
2nd century BC
Encyclopedia
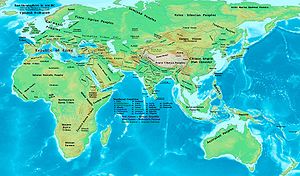
200 BC
Year 200 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Maximus and Cotta...
and ended the last day of 101 BC
101 BC
Year 101 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Marius and Aquillius...
. It is considered part of the Classical
Classical antiquity
Classical antiquity is a broad term for a long period of cultural history centered on the Mediterranean Sea, comprising the interlocking civilizations of ancient Greece and ancient Rome, collectively known as the Greco-Roman world...
era
Era
An era is a commonly used word for long period of time. When used in science, for example geology, eras denote clearly defined periods of time of arbitrary but well defined length, such as for example the Mesozoic era from 252 Ma–66 Ma, delimited by a start event and an end event. When used in...
, although depending on the region being studied, other terms may be more proper (for instance, if regarding only the Eastern Mediterranean, it would best be called part of the Hellenistic period
Hellenistic period
The Hellenistic period or Hellenistic era describes the time which followed the conquests of Alexander the Great. It was so named by the historian J. G. Droysen. During this time, Greek cultural influence and power was at its zenith in Europe and Asia...
).
Overview
Fresh from its victories in the Second Punic WarSecond Punic War
The Second Punic War, also referred to as The Hannibalic War and The War Against Hannibal, lasted from 218 to 201 BC and involved combatants in the western and eastern Mediterranean. This was the second major war between Carthage and the Roman Republic, with the participation of the Berbers on...
, the Roman Republic
Roman Republic
The Roman Republic was the period of the ancient Roman civilization where the government operated as a republic. It began with the overthrow of the Roman monarchy, traditionally dated around 508 BC, and its replacement by a government headed by two consuls, elected annually by the citizens and...
continued its expansion into neighbouring territories, eventually annexing Greece
Greece
Greece , officially the Hellenic Republic , and historically Hellas or the Republic of Greece in English, is a country in southeastern Europe....
, and the North African coast after completely destroying the city of Carthage
Carthage
Carthage , implying it was a 'new Tyre') is a major urban centre that has existed for nearly 3,000 years on the Gulf of Tunis, developing from a Phoenician colony of the 1st millennium BC...
at the end of the Third Punic War
Third Punic War
The Third Punic War was the third and last of the Punic Wars fought between the former Phoenician colony of Carthage, and the Roman Republic...
. Rome's influence was also felt in the near east, as crumbling Hellenistic states like the Seleucid Empire
Seleucid Empire
The Seleucid Empire was a Greek-Macedonian state that was created out of the eastern conquests of Alexander the Great. At the height of its power, it included central Anatolia, the Levant, Mesopotamia, Persia, today's Turkmenistan, Pamir and parts of Pakistan.The Seleucid Empire was a major centre...
were forced to make treaties on Roman terms in order to avoid confrontation with the new masters of the western Mediterranean. The period is noted for the emergence of a new arrogance on the part of the Romans, which manifested itself in provincial corruption, and a shameless lust for wealth and status among the privileged classes. The end of the century witnessed the reforming of the Roman Army
Roman army
The Roman army is the generic term for the terrestrial armed forces deployed by the kingdom of Rome , the Roman Republic , the Roman Empire and its successor, the Byzantine empire...
from a citizen army to a voluntary professional force, under the guidance of the great general and statesman Gaius Marius
Gaius Marius
Gaius Marius was a Roman general and statesman. He was elected consul an unprecedented seven times during his career. He was also noted for his dramatic reforms of Roman armies, authorizing recruitment of landless citizens, eliminating the manipular military formations, and reorganizing the...
—(Marian Reforms
Marian reforms
The Marian reforms of 107 BC were a group of military reforms initiated by Gaius Marius, a statesman and general of the Roman republic.- Roman army before the Marian reforms :...
).
In East Asia, China
China
Chinese civilization may refer to:* China for more general discussion of the country.* Chinese culture* Greater China, the transnational community of ethnic Chinese.* History of China* Sinosphere, the area historically affected by Chinese culture...
reached a high point under the Han Dynasty
Han Dynasty
The Han Dynasty was the second imperial dynasty of China, preceded by the Qin Dynasty and succeeded by the Three Kingdoms . It was founded by the rebel leader Liu Bang, known posthumously as Emperor Gaozu of Han. It was briefly interrupted by the Xin Dynasty of the former regent Wang Mang...
. The Han Empire extended its boundaries from Korea in the east to Vietnam in the South to the borders of modern day Kazakhstan
History of the Han Dynasty
The Han Dynasty , founded by the peasant rebel leader Liu Bang ,From the Shang to the Sui dynasties, Chinese rulers were referred to in later records by their posthumous names, while emperors of the Tang to Yuan dynasties were referred to by their temple names, and emperors of the Ming and Qing...
in the west. Also in the 2nd century BC, the Han dispatched the explorer Zhang Qian
Zhang Qian
Zhang Qian was an imperial envoy to the world outside of China in the 2nd century BCE, during the time of the Han Dynasty...
to explore the lands to the west and to form an alliance with the Yuezhi
Yuezhi
The Yuezhi, or Rouzhi , also known as the Da Yuezhi or Da Rouzhi , were an ancient Central Asian people....
people in order to combat the nomadic tribe of the Xiongnu
Xiongnu
The Xiongnu were ancient nomadic-based people that formed a state or confederation north of the agriculture-based empire of the Han Dynasty. Most of the information on the Xiongnu comes from Chinese sources...
.
Events

- March 14, 190 BC: Solar eclipseSolar eclipseAs seen from the Earth, a solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between the Sun and the Earth, and the Moon fully or partially blocks the Sun as viewed from a location on Earth. This can happen only during a new moon, when the Sun and the Moon are in conjunction as seen from Earth. At least...
recorded in Rome [Livy: Ab Urbe ConditaAb urbe conditaAb urbe condita is Latin for "from the founding of the City ", traditionally set in 753 BC. AUC is a year-numbering system used by some ancient Roman historians to identify particular Roman years...
37.4.4]. - 175 BC175 BCYear 175 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Scaevola and Lepidus...
: Antiochus IV EpiphanesAntiochus IV EpiphanesAntiochus IV Epiphanes ruled the Seleucid Empire from 175 BC until his death in 164 BC. He was a son of King Antiochus III the Great. His original name was Mithridates; he assumed the name Antiochus after he ascended the throne....
, took possession of the SyriaSyriaSyria , officially the Syrian Arab Republic , is a country in Western Asia, bordering Lebanon and the Mediterranean Sea to the West, Turkey to the north, Iraq to the east, Jordan to the south, and Israel to the southwest....
n throne, at the murder of his brother Seleucus IV PhilopatorSeleucus IV PhilopatorSeleucus IV Philopator , ruler of the Hellenistic Seleucid Empire, reigned from 187 BC to 175 BC over a realm consisting of Syria , Mesopotamia, Babylonia and Nearer Iran . He was the second son and successor of Antiochus III the Great and Laodice III...
, which rightly belonged to his nephew Demetrius I SoterDemetrius I SoterDemetrius I , surnamed Soter , was a ruler of the Hellenistic Seleucid Empire....
. - 168 BC168 BCYear 168 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Macedonicus and Crassus...
: Battle of PydnaBattle of PydnaThe Battle of Pydna in 168 BC between Rome and the Macedonian Antigonid dynasty saw the further ascendancy of Rome in the Hellenic/Hellenistic world and the end of the Antigonid line of kings, whose power traced back to Alexander the Great.Paul K...
—The Macedonian phalanxMacedonian phalanxThe Macedonian phalanx is an infantry formation developed by Philip II and used by his son Alexander the Great to conquer the Persian Empire and other armies...
defeated by RomansRoman RepublicThe Roman Republic was the period of the ancient Roman civilization where the government operated as a republic. It began with the overthrow of the Roman monarchy, traditionally dated around 508 BC, and its replacement by a government headed by two consuls, elected annually by the citizens and...
. - June 21, 168 BC: Lunar eclipseLunar eclipseA lunar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes behind the Earth so that the Earth blocks the Sun's rays from striking the Moon. This can occur only when the Sun, Earth, and Moon are aligned exactly, or very closely so, with the Earth in the middle. Hence, a lunar eclipse can only occur the night of a...
recorded in Rome [Livy: Ab Urbe Condita 44.37.8]. - 164 BC164 BCYear 164 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Torquatus and Longinus...
, 25 KislevKislevKislev Kislev Tiberian ; also Chislev is the third month of the civil year and the ninth month of the ecclesiastical year on the Hebrew calendar....
: Judas Maccabaeus, son of Mattathias of the HasmoneanHasmoneanThe Hasmonean dynasty , was the ruling dynasty of Judea and surrounding regions during classical antiquity. Between c. 140 and c. 116 BCE, the dynasty ruled semi-autonomously from the Seleucids in the region of Judea...
family, restores the Temple in JerusalemTemple in JerusalemThe Temple in Jerusalem or Holy Temple , refers to one of a series of structures which were historically located on the Temple Mount in the Old City of Jerusalem, the current site of the Dome of the Rock. Historically, these successive temples stood at this location and functioned as the centre of...
. Events commemorated each year by the festival of HanukkahHanukkahHanukkah , also known as the Festival of Lights, is an eight-day Jewish holiday commemorating the rededication of the Holy Temple in Jerusalem at the time of the Maccabean Revolt of the 2nd century BCE...
. - 147 BC147 BCYear 147 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Aemilianus and Drusus...
: HasmoneanHasmoneanThe Hasmonean dynasty , was the ruling dynasty of Judea and surrounding regions during classical antiquity. Between c. 140 and c. 116 BCE, the dynasty ruled semi-autonomously from the Seleucids in the region of Judea...
victories restore autonomy to JudeaJudeaJudea or Judæa was the name of the mountainous southern part of the historic Land of Israel from the 8th century BCE to the 2nd century CE, when Roman Judea was renamed Syria Palaestina following the Jewish Bar Kokhba revolt.-Etymology:The...
. - 148 BC148 BCYear 148 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Magnus and Caesoninus...
: RomeRomeRome is the capital of Italy and the country's largest and most populated city and comune, with over 2.7 million residents in . The city is located in the central-western portion of the Italian Peninsula, on the Tiber River within the Lazio region of Italy.Rome's history spans two and a half...
conquers MacedonMacedonMacedonia or Macedon was an ancient kingdom, centered in the northeastern part of the Greek peninsula, bordered by Epirus to the west, Paeonia to the north, the region of Thrace to the east and Thessaly to the south....
ia. - 146 BC146 BCYear 146 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Lentulus and Achaicus...
: RomeRomeRome is the capital of Italy and the country's largest and most populated city and comune, with over 2.7 million residents in . The city is located in the central-western portion of the Italian Peninsula, on the Tiber River within the Lazio region of Italy.Rome's history spans two and a half...
destroys and razes the city of CarthageCarthageCarthage , implying it was a 'new Tyre') is a major urban centre that has existed for nearly 3,000 years on the Gulf of Tunis, developing from a Phoenician colony of the 1st millennium BC...
in the Third Punic WarThird Punic WarThe Third Punic War was the third and last of the Punic Wars fought between the former Phoenician colony of Carthage, and the Roman Republic...
.- RomeRomeRome is the capital of Italy and the country's largest and most populated city and comune, with over 2.7 million residents in . The city is located in the central-western portion of the Italian Peninsula, on the Tiber River within the Lazio region of Italy.Rome's history spans two and a half...
conquers CorinthAncient CorinthCorinth, or Korinth was a city-state on the Isthmus of Corinth, the narrow stretch of land that joins the Peloponnesus to the mainland of Greece, roughly halfway between Athens and Sparta. The modern town of Corinth is located approximately northeast of the ancient ruins...
.
- Rome
- 133 BC133 BCYear 133 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Scaevola and Frugi...
: assassination of Tiberius GracchusTiberius GracchusTiberius Sempronius Gracchus was a Roman Populares politician of the 2nd century BC and brother of Gaius Gracchus. As a plebeian tribune, his reforms of agrarian legislation caused political turmoil in the Republic. These reforms threatened the holdings of rich landowners in Italy... - 129 BC129 BCYear 129 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Tuditanus and Aquillius...
: collapse of the Seleucid EmpireSeleucid EmpireThe Seleucid Empire was a Greek-Macedonian state that was created out of the eastern conquests of Alexander the Great. At the height of its power, it included central Anatolia, the Levant, Mesopotamia, Persia, today's Turkmenistan, Pamir and parts of Pakistan.The Seleucid Empire was a major centre...
. - 121 BC121 BCYear 121 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Opimius and Allobrogicus...
: assassination of Gaius GracchusGaius GracchusGaius Sempronius Gracchus was a Roman Populari politician in the 2nd century BC and brother of the ill-fated reformer Tiberius Sempronius Gracchus... - 108 BC108 BCYear 108 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Galba and Hortensius/Scaurus...
: Gojoseon-Han WarGojoseon-Han WarThe Gojoseon–Han War was a campaign launched by the Han Dynasty of China against Wiman Joseon, the last remaining part of Gojoseon after many kingdoms in the Korean peninsula became independent countries, between 109 BC and 108 BC...
—Han DynastyHan DynastyThe Han Dynasty was the second imperial dynasty of China, preceded by the Qin Dynasty and succeeded by the Three Kingdoms . It was founded by the rebel leader Liu Bang, known posthumously as Emperor Gaozu of Han. It was briefly interrupted by the Xin Dynasty of the former regent Wang Mang...
finally destroyed Wanggeom seong, the capital of GojoseonGojoseonGojoseon was an ancient Korean kingdom. Go , meaning "ancient," distinguishes it from the later Joseon Dynasty; Joseon, as it is called in contemporaneous writings, is also romanized as Chosŏn....
. And Han DynastyHan DynastyThe Han Dynasty was the second imperial dynasty of China, preceded by the Qin Dynasty and succeeded by the Three Kingdoms . It was founded by the rebel leader Liu Bang, known posthumously as Emperor Gaozu of Han. It was briefly interrupted by the Xin Dynasty of the former regent Wang Mang...
founded Four Commanderies of HanFour Commanderies of HanThe Four Commanderies of Han are Lelang, Lintun, Xuantu and Zhenfan commanderies in northern Korean Peninsula and part of the Liaodong Peninsula. set up by Emperor Wu of the Han Dynasty in early 2nd century BC after his conquest of Wiman Joseon...
to govern GojoseonGojoseonGojoseon was an ancient Korean kingdom. Go , meaning "ancient," distinguishes it from the later Joseon Dynasty; Joseon, as it is called in contemporaneous writings, is also romanized as Chosŏn....
. - 107 BC107 BCYear 107 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Ravilla and Marius...
: Roman consulConsulConsul was the highest elected office of the Roman Republic and an appointive office under the Empire. The title was also used in other city states and also revived in modern states, notably in the First French Republic...
Gaius MariusGaius MariusGaius Marius was a Roman general and statesman. He was elected consul an unprecedented seven times during his career. He was also noted for his dramatic reforms of Roman armies, authorizing recruitment of landless citizens, eliminating the manipular military formations, and reorganizing the...
passes the Marian ReformsMarian reformsThe Marian reforms of 107 BC were a group of military reforms initiated by Gaius Marius, a statesman and general of the Roman republic.- Roman army before the Marian reforms :...
, which remove all ownership restrictions for joining the Roman Army. - 113 BC113 BCYear 113 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Caprarius and Carbo...
– 101 BC101 BCYear 101 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Marius and Aquillius...
: Migration of the CimbriCimbriThe Cimbri were a tribe from Northern Europe, who, together with the Teutones and the Ambrones threatened the Roman Republic in the late 2nd century BC. The Cimbri were probably Germanic, though some believe them to be of Celtic origin...
and the TeutonsTeutonsThe Teutons or Teutones were mentioned as a Germanic tribe by Greek and Roman authors, notably Strabo and Marcus Velleius Paterculus and normally in close connection with the Cimbri, whose ethnicity is contested between Gauls and Germani...
, defeated at the battles of Aquae SextiaeBattle of Aquae SextiaeThe Battle of Aquae Sextiae took place in 102 BC. After a string of Roman defeats , the Romans under Gaius Marius finally defeated the Teutones and Ambrones.-The battle:...
and VercellaeBattle of VercellaeThe Battle of Vercellae, or Battle of the Raudine Plain, in 101 BC was the Roman victory of Consul Gaius Marius over the invading Germanic Cimbri tribe near the settlement of Vercellae in Cisalpine Gaul....
. - TheravadaTheravadaTheravada ; literally, "the Teaching of the Elders" or "the Ancient Teaching", is the oldest surviving Buddhist school. It was founded in India...
BuddhismBuddhismBuddhism is a religion and philosophy encompassing a variety of traditions, beliefs and practices, largely based on teachings attributed to Siddhartha Gautama, commonly known as the Buddha . The Buddha lived and taught in the northeastern Indian subcontinent some time between the 6th and 4th...
is officially introduced to Sri LankaSri LankaSri Lanka, officially the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka is a country off the southern coast of the Indian subcontinent. Known until 1972 as Ceylon , Sri Lanka is an island surrounded by the Indian Ocean, the Gulf of Mannar and the Palk Strait, and lies in the vicinity of India and the...
by the Venerable Mahinda. - 2nd or 1st century BC1st century BCThe 1st century BC, also known as the last century BC or 1st century BCE, started on the first day of 100 BC and ended on the last day of 1 BC. The AD/BC notation does not use a year zero; however, astronomical year numbering does use a minus sign, so "2 BC" is equal to "year -1"...
: Hagesandros, Polydoros, Athanadoros of RhodesRhodesRhodes is an island in Greece, located in the eastern Aegean Sea. It is the largest of the Dodecanese islands in terms of both land area and population, with a population of 117,007, and also the island group's historical capital. Administratively the island forms a separate municipality within...
make Laocoön and his SonsLaocoön and his SonsThe statue of Laocoön and His Sons , also called the Laocoön Group, is a monumental sculpture in marble now in the Vatican Museums, Rome. The statue is attributed by the Roman author Pliny the Elder to three sculptors from the island of Rhodes: Agesander, Athenodoros and Polydorus...
. Perhaps the original or a Roman copy of the 1st century AD is discovered in 1506. It is now at Musei Vaticani, Museo Pio Clementino, Cortile Ottagono, RomeRomeRome is the capital of Italy and the country's largest and most populated city and comune, with over 2.7 million residents in . The city is located in the central-western portion of the Italian Peninsula, on the Tiber River within the Lazio region of Italy.Rome's history spans two and a half...
. - Porta Augusta, PerugiaPerugiaPerugia is the capital city of the region of Umbria in central Italy, near the River Tiber, and the capital of the province of Perugia. The city is located about north of Rome. It covers a high hilltop and part of the valleys around the area....
, is built. - House of the VettiiHouse of the VettiiIn Pompeii one of the most famous of the luxurious residences is the so-called House of the Vettii, preserved like the rest of the Roman city by the eruption of Vesuvius in 79 AD. The house is named for its owners, two successful freedmen: Aulus Vettius Conviva, an Augustalis, and Aulus Vettius...
, PompeiiPompeiiThe city of Pompeii is a partially buried Roman town-city near modern Naples in the Italian region of Campania, in the territory of the comune of Pompei. Along with Herculaneum, Pompeii was destroyed and completely buried during a long catastrophic eruption of the volcano Mount Vesuvius spanning...
, is built. - Late 2nd century BC – Temple perhaps dedicated to PortunesPortunesIn Roman mythology, Portunes was a god of keys, doors and livestock. He protected the warehouses where grain was stored...
, Forum BoariumForum BoariumThe Forum Boarium was the cattle forum venalium of Ancient Rome and the oldest forum that Rome possessed. It was located on a level piece of land near the Tiber between the Capitoline, the Palatine and Aventine hills. Here, too, is where the first bridges were built...
, RomeRomeRome is the capital of Italy and the country's largest and most populated city and comune, with over 2.7 million residents in . The city is located in the central-western portion of the Italian Peninsula, on the Tiber River within the Lazio region of Italy.Rome's history spans two and a half...
, is built. - Late 2nd century BC or early 1st century BC1st century BCThe 1st century BC, also known as the last century BC or 1st century BCE, started on the first day of 100 BC and ended on the last day of 1 BC. The AD/BC notation does not use a year zero; however, astronomical year numbering does use a minus sign, so "2 BC" is equal to "year -1"...
– Aulus Metellus, found near Perugia, is made. It is now kept at Museo Archeologico Nazionale, FlorenceFlorenceFlorence is the capital city of the Italian region of Tuscany and of the province of Florence. It is the most populous city in Tuscany, with approximately 370,000 inhabitants, expanding to over 1.5 million in the metropolitan area....
. - Shortly before 100 BC the Scythians overran ParthiaParthiaParthia is a region of north-eastern Iran, best known for having been the political and cultural base of the Arsacid dynasty, rulers of the Parthian Empire....
. - Buddhist monks begin to hew caves for their own use out of the stone plateaus in the region of south-central IndiaIndiaIndia , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
known as the Deccan (approximate date). - The Segestani were attacked by the Romans
Significant persons

- AndriscusAndriscusAndriscus, and often called the "pseudo-Philip", was the last King of Macedon , and ruler of Adramyttium in Aeolis ....
, last independent ruler of Macedon - Antiochus IV EpiphanesAntiochus IV EpiphanesAntiochus IV Epiphanes ruled the Seleucid Empire from 175 BC until his death in 164 BC. He was a son of King Antiochus III the Great. His original name was Mithridates; he assumed the name Antiochus after he ascended the throne....
, the last effective ruler of the Seleucid EmpireSeleucid EmpireThe Seleucid Empire was a Greek-Macedonian state that was created out of the eastern conquests of Alexander the Great. At the height of its power, it included central Anatolia, the Levant, Mesopotamia, Persia, today's Turkmenistan, Pamir and parts of Pakistan.The Seleucid Empire was a major centre... - Antiochus VII SidetesAntiochus VII SidetesAntiochus VII Euergetes, nicknamed Sidetes , ruler of the Hellenistic Seleucid Empire, reigned from 138 to 129 BC. He was the last Seleucid king of any stature....
, last King of a United Seleucid EmpireSeleucid EmpireThe Seleucid Empire was a Greek-Macedonian state that was created out of the eastern conquests of Alexander the Great. At the height of its power, it included central Anatolia, the Levant, Mesopotamia, Persia, today's Turkmenistan, Pamir and parts of Pakistan.The Seleucid Empire was a major centre... - Apollonius of PergaApollonius of PergaApollonius of Perga [Pergaeus] was a Greek geometer and astronomer noted for his writings on conic sections. His innovative methodology and terminology, especially in the field of conics, influenced many later scholars including Ptolemy, Francesco Maurolico, Isaac Newton, and René Descartes...
, Greek geometer - Appius Claudius Pulcher, Roman consul and censor
- BoiorixBoiorixBoiorix was a king of the Cimbri tribe. His most notable achievement was a spectacular victory against the Romans at the Battle of Arausio in 105 BC. He was later defeated and slain at the Battle of Vercellae in 101 BC.-References:...
, king of the CimbriCimbriThe Cimbri were a tribe from Northern Europe, who, together with the Teutones and the Ambrones threatened the Roman Republic in the late 2nd century BC. The Cimbri were probably Germanic, though some believe them to be of Celtic origin... - CiceroCiceroMarcus Tullius Cicero , was a Roman philosopher, statesman, lawyer, political theorist, and Roman constitutionalist. He came from a wealthy municipal family of the equestrian order, and is widely considered one of Rome's greatest orators and prose stylists.He introduced the Romans to the chief...
, Roman orator and Statesman (106-43 BC) - FlaccusFlaccus (composer)Flaccus is a composer from the 2nd century BC, of whom little is known. He was either a freedman or a slave of one of Terence's patrons and wrote musical scores for Terence's comedies...
, musical collaboratorComposerA composer is a person who creates music, either by musical notation or oral tradition, for interpretation and performance, or through direct manipulation of sonic material through electronic media...
of Terence - HipparchusHipparchusHipparchus, the common Latinization of the Greek Hipparkhos, can mean:* Hipparchus, the ancient Greek astronomer** Hipparchic cycle, an astronomical cycle he created** Hipparchus , a lunar crater named in his honour...
, considered the greatest astronomical observer - Jonathan MaccabaeusJonathan MaccabaeusJonathan Apphus was leader of the Hasmonean Dynasty of Judea from 161 to 143 BCE. The name Apphus could mean = "the dissembler", "the Wary", or "the diplomat", in allusion to a trait prominent in him -Leader of the Jews:...
, leader of the HasmoneanHasmoneanThe Hasmonean dynasty , was the ruling dynasty of Judea and surrounding regions during classical antiquity. Between c. 140 and c. 116 BCE, the dynasty ruled semi-autonomously from the Seleucids in the region of Judea...
rebellion and first autonomous ruler of JudeaJudeaJudea or Judæa was the name of the mountainous southern part of the historic Land of Israel from the 8th century BCE to the 2nd century CE, when Roman Judea was renamed Syria Palaestina following the Jewish Bar Kokhba revolt.-Etymology:The... - Judas MaccabeusJudas MaccabeusJudah Maccabee was a Kohen and a son of the Jewish priest Mattathias...
, leader of the HasmoneanHasmoneanThe Hasmonean dynasty , was the ruling dynasty of Judea and surrounding regions during classical antiquity. Between c. 140 and c. 116 BCE, the dynasty ruled semi-autonomously from the Seleucids in the region of Judea...
rebellion and its first successful general - Liu AnLiu AnLíu Ān was a Chinese prince and advisor to his nephew, Emperor Wu of Han of the Han Dynasty in China and the legendary inventor of t'ai chi...
, Chinese prince and noted geographerGeographerA geographer is a scholar whose area of study is geography, the study of Earth's natural environment and human society.Although geographers are historically known as people who make maps, map making is actually the field of study of cartography, a subset of geography... - Lucius Aemilius Paullus Macedonicus, Roman general and politician
- Lucius Cornelius SullaLucius Cornelius SullaLucius Cornelius Sulla Felix , known commonly as Sulla, was a Roman general and statesman. He had the rare distinction of holding the office of consul twice, as well as that of dictator...
, Roman general and politician - Lucius Mummius AchaicusLucius Mummius AchaicusLucius Mummius , was a Roman statesman and general, also known as Leucius Mommius. He later received the agnomen Achaicus after conquering Greece.-Praetor:...
, conqueror of CorinthAncient CorinthCorinth, or Korinth was a city-state on the Isthmus of Corinth, the narrow stretch of land that joins the Peloponnesus to the mainland of Greece, roughly halfway between Athens and Sparta. The modern town of Corinth is located approximately northeast of the ancient ruins... - Gaius MariusGaius MariusGaius Marius was a Roman general and statesman. He was elected consul an unprecedented seven times during his career. He was also noted for his dramatic reforms of Roman armies, authorizing recruitment of landless citizens, eliminating the manipular military formations, and reorganizing the...
, Roman general and politician - Perseus of MacedonPerseus of MacedonPerseus was the last king of the Antigonid dynasty, who ruled the successor state in Macedon created upon the death of Alexander the Great...
, last King of the Antigonid dynastyAntigonid dynastyThe Antigonid dynasty was a dynasty of Hellenistic kings descended from Alexander the Great's general Antigonus I Monophthalmus .-History:... - PlautusPlautusTitus Maccius Plautus , commonly known as "Plautus", was a Roman playwright of the Old Latin period. His comedies are the earliest surviving intact works in Latin literature. He wrote Palliata comoedia, the genre devised by the innovator of Latin literature, Livius Andronicus...
, Latin playwrightPlaywrightA playwright, also called a dramatist, is a person who writes plays.The term is not a variant spelling of "playwrite", but something quite distinct: the word wright is an archaic English term for a craftsman or builder... - Quintus Lutatius CatulusQuintus Lutatius CatulusQuintus Lutatius Catulus was consul of the Roman Republic in 102 BC, and the leading public figure of the gens Lutatia of the time. His colleague in the consulship was Gaius Marius, but the two feuded and Catulus sided with Sulla in the civil war of 88–87 BC...
, Roman general - Scipio Aemilianus AfricanusScipio Aemilianus AfricanusPublius Cornelius Scipio Aemilianus Africanus Numantinus , also known as Scipio Aemilianus or Scipio Africanus the Younger, was a leading general and politician of the ancient Roman Republic...
, conqueror of CarthageCarthageCarthage , implying it was a 'new Tyre') is a major urban centre that has existed for nearly 3,000 years on the Gulf of Tunis, developing from a Phoenician colony of the 1st millennium BC... - Sima QianSima QianSima Qian was a Prefect of the Grand Scribes of the Han Dynasty. He is regarded as the father of Chinese historiography for his highly praised work, Records of the Grand Historian , a "Jizhuanti"-style general history of China, covering more than two thousand years from the Yellow Emperor to...
, father of Chinese historiographyChinese historiographyChinese historiography refers to the study of methods and assumptions made in studying Chinese history.-History of Chinese Historians:Record of Chinese history dated back to the Shang Dynasty. The Classic of History, one of the Five Classics of Chinese classic texts is one of the earliest... - TerenceTerencePublius Terentius Afer , better known in English as Terence, was a playwright of the Roman Republic, of North African descent. His comedies were performed for the first time around 170–160 BC. Terentius Lucanus, a Roman senator, brought Terence to Rome as a slave, educated him and later on,...
, Latin playwrightPlaywrightA playwright, also called a dramatist, is a person who writes plays.The term is not a variant spelling of "playwrite", but something quite distinct: the word wright is an archaic English term for a craftsman or builder... - TeutobodTeutobodTeutobod was King of the Teutons. In the late 2nd century BC, together with their neighbours, allies and possible relatives, the Cimbri, the Teutons migrated from their original homes in southern Scandinavia and on the Jutland peninsula of Denmark, south into the Danube valley, southern Gaul and...
, King of the TeutonsTeutonsThe Teutons or Teutones were mentioned as a Germanic tribe by Greek and Roman authors, notably Strabo and Marcus Velleius Paterculus and normally in close connection with the Cimbri, whose ethnicity is contested between Gauls and Germani... - Wei QingWei QingWei Qing , born Zheng Qing in Linfen, Shanxi, was a famous general during Han Dynasty of China, whose campaigns against the Xiongnu earned him great acclaim. He was the younger half-brother of Empress Wei Zifu, making him the the Emperor Wu's brother-in-law...
, a general of Han DynastyHan DynastyThe Han Dynasty was the second imperial dynasty of China, preceded by the Qin Dynasty and succeeded by the Three Kingdoms . It was founded by the rebel leader Liu Bang, known posthumously as Emperor Gaozu of Han. It was briefly interrupted by the Xin Dynasty of the former regent Wang Mang...
, who strike XiongnuXiongnuThe Xiongnu were ancient nomadic-based people that formed a state or confederation north of the agriculture-based empire of the Han Dynasty. Most of the information on the Xiongnu comes from Chinese sources...
deeply leading Chinese army and enabled Han control Western RegionsWestern RegionsThe Western Regions or Xiyu was a historical name specified in the Chinese chronicles between the 3rd century BC to 8th century AD that referred to the regions west of Jade Gate, most often Central Asia or sometimes more specifically the easternmost portion of it The Western Regions or Xiyu was a...
later - Emperor Wu of HanEmperor Wu of HanEmperor Wu of Han , , personal name Liu Che , was the seventh emperor of the Han Dynasty of China, ruling from 141 BC to 87 BC. Emperor Wu is best remembered for the vast territorial expansion that occurred under his reign, as well as the strong and centralized Confucian state he organized...
, considered one of the greatest emperors throughout the History of ChinaHistory of ChinaChinese civilization originated in various regional centers along both the Yellow River and the Yangtze River valleys in the Neolithic era, but the Yellow River is said to be the Cradle of Chinese Civilization. With thousands of years of continuous history, China is one of the world's oldest... - Zhang QianZhang QianZhang Qian was an imperial envoy to the world outside of China in the 2nd century BCE, during the time of the Han Dynasty...
, Chinese diplomat and explorer
Inventions, discoveries, introductions

- The ChineseChinaChinese civilization may refer to:* China for more general discussion of the country.* Chinese culture* Greater China, the transnational community of ethnic Chinese.* History of China* Sinosphere, the area historically affected by Chinese culture...
first produce PaperPaperPaper is a thin material mainly used for writing upon, printing upon, drawing or for packaging. It is produced by pressing together moist fibers, typically cellulose pulp derived from wood, rags or grasses, and drying them into flexible sheets....
. - Silk RoadSilk RoadThe Silk Road or Silk Route refers to a historical network of interlinking trade routes across the Afro-Eurasian landmass that connected East, South, and Western Asia with the Mediterranean and European world, as well as parts of North and East Africa...
between EuropeEuropeEurope is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting...
and AsiaAsiaAsia is the world's largest and most populous continent, located primarily in the eastern and northern hemispheres. It covers 8.7% of the Earth's total surface area and with approximately 3.879 billion people, it hosts 60% of the world's current human population... - HipparchusHipparchusHipparchus, the common Latinization of the Greek Hipparkhos, can mean:* Hipparchus, the ancient Greek astronomer** Hipparchic cycle, an astronomical cycle he created** Hipparchus , a lunar crater named in his honour...
discovers precessionPrecessionPrecession is a change in the orientation of the rotation axis of a rotating body. It can be defined as a change in direction of the rotation axis in which the second Euler angle is constant...
of EarthEarthEarth is the third planet from the Sun, and the densest and fifth-largest of the eight planets in the Solar System. It is also the largest of the Solar System's four terrestrial planets...
's equinoxEquinoxAn equinox occurs twice a year, when the tilt of the Earth's axis is inclined neither away from nor towards the Sun, the center of the Sun being in the same plane as the Earth's equator...
es and compiles first trigonometricTrigonometryTrigonometry is a branch of mathematics that studies triangles and the relationships between their sides and the angles between these sides. Trigonometry defines the trigonometric functions, which describe those relationships and have applicability to cyclical phenomena, such as waves...
tables - Liu AnLiu AnLíu Ān was a Chinese prince and advisor to his nephew, Emperor Wu of Han of the Han Dynasty in China and the legendary inventor of t'ai chi...
invented tofuTofuis a food made by coagulating soy milk and then pressing the resulting curds into soft white blocks. It is part of East Asian and Southeast Asian cuisine such as Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Indonesian, Vietnamese, and others. There are many different varieties of tofu, including fresh tofu and tofu... - The Roman concreteRoman concreteRoman concrete was a material used in construction during the late Roman Republic through the whole history of the Roman Empire. Roman concrete was based on a hydraulic-setting cement with many material qualities similar to modern Portland cement...
(pozzolana) first used - Rotary mill invented by the ancient Greeks
- A system for sending signs to communicate quickly over a long distance is described by Polybios
- The earliest known winnowing machine is depicted in a Han DynastyHan DynastyThe Han Dynasty was the second imperial dynasty of China, preceded by the Qin Dynasty and succeeded by the Three Kingdoms . It was founded by the rebel leader Liu Bang, known posthumously as Emperor Gaozu of Han. It was briefly interrupted by the Xin Dynasty of the former regent Wang Mang...
Chinese tomb model.

