
Lithuanian litas
Encyclopedia
The Lithuanian litas is the currency of Lithuania
. It is divided into 100 centų
(genitive case; singular centas, nominative plural centai). The litas was first introduced in 1922 after World War I
, when Lithuania declared independence and was reintroduced on June 25, 1993, following a period of currency exchange from the ruble
to the litas with the temporary talonas
then in place. The name was modeled after the name of the country (similarly to Latvia
and its lats
). From 1994 to 2002, the litas was pegged
to the U.S. dollar at the rate of 1 to 4. Currently the litas is pegged to the euro
at the rate of 3.4528 to 1. The euro was expected to replace the litas by January 1, 2010, but due to the current rate of inflation and the economic crisis, this date will be delayed for another four years until 1 January 2014.
and ostruble
, both of which had been issued by the occupying German
forces during World War I. The ostmark was known as the auksinas
in Lithuania.
The litas was established at a value of 10 litas = 1US dollar and was subdivided into 100 centų. In the face of world wide economic depression, the litas appeared to be quite a strong and stable currency, reflecting the negligible influence of the depression on the Lithuanian economy. One litas was covered by 0.150462 grams of gold stored by the Bank of Lithuania
in foreign countries. In March 1923, the circulation amounted to 39,412,984 litai, backed by 15,738,964 in actual gold and by 24,000,000 in high exchange securities. It was required that at least one third of the total circulation would be covered by gold and the rest by other assets. By 1938, 1 U.S. dollar was worth about 5.9 litai, falling to about 20 U.S. cents before its disappearance in 1941.
The litas was replaced by the Soviet ruble in April 1941 http://www.globalfinancialdata.com/index.php3?action=detailedinfo&id=3891 after Lithuania was annexed by the Soviet Union
, with 1 litas equal to 0.9 ruble, although the actual value of the litas was about 3-5 rubles. Such an exchange rate provided great profits for the military and party officials. Trying to protect the value of the currency, people started to massively buy which, together with a downfall in production (following nationalization
), caused material shortages. Withdrawals were then limited to 250 litų before the litas was completely abolished.

(1881-1944). The litas coins displayed Jonas Basanavičius
and Vytautas the Great
, which was replaced by a portrait of President Antanas Smetona
.
currency at a rate of 1 litas to 100 talonas.
The Bank of Lithuania was established on March 1, 1990. Ten days later Lithuania declared independence. At first the Lithuanian government negotiated in vain with François Charles Oberthur, a press located in France to print the banknotes. In November 1990 The Bank of Lithuania decided to work with the United States Banknote Corporation (now American Banknote Corporation
). In late fall, 1991 the first shipments of litas banknotes and coins arrived in Lithuania.
In November 1991, the Currency Issue Law was passed and the Litas Committee was created. It had the power to fix the date for the litas to come into circulation, the terms for the withdrawal from circulation of the ruble, the exchange rate of the litas and other conditions. Officials waited for a while for the economy to stabilize to not to expose the young litas to inflation. About 80% of Lithuania's trade was with Russia and the government needed to find a way to smooth the transition from the ruble zone. Also, Lithuania needed to gather funds to form a stabilization fund.
, for example, sold the reserves to the Soviets in 1967. However, in January 1992 it announced that this action was a “betrayal of the people of the Baltic states” and that it would return the originally deposited amount of gold, now worth about 90 million pound sterling
, to the three Baltic states
. Lithuania received 18.5 million pounds or 95,000 ounce
s of gold and remained a customer of the bank. Similarly, in March 1992 Lithuania reclaimed gold from the Bank of France
and later from the Bank of Sweden.
In October 1992, the International Monetary Fund
(Lithuania joined this organization on April 29, 1992) granted the first loan of 23.05 million U.S. dollars to create the stabilization fund. However, it is estimated that at the time of the introduction of the new currency, Lithuania managed to gather only $120 million for the stabilization fund. For a brief while it was kept a secret so as not to further damage the reputation and trust in of the litas.
journalists investigated the production of the litas and found that for a while it was purposely held back. For example, 6 million litas designated to pay for printing the banknotes stayed in a zero interest bearing account for a year in a bank in Sweden. By 1992, the litas was ready for introduction, but the banknotes were of extremely low quality (one could easily counterfeit
them with a simple color printer; especially the 10, 20, and 50 litų banknotes).
Newly elected President Algirdas Brazauskas
dismissed the Chair of the Bank of Lithuania, Vilius Baldišis, for incompetence just two months before the introduction of the litas. Baldišis was later charged for negligence
that cost Lithuania $3,000,000. Some claim that the Russian secret services were behind the affair. Baldišis’ explanation was that he was trying to cut the costs of printing the banknotes and thus did not order better security features. Also, “U.S. Banknote Corporation” was accused of violation of the contract terms.
But when the new issue of litas banknotes was redesigned, reprinted, and introduced in June 1993, it was found that the quality of the money was still too low and the banknotes would have to be redesigned further in the future. All these scandals and the small backup of gold reserve (about $120 million instead of $200 million) damaged the reputation of the litas. Thankfully, the newly appointed chair, Romualdas Visokavičius, moved things quickly and managed to win the trust of the public. Unfortunately, in October he was asked to resign mostly because of his involvement with a private bank "Litimpex."
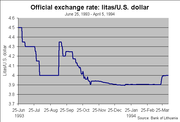 On June 25, 1993, the litas was finally introduced at the rate of 1 litas to 100 talonas
On June 25, 1993, the litas was finally introduced at the rate of 1 litas to 100 talonas
. 1 U.S. dollar was worth 4.5 litai and decreased to about 4.2 a couple of weeks later. Even the introduction of the litas was followed by a scandal. The government allowed the changing of unlimited amounts of talonas to the litas without having to show the source of the talonas. This allowed criminal groups to legalize their funds.
In July, circulation of the talonas was stopped and on August 1, 1993, the litas became the only legal tender. Following the reintroduction of the litas, there was an effort to weed out U.S. dollars from the market. The talonas was never really trusted by the people and the ruble was very unstable. Thus, people started using U.S. dollars as a stable currency. Another alternative was the German mark
, but it was not available in larger quantities. A lot of shops printed prices in several different currencies, including dollars, and the economy was very "dollarised" as it was legal to make trades in foreign currencies.
.jpg) Due to poor banknote quality (both talonas and early litas) it was easy to counterfeit them. Most shops were forced to acquire ultra violet lamps to check for forgeries. One group, for example, printed 500 talonas banknotes in Turkey. It is estimated that their notes totaled 140,000 litas.
Due to poor banknote quality (both talonas and early litas) it was easy to counterfeit them. Most shops were forced to acquire ultra violet lamps to check for forgeries. One group, for example, printed 500 talonas banknotes in Turkey. It is estimated that their notes totaled 140,000 litas.
From April 1, 1994 to February 1, 2002, the litas was pegged to the U.S. dollar at the rate of 4 to 1 (the litas was stable around 3.9 for half a year before the pegging). The main reasons for this fixation was little trust in the emerging monetary system, fear of high fluctuations in currency exchange rates, desire to attract foreign investors, and International Monetary Fund
recommendations. The peg was renewable every year. For a while a peg was considered to a basket of currencies: the European Currency Unit
. At around this time Lithuania also established a currency board
.
From April 1, 1994, the litas was fully backed by gold and other stable securities.
at a rate of 3.4528 to 1; this rate is not expected to change until the litas is completely replaced by the euro. After the peg, Lithuania became a member of the Eurozone
de facto
. Since 28 June 2004, the litas has been part of the ERM II
, the EU's exchange rate mechanism. The design of Lithuanian euro coins
is already prepared.
Lithuania has postponed its euro day several times, since the country does not meet the convergence criteria
. A recent analysis of SEB bankas says that Lithuania could not adopt the euro before 2013 due to the high rate of inflationwhich reached 11% in October 2008well above the Maastricht criterion of 4.2%.
designs showing the Coat of Arms
in the center and the name of the state "Lietuva" in capital letters.
The first coins were minted in the United Kingdom
and arrived in Lithuania on October 31, 1990. Currently, all coins are minted in the state-owned enterprise "Lithuanian Mint", which started its operations in September 1992 and helped to cut the costs of introducing the litas.
Lithuania
Lithuania , officially the Republic of Lithuania is a country in Northern Europe, the biggest of the three Baltic states. It is situated along the southeastern shore of the Baltic Sea, whereby to the west lie Sweden and Denmark...
. It is divided into 100 centų
Cent (currency)
In many national currencies, the cent is a monetary unit that equals 1⁄100 of the basic monetary unit. Etymologically, the word cent derives from the Latin word "centum" meaning hundred. Cent also refers to a coin which is worth one cent....
(genitive case; singular centas, nominative plural centai). The litas was first introduced in 1922 after World War I
World War I
World War I , which was predominantly called the World War or the Great War from its occurrence until 1939, and the First World War or World War I thereafter, was a major war centred in Europe that began on 28 July 1914 and lasted until 11 November 1918...
, when Lithuania declared independence and was reintroduced on June 25, 1993, following a period of currency exchange from the ruble
Soviet ruble
The Soviet ruble or rouble was the currency of the Soviet Union. One ruble is divided into 100 kopeks, ....
to the litas with the temporary talonas
Lithuanian talonas
The talonas was a temporary currency issued in Lithuania between 1991 and 1993. It replaced the Soviet ruble at par and was replaced by the litas at a rate of 100 talonas = 1 litas...
then in place. The name was modeled after the name of the country (similarly to Latvia
Latvia
Latvia , officially the Republic of Latvia , is a country in the Baltic region of Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by Estonia , to the south by Lithuania , to the east by the Russian Federation , to the southeast by Belarus and shares maritime borders to the west with Sweden...
and its lats
Latvian lats
The lats is the currency of Latvia. It is abbreviated as Ls. The lats is sub-divided into 100 santīmi ....
). From 1994 to 2002, the litas was pegged
Fixed exchange rate
A fixed exchange rate, sometimes called a pegged exchange rate, is a type of exchange rate regime wherein a currency's value is matched to the value of another single currency or to a basket of other currencies, or to another measure of value, such as gold.A fixed exchange rate is usually used to...
to the U.S. dollar at the rate of 1 to 4. Currently the litas is pegged to the euro
Euro
The euro is the official currency of the eurozone: 17 of the 27 member states of the European Union. It is also the currency used by the Institutions of the European Union. The eurozone consists of Austria, Belgium, Cyprus, Estonia, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Ireland, Italy, Luxembourg,...
at the rate of 3.4528 to 1. The euro was expected to replace the litas by January 1, 2010, but due to the current rate of inflation and the economic crisis, this date will be delayed for another four years until 1 January 2014.
History
The first litas was introduced on October 2, 1922, replacing the ostmarkGerman ostmark
Ostmark is the name given to a currency denominated in Mark which was issued by Germany in 1918 for use in a part of the eastern areas under German control at that time, the Ober Ost area. The currency consisted of paper money issued on 4 April 1918 by the ‘Darlehnskasse’ in Kowno and was equal to...
and ostruble
German ostruble
Ostruble is the name given to a currency denominated in kopeck and ruble, which was issued by Germany in 1916 for use in the eastern areas under German occupation . It was initially equal to the Russian ruble. The reason for the issue was a shortage of rubles...
, both of which had been issued by the occupying German
German Empire
The German Empire refers to Germany during the "Second Reich" period from the unification of Germany and proclamation of Wilhelm I as German Emperor on 18 January 1871, to 1918, when it became a federal republic after defeat in World War I and the abdication of the Emperor, Wilhelm II.The German...
forces during World War I. The ostmark was known as the auksinas
Lithuanian auksinas
-First Auksinas:The auksinas was the currency of Lithuania in the 17th century. It was a silver coin, sub-divided into 30 grašis, with 3 auksinas = 1 taleris...
in Lithuania.
The litas was established at a value of 10 litas = 1US dollar and was subdivided into 100 centų. In the face of world wide economic depression, the litas appeared to be quite a strong and stable currency, reflecting the negligible influence of the depression on the Lithuanian economy. One litas was covered by 0.150462 grams of gold stored by the Bank of Lithuania
Bank of Lithuania
The Bank of Lithuania is the central bank of the Republic of Lithuania. The Bank of Lithuania is a non-Eurozone member of the European System of Central Banks...
in foreign countries. In March 1923, the circulation amounted to 39,412,984 litai, backed by 15,738,964 in actual gold and by 24,000,000 in high exchange securities. It was required that at least one third of the total circulation would be covered by gold and the rest by other assets. By 1938, 1 U.S. dollar was worth about 5.9 litai, falling to about 20 U.S. cents before its disappearance in 1941.
The litas was replaced by the Soviet ruble in April 1941 http://www.globalfinancialdata.com/index.php3?action=detailedinfo&id=3891 after Lithuania was annexed by the Soviet Union
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union , officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics , was a constitutionally socialist state that existed in Eurasia between 1922 and 1991....
, with 1 litas equal to 0.9 ruble, although the actual value of the litas was about 3-5 rubles. Such an exchange rate provided great profits for the military and party officials. Trying to protect the value of the currency, people started to massively buy which, together with a downfall in production (following nationalization
Nationalization
Nationalisation, also spelled nationalization, is the process of taking an industry or assets into government ownership by a national government or state. Nationalization usually refers to private assets, but may also mean assets owned by lower levels of government, such as municipalities, being...
), caused material shortages. Withdrawals were then limited to 250 litų before the litas was completely abolished.

Coins
Coins were introduced in 1925 in denominations of 1, 2, 5, 10, 20 and 50 centų, 1, 2 and 5 litai, with the litas coins in silver. 10 litų coins were introduced in 1936. All these coins were designed by the sculptor Juozas ZikarasJuozas Zikaras
Juozas Zikaras was a Lithuanian sculptor and artist, who created the design for pre-war Lithuanian litas coins. He is considered to be one of the first professional Lithuanian sculptors.-Biography:...
(1881-1944). The litas coins displayed Jonas Basanavičius
Jonas Basanavicius
Jonas Basanavičius was an activist and proponent of Lithuania's National Revival and founder of the first Lithuanian language newspaper Aušra. He was one of the initiators and the Chairman of the Organizing Committee of the 1905 Congress of Lithuanians, the Great Seimas of Vilnius...
and Vytautas the Great
Vytautas the Great
Vytautas ; styled "the Great" from the 15th century onwards; c. 1350 October 27, 1430) was one of the most famous rulers of medieval Lithuania. Vytautas was the ruler of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania which chiefly encompassed the Lithuanians and Ruthenians...
, which was replaced by a portrait of President Antanas Smetona
Antanas Smetona
Antanas Smetona was one of the most important Lithuanian political figures between World War I and World War II. He served as the first President of Lithuania from April 4, 1919 to June 19, 1920. He again served as the last President of the country from December 19, 1926 to June 15, 1940, before...
.
Banknotes
In 1922, the Bank of Lithuania issued notes in denominations of 1, 2, 5, 10, 20 and 50 centai, 1, 2, 5, 10, 50 and 100 litų. In 1924, 500 and 1000 litų notes were added. Denominations below 5 litai were replaced by coins in 1925.Second litas, 1993-
The litas became Lithuania's currency once more on June 25, 1993, when it replaced the temporary talonasLithuanian talonas
The talonas was a temporary currency issued in Lithuania between 1991 and 1993. It replaced the Soviet ruble at par and was replaced by the litas at a rate of 100 talonas = 1 litas...
currency at a rate of 1 litas to 100 talonas.
Preparatory work
Officials started to prepare for the introduction of the litas even before independence was declared, it was thought to introduce the litas alongside the ruble even if Lithuania remained a part of the Soviet Union. In December 1989, artists were asked to submit sketches of possible coin and banknote designs. Also, a list of famous people was compiled in order to determine who should be featured.The Bank of Lithuania was established on March 1, 1990. Ten days later Lithuania declared independence. At first the Lithuanian government negotiated in vain with François Charles Oberthur, a press located in France to print the banknotes. In November 1990 The Bank of Lithuania decided to work with the United States Banknote Corporation (now American Banknote Corporation
American Bank Note Company
The American Bank Note Company was a major worldwide engraver of national currency and postage stamps. Currently it engraves and prints stock and bond certificates.-History:Robert Scot, the first official engraver of the young U.S...
). In late fall, 1991 the first shipments of litas banknotes and coins arrived in Lithuania.
In November 1991, the Currency Issue Law was passed and the Litas Committee was created. It had the power to fix the date for the litas to come into circulation, the terms for the withdrawal from circulation of the ruble, the exchange rate of the litas and other conditions. Officials waited for a while for the economy to stabilize to not to expose the young litas to inflation. About 80% of Lithuania's trade was with Russia and the government needed to find a way to smooth the transition from the ruble zone. Also, Lithuania needed to gather funds to form a stabilization fund.
Gathering funds
At first, Lithuania did not have gold or any other securities to back up the litas. Lithuania needed to find about 200 million U.S. dollars to form the stabilization fund. First, it sought to recover its pre-war gold reserves (about 10 tons) from France, United Kingdom, Switzerland, etc. In the interwar period Lithuania stored its gold reserve in foreign banks. After the occupation in 1940 those reserves were “nobody’s”: there was no Lithuania and most western countries condemned the occupation as illegal and did not recognize the Soviet Union as a successor. The Bank of EnglandBank of England
The Bank of England is the central bank of the United Kingdom and the model on which most modern central banks have been based. Established in 1694, it is the second oldest central bank in the world...
, for example, sold the reserves to the Soviets in 1967. However, in January 1992 it announced that this action was a “betrayal of the people of the Baltic states” and that it would return the originally deposited amount of gold, now worth about 90 million pound sterling
Pound sterling
The pound sterling , commonly called the pound, is the official currency of the United Kingdom, its Crown Dependencies and the British Overseas Territories of South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands, British Antarctic Territory and Tristan da Cunha. It is subdivided into 100 pence...
, to the three Baltic states
Baltic states
The term Baltic states refers to the Baltic territories which gained independence from the Russian Empire in the wake of World War I: primarily the contiguous trio of Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania ; Finland also fell within the scope of the term after initially gaining independence in the 1920s.The...
. Lithuania received 18.5 million pounds or 95,000 ounce
Ounce
The ounce is a unit of mass with several definitions, the most commonly used of which are equal to approximately 28 grams. The ounce is used in a number of different systems, including various systems of mass that form part of the imperial and United States customary systems...
s of gold and remained a customer of the bank. Similarly, in March 1992 Lithuania reclaimed gold from the Bank of France
Banque de France
The Banque de France is the central bank of France; it is linked to the European Central Bank . Its main charge is to implement the interest rate policy of the European System of Central Banks...
and later from the Bank of Sweden.
In October 1992, the International Monetary Fund
International Monetary Fund
The International Monetary Fund is an organization of 187 countries, working to foster global monetary cooperation, secure financial stability, facilitate international trade, promote high employment and sustainable economic growth, and reduce poverty around the world...
(Lithuania joined this organization on April 29, 1992) granted the first loan of 23.05 million U.S. dollars to create the stabilization fund. However, it is estimated that at the time of the introduction of the new currency, Lithuania managed to gather only $120 million for the stabilization fund. For a brief while it was kept a secret so as not to further damage the reputation and trust in of the litas.
Delayed introduction of the litas
Lietuvos RytasLietuvos Rytas
Lietuvos rytas is a Lithuanian daily newspaper, printed in Vilnius and a TV company. Lietuvos rytas sponsors basketball team BC Lietuvos Rytas and the annual Vilnius Marathon.-External links:*...
journalists investigated the production of the litas and found that for a while it was purposely held back. For example, 6 million litas designated to pay for printing the banknotes stayed in a zero interest bearing account for a year in a bank in Sweden. By 1992, the litas was ready for introduction, but the banknotes were of extremely low quality (one could easily counterfeit
Counterfeit
To counterfeit means to illegally imitate something. Counterfeit products are often produced with the intent to take advantage of the superior value of the imitated product...
them with a simple color printer; especially the 10, 20, and 50 litų banknotes).
Newly elected President Algirdas Brazauskas
Algirdas Brazauskas
Algirdas Mykolas Brazauskas was the first President of a newly independent post-Soviet Union Lithuania from 1993 to 1998 and Prime Minister from 2001 to 2006....
dismissed the Chair of the Bank of Lithuania, Vilius Baldišis, for incompetence just two months before the introduction of the litas. Baldišis was later charged for negligence
Negligence
Negligence is a failure to exercise the care that a reasonably prudent person would exercise in like circumstances. The area of tort law known as negligence involves harm caused by carelessness, not intentional harm.According to Jay M...
that cost Lithuania $3,000,000. Some claim that the Russian secret services were behind the affair. Baldišis’ explanation was that he was trying to cut the costs of printing the banknotes and thus did not order better security features. Also, “U.S. Banknote Corporation” was accused of violation of the contract terms.
But when the new issue of litas banknotes was redesigned, reprinted, and introduced in June 1993, it was found that the quality of the money was still too low and the banknotes would have to be redesigned further in the future. All these scandals and the small backup of gold reserve (about $120 million instead of $200 million) damaged the reputation of the litas. Thankfully, the newly appointed chair, Romualdas Visokavičius, moved things quickly and managed to win the trust of the public. Unfortunately, in October he was asked to resign mostly because of his involvement with a private bank "Litimpex."
Introduction of the litas

Lithuanian talonas
The talonas was a temporary currency issued in Lithuania between 1991 and 1993. It replaced the Soviet ruble at par and was replaced by the litas at a rate of 100 talonas = 1 litas...
. 1 U.S. dollar was worth 4.5 litai and decreased to about 4.2 a couple of weeks later. Even the introduction of the litas was followed by a scandal. The government allowed the changing of unlimited amounts of talonas to the litas without having to show the source of the talonas. This allowed criminal groups to legalize their funds.
In July, circulation of the talonas was stopped and on August 1, 1993, the litas became the only legal tender. Following the reintroduction of the litas, there was an effort to weed out U.S. dollars from the market. The talonas was never really trusted by the people and the ruble was very unstable. Thus, people started using U.S. dollars as a stable currency. Another alternative was the German mark
German mark
The Deutsche Mark |mark]], abbreviated "DM") was the official currency of West Germany and Germany until the adoption of the euro in 2002. It is commonly called the "Deutschmark" in English but not in German. Germans often say "Mark" or "D-Mark"...
, but it was not available in larger quantities. A lot of shops printed prices in several different currencies, including dollars, and the economy was very "dollarised" as it was legal to make trades in foreign currencies.
.jpg)
From April 1, 1994 to February 1, 2002, the litas was pegged to the U.S. dollar at the rate of 4 to 1 (the litas was stable around 3.9 for half a year before the pegging). The main reasons for this fixation was little trust in the emerging monetary system, fear of high fluctuations in currency exchange rates, desire to attract foreign investors, and International Monetary Fund
International Monetary Fund
The International Monetary Fund is an organization of 187 countries, working to foster global monetary cooperation, secure financial stability, facilitate international trade, promote high employment and sustainable economic growth, and reduce poverty around the world...
recommendations. The peg was renewable every year. For a while a peg was considered to a basket of currencies: the European Currency Unit
European Currency Unit
The European Currency Unit was a basket of the currencies of the European Community member states, used as the unit of account of the European Community before being replaced by the euro on 1 January 1999, at parity. The ECU itself replaced the European Unit of Account, also at parity, on 13...
. At around this time Lithuania also established a currency board
Currency board
A currency board is a monetary authority which is required to maintain a fixed exchange rate with a foreign currency. This policy objective requires the conventional objectives of a central bank to be subordinated to the exchange rate target....
.
From April 1, 1994, the litas was fully backed by gold and other stable securities.
The litas and the euro
On 2 February 2002 the litas was pegged to the euroEuro
The euro is the official currency of the eurozone: 17 of the 27 member states of the European Union. It is also the currency used by the Institutions of the European Union. The eurozone consists of Austria, Belgium, Cyprus, Estonia, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Ireland, Italy, Luxembourg,...
at a rate of 3.4528 to 1; this rate is not expected to change until the litas is completely replaced by the euro. After the peg, Lithuania became a member of the Eurozone
Eurozone
The eurozone , officially called the euro area, is an economic and monetary union of seventeen European Union member states that have adopted the euro as their common currency and sole legal tender...
de facto
De facto
De facto is a Latin expression that means "concerning fact." In law, it often means "in practice but not necessarily ordained by law" or "in practice or actuality, but not officially established." It is commonly used in contrast to de jure when referring to matters of law, governance, or...
. Since 28 June 2004, the litas has been part of the ERM II
European Exchange Rate Mechanism
The European Exchange Rate Mechanism, ERM, was a system introduced by the European Community in March 1979, as part of the European Monetary System , to reduce exchange rate variability and achieve monetary stability in Europe, in preparation for Economic and Monetary Union and the introduction of...
, the EU's exchange rate mechanism. The design of Lithuanian euro coins
Lithuanian euro coins
Lithuanian euro coins share a similar national side for all eight coins, and are expected to be issued from 2013 on. The difference between the coins are that one and two euro coins have vertical lines on the outer circle, the fifty, twenty and ten cent coins have horizontal lines on the outer...
is already prepared.
Lithuania has postponed its euro day several times, since the country does not meet the convergence criteria
Convergence criteria
The euro convergence criteria are the criteria for European Union member states to enter the third stage of European Economic and Monetary Union and adopt the euro as their currency...
. A recent analysis of SEB bankas says that Lithuania could not adopt the euro before 2013 due to the high rate of inflationwhich reached 11% in October 2008well above the Maastricht criterion of 4.2%.
Coins
In 1993, coins were introduced (dated 1991) in denominations of 1, 2, 5, 10, 20 and 50 centų, 1, 2 and 5 litai. The 1, 2 and 5 centai pieces were minted in aluminium, the 10, 20 and 50 centų in bronze and the litas coins were of cupro-nickel. In 1997, nickel-brass 10, 20 and 50 centų coins were introduced, followed by cupro-nickel 1 litas and bimetallic 2 and 5 litai in 1998. All have the obverseObverse and reverse
Obverse and its opposite, reverse, refer to the two flat faces of coins and some other two-sided objects, including paper money, flags , seals, medals, drawings, old master prints and other works of art, and printed fabrics. In this usage, obverse means the front face of the object and reverse...
designs showing the Coat of Arms
Coat of arms of Lithuania
The coat of arms of Lithuania, consisting of an armor-clad knight on horseback holding an olden sword and shield, is also known as Vytis . The Lithuanian coat of arms is one of the oldest national coats of arms in Europe...
in the center and the name of the state "Lietuva" in capital letters.
The first coins were minted in the United Kingdom
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
and arrived in Lithuania on October 31, 1990. Currently, all coins are minted in the state-owned enterprise "Lithuanian Mint", which started its operations in September 1992 and helped to cut the costs of introducing the litas.
Banknotes
In 1993, banknotes (dated 1991) were issued in denominations of 10, 20, 50, 100, 200 and 500 litų. Due to poor designs, these were found to be easily copied and a second series of notes was swiftly introduced in denominations of 1, 2, 5, 10, 20 and 50 litų, with only the 100 litų notes of the first series remaining in circulation. 200 litų notes were introduced in 1997, followed by 500 litų in 2000.See also
- Lithuanian euro coinsLithuanian euro coinsLithuanian euro coins share a similar national side for all eight coins, and are expected to be issued from 2013 on. The difference between the coins are that one and two euro coins have vertical lines on the outer circle, the fifty, twenty and ten cent coins have horizontal lines on the outer...
- Lithuanian grammar: Noun modification by numeral — usage of forms litas, litai, litų
- Economy of LithuaniaEconomy of LithuaniaLithuania is a member of the European Union and the biggest economy among three Baltic states. GDP per capita reached USD 17,800 in 2008 and was higher than the ones of all its neighbors – Latvia, Poland, Russia and Belarus....
Further reading
- Documentaries directed by Rimtautas Šilinis "Iš lito istorijos: Banknotai" (From History of the Litas: Banknotes (2004)) and "Iš lito istorijos: Monetos" (From History of the Litas: Coins (2002))
- Bronė Vainauskienė, "Skandalingoji lito istorija" (Scandalous History of Litas (2003)) - collection of articles by Lietuvos RytasLietuvos RytasLietuvos rytas is a Lithuanian daily newspaper, printed in Vilnius and a TV company. Lietuvos rytas sponsors basketball team BC Lietuvos Rytas and the annual Vilnius Marathon.-External links:*...
journalist who spend 6 years investigating the history of the litas in the early years of independence. ISBN 9986-448-12-3

