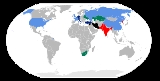
List of countries with nuclear weapons
Unanswered Questions
Encyclopedia
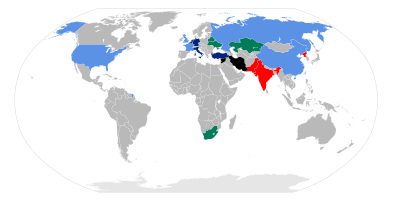
Sovereign state
A sovereign state, or simply, state, is a state with a defined territory on which it exercises internal and external sovereignty, a permanent population, a government, and the capacity to enter into relations with other sovereign states. It is also normally understood to be a state which is neither...
that have successfully detonated nuclear weapons. Five are considered to be "nuclear-weapon states" (NWS) under the terms of the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty
Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty
The Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons, commonly known as the Non-Proliferation Treaty or NPT, is a landmark international treaty whose objective is to prevent the spread of nuclear weapons and weapons technology, to promote cooperation in the peaceful uses of nuclear energy and to...
(NPT). In order of acquisition of nuclear weapons these are: the United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
, Russia
Russia
Russia or , officially known as both Russia and the Russian Federation , is a country in northern Eurasia. It is a federal semi-presidential republic, comprising 83 federal subjects...
(successor state to the Soviet Union
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union , officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics , was a constitutionally socialist state that existed in Eurasia between 1922 and 1991....
), the United Kingdom
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
, France
France
The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
, and China
People's Republic of China
China , officially the People's Republic of China , is the most populous country in the world, with over 1.3 billion citizens. Located in East Asia, the country covers approximately 9.6 million square kilometres...
. Nation
Nation
A nation may refer to a community of people who share a common language, culture, ethnicity, descent, and/or history. In this definition, a nation has no physical borders. However, it can also refer to people who share a common territory and government irrespective of their ethnic make-up...
s that are known or believed to possess nuclear weapon
Nuclear weapon
A nuclear weapon is an explosive device that derives its destructive force from nuclear reactions, either fission or a combination of fission and fusion. Both reactions release vast quantities of energy from relatively small amounts of matter. The first fission bomb test released the same amount...
s are sometimes referred to as the nuclear club.
Since the NPT entered into force in 1970, three states that were not parties to the Treaty have conducted nuclear tests
Nuclear testing
Nuclear weapons tests are experiments carried out to determine the effectiveness, yield and explosive capability of nuclear weapons. Throughout the twentieth century, most nations that have developed nuclear weapons have tested them...
, namely India
India
India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
, Pakistan
Pakistan
Pakistan , officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan is a sovereign state in South Asia. It has a coastline along the Arabian Sea and the Gulf of Oman in the south and is bordered by Afghanistan and Iran in the west, India in the east and China in the far northeast. In the north, Tajikistan...
, and North Korea
North Korea
The Democratic People’s Republic of Korea , , is a country in East Asia, occupying the northern half of the Korean Peninsula. Its capital and largest city is Pyongyang. The Korean Demilitarized Zone serves as the buffer zone between North Korea and South Korea...
. North Korea had been a party to the NPT but withdrew in 2003. Israel is also widely believed to have nuclear weapons, though it has refused to confirm or deny this, and is not known to have conducted a nuclear test.
South Africa
South Africa
The Republic of South Africa is a country in southern Africa. Located at the southern tip of Africa, it is divided into nine provinces, with of coastline on the Atlantic and Indian oceans...
has the unique status of a nation that developed nuclear weapons but has since disassembled its arsenal before joining the NPT.
Statistics
The following is a list of statesSovereign state
A sovereign state, or simply, state, is a state with a defined territory on which it exercises internal and external sovereignty, a permanent population, a government, and the capacity to enter into relations with other sovereign states. It is also normally understood to be a state which is neither...
that have admitted the possession of nuclear weapons, the approximate number of warhead
Warhead
The term warhead refers to the explosive material and detonator that is delivered by a missile, rocket, or torpedo.- Etymology :During the early development of naval torpedoes, they could be equipped with an inert payload that was intended for use during training, test firing and exercises. This...
s under their control, and the year they tested their first weapon. This list is informally known in global politics as the "Nuclear Club." With the exception of Russia and the United States (which have subjected their nuclear forces to independent verification under various treaties) these figures are estimates, in some cases quite unreliable estimates. Also, these figures represent total warheads possessed, rather than deployed. In particular, under the SORT
SORT
The Treaty Between the United States of America and the Russian Federation on Strategic Offensive Reductions , also known as the Treaty of Moscow, was a strategic arms reduction treaty between the United States and Russia that was in force from June 2003 until February 2011 when it was superseded...
treaty thousands of Russian and U.S. nuclear warheads are in inactive stockpiles awaiting processing. The fissile material contained in the warheads can then be recycled for use in nuclear reactors.
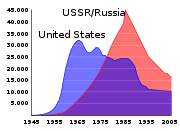
From a high of 65,000 active weapons in 1985, there are now nearly 8,000 active nuclear warheads and more than 22,000 total nuclear warheads in the world in 2010. Many of the decommissioned weapons were simply stored or partially dismantled, not destroyed. As of 2009, the total number was expected to continue to decline by 30%–50% over the next decade.
| Country | Warheads active/totalAll numbers are estimates from the Natural Resources Defense Council Natural Resources Defense Council The Natural Resources Defense Council is a New York City-based, non-profit, non-partisan international environmental advocacy group, with offices in Washington DC, San Francisco, Los Angeles, Chicago, and Beijing... , published in the Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists The Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists is a nontechnical online magazine that covers global security and public policy issues, especially related to the dangers posed by nuclear and other weapons of mass destruction... , unless other references are given. The latest update was on February 19, 2011. If differences between active and total stockpile are known, they are given as two figures separated by a forward slash. If specifics are not available (n.a.), only one figure is given. Stockpile number may not contain all intact warheads if a substantial amount of warheads are scheduled for but have not yet gone through dismantlement; not all "active" warheads are deployed at any given time. When a range of weapons is given (e.g., 0–10), it generally indicates that the estimate is being made on the amount of fissile material that has likely been produced, and the amount of fissile material needed per warhead depends on estimates of a country's proficiency at nuclear weapon design. |
Year of first test | CTBT status |
|---|---|---|---|
| The five nuclear-weapon states under the NPT Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty The Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons, commonly known as the Non-Proliferation Treaty or NPT, is a landmark international treaty whose objective is to prevent the spread of nuclear weapons and weapons technology, to promote cooperation in the peaceful uses of nuclear energy and to... |
|||
 United States United StatesNuclear weapons and the United States The United States was the first country to develop nuclear weapons, and is the only country to have used them in warfare, with the separate bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki in World War II. Before and during the Cold War it conducted over a thousand nuclear tests and developed many long-range... |
1,950 / 8,500 | 1945 ("Trinity Trinity test Trinity was the code name of the first test of a nuclear weapon. This test was conducted by the United States Army on July 16, 1945, in the Jornada del Muerto desert about 35 miles southeast of Socorro, New Mexico, at the new White Sands Proving Ground, which incorporated the Alamogordo Bombing... ) |
Signatory |
 Russia (former Russia (former  Soviet Union) Soviet Union) |
2,430 / 11,000 | 1949 ("RDS-1) | Ratifier |
| United Kingdom Nuclear weapons and the United Kingdom The United Kingdom was the third country to test an independently developed nuclear weapon, in October 1952. It is one of the five "Nuclear Weapons States" under the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty, which the UK ratified in 1968... |
160 / 225 | 1952 ("Hurricane Operation Hurricane Operation Hurricane was the test of the first British atomic device on 3 October 1952. A plutonium implosion device was detonated in the lagoon between the Montebello Islands, Western Australia.... ) |
Ratifier |
 France France |
290 / 300 | 1960 ("Gerboise Bleue Gerboise Bleue Gerboise Bleue was the name of the first French nuclear test. It was an atomic bomb detonated in the middle of the Algerian Sahara desert on 13 February 1960, during the Algerian War... ) |
Ratifier |
 China China |
~180 / 240 | 1964 ("596 596 (nuclear test) 596 is the codename of the People's Republic of China's first nuclear weapons test, detonated on October 16, 1964 at the Lop Nur test site. It was a uranium-235 implosion fission device and had a yield of 22 kilotons... ) |
Signatory |
| Non-NPT Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty The Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons, commonly known as the Non-Proliferation Treaty or NPT, is a landmark international treaty whose objective is to prevent the spread of nuclear weapons and weapons technology, to promote cooperation in the peaceful uses of nuclear energy and to... nuclear powers |
|||
 India India |
n.a. / 80–100 | 1974 ("Smiling Buddha Smiling Buddha The Smiling Buddha, formally designated as Pokhran-I, was the codename given to Republic of India's first nuclear test explosion that took place at the long-constructed Indian Army base, Pokhran Test Range at Pokhran municipality, Rajasthan state on 18 May 1974 at 8:05 a.m.... ) |
Non-signatory |
 Pakistan Pakistan |
n.a. / 90–110 | 1998 ("Chagai-I Chagai-I The Chagai-I was a codename referring to the five underground nuclear tests conducted by Pakistan at 15:15hrs in 28th May of 1998. It was named Chagai-I, as the tests were conducted in the Chagai District... ) |
Non-signatory |
 North Korea North Korea |
n.a. / <10 | 2006 (2006 test 2006 North Korean nuclear test The 2006 North Korean nuclear test was the detonation of a nuclear device conducted on October 9, 2006 by North Korea.North Korea announced its intention to conduct a test on October 3, six days prior, and in doing so became the first nation to give warning of its first nuclear test... ) |
Non-signatory |
| Undeclared nuclear powers | |||
 Israel IsraelNuclear weapons and Israel Israel is widely believed to be the sixth country in the world to have developed nuclear weapons and to be one of four nuclear-armed countries not recognized as a Nuclear Weapons State by the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty , the others being India, Pakistan and North Korea... |
n.a. / 80–200 | possibly 1979 (See Vela Incident Vela Incident The Vela Incident was an unidentified "double flash" of light that was detected by an American Vela Hotel satellite on September 22, 1979.... ) |
Signatory |
Five nuclear-weapon states under the NPT


- The United States developed the first atomic weapons during World War IIWorld War IIWorld War II, or the Second World War , was a global conflict lasting from 1939 to 1945, involving most of the world's nations—including all of the great powers—eventually forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis...
in co-operation with the United Kingdom and Canada as part of the Manhattan ProjectManhattan ProjectThe Manhattan Project was a research and development program, led by the United States with participation from the United Kingdom and Canada, that produced the first atomic bomb during World War II. From 1942 to 1946, the project was under the direction of Major General Leslie Groves of the US Army...
, out of the fear that Nazi GermanyNazi GermanyNazi Germany , also known as the Third Reich , but officially called German Reich from 1933 to 1943 and Greater German Reich from 26 June 1943 onward, is the name commonly used to refer to the state of Germany from 1933 to 1945, when it was a totalitarian dictatorship ruled by...
would develop them first. It tested the first nuclear weapon in 1945 ("Trinity"), and remains the only country to have used nuclear weapons against another nation, during the atomic bombings of Hiroshima and NagasakiAtomic bombings of Hiroshima and NagasakiDuring the final stages of World War II in 1945, the United States conducted two atomic bombings against the cities of Hiroshima and Nagasaki in Japan, the first on August 6, 1945, and the second on August 9, 1945. These two events are the only use of nuclear weapons in war to date.For six months...
. It was the first nation to develop the hydrogen bombNuclear weapon designNuclear weapon designs are physical, chemical, and engineering arrangements that cause the physics package of a nuclear weapon to detonate. There are three basic design types...
, testing an experimental version in 1952 ("Ivy MikeIvy MikeIvy Mike was the codename given to the first United States test of a thermonuclear weapon, in which a major part of the explosive yield came from nuclear fusion. It was detonated on November 1, 1952 by the United States at on Enewetak, an atoll in the Pacific Ocean, as part of Operation Ivy...
") and a deployable weapon in 1954 ("Castle BravoCastle BravoCastle Bravo was the code name given to the first U.S. test of a dry fuel thermonuclear hydrogen bomb device, detonated on March 1, 1954 at Bikini Atoll, Marshall Islands, as the first test of Operation Castle. Castle Bravo was the most powerful nuclear device ever detonated by the United States ,...
"). Throughout the Cold War it continued to modernize and enlarge its nuclear arsenal, but from 1992 on has been involved primarily in a program of Stockpile stewardshipStockpile stewardshipStockpile stewardship refers to the United States program of reliability testing and maintenance of its nuclear weapons without the use of nuclear testing....
. At its Cold War height, the US nuclear arsenal is estimated to have contained over 32,000 warheads (in 1966).
- The Soviet Union tested its first nuclear weapon ("Joe-1") in 1949, in a crash project developed partially with espionage obtained during and after World War IIWorld War IIWorld War II, or the Second World War , was a global conflict lasting from 1939 to 1945, involving most of the world's nations—including all of the great powers—eventually forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis...
(see: Soviet atomic bomb projectSoviet atomic bomb projectThe Soviet project to develop an atomic bomb , was a clandestine research and development program began during and post-World War II, in the wake of the Soviet Union's discovery of the United States' nuclear project...
). The USSR was the second nation to have developed and tested a nuclear weaponNuclear weaponA nuclear weapon is an explosive device that derives its destructive force from nuclear reactions, either fission or a combination of fission and fusion. Both reactions release vast quantities of energy from relatively small amounts of matter. The first fission bomb test released the same amount...
. The direct motivation for their weapons development was to achieve a balance of power during the Cold WarCold WarThe Cold War was the continuing state from roughly 1946 to 1991 of political conflict, military tension, proxy wars, and economic competition between the Communist World—primarily the Soviet Union and its satellite states and allies—and the powers of the Western world, primarily the United States...
. It tested its first megaton-range hydrogen bomb ("RDS-37RDS-37RDS-37 was the Soviet Union's first "true" hydrogen bomb, first tested on November 22, 1955. The weapon had a nominal yield of approximately 3 megatons. It was scaled down to 1.6 megatons for the live test....
") in 1955. The Soviet Union also tested the most powerful explosive ever detonated by humans, ("Tsar BombaTsar BombaTsar Bomba is the nickname for the AN602 hydrogen bomb, the most powerful nuclear weapon ever detonated. It was also referred to as Kuz'kina Mat , in this usage meaning "something that has not been seen before"....
"), with a theoretical yield of 100 megatons, intentionally reduced to 50 when detonated. After its dissolution in 1991, the Soviet weapons entered officially into the possession of the Russian Federation. At its maximum, the Soviet nuclear arsenal is estimated to have contained some 45,000 warheads (in 1988).
- The United Kingdom tested its first nuclear weapon ("HurricaneOperation HurricaneOperation Hurricane was the test of the first British atomic device on 3 October 1952. A plutonium implosion device was detonated in the lagoon between the Montebello Islands, Western Australia....
") in 1952, drawing largely on data gained while collaborating with the United States during the Manhattan ProjectManhattan ProjectThe Manhattan Project was a research and development program, led by the United States with participation from the United Kingdom and Canada, that produced the first atomic bomb during World War II. From 1942 to 1946, the project was under the direction of Major General Leslie Groves of the US Army...
. The United KingdomUnited KingdomThe United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
was the third country in the world after the USA and USSR to develop and test a nuclear weapon. Its programme was motivated to have an independent deterrent against the USSR, while also maintaining its status as a great powerGreat powerA great power is a nation or state that has the ability to exert its influence on a global scale. Great powers characteristically possess military and economic strength and diplomatic and cultural influence which may cause small powers to consider the opinions of great powers before taking actions...
. It tested its first hydrogen bomb in 1957 (Operation GrappleOperation GrappleOperation Grapple, and operations Grapple X, Grapple Y and Grapple Z, were the names of British nuclear tests of the hydrogen bomb. They were held 1956—1958 at Malden Island and Christmas Island in the central Pacific Ocean. Nine nuclear detonations took place during the trials, resulting in...
), making it the third country to do so after the USA and USSR. The UK maintained a fleet of V-bomber strategic bombers and ballistic missile submarines (SSBNs)Ballistic missile submarineA ballistic missile submarine is a submarine equipped to launch ballistic missiles .-Description:Ballistic missile submarines are larger than any other type of submarine, in order to accommodate SLBMs such as the Russian R-29 or the American Trident...
equipped with nuclear weapons during the Cold War. It currently maintains a fleet of four 'Vanguard' classVanguard class submarineThe Vanguard class are the Royal Navy's current nuclear ballistic missile submarines , each armed with up to 16 Trident II Submarine-launched ballistic missiles...
ballistic missile submarines equipped with Trident IITrident missileThe Trident missile is a submarine-launched ballistic missile equipped with multiple independently-targetable reentry vehicles . The Fleet Ballistic Missile is armed with nuclear warheads and is launched from nuclear-powered ballistic missile submarines . Trident missiles are carried by fourteen...
SLBMs. The British government announced a replacement to the current systemBritish replacement of the Trident systemThe British replacement of Trident is a proposal to replace the existing Vanguard class of four Trident ballistic-missile armed submarines with a new class designed to continue a nuclear deterrent after the current boats reach the end of their service lives...
to take place between 2007-2024.
- France tested its first nuclear weapon in 1960 ("Gerboise BleueGerboise BleueGerboise Bleue was the name of the first French nuclear test. It was an atomic bomb detonated in the middle of the Algerian Sahara desert on 13 February 1960, during the Algerian War...
"), based mostly on its own research. It was motivated by the Suez CrisisSuez CrisisThe Suez Crisis, also referred to as the Tripartite Aggression, Suez War was an offensive war fought by France, the United Kingdom, and Israel against Egypt beginning on 29 October 1956. Less than a day after Israel invaded Egypt, Britain and France issued a joint ultimatum to Egypt and Israel,...
diplomatic tension vis-à-vis both the USSR and the Free WorldFree WorldThe Free World is a Cold War-era term often used to describe states not under the rule of the Soviet Union, its Eastern European allies, China, Vietnam, Cuba, and other communist nations. The term often referred to states such as the United States, Canada, and Western European states such as the...
allies United States and United Kingdom. It was also relevant to retain great powerGreat powerA great power is a nation or state that has the ability to exert its influence on a global scale. Great powers characteristically possess military and economic strength and diplomatic and cultural influence which may cause small powers to consider the opinions of great powers before taking actions...
status, alongside the United Kingdom, during the post-colonial Cold WarCold WarThe Cold War was the continuing state from roughly 1946 to 1991 of political conflict, military tension, proxy wars, and economic competition between the Communist World—primarily the Soviet Union and its satellite states and allies—and the powers of the Western world, primarily the United States...
(see: Force de frappeForce de frappeThe Force de Frappe is the designation of what used to be a triad of air-, sea- and land-based nuclear weapons intended for dissuasion, and consequential deterrence...
). France tested its first hydrogen bomb in 1968 ("Opération CanopusCanopus (nuclear test)Canopus was the code name for France's first two-stage thermonuclear test, conducted on August 24, 1968 at Fangataufa atoll...
"). After the Cold War, France has disarmed 175 warheads with the reduction and modernization of its arsenal that has now evolved to a dual system based on submarine-launched ballistic missiles (SLBMs) and medium-range air-to-surface missiles (Rafale fighter-bombers). However new nuclear weapons are in development and reformed nuclear squadrons were trained during Enduring Freedom operations in Afghanistan. In January 2006, President Jacques ChiracJacques ChiracJacques René Chirac is a French politician who served as President of France from 1995 to 2007. He previously served as Prime Minister of France from 1974 to 1976 and from 1986 to 1988 , and as Mayor of Paris from 1977 to 1995.After completing his studies of the DEA's degree at the...
stated a terrorist act or the use of weapons of mass destructionWeapons of mass destructionA weapon of mass destruction is a weapon that can kill and bring significant harm to a large number of humans and/or cause great damage to man-made structures , natural structures , or the biosphere in general...
against France would result in a nuclear counterattack.
- China tested its first nuclear weaponNuclear weaponA nuclear weapon is an explosive device that derives its destructive force from nuclear reactions, either fission or a combination of fission and fusion. Both reactions release vast quantities of energy from relatively small amounts of matter. The first fission bomb test released the same amount...
device ("596596 (nuclear test)596 is the codename of the People's Republic of China's first nuclear weapons test, detonated on October 16, 1964 at the Lop Nur test site. It was a uranium-235 implosion fission device and had a yield of 22 kilotons...
") in 1964 at the Lop NurLop NurLop Lake or Lop Nur is a group of small, now seasonal salt lake sand marshes between the Taklamakan and Kuruktag deserts in the Bayingolin Mongol Autonomous Prefecture, southeastern portion of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region in the People's Republic of China.The lake system into which the Tarim...
test site. The weapon was developed as a deterrent against both the United StatesUnited StatesThe United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
and the Soviet UnionSoviet UnionThe Soviet Union , officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics , was a constitutionally socialist state that existed in Eurasia between 1922 and 1991....
. China would manage to develop a fission bomb capable of being put onto a nuclear missile only two years after its first detonation. It tested its first hydrogen bomb ("Test No. 6Chinese nuclear test No. 6Test No. 6 is the codename for the China's first test of a three-staged thermonuclear device and, also its sixth nuclear weapons test. The device was detonated at Lop Nur Test Base, or often dubbed as Lop Nur Nuclear Weapon Test Base, in Malan, Xinjiang, on 17 June 1967...
") in 1967, a mere 32 months after testing its first nuclear weapon (the shortest fission-to-fusion development known in history). The country is currently thought to have had a stockpile of around 240 warheads, though because of the limited information available, estimates range from 100 to 400. China is the only NPT nuclear-weapon state to give an unqualified negative security assurance due to its "no first useNo first useNo first use refers to a pledge or a policy by a nuclear power not to use nuclear weapons as a means of warfare unless first attacked by an adversary using nuclear weapons...
" policy.
Other states declaring they have nuclear weapons
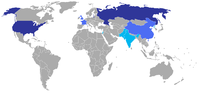
- India is not a Party to the Nuclear Non-Proliferation TreatyNuclear Non-Proliferation TreatyThe Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons, commonly known as the Non-Proliferation Treaty or NPT, is a landmark international treaty whose objective is to prevent the spread of nuclear weapons and weapons technology, to promote cooperation in the peaceful uses of nuclear energy and to...
. India tested what it called a "peaceful nuclear explosivePeaceful nuclear explosionsPeaceful nuclear explosions are nuclear explosions conducted for non-military purposes, such as activities related to economic development including the creation of canals...
" in 1974 (which became known as "Smiling BuddhaSmiling BuddhaThe Smiling Buddha, formally designated as Pokhran-I, was the codename given to Republic of India's first nuclear test explosion that took place at the long-constructed Indian Army base, Pokhran Test Range at Pokhran municipality, Rajasthan state on 18 May 1974 at 8:05 a.m....
"). The test was the first test developed after the creation of the NPT, and created new questions about how civilian nuclear technology could be diverted secretly to weapons purposes (dual-use technologyDual-use technologyDual-use is a term often used in politics and diplomacy to refer to technology which can be used for both peaceful and military aims. It often refers to the proliferation of nuclear weapons, but that of bioweapons is a major issue as well. The scientific reviews Dual-use is a term often used in...
). India's secret development caused great concern and anger particularly from nations, such as Canada, that had supplied it nuclear reactors for peaceful and power generating needs. It appears to have been primarily motivated as a general deterrent, as well as an attempt to project India as a regional power.
- Though India maintained that its nuclear capability was primarily "peaceful", it apparently weaponized two dozen nuclear weapons for delivery by air between 1988 and 1990. But it was not until 1998 that India tested weaponized nuclear warheads ("Operation Shakti"), including a thermonuclear device.
- In July 2005, U.S. PresidentPresident of the United StatesThe President of the United States of America is the head of state and head of government of the United States. The president leads the executive branch of the federal government and is the commander-in-chief of the United States Armed Forces....
George W. BushGeorge W. BushGeorge Walker Bush is an American politician who served as the 43rd President of the United States, from 2001 to 2009. Before that, he was the 46th Governor of Texas, having served from 1995 to 2000....
and Indian Prime Minister Manmohan SinghManmohan SinghManmohan Singh is the 13th and current Prime Minister of India. He is the only Prime Minister since Jawaharlal Nehru to return to power after completing a full five-year term. A Sikh, he is the first non-Hindu to occupy the office. Singh is also the 7th Prime Minister belonging to the Indian...
announced plans to conclude an Indo-US civilian nuclear agreement. This came to fruition through a series of steps that included India’s announced plan to separate its civil and military nuclear programs in March 2006, the passage of the United States-India Peaceful Atomic Energy Cooperation Act by the U.S. Congress in December 2006, the conclusion of a U.S.-India nuclear cooperation agreement in July 2007, approval by the IAEA of an India-specific safeguards agreement, agreement by the Nuclear Suppliers GroupNuclear Suppliers GroupNuclear Suppliers Group is a multinational body concerned with reducing nuclear proliferation by controlling the export and re-transfer of materials that may be applicable to nuclear weapon development and by improving safeguards and protection on existing materials.- History :It was founded in...
to a waiver of export restrictions for India, approval by the U.S. Congress and culminating in the signature of U.S.-India agreement for civil nuclear cooperation in October 2008. The U.S. State Department said it made it "very clear that we will not recognize India as a nuclear-weapon state". The United States is bound by the Hyde Act with India and may cease all cooperation with India if India detonates a nuclear explosive device. The US had further said it is not its intention to assist India in the design, construction or operation of sensitive nuclear technologies through the transfer of dual-use items. In establishing an exemption for India, the Nuclear Suppliers Group reserved the right to consult on any future issues which might trouble it. As of June 2011, India was estimated to have had a stockpile of around 80–100 warheads.
- Pakistan also is not a Party to the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty. Pakistan covertly developed nuclear weapons over many decades, beginning in the late 1970s. Pakistan first delved into nuclear power after the establishment of its first nuclear power plant near KarachiKarachiKarachi is the largest city, main seaport and the main financial centre of Pakistan, as well as the capital of the province of Sindh. The city has an estimated population of 13 to 15 million, while the total metropolitan area has a population of over 18 million...
with equipment and materials supplied mainly by western nations in the early 1970s. Pakistani Prime Minister Zulfiqar Ali Bhutto promised in 1965 that if India can build nuclear weapons then Pakistan would too, "even if we have to eat grass." The United States continued to certify that Pakistan did not possess nuclear weapons until 1990, when sanctions were imposed under the Pressler Amendment, requiring a cutoff of U.S. economic and military assistance to Pakistan. In 1998, Pakistan conducted its first six nuclear testsChagai-IThe Chagai-I was a codename referring to the five underground nuclear tests conducted by Pakistan at 15:15hrs in 28th May of 1998. It was named Chagai-I, as the tests were conducted in the Chagai District...
at the Chagai HillsChagai HillsThe Chagai Hills is a range of granite hills in the Chagai District in Pakistan's Balochistan province.-Location:The Chagai Hills lie in a desert area in the northernmost part of Chagai District north of Pakistan's Ras Koh Hills and south of Afghanistan's Helmand and Nimruz provinces.- Topography...
, in response to the five tests conducted by India a few weeks before. Over the years, Pakistan has developed into a crucial nuclear power.
- In 2004, the Pakistani metallurgist A.Q. Khan, a key figure in Pakistan's nuclear weapons program, confessed to heading an international black market ring involved in selling nuclear weapons technology. In particular, Khan had been selling gas centrifugeGas centrifugeA gas centrifuge is a device that performs isotope separation of gases. A centrifuge relies on the principles of centripetal force accelerating molecules so that particles of different masses are physically separated in a gradient along the radius of a rotating container.A prominent use of gas...
technology to North Korea, Iran, and Libya. Khan denied complicity by the Pakistani government or Army, but this has been called into question by journalists and IAEA officials, and was later contradicted by statements from Khan himself.
- North Korea was a Party to the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty, but announced a withdrawal on January 10, 2003, after the United States accused it of having a secret uranium enrichment program and cut off energy assistance under the 1994 Agreed Framework. In February 2005 the North Koreans claimed to possess functional nuclear weapons, though their lack of a test at the time led many experts to doubt the claim. However, in October 2006, North Korea stated that due to growing intimidation by the USA, it would conduct a nuclear test to confirm its nuclear status. North Korea reported a successful nuclear test on October 9, 2006 (see 2006 North Korean nuclear test2006 North Korean nuclear testThe 2006 North Korean nuclear test was the detonation of a nuclear device conducted on October 9, 2006 by North Korea.North Korea announced its intention to conduct a test on October 3, six days prior, and in doing so became the first nation to give warning of its first nuclear test...
). Most U.S. intelligence officials believe that North Korea did, in fact, test a nuclear device due to radioactive isotopes detected by U.S. aircraft; however, most agree that the test was probably only partially successful. The yieldNuclear weapon yieldThe explosive yield of a nuclear weapon is the amount of energy discharged when a nuclear weapon is detonated, expressed usually in the equivalent mass of trinitrotoluene , either in kilotons or megatons , but sometimes also in terajoules...
may have been less than a kiloton, which is much smaller than the first successful tests of other powers; however, boosted fission weaponBoosted fission weaponA boosted fission weapon usually refers to a type of nuclear bomb that uses a small amount of fusion fuel to increase the rate, and thus yield, of a fission reaction. The neutrons released by the fusion reactions add to the neutrons released in the fission, as well as inducing the fission reactions...
s may have an unboosted yield in this range, which is sufficient to start deuterium-tritiumTritiumTritium is a radioactive isotope of hydrogen. The nucleus of tritium contains one proton and two neutrons, whereas the nucleus of protium contains one proton and no neutrons...
fusion in the boost gas at the center; the fast neutrons from fusion then ensure a full fission yield. North Korea conducted a second, higher yield test on May 25, 2009 (see 2009 North Korean nuclear test2009 North Korean nuclear testThe 2009 North Korean nuclear test was the underground detonation of a nuclear device conducted on 25 May 2009 by North Korea. This was its second nuclear test, the first test having taken place in October 2006. Following the nuclear test, Pyongyang also conducted several missile tests.The test was...
).
Other states believed to have nuclear weapons

- Israel is not a party to the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty and refuses to officially confirm or deny having a nuclear arsenal, or having developed nuclear weapons, or even having a nuclear weapons program. Israel has pledged not to be the first country to introduce nuclear weapons into the region, but is also pursuing a policy of strategic ambiguity with regard to their possession. This is sometimes called a policy of "nuclear opacity": Israel neither confirms nor denies that it possesses nuclear weapons, in what has been interpreted as an attempt to get the benefits of deterrenceDeterrenceDeterrence may refer to:* Deterrence theory, a theory of war, especially regarding nuclear weapons* Deterrence , a theory of justice* Deterrence , a psychological theory...
with a minimum political cost. In the late 1960s, Israeli Ambassador to the US Yitzhak RabinYitzhak Rabin' was an Israeli politician, statesman and general. He was the fifth Prime Minister of Israel, serving two terms in office, 1974–77 and 1992 until his assassination in 1995....
informed the United States State Department, that its understanding of "introducing" such weapons meant that they would be tested and publicly declared, while merely possessing the weapons did not constitute "introducing" them. Israel claims that the Negev Nuclear Research CenterNegev Nuclear Research CenterThe Negev Nuclear Research Center is an Israeli nuclear installation located in the Negev desert, about thirteen kilometers to the south-east of the city of Dimona. The purpose of Dimona is widely assumed to be the manufacturing of nuclear weapons, and the majority of defense experts have...
near DimonaDimonaDimona is an Israeli city in the Negev desert, to the south of Beersheba and west of the Dead Sea above the Arava valley in the Southern District of Israel. Its population at the end of 2007 was 33,600.-History:...
is a research center. However, there is extensive evidence Israel has nuclear weapons or a near-ready nuclear weapons capability. Extensive information about the program in Dimona was also disclosed by technician Mordechai VanunuMordechai VanunuMordechai Vanunu ; is a former Israeli nuclear technician who, citing his opposition to weapons of mass destruction, revealed details of Israel's nuclear weapons program to the British press in 1986. He was subsequently lured to Italy by a Mossad agent, where he was drugged and kidnapped by...
in 1986. - According to the Natural Resources Defense CouncilNatural Resources Defense CouncilThe Natural Resources Defense Council is a New York City-based, non-profit, non-partisan international environmental advocacy group, with offices in Washington DC, San Francisco, Los Angeles, Chicago, and Beijing...
and the Federation of American ScientistsFederation of American ScientistsThe Federation of American Scientists is a nonpartisan, 501 organization intent on using science and scientific analysis to attempt make the world more secure. FAS was founded in 1945 by scientists who worked on the Manhattan Project to develop the first atomic bombs...
, Israel likely possesses around 75–200 weapons. Imagery analysts can identify weapon bunkers, mobile missile launchers, and launch sites in satellite photographs. Israel may have tested a nuclear weapon along with South AfricaSouth AfricaThe Republic of South Africa is a country in southern Africa. Located at the southern tip of Africa, it is divided into nine provinces, with of coastline on the Atlantic and Indian oceans...
in 1979, but this has never been confirmed, and interpretation of the evidence is controversial (see Vela IncidentVela IncidentThe Vela Incident was an unidentified "double flash" of light that was detected by an American Vela Hotel satellite on September 22, 1979....
).
Nuclear weapons sharing
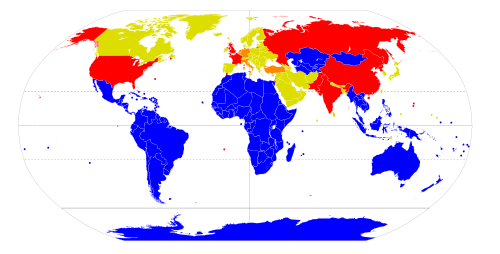
Under NATO nuclear weapons sharing, the United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
has provided nuclear weapons for Belgium
Belgium
Belgium , officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a federal state in Western Europe. It is a founding member of the European Union and hosts the EU's headquarters, and those of several other major international organisations such as NATO.Belgium is also a member of, or affiliated to, many...
, Germany
Germany and weapons of mass destruction
Though Germany is one of the most technologically advanced countries in the world, since World War II it has generally refrained from using this technology to outfit its own armed forces with weapons of mass destruction , although it participates in the NATO nuclear weapons sharing arrangements and...
, Italy
Italy
Italy , officially the Italian Republic languages]] under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, Italy's official name is as follows:;;;;;;;;), is a unitary parliamentary republic in South-Central Europe. To the north it borders France, Switzerland, Austria and...
, the Netherlands
Netherlands and weapons of mass destruction
Although the Netherlands does not have weapons of mass destruction made by itself, the country participates in the NATO nuclear weapons sharing arrangements and trains for delivering U.S...
, and Turkey
Turkey
Turkey , known officially as the Republic of Turkey , is a Eurasian country located in Western Asia and in East Thrace in Southeastern Europe...
to deploy and store. This involves pilots and other staff of the "non-nuclear" NATO states practicing, handling, and delivering the U.S. nuclear bombs, and adapting non-U.S. warplanes to deliver U.S. nuclear bombs. U.S. nuclear weapons were also deployed in Canada
Canada and weapons of mass destruction
Canada does not currently possess any weapons of mass destruction and has signed treaties repudiating possession of them. Canada ratified the Geneva Protocol in 1930 and the Nuclear Non-proliferation Treaty in 1970.- Introduction :...
until 1984, South Korea
South Korea
The Republic of Korea , , is a sovereign state in East Asia, located on the southern portion of the Korean Peninsula. It is neighbored by the People's Republic of China to the west, Japan to the east, North Korea to the north, and the East China Sea and Republic of China to the south...
until 1991, and in Greece
Greece
Greece , officially the Hellenic Republic , and historically Hellas or the Republic of Greece in English, is a country in southeastern Europe....
until 2001 for nuclear sharing purposes. Members of the Non-Aligned Movement
Non-Aligned Movement
The Non-Aligned Movement is a group of states considering themselves not aligned formally with or against any major power bloc. As of 2011, the movement had 120 members and 17 observer countries...
have called on all countries to "refrain from nuclear sharing for military purposes under any kind of security arrangements." The Institute of Strategic Studies Islamabad (ISSI) has criticized the arrangement for allegedly violating Articles I and II of the NPT, arguing that "these Articles do not permit the NWS to delegate the control of their nuclear weapons directly or indirectly to others." NATO has argued that the weapons' sharing is compliant with the NPT because "the U.S. nuclear weapons based in Europe are in the sole possession and under constant and complete custody and control of the United States."
States formerly possessing nuclear weapons
Nuclear weapons have been present in many nations, often as staging grounds under control of other powers. However, in only one instance has a nation given up nuclear weapons after being in control of them; in most cases this has been because of special political circumstances. The fall of the USSRDissolution of the Soviet Union
The dissolution of the Soviet Union was the disintegration of the federal political structures and central government of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics , resulting in the independence of all fifteen republics of the Soviet Union between March 11, 1990 and December 25, 1991...
, for example, left several former Soviet republics
Post-Soviet states
The post-Soviet states, also commonly known as the Former Soviet Union or former Soviet republics, are the 15 independent states that split off from the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics in its dissolution in December 1991...
in possession of nuclear weapons.

- South Africa produced six nuclear weapons in the 1980s, but disassembled them in the early 1990s. In 1979, there was a putative detection of a clandestine nuclear test in the Indian Ocean, and it has long been speculated that it was possibly a test by South Africa, perhaps in collaboration with Israel, though this has never been confirmed (see Vela IncidentVela IncidentThe Vela Incident was an unidentified "double flash" of light that was detected by an American Vela Hotel satellite on September 22, 1979....
). South Africa signed the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty in 1991.
Former Soviet countries
-
 Belarus had 81 single warhead missiles stationed on its territory after the Soviet Union collapsed in 1991. They were all transferred to Russia by 1996. Belarus has signed the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty.
Belarus had 81 single warhead missiles stationed on its territory after the Soviet Union collapsed in 1991. They were all transferred to Russia by 1996. Belarus has signed the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty. -
 Kazakhstan inherited 1,400 nuclear weapons from the Soviet Union, and transferred them all to Russia by 1995. Kazakhstan has signed the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty.
Kazakhstan inherited 1,400 nuclear weapons from the Soviet Union, and transferred them all to Russia by 1995. Kazakhstan has signed the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty. -
 Ukraine has signed the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty. Ukraine inherited about 5,000 nuclear weapons when it became independent from the USSR in 1991, making its nuclear arsenal the third-largest in the world. By 1996, Ukraine had voluntarily disposed of all nuclear weapons within its territory, transferring them to Russia.
Ukraine has signed the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty. Ukraine inherited about 5,000 nuclear weapons when it became independent from the USSR in 1991, making its nuclear arsenal the third-largest in the world. By 1996, Ukraine had voluntarily disposed of all nuclear weapons within its territory, transferring them to Russia.
See also
- Comprehensive Test Ban TreatyComprehensive Test Ban TreatyThe Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty bans all nuclear explosions in all environments, for military or civilian purposes. It was adopted by the United Nations General Assembly on 10 September 1996 but it has not entered into force.-Status:...
- Nuclear disarmamentNuclear disarmamentNuclear disarmament refers to both the act of reducing or eliminating nuclear weapons and to the end state of a nuclear-free world, in which nuclear weapons are completely eliminated....
- Nuclear Non-Proliferation TreatyNuclear Non-Proliferation TreatyThe Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons, commonly known as the Non-Proliferation Treaty or NPT, is a landmark international treaty whose objective is to prevent the spread of nuclear weapons and weapons technology, to promote cooperation in the peaceful uses of nuclear energy and to...
- Nuclear proliferationNuclear proliferationNuclear proliferation is a term now used to describe the spread of nuclear weapons, fissile material, and weapons-applicable nuclear technology and information, to nations which are not recognized as "Nuclear Weapon States" by the Treaty on the Nonproliferation of Nuclear Weapons, also known as the...
- Nuclear Threat Initiative
- Nuclear war
- Nuclear-Weapon-Free ZoneNuclear-Weapon-Free ZoneA nuclear-weapons-free zone, or NWFZ is defined by the United Nations as an agreement which a group of states has freely established by treaty or convention, that bans the use, development, or deployment of nuclear weapons in a given area, that has mechanisms of verification and control to enforce...
- Unsanctioned nuclear activity
- Nuclear terrorismNuclear terrorismNuclear terrorism denotes the use, or threat of the use, of nuclear weapons or radiological weapons in acts of terrorism, includingattacks against facilities where radioactive materials are present...
External links
- Archive of Nuclear Data - List of warheads by country
- Globalsecurity.org World Special Weapons Guide
- The Nuclear Weapon Archive
- Nuclear Notebook from Bulletin of the Atomic ScientistsBulletin of the Atomic ScientistsThe Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists is a nontechnical online magazine that covers global security and public policy issues, especially related to the dangers posed by nuclear and other weapons of mass destruction...
- U.S. Nuclear Weapons in Europe: A review of post-Cold War policy, force levels, and war planning NRDC, February 2005
- Online NewsHour with Jim Lehrer:Tracking Nuclear Proliferation










