Economy of Lithuania
Encyclopedia
Lithuania
is a member of the European Union
and the biggest economy among three Baltic states
. GDP per capita reached USD 17,800 in 2008 and was higher than the ones of all its neighbors – Latvia
, Poland
, Russia
and Belarus
.
GDP per capita in Lithuania is 70% above the world's average of US$10,500. Lithuania has a favorable legislative basis for business as the country is ranked the 3rd in the region of Eastern Europe and Central Asia and the 26th in the world by the Ease of Doing Business Index
prepared by the World Bank Group
. Lithuania is ranked the 30th out of 179 countries in the Index of Economic Freedom
, measured by The Heritage Foundation
. According to the Human Development Report 2011, Lithuania belongs to the group of very high human development
countries.
Having moved away from central planning system in the late 1980s, in 1990, Lithuania was the first to break away from the Soviet Union and become an independent capitalist economy. Lithuania soon implemented liberal reforms and became one of the fastest growing countries in the world last decade, as GDP growth rate was positive 9 years in a row till 2009. It enjoyed high growth rates after entering the European Union along with other Baltic states, leading to the notion of a Baltic Tiger
. Current excellent telecommunication infrastructure and well-educated, multilingual workforce give the possibility to provide high quality business services and produce manufacturing products worldwide.
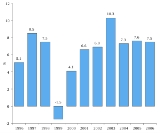
In 2005 the GDP grew by 7.5% and the inflation rate was 3%. GDP growth reached its height in 2007, increasing by 8.9%. Lithuania was the last among the Baltic states to be hit by the economic crisis because its GDP growth rate in 2008 was still positive. In the third quarter of 2009, compared to the previous quarter, GDP grew again by 6.9% after 5 quarters with negative numbers. Rebound in Lithuania's economy in the third quarter was the fastest in the EU. In the last quarter of 2009 Lithuanian economy rose moderately by 0.1%, however the Finance Ministry of Lithuania forecasts that Lithuania's economy will keep growing by 1.6 % in 2010 and by 3.2 % in 2011.
. The tribes maintained close trade contacts with the Roman Empire
. Amber
was the main good provided to the Roman Empire
from Baltic Sea coast, by a long route called the Amber Road
.
Consolidation of the Lithuanian lands began in the late 12th century. Mindaugas
, the first Lithuanian ruler, was crowned as Catholic King of Lithuania in 1253. The expansion of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania
reached its height in the middle of the 14th century under the Grand Duke
Gediminas, who created a strong central government which later spread from the Black Sea
to the Baltic Sea. The duchy was open to everyone. Grand Duke Gediminas issued letters to the Hanseatic league
, offering free access to his domains to men of every order and profession from nobles and knights to tillers of the soil. Economic immigrants had a positive impact, improving the level of handicrafts.
In 1569, the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth was formed by the union of the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania. The economy of the Commonwealth was dominated by feudal agriculture based on the exploitation of the agricultural workforce (serfs). Poland-Lithuania played a significant role in the supply of 16th century Western Europe by exporting three sorts of goods, notably grain (rye), cattle (oxen) and fur. These three articles amounted to nearly 90% of the country's exports to western markets by overland and maritime trade.
The Commonwealth was famous for Europe's first and the world's second modern codified national constitution
, the so-called Constitution of May 3, declared on the 3rd of May, 1791, after the 1788 ratification of the United States Constitution
. Economic and commercial reforms, previously shunned as unimportant by the Szlachta
, were introduced, and the development of industries was encouraged.
Following the partitions of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth
in 1772, 1793 and 1795, the Russian Empire
controlled the majority of Lithuania. One of the most important reforms during the pressure of the Russian Empire that affected economic relations was the Emancipation Reform of 1861 in Russia. The reform amounted to the liquidation of serf dependence previously suffered by peasants and boosted the development of capitalism
.
passed a resolution for the re-establishment of the Independent State of Lithuania. Soon, many economic reforms for sustainable economic growth were implemented. A national currency, called the Lithuanian litas
, was introduced in 1922. It proved to become one of the most stable currencies in Europe during the inter-war period. During the time of its independence, 1918–1940, Lithuania made substantial progress. For example, Lithuania was the second in the world in exporting flax; Lithuanian farm products such as meat, dairy products, many kinds of grain, potatoes, etc. were of superior quality in the world market.
Having taken advantage of favorable international developments, and driven by its foreign policy aims directed against Lithuanian statehood, the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR) occupied Lithuania in 1940. Land and the most important objects for the economy were nationalized, and most of the farms collectivized. Later, many inefficient factories and industry companies, highly dependent on other regions of USSR, were established in Lithuania. Despite that, in 1990, GDP per capita of the Lithuanian Soviet Socialist Republic was USD 8,591, which was above the average for the rest of the Soviet Union of USD 6,871 but lagging behind developed western countries.
The Soviet era brought Lithuania intensive industrialization and economic integration into the USSR, although the level of technology and state concern for environmental, health, and labor issues lagged far behind Western standards. Urbanization
increased from 39% in 1959 to 68% in 1989. From 1949–1952 the Soviets abolished private ownership in agriculture, establishing collective and state farms. Production declined and did not reach pre-war levels until the early 1960s. The intensification of agricultural production through intense chemical use and mechanization eventually doubled production but created additional ecological problems. This changed after independence, when farm production dropped due to difficulties in restructuring the agricultural sector.
During the transitional period former USSR republics, including Lithuania, were characterized by these aspects: overproduction reporting; reluctance to pay taxes by people and enterprises; the reduction of value detraction; overestimation of investment ratios; and politically determined trade among the Soviet countries.
Taking into account the shadow economy, value detraction from products and services, doubtful investments and indirect trade subsidies, Lithuania was not faced with such a huge contraction in GDP as was usually thought and represented in official statistics. On the contrary, Lithuania made structural reforms for future growth and welfare.
One of the most important reforms since Lithuania regained its independence was the privatization
of state owned assets. The first stage of privatization was being implemented in 1991–1995. Citizens were given investment vouchers worth LTL 10.5 billion (USD 2.63 billion) in nominal value, which let them participate in assets selling. By October 1995, they were used as follows: 65% for acquisition of shares; 19% for residential dwellings; 5% for agricultural properties; and 7% remained unused. More than 5700 enterprises with LTL 7 billion (USD 1.75 billion) worth of state capital in book value were sold using four initial privatization methods: share offerings; auctions; best business plans competitions; and hard currency
sales.
The second privatization step began in 1995 by approving a new law that ensured greater diversity of privatization methods and that enabled participation in the selling process without vouchers. During the period 1996–1998, 526 entities were sold for more than LTL 2.3 billion (USD 0.58 billion). Before the reforms, the public sector
totally dominated the economy, whereas the current share of the private sector in GDP increased to over 80%.
The implementation of the monetary reform
was one of the key success factors for the stability of the economy. Lithuania has chosen a currency board system formed and controlled by the Bank of Lithuania
that is independent from any government institution. On 25 June 1993, the Lithuanian litas
was introduced as a free convertible currency, but on the 1st of April, 1994 it was pegged to the United States dollar
at a rate of 4 to 1. The mechanism of the currency board
system enabled Lithuania to stabilize inflation
rates to single digits. The litas soon became a reliable currency as the litas is fully backed by foreign currency. The stable currency rate helped to establish foreign economic relations, therefore leading to a constant growth of foreign trade.
By 1998, the economy had survived the early years of uncertainty and several setbacks, including a banking crisis, and seemed poised for solid growth. However, the collapse of the Russian ruble in August 1998 shocked the economy into negative growth and forced the reorientation of trade from Russia towards the West.
Lithuania was invited to the Helsinki EU summit in December 1999 to begin EU accession talks in early 2000.
After the Russian monetary crisis, the focus of Lithuania's export markets shifted from East to West. In 1997, exports to the Soviet Union's successor entity (the Commonwealth of Independent States
) made up 45% of total Lithuanian exports. This share of exports dropped to 21% of the total in 2006, while exports to EU members increased to 63% of the total.
Exports to the United States made up 4.3% of all Lithuania's exports in 2006, and imports from the United States comprised 2% of total imports. Foreign direct investment
(FDI) in 2005 was 2.6 billion litas, which represented an increase of only 4.6% compared to the same period in the previous year.
Since February 2, 2002 the litas has been pegged to the euro
at a rate of 3.4528 to 1. The rate is not expected to change until Lithuania becomes a member of the Eurozone
. Lithuania was very close to introducing the euro in 2007, but unfortunately the inflation level was somewhat above the Maastricht requirements. The current tough economic situation precludes compliance with the Maastricht criteria on budget balance, so Lithuania cannot expect to have the euro before 2013–2015.
The Vilnius Stock Exchange (VSE), now renamed the NASDAQ OMX Vilnius, started its activity in 1993 and was the first stock exchange in the Baltic states. In 2003, the VSE was acquired by OMX. Since February 27, 2008 the Vilnius Stock Exchange has been a member of NASDAQ OMX Group, which is the world's largest exchange company across six continents, with over 3800 listed companies. The market cap of Vilnius Stock Exchange was LTL 11.7 billion (EUR 3.4 billion) on November 27, 2009 and was twice as large as the ones of Riga and Tallinn Stock Exchanges.
During the last decade (1998–2008) the structure of Lithuania's economy has changed significantly. The biggest changes were recorded in the agricultural sector as the share of total employment decreased from 19.2% in 1998 to just 7.9% in 2008. The service sector plays an increasingly important role in the economy of Lithuania. The share of GDP in financial intermediation and real estate sectors was 17% in 2008 compared to 11% in 1998. The share of total employment in the financial sector in 2008 has doubled compared with 1998.
One of the most important factors for substantial economic expansion was the accession to the WTO in 2001 and the EU in 2004, which enabled free movement of the labour force, capital and trade between the Member States. On the other hand, rapid economic expansion has caused some imbalances in inflation
and balance of payments
. The current account deficit to GDP ratio in 2006–2008 was in double digits and reached its peak at threatening 18.8% in the first quarter of 2008. This was mostly influenced by rapid loan portfolio growth as Scandinavian banks provided cheap credits in Lithuania. The loans directly related to acquisition and development of real estate constituted around half of outstanding bank loans to the private sector. Consumption was affected by credit expansion as well. This led to high inflation of goods and services, as well as trade deficit.
The global credit crunch
which started in 2008 affected the real estate and retail sectors. The construction sector shrank by 46.8% during the first 3 quarters of 2009 and the slump in retail trade was almost 30%. GDP plunged by 15.7% in the first nine months of 2009.
Lithuania was the last among the Baltic states to be hit by the economic crisis because its GDP growth rate in 2008 was still positive. In the third quarter of 2009, compared to the previous quarter, GDP again grew by 6.1% after five quarters with negative numbers. The rebound in Lithuania's economy in the third quarter was the fastest in the EU.
A heavy shock to consumers helped to balance the current account in 2009. Net external assets of the Bank of Lithuania
are at a record height of EUR 5.46 billion. Inflation in Lithuania is no longer a problem. Economic sentiment and confidence of all business activities have rebounded from a record low at the beginning of the year 2009 and suggest further improvements in the economy.
Sectors related to domestic consumption and real estate are still suffering from the economic crisis. However, exporters have started making profits even with lower levels of revenue. The catalysts of growing profit margins are lower raw material prices and staff expense.
system. There are four main types of taxes: personal income tax
(15% + 6% health insurance contribution); value added tax
(21%); corporate profit tax (15%); and social security tax on employers (31% + employee's contribution of 3%). 5% corporate tax for small business was introduced on 1 January 2010. Additional taxes are tax on dividends (0-15% - dividends paid or received are not taxed when an investor controls at least 10% of voting shares in the enterprise for the period of at least 12 months), real estate tax (0.3–1.0%) and a land tax of 1.5% on businesses. The overall tax burden in Lithuania is one of the smallest among all EU countries.
Lithuania attracts foreign investors not only because of small tax burden but also because of a skilled workforce, a well-developed infrastructure and a bigger domestic market than the other two Baltic states combined. Cumulative foreign direct investment
(FDI) at the beginning of the year 2009 was LTL 31.6 billion (EUR 9.2 billion). The manufacturing sector constituted 28% of total FDI, real estate and business activity sector received 20% of total FDI, and financial intermediation a little bit less – 19%. 4/5 of FDI came from the EU countries. Top countries-investors are Sweden (17% of total FDI), Germany (10%) and Denmark (9%).
Lithuania has an ambitious plan to become a Northern European innovation centre by 2020. To reach this goal, it is putting its efforts into attracting FDI to added-value sectors, especially IT services, software development, and consulting services, as well as finance or logistics. Well-known international companies, such as Microsoft
, IBM
, Transcom, Barclays, Siemens
, SEB
, TeliaSonera
, Paroc, Philip Morris
and others, have already established a presence in Lithuania.
Lithuania has prepared an attractive environment for business start-ups in two free economic zone
s (FEZ) in Kaunas
and Klaipėda
. FEZs offer not only developed infrastructure for investments and service support but also tax incentives: a FEZ is free from the corporate tax for the first six years, as well as free from tax on dividends and real estate tax. There are nine industrial sites in Lithuania, which can also provide additional advantages by having a well-developed infrastructure, offering consultancy service and some tax incentives.
The transport infrastructure inherited from the Soviet period is adequate and has been generally well maintained since independence. Its single port
in Klaipėda is ice-free and supplies ferry services to German, Swedish, and Danish ports. There are a few commercial airports; scheduled international services use the facilities at Vilnius
, Kaunas, and Klaipėda. The road system is well developed, including the Via Baltica highway passing through Kaunas.
Border facilities at checkpoints with Poland were significantly improved with the help of EU funds, but long waits had been a frequent phenomenon until 21 December 2007 when the Schengen Agreement
came in force in both countries. Telecommunications have improved greatly since independence as a result of heavy investment. There are currently three large companies providing mobile phone services. http://www.bite.lt/en/ http://www.omnitel.lt/?i3_en http://www.tele2.lt.
(CEE) and is twice the EU-15 average. About 90% of Lithuanians speak at least one foreign language; every second person speaks two foreign languages and every third person speaks English [32].
Lithuania takes the first position in the EU by the number of students in the country. Compared to the EU's average of 15%, only 7% of 18–24 year-old people in Lithuania are not occupied with studies, the lowest percentage in the EU, announced the European Commission
in the end of 2009. School-leavers can choose from 22 universities or 28 colleges for further studies, so 74% of pupils graduated from an upper secondary school continue studies in schools of higher education. Every year more than 30 thousand students graduate from universities or colleges, so the population with higher education is gradually increasing. The most popular higher education programs are business and administration, education science, law, and social sciences.
During the last decade (1998–2008) salaries have more than doubled in Lithuania. Despite this, labour costs in Lithuania are among the lowest in the EU. Average monthly net salary in the third quarter of 2009 was LTL 1665 (EUR 482) and decreased by 6% compared to the same quarter in 2008. The sharpest annual decrease in hourly labour costs in the EU of -10.9% was observed in Lithuania in the third quarter of 2009.
The unemployment rate in Lithuania is very volatile. Since the year 2001, the unemployment rate has decreased from almost 20% to less than 4% in 2007. This could be explained by two main reasons. Firstly, during the time of rapid economic expansion, numerous work places were established. This caused a decrease in the unemployment rate and a rise in staff expenses. Secondly, emigration has also reduced unemployment problems since accession to the EU. However, the current economic crisis has lowered the need for workers, so the unemployment rate increased to 13.8% and then stabilized in the third quarter of 2009.
and Poland.
Lithuania has over 50% of the world's market for high-energy picosecond laser
s, and is a leader in global production of ultra-fast parametric light generators. Lithuanian laser companies were among the first ones in the world to transfer fundamental research into manufacture. Lithuania's laser producers export laser technologies and devices to nearly 100 countries, including EU members, the USA, Japan, Israel, and Switzerland, mostly for universities and corporate laboratories for scientific research purposes.
Recent global broadband
Internet studies show that Lithuania has the fastest Internet in the world, as well as is one of the leading countries in terms of Internet service quality. The broadband speed analysis tool that allows anyone to test their Internet connection Speedtest.net places Lithuania as No. 1 on the list of the world's top countries by upload speed. Lithuania is also on the list of the world's top countries of download speed. Lithuania has one of the highest mobile telephone penetration rates, as well. With a subscription rate of 149 per 100 population, Lithuania is ranked the 8th in the world.
An excellent telecommunication infrastructure and a well-educated, multilingual workforce enable Lithuania to provide high quality business services worldwide. Business services vary from financial to accounting and reporting services. The share of value added in this sector reaches 13%.
Development of shared services and outsourcing
of business processes (BPO) is one of the most promising fields in Lithuania. The research company Datamonitor forecasts a 60% personnel growth by 2009. International companies successfully outsourcing business operations in Lithuania are Barclays Bank PLC, CITCO Group, MIRROR, PricewaterhouseCoopers
, Anthill, Ernst&Young and etc.
Furniture production activity employs more than 50 thousand people. This sector has grown in double-digit numbers over the last three years. The biggest companies in this field work in cooperation with IKEA
and provide high quality products at competitive prices. IKEA also owns one of the biggest wood processing companies in Lithuania.
Companies in the automotive and engineering sector are relatively small but offer flexible services for small and non-standard orders at competitive prices. The sector employs about 3% of the working population and receives 5.6% of FDI. Vilnius Gediminas Technical University
, the biggest technical university in Baltic countries, prepares experts for the sector.
s holding a license from the Bank of Lithuania
and eight foreign bank branches. Most of the banks belong to international corporation
s, mainly Scandinavia
n. The financial sector has demonstrated incredible growth in the last decade (1998–2008). Bank assets were only LTL 11.2 billion (USD 2.8 billion) or 25.5% from GDP at the beginning of the year 2000. Half of the bank assets consisted of loan portfolio.
By the beginning of the year 2009, bank assets grew to LTL 89.7 billion (EUR 26 billion) or 80.8% to GDP, the loan portfolio reached LTL 71.4 billion (EUR 20.7 billion). The loan to GDP ratio was 64%. The growth of deposits was not as fast as that of loans. At the end of 2008, the loan portfolio was almost twice as big as that of deposits. It demonstrated high dependence on external financing. Contraction in the loan portfolio has been recorded over the past year, so the loans to deposits ratio are slowly getting back to healthy levels.
Lithuania had a working nuclear power
plant in Visaginas
, which had a 72% share in electricity generation. However, the government
undertook a commitment to decommission the nuclear power plant by the end of 2009, and the plant was shut on 31 December 2009. The supply of heating energy has been modernized during the last decade (1998–2008). Technological loss in the heat energy system has decreased significantly from 26.2% in the year 2000 to 16.7% in 2008. The amount of air pollution
was reduced by one third. The share of renewable energy
resources in the total fuel balance for heat production increased to almost 20%.
World Heritage site
s, Lithuania receives more than 2.2 million foreign tourists a year. The biggest tourist flows arrive from neighbouring countries: Poland; Russia; Latvia; and Belarus. Other important countries for Lithuania's tourism are Germany, the United Kingdom, Finland and Italy.
sector. 44.8% of the land is arable. Total crop area was 1.8 million hectares in 2008. Cereal
s, wheat
and triticale
are the most popular production of farms. The number of livestock
and poultry
has decreased twofold compared to the 1990s. The number of cattle in Lithuania at the beginning of the year 2009 was 770 thousand, the number of dairy cows was 395 thousand, and the number of poultry was 9.1 million. Lithuanians have changed their habits of foodstuff consumption somewhat. During the period 1992–2008, consumption of vegetables increased by 30% to 86 kg per capita, and consumption of meat
and its products increased by 23% during the same period to 81 kg per capita. On the other hand, consumption of milk
and dairy product
s has decreased to 268 kg per capita by 21%, and the consumption of bread
and grain products decreased to 114 kg per capita by 19% as well.
, Kaunas
and Klaipėda
. These three counties account for 70% of the gross domestic product while having just 59% of the population. Service centers and industry are concentrated there. In five counties (those of Alytus
, Marijampole
, Panevėžys
, Šiauliai
and Tauragė
), GDP per capita is still below 80% of the national average.
In order to achieve balanced regional distribution of GDP, nine public industrial park
s (Akmene Industrial Park, Alytus Industrial Park, Kedainiai Industrial Park, Marijampole Industrial Park, Pagegiai Industrial Park, Panevzys Industrial Park, Radviliskis Industrial Park, Ramygala Industrial Park and Šiauliai Industrial Park) and three private industrial parks (Tauragė Private Industrial Park, Sitkunai Private Industrial Park, Ramučiai Private Logistic and Industrial Park) were established to provide some tax incentives and prepared physical infrastructure.
While the growth in the 1990s was largely constrained to the cities of Vilnius and Klaipėda, in the 2000s the situation changed. Babilonas
real estate development, the largest in the Baltic States
by land area, was conceived in the fifth-largest city Panevėžys
in 2004. In years 2006 - 2008 the large-scale development also reached cities of Kaunas and Šiauliai and some smaller towns.
Region passes through Lithuania. JSC Lithuanian Railways
transports about 44% of the freight carried through the territory of Lithuania. This is a very high indicator compared to other countries of the European Union, where freight transportation by rail amounts to only 10% of the total.
is a regional transport hub connecting the sea, land and railway routes from east and west. Compared to neighbouring Eastern Baltic seaports, the Port of Klaipėda has the widest shipping line network with other seaports. The Port of Klaipėda handles roughly 7,000 ships and 30 million tons of cargo every year, and accepts large-tonnage vessels: dry-cargo vessels up to 70,000 DWT, tankers up to 100,000 DWT and cruise ships up to 270 meters of length. The ice-free seaport of Klaipėda is able to receive Panamax
-type vessels. One of the fastest growing segments of sea transport is passenger traffic. Passenger traffic has increased fourfold since 2002.
(after the completion of several new projects in the third quarter of 2009, the supply of modern warehousing premises has increased by nearly 12% in Vilnius and currently reaches 334,400 m2 of the rentable area). Kaunas
is in the second place (around 200,000 m2), and Klaipėda
in the third (122,500 m2). Since the beginning of the year 2009, prices for warehousing premises have dropped by 20–25% in Vilnius, Kaunas and Klaipėda, and the current level of rents has reached the level of 2003. The costs for renting new warehouses in Vilnius, Kaunas and Klaipėda are similar and reach 2.6 to 4.9 LTL/m2 (0.75 to 1.42 EUR/m2), while the rents of old warehouses are 1.2 to 2.3 LTL/m2 (0.35 to 0.67 EUR/m2).
for such a small country as Lithuania is crucial. The ratio of foreign trade to GDP has always been at least 100%, and for the last several years exceeded it.
The EU is the biggest trade partner of Lithuania with a 58% of total imports and 64% of total exports during the first ten months of the year 2009. The Commonwealth of Independent States
is the second economic union that Lithuania trades the most with, with a share of imports of 34% and a share of exports of 23% during the same period. The vast majority of commodities, including oil, gas and metals have to be imported, mainly from Russia. For this reason, Russia is the biggest import partner of Lithuania.
The import of mineral products has a significant share of 30%, as Lithuania has an oil refinery company owned by Polish concern PKN ORLEN, ORLEN Lietuva, with a refining capacity of 9 million tons a year. The revenues of the company were more than LTL 17 billion (EUR 4.9 billion) in 2008. Orlen Lietuva received 78% of its sales or LTL 13.7 billion (EUR 4 billion) from foreign markets in comparison with total export of Lithuania of LTL 55.5 billion (EUR 16.1 billion) in 2008.
Some sectors are directed mainly at export markets. Transport and logistics export 2/3 of their products and/or services; the biotechnology
industry exports 80%; plastics export 52%; laser
technologies export 86%; metal processing, machinery and electric equipment export 64%; furniture and wood processing
export 55%; textile and clothing export 76%; and the food industry exports 36%.
The total value of natural resource
s in Lithuania reaches LTL 58 billion (EUR 16.8 billion) or 50% of Lithuania's GDP in 2008. The most valuable natural resource in Lithuania is subterranean water, which constitutes more than a half of the total value of natural resources.
Lithuania
Lithuania , officially the Republic of Lithuania is a country in Northern Europe, the biggest of the three Baltic states. It is situated along the southeastern shore of the Baltic Sea, whereby to the west lie Sweden and Denmark...
is a member of the European Union
European Union
The European Union is an economic and political union of 27 independent member states which are located primarily in Europe. The EU traces its origins from the European Coal and Steel Community and the European Economic Community , formed by six countries in 1958...
and the biggest economy among three Baltic states
Baltic states
The term Baltic states refers to the Baltic territories which gained independence from the Russian Empire in the wake of World War I: primarily the contiguous trio of Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania ; Finland also fell within the scope of the term after initially gaining independence in the 1920s.The...
. GDP per capita reached USD 17,800 in 2008 and was higher than the ones of all its neighbors – Latvia
Latvia
Latvia , officially the Republic of Latvia , is a country in the Baltic region of Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by Estonia , to the south by Lithuania , to the east by the Russian Federation , to the southeast by Belarus and shares maritime borders to the west with Sweden...
, Poland
Poland
Poland , officially the Republic of Poland , is a country in Central Europe bordered by Germany to the west; the Czech Republic and Slovakia to the south; Ukraine, Belarus and Lithuania to the east; and the Baltic Sea and Kaliningrad Oblast, a Russian exclave, to the north...
, Russia
Russia
Russia or , officially known as both Russia and the Russian Federation , is a country in northern Eurasia. It is a federal semi-presidential republic, comprising 83 federal subjects...
and Belarus
Belarus
Belarus , officially the Republic of Belarus, is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe, bordered clockwise by Russia to the northeast, Ukraine to the south, Poland to the west, and Lithuania and Latvia to the northwest. Its capital is Minsk; other major cities include Brest, Grodno , Gomel ,...
.
GDP per capita in Lithuania is 70% above the world's average of US$10,500. Lithuania has a favorable legislative basis for business as the country is ranked the 3rd in the region of Eastern Europe and Central Asia and the 26th in the world by the Ease of Doing Business Index
Ease of Doing Business Index
The Ease of Doing Business Index is an index created by the World Bank. Higher rankings indicate better, usually simpler, regulations for businesses and stronger protections of property rights...
prepared by the World Bank Group
World Bank Group
The World Bank Group is a family of five international organizations that makes leveraged loans, generally to poor countries.The Bank came into formal existence on 27 December 1945 following international ratification of the Bretton Woods agreements, which emerged from the United Nations Monetary...
. Lithuania is ranked the 30th out of 179 countries in the Index of Economic Freedom
Index of Economic Freedom
The Index of Economic Freedom is a series of 10 economic measurements created by The Heritage Foundation and The Wall Street Journal. Its stated objective is to measure the degree of economic freedom in the world's nations....
, measured by The Heritage Foundation
The Heritage Foundation
The Heritage Foundation is a conservative American think tank based in Washington, D.C. Heritage's stated mission is to "formulate and promote conservative public policies based on the principles of free enterprise, limited government, individual freedom, traditional American values, and a strong...
. According to the Human Development Report 2011, Lithuania belongs to the group of very high human development
Human Development Index
The Human Development Index is a composite statistic used to rank countries by level of "human development" and separate "very high human development", "high human development", "medium human development", and "low human development" countries...
countries.
Having moved away from central planning system in the late 1980s, in 1990, Lithuania was the first to break away from the Soviet Union and become an independent capitalist economy. Lithuania soon implemented liberal reforms and became one of the fastest growing countries in the world last decade, as GDP growth rate was positive 9 years in a row till 2009. It enjoyed high growth rates after entering the European Union along with other Baltic states, leading to the notion of a Baltic Tiger
Baltic Tiger
Baltic Tiger is a term used to refer to any of the three Baltic states of Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania during their periods of economic boom, which started after the year 2000 and continued until 2006–2007...
. Current excellent telecommunication infrastructure and well-educated, multilingual workforce give the possibility to provide high quality business services and produce manufacturing products worldwide.
In 2005 the GDP grew by 7.5% and the inflation rate was 3%. GDP growth reached its height in 2007, increasing by 8.9%. Lithuania was the last among the Baltic states to be hit by the economic crisis because its GDP growth rate in 2008 was still positive. In the third quarter of 2009, compared to the previous quarter, GDP grew again by 6.9% after 5 quarters with negative numbers. Rebound in Lithuania's economy in the third quarter was the fastest in the EU. In the last quarter of 2009 Lithuanian economy rose moderately by 0.1%, however the Finance Ministry of Lithuania forecasts that Lithuania's economy will keep growing by 1.6 % in 2010 and by 3.2 % in 2011.
History of economy
The history of Lithuania can be divided into 7 major periods. All the periods have some interesting and important facts that had an impact on the economic situation of the country in those times.- Ancient times – Baltic tribes (until the 13th century)
- Grand Duchy of LithuaniaGrand Duchy of LithuaniaThe Grand Duchy of Lithuania was a European state from the 12th /13th century until 1569 and then as a constituent part of Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth until 1791 when Constitution of May 3, 1791 abolished it in favor of unitary state. It was founded by the Lithuanians, one of the polytheistic...
(13th century -1569) - Polish-Lithuanian CommonwealthPolish-Lithuanian CommonwealthThe Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth was a dualistic state of Poland and Lithuania ruled by a common monarch. It was the largest and one of the most populous countries of 16th- and 17th‑century Europe with some and a multi-ethnic population of 11 million at its peak in the early 17th century...
(1569–1795) - Pressure of the Russian EmpireRussian EmpireThe Russian Empire was a state that existed from 1721 until the Russian Revolution of 1917. It was the successor to the Tsardom of Russia and the predecessor of the Soviet Union...
(1795–1914) - Independent Lithuania during the interwar periodInterwar periodInterwar period can refer to any period between two wars. The Interbellum is understood to be the period between the end of the Great War or First World War and the beginning of the Second World War in Europe....
(1918–1940) - Lithuanian Soviet Socialist Republic (1944–1990)
- Republic of Lithuania (since 1990)
History up to the 20th century
The first Lithuanians were a branch of an ancient ethnic group known as the BaltsBalts
The Balts or Baltic peoples , defined as speakers of one of the Baltic languages, a branch of the Indo-European language family, are descended from a group of Indo-European tribes who settled the area between the Jutland peninsula in the west and Moscow, Oka and Volga rivers basins in the east...
. The tribes maintained close trade contacts with the Roman Empire
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire was the post-Republican period of the ancient Roman civilization, characterised by an autocratic form of government and large territorial holdings in Europe and around the Mediterranean....
. Amber
Amber
Amber is fossilized tree resin , which has been appreciated for its color and natural beauty since Neolithic times. Amber is used as an ingredient in perfumes, as a healing agent in folk medicine, and as jewelry. There are five classes of amber, defined on the basis of their chemical constituents...
was the main good provided to the Roman Empire
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire was the post-Republican period of the ancient Roman civilization, characterised by an autocratic form of government and large territorial holdings in Europe and around the Mediterranean....
from Baltic Sea coast, by a long route called the Amber Road
Amber Road
The Amber Road was an ancient trade route for the transfer of amber. As one of the waterways and ancient highways, for centuries the road led from Europe to Asia and back, and from northern Africa to the Baltic Sea....
.
Consolidation of the Lithuanian lands began in the late 12th century. Mindaugas
Mindaugas
Mindaugas was the first known Grand Duke of Lithuania and the only King of Lithuania. Little is known of his origins, early life, or rise to power; he is mentioned in a 1219 treaty as an elder duke, and in 1236 as the leader of all the Lithuanians...
, the first Lithuanian ruler, was crowned as Catholic King of Lithuania in 1253. The expansion of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania
Grand Duchy of Lithuania
The Grand Duchy of Lithuania was a European state from the 12th /13th century until 1569 and then as a constituent part of Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth until 1791 when Constitution of May 3, 1791 abolished it in favor of unitary state. It was founded by the Lithuanians, one of the polytheistic...
reached its height in the middle of the 14th century under the Grand Duke
Grand Duke
The title grand duke is used in Western Europe and particularly in Germanic countries for provincial sovereigns. Grand duke is of a protocolary rank below a king but higher than a sovereign duke. Grand duke is also the usual and established translation of grand prince in languages which do not...
Gediminas, who created a strong central government which later spread from the Black Sea
Black Sea
The Black Sea is bounded by Europe, Anatolia and the Caucasus and is ultimately connected to the Atlantic Ocean via the Mediterranean and the Aegean seas and various straits. The Bosphorus strait connects it to the Sea of Marmara, and the strait of the Dardanelles connects that sea to the Aegean...
to the Baltic Sea. The duchy was open to everyone. Grand Duke Gediminas issued letters to the Hanseatic league
Hanseatic League
The Hanseatic League was an economic alliance of trading cities and their merchant guilds that dominated trade along the coast of Northern Europe...
, offering free access to his domains to men of every order and profession from nobles and knights to tillers of the soil. Economic immigrants had a positive impact, improving the level of handicrafts.
In 1569, the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth was formed by the union of the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania. The economy of the Commonwealth was dominated by feudal agriculture based on the exploitation of the agricultural workforce (serfs). Poland-Lithuania played a significant role in the supply of 16th century Western Europe by exporting three sorts of goods, notably grain (rye), cattle (oxen) and fur. These three articles amounted to nearly 90% of the country's exports to western markets by overland and maritime trade.
The Commonwealth was famous for Europe's first and the world's second modern codified national constitution
Constitution
A constitution is a set of fundamental principles or established precedents according to which a state or other organization is governed. These rules together make up, i.e. constitute, what the entity is...
, the so-called Constitution of May 3, declared on the 3rd of May, 1791, after the 1788 ratification of the United States Constitution
United States Constitution
The Constitution of the United States is the supreme law of the United States of America. It is the framework for the organization of the United States government and for the relationship of the federal government with the states, citizens, and all people within the United States.The first three...
. Economic and commercial reforms, previously shunned as unimportant by the Szlachta
Szlachta
The szlachta was a legally privileged noble class with origins in the Kingdom of Poland. It gained considerable institutional privileges during the 1333-1370 reign of Casimir the Great. In 1413, following a series of tentative personal unions between the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and the Kingdom of...
, were introduced, and the development of industries was encouraged.
Following the partitions of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth
Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth
The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth was a dualistic state of Poland and Lithuania ruled by a common monarch. It was the largest and one of the most populous countries of 16th- and 17th‑century Europe with some and a multi-ethnic population of 11 million at its peak in the early 17th century...
in 1772, 1793 and 1795, the Russian Empire
Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was a state that existed from 1721 until the Russian Revolution of 1917. It was the successor to the Tsardom of Russia and the predecessor of the Soviet Union...
controlled the majority of Lithuania. One of the most important reforms during the pressure of the Russian Empire that affected economic relations was the Emancipation Reform of 1861 in Russia. The reform amounted to the liquidation of serf dependence previously suffered by peasants and boosted the development of capitalism
Capitalism
Capitalism is an economic system that became dominant in the Western world following the demise of feudalism. There is no consensus on the precise definition nor on how the term should be used as a historical category...
.
Lithuania in the 20th century
On February 16, 1918, the Council of LithuaniaCouncil of Lithuania
The Council of Lithuania , after July 11, 1918 The State Council of Lithuania , was convened at the Vilnius Conference that took place between September 18 and 23, 1917. The council was granted the executive authority of the Lithuanian people and was entrusted to establish an independent...
passed a resolution for the re-establishment of the Independent State of Lithuania. Soon, many economic reforms for sustainable economic growth were implemented. A national currency, called the Lithuanian litas
Lithuanian litas
The Lithuanian litas is the currency of Lithuania. It is divided into 100 centų...
, was introduced in 1922. It proved to become one of the most stable currencies in Europe during the inter-war period. During the time of its independence, 1918–1940, Lithuania made substantial progress. For example, Lithuania was the second in the world in exporting flax; Lithuanian farm products such as meat, dairy products, many kinds of grain, potatoes, etc. were of superior quality in the world market.
Having taken advantage of favorable international developments, and driven by its foreign policy aims directed against Lithuanian statehood, the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR) occupied Lithuania in 1940. Land and the most important objects for the economy were nationalized, and most of the farms collectivized. Later, many inefficient factories and industry companies, highly dependent on other regions of USSR, were established in Lithuania. Despite that, in 1990, GDP per capita of the Lithuanian Soviet Socialist Republic was USD 8,591, which was above the average for the rest of the Soviet Union of USD 6,871 but lagging behind developed western countries.
The Soviet era brought Lithuania intensive industrialization and economic integration into the USSR, although the level of technology and state concern for environmental, health, and labor issues lagged far behind Western standards. Urbanization
Urbanization
Urbanization, urbanisation or urban drift is the physical growth of urban areas as a result of global change. The United Nations projected that half of the world's population would live in urban areas at the end of 2008....
increased from 39% in 1959 to 68% in 1989. From 1949–1952 the Soviets abolished private ownership in agriculture, establishing collective and state farms. Production declined and did not reach pre-war levels until the early 1960s. The intensification of agricultural production through intense chemical use and mechanization eventually doubled production but created additional ecological problems. This changed after independence, when farm production dropped due to difficulties in restructuring the agricultural sector.
The myth of Lithuania's economic collapse
According to official statistics, towards the end of central planning economic output plunged in all Soviet-type countries during the transition from central planning to a market economy. The total registered declines in GDP range from 13 to 77% in Eastern Europe. However, both Soviet period and early transition period statistics were deeply flawed and do not represent the real situation and processes in Eastern Europe and Lithuania.During the transitional period former USSR republics, including Lithuania, were characterized by these aspects: overproduction reporting; reluctance to pay taxes by people and enterprises; the reduction of value detraction; overestimation of investment ratios; and politically determined trade among the Soviet countries.
Taking into account the shadow economy, value detraction from products and services, doubtful investments and indirect trade subsidies, Lithuania was not faced with such a huge contraction in GDP as was usually thought and represented in official statistics. On the contrary, Lithuania made structural reforms for future growth and welfare.
Development since the 1990s
Reforms since the mid-1990s have given Lithuania an open and rapidly growing economy. Open to global trade and investment, Lithuania now enjoys high degrees of business, fiscal and financial freedom. Regulation is relatively transparent and efficient. Foreign capital and domestic capital are subject to the same rules as Lithuania is a member of the EU and the WTO. The financial sector is advanced, regionally integrated, and subject to few intrusive regulations.One of the most important reforms since Lithuania regained its independence was the privatization
Privatization
Privatization is the incidence or process of transferring ownership of a business, enterprise, agency or public service from the public sector to the private sector or to private non-profit organizations...
of state owned assets. The first stage of privatization was being implemented in 1991–1995. Citizens were given investment vouchers worth LTL 10.5 billion (USD 2.63 billion) in nominal value, which let them participate in assets selling. By October 1995, they were used as follows: 65% for acquisition of shares; 19% for residential dwellings; 5% for agricultural properties; and 7% remained unused. More than 5700 enterprises with LTL 7 billion (USD 1.75 billion) worth of state capital in book value were sold using four initial privatization methods: share offerings; auctions; best business plans competitions; and hard currency
Hard currency
Hard currency , in economics, refers to a globally traded currency that is expected to serve as a reliable and stable store of value...
sales.
The second privatization step began in 1995 by approving a new law that ensured greater diversity of privatization methods and that enabled participation in the selling process without vouchers. During the period 1996–1998, 526 entities were sold for more than LTL 2.3 billion (USD 0.58 billion). Before the reforms, the public sector
Public sector
The public sector, sometimes referred to as the state sector, is a part of the state that deals with either the production, delivery and allocation of goods and services by and for the government or its citizens, whether national, regional or local/municipal.Examples of public sector activity range...
totally dominated the economy, whereas the current share of the private sector in GDP increased to over 80%.
The implementation of the monetary reform
Monetary reform
Monetary reform describes any movement or theory that proposes a different system of supplying money and financing the economy from the current system.Monetary reformers may advocate any of the following, among other proposals:...
was one of the key success factors for the stability of the economy. Lithuania has chosen a currency board system formed and controlled by the Bank of Lithuania
Bank of Lithuania
The Bank of Lithuania is the central bank of the Republic of Lithuania. The Bank of Lithuania is a non-Eurozone member of the European System of Central Banks...
that is independent from any government institution. On 25 June 1993, the Lithuanian litas
Lithuanian litas
The Lithuanian litas is the currency of Lithuania. It is divided into 100 centų...
was introduced as a free convertible currency, but on the 1st of April, 1994 it was pegged to the United States dollar
United States dollar
The United States dollar , also referred to as the American dollar, is the official currency of the United States of America. It is divided into 100 smaller units called cents or pennies....
at a rate of 4 to 1. The mechanism of the currency board
Currency board
A currency board is a monetary authority which is required to maintain a fixed exchange rate with a foreign currency. This policy objective requires the conventional objectives of a central bank to be subordinated to the exchange rate target....
system enabled Lithuania to stabilize inflation
Inflation
In economics, inflation is a rise in the general level of prices of goods and services in an economy over a period of time.When the general price level rises, each unit of currency buys fewer goods and services. Consequently, inflation also reflects an erosion in the purchasing power of money – a...
rates to single digits. The litas soon became a reliable currency as the litas is fully backed by foreign currency. The stable currency rate helped to establish foreign economic relations, therefore leading to a constant growth of foreign trade.
By 1998, the economy had survived the early years of uncertainty and several setbacks, including a banking crisis, and seemed poised for solid growth. However, the collapse of the Russian ruble in August 1998 shocked the economy into negative growth and forced the reorientation of trade from Russia towards the West.
Lithuania was invited to the Helsinki EU summit in December 1999 to begin EU accession talks in early 2000.
After the Russian monetary crisis, the focus of Lithuania's export markets shifted from East to West. In 1997, exports to the Soviet Union's successor entity (the Commonwealth of Independent States
Commonwealth of Independent States
The Commonwealth of Independent States is a regional organization whose participating countries are former Soviet Republics, formed during the breakup of the Soviet Union....
) made up 45% of total Lithuanian exports. This share of exports dropped to 21% of the total in 2006, while exports to EU members increased to 63% of the total.
Exports to the United States made up 4.3% of all Lithuania's exports in 2006, and imports from the United States comprised 2% of total imports. Foreign direct investment
Foreign direct investment
Foreign direct investment or foreign investment refers to the net inflows of investment to acquire a lasting management interest in an enterprise operating in an economy other than that of the investor.. It is the sum of equity capital,other long-term capital, and short-term capital as shown in...
(FDI) in 2005 was 2.6 billion litas, which represented an increase of only 4.6% compared to the same period in the previous year.
Since February 2, 2002 the litas has been pegged to the euro
Euro
The euro is the official currency of the eurozone: 17 of the 27 member states of the European Union. It is also the currency used by the Institutions of the European Union. The eurozone consists of Austria, Belgium, Cyprus, Estonia, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Ireland, Italy, Luxembourg,...
at a rate of 3.4528 to 1. The rate is not expected to change until Lithuania becomes a member of the Eurozone
Eurozone
The eurozone , officially called the euro area, is an economic and monetary union of seventeen European Union member states that have adopted the euro as their common currency and sole legal tender...
. Lithuania was very close to introducing the euro in 2007, but unfortunately the inflation level was somewhat above the Maastricht requirements. The current tough economic situation precludes compliance with the Maastricht criteria on budget balance, so Lithuania cannot expect to have the euro before 2013–2015.
The Vilnius Stock Exchange (VSE), now renamed the NASDAQ OMX Vilnius, started its activity in 1993 and was the first stock exchange in the Baltic states. In 2003, the VSE was acquired by OMX. Since February 27, 2008 the Vilnius Stock Exchange has been a member of NASDAQ OMX Group, which is the world's largest exchange company across six continents, with over 3800 listed companies. The market cap of Vilnius Stock Exchange was LTL 11.7 billion (EUR 3.4 billion) on November 27, 2009 and was twice as large as the ones of Riga and Tallinn Stock Exchanges.
During the last decade (1998–2008) the structure of Lithuania's economy has changed significantly. The biggest changes were recorded in the agricultural sector as the share of total employment decreased from 19.2% in 1998 to just 7.9% in 2008. The service sector plays an increasingly important role in the economy of Lithuania. The share of GDP in financial intermediation and real estate sectors was 17% in 2008 compared to 11% in 1998. The share of total employment in the financial sector in 2008 has doubled compared with 1998.
| Economic activity | GDP, 1998 | Employment, 1998 | GDP, 2000 | Employment, 2000 | GDP, 2004 | Employment, 2004 | GDP, 2008 | Employment, 2008 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Trade; hotels and restaurants; transport, storage and communication | 27.3% | 22.6% | 30.2% | 22.8% | 31.7% | 24.7% | 30.1% | 27.5% |
| Industry | 22.8% | 22.1% | 23.8% | 20.8% | 25.8% | 20.1% | 21.5% | 19.6% |
| Public administration; services for social sphere | 21.7% | 25.5% | 21.2% | 27.6% | 18.2% | 26.3% | 17.5% | 26.1% |
| Financial intermediation; real estate | 11.2% | 4.0% | 12.5% | 4.1% | 12.4% | 4.9% | 16.6% | 8.0% |
| Construction | 8.3% | 6.7% | 6.0% | 6.0% | 7.2% | 8.1% | 10.0% | 10.9% |
| Agriculture | 8.7% | 19.2% | 6.3% | 18.7% | 4.7% | 15.8% | 4.4% | 7.9% |
Lithuania in the 21st century
The economy of Lithuania was one of the fastest growing in the world last decade (1998–2008) as GDP growth rate was positive 9 years in a row. Since the year 2000 GDP has almost doubled with a growth rate of 77%.One of the most important factors for substantial economic expansion was the accession to the WTO in 2001 and the EU in 2004, which enabled free movement of the labour force, capital and trade between the Member States. On the other hand, rapid economic expansion has caused some imbalances in inflation
Inflation
In economics, inflation is a rise in the general level of prices of goods and services in an economy over a period of time.When the general price level rises, each unit of currency buys fewer goods and services. Consequently, inflation also reflects an erosion in the purchasing power of money – a...
and balance of payments
Balance of payments
Balance of payments accounts are an accounting record of all monetary transactions between a country and the rest of the world.These transactions include payments for the country's exports and imports of goods, services, financial capital, and financial transfers...
. The current account deficit to GDP ratio in 2006–2008 was in double digits and reached its peak at threatening 18.8% in the first quarter of 2008. This was mostly influenced by rapid loan portfolio growth as Scandinavian banks provided cheap credits in Lithuania. The loans directly related to acquisition and development of real estate constituted around half of outstanding bank loans to the private sector. Consumption was affected by credit expansion as well. This led to high inflation of goods and services, as well as trade deficit.
The global credit crunch
Credit crunch
A credit crunch is a reduction in the general availability of loans or a sudden tightening of the conditions required to obtain a loan from the banks. A credit crunch generally involves a reduction in the availability of credit independent of a rise in official interest rates...
which started in 2008 affected the real estate and retail sectors. The construction sector shrank by 46.8% during the first 3 quarters of 2009 and the slump in retail trade was almost 30%. GDP plunged by 15.7% in the first nine months of 2009.
Lithuania was the last among the Baltic states to be hit by the economic crisis because its GDP growth rate in 2008 was still positive. In the third quarter of 2009, compared to the previous quarter, GDP again grew by 6.1% after five quarters with negative numbers. The rebound in Lithuania's economy in the third quarter was the fastest in the EU.
A heavy shock to consumers helped to balance the current account in 2009. Net external assets of the Bank of Lithuania
Bank of Lithuania
The Bank of Lithuania is the central bank of the Republic of Lithuania. The Bank of Lithuania is a non-Eurozone member of the European System of Central Banks...
are at a record height of EUR 5.46 billion. Inflation in Lithuania is no longer a problem. Economic sentiment and confidence of all business activities have rebounded from a record low at the beginning of the year 2009 and suggest further improvements in the economy.
Sectors related to domestic consumption and real estate are still suffering from the economic crisis. However, exporters have started making profits even with lower levels of revenue. The catalysts of growing profit margins are lower raw material prices and staff expense.
Tax system
Lithuania has a favorable taxTax
To tax is to impose a financial charge or other levy upon a taxpayer by a state or the functional equivalent of a state such that failure to pay is punishable by law. Taxes are also imposed by many subnational entities...
system. There are four main types of taxes: personal income tax
Income tax
An income tax is a tax levied on the income of individuals or businesses . Various income tax systems exist, with varying degrees of tax incidence. Income taxation can be progressive, proportional, or regressive. When the tax is levied on the income of companies, it is often called a corporate...
(15% + 6% health insurance contribution); value added tax
Value added tax
A value added tax or value-added tax is a form of consumption tax. From the perspective of the buyer, it is a tax on the purchase price. From that of the seller, it is a tax only on the "value added" to a product, material or service, from an accounting point of view, by this stage of its...
(21%); corporate profit tax (15%); and social security tax on employers (31% + employee's contribution of 3%). 5% corporate tax for small business was introduced on 1 January 2010. Additional taxes are tax on dividends (0-15% - dividends paid or received are not taxed when an investor controls at least 10% of voting shares in the enterprise for the period of at least 12 months), real estate tax (0.3–1.0%) and a land tax of 1.5% on businesses. The overall tax burden in Lithuania is one of the smallest among all EU countries.
Lithuania attracts foreign investors not only because of small tax burden but also because of a skilled workforce, a well-developed infrastructure and a bigger domestic market than the other two Baltic states combined. Cumulative foreign direct investment
Foreign direct investment
Foreign direct investment or foreign investment refers to the net inflows of investment to acquire a lasting management interest in an enterprise operating in an economy other than that of the investor.. It is the sum of equity capital,other long-term capital, and short-term capital as shown in...
(FDI) at the beginning of the year 2009 was LTL 31.6 billion (EUR 9.2 billion). The manufacturing sector constituted 28% of total FDI, real estate and business activity sector received 20% of total FDI, and financial intermediation a little bit less – 19%. 4/5 of FDI came from the EU countries. Top countries-investors are Sweden (17% of total FDI), Germany (10%) and Denmark (9%).
Lithuania has an ambitious plan to become a Northern European innovation centre by 2020. To reach this goal, it is putting its efforts into attracting FDI to added-value sectors, especially IT services, software development, and consulting services, as well as finance or logistics. Well-known international companies, such as Microsoft
Microsoft
Microsoft Corporation is an American public multinational corporation headquartered in Redmond, Washington, USA that develops, manufactures, licenses, and supports a wide range of products and services predominantly related to computing through its various product divisions...
, IBM
IBM
International Business Machines Corporation or IBM is an American multinational technology and consulting corporation headquartered in Armonk, New York, United States. IBM manufactures and sells computer hardware and software, and it offers infrastructure, hosting and consulting services in areas...
, Transcom, Barclays, Siemens
Siemens
Siemens may refer toSiemens, a German family name carried by generations of telecommunications industrialists, including:* Werner von Siemens , inventor, founder of Siemens AG...
, SEB
Seb
Seb is a diminutive of the given name Sebastian. "Seb" may also refer to:*A god in Egyptian mythology also known as Geb*Sebastian 'Seb' Coe , British athlete and politician*Seb Fontaine, DJ with English dance/electronica outfit Reflekt...
, TeliaSonera
TeliaSonera
TeliaSonera AB is the dominant telephone company and mobile network operator in Sweden and Finland. The company has operations in other countries in Northern, Eastern Europe, Central Asia and Spain, with a total of 150 million mobile customers...
, Paroc, Philip Morris
Altria Group
Altria Group, Inc. is based in Henrico County, Virginia, and is the parent company of Philip Morris USA, John Middleton, Inc., U.S. Smokeless Tobacco Company, Inc., Philip Morris Capital Corporation, and Chateau Ste. Michelle Wine Estates. It is one of the world's largest tobacco corporations...
and others, have already established a presence in Lithuania.
Lithuania has prepared an attractive environment for business start-ups in two free economic zone
Free economic zone
Many countries have, or have had at some time, designated areas where companies are taxed very lightly or not at all to encourage development or for some other reason...
s (FEZ) in Kaunas
Kaunas
Kaunas is the second-largest city in Lithuania and has historically been a leading centre of Lithuanian economic, academic, and cultural life. Kaunas was the biggest city and the center of a powiat in Trakai Voivodeship of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania since 1413. During Russian Empire occupation...
and Klaipėda
Klaipeda
Klaipėda is a city in Lithuania situated at the mouth of the Nemunas River where it flows into the Baltic Sea. It is the third largest city in Lithuania and the capital of Klaipėda County....
. FEZs offer not only developed infrastructure for investments and service support but also tax incentives: a FEZ is free from the corporate tax for the first six years, as well as free from tax on dividends and real estate tax. There are nine industrial sites in Lithuania, which can also provide additional advantages by having a well-developed infrastructure, offering consultancy service and some tax incentives.
The transport infrastructure inherited from the Soviet period is adequate and has been generally well maintained since independence. Its single port
Port of Klaipeda
The Port of Klaipėda is a seaport located in Klaipėda, Lithuania. It is one of the few ice-free ports in northernmost Europe, and the largest in Lithuania...
in Klaipėda is ice-free and supplies ferry services to German, Swedish, and Danish ports. There are a few commercial airports; scheduled international services use the facilities at Vilnius
Vilnius
Vilnius is the capital of Lithuania, and its largest city, with a population of 560,190 as of 2010. It is the seat of the Vilnius city municipality and of the Vilnius district municipality. It is also the capital of Vilnius County...
, Kaunas, and Klaipėda. The road system is well developed, including the Via Baltica highway passing through Kaunas.
Border facilities at checkpoints with Poland were significantly improved with the help of EU funds, but long waits had been a frequent phenomenon until 21 December 2007 when the Schengen Agreement
Schengen Agreement
The Schengen Agreement is a treaty signed on 14 June 1985 near the town of Schengen in Luxembourg, between five of the ten member states of the European Economic Community. It was supplemented by the Convention implementing the Schengen Agreement 5 years later...
came in force in both countries. Telecommunications have improved greatly since independence as a result of heavy investment. There are currently three large companies providing mobile phone services. http://www.bite.lt/en/ http://www.omnitel.lt/?i3_en http://www.tele2.lt.
Workforce
The number of the population aged 15 years and over is 2.85 million, and 1.52 million of them were employed in 2008. The population with higher education was 0.54 million, or more than 35% of employed people. This ratio demonstrates that workforce in Lithuania is one of the best-educated in Central and Eastern EuropeCentral and Eastern Europe
Central and Eastern Europe is a term describing former communist states in Europe, after the collapse of the Iron Curtain in 1989/90. In scholarly literature the abbreviations CEE or CEEC are often used for this concept...
(CEE) and is twice the EU-15 average. About 90% of Lithuanians speak at least one foreign language; every second person speaks two foreign languages and every third person speaks English [32].
Lithuania takes the first position in the EU by the number of students in the country. Compared to the EU's average of 15%, only 7% of 18–24 year-old people in Lithuania are not occupied with studies, the lowest percentage in the EU, announced the European Commission
European Commission
The European Commission is the executive body of the European Union. The body is responsible for proposing legislation, implementing decisions, upholding the Union's treaties and the general day-to-day running of the Union....
in the end of 2009. School-leavers can choose from 22 universities or 28 colleges for further studies, so 74% of pupils graduated from an upper secondary school continue studies in schools of higher education. Every year more than 30 thousand students graduate from universities or colleges, so the population with higher education is gradually increasing. The most popular higher education programs are business and administration, education science, law, and social sciences.
During the last decade (1998–2008) salaries have more than doubled in Lithuania. Despite this, labour costs in Lithuania are among the lowest in the EU. Average monthly net salary in the third quarter of 2009 was LTL 1665 (EUR 482) and decreased by 6% compared to the same quarter in 2008. The sharpest annual decrease in hourly labour costs in the EU of -10.9% was observed in Lithuania in the third quarter of 2009.
The unemployment rate in Lithuania is very volatile. Since the year 2001, the unemployment rate has decreased from almost 20% to less than 4% in 2007. This could be explained by two main reasons. Firstly, during the time of rapid economic expansion, numerous work places were established. This caused a decrease in the unemployment rate and a rise in staff expenses. Secondly, emigration has also reduced unemployment problems since accession to the EU. However, the current economic crisis has lowered the need for workers, so the unemployment rate increased to 13.8% and then stabilized in the third quarter of 2009.
High value added production
High value added production is increasing in Lithuania. Several companies produce pharmaceutical substances, components for molecular diagnostics and other sophisticated biotech products. 80% of the production is exported to more than 70 countries. Lithuanian pharmaceutical companies are expanding to foreign markets by acquiring companies in SlovakiaSlovakia
The Slovak Republic is a landlocked state in Central Europe. It has a population of over five million and an area of about . Slovakia is bordered by the Czech Republic and Austria to the west, Poland to the north, Ukraine to the east and Hungary to the south...
and Poland.
Lithuania has over 50% of the world's market for high-energy picosecond laser
Laser
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of photons. The term "laser" originated as an acronym for Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation...
s, and is a leader in global production of ultra-fast parametric light generators. Lithuanian laser companies were among the first ones in the world to transfer fundamental research into manufacture. Lithuania's laser producers export laser technologies and devices to nearly 100 countries, including EU members, the USA, Japan, Israel, and Switzerland, mostly for universities and corporate laboratories for scientific research purposes.
Recent global broadband
Broadband
The term broadband refers to a telecommunications signal or device of greater bandwidth, in some sense, than another standard or usual signal or device . Different criteria for "broad" have been applied in different contexts and at different times...
Internet studies show that Lithuania has the fastest Internet in the world, as well as is one of the leading countries in terms of Internet service quality. The broadband speed analysis tool that allows anyone to test their Internet connection Speedtest.net places Lithuania as No. 1 on the list of the world's top countries by upload speed. Lithuania is also on the list of the world's top countries of download speed. Lithuania has one of the highest mobile telephone penetration rates, as well. With a subscription rate of 149 per 100 population, Lithuania is ranked the 8th in the world.
An excellent telecommunication infrastructure and a well-educated, multilingual workforce enable Lithuania to provide high quality business services worldwide. Business services vary from financial to accounting and reporting services. The share of value added in this sector reaches 13%.
Service sector
The service sector accounts for the largest share of GDP. One of the most important sub-sectors is information and communication technologies. 37 thousand employees work for more than 2000 ICT companies. ICT received 9.5% of total FDI. 11 out of 20 biggest IT companies from Baltic countries are based in Lithuania. Lithuania exported 31% of its IT services in the first quarter of 2009.Development of shared services and outsourcing
Outsourcing
Outsourcing is the process of contracting a business function to someone else.-Overview:The term outsourcing is used inconsistently but usually involves the contracting out of a business function - commonly one previously performed in-house - to an external provider...
of business processes (BPO) is one of the most promising fields in Lithuania. The research company Datamonitor forecasts a 60% personnel growth by 2009. International companies successfully outsourcing business operations in Lithuania are Barclays Bank PLC, CITCO Group, MIRROR, PricewaterhouseCoopers
PricewaterhouseCoopers
PricewaterhouseCoopers is a global professional services firm headquartered in London, United Kingdom. It is the world's largest professional services firm measured by revenues and one of the "Big Four" accountancy firms....
, Anthill, Ernst&Young and etc.
Manufacturing
Manufacturing constitutes the biggest part of gross value added in Lithuania. More than 57 thousand people were employed in food processing in 2008. The food processing sector constitutes 11% of total exports. Dairy products, especially cheese, are well known in neighbouring countries. Another important manufacturing activity is chemical products. 80% of production is exported so chemical products constitute 12.5% of total exports.Furniture production activity employs more than 50 thousand people. This sector has grown in double-digit numbers over the last three years. The biggest companies in this field work in cooperation with IKEA
IKEA
IKEA is a privately held, international home products company that designs and sells ready-to-assemble furniture such as beds and desks, appliances and home accessories. The company is the world's largest furniture retailer...
and provide high quality products at competitive prices. IKEA also owns one of the biggest wood processing companies in Lithuania.
Companies in the automotive and engineering sector are relatively small but offer flexible services for small and non-standard orders at competitive prices. The sector employs about 3% of the working population and receives 5.6% of FDI. Vilnius Gediminas Technical University
Vilnius Gediminas Technical University
Vilnius Gediminas Technical University is a state higher academic school which has the rights of legal entity. The University is a non-profit institution, which was established by the Parliament of the Republic of Lithuania....
, the biggest technical university in Baltic countries, prepares experts for the sector.
Financial sector
The financial sector concentrates mostly on the domestic market. There are nine commercial bankBank
A bank is a financial institution that serves as a financial intermediary. The term "bank" may refer to one of several related types of entities:...
s holding a license from the Bank of Lithuania
Bank of Lithuania
The Bank of Lithuania is the central bank of the Republic of Lithuania. The Bank of Lithuania is a non-Eurozone member of the European System of Central Banks...
and eight foreign bank branches. Most of the banks belong to international corporation
Corporation
A corporation is created under the laws of a state as a separate legal entity that has privileges and liabilities that are distinct from those of its members. There are many different forms of corporations, most of which are used to conduct business. Early corporations were established by charter...
s, mainly Scandinavia
Scandinavia
Scandinavia is a cultural, historical and ethno-linguistic region in northern Europe that includes the three kingdoms of Denmark, Norway and Sweden, characterized by their common ethno-cultural heritage and language. Modern Norway and Sweden proper are situated on the Scandinavian Peninsula,...
n. The financial sector has demonstrated incredible growth in the last decade (1998–2008). Bank assets were only LTL 11.2 billion (USD 2.8 billion) or 25.5% from GDP at the beginning of the year 2000. Half of the bank assets consisted of loan portfolio.
By the beginning of the year 2009, bank assets grew to LTL 89.7 billion (EUR 26 billion) or 80.8% to GDP, the loan portfolio reached LTL 71.4 billion (EUR 20.7 billion). The loan to GDP ratio was 64%. The growth of deposits was not as fast as that of loans. At the end of 2008, the loan portfolio was almost twice as big as that of deposits. It demonstrated high dependence on external financing. Contraction in the loan portfolio has been recorded over the past year, so the loans to deposits ratio are slowly getting back to healthy levels.
Utilities sector
The utilities sector accounts for more than 3% of gross value added in Lithuania. Electricity production exceeded 12 billion kWh in 2007, and consumption exceeded 9.6 billion kWh [49]. Electricity production surplus is exported.Lithuania had a working nuclear power
Nuclear power
Nuclear power is the use of sustained nuclear fission to generate heat and electricity. Nuclear power plants provide about 6% of the world's energy and 13–14% of the world's electricity, with the U.S., France, and Japan together accounting for about 50% of nuclear generated electricity...
plant in Visaginas
Visaginas
Visaginas is a city with municipal rights in eastern Lithuania, situated near the country's biggest lake, Drūkšiai. Its administrative boundaries are in the process of being defined. The Vilnius–Daugavpils railway runs alongside the town, providing convenient communication with Vilnius and...
, which had a 72% share in electricity generation. However, the government
Government
Government refers to the legislators, administrators, and arbitrators in the administrative bureaucracy who control a state at a given time, and to the system of government by which they are organized...
undertook a commitment to decommission the nuclear power plant by the end of 2009, and the plant was shut on 31 December 2009. The supply of heating energy has been modernized during the last decade (1998–2008). Technological loss in the heat energy system has decreased significantly from 26.2% in the year 2000 to 16.7% in 2008. The amount of air pollution
Pollution
Pollution is the introduction of contaminants into a natural environment that causes instability, disorder, harm or discomfort to the ecosystem i.e. physical systems or living organisms. Pollution can take the form of chemical substances or energy, such as noise, heat or light...
was reduced by one third. The share of renewable energy
Renewable energy
Renewable energy is energy which comes from natural resources such as sunlight, wind, rain, tides, and geothermal heat, which are renewable . About 16% of global final energy consumption comes from renewables, with 10% coming from traditional biomass, which is mainly used for heating, and 3.4% from...
resources in the total fuel balance for heat production increased to almost 20%.
Tourism
The tourism sector is becoming increasingly important for the economy of Lithuania. It constituted almost 3% of GDP in 2008. Having an untouched ecological countryside with rich natural resources (22 000 rivers and rivulets, and about 3000 lakes), a well-developed rural tourism network, a unique coastal area of almost 100 km and four UNESCOUNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations...
World Heritage site
World Heritage Site
A UNESCO World Heritage Site is a place that is listed by the UNESCO as of special cultural or physical significance...
s, Lithuania receives more than 2.2 million foreign tourists a year. The biggest tourist flows arrive from neighbouring countries: Poland; Russia; Latvia; and Belarus. Other important countries for Lithuania's tourism are Germany, the United Kingdom, Finland and Italy.
Agriculture
Despite a decreased share in GDP, the agricultural sector is still important for Lithuania as it employs almost 8% of the work force and supplies materials for the food processingFood processing
Food processing is the set of methods and techniques used to transform raw ingredients into food or to transform food into other forms for consumption by humans or animals either in the home or by the food processing industry...
sector. 44.8% of the land is arable. Total crop area was 1.8 million hectares in 2008. Cereal
Cereal
Cereals are grasses cultivated for the edible components of their grain , composed of the endosperm, germ, and bran...
s, wheat
Wheat
Wheat is a cereal grain, originally from the Levant region of the Near East, but now cultivated worldwide. In 2007 world production of wheat was 607 million tons, making it the third most-produced cereal after maize and rice...
and triticale
Triticale
Triticale is a hybrid of wheat and rye first bred in laboratories during the late 19th century. The grain was originally bred in Scotland and Sweden. Commercially available triticale is almost always a second generation hybrid, i.e., a cross between two kinds of primary triticales...
are the most popular production of farms. The number of livestock
Livestock
Livestock refers to one or more domesticated animals raised in an agricultural setting to produce commodities such as food, fiber and labor. The term "livestock" as used in this article does not include poultry or farmed fish; however the inclusion of these, especially poultry, within the meaning...
and poultry
Poultry
Poultry are domesticated birds kept by humans for the purpose of producing eggs, meat, and/or feathers. These most typically are members of the superorder Galloanserae , especially the order Galliformes and the family Anatidae , commonly known as "waterfowl"...
has decreased twofold compared to the 1990s. The number of cattle in Lithuania at the beginning of the year 2009 was 770 thousand, the number of dairy cows was 395 thousand, and the number of poultry was 9.1 million. Lithuanians have changed their habits of foodstuff consumption somewhat. During the period 1992–2008, consumption of vegetables increased by 30% to 86 kg per capita, and consumption of meat
Meat
Meat is animal flesh that is used as food. Most often, this means the skeletal muscle and associated fat and other tissues, but it may also describe other edible tissues such as organs and offal...
and its products increased by 23% during the same period to 81 kg per capita. On the other hand, consumption of milk
Milk
Milk is a white liquid produced by the mammary glands of mammals. It is the primary source of nutrition for young mammals before they are able to digest other types of food. Early-lactation milk contains colostrum, which carries the mother's antibodies to the baby and can reduce the risk of many...
and dairy product
Dairy product
Dairy products are generally defined as foods produced from cow's or domestic buffalo's milk. They are usually high-energy-yielding food products. A production plant for such processing is called a dairy or a dairy factory. Raw milk for processing comes mainly from cows, and, to a lesser extent,...
s has decreased to 268 kg per capita by 21%, and the consumption of bread
Bread
Bread is a staple food prepared by cooking a dough of flour and water and often additional ingredients. Doughs are usually baked, but in some cuisines breads are steamed , fried , or baked on an unoiled frying pan . It may be leavened or unleavened...
and grain products decreased to 114 kg per capita by 19% as well.
| Economic activity | 2008 |
|---|---|
| Manufacturing | 17.9% |
| Wholesale and retail trade; repair of goods | 16.6% |
| Real estate, renting and business activities | 13.1% |
| Transport, storage and communication | 12.1% |
| Construction | 10.0% |
| Public administration and defense; compulsory social security | 6.7% |
| Education | 4.9% |
| Agriculture, hunting and forestry | 4.3% |
| Financial intermediation | 3.5% |
| Health and social work | 3.3% |
| Electricity, gas and water supply | 3.1% |
| Other community, social and personal service activities | 2.5% |
| Hotels and restaurants | 1.3% |
| Mining and quarrying | 0.4% |
| Activities of households | 0.1% |
| Fishing | 0.1% |
Regional situation
Lithuania is divided into 10 counties. There are five cities with a population over 100 thousand and twelve cities of over 30 thousand people. The gross regional product is concentrated in the three largest counties – VilniusVilnius
Vilnius is the capital of Lithuania, and its largest city, with a population of 560,190 as of 2010. It is the seat of the Vilnius city municipality and of the Vilnius district municipality. It is also the capital of Vilnius County...
, Kaunas
Kaunas
Kaunas is the second-largest city in Lithuania and has historically been a leading centre of Lithuanian economic, academic, and cultural life. Kaunas was the biggest city and the center of a powiat in Trakai Voivodeship of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania since 1413. During Russian Empire occupation...
and Klaipėda
Klaipeda
Klaipėda is a city in Lithuania situated at the mouth of the Nemunas River where it flows into the Baltic Sea. It is the third largest city in Lithuania and the capital of Klaipėda County....
. These three counties account for 70% of the gross domestic product while having just 59% of the population. Service centers and industry are concentrated there. In five counties (those of Alytus
Alytus
Alytus is a city with municipal rights in southern Lithuania. It is the capital of Alytus County. Its population in 2007 was 68,835. Alytus is the historical centre of the Dzūkija region. The city lies on the banks of the Nemunas River. The major highways linking Vilnius, Kaunas, Lazdijai, and...
, Marijampole
Marijampole
Marijampolė is an industrial city and the capital of the Marijampolė County in the south of Lithuania, bordering Poland and Russian Kaliningrad oblast, and Lake Vištytis. The population of Marijampolė is 48,700...
, Panevėžys
Panevežys
Panevėžys see also other names, is the fifth largest city in Lithuania. As of 2008, it occupied 50 square kilometers with 113,653 inhabitants. The largest multifunctional arena in Panevėžys is the Cido Arena...
, Šiauliai
Šiauliai
Šiauliai , is the fourth largest city in Lithuania, with a population of 133,900. It is the capital of Šiauliai County. Unofficially, the city is the capital of Northern Lithuania.-Names:...
and Tauragė
Taurage
Tauragė is an industrial city in Lithuania, and the capital of Tauragė County. In 2011, its population was 26,444. Tauragė is situated on the Jūra River, close to the border with the Kaliningrad Oblast, and not far from the Baltic Sea coast....
), GDP per capita is still below 80% of the national average.
In order to achieve balanced regional distribution of GDP, nine public industrial park
Industrial park
An industrial park is an area zoned and planned for the purpose of industrial development...
s (Akmene Industrial Park, Alytus Industrial Park, Kedainiai Industrial Park, Marijampole Industrial Park, Pagegiai Industrial Park, Panevzys Industrial Park, Radviliskis Industrial Park, Ramygala Industrial Park and Šiauliai Industrial Park) and three private industrial parks (Tauragė Private Industrial Park, Sitkunai Private Industrial Park, Ramučiai Private Logistic and Industrial Park) were established to provide some tax incentives and prepared physical infrastructure.
While the growth in the 1990s was largely constrained to the cities of Vilnius and Klaipėda, in the 2000s the situation changed. Babilonas
Babilonas
Babilonas is a privately developed district of retail, commercial, residential and public buildings in Panevėžys, Lithuania....
real estate development, the largest in the Baltic States
Baltic states
The term Baltic states refers to the Baltic territories which gained independence from the Russian Empire in the wake of World War I: primarily the contiguous trio of Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania ; Finland also fell within the scope of the term after initially gaining independence in the 1920s.The...
by land area, was conceived in the fifth-largest city Panevėžys
Panevežys
Panevėžys see also other names, is the fifth largest city in Lithuania. As of 2008, it occupied 50 square kilometers with 113,653 inhabitants. The largest multifunctional arena in Panevėžys is the Cido Arena...
in 2004. In years 2006 - 2008 the large-scale development also reached cities of Kaunas and Šiauliai and some smaller towns.
Infrastructure
The transport, storage and communication sector has increased its importance to the economy of Lithuania. In 2008, it accounted for 12.1% of GDP compared to 9.1% in 1996. Lithuania became a well-developed transport corridor between the East and the West. Having a high-quality and dense road network, Lithuania has achieved significant growth in the amount of goods carried both by road and by rail transport. The volume of goods transported by road transport has increased fivefold since 1996. The total length of roadways is more than 80 thousand km, and 90% of them are paved. The government is demonstrating high attention to the quality of road infrastructure by increasing their funding. The funding of roads exceeded LTL 1.75 billion (EUR 0.5 billion) in 2008.Railways
Railway transport in Lithuania provides long-distance passenger and cargo services. Railways carry approximately 50 million tons of cargo and 7 million passengers a year. Direct rail routes link Lithuania with Russia, Belarus, Latvia, Poland, and Germany. Also, the main transit route between Russia and Russia's KaliningradKaliningrad
Kaliningrad is a seaport and the administrative center of Kaliningrad Oblast, the Russian exclave between Poland and Lithuania on the Baltic Sea...
Region passes through Lithuania. JSC Lithuanian Railways
Lithuanian Railways
Lithuanian Railways is the national, state-owned railway company of Lithuania. It operates all the railway lines in the country.Lithuanian Railways' main network consists of 1749 km of broad gauge railway of which 122 km are electrified. They also operate 22 km of standard gauge...
transports about 44% of the freight carried through the territory of Lithuania. This is a very high indicator compared to other countries of the European Union, where freight transportation by rail amounts to only 10% of the total.
Sea port
The northern-most and one of the few ice-free seaports on the eastern shore of the Baltic Sea is located in the western part of Lithuania. The Port of KlaipėdaPort of Klaipeda
The Port of Klaipėda is a seaport located in Klaipėda, Lithuania. It is one of the few ice-free ports in northernmost Europe, and the largest in Lithuania...
is a regional transport hub connecting the sea, land and railway routes from east and west. Compared to neighbouring Eastern Baltic seaports, the Port of Klaipėda has the widest shipping line network with other seaports. The Port of Klaipėda handles roughly 7,000 ships and 30 million tons of cargo every year, and accepts large-tonnage vessels: dry-cargo vessels up to 70,000 DWT, tankers up to 100,000 DWT and cruise ships up to 270 meters of length. The ice-free seaport of Klaipėda is able to receive Panamax
Panamax
Panamax and New Panamax are popular terms for the size limits for ships traveling through the Panama Canal. Formally, the limits and requirements are published by the Panama Canal Authority titled "Vessel Requirements"...
-type vessels. One of the fastest growing segments of sea transport is passenger traffic. Passenger traffic has increased fourfold since 2002.
Warehousing
There are more than 600,000 m2 of modern logistics and warehousing facilities in Lithuania. The biggest supply of new, modern warehousing facilities is in the capital city VilniusVilnius
Vilnius is the capital of Lithuania, and its largest city, with a population of 560,190 as of 2010. It is the seat of the Vilnius city municipality and of the Vilnius district municipality. It is also the capital of Vilnius County...
(after the completion of several new projects in the third quarter of 2009, the supply of modern warehousing premises has increased by nearly 12% in Vilnius and currently reaches 334,400 m2 of the rentable area). Kaunas
Kaunas
Kaunas is the second-largest city in Lithuania and has historically been a leading centre of Lithuanian economic, academic, and cultural life. Kaunas was the biggest city and the center of a powiat in Trakai Voivodeship of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania since 1413. During Russian Empire occupation...
is in the second place (around 200,000 m2), and Klaipėda
Klaipeda
Klaipėda is a city in Lithuania situated at the mouth of the Nemunas River where it flows into the Baltic Sea. It is the third largest city in Lithuania and the capital of Klaipėda County....
in the third (122,500 m2). Since the beginning of the year 2009, prices for warehousing premises have dropped by 20–25% in Vilnius, Kaunas and Klaipėda, and the current level of rents has reached the level of 2003. The costs for renting new warehouses in Vilnius, Kaunas and Klaipėda are similar and reach 2.6 to 4.9 LTL/m2 (0.75 to 1.42 EUR/m2), while the rents of old warehouses are 1.2 to 2.3 LTL/m2 (0.35 to 0.67 EUR/m2).
International trade
International tradeInternational trade
International trade is the exchange of capital, goods, and services across international borders or territories. In most countries, such trade represents a significant share of gross domestic product...
for such a small country as Lithuania is crucial. The ratio of foreign trade to GDP has always been at least 100%, and for the last several years exceeded it.
The EU is the biggest trade partner of Lithuania with a 58% of total imports and 64% of total exports during the first ten months of the year 2009. The Commonwealth of Independent States
Commonwealth of Independent States
The Commonwealth of Independent States is a regional organization whose participating countries are former Soviet Republics, formed during the breakup of the Soviet Union....
is the second economic union that Lithuania trades the most with, with a share of imports of 34% and a share of exports of 23% during the same period. The vast majority of commodities, including oil, gas and metals have to be imported, mainly from Russia. For this reason, Russia is the biggest import partner of Lithuania.
The import of mineral products has a significant share of 30%, as Lithuania has an oil refinery company owned by Polish concern PKN ORLEN, ORLEN Lietuva, with a refining capacity of 9 million tons a year. The revenues of the company were more than LTL 17 billion (EUR 4.9 billion) in 2008. Orlen Lietuva received 78% of its sales or LTL 13.7 billion (EUR 4 billion) from foreign markets in comparison with total export of Lithuania of LTL 55.5 billion (EUR 16.1 billion) in 2008.
Some sectors are directed mainly at export markets. Transport and logistics export 2/3 of their products and/or services; the biotechnology
Biotechnology
Biotechnology is a field of applied biology that involves the use of living organisms and bioprocesses in engineering, technology, medicine and other fields requiring bioproducts. Biotechnology also utilizes these products for manufacturing purpose...
industry exports 80%; plastics export 52%; laser
Laser
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of photons. The term "laser" originated as an acronym for Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation...
technologies export 86%; metal processing, machinery and electric equipment export 64%; furniture and wood processing
Wood processing
Wood processing is an engineering discipline comprising the production of forest products, such as pulp and paper, construction materials, and tall oil...
export 55%; textile and clothing export 76%; and the food industry exports 36%.
The total value of natural resource
Natural resource
Natural resources occur naturally within environments that exist relatively undisturbed by mankind, in a natural form. A natural resource is often characterized by amounts of biodiversity and geodiversity existent in various ecosystems....
s in Lithuania reaches LTL 58 billion (EUR 16.8 billion) or 50% of Lithuania's GDP in 2008. The most valuable natural resource in Lithuania is subterranean water, which constitutes more than a half of the total value of natural resources.
| Country | Import | Country | Export |
|---|---|---|---|
 EU EUEuropean Union The European Union is an economic and political union of 27 independent member states which are located primarily in Europe. The EU traces its origins from the European Coal and Steel Community and the European Economic Community , formed by six countries in 1958... |
56.5% |  EU EUEuropean Union The European Union is an economic and political union of 27 independent member states which are located primarily in Europe. The EU traces its origins from the European Coal and Steel Community and the European Economic Community , formed by six countries in 1958... |
60.9% |
 Russia Russia |
32.6% |  Russia Russia |
15.6% |
 Germany Germany |
10.5% |  Germany Germany |
9.8% |
 Poland Poland |
8.8% |  Latvia LatviaLatvia Latvia , officially the Republic of Latvia , is a country in the Baltic region of Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by Estonia , to the south by Lithuania , to the east by the Russian Federation , to the southeast by Belarus and shares maritime borders to the west with Sweden... |
9.3% |
 Latvia LatviaLatvia Latvia , officially the Republic of Latvia , is a country in the Baltic region of Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by Estonia , to the south by Lithuania , to the east by the Russian Federation , to the southeast by Belarus and shares maritime borders to the west with Sweden... |
6.3% |  Poland Poland |
7.7% |
 Netherlands Netherlands |
4.4% |  Netherlands Netherlands |
5.5% |
 Italy Italy |
3.3% |  Belarus BelarusBelarus Belarus , officially the Republic of Belarus, is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe, bordered clockwise by Russia to the northeast, Ukraine to the south, Poland to the west, and Lithuania and Latvia to the northwest. Its capital is Minsk; other major cities include Brest, Grodno , Gomel ,... |
5.2% |
 Sweden Sweden |
3.2% |  Estonia EstoniaEstonia Estonia , officially the Republic of Estonia , is a state in the Baltic region of Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland, to the west by the Baltic Sea, to the south by Latvia , and to the east by Lake Peipsi and the Russian Federation . Across the Baltic Sea lies... |
5.0% |
 Belgium Belgium |
3.2% |  United Kingdom United Kingdom |
4.9% |
 Estonia EstoniaEstonia Estonia , officially the Republic of Estonia , is a state in the Baltic region of Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland, to the west by the Baltic Sea, to the south by Latvia , and to the east by Lake Peipsi and the Russian Federation . Across the Baltic Sea lies... |
2.8% |  Ukraine UkraineUkraine Ukraine is a country in Eastern Europe. It has an area of 603,628 km², making it the second largest contiguous country on the European continent, after Russia... |
3.6% |
 France France |
2.5% |  Sweden Sweden |
3.6% |
| Combined Nomenclature | Export | Combined Nomenclature | Import |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mineral products | 21.6% | Mineral products | 29.7% |
| Machinery and mechanical appliances; electrical equipment | 9.8% | Machinery and mechanical appliances; electrical equipment | 12.6% |
| Products of the chemical industries | 9.3% | Products of the chemical industries | 12.4% |
| Prepared foodstuffs; beverages and tobacco | 7.1% | Vehicles and transport equipment | 6.4% |
| Plastics; rubber and articles thereof | 6.9% | Prepared foodstuffs; beverages and tobacco | 5.9% |
| Textiles and textile articles | 6.7% | Textiles and textile articles | 5.2% |
| Vehicles and transport equipment | 6.6% | Base metals and articles of base metal | 5.0% |
| Miscellaneous manufactured articles | 6.4% | Plastics; rubber and articles thereof | 4.6% |
| Vegetable products | 6.3% | Vegetable products | 4.3% |
| Live animals; animal products | 5.7% | Live animals; animal products | 3.6% |
See also
- Lithuania's Department of Statistics
- Public Organization "Invest Lithuania"
- Economy of EuropeEconomy of EuropeThe economy of Europe comprises more than 731 million people in 48 different states. Like other continents, the wealth of Europe's states varies, although the poorest are well above the poorest states of other continents in terms of GDP and living standards. The difference in wealth across...
- LithuaniaLithuaniaLithuania , officially the Republic of Lithuania is a country in Northern Europe, the biggest of the three Baltic states. It is situated along the southeastern shore of the Baltic Sea, whereby to the west lie Sweden and Denmark...

