
Kingdom of Prussia
Encyclopedia
The Kingdom of Prussia was a German
kingdom
from 1701 to 1918. Until the defeat of Germany
in World War I
, it comprised almost two-thirds of the area of the German Empire
. It took its name from the territory of Prussia
, although its power base was Brandenburg
.
by the House of Hohenzollern
("Brandenburg-Prussia
"). In the course of the Second Northern War
, the Treaty of Labiau
and the Treaty of Wehlau-Bromberg granted the Hohenzollern sovereignty in the Prussian duchy. Thus, in return for an alliance against France in the War of the Spanish Succession
, Elector Frederick III crowned himself King in Prussia
as Frederick I
in 1701. Technically, no kingdoms could exist in the Holy Roman Empire except for Bohemia
. However, Frederick took the line that since Prussia had never belonged to the Empire and the Hohenzollerns were fully sovereign over it, he could elevate Prussia to a kingdom. The title "King in Prussia" was adopted because they were still only electors within that portion of Prussia that was still part of the Holy Roman Empire. It was not until 1772 that the title was changed to "King of Prussia."
, to the Hohenzollern
heartland of Brandenburg
, to the exclaves of Cleves
, Mark and Ravensberg in the Rhineland
. In 1708, approximately one third of the population of the Duchy of Prussia fell victim to the bubonic plague
. The plague reached Prenzlau
in August 1710, but eventually receded before it could reach the capital Berlin
, which was only 80 km (49.7 mi) away.
Sweden
's defeat by Russia
, Saxony
, Poland
, Denmark–Norway
, Hanover
, and Prussia in the Great Northern War
(1700–1721) marked the end of significant Swedish power on the southern shores of the Baltic Sea
. In the course of the Pomeranian campaign and by the Prusso-Swedish Treaty of Stockholm
(January 1720), Prussia gained southern Swedish Pomerania
with Stettin (Szczecin)
. Already in 1529, the Hohenzollerns
of Brandenburg had secured the reversion
to the Duchy of Pomerania
after a series of conflicts
, and acquired
its eastern part following the Peace of Westphalia
.
During this time, the trends set in motion by the Great Elector reached their culmination, as the Junker
s, the landed aristocracy, were welded to the Prussian Army
. This era also saw the rise of compulsory education in Germany. King Frederick William I
inaugurated the Prussian compulsory system in 1717.
(Frederick the Great) came to the throne. Using the pretext of a 1537 treaty (vetoed by Emperor Ferdinand I
) by which parts of Silesia
were to pass to Brandenburg
after the extinction of its ruling Piast dynasty
, Frederick invaded Silesia, thereby beginning the War of the Austrian Succession
. After rapidly occupying Silesia, Frederick offered to protect Archduchess Maria Theresa of Austria
if the province were turned over to him. The offer was rejected, but Austria faced several other opponents, and Frederick was eventually able to gain formal cession with the Treaty of Berlin
in 1742.
To the surprise of many, Austria managed to renew the war successfully. In 1744 Frederick invaded again to forestall reprisals and to claim, this time, the province of Bohemia
. He failed, but French
pressure on Austria's ally Great Britain
led to a series of treaties and compromises, culminating in the 1748 Treaty of Aix-la-Chapelle
that restored peace and left Prussia in possession of most of Silesia.
Humiliated by the cession of Silesia, Austria worked to secure an alliance with France and Russia (the "Diplomatic Revolution
"), while Prussia drifted into Great Britain's camp forming the Anglo-Prussian Alliance
. When Frederick preemptively invaded Saxony and Bohemia over the course of a few months in 1756–1757, he initiated the Seven Years' War
which might also be considered the first world war since it was fought in the three continents (France and Great Britain's colonies).
This war was a desperate struggle for the Prussian Army
, and the fact that it managed to fight much of Europe to a draw bears witness to Frederick's military skills. Facing Austria, Russia, France, and Sweden simultaneously, and with only Hanover (and the non-continental British) as notable allies, Frederick managed to prevent serious invasion until October 1760, when the Russian army briefly occupied Berlin
and Königsberg
. The situation became progressively grimmer, however, until the death of Empress Elizabeth of Russia (Miracle of the House of Brandenburg). The accession of the Prussophile Peter III
relieved the pressure on the eastern front. Sweden also exited the war at about the same time.
Defeating the Austrian army at the Battle of Burkersdorf
and relying on continuing British success against France in the war's colonial theatres, Prussia was finally able to force a status quo ante bellum
on the continent. This result confirmed Prussia's major role within the German states and established the country as a European great power
. Frederick, appalled by the near-defeat of Prussia, lived out his days as a much more peaceable ruler.
had gradually weakened during the 18th century. Alarmed by increasing Russian influences in Polish affairs and by a possible expansion of the Russian Empire
, Frederick was instrumental in initiating the first of the Partitions of Poland
between Russia, Prussia, and Austria in 1772 to maintain a balance of power
. The Kingdom of Prussia annexed most of the Polish province of Royal Prussia
, including Warmia
; the annexed land was organized the following year into the Province of West Prussia. The new territory connected the Province of East Prussia
(the territory previously known as the Duchy of Prussia) with the Province of Pomerania, uniting the kingdom's eastern territories.
After Frederick died in 1786, his nephew Fredrick William II
continued the partitions, gaining a large part of western Poland in 1793.
In 1795, the Kingdom of Poland ceased to exist and a large area (including Warsaw
) to the south of East Prussia became part of Prussia. These new territories were organized into the Provinces of New Silesia
, South Prussia
, and New East Prussia
.
(1795) ended the War of the First Coalition against France. In it, the First French Republic and Prussia had stipulated that the latter would ensure the Holy Roman Empire
's neutrality in all the latter's territories north of the demarcation line of the river Main, including the British continental dominions of the Electorate of Hanover
and the Duchies of Bremen-Verden
. To this end, Hanover (including Bremen-Verden) also had to provide troops for the so-called demarcation army maintaining this state of armed neutrality.
In the course of the War of the Second Coalition against France
(1799–1802) Napoléon Bonaparte urged Prussia to occupy the continental British dominions. In 1801 24,000 Prussian soldiers invaded, surprising Hanover, which surrendered without a fight. In April 1801 the Prussian troops arrived in Bremen-Verden's capital Stade
and stayed there until October of the same year. The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland
first ignored Prussia's hostility, but when it joined the pro-French coalition of armed 'neutral' powers such as Denmark-Norway and Russia
, Britain started to capture Prussian sea vessels. After the Battle of Copenhagen (1801)
the coalition fell apart and Prussia withdrew again its troops.
At Napoléon's instigation, Prussia recaptured British Hanover and Bremen-Verden in early 1806. On August 6, the same year the Holy Roman Empire
was dissolved as a result of Napoléon's victories over Austria
. The title of Kurfürst (Prince-elector
) of Brandenburg became meaningless, and was dropped. Before this time, the Hohenzollern sovereign had held many titles and crowns, from Supreme Governor of the Protestant Churches (summus episcopus) to King, Elector, Grand Duke, Duke for the various regions and realms under his rule. After 1806, Frederick William III was simply King of Prussia and summus episcopus.
But when Prussia, after it turned against the French Empire, was defeated in the Battle of Jena-Auerstedt
(November 11, 1806), King Frederick William III was forced to temporarily flee to remote Memel
. After the Treaties of Tilsit
in 1807, Prussia lost about half of its territory, including the land gained from the Second and Third Partitions of Poland
(which now fell to the Duchy of Warsaw
) and all land west of the Elbe River. France recaptured Prussian-occupied Hanover, including Bremen-Verden. The remainder of the kingdom was occupied by French troops (at Prussia’s expense) and the king was obliged to make an alliance with France and join the Continental System
.
After the defeat of Napoleon in Russia, Prussia quit the alliance and took part in the Sixth Coalition during the "Wars of Liberation" (Befreiungskriege) against the French occupation. Prussian troops under Marshal Gebhard Leberecht von Blücher
contributed crucially in the Battle of Waterloo
of 1815 to the final victory over Napoleon.
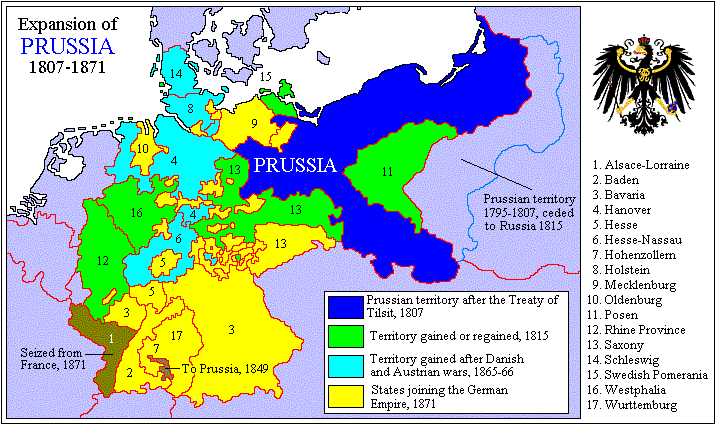 Prussia’s reward for its part in France's defeat came at the Congress of Vienna
Prussia’s reward for its part in France's defeat came at the Congress of Vienna
, where Prussia was granted most of its lost territories and considerably more, including 40% of the Kingdom of Saxony
and much of the Rhineland
. Much of the territory annexed in the Third Partition of Poland was granted to Congress Poland
under Russian rule.
With these Prussian gains in territory, the kingdom was reorganised into ten provinces. Most of the kingdom, aside from the Provinces of East Prussia
, West Prussia
, and Posen
, became part of the new German Confederation
, a confederacy
of 39 sovereign states replacing the defunct Holy Roman Empire
.
Frederick William III submitted Prussia to a number of administrative reforms, among others reorganising the government by way of ministries, which remained formative for the following hundred years.
As to religion, reformed Calvinist Frederick William III—as Supreme Governor of the Protestant Churches—asserted his long-cherished project (started in 1798) to unite the Lutheran and the Reformed Church in 1817, (see Prussian Union
). The Calvinist minority, strongly supported by its co-religionist Frederick William III, and the partially reluctant Lutheran majority formed the united
Protestant Evangelical Church in Prussia. However, ensuing quarrels causing a permanent schism
among the Lutherans into united and Old Lutherans
by 1830.
As a consequence of the Revolutions of 1848
, the Principalities of Hohenzollern-Sigmaringen
and Hohenzollern-Hechingen
(ruled by a Catholic
cadet branch of the House of Hohenzollern) were annexed by Prussia in 1850, later united as Province of Hohenzollern
.
between the formation of a single German nation and the conservation of the current collection of smaller German states and kingdoms. The creation of the German Customs Union (Zollverein
) in 1834, which excluded the Austrian Empire
, increased Prussian influence over the member states. As a consequence of the Revolutions of 1848
, King Frederick William IV
was offered the crown of a united Germany by the Frankfurt Parliament
. Frederick William refused the offer on the grounds that revolutionary assemblies could not grant royal titles. But there were two other reasons why he refused: to do so would have done little to end the internal power struggle between Austria and Prussia, and all Prussian kings (up to and including William I
) feared that the formation of a German Empire
would mean the end of Prussia’s independence within the German states.
In 1848, actions taken by Denmark
towards the Duchies of Schleswig
and Holstein
led to the First War of Schleswig
(1848–51) between Denmark and the German Confederation
. Denmark won.
Frederick William issued Prussia's first constitution
by his own authority in 1850. This document—moderate by the standards of the time but conservative by today's standards—provided for a two-house parliament. The lower house, or Landtag
was elected by all taxpayers, who were divided into three classes
whose votes were weighted according to the amount of taxes paid. Women and those who paid no taxes had no vote. This allowed just over one-third of the voters to choose 85% of the legislature, all but assuring dominance by the more well-to-do men of the population. The upper house, which was later renamed the Herrenhaus
("House of Lords"), was appointed by the king. He retained full executive authority and ministers were responsible only to him (indeed, as late as 1910, Prussian kings believed that they ruled by divine right
). As a result, the grip of the landowning classes, the Junker
s, remained unbroken, especially in the eastern provinces.
Frederick William suffered a stroke in 1857, and his younger brother, Crown Prince Wilhelm, became regent. Wilhelm pursued a considerably more moderate course, and gained enough power that, by Frederick William's death in 1861, he was able to become king in his own right as William I
. However, shortly after gaining the throne, he faced a dispute with his parliament over the size of the army. The parliament, dominated by the liberals, balked at William's desire to increase the number of regiments and withheld approval of the budget to pay for its cost. A deadlock ensued, and William seriously considered abdicating in favour of his son, Crown Prince Frederick William. He was, however, persuaded to appoint as prime minister Otto von Bismarck
, his ambassador to France. Bismarck took office on September 23, 1862.
Although Bismarck had a reputation as an unyielding conservative, he was initially inclined to seek a compromise over the budget issue. However, William refused to consider it; he viewed defense issues as the crown's personal province. Forced into a policy of confrontation, Bismarck came up with a novel theory. Under the constitution, the king and the parliament were responsible for agreeing on the budget. Bismarck argued that since they had failed to come to an agreement, there was a "hole" in the constitution, and the government had to continue to collect taxes and disburse funds in accordance with the old budget in order to keep functioning. The government thus operated without a new budget from 1862 to 1866, allowing Bismarck to implement William's military reforms.
The liberals violently denounced Bismarck as a violator of the law. However, Bismarck's real plan was an accommodation with liberalism. He had come to believe that German unification was inevitable, but that the conservative forces had to take the lead in the drive toward creating a unified nation in order to keep from being eclipsed. He also believed that the middle-class liberals wanted a unified Germany more than they wanted to break the grip of the traditional forces over society. He thus embarked on a drive to create a united Germany under Prussian leadership, and guided Prussia through three wars which ultimately achieved this goal.
The first of these wars was the Second War of Schleswig
(1864), which Prussia initiated and succeeded in gaining the assistance of Austria. Denmark was soundly defeated and surrendered both Schleswig and Holstein, to Prussia and Austria respectively.
 The divided administration of Schleswig and Holstein then became the trigger for the Austro-Prussian War
The divided administration of Schleswig and Holstein then became the trigger for the Austro-Prussian War
(1866 – also known as the Seven Weeks’ War), where Prussia, allied with the Kingdom of Italy
and various northern German states, declared war on the Austrian Empire. The Austrian-led coalition was crushed, and Prussia annexed four of its smaller allies—the Kingdom of Hanover
, the Electorate of Hesse
, the Duchy of Nassau and the Free City of Frankfurt
. Prussia also annexed Schleswig and Holstein, and also effectively annexed Saxe-Lauenburg by forcing it into a personal union
with Prussia (which was turned into a full union in 1876). King William initially wanted to take territory from Austria itself, but Bismarck persuaded him to abandon the idea. While Bismarck wanted Austria to play no future role in German affairs, he still saw that Austria could be a valuable future ally.
With these gains in territory, the Prussian possessions in the Rhineland and Westphalia were connected to the rest of the kingdom for the first time. Counting the de facto annexation of Saxe-Lauenburg, Prussia now stretched uninterrupted across the northern two-thirds of Germany. It would remain at this size until the overthrow of the monarchy in 1918.
Bismarck used this opportunity to end the budget dispute with parliament. He proposed a bill of indemnity granting him retroactive approval for governing without a legal budget. He guessed, correctly as it turned out, that this would lead to a split between his liberal adversaries. While some of them argued that there could be no compromise with the principle of constitutional government, most of the liberals decided to support the bill in hopes of winning more freedom in the future.
The German Confederation was dissolved as part of the war. In its place, Prussia cajoled the 21 states north of the Main into forming the North German Confederation
in 1867. Prussia was the dominant state in this new grouping, with four-fifths of its territory and population. Its near-total control was cemented in a constitution written by Bismarck. Executive power was vested in a president—an office vested in the Prussian crown according to hereditary right. He was assisted by a chancellor responsible only to him. There was also a two-house parliament. The lower house, or Reichstag
(Diet), was elected by universal male suffrage. The upper house, or Bundesrat (Federal Council) was appointed by the state governments. The Bundesrat was, in practice, the stronger chamber. Prussia had 17 of 43 votes, and could easily control proceedings through alliances with the other states. For all intents and purposes, the new grouping was dominated by Bismarck. He served as his own foreign minister for virtually his entire tenure as prime minister of Prussia, and in that capacity was able to instruct the Prussian delegates to the Bundesrat.
The southern German states (except Austria) were forced to accept military alliances with Prussia, and Prussia began steps to merge them with the North German Confederation. Bismarck’s planned Kleindeutschland unification of Germany
had come considerably closer to realisation.
The final act was the Franco-Prussian War
(1870), where Bismarck maneuvered Emperor Napoleon III of France
into declaring war on Prussia. Activating the German alliances put in place after the Austro-Prussian War, the German states came together and swiftly defeated France
. Even before then, Bismarck was able to complete the work of unifying Germany under Prussian leadership. The patriotic fervour aroused by the war with France was too much for the remaining opponents of a unified nation to overcome, and on 18 January 1871 (the 170th anniversary of the coronation of the first Prussian king, Frederick I
), the German Empire
was proclaimed in the Hall of Mirrors
at Versailles
outside of Paris
, while the French capital was still under siege
. King William became the first emperor of a unified Germany.
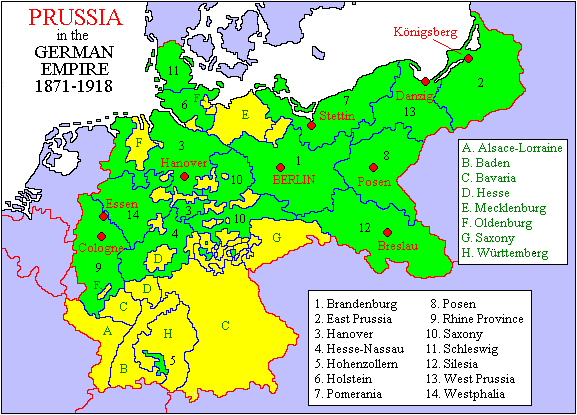 Bismarck's new empire was the most powerful state on the Continent. Prussia's dominance over the new empire was almost as absolute as it was with the North German Confederation. It included two-thirds of the empire's territory and three-fifths of its population. The imperial crown was a hereditary office of the House of Hohenzollern. Prussia also had a large plurality of seats in the Bundesrat, and as before could control the proceedings with the support of its allies in the secondary states.
Bismarck's new empire was the most powerful state on the Continent. Prussia's dominance over the new empire was almost as absolute as it was with the North German Confederation. It included two-thirds of the empire's territory and three-fifths of its population. The imperial crown was a hereditary office of the House of Hohenzollern. Prussia also had a large plurality of seats in the Bundesrat, and as before could control the proceedings with the support of its allies in the secondary states.
However, the seeds for future problems lay in a gross disparity between the imperial and Prussian systems. The empire granted the vote to all men over 25. However, Prussia retained its restrictive three-class voting system, in which the well-to-do had 17.5 times the voting power of the rest of the population. Since the imperial chancellor was, except for two periods (January–November 1873 and 1892–94) also prime minister of Prussia, this meant that for most of the empire's existence, the king/emperor and prime minister/chancellor had to seek majorities from legislatures elected by two completely different franchises.
At the time of the empire's creation, both Prussia and Germany were roughly two-thirds rural. Within 20 years, the situation was reversed; the cities and towns accounted for two-thirds of the population. However, in both the kingdom and the empire, the constituencies were never redrawn to reflect the growing population and influence of the cities and towns. This meant that rural areas were grossly overrepresented from the 1890s onward.
Bismarck realised that the rest of Europe was skeptical of his powerful new Reich, and turned his attention to preserving peace with such acts as the Congress of Berlin
. The new German Empire improved its already-strong relations with Britain. The ties between London and Berlin had already been sealed with a golden braid in 1858, when Crown Prince Frederick William of Prussia married Princess Victoria
of Britain.
William I
died in 1888, and the Crown Prince succeeded to the throne as Frederick III
. The new emperor, a decided Anglophile, planned to transform Prussia and the empire into a more liberal and democratic monarchy on the British model. However, he died after only 99 days on the throne and was succeeded by his 29-year old son, William II
. As a boy, William had rebelled against his parents' efforts to mould him as a liberal, and had become thoroughly Prussianised under Bismarck's tutelage. The new Kaiser rapidly soured relations with the British
and Russian
royal families (despite being closely related to them), becoming their rival and ultimately their enemy.
until the Revolutions of 1848 in the German states
, after which Prussia became a constitutional monarchy
and Adolf Heinrich von Arnim-Boitzenburg
was elected as Prussia's first prime minister
. Following Prussia's first constitution
, a two-house parliament was formed. The lower house, or Landtag was elected by all taxpayers, who were divided into three classes
according to the amount of taxes paid. This allowed just over 25% of the voters to choose 85% of the legislature, all but assuring dominance by the more well-to-do elements of the population. The upper house, which was later renamed the Prussian House of Lords
, was appointed by the king. He retained full executive authority and ministers were responsible only to him. As a result, the grip of the landowning classes, the Junker
s, remained unbroken, especially in the eastern provinces. Prussian Secret Police
, formed in response to the Revolutions of 1848 in the German states
, aided the conservative government.
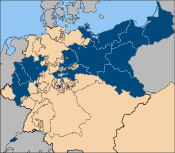
 The original core regions of the Kingdom of Prussia were the Margraviate of Brandenburg
The original core regions of the Kingdom of Prussia were the Margraviate of Brandenburg
and the Duchy of Prussia which together formed Brandenburg-Prussia
. A Further Pomeranian province had been held by Prussia since 1653. Combined with Swedish Pomerania
, gained from Sweden in 1720 and 1815, this region formed the Province of Pomerania. Prussian gains in the Silesian Wars
led to the formation of the Province of Silesia
in 1740.
After the First Partition of Poland
in 1772, the newly-annexed Royal Prussia
and Warmia
became the Province of West Prussia, while the Duchy of Prussia (along with part of Warmia) became the Province of East Prussia
. Other annexations along the Noteć (Netze) River
became the Netze District
. Following the second and third partitions (1793–1795), the new Prussian annexations became the Provinces of New Silesia
, South Prussia
, and New East Prussia
, with the Netze District redivided between West and South Prussia. These three provinces were ultimately lost to Congress Poland
after the Congress of Vienna
in 1815, except for the western part of South Prussia, which would form part of the Grand Duchy of Posen.
Following the major western gains made by Prussia after the Vienna Congress, a total of ten provinces were established, each one subdivided further into smaller administrative regions known as Regierungsbezirk
e. The provinces were:
In 1822, the provinces of Jülich-Cleves-Berg and the Lower Rhine were merged to form the Rhine Province
. In 1829, the Provinces of East and West Prussia merged to form the Province of Prussia
, but the separate provinces were reformed in 1878. The principalities of Hohenzollern-Sigmaringen
and Hohenzollern-Hechingen
were annexed in 1850 to form the Province of Hohenzollern
.
After Prussia's victory in the 1866 Austro-Prussian War
, territories annexed by Prussia were reorganised into three new provinces: Hanover
, Hesse-Nassau
and Schleswig-Holstein
.
Germany
Germany , officially the Federal Republic of Germany , is a federal parliamentary republic in Europe. The country consists of 16 states while the capital and largest city is Berlin. Germany covers an area of 357,021 km2 and has a largely temperate seasonal climate...
kingdom
Monarchy
A monarchy is a form of government in which the office of head of state is usually held until death or abdication and is often hereditary and includes a royal house. In some cases, the monarch is elected...
from 1701 to 1918. Until the defeat of Germany
Germany
Germany , officially the Federal Republic of Germany , is a federal parliamentary republic in Europe. The country consists of 16 states while the capital and largest city is Berlin. Germany covers an area of 357,021 km2 and has a largely temperate seasonal climate...
in World War I
World War I
World War I , which was predominantly called the World War or the Great War from its occurrence until 1939, and the First World War or World War I thereafter, was a major war centred in Europe that began on 28 July 1914 and lasted until 11 November 1918...
, it comprised almost two-thirds of the area of the German Empire
German Empire
The German Empire refers to Germany during the "Second Reich" period from the unification of Germany and proclamation of Wilhelm I as German Emperor on 18 January 1871, to 1918, when it became a federal republic after defeat in World War I and the abdication of the Emperor, Wilhelm II.The German...
. It took its name from the territory of Prussia
Prussia (region)
Prussia is a historical region in Central Europe extending from the south-eastern coast of the Baltic Sea to the Masurian Lake District. It is now divided between Poland, Russia, and Lithuania...
, although its power base was Brandenburg
Margraviate of Brandenburg
The Margraviate of Brandenburg was a major principality of the Holy Roman Empire from 1157 to 1806. Also known as the March of Brandenburg , it played a pivotal role in the history of Germany and Central Europe....
.
Establishment
Since 1618, the Electorate of Brandenburg and the Duchy of Prussia were ruled in personal unionPersonal union
A personal union is the combination by which two or more different states have the same monarch while their boundaries, their laws and their interests remain distinct. It should not be confused with a federation which is internationally considered a single state...
by the House of Hohenzollern
House of Hohenzollern
The House of Hohenzollern is a noble family and royal dynasty of electors, kings and emperors of Prussia, Germany and Romania. It originated in the area around the town of Hechingen in Swabia during the 11th century. They took their name from their ancestral home, the Burg Hohenzollern castle near...
("Brandenburg-Prussia
Brandenburg-Prussia
Brandenburg-Prussia is the historiographic denomination for the Early Modern realm of the Brandenburgian Hohenzollerns between 1618 and 1701. Based in the Electorate of Brandenburg, the main branch of the Hohenzollern intermarried with the branch ruling the Duchy of Prussia, and secured succession...
"). In the course of the Second Northern War
Second Northern War
The Second Northern War was fought between Sweden and its adversaries the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth , Russia , Brandenburg-Prussia , the Habsburg Monarchy and Denmark–Norway...
, the Treaty of Labiau
Treaty of Labiau
The Treaty of Labiau was a treaty signed between Frederick William I, Elector of Brandenburg and Charles X Gustav of Sweden on 10 November / 20 November 1656 in Labiau...
and the Treaty of Wehlau-Bromberg granted the Hohenzollern sovereignty in the Prussian duchy. Thus, in return for an alliance against France in the War of the Spanish Succession
War of the Spanish Succession
The War of the Spanish Succession was fought among several European powers, including a divided Spain, over the possible unification of the Kingdoms of Spain and France under one Bourbon monarch. As France and Spain were among the most powerful states of Europe, such a unification would have...
, Elector Frederick III crowned himself King in Prussia
King in Prussia
King in Prussia was a title used by the Electors of Brandenburg from 1701 to 1772. Subsequently they used the title King of Prussia....
as Frederick I
Frederick I of Prussia
Frederick I , of the Hohenzollern dynasty, was Elector of Brandenburg and Duke of Prussia in personal union . The latter function he upgraded to royalty, becoming the first King in Prussia . From 1707 he was in personal union the sovereign prince of the Principality of Neuchâtel...
in 1701. Technically, no kingdoms could exist in the Holy Roman Empire except for Bohemia
Kingdom of Bohemia
The Kingdom of Bohemia was a country located in the region of Bohemia in Central Europe, most of whose territory is currently located in the modern-day Czech Republic. The King was Elector of Holy Roman Empire until its dissolution in 1806, whereupon it became part of the Austrian Empire, and...
. However, Frederick took the line that since Prussia had never belonged to the Empire and the Hohenzollerns were fully sovereign over it, he could elevate Prussia to a kingdom. The title "King in Prussia" was adopted because they were still only electors within that portion of Prussia that was still part of the Holy Roman Empire. It was not until 1772 that the title was changed to "King of Prussia."
1701–1740: Early History
The new Kingdom of Prussia was very poor—still having not fully recovered from the devastation of the Thirty Years’ War—and its territory was scattered across over 1200 km (745.6 mi): from the lands of the Duchy of Prussia on the south-east coast of the Baltic SeaBaltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is a brackish mediterranean sea located in Northern Europe, from 53°N to 66°N latitude and from 20°E to 26°E longitude. It is bounded by the Scandinavian Peninsula, the mainland of Europe, and the Danish islands. It drains into the Kattegat by way of the Øresund, the Great Belt and...
, to the Hohenzollern
House of Hohenzollern
The House of Hohenzollern is a noble family and royal dynasty of electors, kings and emperors of Prussia, Germany and Romania. It originated in the area around the town of Hechingen in Swabia during the 11th century. They took their name from their ancestral home, the Burg Hohenzollern castle near...
heartland of Brandenburg
Margraviate of Brandenburg
The Margraviate of Brandenburg was a major principality of the Holy Roman Empire from 1157 to 1806. Also known as the March of Brandenburg , it played a pivotal role in the history of Germany and Central Europe....
, to the exclaves of Cleves
Duchy of Cleves
The Duchy of Cleves was a State of the Holy Roman Empire. It was situated in the northern Rhineland on both sides of the Lower Rhine, around its capital Cleves and the town of Wesel, bordering the lands of the Prince-Bishopric of Münster in the east and the Duchy of Brabant in the west...
, Mark and Ravensberg in the Rhineland
Rhineland
Historically, the Rhinelands refers to a loosely-defined region embracing the land on either bank of the River Rhine in central Europe....
. In 1708, approximately one third of the population of the Duchy of Prussia fell victim to the bubonic plague
Bubonic plague
Plague is a deadly infectious disease that is caused by the enterobacteria Yersinia pestis, named after the French-Swiss bacteriologist Alexandre Yersin. Primarily carried by rodents and spread to humans via fleas, the disease is notorious throughout history, due to the unrivaled scale of death...
. The plague reached Prenzlau
Prenzlau
Prenzlau , a city in the Uckermark District of Brandenburg in Germany, had a population of about 21,000 in 2005.-International relations:Prenzlau is twinned with: Uster, Switzerland Barlinek, Poland Świdwin, Poland...
in August 1710, but eventually receded before it could reach the capital Berlin
Berlin
Berlin is the capital city of Germany and is one of the 16 states of Germany. With a population of 3.45 million people, Berlin is Germany's largest city. It is the second most populous city proper and the seventh most populous urban area in the European Union...
, which was only 80 km (49.7 mi) away.
Sweden
Swedish Empire
The Swedish Empire refers to the Kingdom of Sweden between 1561 and 1721 . During this time, Sweden was one of the great European powers. In Swedish, the period is called Stormaktstiden, literally meaning "the Great Power Era"...
's defeat by Russia
Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was a state that existed from 1721 until the Russian Revolution of 1917. It was the successor to the Tsardom of Russia and the predecessor of the Soviet Union...
, Saxony
Electorate of Saxony
The Electorate of Saxony , sometimes referred to as Upper Saxony, was a State of the Holy Roman Empire. It was established when Emperor Charles IV raised the Ascanian duchy of Saxe-Wittenberg to the status of an Electorate by the Golden Bull of 1356...
, Poland
Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth
The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth was a dualistic state of Poland and Lithuania ruled by a common monarch. It was the largest and one of the most populous countries of 16th- and 17th‑century Europe with some and a multi-ethnic population of 11 million at its peak in the early 17th century...
, Denmark–Norway
Denmark–Norway
Denmark–Norway is the historiographical name for a former political entity consisting of the kingdoms of Denmark and Norway, including the originally Norwegian dependencies of Iceland, Greenland and the Faroe Islands...
, Hanover
Electorate of Hanover
The Electorate of Brunswick-Lüneburg was the ninth Electorate of the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation...
, and Prussia in the Great Northern War
Great Northern War
The Great Northern War was a conflict in which a coalition led by the Tsardom of Russia successfully contested the supremacy of the Swedish Empire in northern Central Europe and Eastern Europe. The initial leaders of the anti-Swedish alliance were Peter I the Great of Russia, Frederick IV of...
(1700–1721) marked the end of significant Swedish power on the southern shores of the Baltic Sea
Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is a brackish mediterranean sea located in Northern Europe, from 53°N to 66°N latitude and from 20°E to 26°E longitude. It is bounded by the Scandinavian Peninsula, the mainland of Europe, and the Danish islands. It drains into the Kattegat by way of the Øresund, the Great Belt and...
. In the course of the Pomeranian campaign and by the Prusso-Swedish Treaty of Stockholm
Treaty of Stockholm (Great Northern War)
With the death of Charles XII of Sweden in 1718 it was obvious that the Great Northern War was coming to a close. His successor Frederick I began negotiating the Treaty of Stockholm, which refers to the two treaties signed in 1719 and 1720 that ended the war between Sweden on one side and Hanover...
(January 1720), Prussia gained southern Swedish Pomerania
Swedish Pomerania
Swedish Pomerania was a Dominion under the Swedish Crown from 1630 to 1815, situated on what is now the Baltic coast of Germany and Poland. Following the Polish War and the Thirty Years' War, Sweden held extensive control over the lands on the southern Baltic coast, including Pomerania and parts...
with Stettin (Szczecin)
Szczecin
Szczecin , is the capital city of the West Pomeranian Voivodeship in Poland. It is the country's seventh-largest city and the largest seaport in Poland on the Baltic Sea. As of June 2009 the population was 406,427....
. Already in 1529, the Hohenzollerns
House of Hohenzollern
The House of Hohenzollern is a noble family and royal dynasty of electors, kings and emperors of Prussia, Germany and Romania. It originated in the area around the town of Hechingen in Swabia during the 11th century. They took their name from their ancestral home, the Burg Hohenzollern castle near...
of Brandenburg had secured the reversion
Treaty of Grimnitz
The Treaty of Grimnitz was the final settlement of a long-standing dispute between the House of Pomerania and the House of Hohenzollern regarding the legal status and succession in the Duchy of Pomerania. It renewed and amended the Treaty of Pyritz of 1493.With some formal caveats, the House of...
to the Duchy of Pomerania
Duchy of Pomerania
The Duchy of Pomerania was a duchy in Pomerania on the southern coast of the Baltic Sea, ruled by dukes of the House of Pomerania ....
after a series of conflicts
Brandenburg-Pomeranian conflict
Starting in the 12th century, the Margraviate, later Electorate of Brandenburg was in conflict with the neighboring Duchy of Pomerania over frontier territories claimed by both Brandenburg and Pomerania, and over the status of the Pomeranian duchy, which Brandenburg claimed as a fief, whereas...
, and acquired
Treaty of Stettin (1653)
The Treaty of Stettin of 4 May 1653 settled a dispute between Brandenburg and Sweden, who both claimed succession in the Duchy of Pomerania after the extinction of the local House of Pomerania during the Thirty Years' War. Brandenburg's claims were based on the Treaty of Grimnitz , while Sweden's...
its eastern part following the Peace of Westphalia
Peace of Westphalia
The Peace of Westphalia was a series of peace treaties signed between May and October of 1648 in Osnabrück and Münster. These treaties ended the Thirty Years' War in the Holy Roman Empire, and the Eighty Years' War between Spain and the Dutch Republic, with Spain formally recognizing the...
.
During this time, the trends set in motion by the Great Elector reached their culmination, as the Junker
Junker
A Junker was a member of the landed nobility of Prussia and eastern Germany. These families were mostly part of the German Uradel and carried on the colonization and Christianization of the northeastern European territories during the medieval Ostsiedlung. The abbreviation of Junker is Jkr...
s, the landed aristocracy, were welded to the Prussian Army
Prussian Army
The Royal Prussian Army was the army of the Kingdom of Prussia. It was vital to the development of Brandenburg-Prussia as a European power.The Prussian Army had its roots in the meager mercenary forces of Brandenburg during the Thirty Years' War...
. This era also saw the rise of compulsory education in Germany. King Frederick William I
Frederick William I of Prussia
Frederick William I of the House of Hohenzollern, was the King in Prussia and Elector of Brandenburg from 1713 until his death...
inaugurated the Prussian compulsory system in 1717.
1740–1760: The Silesian Wars
In 1740, King Frederick IIFrederick II of Prussia
Frederick II was a King in Prussia and a King of Prussia from the Hohenzollern dynasty. In his role as a prince-elector of the Holy Roman Empire, he was also Elector of Brandenburg. He was in personal union the sovereign prince of the Principality of Neuchâtel...
(Frederick the Great) came to the throne. Using the pretext of a 1537 treaty (vetoed by Emperor Ferdinand I
Ferdinand I, Holy Roman Emperor
Ferdinand I was Holy Roman Emperor from 1558 and king of Bohemia and Hungary from 1526 until his death. Before his accession, he ruled the Austrian hereditary lands of the Habsburgs in the name of his elder brother, Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor.The key events during his reign were the contest...
) by which parts of Silesia
Silesia
Silesia is a historical region of Central Europe located mostly in Poland, with smaller parts also in the Czech Republic, and Germany.Silesia is rich in mineral and natural resources, and includes several important industrial areas. Silesia's largest city and historical capital is Wrocław...
were to pass to Brandenburg
Margraviate of Brandenburg
The Margraviate of Brandenburg was a major principality of the Holy Roman Empire from 1157 to 1806. Also known as the March of Brandenburg , it played a pivotal role in the history of Germany and Central Europe....
after the extinction of its ruling Piast dynasty
Piast dynasty
The Piast dynasty was the first historical ruling dynasty of Poland. It began with the semi-legendary Piast Kołodziej . The first historical ruler was Duke Mieszko I . The Piasts' royal rule in Poland ended in 1370 with the death of king Casimir the Great...
, Frederick invaded Silesia, thereby beginning the War of the Austrian Succession
War of the Austrian Succession
The War of the Austrian Succession – including King George's War in North America, the Anglo-Spanish War of Jenkins' Ear, and two of the three Silesian wars – involved most of the powers of Europe over the question of Maria Theresa's succession to the realms of the House of Habsburg.The...
. After rapidly occupying Silesia, Frederick offered to protect Archduchess Maria Theresa of Austria
Maria Theresa of Austria
Maria Theresa Walburga Amalia Christina was the only female ruler of the Habsburg dominions and the last of the House of Habsburg. She was the sovereign of Austria, Hungary, Croatia, Bohemia, Mantua, Milan, Lodomeria and Galicia, the Austrian Netherlands and Parma...
if the province were turned over to him. The offer was rejected, but Austria faced several other opponents, and Frederick was eventually able to gain formal cession with the Treaty of Berlin
Treaty of Berlin (1742)
The Treaty of Berlin between the Habsburg archduchess Maria Theresa of Austria, who was also Queen of Bohemia, and the Prussian king Frederick the Great was signed on July 28, 1742 in Berlin...
in 1742.
To the surprise of many, Austria managed to renew the war successfully. In 1744 Frederick invaded again to forestall reprisals and to claim, this time, the province of Bohemia
Kingdom of Bohemia
The Kingdom of Bohemia was a country located in the region of Bohemia in Central Europe, most of whose territory is currently located in the modern-day Czech Republic. The King was Elector of Holy Roman Empire until its dissolution in 1806, whereupon it became part of the Austrian Empire, and...
. He failed, but French
Ancien Régime in France
The Ancien Régime refers primarily to the aristocratic, social and political system established in France from the 15th century to the 18th century under the late Valois and Bourbon dynasties...
pressure on Austria's ally Great Britain
Kingdom of Great Britain
The former Kingdom of Great Britain, sometimes described as the 'United Kingdom of Great Britain', That the Two Kingdoms of Scotland and England, shall upon the 1st May next ensuing the date hereof, and forever after, be United into One Kingdom by the Name of GREAT BRITAIN. was a sovereign...
led to a series of treaties and compromises, culminating in the 1748 Treaty of Aix-la-Chapelle
Treaty of Aix-la-Chapelle (1748)
The Treaty of Aix-la-Chapelle of 1748 ended the War of the Austrian Succession following a congress assembled at the Imperial Free City of Aachen—Aix-la-Chapelle in French—in the west of the Holy Roman Empire, on 24 April 1748...
that restored peace and left Prussia in possession of most of Silesia.
Humiliated by the cession of Silesia, Austria worked to secure an alliance with France and Russia (the "Diplomatic Revolution
Diplomatic Revolution
The Diplomatic Revolution of 1756 is a term applied to the reversal of longstanding diplomatic alliances which were upheld until the War of the Austrian Succession and then reversed in the Seven Years' War; the shift has also been known as "the great change of partners"...
"), while Prussia drifted into Great Britain's camp forming the Anglo-Prussian Alliance
Anglo-Prussian Alliance
The Anglo-Prussian Alliance was a military alliance created by the Westminster Convention between Great Britain and Prussia which lasted formally between 1756 and 1762 during the Seven Years' War. It allowed Britain to concentrate the majority of its efforts against the colonial possessions of the...
. When Frederick preemptively invaded Saxony and Bohemia over the course of a few months in 1756–1757, he initiated the Seven Years' War
Seven Years' War
The Seven Years' War was a global military war between 1756 and 1763, involving most of the great powers of the time and affecting Europe, North America, Central America, the West African coast, India, and the Philippines...
which might also be considered the first world war since it was fought in the three continents (France and Great Britain's colonies).
This war was a desperate struggle for the Prussian Army
Prussian Army
The Royal Prussian Army was the army of the Kingdom of Prussia. It was vital to the development of Brandenburg-Prussia as a European power.The Prussian Army had its roots in the meager mercenary forces of Brandenburg during the Thirty Years' War...
, and the fact that it managed to fight much of Europe to a draw bears witness to Frederick's military skills. Facing Austria, Russia, France, and Sweden simultaneously, and with only Hanover (and the non-continental British) as notable allies, Frederick managed to prevent serious invasion until October 1760, when the Russian army briefly occupied Berlin
Berlin
Berlin is the capital city of Germany and is one of the 16 states of Germany. With a population of 3.45 million people, Berlin is Germany's largest city. It is the second most populous city proper and the seventh most populous urban area in the European Union...
and Königsberg
Königsberg
Königsberg was the capital of East Prussia from the Late Middle Ages until 1945 as well as the northernmost and easternmost German city with 286,666 inhabitants . Due to the multicultural society in and around the city, there are several local names for it...
. The situation became progressively grimmer, however, until the death of Empress Elizabeth of Russia (Miracle of the House of Brandenburg). The accession of the Prussophile Peter III
Peter III of Russia
Peter III was Emperor of Russia for six months in 1762. He was very pro-Prussian, which made him an unpopular leader. He was supposedly assassinated as a result of a conspiracy led by his wife, who succeeded him to the throne as Catherine II.-Early life and character:Peter was born in Kiel, in...
relieved the pressure on the eastern front. Sweden also exited the war at about the same time.
Defeating the Austrian army at the Battle of Burkersdorf
Battle of Burkersdorf
The Battle of Burkersdorf was a battle fought on July 21, 1762 during the Seven Years' War. A Prussian army of 40,000 men fought an Austrian army of around 30,000 men....
and relying on continuing British success against France in the war's colonial theatres, Prussia was finally able to force a status quo ante bellum
Status quo ante bellum
The term status quo ante bellum is Latin, meaning literally "the state in which things were before the war".The term was originally used in treaties to refer to the withdrawal of enemy troops and the restoration of prewar leadership. When used as such, it means that no side gains or loses...
on the continent. This result confirmed Prussia's major role within the German states and established the country as a European great power
Great power
A great power is a nation or state that has the ability to exert its influence on a global scale. Great powers characteristically possess military and economic strength and diplomatic and cultural influence which may cause small powers to consider the opinions of great powers before taking actions...
. Frederick, appalled by the near-defeat of Prussia, lived out his days as a much more peaceable ruler.
1772, 1793, & 1795: Partitions of Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth
To the east and south of Prussia, the Polish-Lithuanian CommonwealthPolish-Lithuanian Commonwealth
The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth was a dualistic state of Poland and Lithuania ruled by a common monarch. It was the largest and one of the most populous countries of 16th- and 17th‑century Europe with some and a multi-ethnic population of 11 million at its peak in the early 17th century...
had gradually weakened during the 18th century. Alarmed by increasing Russian influences in Polish affairs and by a possible expansion of the Russian Empire
Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was a state that existed from 1721 until the Russian Revolution of 1917. It was the successor to the Tsardom of Russia and the predecessor of the Soviet Union...
, Frederick was instrumental in initiating the first of the Partitions of Poland
Partitions of Poland
The Partitions of Poland or Partitions of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth took place in the second half of the 18th century and ended the existence of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, resulting in the elimination of sovereign Poland for 123 years...
between Russia, Prussia, and Austria in 1772 to maintain a balance of power
Balance of power in international relations
In international relations, a balance of power exists when there is parity or stability between competing forces. The concept describes a state of affairs in the international system and explains the behavior of states in that system...
. The Kingdom of Prussia annexed most of the Polish province of Royal Prussia
Royal Prussia
Royal Prussia was a Region of the Kingdom of Poland and of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth . Polish Prussia included Pomerelia, Chełmno Land , Malbork Voivodeship , Gdańsk , Toruń , and Elbląg . It is distinguished from Ducal Prussia...
, including Warmia
Warmia
Warmia or Ermland is a region between Pomerelia and Masuria in northeastern Poland. Together with Masuria, it forms the Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship....
; the annexed land was organized the following year into the Province of West Prussia. The new territory connected the Province of East Prussia
Province of East Prussia
The Province of East Prussia was a province of Prussia from 1773–1829 and 1878-1945. Composed of the historical region East Prussia, the province's capital was Königsberg ....
(the territory previously known as the Duchy of Prussia) with the Province of Pomerania, uniting the kingdom's eastern territories.
After Frederick died in 1786, his nephew Fredrick William II
Frederick William II of Prussia
Frederick William II was the King of Prussia, reigning from 1786 until his death. He was in personal union the Prince-Elector of Brandenburg and the sovereign prince of the Principality of Neuchâtel.-Early life:...
continued the partitions, gaining a large part of western Poland in 1793.
In 1795, the Kingdom of Poland ceased to exist and a large area (including Warsaw
Warsaw
Warsaw is the capital and largest city of Poland. It is located on the Vistula River, roughly from the Baltic Sea and from the Carpathian Mountains. Its population in 2010 was estimated at 1,716,855 residents with a greater metropolitan area of 2,631,902 residents, making Warsaw the 10th most...
) to the south of East Prussia became part of Prussia. These new territories were organized into the Provinces of New Silesia
New Silesia
New Silesia was a small province of the Kingdom of Prussia from 1795 to 1807, created after the Third Partition of Poland. It was located northwest of Kraków and southeast of Częstochowa, in the lands that had been part of the Silesian Duchy of Siewierz and the adjacent Polish historical province...
, South Prussia
South Prussia
South Prussia was a province of the Kingdom of Prussia from 1793 to 1807. It was created out of territory annexed in the Second Partition of Poland and included in 1793*the Poznań, Kalisz and Gniezno Voivodeships of Greater Poland;...
, and New East Prussia
New East Prussia
New East Prussia was a province of the Kingdom of Prussia from 1795 to 1807. It was created out of territory annexed in the Third Partition of Poland and included parts of Masovia and Podlaskie...
.
1801–1815: Napoleonic Wars
The Treaty of BaselPeace of Basel
The Peace of Basel of 1795 consists of three peace treaties involving France .* The first of the three treaties of 1795, France made peace with Prussia on 5 April; , * The Second was with Spain on 22 July, ending the War of the Pyrenees; and*...
(1795) ended the War of the First Coalition against France. In it, the First French Republic and Prussia had stipulated that the latter would ensure the Holy Roman Empire
Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a realm that existed from 962 to 1806 in Central Europe.It was ruled by the Holy Roman Emperor. Its character changed during the Middle Ages and the Early Modern period, when the power of the emperor gradually weakened in favour of the princes...
's neutrality in all the latter's territories north of the demarcation line of the river Main, including the British continental dominions of the Electorate of Hanover
Electorate of Hanover
The Electorate of Brunswick-Lüneburg was the ninth Electorate of the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation...
and the Duchies of Bremen-Verden
Bremen-Verden
Bremen-Verden, formally the Duchies of Bremen and Verden , were two territories and immediate fiefs of the Holy Roman Empire, which emerged and gained Imperial immediacy in 1180...
. To this end, Hanover (including Bremen-Verden) also had to provide troops for the so-called demarcation army maintaining this state of armed neutrality.
In the course of the War of the Second Coalition against France
War of the Second Coalition
The "Second Coalition" was the second attempt by European monarchs, led by the Habsburg Monarchy of Austria and the Russian Empire, to contain or eliminate Revolutionary France. They formed a new alliance and attempted to roll back France's previous military conquests...
(1799–1802) Napoléon Bonaparte urged Prussia to occupy the continental British dominions. In 1801 24,000 Prussian soldiers invaded, surprising Hanover, which surrendered without a fight. In April 1801 the Prussian troops arrived in Bremen-Verden's capital Stade
Stade
Stade is a city in Lower Saxony, Germany and part of the Hamburg Metropolitan Region . It is the seat of the district named after it...
and stayed there until October of the same year. The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland
United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland was the formal name of the United Kingdom during the period when what is now the Republic of Ireland formed a part of it....
first ignored Prussia's hostility, but when it joined the pro-French coalition of armed 'neutral' powers such as Denmark-Norway and Russia
Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was a state that existed from 1721 until the Russian Revolution of 1917. It was the successor to the Tsardom of Russia and the predecessor of the Soviet Union...
, Britain started to capture Prussian sea vessels. After the Battle of Copenhagen (1801)
Battle of Copenhagen (1801)
The Battle of Copenhagen was an engagement which saw a British fleet under the command of Admiral Sir Hyde Parker fight and strategically defeat a Danish-Norwegian fleet anchored just off Copenhagen on 2 April 1801. Vice-Admiral Horatio Nelson led the main attack. He famously disobeyed Parker's...
the coalition fell apart and Prussia withdrew again its troops.
At Napoléon's instigation, Prussia recaptured British Hanover and Bremen-Verden in early 1806. On August 6, the same year the Holy Roman Empire
Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a realm that existed from 962 to 1806 in Central Europe.It was ruled by the Holy Roman Emperor. Its character changed during the Middle Ages and the Early Modern period, when the power of the emperor gradually weakened in favour of the princes...
was dissolved as a result of Napoléon's victories over Austria
Archduchy of Austria
The Archduchy of Austria , one of the most important states within the Holy Roman Empire, was the nucleus of the Habsburg Monarchy and the predecessor of the Austrian Empire...
. The title of Kurfürst (Prince-elector
Prince-elector
The Prince-electors of the Holy Roman Empire were the members of the electoral college of the Holy Roman Empire, having the function of electing the Roman king or, from the middle of the 16th century onwards, directly the Holy Roman Emperor.The heir-apparent to a prince-elector was known as an...
) of Brandenburg became meaningless, and was dropped. Before this time, the Hohenzollern sovereign had held many titles and crowns, from Supreme Governor of the Protestant Churches (summus episcopus) to King, Elector, Grand Duke, Duke for the various regions and realms under his rule. After 1806, Frederick William III was simply King of Prussia and summus episcopus.
But when Prussia, after it turned against the French Empire, was defeated in the Battle of Jena-Auerstedt
Battle of Jena-Auerstedt
The twin battles of Jena and Auerstedt were fought on 14 October 1806 on the plateau west of the river Saale in today's Germany, between the forces of Napoleon I of France and Frederick William III of Prussia...
(November 11, 1806), King Frederick William III was forced to temporarily flee to remote Memel
Klaipeda
Klaipėda is a city in Lithuania situated at the mouth of the Nemunas River where it flows into the Baltic Sea. It is the third largest city in Lithuania and the capital of Klaipėda County....
. After the Treaties of Tilsit
Treaties of Tilsit
The Treaties of Tilsit were two agreements signed by Napoleon I of France in the town of Tilsit in July, 1807 in the aftermath of his victory at Friedland. The first was signed on 7 July, between Tsar Alexander I of Russia and Napoleon I of France, when they met on a raft in the middle of the Neman...
in 1807, Prussia lost about half of its territory, including the land gained from the Second and Third Partitions of Poland
Partitions of Poland
The Partitions of Poland or Partitions of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth took place in the second half of the 18th century and ended the existence of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, resulting in the elimination of sovereign Poland for 123 years...
(which now fell to the Duchy of Warsaw
Duchy of Warsaw
The Duchy of Warsaw was a Polish state established by Napoleon I in 1807 from the Polish lands ceded by the Kingdom of Prussia under the terms of the Treaties of Tilsit. The duchy was held in personal union by one of Napoleon's allies, King Frederick Augustus I of Saxony...
) and all land west of the Elbe River. France recaptured Prussian-occupied Hanover, including Bremen-Verden. The remainder of the kingdom was occupied by French troops (at Prussia’s expense) and the king was obliged to make an alliance with France and join the Continental System
Continental System
The Continental System or Continental Blockade was the foreign policy of Napoleon I of France in his struggle against the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland during the Napoleonic Wars. It was a large-scale embargo against British trade, which began on November 21, 1806...
.
After the defeat of Napoleon in Russia, Prussia quit the alliance and took part in the Sixth Coalition during the "Wars of Liberation" (Befreiungskriege) against the French occupation. Prussian troops under Marshal Gebhard Leberecht von Blücher
Gebhard Leberecht von Blücher
Gebhard Leberecht von Blücher, Fürst von Wahlstatt , Graf , later elevated to Fürst von Wahlstatt, was a Prussian Generalfeldmarschall who led his army against Napoleon I at the Battle of the Nations at Leipzig in 1813 and at the Battle of Waterloo in 1815 with the Duke of Wellington.He is...
contributed crucially in the Battle of Waterloo
Battle of Waterloo
The Battle of Waterloo was fought on Sunday 18 June 1815 near Waterloo in present-day Belgium, then part of the United Kingdom of the Netherlands...
of 1815 to the final victory over Napoleon.
1815: After Napoleon

Congress of Vienna
The Congress of Vienna was a conference of ambassadors of European states chaired by Klemens Wenzel von Metternich, and held in Vienna from September, 1814 to June, 1815. The objective of the Congress was to settle the many issues arising from the French Revolutionary Wars, the Napoleonic Wars,...
, where Prussia was granted most of its lost territories and considerably more, including 40% of the Kingdom of Saxony
Kingdom of Saxony
The Kingdom of Saxony , lasting between 1806 and 1918, was an independent member of a number of historical confederacies in Napoleonic through post-Napoleonic Germany. From 1871 it was part of the German Empire. It became a Free state in the era of Weimar Republic in 1918 after the end of World War...
and much of the Rhineland
Rhineland
Historically, the Rhinelands refers to a loosely-defined region embracing the land on either bank of the River Rhine in central Europe....
. Much of the territory annexed in the Third Partition of Poland was granted to Congress Poland
Congress Poland
The Kingdom of Poland , informally known as Congress Poland , created in 1815 by the Congress of Vienna, was a personal union of the Russian parcel of Poland with the Russian Empire...
under Russian rule.
With these Prussian gains in territory, the kingdom was reorganised into ten provinces. Most of the kingdom, aside from the Provinces of East Prussia
East Prussia
East Prussia is the main part of the region of Prussia along the southeastern Baltic Coast from the 13th century to the end of World War II in May 1945. From 1772–1829 and 1878–1945, the Province of East Prussia was part of the German state of Prussia. The capital city was Königsberg.East Prussia...
, West Prussia
West Prussia
West Prussia was a province of the Kingdom of Prussia from 1773–1824 and 1878–1919/20 which was created out of the earlier Polish province of Royal Prussia...
, and Posen
Province of Posen
The Province of Posen was a province of Prussia from 1848–1918 and as such part of the German Empire from 1871 to 1918. The area was about 29,000 km2....
, became part of the new German Confederation
German Confederation
The German Confederation was the loose association of Central European states created by the Congress of Vienna in 1815 to coordinate the economies of separate German-speaking countries. It acted as a buffer between the powerful states of Austria and Prussia...
, a confederacy
Confederation
A confederation in modern political terms is a permanent union of political units for common action in relation to other units. Usually created by treaty but often later adopting a common constitution, confederations tend to be established for dealing with critical issues such as defense, foreign...
of 39 sovereign states replacing the defunct Holy Roman Empire
Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a realm that existed from 962 to 1806 in Central Europe.It was ruled by the Holy Roman Emperor. Its character changed during the Middle Ages and the Early Modern period, when the power of the emperor gradually weakened in favour of the princes...
.
Frederick William III submitted Prussia to a number of administrative reforms, among others reorganising the government by way of ministries, which remained formative for the following hundred years.
As to religion, reformed Calvinist Frederick William III—as Supreme Governor of the Protestant Churches—asserted his long-cherished project (started in 1798) to unite the Lutheran and the Reformed Church in 1817, (see Prussian Union
Prussian Union (Evangelical Christian Church)
The Prussian Union was the merger of the Lutheran Church and the Reformed Church in Prussia, by a series of decrees – among them the Unionsurkunde – by King Frederick William III...
). The Calvinist minority, strongly supported by its co-religionist Frederick William III, and the partially reluctant Lutheran majority formed the united
United and uniting churches
United and uniting churches are churches formed from the merger or other form of union of two or more different Protestant denominations.Perhaps the oldest example of a united church is found in Germany, where the Evangelical Church in Germany is a federation of Lutheran, United and Reformed...
Protestant Evangelical Church in Prussia. However, ensuing quarrels causing a permanent schism
Schism (religion)
A schism , from Greek σχίσμα, skhísma , is a division between people, usually belonging to an organization or movement religious denomination. The word is most frequently applied to a break of communion between two sections of Christianity that were previously a single body, or to a division within...
among the Lutherans into united and Old Lutherans
Old Lutherans
Old Lutherans refers to those German Lutherans who refused to join the Prussian Union in the 1830s and 1840s.Attempted suppression of the Old Lutherans led many to immigrate to Australia and the United States, resulting in the creation of significant Lutheran denominations in those countries.The...
by 1830.
As a consequence of the Revolutions of 1848
Revolutions of 1848
The European Revolutions of 1848, known in some countries as the Spring of Nations, Springtime of the Peoples or the Year of Revolution, were a series of political upheavals throughout Europe in 1848. It was the first Europe-wide collapse of traditional authority, but within a year reactionary...
, the Principalities of Hohenzollern-Sigmaringen
Hohenzollern-Sigmaringen
-Noble jurisdictions:Prince Karl Eitel of Hohenzollern-Sigmaringen, and descendants of his nephew Ferdinand ruled over the Kingdom of Romania, as Karl Eitel did not have children...
and Hohenzollern-Hechingen
Hohenzollern-Hechingen
Hohenzollern-Hechingen was a county and principality in southwestern Germany. Its rulers belonged to a branch of the senior Swabian branch of the Hohenzollern dynasty.-History:...
(ruled by a Catholic
Catholic
The word catholic comes from the Greek phrase , meaning "on the whole," "according to the whole" or "in general", and is a combination of the Greek words meaning "about" and meaning "whole"...
cadet branch of the House of Hohenzollern) were annexed by Prussia in 1850, later united as Province of Hohenzollern
Province of Hohenzollern
Hohenzollern was a de facto province of the Kingdom of Prussia. It was created in 1850 by joining the principalities of Hohenzollern-Sigmaringen and Hohenzollern-Hechingen after both formerly independently ruling Catholic princely lines of the House of Hohenzollern had handed over their...
.
1848–1871: The German wars of unification
For the following half-century after the Congress of Vienna, there was a conflict of ideals within the German ConfederationGerman Confederation
The German Confederation was the loose association of Central European states created by the Congress of Vienna in 1815 to coordinate the economies of separate German-speaking countries. It acted as a buffer between the powerful states of Austria and Prussia...
between the formation of a single German nation and the conservation of the current collection of smaller German states and kingdoms. The creation of the German Customs Union (Zollverein
Zollverein
thumb|upright=1.2|The German Zollverein 1834–1919blue = Prussia in 1834 grey= Included region until 1866yellow= Excluded after 1866red = Borders of the German Union of 1828 pink= Relevant others until 1834...
) in 1834, which excluded the Austrian Empire
Austrian Empire
The Austrian Empire was a modern era successor empire, which was centered on what is today's Austria and which officially lasted from 1804 to 1867. It was followed by the Empire of Austria-Hungary, whose proclamation was a diplomatic move that elevated Hungary's status within the Austrian Empire...
, increased Prussian influence over the member states. As a consequence of the Revolutions of 1848
Revolutions of 1848
The European Revolutions of 1848, known in some countries as the Spring of Nations, Springtime of the Peoples or the Year of Revolution, were a series of political upheavals throughout Europe in 1848. It was the first Europe-wide collapse of traditional authority, but within a year reactionary...
, King Frederick William IV
Frederick William IV of Prussia
|align=right|Upon his accession, he toned down the reactionary policies enacted by his father, easing press censorship and promising to enact a constitution at some point, but he refused to enact a popular legislative assembly, preferring to work with the aristocracy through "united committees" of...
was offered the crown of a united Germany by the Frankfurt Parliament
Frankfurt Parliament
The Frankfurt Assembly was the first freely elected parliament for all of Germany. Session was held from May 18, 1848 to May 31, 1849 in the Paulskirche at Frankfurt am Main...
. Frederick William refused the offer on the grounds that revolutionary assemblies could not grant royal titles. But there were two other reasons why he refused: to do so would have done little to end the internal power struggle between Austria and Prussia, and all Prussian kings (up to and including William I
William I, German Emperor
William I, also known as Wilhelm I , of the House of Hohenzollern was the King of Prussia and the first German Emperor .Under the leadership of William and his Chancellor Otto von Bismarck, Prussia achieved the unification of Germany and the...
) feared that the formation of a German Empire
German Empire
The German Empire refers to Germany during the "Second Reich" period from the unification of Germany and proclamation of Wilhelm I as German Emperor on 18 January 1871, to 1918, when it became a federal republic after defeat in World War I and the abdication of the Emperor, Wilhelm II.The German...
would mean the end of Prussia’s independence within the German states.
In 1848, actions taken by Denmark
Denmark
Denmark is a Scandinavian country in Northern Europe. The countries of Denmark and Greenland, as well as the Faroe Islands, constitute the Kingdom of Denmark . It is the southernmost of the Nordic countries, southwest of Sweden and south of Norway, and bordered to the south by Germany. Denmark...
towards the Duchies of Schleswig
Schleswig
Schleswig or South Jutland is a region covering the area about 60 km north and 70 km south of the border between Germany and Denmark; the territory has been divided between the two countries since 1920, with Northern Schleswig in Denmark and Southern Schleswig in Germany...
and Holstein
Holstein
Holstein is the region between the rivers Elbe and Eider. It is part of Schleswig-Holstein, the northernmost state of Germany....
led to the First War of Schleswig
First War of Schleswig
The First Schleswig War or Three Years' War was the first round of military conflict in southern Denmark and northern Germany rooted in the Schleswig-Holstein Question, contesting the issue of who should control the Duchies of Schleswig and Holstein. The war, which lasted from 1848–1851,...
(1848–51) between Denmark and the German Confederation
German Confederation
The German Confederation was the loose association of Central European states created by the Congress of Vienna in 1815 to coordinate the economies of separate German-speaking countries. It acted as a buffer between the powerful states of Austria and Prussia...
. Denmark won.
Frederick William issued Prussia's first constitution
Constitution of the Kingdom of Prussia
The Constitution of the Kingdom of Prussia was adopted in 1850 and amended in the following years. This constitution was far less liberal than the federal constitution of the German Empire....
by his own authority in 1850. This document—moderate by the standards of the time but conservative by today's standards—provided for a two-house parliament. The lower house, or Landtag
Landtag
A Landtag is a representative assembly or parliament in German-speaking countries with some legislative authority.- Name :...
was elected by all taxpayers, who were divided into three classes
Prussian three-class franchise
After the 1848 revolutions in the German states, the Prussian three-class franchise system was introduced in 1849 by the Prussian king Friedrich Wilhelm IV for the election of the Lower House of the Prussian state parliament. It was completely abolished only in 1918...
whose votes were weighted according to the amount of taxes paid. Women and those who paid no taxes had no vote. This allowed just over one-third of the voters to choose 85% of the legislature, all but assuring dominance by the more well-to-do men of the population. The upper house, which was later renamed the Herrenhaus
Prussian House of Lords
The Prussian House of Lords was the first chamber of the Parliament of the Kingdom of Prussia from 1850-1918. The second chamber was the Prussian House of Representatives . The House of Lords was created on January 31, 1850 with the adoption of the Constitution of the Kingdom of Prussia...
("House of Lords"), was appointed by the king. He retained full executive authority and ministers were responsible only to him (indeed, as late as 1910, Prussian kings believed that they ruled by divine right
Divine Right of Kings
The divine right of kings or divine-right theory of kingship is a political and religious doctrine of royal and political legitimacy. It asserts that a monarch is subject to no earthly authority, deriving his right to rule directly from the will of God...
). As a result, the grip of the landowning classes, the Junker
Junker
A Junker was a member of the landed nobility of Prussia and eastern Germany. These families were mostly part of the German Uradel and carried on the colonization and Christianization of the northeastern European territories during the medieval Ostsiedlung. The abbreviation of Junker is Jkr...
s, remained unbroken, especially in the eastern provinces.
Frederick William suffered a stroke in 1857, and his younger brother, Crown Prince Wilhelm, became regent. Wilhelm pursued a considerably more moderate course, and gained enough power that, by Frederick William's death in 1861, he was able to become king in his own right as William I
William I, German Emperor
William I, also known as Wilhelm I , of the House of Hohenzollern was the King of Prussia and the first German Emperor .Under the leadership of William and his Chancellor Otto von Bismarck, Prussia achieved the unification of Germany and the...
. However, shortly after gaining the throne, he faced a dispute with his parliament over the size of the army. The parliament, dominated by the liberals, balked at William's desire to increase the number of regiments and withheld approval of the budget to pay for its cost. A deadlock ensued, and William seriously considered abdicating in favour of his son, Crown Prince Frederick William. He was, however, persuaded to appoint as prime minister Otto von Bismarck
Otto von Bismarck
Otto Eduard Leopold, Prince of Bismarck, Duke of Lauenburg , simply known as Otto von Bismarck, was a Prussian-German statesman whose actions unified Germany, made it a major player in world affairs, and created a balance of power that kept Europe at peace after 1871.As Minister President of...
, his ambassador to France. Bismarck took office on September 23, 1862.
Although Bismarck had a reputation as an unyielding conservative, he was initially inclined to seek a compromise over the budget issue. However, William refused to consider it; he viewed defense issues as the crown's personal province. Forced into a policy of confrontation, Bismarck came up with a novel theory. Under the constitution, the king and the parliament were responsible for agreeing on the budget. Bismarck argued that since they had failed to come to an agreement, there was a "hole" in the constitution, and the government had to continue to collect taxes and disburse funds in accordance with the old budget in order to keep functioning. The government thus operated without a new budget from 1862 to 1866, allowing Bismarck to implement William's military reforms.
The liberals violently denounced Bismarck as a violator of the law. However, Bismarck's real plan was an accommodation with liberalism. He had come to believe that German unification was inevitable, but that the conservative forces had to take the lead in the drive toward creating a unified nation in order to keep from being eclipsed. He also believed that the middle-class liberals wanted a unified Germany more than they wanted to break the grip of the traditional forces over society. He thus embarked on a drive to create a united Germany under Prussian leadership, and guided Prussia through three wars which ultimately achieved this goal.
The first of these wars was the Second War of Schleswig
Second War of Schleswig
The Second Schleswig War was the second military conflict as a result of the Schleswig-Holstein Question. It began on 1 February 1864, when Prussian forces crossed the border into Schleswig.Denmark fought Prussia and Austria...
(1864), which Prussia initiated and succeeded in gaining the assistance of Austria. Denmark was soundly defeated and surrendered both Schleswig and Holstein, to Prussia and Austria respectively.

Austro-Prussian War
The Austro-Prussian War was a war fought in 1866 between the German Confederation under the leadership of the Austrian Empire and its German allies on one side and the Kingdom of Prussia with its German allies and Italy on the...
(1866 – also known as the Seven Weeks’ War), where Prussia, allied with the Kingdom of Italy
Kingdom of Italy (1861–1946)
The Kingdom of Italy was a state forged in 1861 by the unification of Italy under the influence of the Kingdom of Sardinia, which was its legal predecessor state...
and various northern German states, declared war on the Austrian Empire. The Austrian-led coalition was crushed, and Prussia annexed four of its smaller allies—the Kingdom of Hanover
Kingdom of Hanover
The Kingdom of Hanover was established in October 1814 by the Congress of Vienna, with the restoration of George III to his Hanoverian territories after the Napoleonic era. It succeeded the former Electorate of Brunswick-Lüneburg , and joined with 38 other sovereign states in the German...
, the Electorate of Hesse
Hesse-Kassel
The Landgraviate of Hesse-Kassel or Hesse-Cassel was a state in the Holy Roman Empire under Imperial immediacy that came into existence when the Landgraviate of Hesse was divided in 1567 upon the death of Philip I, Landgrave of Hesse. His eldest son William IV inherited the northern half and the...
, the Duchy of Nassau and the Free City of Frankfurt
Free City of Frankfurt
For almost five centuries, the German city of Frankfurt am Main was a city-state within two major Germanic states:*The Holy Roman Empire as the Free Imperial City of Frankfurt...
. Prussia also annexed Schleswig and Holstein, and also effectively annexed Saxe-Lauenburg by forcing it into a personal union
Personal union
A personal union is the combination by which two or more different states have the same monarch while their boundaries, their laws and their interests remain distinct. It should not be confused with a federation which is internationally considered a single state...
with Prussia (which was turned into a full union in 1876). King William initially wanted to take territory from Austria itself, but Bismarck persuaded him to abandon the idea. While Bismarck wanted Austria to play no future role in German affairs, he still saw that Austria could be a valuable future ally.
With these gains in territory, the Prussian possessions in the Rhineland and Westphalia were connected to the rest of the kingdom for the first time. Counting the de facto annexation of Saxe-Lauenburg, Prussia now stretched uninterrupted across the northern two-thirds of Germany. It would remain at this size until the overthrow of the monarchy in 1918.
Bismarck used this opportunity to end the budget dispute with parliament. He proposed a bill of indemnity granting him retroactive approval for governing without a legal budget. He guessed, correctly as it turned out, that this would lead to a split between his liberal adversaries. While some of them argued that there could be no compromise with the principle of constitutional government, most of the liberals decided to support the bill in hopes of winning more freedom in the future.
The German Confederation was dissolved as part of the war. In its place, Prussia cajoled the 21 states north of the Main into forming the North German Confederation
North German Confederation
The North German Confederation 1866–71, was a federation of 22 independent states of northern Germany. It was formed by a constitution accepted by the member states in 1867 and controlled military and foreign policy. It included the new Reichstag, a parliament elected by universal manhood...
in 1867. Prussia was the dominant state in this new grouping, with four-fifths of its territory and population. Its near-total control was cemented in a constitution written by Bismarck. Executive power was vested in a president—an office vested in the Prussian crown according to hereditary right. He was assisted by a chancellor responsible only to him. There was also a two-house parliament. The lower house, or Reichstag
Reichstag (German Empire)
The Reichstag was the parliament of the North German Confederation , and of the German Reich ....
(Diet), was elected by universal male suffrage. The upper house, or Bundesrat (Federal Council) was appointed by the state governments. The Bundesrat was, in practice, the stronger chamber. Prussia had 17 of 43 votes, and could easily control proceedings through alliances with the other states. For all intents and purposes, the new grouping was dominated by Bismarck. He served as his own foreign minister for virtually his entire tenure as prime minister of Prussia, and in that capacity was able to instruct the Prussian delegates to the Bundesrat.
The southern German states (except Austria) were forced to accept military alliances with Prussia, and Prussia began steps to merge them with the North German Confederation. Bismarck’s planned Kleindeutschland unification of Germany
Unification of Germany
The formal unification of Germany into a politically and administratively integrated nation state officially occurred on 18 January 1871 at the Versailles Palace's Hall of Mirrors in France. Princes of the German states gathered there to proclaim Wilhelm of Prussia as Emperor Wilhelm of the German...
had come considerably closer to realisation.
The final act was the Franco-Prussian War
Franco-Prussian War
The Franco-Prussian War or Franco-German War, often referred to in France as the 1870 War was a conflict between the Second French Empire and the Kingdom of Prussia. Prussia was aided by the North German Confederation, of which it was a member, and the South German states of Baden, Württemberg and...
(1870), where Bismarck maneuvered Emperor Napoleon III of France
Napoleon III of France
Louis-Napoléon Bonaparte was the President of the French Second Republic and as Napoleon III, the ruler of the Second French Empire. He was the nephew and heir of Napoleon I, christened as Charles Louis Napoléon Bonaparte...
into declaring war on Prussia. Activating the German alliances put in place after the Austro-Prussian War, the German states came together and swiftly defeated France
Second French Empire
The Second French Empire or French Empire was the Imperial Bonapartist regime of Napoleon III from 1852 to 1870, between the Second Republic and the Third Republic, in France.-Rule of Napoleon III:...
. Even before then, Bismarck was able to complete the work of unifying Germany under Prussian leadership. The patriotic fervour aroused by the war with France was too much for the remaining opponents of a unified nation to overcome, and on 18 January 1871 (the 170th anniversary of the coronation of the first Prussian king, Frederick I
Frederick I of Prussia
Frederick I , of the Hohenzollern dynasty, was Elector of Brandenburg and Duke of Prussia in personal union . The latter function he upgraded to royalty, becoming the first King in Prussia . From 1707 he was in personal union the sovereign prince of the Principality of Neuchâtel...
), the German Empire
German Empire
The German Empire refers to Germany during the "Second Reich" period from the unification of Germany and proclamation of Wilhelm I as German Emperor on 18 January 1871, to 1918, when it became a federal republic after defeat in World War I and the abdication of the Emperor, Wilhelm II.The German...
was proclaimed in the Hall of Mirrors
Palace of Versailles
The Palace of Versailles , or simply Versailles, is a royal château in Versailles in the Île-de-France region of France. In French it is the Château de Versailles....
at Versailles
Versailles
Versailles , a city renowned for its château, the Palace of Versailles, was the de facto capital of the kingdom of France for over a century, from 1682 to 1789. It is now a wealthy suburb of Paris and remains an important administrative and judicial centre...
outside of Paris
Paris
Paris is the capital and largest city in France, situated on the river Seine, in northern France, at the heart of the Île-de-France region...
, while the French capital was still under siege
Siege of Paris
The Siege of Paris, lasting from September 19, 1870 – January 28, 1871, and the consequent capture of the city by Prussian forces led to French defeat in the Franco-Prussian War and the establishment of the German Empire as well as the Paris Commune....
. King William became the first emperor of a unified Germany.
1871–1918: peak and fall

However, the seeds for future problems lay in a gross disparity between the imperial and Prussian systems. The empire granted the vote to all men over 25. However, Prussia retained its restrictive three-class voting system, in which the well-to-do had 17.5 times the voting power of the rest of the population. Since the imperial chancellor was, except for two periods (January–November 1873 and 1892–94) also prime minister of Prussia, this meant that for most of the empire's existence, the king/emperor and prime minister/chancellor had to seek majorities from legislatures elected by two completely different franchises.
At the time of the empire's creation, both Prussia and Germany were roughly two-thirds rural. Within 20 years, the situation was reversed; the cities and towns accounted for two-thirds of the population. However, in both the kingdom and the empire, the constituencies were never redrawn to reflect the growing population and influence of the cities and towns. This meant that rural areas were grossly overrepresented from the 1890s onward.
Bismarck realised that the rest of Europe was skeptical of his powerful new Reich, and turned his attention to preserving peace with such acts as the Congress of Berlin
Congress of Berlin
The Congress of Berlin was a meeting of the European Great Powers' and the Ottoman Empire's leading statesmen in Berlin in 1878. In the wake of the Russo-Turkish War of 1877–78, the meeting's aim was to reorganize the countries of the Balkans...
. The new German Empire improved its already-strong relations with Britain. The ties between London and Berlin had already been sealed with a golden braid in 1858, when Crown Prince Frederick William of Prussia married Princess Victoria
Victoria, Princess Royal
The Princess Victoria, Princess Royal was the eldest child of Queen Victoria of the United Kingdom and Prince Albert. She was created Princess Royal of the United Kingdom in 1841. She became German Empress and Queen of Prussia by marriage to German Emperor Frederick III...
of Britain.
William I
William I, German Emperor
William I, also known as Wilhelm I , of the House of Hohenzollern was the King of Prussia and the first German Emperor .Under the leadership of William and his Chancellor Otto von Bismarck, Prussia achieved the unification of Germany and the...
died in 1888, and the Crown Prince succeeded to the throne as Frederick III
Frederick III, German Emperor
Frederick III was German Emperor and King of Prussia for 99 days in 1888, the Year of the Three Emperors. Friedrich Wilhelm Nikolaus Karl known informally as Fritz, was the only son of Emperor William I and was raised in his family's tradition of military service...
. The new emperor, a decided Anglophile, planned to transform Prussia and the empire into a more liberal and democratic monarchy on the British model. However, he died after only 99 days on the throne and was succeeded by his 29-year old son, William II
William II, German Emperor
Wilhelm II was the last German Emperor and King of Prussia, ruling the German Empire and the Kingdom of Prussia from 15 June 1888 to 9 November 1918. He was a grandson of the British Queen Victoria and related to many monarchs and princes of Europe...
. As a boy, William had rebelled against his parents' efforts to mould him as a liberal, and had become thoroughly Prussianised under Bismarck's tutelage. The new Kaiser rapidly soured relations with the British
House of Windsor
The House of Windsor is the royal house of the Commonwealth realms. It was founded by King George V by royal proclamation on the 17 July 1917, when he changed the name of his family from the German Saxe-Coburg and Gotha to the English Windsor, due to the anti-German sentiment in the United Kingdom...
and Russian
Romanov
The House of Romanov was the second and last imperial dynasty to rule over Russia, reigning from 1613 until the February Revolution abolished the crown in 1917...
royal families (despite being closely related to them), becoming their rival and ultimately their enemy.
Politics
The Kingdom of Prussia was an absolute monarchyAbsolute monarchy
Absolute monarchy is a monarchical form of government in which the monarch exercises ultimate governing authority as head of state and head of government, his or her power not being limited by a constitution or by the law. An absolute monarch thus wields unrestricted political power over the...
until the Revolutions of 1848 in the German states
Revolutions of 1848 in the German states
The Revolutions of 1848 in the German states, also called the March Revolution – part of the Revolutions of 1848 that broke out in many countries of Europe – were a series of loosely coordinated protests and rebellions in the states of the German Confederation, including the Austrian Empire...
, after which Prussia became a constitutional monarchy
Constitutional monarchy
Constitutional monarchy is a form of government in which a monarch acts as head of state within the parameters of a constitution, whether it be a written, uncodified or blended constitution...
and Adolf Heinrich von Arnim-Boitzenburg
Adolf Heinrich von Arnim-Boitzenburg
Adolf Heinrich Graf Arnim-Boitzenburg was a German statesman, and the first Prime Minister of Prussia.After finishing his studies, he joined the Prussian civil service and soon became Landrat in the Uckermark. In 1833 he became Regierungspräsident in the Regierungsbezirk Stralsund...
was elected as Prussia's first prime minister
Prime Minister of Prussia
The office of Minister President or Prime Minister of Prussia existed in one form or another from 1702 until the dissolution of Prussia in 1947. When Prussia was an independent kingdom the Minister President or Prime Minister functioned as the King's Chief Minister and presided over the Prussian...
. Following Prussia's first constitution
Constitution of the Kingdom of Prussia
The Constitution of the Kingdom of Prussia was adopted in 1850 and amended in the following years. This constitution was far less liberal than the federal constitution of the German Empire....
, a two-house parliament was formed. The lower house, or Landtag was elected by all taxpayers, who were divided into three classes
Prussian three-class franchise
After the 1848 revolutions in the German states, the Prussian three-class franchise system was introduced in 1849 by the Prussian king Friedrich Wilhelm IV for the election of the Lower House of the Prussian state parliament. It was completely abolished only in 1918...
according to the amount of taxes paid. This allowed just over 25% of the voters to choose 85% of the legislature, all but assuring dominance by the more well-to-do elements of the population. The upper house, which was later renamed the Prussian House of Lords
Prussian House of Lords
The Prussian House of Lords was the first chamber of the Parliament of the Kingdom of Prussia from 1850-1918. The second chamber was the Prussian House of Representatives . The House of Lords was created on January 31, 1850 with the adoption of the Constitution of the Kingdom of Prussia...
, was appointed by the king. He retained full executive authority and ministers were responsible only to him. As a result, the grip of the landowning classes, the Junker
Junker
A Junker was a member of the landed nobility of Prussia and eastern Germany. These families were mostly part of the German Uradel and carried on the colonization and Christianization of the northeastern European territories during the medieval Ostsiedlung. The abbreviation of Junker is Jkr...
s, remained unbroken, especially in the eastern provinces. Prussian Secret Police
Prussian Secret Police
The Prussian Secret Police was the state police agency of the German state of Prussia in the 19th century and early 20th century.In 1851 Police Union of German States was set up by the police forces of Austria, Prussia, Bavaria, Saxony, Hanover, Baden, and Württemberg...
, formed in response to the Revolutions of 1848 in the German states
Revolutions of 1848 in the German states
The Revolutions of 1848 in the German states, also called the March Revolution – part of the Revolutions of 1848 that broke out in many countries of Europe – were a series of loosely coordinated protests and rebellions in the states of the German Confederation, including the Austrian Empire...
, aided the conservative government.
Subdivisions


Margraviate of Brandenburg
The Margraviate of Brandenburg was a major principality of the Holy Roman Empire from 1157 to 1806. Also known as the March of Brandenburg , it played a pivotal role in the history of Germany and Central Europe....
and the Duchy of Prussia which together formed Brandenburg-Prussia
Brandenburg-Prussia
Brandenburg-Prussia is the historiographic denomination for the Early Modern realm of the Brandenburgian Hohenzollerns between 1618 and 1701. Based in the Electorate of Brandenburg, the main branch of the Hohenzollern intermarried with the branch ruling the Duchy of Prussia, and secured succession...
. A Further Pomeranian province had been held by Prussia since 1653. Combined with Swedish Pomerania
Swedish Pomerania
Swedish Pomerania was a Dominion under the Swedish Crown from 1630 to 1815, situated on what is now the Baltic coast of Germany and Poland. Following the Polish War and the Thirty Years' War, Sweden held extensive control over the lands on the southern Baltic coast, including Pomerania and parts...
, gained from Sweden in 1720 and 1815, this region formed the Province of Pomerania. Prussian gains in the Silesian Wars
Silesian Wars
The Silesian Wars were a series of wars between Prussia and Austria for control of Silesia. They formed parts of the larger War of the Austrian Succession and Seven Years' War. They eventually ended with Silesia being incorporated into Prussia, and Austrian recognition of this...
led to the formation of the Province of Silesia
Province of Silesia
The Province of Silesia was a province of the Kingdom of Prussia from 1815 to 1919.-Geography:The territory comprised the bulk of the former Bohemian crown land of Silesia and the County of Kladsko, which King Frederick the Great had conquered from the Austrian Habsburg Monarchy in the 18th...
in 1740.
After the First Partition of Poland
First Partition of Poland
The First Partition of Poland or First Partition of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth took place in 1772 as the first of three partitions that ended the existence of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth by 1795. Growth in the Russian Empire's power, threatening the Kingdom of Prussia and the...
in 1772, the newly-annexed Royal Prussia
Royal Prussia
Royal Prussia was a Region of the Kingdom of Poland and of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth . Polish Prussia included Pomerelia, Chełmno Land , Malbork Voivodeship , Gdańsk , Toruń , and Elbląg . It is distinguished from Ducal Prussia...
and Warmia
Warmia
Warmia or Ermland is a region between Pomerelia and Masuria in northeastern Poland. Together with Masuria, it forms the Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship....
became the Province of West Prussia, while the Duchy of Prussia (along with part of Warmia) became the Province of East Prussia
Province of East Prussia
The Province of East Prussia was a province of Prussia from 1773–1829 and 1878-1945. Composed of the historical region East Prussia, the province's capital was Königsberg ....
. Other annexations along the Noteć (Netze) River
Notec
Noteć is a river in central Poland with a length of 388 km and a basin area of 17,330 km². It is a tributary of the Warta river and lies completely within Poland....
became the Netze District
Netze District
The Netze District or District of the Netze was a territory in the Kingdom of Prussia from 1772 until 1807. It included the urban centers of Bydgoszcz , Inowrocław , Piła and Wałcz and was given its name for the Noteć River that traversed it.Beside Royal Prussia, a land of the Polish Crown...
. Following the second and third partitions (1793–1795), the new Prussian annexations became the Provinces of New Silesia
New Silesia
New Silesia was a small province of the Kingdom of Prussia from 1795 to 1807, created after the Third Partition of Poland. It was located northwest of Kraków and southeast of Częstochowa, in the lands that had been part of the Silesian Duchy of Siewierz and the adjacent Polish historical province...
, South Prussia
South Prussia
South Prussia was a province of the Kingdom of Prussia from 1793 to 1807. It was created out of territory annexed in the Second Partition of Poland and included in 1793*the Poznań, Kalisz and Gniezno Voivodeships of Greater Poland;...
, and New East Prussia
New East Prussia
New East Prussia was a province of the Kingdom of Prussia from 1795 to 1807. It was created out of territory annexed in the Third Partition of Poland and included parts of Masovia and Podlaskie...
, with the Netze District redivided between West and South Prussia. These three provinces were ultimately lost to Congress Poland
Congress Poland
The Kingdom of Poland , informally known as Congress Poland , created in 1815 by the Congress of Vienna, was a personal union of the Russian parcel of Poland with the Russian Empire...
after the Congress of Vienna
Congress of Vienna
The Congress of Vienna was a conference of ambassadors of European states chaired by Klemens Wenzel von Metternich, and held in Vienna from September, 1814 to June, 1815. The objective of the Congress was to settle the many issues arising from the French Revolutionary Wars, the Napoleonic Wars,...
in 1815, except for the western part of South Prussia, which would form part of the Grand Duchy of Posen.
Following the major western gains made by Prussia after the Vienna Congress, a total of ten provinces were established, each one subdivided further into smaller administrative regions known as Regierungsbezirk
Regierungsbezirk
In Germany, a Government District, in German: Regierungsbezirk – is a subdivision of certain federal states .They are above the Kreise, Landkreise, and kreisfreie Städte...
e. The provinces were:
- Province of BrandenburgProvince of BrandenburgThe Province of Brandenburg was a province of the Kingdom of Prussia and the Free State of Prussia from 1815 to 1946.-History:The first people who are known to have inhabited Brandenburg were the Suevi. They were succeeded by the Slavonians, whom Henry II conquered and converted to Christianity in...
- Province of East PrussiaProvince of East PrussiaThe Province of East Prussia was a province of Prussia from 1773–1829 and 1878-1945. Composed of the historical region East Prussia, the province's capital was Königsberg ....
- Province of Jülich-Cleves-BergProvince of Jülich-Cleves-BergThe Province of Jülich-Cleves-Berg was a province of the Kingdom of Prussia from 1815–22. The province was largely made up of the land held by the former United Duchies of Jülich-Cleves-Berg...
- Grand Duchy of the Lower RhineGrand Duchy of the Lower RhineThe Grand Duchy of the Lower Rhine , or simply known as the Lower Rhine Province was a province of the Kingdom of Prussia and existed from 1815 to 1822....
- Province of Pomerania
- Grand Duchy of Posen (authonomus, outside of German ConfederationGerman ConfederationThe German Confederation was the loose association of Central European states created by the Congress of Vienna in 1815 to coordinate the economies of separate German-speaking countries. It acted as a buffer between the powerful states of Austria and Prussia...
) - Province of SaxonyProvince of SaxonyThe Province of Saxony was a province of the Kingdom of Prussia and later the Free State of Prussia from 1816 until 1945. Its capital was Magdeburg.-History:The province was created in 1816 out of the following territories:...
- Province of SilesiaProvince of SilesiaThe Province of Silesia was a province of the Kingdom of Prussia from 1815 to 1919.-Geography:The territory comprised the bulk of the former Bohemian crown land of Silesia and the County of Kladsko, which King Frederick the Great had conquered from the Austrian Habsburg Monarchy in the 18th...
- Province of West Prussia
- Province of WestphaliaProvince of WestphaliaThe Province of Westphalia was a province of the Kingdom of Prussia and the Free State of Prussia from 1815 to 1946.-History:Napoleon Bonaparte founded the Kingdom of Westphalia, which was a client state of the First French Empire from 1807 to 1813...
In 1822, the provinces of Jülich-Cleves-Berg and the Lower Rhine were merged to form the Rhine Province
Rhine Province
The Rhine Province , also known as Rhenish Prussia or synonymous to the Rhineland , was the westernmost province of the Kingdom of Prussia and the Free State of Prussia, within the German Reich, from 1822-1946. It was created from the provinces of the Lower Rhine and Jülich-Cleves-Berg...
. In 1829, the Provinces of East and West Prussia merged to form the Province of Prussia
Province of Prussia
The Province of Prussia was a province of the Kingdom of Prussia from 1829-1878 created out of the provinces of East Prussia and West Prussia....
, but the separate provinces were reformed in 1878. The principalities of Hohenzollern-Sigmaringen
Hohenzollern-Sigmaringen
-Noble jurisdictions:Prince Karl Eitel of Hohenzollern-Sigmaringen, and descendants of his nephew Ferdinand ruled over the Kingdom of Romania, as Karl Eitel did not have children...
and Hohenzollern-Hechingen
Hohenzollern-Hechingen
Hohenzollern-Hechingen was a county and principality in southwestern Germany. Its rulers belonged to a branch of the senior Swabian branch of the Hohenzollern dynasty.-History:...
were annexed in 1850 to form the Province of Hohenzollern
Province of Hohenzollern
Hohenzollern was a de facto province of the Kingdom of Prussia. It was created in 1850 by joining the principalities of Hohenzollern-Sigmaringen and Hohenzollern-Hechingen after both formerly independently ruling Catholic princely lines of the House of Hohenzollern had handed over their...
.
After Prussia's victory in the 1866 Austro-Prussian War
Austro-Prussian War
The Austro-Prussian War was a war fought in 1866 between the German Confederation under the leadership of the Austrian Empire and its German allies on one side and the Kingdom of Prussia with its German allies and Italy on the...
, territories annexed by Prussia were reorganised into three new provinces: Hanover
Province of Hanover
The Province of Hanover was a province of the Kingdom of Prussia and the Free State of Prussia from 1868 to 1946.During the Austro-Prussian War, the Kingdom of Hanover had attempted to maintain a neutral position, along with some other member states of the German Confederation...
, Hesse-Nassau
Province of Hesse-Nassau
Hesse-Nassau Province was a province of the Kingdom of Prussia from 1868-1918, then a province of the Free State of Prussia until 1944.Hesse-Nassau was created as a consequence of the Austro-Prussian War of 1866 by combining the previously independent Hesse-Kassel , the Duchy of Nassau, the Free...
and Schleswig-Holstein
Province of Schleswig-Holstein
The Province of Schleswig-Holstein was a province of the Kingdom of Prussia and the Free State of Prussia from 1868 to 1946. It was created from the Duchies of Schleswig and Holstein, which had been conquered by Prussia and the Austrian Empire from Denmark in the Second War of Schleswig in 1864...
.
See also
- List of Kings of Prussia
- Prussian ArmyPrussian ArmyThe Royal Prussian Army was the army of the Kingdom of Prussia. It was vital to the development of Brandenburg-Prussia as a European power.The Prussian Army had its roots in the meager mercenary forces of Brandenburg during the Thirty Years' War...
- Free State of Prussia
- Prussian Crown JewelsPrussian Crown JewelsThe Prussian Crown Jewels is a set of crowns, orb and scepters used to crown Kings of Prussia of the Hohenzollern dynasty. After the King of Prussia became German Kaiser on the establishment of the German Empire on January 18, 1871, they were no longer used as the position of King of Prussia while...
- Prussian virtuesPrussian virtuesThe term Prussian virtues refers to an unfixed canon of several Lutheran virtues dating from the Enlightenment. Prussian virtues and the Prussian value system have influenced aspects of wider German culture.- Historical Development :...
- History of GermanyHistory of GermanyThe concept of Germany as a distinct region in central Europe can be traced to Roman commander Julius Caesar, who referred to the unconquered area east of the Rhine as Germania, thus distinguishing it from Gaul , which he had conquered. The victory of the Germanic tribes in the Battle of the...
- Kreis in PrussiaKreis in PrussiaPrussian districts were administrative units in the former German state of Prussia. The districts , also known as counties, usually took the name of the district's capital . A typical district had a rough diameter of 20 to 40 miles, though few were circular in shape...

