
Rectified cubic honeycomb
Encyclopedia
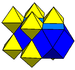 |
|
| Type | Uniform honeycomb Convex uniform honeycomb In geometry, a convex uniform honeycomb is a uniform tessellation which fills three-dimensional Euclidean space with non-overlapping convex uniform polyhedral cells.Twenty-eight such honeycombs exist:* the familiar cubic honeycomb and 7 truncations thereof;... |
| Schläfli symbol | t1{4,3,4} |
| Coxeter-Dynkin diagram Coxeter-Dynkin diagram In geometry, a Coxeter–Dynkin diagram is a graph with numerically labeled edges representing the spatial relations between a collection of mirrors... s |
|
| Vertex figure | Cuboid Cuboid In geometry, a cuboid is a solid figure bounded by six faces, forming a convex polyhedron. There are two competing definitions of a cuboid in mathematical literature... |
| Coxeter group Coxeter group In mathematics, a Coxeter group, named after H.S.M. Coxeter, is an abstract group that admits a formal description in terms of mirror symmetries. Indeed, the finite Coxeter groups are precisely the finite Euclidean reflection groups; the symmetry groups of regular polyhedra are an example... |
 , [4,3,4] , [4,3,4] |
| Dual | Square bipyramidal honeycomb |
| Properties | vertex-transitive Vertex-transitive In geometry, a polytope is isogonal or vertex-transitive if, loosely speaking, all its vertices are the same... , edge-transitive |
Tessellation
A tessellation or tiling of the plane is a pattern of plane figures that fills the plane with no overlaps and no gaps. One may also speak of tessellations of parts of the plane or of other surfaces. Generalizations to higher dimensions are also possible. Tessellations frequently appeared in the art...
(or honeycomb
Honeycomb (geometry)
In geometry, a honeycomb is a space filling or close packing of polyhedral or higher-dimensional cells, so that there are no gaps. It is an example of the more general mathematical tiling or tessellation in any number of dimensions....
) in Euclidean 3-space. It is composed of octahedra
Octahedron
In geometry, an octahedron is a polyhedron with eight faces. A regular octahedron is a Platonic solid composed of eight equilateral triangles, four of which meet at each vertex....
and cuboctahedra
Cuboctahedron
In geometry, a cuboctahedron is a polyhedron with eight triangular faces and six square faces. A cuboctahedron has 12 identical vertices, with two triangles and two squares meeting at each, and 24 identical edges, each separating a triangle from a square. As such it is a quasiregular polyhedron,...
in a ratio of 1:1.
-
-
- {|class=wikitable
-
!
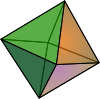
Octahedron
!
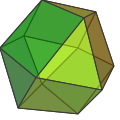
Cuboctahedron
|}
Symmetry
There are four uniform coloringUniform coloring
In geometry, a uniform coloring is a property of a uniform figure that is colored to be vertex-transitive...
s for the cells of this honeycomb with reflective symmetry, listed by their Coxeter group
Coxeter group
In mathematics, a Coxeter group, named after H.S.M. Coxeter, is an abstract group that admits a formal description in terms of mirror symmetries. Indeed, the finite Coxeter groups are precisely the finite Euclidean reflection groups; the symmetry groups of regular polyhedra are an example...
, and Wythoff construction
Wythoff construction
In geometry, a Wythoff construction, named after mathematician Willem Abraham Wythoff, is a method for constructing a uniform polyhedron or plane tiling. It is often referred to as Wythoff's kaleidoscopic construction.- Construction process :...
name, and the Coxeter-Dynkin diagram
Coxeter-Dynkin diagram
In geometry, a Coxeter–Dynkin diagram is a graph with numerically labeled edges representing the spatial relations between a collection of mirrors...
below.
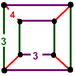
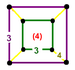
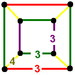
| Symmetry | [4,3,4],  |
[4,31,1],  |
[4,31,1],  |
[3[4]],  |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Rectified cubic | Rectified alternate cubic | Cantellated alternate cubic | Birectified quarter cubic |
| Coloring |  |
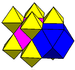 |
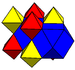 |
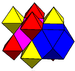 |
| Coxeter Coxeter-Dynkin diagram In geometry, a Coxeter–Dynkin diagram is a graph with numerically labeled edges representing the spatial relations between a collection of mirrors... |
||||
| Vertex figure Vertex figure In geometry a vertex figure is, broadly speaking, the figure exposed when a corner of a polyhedron or polytope is sliced off.-Definitions - theme and variations:... |
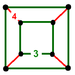 |
 |
 |
 |

