
G-block
Encyclopedia
There are currently seven periods in the periodic table
of chemical elements, culminating with atomic number
118
. If further elements with higher atomic numbers than this are discovered, they will be placed in additional periods, laid out (as with the existing periods) to illustrate periodically recurring trends in the properties of the elements concerned. Any additional periods are expected to contain a larger number of elements than the seventh period, as they are calculated to have an additional so-called g-block, containing 18 elements with partially filled g-orbital
s in each period. An eight-period table containing this block was suggested by Glenn T. Seaborg
in 1969.
No elements in this region have been synthesized or discovered in nature. The first element of the g-block may have atomic number
121, and thus would have the systematic name
unbiunium
. Elements in this region are likely to be highly unstable with respect to radioactive decay
, and have extremely short half lives, although element 126
is hypothesized to be within an island of stability
that is resistant to fission but not to alpha decay
. It is not clear how many elements beyond the expected island of stability are physically possible, if period 8 is complete, or if there is a period 9.
According to the orbital approximation in quantum mechanical
descriptions of atomic structure, the g-block would correspond to elements with partially-filled g-orbitals. However, spin-orbit coupling effects reduce the validity of the orbital approximation substantially for elements of high atomic number
.
suggested that the highest possible element may be under Z=130. However, if higher elements do exist, it is unlikely that they can be meaningfully assigned to the periodic table above approximately Z=173, as discussed in the next section. This chart therefore ends at that number, without meaning to imply that all of those 173 elements are actually possible, nor to imply that heavier elements are not possible. (See also extended periodic table (large version)
.)
All of these hypothetical undiscovered elements are named by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry
(IUPAC) systematic element name
standard which creates a generic name for use until the element has been discovered, confirmed, and an official name approved.
, synthesis has been attempted for only ununennium
, unbinilium
, unbibium
, unbiquadium
and unbihexium
. (Z = 119, 120, 122, 124 and 126)
The positioning of the g-block in the table (to the left of the f-block, to the right, or in between) is speculative. The positions shown in the table above correspond to the assumption that the Madelung rule
will continue to hold for higher atomic numbers; this assumption may or may not be true. At element 118, the orbitals 1s, 2s, 2p, 3s, 3p, 3d, 4s, 4p, 4d, 4f, 5s, 5p, 5d, 5f, 6s, 6p, 6d, 7s and 7p are assumed to be filled, with the remaining orbitals unfilled. The orbitals of the eighth period are predicted to be filled in the order 8s, 5g, 6f, 7d, 8p. However, after approximately element 120, the proximity of the electron shells makes placement in a simple table problematic.
. He predicts that the orbital shells will fill up in this order:
He also suggests that period 8 be split into three parts:
. However, it is likely that the periodic table actually ends much earlier, possibly soon after the island of stability
, which is expected to center around Z = 126.
Additionally the extension of the periodic and nuclides tables is restricted by the proton and the neutron drip lines
.
exhibits difficulty for atoms with atomic number greater than 137
, for the speed of an electron in a 1s electron orbital
, v, is given by
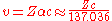
where Z is the atomic number
, and α is the fine structure constant, a measure of the strength of electromagnetic interactions. Under this approximation, any element with an atomic number of greater than 137 would require 1s electrons to be traveling swifter than c, the speed of light
. Hence a non-relativistic model such as the Bohr model is inadequate for such calculations.
Dirac equation
also has problems for Z > 137, for the ground state energy is
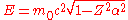
where m0 is the rest mass of the electron. For Z > 137, the wave function of the Dirac ground state is oscillatory, rather than bound, and there is no gap between the positive and negative energy spectra, as in the Klein paradox
. Richard Feynman
pointed out this effect, so the last element expected under this model, 137 (untriseptium
), is sometimes called feynmanium (symbol: Fy).
However, a realistic calculation has to take into account the finite extension of the nuclear-charge distribution. This results in a critical Z of ≈ 173 (unsepttrium), such that neutral atoms may be limited to elements equal to or lower than this. Higher elements could only exist as ions, for example as salts.
Periodic table
The periodic table of the chemical elements is a tabular display of the 118 known chemical elements organized by selected properties of their atomic structures. Elements are presented by increasing atomic number, the number of protons in an atom's atomic nucleus...
of chemical elements, culminating with atomic number
Atomic number
In chemistry and physics, the atomic number is the number of protons found in the nucleus of an atom and therefore identical to the charge number of the nucleus. It is conventionally represented by the symbol Z. The atomic number uniquely identifies a chemical element...
118
Ununoctium
Ununoctium is the temporary IUPAC name for the transactinide element having the atomic number 118 and temporary element symbol Uuo. It is also known as eka-radon or element 118, and on the periodic table of the elements it is a p-block element and the last one of the 7th period. Ununoctium is...
. If further elements with higher atomic numbers than this are discovered, they will be placed in additional periods, laid out (as with the existing periods) to illustrate periodically recurring trends in the properties of the elements concerned. Any additional periods are expected to contain a larger number of elements than the seventh period, as they are calculated to have an additional so-called g-block, containing 18 elements with partially filled g-orbital
Atomic orbital
An atomic orbital is a mathematical function that describes the wave-like behavior of either one electron or a pair of electrons in an atom. This function can be used to calculate the probability of finding any electron of an atom in any specific region around the atom's nucleus...
s in each period. An eight-period table containing this block was suggested by Glenn T. Seaborg
Glenn T. Seaborg
Glenn Theodore Seaborg was an American scientist who won the 1951 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for "discoveries in the chemistry of the transuranium elements", contributed to the discovery and isolation of ten elements, and developed the actinide concept, which led to the current arrangement of the...
in 1969.
No elements in this region have been synthesized or discovered in nature. The first element of the g-block may have atomic number
Atomic number
In chemistry and physics, the atomic number is the number of protons found in the nucleus of an atom and therefore identical to the charge number of the nucleus. It is conventionally represented by the symbol Z. The atomic number uniquely identifies a chemical element...
121, and thus would have the systematic name
Systematic element name
A systematic element name is the temporary name and symbol assigned to newly synthesized and not yet synthesized chemical elements. In chemistry, a transuranic element receives a permanent name and symbol only after its synthesis has been confirmed. In some cases, this has been a protracted and...
unbiunium
Unbiunium
Unbiunium , also known as eka-actinium or element 121, is the temporary name of a hypothetical chemical element in the periodic table that has the temporary symbol Ubu and has the atomic number 121. It would be the first element in the g-block of the periodic table...
. Elements in this region are likely to be highly unstable with respect to radioactive decay
Radioactive decay
Radioactive decay is the process by which an atomic nucleus of an unstable atom loses energy by emitting ionizing particles . The emission is spontaneous, in that the atom decays without any physical interaction with another particle from outside the atom...
, and have extremely short half lives, although element 126
Unbihexium
Unbihexium , also known as eka-plutonium or element 126, is a hypothetical chemical element with atomic number 126 and symbol Ubh. It is of interest because of its location at the peak of the hypothesized island of stability.-History:...
is hypothesized to be within an island of stability
Island of stability
The island of stability in nuclear physics describes a set of as-yet undiscovered isotopes of transuranium elements which are theorized to be much more stable than others...
that is resistant to fission but not to alpha decay
Alpha decay
Alpha decay is a type of radioactive decay in which an atomic nucleus emits an alpha particle and thereby transforms into an atom with a mass number 4 less and atomic number 2 less...
. It is not clear how many elements beyond the expected island of stability are physically possible, if period 8 is complete, or if there is a period 9.
According to the orbital approximation in quantum mechanical
Quantum mechanics
Quantum mechanics, also known as quantum physics or quantum theory, is a branch of physics providing a mathematical description of much of the dual particle-like and wave-like behavior and interactions of energy and matter. It departs from classical mechanics primarily at the atomic and subatomic...
descriptions of atomic structure, the g-block would correspond to elements with partially-filled g-orbitals. However, spin-orbit coupling effects reduce the validity of the orbital approximation substantially for elements of high atomic number
Atomic number
In chemistry and physics, the atomic number is the number of protons found in the nucleus of an atom and therefore identical to the charge number of the nucleus. It is conventionally represented by the symbol Z. The atomic number uniquely identifies a chemical element...
.
Extended periodic table, including the g-block
It is unknown how far the periodic table might extend beyond the known 118 elements. Glenn T. SeaborgGlenn T. Seaborg
Glenn Theodore Seaborg was an American scientist who won the 1951 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for "discoveries in the chemistry of the transuranium elements", contributed to the discovery and isolation of ten elements, and developed the actinide concept, which led to the current arrangement of the...
suggested that the highest possible element may be under Z=130. However, if higher elements do exist, it is unlikely that they can be meaningfully assigned to the periodic table above approximately Z=173, as discussed in the next section. This chart therefore ends at that number, without meaning to imply that all of those 173 elements are actually possible, nor to imply that heavier elements are not possible. (See also extended periodic table (large version)
Extended periodic table (large version)
This is a large version of the extended periodic table and contains the symbol, atomic number and mean atomic mass value for the natural isotopic composition of each element....
.)
| 1 | 1 H Hydrogen Hydrogen is the chemical element with atomic number 1. It is represented by the symbol H. With an average atomic weight of , hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant chemical element, constituting roughly 75% of the Universe's chemical elemental mass. Stars in the main sequence are mainly... |
2 He Helium Helium is the chemical element with atomic number 2 and an atomic weight of 4.002602, which is represented by the symbol He. It is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, inert, monatomic gas that heads the noble gas group in the periodic table... |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3 Li Lithium Lithium is a soft, silver-white metal that belongs to the alkali metal group of chemical elements. It is represented by the symbol Li, and it has the atomic number 3. Under standard conditions it is the lightest metal and the least dense solid element. Like all alkali metals, lithium is highly... |
4 Be Beryllium Beryllium is the chemical element with the symbol Be and atomic number 4. It is a divalent element which occurs naturally only in combination with other elements in minerals. Notable gemstones which contain beryllium include beryl and chrysoberyl... |
5 B Boron Boron is the chemical element with atomic number 5 and the chemical symbol B. Boron is a metalloid. Because boron is not produced by stellar nucleosynthesis, it is a low-abundance element in both the solar system and the Earth's crust. However, boron is concentrated on Earth by the... |
6 C Carbon Carbon is the chemical element with symbol C and atomic number 6. As a member of group 14 on the periodic table, it is nonmetallic and tetravalent—making four electrons available to form covalent chemical bonds... |
7 N Nitrogen Nitrogen is a chemical element that has the symbol N, atomic number of 7 and atomic mass 14.00674 u. Elemental nitrogen is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, and mostly inert diatomic gas at standard conditions, constituting 78.08% by volume of Earth's atmosphere... |
8 O Oxygen Oxygen is the element with atomic number 8 and represented by the symbol O. Its name derives from the Greek roots ὀξύς and -γενής , because at the time of naming, it was mistakenly thought that all acids required oxygen in their composition... |
9 F Fluorine Fluorine is the chemical element with atomic number 9, represented by the symbol F. It is the lightest element of the halogen column of the periodic table and has a single stable isotope, fluorine-19. At standard pressure and temperature, fluorine is a pale yellow gas composed of diatomic... |
10 Ne Neon Neon is the chemical element that has the symbol Ne and an atomic number of 10. Although a very common element in the universe, it is rare on Earth. A colorless, inert noble gas under standard conditions, neon gives a distinct reddish-orange glow when used in either low-voltage neon glow lamps or... |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 11 Na Sodium Sodium is a chemical element with the symbol Na and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal and is a member of the alkali metals; its only stable isotope is 23Na. It is an abundant element that exists in numerous minerals, most commonly as sodium chloride... |
12 Mg Magnesium Magnesium is a chemical element with the symbol Mg, atomic number 12, and common oxidation number +2. It is an alkaline earth metal and the eighth most abundant element in the Earth's crust and ninth in the known universe as a whole... |
13 Al Aluminium Aluminium or aluminum is a silvery white member of the boron group of chemical elements. It has the symbol Al, and its atomic number is 13. It is not soluble in water under normal circumstances.... |
14 Si Silicon Silicon is a chemical element with the symbol Si and atomic number 14. A tetravalent metalloid, it is less reactive than its chemical analog carbon, the nonmetal directly above it in the periodic table, but more reactive than germanium, the metalloid directly below it in the table... |
15 P Phosphorus Phosphorus is the chemical element that has the symbol P and atomic number 15. A multivalent nonmetal of the nitrogen group, phosphorus as a mineral is almost always present in its maximally oxidized state, as inorganic phosphate rocks... |
16 S Sulfur Sulfur or sulphur is the chemical element with atomic number 16. In the periodic table it is represented by the symbol S. It is an abundant, multivalent non-metal. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms form cyclic octatomic molecules with chemical formula S8. Elemental sulfur is a bright yellow... |
17 Cl Chlorine Chlorine is the chemical element with atomic number 17 and symbol Cl. It is the second lightest halogen, found in the periodic table in group 17. The element forms diatomic molecules under standard conditions, called dichlorine... |
18 Ar Argon Argon is a chemical element represented by the symbol Ar. Argon has atomic number 18 and is the third element in group 18 of the periodic table . Argon is the third most common gas in the Earth's atmosphere, at 0.93%, making it more common than carbon dioxide... |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 19 K Potassium Potassium is the chemical element with the symbol K and atomic number 19. Elemental potassium is a soft silvery-white alkali metal that oxidizes rapidly in air and is very reactive with water, generating sufficient heat to ignite the hydrogen emitted in the reaction.Potassium and sodium are... |
20 Ca Calcium Calcium is the chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. It has an atomic mass of 40.078 amu. Calcium is a soft gray alkaline earth metal, and is the fifth-most-abundant element by mass in the Earth's crust... |
21 Sc Scandium Scandium is a chemical element with symbol Sc and atomic number 21. A silvery-white metallic transition metal, it has historically been sometimes classified as a rare earth element, together with yttrium and the lanthanoids... |
22 Ti Titanium Titanium is a chemical element with the symbol Ti and atomic number 22. It has a low density and is a strong, lustrous, corrosion-resistant transition metal with a silver color.... |
23 V Vanadium Vanadium is a chemical element with the symbol V and atomic number 23. It is a hard, silvery gray, ductile and malleable transition metal. The formation of an oxide layer stabilizes the metal against oxidation. The element is found only in chemically combined form in nature... |
24 Cr Chromium Chromium is a chemical element which has the symbol Cr and atomic number 24. It is the first element in Group 6. It is a steely-gray, lustrous, hard metal that takes a high polish and has a high melting point. It is also odorless, tasteless, and malleable... |
25 Mn Manganese Manganese is a chemical element, designated by the symbol Mn. It has the atomic number 25. It is found as a free element in nature , and in many minerals... |
26 Fe Iron Iron is a chemical element with the symbol Fe and atomic number 26. It is a metal in the first transition series. It is the most common element forming the planet Earth as a whole, forming much of Earth's outer and inner core. It is the fourth most common element in the Earth's crust... |
27 Co Cobalt Cobalt is a chemical element with symbol Co and atomic number 27. It is found naturally only in chemically combined form. The free element, produced by reductive smelting, is a hard, lustrous, silver-gray metal.... |
28 Ni Nickel Nickel is a chemical element with the chemical symbol Ni and atomic number 28. It is a silvery-white lustrous metal with a slight golden tinge. Nickel belongs to the transition metals and is hard and ductile... |
29 Cu Copper Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu and atomic number 29. It is a ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. Pure copper is soft and malleable; an exposed surface has a reddish-orange tarnish... |
30 Zn Zinc Zinc , or spelter , is a metallic chemical element; it has the symbol Zn and atomic number 30. It is the first element in group 12 of the periodic table. Zinc is, in some respects, chemically similar to magnesium, because its ion is of similar size and its only common oxidation state is +2... |
31 Ga Gallium Gallium is a chemical element that has the symbol Ga and atomic number 31. Elemental gallium does not occur in nature, but as the gallium salt in trace amounts in bauxite and zinc ores. A soft silvery metallic poor metal, elemental gallium is a brittle solid at low temperatures. As it liquefies... |
32 Ge Germanium Germanium is a chemical element with the symbol Ge and atomic number 32. It is a lustrous, hard, grayish-white metalloid in the carbon group, chemically similar to its group neighbors tin and silicon. The isolated element is a semiconductor, with an appearance most similar to elemental silicon.... |
33 As Arsenic Arsenic is a chemical element with the symbol As, atomic number 33 and relative atomic mass 74.92. Arsenic occurs in many minerals, usually in conjunction with sulfur and metals, and also as a pure elemental crystal. It was first documented by Albertus Magnus in 1250.Arsenic is a metalloid... |
34 Se Selenium Selenium is a chemical element with atomic number 34, chemical symbol Se, and an atomic mass of 78.96. It is a nonmetal, whose properties are intermediate between those of adjacent chalcogen elements sulfur and tellurium... |
35 Br Bromine Bromine ") is a chemical element with the symbol Br, an atomic number of 35, and an atomic mass of 79.904. It is in the halogen element group. The element was isolated independently by two chemists, Carl Jacob Löwig and Antoine Jerome Balard, in 1825–1826... |
36 Kr Krypton Krypton is a chemical element with the symbol Kr and atomic number 36. It is a member of Group 18 and Period 4 elements. A colorless, odorless, tasteless noble gas, krypton occurs in trace amounts in the atmosphere, is isolated by fractionally distilling liquified air, and is often used with other... |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 37 Rb Rubidium Rubidium is a chemical element with the symbol Rb and atomic number 37. Rubidium is a soft, silvery-white metallic element of the alkali metal group. Its atomic mass is 85.4678. Elemental rubidium is highly reactive, with properties similar to those of other elements in group 1, such as very rapid... |
38 Sr Strontium Strontium is a chemical element with the symbol Sr and the atomic number 38. An alkaline earth metal, strontium is a soft silver-white or yellowish metallic element that is highly reactive chemically. The metal turns yellow when exposed to air. It occurs naturally in the minerals celestine and... |
39 Y Yttrium Yttrium is a chemical element with symbol Y and atomic number 39. It is a silvery-metallic transition metal chemically similar to the lanthanides and it has often been classified as a "rare earth element". Yttrium is almost always found combined with the lanthanides in rare earth minerals and is... |
40 Zr Zirconium Zirconium is a chemical element with the symbol Zr and atomic number 40. The name of zirconium is taken from the mineral zircon. Its atomic mass is 91.224. It is a lustrous, grey-white, strong transition metal that resembles titanium... |
41 Nb Niobium Niobium or columbium , is a chemical element with the symbol Nb and atomic number 41. It's a soft, grey, ductile transition metal, which is often found in the pyrochlore mineral, the main commercial source for niobium, and columbite... |
42 Mo Molybdenum Molybdenum , is a Group 6 chemical element with the symbol Mo and atomic number 42. The name is from Neo-Latin Molybdaenum, from Ancient Greek , meaning lead, itself proposed as a loanword from Anatolian Luvian and Lydian languages, since its ores were confused with lead ores... |
43 Tc Technetium Technetium is the chemical element with atomic number 43 and symbol Tc. It is the lowest atomic number element without any stable isotopes; every form of it is radioactive. Nearly all technetium is produced synthetically and only minute amounts are found in nature... |
44 Ru Ruthenium Ruthenium is a chemical element with symbol Ru and atomic number 44. It is a rare transition metal belonging to the platinum group of the periodic table. Like the other metals of the platinum group, ruthenium is inert to most chemicals. The Russian scientist Karl Ernst Claus discovered the element... |
45 Rh Rhodium Rhodium is a chemical element that is a rare, silvery-white, hard and chemically inert transition metal and a member of the platinum group. It has the chemical symbol Rh and atomic number 45. It is composed of only one isotope, 103Rh. Naturally occurring rhodium is found as the free metal, alloyed... |
46 Pd Palladium Palladium is a chemical element with the chemical symbol Pd and an atomic number of 46. It is a rare and lustrous silvery-white metal discovered in 1803 by William Hyde Wollaston. He named it after the asteroid Pallas, which was itself named after the epithet of the Greek goddess Athena, acquired... |
47 Ag Silver Silver is a metallic chemical element with the chemical symbol Ag and atomic number 47. A soft, white, lustrous transition metal, it has the highest electrical conductivity of any element and the highest thermal conductivity of any metal... |
48 Cd Cadmium Cadmium is a chemical element with the symbol Cd and atomic number 48. This soft, bluish-white metal is chemically similar to the two other stable metals in group 12, zinc and mercury. Similar to zinc, it prefers oxidation state +2 in most of its compounds and similar to mercury it shows a low... |
49 In Indium Indium is a chemical element with the symbol In and atomic number 49. This rare, very soft, malleable and easily fusible post-transition metal is chemically similar to gallium and thallium, and shows the intermediate properties between these two... |
50 Sn Tin Tin is a chemical element with the symbol Sn and atomic number 50. It is a main group metal in group 14 of the periodic table. Tin shows chemical similarity to both neighboring group 14 elements, germanium and lead and has two possible oxidation states, +2 and the slightly more stable +4... |
51 Sb Antimony Antimony is a toxic chemical element with the symbol Sb and an atomic number of 51. A lustrous grey metalloid, it is found in nature mainly as the sulfide mineral stibnite... |
52 Te |
53 I Iodine Iodine is a chemical element with the symbol I and atomic number 53. The name is pronounced , , or . The name is from the , meaning violet or purple, due to the color of elemental iodine vapor.... |
54 Xe Xenon Xenon is a chemical element with the symbol Xe and atomic number 54. The element name is pronounced or . A colorless, heavy, odorless noble gas, xenon occurs in the Earth's atmosphere in trace amounts... |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 55 Cs Caesium Caesium or cesium is the chemical element with the symbol Cs and atomic number 55. It is a soft, silvery-gold alkali metal with a melting point of 28 °C , which makes it one of only five elemental metals that are liquid at room temperature... |
56 Ba Barium Barium is a chemical element with the symbol Ba and atomic number 56. It is the fifth element in Group 2, a soft silvery metallic alkaline earth metal. Barium is never found in nature in its pure form due to its reactivity with air. Its oxide is historically known as baryta but it reacts with... |
57 La Lanthanum Lanthanum is a chemical element with the symbol La and atomic number 57.Lanthanum is a silvery white metallic element that belongs to group 3 of the periodic table and is the first element of the lanthanide series. It is found in some rare-earth minerals, usually in combination with cerium and... |
58 Ce Cerium Cerium is a chemical element with the symbol Ce and atomic number 58. It is a soft, silvery, ductile metal which easily oxidizes in air. Cerium was named after the dwarf planet . Cerium is the most abundant of the rare earth elements, making up about 0.0046% of the Earth's crust by weight... |
59 Pr Praseodymium Praseodymium is a chemical element that has the symbol Pr and atomic number 59. Praseodymium is a soft, silvery, malleable and ductile metal in the lanthanide group. It is too reactive to be found in native form, and when artificially prepared, it slowly develops a green oxide coating.The element... |
60 Nd Neodymium Neodymium is a chemical element with the symbol Nd and atomic number 60. It is a soft silvery metal that tarnishes in air. Neodymium was discovered in 1885 by the Austrian chemist Carl Auer von Welsbach. It is present in significant quantities in the ore minerals monazite and bastnäsite... |
61 Pm Promethium Promethium is a chemical element with the symbol Pm and atomic number 61. It is notable for being the only exclusively radioactive element besides technetium that is followed by chemical elements with stable isotopes.- Prediction :... |
62 Sm Samarium Samarium is a chemical element with the symbol Sm, atomic number 62 and atomic weight 150.36. It is a moderately hard silvery metal which readily oxidizes in air. Being a typical member of the lanthanide series, samarium usually assumes the oxidation state +3... |
63 Eu Europium Europium is a chemical element with the symbol Eu and atomic number 63. It is named after the continent of Europe. It is a moderately hard silvery metal which readily oxidizes in air and water... |
64 Gd Gadolinium Gadolinium is a chemical element with the symbol Gd and atomic number 64. It is a silvery-white, malleable and ductile rare-earth metal. It is found in nature only in combined form. Gadolinium was first detected spectroscopically in 1880 by de Marignac who separated its oxide and is credited with... |
65 Tb Terbium Terbium is a chemical element with the symbol Tb and atomic number 65. It is a silvery-white rare earth metal that is malleable, ductile and soft enough to be cut with a knife... |
66 Dy Dysprosium Dysprosium is a chemical element with the symbol Dy and atomic number 66. It is a rare earth element with a metallic silver luster. Dysprosium is never found in nature as a free element, though it is found in various minerals, such as xenotime... |
67 Ho Holmium Holmium is a chemical element with the symbol Ho and atomic number 67. Part of the lanthanide series, holmium is a rare earth element. Its oxide was first isolated from rare earth ores in 1878 and the element was named after the city of Stockholm.... |
68 Er Erbium Erbium is a chemical element in the lanthanide series, with the symbol Er and atomic number 68. A silvery-white solid metal when artificially isolated, natural erbium is always found in chemical combination with other elements on Earth... |
69 Tm Thulium Thulium is a chemical element that has the symbol Tm and atomic number 69. Thulium is the second least abundant of the lanthanides . It is an easily workable metal with a bright silvery-gray luster... |
70 Yb Ytterbium Ytterbium is a chemical element with the symbol Yb and atomic number 70. A soft silvery metallic element, ytterbium is a rare earth element of the lanthanide series and is found in the minerals gadolinite, monazite, and xenotime. The element is sometimes associated with yttrium or other related... |
71 Lu |
72 Hf Hafnium Hafnium is a chemical element with the symbol Hf and atomic number 72. A lustrous, silvery gray, tetravalent transition metal, hafnium chemically resembles zirconium and is found in zirconium minerals. Its existence was predicted by Dmitri Mendeleev in 1869. Hafnium was the penultimate stable... |
73 Ta Tantalum Tantalum is a chemical element with the symbol Ta and atomic number 73. Previously known as tantalium, the name comes from Tantalus, a character in Greek mythology. Tantalum is a rare, hard, blue-gray, lustrous transition metal that is highly corrosion resistant. It is part of the refractory... |
74 W Tungsten Tungsten , also known as wolfram , is a chemical element with the chemical symbol W and atomic number 74.A hard, rare metal under standard conditions when uncombined, tungsten is found naturally on Earth only in chemical compounds. It was identified as a new element in 1781, and first isolated as... |
75 Re Rhenium Rhenium is a chemical element with the symbol Re and atomic number 75. It is a silvery-white, heavy, third-row transition metal in group 7 of the periodic table. With an average concentration of 1 part per billion , rhenium is one of the rarest elements in the Earth's crust. The free element has... |
76 Os Osmium Osmium is a chemical element with the symbol Os and atomic number 76. Osmium is a hard, brittle, blue-gray or blue-blacktransition metal in the platinum family, and is the densest natural element. Osmium is twice as dense as lead. The density of osmium is , slightly greater than that of iridium,... |
77 Ir Iridium Iridium is the chemical element with atomic number 77, and is represented by the symbol Ir. A very hard, brittle, silvery-white transition metal of the platinum family, iridium is the second-densest element and is the most corrosion-resistant metal, even at temperatures as high as 2000 °C... |
78 Pt Platinum Platinum is a chemical element with the chemical symbol Pt and an atomic number of 78. Its name is derived from the Spanish term platina del Pinto, which is literally translated into "little silver of the Pinto River." It is a dense, malleable, ductile, precious, gray-white transition metal... |
79 Au Gold Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au and an atomic number of 79. Gold is a dense, soft, shiny, malleable and ductile metal. Pure gold has a bright yellow color and luster traditionally considered attractive, which it maintains without oxidizing in air or water. Chemically, gold is a... |
80 Hg Mercury (element) Mercury is a chemical element with the symbol Hg and atomic number 80. It is also known as quicksilver or hydrargyrum... |
81 Tl Thallium Thallium is a chemical element with the symbol Tl and atomic number 81. This soft gray poor metal resembles tin but discolors when exposed to air. The two chemists William Crookes and Claude-Auguste Lamy discovered thallium independently in 1861 by the newly developed method of flame spectroscopy... |
82 Pb Lead Lead is a main-group element in the carbon group with the symbol Pb and atomic number 82. Lead is a soft, malleable poor metal. It is also counted as one of the heavy metals. Metallic lead has a bluish-white color after being freshly cut, but it soon tarnishes to a dull grayish color when exposed... |
83 Bi Bismuth Bismuth is a chemical element with symbol Bi and atomic number 83. Bismuth, a trivalent poor metal, chemically resembles arsenic and antimony. Elemental bismuth may occur naturally uncombined, although its sulfide and oxide form important commercial ores. The free element is 86% as dense as lead... |
84 Po Polonium Polonium is a chemical element with the symbol Po and atomic number 84, discovered in 1898 by Marie Skłodowska-Curie and Pierre Curie. A rare and highly radioactive element, polonium is chemically similar to bismuth and tellurium, and it occurs in uranium ores. Polonium has been studied for... |
85 At Astatine Astatine is a radioactive chemical element with the symbol At and atomic number 85. It occurs on the Earth only as the result of decay of heavier elements, and decays away rapidly, so much less is known about this element than its upper neighbors in the periodic table... |
86 Rn Radon Radon is a chemical element with symbol Rn and atomic number 86. It is a radioactive, colorless, odorless, tasteless noble gas, occurring naturally as the decay product of uranium or thorium. Its most stable isotope, 222Rn, has a half-life of 3.8 days... |
|||||||||||||||||||
| 87 Fr Francium Francium is a chemical element with symbol Fr and atomic number 87. It was formerly known as eka-caesium and actinium K.Actually the least unstable isotope, francium-223 It has the lowest electronegativity of all known elements, and is the second rarest naturally occurring element... |
88 Ra Radium Radium is a chemical element with atomic number 88, represented by the symbol Ra. Radium is an almost pure-white alkaline earth metal, but it readily oxidizes on exposure to air, becoming black in color. All isotopes of radium are highly radioactive, with the most stable isotope being radium-226,... |
89 Ac Actinium Actinium is a radioactive chemical element with the symbol Ac and atomic number 89, which was discovered in 1899. It was the first non-primordial radioactive element to be isolated. Polonium, radium and radon were observed before actinium, but they were not isolated until 1902... |
90 Th Thorium Thorium is a natural radioactive chemical element with the symbol Th and atomic number 90. It was discovered in 1828 and named after Thor, the Norse god of thunder.... |
91 Pa Protactinium Protactinium is a chemical element with the symbol Pa and atomic number 91. It is a dense, silvery-gray metal which readily reacts with oxygen, water vapor and inorganic acids. It forms various chemical compounds where protactinium is usually present in the oxidation state +5, but can also assume... |
92 U Uranium Uranium is a silvery-white metallic chemical element in the actinide series of the periodic table, with atomic number 92. It is assigned the chemical symbol U. A uranium atom has 92 protons and 92 electrons, of which 6 are valence electrons... |
93 Np Neptunium Neptunium is a chemical element with the symbol Np and atomic number 93. A radioactive metal, neptunium is the first transuranic element and belongs to the actinide series. Its most stable isotope, 237Np, is a by-product of nuclear reactors and plutonium production and it can be used as a... |
94 Pu Plutonium Plutonium is a transuranic radioactive chemical element with the chemical symbol Pu and atomic number 94. It is an actinide metal of silvery-gray appearance that tarnishes when exposed to air, forming a dull coating when oxidized. The element normally exhibits six allotropes and four oxidation... |
95 Am Americium Americium is a synthetic element that has the symbol Am and atomic number 95. This transuranic element of the actinide series is located in the periodic table below the lanthanide element europium, and thus by analogy was named after another continent, America.Americium was first produced in 1944... |
96 Cm Curium Curium is a synthetic chemical element with the symbol Cm and atomic number 96. This radioactive transuranic element of the actinide series was named after Marie Skłodowska-Curie and her husband Pierre Curie. Curium was first intentionally produced and identified in summer 1944 by the group of... |
97 Bk Berkelium Berkelium , is a synthetic element with the symbol Bk and atomic number 97, a member of the actinide and transuranium element series. It is named after the city of Berkeley, California, the location of the University of California Radiation Laboratory where it was discovered in December 1949... |
98 Cf Californium Californium is a radioactive metallic chemical element with the symbol Cf and atomic number 98. The element was first made in the laboratory in 1950 by bombarding curium with alpha particles at the University of California, Berkeley. It is the ninth member of the actinide series and was the... |
99 Es Einsteinium Einsteinium is a synthetic element with the symbol Es and atomic number 99. It is the seventh transuranic element, and an actinide.Einsteinium was discovered in the debris of the first hydrogen bomb explosion in 1952, and named after Albert Einstein... |
100 Fm Fermium Fermium is a synthetic element with the symbol Fm. It is the 100th element in the periodic table and a member of the actinide series. It is the heaviest element that can be formed by neutron bombardment of lighter elements, and hence the last element that can be prepared in macroscopic quantities,... |
101 Md Mendelevium Mendelevium is a synthetic element with the symbol Md and the atomic number 101. A metallic radioactive transuranic element in the actinide series, mendelevium is usually synthesized by bombarding einsteinium with alpha particles. It was named after Dmitri Ivanovich Mendeleev, who created the... |
102 No Nobelium Nobelium is a synthetic element with the symbol No and atomic number 102. It was first correctly identified in 1966 by scientists at the Flerov Laboratory of Nuclear Reactions in Dubna, Soviet Union... |
103 Lr Lawrencium Lawrencium is a radioactive synthetic chemical element with the symbol Lr and atomic number 103. In the periodic table of the elements, it is a period 7 d-block element and the last element of actinide series... |
104 Rf Rutherfordium Rutherfordium is a chemical element with symbol Rf and atomic number 104, named in honor of New Zealand physicist Ernest Rutherford. It is a synthetic element and radioactive; the most stable known isotope, 267Rf, has a half-life of approximately 1.3 hours.In the periodic table of the elements,... |
105 Db Dubnium The Soviet team proposed the name nielsbohrium in honor of the Danish nuclear physicist Niels Bohr. The American team proposed that the new element should be named hahnium , in honor of the late German chemist Otto Hahn... |
106 Sg Seaborgium Seaborgium is a synthetic chemical element with the symbol Sg and atomic number 106.Seaborgium is a synthetic element whose most stable isotope 271Sg has a half-life of 1.9 minutes. A new isotope 269Sg has a potentially slightly longer half-life based on the observation of a single decay... |
107 Bh Bohrium Bohrium is a chemical element with the symbol Bh and atomic number 107 and is the heaviest member of group 7 .It is a synthetic element whose most stable known isotope, 270Bh, has a half-life of 61 seconds... |
108 Hs Hassium Hassium is a synthetic element with the symbol Hs and atomic number 108. It is the heaviest member of the group 8 elements. The element was first observed in 1984... |
109 Mt Meitnerium Meitnerium is a chemical element with the symbol Mt and atomic number 109. It is placed as the heaviest member of group 9 in the periodic table but a sufficiently stable isotope is not known at this time which would allow chemical experiments to confirm its position, unlike its lighter... |
110 Ds Darmstadtium Darmstadtium is a chemical element with the symbol Ds and atomic number 110. It is placed as the heaviest member of group 10, but no known isotope is sufficiently stable to allow chemical experiments to confirm its placing in that group... |
111 Rg Roentgenium Roentgenium is a synthetic radioactive chemical element with the symbol Rg and atomic number 111. It is placed as the heaviest member of the group 11 elements, although a sufficiently stable isotope has not yet been produced in a sufficient amount that would confirm this position as a heavier... |
112 Cn |
113 Uut Ununtrium Ununtrium is the temporary name of a synthetic element with the temporary symbol Uut and atomic number 113.It is placed as the heaviest member of the group 13 elements although a sufficiently stable isotope is not known at this time that would allow chemical experiments to confirm its position... |
114 Uuq Ununquadium Ununquadium is the temporary name of a radioactive chemical element with the temporary symbol Uuq and atomic number 114. There is no proposed name yet, although flerovium has been discussed in the media.About 80 decays of atoms of... |
115 Uup Ununpentium Ununpentium is the temporary name of a synthetic superheavy element in the periodic table that has the temporary symbol Uup and has the atomic number 115.... |
116 Uuh Ununhexium Ununhexium is the temporary name of a synthetic superheavy element with the temporary symbol Uuh and atomic number 116. There is no proposed name yet although moscovium has been discussed in the media.It is placed as the heaviest member of group 16 although a sufficiently stable isotope is... |
117 Uus Ununseptium Ununseptium is the temporary name of a superheavy artificial chemical element with temporary symbol Uus and atomic number 117. Six atoms were detected by a joint Russia–US collaboration at Dubna, Moscow Oblast, Russia, in 2009–10... |
118 Uuo Ununoctium Ununoctium is the temporary IUPAC name for the transactinide element having the atomic number 118 and temporary element symbol Uuo. It is also known as eka-radon or element 118, and on the periodic table of the elements it is a p-block element and the last one of the 7th period. Ununoctium is... |
|||||||||||||||||||
| 119 Uue Ununennium Ununennium also known as eka-francium or element 119, is the temporary name of a hypothetical chemical element in the periodic table that has the temporary symbol Uue and has the atomic number 119. To date, attempted syntheses of this element have been unsuccessful. Since it is below the alkali... |
120 Ubn Unbinilium Unbinilium , also called eka-radium or element 120, is the temporary, systematic element name of a hypothetical chemical element in the periodic table that has the temporary symbol Ubn and has the atomic number 120.... |
121 Ubu Unbiunium Unbiunium , also known as eka-actinium or element 121, is the temporary name of a hypothetical chemical element in the periodic table that has the temporary symbol Ubu and has the atomic number 121. It would be the first element in the g-block of the periodic table... |
122 Ubb Unbibium Unbibium , also referred to as eka-thorium or element 122, is the temporary name of a currently unknown chemical element in the periodic table that has the temporary symbol Ubb and the atomic number 122.... |
123 Ubt |
124 Ubq Unbiquadium Unbiquadium , also known as eka-uranium or element 124, is the temporary name of a hypothetical element in the periodic table that has the temporary symbol Ubq and atomic number 124.... |
125 Ubp |
126 Ubh Unbihexium Unbihexium , also known as eka-plutonium or element 126, is a hypothetical chemical element with atomic number 126 and symbol Ubh. It is of interest because of its location at the peak of the hypothesized island of stability.-History:... |
127 Ubs |
128 Ubo |
129 Ube |
130 Utn |
131 Utu |
132 Utb |
133 Utt |
134 Utq |
135 Utp |
136 Uth |
137 Uts Untriseptium Untriseptium , also known as eka-dubnium or element 137, is a hypothetical chemical element which has not been observed to occur naturally, nor has it yet been synthesised. Due to drip instabilities, it is not known if this element is physically possible... |
138 Uto |
139 Ute |
140 Uqn |
141 Uqu |
142 Uqb |
143 Uqt |
144 Uqq |
145 Uqp |
146 Uqh |
147 Uqs |
148 Uqo |
149 Uqe |
150 Upn |
151 Upu |
152 Upb |
153 Upt |
154 Upq |
155 Upp |
156 Uph |
157 Ups |
158 Upo |
159 Upe |
160 Uhn |
161 Uhu |
162 Uhb |
163 Uht |
164 Uhq |
165 Uhp |
166 Uhh |
167 Uhs |
168 Uho |
|
| 169 Uhe |
170 Usn |
171 Usu |
172 Usb |
173 Ust |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
All of these hypothetical undiscovered elements are named by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry
International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry
The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry is an international federation of National Adhering Organizations that represents chemists in individual countries. It is a member of the International Council for Science . The international headquarters of IUPAC is located in Zürich,...
(IUPAC) systematic element name
Systematic element name
A systematic element name is the temporary name and symbol assigned to newly synthesized and not yet synthesized chemical elements. In chemistry, a transuranic element receives a permanent name and symbol only after its synthesis has been confirmed. In some cases, this has been a protracted and...
standard which creates a generic name for use until the element has been discovered, confirmed, and an official name approved.
, synthesis has been attempted for only ununennium
Ununennium
Ununennium also known as eka-francium or element 119, is the temporary name of a hypothetical chemical element in the periodic table that has the temporary symbol Uue and has the atomic number 119. To date, attempted syntheses of this element have been unsuccessful. Since it is below the alkali...
, unbinilium
Unbinilium
Unbinilium , also called eka-radium or element 120, is the temporary, systematic element name of a hypothetical chemical element in the periodic table that has the temporary symbol Ubn and has the atomic number 120....
, unbibium
Unbibium
Unbibium , also referred to as eka-thorium or element 122, is the temporary name of a currently unknown chemical element in the periodic table that has the temporary symbol Ubb and the atomic number 122....
, unbiquadium
Unbiquadium
Unbiquadium , also known as eka-uranium or element 124, is the temporary name of a hypothetical element in the periodic table that has the temporary symbol Ubq and atomic number 124....
and unbihexium
Unbihexium
Unbihexium , also known as eka-plutonium or element 126, is a hypothetical chemical element with atomic number 126 and symbol Ubh. It is of interest because of its location at the peak of the hypothesized island of stability.-History:...
. (Z = 119, 120, 122, 124 and 126)
The positioning of the g-block in the table (to the left of the f-block, to the right, or in between) is speculative. The positions shown in the table above correspond to the assumption that the Madelung rule
Aufbau principle
The Aufbau principle is used to determine the electron configuration of an atom, molecule or ion. The principle postulates a hypothetical process in which an atom is "built up" by progressively adding electrons...
will continue to hold for higher atomic numbers; this assumption may or may not be true. At element 118, the orbitals 1s, 2s, 2p, 3s, 3p, 3d, 4s, 4p, 4d, 4f, 5s, 5p, 5d, 5f, 6s, 6p, 6d, 7s and 7p are assumed to be filled, with the remaining orbitals unfilled. The orbitals of the eighth period are predicted to be filled in the order 8s, 5g, 6f, 7d, 8p. However, after approximately element 120, the proximity of the electron shells makes placement in a simple table problematic.
Pyykkö model
Not all models show the higher elements following the pattern established by lighter elements. Pekka Pyykkö, for example, used computer modeling to calculate the positions of elements up to Z=172, and found that several were displaced from the Madelung energy-ordering ruleAufbau principle
The Aufbau principle is used to determine the electron configuration of an atom, molecule or ion. The principle postulates a hypothetical process in which an atom is "built up" by progressively adding electrons...
. He predicts that the orbital shells will fill up in this order:
- 8s,
- 5g,
- the first two spaces of 8p,
- 6f,
- 7d,
- 9s,
- the first two spaces of 9p,
- the rest of 8p.
He also suggests that period 8 be split into three parts:
- 8a, containing 8s,
- 8b, containing the first two elements of 8p,
- 8c, containing 7d and the rest of 8p.
| 8 | 119 Uue Ununennium Ununennium also known as eka-francium or element 119, is the temporary name of a hypothetical chemical element in the periodic table that has the temporary symbol Uue and has the atomic number 119. To date, attempted syntheses of this element have been unsuccessful. Since it is below the alkali... |
120 Ubn Unbinilium Unbinilium , also called eka-radium or element 120, is the temporary, systematic element name of a hypothetical chemical element in the periodic table that has the temporary symbol Ubn and has the atomic number 120.... |
121 Ubu Unbiunium Unbiunium , also known as eka-actinium or element 121, is the temporary name of a hypothetical chemical element in the periodic table that has the temporary symbol Ubu and has the atomic number 121. It would be the first element in the g-block of the periodic table... |
122 Ubb Unbibium Unbibium , also referred to as eka-thorium or element 122, is the temporary name of a currently unknown chemical element in the periodic table that has the temporary symbol Ubb and the atomic number 122.... |
123 Ubt |
124 Ubq Unbiquadium Unbiquadium , also known as eka-uranium or element 124, is the temporary name of a hypothetical element in the periodic table that has the temporary symbol Ubq and atomic number 124.... |
125 Ubp |
126 Ubh Unbihexium Unbihexium , also known as eka-plutonium or element 126, is a hypothetical chemical element with atomic number 126 and symbol Ubh. It is of interest because of its location at the peak of the hypothesized island of stability.-History:... |
127 Ubs |
128 Ubo |
129 Ube |
130 Utn |
131 Utu |
132 Utb |
133 Utt |
134 Utq |
135 Utp |
136 Uth |
137 Uts Untriseptium Untriseptium , also known as eka-dubnium or element 137, is a hypothetical chemical element which has not been observed to occur naturally, nor has it yet been synthesised. Due to drip instabilities, it is not known if this element is physically possible... |
138 Uto |
141 Uqu |
142 Uqb |
143 Uqt |
144 Uqq |
145 Uqp |
146 Uqh |
147 Uqs |
148 Uqo |
149 Uqe |
150 Upn |
151 Upu |
152 Upb |
153 Upt |
154 Upq |
155 Upp |
156 Uph |
157 Ups |
158 Upo |
159 Upe |
160 Uhn |
161 Uhu |
162 Uhb |
163 Uht |
164 Uhq |
139 Ute |
140 Uqn |
169 Uhe |
170 Usn |
171 Usu |
172 Usb |
| 9 | 165 Uhp |
166 Uhh |
167 Uhs |
168 Uho |
End of the periodic table
The number of physically possible elements is unknown. The light-speed limit on electrons orbiting in ever-bigger electron shells theoretically limits neutral atoms to a Z of approximately 137, after which it would be nonsensical to assign the elements to blocks on the basis of electron configurationElectron configuration
In atomic physics and quantum chemistry, electron configuration is the arrangement of electrons of an atom, a molecule, or other physical structure...
. However, it is likely that the periodic table actually ends much earlier, possibly soon after the island of stability
Island of stability
The island of stability in nuclear physics describes a set of as-yet undiscovered isotopes of transuranium elements which are theorized to be much more stable than others...
, which is expected to center around Z = 126.
Additionally the extension of the periodic and nuclides tables is restricted by the proton and the neutron drip lines
Nuclear drip line
In nuclear physics, the boundaries for nuclear particle-stability are conceptualized as drip lines. The nuclear landscape is understood by plotting boxes, each of which represents a unique nuclear species, on a graph with the number of neutrons increasing on the abscissa and number of protons...
.
Bohr model breakdown
The Bohr modelBohr model
In atomic physics, the Bohr model, introduced by Niels Bohr in 1913, depicts the atom as a small, positively charged nucleus surrounded by electrons that travel in circular orbits around the nucleus—similar in structure to the solar system, but with electrostatic forces providing attraction,...
exhibits difficulty for atoms with atomic number greater than 137
Untriseptium
Untriseptium , also known as eka-dubnium or element 137, is a hypothetical chemical element which has not been observed to occur naturally, nor has it yet been synthesised. Due to drip instabilities, it is not known if this element is physically possible...
, for the speed of an electron in a 1s electron orbital
Atomic orbital
An atomic orbital is a mathematical function that describes the wave-like behavior of either one electron or a pair of electrons in an atom. This function can be used to calculate the probability of finding any electron of an atom in any specific region around the atom's nucleus...
, v, is given by
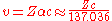
where Z is the atomic number
Atomic number
In chemistry and physics, the atomic number is the number of protons found in the nucleus of an atom and therefore identical to the charge number of the nucleus. It is conventionally represented by the symbol Z. The atomic number uniquely identifies a chemical element...
, and α is the fine structure constant, a measure of the strength of electromagnetic interactions. Under this approximation, any element with an atomic number of greater than 137 would require 1s electrons to be traveling swifter than c, the speed of light
Speed of light
The speed of light in vacuum, usually denoted by c, is a physical constant important in many areas of physics. Its value is 299,792,458 metres per second, a figure that is exact since the length of the metre is defined from this constant and the international standard for time...
. Hence a non-relativistic model such as the Bohr model is inadequate for such calculations.
The Dirac equation
The semi-relativisticTheory of relativity
The theory of relativity, or simply relativity, encompasses two theories of Albert Einstein: special relativity and general relativity. However, the word relativity is sometimes used in reference to Galilean invariance....
Dirac equation
Dirac equation
The Dirac equation is a relativistic quantum mechanical wave equation formulated by British physicist Paul Dirac in 1928. It provided a description of elementary spin-½ particles, such as electrons, consistent with both the principles of quantum mechanics and the theory of special relativity, and...
also has problems for Z > 137, for the ground state energy is
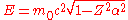
where m0 is the rest mass of the electron. For Z > 137, the wave function of the Dirac ground state is oscillatory, rather than bound, and there is no gap between the positive and negative energy spectra, as in the Klein paradox
Klein paradox
In 1929, physicist Oskar Klein obtained a surprising result by applying the Dirac equation to the familiar problem of electron scattering from a potential barrier. In nonrelativistic quantum mechanics, electron tunneling into a barrier is observed, with exponential damping...
. Richard Feynman
Richard Feynman
Richard Phillips Feynman was an American physicist known for his work in the path integral formulation of quantum mechanics, the theory of quantum electrodynamics and the physics of the superfluidity of supercooled liquid helium, as well as in particle physics...
pointed out this effect, so the last element expected under this model, 137 (untriseptium
Untriseptium
Untriseptium , also known as eka-dubnium or element 137, is a hypothetical chemical element which has not been observed to occur naturally, nor has it yet been synthesised. Due to drip instabilities, it is not known if this element is physically possible...
), is sometimes called feynmanium (symbol: Fy).
However, a realistic calculation has to take into account the finite extension of the nuclear-charge distribution. This results in a critical Z of ≈ 173 (unsepttrium), such that neutral atoms may be limited to elements equal to or lower than this. Higher elements could only exist as ions, for example as salts.
See also
- Electron configurationElectron configurationIn atomic physics and quantum chemistry, electron configuration is the arrangement of electrons of an atom, a molecule, or other physical structure...
- Nuclear shell model
- Table of nuclides (combined)
- Period 8 elementPeriod 8 elementA period 8 element is any one of 50 hypothetical chemical elements belonging to an eighth period of the periodic table of the elements. They may be referred to using IUPAC systematic element names. None of these elements have been created, and it is possible that none have isotopes with stable...

