
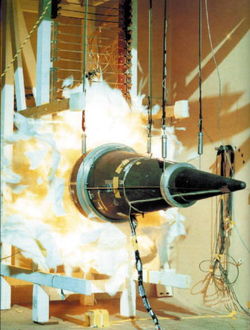
Stockpile stewardship
Encyclopedia
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
program of reliability testing and maintenance of its nuclear weapon
Nuclear weapon
A nuclear weapon is an explosive device that derives its destructive force from nuclear reactions, either fission or a combination of fission and fusion. Both reactions release vast quantities of energy from relatively small amounts of matter. The first fission bomb test released the same amount...
s without the use of nuclear testing
Nuclear testing
Nuclear weapons tests are experiments carried out to determine the effectiveness, yield and explosive capability of nuclear weapons. Throughout the twentieth century, most nations that have developed nuclear weapons have tested them...
.
Because no new nuclear weapons have been developed by the United States since 1992, even its youngest weapons are at least years old. Aging weapons can fail or act unpredictably in a number of ways: the high explosives that condense their fissile
Fissile
In nuclear engineering, a fissile material is one that is capable of sustaining a chain reaction of nuclear fission. By definition, fissile materials can sustain a chain reaction with neutrons of any energy. The predominant neutron energy may be typified by either slow neutrons or fast neutrons...
material can chemically degrade, their electronic components can suffer from decay, their radioactive plutonium
Plutonium
Plutonium is a transuranic radioactive chemical element with the chemical symbol Pu and atomic number 94. It is an actinide metal of silvery-gray appearance that tarnishes when exposed to air, forming a dull coating when oxidized. The element normally exhibits six allotropes and four oxidation...
/uranium
Uranium
Uranium is a silvery-white metallic chemical element in the actinide series of the periodic table, with atomic number 92. It is assigned the chemical symbol U. A uranium atom has 92 protons and 92 electrons, of which 6 are valence electrons...
cores are potentially unreliable, and the isotopes used by thermonuclear weapons may be chemically unstable as well.
Since the United States has also not tested nuclear weapons since 1992, this leaves the task of its stockpile maintenance resting on the use of simulations (using non-nuclear explosives tests and supercomputer
Supercomputer
A supercomputer is a computer at the frontline of current processing capacity, particularly speed of calculation.Supercomputers are used for highly calculation-intensive tasks such as problems including quantum physics, weather forecasting, climate research, molecular modeling A supercomputer is a...
s, among other methods) and applications of scientific knowledge about physics
Physics
Physics is a natural science that involves the study of matter and its motion through spacetime, along with related concepts such as energy and force. More broadly, it is the general analysis of nature, conducted in order to understand how the universe behaves.Physics is one of the oldest academic...
and chemistry
Chemistry
Chemistry is the science of matter, especially its chemical reactions, but also its composition, structure and properties. Chemistry is concerned with atoms and their interactions with other atoms, and particularly with the properties of chemical bonds....
to the specific problems of weapons aging (the latter method is what is meant when various agencies refer to their work as "science-based"). It also involves the manufacture of additional plutonium "pits" to replace ones of unknown quality, and finding other methods to increase the lifespan of existing warheads and maintain a confident nuclear deterrent.
Most work for stockpile stewardship is undertaken at United States Department of Energy National Laboratories
United States Department of Energy National Laboratories
The United States Department of Energy National Laboratories and Technology Centers are a system of facilities and laboratories overseen by the United States Department of Energy for the purpose of advancing science and helping promote the economic and defensive national interests of the United...
, mostly at Los Alamos National Laboratory
Los Alamos National Laboratory
Los Alamos National Laboratory is a United States Department of Energy national laboratory, managed and operated by Los Alamos National Security , located in Los Alamos, New Mexico...
, Sandia National Laboratories
Sandia National Laboratories
The Sandia National Laboratories, managed and operated by the Sandia Corporation , are two major United States Department of Energy research and development national laboratories....
, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory
The Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory , just outside Livermore, California, is a Federally Funded Research and Development Center founded by the University of California in 1952...
, the Nevada Test Site
Nevada Test Site
The Nevada National Security Site , previously the Nevada Test Site , is a United States Department of Energy reservation located in southeastern Nye County, Nevada, about northwest of the city of Las Vegas...
, and Department of Energy
United States Department of Energy
The United States Department of Energy is a Cabinet-level department of the United States government concerned with the United States' policies regarding energy and safety in handling nuclear material...
productions facilities, which employ around 27,500 personnel and cost billions of dollars per year to operate.
Stockpile Stewardship and Management Program
The Stockpile Stewardship and Management Program is a United States Department of EnergyUnited States Department of Energy
The United States Department of Energy is a Cabinet-level department of the United States government concerned with the United States' policies regarding energy and safety in handling nuclear material...
program to ensure that the nuclear capabilities of the United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
are not eroded as nuclear weapons age. It costs more than $4 billion annually to test nuclear weapons and build advanced science facilities, such as the National Ignition Facility
National Ignition Facility
The National Ignition Facility, or NIF is a large, laser-based inertial confinement fusion research device located at the Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory in Livermore, California. NIF uses powerful lasers to heat and compress a small amount of hydrogen fuel to the point where nuclear fusion...
(NIF). Such facilities have been deemed necessary under the program since President Bill Clinton
Bill Clinton
William Jefferson "Bill" Clinton is an American politician who served as the 42nd President of the United States from 1993 to 2001. Inaugurated at age 46, he was the third-youngest president. He took office at the end of the Cold War, and was the first president of the baby boomer generation...
signed the Comprehensive Test Ban Treaty
Comprehensive Test Ban Treaty
The Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty bans all nuclear explosions in all environments, for military or civilian purposes. It was adopted by the United Nations General Assembly on 10 September 1996 but it has not entered into force.-Status:...
in 1996.

