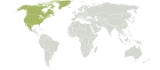
Nearctic
Encyclopedia
The Nearctic is one of the eight terrestrial ecozone
s dividing the Earth's land surface.
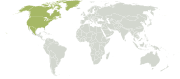 The Nearctic ecozone covers most of North America
The Nearctic ecozone covers most of North America
, including Greenland
and the highlands of Mexico
. Southern Mexico, southern Florida
, Central America
, and the Caribbean
islands are part of the Neotropic
ecozone, together with South America
.
bioregion extends across the northern portion of the continent, from the Aleutian Islands to Newfoundland
. It includes the Nearctic's Arctic Tundra and Boreal forest ecoregions.
In terms of floristic province
s, it is represented by part of the Canadian Province of the Circumboreal Region
.
of the eastern United States and southeastern Canada, the Great Plains
temperate grasslands
of the central United States and south-central Canada, and the Temperate coniferous forests
of the southeastern United States.
In terms of floristic province
s, it is represented by the North American Atlantic Region
and part of the Canadian Province of the Circumboreal Region
.
of the coastal and mountain regions of southern Alaska, western Canada, and the western United States from the Pacific Coast
and Northern California
to the Rocky Mountains
, as well as the cold-winter intermountain deserts and xeric shrublands
and temperate grasslands and shrublands of the western United States
.
In terms of floristic province
s, it is represented by the Rocky Mountain Region
.
, and the Southwestern United States
, including the Chihuahuan
, Sonoran
, and Mojave
deserts. The Mediterranean climate
ecoregion
s of the Southern
and Central Coast of California
include the California chaparral and woodlands
, California coastal sage and chaparral
, California interior chaparral and woodlands
, and California montane chaparral and woodlands
.
The bioregion also includes the warm temperate and subtropical pine and pine-oak forests, including the Arizona Mountains forests
and the Sierra Madre Occidental
, Sierra Madre Oriental
, and Sierra Juarez and San Pedro Martir
pine-oak forests.
In terms of floristic province
s, it is represented by the Madrean Region
.
, these continents were separated for about 180 million years, and evolved very different plant and animal lineages. When the ancient supercontinent of Pangaea
split into two about 180 million years ago, North America remained joined to Eurasia
as part of the supercontinent of Laurasia
, while South America was part of the supercontinent of Gondwana
. North America later split from Eurasia. North America has been joined by land bridges to both Asia
and South America since then, which allowed an exchange of plant and animal species
between the continents, the Great American Interchange
.
A former land bridge across the Bering Strait
between Asia and North America allowed many plants and animals to move between these continents, and the Nearctic ecozone shares many plants and animals with the Palearctic
. The two ecozones are sometimes included in a single Holarctic
ecozone.
Many large animals, or megafauna
, including horse
s, camel
s, mammoth
s, mastodonts, ground sloth
s, sabre-tooth cats (Smilodon
), the giant short-faced bear
(Arctodus simus), and the cheetah
, became extinct in North America at the end of the Pleistocene
epoch (ice ages), at the same time the first evidence of humans appeared, in what is called the Holocene extinction event
. Previously, it was believed that the megafaunal extinctions were caused by the changing climate, but many scientists now believe that while the climate change contributed to these extinctions, the primary cause was hunting by newly-arrived humans or, in the case of some large predators, extinction resulting from prey becoming scarce. The American bison
(Bison bison), brown bear
or grizzly bear (Ursus arctos), and elk
or wapiti (Cervus canadensis) entered North America around the same time as the first humans, and expanded rapidly, filling ecological niches left empty by the newly-extinct North American megafauna.
family, the wrentit
s (Timaliinae), is endemic to the Nearctic region. The Holarctic has four endemic families: divers
(Gaviidae), grouse
(Tetraoninae), auk
s (Alcidae), and the waxwing
s (Bombycillidae). The scarab beetle families Pleocomidae and Diphyllostomatidae (Coleoptera) are also endemic to the Nearctic. The fly species Cynomya cadaverina
is also found in high numbers in this area.
Plants families endemic or nearly endemic to the Nearctic include Crossosomataceae
, Simmondsiaceae
, and Limnanthaceae
.
Ecozone
An ecozone is the broadest biogeographic division of the Earth's land surface, based on distributional patterns of terrestrial organisms.Ecozones delineate large areas of the Earth's surface within which organisms have been evolving in relative isolation over long periods of time, separated from...
s dividing the Earth's land surface.

North America
North America is a continent wholly within the Northern Hemisphere and almost wholly within the Western Hemisphere. It is also considered a northern subcontinent of the Americas...
, including Greenland
Greenland
Greenland is an autonomous country within the Kingdom of Denmark, located between the Arctic and Atlantic Oceans, east of the Canadian Arctic Archipelago. Though physiographically a part of the continent of North America, Greenland has been politically and culturally associated with Europe for...
and the highlands of Mexico
Mexico
The United Mexican States , commonly known as Mexico , is a federal constitutional republic in North America. It is bordered on the north by the United States; on the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; on the southeast by Guatemala, Belize, and the Caribbean Sea; and on the east by the Gulf of...
. Southern Mexico, southern Florida
Florida
Florida is a state in the southeastern United States, located on the nation's Atlantic and Gulf coasts. It is bordered to the west by the Gulf of Mexico, to the north by Alabama and Georgia and to the east by the Atlantic Ocean. With a population of 18,801,310 as measured by the 2010 census, it...
, Central America
Central America
Central America is the central geographic region of the Americas. It is the southernmost, isthmian portion of the North American continent, which connects with South America on the southeast. When considered part of the unified continental model, it is considered a subcontinent...
, and the Caribbean
Caribbean
The Caribbean is a crescent-shaped group of islands more than 2,000 miles long separating the Gulf of Mexico and the Caribbean Sea, to the west and south, from the Atlantic Ocean, to the east and north...
islands are part of the Neotropic
Neotropic
In biogeography, the Neotropic or Neotropical zone is one of the eight terrestrial ecozones. This ecozone includes South and Central America, the Mexican lowlands, the Caribbean islands, and southern Florida, because these regions share a large number of plant and animal groups.It is sometimes used...
ecozone, together with South America
South America
South America is a continent situated in the Western Hemisphere, mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere. The continent is also considered a subcontinent of the Americas. It is bordered on the west by the Pacific Ocean and on the north and east...
.
Major ecological regions
The World Wildlife Fund (WWF) divides the Nearctic into four Bioregions, defined as "geographic clusters of ecoregions that may span several habitat types, but have strong biogeographic affinities, particularly at taxonomic levels higher than the species level (genus, family)."Canadian Shield
The Canadian ShieldCanadian Shield
The Canadian Shield, also called the Laurentian Plateau, or Bouclier Canadien , is a vast geological shield covered by a thin layer of soil that forms the nucleus of the North American or Laurentia craton. It is an area mostly composed of igneous rock which relates to its long volcanic history...
bioregion extends across the northern portion of the continent, from the Aleutian Islands to Newfoundland
Newfoundland and Labrador
Newfoundland and Labrador is the easternmost province of Canada. Situated in the country's Atlantic region, it incorporates the island of Newfoundland and mainland Labrador with a combined area of . As of April 2011, the province's estimated population is 508,400...
. It includes the Nearctic's Arctic Tundra and Boreal forest ecoregions.
In terms of floristic province
Floristic province
A phytochorion, in phytogeography, is a geographic area with a relatively uniform composition of plant species. Adjacent phytochoria do not usually have a sharp boundary, but rather a soft one, a transitional area in which many species from both regions overlap...
s, it is represented by part of the Canadian Province of the Circumboreal Region
Circumboreal Region
The Circumboreal Region is a floristic region within the Holarctic Kingdom in Eurasia and North America, as delineated by such geobotanists as Josias Braun-Blanquet and Armen Takhtajan....
.
Eastern North America
The Eastern North America bioregion includes the Temperate broadleaf and mixed forestsTemperate broadleaf and mixed forests
Mixed forests are a temperate and humid biome. The typical structure of these forests includes four layers. The uppermost layer is the canopy composed of tall mature trees ranging from 33 to 66 m high. Below the canopy is the three-layered, shade-tolerant understory that is roughly 9 to...
of the eastern United States and southeastern Canada, the Great Plains
Great Plains
The Great Plains are a broad expanse of flat land, much of it covered in prairie, steppe and grassland, which lies west of the Mississippi River and east of the Rocky Mountains in the United States and Canada. This area covers parts of the U.S...
temperate grasslands
Temperate grasslands, savannas, and shrublands
Temperate grasslands, savannas, and shrublands is a terrestrial biome whose predominant vegetation consists of grasses and/or shrubs. The climate is temperate and semi-arid to semi-humid....
of the central United States and south-central Canada, and the Temperate coniferous forests
Temperate coniferous forests
Temperate coniferous forest is a terrestrial biome found in temperate regions of the world with warm summers and cool winters and adequate rainfall to sustain a forest. In most temperate coniferous forests, evergreen conifers predominate, while some are a mix of conifers and broadleaf evergreen...
of the southeastern United States.
In terms of floristic province
Floristic province
A phytochorion, in phytogeography, is a geographic area with a relatively uniform composition of plant species. Adjacent phytochoria do not usually have a sharp boundary, but rather a soft one, a transitional area in which many species from both regions overlap...
s, it is represented by the North American Atlantic Region
North American Atlantic Region
North American Atlantic Region is a floristic region within the Holarctic Kingdom identified by Armen Takhtajan and Robert F. Thorne, spanning from the Atlantic and Gulf coasts to the Great Plains and comprising a major part of the United States and southeastern portions of Canada...
and part of the Canadian Province of the Circumboreal Region
Circumboreal Region
The Circumboreal Region is a floristic region within the Holarctic Kingdom in Eurasia and North America, as delineated by such geobotanists as Josias Braun-Blanquet and Armen Takhtajan....
.
Western North America
The Western North America bioregion includes the Temperate coniferous forestsTemperate coniferous forests
Temperate coniferous forest is a terrestrial biome found in temperate regions of the world with warm summers and cool winters and adequate rainfall to sustain a forest. In most temperate coniferous forests, evergreen conifers predominate, while some are a mix of conifers and broadleaf evergreen...
of the coastal and mountain regions of southern Alaska, western Canada, and the western United States from the Pacific Coast
West Coast of the United States
West Coast or Pacific Coast are terms for the westernmost coastal states of the United States. The term most often refers to the states of California, Oregon, and Washington. Although not part of the contiguous United States, Alaska and Hawaii do border the Pacific Ocean but can't be included in...
and Northern California
Northern California
Northern California is the northern portion of the U.S. state of California. The San Francisco Bay Area , and Sacramento as well as its metropolitan area are the main population centers...
to the Rocky Mountains
Rocky Mountains
The Rocky Mountains are a major mountain range in western North America. The Rocky Mountains stretch more than from the northernmost part of British Columbia, in western Canada, to New Mexico, in the southwestern United States...
, as well as the cold-winter intermountain deserts and xeric shrublands
Deserts and xeric shrublands
Deserts and xeric shrublands is a biome characterized by, relating to, or requiring only a small amount of moisture.-Definition and occurrence:...
and temperate grasslands and shrublands of the western United States
Western United States
.The Western United States, commonly referred to as the American West or simply "the West," traditionally refers to the region comprising the westernmost states of the United States. Because the U.S. expanded westward after its founding, the meaning of the West has evolved over time...
.
In terms of floristic province
Floristic province
A phytochorion, in phytogeography, is a geographic area with a relatively uniform composition of plant species. Adjacent phytochoria do not usually have a sharp boundary, but rather a soft one, a transitional area in which many species from both regions overlap...
s, it is represented by the Rocky Mountain Region
Rocky Mountain Region
The Rocky Mountain Floristic Region, also known as the Rocky Mountain Floristic Province, is a floristic region within the Holarctic Kingdom in western North America delineated by Armen Takhtajan and Robert F...
.
Northern Mexico and Southwestern North America
The Northern Mexico bioregion includes the mild-winter to cold-winter deserts and xeric shrublands of northern Mexico, Southern CaliforniaCalifornia
California is a state located on the West Coast of the United States. It is by far the most populous U.S. state, and the third-largest by land area...
, and the Southwestern United States
Southwestern United States
The Southwestern United States is a region defined in different ways by different sources. Broad definitions include nearly a quarter of the United States, including Arizona, California, Colorado, Nevada, New Mexico, Oklahoma, Texas and Utah...
, including the Chihuahuan
Chihuahuan Desert
The Chihuahuan Desert is a desert, and an ecoregion designation, that straddles the U.S.-Mexico border in the central and northern portions of the Mexican Plateau, bordered on the west by the extensive Sierra Madre Occidental range, and overlaying northern portions of the east range, the Sierra...
, Sonoran
Sonoran Desert
The Sonoran Desert is a North American desert which straddles part of the United States-Mexico border and covers large parts of the U.S. states of Arizona and California and the northwest Mexican states of Sonora, Baja California, and Baja California Sur. It is one of the largest and hottest...
, and Mojave
Mojave Desert
The Mojave Desert occupies a significant portion of southeastern California and smaller parts of central California, southern Nevada, southwestern Utah and northwestern Arizona, in the United States...
deserts. The Mediterranean climate
Mediterranean climate
A Mediterranean climate is the climate typical of most of the lands in the Mediterranean Basin, and is a particular variety of subtropical climate...
ecoregion
Ecoregion
An ecoregion , sometimes called a bioregion, is an ecologically and geographically defined area that is smaller than an ecozone and larger than an ecosystem. Ecoregions cover relatively large areas of land or water, and contain characteristic, geographically distinct assemblages of natural...
s of the Southern
Southern California
Southern California is a megaregion, or megapolitan area, in the southern area of the U.S. state of California. Large urban areas include Greater Los Angeles and Greater San Diego. The urban area stretches along the coast from Ventura through the Southland and Inland Empire to San Diego...
and Central Coast of California
Central Coast of California
The Central Coast is an area of California, United States, roughly spanning the area between the Monterey Bay and Point Conception. It extends through Santa Cruz County, San Benito County, Monterey County, San Luis Obispo County, and Santa Barbara County...
include the California chaparral and woodlands
California chaparral and woodlands
The California chaparral and woodlands is a terrestrial ecoregion of lower northern, central, and southern California and northwestern Baja California , located on the west coast of North America...
, California coastal sage and chaparral
California coastal sage and chaparral ecoregion
The California coastal sage and chaparral, a sub-ecoregion of the California chaparral and woodlands ecoregion, is found in southwestern California and northwestern Baja California in Mexico.-Location:...
, California interior chaparral and woodlands
California interior chaparral and woodlands
The California interior chaparral and woodlands ecoregion covers in an elliptical ring around the California Central Valley. It occurs on hills and mountains ranging from to . It is part of the Mediterranean forests, woodlands, and scrub biome, with cool, wet winters and hot, dry summers...
, and California montane chaparral and woodlands
California montane chaparral and woodlands
The California montane chaparral and woodlands ecoregion covers , including the mountains of the Transverse, Peninsular, and Santa Lucia Ranges of California. It is part of the Mediterranean forests, woodlands, and scrub biome, with cool, wet winters and hot, dry summers...
.
The bioregion also includes the warm temperate and subtropical pine and pine-oak forests, including the Arizona Mountains forests
Arizona Mountains forests
The Arizona Mountains forests are a temperate coniferous forests ecoregion of the southwest United States with a rich variety of woodland habitats and wildlife.-Setting:...
and the Sierra Madre Occidental
Sierra Madre Occidental pine-oak forests
The Sierra Madre Occidental pine-oak forests are a subtropical coniferous forest ecoregion of the Sierra Madre Occidental range of western Mexico and the southwestern United States...
, Sierra Madre Oriental
Sierra Madre Oriental pine-oak forests
The Sierra Madre Oriental pine-oak forests are a subtropical coniferous forest ecoregion of northeastern and Central Mexico, extending into the state of Texas in the United States.-Setting:...
, and Sierra Juarez and San Pedro Martir
Sierra Juarez and San Pedro Martir pine-oak forests
The Sierra Juárez and San Pedro Mártir pine-oak forests is an ecoregion, in the Temperate coniferous forests biome, that covers the higher elevations of the Sierra Juárez and Sierra San Pedro Mártir ranges, of the Peninsular Ranges, in the northern Baja California Peninsula of Mexico, near the...
pine-oak forests.
In terms of floristic province
Floristic province
A phytochorion, in phytogeography, is a geographic area with a relatively uniform composition of plant species. Adjacent phytochoria do not usually have a sharp boundary, but rather a soft one, a transitional area in which many species from both regions overlap...
s, it is represented by the Madrean Region
Madrean Region
The Madrean Region is a floristic region within the Holarctic Kingdom in North America, as delineated by Armen Takhtajan and Robert F. Thorne...
.
History
Although North America and South America are presently joined by the Isthmus of PanamaIsthmus of Panama
The Isthmus of Panama, also historically known as the Isthmus of Darien, is the narrow strip of land that lies between the Caribbean Sea and the Pacific Ocean, linking North and South America. It contains the country of Panama and the Panama Canal...
, these continents were separated for about 180 million years, and evolved very different plant and animal lineages. When the ancient supercontinent of Pangaea
Pangaea
Pangaea, Pangæa, or Pangea is hypothesized as a supercontinent that existed during the Paleozoic and Mesozoic eras about 250 million years ago, before the component continents were separated into their current configuration....
split into two about 180 million years ago, North America remained joined to Eurasia
Eurasia
Eurasia is a continent or supercontinent comprising the traditional continents of Europe and Asia ; covering about 52,990,000 km2 or about 10.6% of the Earth's surface located primarily in the eastern and northern hemispheres...
as part of the supercontinent of Laurasia
Laurasia
In paleogeography, Laurasia was the northernmost of two supercontinents that formed part of the Pangaea supercontinent from approximately...
, while South America was part of the supercontinent of Gondwana
Gondwana
In paleogeography, Gondwana , originally Gondwanaland, was the southernmost of two supercontinents that later became parts of the Pangaea supercontinent. It existed from approximately 510 to 180 million years ago . Gondwana is believed to have sutured between ca. 570 and 510 Mya,...
. North America later split from Eurasia. North America has been joined by land bridges to both Asia
Asia
Asia is the world's largest and most populous continent, located primarily in the eastern and northern hemispheres. It covers 8.7% of the Earth's total surface area and with approximately 3.879 billion people, it hosts 60% of the world's current human population...
and South America since then, which allowed an exchange of plant and animal species
Species
In biology, a species is one of the basic units of biological classification and a taxonomic rank. A species is often defined as a group of organisms capable of interbreeding and producing fertile offspring. While in many cases this definition is adequate, more precise or differing measures are...
between the continents, the Great American Interchange
Great American Interchange
The Great American Interchange was an important paleozoogeographic event in which land and freshwater fauna migrated from North America via Central America to South America and vice versa, as the volcanic Isthmus of Panama rose up from the sea floor and bridged the formerly separated continents...
.
A former land bridge across the Bering Strait
Bering Strait
The Bering Strait , known to natives as Imakpik, is a sea strait between Cape Dezhnev, Chukotka Autonomous Okrug, Russia, the easternmost point of the Asian continent and Cape Prince of Wales, Alaska, USA, the westernmost point of the North American continent, with latitude of about 65°40'N,...
between Asia and North America allowed many plants and animals to move between these continents, and the Nearctic ecozone shares many plants and animals with the Palearctic
Palearctic
The Palearctic or Palaearctic is one of the eight ecozones dividing the Earth's surface.Physically, the Palearctic is the largest ecozone...
. The two ecozones are sometimes included in a single Holarctic
Holarctic
The Holarctic ecozone refers to the habitats found throughout the northern continents of the world as a whole. This region is divided into the Palearctic, consisting of Northern Africa and all of Eurasia, with the exception of Southeast Asia and the Indian subcontinent, and the Nearctic,...
ecozone.
Many large animals, or megafauna
Megafauna
In terrestrial zoology, megafauna are "giant", "very large" or "large" animals. The most common thresholds used are or...
, including horse
Horse
The horse is one of two extant subspecies of Equus ferus, or the wild horse. It is a single-hooved mammal belonging to the taxonomic family Equidae. The horse has evolved over the past 45 to 55 million years from a small multi-toed creature into the large, single-toed animal of today...
s, camel
Camel
A camel is an even-toed ungulate within the genus Camelus, bearing distinctive fatty deposits known as humps on its back. There are two species of camels: the dromedary or Arabian camel has a single hump, and the bactrian has two humps. Dromedaries are native to the dry desert areas of West Asia,...
s, mammoth
Mammoth
A mammoth is any species of the extinct genus Mammuthus. These proboscideans are members of Elephantidae, the family of elephants and mammoths, and close relatives of modern elephants. They were often equipped with long curved tusks and, in northern species, a covering of long hair...
s, mastodonts, ground sloth
Ground sloth
Ground sloths are a diverse group of extinct sloths, in the mammalian superorder Xenarthra. Their most recent survivors lived in the Antilles, where it has been proposed they may have survived until 1550 CE; however, the youngest AMS radiocarbon date reported is 4190 BP, calibrated to c. 4700 BP...
s, sabre-tooth cats (Smilodon
Smilodon
Smilodon , often called a saber-toothed cat or saber-toothed tiger, is an extinct genus of machairodonts. This saber-toothed cat was endemic to North America and South America, living from near the beginning through the very end of the Pleistocene epoch .-Etymology:The nickname "saber-tooth" refers...
), the giant short-faced bear
Bear
Bears are mammals of the family Ursidae. Bears are classified as caniforms, or doglike carnivorans, with the pinnipeds being their closest living relatives. Although there are only eight living species of bear, they are widespread, appearing in a wide variety of habitats throughout the Northern...
(Arctodus simus), and the cheetah
Cheetah
The cheetah is a large-sized feline inhabiting most of Africa and parts of the Middle East. The cheetah is the only extant member of the genus Acinonyx, most notable for modifications in the species' paws...
, became extinct in North America at the end of the Pleistocene
Pleistocene
The Pleistocene is the epoch from 2,588,000 to 11,700 years BP that spans the world's recent period of repeated glaciations. The name pleistocene is derived from the Greek and ....
epoch (ice ages), at the same time the first evidence of humans appeared, in what is called the Holocene extinction event
Holocene extinction event
The Holocene extinction refers to the extinction of species during the present Holocene epoch . The large number of extinctions span numerous families of plants and animals including mammals, birds, amphibians, reptiles and arthropods; a sizeable fraction of these extinctions are occurring in the...
. Previously, it was believed that the megafaunal extinctions were caused by the changing climate, but many scientists now believe that while the climate change contributed to these extinctions, the primary cause was hunting by newly-arrived humans or, in the case of some large predators, extinction resulting from prey becoming scarce. The American bison
American Bison
The American bison , also commonly known as the American buffalo, is a North American species of bison that once roamed the grasslands of North America in massive herds...
(Bison bison), brown bear
Brown Bear
The brown bear is a large bear distributed across much of northern Eurasia and North America. It can weigh from and its largest subspecies, the Kodiak Bear, rivals the polar bear as the largest member of the bear family and as the largest land-based predator.There are several recognized...
or grizzly bear (Ursus arctos), and elk
Elk
The Elk is the large deer, also called Cervus canadensis or wapiti, of North America and eastern Asia.Elk may also refer to:Other antlered mammals:...
or wapiti (Cervus canadensis) entered North America around the same time as the first humans, and expanded rapidly, filling ecological niches left empty by the newly-extinct North American megafauna.
Flora and fauna that originated in the Nearctic
Animals originally unique to the Nearctic include:- Family CanidaeCanidaeCanidae is the biological family of carnivorous and omnivorous mammals that includes wolves, foxes, jackals, coyotes, and domestic dogs. A member of this family is called a canid . The Canidae family is divided into two tribes: Canini and Vulpini...
, dogDogThe domestic dog is a domesticated form of the gray wolf, a member of the Canidae family of the order Carnivora. The term is used for both feral and pet varieties. The dog may have been the first animal to be domesticated, and has been the most widely kept working, hunting, and companion animal in...
s, wolves, foxesFoxFox is a common name for many species of omnivorous mammals belonging to the Canidae family. Foxes are small to medium-sized canids , characterized by possessing a long narrow snout, and a bushy tail .Members of about 37 species are referred to as foxes, of which only 12 species actually belong to...
, and coyoteCoyoteThe coyote , also known as the American jackal or the prairie wolf, is a species of canine found throughout North and Central America, ranging from Panama in the south, north through Mexico, the United States and Canada...
s - Family Camelidae, camelCamelA camel is an even-toed ungulate within the genus Camelus, bearing distinctive fatty deposits known as humps on its back. There are two species of camels: the dromedary or Arabian camel has a single hump, and the bactrian has two humps. Dromedaries are native to the dry desert areas of West Asia,...
s and their South American relatives including the llamaLlamaThe llama is a South American camelid, widely used as a meat and pack animal by Andean cultures since pre-Hispanic times....
. The last North American Camelids went extinct during the last ice age. - Family EquidaeEquidaeEquidae is the taxonomic family of horses and related animals, including the extant horses, donkeys, and zebras, and many other species known only from fossils. All extant species are in the genus Equus...
, horseHorseThe horse is one of two extant subspecies of Equus ferus, or the wild horse. It is a single-hooved mammal belonging to the taxonomic family Equidae. The horse has evolved over the past 45 to 55 million years from a small multi-toed creature into the large, single-toed animal of today...
s and their relatives. - Family Antilocapridae, which includes the pronghornPronghornThe pronghorn is a species of artiodactyl mammal endemic to interior western and central North America. Though not an antelope, it is often known colloquially in North America as the prong buck, pronghorn antelope, or simply antelope, as it closely resembles the true antelopes of the Old World and...
- TremarctinaeTremarctinaeTremarctinae is a term for the subfamily of Ursidae containing one living representative, the Spectacled Bear of South America, and several extinct species from four genera: the Florida spectacled bear , the North American short-faced bears of genera Plionarctos and Arctodus Tremarctinae is a...
, or short-faced, bears, including the extinct giant short-faced bear (Arctodus simius). The last remaining member of the group is the spectacled bearSpectacled BearThe spectacled bear , also known as the Andean bear and locally as ukuko, jukumari or ucumari, is the last remaining short-faced bear and the closest living relative to the Florida spectacled bear and short-faced bears of the Middle Pleistocene to Late Pleistocene age.The spectacled bear is a...
(Tremarctos ornatus) of South America. - The now-extinct American cheetah (Miracinonyx)
Flora and fauna endemic to the Nearctic
One birdBird
Birds are feathered, winged, bipedal, endothermic , egg-laying, vertebrate animals. Around 10,000 living species and 188 families makes them the most speciose class of tetrapod vertebrates. They inhabit ecosystems across the globe, from the Arctic to the Antarctic. Extant birds range in size from...
family, the wrentit
Wrentit
The Wrentit is a small bird that lives in chaparral and bushland. It is the only species in the genus Chamaea....
s (Timaliinae), is endemic to the Nearctic region. The Holarctic has four endemic families: divers
Loon
The loons or divers are a group of aquatic birds found in many parts of North America and northern Eurasia...
(Gaviidae), grouse
Grouse
Grouse are a group of birds from the order Galliformes. They are sometimes considered a family Tetraonidae, though the American Ornithologists' Union and many others include grouse as a subfamily Tetraoninae in the family Phasianidae...
(Tetraoninae), auk
Auk
An auk is a bird of the family Alcidae in the order Charadriiformes. Auks are superficially similar to penguins due to their black-and-white colours, their upright posture and some of their habits...
s (Alcidae), and the waxwing
Waxwing
The waxwings form the genus Bombycilla of passerine birds. According to most authorities, this is the only genus placed in the family Bombycillidae.-Description:Waxwings are characterised by soft silky plumage...
s (Bombycillidae). The scarab beetle families Pleocomidae and Diphyllostomatidae (Coleoptera) are also endemic to the Nearctic. The fly species Cynomya cadaverina
Cynomya cadaverina
Cynomya cadaverina, also known as the shiny blue bottle fly, is a member of the family Calliphoridae, which includes both blow flies, as well as bottle flies. In recent years, this family has become a forensically important facet in many medicocriminal investigations in the growing field of...
is also found in high numbers in this area.
Plants families endemic or nearly endemic to the Nearctic include Crossosomataceae
Crossosomataceae
Crossosomataceae is a small plant family, consisting of three genera of shrubs found only in the dry parts of the American southwest and Mexico.-External links:...
, Simmondsiaceae
Simmondsiaceae
Simmondsiaceae or the Jojoba Family is a family of flowering plants. The family is not recognized by all taxonomic systems, the single species, Simmondsia chinensis, often being treated as belonging to family Buxaceae....
, and Limnanthaceae
Limnanthaceae
Limnanthaceae are a small family of annual herbs occurring throughout temperate North America. There are eight species and nineteen taxa currently recognized. Members of this family are prominent in vernal pool communities of California. Some taxa have been domesticated for use as an oil seed crop...
.

