
Drawing
Encyclopedia

Graphite
The mineral graphite is one of the allotropes of carbon. It was named by Abraham Gottlob Werner in 1789 from the Ancient Greek γράφω , "to draw/write", for its use in pencils, where it is commonly called lead . Unlike diamond , graphite is an electrical conductor, a semimetal...
pencil
Pencil
A pencil is a writing implement or art medium usually constructed of a narrow, solid pigment core inside a protective casing. The case prevents the core from breaking, and also from marking the user’s hand during use....
s, pen and ink, ink
Ink
Ink is a liquid or paste that contains pigments and/or dyes and is used to color a surface to produce an image, text, or design. Ink is used for drawing and/or writing with a pen, brush, or quill...
ed brush
Brush
A brush is a tool with bristles, wire or other filaments, used for cleaning, grooming hair, make up, painting, surface finishing and for many other purposes. It is one of the most basic and versatile tools known to mankind, and the average household may contain several dozen varieties...
es, wax color pencils, crayon
Crayon
A crayon is a stick of colored wax, charcoal, chalk, or other materials used for writing, coloring, drawing, and other methods of illustration. A crayon made of oiled chalk is called an oil pastel; when made of pigment with a dry binder, it is simply a pastel; both are popular media for color...
s, charcoal
Charcoal
Charcoal is the dark grey residue consisting of carbon, and any remaining ash, obtained by removing water and other volatile constituents from animal and vegetation substances. Charcoal is usually produced by slow pyrolysis, the heating of wood or other substances in the absence of oxygen...
, chalk
Chalk
Chalk is a soft, white, porous sedimentary rock, a form of limestone composed of the mineral calcite. Calcite is calcium carbonate or CaCO3. It forms under reasonably deep marine conditions from the gradual accumulation of minute calcite plates shed from micro-organisms called coccolithophores....
, pastel
Pastel
Pastel is an art medium in the form of a stick, consisting of pure powdered pigment and a binder. The pigments used in pastels are the same as those used to produce all colored art media, including oil paints; the binder is of a neutral hue and low saturation....
s, markers
Marker pen
thumb|MarkerA marker pen, marking pen, felt-tip pen, flow or marker, is a pen which has its own ink-source, and usually a tip made of a porous, pressed fibres; such as felt or nylon.-Permanent marker:...
, stylus
Stylus
A stylus is a writing utensil, or a small tool for some other form of marking or shaping, for example in pottery. The word is also used for a computer accessory . It usually refers to a narrow elongated staff, similar to a modern ballpoint pen. Many styli are heavily curved to be held more easily...
es, and various metals (such as silverpoint
Silverpoint
Silverpoint is a traditional drawing technique first used by Medieval scribes on manuscripts.-History:A silverpoint drawing is made by dragging a silver rod or wire across a surface, often prepared with gesso or primer. Silverpoint is one of several types of metalpoint used by scribes, craftsmen...
).
An artist who practices or works in drawing may be called a draughtsman
Draughtsman
A draughtsman or draftsman , is a person skilled in drawing, either:*drawing for artistic purposes, or*technical drawing for practical purposes such as architecture or engineering...
or draftsman.
A small amount of material is released onto the two dimensional medium, leaving a visible mark. The most common support for drawing is paper
Paper
Paper is a thin material mainly used for writing upon, printing upon, drawing or for packaging. It is produced by pressing together moist fibers, typically cellulose pulp derived from wood, rags or grasses, and drying them into flexible sheets....
, although other materials, such as cardboard
Paperboard
Paperboard is a thick paper based material. While there is no rigid differentiation between paper and paperboard, paperboard is generally thicker than paper. According to ISO standards, paperboard is a paper with a basis weight above 224 g/m2, but there are exceptions. Paperboard can be single...
, plastic, leather
Leather
Leather is a durable and flexible material created via the tanning of putrescible animal rawhide and skin, primarily cattlehide. It can be produced through different manufacturing processes, ranging from cottage industry to heavy industry.-Forms:...
, canvas
Canvas
Canvas is an extremely heavy-duty plain-woven fabric used for making sails, tents, marquees, backpacks, and other items for which sturdiness is required. It is also popularly used by artists as a painting surface, typically stretched across a wooden frame...
, and board
Lumber
Lumber or timber is wood in any of its stages from felling through readiness for use as structural material for construction, or wood pulp for paper production....
, may be used. Temporary drawings may be made on a blackboard
Blackboard
A chalkboard is a reusable writing surface.Blackboard may also refer to:* Blackboards are synonymous with "boards of infamy", an element of agitation-propaganda in the Soviet Union in 1930s, coincidental with Holodomor...
or whiteboard
Whiteboard
A whiteboard is a name for any glossy, usually white surface for nonpermanent markings. Whiteboards are analogous to chalkboards, allowing rapid marking and erasing of markings on their surface...
or indeed almost anything. The medium has been a popular and fundamental means of public expression throughout human history. The relatively easy availability of basic drawing instruments makes drawing more universal than most other media.
Overview

Tracing paper
Tracing paper is a type of translucent paper. It is made by immersing uncut and unloaded paper of good quality in sulphuric acid for a few seconds. The acid converts some of the cellulose into amyloid form having a gelatinous and impermeable character. When the treated paper is thoroughly washed...
), around the outline of preexisting shapes that show through the paper—is also not considered fine art, although it may be part of the draughtsman's preparation.
The word drawing is both (1) a noun and (2) the present-participle and gerund forms of the verb draw. To draw is to produce a drawing. A quick, unrefined drawing may be called a sketch
Sketch (drawing)
A sketch is a rapidly executed freehand drawing that is not usually intended as a finished work...
.
Drawing is generally concerned with the marking of lines and areas of tone onto paper. Traditional drawings were monochrome, or at least had little colour, while modern colored-pencil drawings may approach or cross a boundary between drawing and painting. In Western terminology, however, drawing is distinct from painting, even though similar media often are employed in both tasks. Dry media, normally associated with drawing, such as chalk, may be used in pastel
Pastel
Pastel is an art medium in the form of a stick, consisting of pure powdered pigment and a binder. The pigments used in pastels are the same as those used to produce all colored art media, including oil paints; the binder is of a neutral hue and low saturation....
paintings. Drawing may be done with a liquid medium, applied with brushes or pens. Similar supports likewise can serve both: painting generally involves the application of liquid paint onto prepared canvas or panels, but sometimes an underdrawing
Underdrawing
Underdrawing is the drawing done on a painting ground before paint is applied, for example, an imprimatura or an underpainting. Underdrawing was used extensively by 15th century painters like Jan van Eyck and Rogier van der Weyden. These artists "underdrew" with a brush, using hatching strokes for...
is drawn first on that same support. Drawing is often exploratory, with considerable emphasis on observation, problem-solving, and composition. Drawing is also regularly used in preparation for a painting, further obfuscating their distinction.
History

Art
Art is the product or process of deliberately arranging items in a way that influences and affects one or more of the senses, emotions, and intellect....
or drawing was established. Sketches and paintings have been produced since prehistoric times, as demonstrated by cave and rock paintings. By the 12th to 13th centuries A.D., monks were preparing illuminated manuscripts on vellum and parchment in monasteries throughout Europe and were using lead styli to draw lines for their writings and for the outlines for their illuminations. Soon artists generally were using silver
Silver
Silver is a metallic chemical element with the chemical symbol Ag and atomic number 47. A soft, white, lustrous transition metal, it has the highest electrical conductivity of any element and the highest thermal conductivity of any metal...
to make drawings and underdrawings. Initially they used and re-used wooden tablets with prepared ground for these drawings. When paper became generally available, from the 14th century onwards, artists' drawings, both preparatory studies and finished works, became increasingly common.
Notable Draftsmen
Since the 14th century, each century has produced artists who have created great drawings.- Notable draftsmen of the 14th, 15th and 16th centuries include Leonardo da VinciLeonardo da VinciLeonardo di ser Piero da Vinci was an Italian Renaissance polymath: painter, sculptor, architect, musician, scientist, mathematician, engineer, inventor, anatomist, geologist, cartographer, botanist and writer whose genius, perhaps more than that of any other figure, epitomized the Renaissance...
, Albrecht DürerAlbrecht DürerAlbrecht Dürer was a German painter, printmaker, engraver, mathematician, and theorist from Nuremberg. His prints established his reputation across Europe when he was still in his twenties, and he has been conventionally regarded as the greatest artist of the Northern Renaissance ever since...
, MichelangeloMichelangeloMichelangelo di Lodovico Buonarroti Simoni , commonly known as Michelangelo, was an Italian Renaissance painter, sculptor, architect, poet, and engineer who exerted an unparalleled influence on the development of Western art...
, RaphaelRaphaelRaffaello Sanzio da Urbino , better known simply as Raphael, was an Italian painter and architect of the High Renaissance. His work is admired for its clarity of form and ease of composition and for its visual achievement of the Neoplatonic ideal of human grandeur...
, and DonatelloDonatelloDonato di Niccolò di Betto Bardi , also known as Donatello, was an early Renaissance Italian artist and sculptor from Florence...
. - Notable draftsmen of the 17th century include ClaudeClaude LorrainClaude Lorrain, , traditionally just Claude in English Claude Lorrain, , traditionally just Claude in English (also Claude Gellée, his real name, or in French Claude Gellée, , dit le Lorrain) Claude Lorrain, , traditionally just Claude in English (also Claude Gellée, his real name, or in French...
, Nicolas PoussinNicolas PoussinNicolas Poussin was a French painter in the classical style. His work predominantly features clarity, logic, and order, and favors line over color. His work serves as an alternative to the dominant Baroque style of the 17th century...
, Rembrandt, Guercino, and Peter Paul Rubens. - Notable draftsmen of the 18th century include Jean-Honoré FragonardJean-Honoré FragonardJean-Honoré Fragonard was a French painter and printmaker whose late Rococo manner was distinguished by remarkable facility, exuberance, and hedonism. One of the most prolific artists active in the last decades of the Ancien Régime, Fragonard produced more than 550 paintings , of which only five...
, Giovanni Battista TiepoloGiovanni Battista TiepoloGiovanni Battista Tiepolo , also known as Gianbattista or Giambattista Tiepolo, was an Italian painter and printmaker from the Republic of Venice...
, and Antoine WatteauAntoine WatteauJean-Antoine Watteau was a French painter whose brief career spurred the revival of interest in colour and movement...
. - Notable draftsmen of the 19th century include Paul CézannePaul CézannePaul Cézanne was a French artist and Post-Impressionist painter whose work laid the foundations of the transition from the 19th century conception of artistic endeavour to a new and radically different world of art in the 20th century. Cézanne can be said to form the bridge between late 19th...
, Aubrey BeardsleyAubrey BeardsleyAubrey Vincent Beardsley was an English illustrator and author. His drawings, done in black ink and influenced by the style of Japanese woodcuts, emphasized the grotesque, the decadent, and the erotic. He was a leading figure in the Aesthetic movement which also included Oscar Wilde and James A....
, Jacques Louis David, Pierre-Paul Prud'hon, Edgar DegasEdgar DegasEdgar Degas[p] , born Hilaire-Germain-Edgar De Gas, was a French artist famous for his work in painting, sculpture, printmaking and drawing. He is regarded as one of the founders of Impressionism although he rejected the term, and preferred to be called a realist...
, Théodore GéricaultThéodore GéricaultJean-Louis André Théodore Géricault was a profoundly influential French artist, painter and lithographer, known for The Raft of the Medusa and other paintings...
, Francisco GoyaFrancisco GoyaFrancisco José de Goya y Lucientes was a Spanish romantic painter and printmaker regarded both as the last of the Old Masters and the first of the moderns. Goya was a court painter to the Spanish Crown, and through his works was both a commentator on and chronicler of his era...
, Jean Ingres, Odilon RedonOdilon RedonBertrand-Jean Redon, better known as Odilon Redon was a French symbolist painter, printmaker, draughtsman and pastellist.-Life:...
, Henri de Toulouse-LautrecHenri de Toulouse-LautrecHenri Marie Raymond de Toulouse-Lautrec-Monfa or simply Henri de Toulouse-Lautrec was a French painter, printmaker, draughtsman, and illustrator, whose immersion in the colourful and theatrical life of fin de siècle Paris yielded an œuvre of exciting, elegant and provocative images of the modern...
, Honoré DaumierHonoré DaumierHonoré Daumier was a French printmaker, caricaturist, painter, and sculptor, whose many works offer commentary on social and political life in France in the 19th century....
, and Vincent van GoghVincent van GoghVincent Willem van Gogh , and used Brabant dialect in his writing; it is therefore likely that he himself pronounced his name with a Brabant accent: , with a voiced V and palatalized G and gh. In France, where much of his work was produced, it is...
. - Notable draftsmen of the 20th century include Käthe KollwitzKäthe KollwitzKäthe Kollwitz was a German painter, printmaker, and sculptor whose work offered an eloquent and often searing account of the human condition in the first half of the 20th century...
, Max BeckmannMax BeckmannMax Beckmann was a German painter, draftsman, printmaker, sculptor, and writer. Although he is classified as an Expressionist artist, he rejected both the term and the movement...
, Jean DubuffetJean DubuffetJean Philippe Arthur Dubuffet was a French painter and sculptor. His idealistic approach to aesthetics embraced so called "low art" and eschewed traditional standards of beauty in favor of what he believed to be a more authentic and humanistic approach to image-making.-Life and work:Dubuffet was...
, Egon SchieleEgon SchieleEgon Schiele was an Austrian painter. A protégé of Gustav Klimt, Schiele was a major figurative painter of the early 20th century. His work is noted for its intensity, and the many self-portraits the artist produced...
, Arshile GorkyArshile GorkyArshile Gorky was an Armenian-born American painter who had a seminal influence on Abstract Expressionism. As such, his works were often speculated to have been informed by the suffering and loss he experienced of the Armenian genocide.-Early life:...
, Paul KleePaul KleePaul Klee was born in Münchenbuchsee, Switzerland, and is considered both a German and a Swiss painter. His highly individual style was influenced by movements in art that included expressionism, cubism, and surrealism. He was, as well, a student of orientalism...
, Oscar Kokoschka, Alphonse Mucha, M. C. EscherM. C. EscherMaurits Cornelis Escher , usually referred to as M. C. Escher , was a Dutch graphic artist. He is known for his often mathematically inspired woodcuts, lithographs, and mezzotints...
, André MassonAndré MassonAndré-Aimé-René Masson was a French artist.-Biography:Masson was born in Balagny-sur-Thérain, Oise, but was brought up in Belgium. He began his study of art at the age of eleven in Brussels, at the Académie Royale des Beaux-Arts under the guidance of Constant Montald, and later he studied in Paris...
, Jules Pascin, and Pablo PicassoPablo PicassoPablo Diego José Francisco de Paula Juan Nepomuceno María de los Remedios Cipriano de la Santísima Trinidad Ruiz y Picasso known as Pablo Ruiz Picasso was a Spanish expatriate painter, sculptor, printmaker, ceramicist, and stage designer, one of the greatest and most influential artists of the...
.
Media
The medium is the means by which ink, pigment or color are delivered onto the drawing surface. Most drawing media are either dry (e.g. graphiteGraphite
The mineral graphite is one of the allotropes of carbon. It was named by Abraham Gottlob Werner in 1789 from the Ancient Greek γράφω , "to draw/write", for its use in pencils, where it is commonly called lead . Unlike diamond , graphite is an electrical conductor, a semimetal...
, charcoal
Charcoal
Charcoal is the dark grey residue consisting of carbon, and any remaining ash, obtained by removing water and other volatile constituents from animal and vegetation substances. Charcoal is usually produced by slow pyrolysis, the heating of wood or other substances in the absence of oxygen...
, pastels, Conté
Conté
Conté, also known as Conté sticks or Conté crayons, are a drawing medium composed of compressed powdered graphite or charcoal mixed with a wax or clay base, square in cross-section...
, silverpoint
Silverpoint
Silverpoint is a traditional drawing technique first used by Medieval scribes on manuscripts.-History:A silverpoint drawing is made by dragging a silver rod or wire across a surface, often prepared with gesso or primer. Silverpoint is one of several types of metalpoint used by scribes, craftsmen...
), or use a fluid solvent or carrier (marker, pen and ink). Watercolor pencils can be used dry like ordinary pencils, then moistened with a wet brush to get various painterly effects. Very rarely, artists have drawn with (usually decoded) invisible ink
Invisible ink
Invisible ink, also known as security ink, is a substance used for writing, which is invisible either on application or soon thereafter, and which later on can be made visible by some means. Invisible ink is one form of steganography, and it has been used in espionage...
. Metalpoint drawing usually employs either of two metals: silver or lead.
More rarely used are gold, platinum, copper, brass, bronze and tinpoint.
Applying media
Almost all draughtsmen use their hands and fingers to apply the media, with the exception of some handicapped individuals who draw with their mouth or feet.Prior to working on an image, the artist will likely want to gain an understanding of how the various media will work. The different drawing implements can be tried on practice sheets in order to determine value and texture, and how to apply the implement in order to produce various effects.
The stroke of the drawing implement can be used to control the appearance of the image. Ink drawings typically use hatching
Hatching
Hatching is an artistic technique used to create tonal or shading effects by drawing closely spaced parallel lines...
, which consists of groups of parallel lines. Cross-hatching uses hatching in two or more different directions to create a darker tone. Broken hatching, or lines with intermittent breaks, is used to form lighter tones, and by controlling the density of the breaks a graduation of tone can be achieved. Stippling, uses dots to produce tone, texture or shade
Shade
Shade is the blocking of sunlight by any object, and also the shadow created by that object. Shade also consists of the colors grey, black, white, etc...
.
Sketch
Sketch (drawing)
A sketch is a rapidly executed freehand drawing that is not usually intended as a finished work...
drawings use similar techniques, although with pencils and drawing sticks continuous variations in tone can be achieved. For best results the lines in a sketch are typically drawn to follow the contour curves of the surface, thus producing a depth effect. When drawing hair, the lines of the sketch follow the direction of the hair growth.
Typically a drawing will be filled in based on which hand the artist favors. A right-handed artist will want to draw from left to right in order to avoid smearing the image. Sometimes the artist will want to leave a section of the image blank while filling in the remainder of the picture. A frisket can be used for this purpose. The shape of the area to be preserved is cut out of the frisket
Frisket
A frisket is any material that protects areas of a work from unintended change.-Letterpress:On a sheet-fed letterpress printing machine, a frisket is a sheet of oiled paper that covers the space between the type or cuts and the edge of the paper that is to be printed...
, and the resulting shape is then applied to the drawing surface. This will protect the surface from receiving any stray marks before it is ready to be filled in.
Another method to preserve a section of the image is to apply a spray-on fixative to the surface. This will hold loose material more firmly to the sheet and prevent it from smearing. However the fixative spray typically uses chemicals that can negatively affect the respiratory system, so it should be employed in a well-ventilated area such as outdoors.
Materials
Paper comes in a variety of different sizes and qualities, ranging from newspaper grade up to high quality and relatively expensive paper sold as individual sheets. Papers can vary in texture, hue, acidity, and strength when wet. Smooth paper is good for rendering fine detail, but a more "toothy" paper will hold the drawing material better. Thus a coarser material is useful for producing deeper contrast.Newsprint and typing paper may be useful for practice and rough sketches. Tracing paper is used to experiment over a half-finished drawing, and to transfer a design from one sheet to another. Cartridge paper is the basic type of drawing paper sold in pads. Bristol board and even heavier acid-free boards, frequently with smooth finishes, are used for drawing fine detail and do not distort when wet media (ink, washes) are applied. Vellum is extremely smooth and suitable for very fine detail. Coldpressed watercolor paper may be favored for ink drawing due to its texture.
Acid-free, archival quality paper keeps its color and texture far longer than wood pulp
Wood pulp
Pulp is a lignocellulosic fibrous material prepared by chemically or mechanically separating cellulose fibres from wood, fibre crops or waste paper. Wood pulp is the most common raw material in papermaking.-History:...
based paper such as newsprint
Newsprint
Newsprint is a low-cost, non-archival paper most commonly used to print newspapers, and other publications and advertising material. It usually has an off-white cast and distinctive feel. It is designed for use in printing presses that employ a long web of paper rather than individual sheets of...
, which will turn yellow and become brittle much sooner.
The basic tools are a drawing board
Drawing board
A drawing board is, in its antique form, a kind of multipurpose desk which can be used for any kind of drawing, writing or impromptu sketching on a large sheet of paper or for reading a large format book or other oversized document or for drafting precise technical illustrations...
or table, pencil sharpener
Pencil sharpener
A pencil sharpener is a device for sharpening a pencil's writing point by shaving away its worn surface. Pencil sharpeners may be operated manually or by an electric motor.-History:...
and eraser
Eraser
An eraser or rubber is an article of stationery that is used for rubbing out pencil markings. Erasers have a rubbery consistency and are often white or pink, although modern materials allow them to be made in any color. Many pencils are equipped with an eraser on one end...
, and for ink drawing, blotting paper
Blotting paper
Blotting paper is a highly absorbent type of paper or other material. It is used to absorb an excess of liquid substances from the surface of writing paper or objects. It is also commonly used as a beauty tool to absorb excess oil from the skin.-Manufacture:Blotting paper is made from different...
. Other tools used are circle compass, ruler
Ruler
A ruler, sometimes called a rule or line gauge, is an instrument used in geometry, technical drawing, printing and engineering/building to measure distances and/or to rule straight lines...
, and set square
Set square
A set square or triangle is an object used in engineering and technical drawing, with the aim of providing a straightedge at a right angle or other particular planar angle to a baseline....
. Fixative
Fixative
A fixative is a stabilizing or preservative agent:*Fixative , a liquid usually sprayed over a finished piece of artwork to better preserve it and prevent smudging...
is used to prevent pencil and crayon marks from smudging. Drafting tape
Drafting tape
Drafting Tape, also known as "the second most useful tape in the world", is similar to duct tape in that is has a wide variety of uses, but differs in several key areas....
is used to secure paper to drawing surface, and also to mask an area to keep it free of accidental marks sprayed or spattered materials and washes. An easel or slanted table is used to keep the drawing surface in a suitable position, which is generally more horizontal than the position used in painting.
Tone

Blending uses an implement to soften or spread the original drawing strokes. Blending is most easily done with a medium that does not immediately fix
Fixative
A fixative is a stabilizing or preservative agent:*Fixative , a liquid usually sprayed over a finished piece of artwork to better preserve it and prevent smudging...
itself, such as graphite, chalk, or charcoal, although freshly applied ink can be smudged, wet or dry, for some effects. For shading and blending, the artist can use a blending stump
Tortillon
A tortillon is a cylindrical drawing tool, tapered at the ends and usually made of rolled paper, used by artists to smudge or blend marks made with charcoal, Conté crayon, pencil or other drawing media....
, tissue
Facial tissue
Facial tissue and paper handkerchief refers to a class of soft, absorbent, disposable papers that is suitable for use on the face. They are disposable alternatives for cloth handkerchiefs...
, a kneaded eraser
Kneaded eraser
The kneaded eraser/putty rubber is a tool for artists. It is usually made of a grey or white pliable material that resembles putty or gum. It functions by "absorbing" and "picking up" graphite and charcoal particles...
, a fingertip, or any combination of them. A piece of chamois
Chamois leather
Chamois leather , sometimes known as a shammy, is a type of porous leather that is favored for its gentle, non-abrasive composition and exceptional absorption properties...
is useful for creating smooth textures, and for removing material to lighten the tone. Continuous tone can be achieved with graphite on a smooth surface without blending, but the technique is laborious, involving small circular or oval strokes with a somewhat blunt point.
Shading techniques that also introduce texture to the drawing include hatching
Hatching
Hatching is an artistic technique used to create tonal or shading effects by drawing closely spaced parallel lines...
and stippling
Stippling
Stippling is the creation of a pattern simulating varying degrees of solidity or shading by using small dots. Such a pattern may occur in nature and these effects are frequently emulated by artists.-Art:...
. There are a number of other methods for producing texture in the picture: in addition to choosing a suitable paper, the type of drawing material and the drawing technique will result in different textures. Texture can be made to appear more realistic when it is drawn next to a contrasting texture; a coarse texture will be more obvious when placed next to a smoothly blended area. A similar effect can be achieved by drawing different tones close together; a light edge next to a dark background will stand out to the eye, and almost appear to float above the surface.
Layout
Measuring the dimensions of a subject while blocking in the drawing is an important step in producing a realistic rendition of the subject. Tools such as a compassCompass (drafting)
A compass or pair of compasses is a technical drawing instrument that can be used for inscribing circles or arcs. As dividers, they can also be used as a tool to measure distances, in particular on maps...
can be used to measure the angles of different sides. These angles can be reproduced on the drawing surface and then rechecked to make sure they are accurate. Another form of measurement is to compare the relative sizes of different parts of the subject with each other. A finger placed at a point along the drawing implement can be used to compare that dimension with other parts of the image. A ruler
Ruler
A ruler, sometimes called a rule or line gauge, is an instrument used in geometry, technical drawing, printing and engineering/building to measure distances and/or to rule straight lines...
can be used both as a straightedge
Straightedge
A straightedge is a tool with an edge free from curves, or straight, used for transcribing straight lines, or checking the straightness of lines...
and a device to compute proportions.
When attempting to draw a complicated shape such as a human figure, it is helpful at first to represent the form with a set of primitive shapes. Almost any form can be represented by some combination of the cube, sphere, cylinder, and cone. Once these basic shapes have been assembled into a likeness, then the drawing can be refined into a more accurate and polished form. The lines of the primitive shapes are removed and replaced by the final likeness. Drawing the underlying construction is a fundamental skill for representational art and is taught in many books and schools, as its correct application will resolve most uncertainties about smaller details and make the final image look self-consistent.
A more refined art of figure drawing
Figure drawing
In art, a figure drawing is a study of the human form in its various shapes and body postures - sitting, standing or even sleeping. It is a study or stylized depiction of the human form, with the line and form of the human figure as the primary objective, rather than the subject person. It is a...
relies upon the artist possessing a deep understanding of anatomy and the human proportions. A trained artist is familiar with the skeleton structure, joint location, muscle placement, tendon movement, and how the different parts work together during movement. This allows the artist to render more natural poses that do not appear artificially stiff. The artist is also familiar with how the proportions vary depending on the age of the subject, particularly when drawing a portrait.
Perspective
Linear perspectivePerspective (graphical)
Perspective in the graphic arts, such as drawing, is an approximate representation, on a flat surface , of an image as it is seen by the eye...
is a method of portraying objects on a flat surface so that the dimensions shrink with distance. The parallel, straight edges of any object, whether a building or a table, will follow lines that eventually converge at infinity. Typically this point of convergence will be along the horizon, as buildings are built level with the flat surface. When multiple structures are aligned with each other, such as buildings along a street, the horizontal tops and bottoms of the structures will all typically converge at a vanishing point.
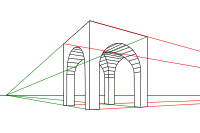
Depth can also be portrayed by several techniques in addition to the perspective approach above. Objects of similar size should appear ever smaller the further they are from the viewer. Thus the back wheel of a cart will appear slightly smaller than the front wheel. Depth can be portrayed through the use of texture. As the texture of an object gets further away it becomes more compressed and busy, taking on an entirely different character than if it was close. Depth can also be portrayed by reducing the amount of contrast of more distant objects, and also by making the colors more pale. This will reproduce the effect of atmospheric haze, and cause the eye to focus primarily on objects drawn in the foreground.
Artistry
_-_study_of_a_seated_veiled_female_figure_(19th_century).png)
Composition (visual arts)
In the visual arts – in particular painting, graphic design, photography and sculpture – composition is the placement or arrangement of visual elements or ingredients in a work of art or a photograph, as distinct from the subject of a work...
of the image is an important element in producing an interesting work of artistic merit
Artistic merit
Artistic merit is a term that is used in relation to cultural products when referring to the judgment of their perceived quality or value as works of art....
. The artist plans the placement of elements in the art in order to communicate ideas and feelings with the viewer. The composition can determine the focus of the art, and result in a harmonious whole that is aesthetically appealing and stimulating.
The illumination
Illumination (image)
Processing of illumination is an important concept in computer vision and computer graphics....
of the subject is also a key element in creating an artistic piece, and the interplay of light and shadow
Chiaroscuro
Chiaroscuro in art is "an Italian term which literally means 'light-dark'. In paintings the description refers to clear tonal contrasts which are often used to suggest the volume and modelling of the subjects depicted"....
is a valuable method in the artist's toolbox. The placement of the light sources
Three-point lighting
Three-point lighting is a standard method used in visual media such as video, film, still photography and computer-generated imagery. By using three separate positions, the photographer can illuminate the shot's subject however desired, while also controlling the shading and shadows produced by...
can make a considerable difference in the type of message that is being presented. Multiple light sources can wash out any wrinkles in a person's face, for instance, and give a more youthful appearance. In contrast, a single light source, such as harsh daylight, can serve to highlight any texture or interesting features.
When drawing an object or figure, the skilled artist pays attention to both the area within the silhouette and what lies outside. The exterior is termed the negative space
Negative space
Negative space, in art, is the space around and between the subject of an image. Negative space may be most evident when the space around a subject, and not the subject itself, forms an interesting or artistically relevant shape, and such space is occasionally used to artistic effect as the "real"...
, and can be as important in the representation as the figure. Objects placed in the background of the figure should appear properly placed wherever they can be viewed.
A study
Study (drawing)
In art, a study is a drawing, sketch or painting done in preparation for a finished piece, or as visual notes. A study can have more impact than a more-elaborately planned work, due to the fresh insights the artist is gaining while exploring his/her subject. The excitement of discovery can give a...
is a draft drawing that is made in preparation for a planned final image. Studies can be used to determine the appearances of specific parts of the completed image, or for experimenting with the best approach for accomplishing the end goal. However a well-crafted study can be a piece of art in its own right, and many hours of careful work can go into completing a study.
Digital illustration
Computer art
Computer art
Computer art is any art in which computers play a role in production or display of the artwork. Such art can be an image, sound, animation, video, CD-ROM, DVD-ROM, videogame, web site, algorithm, performance or gallery installation...
is the use of digital
Digital
A digital system is a data technology that uses discrete values. By contrast, non-digital systems use a continuous range of values to represent information...
tools to produce images under the direct manipulation of the artist, usually through a pointing device such as a tablet
Graphics tablet
A graphics tablet is a computer input device that enables a user to hand-draw images and graphics, similar to the way a person draws images with a pencil and paper. These tablets may also be used to capture data or handwritten signatures...
or a mouse. It is distinguished from computer-generated art
Generative art
Generative art refers to art that has been generated, composed, or constructed in an algorithmic manner through the use of systems defined by computer software algorithms, or similar mathematical or mechanical or randomised autonomous processes....
, which is produced by a computer using mathematical models created by the artist.
Computer art is also distinct from digital manipulation of photographs
Photo editing
Photo editing can refer to:* Image editing techniques applied to photographs.* The cultural impact and ethical concerns of photo manipulation....
, in that it is an original construction "from scratch". Photographic elements may be incorporated into such works, but they are not the primary basis or source for them.
See also
- Architectural drawingArchitectural drawingAn architectural drawing or architect's drawing is a technical drawing of a building that falls within the definition of architecture...
- Color theoryColor theoryIn the visual arts, color theory is a body of practical guidance to color mixing and the visual impacts of specific color combinations. Although color theory principles first appeared in the writings of Leone Battista Alberti and the notebooks of Leonardo da Vinci , a tradition of "colory theory"...
- CompositionComposition (visual arts)In the visual arts – in particular painting, graphic design, photography and sculpture – composition is the placement or arrangement of visual elements or ingredients in a work of art or a photograph, as distinct from the subject of a work...
- DiagramDiagramA diagram is a two-dimensional geometric symbolic representation of information according to some visualization technique. Sometimes, the technique uses a three-dimensional visualization which is then projected onto the two-dimensional surface...
- Digital illustrationDigital illustrationComputer illustration or digital illustration is the use of digital tools to produce images under the direct manipulation of the artist, usually through a pointing device such as a tablet or a mouse. It is distinguished from computer-generated art, which is produced by a computer using mathematical...
- Engineering drawingEngineering drawingAn engineering drawing, a type of technical drawing, is used to fully and clearly define requirements for engineered items.Engineering drawing produces engineering drawings . More than just the drawing of pictures, it is also a language—a graphical language that communicates ideas and information...
- Figure drawingFigure drawingIn art, a figure drawing is a study of the human form in its various shapes and body postures - sitting, standing or even sleeping. It is a study or stylized depiction of the human form, with the line and form of the human figure as the primary objective, rather than the subject person. It is a...
- GPS drawingGPS drawingGPS Drawing combines art, travelling and technology and is a method of drawing that uses GPS to create large-scale artwork.-Methods:...
- IllustrationIllustrationAn illustration is a displayed visualization form presented as a drawing, painting, photograph or other work of art that is created to elucidate or dictate sensual information by providing a visual representation graphically.- Early history :The earliest forms of illustration were prehistoric...
- Multi-SketchMulti-sketchMulti-sketch is an animation method of story-telling where a sequence of hand-drawn sketches are created simultaneously while narrating it with voice...
- PenPenA pen is a device used to apply ink to a surface, usually paper, for writing or drawing. Historically, reed pens, quill pens, and dip pens were used, with a nib of some sort to be dipped in the ink. Ruling pens allow precise adjustment of line width, and still find a few specialized uses, but...
- Sketch (drawing)Sketch (drawing)A sketch is a rapidly executed freehand drawing that is not usually intended as a finished work...
- Technical drawingTechnical drawingTechnical drawing, also known as drafting or draughting, is the act and discipline of composing plans that visually communicate how something functions or has to be constructed.Drafting is the language of industry....
- Traditional animationTraditional animationTraditional animation, is an animation technique where each frame is drawn by hand...
- Academy figureAcademy figureAn academy figure is a drawing, painting or sculpture of the nude human body executed after a live model, typically at half life size.It is a common exercise required of students at art schools and academies, both in the past and present, hence the name....
Further reading
- Betty Edwards, The New Drawing on the Right Side of the Brain, HarperCollins Publishers Ltd; 3Rev Ed edition, 2001, ISBN 978-0007116454
- Brommer, Gerald F. Exploring Drawing. Worcester, Massachusetts: Davis Publications. 1988.
- Bodley Gallery, New York, N.Y., Modern master drawings, 1971, OCLC 37498294.
- Frank Lohan, Pen & Ink Techniques, Contemporary Books, 1978, ISBN 0-8092-7438-8.
- J. D. Hillberry, Drawing Realistic Textures in Pencil, North Light Books, 1999, ISBN 0-89134-868-9.
- Landa, Robin. Take a line for a walk: A Creativity Journal. Boston: Wadsworth, 2011. ISBN: 978-1111839222
- Spears, Heather. The Creative Eye. London: Arcturus. 2007. ISBN 978-0-572-03315-6.
- World Book, Inc. The World Book Encyclopedia Volume 5, 1988, ISBN 0-7166-0089-7.
- Drawing/Thinking: Confronting an Electronic Age, edited by Marc Treib, 2008, ISBN, 0-415-77560-4.
External links
- Timeline of Drawing Development in Children
- On Drawing, an essay about the craft of drawing, by artist Norman Nason

