issues until a later time.
The Hudson's Bay Company
Hudson's Bay Company
The Hudson's Bay Company , abbreviated HBC, or "The Bay" is the oldest commercial corporation in North America and one of the oldest in the world. A fur trading business for much of its existence, today Hudson's Bay Company owns and operates retail stores throughout Canada...
(HBC) merged with the North West Company in 1821. That same year, the U.K. Parliament passed a statute requiring that the laws of Upper Canada
Upper Canada
The Province of Upper Canada was a political division in British Canada established in 1791 by the British Empire to govern the central third of the lands in British North America and to accommodate Loyalist refugees from the United States of America after the American Revolution...
be enforced by the HBC in Rupert's Land
Rupert's Land
Rupert's Land, or Prince Rupert's Land, was a territory in British North America, consisting of the Hudson Bay drainage basin that was nominally owned by the Hudson's Bay Company for 200 years from 1670 to 1870, although numerous aboriginal groups lived in the same territory and disputed the...
and the Columbia District
Columbia District
The Columbia District was a fur trading district in the Pacific Northwest region of British North America in the 19th century. It was explored by the North West Company between 1793 and 1811, and established as an operating fur district around 1810...
. The HBC's Pacific Headquarters at Fort Vancouver
Fort Vancouver
Fort Vancouver was a 19th century fur trading outpost along the Columbia River that served as the headquarters of the Hudson's Bay Company in the company's Columbia District...
became the center of activity in the Pacific Northwest.
The HBC held a license to trade with the populous aboriginal peoples of the region, and its network of trading posts and routes extended southward from New Caledonia
New Caledonia (Canada)
New Caledonia was the name given to a district of the Hudson's Bay Company that comprised the territory largely coterminous with the present-day province of British Columbia, Canada. Though not a British colony, New Caledonia was part of the British claim to North America. Its administrative...
, another HBC fur-trade district, into the Columbia basin. The HBC's headquarters for the entire region became established at Fort Vancouver
Fort Vancouver
Fort Vancouver was a 19th century fur trading outpost along the Columbia River that served as the headquarters of the Hudson's Bay Company in the company's Columbia District...
(near today's Vancouver, Washington
Vancouver, Washington
Vancouver is a city on the north bank of the Columbia River in the U.S. state of Washington. Incorporated in 1857, it is the fourth largest city in the state with a 2010 census population of 161,791 as of April 1, 2010...
) in 1824, which became the centre of a thriving colony of mixed origin, including Scottish Canadians and Scots
Scottish people
The Scottish people , or Scots, are a nation and ethnic group native to Scotland. Historically they emerged from an amalgamation of the Picts and Gaels, incorporating neighbouring Britons to the south as well as invading Germanic peoples such as the Anglo-Saxons and the Norse.In modern use,...
, English
English people
The English are a nation and ethnic group native to England, who speak English. The English identity is of early mediaeval origin, when they were known in Old English as the Anglecynn. England is now a country of the United Kingdom, and the majority of English people in England are British Citizens...
, French Canadian
French Canadian
French Canadian or Francophone Canadian, , generally refers to the descendents of French colonists who arrived in New France in the 17th and 18th centuries...
s, Hawaiians
Native Hawaiians
Native Hawaiians refers to the indigenous Polynesian people of the Hawaiian Islands or their descendants. Native Hawaiians trace their ancestry back to the original Polynesian settlers of Hawaii.According to the U.S...
, Algonkians
Algonquian peoples
The Algonquian are one of the most populous and widespread North American native language groups, with tribes originally numbering in the hundreds. Today hundreds of thousands of individuals identify with various Algonquian peoples...
and Iroquois
Iroquois
The Iroquois , also known as the Haudenosaunee or the "People of the Longhouse", are an association of several tribes of indigenous people of North America...
, as well as the offspring of company employees who had intermarried with various local native populations.
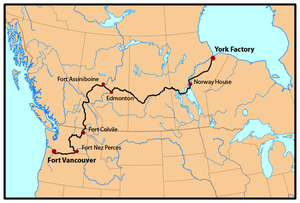
London
London is the capital city of :England and the :United Kingdom, the largest metropolitan area in the United Kingdom, and the largest urban zone in the European Union by most measures. Located on the River Thames, London has been a major settlement for two millennia, its history going back to its...
twice annually via Hudson Bay
Hudson Bay
Hudson Bay , sometimes called Hudson's Bay, is a large body of saltwater in northeastern Canada. It drains a very large area, about , that includes parts of Ontario, Quebec, Saskatchewan, Alberta, most of Manitoba, southeastern Nunavut, as well as parts of North Dakota, South Dakota, Minnesota,...
and the York Factory Express
York Factory Express
The York Factory Express, usually called "the Express" and also called the Columbia Express and the Communication, was a brigade operated by Hudson's Bay Company in the early 19th century connecting York Factory and Fort Vancouver. It was named "express" because it was not used only to transport...
trade route. Fort Vancouver was the nexus for the fur trade on the Pacific Coast; its influence reached from Rupert's Land
Rupert's Land
Rupert's Land, or Prince Rupert's Land, was a territory in British North America, consisting of the Hudson Bay drainage basin that was nominally owned by the Hudson's Bay Company for 200 years from 1670 to 1870, although numerous aboriginal groups lived in the same territory and disputed the...
and the Rocky Mountains
Rocky Mountains
The Rocky Mountains are a major mountain range in western North America. The Rocky Mountains stretch more than from the northernmost part of British Columbia, in western Canada, to New Mexico, in the southwestern United States...
in the east to the Hawaiian Islands
Hawaiian Islands
The Hawaiian Islands are an archipelago of eight major islands, several atolls, numerous smaller islets, and undersea seamounts in the North Pacific Ocean, extending some 1,500 miles from the island of Hawaii in the south to northernmost Kure Atoll...
, and from Russian Alaska
Russian Alaska
Russian America was the name of Russian colonial possessions in the Americas from 1733 to 1867 that today is the U.S. state of Alaska and settlements farther south in California and Hawaii...
to Mexican California. At its pinnacle in the late 1830s and early 1840s, Fort Vancouver watched over 34 outposts, 24 ports, six ships, and 600 employees.
Early American activity in the region included Fort William
Fort William (Oregon)
Fort William was a fur trading outpost built by American Nathaniel Jarvis Wyeth in 1834. It was located on the Columbia River on Wappatoo Island in what is now part of Portland, Oregon. It was the site of a murder and the first Euro-American trial in what is now the state of Oregon...
on present day Sauvie Island
Sauvie Island
Sauvie Island, in the U.S. state of Oregon, originally Wapato Island or Wappatoo Island, is the largest island along the Columbia River, at 26,000 acres , and the largest river island in the United States...
, the establishment of the Methodist Mission
Oregon Mission
The Oregon Mission began as an effort by the Methodist Episcopal Church to convert the native Indians of the far west to Christianity. This mission, under the leadership of Jason Lee, largely failed in its initial goal, but played a significant role in the westward expansion of the United States...
in the Willamette Valley
Willamette Valley
The Willamette Valley is the most populated region in the state of Oregon of the United States. Located in the state's northwest, the region is surrounded by tall mountain ranges to the east, west and south and the valley's floor is broad, flat and fertile because of Ice Age conditions...
and the Whitman Mission
Whitman Mission National Historic Site
Whitman Mission National Historic Site is a United States National Historic Site located just west of Walla Walla, Washington, at the site of the former Whitman Mission at Waiilatpu. On November 29, 1847, the family of Dr. Marcus Whitman and others were massacred by Native Americans of the Cayuse...
east of the Cascades
Cascade Range
The Cascade Range is a major mountain range of western North America, extending from southern British Columbia through Washington and Oregon to Northern California. It includes both non-volcanic mountains, such as the North Cascades, and the notable volcanoes known as the High Cascades...
, a saw mill in the Willamette Valley partly owned by Ewing Young
Ewing Young
Ewing Young was an American fur trapper and trader from Tennessee who traveled Mexican southwestern North America and California before settling in the Oregon Country. As a prominent and wealthy citizen there, his death was the impetus for the early formation of government in what became the state...
, a grist mill also in the valley built in 1834, the Willamette Cattle Company
Willamette Cattle Company
The Willamette Cattle Company was formed in 1837 by pioneers in the Willamette Valley of present day Oregon, United States. The company was formed with the express purpose of purchasing cattle in California to bring to Oregon Country...
organized in 1837 to bring over 600 head of cattle to the Willamette Valley, as well as ongoing Maritime Fur Trade
Maritime Fur Trade
The Maritime Fur Trade was a ship-based fur trade system that focused on acquiring furs of sea otters and other animals from the indigenous peoples of the Pacific Northwest Coast and natives of Alaska. The furs were mostly sold in China in exchange for tea, silks, porcelain, and other Chinese...
vessels.
Since the HBC officially discouraged settlement because it interfered with the lucrative fur trade, negotiations over the decades failed to settle upon a compromise boundary along the Columbia River. Strained relationships grew worse as American settlers began trickling into the region in the 1830s, and tensions escalated when settlers started arriving in large numbers in the 1840s along the Oregon Trail
Oregon Trail
The Oregon Trail is a historic east-west wagon route that connected the Missouri River to valleys in Oregon and locations in between.After 1840 steam-powered riverboats and steamboats traversing up and down the Ohio, Mississippi and Missouri rivers sped settlement and development in the flat...
.
Joint occupation
The dispute arose as a result of competing claims between the United States and the United Kingdom to the Oregon Country, which consisted of what is now the Pacific NorthwestPacific Northwest
The Pacific Northwest is a region in northwestern North America, bounded by the Pacific Ocean to the west and, loosely, by the Rocky Mountains on the east. Definitions of the region vary and there is no commonly agreed upon boundary, even among Pacific Northwesterners. A common concept of the...
of the United States and southern British Columbia
British Columbia
British Columbia is the westernmost of Canada's provinces and is known for its natural beauty, as reflected in its Latin motto, Splendor sine occasu . Its name was chosen by Queen Victoria in 1858...
, Canada
Canada
Canada is a North American country consisting of ten provinces and three territories. Located in the northern part of the continent, it extends from the Atlantic Ocean in the east to the Pacific Ocean in the west, and northward into the Arctic Ocean...
. Both nations claimed the region based on earlier exploration and the "right of discovery". Following long European precedent, both sides recognized only limited sovereign rights of the indigenous population
Indigenous peoples of the Americas
The indigenous peoples of the Americas are the pre-Columbian inhabitants of North and South America, their descendants and other ethnic groups who are identified with those peoples. Indigenous peoples are known in Canada as Aboriginal peoples, and in the United States as Native Americans...
.
In 1818, diplomats of the two countries attempted to negotiate a boundary between the rival claims. The Americans suggested dividing the Oregon Country along the 49th parallel
49th parallel north
The 49th parallel north is a circle of latitude that is 49 degrees north of the Earth's equatorial plane. It crosses Europe, Asia, the Pacific Ocean, North America, and the Atlantic Ocean....
, which was the border between the United States and British North America
British North America
British North America is a historical term. It consisted of the colonies and territories of the British Empire in continental North America after the end of the American Revolutionary War and the recognition of American independence in 1783.At the start of the Revolutionary War in 1775 the British...
east of the Rocky Mountains
Rocky Mountains
The Rocky Mountains are a major mountain range in western North America. The Rocky Mountains stretch more than from the northernmost part of British Columbia, in western Canada, to New Mexico, in the southwestern United States...
. British diplomats wanted a border further south along the Columbia River
Columbia River
The Columbia River is the largest river in the Pacific Northwest region of North America. The river rises in the Rocky Mountains of British Columbia, Canada, flows northwest and then south into the U.S. state of Washington, then turns west to form most of the border between Washington and the state...
, so as to maintain the North West Company
North West Company
The North West Company was a fur trading business headquartered in Montreal from 1779 to 1821. It competed with increasing success against the Hudson's Bay Company in what was to become Western Canada...
"s (later the Hudson's Bay Company
Hudson's Bay Company
The Hudson's Bay Company , abbreviated HBC, or "The Bay" is the oldest commercial corporation in North America and one of the oldest in the world. A fur trading business for much of its existence, today Hudson's Bay Company owns and operates retail stores throughout Canada...
) control of the lucrative fur trade
Fur trade
The fur trade is a worldwide industry dealing in the acquisition and sale of animal fur. Since the establishment of world market for in the early modern period furs of boreal, polar and cold temperate mammalian animals have been the most valued...
along that river. As a compromise, the Anglo-American Convention of 1818
Treaty of 1818
The Convention respecting fisheries, boundary and the restoration of slaves between the United States of America and the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, also known as the London Convention, Anglo-American Convention of 1818, Convention of 1818, or simply the Treaty of 1818, was a...
(or Treaty of 1818), which settled most other disputes from the War of 1812
War of 1812
The War of 1812 was a military conflict fought between the forces of the United States of America and those of the British Empire. The Americans declared war in 1812 for several reasons, including trade restrictions because of Britain's ongoing war with France, impressment of American merchant...
, called for the joint occupation of the region for ten years. As the expiration of the ten-year agreement approached, a second round of negotiations from 1825 to 1827 failed to resolve the issue, and so the joint occupation agreement was renewed, this time with the stipulation that a one-year notice had to be given when either party intended to abrogate the agreement.
Early in the 1840s, negotiations that produced the 1842 Webster-Ashburton Treaty
Webster-Ashburton Treaty
The Webster–Ashburton Treaty, signed August 9, 1842, was a treaty resolving several border issues between the United States and the British North American colonies...
(a border settlement in the east) addressed the Oregon question once again. British negotiators still pressed for the Columbia River boundary, which the Americans would not accept since it would deny the U.S. an easily accessible deep water port on the Pacific Ocean
Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest of the Earth's oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic in the north to the Southern Ocean in the south, bounded by Asia and Australia in the west, and the Americas in the east.At 165.2 million square kilometres in area, this largest division of the World...
, and so no adjustment to the existing agreement was made. By this time, American settlers were steadily pouring into the region along the Oregon Trail
Oregon Trail
The Oregon Trail is a historic east-west wagon route that connected the Missouri River to valleys in Oregon and locations in between.After 1840 steam-powered riverboats and steamboats traversing up and down the Ohio, Mississippi and Missouri rivers sped settlement and development in the flat...
, a development that some observers—both British and American—realized would eventually decide the issue.
The HBC belatedly reversed its policy on colonization. In 1841, on orders from HBC Governor Sir George Simpson
George Simpson (administrator)
Sir George Simpson was a Scots-Quebecer and employee of the Hudson's Bay Company . His title was Governor-in-Chief of Rupert's Land and administrator over the Northwest Territories and Columbia Department in British North America from 1821 to 1860.-Early years:George Simpson was born in Dingwall,...
, James Sinclair
James Sinclair (fur trapper)
James Sinclair was a trader and explorer with the Hudson's Bay Company. He was the son of Hudson's Bay Company factor William Sinclair, from Eastaquoy in Harray, and his Cree wife, Nahovway. He was a brother of William Sinclair. James was born in Rupert's Land and educated in Scotland at Edinburgh...
guided nearly 200 settlers from the Red River Colony
Red River Colony
The Red River Colony was a colonization project set up by Thomas Douglas, 5th Earl of Selkirk in 1811 on of land granted to him by the Hudson's Bay Company under what is referred to as the Selkirk Concession. The colony along the Red River of the North was never very successful...
west in an attempt to retain the area for Britain.
In 1843, John C. Calhoun
John C. Calhoun
John Caldwell Calhoun was a leading politician and political theorist from South Carolina during the first half of the 19th century. Calhoun eloquently spoke out on every issue of his day, but often changed positions. Calhoun began his political career as a nationalist, modernizer, and proponent...
famously declared that the U.S. government should pursue a policy of "wise and masterly inactivity" in Oregon, letting settlement determine the eventual boundary. That year over 700 U.S settlers arrived via the Oregon Trail in the "Great Migration". The Provisional Government of Oregon
Provisional Government of Oregon
The Provisional Government of Oregon was a popularly elected government created in the Oregon Country, in the Pacific Northwest region of North America. It existed from May 2, 1843 until March 3, 1849. Created at a time when no country had sovereignty over the region, this independent government...
was established that year. Many of Calhoun's fellow Democrats
Democratic Party (United States)
The Democratic Party is one of two major contemporary political parties in the United States, along with the Republican Party. The party's socially liberal and progressive platform is largely considered center-left in the U.S. political spectrum. The party has the lengthiest record of continuous...
, however, soon began to advocate a more direct approach.
Election of 1844
| Important figures in the Oregon question | |
|---|---|
| United States | United Kingdom |
| James K. Polk James K. Polk James Knox Polk was the 11th President of the United States . Polk was born in Mecklenburg County, North Carolina. He later lived in and represented Tennessee. A Democrat, Polk served as the 17th Speaker of the House of Representatives and the 12th Governor of Tennessee... President President of the United States The President of the United States of America is the head of state and head of government of the United States. The president leads the executive branch of the federal government and is the commander-in-chief of the United States Armed Forces.... |
Robert Peel Robert Peel Sir Robert Peel, 2nd Baronet was a British Conservative statesman who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 10 December 1834 to 8 April 1835, and again from 30 August 1841 to 29 June 1846... Prime Minister Prime Minister of the United Kingdom The Prime Minister of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland is the Head of Her Majesty's Government in the United Kingdom. The Prime Minister and Cabinet are collectively accountable for their policies and actions to the Sovereign, to Parliament, to their political party and... |
| James Buchanan James Buchanan James Buchanan, Jr. was the 15th President of the United States . He is the only president from Pennsylvania, the only president who remained a lifelong bachelor and the last to be born in the 18th century.... Secretary of State United States Secretary of State The United States Secretary of State is the head of the United States Department of State, concerned with foreign affairs. The Secretary is a member of the Cabinet and the highest-ranking cabinet secretary both in line of succession and order of precedence... |
Earl of Aberdeen George Hamilton-Gordon, 4th Earl of Aberdeen George Hamilton-Gordon, 4th Earl of Aberdeen KG, KT, FRS, PC , styled Lord Haddo from 1791 to 1801, was a Scottish politician, successively a Tory, Conservative and Peelite, who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 1852 until 1855.-Early life:Born in Edinburgh on 28 January 1784, he... Foreign Secretary |
| Louis McLane Louis McLane Louis McLane was an American lawyer and politician from Wilmington, in New Castle County, Delaware, and Baltimore, Maryland. He was a veteran of the War of 1812 and a member of the Federalist Party and later the Democratic Party. He served as the U.S. Representative from Delaware, U.S. Senator... Minister to the UK United States Ambassador to the United Kingdom The office of United States Ambassador to the United Kingdom was traditionally, and still is very much so today due to the Special Relationship, the most prestigious position in the United States Foreign Service... |
Richard Pakenham Minister in Washington |
At the 1844 Democratic National Convention
1844 Democratic National Convention
In 1844, the Democratic Party held their National Convention in Baltimore. At first, the Democrats were split; the three nominees for the Presidential candidate were:* Martin van Buren, a former president and leader of the dominant Jacksonian faction...
, the party platform
Party platform
A party platform, or platform sometimes also referred to as a manifesto, is a list of the actions which a political party, individual candidate, or other organization supports in order to appeal to the general public for the purpose of having said peoples' candidates voted into political office or...
called for the annexation of Texas and asserted that the United States had a "clear and unquestionable" claim to "the whole" of Oregon and "that no portion of the same ought to be ceded to England or any other power." By informally tying the Oregon dispute to the more controversial Texas debate, the Democrats appealed to both Northern expansionists, who were more adamant about the Oregon boundary, and Southern expansionists, who focused on annexing Texas. Democratic candidate James K. Polk
James K. Polk
James Knox Polk was the 11th President of the United States . Polk was born in Mecklenburg County, North Carolina. He later lived in and represented Tennessee. A Democrat, Polk served as the 17th Speaker of the House of Representatives and the 12th Governor of Tennessee...
went on to win a narrow victory over Whig candidate Henry Clay
Henry Clay
Henry Clay, Sr. , was a lawyer, politician and skilled orator who represented Kentucky separately in both the Senate and in the House of Representatives...
, in part because Clay had taken a stand against expansion. "Fifty-four Forty or Fight!" was not yet coined during this election; one actual Democratic campaign slogan from this election (used in Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania
The Commonwealth of Pennsylvania is a U.S. state that is located in the Northeastern and Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States. The state borders Delaware and Maryland to the south, West Virginia to the southwest, Ohio to the west, New York and Ontario, Canada, to the north, and New Jersey to...
) was the more mundane "Polk, Dallas
George M. Dallas
George Mifflin Dallas was a U.S. Senator from Pennsylvania and the 11th Vice President of the United States , serving under James K. Polk.-Family and early life:...
, and the Tariff of '42
Tariff of 1842
The Tariff of 1842, or Black Tariff as it became known, was a protectionist tariff schedule adopted in the United States to reverse the effects of the Compromise Tariff of 1833...
".
In his March 1845 inaugural address, President Polk quoted from the party platform, saying that the U.S. title to Oregon was "clear and unquestionable". Tensions grew, with both sides moving to strengthen border fortifications in anticipation of war. Despite Polk's bold language, he was actually prepared to compromise, and had no real desire to go to war over Oregon. He believed that a firm stance would compel the British to accept a resolution agreeable to the United States, writing that "the only way to treat John Bull
John Bull
John Bull is a national personification of Britain in general and England in particular, especially in political cartoons and similar graphic works. He is usually depicted as a stout, middle-aged man, often wearing a Union Flag waistcoat.-Origin:...
was to look him straight in the eye". But Polk's position on Oregon was not mere posturing: he genuinely believed that the U.S. had a legitimate claim to the entire region. He rejected British offers to settle the dispute through arbitration, fearing that no impartial third party could be found.
Prime Minister Robert Peel
Robert Peel
Sir Robert Peel, 2nd Baronet was a British Conservative statesman who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 10 December 1834 to 8 April 1835, and again from 30 August 1841 to 29 June 1846...
's Foreign Secretary, the Earl of Aberdeen
George Hamilton-Gordon, 4th Earl of Aberdeen
George Hamilton-Gordon, 4th Earl of Aberdeen KG, KT, FRS, PC , styled Lord Haddo from 1791 to 1801, was a Scottish politician, successively a Tory, Conservative and Peelite, who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 1852 until 1855.-Early life:Born in Edinburgh on 28 January 1784, he...
, also had no intention of going to war over a region that was of diminishing economic value to the United Kingdom. Furthermore, the United States was an important trading partner. With the onset of famine in Ireland, the United Kingdom faced a food crisis, and had an increasing need for American wheat. Aberdeen had already decided to accept the U.S. proposal for a boundary along the 49th parallel, and he instructed Richard Pakenham, his minister in the U.S., to keep negotiations open.
On the other hand, Aberdeen and Pakenham were negotiating from a position of strength. The key was the overwhelming naval power which Britain could have brought to bear against the United States, combined with a diplomatic and political landscape that ultimately favored the British government's aim of protecting her interests robustly but without resort to armed conflict.
Local interests were protected by the 80-gun ship-of-the-line HMS Collingwood
HMS Collingwood (1841)
HMS Collingwood was an 80-gun two-deck second rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, launched on 17 August 1841 at Pembroke Dockyard.She was fitted with screw propulsion in 1861, and sold out of the navy in 1867.-References:...
under the CinC Rear Admiral Sir George Seymour
George Seymour
George Seymour may refer to:*Sir George Seymour, English knight*George Francis Seymour , British admiral*Lord George Seymour , British politician*George Hamilton Seymour , British diplomat, son of the above...
. During the crisis his squadron was augmented by HMS America
HMS America (1810)
HMS America was a 74-gun third rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, launched on 21 April 1810 at Blackwall Yard.In 1827 America was cut down into a fourth rate, and was broken up in 1867....
(74 guns), under the command of Captain John Gordon (younger brother of the Foreign Secretary), an officer whose misjudgement during the crisis – in contrast to Seymour’s exemplary behavior – led to his court-martial and reprimand.
Ultimately British politicians and naval officers recognized that any conflict over the Oregon boundary, however undesirable, would be decided, like the War of 1812, on the Eastern Seaboard of the U.S. and the Great Lakes. It was here that the full influence of British naval dominance could be brought to bear and it was this influence that played most strongly upon American decision-making during the crisis, especially their decision to compromise. From London, McLane reported that the British were prepared “to commission immediately some thirty ships-of-the-line in addition to steamers and other vessels held in reserve.” Polk’s bluff had been called.
Against this background, skillful diplomacy by the Peel government offered Polk the chance to back down, which was a course he accepted. A repeat of the War of 1812 was not on anyone’s agenda, and with no prospect of French support over such a trivial point Polk had little choice.
Whilst the Hudson’s Bay Company gradually lost commercial dominance over Oregon, the company’s interests were increasingly turning towards shipping which rendered the Columbia River less important than Vancouver Island. Shipping and trade interests could be protected by the development of the Esquimalt
CFB Esquimalt
Canadian Forces Base Esquimalt is Canada's Pacific Coast naval base and home port to Maritime Forces Pacific and Joint Task Force Pacific Headquarters....
naval base and RN squadron based there
Pacific Station
The Pacific Station, often referred to as the Pacific Squadron, was one of the geographical divisions into which the Royal Navy divided its worldwide responsibilities...
.
Although the Royal Navy’s presence locally may not have been superior, vast overall superiority to the U.S. Navy enabled Britain’s politicians to secure their central objective of defeating the wild assertions of American politicians, retaining Vancouver island and avoiding a potentially costly, distracting war with a major trading partner at seemingly small cost at a time when the European continental balance was a far more pressing issue.
A complicating factor in the negotiations was the issue of navigation on the Columbia River. Polk's predecessor, John Tyler
John Tyler
John Tyler was the tenth President of the United States . A native of Virginia, Tyler served as a state legislator, governor, U.S. representative, and U.S. senator before being elected Vice President . He was the first to succeed to the office of President following the death of a predecessor...
, had offered the British unrestricted navigation on the river if they would accept a boundary along the 49th parallel. In the summer of 1845, the Polk administration renewed the proposal to divide Oregon along the 49th parallel, but this time without conceding navigation rights. Because this proposal fell short of the Tyler administration's earlier offer, Pakenham rejected the offer without first contacting London. Offended, Polk officially withdrew the proposal on August 30, 1845 and broke off negotiations. Aberdeen censured Pakenham for this diplomatic blunder, and attempted to renew the dialogue. By then, however, Polk was suspicious of British intentions, and under increasing political pressure not to compromise. He declined to reopen negotiations.
Slogans and war crisis

John L. O'Sullivan
John Louis O'Sullivan was an American columnist and editor who used the term "Manifest Destiny" in 1845 to promote the annexation of Texas and the Oregon Country to the United States. O'Sullivan was an influential political writer and advocate for the Democratic Party at that time, but he faded...
argued that the United States should claim all of Oregon "by the right of our manifest destiny to overspread and to possess the whole of the continent". Soon afterwards, the term "Manifest Destiny
Manifest Destiny
Manifest Destiny was the 19th century American belief that the United States was destined to expand across the continent. It was used by Democrat-Republicans in the 1840s to justify the war with Mexico; the concept was denounced by Whigs, and fell into disuse after the mid-19th century.Advocates of...
" became a standard phrase for expansionists, and a permanent part of the American lexicon. O'Sullivan's version of "Manifest Destiny" was not a call for war, but such calls were soon forthcoming.
In his annual address
State of the Union Address
The State of the Union is an annual address presented by the President of the United States to the United States Congress. The address not only reports on the condition of the nation but also allows the president to outline his legislative agenda and his national priorities.The practice arises...
to Congress on December 2, 1845, Polk recommended giving the British the required one-year notice of the termination of the joint occupation agreement. In Congress, Democratic expansionists from the Midwest
Midwestern United States
The Midwestern United States is one of the four U.S. geographic regions defined by the United States Census Bureau, providing an official definition of the American Midwest....
, led by Senators Lewis Cass
Lewis Cass
Lewis Cass was an American military officer and politician. During his long political career, Cass served as a governor of the Michigan Territory, an American ambassador, a U.S. Senator representing Michigan, and co-founder as well as first Masonic Grand Master of the Grand Lodge of Michigan...
of Michigan
Michigan
Michigan is a U.S. state located in the Great Lakes Region of the United States of America. The name Michigan is the French form of the Ojibwa word mishigamaa, meaning "large water" or "large lake"....
, Edward A. Hannegan
Edward A. Hannegan
Edward Allen Hannegan was a United States Representative and Senator from Indiana.-Early life and education:...
of Indiana
Indiana
Indiana is a US state, admitted to the United States as the 19th on December 11, 1816. It is located in the Midwestern United States and Great Lakes Region. With 6,483,802 residents, the state is ranked 15th in population and 16th in population density. Indiana is ranked 38th in land area and is...
, and William Allen
William Allen (governor)
William Allen was an Democratic Representative, Senator and 31st Governor of Ohio. He moved to the U.S. state of Ohio after his parents died, residing in Chillicothe, Ohio....
of Ohio
Ohio
Ohio is a Midwestern state in the United States. The 34th largest state by area in the U.S.,it is the 7th‑most populous with over 11.5 million residents, containing several major American cities and seven metropolitan areas with populations of 500,000 or more.The state's capital is Columbus...
, called for war with the United Kingdom rather than accepting anything short of all of Oregon up to Parallel 54°40′ north. (54°40′ was then the southern boundary of the Russian claim to Alaska
Russian Alaska
Russian America was the name of Russian colonial possessions in the Americas from 1733 to 1867 that today is the U.S. state of Alaska and settlements farther south in California and Hawaii...
.) The slogan "Fifty-Four Forty or Fight" appeared by January 1846, driven in part by the Democratic press. The phrase is frequently misidentified as a campaign slogan from the election of 1844, even in many textbooks. Bartlett's Familiar Quotations
Bartlett's Familiar Quotations
Bartlett's Familiar Quotations, often simply called Bartlett's, is an American reference work that is the longest-lived and most widely distributed collection of quotations...
attributes the slogan to William Allen.
The calls to war were fueled by a number of factors, including traditional distrust of the British
Anglophobia
Anglophobia means hatred or fear of England or the English people. The term is sometimes used more loosely for general Anti-British sentiment...
and a belief that the U.S. had the better claim and would make better use of the land. Moderates warned that the U.S. could not win a war against the world's greatest power
British Empire
The British Empire comprised the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom. It originated with the overseas colonies and trading posts established by England in the late 16th and early 17th centuries. At its height, it was the...
, and that negotiation could still achieve U.S. territorial goals. Although the debate in the U.S. was not strictly divided along party or sectional lines, many who clamored for the 54°40′ border were Northerners upset that Polk, a Southern slave owner, had been uncompromising in his pursuit of Texas, a cause deemed favorable to Southern slave owners, but willing to compromise on Oregon. As historian David M. Pletcher noted, "Fifty-Four Forty or Fight" seemed to be directed at the southern aristocracy in the U.S. as much as at the United Kingdom.
Resolution and treaty
The Polk administration then made it known that the British government should offer terms to settle the issue. Time was of the essence, because it was well known that the Peel government
Robert Peel
Sir Robert Peel, 2nd Baronet was a British Conservative statesman who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 10 December 1834 to 8 April 1835, and again from 30 August 1841 to 29 June 1846...
would fall with the impending repeal of the corn laws
Corn Laws
The Corn Laws were trade barriers designed to protect cereal producers in the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland against competition from less expensive foreign imports between 1815 and 1846. The barriers were introduced by the Importation Act 1815 and repealed by the Importation Act 1846...
in the United Kingdom, and then negotiations would have to begin again with a new ministry. Aberdeen and Louis McLane
Louis McLane
Louis McLane was an American lawyer and politician from Wilmington, in New Castle County, Delaware, and Baltimore, Maryland. He was a veteran of the War of 1812 and a member of the Federalist Party and later the Democratic Party. He served as the U.S. Representative from Delaware, U.S. Senator...
, the American minister in the United Kingdom, quickly worked out a compromise and sent it to the United States. There, Pakenham and U.S. Secretary of State James Buchanan
James Buchanan
James Buchanan, Jr. was the 15th President of the United States . He is the only president from Pennsylvania, the only president who remained a lifelong bachelor and the last to be born in the 18th century....
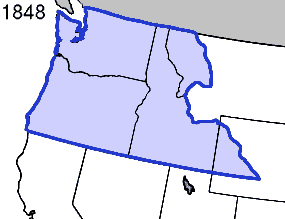
drew up a formal treaty, known as the Oregon Treaty, which was ratified by the Senate on June 18, 1846 by a vote of 41–14. The border was set at the 49th parallel, the original U.S. proposal, with navigation rights on the Columbia River granted to British subjects living in the area. Senator William Allen, one of the most outspoken advocates of the 54° 40' claim, felt betrayed by Polk and resigned his chairmanship of the Foreign Relations Committee.
The terms of the Oregon Treaty were essentially the same ones that had been offered earlier by the Tyler administration, and thus represented a diplomatic victory for Polk. However, Polk has often been criticized for his handling of the Oregon question. Historian Sam W. Haynes characterizes Polk's policy as "brinkmanship
Brinkmanship
Brinkmanship is the practice of pushing dangerous events to the verge of disaster in order to achieve the most advantageous outcome...
" which "brought the United States perilously close to a needless and potentially disastrous conflict". David M. Pletcher notes that while Polk's bellicose stance was the by-product of internal American politics, the war crisis was "largely of his own creation" and might have been avoided "with more sophisticated diplomacy".
Ambiguities in the wording of the Oregon Treaty regarding the route of the boundary, which was to follow "the deepest channel" out to the Strait of Juan de Fuca and beyond to the open ocean resulted in the Pig War
Pig War
The Pig War was a confrontation in 1859 between the United States and the British Empire over the boundary between the US and British North America. The territory in dispute was the San Juan Islands, which lie between Vancouver Island and the North American mainland...
; another boundary dispute in 1859 over the San Juan Islands
San Juan Islands
The San Juan Islands are an archipelago in the northwest corner of the contiguous United States between the US mainland and Vancouver Island, British Columbia, Canada. The San Juan Islands are part of the U.S...
. The dispute was peacefully resolved after a decade of confrontation and military bluster during which the local British authorities consistently lobbied London to seize back the Puget Sound region entirely, as the Americans were busy elsewhere with the Civil War. The San Juan's dispute was not resolved until 1872; when the pursuant to the Treaty of Washington (1871)
Treaty of Washington (1871)
The Treaty of Washington was a treaty signed and ratified by Great Britain and the United States in 1871 that settled various disputes between the countries, in particular the Alabama Claims.-Background:...
an arbitrator (the German Emperor) chose the American-preferred marine boundary via Haro Strait
Haro Strait
Haro Strait, often referred to as the Haro Straits because it is really a series of straits, is one of the main channels connecting the Strait of Georgia to the Strait of Juan de Fuca, separating Vancouver Island and the Gulf Islands in British Columbia, Canada from the San Juan Islands of...
, to the west of the islands, over the British preference for Rosario Strait
Rosario Strait
Rosario Strait is a strait in northern Washington state, separating Island and San Juan Counties. It extends from the Strait of Juan de Fuca about north to the Strait of Georgia...
which lay to their east.
Upper Canada
Upper Canada
The Province of Upper Canada was a political division in British Canada established in 1791 by the British Empire to govern the central third of the lands in British North America and to accommodate Loyalist refugees from the United States of America after the American Revolution...
politicians and public, already angry with the Oregon Treaty, were once again upset that Britain had not looked after their interests and sought greater autonomy in international affairs.
Historical maps
The boundary between British and American territory was shown differently in maps at the time:See also
- Adams-Onís TreatyAdams-Onís TreatyThe Adams–Onís Treaty of 1819, also known as the Transcontinental Treaty or the Purchase of Florida, was a treaty between the United States and Spain in 1819 that gave Florida to the U.S. and set out a boundary between the U.S. and New Spain . It settled a standing border dispute between the two...
of 1819, between U.S. and Spain, resolved borders from Florida to the Pacific Ocean. - Alaska boundary disputeAlaska Boundary DisputeThe Alaska boundary dispute was a territorial dispute between the United States and Canada . It was resolved by arbitration in 1903. The dispute had been going on between the Russian and British Empires since 1821, and was inherited by the United States as a consequence of the Alaska Purchase in...
, mid-to-late-19th century, resolved in 1903, resolved border between Alaska and British Columbia. - Pig WarPig WarThe Pig War was a confrontation in 1859 between the United States and the British Empire over the boundary between the US and British North America. The territory in dispute was the San Juan Islands, which lie between Vancouver Island and the North American mainland...
- Webster-Ashburton TreatyWebster-Ashburton TreatyThe Webster–Ashburton Treaty, signed August 9, 1842, was a treaty resolving several border issues between the United States and the British North American colonies...
of 1842, primarily concerned the border between Maine and New Brunswick, but reaffirmed other aspects of the U.S.–Canadian border.
External links
Party platform and speeches- 1844 Democratic platform, which asserted that the U.S. "title to the whole of the Territory of Oregon is clear and unquestionable"
- Polk's March 1845 inaugural address, in which he reasserted the "clear and unquestionable" claim
- Polk's December 1845 message to Congress, in which he called for the end of the joint occupation of Oregon
Political cartoons from Harper's Weekly
Harper's Weekly
Harper's Weekly was an American political magazine based in New York City. Published by Harper & Brothers from 1857 until 1916, it featured foreign and domestic news, fiction, essays on many subjects, and humor...
, 1846
- "Polk's Dream", in which the Devil, disguised as Andrew Jackson, advises Polk to fight for the 54°40′ line
- "Present Presidential Position", in which the Democratic Party's "jackass" is standing on the 54°40′ line
- "Ultimatum on the Oregon Question", Polk talks with Queen Victoria, while others make comments
- "War! or No War!", two Irish immigrants face off over the boundary question
Other
- Fifty-Four Forty or Fight at About.com, an example of a reference that mistakenly describes the phrase as an 1844 campaign slogan
- Another reference work that mistakenly ascribes the slogan Fifty-Four Forty or Fight to Polk is the Encyclopædia BritannicaEncyclopædia BritannicaThe Encyclopædia Britannica , published by Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc., is a general knowledge English-language encyclopaedia that is available in print, as a DVD, and on the Internet. It is written and continuously updated by about 100 full-time editors and more than 4,000 expert...
. URL last accessed December 16, 2005. - 54-40 or Fight shows the quilt block named after the slogan. In this time period, women frequently used quilts to express their political views.
Further reading
- Sir James Douglas, Chapter V The Oregon Boundary, Robert Hamilton Coats and R. Edward Gosnell , publ. Morang, Toronto, 1908

