
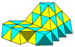
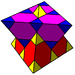
Convex uniform honeycomb
Encyclopedia
Geometry
Geometry arose as the field of knowledge dealing with spatial relationships. Geometry was one of the two fields of pre-modern mathematics, the other being the study of numbers ....
, a convex uniform honeycomb is a uniform
Uniform polytope
A uniform polytope is a vertex-transitive polytope made from uniform polytope facets of a lower dimension. Uniform polytopes of 2 dimensions are the regular polygons....
tessellation
Tessellation
A tessellation or tiling of the plane is a pattern of plane figures that fills the plane with no overlaps and no gaps. One may also speak of tessellations of parts of the plane or of other surfaces. Generalizations to higher dimensions are also possible. Tessellations frequently appeared in the art...
which fills three-dimensional Euclidean space
Euclidean space
In mathematics, Euclidean space is the Euclidean plane and three-dimensional space of Euclidean geometry, as well as the generalizations of these notions to higher dimensions...
with non-overlapping convex uniform polyhedral
Uniform polyhedron
A uniform polyhedron is a polyhedron which has regular polygons as faces and is vertex-transitive...
cells.
Twenty-eight such honeycombs exist:
- the familiar cubic honeycombCubic honeycombThe cubic honeycomb is the only regular space-filling tessellation in Euclidean 3-space, made up of cubic cells. It has 4 cubes around every edge, and 8 cubes around each vertex. Its vertex figure is a regular octahedron....
and 7 truncations thereof; - the alternated cubic honeycomb and 4 truncations thereof;
- 10 prismatic forms based on the uniform plane tilings (11 if including the cubic honeycomb);
- 5 modifications of some of the above by elongation and/or gyration.
They can be considered the three-dimensional analogue to the uniform tilings of the plane.
History
- 1900: Thorold GossetThorold GossetThorold Gosset was an English lawyer and an amateur mathematician. In mathematics, he is noted for discovering and classifying the semiregular polytopes in dimensions four and higher.According to H. S. M...
enumerated the list of semiregular convex polytopes with regular cells (Platonic solidPlatonic solidIn geometry, a Platonic solid is a convex polyhedron that is regular, in the sense of a regular polygon. Specifically, the faces of a Platonic solid are congruent regular polygons, with the same number of faces meeting at each vertex; thus, all its edges are congruent, as are its vertices and...
s) in his publication On the Regular and Semi-Regular Figures in Space of n Dimensions, including one regular cubic honeycomb, and two semiregular forms with tetrahedra and octahedra. - 1905: Alfredo AndreiniAlfredo AndreiniAlfredo Andreini was an Italian physician and entomologist.He carried out a large collection of insects collected in particular from Cape Verde and in Libya and Eritrea...
enumerated 25 of these tessellations. - 1991: Norman Johnson's manuscript Uniform Polytopes identified the complete list of 28.
- 1994: Branko GrünbaumBranko GrünbaumBranko Grünbaum is a Croatian-born mathematician and a professor emeritus at the University of Washington in Seattle. He received his Ph.D. in 1957 from Hebrew University of Jerusalem in Israel....
, in his paper Uniform tilings of 3-space, also independently enumerated all 28, after discovering errors in Andreini's publication. He found the 1905 paper, which listed 25, had 1 wrong, and 4 being missing. Grünbaum states in this paper that Norman Johnson deserves priority for achieving the same enumeration in 1991. He also mentions that I. Alexeyev of Russia had contacted him regarding a putative enumeration of these forms, but that Grünbaum was unable to verify this at the time. - 2006: George OlshevskyGeorge OlshevskyGeorge Olshevsky is a freelance editor, writer, publisher, amateur paleontologist, and mathematician living in San Diego, California.Olshevsky maintains the comprehensive online Dinosaur Genera List...
, in his manuscript Uniform Panoploid Tetracombs, along with repeating the derived list of 11 convex uniform tilings, and 28 convex uniform honeycombs, expands a further derived list of 143 convex uniform tetracombs (Honeycombs of uniform polychoronUniform polychoronIn geometry, a uniform polychoron is a polychoron or 4-polytope which is vertex-transitive and whose cells are uniform polyhedra....
s in 4-space).
Only 14 of the convex uniform polyhedra appear in these patterns:
- three of the five Platonic solidPlatonic solidIn geometry, a Platonic solid is a convex polyhedron that is regular, in the sense of a regular polygon. Specifically, the faces of a Platonic solid are congruent regular polygons, with the same number of faces meeting at each vertex; thus, all its edges are congruent, as are its vertices and...
s, - six of the thirteen Archimedean solidArchimedean solidIn geometry an Archimedean solid is a highly symmetric, semi-regular convex polyhedron composed of two or more types of regular polygons meeting in identical vertices...
s, and - five of the infinite family of prismPrism (geometry)In geometry, a prism is a polyhedron with an n-sided polygonal base, a translated copy , and n other faces joining corresponding sides of the two bases. All cross-sections parallel to the base faces are the same. Prisms are named for their base, so a prism with a pentagonal base is called a...
s.
Names
This set can be called the regular and semiregular honeycombs. It has been called the Archimedean honeycombs by analogy with the convex uniform (non-regular) polyhedra, commonly called Archimedean solidArchimedean solid
In geometry an Archimedean solid is a highly symmetric, semi-regular convex polyhedron composed of two or more types of regular polygons meeting in identical vertices...
s. Recently Conway
John Horton Conway
John Horton Conway is a prolific mathematician active in the theory of finite groups, knot theory, number theory, combinatorial game theory and coding theory...
has suggested naming the set as the Architectonic tessellations and the dual honeycombs as the Catoptric tessellations.
The individual honeycombs are listed with names given to them by Norman Johnson. (Some of the terms used below are defined in Uniform polychoron#Geometric derivations.)
For cross-referencing, they are given with list indices from [A]ndreini (1-22), [W]illiams(1-2,9-19), [J]ohnson (11-19, 21-25, 31-34, 41-49, 51-52, 61-65), and [G]runbaum(1-28).
Compact Euclidean uniform tessellations (by their infinite Coxeter group families)
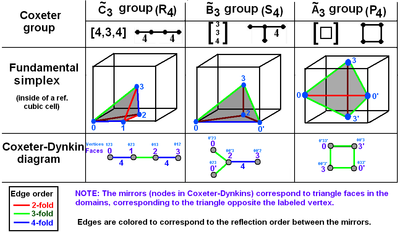
Coxeter group
In mathematics, a Coxeter group, named after H.S.M. Coxeter, is an abstract group that admits a formal description in terms of mirror symmetries. Indeed, the finite Coxeter groups are precisely the finite Euclidean reflection groups; the symmetry groups of regular polyhedra are an example...
s for 3-space are:
- The
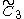 , [4,3,4], cubic, (8 unique forms plus one alternation)
, [4,3,4], cubic, (8 unique forms plus one alternation) - The
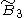 , [4,31,1], alternated cubic, (11 forms, 3 new)
, [4,31,1], alternated cubic, (11 forms, 3 new) - The
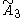 cyclic group, [(3,3,3,3)], (5 forms, one new)
cyclic group, [(3,3,3,3)], (5 forms, one new)
In addition there are 5 special honeycombs which don't have pure reflectional symmetry and are constructed from reflectional forms with elongation and gyration operations.
The total unique honeycombs above are 18.
The prismatic stacks from infinite Coxeter groups for 3-space are:
- The
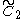 x
x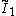 , [4,4]x[∞] prismatic group, (2 new forms)
, [4,4]x[∞] prismatic group, (2 new forms) - The
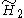 x
x , [6,3]x[∞] prismatic group, (7 unique forms)
, [6,3]x[∞] prismatic group, (7 unique forms) - The
 x
x , (3 3 3)x[∞] prismatic group, (No new forms)
, (3 3 3)x[∞] prismatic group, (No new forms) - The
 x
x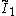 x
x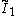 , [∞]x[∞]x[∞] prismatic group, (These all become a cubic honeycomb)
, [∞]x[∞]x[∞] prismatic group, (These all become a cubic honeycomb)
In addition there is one special elongated form of the triangular prismatic honeycomb.
The total unique prismatic honeycombs above (excluding the cubic counted previously) are 10.
Combining these counts, 18 and 10 gives us the total 28 uniform honeycombs.
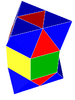
The C~3, [4,3,4] group (cubic)
The regular cubic honeycomb, represented by Schläfli symbol {4,3,4}, offers seven unique derived uniform honeycombs via truncation operations. (One redundant form, the runcinated cubic honeycomb, is included for completeness though identical to the cubic honeycomb.)| Reference Indices |
Honeycomb name Coxeter-Dynkin Coxeter-Dynkin diagram In geometry, a Coxeter–Dynkin diagram is a graph with numerically labeled edges representing the spatial relations between a collection of mirrors... and Schläfli symbols |
Cell counts/vertex and positions in cubic honeycomb |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Solids (Partial) |
Frames (Perspective) |
Vertex figure Vertex figure In geometry a vertex figure is, broadly speaking, the figure exposed when a corner of a polyhedron or polytope is sliced off.-Definitions - theme and variations:... |
||||||
| J11,15 A1 W1 G22 |
cubic Cubic honeycomb The cubic honeycomb is the only regular space-filling tessellation in Euclidean 3-space, made up of cubic cells. It has 4 cubes around every edge, and 8 cubes around each vertex. Its vertex figure is a regular octahedron.... t0{4,3,4} |
(8) (4.4.4) Cube In geometry, a cube is a three-dimensional solid object bounded by six square faces, facets or sides, with three meeting at each vertex. The cube can also be called a regular hexahedron and is one of the five Platonic solids. It is a special kind of square prism, of rectangular parallelepiped and... |
 |
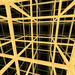 |
 octahedron Octahedron In geometry, an octahedron is a polyhedron with eight faces. A regular octahedron is a Platonic solid composed of eight equilateral triangles, four of which meet at each vertex.... |
|||
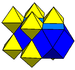
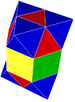
| J12,32 A15 W14 G7 |
rectified cubic Rectified cubic honeycomb The rectified cubic honeycomb is a uniform space-filling tessellation in Euclidean 3-space. It is composed of octahedra and cuboctahedra in a ratio of 1:1.- Symmetry :... t1{4,3,4} |
(2) (3.3.3.3) Octahedron In geometry, an octahedron is a polyhedron with eight faces. A regular octahedron is a Platonic solid composed of eight equilateral triangles, four of which meet at each vertex.... |
(4) (3.4.3.4) Cuboctahedron In geometry, a cuboctahedron is a polyhedron with eight triangular faces and six square faces. A cuboctahedron has 12 identical vertices, with two triangles and two squares meeting at each, and 24 identical edges, each separating a triangle from a square. As such it is a quasiregular polyhedron,... |
 |
 |
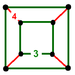 cuboid Cuboid In geometry, a cuboid is a solid figure bounded by six faces, forming a convex polyhedron. There are two competing definitions of a cuboid in mathematical literature... |
||
| J13 A14 W15 G8 |
truncated cubic Truncated cubic honeycomb The truncated cubic honeycomb is a uniform space-filling tessellation in Euclidean 3-space. It is composed of truncated cubes and octahedra in a ratio of 1:1.- Symmetry :... t0,1{4,3,4} |
(1) (3.3.3.3) Octahedron In geometry, an octahedron is a polyhedron with eight faces. A regular octahedron is a Platonic solid composed of eight equilateral triangles, four of which meet at each vertex.... |
(4)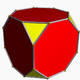 (3.8.8) Truncated cube In geometry, the truncated cube, or truncated hexahedron, is an Archimedean solid. It has 14 regular faces , 36 edges, and 24 vertices.... |
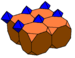 |
 |
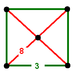 square pyramid Square pyramid In geometry, a square pyramid is a pyramid having a square base. If the apex is perpendicularly above the center of the square, it will have C4v symmetry.- Johnson solid :... |
||
| J14 A17 W12 G9 |
cantellated cubic Cantellated cubic honeycomb The cantellated cubic honeycomb is a uniform space-filling tessellation in Euclidean 3-space. It is composed of small rhombicuboctahedra, cuboctahedra, and cubes in a ratio of 1:1:3.- References :... t0,2{4,3,4} |
(1) (3.4.3.4) Cuboctahedron In geometry, a cuboctahedron is a polyhedron with eight triangular faces and six square faces. A cuboctahedron has 12 identical vertices, with two triangles and two squares meeting at each, and 24 identical edges, each separating a triangle from a square. As such it is a quasiregular polyhedron,... |
(2) (4.4.4) Cube In geometry, a cube is a three-dimensional solid object bounded by six square faces, facets or sides, with three meeting at each vertex. The cube can also be called a regular hexahedron and is one of the five Platonic solids. It is a special kind of square prism, of rectangular parallelepiped and... |
(2) (3.4.4.4) Rhombicuboctahedron In geometry, the rhombicuboctahedron, or small rhombicuboctahedron, is an Archimedean solid with eight triangular and eighteen square faces. There are 24 identical vertices, with one triangle and three squares meeting at each. Note that six of the squares only share vertices with the triangles... |
 |
 |
 obilique triangular prism Triangular prism In geometry, a triangular prism is a three-sided prism; it is a polyhedron made of a triangular base, a translated copy, and 3 faces joining corresponding sides.... |
|
| J11,15 | runcinated cubic (same as regular cubic Cubic honeycomb The cubic honeycomb is the only regular space-filling tessellation in Euclidean 3-space, made up of cubic cells. It has 4 cubes around every edge, and 8 cubes around each vertex. Its vertex figure is a regular octahedron.... ) t0,3{4,3,4} |
(1) (4.4.4) Cube In geometry, a cube is a three-dimensional solid object bounded by six square faces, facets or sides, with three meeting at each vertex. The cube can also be called a regular hexahedron and is one of the five Platonic solids. It is a special kind of square prism, of rectangular parallelepiped and... |
(3) (4.4.4) Cube In geometry, a cube is a three-dimensional solid object bounded by six square faces, facets or sides, with three meeting at each vertex. The cube can also be called a regular hexahedron and is one of the five Platonic solids. It is a special kind of square prism, of rectangular parallelepiped and... |
(3) (4.4.4) Cube In geometry, a cube is a three-dimensional solid object bounded by six square faces, facets or sides, with three meeting at each vertex. The cube can also be called a regular hexahedron and is one of the five Platonic solids. It is a special kind of square prism, of rectangular parallelepiped and... |
(1) (4.4.4) Cube In geometry, a cube is a three-dimensional solid object bounded by six square faces, facets or sides, with three meeting at each vertex. The cube can also be called a regular hexahedron and is one of the five Platonic solids. It is a special kind of square prism, of rectangular parallelepiped and... |
 |
 |
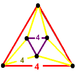 octahedron Octahedron In geometry, an octahedron is a polyhedron with eight faces. A regular octahedron is a Platonic solid composed of eight equilateral triangles, four of which meet at each vertex.... |
| J16 A3 W2 G28 |
bitruncated cubic Bitruncated cubic honeycomb The bitruncated cubic honeycomb is a space-filling tessellation in Euclidean 3-space made up of truncated octahedra.It is one of 28 uniform honeycombs. It has 4 truncated octahedra around each vertex.... t1,2{4,3,4} |
(2) (4.6.6) Truncated octahedron In geometry, the truncated octahedron is an Archimedean solid. It has 14 faces , 36 edges, and 24 vertices. Since each of its faces has point symmetry the truncated octahedron is a zonohedron.... |
(2) (4.6.6) Truncated octahedron In geometry, the truncated octahedron is an Archimedean solid. It has 14 faces , 36 edges, and 24 vertices. Since each of its faces has point symmetry the truncated octahedron is a zonohedron.... |
 |
 |
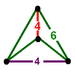 (disphenoid tetrahedron) |
||
| J17 A18 W13 G25 |
cantitruncated cubic Cantitruncated cubic honeycomb The cantitruncated cubic honeycomb is a uniform space-filling tessellation in Euclidean 3-space, made up of truncated cuboctahedra, truncated octahedra, and cubes in a ratio of 1:1:3.- Uniform colorings :... t0,1,2{4,3,4} |
(1) (4.6.6) Truncated octahedron In geometry, the truncated octahedron is an Archimedean solid. It has 14 faces , 36 edges, and 24 vertices. Since each of its faces has point symmetry the truncated octahedron is a zonohedron.... |
(1) (4.4.4) Cube In geometry, a cube is a three-dimensional solid object bounded by six square faces, facets or sides, with three meeting at each vertex. The cube can also be called a regular hexahedron and is one of the five Platonic solids. It is a special kind of square prism, of rectangular parallelepiped and... |
(2)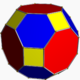 (4.6.8) Truncated cuboctahedron In geometry, the truncated cuboctahedron is an Archimedean solid. It has 12 square faces, 8 regular hexagonal faces, 6 regular octagonal faces, 48 vertices and 72 edges... |
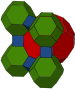 |
 |
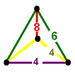 irregular tetrahedron Tetrahedron In geometry, a tetrahedron is a polyhedron composed of four triangular faces, three of which meet at each vertex. A regular tetrahedron is one in which the four triangles are regular, or "equilateral", and is one of the Platonic solids... |
|
| J18 A19 W19 G20 |
runcitruncated cubic Runcitruncated cubic honeycomb The runcitruncated cubic honeycomb is a uniform space-filling tessellation in Euclidean 3-space. It is composed of small rhombicuboctahedra, truncated cubes, octagonal prisms, and cubes in a ratio of 1:1:3:3.... t0,1,3{4,3,4} |
(1) (3.4.4.4) Rhombicuboctahedron In geometry, the rhombicuboctahedron, or small rhombicuboctahedron, is an Archimedean solid with eight triangular and eighteen square faces. There are 24 identical vertices, with one triangle and three squares meeting at each. Note that six of the squares only share vertices with the triangles... |
(1) (4.4.4) Cube In geometry, a cube is a three-dimensional solid object bounded by six square faces, facets or sides, with three meeting at each vertex. The cube can also be called a regular hexahedron and is one of the five Platonic solids. It is a special kind of square prism, of rectangular parallelepiped and... |
(2) (4.4.8) Octagonal prism In geometry, the octagonal prism is the sixth in an infinite set of prisms, formed by square sides and two regular octagon caps.If faces are all regular, it is a semiregular polyhedron.- Use :... |
(1) (3.8.8) Truncated cube In geometry, the truncated cube, or truncated hexahedron, is an Archimedean solid. It has 14 regular faces , 36 edges, and 24 vertices.... |
 |
 |
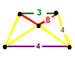 oblique trapezoidal pyramid |
| J19 A22 W18 G27 |
omnitruncated cubic Omnitruncated cubic honeycomb The omnitruncated cubic honeycomb is a uniform space-filling tessellation in Euclidean 3-space. It is composed of truncated cuboctahedra and octagonal prisms in a ratio of 1:3.A wireframe rendering- References :... t0,1,2,3{4,3,4} |
(1) (4.6.8) Truncated cuboctahedron In geometry, the truncated cuboctahedron is an Archimedean solid. It has 12 square faces, 8 regular hexagonal faces, 6 regular octagonal faces, 48 vertices and 72 edges... |
(1) (4.4.8) Octagonal prism In geometry, the octagonal prism is the sixth in an infinite set of prisms, formed by square sides and two regular octagon caps.If faces are all regular, it is a semiregular polyhedron.- Use :... |
(1) (4.4.8) Octagonal prism In geometry, the octagonal prism is the sixth in an infinite set of prisms, formed by square sides and two regular octagon caps.If faces are all regular, it is a semiregular polyhedron.- Use :... |
(1) (4.6.8) Truncated cuboctahedron In geometry, the truncated cuboctahedron is an Archimedean solid. It has 12 square faces, 8 regular hexagonal faces, 6 regular octagonal faces, 48 vertices and 72 edges... |
 |
 |
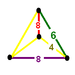 irregular tetrahedron Tetrahedron In geometry, a tetrahedron is a polyhedron composed of four triangular faces, three of which meet at each vertex. A regular tetrahedron is one in which the four triangles are regular, or "equilateral", and is one of the Platonic solids... |
| J21,31,51 A2 W9 G1 |
alternated cubic Tetrahedral-octahedral honeycomb The tetrahedral-octahedral honeycomb or alternated cubic honeycomb is a space-filling tessellation in Euclidean 3-space. It is composed of alternating octahedra and tetrahedra in a ratio of 1:2.... h0{4,3,4} |
(6) (3.3.3.3) Octahedron In geometry, an octahedron is a polyhedron with eight faces. A regular octahedron is a Platonic solid composed of eight equilateral triangles, four of which meet at each vertex.... |
(8) (3.3.3) Tetrahedron In geometry, a tetrahedron is a polyhedron composed of four triangular faces, three of which meet at each vertex. A regular tetrahedron is one in which the four triangles are regular, or "equilateral", and is one of the Platonic solids... |
 |
 |
cuboctahedron Cuboctahedron In geometry, a cuboctahedron is a polyhedron with eight triangular faces and six square faces. A cuboctahedron has 12 identical vertices, with two triangles and two squares meeting at each, and 24 identical edges, each separating a triangle from a square. As such it is a quasiregular polyhedron,... |
B~4, [4,31,1] group
The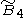 group offers 11 derived forms via truncation operations, four being unique uniform honeycombs.
group offers 11 derived forms via truncation operations, four being unique uniform honeycombs.The honeycombs from this group are called alternated cubic because the first form can be seen as a cubic honeycomb with alternate vertices removed, reducing cubic cells to tetrahedra and creating octahedron cells in the gaps.
Nodes are indexed left to right as 0,1,0',3 with 0' being below and interchangeable with 0. The alternate cubic names given are based on this ordering.
| Referenced indices |
Honeycomb name Coxeter-Dynkin diagram Coxeter-Dynkin diagram In geometry, a Coxeter–Dynkin diagram is a graph with numerically labeled edges representing the spatial relations between a collection of mirrors... |
Cells by location (and count around each vertex) |
Solids (Partial) |
Frames (Perspective) |
vertex figure Vertex figure In geometry a vertex figure is, broadly speaking, the figure exposed when a corner of a polyhedron or polytope is sliced off.-Definitions - theme and variations:... |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| J21,31,51 A2 W9 G1 |
alternated cubic Tetrahedral-octahedral honeycomb The tetrahedral-octahedral honeycomb or alternated cubic honeycomb is a space-filling tessellation in Euclidean 3-space. It is composed of alternating octahedra and tetrahedra in a ratio of 1:2.... |
 (6) (6)(3.3.3.3) Octahedron In geometry, an octahedron is a polyhedron with eight faces. A regular octahedron is a Platonic solid composed of eight equilateral triangles, four of which meet at each vertex.... |
 (8) (8)(3.3.3) Tetrahedron In geometry, a tetrahedron is a polyhedron composed of four triangular faces, three of which meet at each vertex. A regular tetrahedron is one in which the four triangles are regular, or "equilateral", and is one of the Platonic solids... |
 |
 |
cuboctahedron Cuboctahedron In geometry, a cuboctahedron is a polyhedron with eight triangular faces and six square faces. A cuboctahedron has 12 identical vertices, with two triangles and two squares meeting at each, and 24 identical edges, each separating a triangle from a square. As such it is a quasiregular polyhedron,... |
||
| J22,34 A21 W17 G10 |
truncated alternated cubic Truncated alternated cubic honeycomb The truncated alternated cubic honeycomb is a uniform space-filling tessellation in Euclidean 3-space. It is composed of truncated octahedra, cuboctahedra and truncated tetrahedra in a ratio of 1:1:2. Its vertex figure is a rectangular pyramid.... |
 (1) (1)(3.4.3.4) Cuboctahedron In geometry, a cuboctahedron is a polyhedron with eight triangular faces and six square faces. A cuboctahedron has 12 identical vertices, with two triangles and two squares meeting at each, and 24 identical edges, each separating a triangle from a square. As such it is a quasiregular polyhedron,... |
 (2) (2)(4.6.6) Truncated octahedron In geometry, the truncated octahedron is an Archimedean solid. It has 14 faces , 36 edges, and 24 vertices. Since each of its faces has point symmetry the truncated octahedron is a zonohedron.... |
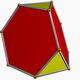 (2) (2)(3.6.6) Truncated tetrahedron In geometry, the truncated tetrahedron is an Archimedean solid. It has 4 regular hexagonal faces, 4 regular triangular faces, 12 vertices and 18 edges.- Area and volume :... |
 |
 |
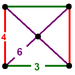 rectangular pyramid |
|
| J12,32 A15 W14 G7 |
rectified cubic Rectified cubic honeycomb The rectified cubic honeycomb is a uniform space-filling tessellation in Euclidean 3-space. It is composed of octahedra and cuboctahedra in a ratio of 1:1.- Symmetry :... (rectified alternate cubic) |
 (2) (2)(3.4.3.4) Cuboctahedron In geometry, a cuboctahedron is a polyhedron with eight triangular faces and six square faces. A cuboctahedron has 12 identical vertices, with two triangles and two squares meeting at each, and 24 identical edges, each separating a triangle from a square. As such it is a quasiregular polyhedron,... |
 (2) (2)(3.4.3.4) Cuboctahedron In geometry, a cuboctahedron is a polyhedron with eight triangular faces and six square faces. A cuboctahedron has 12 identical vertices, with two triangles and two squares meeting at each, and 24 identical edges, each separating a triangle from a square. As such it is a quasiregular polyhedron,... |
 (2) (2)(3.3.3.3) Octahedron In geometry, an octahedron is a polyhedron with eight faces. A regular octahedron is a Platonic solid composed of eight equilateral triangles, four of which meet at each vertex.... |
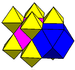 |
 |
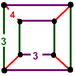 cuboid Cuboid In geometry, a cuboid is a solid figure bounded by six faces, forming a convex polyhedron. There are two competing definitions of a cuboid in mathematical literature... |
|
| J12,32 A15 W14 G7 |
rectified cubic Rectified cubic honeycomb The rectified cubic honeycomb is a uniform space-filling tessellation in Euclidean 3-space. It is composed of octahedra and cuboctahedra in a ratio of 1:1.- Symmetry :... (cantellated alternate cubic) |
 (1) (1)(3.3.3.3) Octahedron In geometry, an octahedron is a polyhedron with eight faces. A regular octahedron is a Platonic solid composed of eight equilateral triangles, four of which meet at each vertex.... |
 (1) (1)(3.3.3.3) Octahedron In geometry, an octahedron is a polyhedron with eight faces. A regular octahedron is a Platonic solid composed of eight equilateral triangles, four of which meet at each vertex.... |
 (4) (4)(3.4.3.4) Cuboctahedron In geometry, a cuboctahedron is a polyhedron with eight triangular faces and six square faces. A cuboctahedron has 12 identical vertices, with two triangles and two squares meeting at each, and 24 identical edges, each separating a triangle from a square. As such it is a quasiregular polyhedron,... |
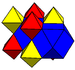 |
 |
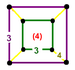 cuboid Cuboid In geometry, a cuboid is a solid figure bounded by six faces, forming a convex polyhedron. There are two competing definitions of a cuboid in mathematical literature... |
|
| J16 A3 W2 G28 |
bitruncated cubic Bitruncated cubic honeycomb The bitruncated cubic honeycomb is a space-filling tessellation in Euclidean 3-space made up of truncated octahedra.It is one of 28 uniform honeycombs. It has 4 truncated octahedra around each vertex.... (cantitruncated alternate cubic) |
 (1) (1)(4.6.6) Truncated octahedron In geometry, the truncated octahedron is an Archimedean solid. It has 14 faces , 36 edges, and 24 vertices. Since each of its faces has point symmetry the truncated octahedron is a zonohedron.... |
 (1) (1)(4.6.6) Truncated octahedron In geometry, the truncated octahedron is an Archimedean solid. It has 14 faces , 36 edges, and 24 vertices. Since each of its faces has point symmetry the truncated octahedron is a zonohedron.... |
 (2) (2)(4.6.6) Truncated octahedron In geometry, the truncated octahedron is an Archimedean solid. It has 14 faces , 36 edges, and 24 vertices. Since each of its faces has point symmetry the truncated octahedron is a zonohedron.... |
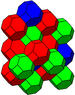 |
 |
 isosceles tetrahedron Tetrahedron In geometry, a tetrahedron is a polyhedron composed of four triangular faces, three of which meet at each vertex. A regular tetrahedron is one in which the four triangles are regular, or "equilateral", and is one of the Platonic solids... |
|
| J13 A14 W15 G8 |
truncated cubic Truncated cubic honeycomb The truncated cubic honeycomb is a uniform space-filling tessellation in Euclidean 3-space. It is composed of truncated cubes and octahedra in a ratio of 1:1.- Symmetry :... (bicantellated alternate cubic) |
 (2) (2)(3.8.8) Truncated cube In geometry, the truncated cube, or truncated hexahedron, is an Archimedean solid. It has 14 regular faces , 36 edges, and 24 vertices.... |
 (2) (2)(3.8.8) Truncated cube In geometry, the truncated cube, or truncated hexahedron, is an Archimedean solid. It has 14 regular faces , 36 edges, and 24 vertices.... |
 (1) (1)(3.3.3.3) Octahedron In geometry, an octahedron is a polyhedron with eight faces. A regular octahedron is a Platonic solid composed of eight equilateral triangles, four of which meet at each vertex.... |
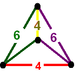
 |
 |
 square pyramid Square pyramid In geometry, a square pyramid is a pyramid having a square base. If the apex is perpendicularly above the center of the square, it will have C4v symmetry.- Johnson solid :... |
|
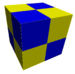
| J11,15 A1 W1 G22 |
cubic Cubic honeycomb The cubic honeycomb is the only regular space-filling tessellation in Euclidean 3-space, made up of cubic cells. It has 4 cubes around every edge, and 8 cubes around each vertex. Its vertex figure is a regular octahedron.... (trirectified alternate cubic) |
 (4) (4)(4.4.4) Cube In geometry, a cube is a three-dimensional solid object bounded by six square faces, facets or sides, with three meeting at each vertex. The cube can also be called a regular hexahedron and is one of the five Platonic solids. It is a special kind of square prism, of rectangular parallelepiped and... |
 (4) (4)(4.4.4) Cube In geometry, a cube is a three-dimensional solid object bounded by six square faces, facets or sides, with three meeting at each vertex. The cube can also be called a regular hexahedron and is one of the five Platonic solids. It is a special kind of square prism, of rectangular parallelepiped and... |
 |
 |
 octahedron Octahedron In geometry, an octahedron is a polyhedron with eight faces. A regular octahedron is a Platonic solid composed of eight equilateral triangles, four of which meet at each vertex.... |
||
| J23 A16 W11 G5 |
runcinated alternated cubic Runcinated alternated cubic honeycomb The runcinated alternated cubic honeycomb is a uniform space-filling tessellation in Euclidean 3-space. It is composed of small rhombicuboctahedra, cubes, and tetrahedra in a ratio of 1:1:2.- References :... |
 (1) (1)cube Cube In geometry, a cube is a three-dimensional solid object bounded by six square faces, facets or sides, with three meeting at each vertex. The cube can also be called a regular hexahedron and is one of the five Platonic solids. It is a special kind of square prism, of rectangular parallelepiped and... |
 (3) (3)(3.4.4.4) Rhombicuboctahedron In geometry, the rhombicuboctahedron, or small rhombicuboctahedron, is an Archimedean solid with eight triangular and eighteen square faces. There are 24 identical vertices, with one triangle and three squares meeting at each. Note that six of the squares only share vertices with the triangles... |
 (1) (1)(3.3.3) Tetrahedron In geometry, a tetrahedron is a polyhedron composed of four triangular faces, three of which meet at each vertex. A regular tetrahedron is one in which the four triangles are regular, or "equilateral", and is one of the Platonic solids... |
 |
 |
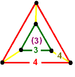 tapered triangular prism Triangular prism In geometry, a triangular prism is a three-sided prism; it is a polyhedron made of a triangular base, a translated copy, and 3 faces joining corresponding sides.... |
|
| J14 A17 W12 G9 |
cantellated cubic Cantellated cubic honeycomb The cantellated cubic honeycomb is a uniform space-filling tessellation in Euclidean 3-space. It is composed of small rhombicuboctahedra, cuboctahedra, and cubes in a ratio of 1:1:3.- References :... (runcicantellated alternate cubic) |
 (1) (1)(3.4.4.4) Rhombicuboctahedron In geometry, the rhombicuboctahedron, or small rhombicuboctahedron, is an Archimedean solid with eight triangular and eighteen square faces. There are 24 identical vertices, with one triangle and three squares meeting at each. Note that six of the squares only share vertices with the triangles... |
 (2) (2)(4.4.4) Cube In geometry, a cube is a three-dimensional solid object bounded by six square faces, facets or sides, with three meeting at each vertex. The cube can also be called a regular hexahedron and is one of the five Platonic solids. It is a special kind of square prism, of rectangular parallelepiped and... |
 (1) (1)(3.4.4.4) Rhombicuboctahedron In geometry, the rhombicuboctahedron, or small rhombicuboctahedron, is an Archimedean solid with eight triangular and eighteen square faces. There are 24 identical vertices, with one triangle and three squares meeting at each. Note that six of the squares only share vertices with the triangles... |
 (1) (1)(3.4.3.4) Cuboctahedron In geometry, a cuboctahedron is a polyhedron with eight triangular faces and six square faces. A cuboctahedron has 12 identical vertices, with two triangles and two squares meeting at each, and 24 identical edges, each separating a triangle from a square. As such it is a quasiregular polyhedron,... |
 |
 |
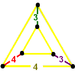 obilique triangular prism Triangular prism In geometry, a triangular prism is a three-sided prism; it is a polyhedron made of a triangular base, a translated copy, and 3 faces joining corresponding sides.... |
| J24 A20 W16 G21 |
cantitruncated alternated cubic Cantitruncated alternated cubic honeycomb The cantitruncated alternated cubic honeycomb is a uniform space-filling tessellation in Euclidean 3-space. It is composed of truncated cuboctahedra, truncated cubes and truncated tetrahedra in a ratio of 1:1:2.- References :... (or runcitruncated alternate cubic) |
 (1) (1)(3.8.8) Truncated cube In geometry, the truncated cube, or truncated hexahedron, is an Archimedean solid. It has 14 regular faces , 36 edges, and 24 vertices.... |
 (2) (2)(4.6.8) Truncated cuboctahedron In geometry, the truncated cuboctahedron is an Archimedean solid. It has 12 square faces, 8 regular hexagonal faces, 6 regular octagonal faces, 48 vertices and 72 edges... |
 (1) (1)(3.6.6) Truncated tetrahedron In geometry, the truncated tetrahedron is an Archimedean solid. It has 4 regular hexagonal faces, 4 regular triangular faces, 12 vertices and 18 edges.- Area and volume :... |
 |
 |
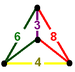 Irregular tetrahedron Tetrahedron In geometry, a tetrahedron is a polyhedron composed of four triangular faces, three of which meet at each vertex. A regular tetrahedron is one in which the four triangles are regular, or "equilateral", and is one of the Platonic solids... |
|
| J17 A18 W13 G25 |
cantitruncated cubic Cantitruncated cubic honeycomb The cantitruncated cubic honeycomb is a uniform space-filling tessellation in Euclidean 3-space, made up of truncated cuboctahedra, truncated octahedra, and cubes in a ratio of 1:1:3.- Uniform colorings :... (omnitruncated alternated cubic) |
 (1) (1)(4.6.8) Truncated cuboctahedron In geometry, the truncated cuboctahedron is an Archimedean solid. It has 12 square faces, 8 regular hexagonal faces, 6 regular octagonal faces, 48 vertices and 72 edges... |
 (1) (1)(4.4.4) Cube In geometry, a cube is a three-dimensional solid object bounded by six square faces, facets or sides, with three meeting at each vertex. The cube can also be called a regular hexahedron and is one of the five Platonic solids. It is a special kind of square prism, of rectangular parallelepiped and... |
 (1) (1)(4.6.8) Truncated cuboctahedron In geometry, the truncated cuboctahedron is an Archimedean solid. It has 12 square faces, 8 regular hexagonal faces, 6 regular octagonal faces, 48 vertices and 72 edges... |
 (1) (1)(4.6.6) Truncated octahedron In geometry, the truncated octahedron is an Archimedean solid. It has 14 faces , 36 edges, and 24 vertices. Since each of its faces has point symmetry the truncated octahedron is a zonohedron.... |
 |
 |
 irregular tetrahedron Tetrahedron In geometry, a tetrahedron is a polyhedron composed of four triangular faces, three of which meet at each vertex. A regular tetrahedron is one in which the four triangles are regular, or "equilateral", and is one of the Platonic solids... |
A~3, [(3,3,3,3)] group
There are 5 forms constructed from the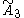 group, of which only the quarter cubic honeycomb is unique.
group, of which only the quarter cubic honeycomb is unique.| Referenced indices |
Honeycomb name Coxeter-Dynkin diagram Coxeter-Dynkin diagram In geometry, a Coxeter–Dynkin diagram is a graph with numerically labeled edges representing the spatial relations between a collection of mirrors... |
Cells by location (and count around each vertex) |
Solids (Partial) |
Frames (Perspective) |
vertex figure Vertex figure In geometry a vertex figure is, broadly speaking, the figure exposed when a corner of a polyhedron or polytope is sliced off.-Definitions - theme and variations:... |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| J21,31,51 A2 W9 G1 |
alternated cubic Tetrahedral-octahedral honeycomb The tetrahedral-octahedral honeycomb or alternated cubic honeycomb is a space-filling tessellation in Euclidean 3-space. It is composed of alternating octahedra and tetrahedra in a ratio of 1:2.... |
 (4) (4)(3.3.3) Tetrahedron In geometry, a tetrahedron is a polyhedron composed of four triangular faces, three of which meet at each vertex. A regular tetrahedron is one in which the four triangles are regular, or "equilateral", and is one of the Platonic solids... |
 (6) (6)(3.3.3.3) Octahedron In geometry, an octahedron is a polyhedron with eight faces. A regular octahedron is a Platonic solid composed of eight equilateral triangles, four of which meet at each vertex.... |
 (4) (4)(3.3.3) Tetrahedron In geometry, a tetrahedron is a polyhedron composed of four triangular faces, three of which meet at each vertex. A regular tetrahedron is one in which the four triangles are regular, or "equilateral", and is one of the Platonic solids... |
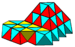 |
 |
cuboctahedron Cuboctahedron In geometry, a cuboctahedron is a polyhedron with eight triangular faces and six square faces. A cuboctahedron has 12 identical vertices, with two triangles and two squares meeting at each, and 24 identical edges, each separating a triangle from a square. As such it is a quasiregular polyhedron,... |
|
| J12,32 A15 W14 G7 |
rectified cubic Rectified cubic honeycomb The rectified cubic honeycomb is a uniform space-filling tessellation in Euclidean 3-space. It is composed of octahedra and cuboctahedra in a ratio of 1:1.- Symmetry :... |
 (2) (2)(3.4.3.4) Cuboctahedron In geometry, a cuboctahedron is a polyhedron with eight triangular faces and six square faces. A cuboctahedron has 12 identical vertices, with two triangles and two squares meeting at each, and 24 identical edges, each separating a triangle from a square. As such it is a quasiregular polyhedron,... |
 (1) (1)(3.3.3.3) Octahedron In geometry, an octahedron is a polyhedron with eight faces. A regular octahedron is a Platonic solid composed of eight equilateral triangles, four of which meet at each vertex.... |
 (2) (2)(3.4.3.4) Cuboctahedron In geometry, a cuboctahedron is a polyhedron with eight triangular faces and six square faces. A cuboctahedron has 12 identical vertices, with two triangles and two squares meeting at each, and 24 identical edges, each separating a triangle from a square. As such it is a quasiregular polyhedron,... |
 (1) (1)(3.3.3.3) Octahedron In geometry, an octahedron is a polyhedron with eight faces. A regular octahedron is a Platonic solid composed of eight equilateral triangles, four of which meet at each vertex.... |
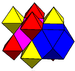 |
 |
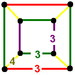 cuboid Cuboid In geometry, a cuboid is a solid figure bounded by six faces, forming a convex polyhedron. There are two competing definitions of a cuboid in mathematical literature... |
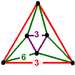
| J25,33 A13 W10 G6 |
quarter cubic Quarter cubic honeycomb The quarter cubic honeycomb is a space-filling tessellation in Euclidean 3-space. It is composed of tetrahedra and truncated tetrahedra in a ratio of 1:1... |
 (1) (1)(3.3.3) Tetrahedron In geometry, a tetrahedron is a polyhedron composed of four triangular faces, three of which meet at each vertex. A regular tetrahedron is one in which the four triangles are regular, or "equilateral", and is one of the Platonic solids... |
 (1) (1)(3.3.3) Tetrahedron In geometry, a tetrahedron is a polyhedron composed of four triangular faces, three of which meet at each vertex. A regular tetrahedron is one in which the four triangles are regular, or "equilateral", and is one of the Platonic solids... |
 (3) (3)(3.6.6) Truncated tetrahedron In geometry, the truncated tetrahedron is an Archimedean solid. It has 4 regular hexagonal faces, 4 regular triangular faces, 12 vertices and 18 edges.- Area and volume :... |
 (3) (3)(3.6.6) Truncated tetrahedron In geometry, the truncated tetrahedron is an Archimedean solid. It has 4 regular hexagonal faces, 4 regular triangular faces, 12 vertices and 18 edges.- Area and volume :... |
 |
 |
 triangular antiprism |
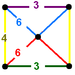
| J22,34 A21 W17 G10 |
truncated alternated cubic Truncated alternated cubic honeycomb The truncated alternated cubic honeycomb is a uniform space-filling tessellation in Euclidean 3-space. It is composed of truncated octahedra, cuboctahedra and truncated tetrahedra in a ratio of 1:1:2. Its vertex figure is a rectangular pyramid.... |
 (1) (1)(3.6.6) Truncated tetrahedron In geometry, the truncated tetrahedron is an Archimedean solid. It has 4 regular hexagonal faces, 4 regular triangular faces, 12 vertices and 18 edges.- Area and volume :... |
 (1) (1)(3.4.3.4) Cuboctahedron In geometry, a cuboctahedron is a polyhedron with eight triangular faces and six square faces. A cuboctahedron has 12 identical vertices, with two triangles and two squares meeting at each, and 24 identical edges, each separating a triangle from a square. As such it is a quasiregular polyhedron,... |
 (1) (1)(3.6.6) Truncated tetrahedron In geometry, the truncated tetrahedron is an Archimedean solid. It has 4 regular hexagonal faces, 4 regular triangular faces, 12 vertices and 18 edges.- Area and volume :... |
 (2) (2)(4.6.6) Truncated octahedron In geometry, the truncated octahedron is an Archimedean solid. It has 14 faces , 36 edges, and 24 vertices. Since each of its faces has point symmetry the truncated octahedron is a zonohedron.... |
 |
 |
 Rectangular pyramid |
| J16 A3 W2 G28 |
bitruncated cubic Bitruncated cubic honeycomb The bitruncated cubic honeycomb is a space-filling tessellation in Euclidean 3-space made up of truncated octahedra.It is one of 28 uniform honeycombs. It has 4 truncated octahedra around each vertex.... |
 (1) (1)(4.6.6) Truncated octahedron In geometry, the truncated octahedron is an Archimedean solid. It has 14 faces , 36 edges, and 24 vertices. Since each of its faces has point symmetry the truncated octahedron is a zonohedron.... |
 (1) (1)(4.6.6) Truncated octahedron In geometry, the truncated octahedron is an Archimedean solid. It has 14 faces , 36 edges, and 24 vertices. Since each of its faces has point symmetry the truncated octahedron is a zonohedron.... |
 (1) (1)(4.6.6) Truncated octahedron In geometry, the truncated octahedron is an Archimedean solid. It has 14 faces , 36 edges, and 24 vertices. Since each of its faces has point symmetry the truncated octahedron is a zonohedron.... |
 (1) (1)(4.6.6) Truncated octahedron In geometry, the truncated octahedron is an Archimedean solid. It has 14 faces , 36 edges, and 24 vertices. Since each of its faces has point symmetry the truncated octahedron is a zonohedron.... |
 |
 |
 isosceles tetrahedron Tetrahedron In geometry, a tetrahedron is a polyhedron composed of four triangular faces, three of which meet at each vertex. A regular tetrahedron is one in which the four triangles are regular, or "equilateral", and is one of the Platonic solids... |
Nonwythoffian forms (gyrated and elongated)
Three more uniform honeycombs are generated by breaking one or another of the above honeycombs where its faces form a continuous plane, then rotating alternate layers by 60 or 90 degrees (gyration) and/or inserting a layer of prisms (elongation).The elongated and gyroelongated alternated cubic tilings have the same vertex figure, but are not alike. In the elongated form, each prism meets a tetrahedron at one triangular end and an octahedron at the other. In the gyroelongated form, prisms that meet tetrahedra at both ends alternate with prisms that meet octahedra at both ends.
The gyroelongated triangular prismatic tiling has the same vertex figure as one of the plain prismatic tilings; the two may be derived from the gyrated and plain triangular prismatic tilings, respectively, by inserting layers of cubes.
| Referenced indices |
symbol | Honeycomb name | cell types (# at each vertex) | Solids (Partial) |
Frames (Perspective) |
vertex figure Vertex figure In geometry a vertex figure is, broadly speaking, the figure exposed when a corner of a polyhedron or polytope is sliced off.-Definitions - theme and variations:... |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| J52 A2' G2 |
h{4,3,4}:g | gyrated alternated cubic | tetrahedron Tetrahedron In geometry, a tetrahedron is a polyhedron composed of four triangular faces, three of which meet at each vertex. A regular tetrahedron is one in which the four triangles are regular, or "equilateral", and is one of the Platonic solids... (8) octahedron Octahedron In geometry, an octahedron is a polyhedron with eight faces. A regular octahedron is a Platonic solid composed of eight equilateral triangles, four of which meet at each vertex.... (6) |
 |
 |
 triangular orthobicupola Triangular orthobicupola In geometry, the triangular orthobicupola is one of the Johnson solids . As the name suggests, it can be constructed by attaching two triangular cupolas along their bases... |
| J61 A? G3 |
h{4,3,4}:ge | gyroelongated alternated cubic Gyroelongated alternated cubic honeycomb The gyroelongated alternated cubic honeycomb is a space-filling tessellation in Euclidean 3-space. It is composed of octahedra, triangular prisms, and tetrahedra in a ratio of 1:2:2.... |
triangular prism Triangular prism In geometry, a triangular prism is a three-sided prism; it is a polyhedron made of a triangular base, a translated copy, and 3 faces joining corresponding sides.... (6) tetrahedron Tetrahedron In geometry, a tetrahedron is a polyhedron composed of four triangular faces, three of which meet at each vertex. A regular tetrahedron is one in which the four triangles are regular, or "equilateral", and is one of the Platonic solids... (4) octahedron Octahedron In geometry, an octahedron is a polyhedron with eight faces. A regular octahedron is a Platonic solid composed of eight equilateral triangles, four of which meet at each vertex.... (3) |
 |
 |
- |
| J62 A? G4 |
h{4,3,4}:e | elongated alternated cubic Elongated alternated cubic honeycomb The elongated alternated cubic honeycomb is a space-filling tessellation in Euclidean 3-space. It is composed of octahedra, triangular prisms, and tetrahedra in a ratio of 1:2:2.... |
triangular prism Triangular prism In geometry, a triangular prism is a three-sided prism; it is a polyhedron made of a triangular base, a translated copy, and 3 faces joining corresponding sides.... (6) tetrahedron Tetrahedron In geometry, a tetrahedron is a polyhedron composed of four triangular faces, three of which meet at each vertex. A regular tetrahedron is one in which the four triangles are regular, or "equilateral", and is one of the Platonic solids... (4) octahedron Octahedron In geometry, an octahedron is a polyhedron with eight faces. A regular octahedron is a Platonic solid composed of eight equilateral triangles, four of which meet at each vertex.... (3) |
 |
 |
 |
| J63 A? G12 |
{3,6}:g x {∞} | gyrated triangular prismatic Gyrated triangular prismatic honeycomb The gyrated triangular prismatic honeycomb is a space-filling tessellation in Euclidean 3-space made up of triangular prisms. It is vertex-uniform with 12 triangular prisms per vertex.... |
triangular prism Triangular prism In geometry, a triangular prism is a three-sided prism; it is a polyhedron made of a triangular base, a translated copy, and 3 faces joining corresponding sides.... (12) |
 |
 |
 |
| J64 A? G15 |
{3,6}:ge x {∞} | gyroelongated triangular prismatic Gyroelongated triangular prismatic honeycomb The gyroelongated triangular prismatic honeycomb is a uniform space-filling tessellation in Euclidean 3-space. It is composed of cubes and triangular prisms in a ratio of 1:2.... |
triangular prism Triangular prism In geometry, a triangular prism is a three-sided prism; it is a polyhedron made of a triangular base, a translated copy, and 3 faces joining corresponding sides.... (6) cube Cube In geometry, a cube is a three-dimensional solid object bounded by six square faces, facets or sides, with three meeting at each vertex. The cube can also be called a regular hexahedron and is one of the five Platonic solids. It is a special kind of square prism, of rectangular parallelepiped and... (4) |
 |
 |
 |
Prismatic stacks
Eleven prismatic tilings are obtained by stacking the eleven uniform plane tilingsTiling by regular polygons
Plane tilings by regular polygons have been widely used since antiquity. The first systematic mathematical treatment was that of Kepler in Harmonices Mundi.- Regular tilings :...
, shown below, in parallel layers. (One of these honeycombs is the cubic, shown above.) The vertex figure
Vertex figure
In geometry a vertex figure is, broadly speaking, the figure exposed when a corner of a polyhedron or polytope is sliced off.-Definitions - theme and variations:...
of each is an irregular bipyramid
Bipyramid
An n-gonal bipyramid or dipyramid is a polyhedron formed by joining an n-gonal pyramid and its mirror image base-to-base.The referenced n-gon in the name of the bipyramids is not an external face but an internal one, existing on the primary symmetry plane which connects the two pyramid halves.The...
whose faces are isosceles triangles.
The C~2xI~1(∞), [4,4] x [∞], prismatic group
There's only 3 unique honeycombs from the square tiling, but all 6 tiling truncations are listed below for completeness, and tiling images are shown by colors corresponding to each form.| Indices | Coxeter-Dynkin Coxeter-Dynkin diagram In geometry, a Coxeter–Dynkin diagram is a graph with numerically labeled edges representing the spatial relations between a collection of mirrors... and Schläfli symbols |
Honeycomb name | Plane tiling |
Solids (Partial) |
Tiling |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| J11,15 A1 G22 |
{4,4} x {∞} |
Cubic Cubic honeycomb The cubic honeycomb is the only regular space-filling tessellation in Euclidean 3-space, made up of cubic cells. It has 4 cubes around every edge, and 8 cubes around each vertex. Its vertex figure is a regular octahedron.... (Square prismatic) |
(4.4.4.4) |  |
 |
| J45 A6 G24 |
t0,1{4,4} x {∞} |
Truncated/Bitruncated square prismatic Truncated square prismatic honeycomb The truncated square prismatic honeycomb is a space-filling tessellation in Euclidean 3-space. It is composed of octagonal prisms and cubes in a ratio of 1:1.It is constructed from a truncated square tiling extruded into prisms.... |
(4.8.8) Truncated square tiling In geometry, the truncated square tiling is a semiregular tiling of the Euclidean plane. There is one square and two octagons on each vertex. This is the only edge-to-edge tiling by regular convex polygons which contains an octagon... |
 |
 |
| J11,15 A1 G22 |
t1{4,4} x {∞} |
Cubic Cubic honeycomb The cubic honeycomb is the only regular space-filling tessellation in Euclidean 3-space, made up of cubic cells. It has 4 cubes around every edge, and 8 cubes around each vertex. Its vertex figure is a regular octahedron.... (Rectified square prismatic) |
(4.4.4.4) | 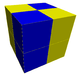 |
 |
| J11,15 A1 G22 |
t0,2{4,4} x {∞} |
Cubic Cubic honeycomb The cubic honeycomb is the only regular space-filling tessellation in Euclidean 3-space, made up of cubic cells. It has 4 cubes around every edge, and 8 cubes around each vertex. Its vertex figure is a regular octahedron.... (Cantellated square prismatic) |
(4.4.4.4) |  |
 |
| J45 A6 G24 |
t0,1,2{4,4} x {∞} |
Truncated square prismatic Truncated square prismatic honeycomb The truncated square prismatic honeycomb is a space-filling tessellation in Euclidean 3-space. It is composed of octagonal prisms and cubes in a ratio of 1:1.It is constructed from a truncated square tiling extruded into prisms.... (Omnitruncated square prismatic) |
(4.8.8) Truncated square tiling In geometry, the truncated square tiling is a semiregular tiling of the Euclidean plane. There is one square and two octagons on each vertex. This is the only edge-to-edge tiling by regular convex polygons which contains an octagon... |
 |
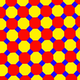 |
| J44 A11 G14 |
s{4,4} x {∞} |
Snub square prismatic Snub square prismatic honeycomb The snub square prismatic honeycomb is a space-filling tessellation in Euclidean 3-space. It is composed of cubes and triangular prisms in a ratio of 1:2.It is constructed from a Snub square tiling extruded into prisms.... |
(3.3.4.3.4) |  |
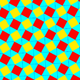 |
The G~2xI~1(∞), [6,3] x [∞] prismatic group
| Indices | Coxeter-Dynkin Coxeter-Dynkin diagram In geometry, a Coxeter–Dynkin diagram is a graph with numerically labeled edges representing the spatial relations between a collection of mirrors... and Schläfli symbols |
Honeycomb name | Plane tiling |
Solids (Partial) |
Tiling |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| J42 A5 G26 |
t0{6,3} x {∞} |
Hexagonal prismatic Hexagonal prismatic honeycomb The hexagonal prismatic honeycomb is a space-filling tessellation in Euclidean 3-space made up of hexagonal prisms.It is constructed from a hexagonal tiling extruded into prisms.It is one of 28 convex uniform honeycombs.- References :... |
(63) |  |
 |
| J46 A7 G19 |
t0,1{6,3} x {∞} |
Truncated hexagonal prismatic Truncated hexagonal prismatic honeycomb The truncated hexagonal prismatic honeycomb is a space-filling tessellation in Euclidean 3-space. It is composed of dodecagonal prisms, and triangular prisms in a ratio of 1:2.... |
(3.12.12) Truncated hexagonal tiling In geometry, the truncated hexagonal tiling is a semiregular tiling of the Euclidean plane. There are 2 dodecagons and one triangle on each vertex.... |
 |
 |
| J43 A8 G18 |
t1{6,3} x {∞} |
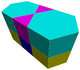
Trihexagonal prismatic Triangular-hexagonal prismatic honeycomb The triangular-hexagonal prismatic honeycomb is a space-filling tessellation in Euclidean 3-space. It is composed of hexagonal prisms and triangular prisms in a ratio of 1:2.It is constructed from a trihexagonal tiling extruded into prisms.... |
(3.6.3.6) Trihexagonal tiling In geometry, the trihexagonal tiling is a semiregular tiling of the Euclidean plane. There are two triangles and two hexagons alternating on each vertex... |
 |
 |
| J42 A5 G26 |
t1,2{6,3} x {∞} |
Truncated triangular prismatic Hexagonal prismatic Hexagonal prismatic honeycomb The hexagonal prismatic honeycomb is a space-filling tessellation in Euclidean 3-space made up of hexagonal prisms.It is constructed from a hexagonal tiling extruded into prisms.It is one of 28 convex uniform honeycombs.- References :... |
(6.6.6) | 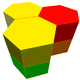 |
 |
| J41 A4 G11 |
t2{6,3} x {∞} |
Triangular prismatic Triangular prismatic honeycomb The triangular prismatic honeycomb is a space-filling tessellation in Euclidean 3-space. It is composed entirely of triangular prisms.It is constructed from a triangular tiling extruded into prisms.It is one of 28 convex uniform honeycombs.... |
(36) |  |
 |
| J47 A9 G16 |
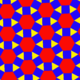
t0,2{6,3} x {∞} |
Rhombi-trihexagonal prismatic Rhombitriangular-hexagonal prismatic honeycomb The rhombitriangular-hexagonal prismatic honeycomb is a space-filling tessellation in Euclidean 3-space. It is composed of hexagonal prisms, cubes, and triangular prisms in a ratio of 1:3:2.... |
(3.4.6.4) | 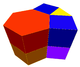 |
 |
| J49 A10 G23 |
t0,1,2{6,3} x {∞} |
Omnitruncated trihexagonal prismatic Omnitruncated triangular-hexagonal prismatic honeycomb The omnitruncated triangular-hexagonal prismatic honeycomb is a space-filling tessellation in Euclidean 3-space. It is composed of dodecagonal prisms, hexagonal prisms, and cubes in a ratio of 1:2:3.... |
(4.6.12) | 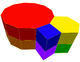 |
 |
| J48 A12 G17 |
s{6,3} x {∞} |
Snub trihexagonal prismatic Snub triangular-hexagonal prismatic honeycomb The Snub triangular-hexagonal prismatic honeycomb is a space-filling tessellation in Euclidean 3-space. It is composed of hexagonal prisms and triangular prisms in a ratio of 1:8.... |
(3.3.3.3.6) Snub hexagonal tiling In geometry, the Snub hexagonal tiling is a semiregular tiling of the Euclidean plane. There are four triangles and one hexagon on each vertex... |
 |
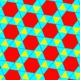 |
| J65 A11' G13 |
{3,6}:e x {∞} | elongated triangular prismatic Elongated triangular prismatic honeycomb The elongated triangular prismatic honeycomb is a space-filling tessellation in Euclidean 3-space. It is composed of cubes and triangular prisms in a ratio of 1:2.It is constructed from an elongated triangular tiling extruded into prisms.... |
(3.3.3.4.4) Elongated triangular tiling In geometry, the elongated triangular tiling is a semiregular tiling of the Euclidean plane. There are three triangles and two squares on each vertex.Conway calls it a isosnub quadrille.... |
 |
 |
Examples
All 28 of these tessellations are found in crystalCrystal
A crystal or crystalline solid is a solid material whose constituent atoms, molecules, or ions are arranged in an orderly repeating pattern extending in all three spatial dimensions. The scientific study of crystals and crystal formation is known as crystallography...
arrangements.
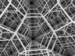
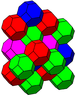
The alternated cubic honeycomb
Tetrahedral-octahedral honeycomb
The tetrahedral-octahedral honeycomb or alternated cubic honeycomb is a space-filling tessellation in Euclidean 3-space. It is composed of alternating octahedra and tetrahedra in a ratio of 1:2....
is of special importance since its vertices form a cubic close-packing
Close-packing
In geometry, close-packing of equal spheres is a dense arrangement of congruent spheres in an infinite, regular arrangement . Carl Friedrich Gauss proved that the highest average density – that is, the greatest fraction of space occupied by spheres – that can be achieved by a regular lattice...
of spheres. The space-filling truss
Truss
In architecture and structural engineering, a truss is a structure comprising one or more triangular units constructed with straight members whose ends are connected at joints referred to as nodes. External forces and reactions to those forces are considered to act only at the nodes and result in...
of packed octahedra and tetrahedra was apparently first discovered by Alexander Graham Bell
Alexander Graham Bell
Alexander Graham Bell was an eminent scientist, inventor, engineer and innovator who is credited with inventing the first practical telephone....
and independently re-discovered by Buckminster Fuller
Buckminster Fuller
Richard Buckminster “Bucky” Fuller was an American systems theorist, author, designer, inventor, futurist and second president of Mensa International, the high IQ society....
(who called it the octet truss and patented it in the 1940s).
http://tabletoptelephone.com/~hopspage/Fuller.html
http://members.cruzio.com/~devarco/energy.htm
http://www.n55.dk/MANUALS/DISCUSSIONS/OTHER_TEXTS/CM_TEXT.html
http://www.cjfearnley.com/fuller-faq-2.html. Octet trusses are now among the most common types of truss used in construction.
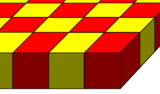
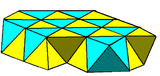
Noncompact forms
 |
 |
If cells are allowed to be uniform tiling
Uniform tiling
In geometry, a uniform tiling is a tessellation of the plane by regular polygon faces with the restriction of being vertex-uniform.Uniform tilings can exist in both the Euclidean plane and hyperbolic plane...
s, more uniform honeycombs can be defined:
Families:
 x
x : [4,4]x[ ] Cubic prismatic slab honeycomb (3 forms)
: [4,4]x[ ] Cubic prismatic slab honeycomb (3 forms) x
x : [6,3]x[ ] Tri-hexagonal prismatic slab honeycomb (8 forms)
: [6,3]x[ ] Tri-hexagonal prismatic slab honeycomb (8 forms)-
 x
x : (3 3 3)x[ ] Triangular prismatic slab (No new forms)
: (3 3 3)x[ ] Triangular prismatic slab (No new forms)  x
x x
x : [∞]x[ ]x[ ] = Cubic column honeycomb (1 form)
: [∞]x[ ]x[ ] = Cubic column honeycomb (1 form) x
x : [p]x[∞] Prismatic column honeycomb
: [p]x[∞] Prismatic column honeycomb-
 x
x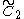 x
x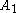 : [∞]x[∞]x[ ] = [4,4]x[ ] - = (Same as cubic slab honeycomb family)
: [∞]x[∞]x[ ] = [4,4]x[ ] - = (Same as cubic slab honeycomb family)
Hyperbolic forms

Coxeter group
In mathematics, a Coxeter group, named after H.S.M. Coxeter, is an abstract group that admits a formal description in terms of mirror symmetries. Indeed, the finite Coxeter groups are precisely the finite Euclidean reflection groups; the symmetry groups of regular polyhedra are an example...
families of compact uniform honeycombs in hyperbolic 3-space
Hyperbolic space
In mathematics, hyperbolic space is a type of non-Euclidean geometry. Whereas spherical geometry has a constant positive curvature, hyperbolic geometry has a negative curvature: every point in hyperbolic space is a saddle point...
, generated as Wythoff construction
Wythoff construction
In geometry, a Wythoff construction, named after mathematician Willem Abraham Wythoff, is a method for constructing a uniform polyhedron or plane tiling. It is often referred to as Wythoff's kaleidoscopic construction.- Construction process :...
s, and represented by ring permutations of the Coxeter-Dynkin diagram
Coxeter-Dynkin diagram
In geometry, a Coxeter–Dynkin diagram is a graph with numerically labeled edges representing the spatial relations between a collection of mirrors...
s for each family.
From these 9 families, there are a total of 76 unique honeycombs generated:
- [3,5,3] : - 9 forms
- [5,3,4] : - 15 forms
- [5,3,5] : - 9 forms
- [5,31,1] : - 11 forms (7 overlap with [5,3,4] family, 4 are unique)
- (4 3 3 3) : - 9 forms
- (4 3 4 3) : - 6 forms
- (5 3 3 3) : - 9 forms
- (5 3 4 3) : - 9 forms
- (5 3 5 3) : - 6 forms
The full list of hyperbolic uniform honeycombs has not been proven and an unknown number of non-Wythoffian exist. One known example is in the {3,5,3} family.
There are also 23 noncompact Coxeter groups of rank 4. These families can produce uniform honeycombs with unbounded facets or vertex figure, including ideal vertices at infinity:
| 7 | , , , , , , |
|---|---|
| 7 | , , ,, , , |
| 6 | , , , , , |
| 3 | , , |
External links
- Uniform Honeycombs in 3-Space VRML models
- Elementary Honeycombs Vertex transitive space filling honeycombs with non-uniform cells.
- Uniform partitions of 3-space, their relatives and embedding, 1999
- The Uniform Polyhedra
- Virtual Reality Polyhedra The Encyclopedia of Polyhedra
- octet truss animation
- Review: A. F. Wells, Three-dimensional nets and polyhedra, H. S. M. Coxeter (Source: Bull. Amer. Math. Soc. Volume 84, Number 3 (1978), 466-470.)

